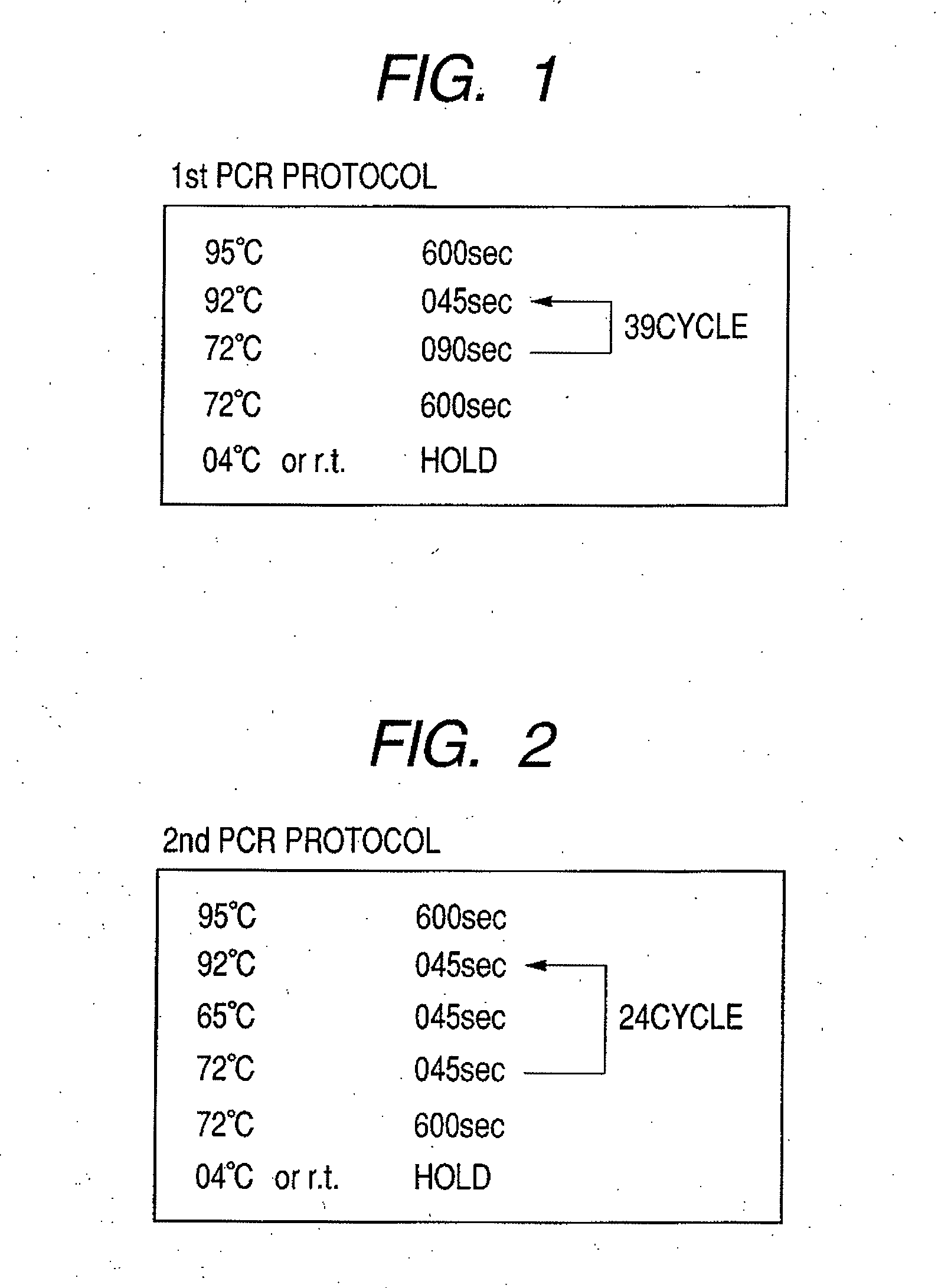
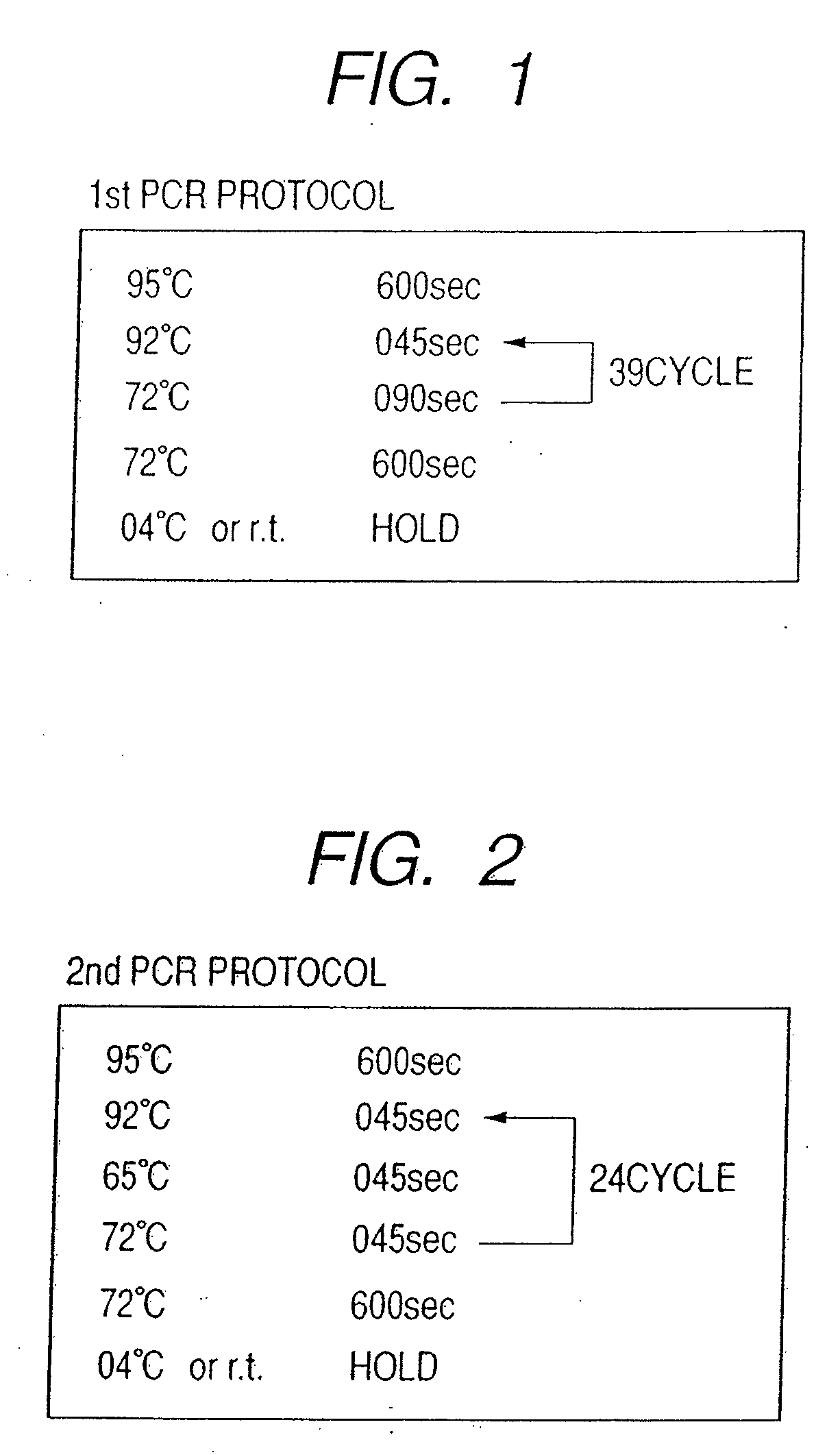
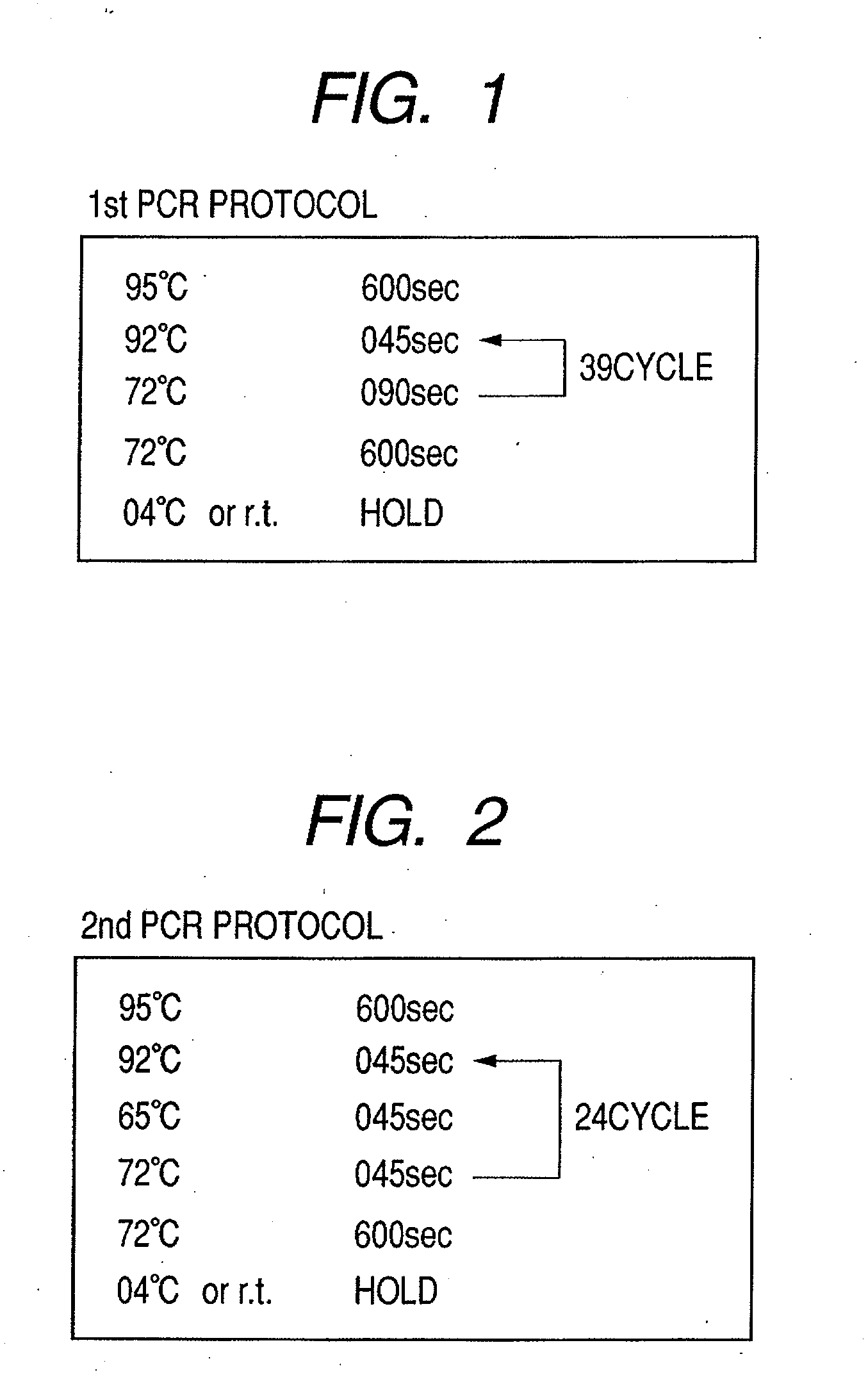
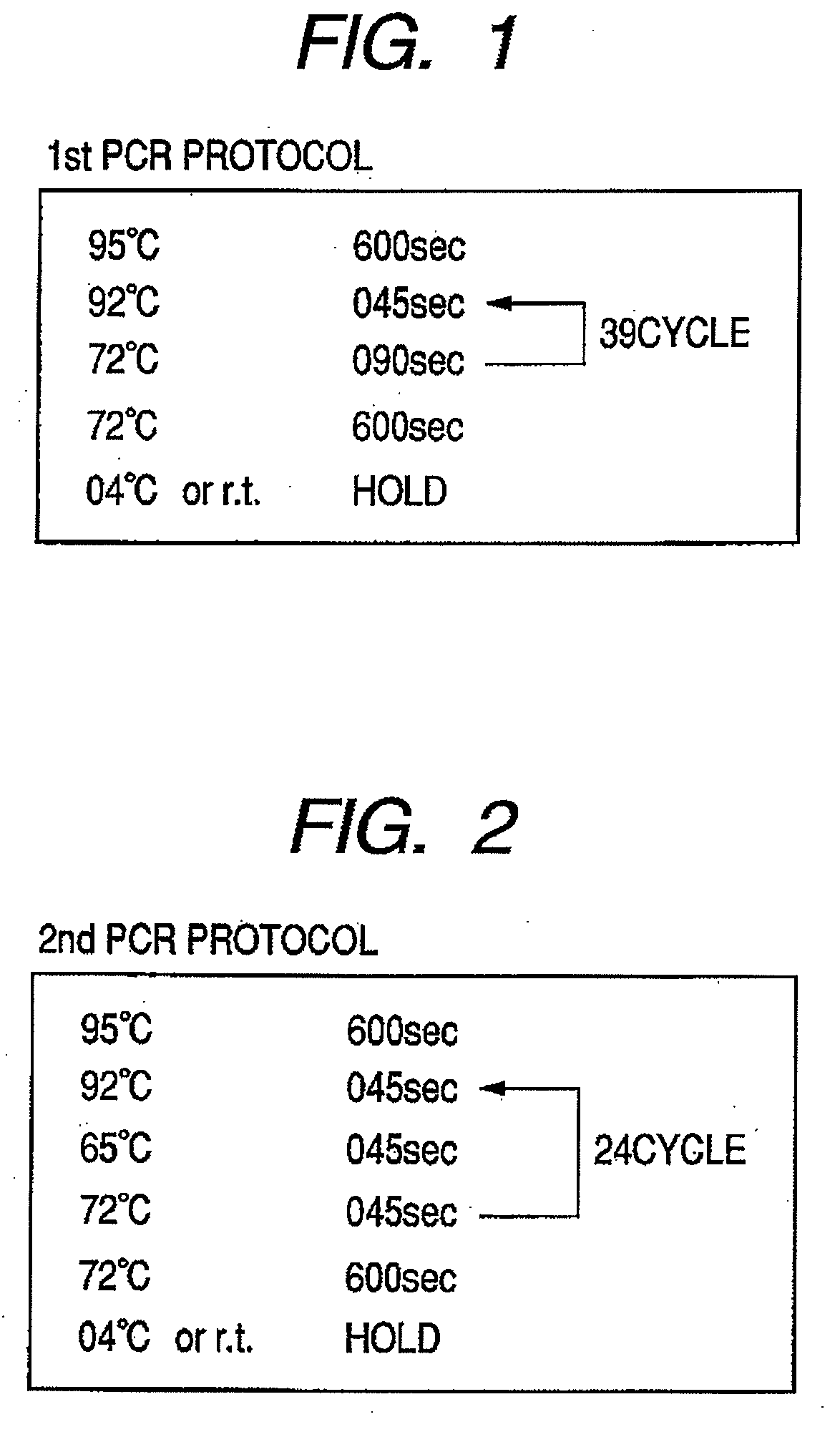
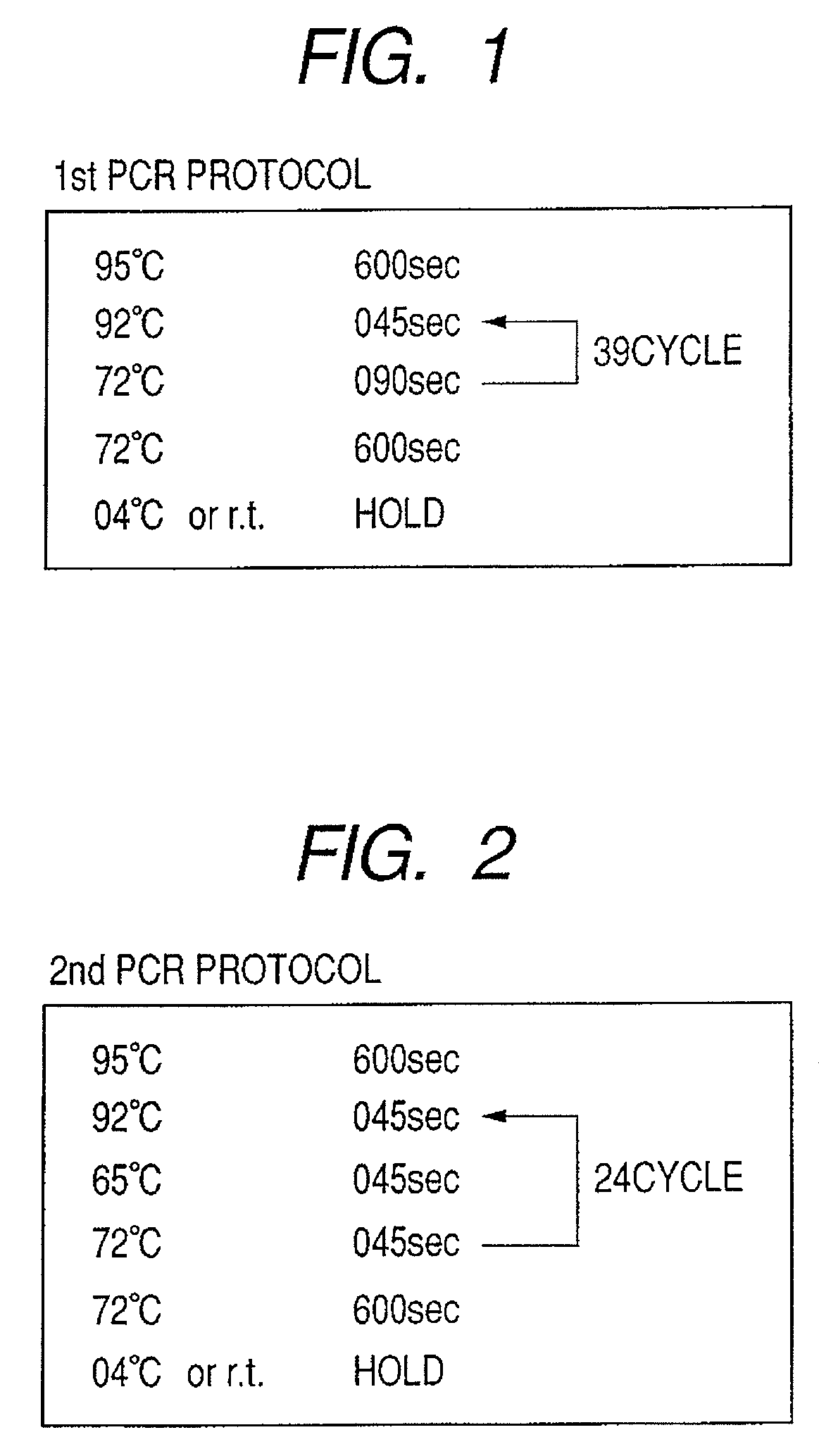
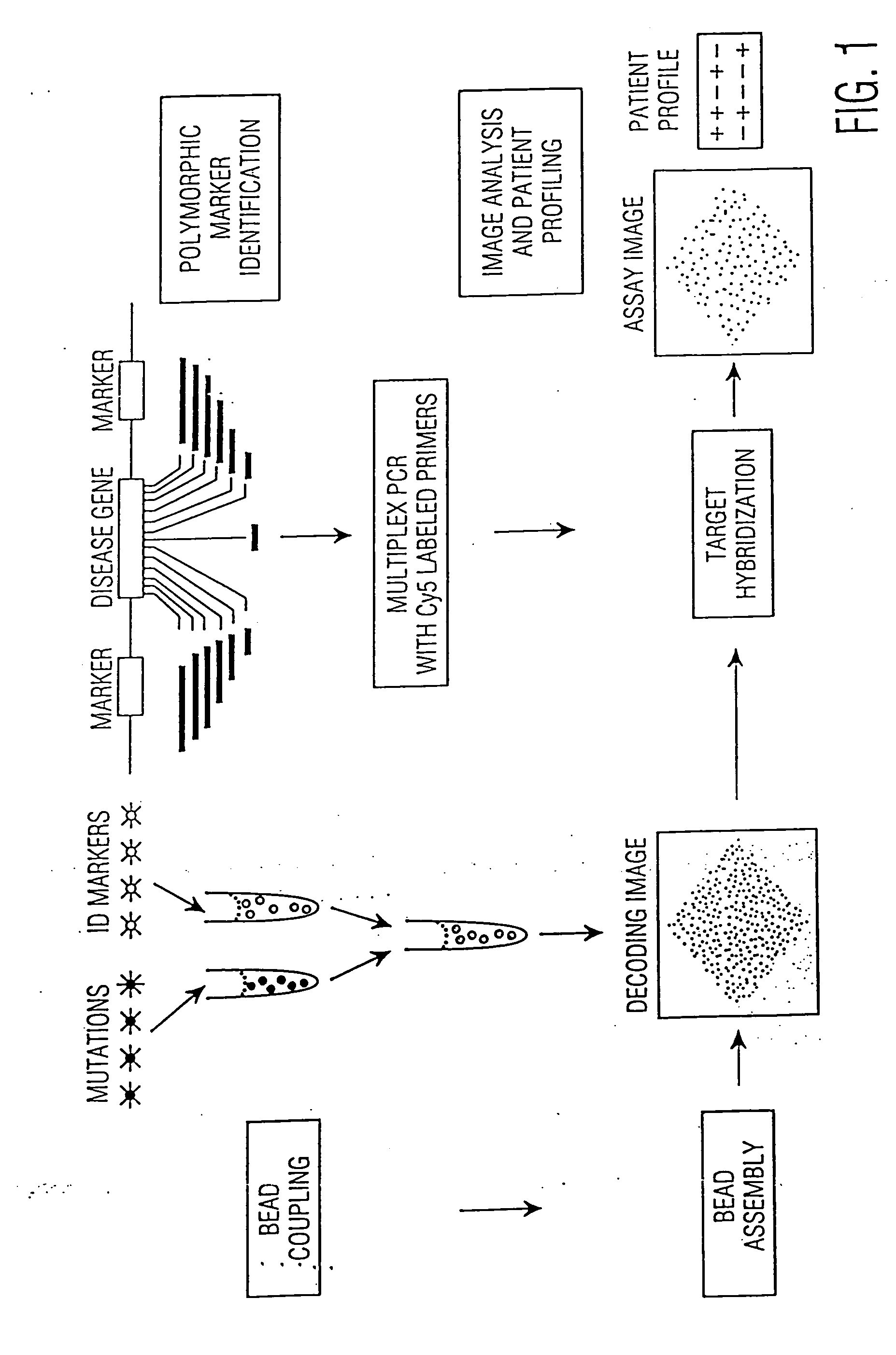
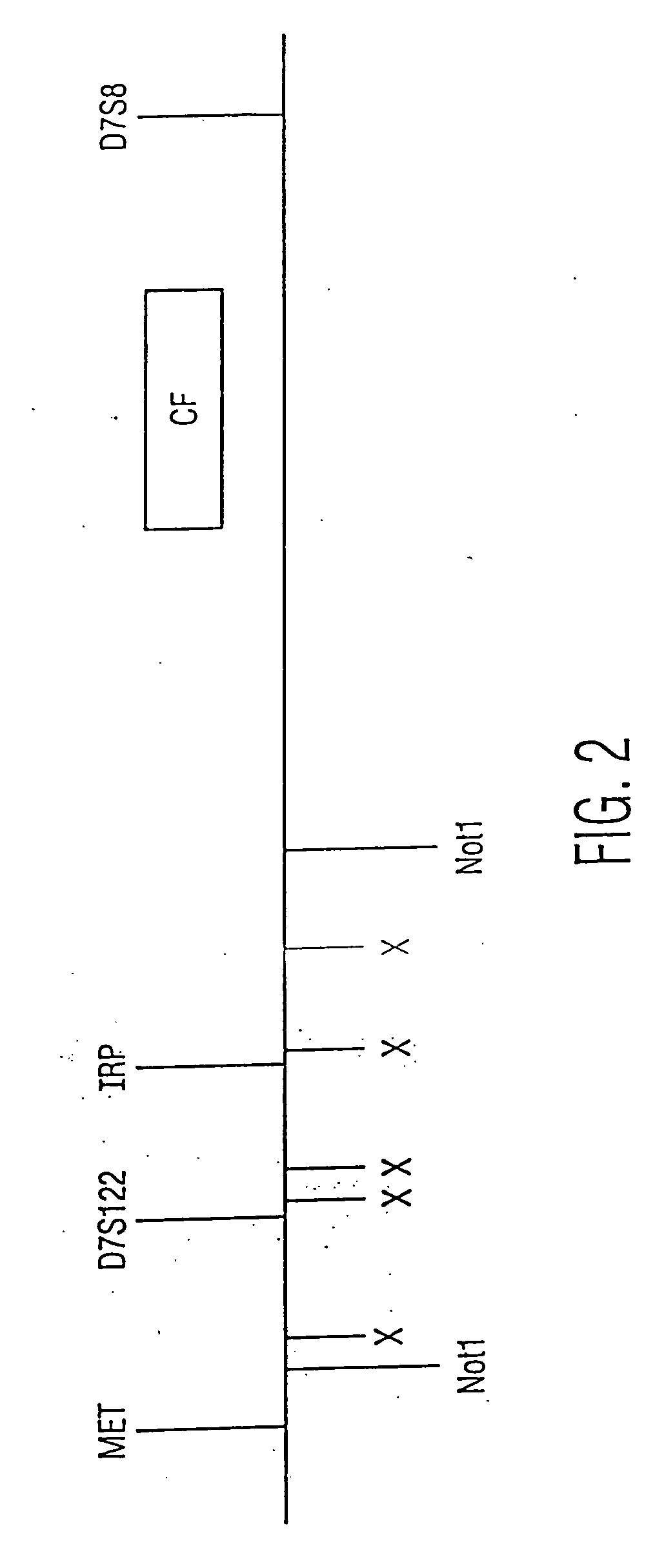
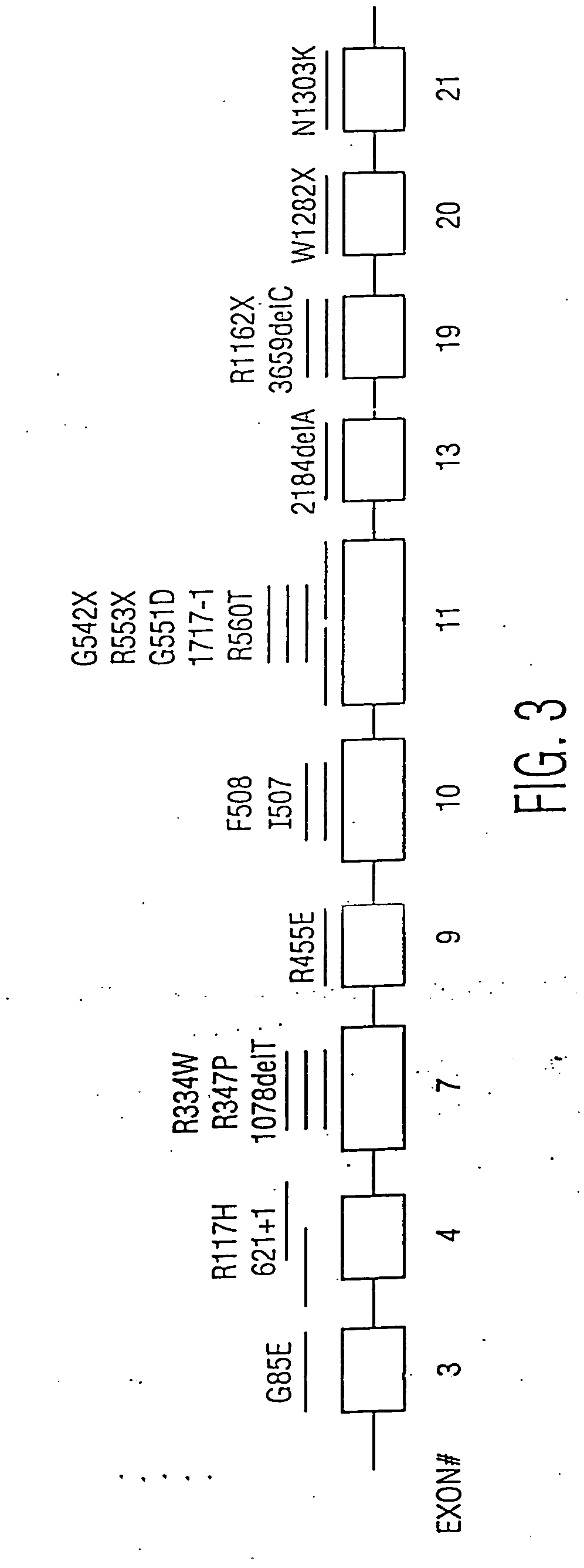
Patents
Literature
122 results about "Genetic Screening (procedure)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
