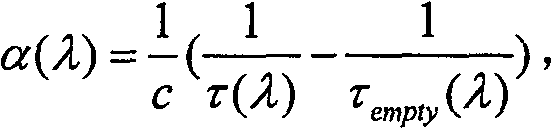Patents
Literature
47 results about "Absolute concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absolute concentration, n a state of mind held by a practitioner of Tibetan medicine during a session with a patient. As a result of continual instruction and training, the practitioner can focus on the patient with-out being distracted by thoughts of anticipated future or past occurrences.
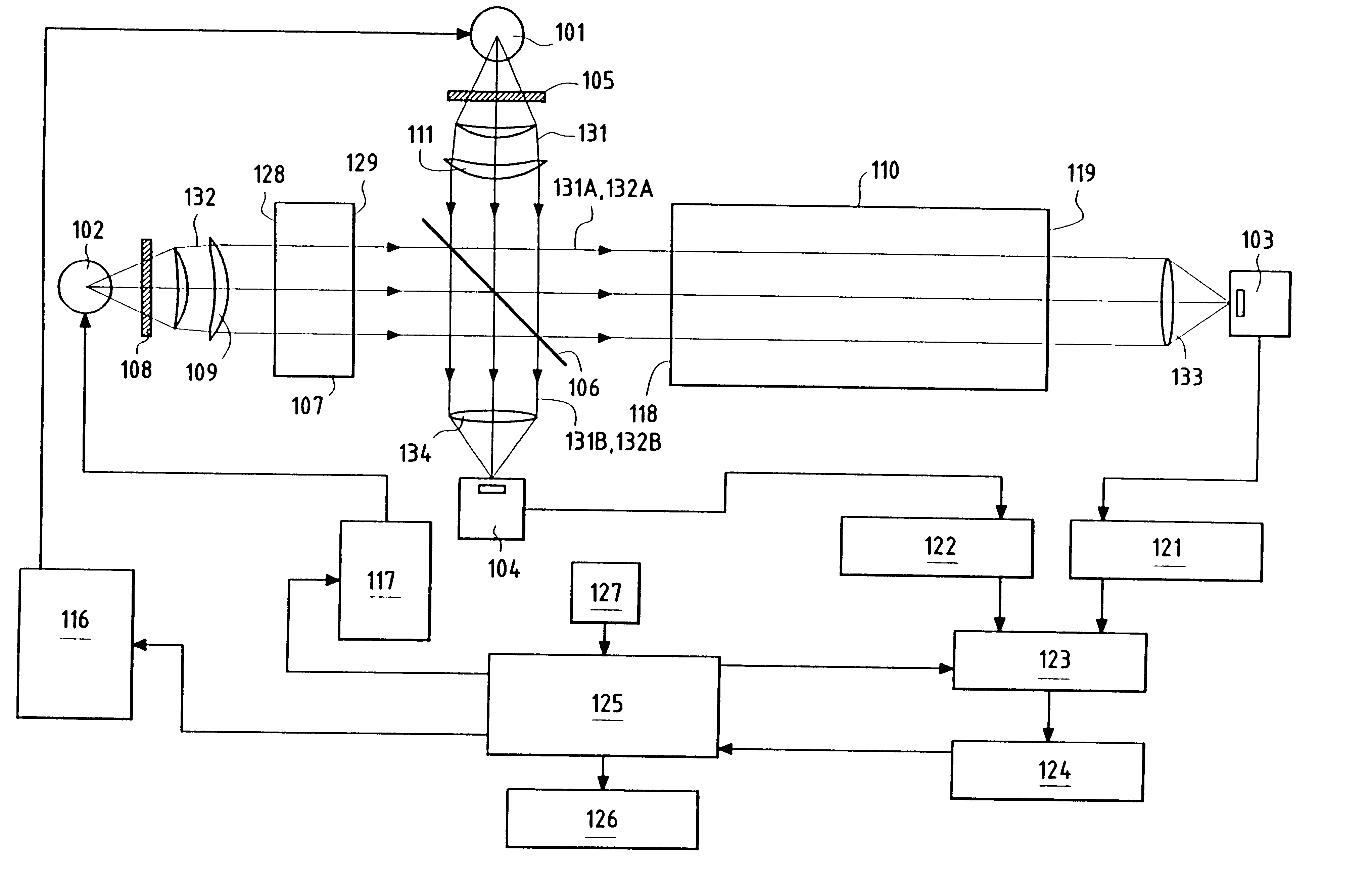
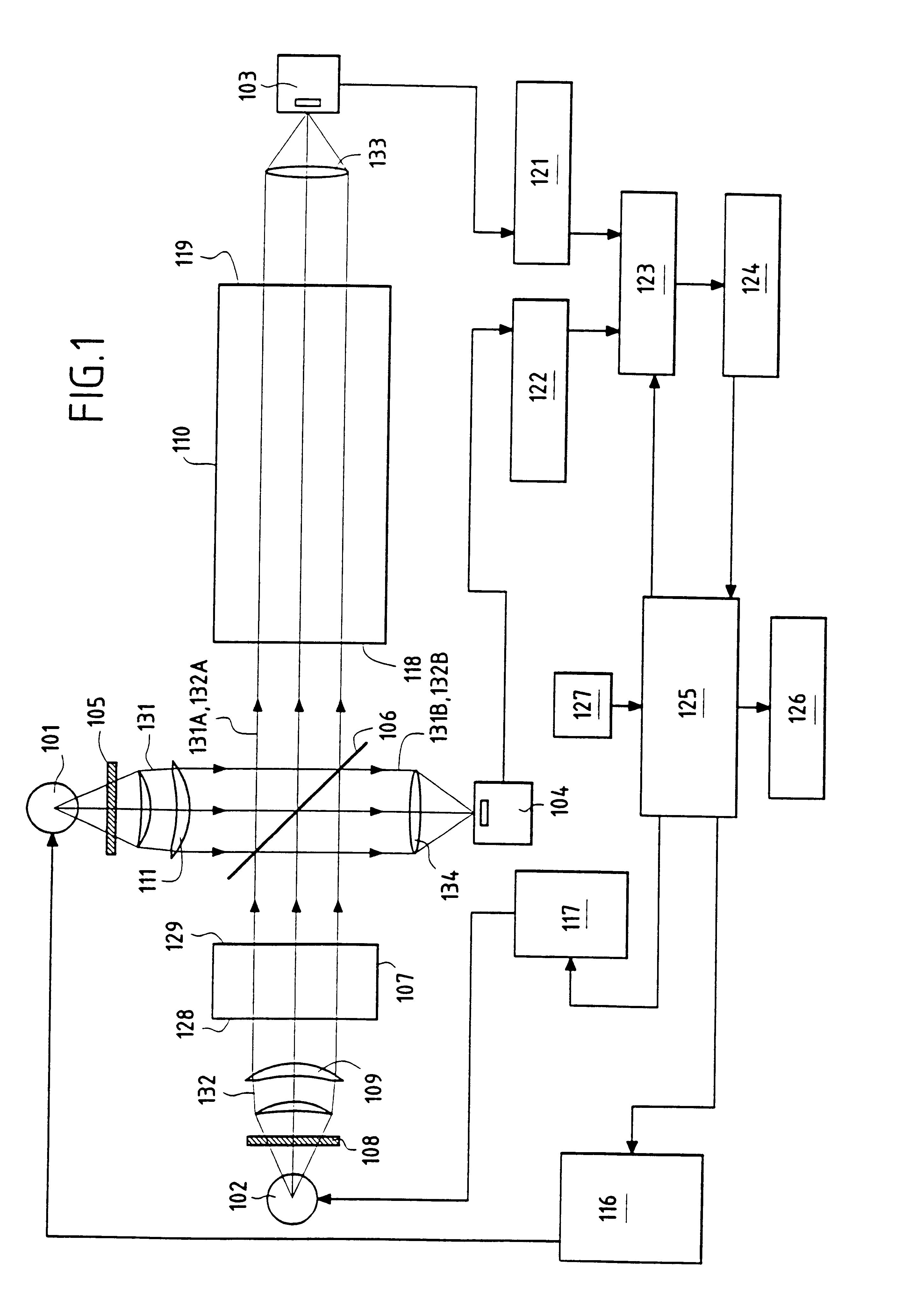
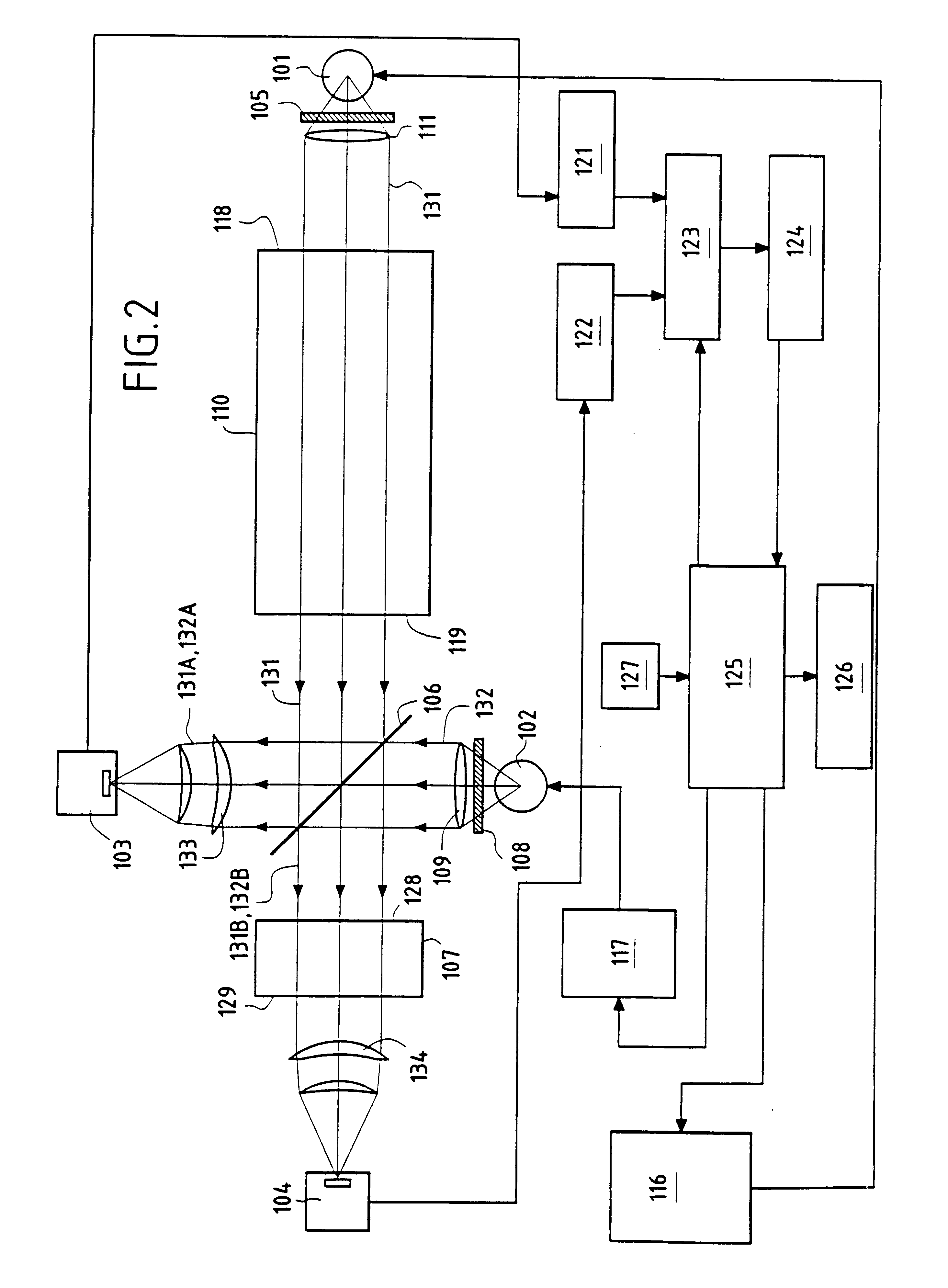
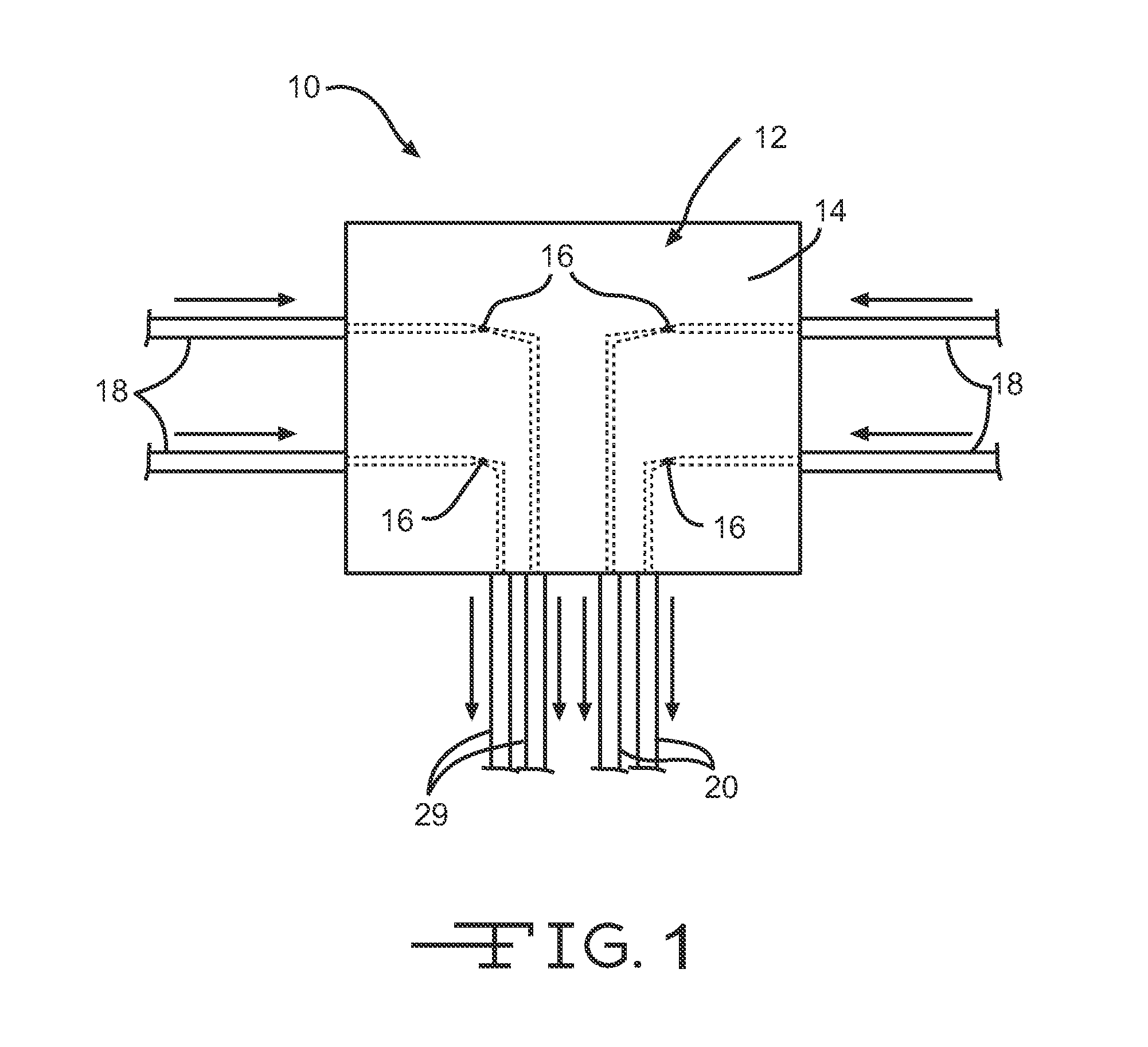
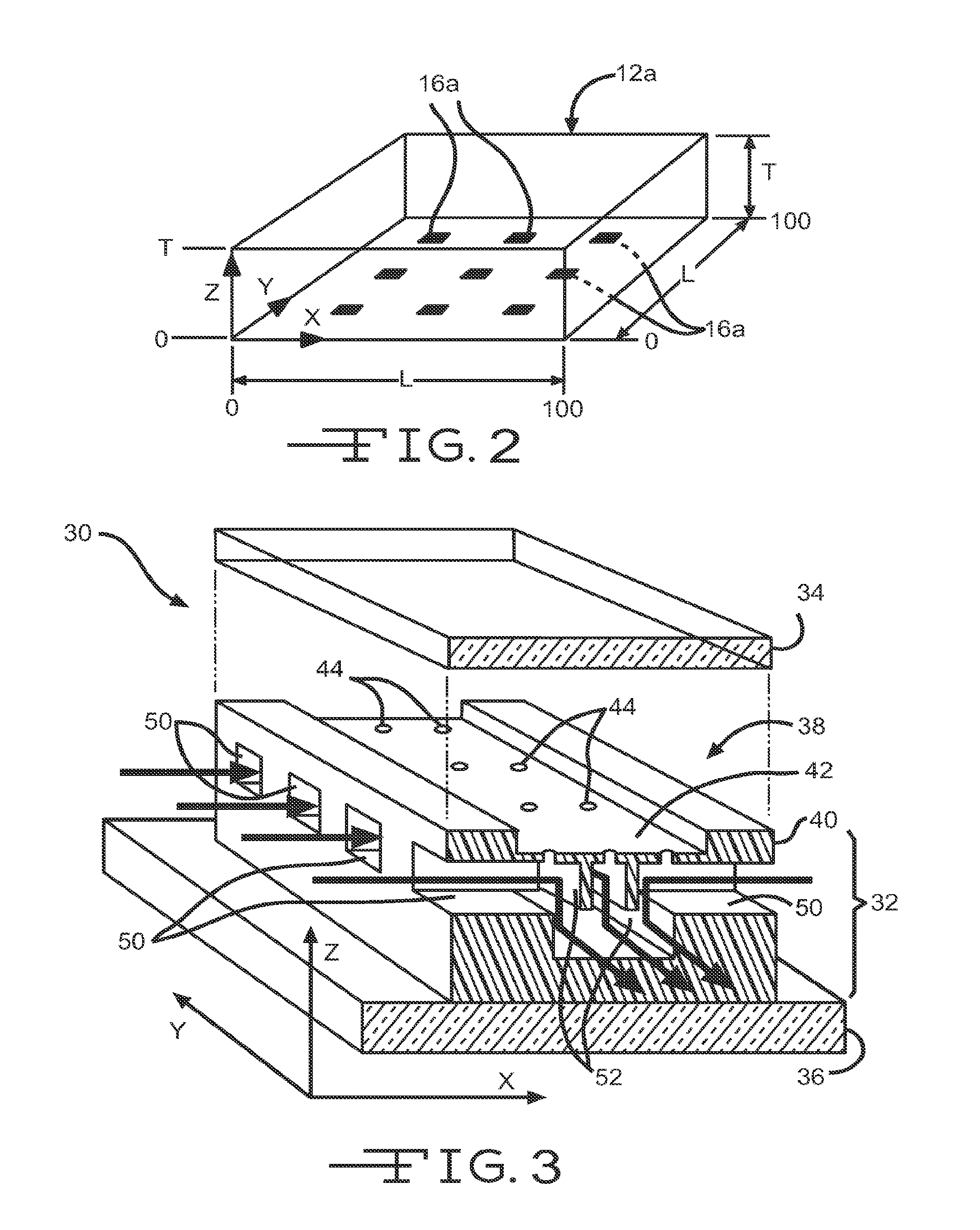
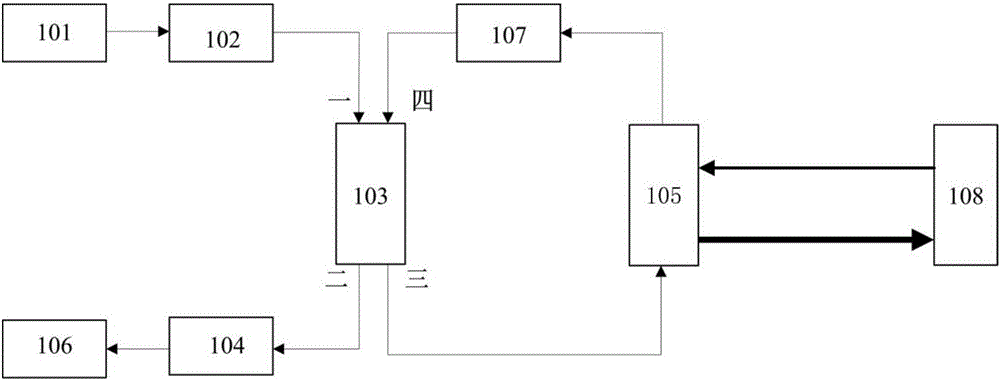
Method and apparatus for detecting gases
InactiveUS20020050567A1High sensitivityGood choiceRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsBeam splitterTagged Image File Format
The apparatus for detecting the presence of a particular gas within a mixture of gases comprises first and second emitter means for emitting measurement and reference electromagnetic radiation beams respectively, which beams are activated in alternation, a measurement cell, a filter cell, first and second detector means for detecting electromagnetic radiation beams, a beam splitter, and acquisition and processing means for synchronously acquiring and processing the four signals <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00001"> <number>1< / number> U S 1 , U S 2 , U R 1 , U R 2 <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00001" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00001.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00001" wi="216.027" he="11.02815" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00001.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> delivered by the first and second detector means in succession when the first and second emitter means are respectively activated so as to determine the absolute concentration of the gas to be detected on the basis of the ratio <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00002"> <number>2< / number> R = ( U S 1 x U R 2 ) / ( U S 2 x U R 1 ) <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00002" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00002.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00002" wi="216.027" he="11.02815" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00002.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> between the four signals, in which <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00003"> <number>3< / number> U S 1 and U S 2 <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00003" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00003.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00003" wi="216.027" he="11.02815" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00003.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> respectively represent the signals delivered by the first and second detector means when the first emitter means is activated, and <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00004"> <number>4< / number> U R 1 and U R 2 <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00004" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00004.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00004" wi="216.027" he="11.02815" file="US20020050567A1-20020502-M00004.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> respectively represent the signals delivered by the first and second detector means when the second emitter means is activated.
