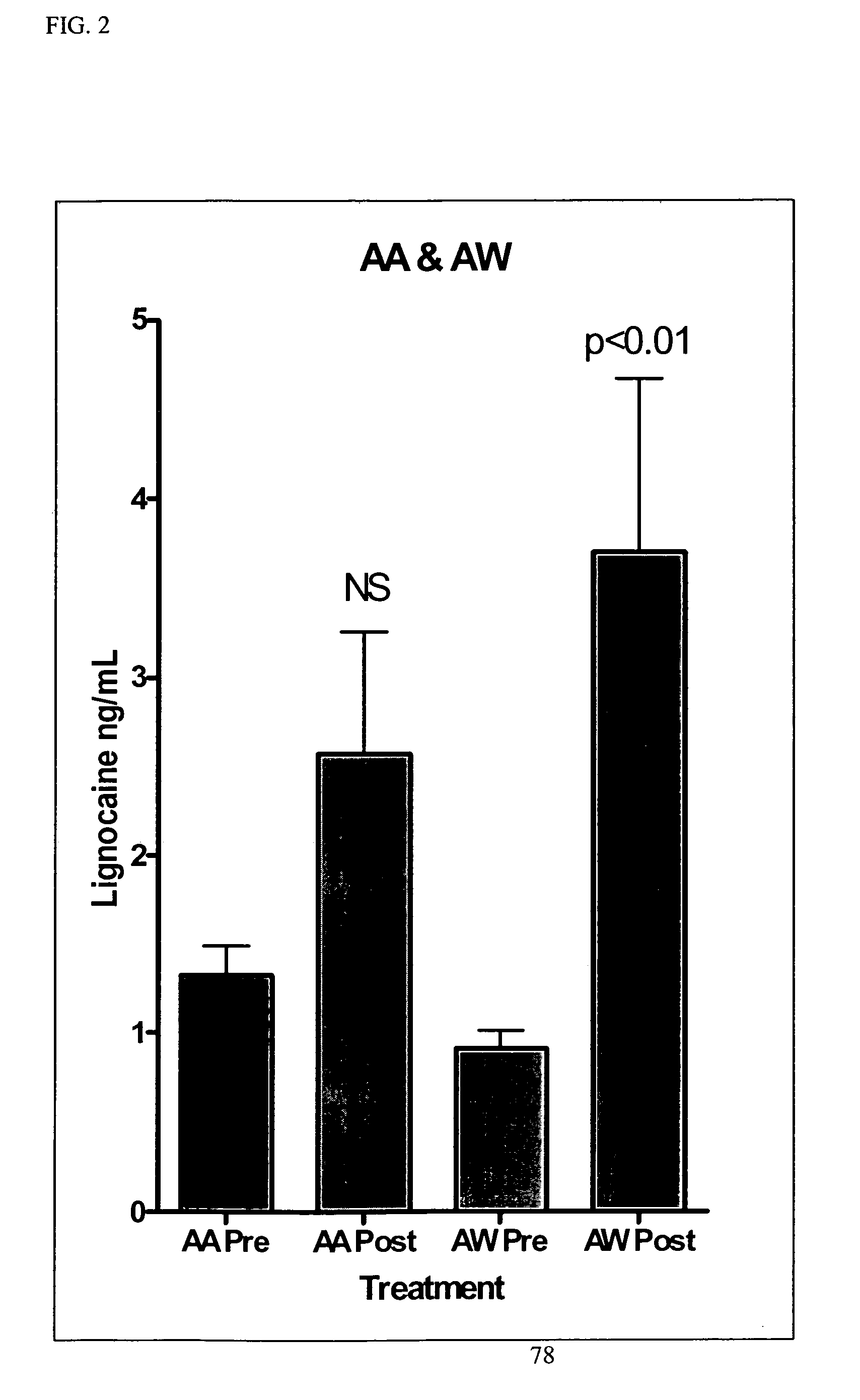
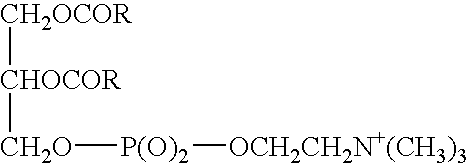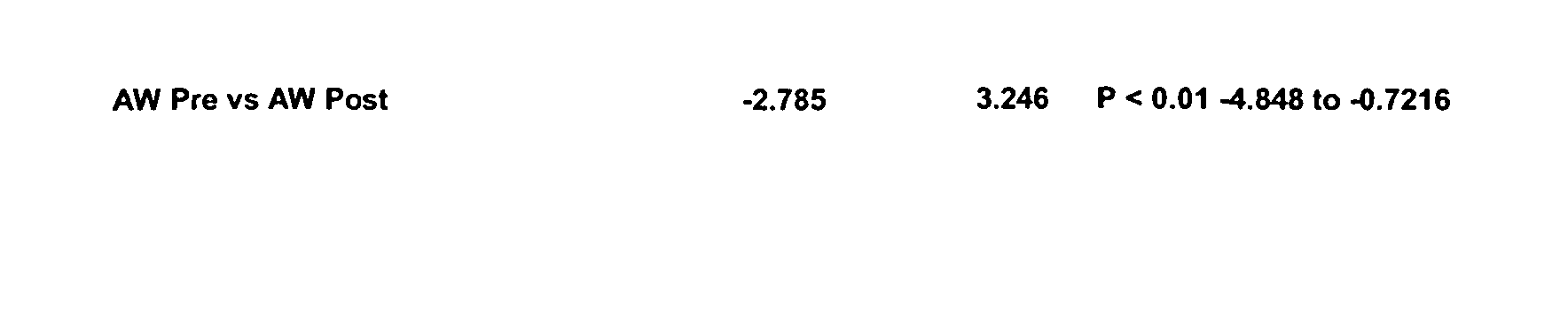Patents
Literature
116 results about "Cellular energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular Energy is a potent formula that contains research-backed ingredients for supporting energy production in mitochondria, as well as many other benefits. ◆ The nutrients found in Cellular Energy help these organelles efficiently carry out their role in producing ATP - the energy currency of cells. ◆.
Methods and compositions for treatment of free radical injury
InactiveUS20060121016A1Reduction of tissue level oxidative damage toBiocideDipeptide ingredientsAntioxidantCell membrane
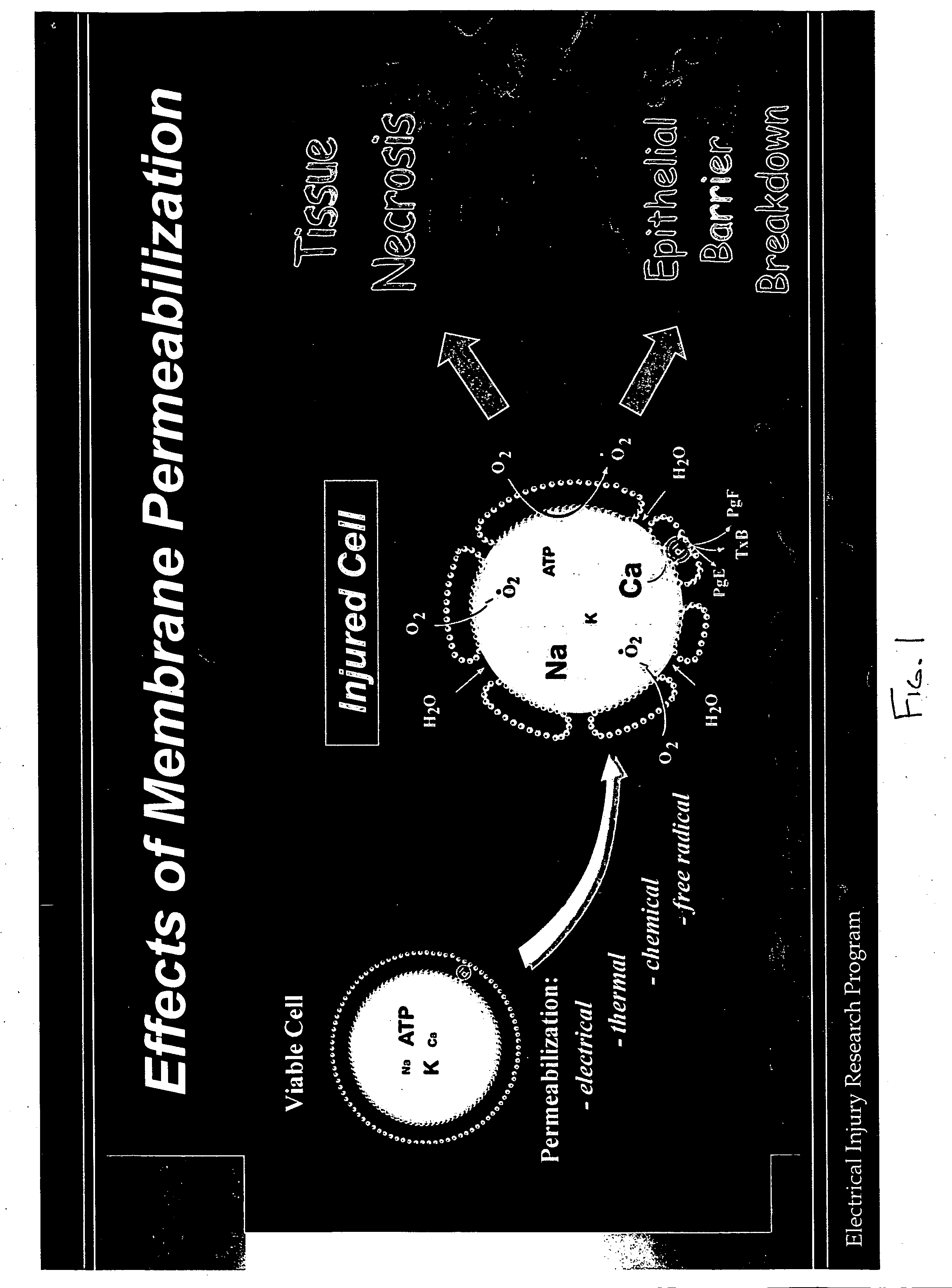
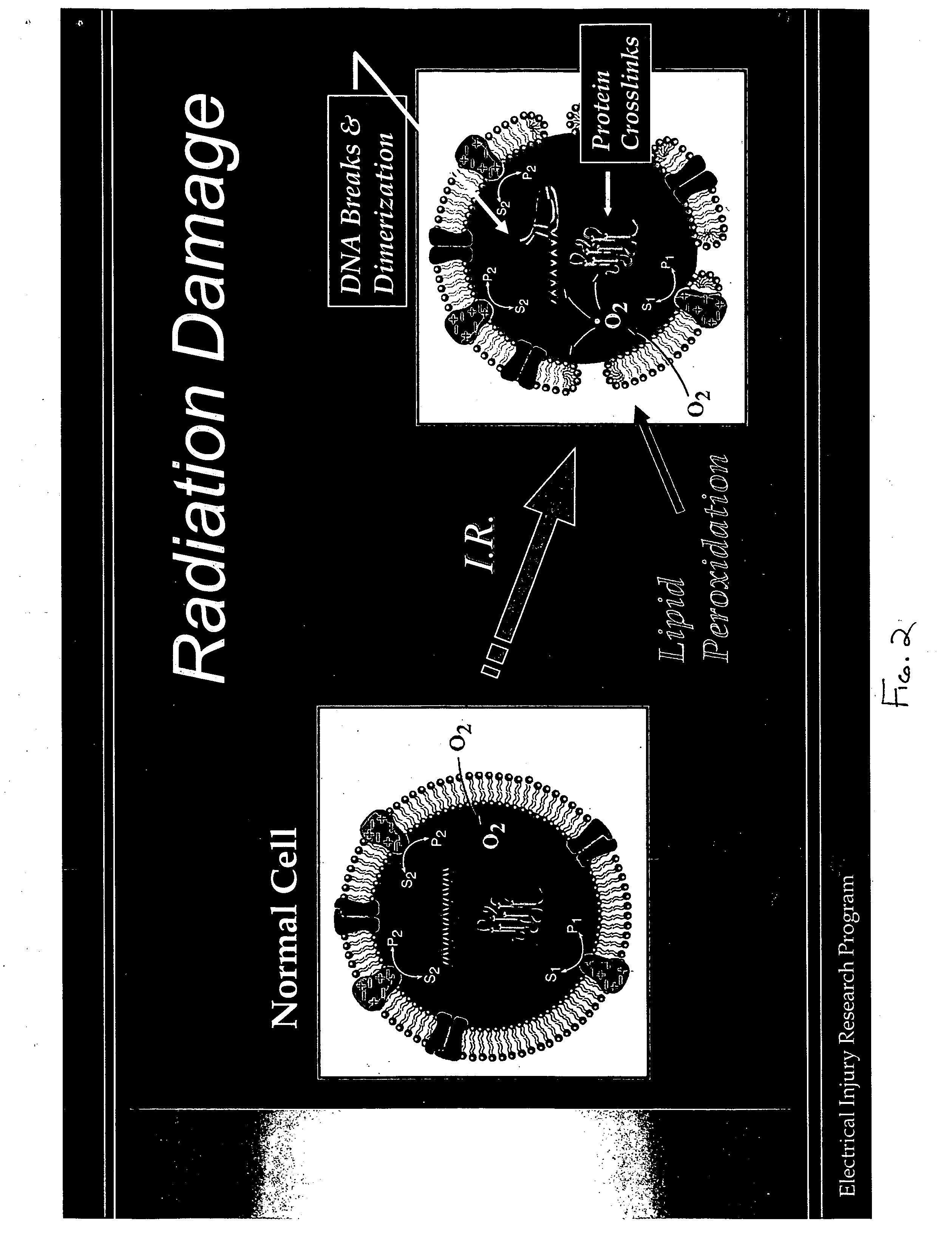
Therapeutic methods and compositions useful for the prevention and / or treatment of cellular membrane damage leading to or resulting from peroxidation of the cellular membrane and a breakdown of the barrier function of the cellular membrane. A therapeutic composition includes a combination of a membrane sealing sealing surfactant and a cofactor treatment consisting of an antioxidant and a cellular energy store. To affect this goal, the permeability of damaged cellular membranes is reestablished by the membrane sealing surfactant, effectively “sealing” the injured membranes. To facilitate rapid tissue recovery, cellular energy levels can be reestablished through addition of a cellular energy source such as, for example, MgCl2-ATP which, serves a further dual benefit of improving the cellular ion balance. Addition of an antioxidant eliminates the generation of Reactive Oxygen intermediates and enhances the metabolism of free radicals.
Owner:MAROON BIOTECH
Coenzyme Q10, lactoferrin and angiogenin compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070253941A1Efficient assimilationReduce frequencyOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAngiogeninFunctional health
Methods of enhancing the bio-availability of coenzyme Q10, and methods of supporting the cardiovascular system to accommodate the increase in cellular energy synthesis as a result of the bio-availability of coenzyme Q10 are described. Compositions which include coenzyme Q10, lactoferrin and / or angiogenin are described for use in the related methods, for multi-functional health applications.