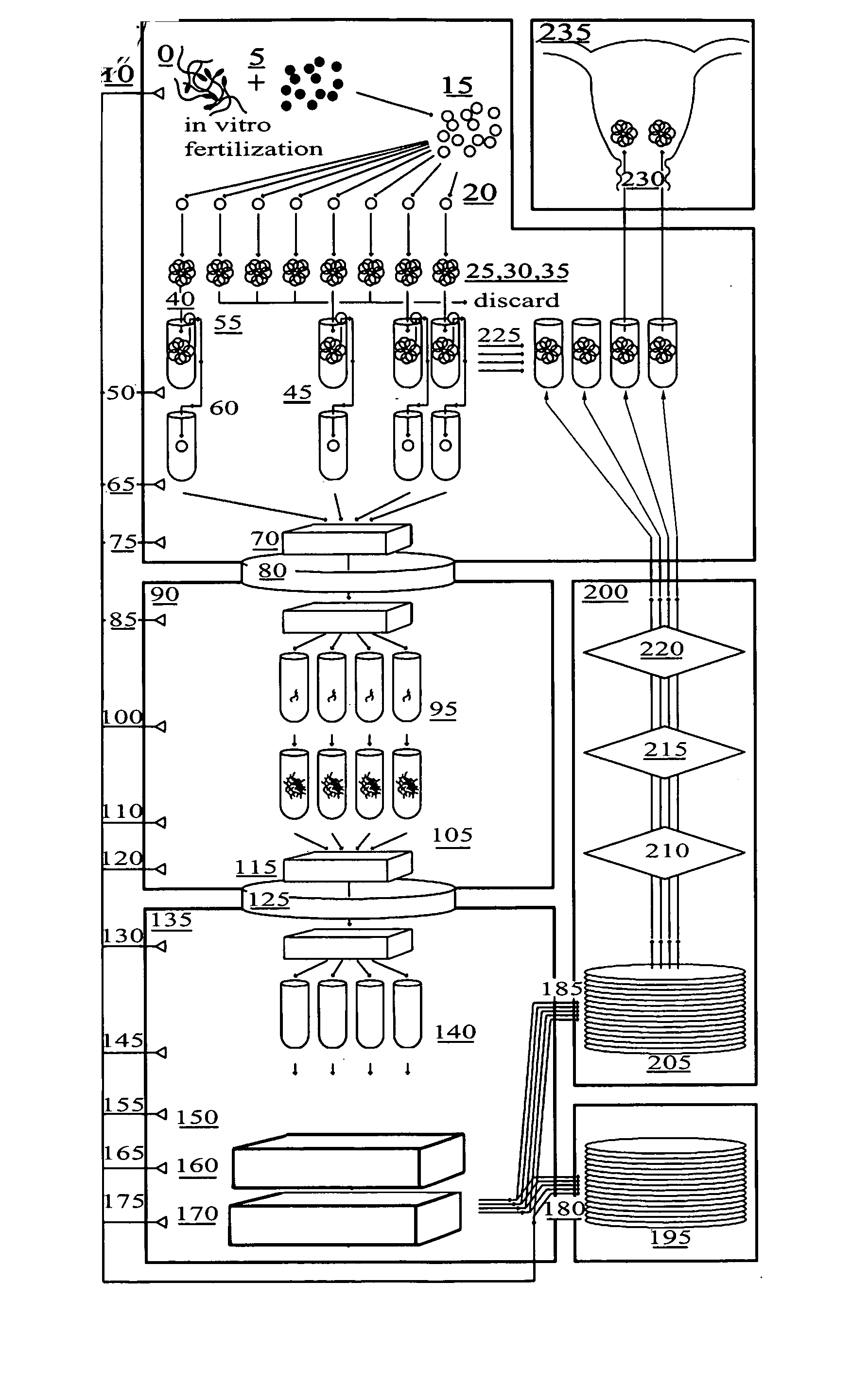
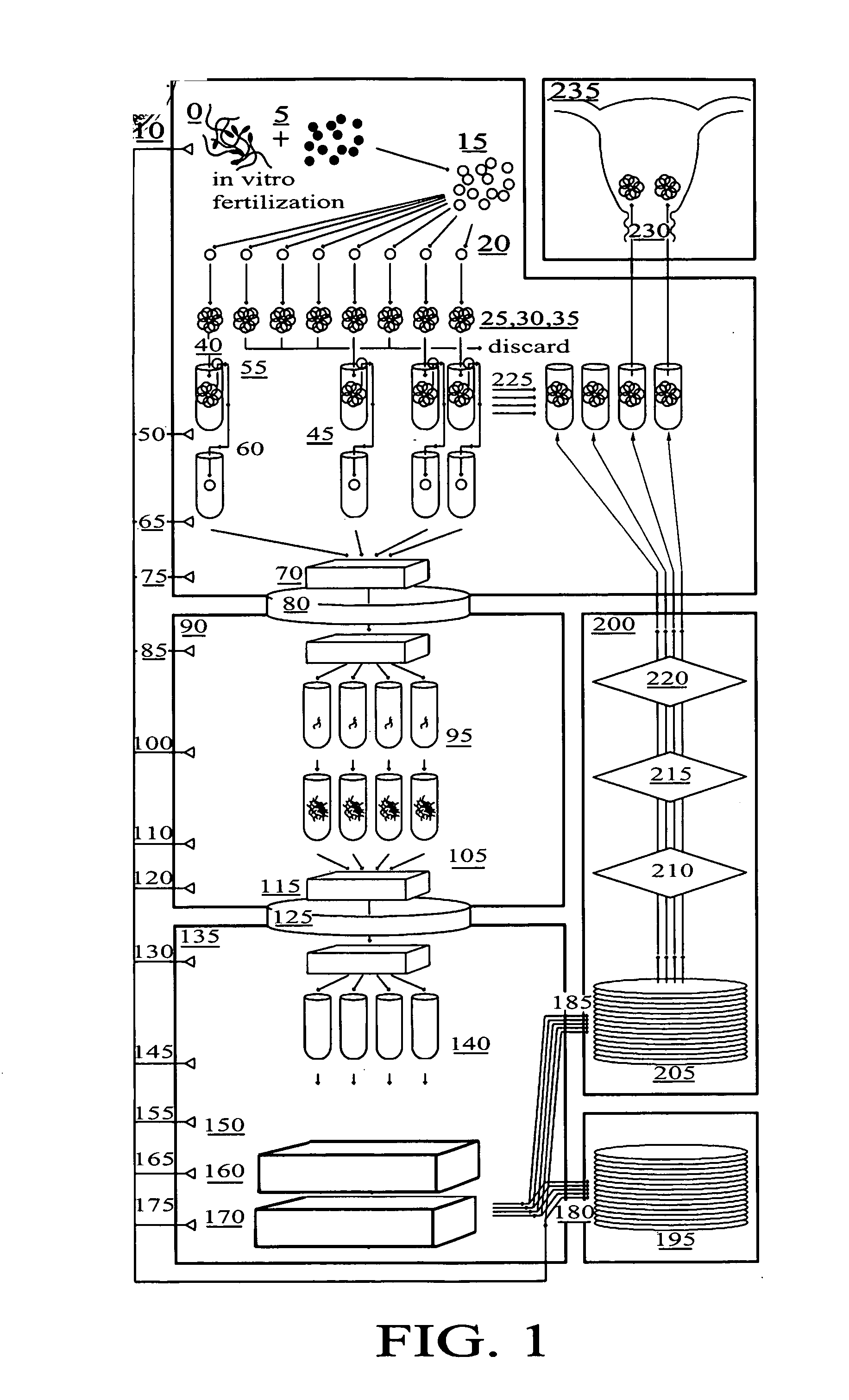
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: Genetic testing procedures that are performed on human embryos prior to the implantation as part of an in vitro fertilization procedure. Pre-implantation testing is used when individuals try to conceive a child through in vitro fertilization.