Owner:GAZ DE FRANCE +1
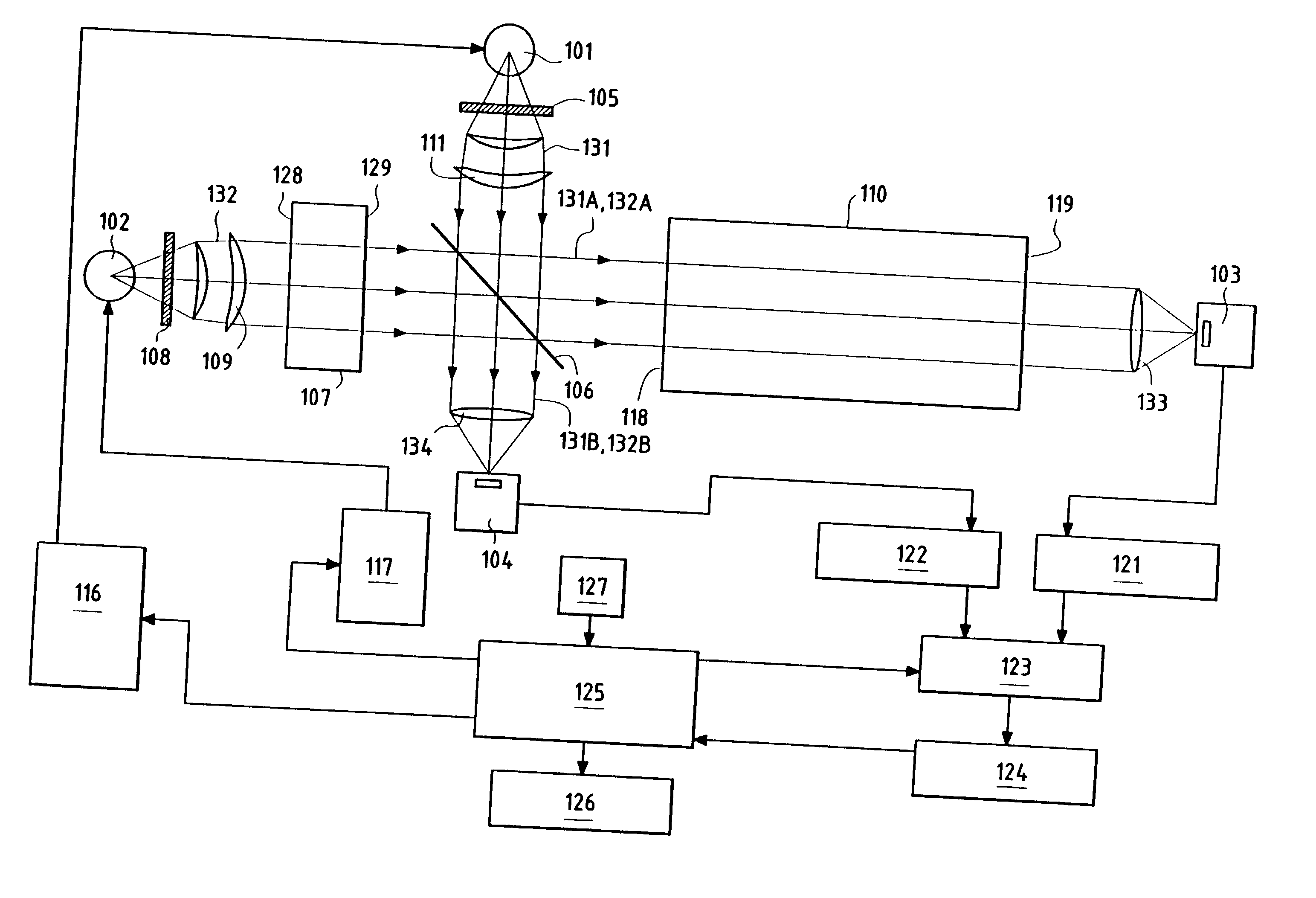
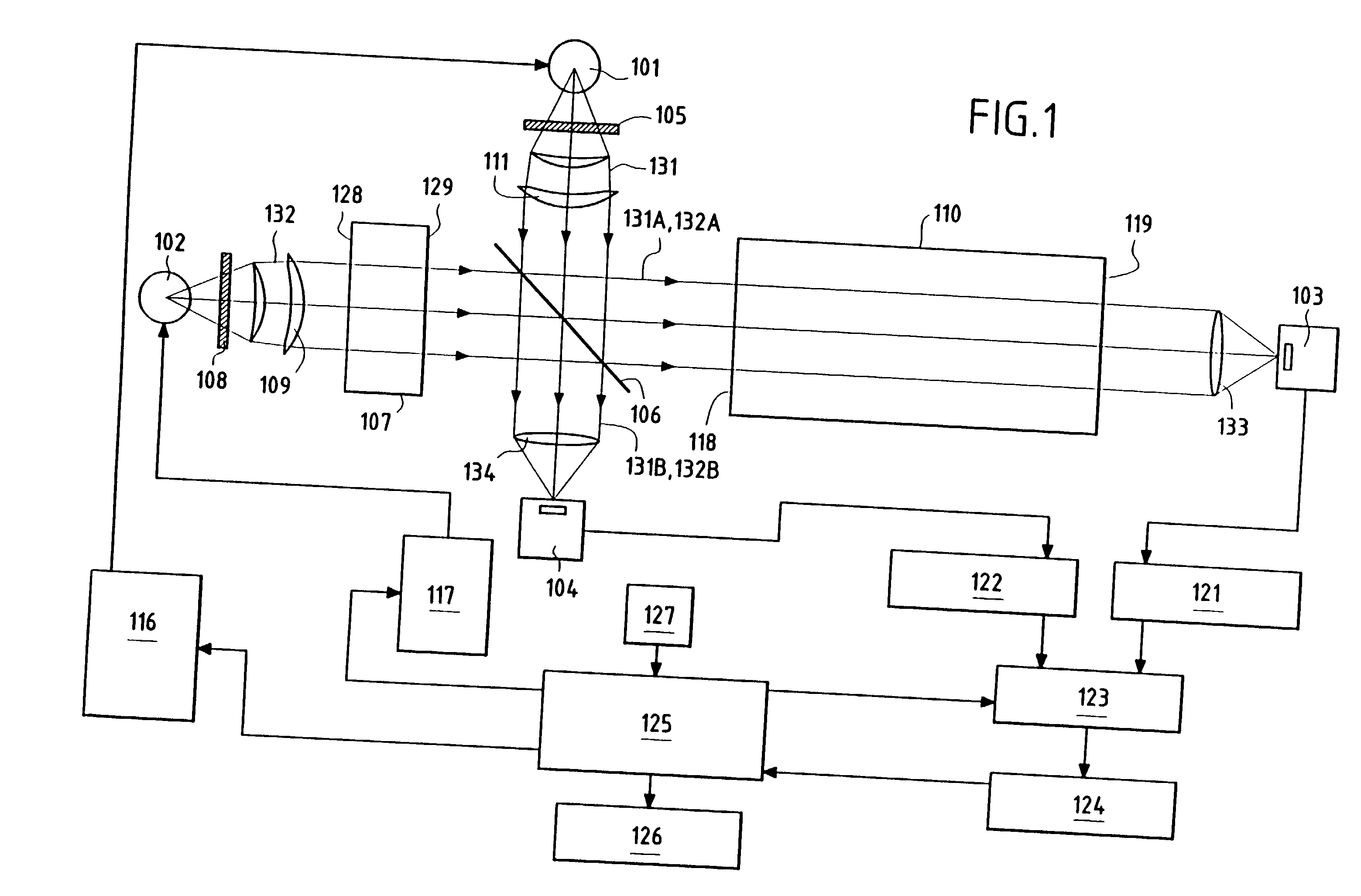
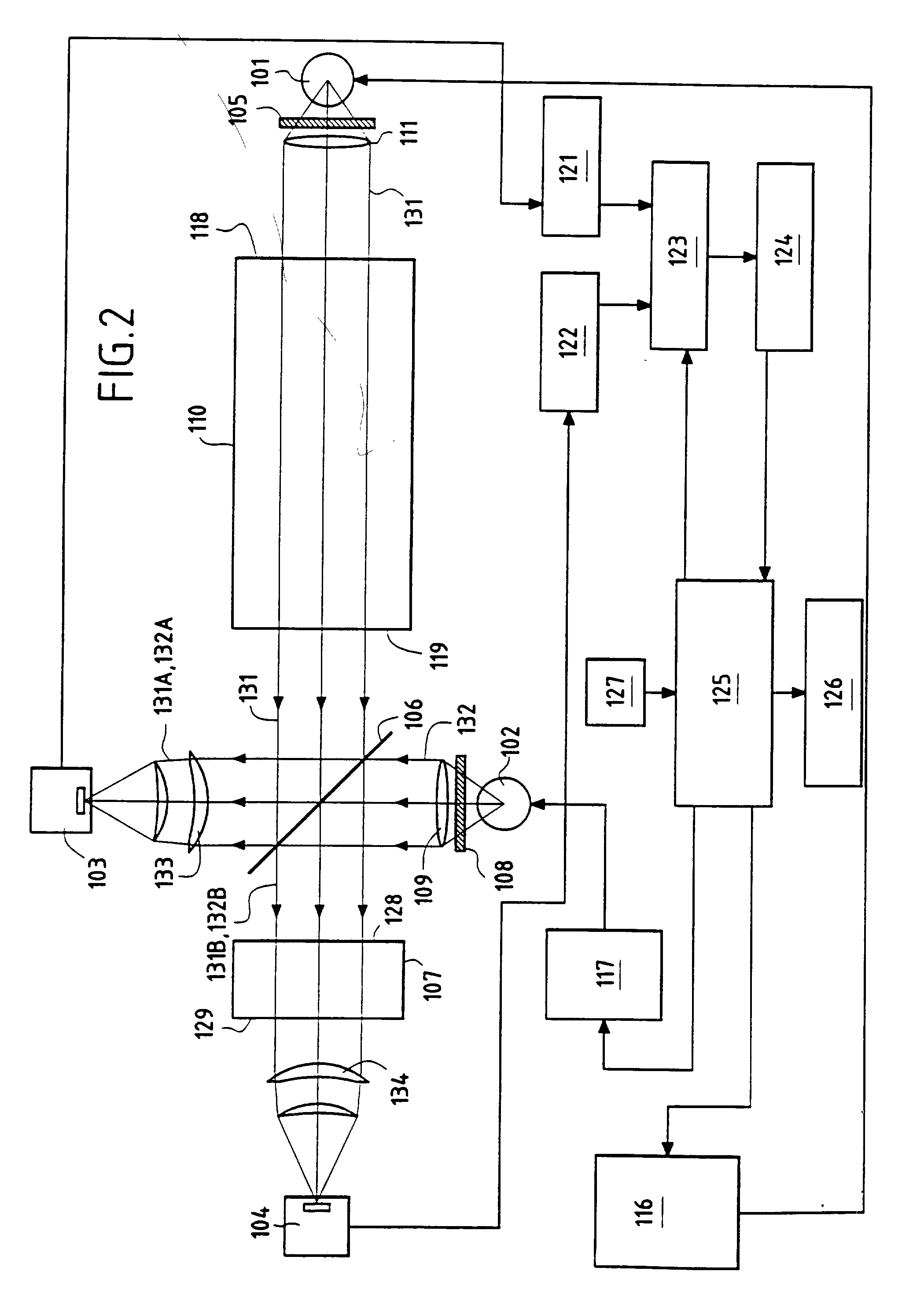
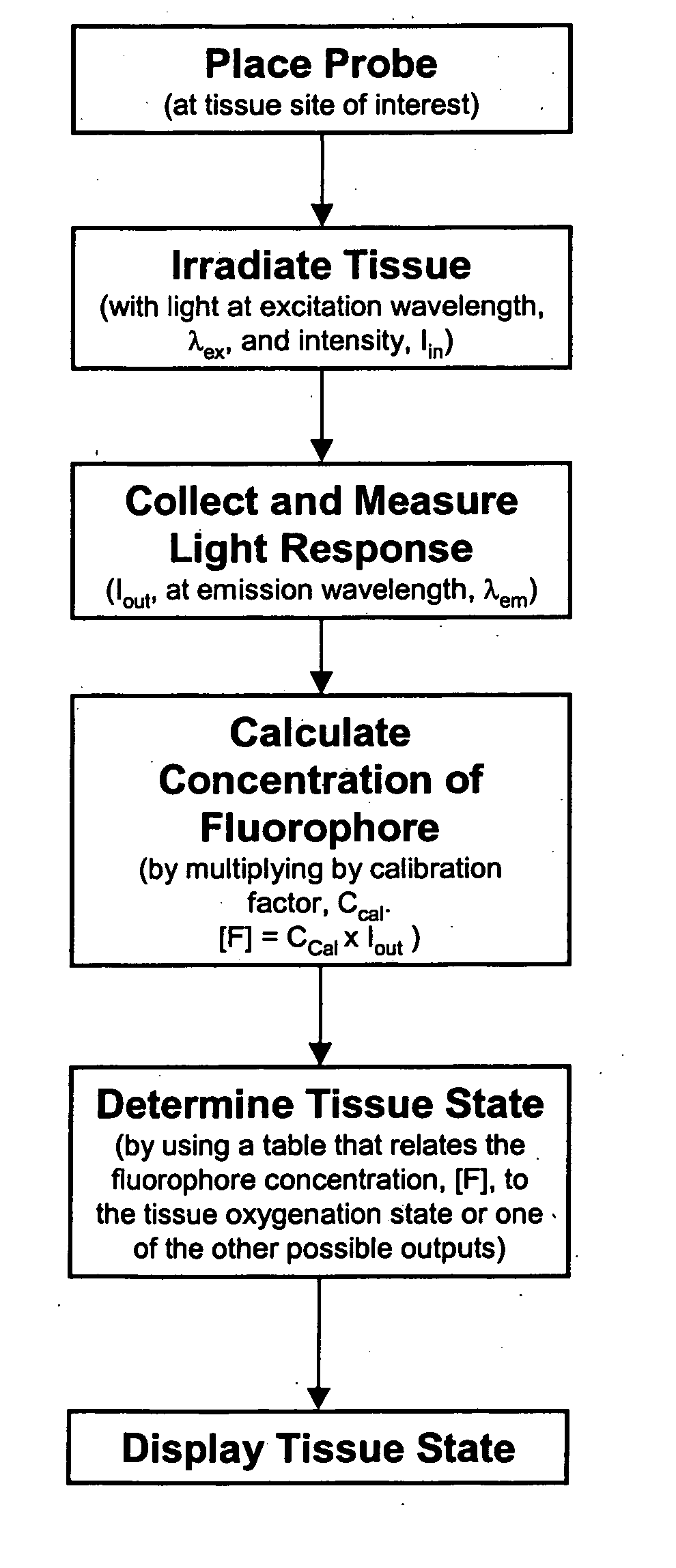
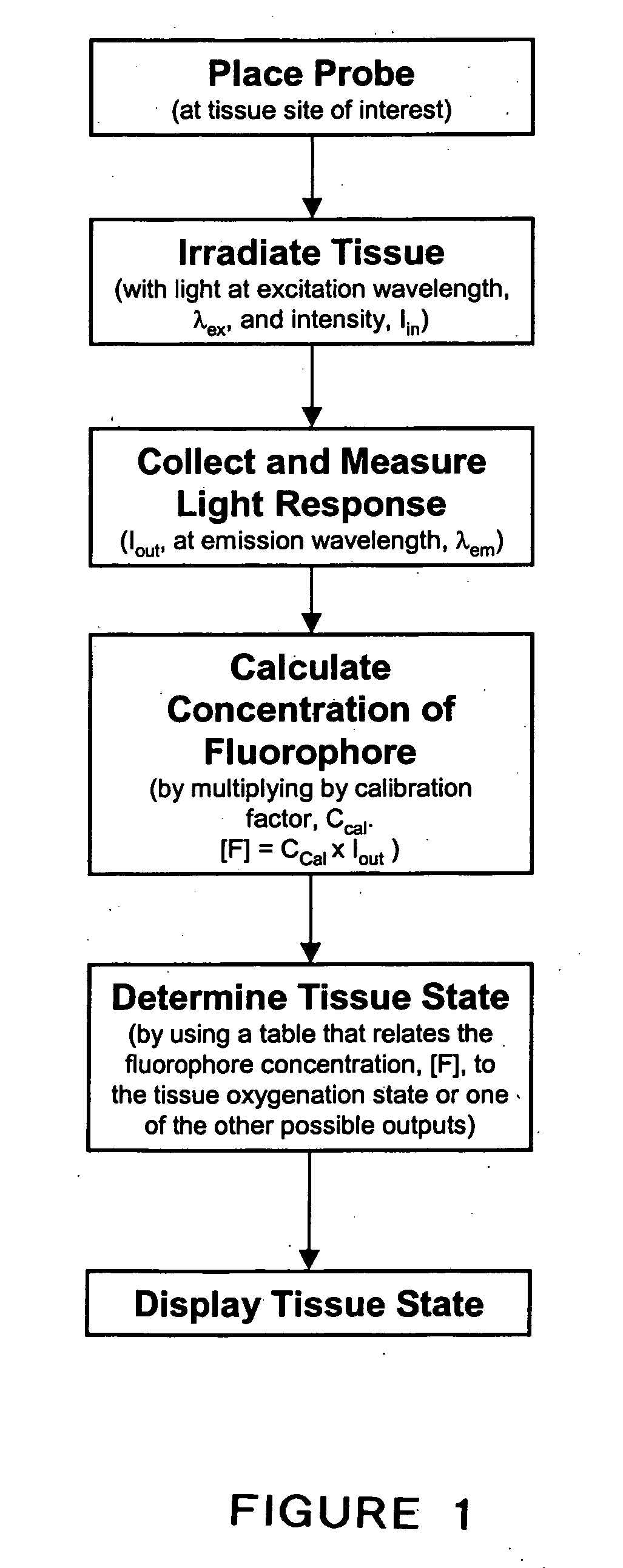
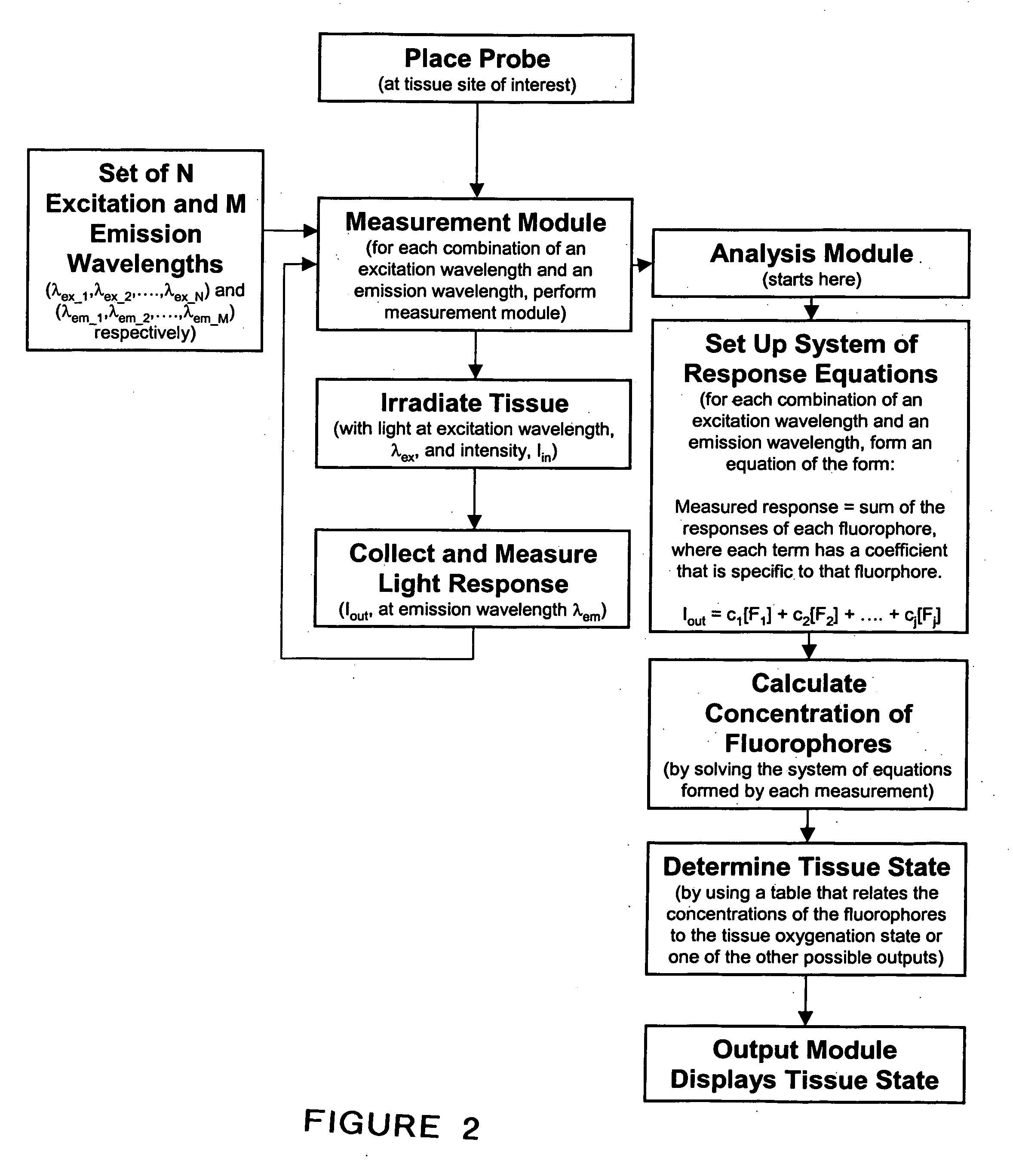
System and method for monitoring of end organ oxygenation by measurement of in vivo cellular energy status
A method is provided of measuring in vivo of an endogenous fluorophore in a tissue site. A known excitation wavelength of the endogenous flurophore is selected within a range of wavelengths at which the endogenous flurophore undergoes fluorescence. The tissue site is irradiated with irradiated light having at least the selected excitation wavelength within the range of wavelengths. A fluorescence emission of the tissue site resulting from the irradiation thereof is detected. A relative or absolute concentration of the endogenous fluorophore is determined by multiplying it by a calibration factor that depends one at least one of, a known excitation and emission property of the endogenous fluorophore, an intensity of the irradiated light, optical properties of an excitation probe, and specific properties of the tissue. The relative or absolute concentration of the endogenous fluorphore is used to estimate at least one of a, in vivo cellular energy production status or state of end-organ tissue oxygenation.
Owner:EPOC
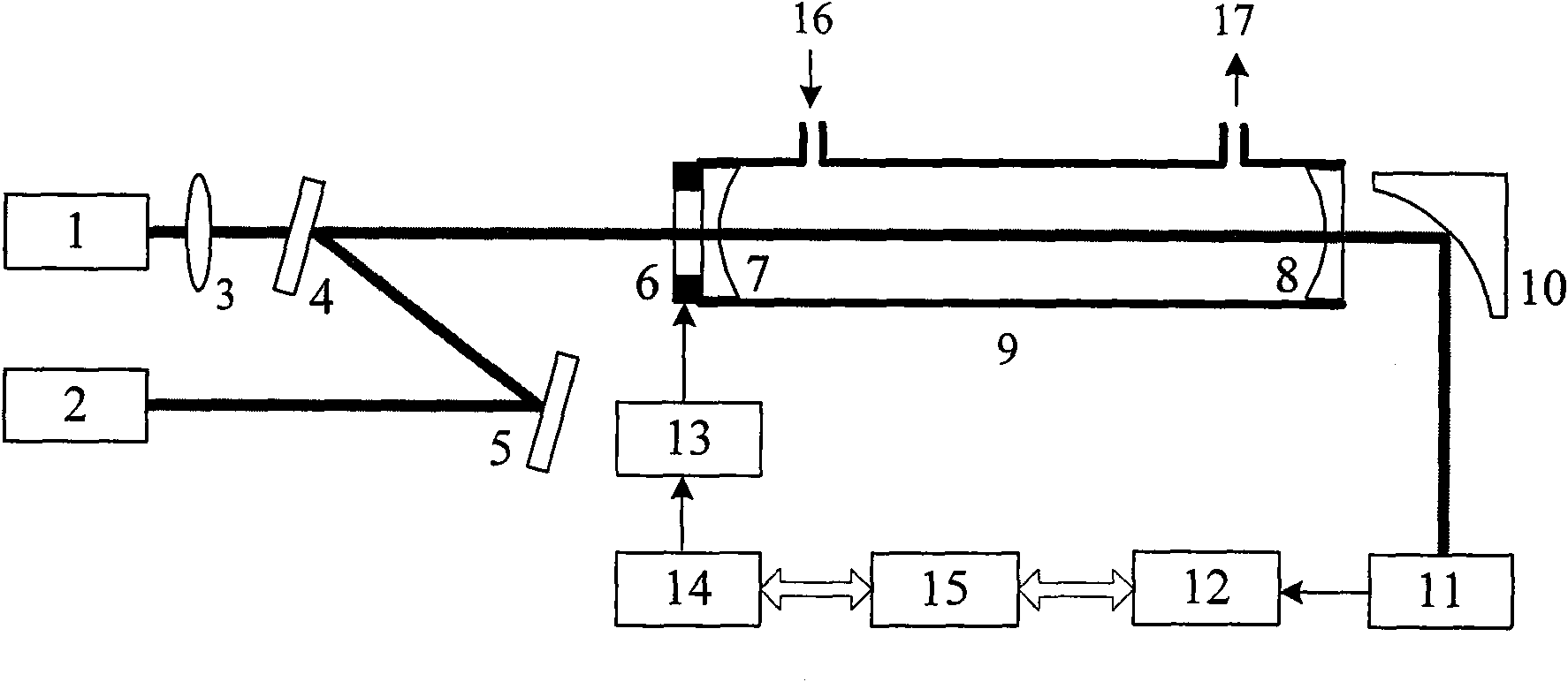
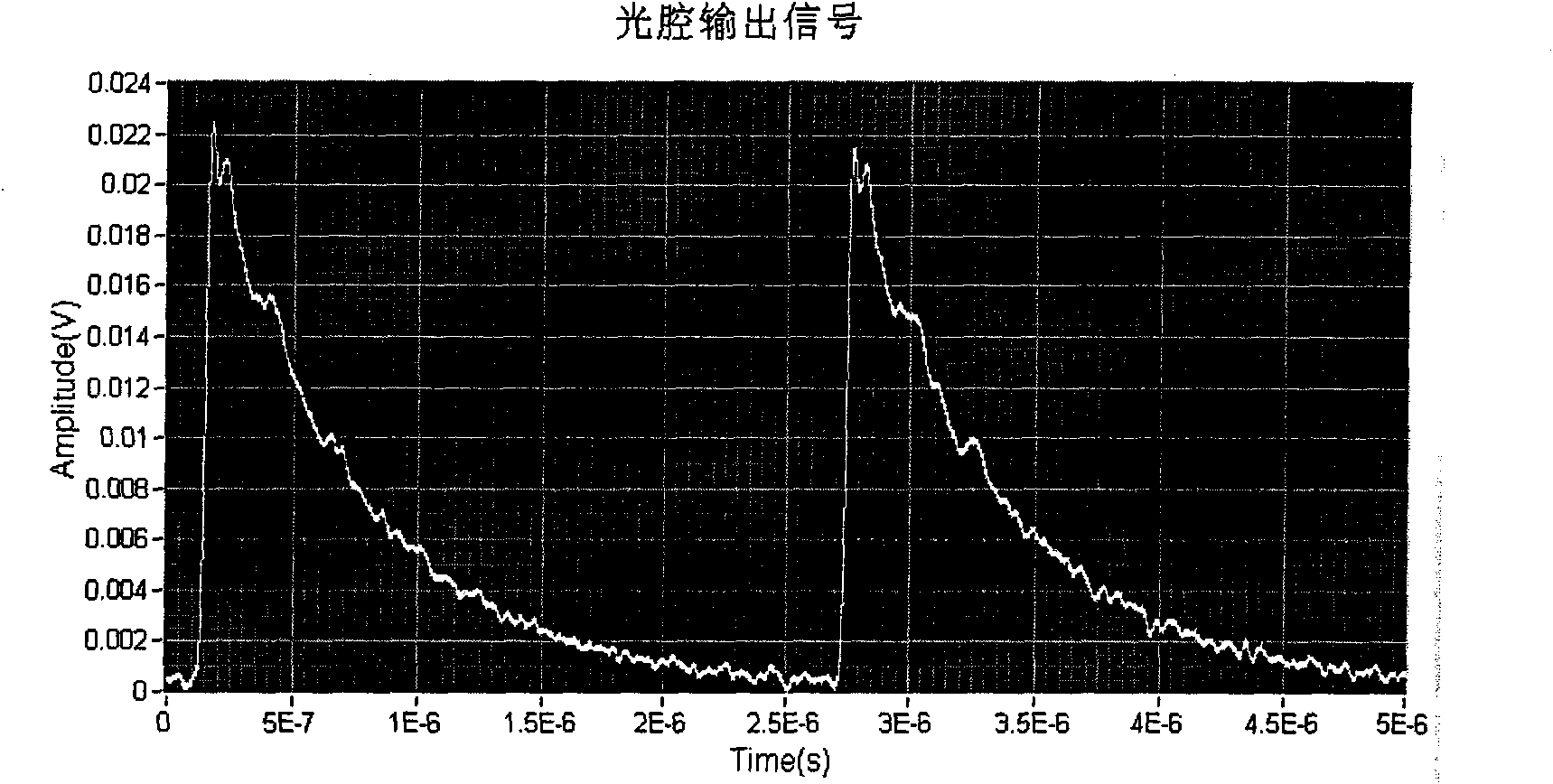
Infrared cavity ring-down spectroscopy trace gas detection method based on quantum cascade laser
InactiveCN101644673AEquivalent absorption lengthGood choiceColor/spectral properties measurementsAction spectrumPeak value
The invention discloses an infrared cavity ring-down spectroscopy trace gas detection method based on quantum cascade laser; comprising the following steps: using a tunable quantum cascade laser as alight source, and selecting measuring waveband and wavelength scan step length aiming at spectrum line characteristic of the gas to be detected; respectively measuring the cavity ring-down time of each wavelength in the cavity with absorption or without absorption by cavity ring-down technique, and calculating the gas absorption coefficient of corresponding wavelength so as to obtain a relation curve that is an absorption spectrogram of the measured gas absorption coefficient and toned laser wavelength. The spectrogram is contrasted with spectrum line characteristic of corresponding gas in HITRAN database, thereby being capable of analyzing and determining weather the measured gas contains the predetermined gas component; the absolute concentration of the gas to be measured can be calculated and obtained and the absolute concentration of the gas to be measured can be measured through scaling measurement by using absorption peak wavelength of the absorption spectrum as the best detection wavelength and the relation among the gas absorption coefficient of the wavelength, the absorption cross section and concentration. The method has high measuring sensitivity and high property of resisting interference so that the fast and exact on-line analysis and detection of multiple trace gases are easily realized.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for detecting gases
InactiveUS6509567B2High sensitivityGood choiceRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsBeam splitterLight beam
Owner:GAZ DE FRANCE +1
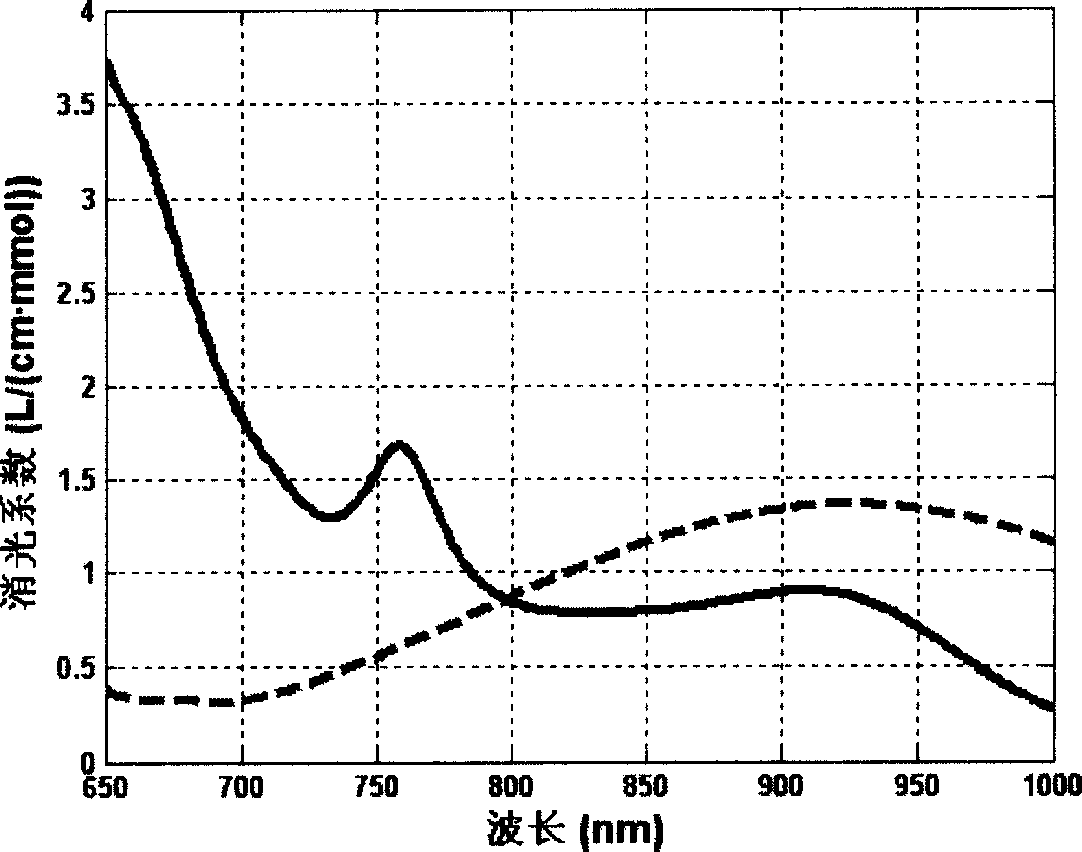
Method for testing absolute volume of concentration of oxidized hemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin in human tissue
ActiveCN1911172AHelp to understand blood volumeUnderstanding blood volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringHemoglobin FHEMOGLOBIN I
A method for measuring the absolute concentration of oxygenated and reduced hemoglobin in human tissue features that its sensor is composed of 2 photoelectric receiving tubes and at least 3 light sources with different wavelengths, which are arranged on a straight line at intervals. Said absolute concentration can be calculated out. Said light source can emit respectively red light and near infrared light.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Microfluidic Device and Related Methods
InactiveUS20120135446A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningDiffusionConcentration gradient
A combinatorial microenvironment generator is configured for the generation of arbitrary, user-defined, steady-state, concentration gradients with negligible to no flow through the growth medium to perturb diffusion gradients or cellular growth. More importantly, the absolute concentrations and / or gradients can be dynamically altered upon request both spatially and temporally to impose tailored concentration fields for in-situ stimulus studies. Here, diffusion occurs via an array of ports, each of which can be an independently controlled source / sink. Together, the array of ports establishes a user-defined, 3D concentration profile. Useful methods related to this device are also provided.