Owner:NAIDU LP
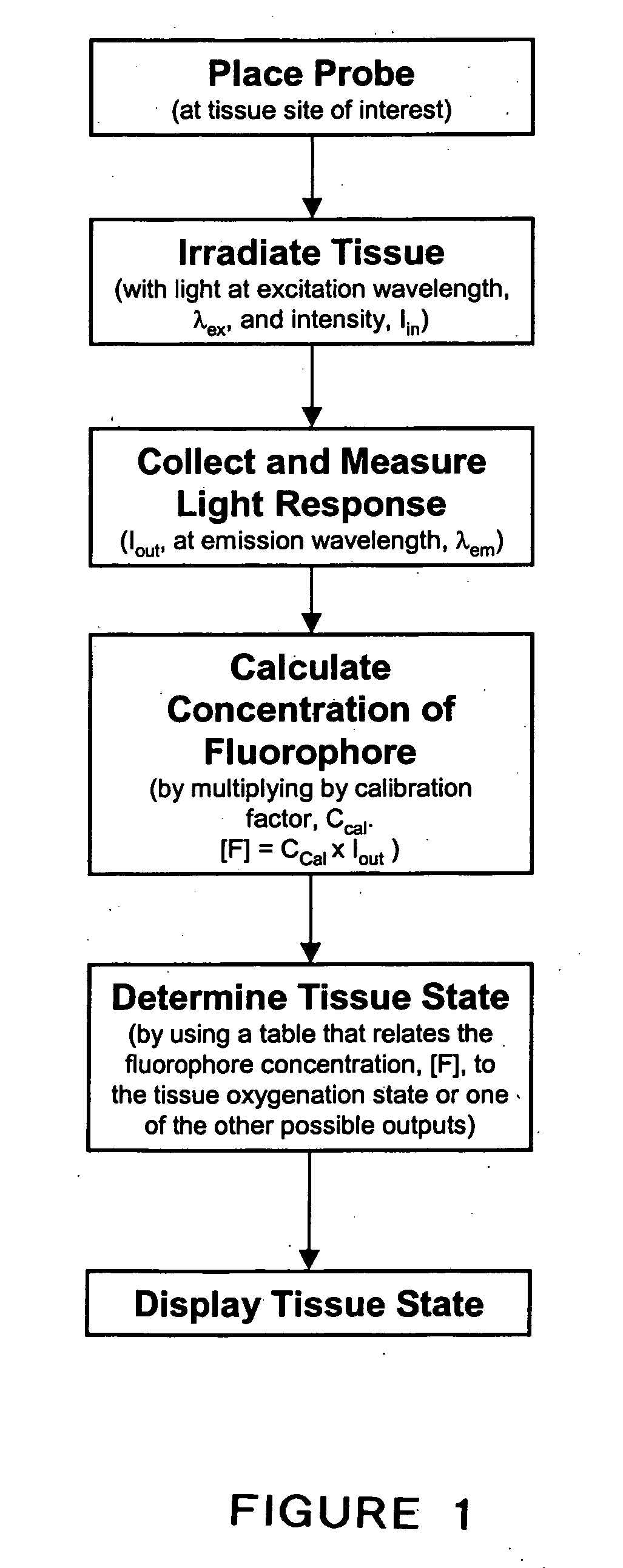
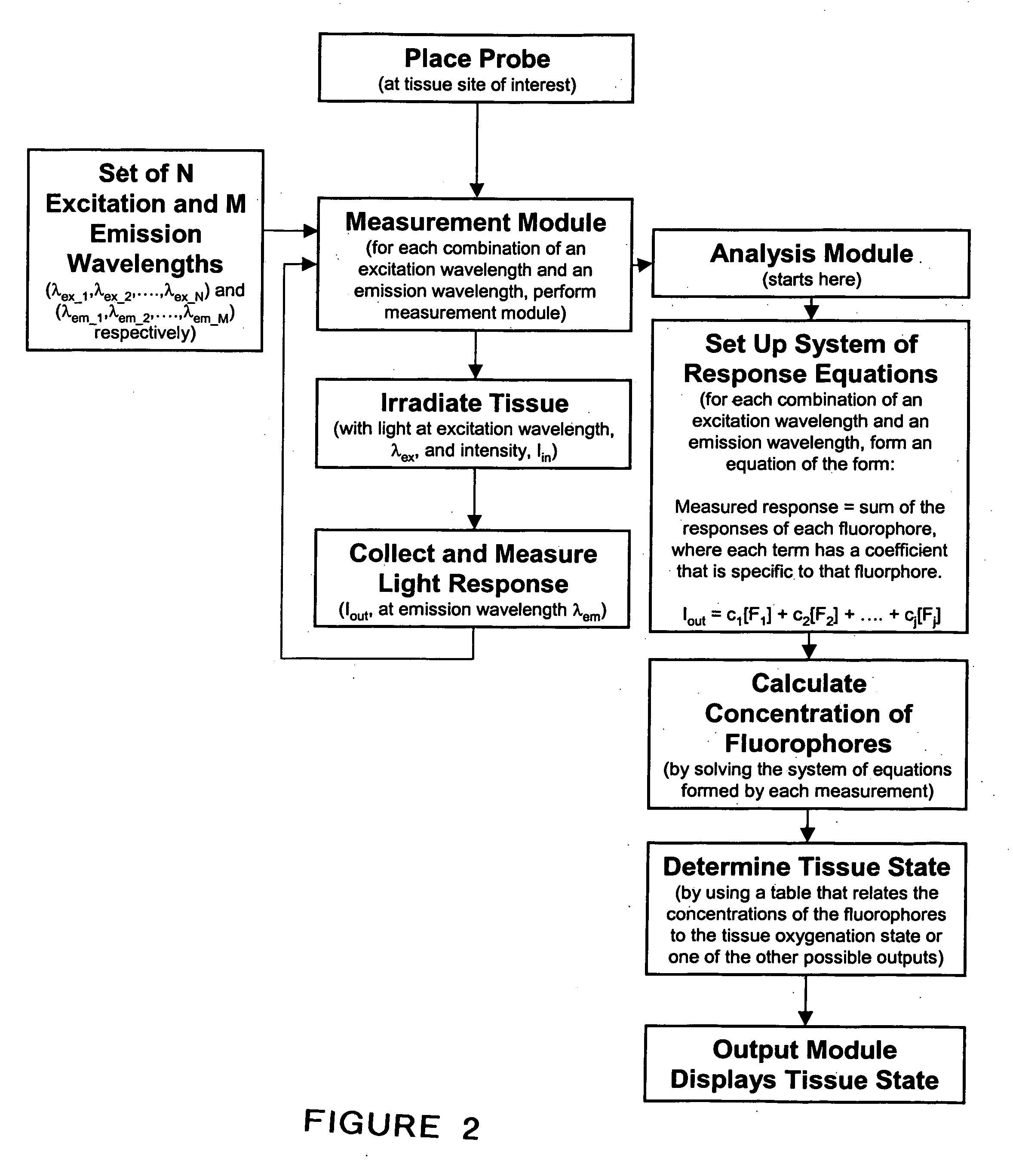
System and method for monitoring of end organ oxygenation by measurement of in vivo cellular energy status
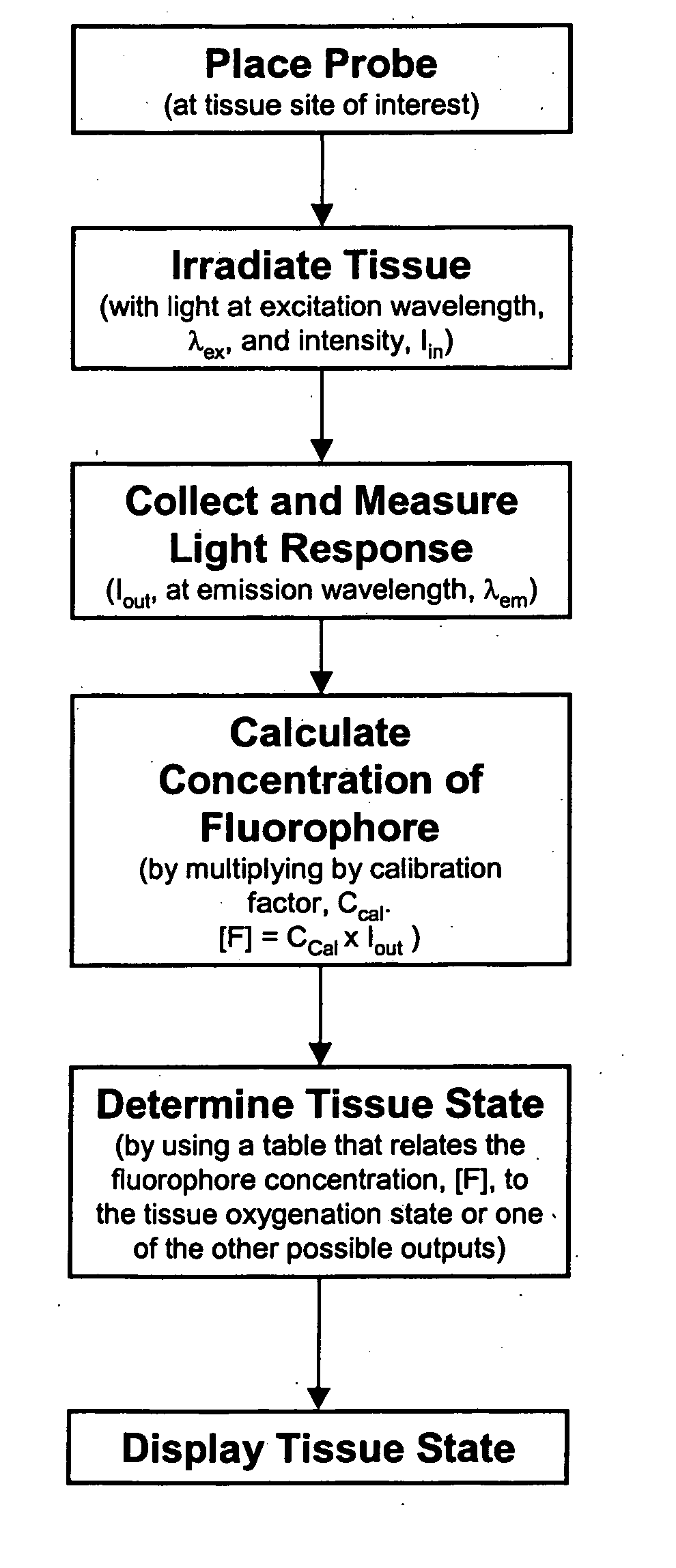
A method is provided of measuring in vivo of an endogenous fluorophore in a tissue site. A known excitation wavelength of the endogenous flurophore is selected within a range of wavelengths at which the endogenous flurophore undergoes fluorescence. The tissue site is irradiated with irradiated light having at least the selected excitation wavelength within the range of wavelengths. A fluorescence emission of the tissue site resulting from the irradiation thereof is detected. A relative or absolute concentration of the endogenous fluorophore is determined by multiplying it by a calibration factor that depends one at least one of, a known excitation and emission property of the endogenous fluorophore, an intensity of the irradiated light, optical properties of an excitation probe, and specific properties of the tissue. The relative or absolute concentration of the endogenous fluorphore is used to estimate at least one of a, in vivo cellular energy production status or state of end-organ tissue oxygenation.
Owner:EPOC
Composition for enhancing cellular energy
InactiveUS20060292134A1Improve bioavailabilityIncreasing subject 's relative intensityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationArginine
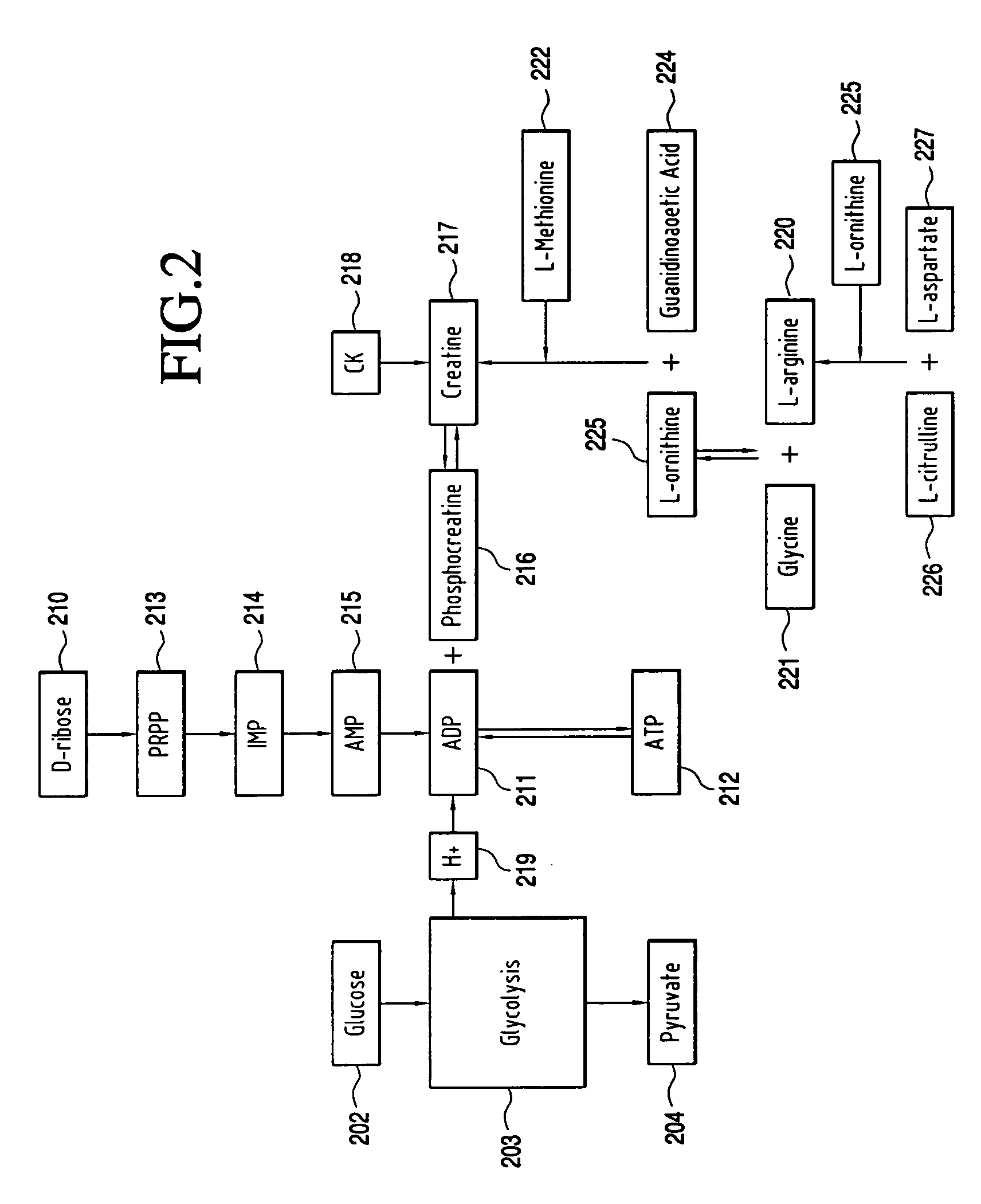
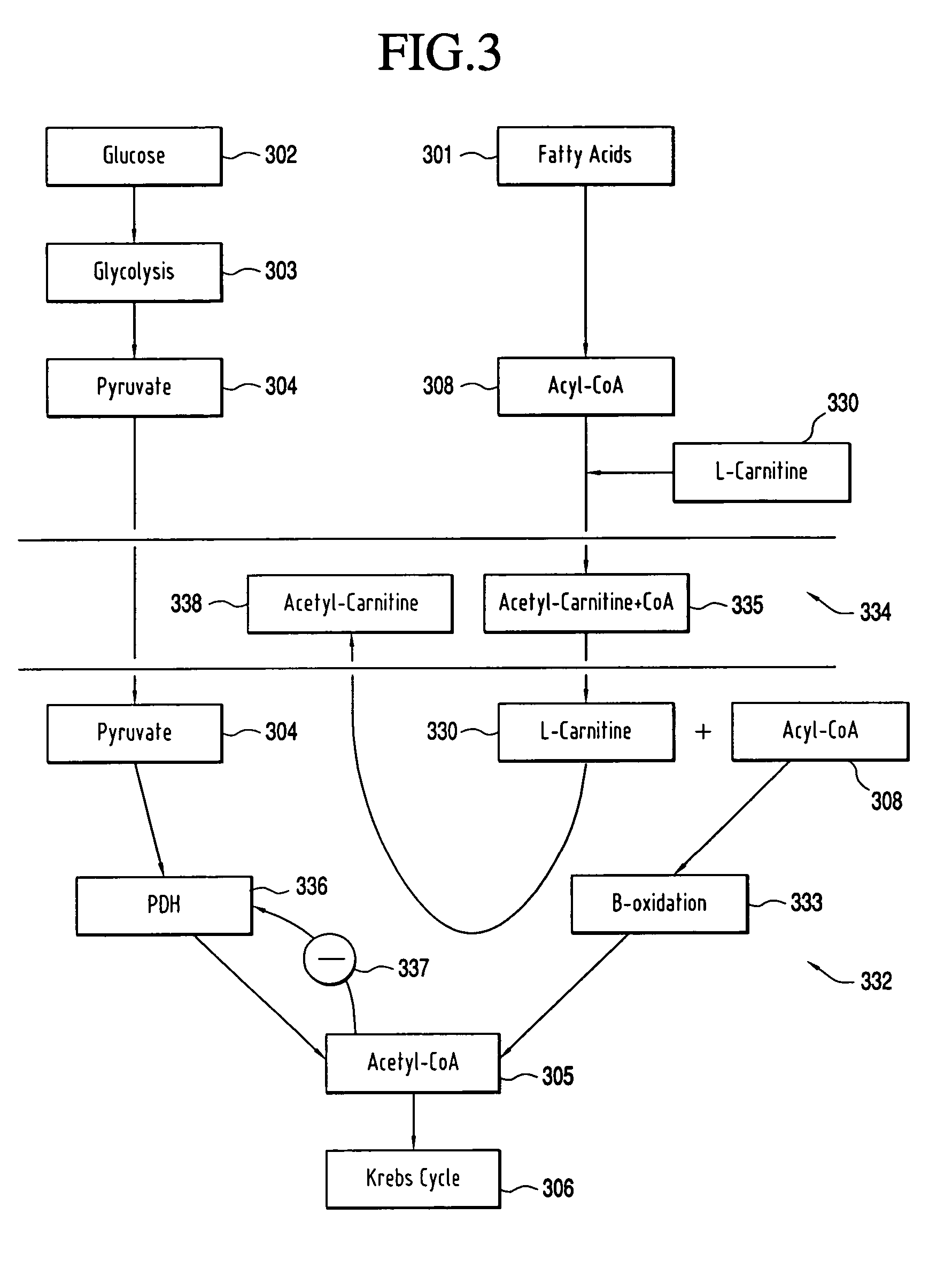
A composition for enhancing cellular energy that includes creatine, L-arginine-α-ketoglutarate, D-ribose, L-carnitine, L-citrulline, and pyruvate. The composition is administering to a subject to enhance cellular energy, to increase relative intensity of physical activity performed by the subject, to increase endurance of the subject during the physical activity and to increase the muscle mass of the subject.