Genetic analysis and authentication
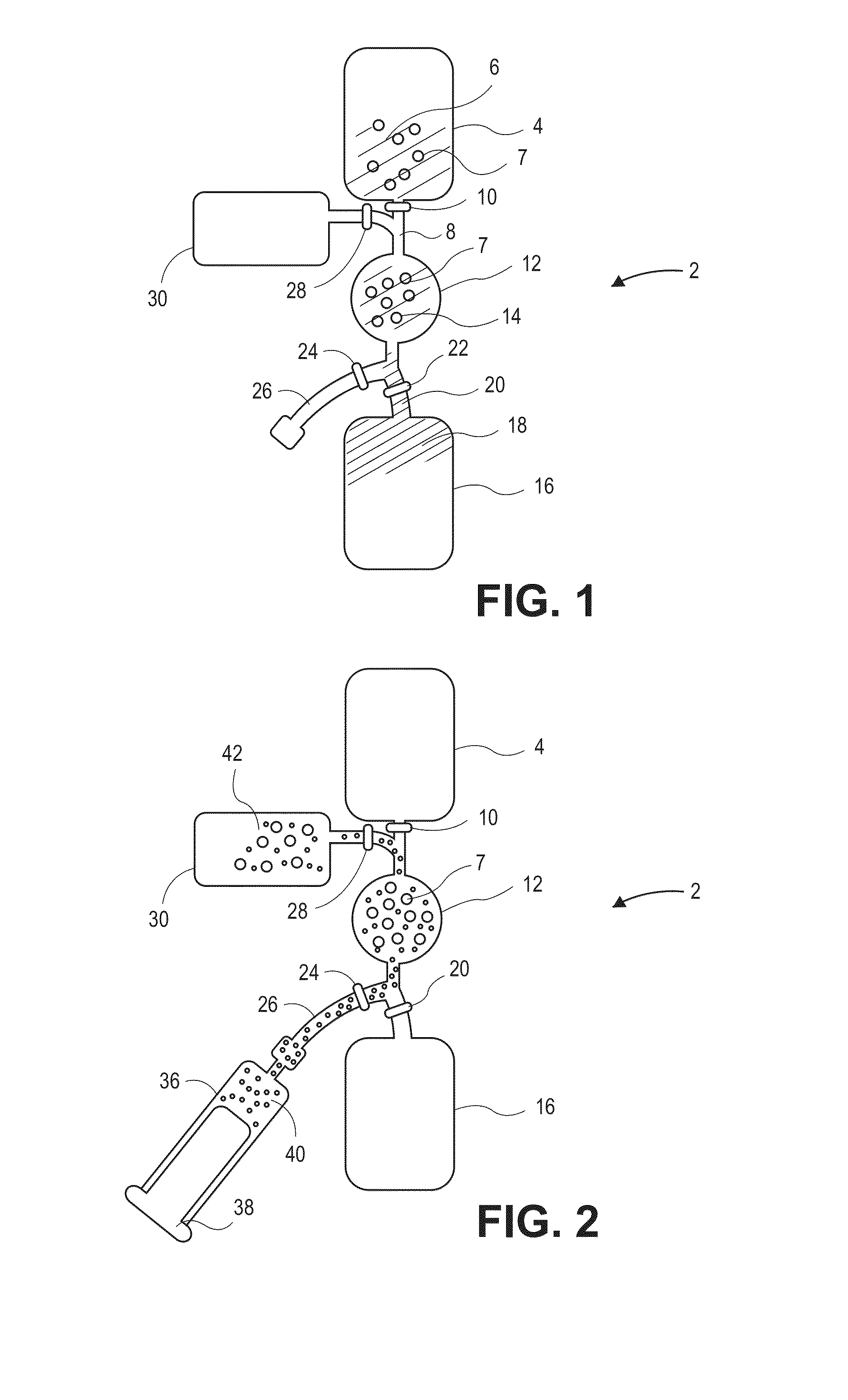
InactiveUS7157228B2Reduce morbidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyGenetic Screening (procedure)
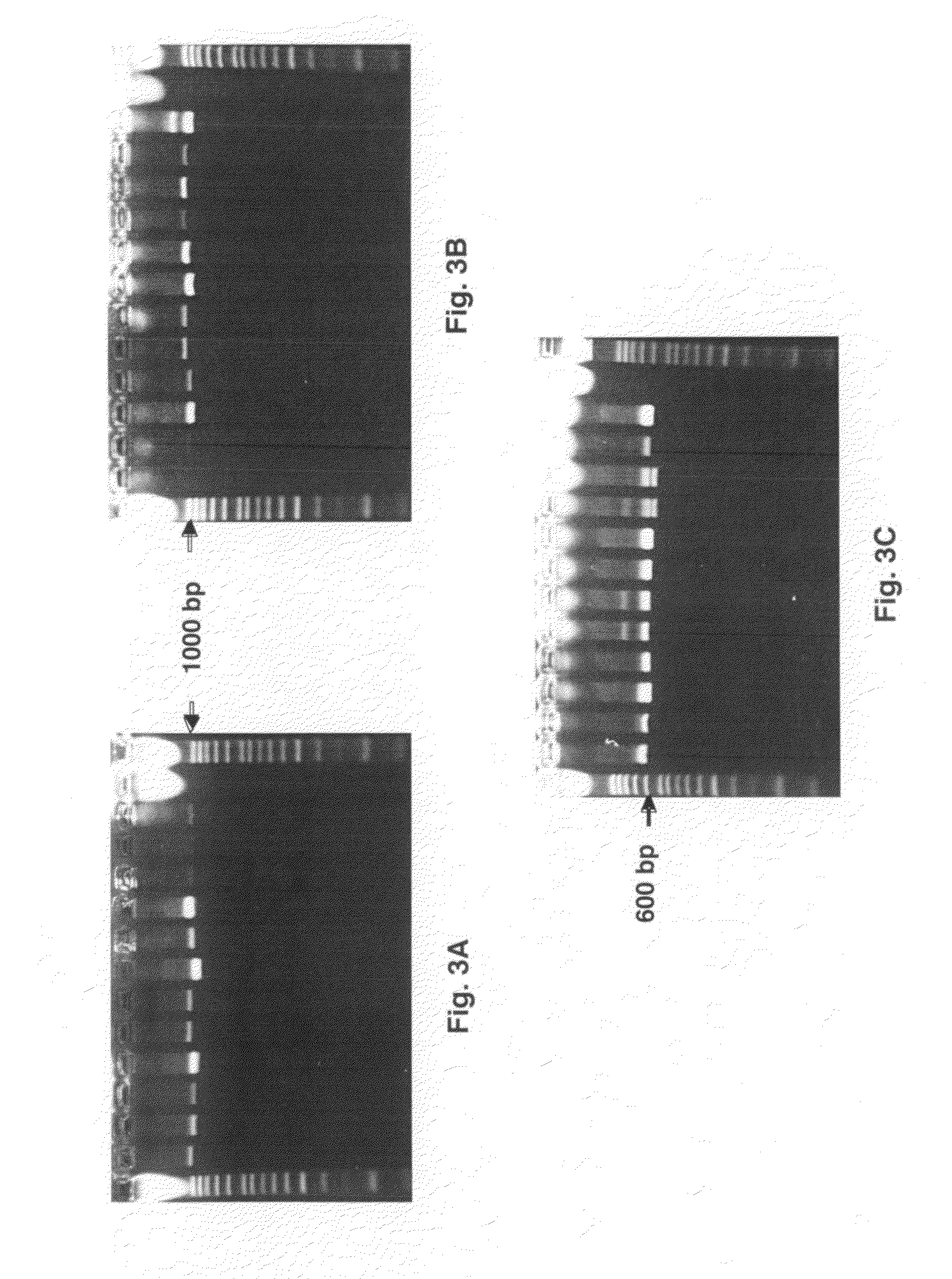
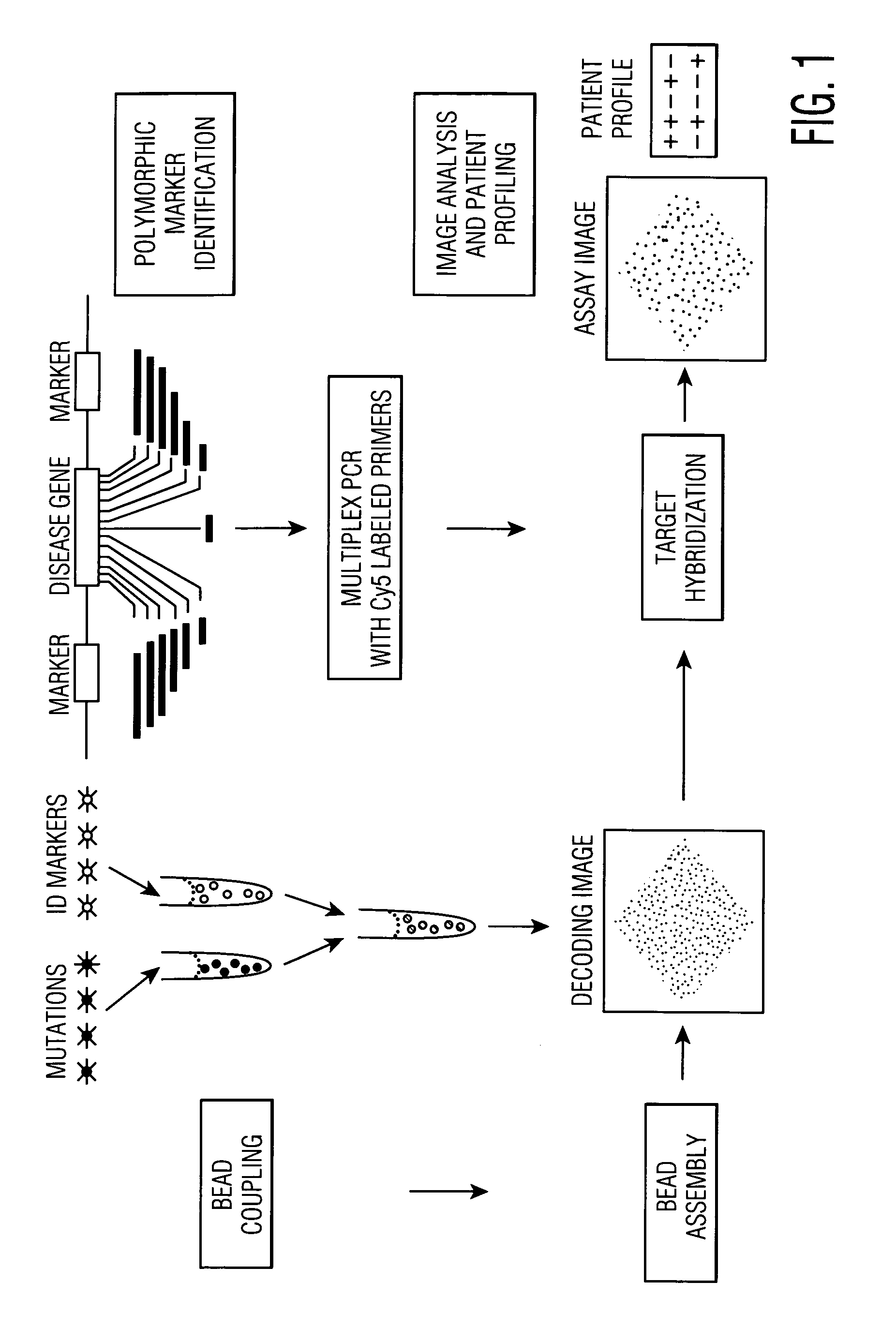
This invention provides compositions and methods for genetic testing of an organism and for correlating the results of the genetic testing with a unique marker that unambiguously identifies the organism. The markers may be internal markers, such as for example single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), short tandem repeats (STRs), or other sites within a genomic locus. Alternatively, the markers may be external, such that they are separately added to the genetic sample before testing.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
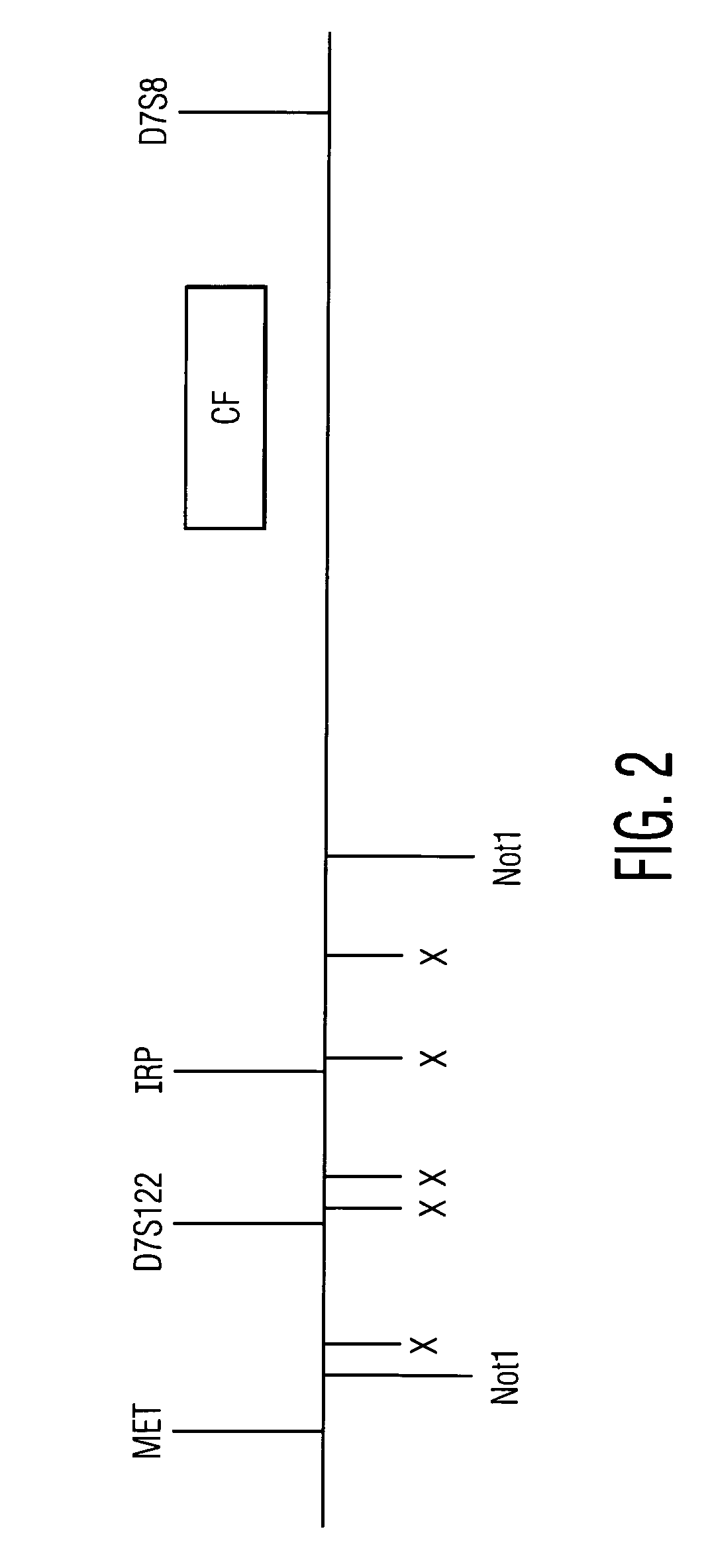
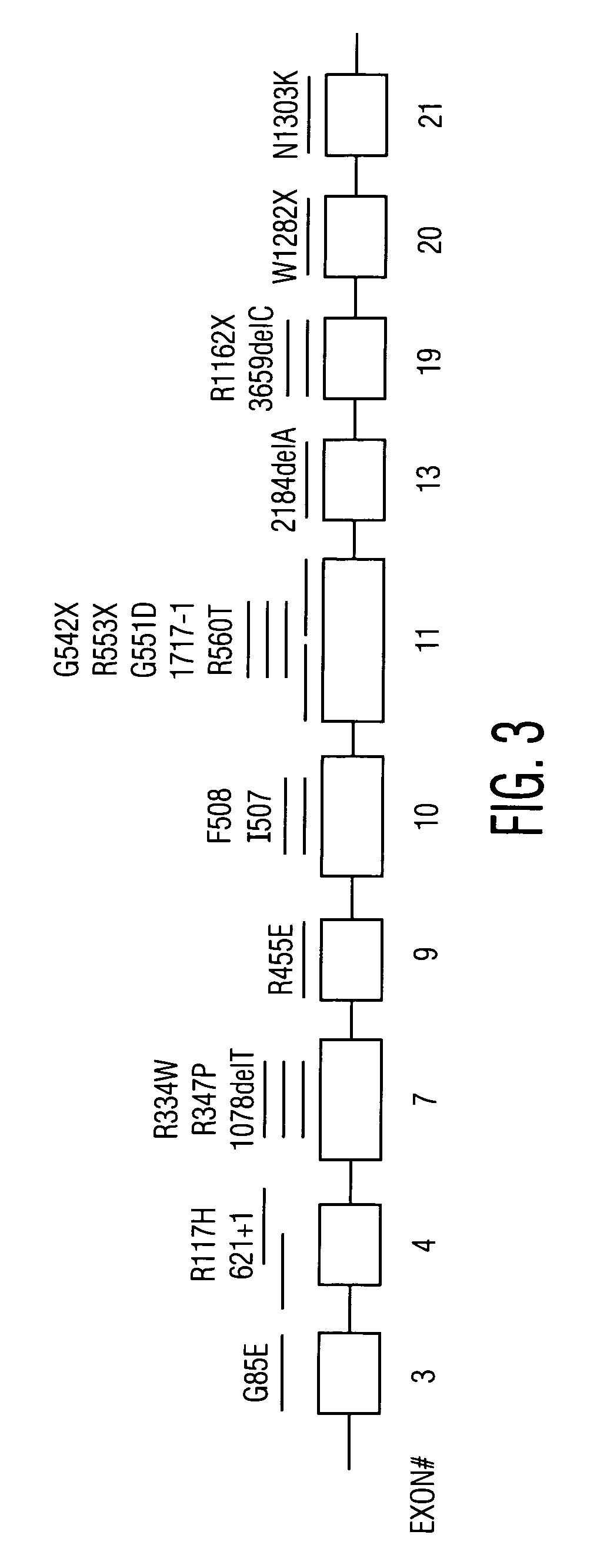
Method for genetic testing of human embryos for chromosome abnormalities, segregating genetic disorders with or without a known mutation and mitochondrial disorders following in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and embryo biopsy
InactiveUS20080085836A1Reduce significant riskImprove the level ofLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationLess invasiveContamination
We describe a method for interrogating the content and primary structure of DNA by microarray analyses and to provide comprehensive genetic screening and diagnostics prior to embryo transfer within an IVF setting. We will accomplish this by the following claims: 1) an optimized embryo grading system, 2) a less invasive embryo biopsy with reduced cellular contamination, 3) an optimized DNA amplification protocol for single cells, 4) identify aneuploidy and structural chromosome abnormalities using microarrays, 5) identifying sub-telomeric chromosome rearrangements, 6) a modified DNA fingerprinting protocol, 7) determine imprinting and epigenetic changes in developing embryos, 8) performing genome-wide scans to clarify / diagnose multi-factorial genetic disease and to determine genotype / haplotype patterns that may predict future disease, 9) determining single gene disorders with or without a known DNA mutation, 10) determining mtDNA mutations and / or the combination of mtDNA and genomic (nuclear) DNA aberrations that cause genetic disease.
