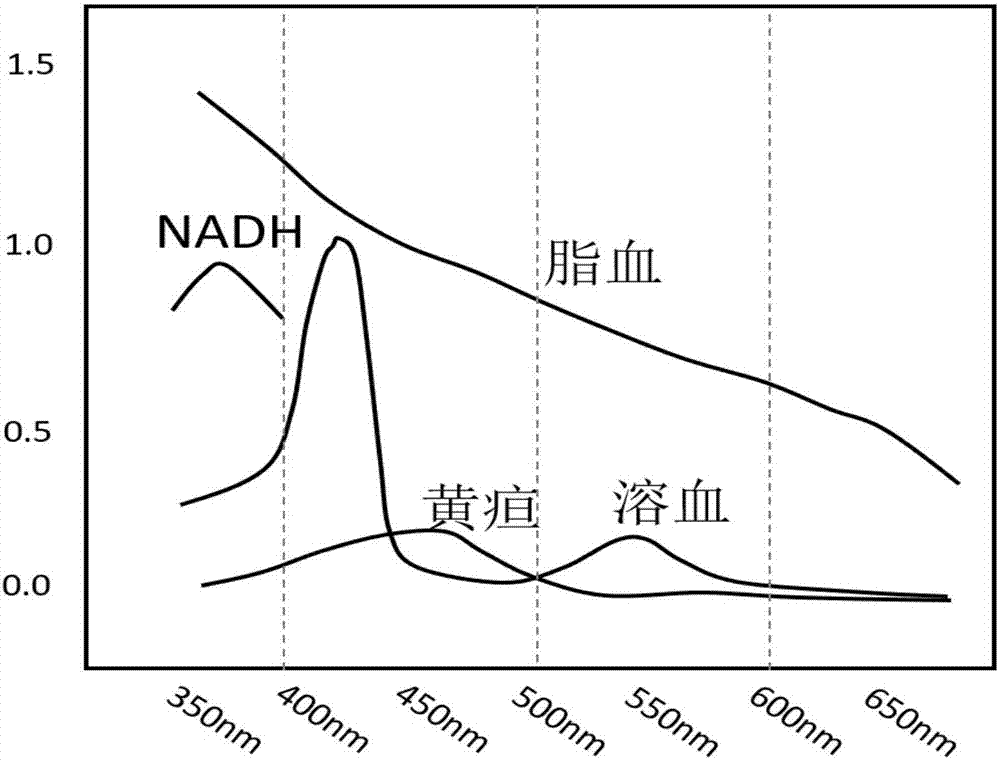
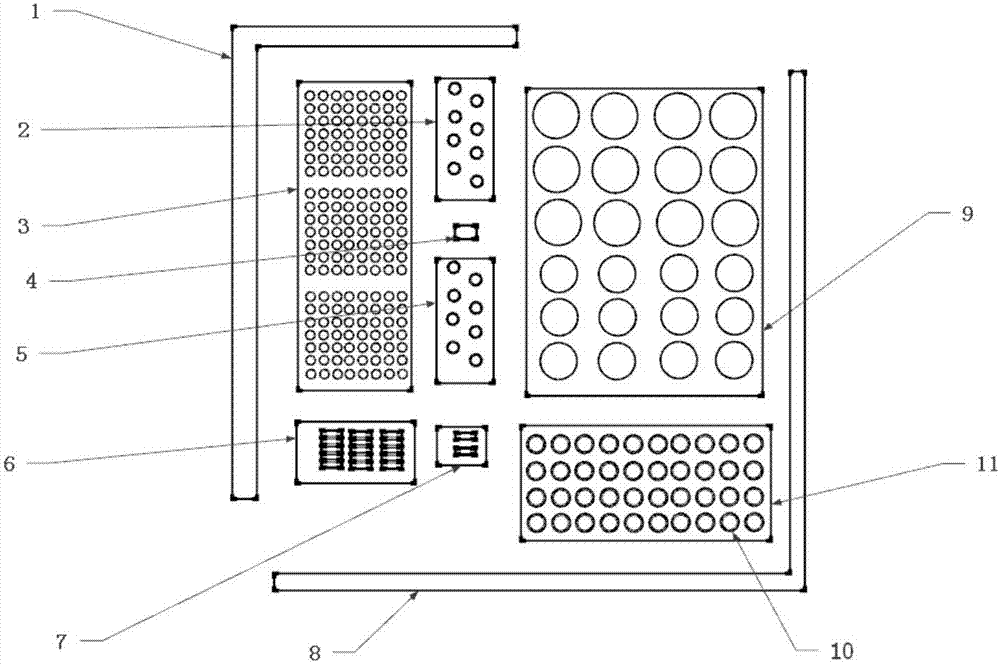
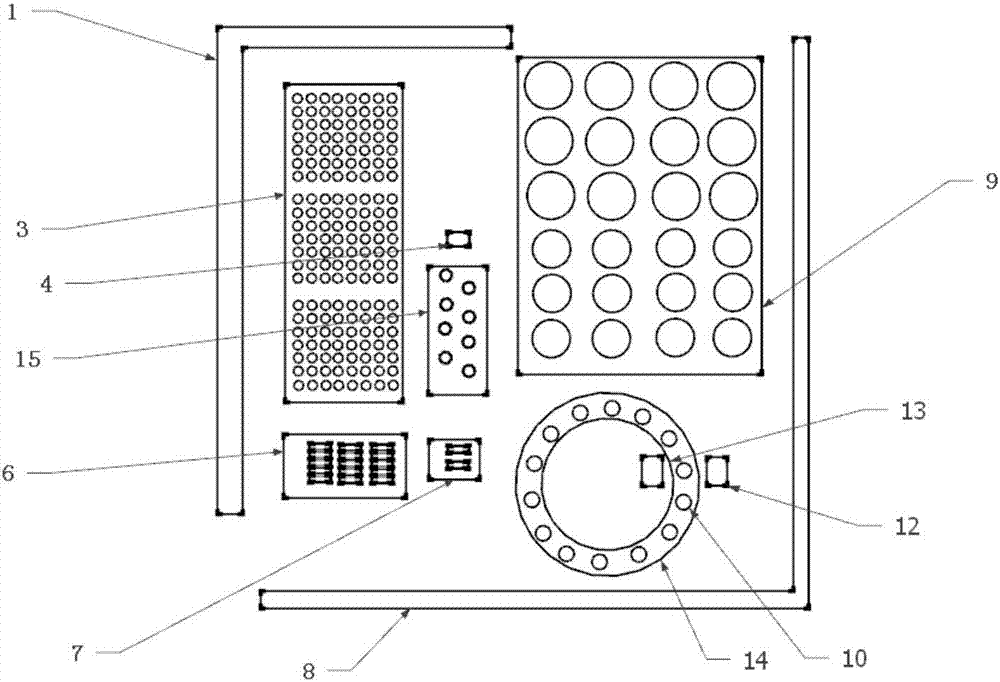
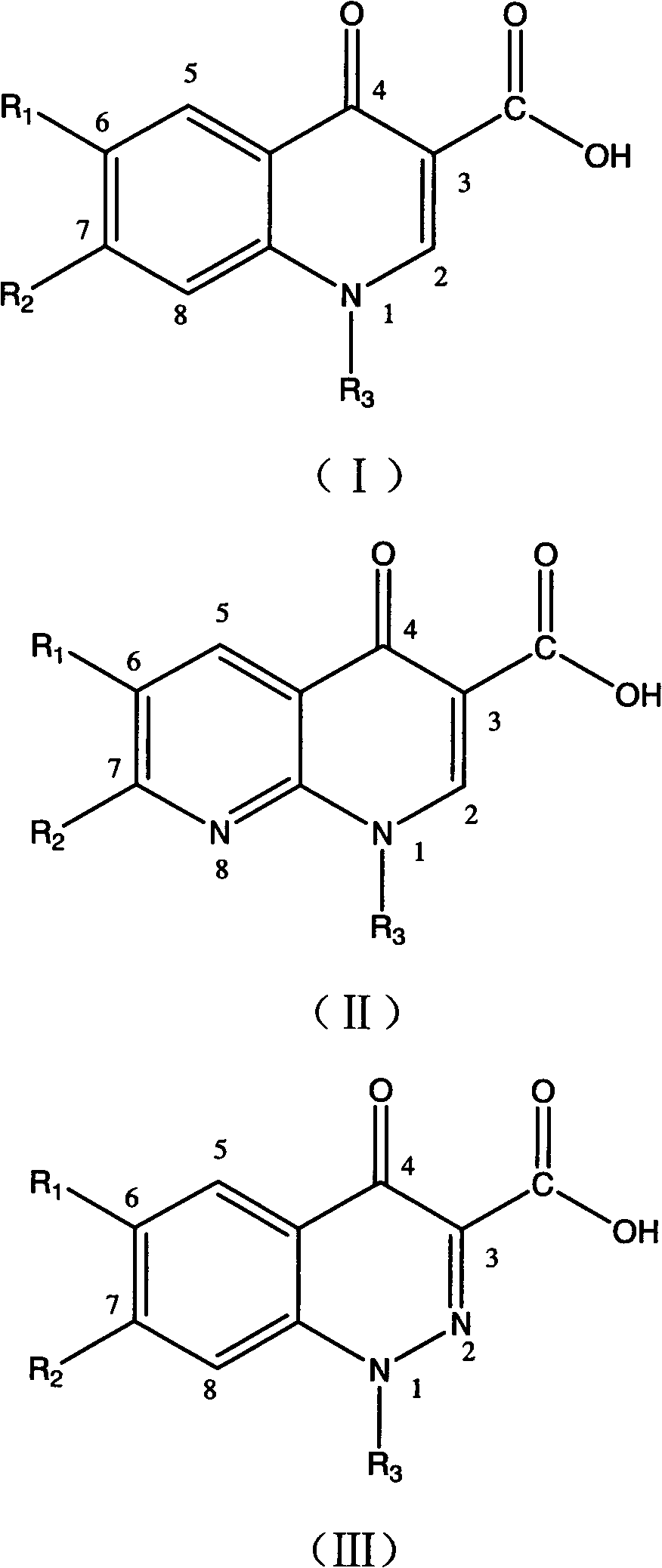
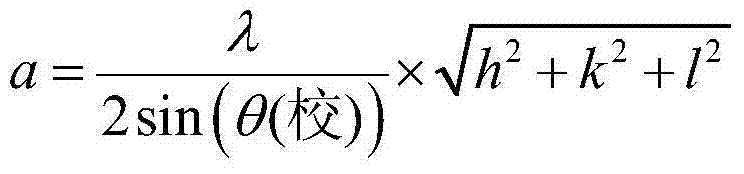Patents
Literature
63results about How to "Low cost of reagents" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
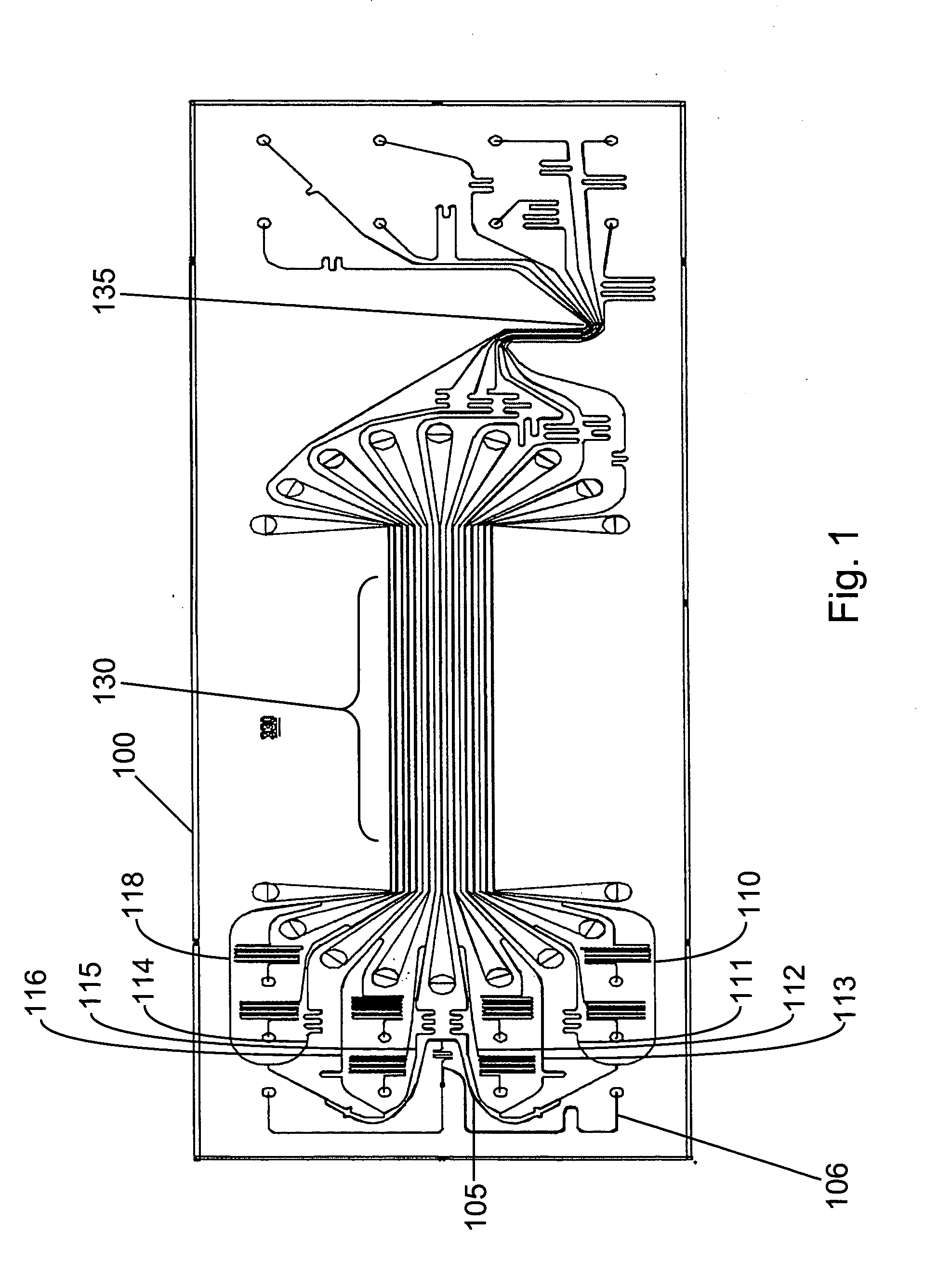
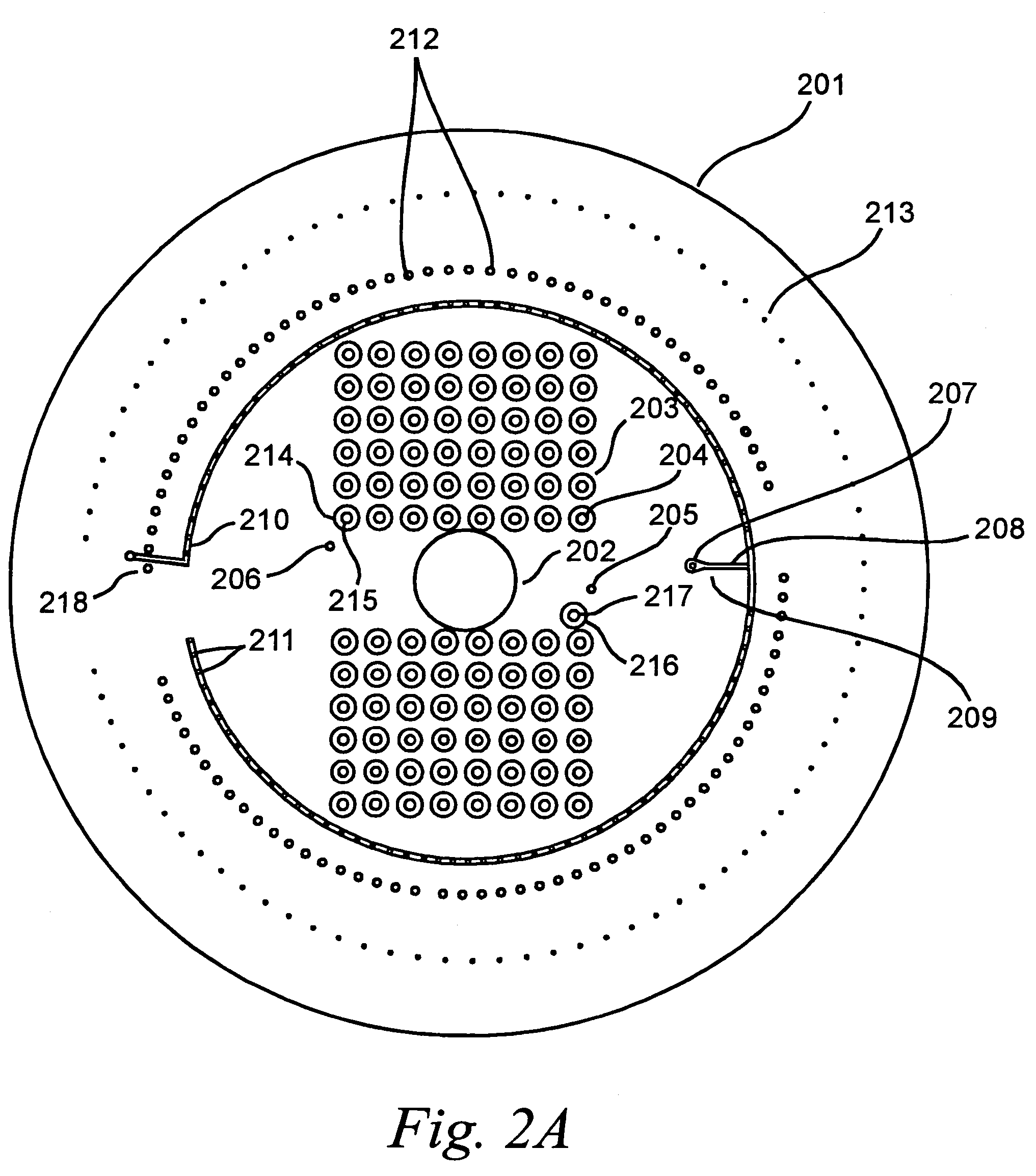
Single molecule amplification and detection of DNA length
InactiveUS20050042639A1Reliable resultsImprove reliabilityHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementStatistical analysisDNA