Owner:ADVOCARE INT
Method of generating hydrogen in drinking water using an enerceutical product added to magnesium in a hydrogen permeable but solute impermeable container
InactiveUS20100008850A1Increased hydrogen productionImprove usabilityHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionDialysis membranesWater use
Consuming water with increased hydrogen content can provide clinical benefits to humans and animals through a non-mitochondria alternative cellular energy (ACE) pathway and also as an antioxidant. This application discloses that the hydrogen content of drinking water can be safely increased by placing into the water a hydrogen generating device, such as a mixture of metallic magnesium and EH-101 (HB-101) containing solution, whereby the device allows for the selective passage of the generated hydrogen but restricts the passage of magnesium and EH-101 (HB-101) components. This partitioning of hydrogen from EH-101 (HB-101) components is achieved by using either reverse osmosis membrane, low density plastic material such as polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC or Saran), or low molecular weight cutoff dialysis membrane to create a sealed container of the magnesium and magnesium chloride, that can be placed into drinkable water. The EH-101 (HB-101) can be initially placed into a breakable inner compartment within the hydrogen permeable container. This compartment can be easily broken by simple squeezing just prior to placing the device into the water that is intended to have its hydrogen content increased. The increased hydrogen content can be assessed by the capacity of the water to decolorize a potassium permanganate test sample.
Owner:MARTIN WILLIAM JOHN
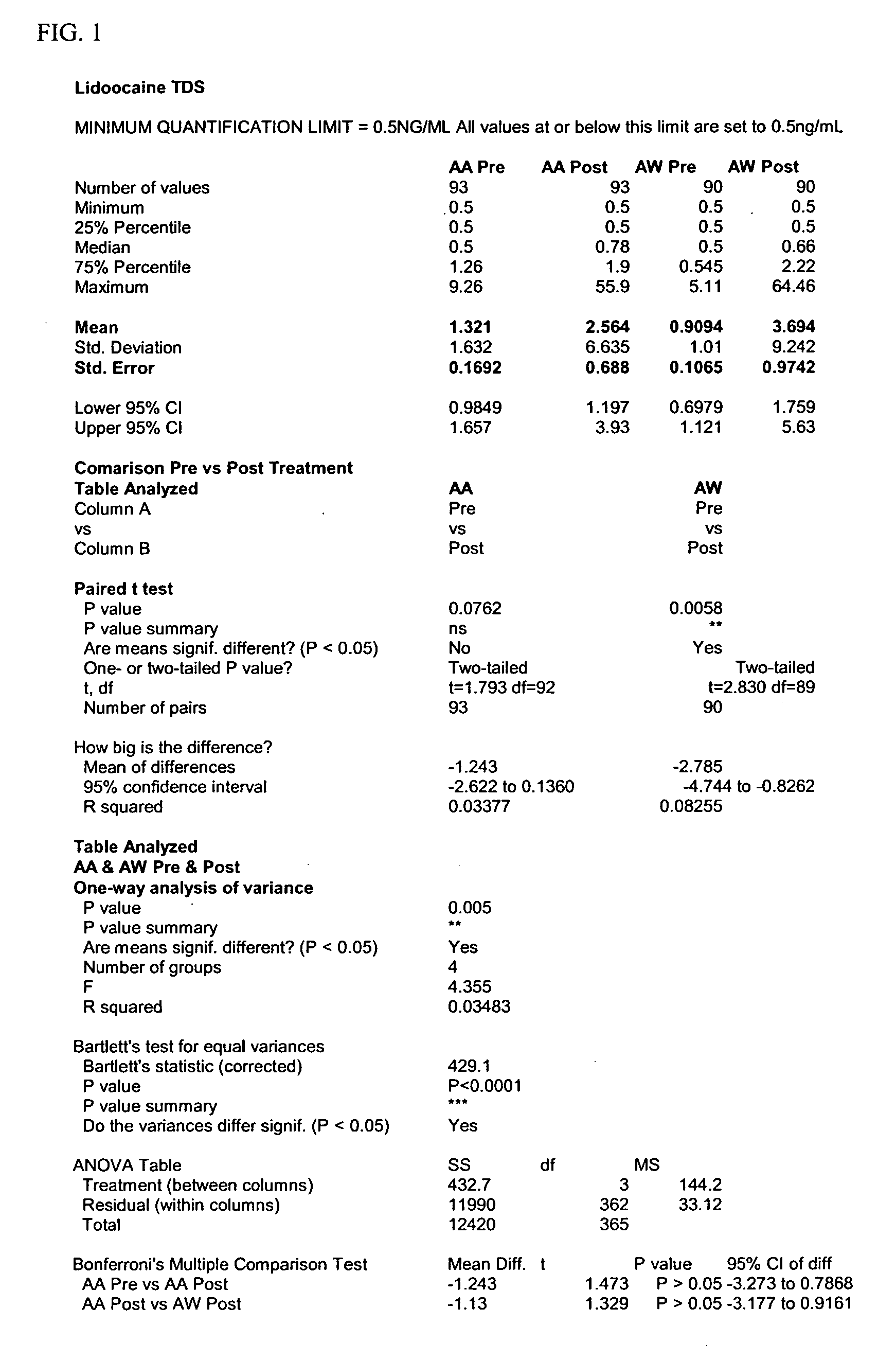
Compositions for rapid and non-irritating transdermal delivery of pharmaceutically active agents and methods for formulating such compositions and delivery thereof
InactiveUS20030104040A1Effective and safe and rapid transmigrationIntact skinCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsActive agentDrug activity
A transdermal delivery system (TDS) for use in treatment of living bodies may be applied as an open (liquid, gel) or closed (patch) article. The TDS is composed of a particular active agent which dictates an associated selection of certain solvents, solvent modifiers, solute modifiers and skin stabilizers with which the medicament forms a true solution that rapidly crosses the skin barrier. The associated selection of the particular solvents, solvent modifiers, solute modifiers and skin stabilizers is based on a balancing of the molecular properties of all the components against the molecular properties of all the components plus the particular active agent. The TDS may also include a source of cellular energy to induce CAMP or cGMP. The TDS improves delivery of active agents having a molecular weight greater than 340 Daltons and increases dosage above 0.25 mg / day for such active agents.
Owner:TRANSDERMAL DELIVERY SOLUTIONS
Methods for increasing cellular energy expenditure
InactiveUS20080031968A1Increased cellular energy expenditureImprove metabolic controlCompound screeningApoptosis detectionG protein-coupled receptorAgonist
The present invention is directed to methods of treating a human for a variety of conditions by administering an agonist of the G protein coupled receptor TGR5. In addition, the invention includes methods for determining whether a test compound is likely to be effective in treating one of these conditions by assaying it for its ability to raise intracellular iodothyronine deiodinase levels or for its ability to bind to and activate TGR5.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Nonsymbiotic plant hemoglobins to maintain cell energy status
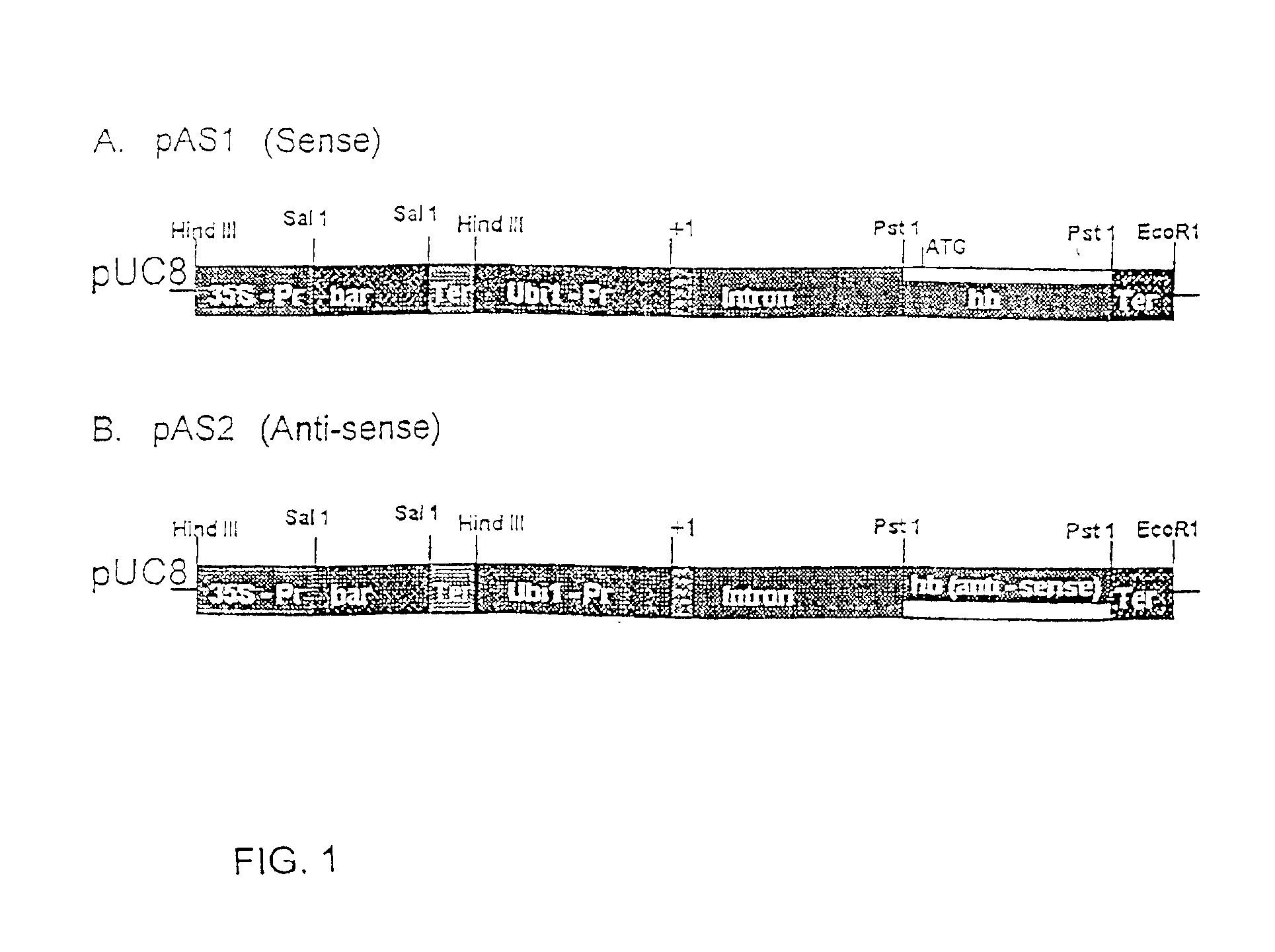
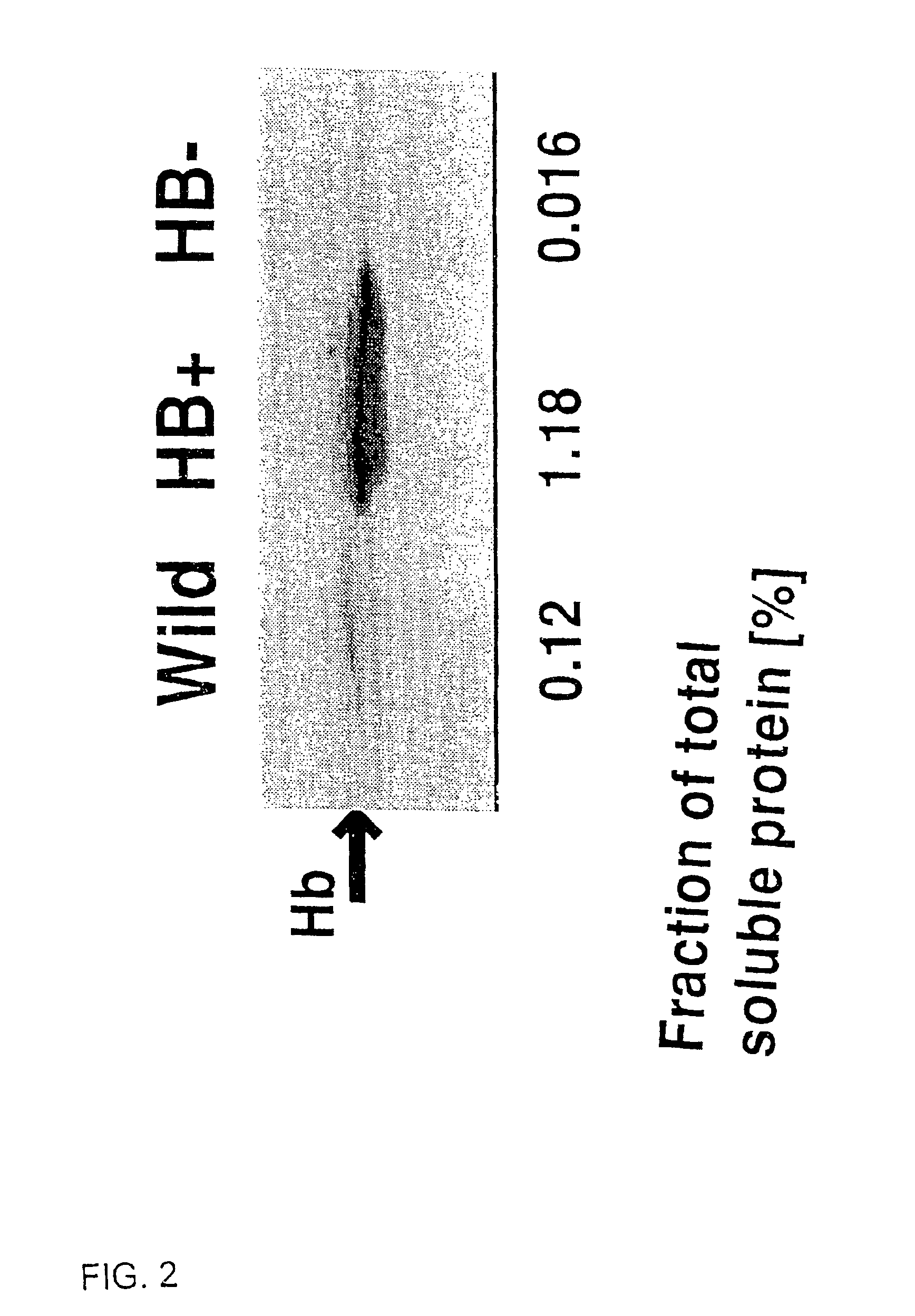
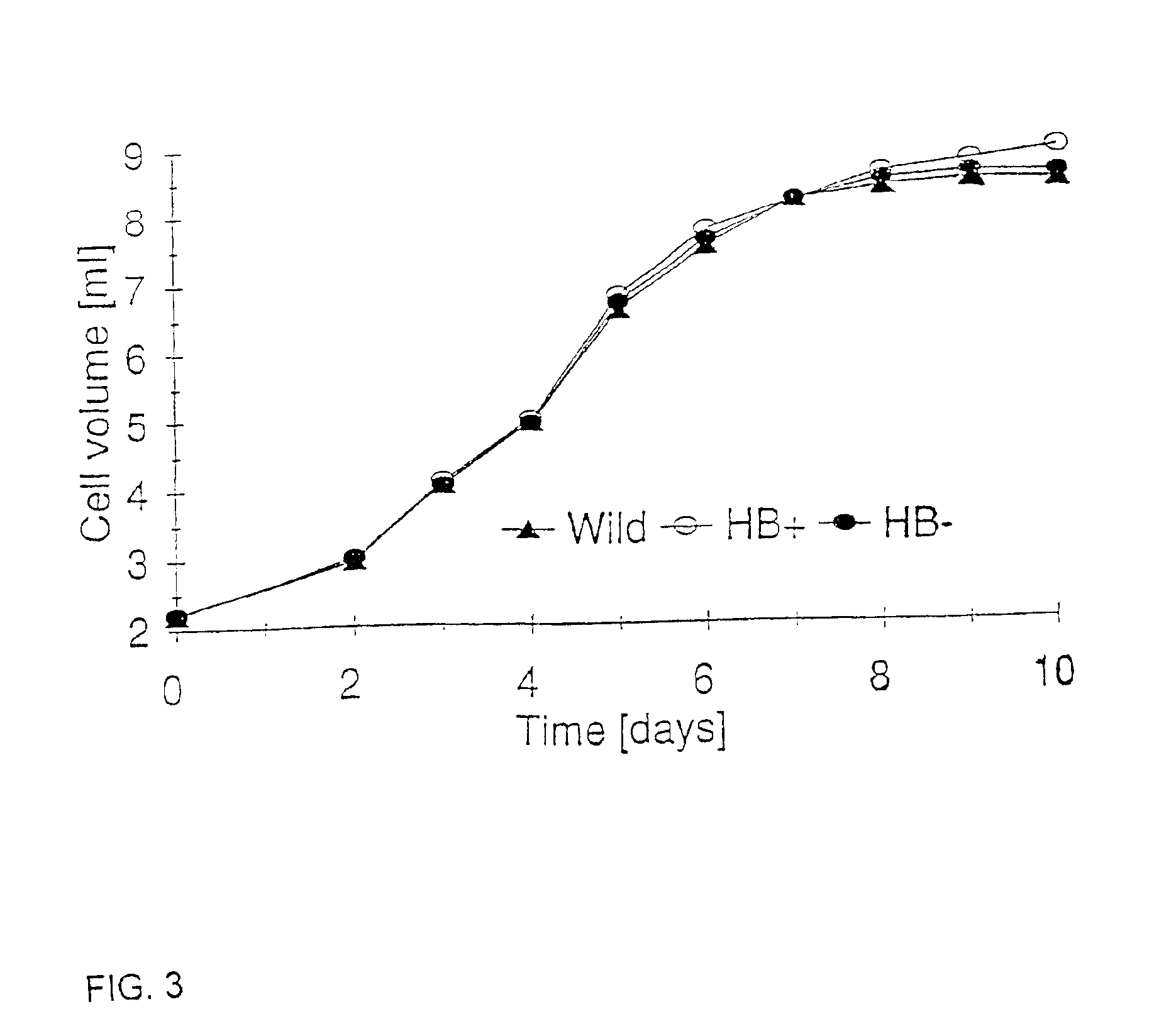
InactiveUS6936749B1Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesBacteriaSubstrate-level phosphorylationProgenitor
Nonsymbiotic hemoglobins are broadly present across evolution; however, the function of these proteins is unknown. Cultured maize cells have been transformed to constitutively express a barley hemoglobin gene in either the sense (HB+) or antisense (HB−) orientation. Hemoglobin protein in the transformed cell lines was correspondingly higher or lower than in wild type cells under normal atmospheric conditions. Limiting oxygen availability, by placing the cells in a nitrogen atmosphere for 12 hours, had little effect on the energy status of cells constitutively expressing hemoglobin, but had a pronounced effect on both wild type and HB− cells, where ATP levels declined by 27% and 61% respectively. Energy charge was relatively unaffected by the treatment in HB+ and wild type cells, but was reduced from 0.91 to 0.73 in HB− cells suggesting that the latter were incapable of maintaining their energy status under the low oxygen regime. Similar results were observed with P. aeruginosa cells transformed with an Hb expression vector. It is suggested that nonsymbiotic hemoglobins act to maintain the energy status of cells in low oxygen environments and that they accomplish this effect by promoting glycolytic flux through NADH oxidation, resulting in increased substrate level phosphorylation. Nonsymbiotic hemoglobins are likely ancestors of an early form of hemoglobin that sequestered oxygen in low oxygen environments, providing a source of oxygen to oxidize NADH to provide ATP for cell growth and development. This in turn suggests that cells containing increased levels of Hb protein will survive longer under low oxygen tension or high energy demand.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
Molecules to perfect HbA1c levels
InactiveUS9254250B1Enhanced utilization and regulationFavorable cellular milieuCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCellular respirationAcute hyperglycaemia
This invention is of particular use to patients with Diabetes Mellitus. It uses alkyl analogs of the methyl pyruvate (MP) family to provide energy and improve insulin and glucose homeostasis via accelerated intracellular delivery of protons and ATP from each MP. The energy upregulates cellular cross talk and networking resulting in a surge of ATP enabling NADH (via glycolysis) that enables pancreatic islet cells to obtain increased ATP allowing excess insulin manufacture. This process improves cellular respiration and expedites protein, lipid and hormone manufacture. The increased energy also enables telomeres and delays Hayflick limit. Instead of cellular repair, silence, or apoptosis, energy is allocated for cell / organ function. This invention curbs inflammation and ROS by idealizing cellular respiration and diminishing hyperglycemia. In turn a reduction of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), lessened target RNA and nucleic acid toxins, i.e., diminished HbA1c occurs. By decreased drain of cellular energy, genomic function improves.