Owner:KEARNS WILLIAM G +1
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080124733A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesMicrobiology
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 90 to 91 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20080161192A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 87 to 89 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Apparatus and method for luminometric assay
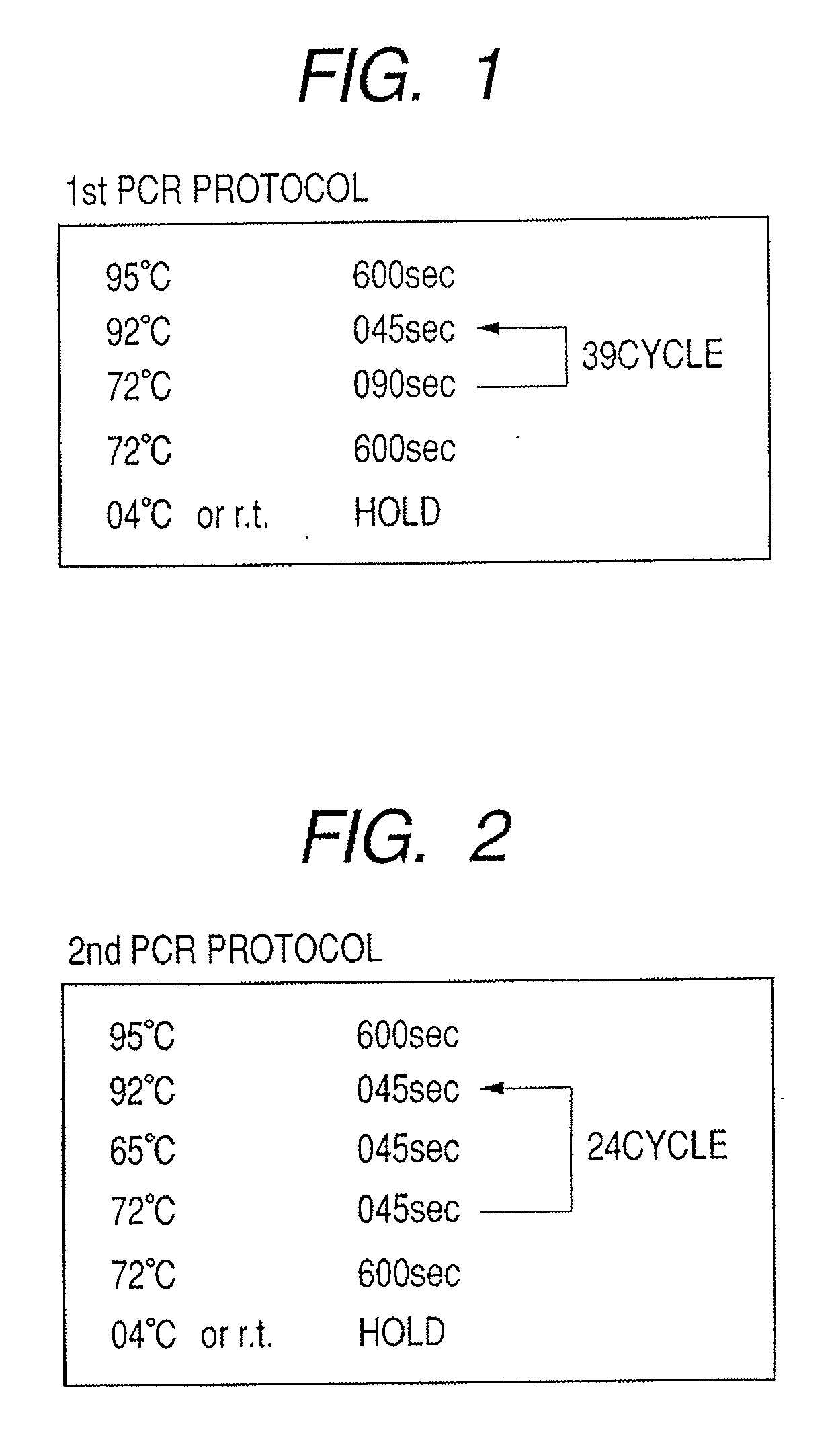
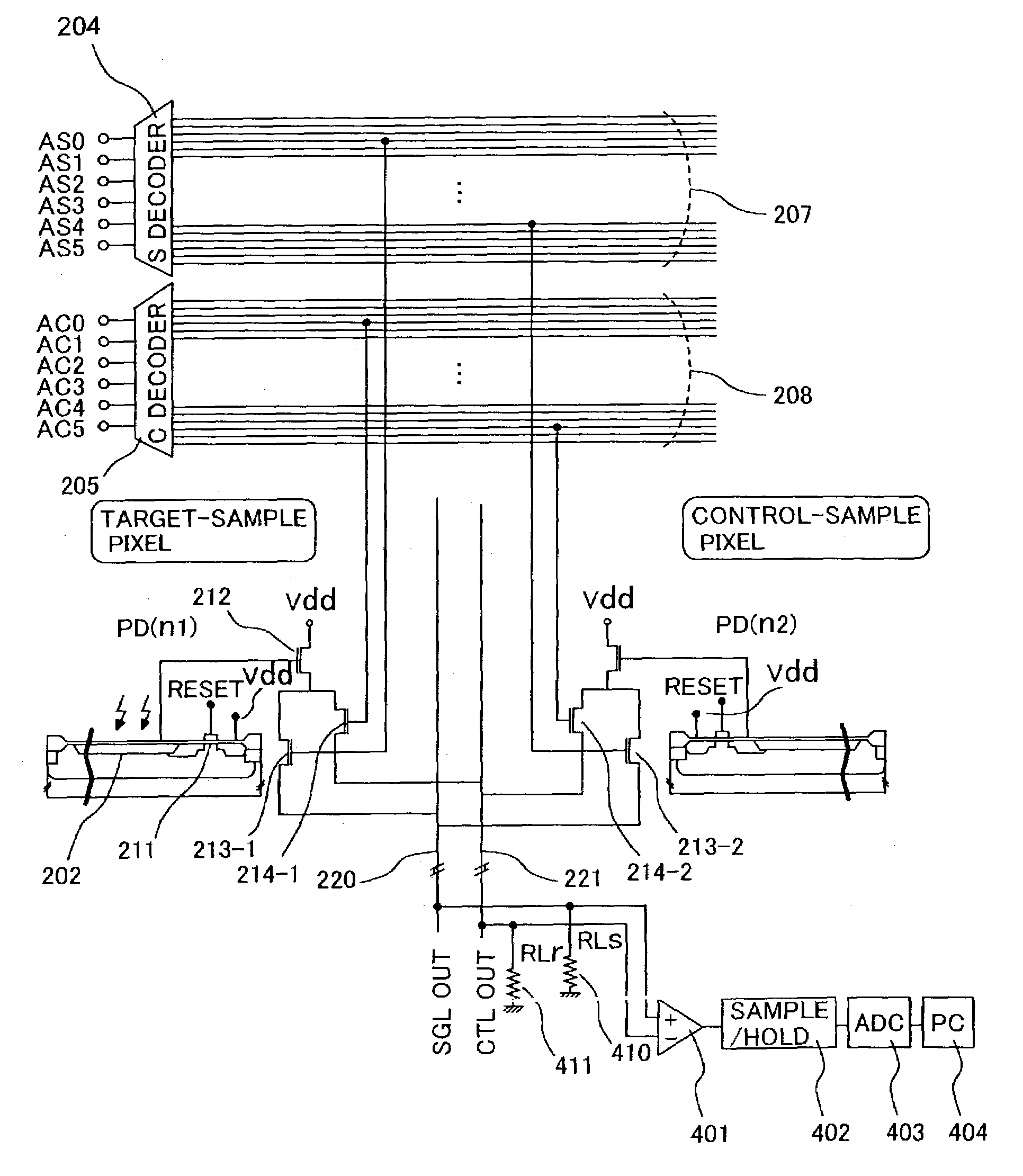
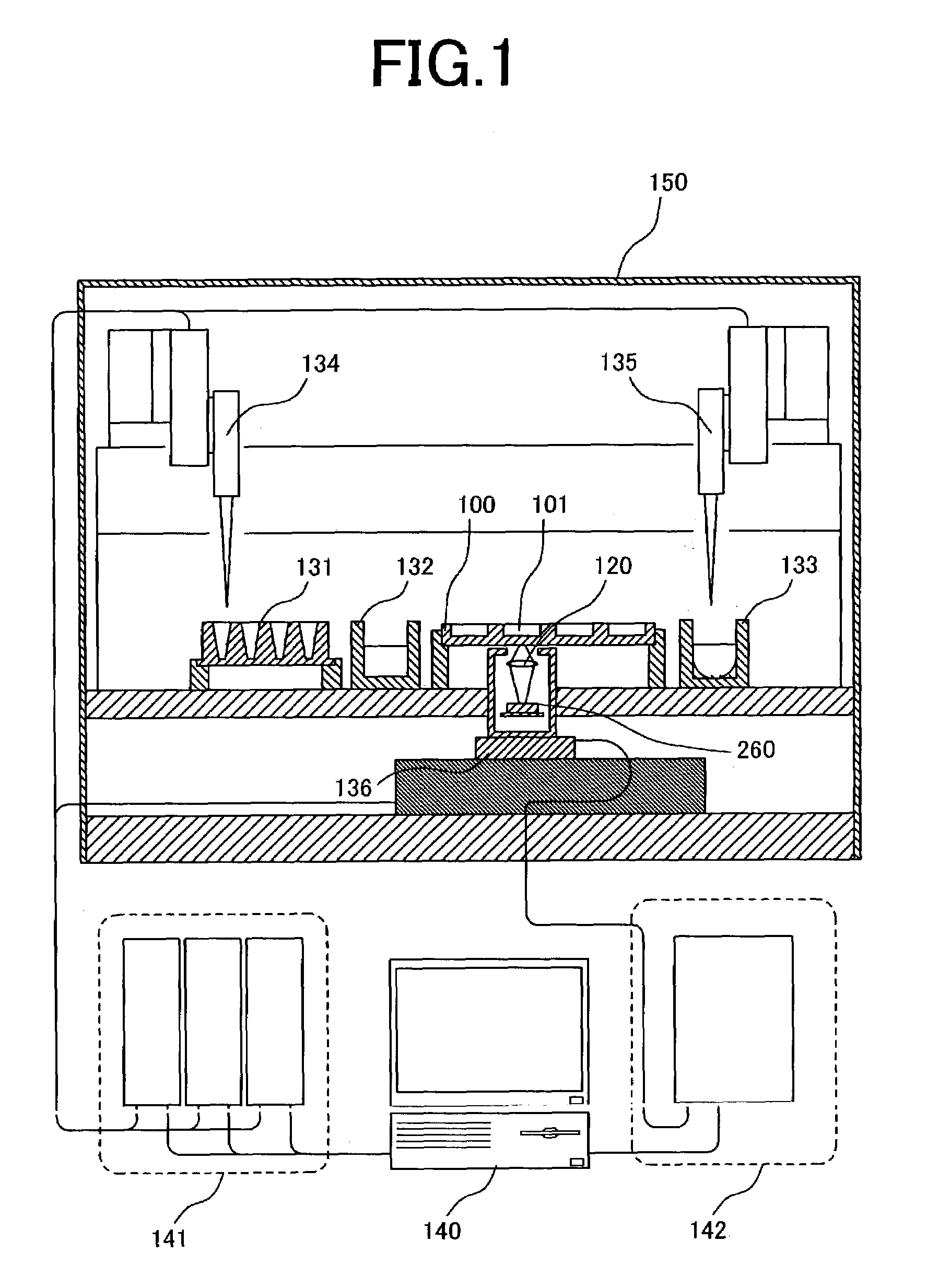
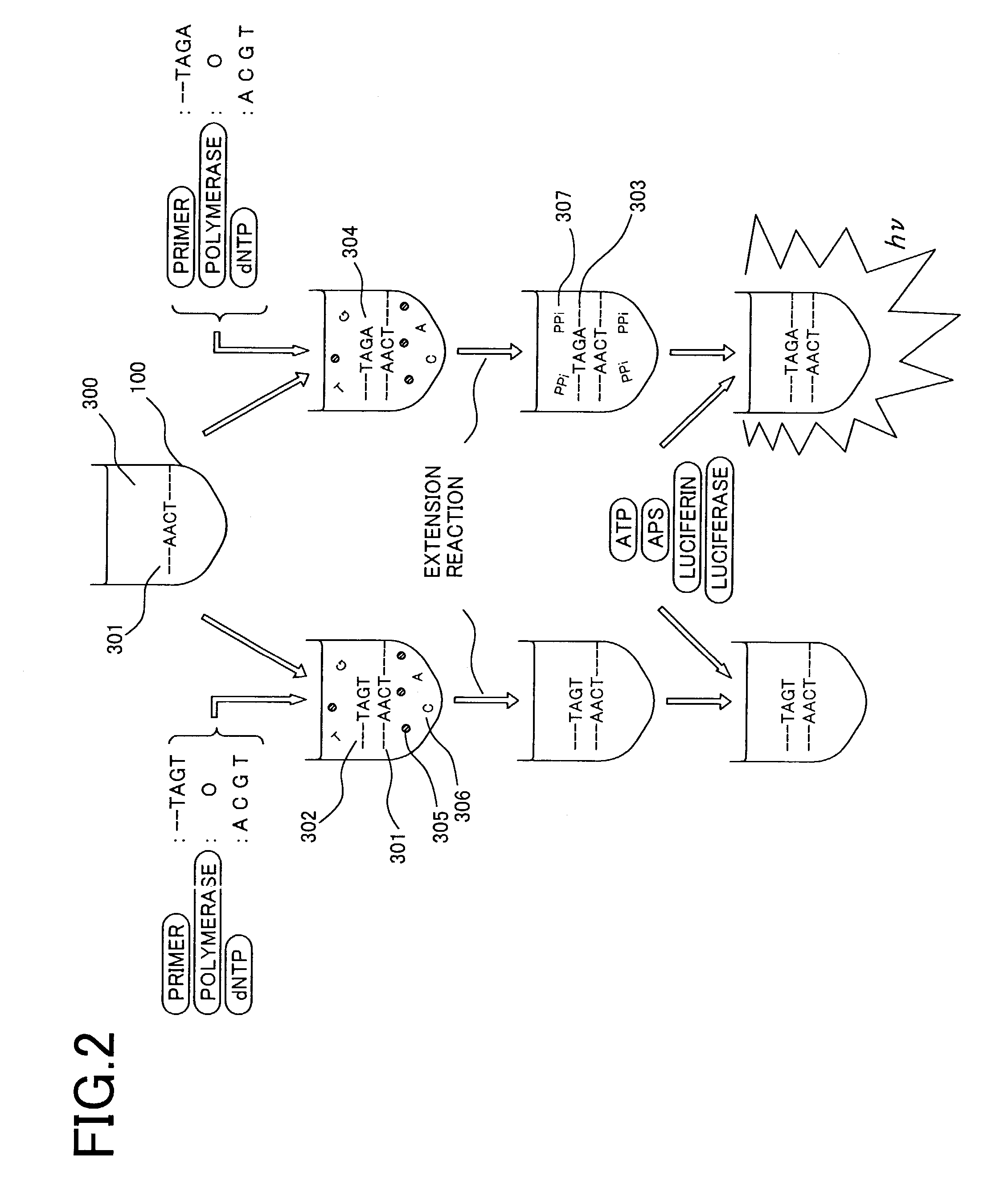
InactiveUS7163822B2Low cost of reagentsLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTelevision system detailsSensor arrayAssay
A small sized, cost-effective genetic testing apparatus that provides high sensitivity testing, for performing genetic testing simply and at low cost. An optical sensor array for the apparatus and method for luminometric assay comprises a means that simultaneously selects 2 pixels and detects minute amounts of chemiluminescence by obtaining the differential output of the respective signals.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20090130669A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 92 to 93 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of genetic testing in heritable arrhythmia syndrome patients
InactiveUS20050142591A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSyndrome patientGenetic Screening (procedure)
A method of diagnosing heritable arrhythmia syndrome in a patient is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of (a) isolating a nucleic acid sample from the patient and (b) comparing the nucleic acid sample to the compendium of novel DNA mutations disclosed in Table 1, wherein the comparison is to the mutations described from at least one of the genes selected from the group consisting of KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, and KCNE2.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20090305262A1Quickly and precisely detectAccurate identificationSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesNucleic Acid ProbesMicrobiology
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 56 to 58 or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20090130670A1Quickly and precisely detectAccurate identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesMicrobiology
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequence of SEQ ID NO. 94 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20090305260A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 59 to 61 or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20090130668A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 78 to 80 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods and devices for obtaining and analyzing cells
InactiveUS20130130265A1Microbiological testing/measurementOn/in organic carrierGenetic MaterialsGenetic Screening (procedure)
A method for concentrating and isolating nucleated cells, such as maternal and fetal nucleated red blood cells (nRBCs), in a maternal whole blood sample. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for preparing to analyze and analyzing the sample for identification of fetal genetic material as part of prenatal genetic testing. The invention also pertains to methods and apparatus for discriminating fetal nucleated red blood cells from maternal nucleated red blood cells obtained from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman.
Owner:CELLSCAPE CORP
Anonymous testing system and kit
Disclosed are methods and kits for conducting anonymous genetic testing. The methods and kits include provide a patient with an Alias ID and Password. The Alias ID is used to track a genetic sample from the patient. Both the Alias ID and Password are then used by the patient to obtain the results of the genetic test. The methods and kits allow a patient to have a genetic test performed while remaining anonymous.