Owner:MAINE INST FOR HUMAN GENETICS & HEALTH +1
Antigen antibody complex dissociation liquid kit and application thereof
InactiveCN101832999AFacilitate dissociationIncrease the absolute concentration valueBiological testingSerum igeBlood plasma
The invention discloses an antigen antibody complex dissociation liquid kit, which is prepared by blending reagents of 0.3 volume percent of Triton-X100, 1.5 volume percent of lauryl sodium sulfate and 1.5 volume percent of 3-[(3-cholane amidopropyl)-dimethylammonium]propanesulfonic acid in equal amount. The invention also discloses application of the kit in separating a pathogenic antigen antibody complex. The kit of the invention effectively realizes rapid dissociation of the pathogenic antigen antibody complex in a serum or blood plasma sample to be detected, increases the absolute concentration value of an antigen and an antibody, and greatly improves the detection sensitivity of the sample to be detected.
Owner:山东莱博生物科技有限公司
Lipoprotein (a) detection kit
The invention discloses a lipoprotein (a) detection kit which is characterized by consisting of a reagent 1, a reagent 2 and a working calibration solution. The reagent 1 consists of a buffer solution, bull serum albumin (BSA), a surfactant, goat IgG and NaN3; the reagent 2 consists of a buffer solution, a lipoprotein (a) monoclonal antibody latex microsphere, BSA, the surfactant, the goat IgG, a stabilizer and NaN3. The lipoprotein (a) detection kit can be applied to a fully automatic biochemical analyzer, the detection result is high in accuracy, and the lipoprotein (a) has high comparability with absolute concentration of lipoprotein (a) of different crowds and different sizes. Moreover, the lipoprotein (a) detection kit does not have a cross reaction with plasminogen, is not interfered by rheumatoid factors and is high in reagent stability, convenient to use and convenient for large-scale popularization, only a monoclonal antibody of the lipoprotein (a) is needed, and the preparation cost and time of the kit are saved.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
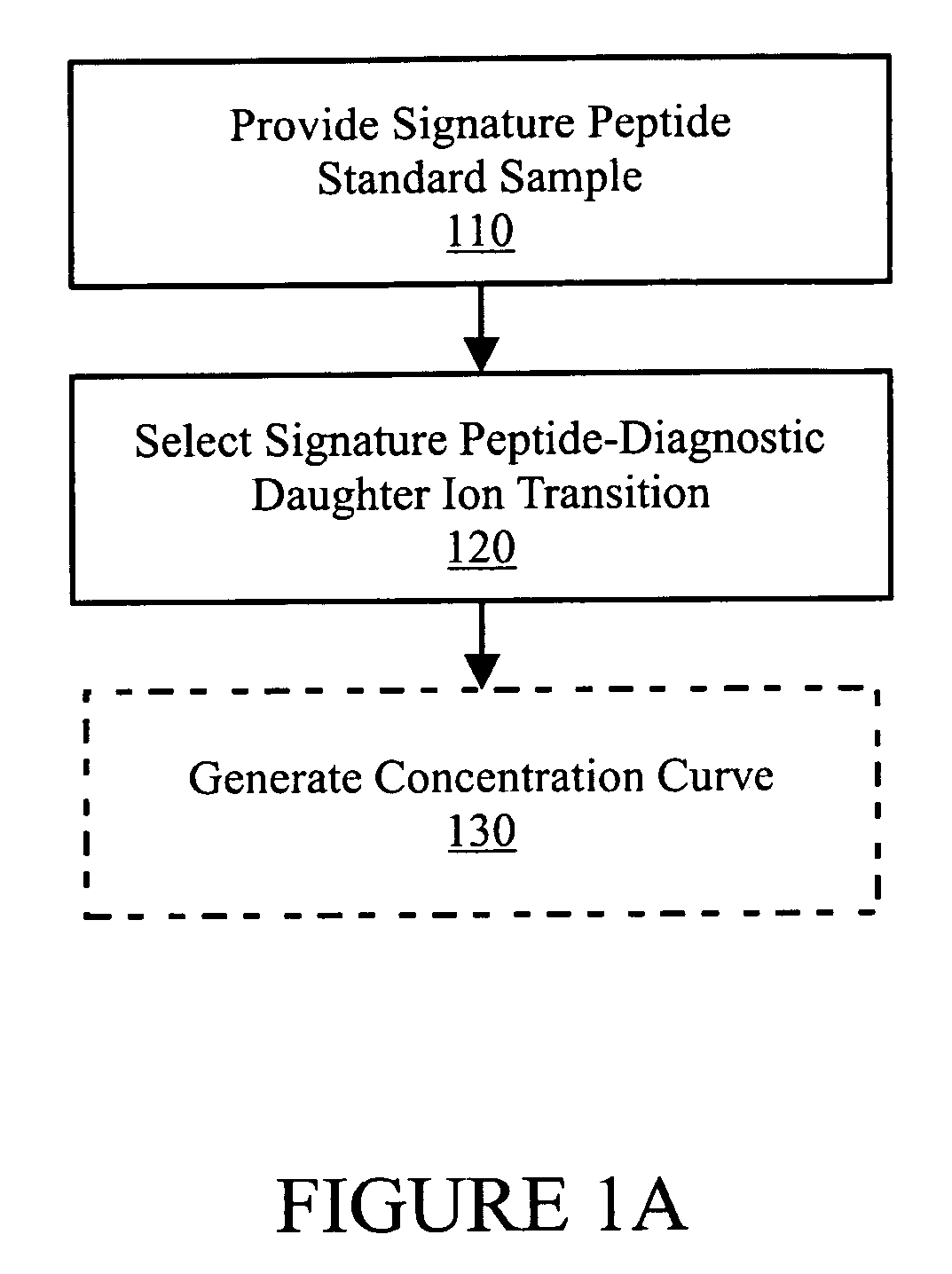
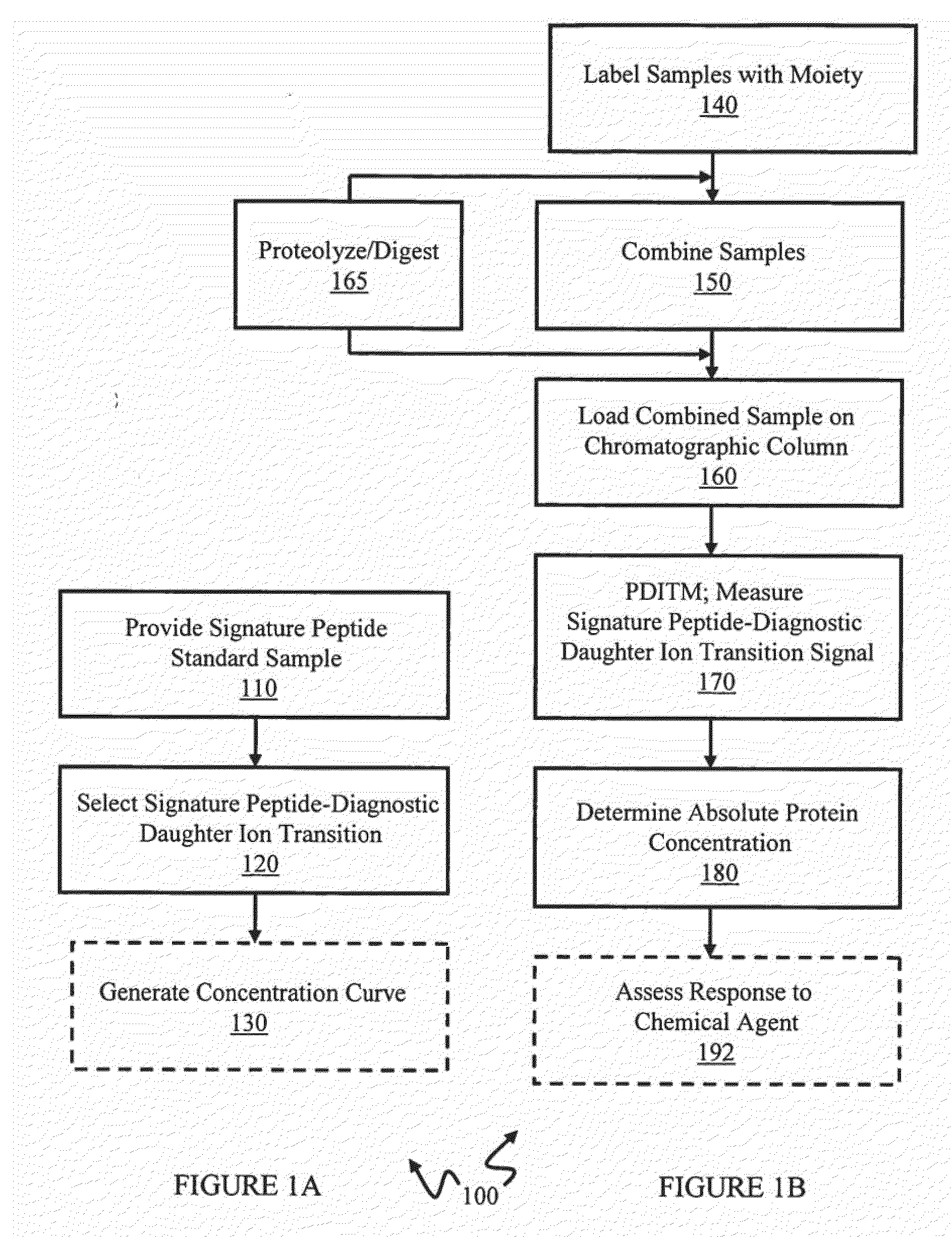
Expression quantification using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060078960A1Easy to identifyHelp studyParticle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometry imagingProtein mass spectrometry
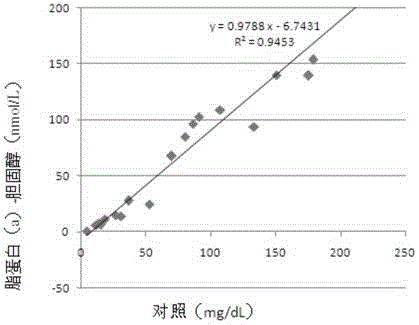
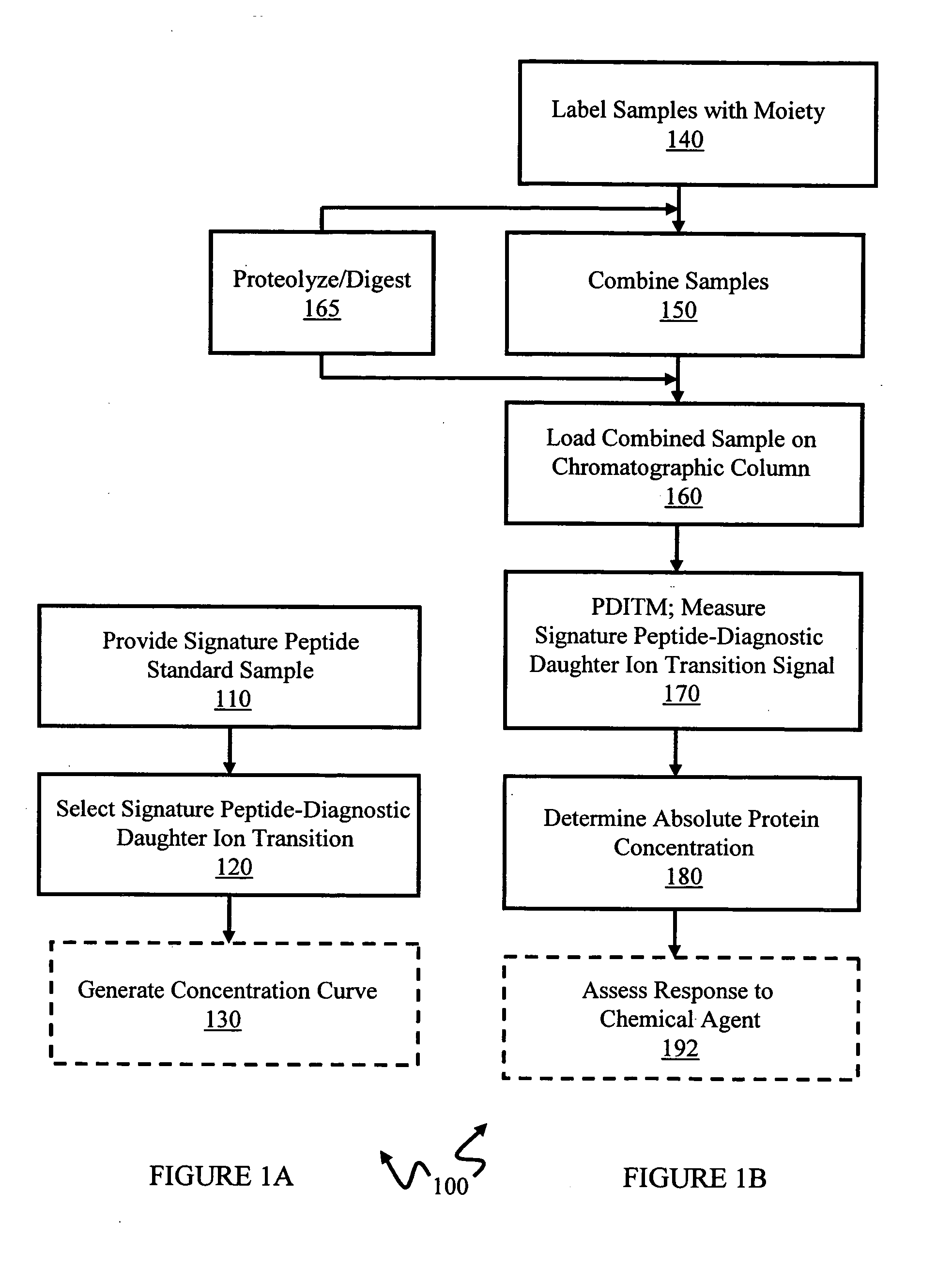
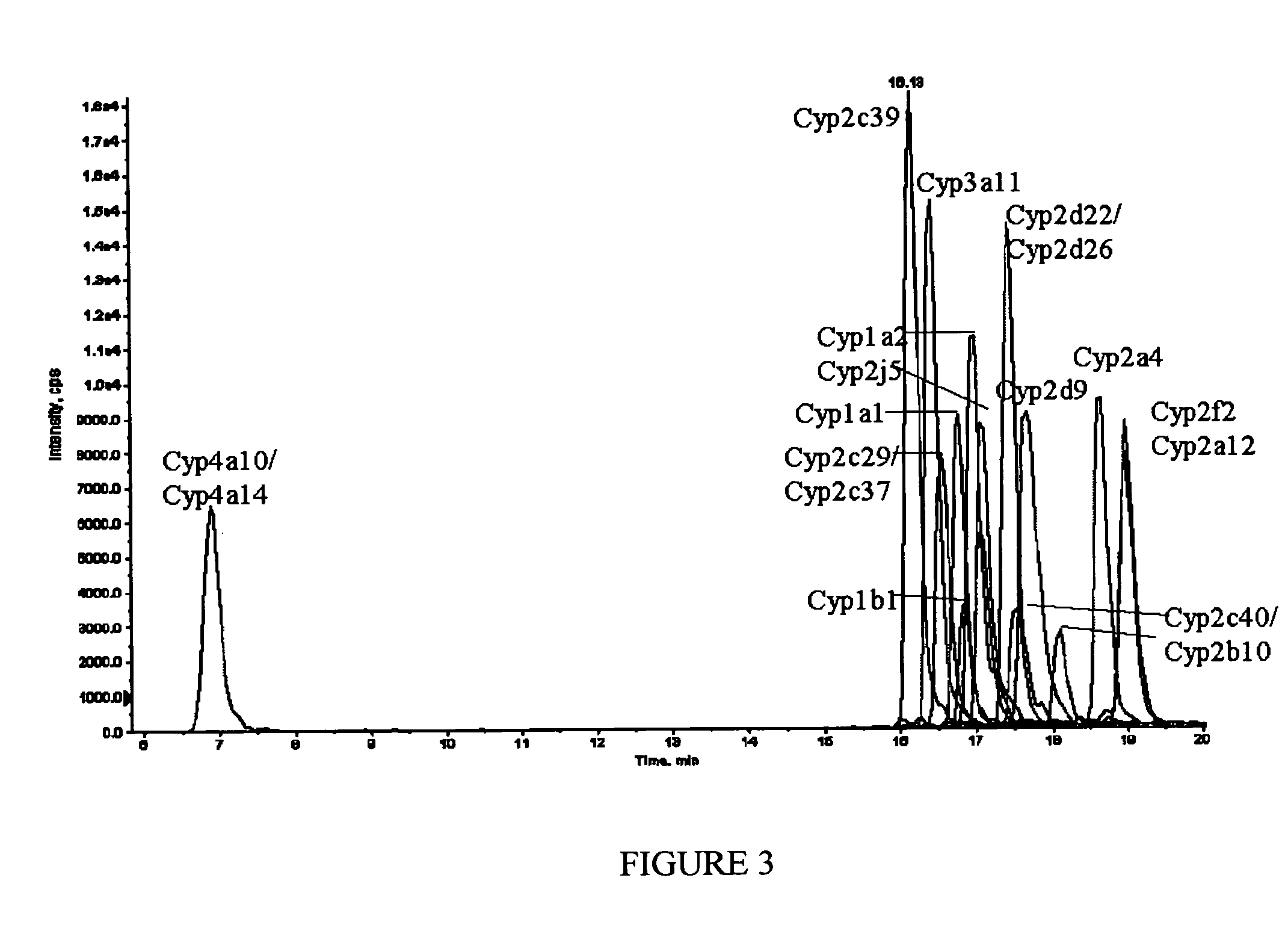
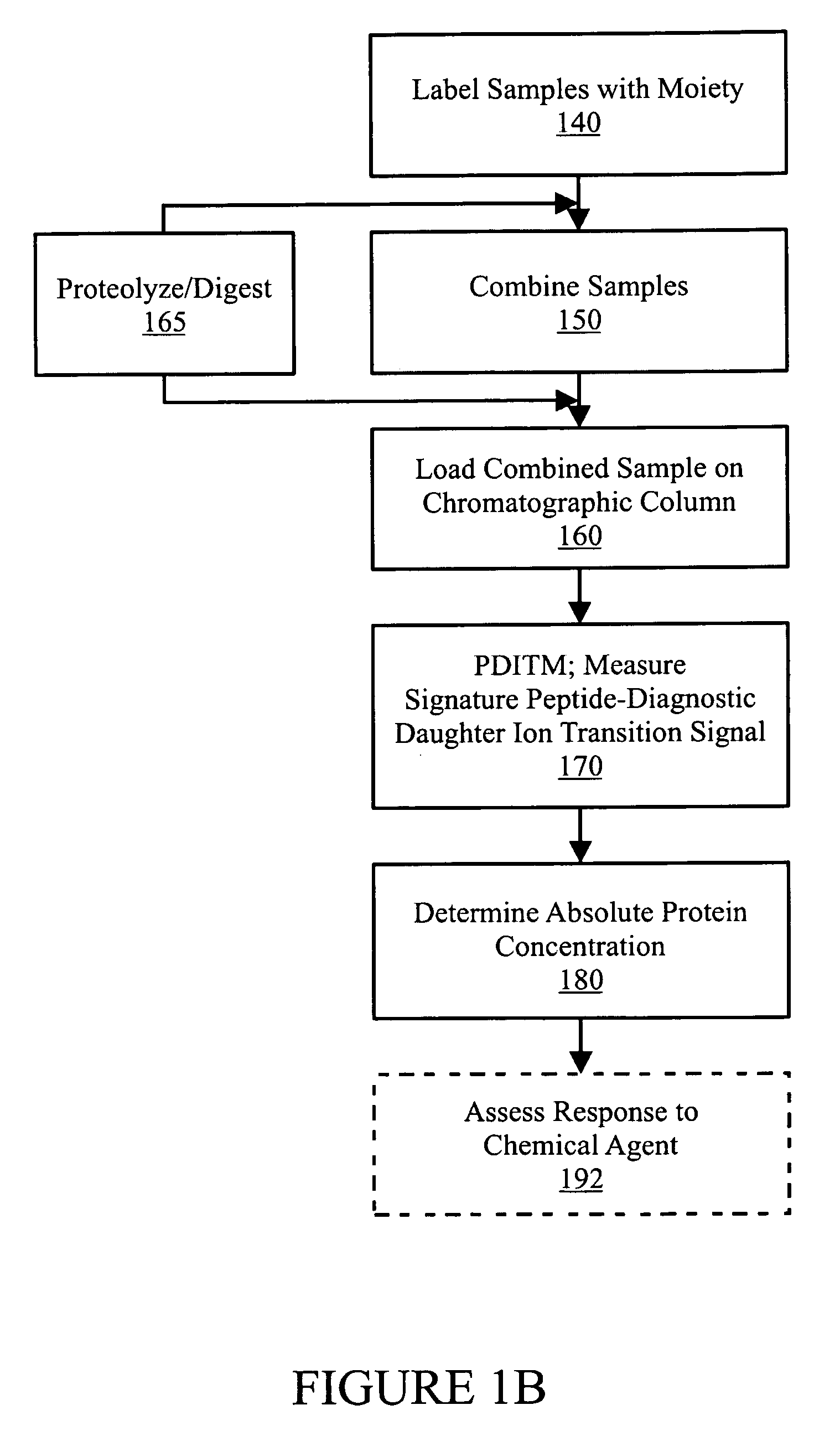
In various aspects, the present teachings provide systems, methods, assays and kits for the absolute quantitation of protein expression. In various aspects, the present teachings provide methods of determining the concentration of one or more proteins of interest in one or more samples of interest. In various aspects, the present teachings provide methods of determining the absolute concentration of one or more isoforms of a protein using standard samples of signature protein fragments and parent-daughter ion transition monitoring (PDITM). In various embodiments, the absolute concentration of multiple isoforms of a biomolecule in a sample, multiple proteins in a biological process, a combination of multiple samples, or combinations thereof, can be determined in a multiplex fashion using the present teachings. In various aspects, provided are methods of assessing the response of a biological system to a chemical agent.