Owner:NEVILLE PHARMA
Composition for enhancing cellular energy
InactiveUS7645742B2Increase ease of administration and bioavailabilityIncreasing subject 's relative intensityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPyruvic acid
Owner:ADVOCARE INT
Method of generating hydrogen and of selectively transferring the generated hydrogen to drinking water as a potential source of alternative cellular energy (ACE)
InactiveUS20100008849A1Increased hydrogen productionImprove usabilityHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAntioxidantReverse osmosis
Consuming water with increased hydrogen content can provide clinical benefits to humans and animals through a non-mitochondria alternative cellular energy (ACE) pathway and also as an antioxidant. This application discloses that the hydrogen content of drinking water can be safely increased by placing into the water a hydrogen generating device, such as a mixture of metallic magnesium and magnesium chloride containing solution, whereby the device allows for the selective passage of the generated hydrogen but restricts the passage of magnesium and magnesium ions. This partitioning of hydrogen from magnesium ions is achieved by using either reverse osmosis membrane or low density plastic material such as polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC or Saran), to create a sealed container of the magnesium and magnesium chloride, that can be placed into drinkable water. The magnesium chloride can be initially placed into a breakable inner compartment within the hydrogen permeable container. This compartment can be easily broken by simple squeezing just prior to placing the device into the water that is intended to have its hydrogen content increased. The increased hydrogen content can be assessed by the capacity of the water to decolorize a potassium permanganate test sample.
Owner:MARTIN WILLIAM JOHN
Organ and biological tissue preservation cold storage solution
InactiveUS20020115634A1Prolonged plasma half-lifePronounced growth-suppressing propertyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineOxygen
Cold storage solutions for the preservation of organs and biological tissues prior to implantation, including a cellular energy production stimulator under anaerobic conditions, an anti-inflammatory agent, and an oxygen free radical scavenger.
Owner:ORGAN RECOVERY SYST +1
Method and composition for treating mammalian diseases and injuries which cause pain, erythema, swelling, crusting, ischemia scarring and excess white blood cell infiltration
InactiveUS7122578B2Reducing undesired inflammatory responseIncrease cellular metabolic rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCellular componentAntioxidant
A method for treating the disease state in mammals caused by mammalian cells involved in the inflammatory response is disclosed. Mammalian cells participating in the inflammatory response are contacted with an inflammatory suppressor selected from the group consisting of alpha-keto acids and their salts which reduce the undesired inflammatory response and is an antioxidant. The inflammatory suppressor may further provide a cellular energy source and be a building block in the cellular synthesis of other cellular components. Compositions for reducing and treating undesired inflammatory response such as pain, swelling, erythema, crusting, scarring, itching, also disclosed.
Owner:MARTIN ALAIN
Treatment of type ii diabetes and diabetes-associated diseases with safe chemical mitochondrial uncouplers
InactiveUS20130231312A1Effective of plasma glucose levelHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseSide effect
This application discloses methods for treating, preventing and / or alleviating the symptoms of type II diabetes and diabetes-related disorders or complications. The invention provides a novel approach to treating and managing disorders and symptoms related to elevated plasma glucose concentrations and insulin resistance, characterized by few side effects and low toxicity. In particular, the invention provides 2-hydroxy-benzoic anilide compounds and derivatives, and compositions thereof, which can control blood-glucose and increase insulin sensitivity by reducing plasma glucose concentration and cellular energy efficiency.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Coenzyme Q10, lactoferrin and angiogenin compositions and uses thereof