Owner:TYLER TROY S +1
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS7867711B2Quickly and precisely detectAccurate identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesMicrobiology
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 87 to 89 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
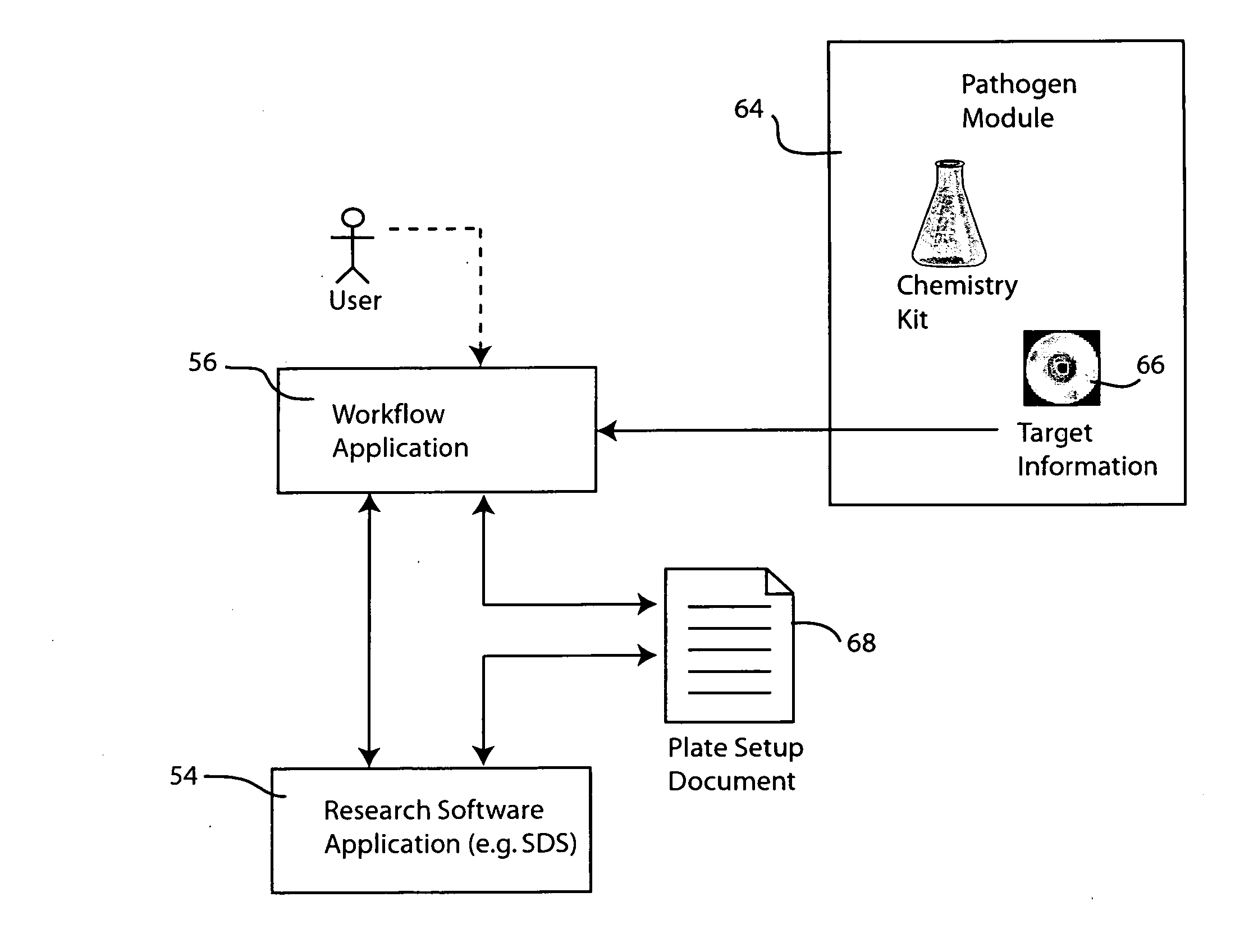
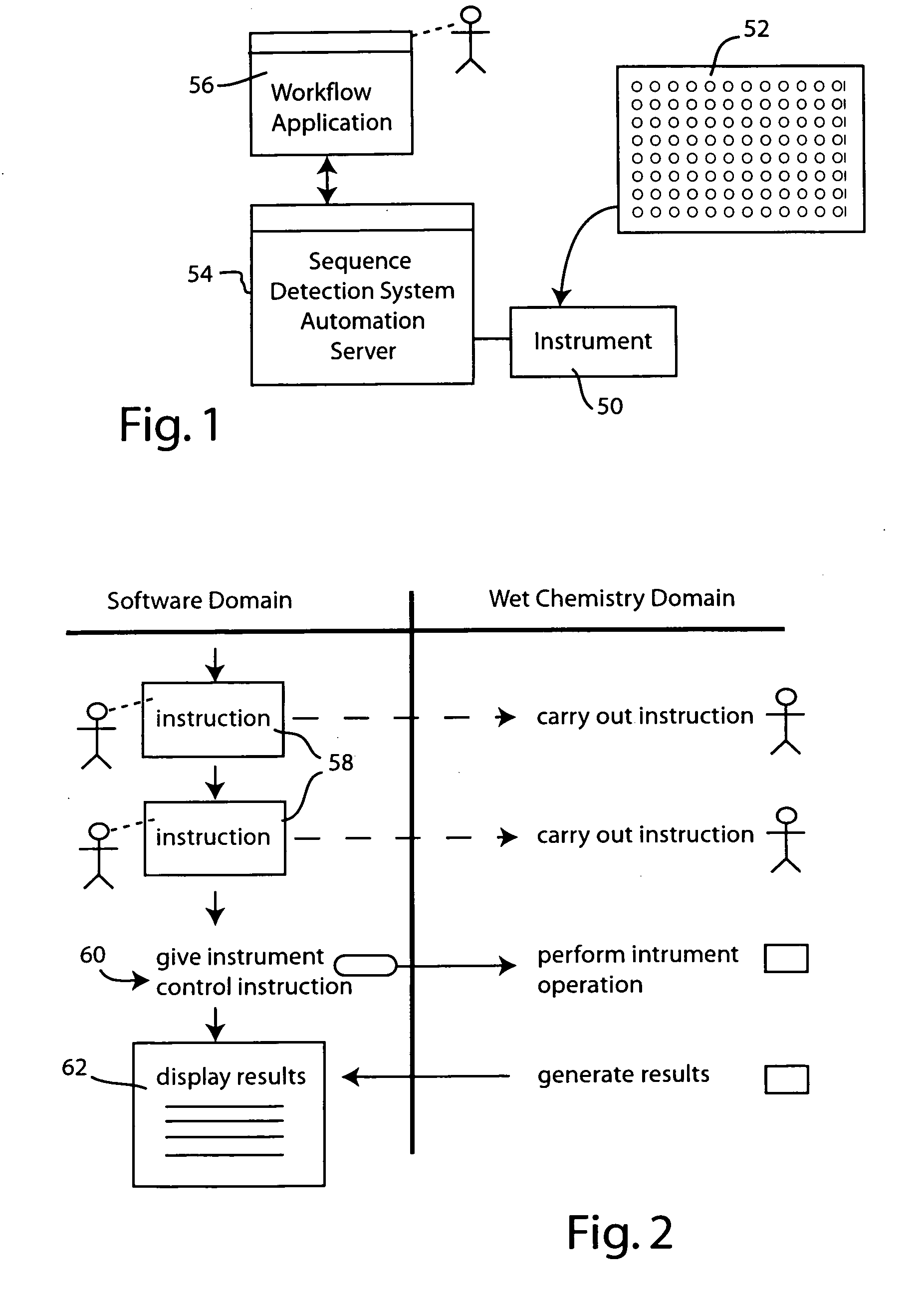
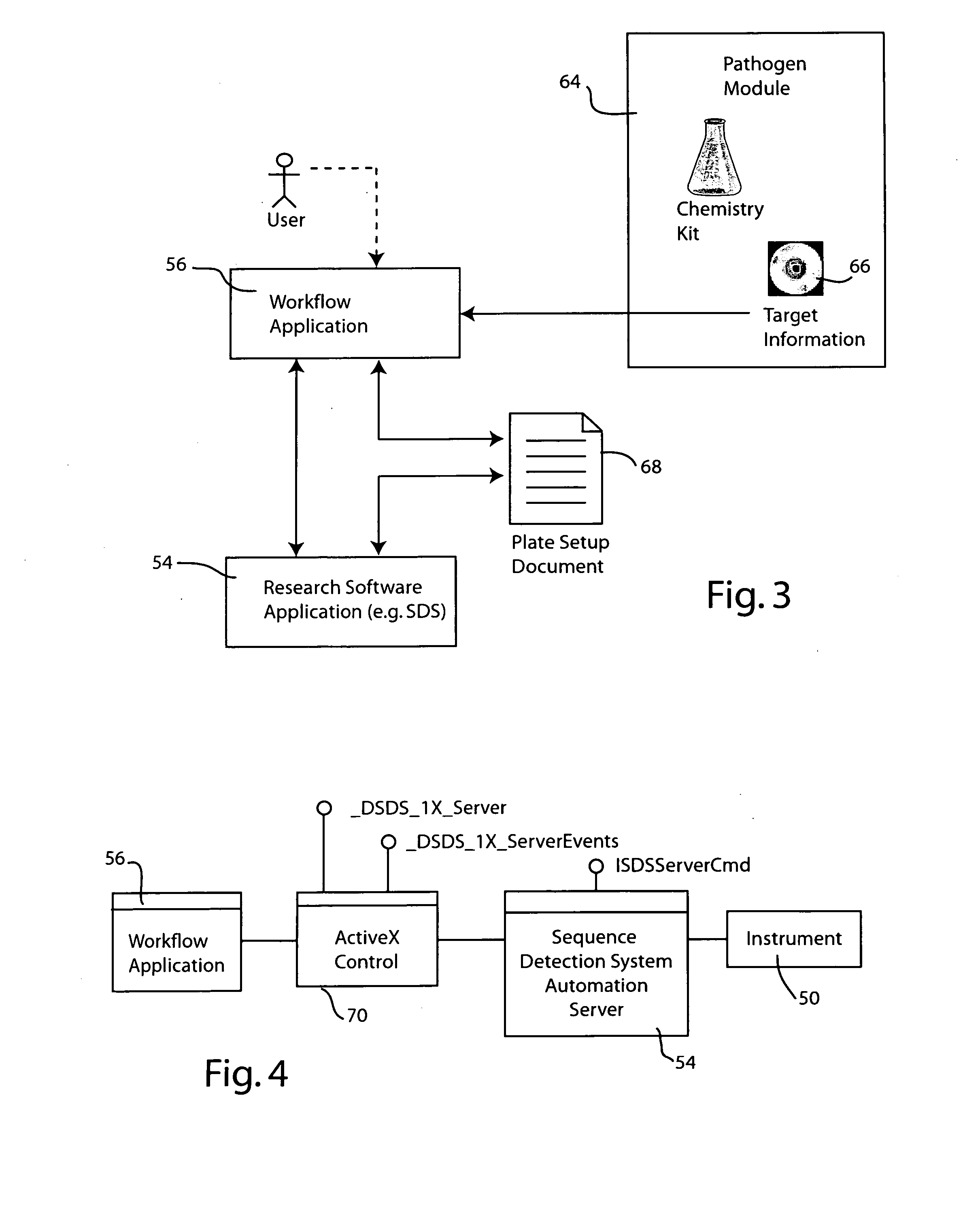
Systems and methods for generating automated software workflows for biological testing
InactiveUS20070112804A1Digital data processing detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementSoftware engineeringLearning curve
The workflow application integrates with a research software application associated with a laboratory instrument to provide a user with step-by-step instructions on how to follow the workflow steps of a laboratory experiment. The instructions are dynamically tailored, according to the nature of the workflow, the samples being experimented upon and / or the operating states of the instrument and / or the research software application. The workflow application significantly reduces the learning curve to operate sophisticated laboratory instruments. In a genetic testing instrument the workflow application can prescribe the need for control samples and can optimize the layout of samples within the instrument's sample receiving plate or fixture.
Owner:APPLERA
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS20110003283A1Quickly and precisely identifiedAccurate distinctionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NO. 55 or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
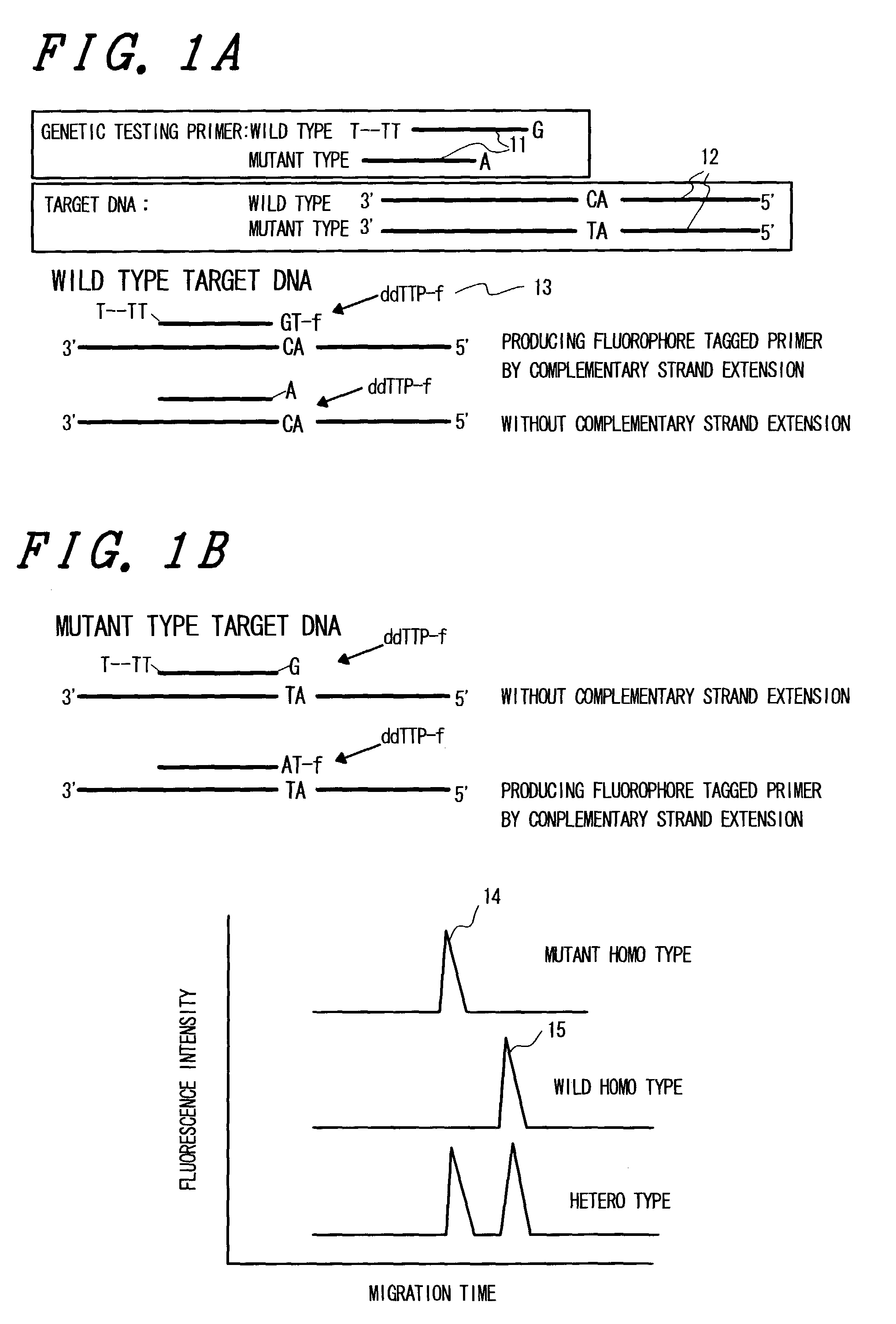
Genetic analysis method
InactiveUS7049104B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFluorescenceElectrophoresis
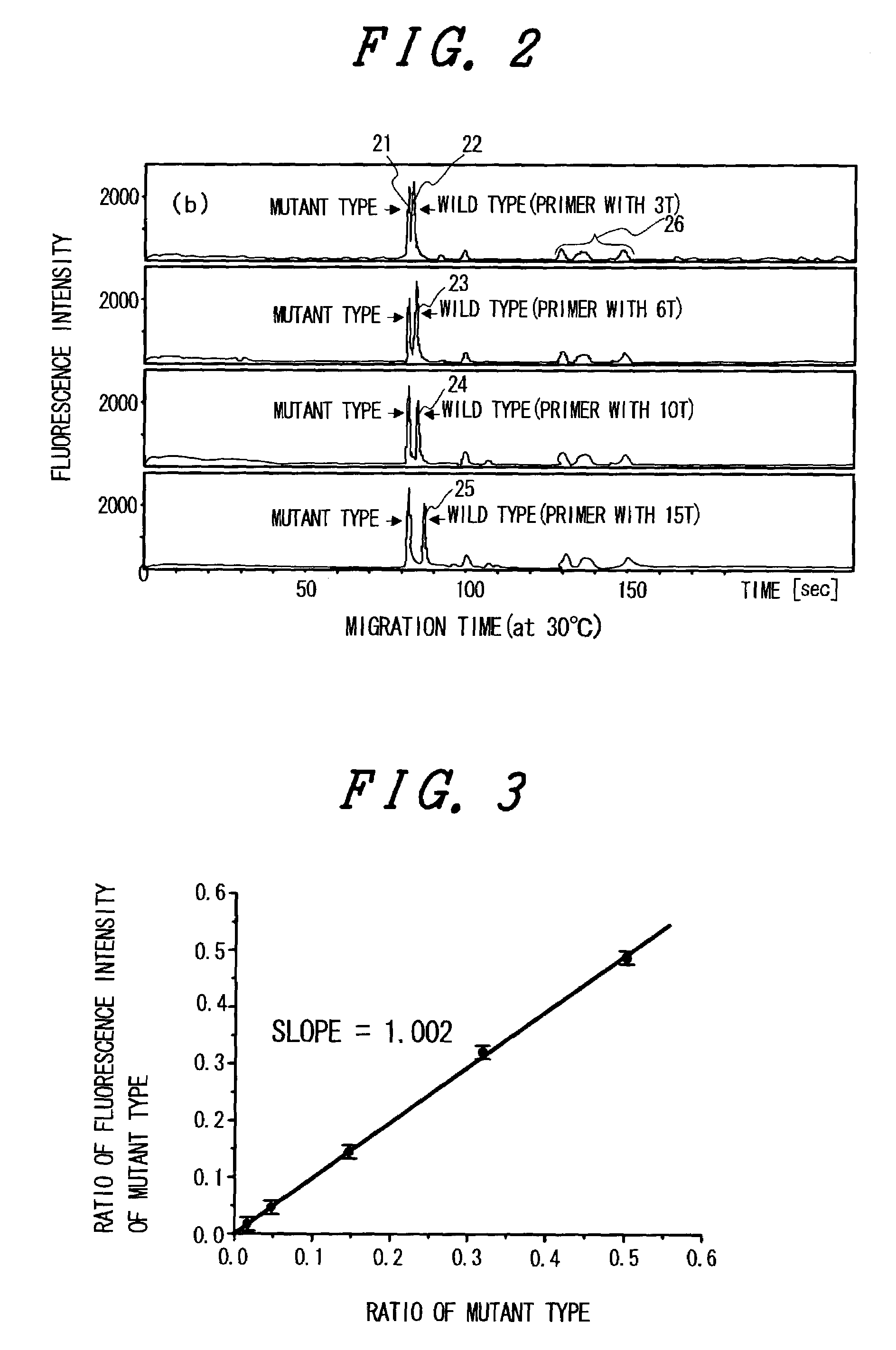
The present invention relates to a quick and simple method for genetic testing, particularly for SNP testing, using two kinds of primers which are complementary to a mutant target and a wild-type target, respectively, and different in length or migration speed in electrophoresis. These probes are allowed to hybridize with targets, fluorophore-tagged nucleotides are attached to the primers, and electrophoresis is carried out for discriminatory detection.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Peritoneal metastasis prediction model of gastric cancer based on 22 genes and application thereof
ActiveCN107586852AImprove survival rateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadRPS27A
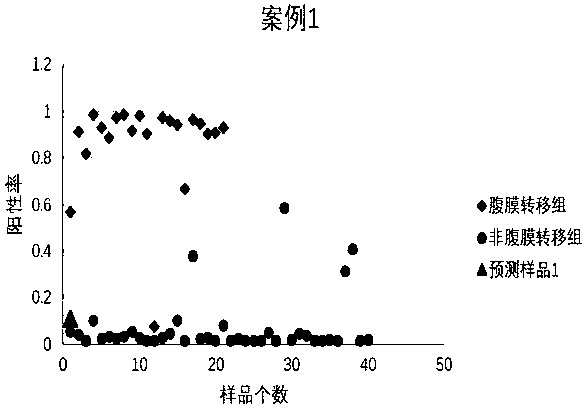
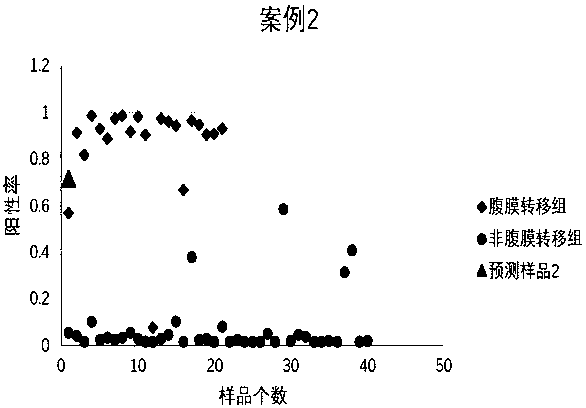
The invention belongs to the field of genetic testing and provides a peritoneal metastasis prediction model of a gastric cancer based on 22 genes and application thereof, including PCLO, UGGT1, ZNF714, KIAA0825, COL23A1, MED1, NPAS2, TTC14, RPS27A, ASPH, ARHGEF12, SIK1, PAPPA, HHIPL1, MYO9B, ITPKB, ZNF862, MKNK1, MUC6, TRRAP, DUOX1 and KRTAP5-2; a risk of peritoneal metastasis is predicted effectively and specifically, according to SVM of a selected classifier and a positive judgment threshold value of 0.5. The application of the gene model of the invention is helpful for predicting the metastasis of patients with gastric cancer and has important value and significance for taking timely and effective clinical measures, making an individualized diagnosis and treatment plan and finally improving a survival rate of the patients with the gastric cancer.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV UNION HOSPITAL +1
Methods and devices for obtaining and analyzing cells
InactiveUS20130130930A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenetic MaterialsGenetic Screening (procedure)
A method for concentrating and isolating nucleated cells, such as maternal and fetal nucleated red blood cells (nRBCs), in a maternal whole blood sample. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for preparing to analyze and analyzing the sample for identification of fetal genetic material as part of prenatal genetic testing. The invention also pertains to methods and apparatus for discriminating fetal nucleated red blood cells from maternal nucleated red blood cells obtained from a blood sample taken from a pregnant woman.