Methods and systems for performing single molecule amplification for detection, quantification and statistical analysis of nucleic acids are provided. Methods and systems are provided for determining and quantifying lengths of nucleic acids of interest.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
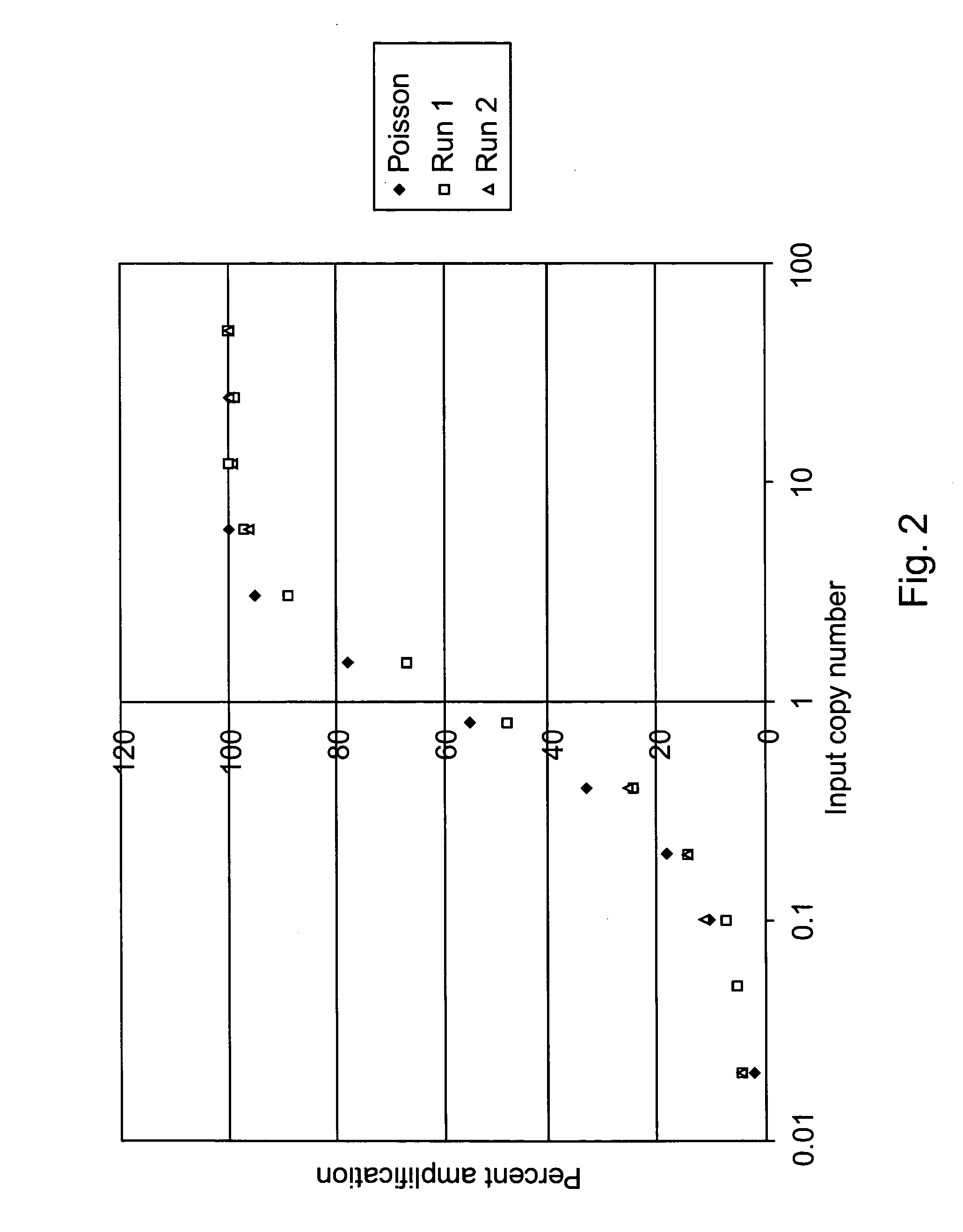
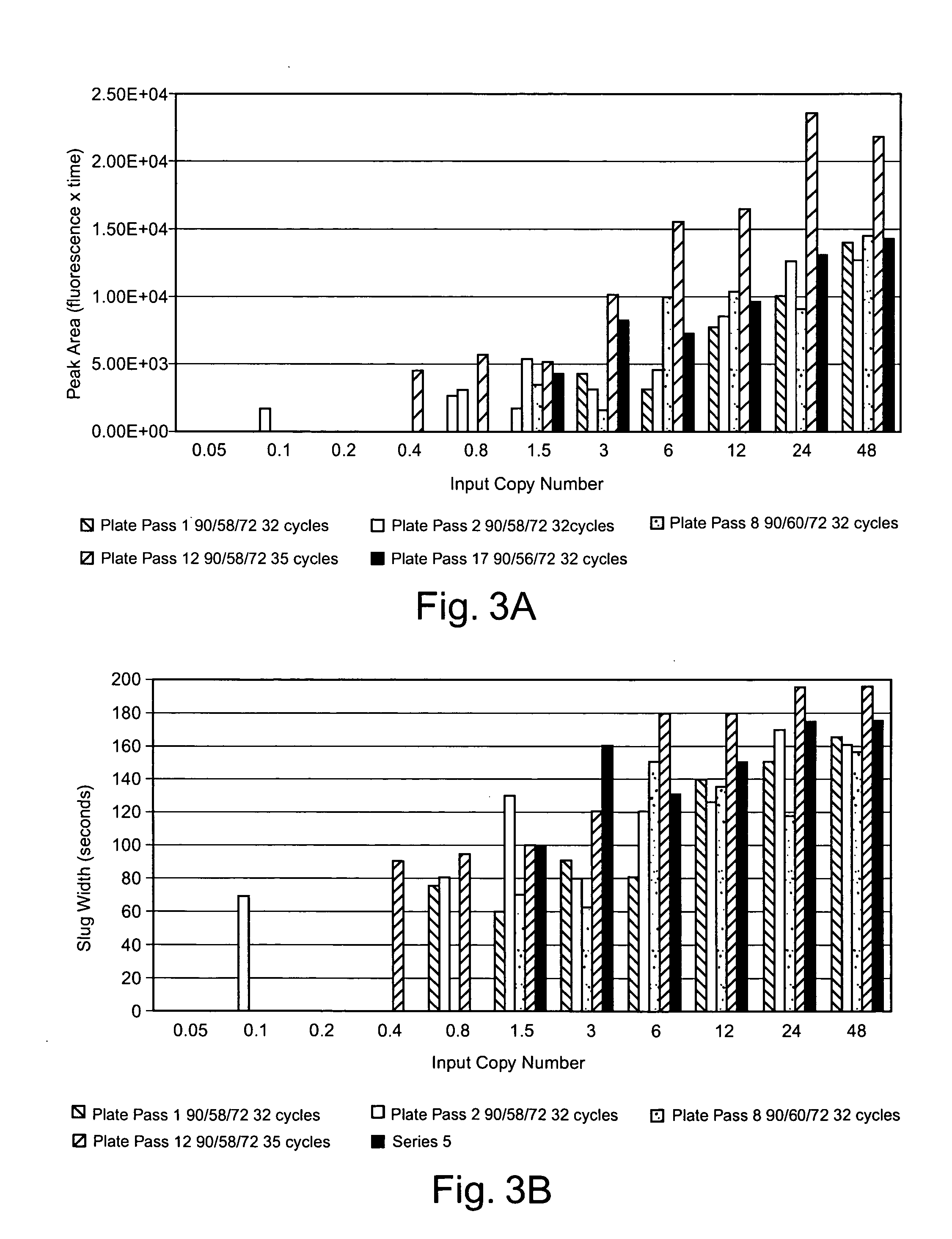
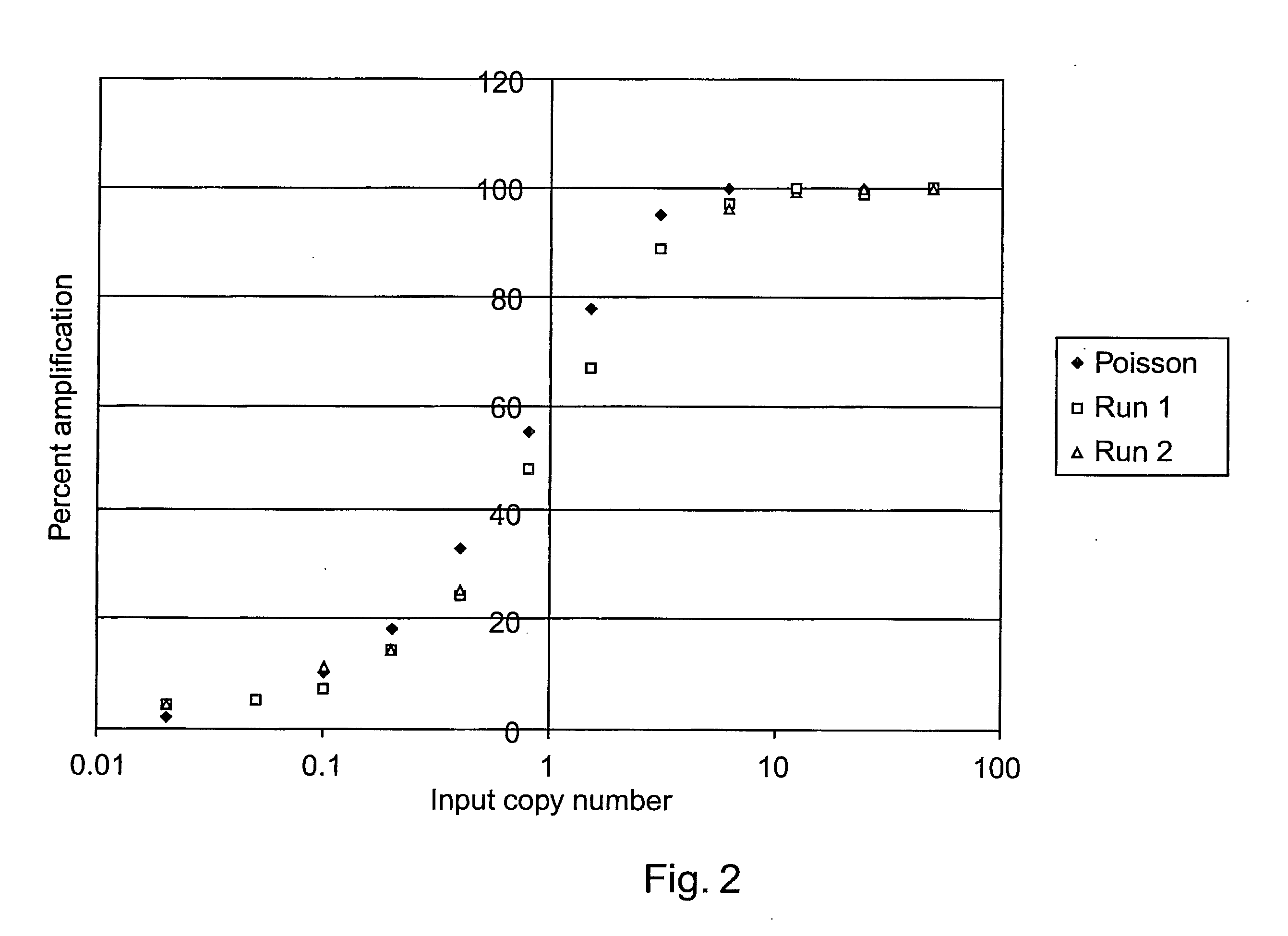
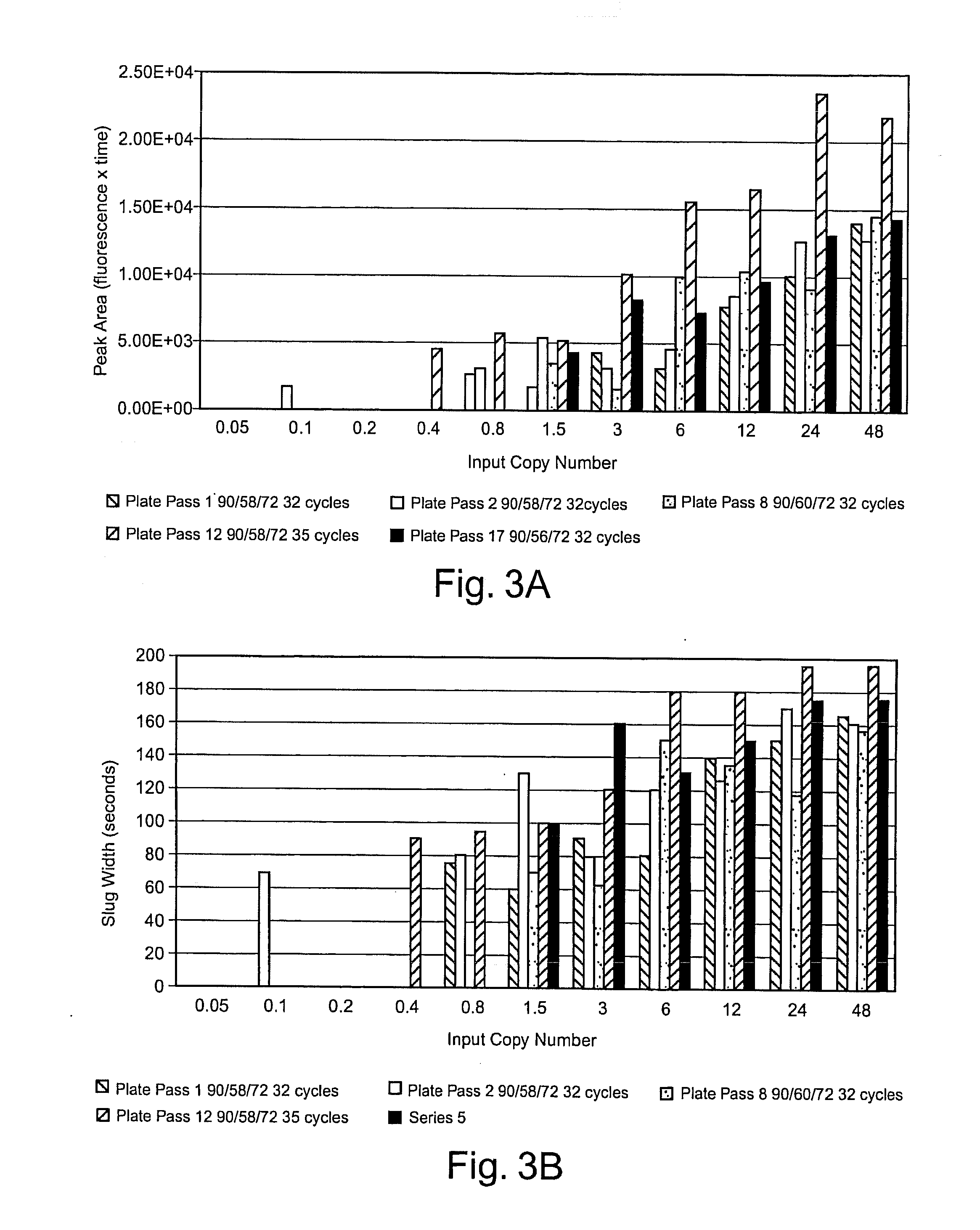
Methods of detecting low copy nucleic acids
ActiveUS20080090244A1Reduce cross contaminationReduce pollutionHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementEmulsionChemistry
Methods are provided for detecting low copy nucleic acids of interest in a sample. In one method, a sample comprising a nucleic acid of interest is aliquotted into a plurality of reaction mixtures, at least two of which are single-copy reaction mixtures. The reaction mixtures are subjected to one or more amplification reactions while flowing through a channel of a microfluidic device. At least one of the reaction mixtures is formulated in an aqueous phase of an emulsion comprising aqueous droplets suspended in an immiscible liquid. The nucleic acid of interest is present as a single copy in at least one aqueous droplet of the aqueous phase prior to performing the amplification reaction(s). Amplification is performed on the reaction mixture when it is formulated in the emulsion. The nucleic acid is continuously flowed during a plurality of steps of the method.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
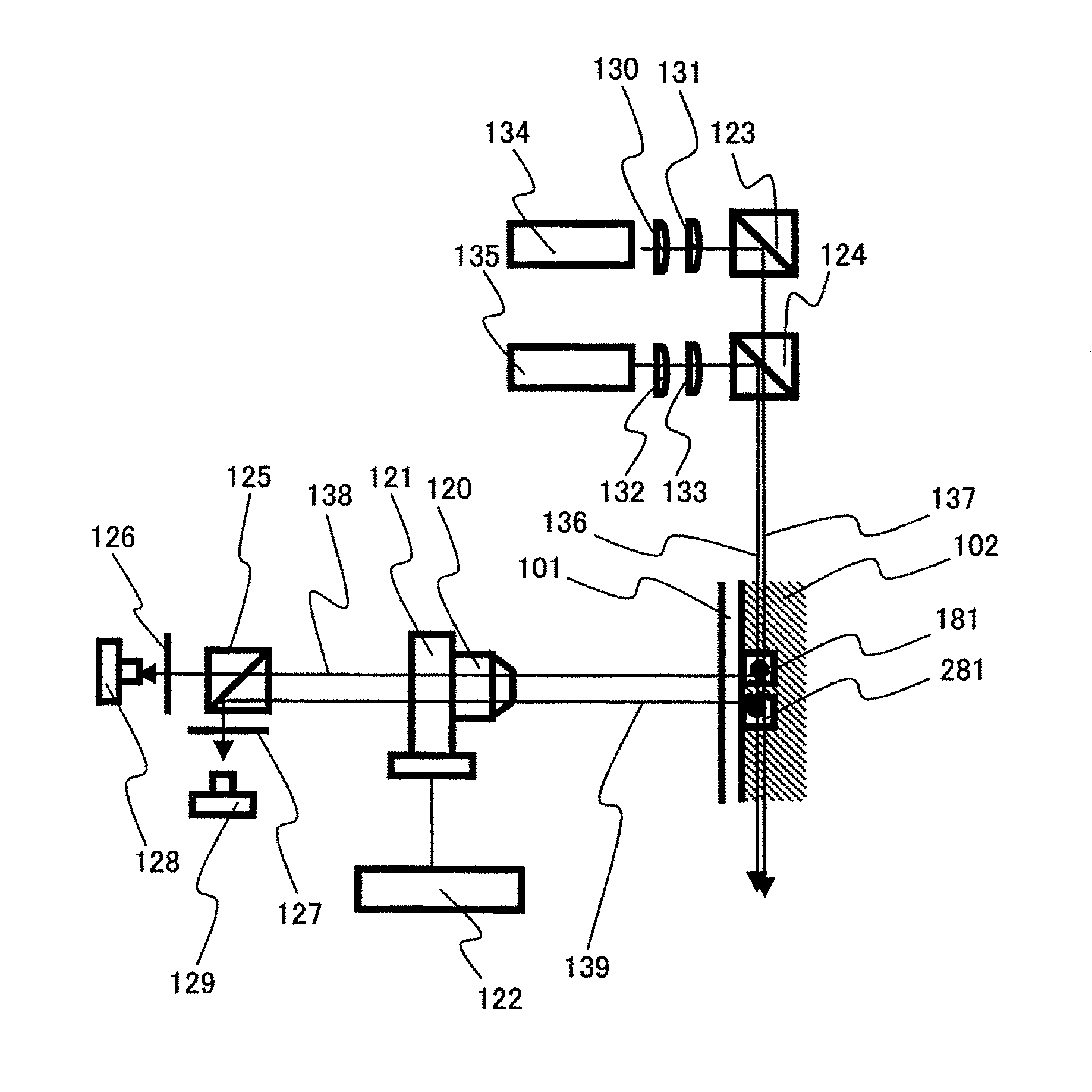
Thermal cycler for automatic performance of the polymerase chain reaction with close temperature control
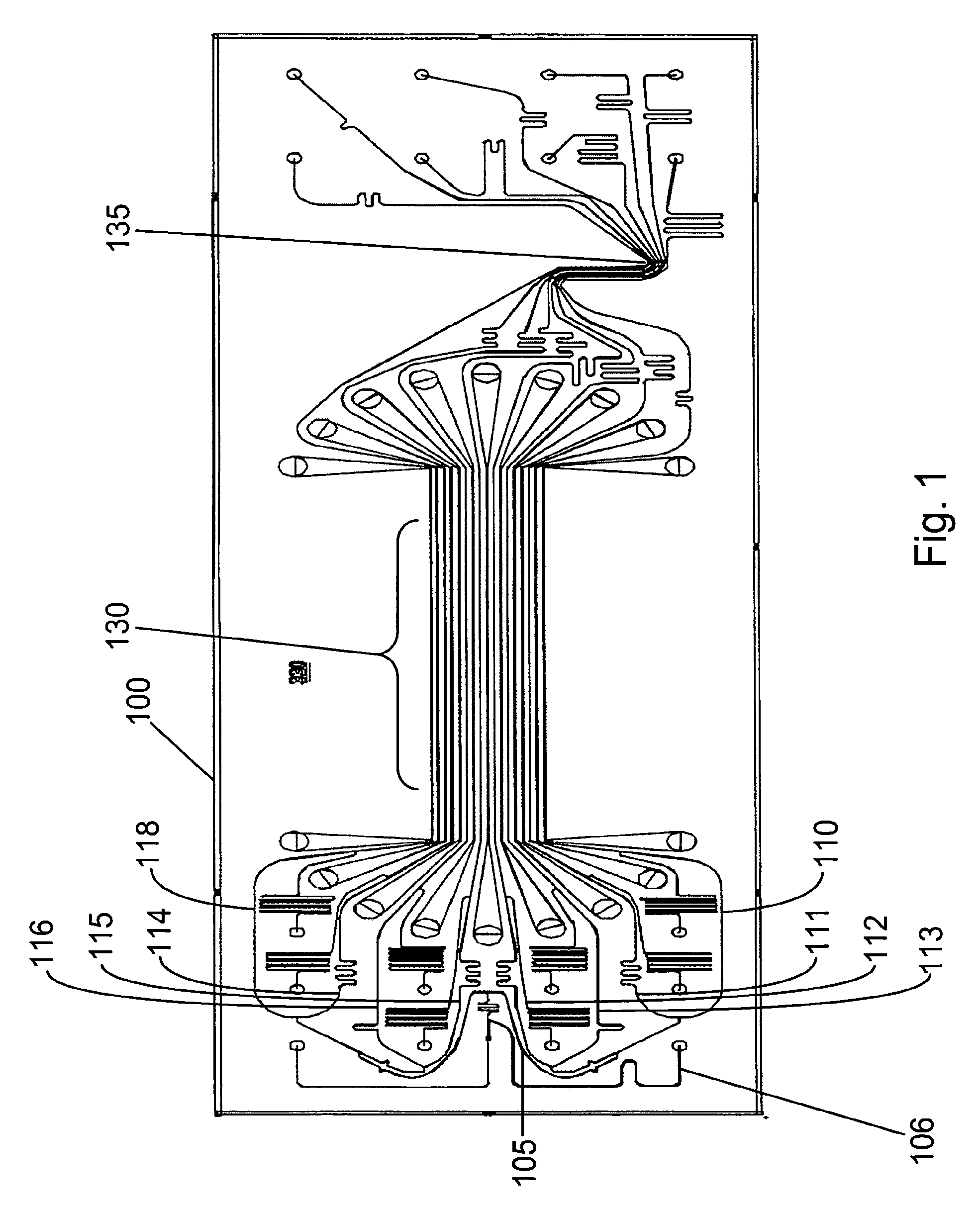
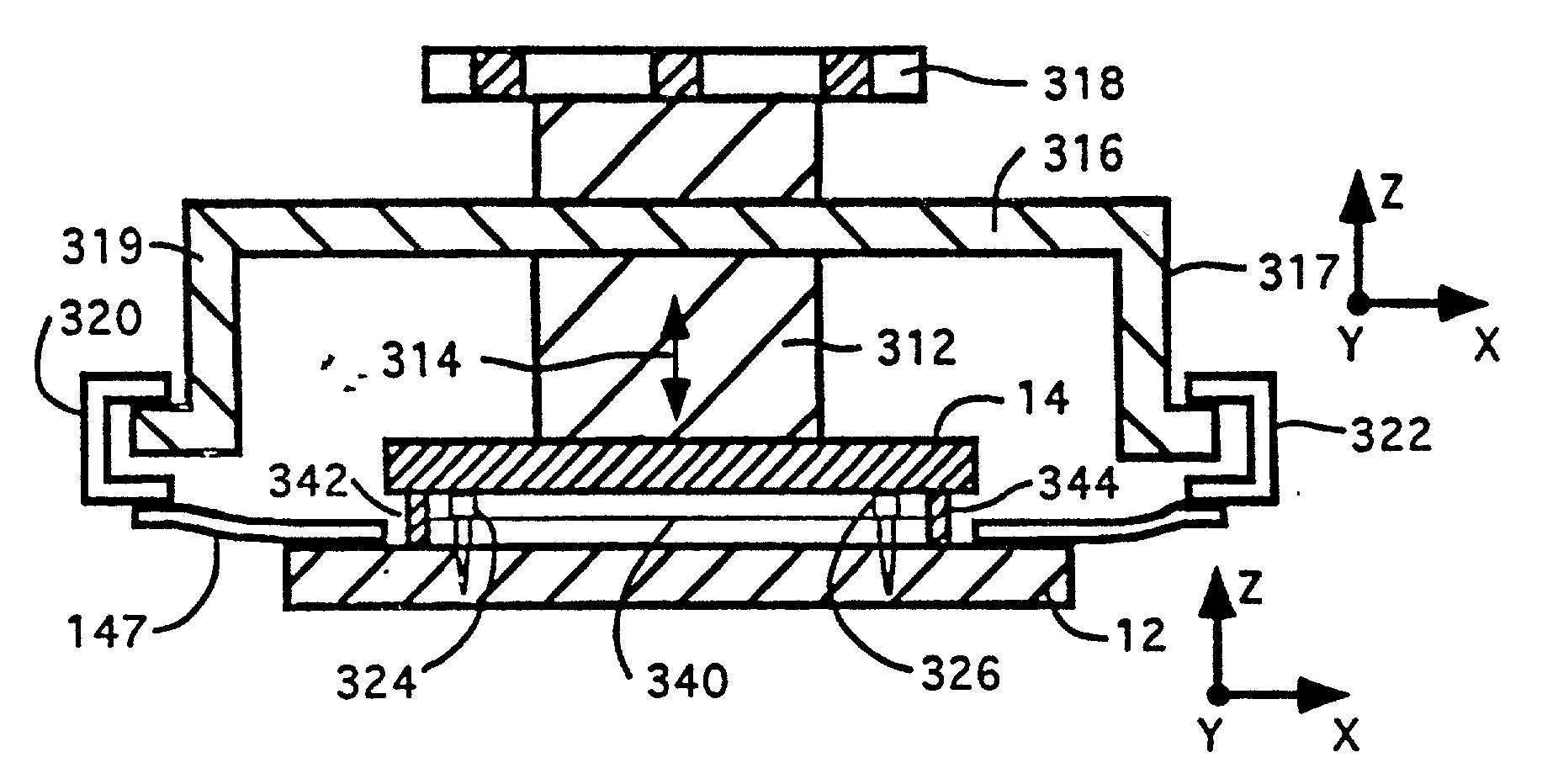
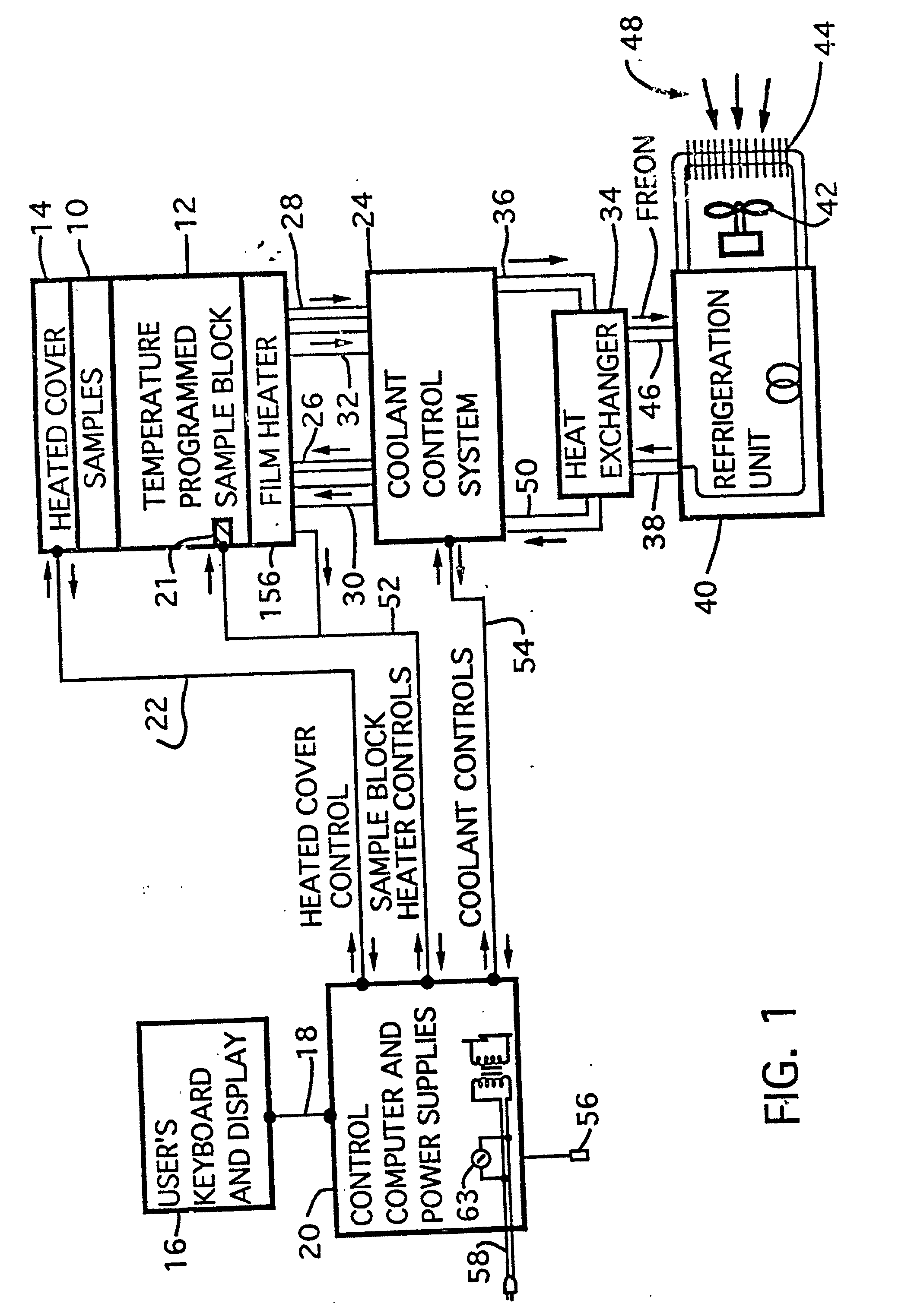
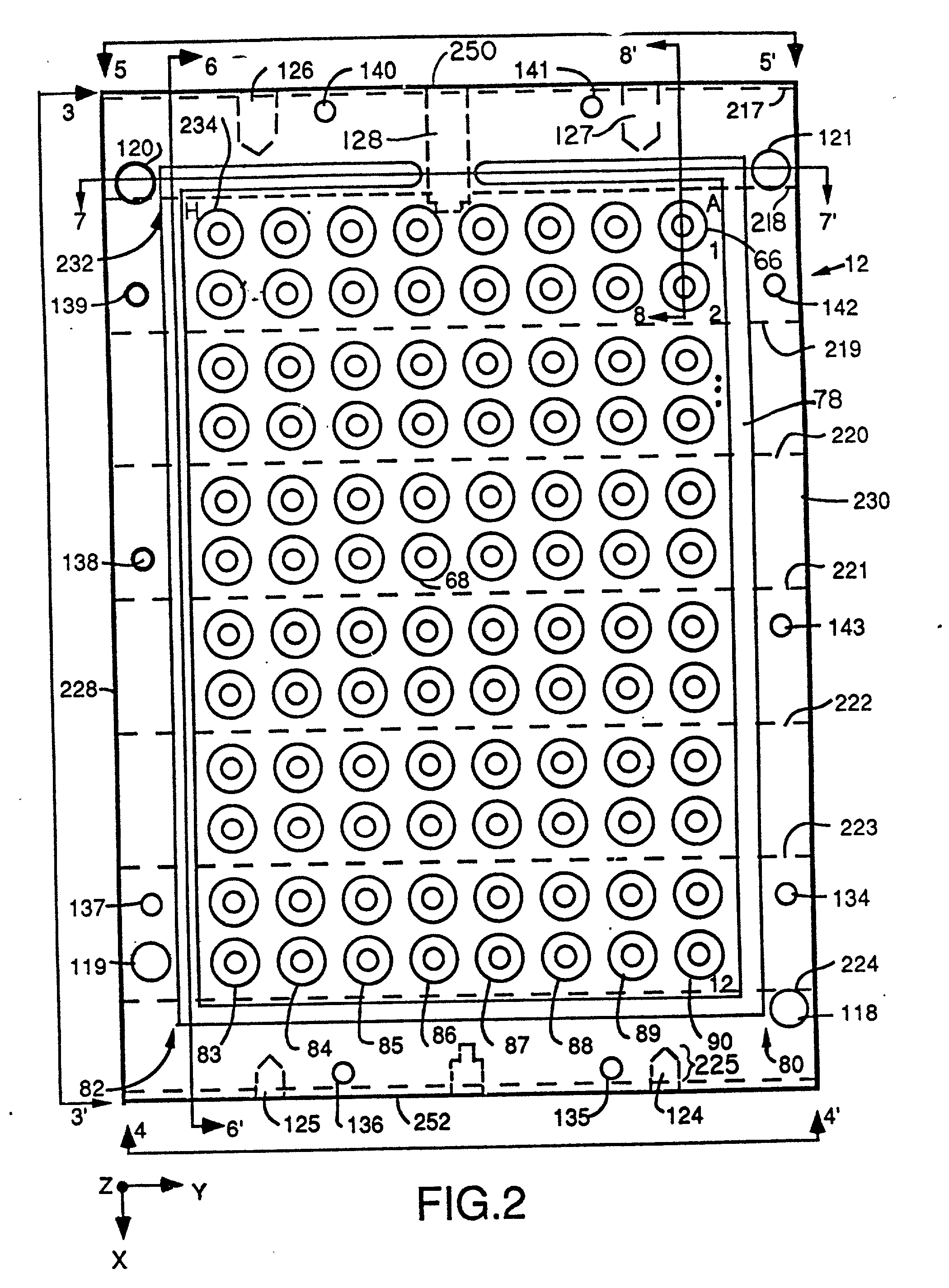
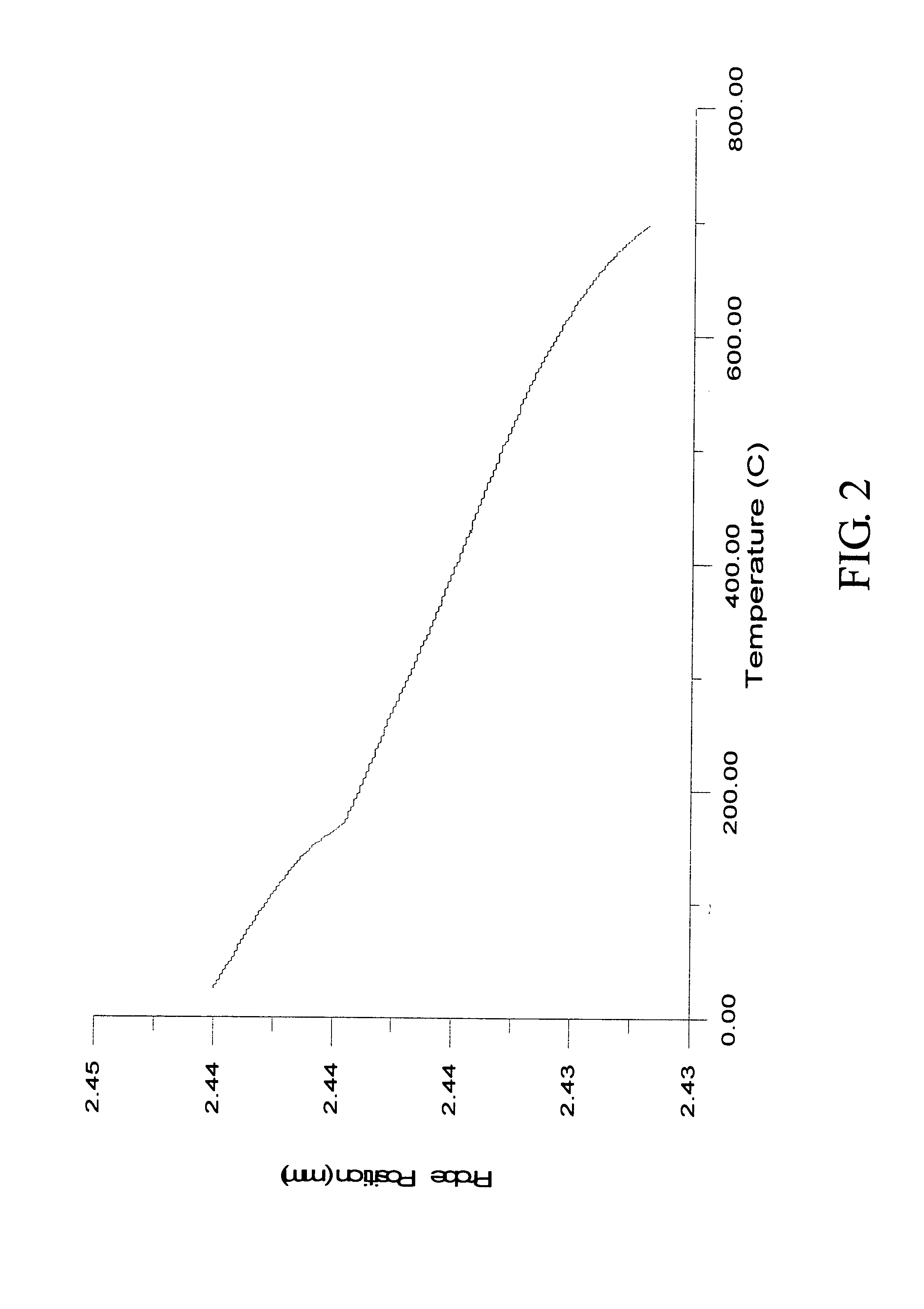
InactiveUS20020072112A1Shorten cycle timeLow cost of reagentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlSolenoid valve