Methods of enhancing the bio-availability of coenzyme Q10, and methods of supporting the cardiovascular system to accommodate the increase in cellular energy synthesis as a result of the bio-availability of coenzyme Q10 are described. Compositions which include coenzyme Q10, lactoferrin and / or angiogenin are described for use in the related methods, for multi-functional health applications.
Owner:NAIDU LP
Methods and compositions for preserving tissues and organs
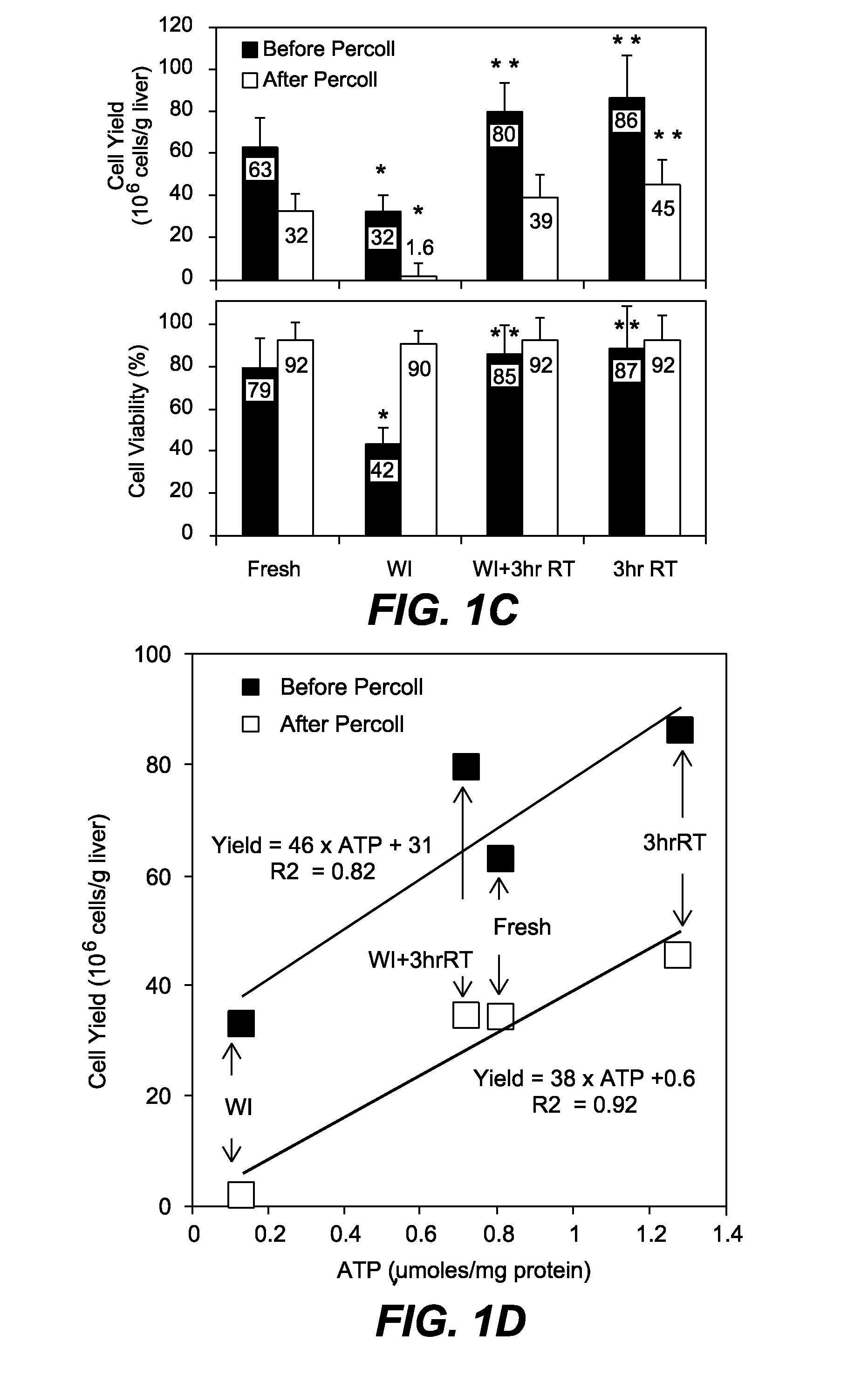
ActiveUS20140030231A1Extend and preserve viabilityReduces reperfusionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementOrgan ViabilityMetabolic Suppression
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to determine viability of an organ for transplantation and other medical purposes. One aspect of the invention relates to a method for assessing the viability of an organ by measuring the energy parameters to determine the energy level of the organ by determining the stored cellular energy (e.g., ATP levels), and / or energy consumption over a particular time period of viability. The energy parameters can be compared to reference energy parameters as a highly accurate and reliable prediction of viable cell yield, and organ viability. Another aspect of the invention relates methods to preserve or extend the time period of viability of an organ any combination of (i) preservation perfusion of the organ to prevent ischemic damage, (ii) chemical metabolic suppression of the organ e.g., using metabolic suppressants, (iii) metabolic suppression by physical or environmental conditions, e.g., sub-zero non-freezing storage.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Composition and methods for the treatment of cancer
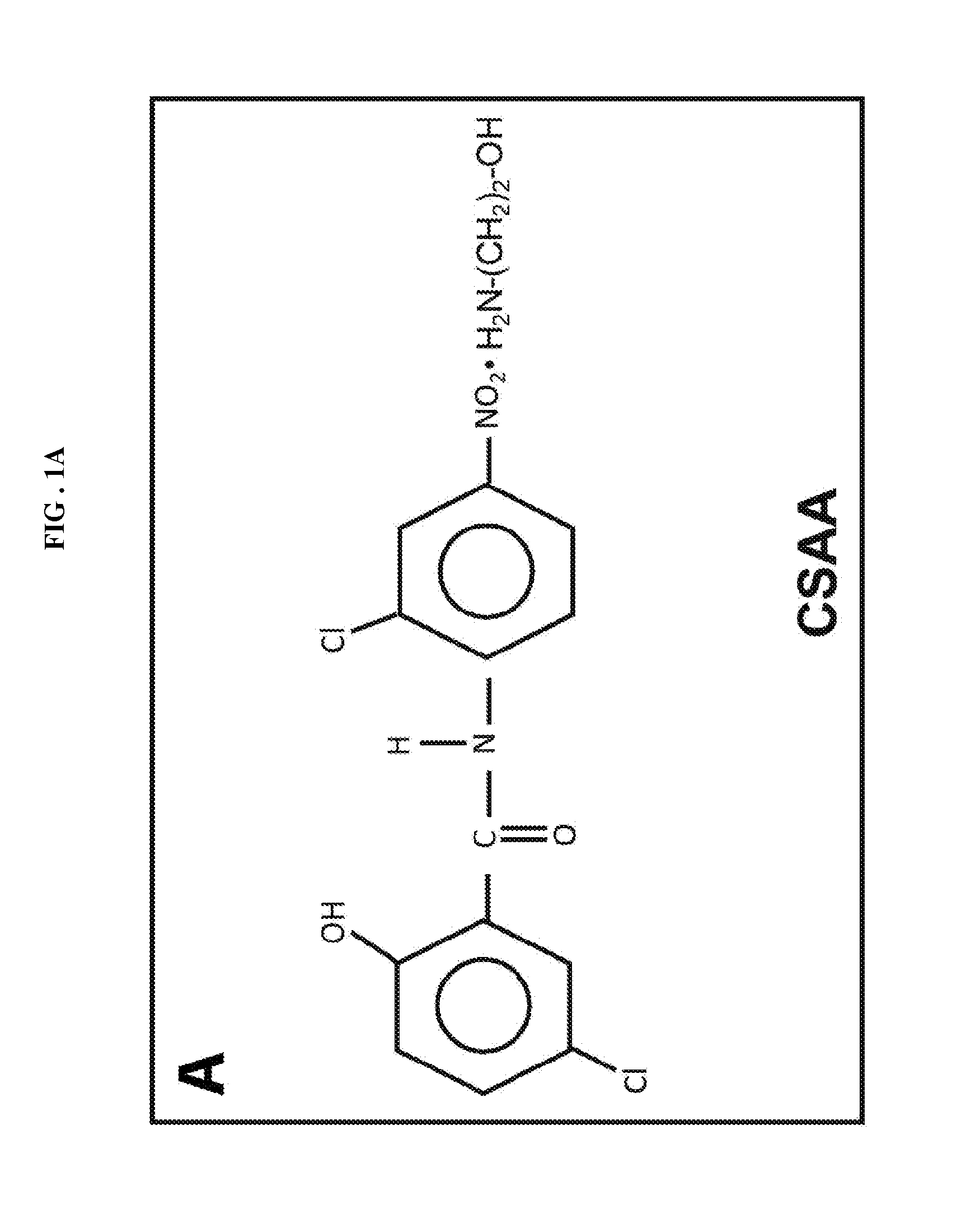
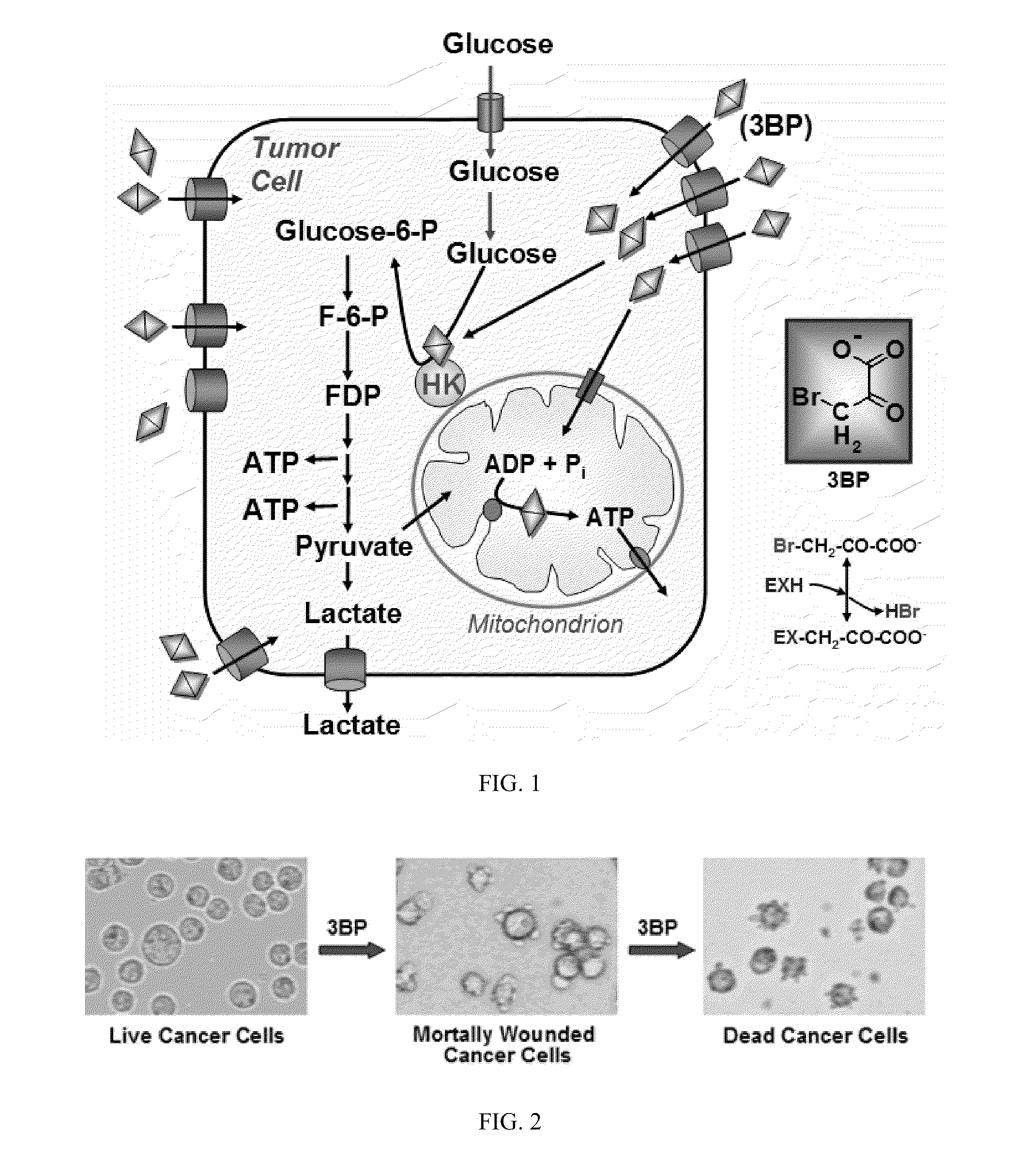
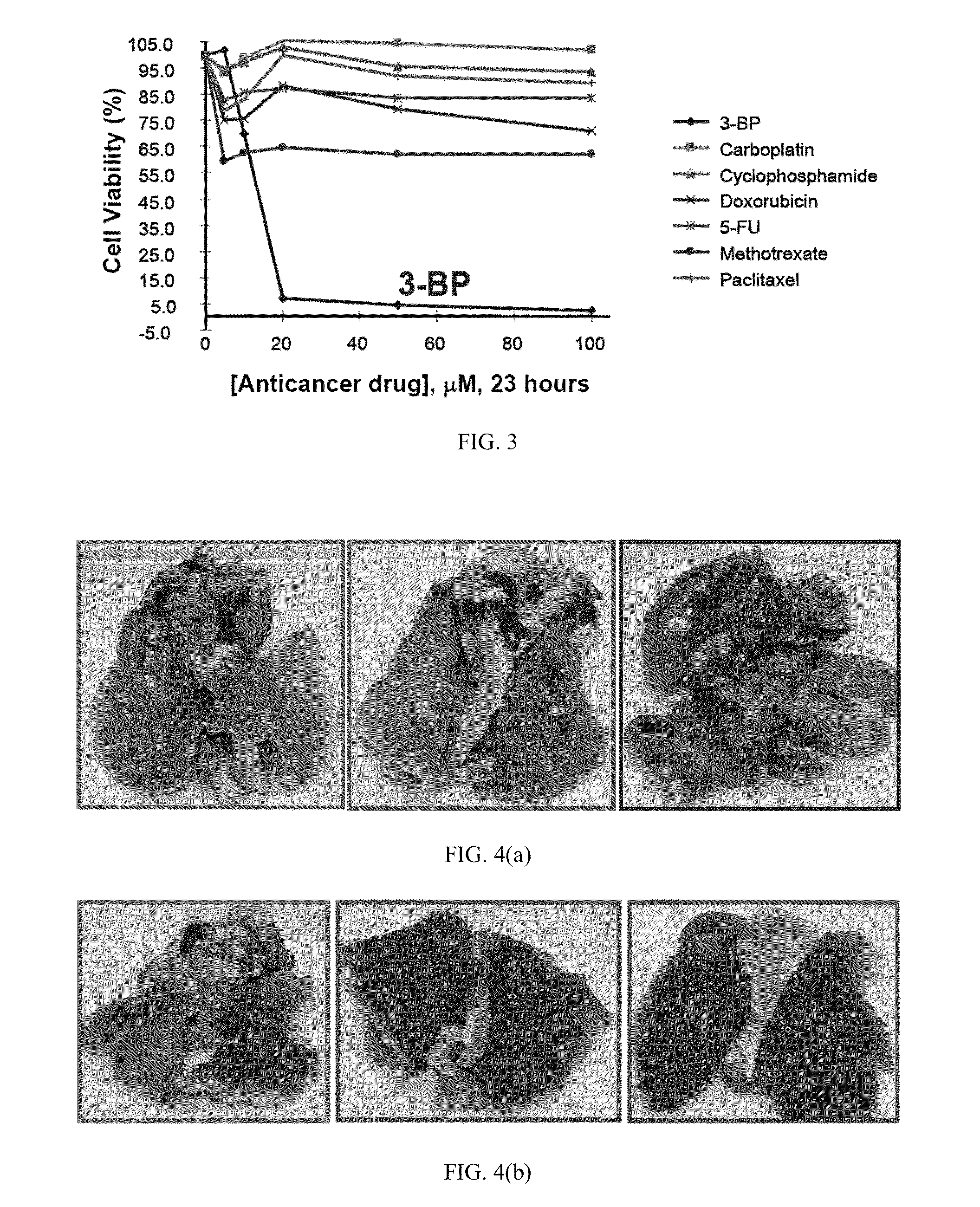
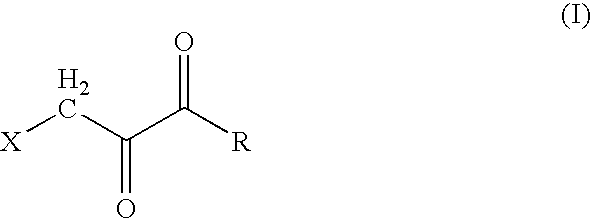
The present invention discloses anti-cancer compositions, and associated methods, including an anti-cancer composition comprising: a cellular energy inhibitor having the structure according to formula Iwherein X is selected from the group consisting of: a nitro, an imidazole, a halide, sulfonate, a carboxylate, an alkoxide, and amine oxide; and R is selected from the group consisting of: OR′, N(R″)2, C(O)R′″, C1-C6 alkyl, C6-C12 aryl, C1-C6 heteroalkyl, a C6-C12 heteroaryl, H, and an alkali metal; where R′ represents H, alkali metal, C1-C6 alkyl, C6-C12 aryl or C(O)R′″, R″ represents H, C1-C6 alkyl, or C6-C12 aryl, and R′″ represents H, C1-C20 alkyl or C6-C12 aryl. The anti-cancer composition can additionally comprise at least one sugar, which stabilizes the cellular energy inhibitor by substantially preventing the inhibitor from hydrolyzing. Also, the anti-cancer composition can comprise a glycolysis inhibitor. Further, the anti-cancer composition can comprise a biological buffer that is present in an amount sufficient to at least partially deacidify the cellular energy inhibitor and neutralize metabolic by-products of the cellular energy inhibitor.
Owner:KODISCOVERY LLC
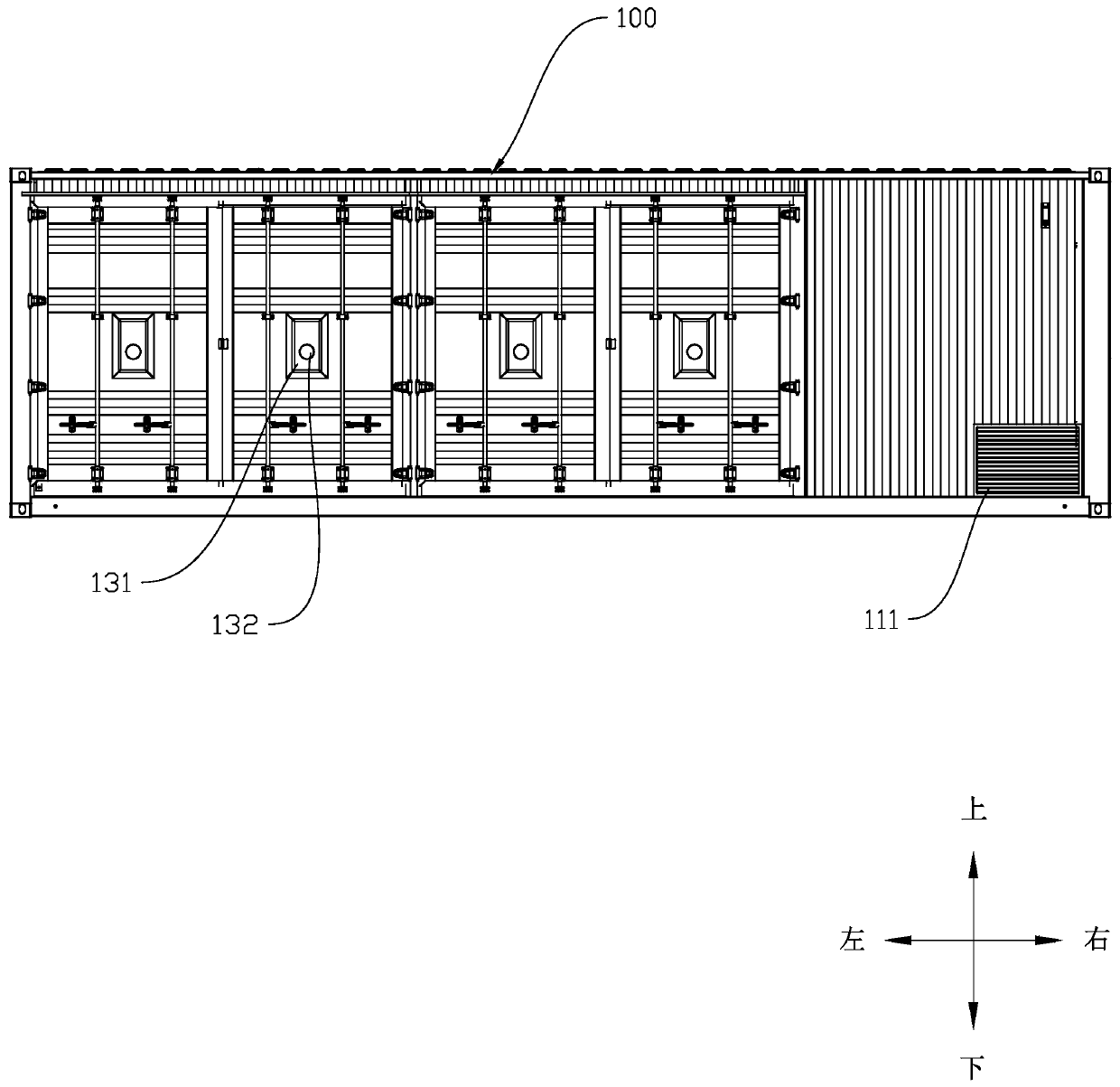
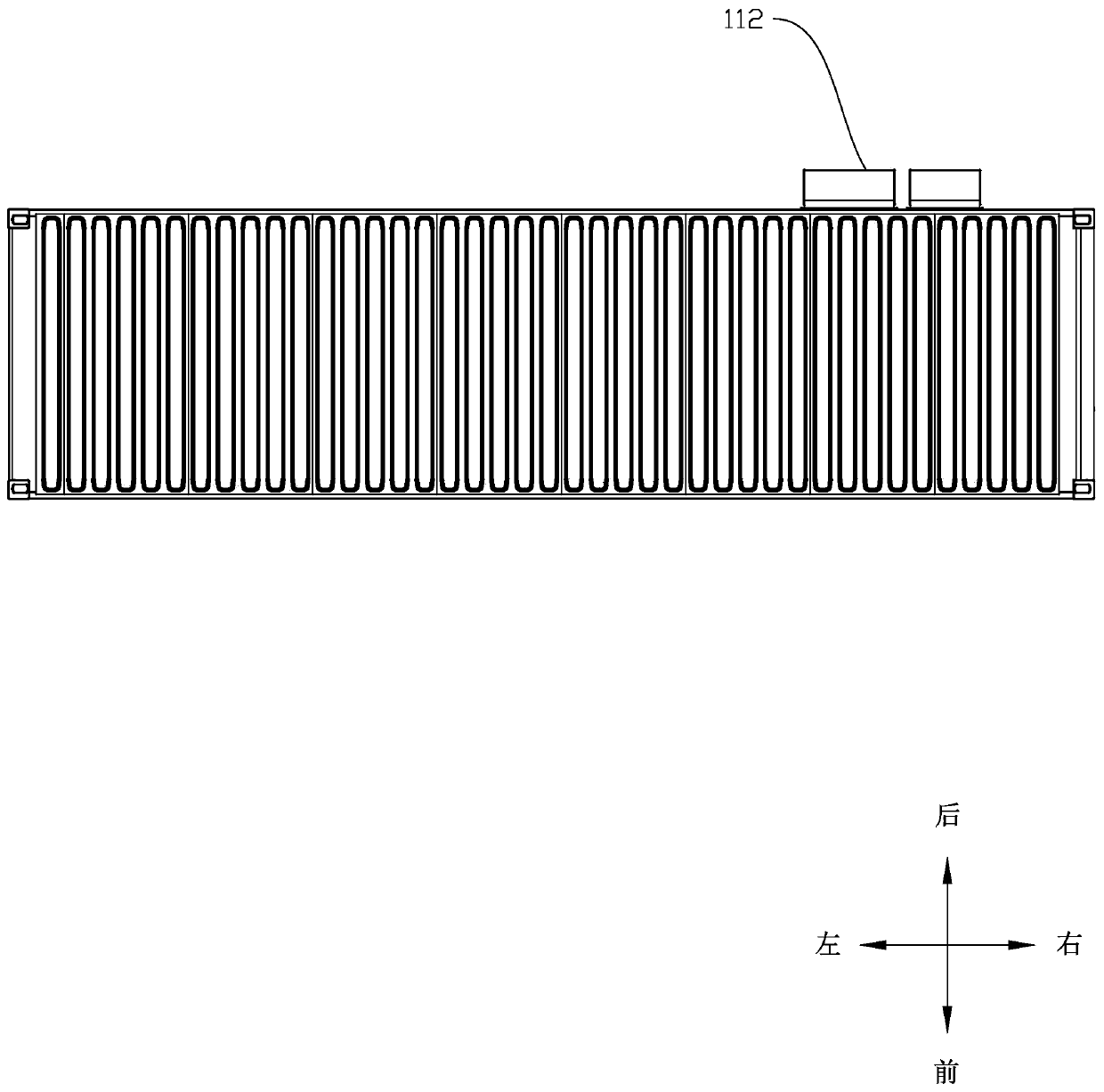
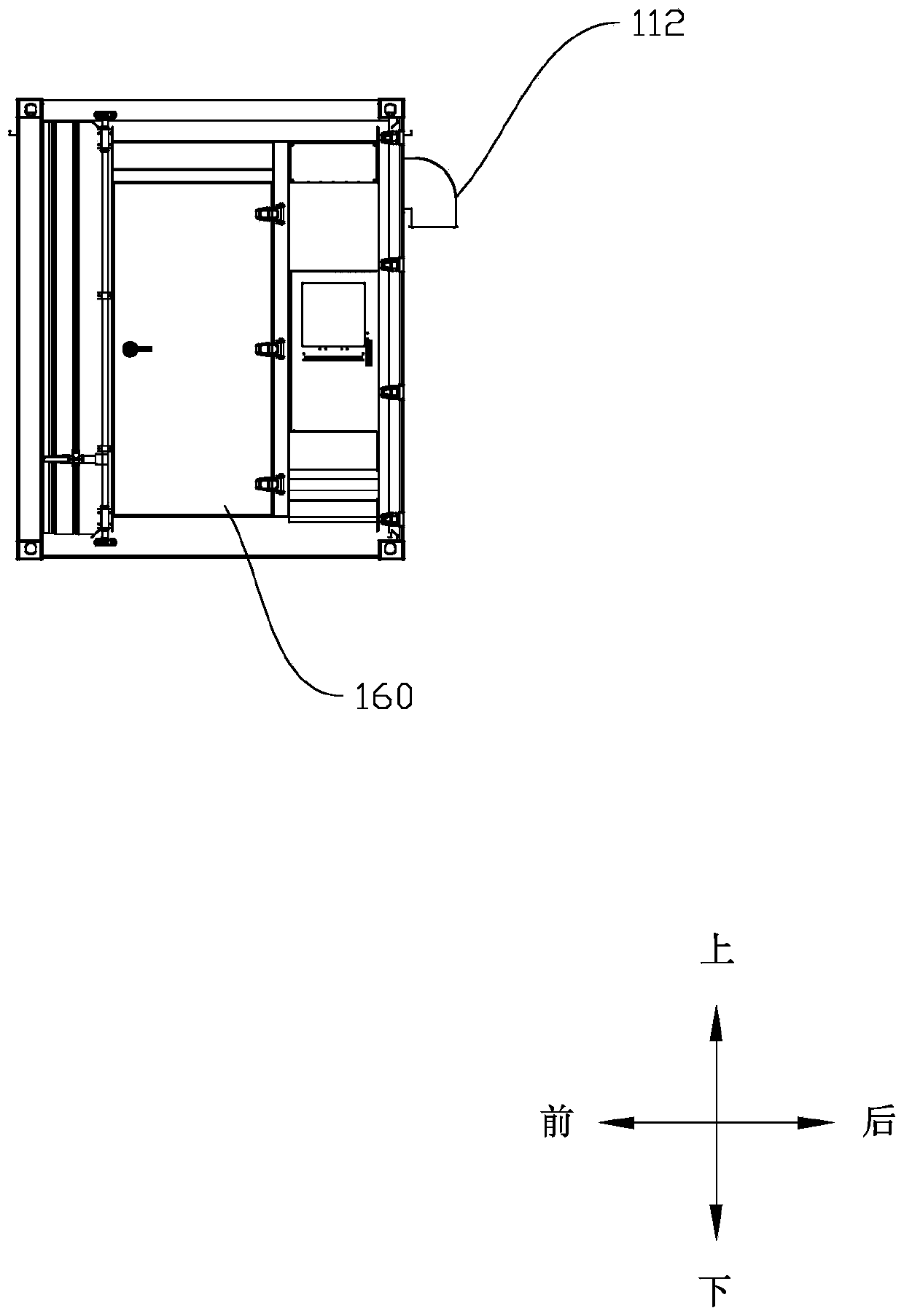
Cellular energy storage container
PendingCN111326824AGuaranteed performanceSmall temperature differenceSecondary cellsFire rescueCold airAir volume
The invention discloses a cellular energy storage container. The cellular energy storage container comprises: a container body, wherein a battery compartment is arranged in the container body, and thebattery compartment is divided into a plurality of unit compartments; battery racks, wherein each unit bin is internally provided with the corresponding battery rack; and heat dissipation devices, wherein each unit bin is internally provided with the corresponding heat dissipation device, each heat dissipation device comprises an air conditioner and an air duct wall, an air outlet of each air conditioner is communicated with an air inlet of the corresponding air duct wall, and an air outlet of each air duct wall faces the battery rack. According to the invention, each unit bin is an independent space, each unit bin is subjected to independent heat dissipation by a heat dissipation device, even if the heat emitted by the battery modules in the unit cabins is inconsistent, the battery modules in the unit cabins can be located in a temperature area with stable performance by adjusting the air volume of the air conditioner and adjusting the temperature of cold air blown out by the air conditioner, and then the performance of the energy storage container is guaranteed on the whole.