Owner:APPLERA
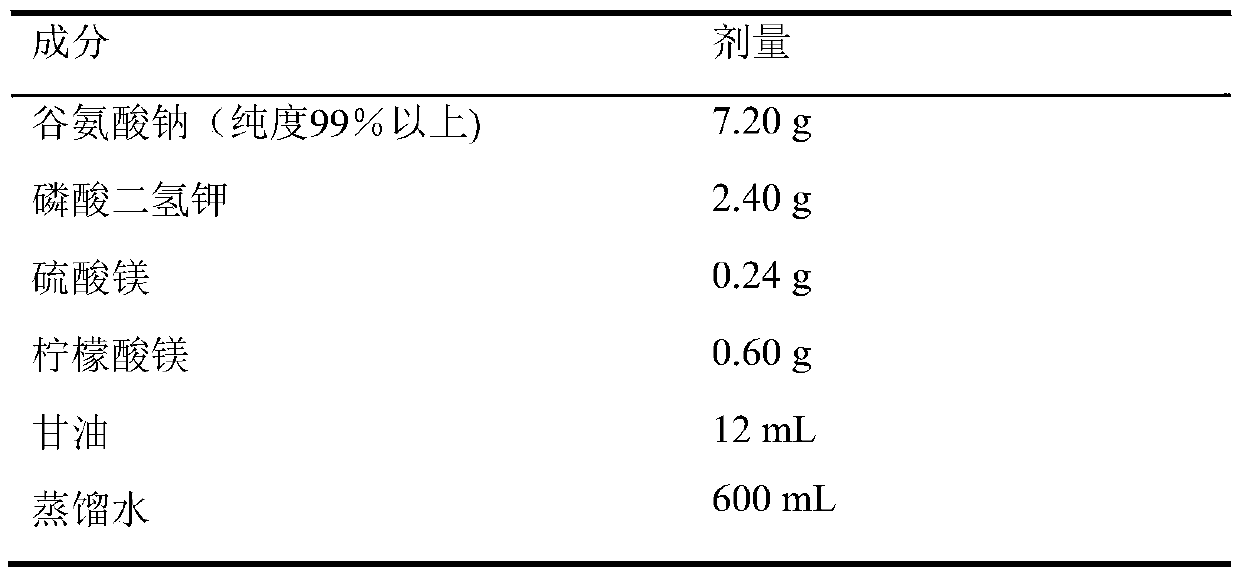
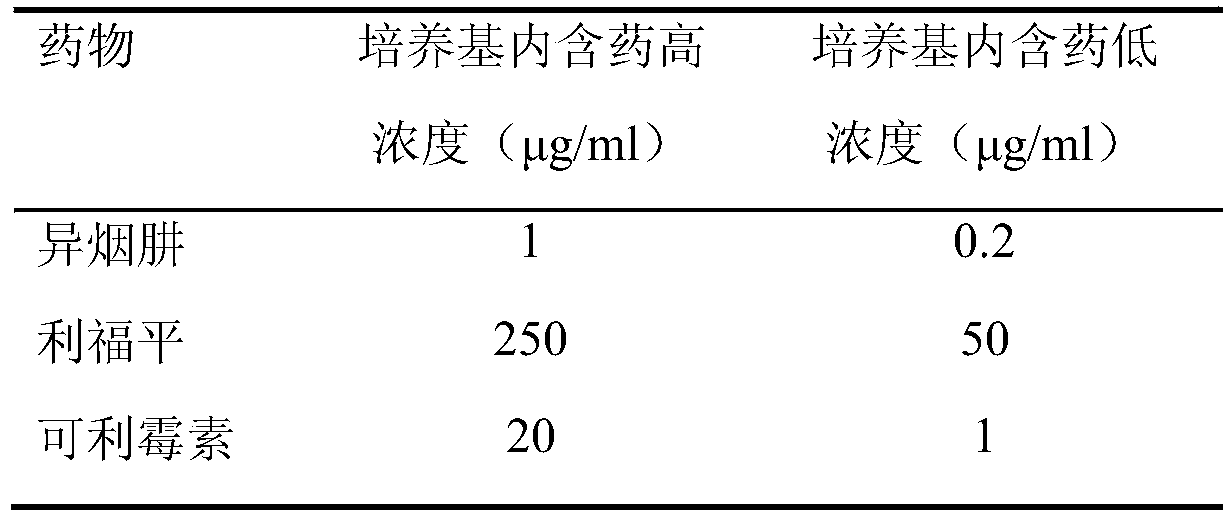
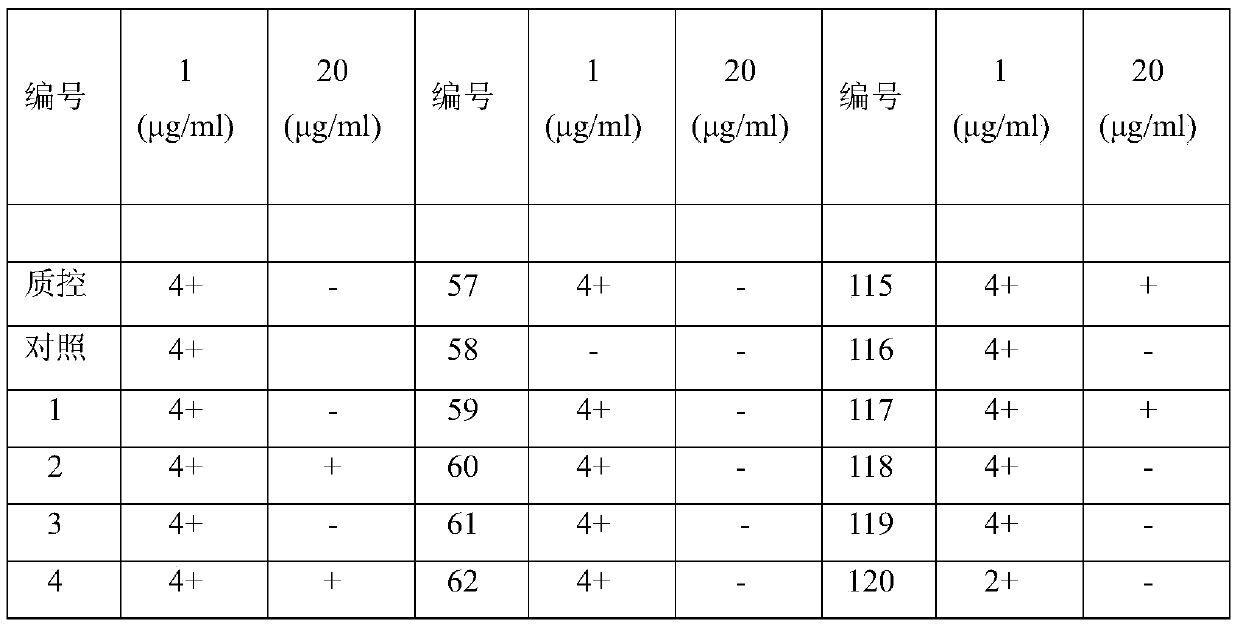
Application of kelimycin in mycobacterium tuberculosis infection resistance
The invention relates to application of kelimycin in mycobacterium tuberculosis infection resistance. The application comprises the following main steps: clinical first-line antitubercular drugs isoniazide and rifamycin are used as contrast, and the antimycobacterial activity of kelimycin is detected by adopting an absolute concentration method. The result indicates that the activity of kelimycin on clinically separated mycobacterium tuberculosis including drug-resistance bacteria is remarkably superior to those of the clinical first-line contrast drugs isoniazide and rifamycin, and novel application of kelimycin is expected to be developed in treatment of tubercle bacillus infected diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGLIAN PHARMA CO LTD
Expression quantification using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20070054345A1Facilitate validationConvenient verificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisOrganismal ProcessMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
In various aspects, the present teachings provide systems, methods, assays and kits for the absolute quantitation of protein expression. In various aspects, the present teachings provide methods of determining the concentration of one or more proteins of interest in one or more samples of interest. In various aspects, the present teachings provide methods of determining the absolute concentration of one or more isoforms of a protein using standard samples of signature protein fragments and parent-daughter ion transition monitoring (PDITM). In various embodiments, the absolute concentration of multiple isoforms of a biomolecule in a sample, multiple proteins in a biological process, a combination of multiple samples, or combinations thereof, can be determined in a multiplex fashion using the present teachings. In various aspects, provided are methods of assessing the response of a biological system to a chemical agent.
Owner:APPLERA
Microfluidic device and related methods
InactiveUS20150111239A1Compound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDiffusionConcentration gradient
A combinatorial microenvironment generator is configured for the generation of arbitrary, user-defined, steady-state, concentration gradients with negligible to no flow through the growth medium to perturb diffusion gradients or cellular growth. More importantly, the absolute concentrations and / or gradients can be dynamically altered upon request both spatially and temporally to impose tailored concentration fields for in-situ stimulus studies. Here, diffusion occurs via an array of ports, each of which can be an independently controlled source / sink. Together, the array of ports establishes a user-defined, 3D concentration profile. Useful methods related to this device are also provided.
Owner:MAINE INST FOR HUMAN GENETICS & HEALTH +1
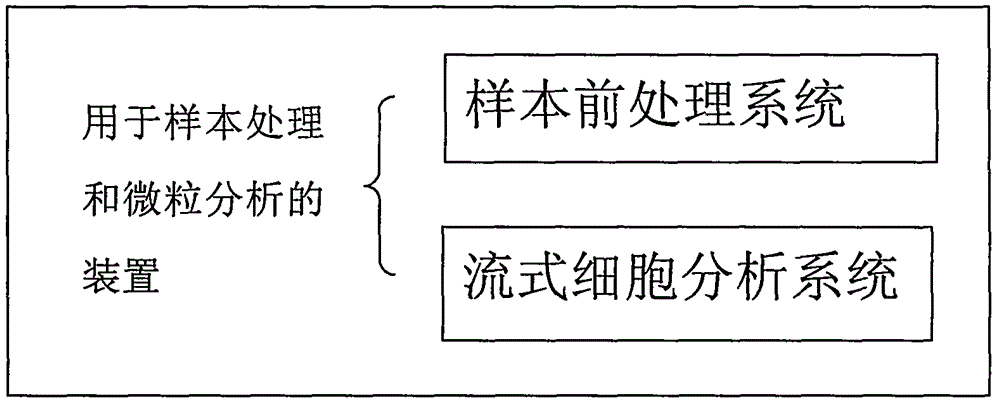
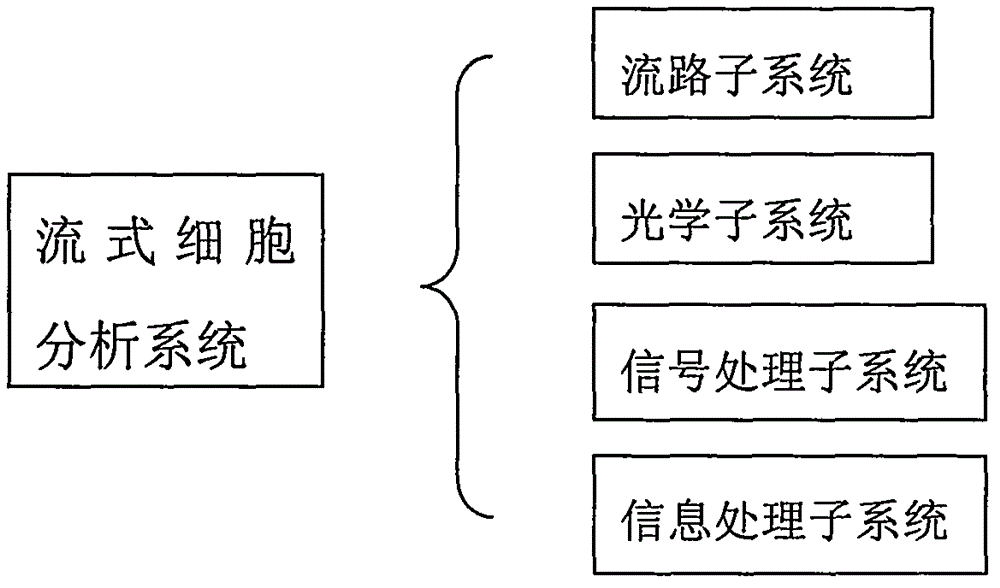
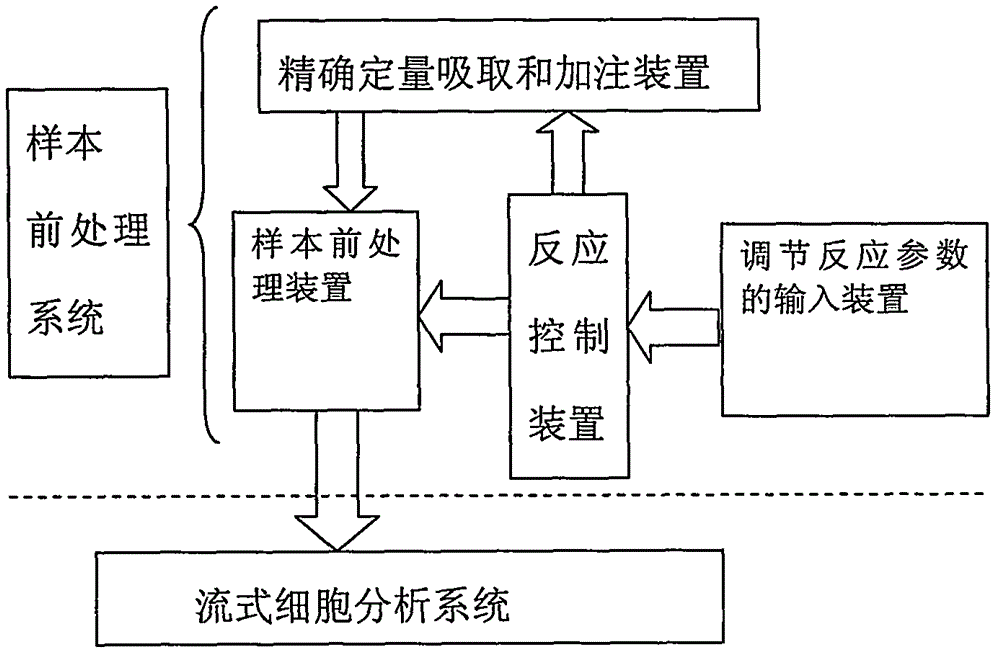
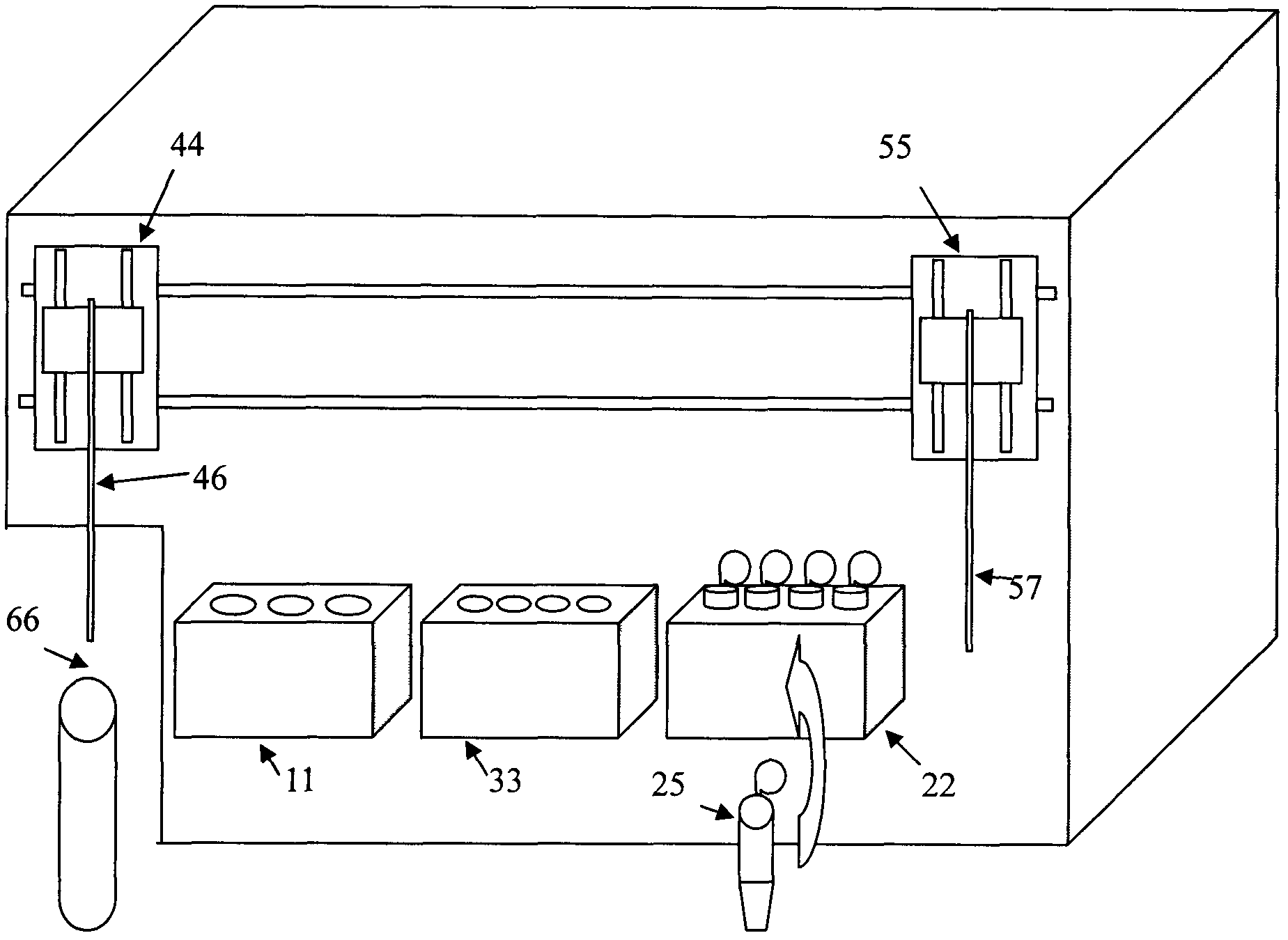
Automatic device for sample treatment and particle analysis, and method for sample treatment and particle analysis
InactiveCN103823073ARealize measurementEnsure consistencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroparticleAbsolute concentration
The invention discloses an automatic device for sample treatment and particle analysis, and a method for sample treatment and particle analysis. A sample pretreatment system in the device comprises a sample pretreatment device, an input device for reaction parameter adjustments, a precise quantitative pipetting and adding device, and a reaction control device; a flow cytometry analysis system in the device can acquire the absolute concentration of a certain kind of targets to be tested. The invention further discloses various work modes in which the device is used for the analysis of the targets to be tested. Through the device and the method disclosed by the invention, the processes of marking reactions, hemolytic reactions and the like can be automatically and precisely controlled, and the parameters such as reaction time and reaction dosage can be adjusted by an operator as needed, so that the experiment consistency and repeatability can be ensured; an absolute concentration analysis of the targets to be tested can be carried out without extra labor or equipment.
Owner:上海纳衍生物科技有限公司
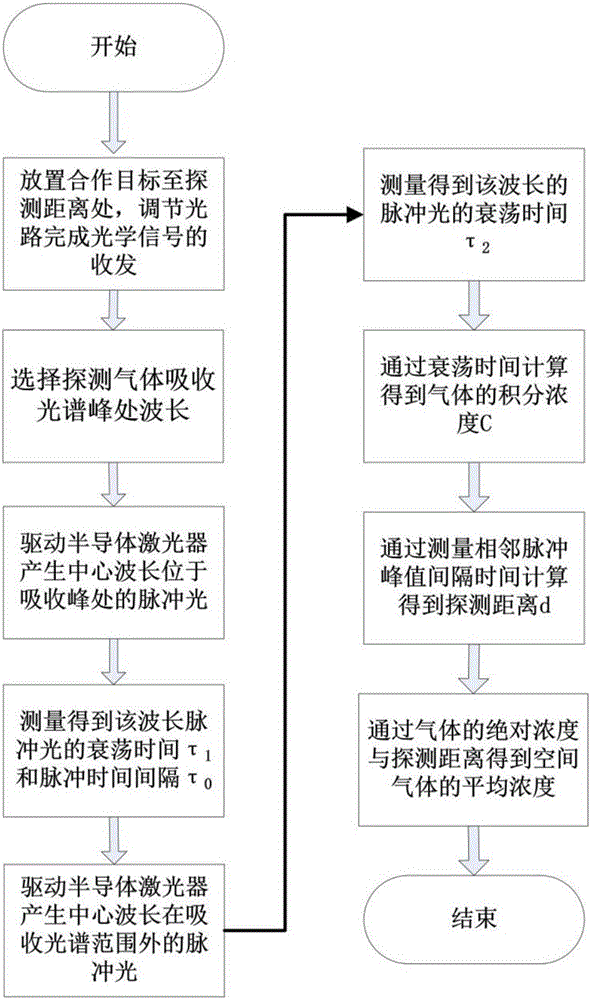
Device and method for measuring mean concentration of gas in open space
ActiveCN105067563AGood coupling efficiencyReduce mistakesColor/spectral properties measurementsErbium dopingOpto electronic
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the mean concentration of gas in open space. The device comprises a semiconductor laser, a semiconductor laser controller, an optical fiber coupler, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a photoelectric detector, an optical transceiving antenna, a single-mode optical fiber and a data processing unit. According to the method, a cavity ring-down technology is used to measure the cavity ring-down time of a laser at a wavelength of an absorption spectrum peak of to-be-measured gas and a laser at a wavelength out of the absorption spectrum range respectively, the absorption coefficient of the gas is obtained through calculation, and then the absolute concentration of the gas is solved through calculation according to the relation of the gas absorption coefficient, the absorption section and the concentration; meanwhile, a detection distance calculated through measurement of the time interval of ring-down pulse; the mean concentration of the gas is obtained through calculation on the basis of the known integrated concentration of the gas in the open space and detection distance. The method has the characteristics of high measurement sensitivity and high anti-interference capacity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of determining a measurement value on the basis of single molecule events
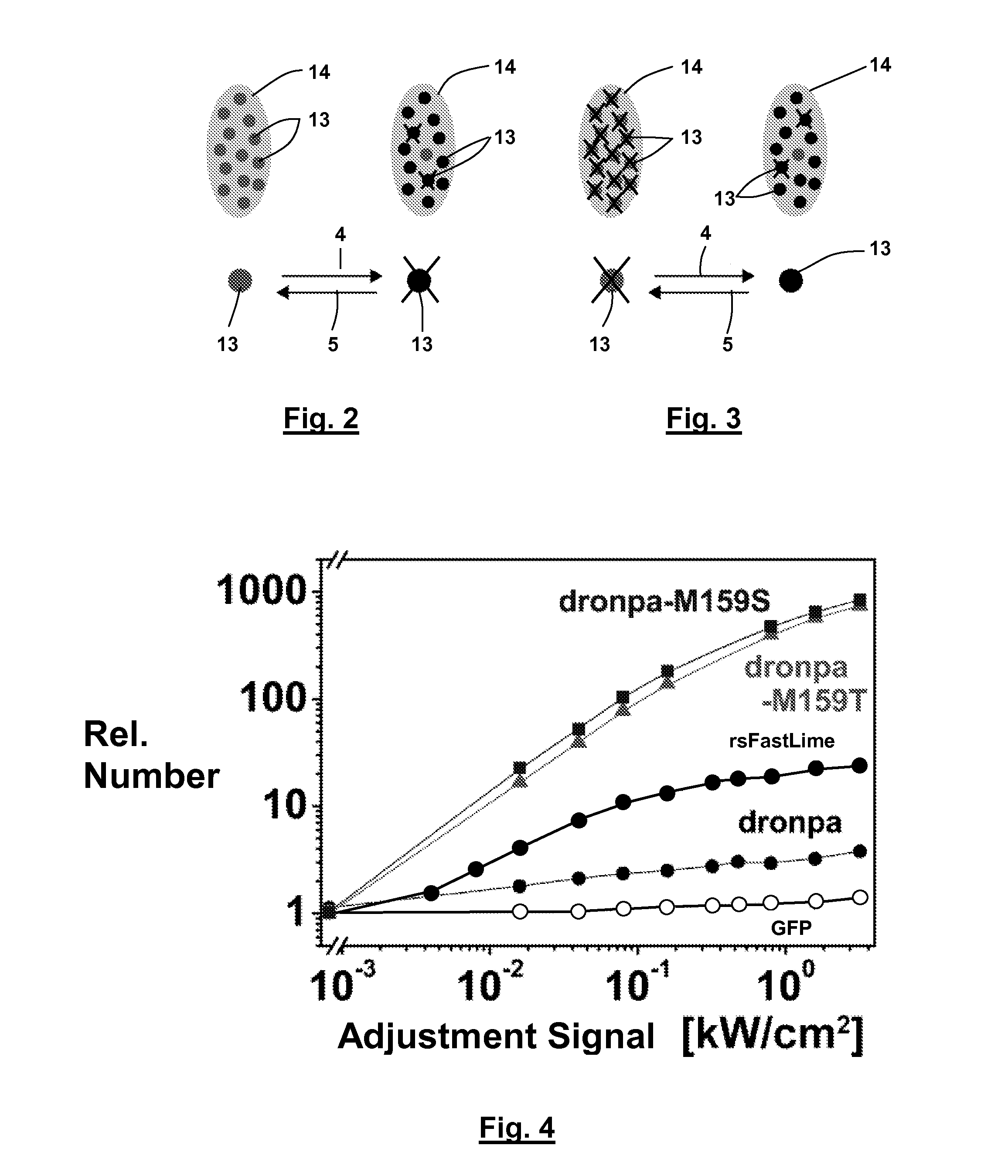
A method of determining a measurement value on the basis of a plurality of single molecule events of marker molecules in a sample comprises the steps of selecting the marker molecules from a group of marker molecules which are transferable between a measurable state in which a measurement signal necessary for determining the at least one measurement value is obtainable from the marker molecules and a non-measurable state, of providing the marker molecules in the sample at such an absolute concentration that the at least one measurement value is not determinable, if all marker molecules are in their measurable state, and adjusting a measurement concentration of the marker molecules in the measurable state by means of applying the physical signal to the sample at such an intensity that the at least one measurement value is determinable within a defined measurement area of the sample.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Apparatus and apparatus control method for the quantitative concentration determination of selected substances filtered out of a patient's body in a fluid
ActiveUS9423338B2Easy to integrateDifficult to doseInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsDialysis systemsExtinctionQuantitative determination
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for determining a substance in a fluid excreted / extracted from the body or spent dialysate, e.g., for determining a quality measure for the dialysis, such as the concentration of selected toxic substances, and / or for determining a removed total quantity of uremic toxins during a dialysis with a dialysis apparatus. A concentration of a substance in the fluid may be determined by: detecting, by an absorption sensor, a first extinction signal of the fluid at an analysis wavelength at a defined first pH value of the fluid; adjusting, by a pH adjusting device, a second pH value of the fluid which differs from the first pH value; detecting, by the absorption sensor, a second extinction signal of the fluid at the analysis wavelength at the second pH value; and processing / comparing the two extinction signals for the first and the second pH values and determining an absolute concentration of the substance dissolved in the fluid.