An instrument for performing highly accurate PCR employing a sample block in microtiter tray format. The sample block has local balance and local symmetry. A three zone film heater controlled by a computer and ramp cooling solenoid valves also controlled by the computer for gating coolant flow through the block controls the block temperature. Constant bias cooling is used for small changes. Sample temperature is calculated instead of measured. A platen deforms plastic caps to apply a minimum acceptable threshold force for seating the tubes and thermally isolates them. A cover isolates the block. The control software includes diagnostics. An install program tests and characterizes the instrument. A new user interface is used. Disposable, multipiece plastic microtiter trays to give individual freedom to sample tubes are taught.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Nucleic acid arrays for monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes
InactiveUS20050221354A1Reagent cost per experimentRobust overall probe set signal valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDrug targetPolynucleotide
The present invention provides nucleic acid arrays and methods of using the same for detecting or monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes. Non-limiting examples of drug target genes include kinase genes, phosphatase genes, protease genes, G-protein coupled receptor genes, nuclear hormone receptor genes, and ion channel genes. The present invention also provides methods of using nucleic acid arrays for the identification or validation of drugs or drug targets. In one embodiment, a nucleic acid array of the present invention is concentrated with probes for drug target genes. These probes constitute a substantial portion of all of the polynucleotide probes that are stably attached to the nucleic acid array, and can hybridize under stringent or nucleic acid array hybridization conditions to the tiling sequences selected from Attachment C, or the complements thereof.