Owner:SHENZHEN CLOU ELECTRONICS
Compositions and methods for preventing infection of a wound and for advancing the healing process
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods that are effective in controlling and preventing bacterial, viral and fungal infections in the living tissue of plants, humans and animals, and in advancing the healing process for wounds to that tissue. The disclosed compositions comprise a biocidal system, a pH buffer, and one or more of a surfactant, a cellular energy supplement, an inflammation reducer, a clotting agent, an electrolytic system, a lattice forming system, and for plants a fungicide, all in an aqueous composition.
Owner:NBIP
Energy Charged Liquids to Enhance Enerceutical Activation of the Alternative Cellular Energy (ACE) Pathway in the Therapy of Diseases
InactiveUS20120152755A1Improve abilitiesMore ACEElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesTissue repairUltraviolet lights
The alternative cellular energy (ACE) pathway provides a non-immunological defense mechanism against infectious diseases and can also function as an effective, non-scarring, tissue repair mechanism in response to injury. The ACE pathway can be activated using energy obtained from the ultraviolet light illumination of neutral red dissolved in alcohol. The effectiveness of the alcohol used in this procedure is significantly increased by first bubbling air containing “Water Gas” (otherwise referred to as Brown's Gas or HHO) through the alcohol. The Water Gas is considered as providing an additional charge to the alcohol. Water Gas can similarly be used to charge water and other liquids and to, thereby, increase the liquid's capacity to interact with various dyes, such as neutral red, and with other enerceuticals, which are regarded as being representative of the body's ACE pigments. Various uses are disclosed for using Water Gas charged alcohol and Water Gas charged water, for the therapeutic activation of the ACE pathway.
Owner:MARTIN WILLIAM JOHN
Composition and application thereof to preparation of skin care products for regulating skin biorhythm
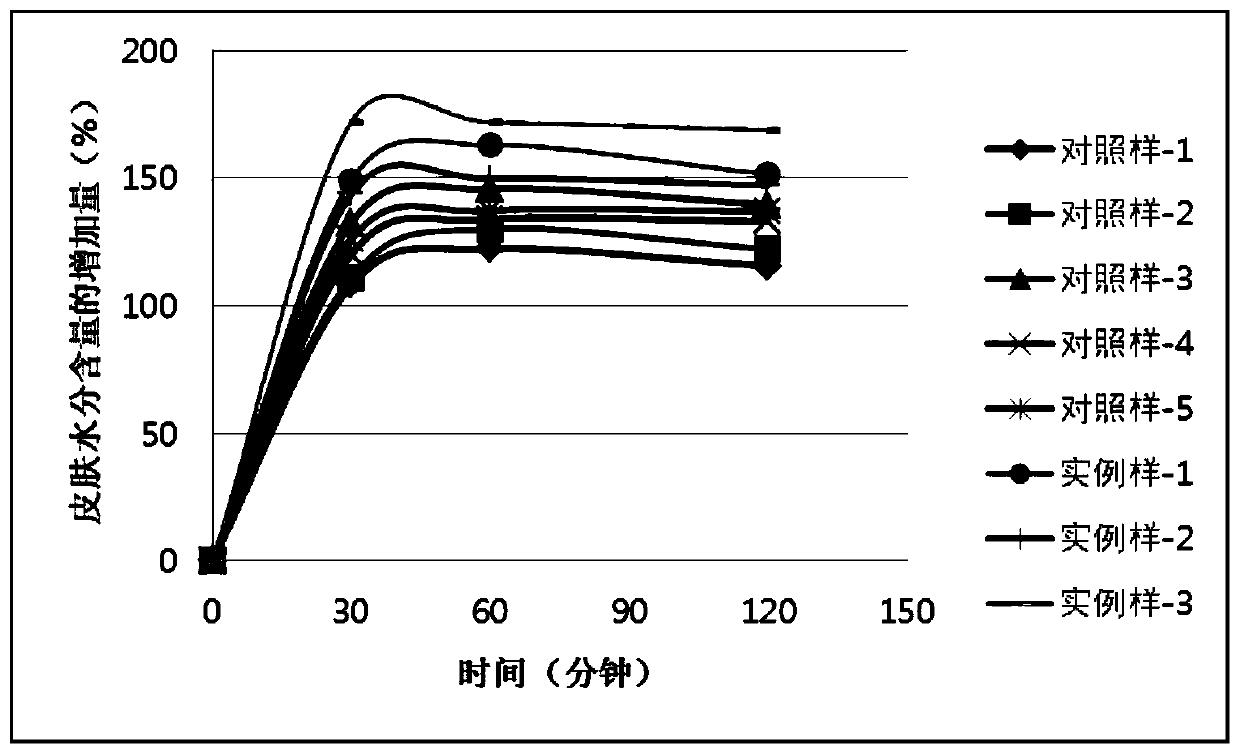
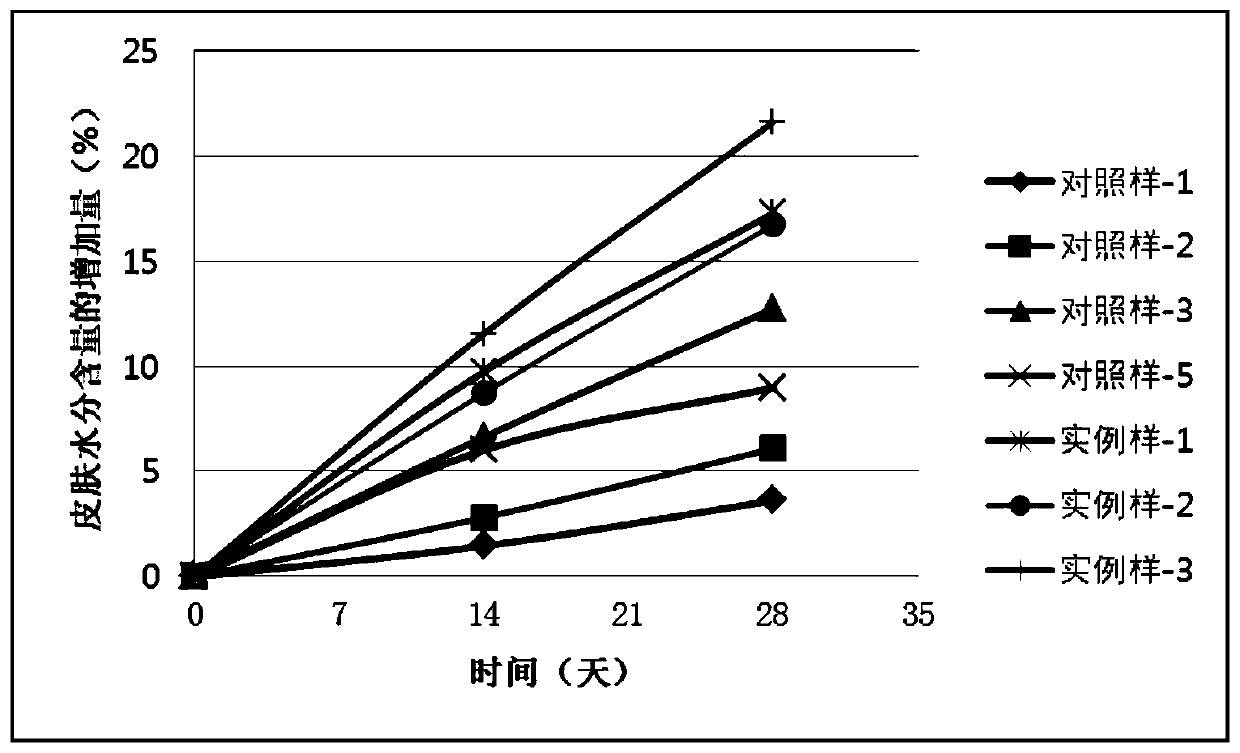
ActiveCN110448478AGood moisturizingPromotes cellular energy synthesisCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycoproteinAmino acid
The invention relates to the technical field of skin care products, in particular to a composition and an application thereof to preparation of skin care products for regulating skin biorhythm. The composition provided by the invention comprises adenosine, a skin conditioning agent A containing glycoprotein and amino acids, and a skin conditioning agent B containing glutamylamidoethyl Imidazole. Through interaction and inter-promotion of the components, favorable effects of replenishing water, moisturizing and promoting cell energy synthesis can be realized. The composition is used for preparing cosmetics, and can solve a series of problems of skin and muscle of people staying up later or all night.
Owner:HUNAN YUJIA COSMETICS MFG CO LTD
Transdermal delivery system
InactiveUS20060121103A1Improved release profileReduce absorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAbsorbent padsSolventCellular energy
A transdermal delivery system (TDS) for use in treatment of living bodies may be applied as an open (liquid, gel) or closed (patch) article. The TDS is composed of a particular active agent which dictates an associated selection of certain solvents, solvent modifiers, solute modifiers and skin stabilizers with which the medicament forms a true solution that rapidly crosses the skin barrier. The associated selection of the particular solvents, solvent modifiers, solute modifiers and skin stabilizers is based on a balancing of the molecular properties of all the components against the molecular properties of all the components plus the particular active agent. The TDS includes solvent complex modifiers for regulating the rate of absorption of the active agent. The TDS may also include a source of cellular energy to induce CAMP or cGMP. The TDS improves delivery of active agents having a molecular weight greater than 340 Daltons and increases dosage above 0.25 mg / day for such active agents.
Owner:KIRBY KENNETH +1
Cell nutrition enhancing health product preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105341917AImprove regenerative abilityIncrease supplyYeast food ingredientsNatural extract food ingredientsBiotechnologySide effect
The present invention discloses a cell nutrition enhancing health product preparation and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of health care products, the cell nutrition enhancing health product preparation is made from the following materials: wall-broken ganoderma lucidum spore powder, selenium-rich yeast, dendrobium officinale freeze-dried powder, ganoderma lucidum extract, astragalus extract, wolfberry extract, rhizoma polygonati powder, Ganoderma sinensis powder, Antrodia powder, American ginseng powder, lentinan, pine pollen, spirulina powder and royal jelly powder, the cell nutrition enhancing health product preparation can activate the electronic delivery system on mitochondrial inner membrane, increase cell mitochondrial ATP production, fundamentally supplement cellular energy, eliminate cell fatigue, and enhance cell regeneration ability, and is free of side effects, by insisting on taking, the cell nutrition enhancing health product preparation helps to enhance physique and improve health state, and is suitable for the sub-health crowd to take.