Owner:B BRAUN AVITUM
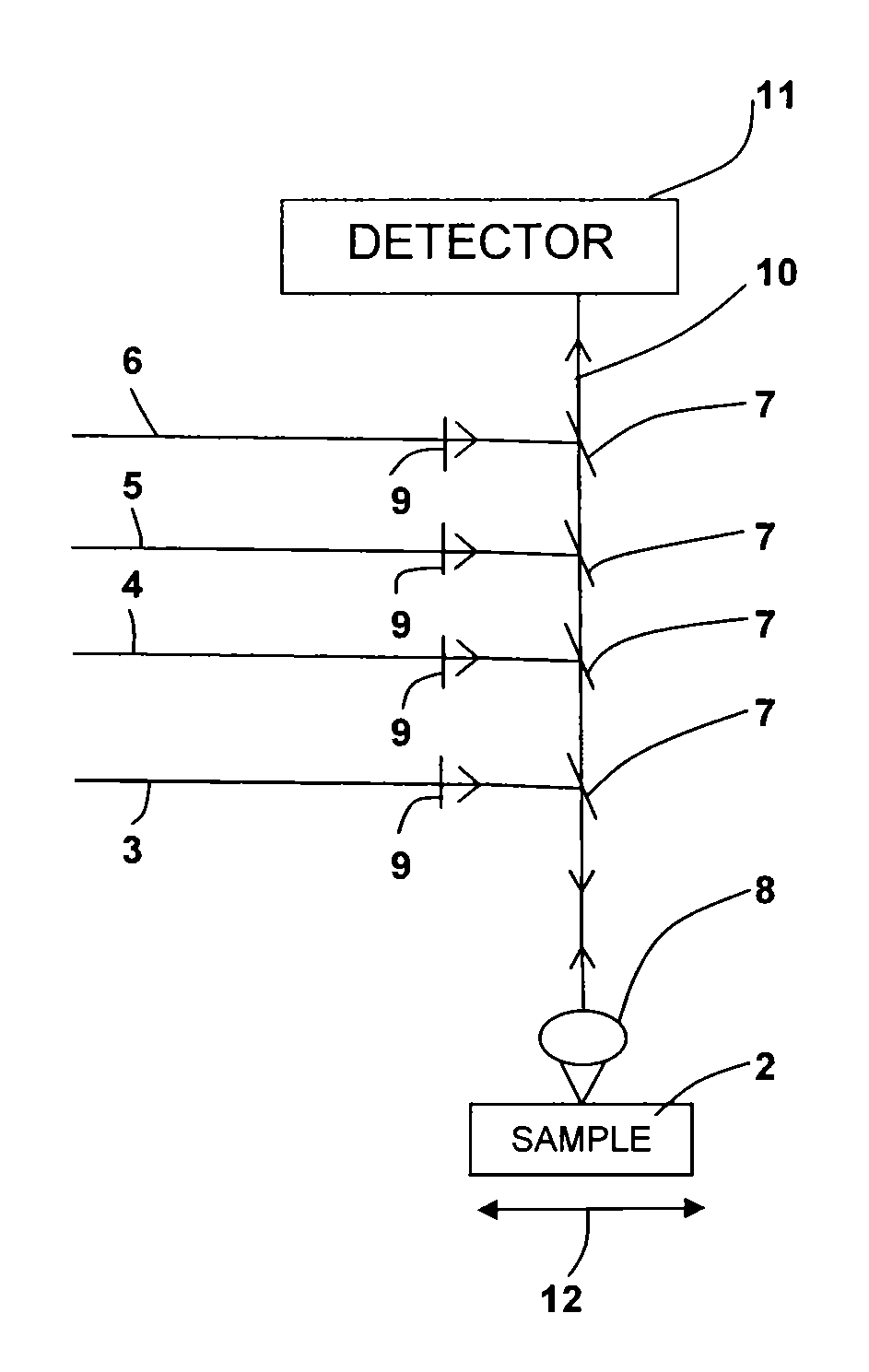
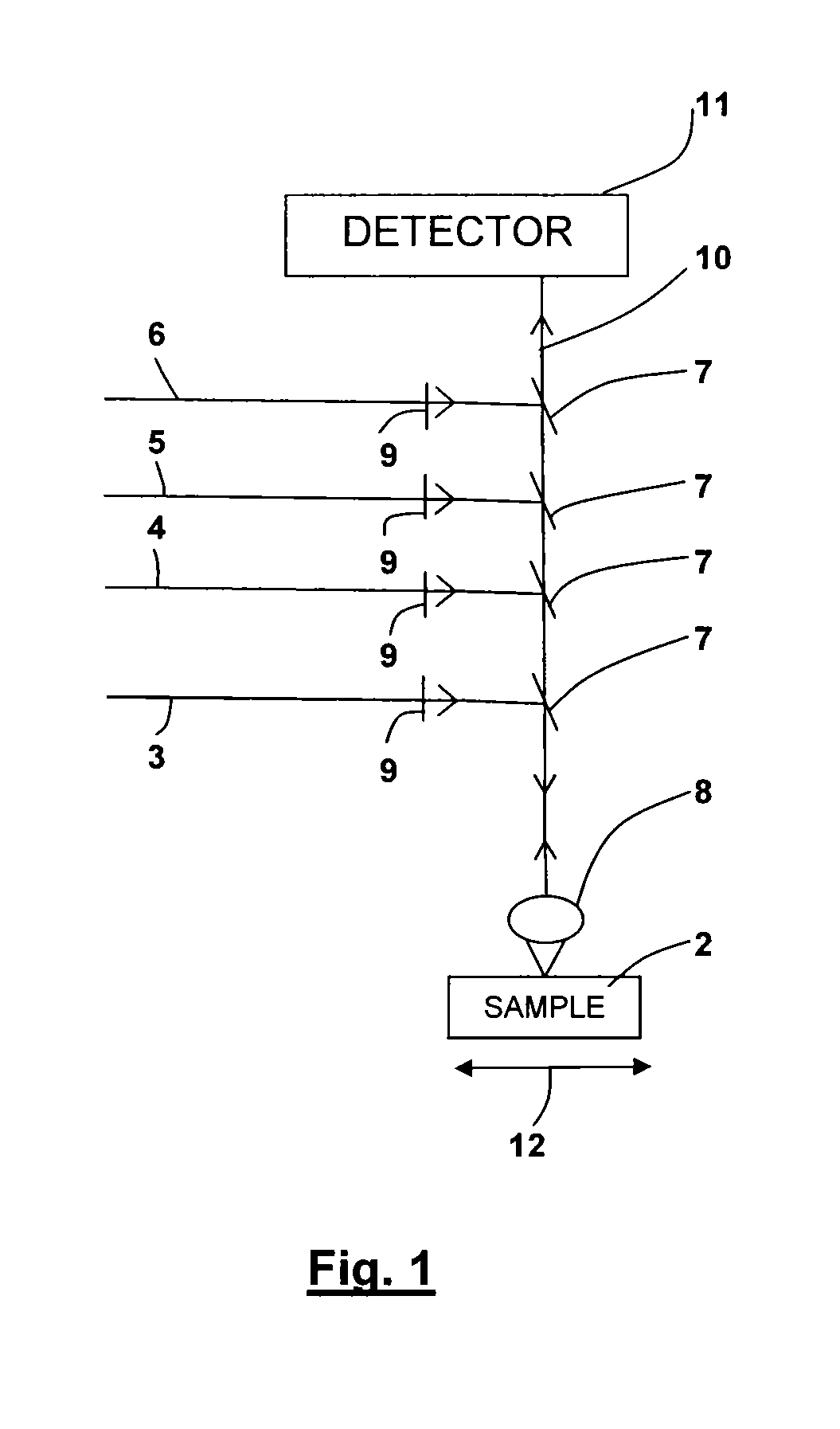
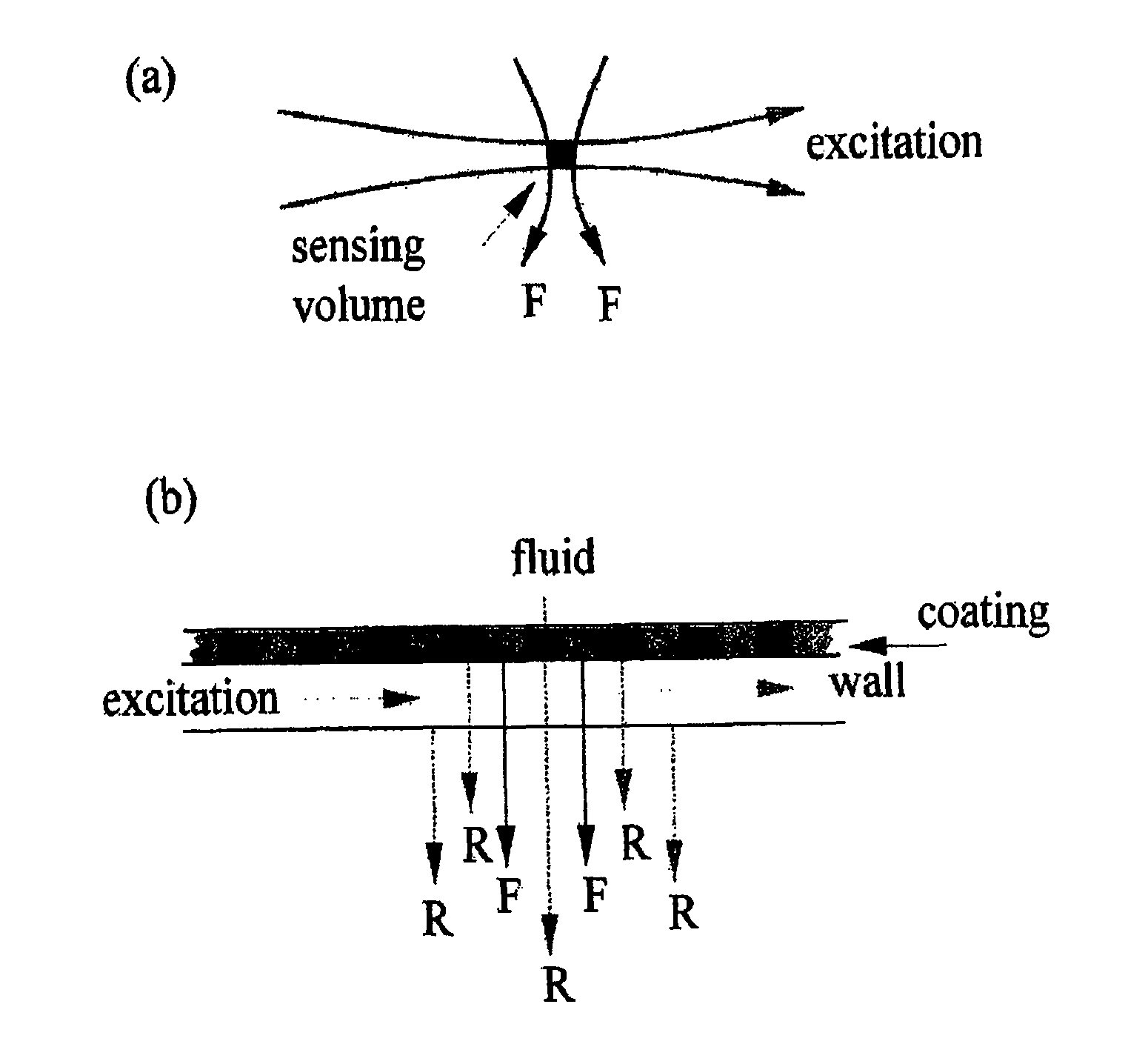
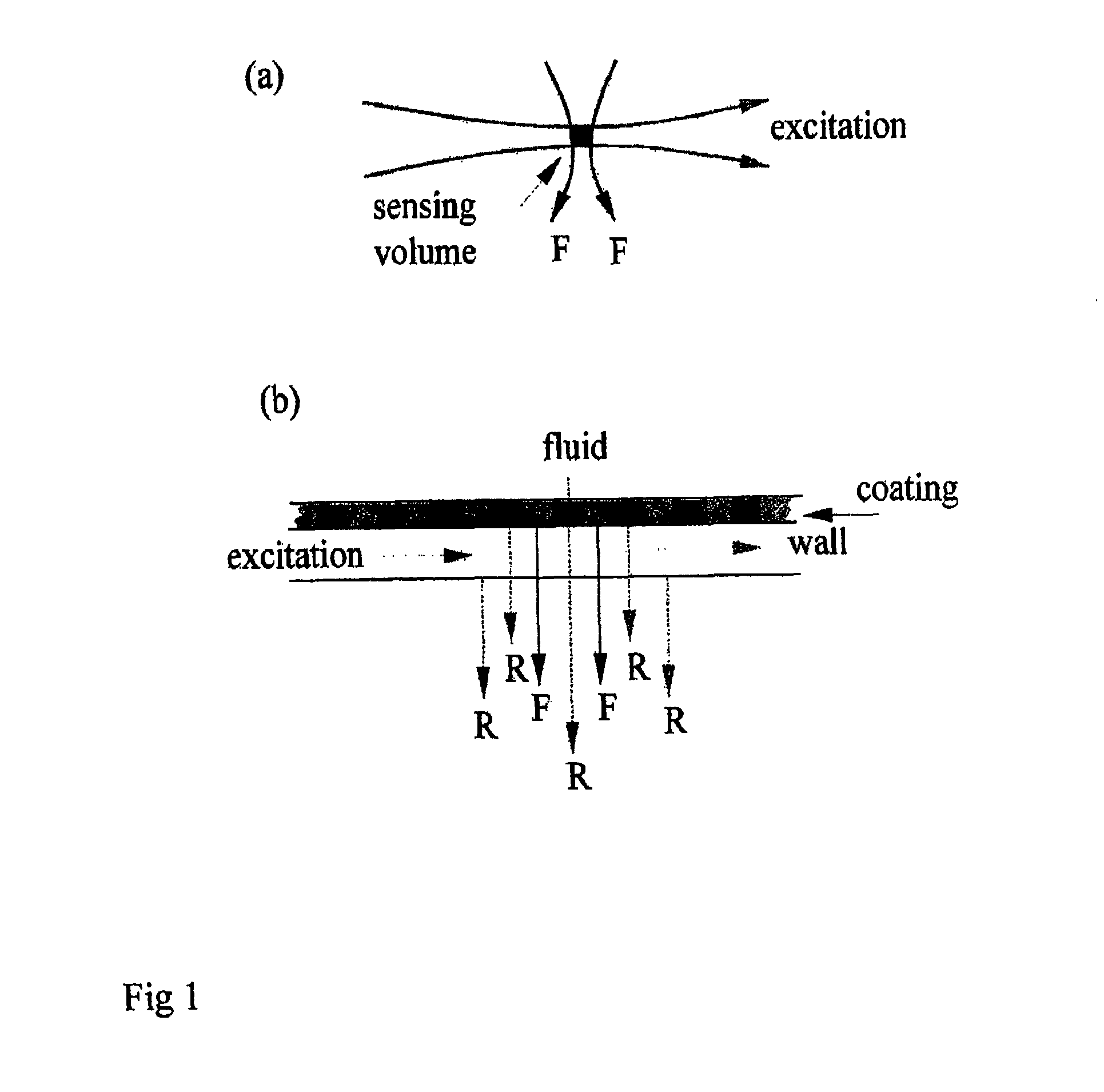
Dual detector capillary waveguide biosensor and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20100163748A1PhotometryScattering properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
A method for fluorescence detection that provides control of experimental and molecular factors and reliably predicts of concentration from fluorescence intensity measurements utilizing capillary-based flow sensors utilizing a dual detector approach to provide instantaneous normalization of the fluorescent intensity by the Rayleigh scattered intensity measured from the same sensing volume, insensitive to various experimental parameters for prediction of absolute concentrations of fluorescent solutes.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
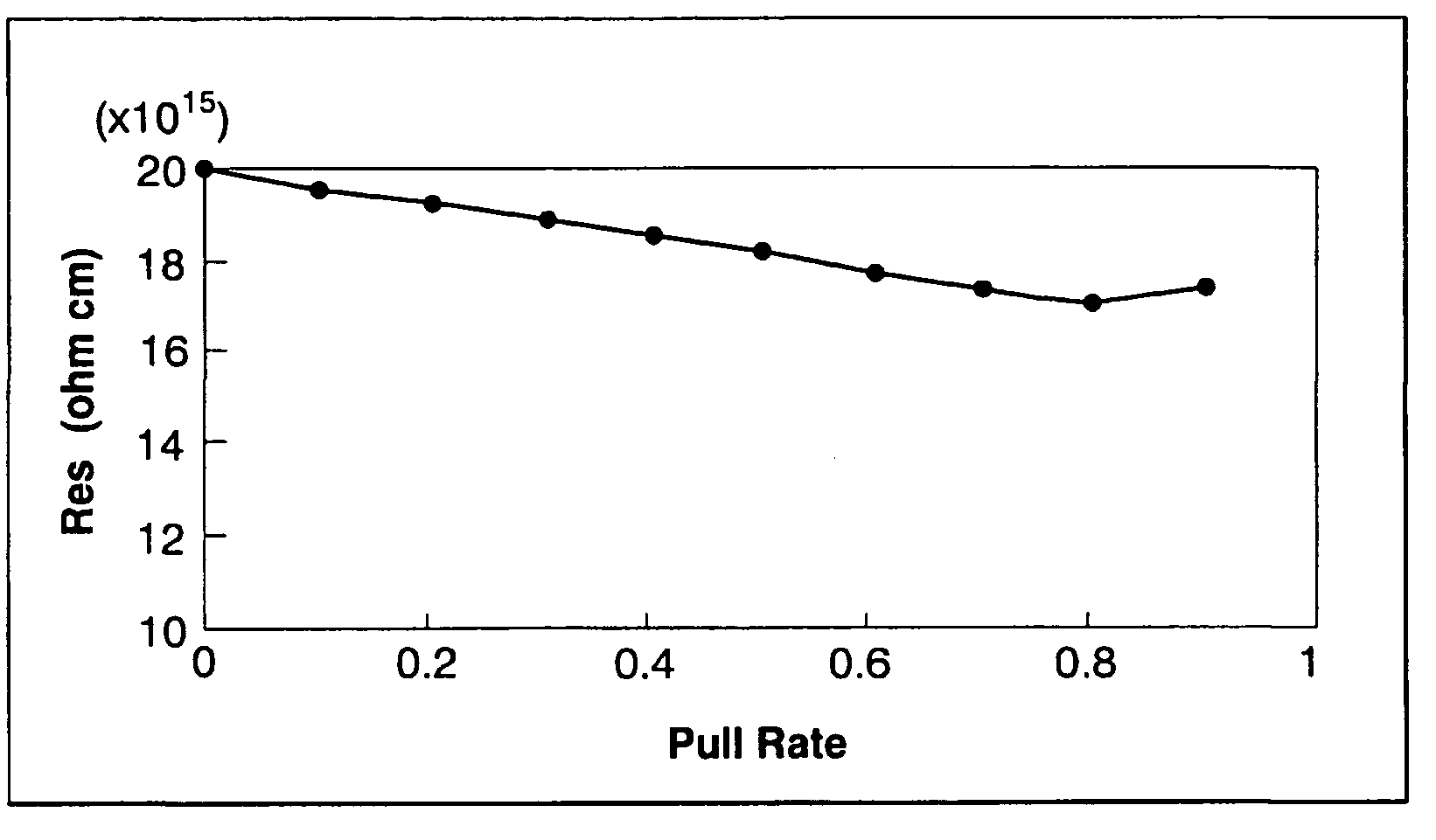
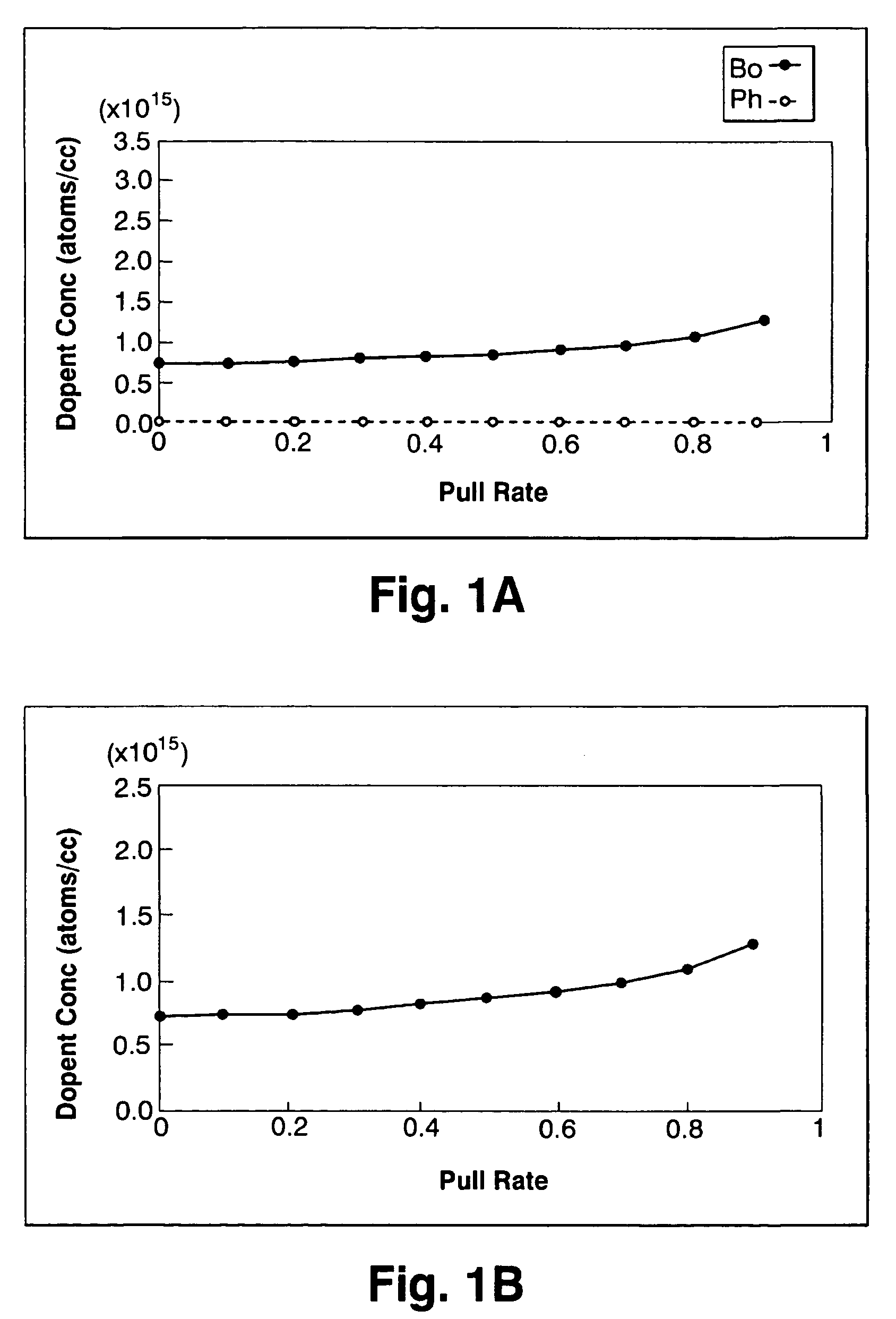
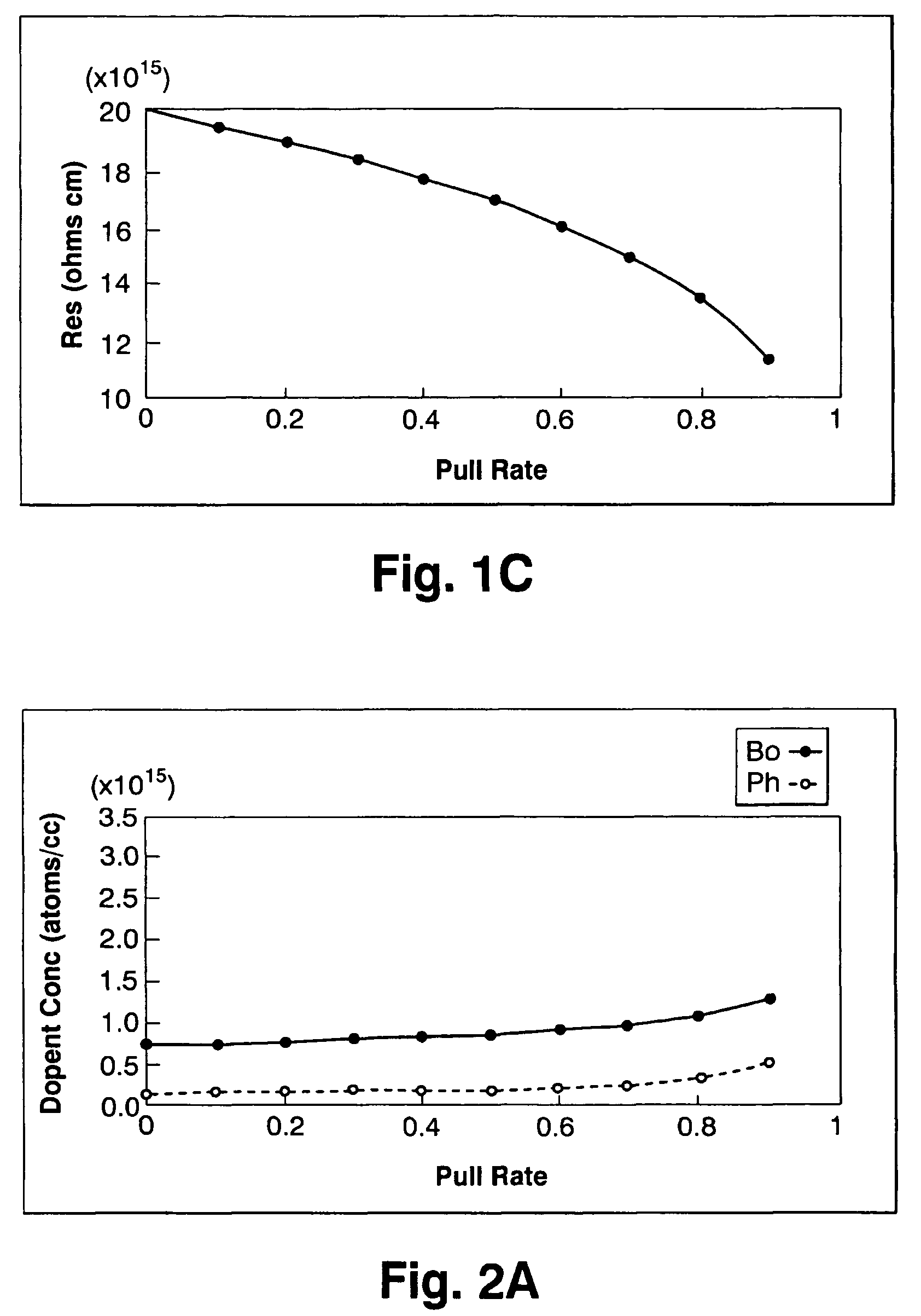
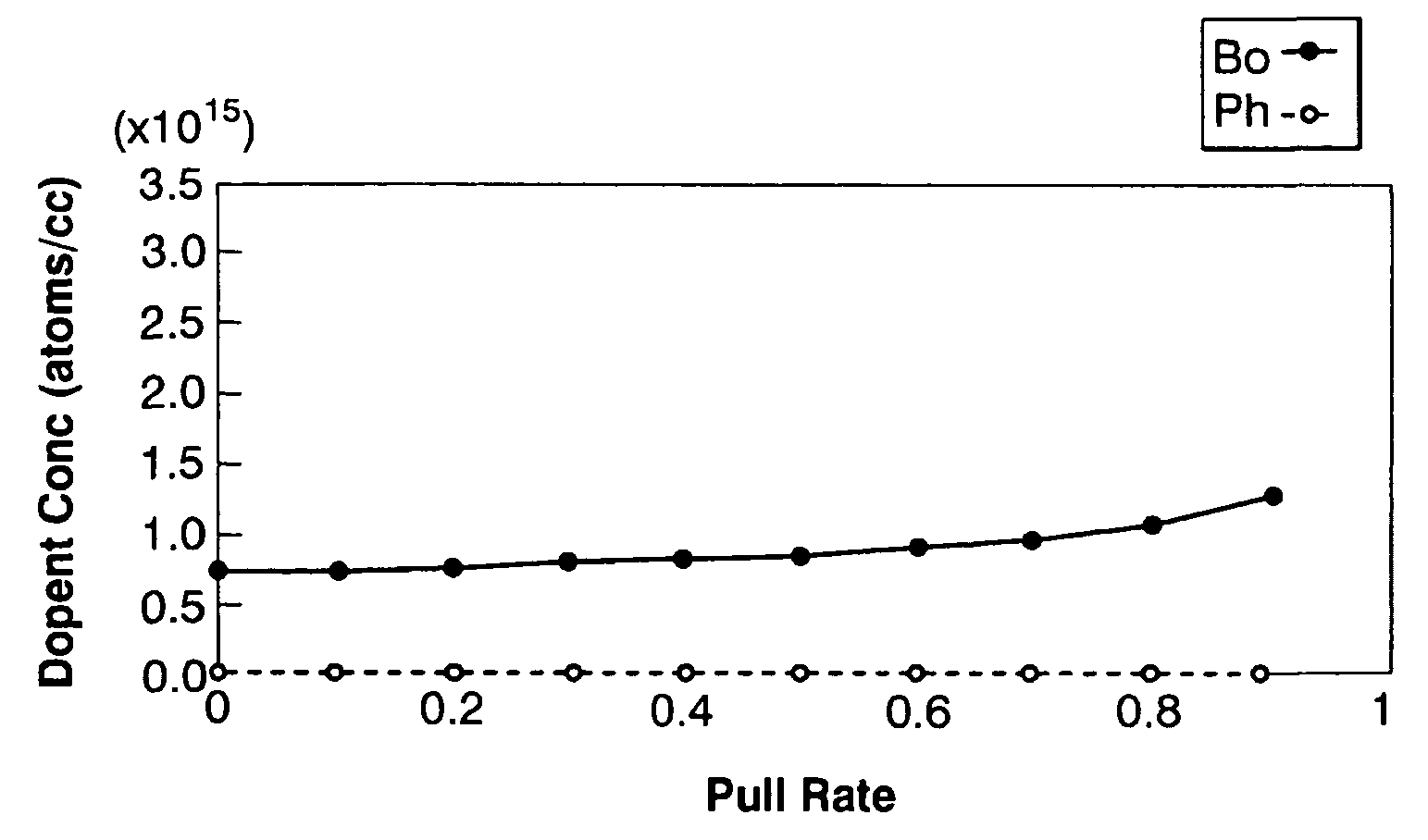
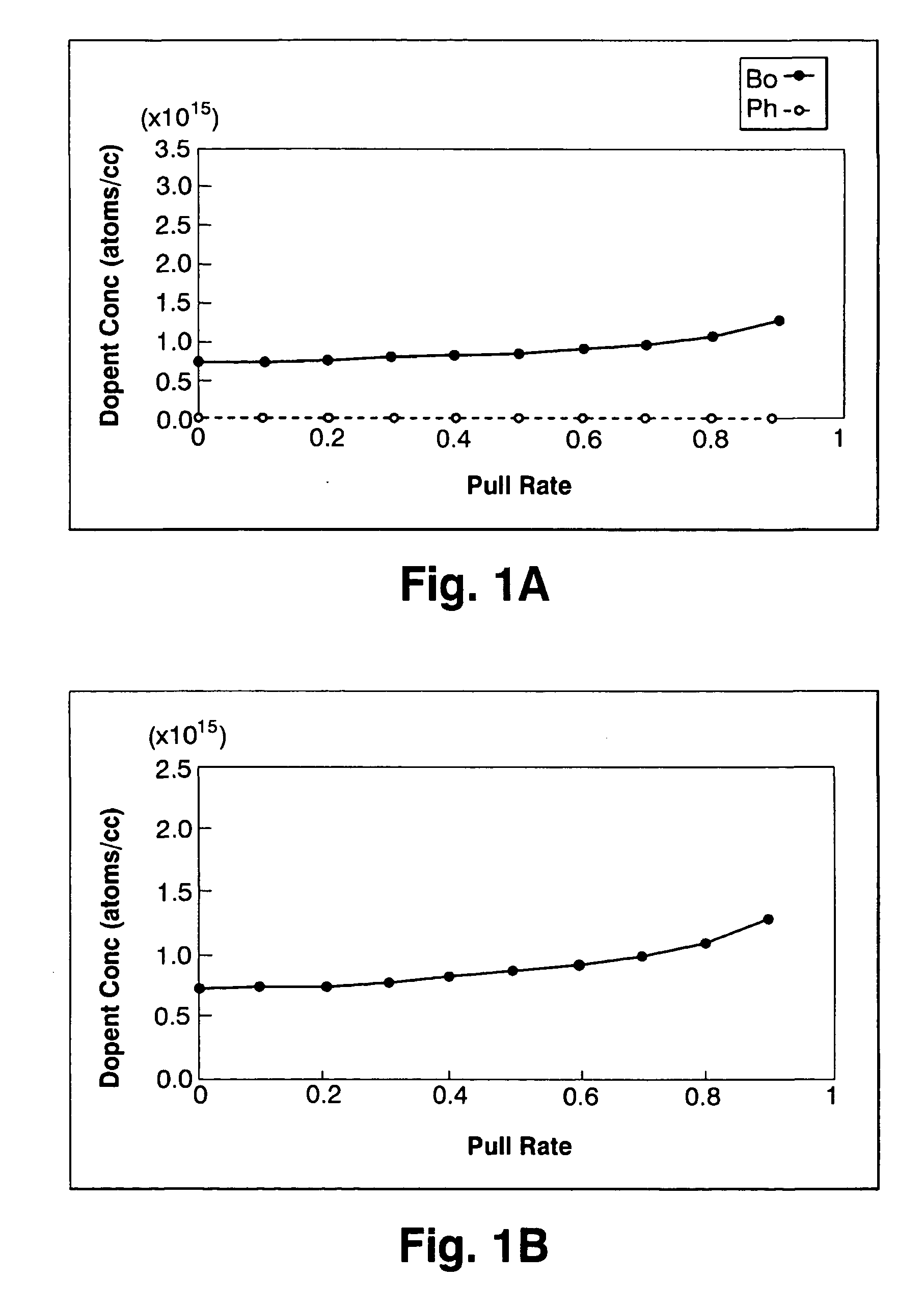
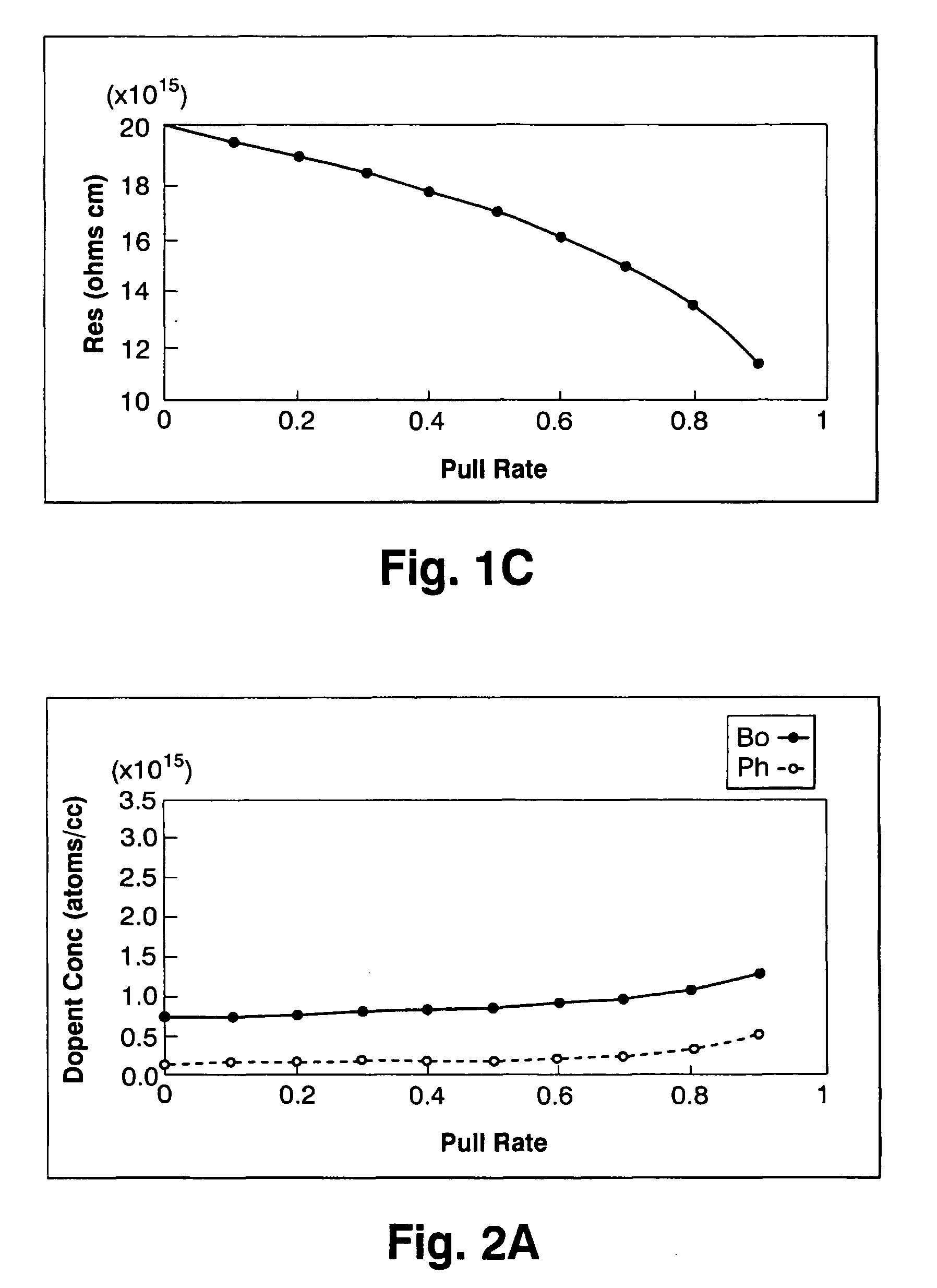
Silicon single crystal and method for growing silicon single crystal
ActiveUS7214267B2Improve the overall coefficientIncrease productionPolycrystalline material growthSiliconCzochralski methodSingle crystal
A silicon single crystal and a method for growing a silicon single crystal are provided. A p-type silicon single crystal is grown with a uniform resistivity value in a pulling direction. Pulling is conducted by the Czochralski method from molten silicon obtained by adding phosphorus to an initial melt in an amount equivalent to 25˜35% of an absolute concentration (atoms / cc) of boron contained in the melt.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Silicon single crystal and method for growing silicon single crystal
ActiveUS20050252442A1Improve the overall coefficientIncrease productionPolycrystalline material growthSiliconCzochralski methodSingle crystal
A silicon single crystal and a method for growing a silicon single crystal are provided. A p-type silicon single crystal is grown with a uniform resistivity value in a pulling direction. Pulling is conducted by the Czochralski method from molten silicon obtained by adding phosphorus to an initial melt in an amount equivalent to 25˜35% of an absolute concentration (atoms / cc) of boron contained in the melt.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Expression Quantification Using Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20100227352A1Easy to observeEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisStandard samplesChemical agent
Owner:APPLERA +1
Graphene field effect transistor array biosensor and preparation method and detection method thereof
ActiveCN108956742AAvoid non-specific bindingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAntigenTransistor
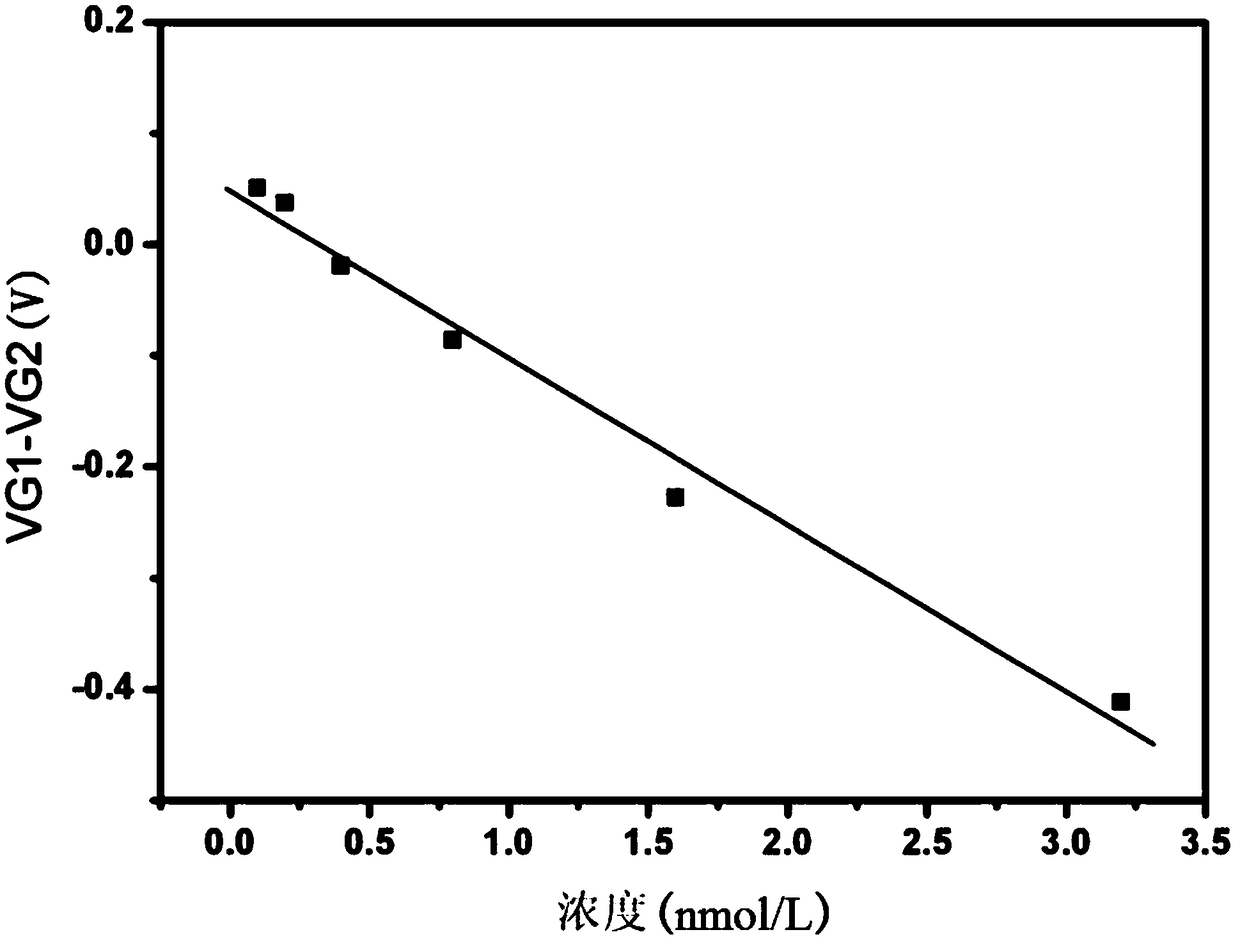