Owner:CELLSCAPE CORP
Probe, probe set, probe-immobilized carrier, and genetic testing method
InactiveUS7838656B2Quickly and precisely detectAccurate identificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesNucleic Acid Probes
A nucleic acid probe for classification of pathogenic bacterial species is capable of collectively detecting bacterial strains of the same species and differentially detecting them from other bacterial species. Any one of the base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 73 to 75 and complementary or modified sequences thereof or a combination of at least two of them is used for detecting the gene of an infectious disease pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:CANON KK
Determination of the number of tandem repeat nucleotides using encoded probe-displaying beads
InactiveUS20060257916A1Reduce morbidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyGenetic Screening (procedure)
This invention provides compositions and methods for genetic testing of an organism and for correlating the results of the genetic testing with a unique marker that unambiguously identifies the organism. The markers may be internal markers, such as for example single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), short tandem repeats (STRs), or other sites within a genomic locus. Alternatively, the markers may be external, such that they are separately added to the genetic sample before testing.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Pulmonary artery hypertension treatment drug stem cell screening model and application thereof
The invention belongs to a novel pulmonary artery hypertension treatment drug screening technology established by applying a stem cell technology; with a BMP signal downstream key gene Id1 as a target spot, a double-report-gene original is designed and inserted into an Id1 genome to construct a restructuring carrier, the carrier is transferred into a human embryonic stem cell strain, and a stable-expression CGMCC11091 cell strain is obtained; the CGMCC11091 cell strain is stimulated by a to-be-tested anti pulmonary artery hypertension compound, then cells are cracked by a cell cracking fluid, according to a genetic testing system, the method detects luciferase expression activity, with the Id1 promoter driven double-report-gene expression quantity as an indicator, and a pulmonary artery hypertension treating compound screening model having Id1 expression up-regulated is obtained. The invention also discloses an application of the model in screening regulators for up-regulation of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signals, regulators for up-regulation of expression level of BMP-2 acceptors, preparations for improving the pulmonary artery blood hemodynamics, preparations for improving pulmonary vascular reconstitution, pulmonary artery hypertension treatment drugs and cardiopulmonary vascular disease treatment drugs.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
LAMP-based (loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based) visual fluorogenic and chromogenic genetic testing method for microorganisms
InactiveCN102586438AMeet the requirements for rapid detection of pathogenic microorganismsThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroorganismFluorescence
The invention discloses an LAMP-based visual fluorogenic and chromogenic genetic testing method for microorganisms, which relates to a genetic testing method for microorganisms. The testing method includes the following steps: (1) buffered peptone water (BPW) is used for culturing a sample to be tested according to a national standard method for 4 hours; (2) a water boiling method is used for extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from the sample to be tested; (3) the DNA is added into an LAMP reaction system, and the temperature of 65 DEG C is kept for 1 hour; (4) by means of comparison with a control group, the result of the sample to be tested is observed with naked eyes, and qualitative analysis is carried out on the sample. Compared with the conventional culture method, the genetic testing method has the advantages that: testing is rapid, only taking 5 hours, and plus the extraction of the sample DNA, testing takes less than 6 hours in total; the specificity is good, and the sensitivity is high; the steps are simple, and the repeatability is high; and a plurality of samples can be tested at the same time. The genetic testing method can qualitatively test microorganisms, and can take the place of the conventional culture method and the serological testing method which are used up to now.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
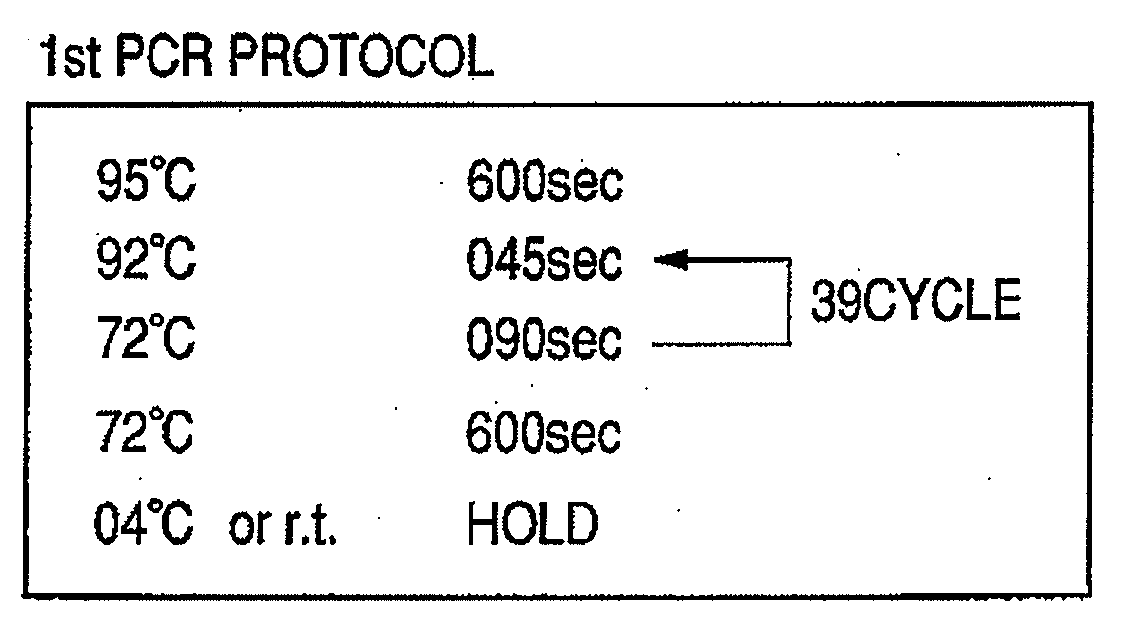
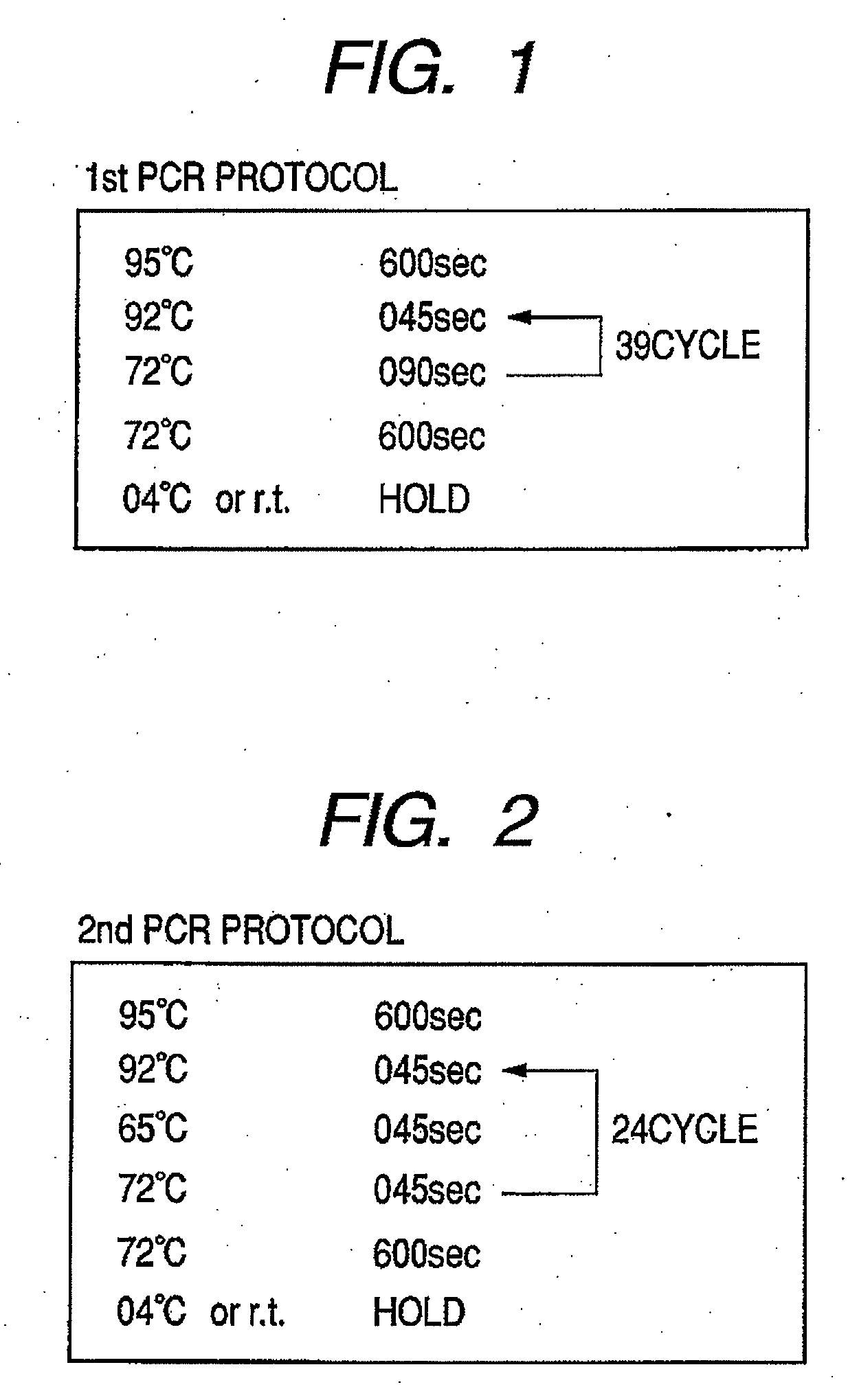
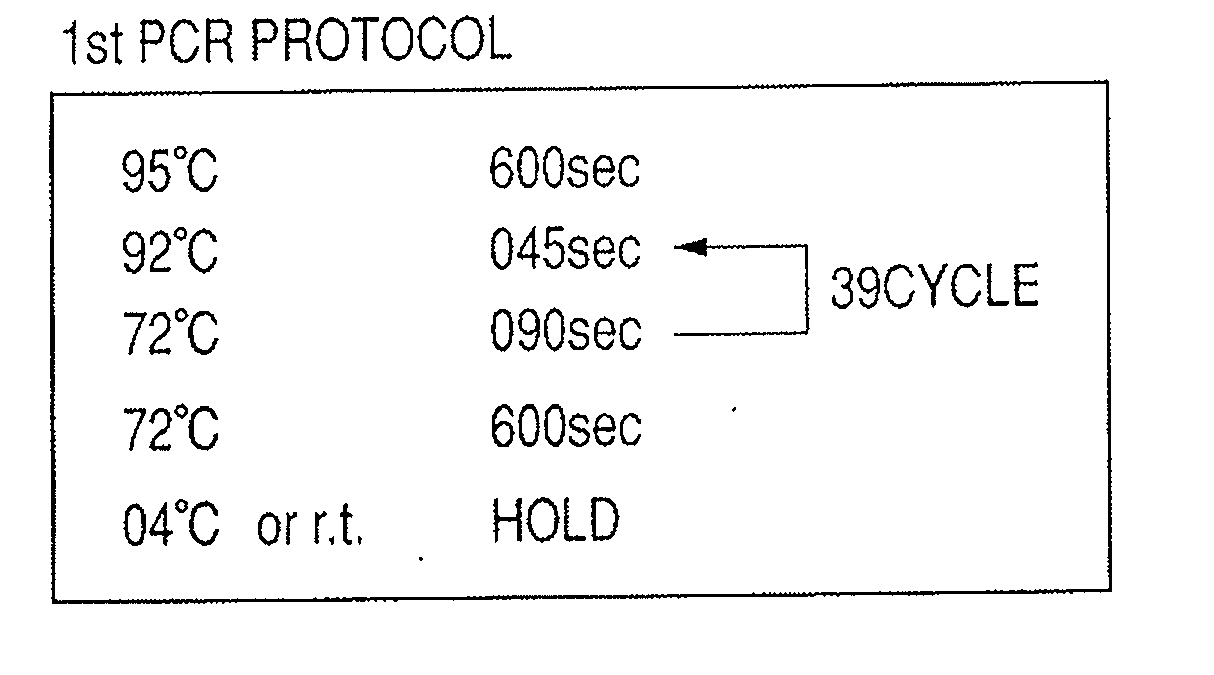
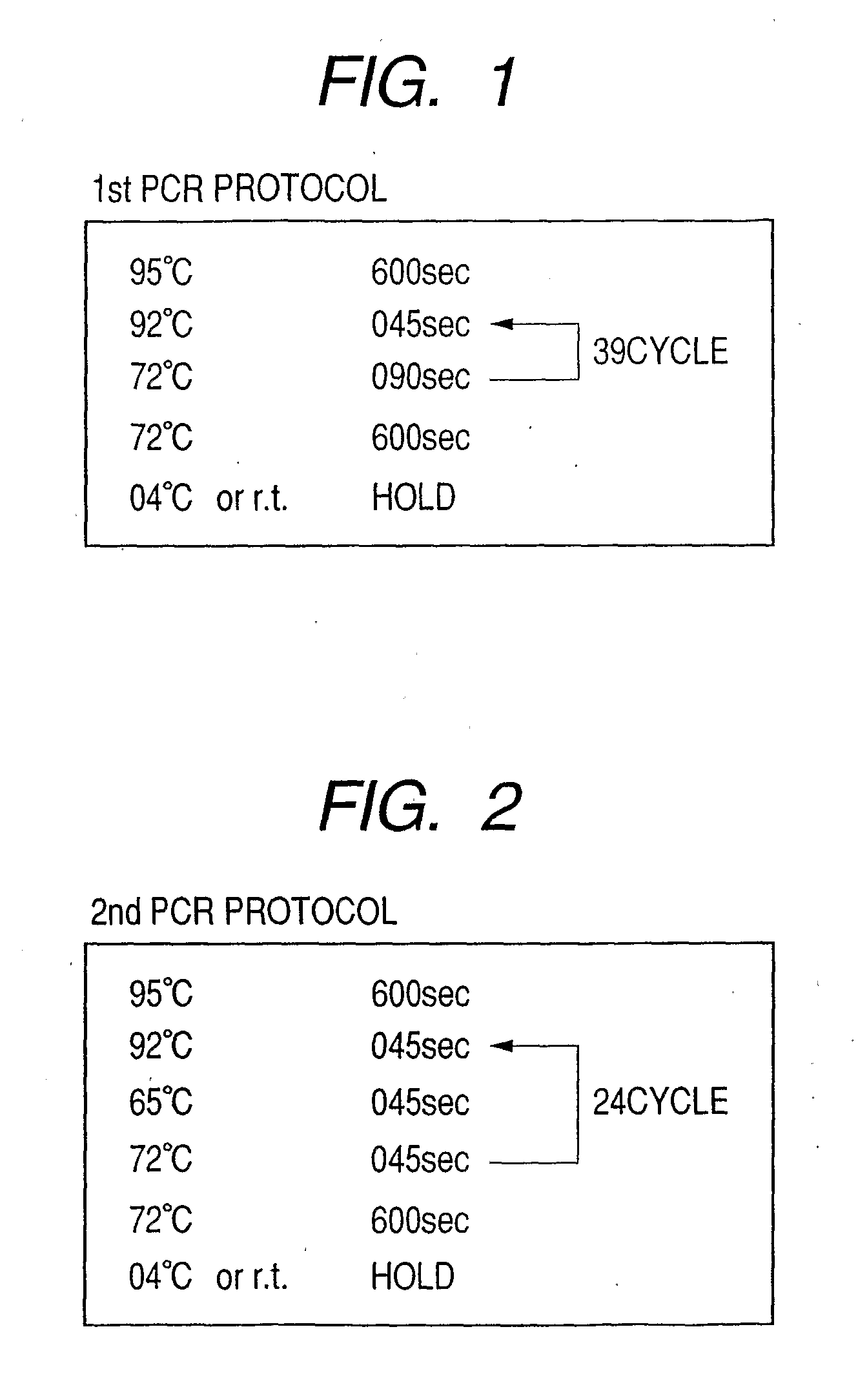
Methods for PCR and HLA typing using unpurified samples
Provided are methods for amplifying a gene or RNA or sets thereof of interest using a tandem PCR process. The primers in the first PCR or set of PCR reactions are locus-specific. The primers in the second PCR or set of PCR reactions are specific for a sub-sequence of the locus-specific primers and completely consumed during the second PCR amplification. For RNA amplification, the first PCR is reverse transcription and the resulting cDNA(s) provide a template for cRNA synthesis, endpoint PCR or real time PCR. Also provided is a tandem PCR method which accepts raw, completely unpurified mouthwash, cheek swabs and ORAGENE™-stabilized saliva as the sample input, the resulting amplicons serving as the substrate for complex, microarray-based genetic testing. Also provided is a method of allelotyping a gene or set thereof by amplifying the gene(s) using tandem PCR on DNA or RNA comprising the sample.