Owner:安徽千方生物科技有限公司
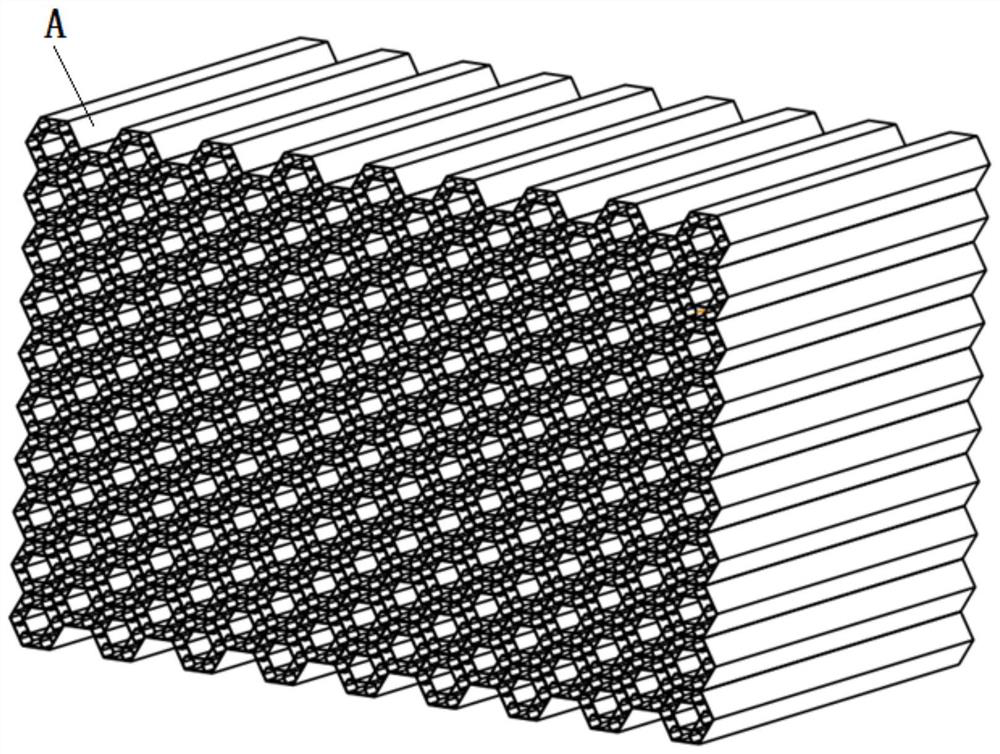
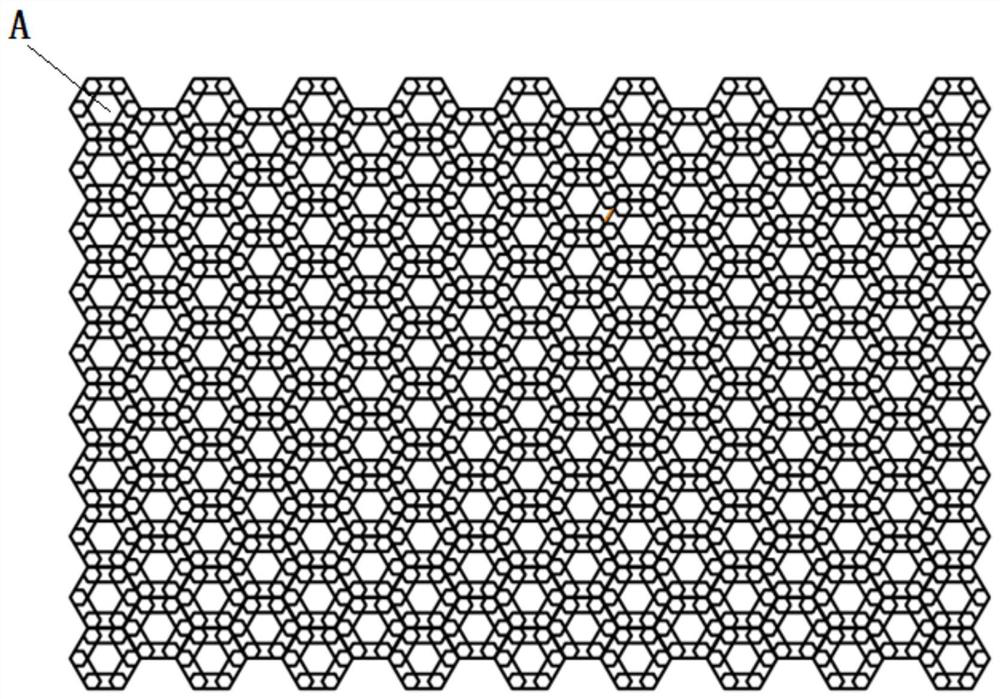
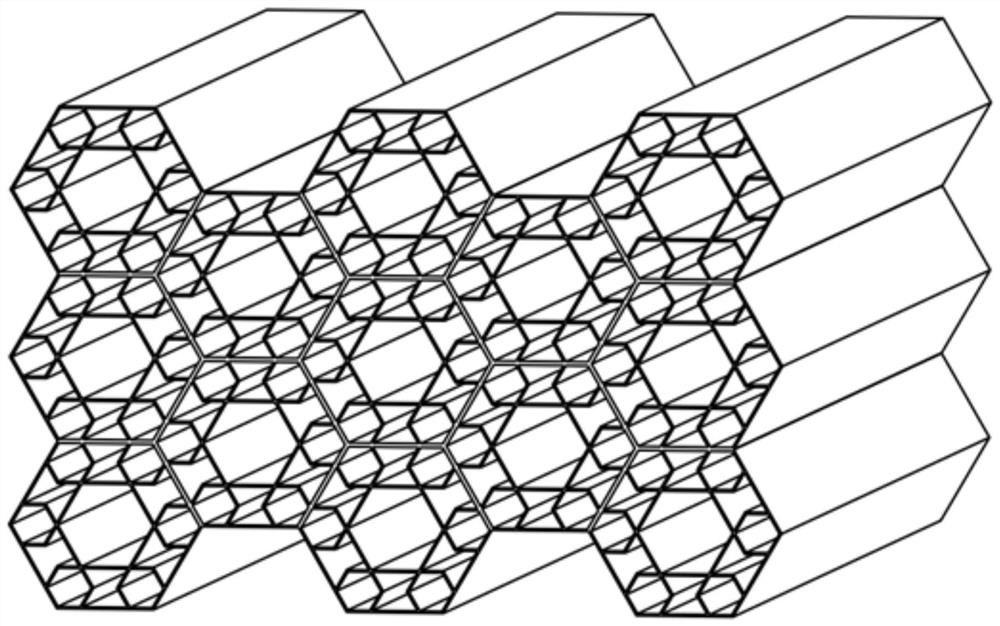
Bionic composite energy absorption structure with impact angle adaptability
ActiveCN112224163ASolve the problem of energy absorptionImprove crashworthinessBumpersEngineeringCellular energy
A bionic composite energy absorption structure with impact angle adaptability comprises micro-cellular energy absorbers which are sequentially arranged in the X direction and the Y direction, whereineach micro-cellular energy absorber comprises a first regular hexagonal prism energy absorber, a second regular hexagonal prism energy absorber and a V-shaped connecting arm. The second regular hexagonal prism energy absorber is arranged in the first regular hexagonal prism energy absorber, and two opposite side edges of the second regular hexagonal prism energy absorber and two opposite side edges of the first regular hexagonal prism energy absorber are located on the same straight line; every two V-shaped connecting arms in the twelve V-shaped connecting arms form a group, one ends of everytwo V-shaped connecting arms are fixed to the side edge of the second regular hexagonal prism energy absorber after being in butt joint, the other ends of the two V-shaped connecting arms are fixed tothe two side faces of the first regular hexagonal prism energy absorber respectively, and six regular hexagonal prism reverse resistance energy absorption units are formed; a hexagonal negative poisson ratio energy absorption unit with the two sides concaved inwards is arranged between every two adjacent regular hexagonal prism reverse resistance energy absorption units. The structure has excellent energy absorption performance under the working conditions of axial and large-angle collision.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods for Increasing the Kinetic Activity of Alcohol, Water and Other Liquids, so as to Render the Liquids More Useful in Enhancing the Alternative Cellular Energy Pathway in the Prevention and Therapy of Diseases
InactiveUS20120207850A1Easily discernable increased activityHigh activityCosmetic preparationsBiocideDiseaseSound energy
The kinetic energy of liquids can be increased by several methods described in the present application. The methods include exposure to a magnetic field provided by a rotating or vibrating magnet; exposure to an electromagnetic field provided by an electrical power cord; and placement of the liquid within the vicinity of electrostatic energy and / or sound energy. A previously described method is the bubbling of electrolysis-generated water gas (Brown's Gas) into the liquid. The increased kinetic energy can be demonstrated using a previously described neutral red dye kinetic assay (NR-Kinetic assay). Energized liquids include alcohol, alcoholic beverages and water. The use of the energized solutions to enhance the alternative cellular energy (ACE) pathway in the therapy of individuals is described.
Owner:MARTIN WILLIAM JOHN
Enerceutical mediated activation of the Alternative Cellular Energy (ACE) pathway in the therapy of diseases
InactiveUS20090280193A1Easy to moveSimplifying assayBiocideDrug compositionsNutritional deficiencyFluorescence
Alternative cellular energy pigments (ACE-pigments) provide a source of cellular energy other than that provided through the oxidative metabolism of foods, or in the case of plants and certain bacteria, through the process of photosynthesis. In some patients, ACE pigments exist in a form that can be further energized or activated using ultraviolet (UV) light, especially if the reaction is initially triggered by the presence of suitable dyes, such as neutral red. A method is described to further enhance the activation of the ACE pathway in humans and animals deprived of ACE. The method comprises using natural or man-made sources of ACE products (enerceuticals), with or without the inclusion of a suitable dye, such as neutral red; or other activating components, such as magnesium chloride; with the combined mixture being put into a UV transparent container, such as a plastic bag, or placed on some other material, which can be laid onto the skin and illuminated with a UV light source. The process of activating the ACE pathway is evidenced by UV inducible fluorescence seen within areas of the patients' skin and / or mucus membranes. This fluorescence fades as the ACE pathway becomes fully activated. Activating the ACE pathway can have therapeutic benefits in various infectious and non-infectious diseases including illnesses attributed to infections with stealth adapted and conventional viruses and diseases attributed to an inadequacy of the mitochondria and associated metabolic pathways, including states of hypoxia and nutritional deficiencies.