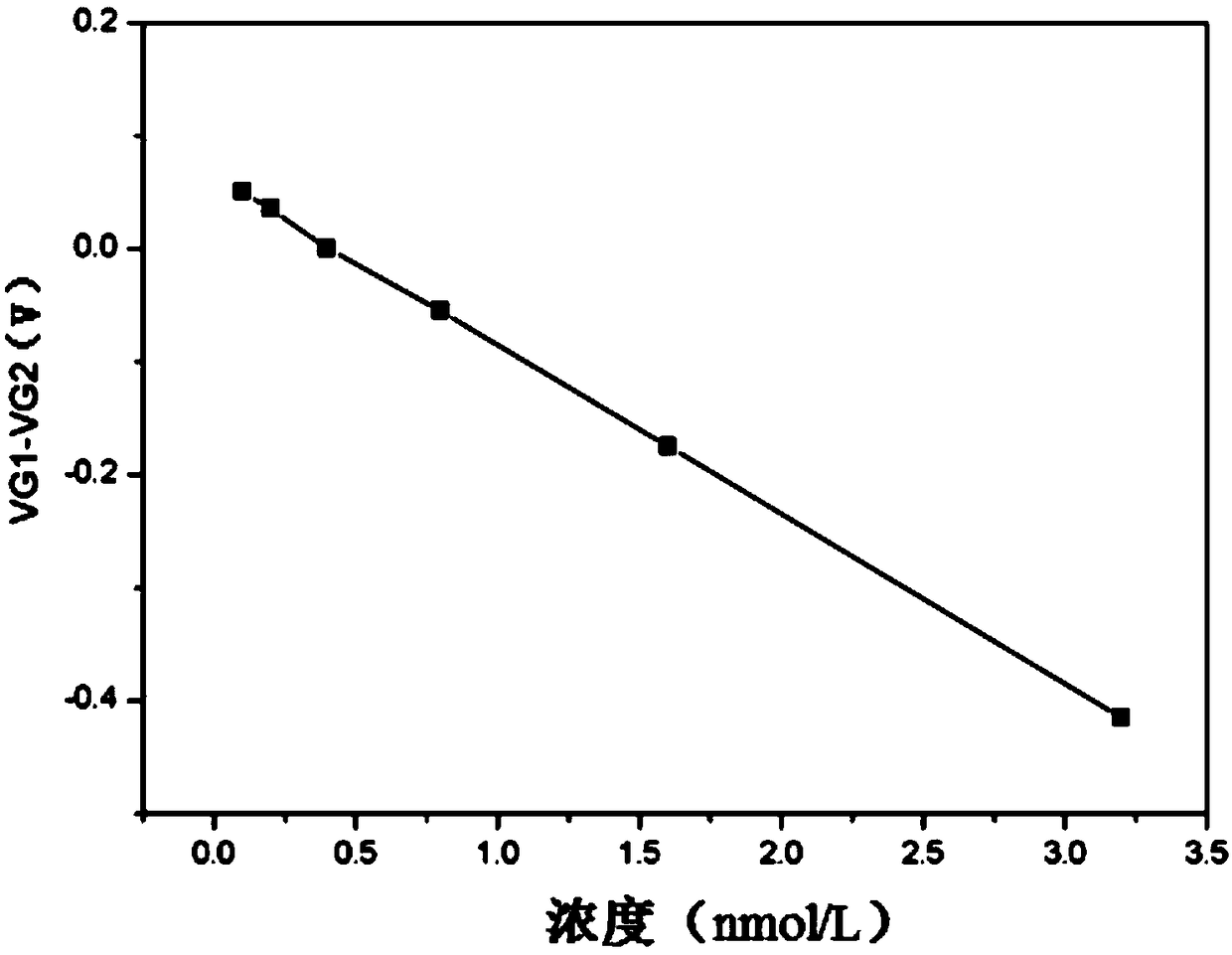
The invention relates to a graphene field effect transistor array biosensor and a preparation method and a detection method thereof. The invention relates to a biosensor and a preparation method and adetection method thereof, aiming at solving the problem of relatively low accuracy in the detection process of the existing graphene field effect transistor array biosensor. The sensor comprises a silicon substrate, an oxidization layer, a first metal grid electrode, a second metal grid electrode, a gate insulating layer, a first graphene conductive channel layer, a second graphene conductive channel layer, a first group source, a leakage electrode, a second group source and a leakage electrode; the preparation method comprises the following steps: I. making a transistor structure; II. performing aldehyde treatment on the graphene surface; III. modifying a detection unit graphene surface to capture antibody molecules; and IV. closing the remaining active sites on the graphene surfaces ofa detection unit and a reference unit; the detection method comprises the following steps: soaking the sensor in a solution containing be-detected antigen, and detecting the voltage at the graphene dirac point of the detection unit and the reference unit, to obtain the absolute concentration of the to-be-detected substance solution, wherein a difference value corresponds to a standard working curve.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV +1
Method for distinguishing outbreak cause of algae in environment by utilizing molecular ion spectroscopy
InactiveCN101858883AAccurate discriminationNo damageMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicro imagingAutomatic control
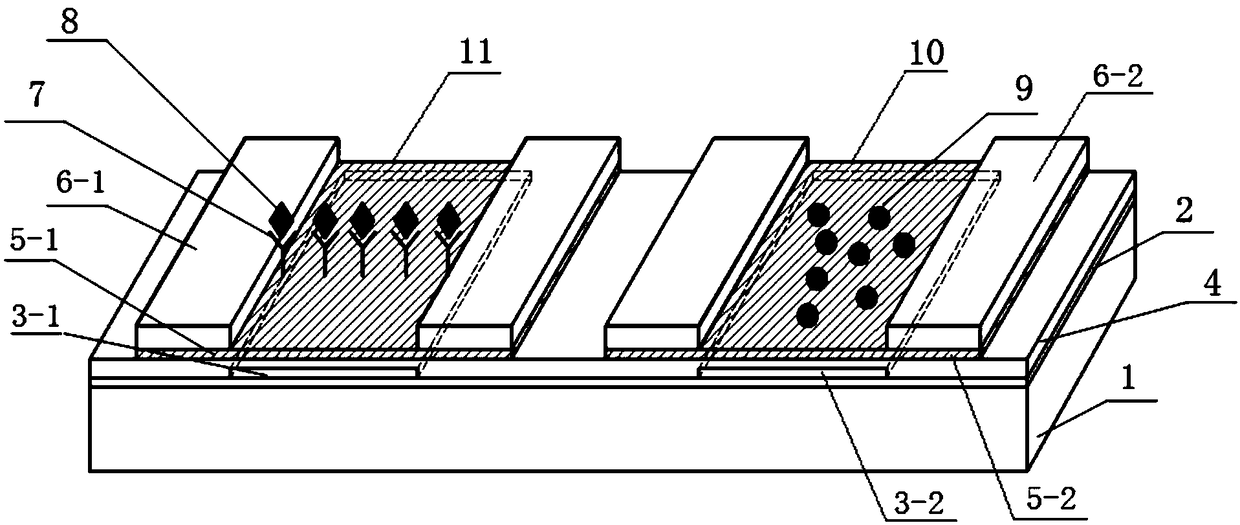
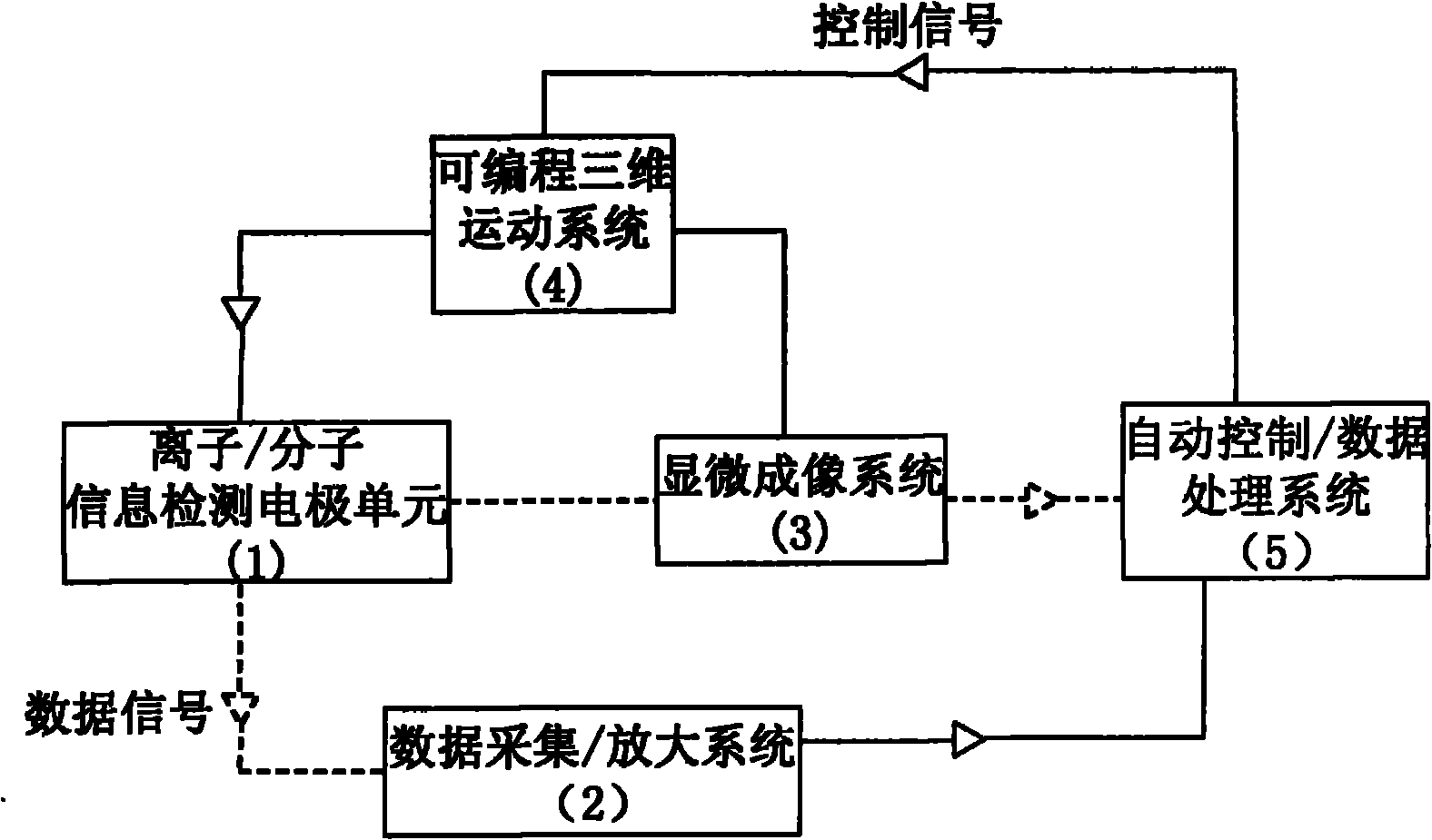
The invention provides a method for distinguishing the outbreak cause of algae in the environment by utilizing a non-invasive way to detect molecular ion spectrum. The technical system comprises an ion / molecule information detection electrode unit (1), a data acquisition / amplification system (2), a micro-imaging system (3), a programmable three-dimensional motion system (4) and an automatic control / data processing system (5). Under the premise of not contacting algae in a real living environment, the invention adopts a manual or programmatic method to measure the absolute concentration, flow rate and three-dimensional motion direction and other parameters of ion / molecule in and out of the surface of the algae at real time according to the setting of researchers so as to obtain the molecular ion spectrum related to the outbreak of the algae in the environment, and directly represents the relationship between physiological activity process of the algae in the real living environment and environmental factors. The method is non-invasive to the algae, has comprehensive data collection, quick and accurate analysis results, and effectively saves manpower and financial cost.