Owner:GENOMICS USA
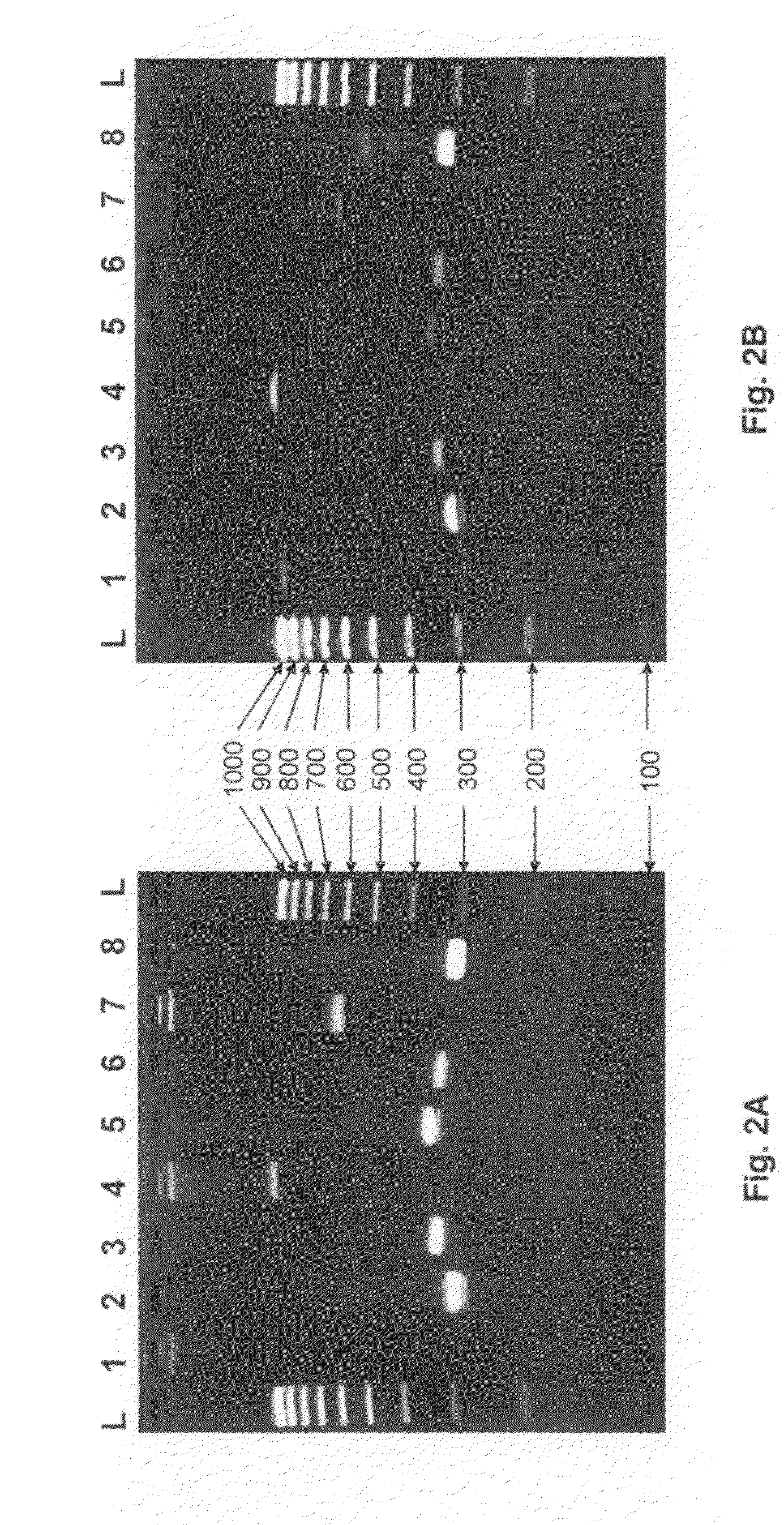
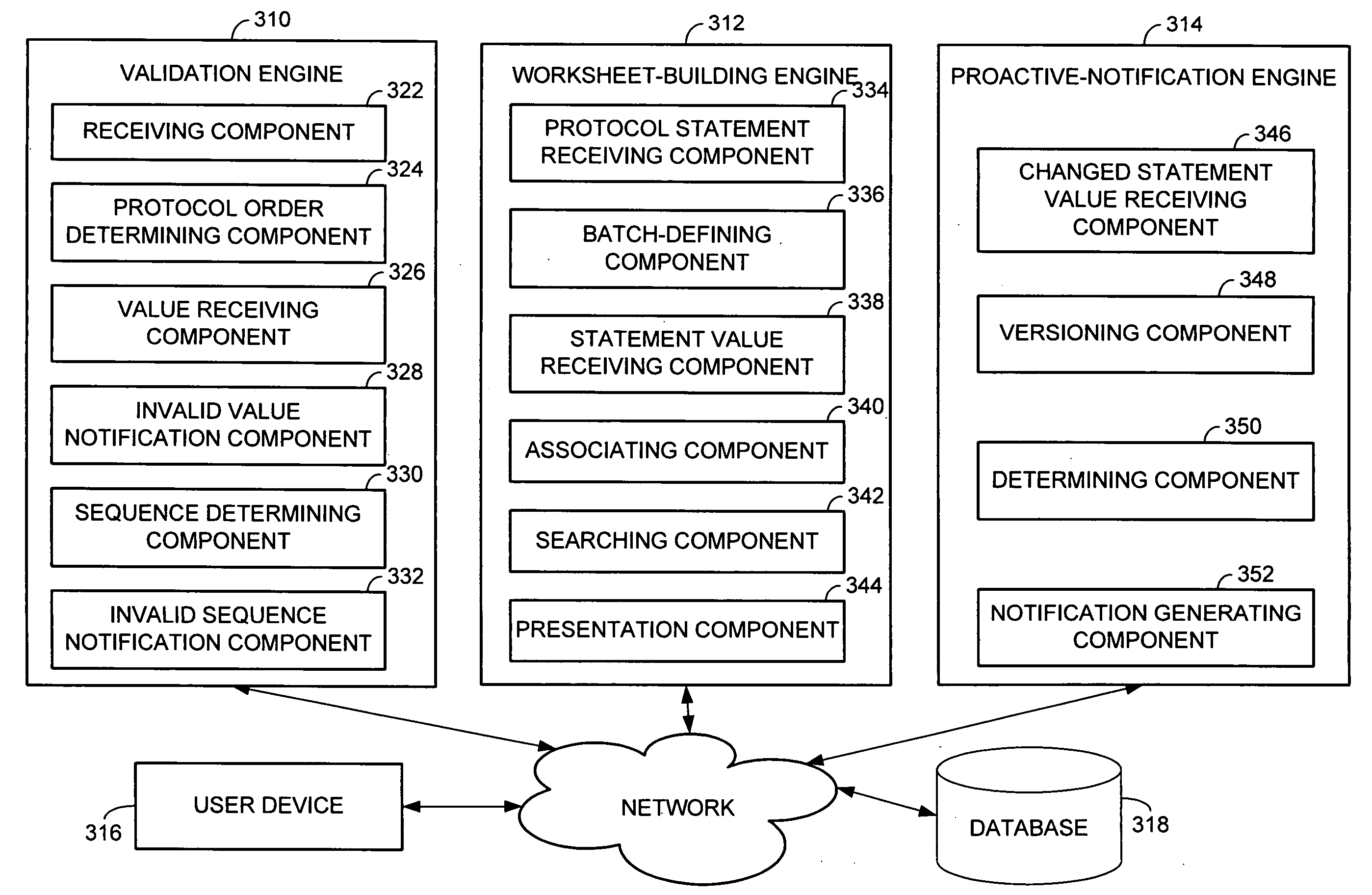
Backing up a protocol order associated with genetic testing
InactiveUS20090106333A1Shorten the timeThe result is accurateComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionPatient personal data managementGenetic Screening (procedure)Molecular diagnostics
Computerized methods and systems for creating and documenting protocol orders in a molecular diagnostic laboratory environment are provided. Utilizing the methods and systems described herein, protocol statements may require values to be entered in association therewith prior to permitting access to subsequent protocol orders. Accordingly, more accurate test runs and, consequently, more accurate test results, may be achieved. Additionally, as values associated with protocol statements are electronically captured, in accordance with embodiments hereof, such values may be searched to evaluate trends or identify protocol orders and / or results that may be affected by a later discovered error or the like. Moreover, backing up a protocol order includes providing a backup protocol order for selection, in the event that an alternative test result is desired.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
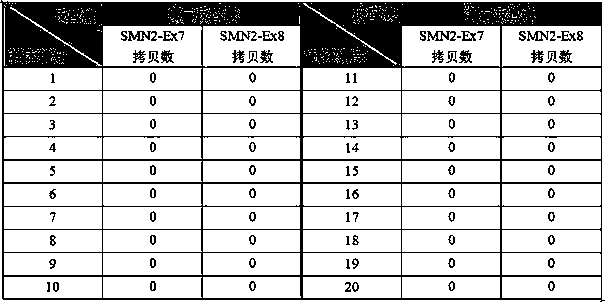
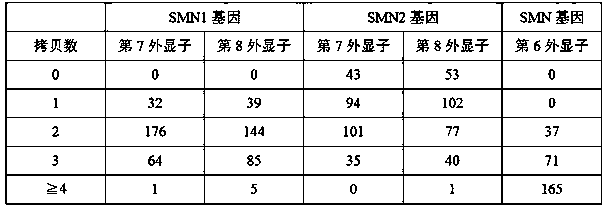
Relative quantifying kit used for detecting copy number of survival genes of human motor neurons
InactiveCN109554459AImprove accuracySmall sample sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesPrimary motor neuron
The invention relates to the field of genetic testing, and specifically relates to a kit used for detecting the copy number of survival genes of human motor neurons. According to the kit used for detecting the copy number of the survival genes of the human motor neurons, a multifluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is adopted for detecting the copy number of the survival genes of thehuman motor neurons; and specific primers and probes for exons 7 and 8 of SMN1 gene, exons 7 and 8 of SMN2 gene, exon 6 of SMN gene and internal reference gene cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator(CFTR) are separately designed. The kit is smartly designed, so that, relative quantifying can be separately performed on the copy number of the exons 7 and 8 of the SMN1 gene, the exons 7 and 8 of the SMN2 gene as well as the exon 6 of the SMN gene by adopting 3 independent PCR reactions. The kit is easy to operate, strong in specificity and excellent in sensitivity. Thus, the result of the copynumber of the exon 6 of the SMN gene can be improved in terms of accuracy; so that, the kit is more suitable for clinical classifying of patients with spinal muscular atrophy and screening of carriers.
Owner:DEBIQI BIOTECH XIAMEN
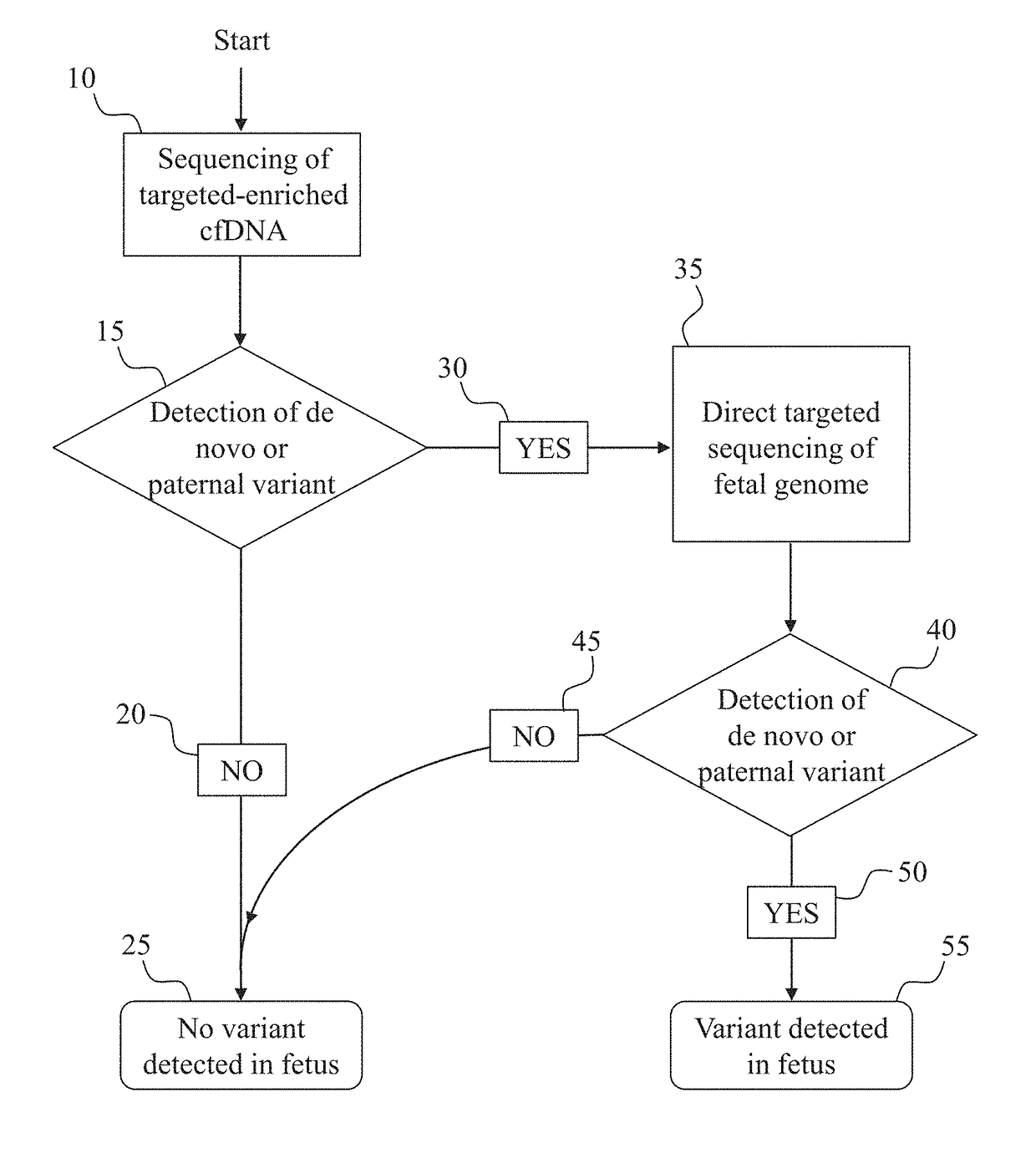
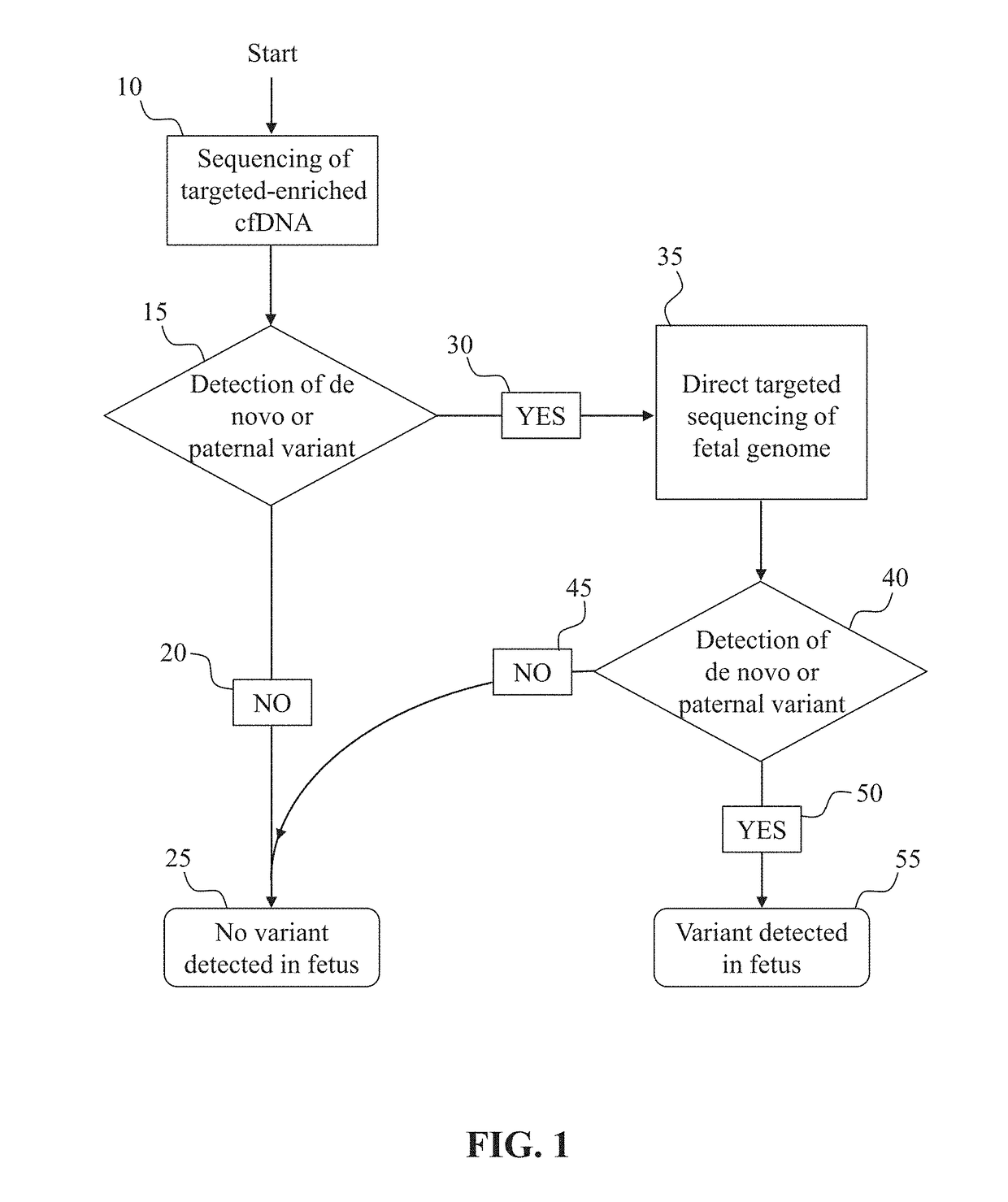
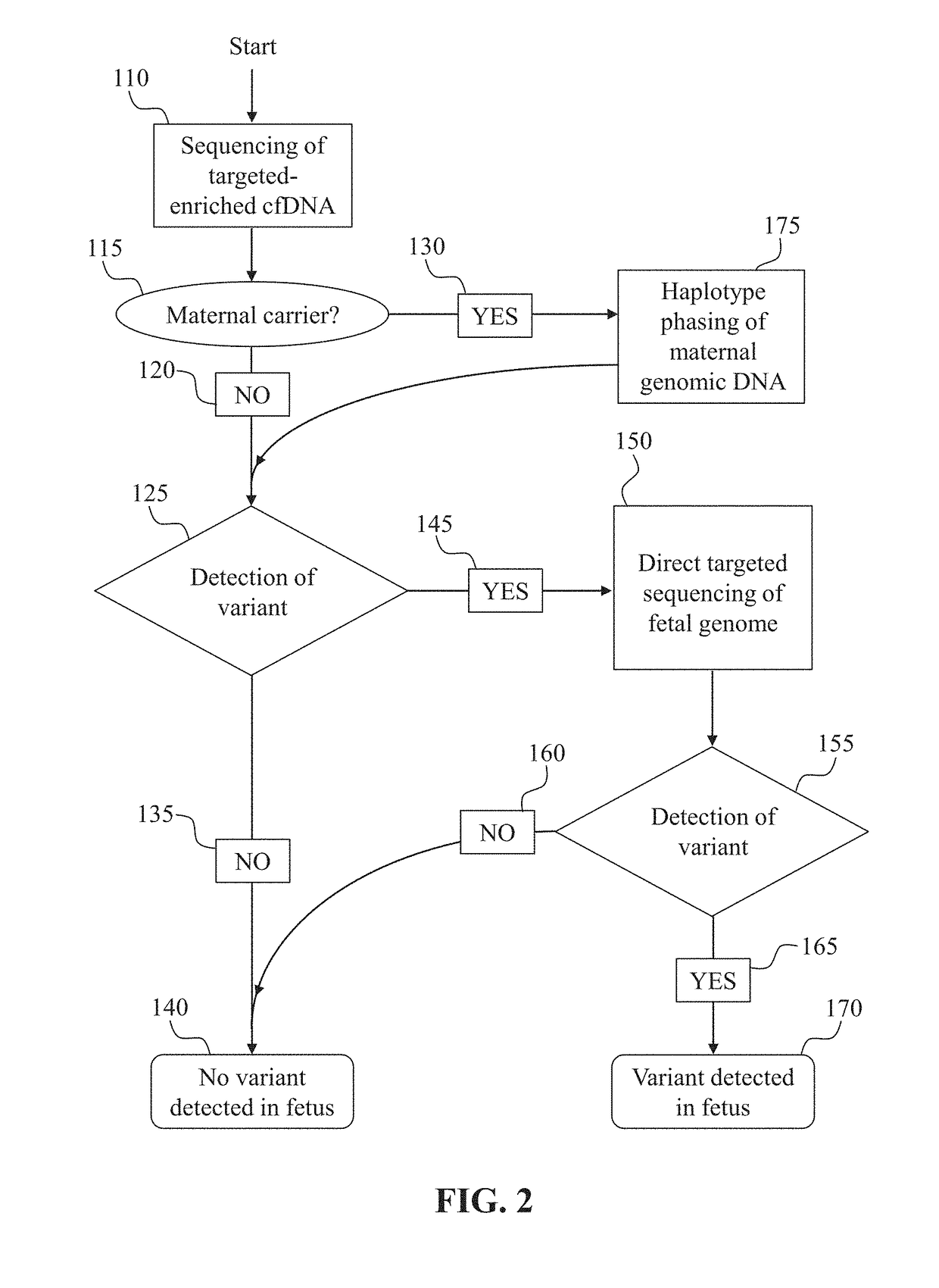
Noninvasive prenatal diagnostic methods
Prenatal genetic testing allows early detection of genetic disease in a fetus. Described herein are methods of detecting the presence or absence of a genetic variant in a region of interest in the genome of a fetus in a pregnant woman. The methods are noninvasive, and can use cell-free DNA (cfDNA) present in the plasma of the pregnant woman. A DNA library is constructed from the cfDNA, and DNA molecules comprising the region of interest or portions thereof are enriched and analyzed, for example by sequencing. The methods described herein can also rely on constructing a maternal haplotype to provide even higher resolution fetal genetic variant determination.