Owner:MI HOPE
Metabolism regulating and liver protecting nutritional supplement, preparation method and applications thereof
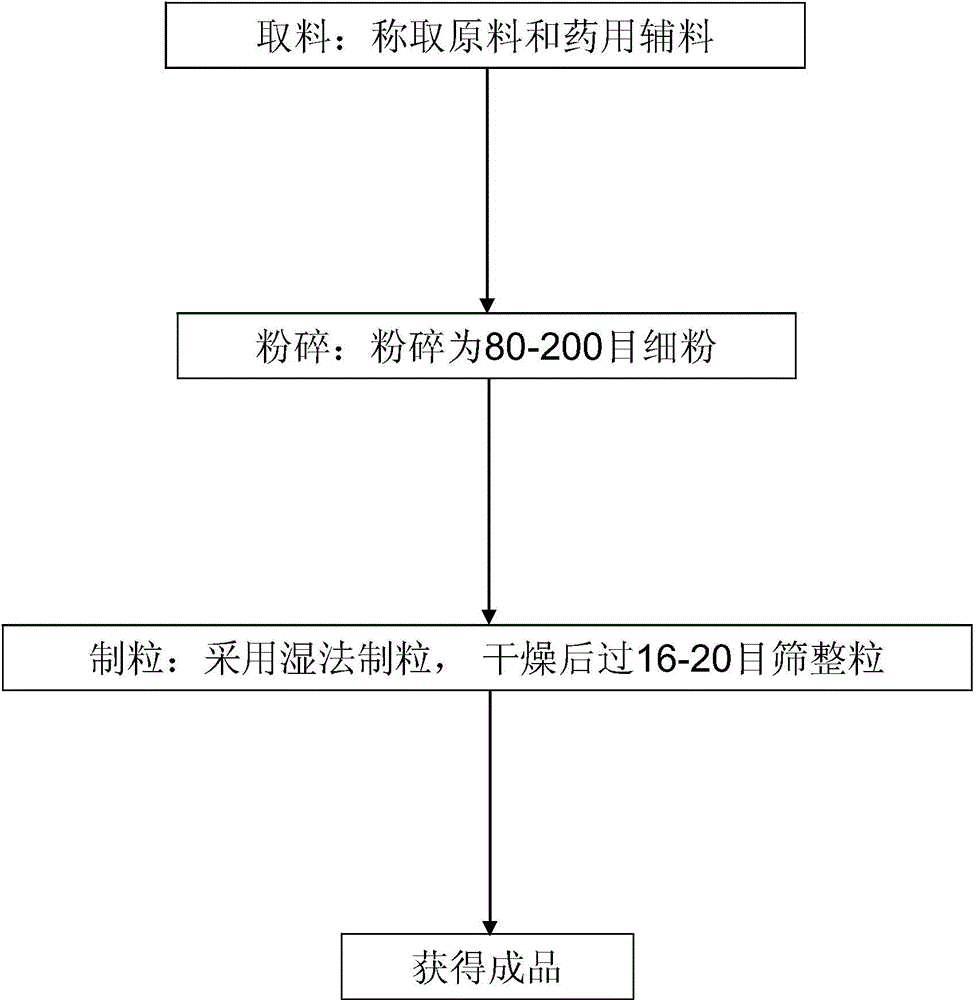
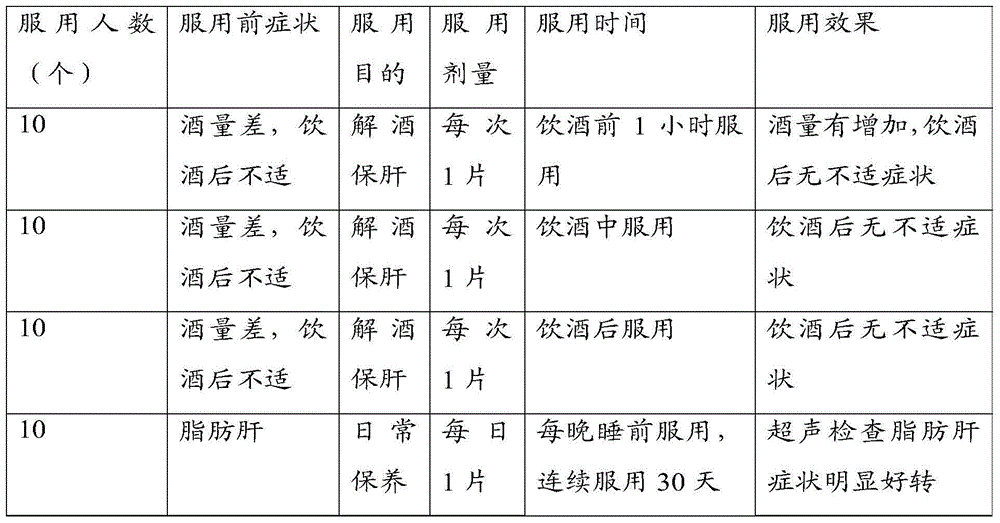
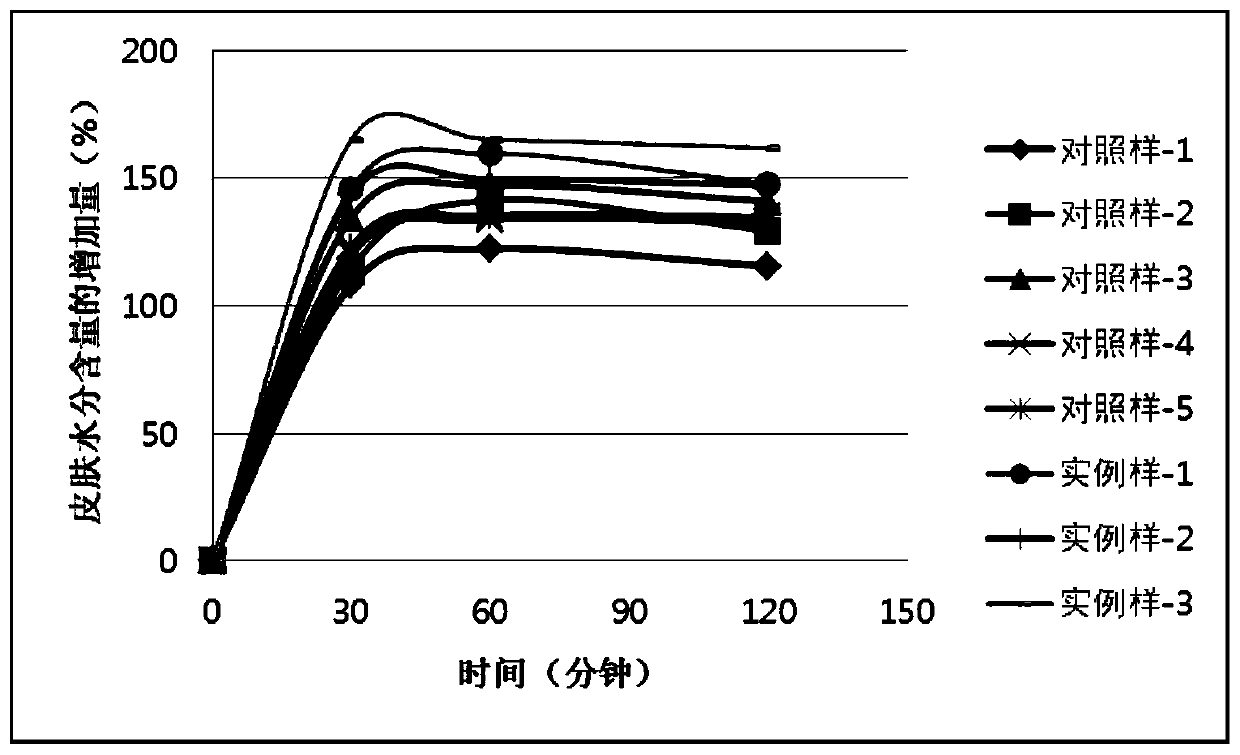
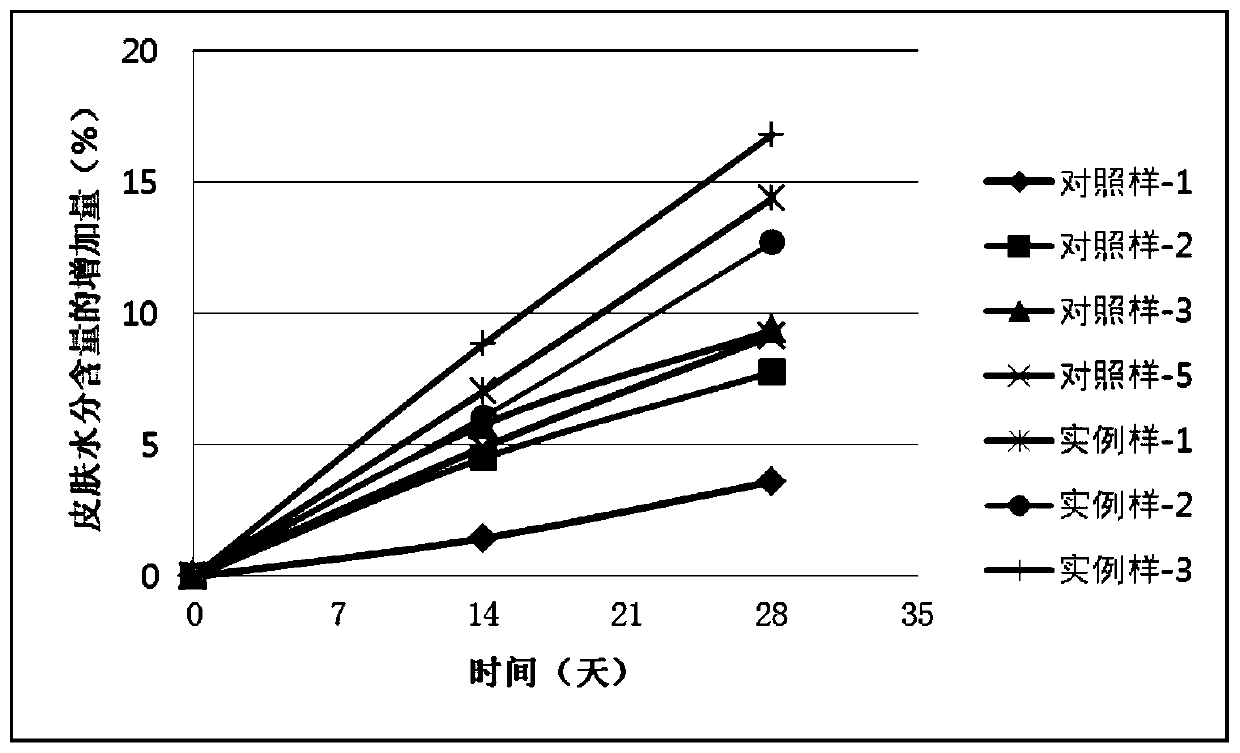
The present invention provides a metabolism regulating and liver protecting nutritional supplement, a preparation method and applications thereof. The metabolism regulating and liver protecting nutritional supplement contains 10 to 50 parts of alpha-ketoglutarate bis-arginine and is effervescent tablet or buccal tablet. On the other hand, the present invention provides a preparation method for the metabolism regulating and liver protecting nutritional supplement. The method comprises four steps of dispensation, pulverization, pelletization, and obtain the finished product. The present invention also provides applications of the metabolism regulating and liver protecting nutritional supplement on alleviating hangover to protect liver and daily care. The metabolism regulating and liver protecting nutritional supplement can regulate the liver dysfunction, and can directly and quickly provide nutrient and plenty of cell energy for liver cells to absorb and utilize, thereby maintaining the normal functions and health of the liver
Owner:何瑞红
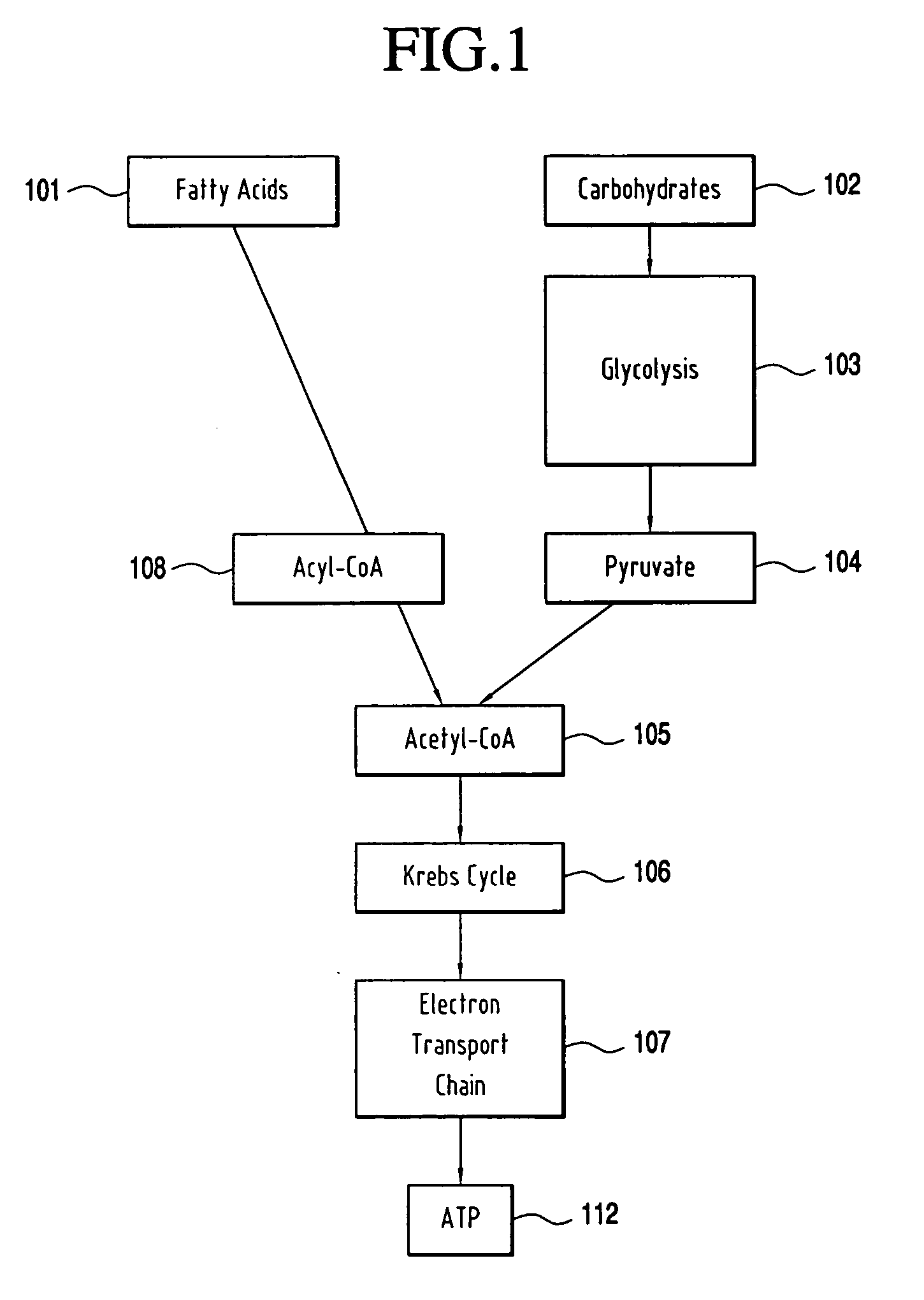
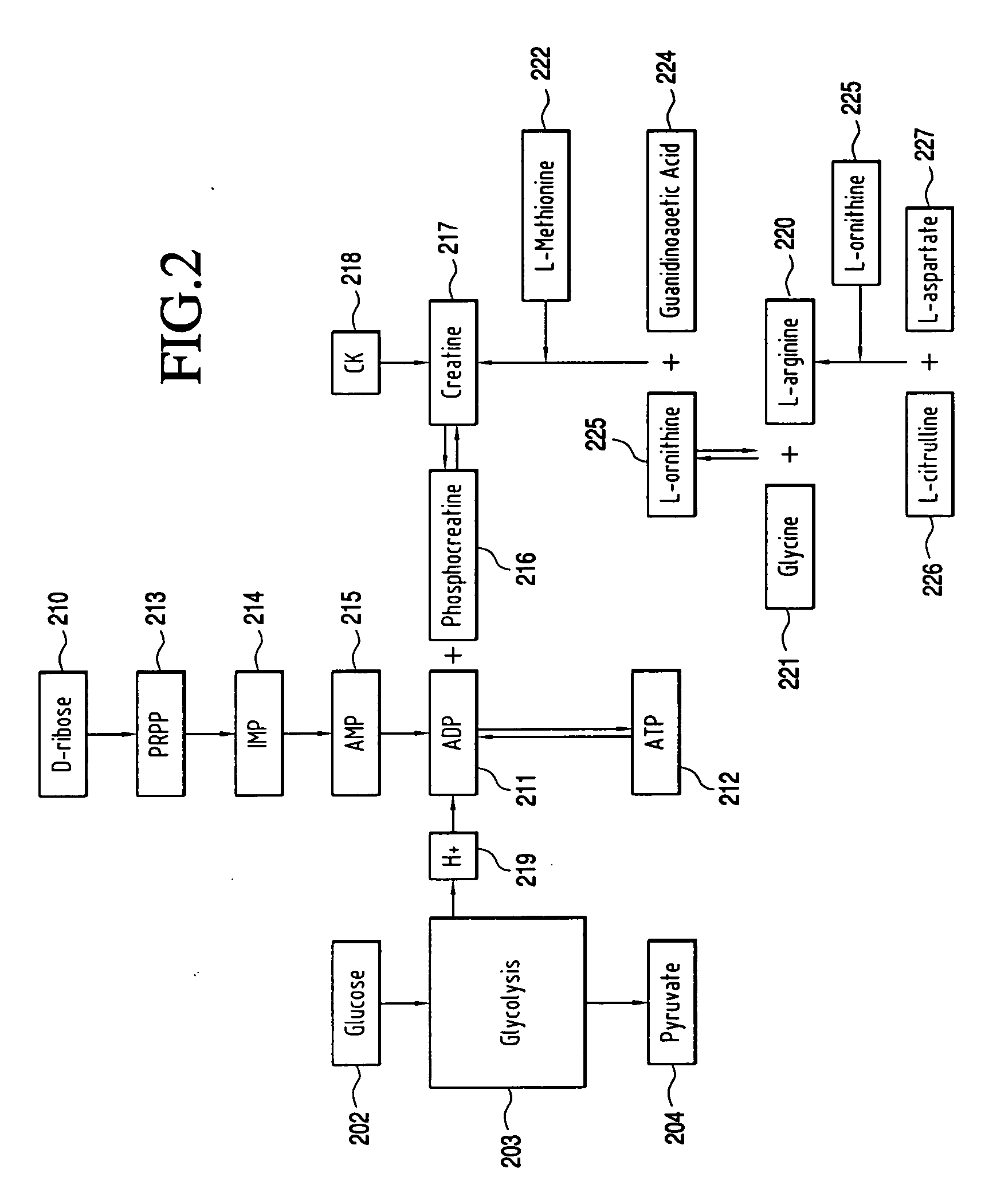
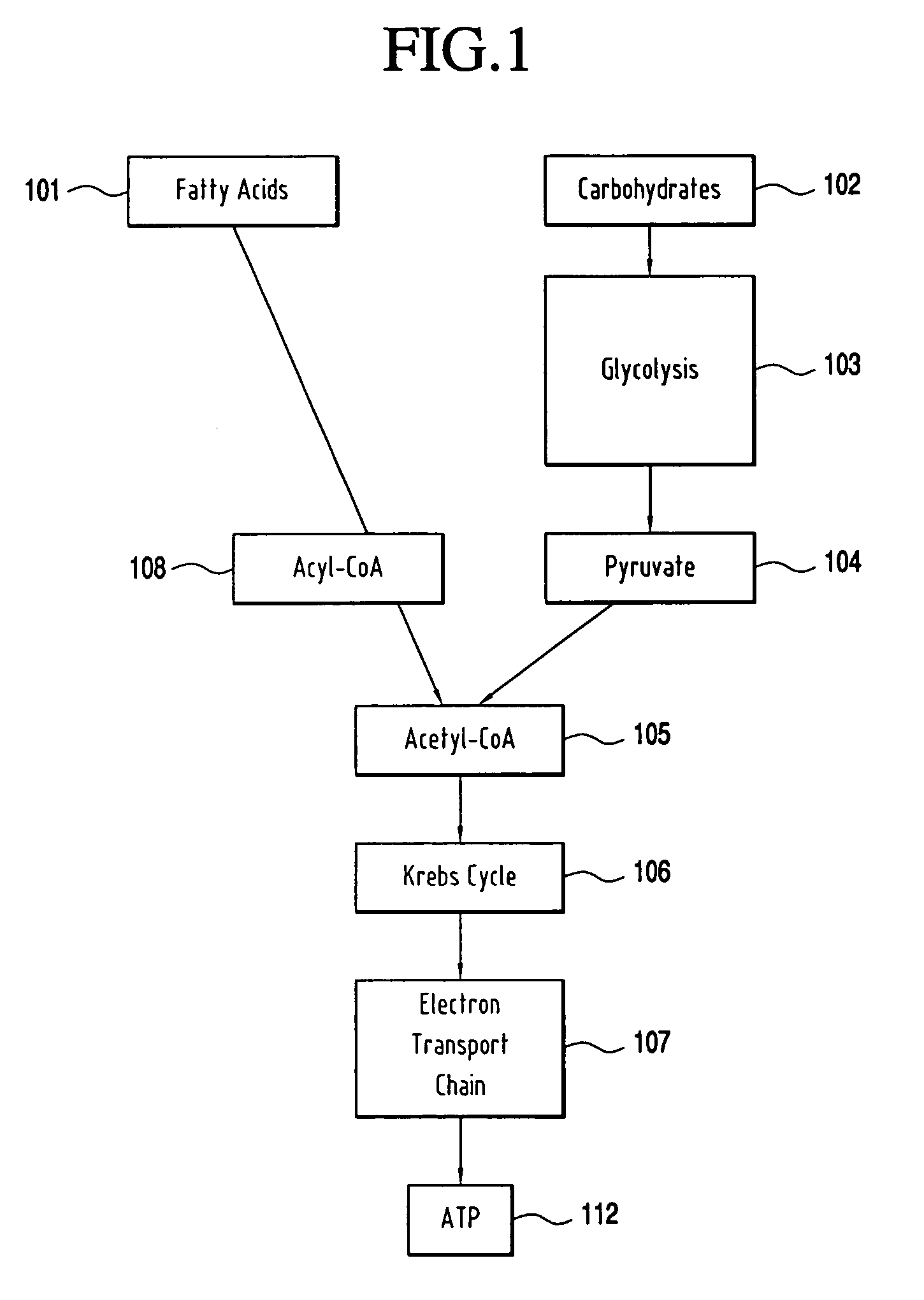
Use of methyl pyruvate to increase cellular energy production downstream of glycolysis for the PARP-1 ablation of HIV without necrotic cell death caused by continuous, chronic PARP-1 activation through the concomitant depletion of ATP and NAD.
InactiveUS20060111442A1Suppression problemPrecise functionBiocideAntiviralsMethyl pyruvateReceptor Inhibition
The present invention relates to the use of methyl pyruvic acid (a methyl ester of pyruvic acid) and / or methyl pyruvate (methyl pyruvate is the ionized form of methyl pyruvic acid) for the purpose of increasing cellular energy production thereby providing energy for the continuous activation of PARP-1 and up-regulation of PPAR. It is well known that chronic activation of PARP causes ATP and NAD depletion with concomitant cell death. PARP is known to prevent HIV replication by competitive receptor inhibition. Use of methyl pyruvate and / or methyl pyruvic acid can be effective when administered orally or infused on either a chronic and / or acute basis. In the following text, the terms “methyl pyruvate, methyl pyruvate compounds, methyl pyruvic acid” are used interchangeably.
Owner:ANTOSH & MEDURI HLDG CORP
Coenzyme Q10 capsules and preparation technology thereof
InactiveCN107496374AImprove immunityImprove antioxidant capacityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses coenzyme Q10 capsules and preparation technology thereof. The coenzyme Q10 capsules comprise, 6-10% of coenzyme Q10, 78-85% of microcrystalline cellulose, 8-11% of dextrin, and 1-2% of silica. The preparation technology is simple, and the prepared capsules can activate nutrition of cells of the human body and cell energy, and have the function of improving immunity of the human body, enhancing oxidation resistance, delaying aging and improving vitality of the human body.
Owner:康道生物(南通)有限公司
Composition and application thereof to preparation of skin care products to repair of damaged skin and muscle caused by staying up late or all night
ActiveCN110496090APromote energy synthesisPromote proliferationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdenosineLeucojum aestivum bulb extract
The invention relates to the technical field of skin care products, in particular to a composition and an application thereof to preparation of skin care products to repair of damaged skin and musclecaused by staying up late or all night. The composition provided by the invention comprises adenosine, a leucojum aestivum bulb extract and sodium hyaluronate. Through interaction and inter-promotionof the components, favorable effects of replenishing water, moisturizing, restoring skin glossiness, promoting cell energy synthesis, and promoting cell proliferation are realized. The composition isused for preparing cosmetics, so that a series of problems of skin and muscle of people staying up late or all night can be solved.
Owner:HUNAN YUJIA COSMETICS MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com