Owner:XUYUE BEIJING
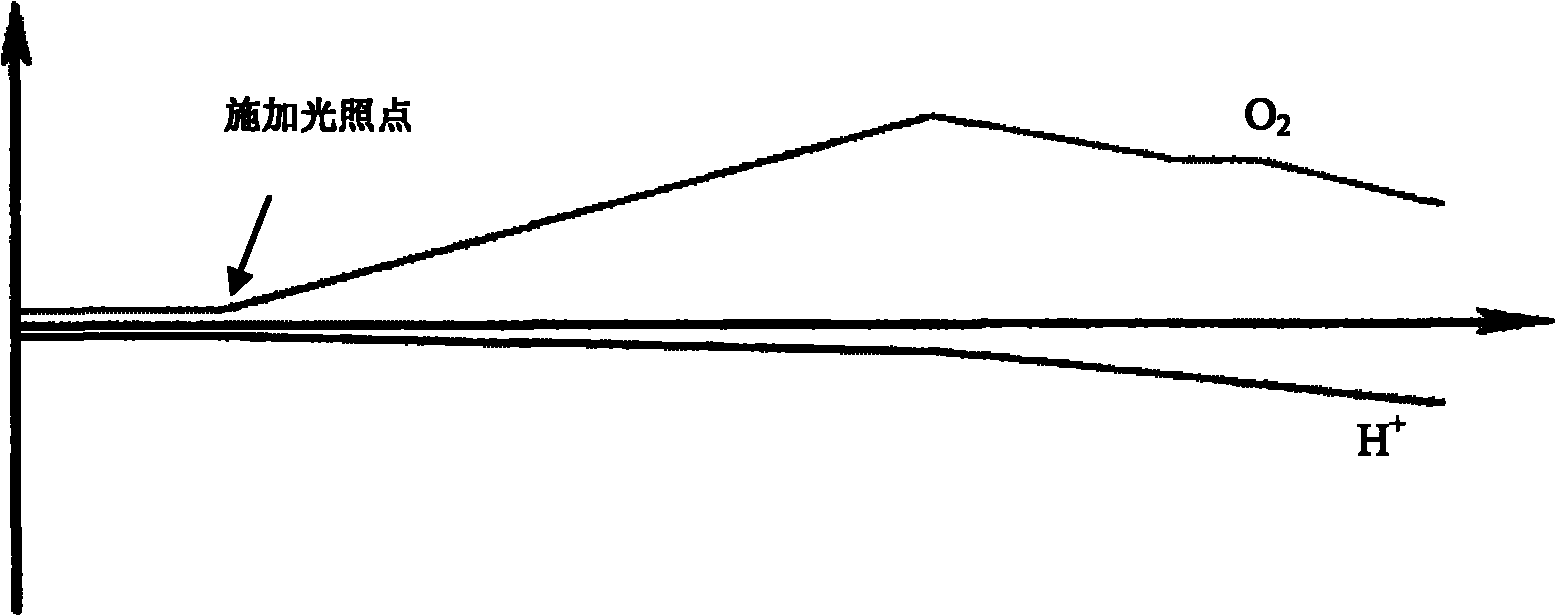
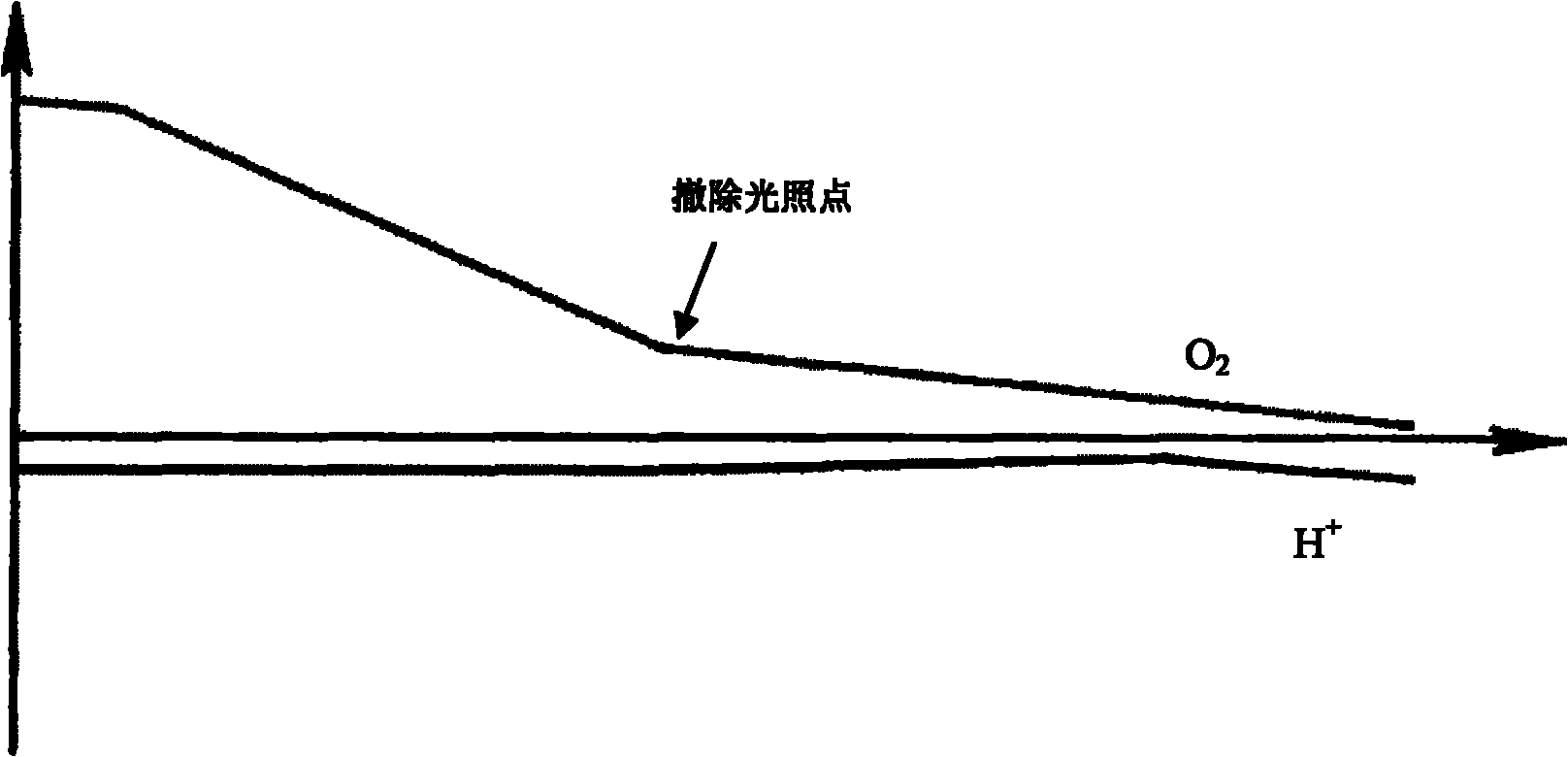
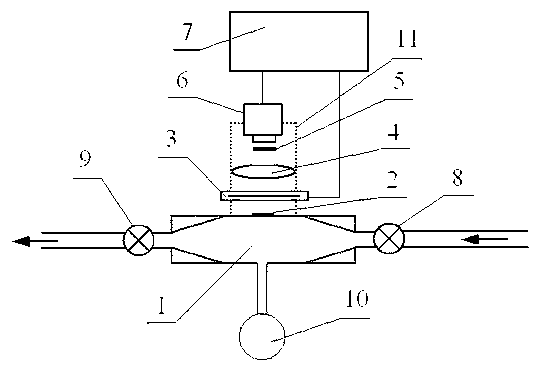
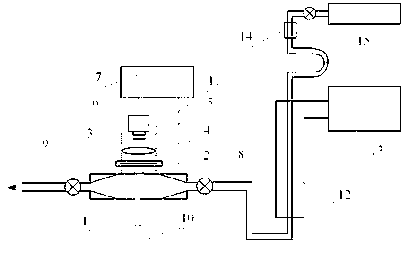
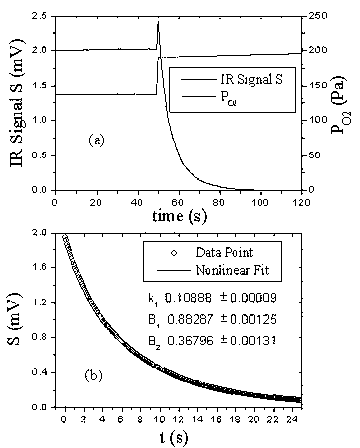
Method and device for measuring absolute concentration of singlet-state oxygen
InactiveCN102759506ASimple structureLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansDynamic modelsData acquisition
The invention provides a method and device for measuring the absolute concentration of singlet-state oxygen (O2(al(delta)). The device comprises a static pool, an infrared detection system and a data acquisition system, wherein the infrared detection system is composed of a chopper, a lens, a narrow-band interference optical filter, an infrared detector and a phase-locked amplifier. In the invention, by monitoring the infrared radiation attenuation change of O2(al(delta)) at 1.27 microns in the static pool and combining the dynamic model analysis in the static pool, the absolute response coefficient of the infrared detection system can be automatically calibrated, and the absolute concentration of O2(al(delta)) can be further measured in real time. Moreover, the infrared attenuation method of the static pool can be applied to the real-time measurement for any flowing system containing O2(al(delta)) by use of a 'flowing-stopping' technology.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Experimental device and experimental method for detecting OH concentration by utilizing SDBD (Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge) and emission spectrum
ActiveCN106872417APromote absorptionEasy to detectAnalysis by electrical excitationNanosecondExperimental methods
The invention discloses an experimental device and an experimental method for detecting OH concentration by utilizing SDBD (Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge) and emission spectrum and belongs to the technical field of plasma. The experimental device is mainly composed of a circular line-line type SDBD generator (1), a power system (2), an air supply system (3), an ultraviolet source system (4) and an emission spectrum diagnosis system (5). The method comprises the following steps: generating surface dielectric barrier discharge plasma by nanosecond pulses power supply excitation, and detecting the absolute concentration of OH free radical in the plasma by utilizing the ultraviolet source and emission spectrum technology. When the absolute concentration of OH is detected, only the emission spectrum of ultraviolet light is detected, then the emission spectrum of the ultraviolet light passing through a discharge plasma area is detected, and finally, the absolute concentration of OH free radical is calculated. According to the device and method disclosed by the invention, the defects in the traditional technology that the operation is complicated, the equipment is expensive and the like when the absolute concentration of active species is detected can be overcome.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Methods for extracting and measuring concentrations of biomolecules in complex matrices without the need for immunocapture
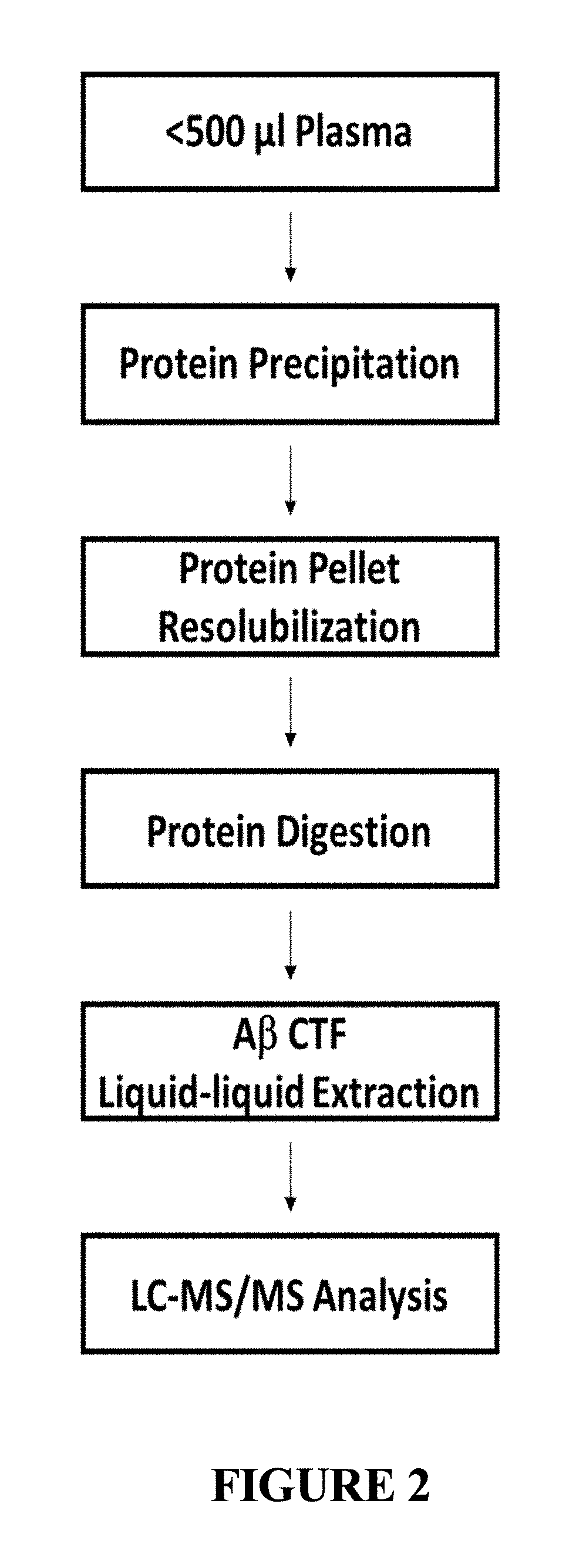
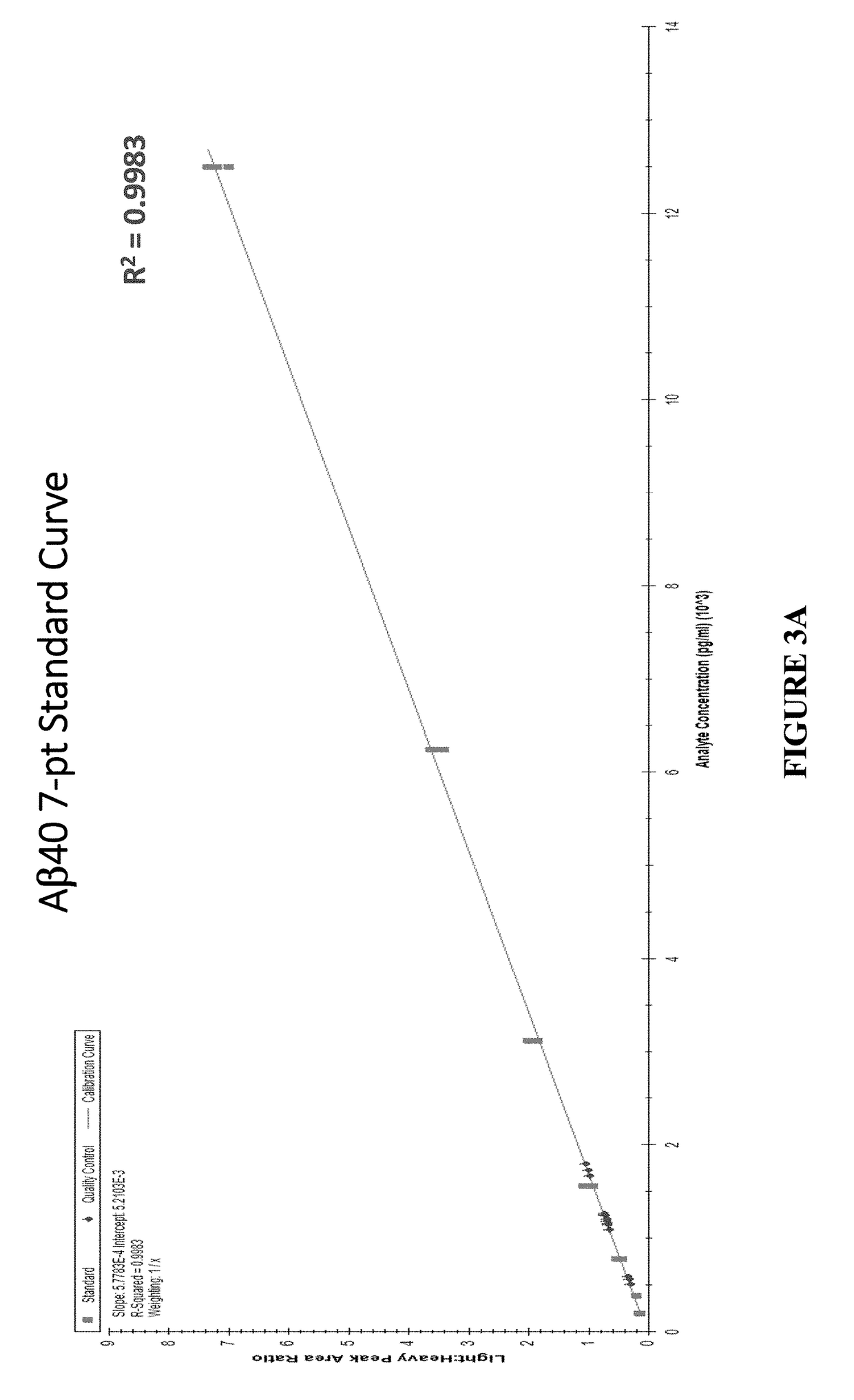
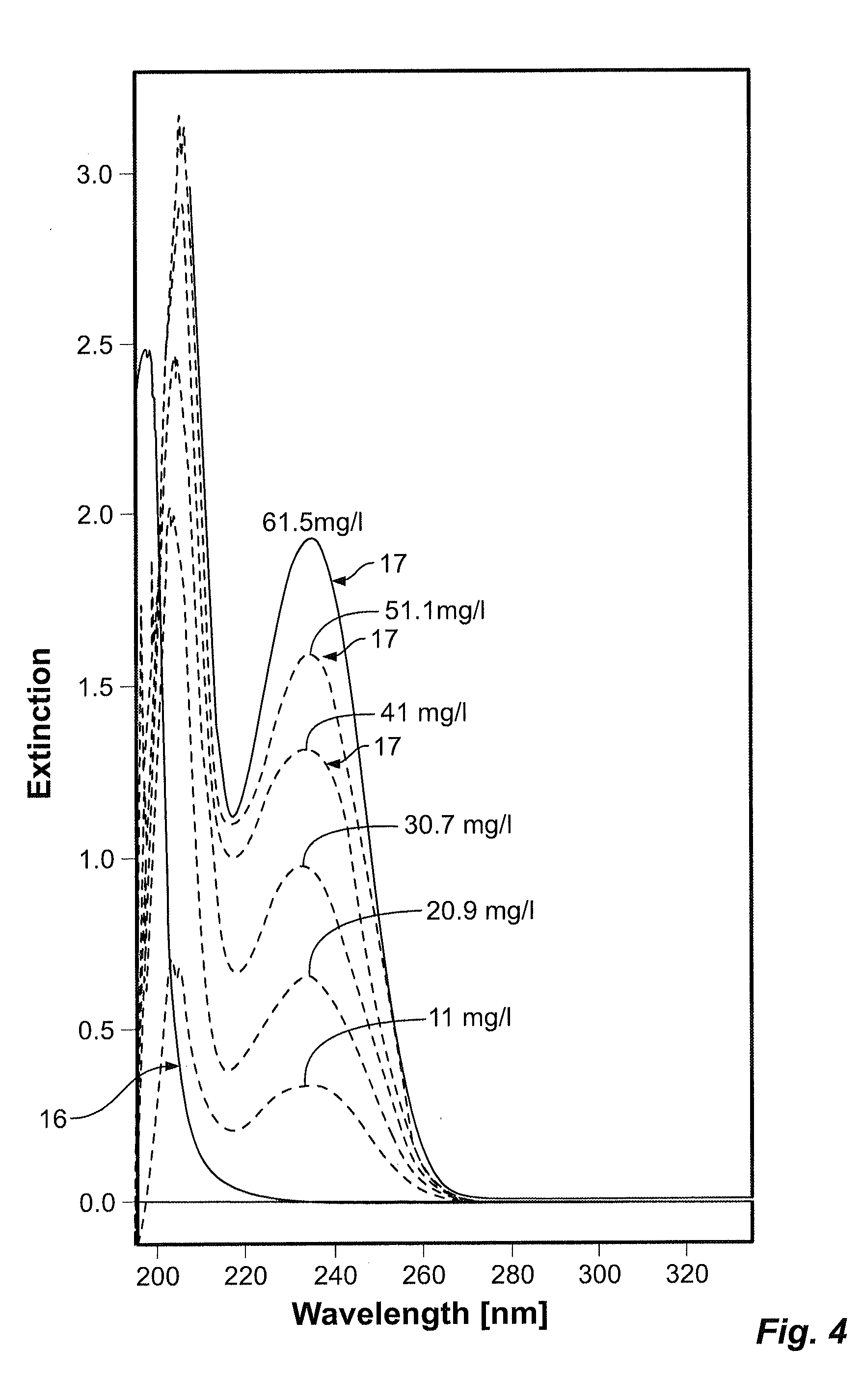
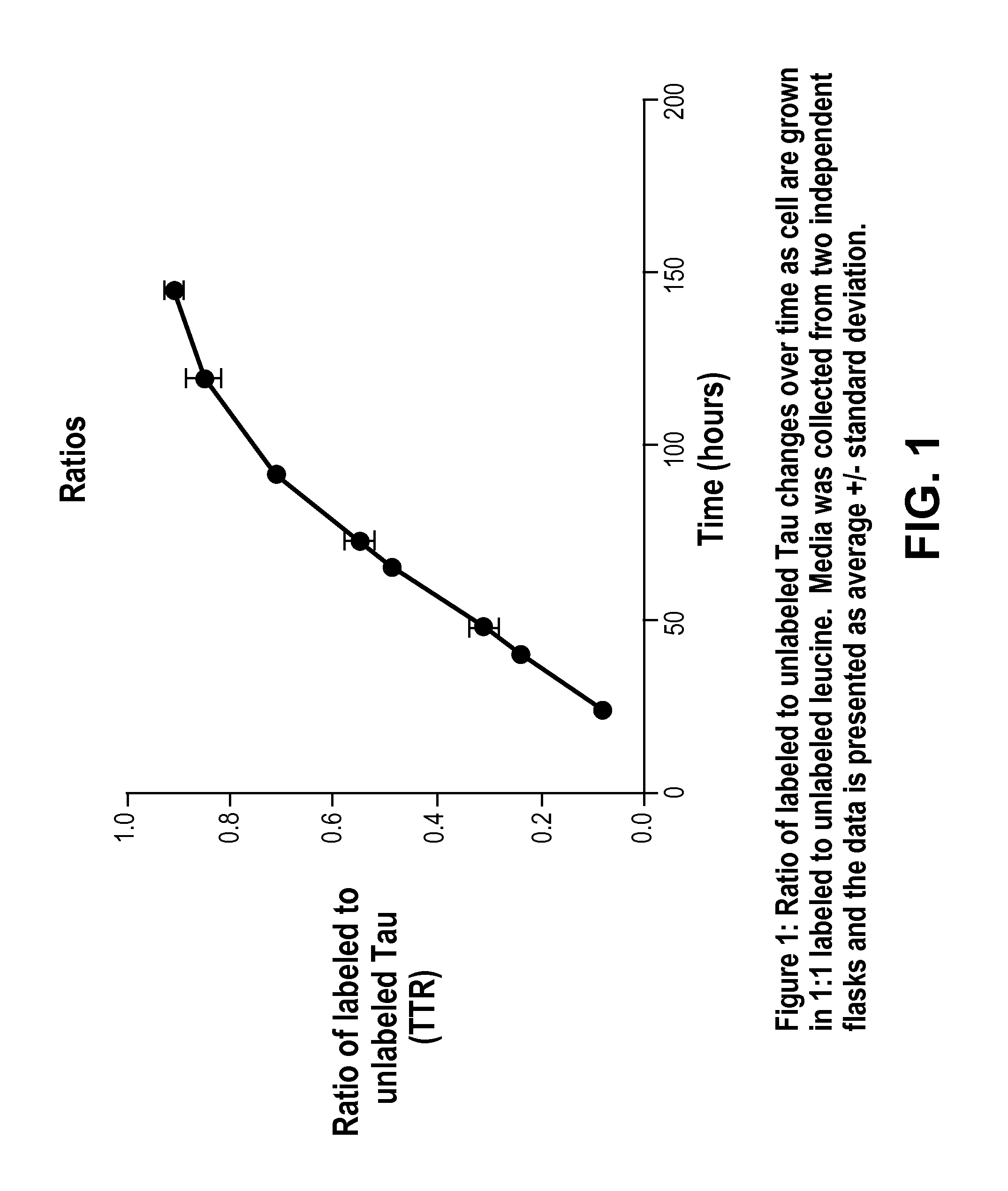
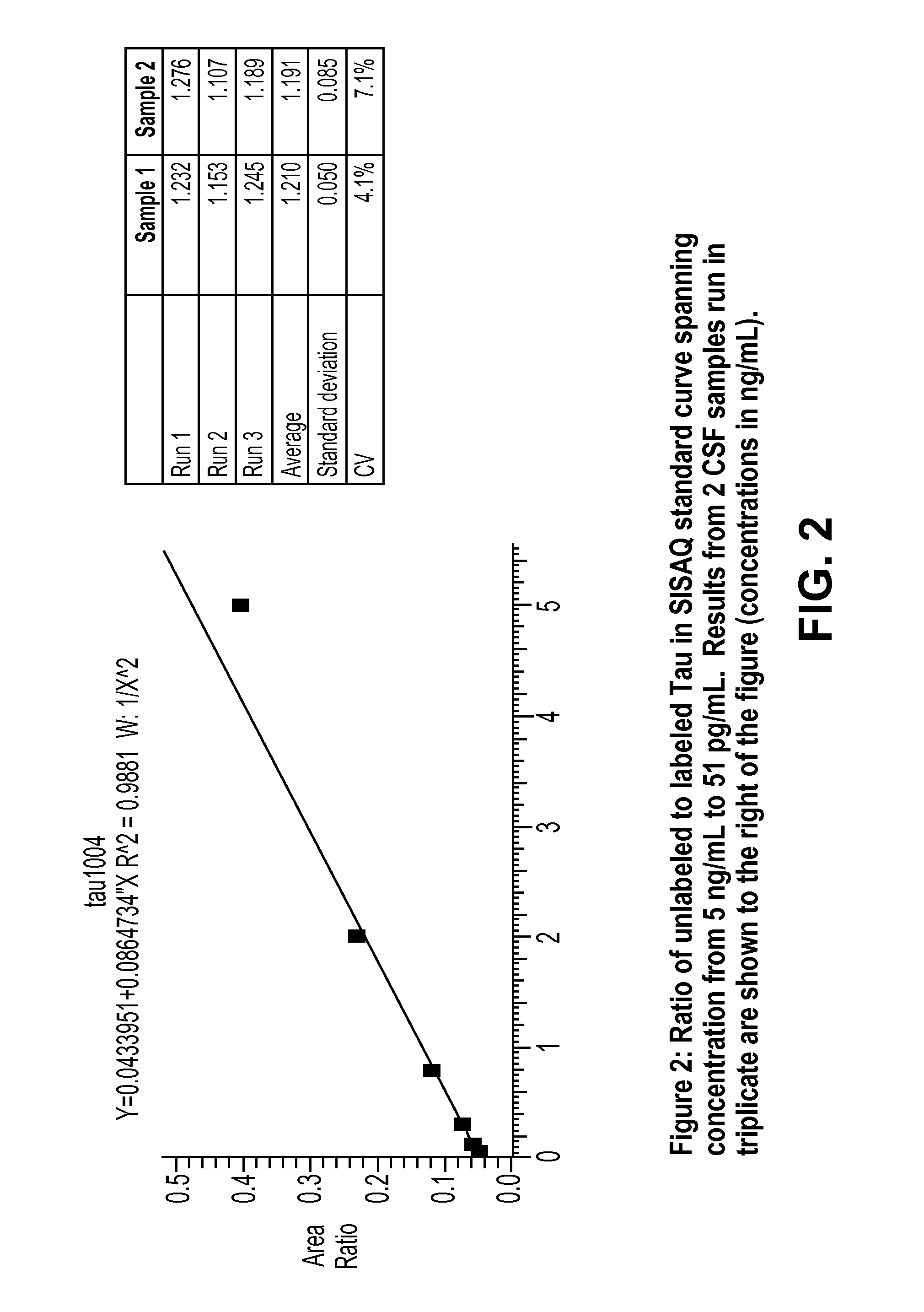
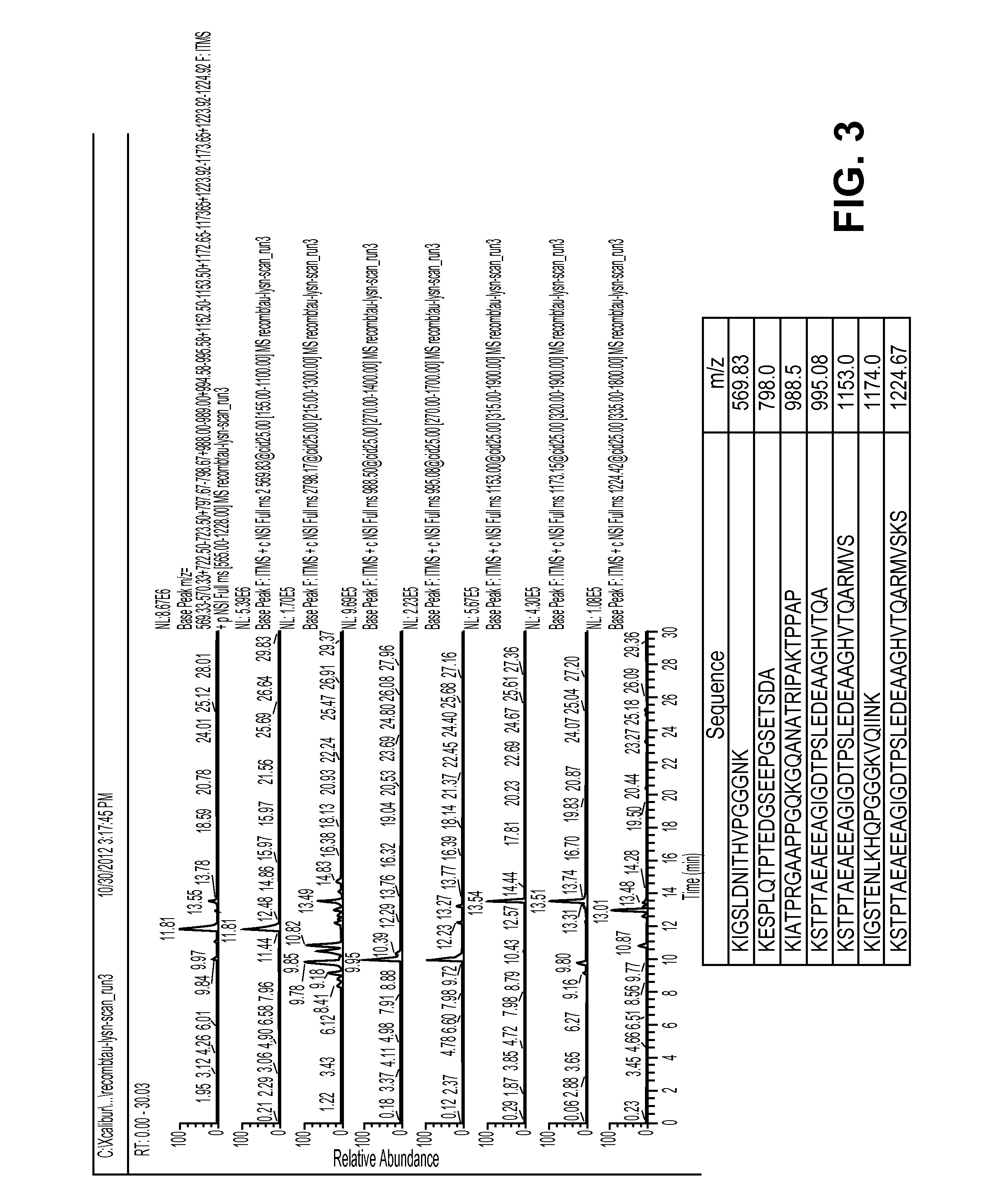
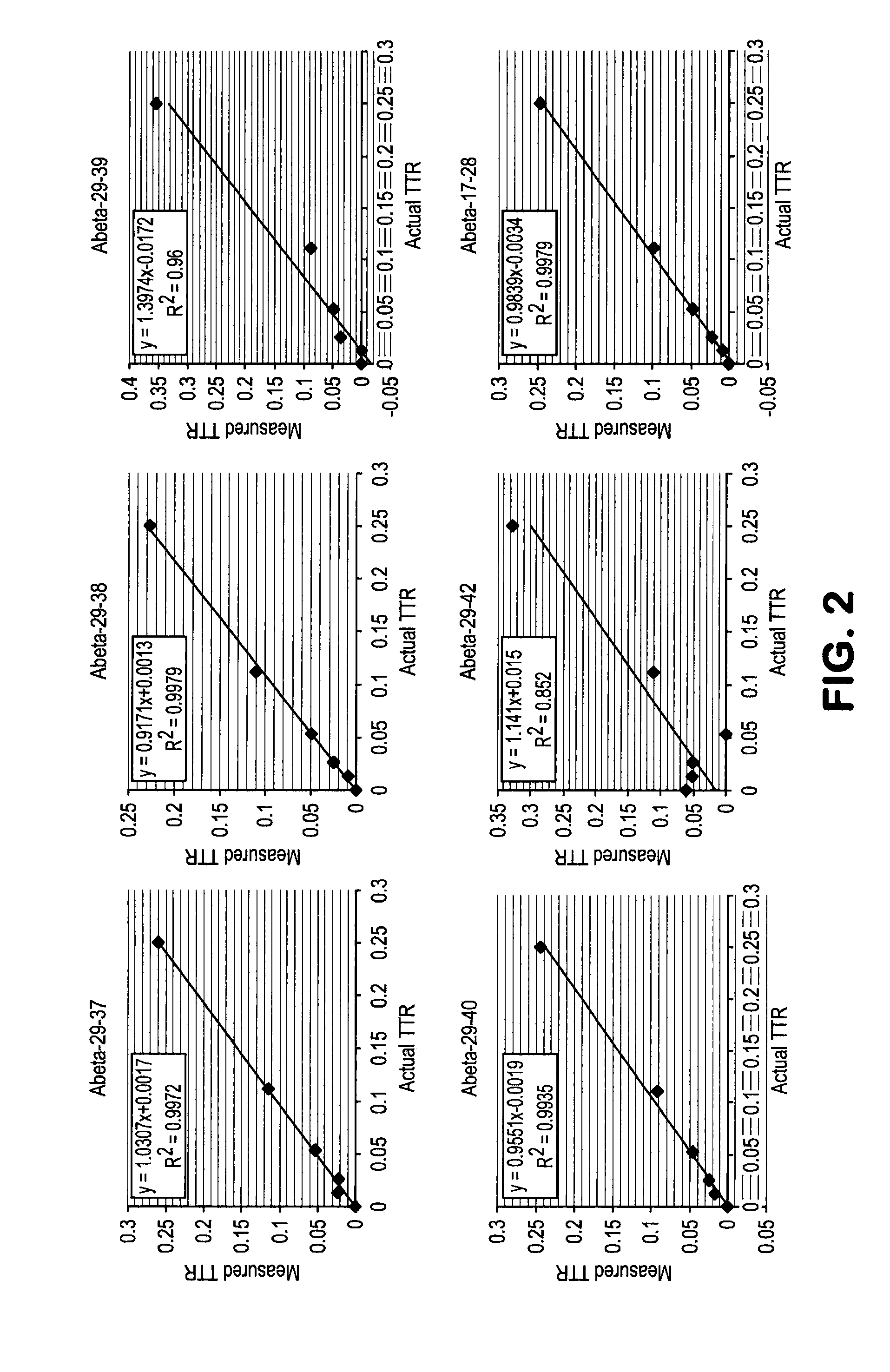
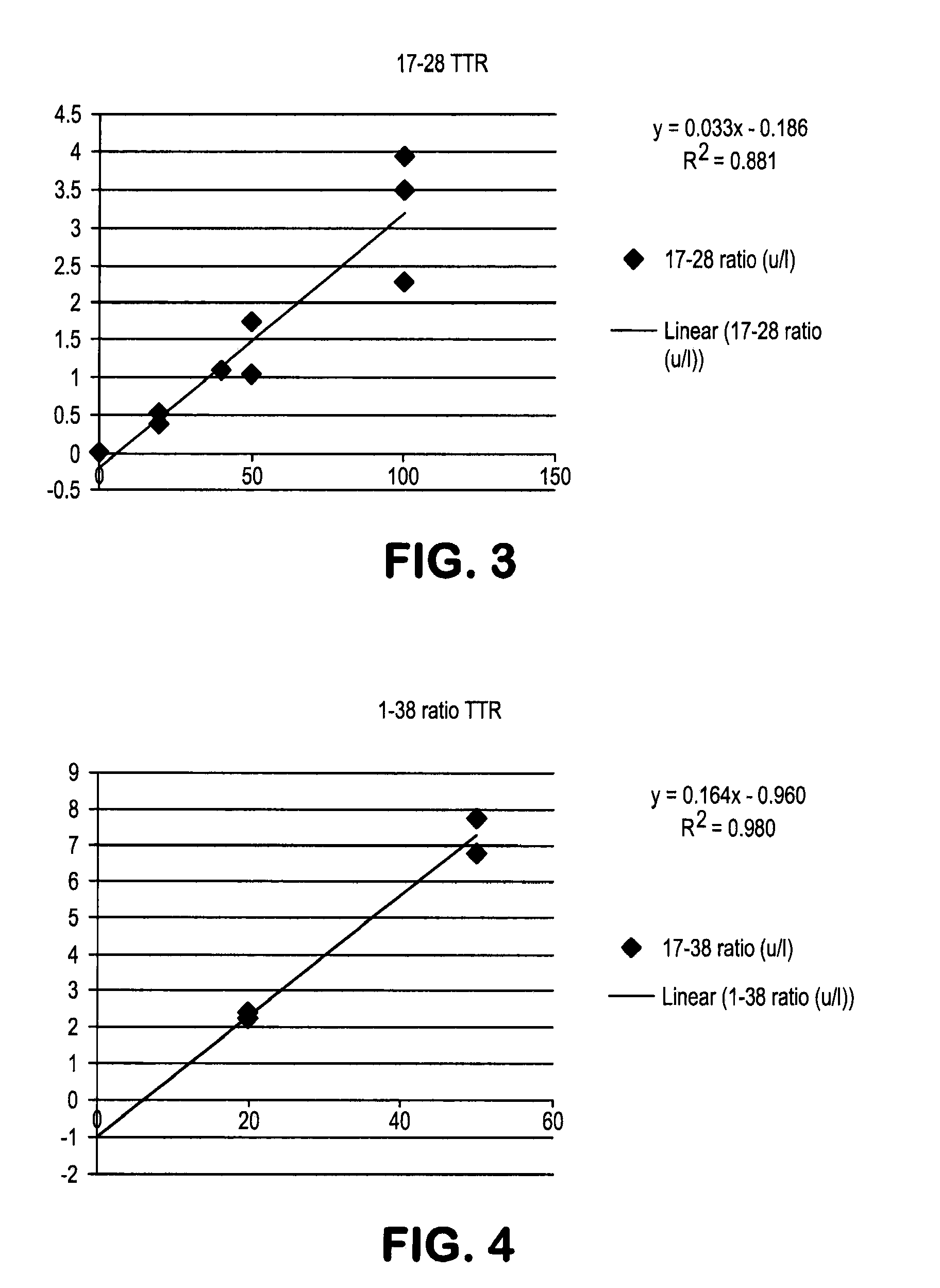
Extraction and separation methods that can be used to quantify the absolute concentrations of one or more low abundance biomolecules present in biological fluids and tissues, without the need for antibody enrichment or reliance on an antibody for quantification are provided. These biomolecules can be biomarkers used to diagnose and monitor disease progression. As an example, these methods are applied to human plasma and CSF, and used to quantify Alzheimer's disease biomarkers.
Owner:C2N DIAGNOSTICS
Apparatus and apparatus control method for the quantitative concentration determination of selected substances filtered out of a patient's body in a fluid
ActiveUS20150323447A1Easy to integrateHigh measurement accuracyInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsMedical devicesExtinctionMedicine