Owner:MYRIAD WOMENS HEALTH INC
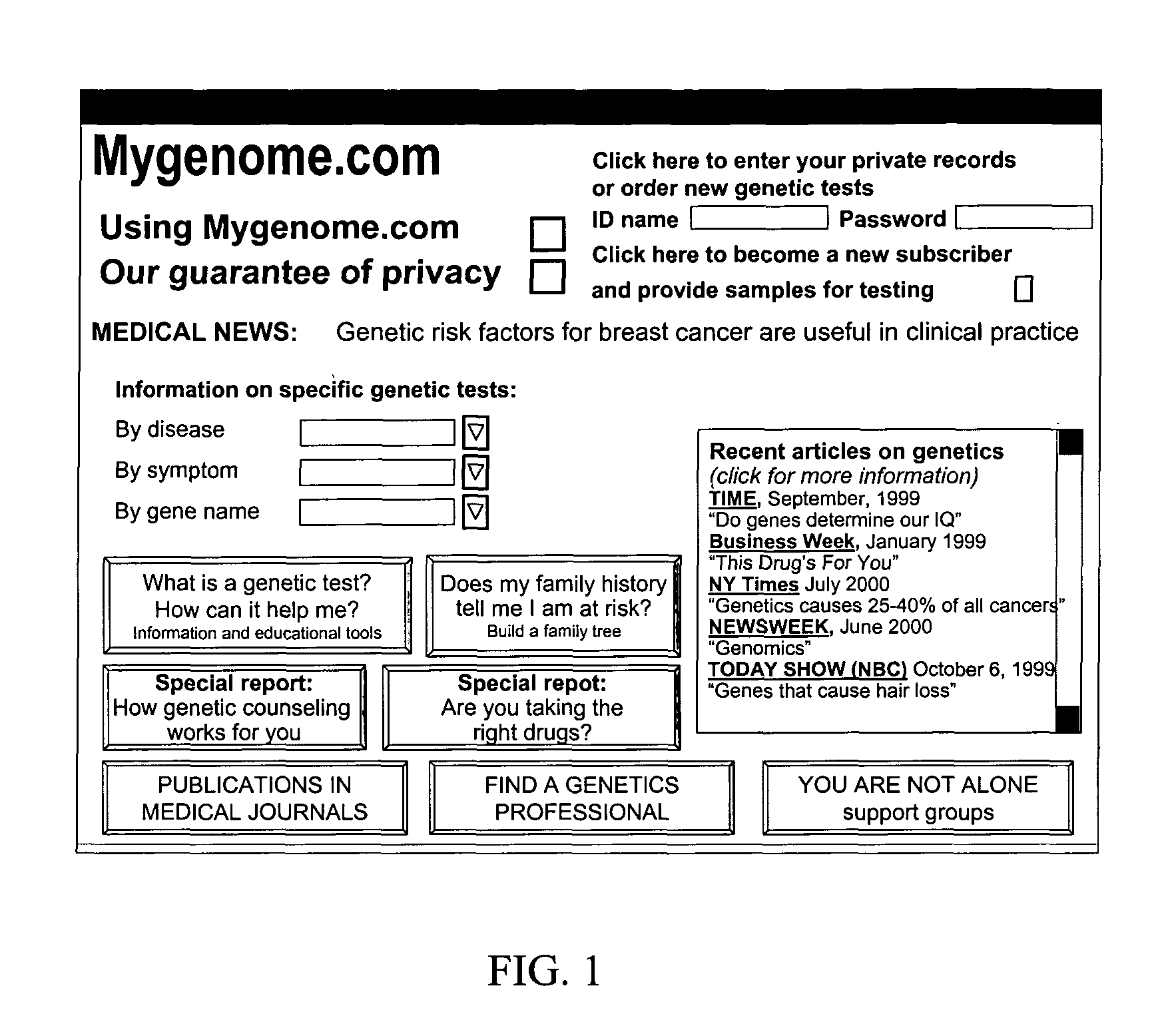
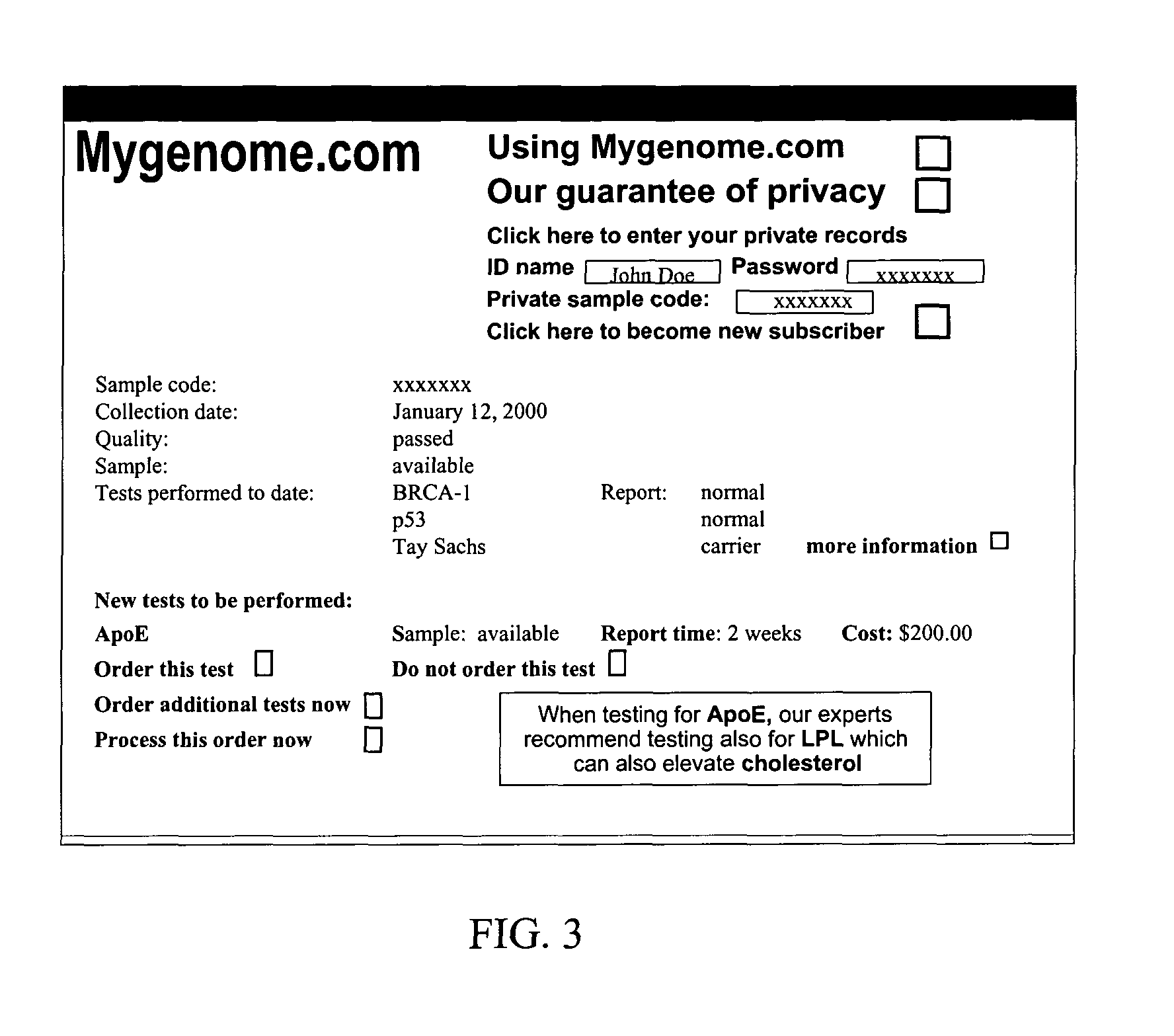
Method for increasing utilization of genetic testing
This invention describes a method and site for providing genetic testing using the Internet which enables individuals to access genetic testing as well as methods that ensure privacy in the selection of genetic tests, payment, performance of tests, delivery of results, interpretation of results, and genetic counseling. These methods will increase the utilization of genetic testing by individuals.
Owner:NAT BIOMEDICAL RES FOUND A CORP OF NY
System for tracing animal products
ActiveUS7229764B2Reduce usageImprove system robustnessSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal scienceAnimal product
The present invention provides a genetic testing system that ensures complete traceability of animals and food products and involves a method of uniquely identifying animals for data collection, records management and retrieval purposes involving a novel method of genetic analysis using individual DNA fingerprinting of parentage of individual animal to effectively provide for full traceability of animals from birth to consumption.
Owner:PIG IMPROVEMENT UK
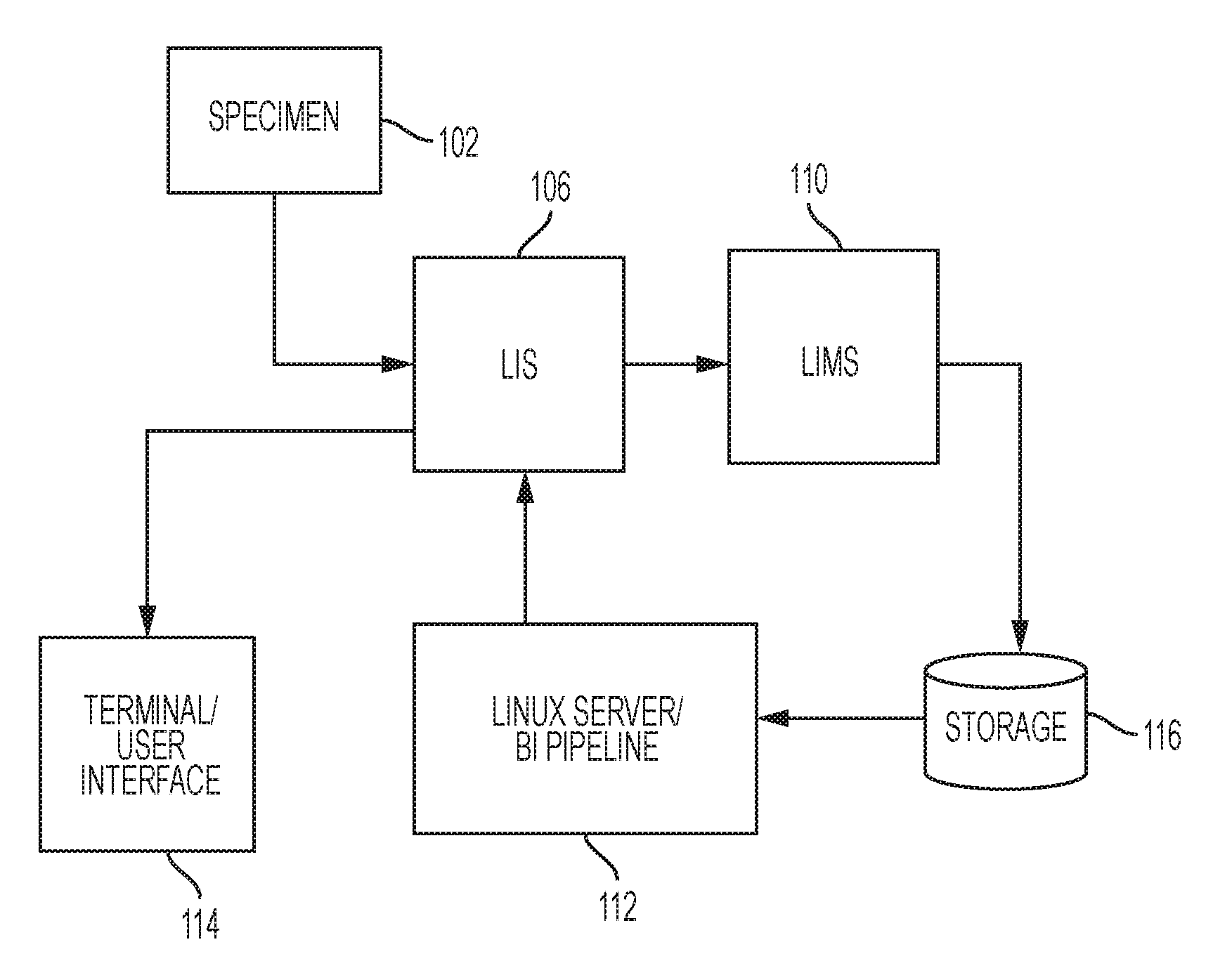
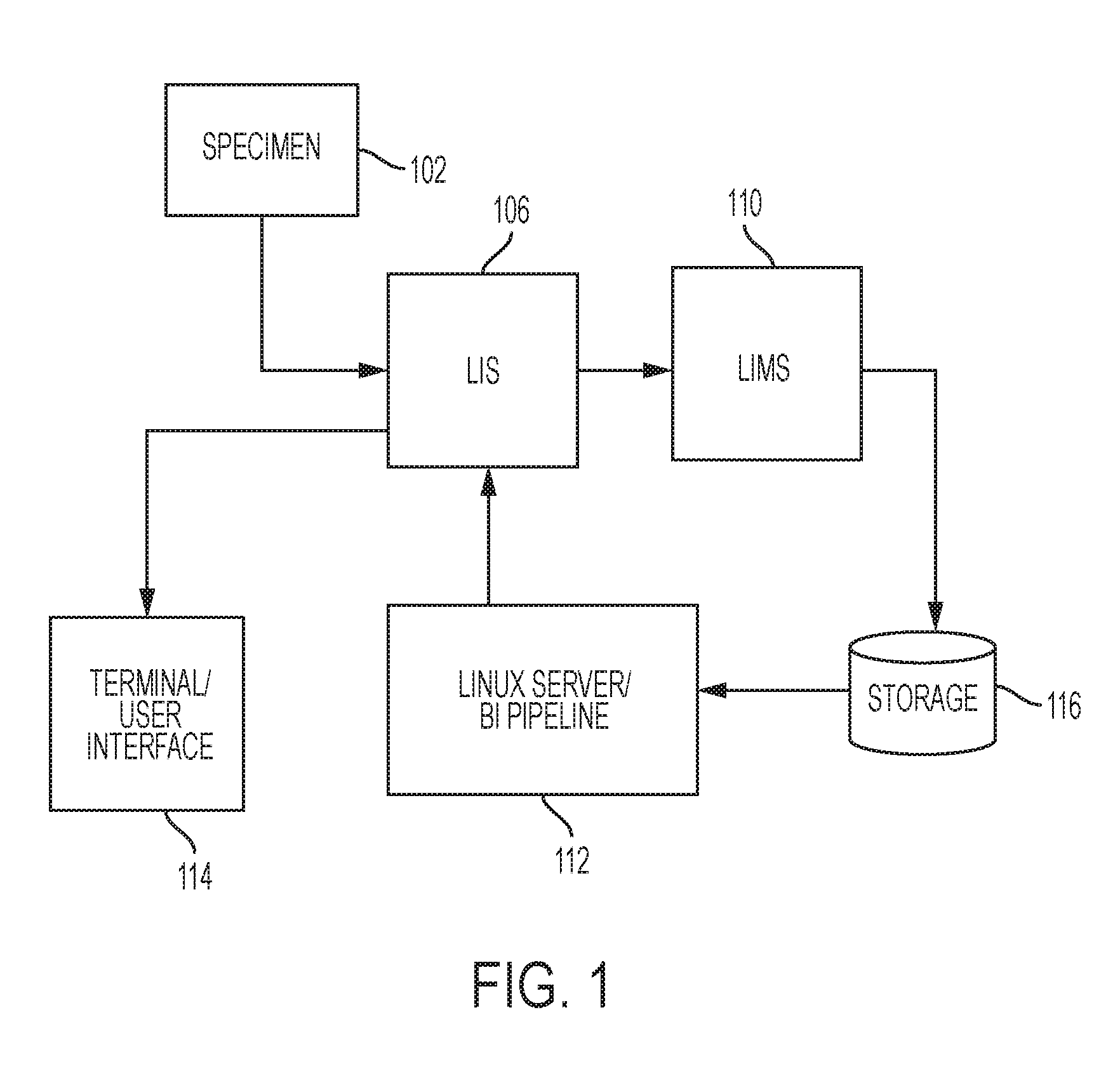
System, method and graphical user interface for creating modular, patient transportable genomic analytic data
Systems and methods may be provided for the generation, online viewing and display of the level of significance, and printing of reports created by the analysis and diagnosis of DNA, mRNA, protein derived from blood, urine, stool, tissue and organ specimens provided to clinical laboratories by client / physicians. These reports graphically and tabularly indicate the severity, diagnosis and prognosis of the specimen and include visual analysis, textual analysis, prognostic and treatment information. Systems and methods are also provided for the generation, online viewing and printing of prognostic fact sheets that are related to other disease states based on the genetic testing results of a specimen, and for the generation, online viewing and printing of comprehensive patient genotype result and drug recommendation by specialty.
Owner:ADMERA HEALTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com