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for determining a substance in a fluid excreted / extracted from the body or spent dialysate, e.g., for determining a quality measure for the dialysis, such as the concentration of selected toxic substances, and / or for determining a removed total quantity of uremic toxins during a dialysis with a dialysis apparatus. A concentration of a substance in the fluid may be determined by: detecting, by an absorption sensor, a first extinction signal of the fluid at an analysis wavelength at a defined first pH value of the fluid; adjusting, by a pH adjusting device, a second pH value of the fluid which differs from the first pH value; detecting, by the absorption sensor, a second extinction signal of the fluid at the analysis wavelength at the second pH value; and processing / comparing the two extinction signals for the first and the second pH values and determining an absolute concentration of the substance dissolved in the fluid.
Owner:B BRAUN AVITUM
Methods for Measuring Concentrations of Biomolecules
InactiveUS20140315327A1Mass spectrometric analysisDisease diagnosisNervous systemAbsolute concentration
The present invention provides methods for measuring the absolute concentration of a biomolecule of interest in a subject. Such biomolecules may be implicated in one or more neurological and neurodegenerative diseases or disorders. Also provided is a method for determining whether a therapeutic agent affects the in vivo metabolism of a central nervous system derived biomolecule. Also provided are kits for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:C2N DIAGNOSTICS
Automatic device and methods for particle analysis
InactiveCN103175766AFlexible analysisEliminate processingIndividual particle analysisAbsolute concentrationHandling system
The invention discloses automatic device and methods for particle analysis. The device comprises a flow cytometry analysis system which can obtain absolute concentration (quantity / liter) of a target object to be tested. The device also comprises a sample pre-treatment system and comprises hemolysis and cell classification reaction pool, a marker storage pool, a marker reaction pool, a sample drawing needle device, a marker drawing needle device and a sample sampling position. The invention also discloses various methods for analyzing the target object to be tested by the device and concrete operation steps. By utilizing the device and the methods disclosed by the invention, automatic sample treatment and analysis can be carried out; an artificial sample pre-treatment process is removed; meanwhile, the quantity of the added markers can be adaptively adjusted aiming at the sample to be marked; and the optimal reaction ratio of the marker and the object to be marked is adaptively determined in the device; and the analysis accuracy and rapidity are improved.
Owner:陶靖
Methods for measuring concentrations of biomolecules
The present invention provides methods for measuring the absolute concentration of a biomolecule of interest in a subject. Such biomolecules may be implicated in one or more neurological and neurodegenerative diseases or disorders. Also provided is a method for determining whether a therapeutic agent affects the in vivo metabolism of a central nervous system derived biomolecule. Also provided are kits for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:C2N DIAGNOSTICS
Method and arrangement for producing an N-semiconductive indium sulfide thin layer
InactiveUS8143145B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin layerAbsolute concentration
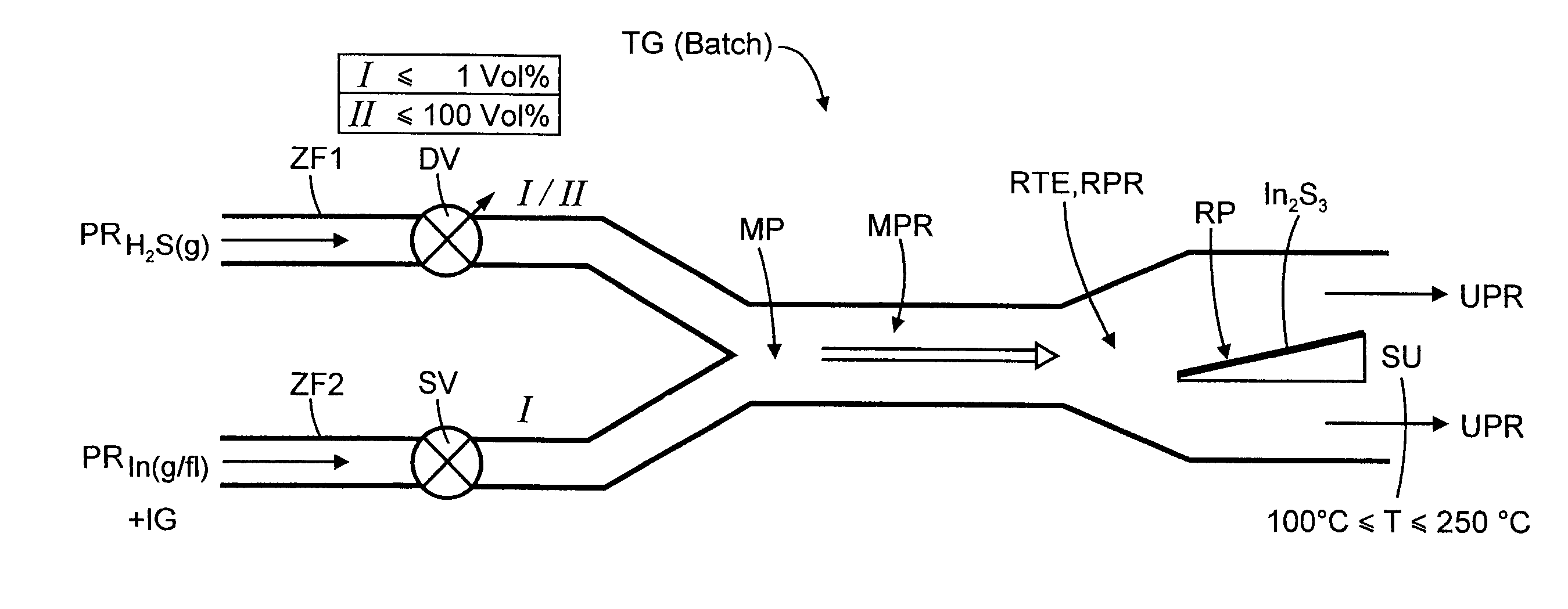
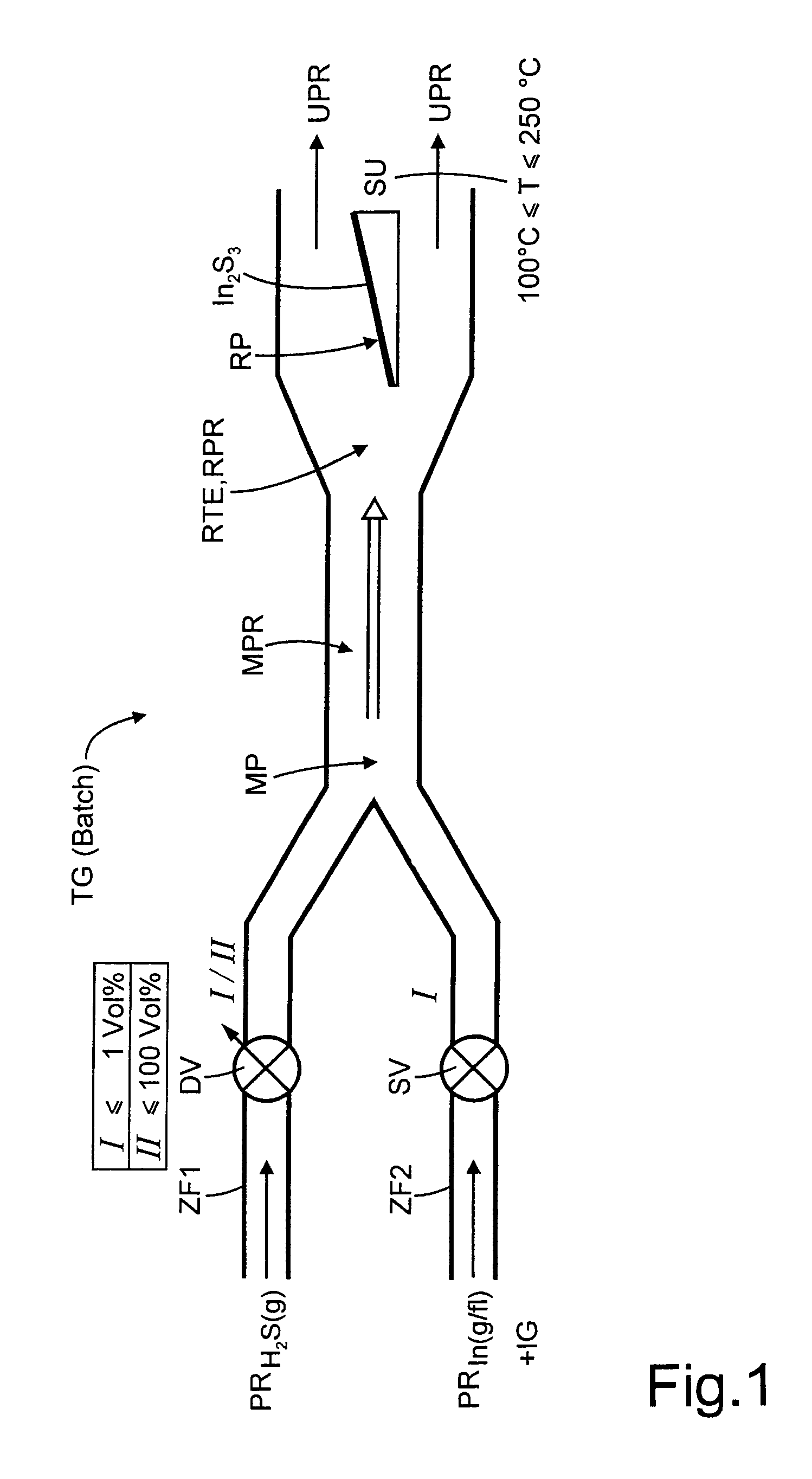
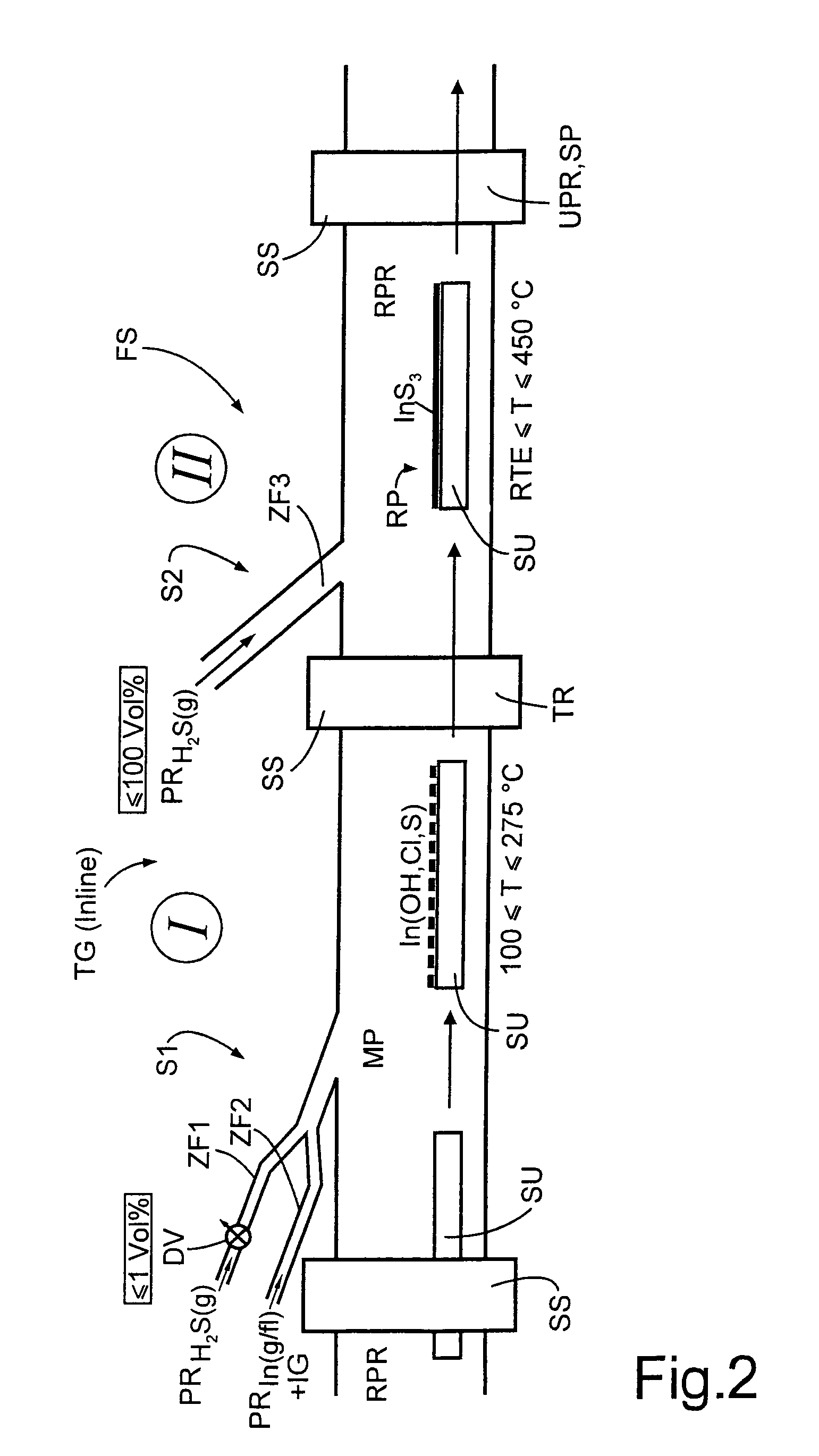
A method of producing, at atmospheric pressure, an n-type semiconductive indium sulfide thin film on a substrate using an indium-containing precursor, hydrogen sulfide as a reactive gaseous precursor, and an inert carrier gas stream includes cyclically repeating first and second steps so as to produce an indium sulfide thin film of a desired thickness. The first method phase includes converting the indium-containing precursor to at least one of a dissolved and a gaseous phase, heating the substrate to a temperature in a range of 100° C. to 275° C., directing the indium containing precursor onto the substrate and supplying hydrogen sulfide to the indium-containing precursor in a mixing zone in an amount so as to provide an absolute concentration of hydrogen sulfide that is greater than zero and no greater than 1% by volume. The indium concentration of the indium-containing precursor is set so as to produce a compact In(OHx,Xy,Sz)3 film, where X=halide and x+y+2z=1 with z≠0. The second step includes setting a temperature of the substrate in a range of 18° C. and 450° C. and directing hydrogen sulfide onto the substrate in an absolute concentration up to 100%.
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT BERLIN FUER MATERIALIEN & ENERGIE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com