Owner:WYETH
Apparatus and method for luminometric assay
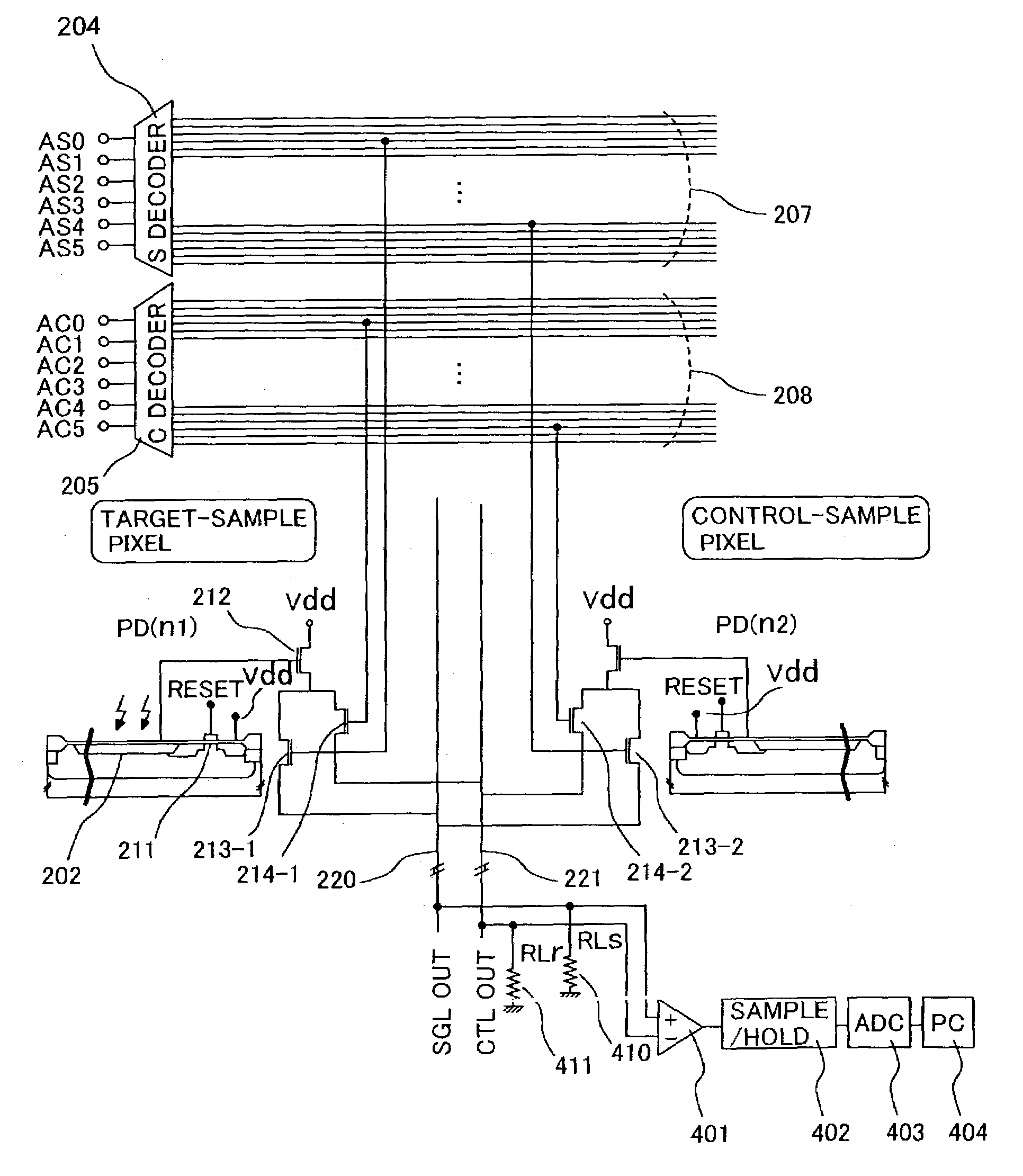
InactiveUS7163822B2Low cost of reagentsLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTelevision system detailsSensor arrayAssay
A small sized, cost-effective genetic testing apparatus that provides high sensitivity testing, for performing genetic testing simply and at low cost. An optical sensor array for the apparatus and method for luminometric assay comprises a means that simultaneously selects 2 pixels and detects minute amounts of chemiluminescence by obtaining the differential output of the respective signals.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for extracting gold from waste circuit boards
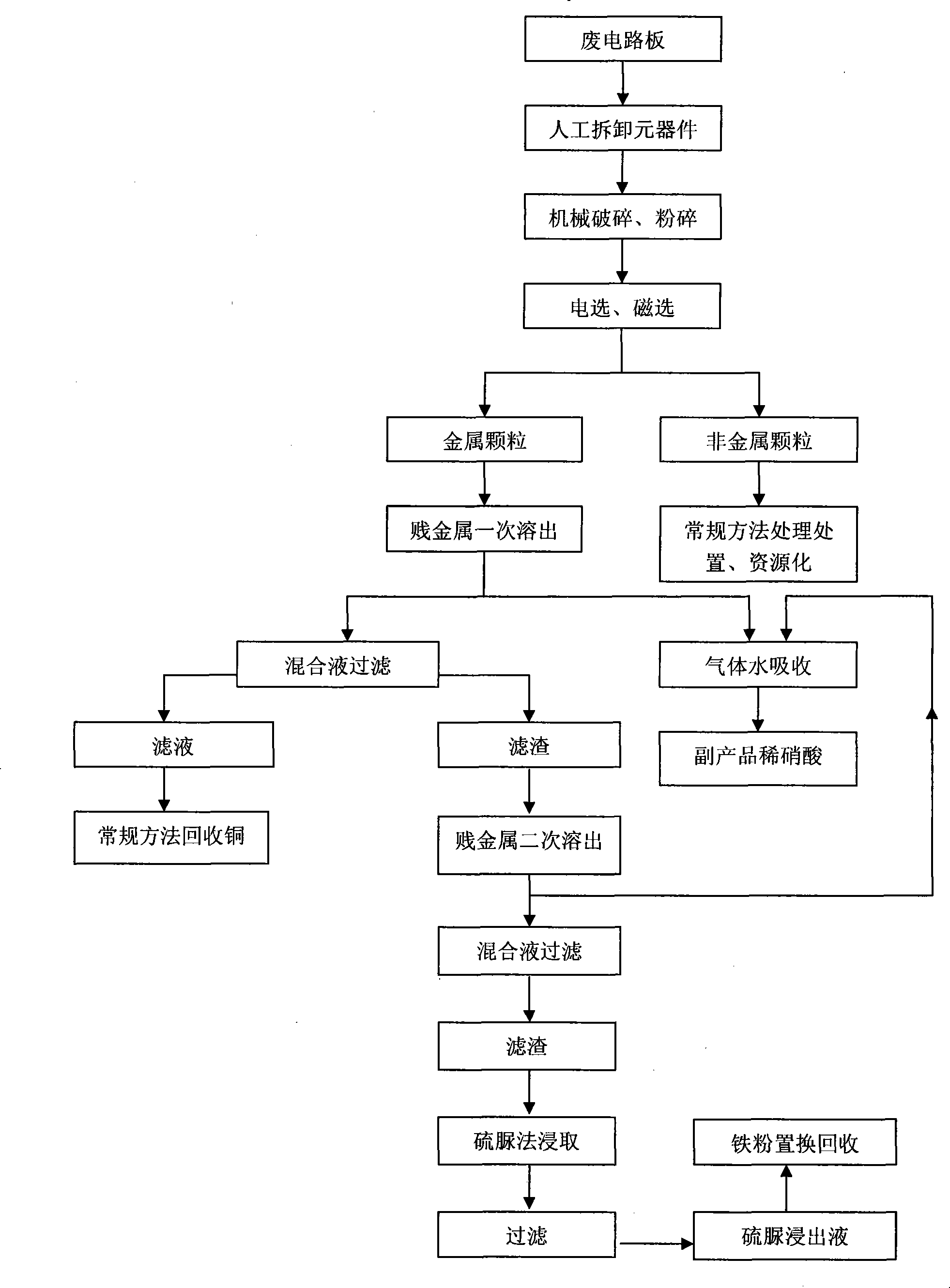
InactiveCN101230421ALow cost of reagentsReduce the formation of nitrogen oxidesProcess efficiency improvementNitrogen oxidesPre treatment
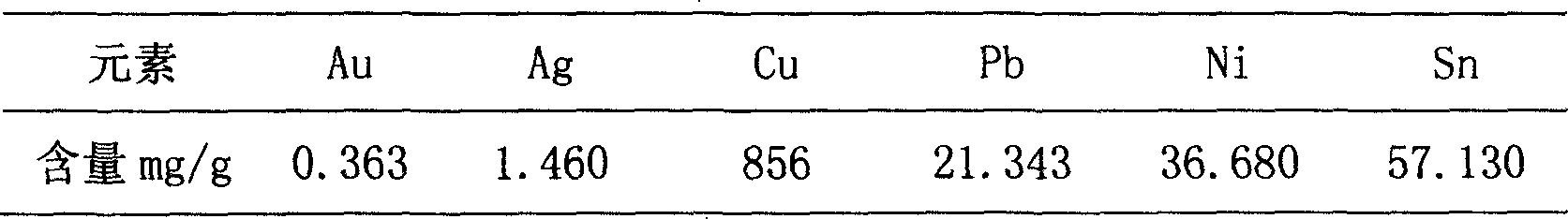
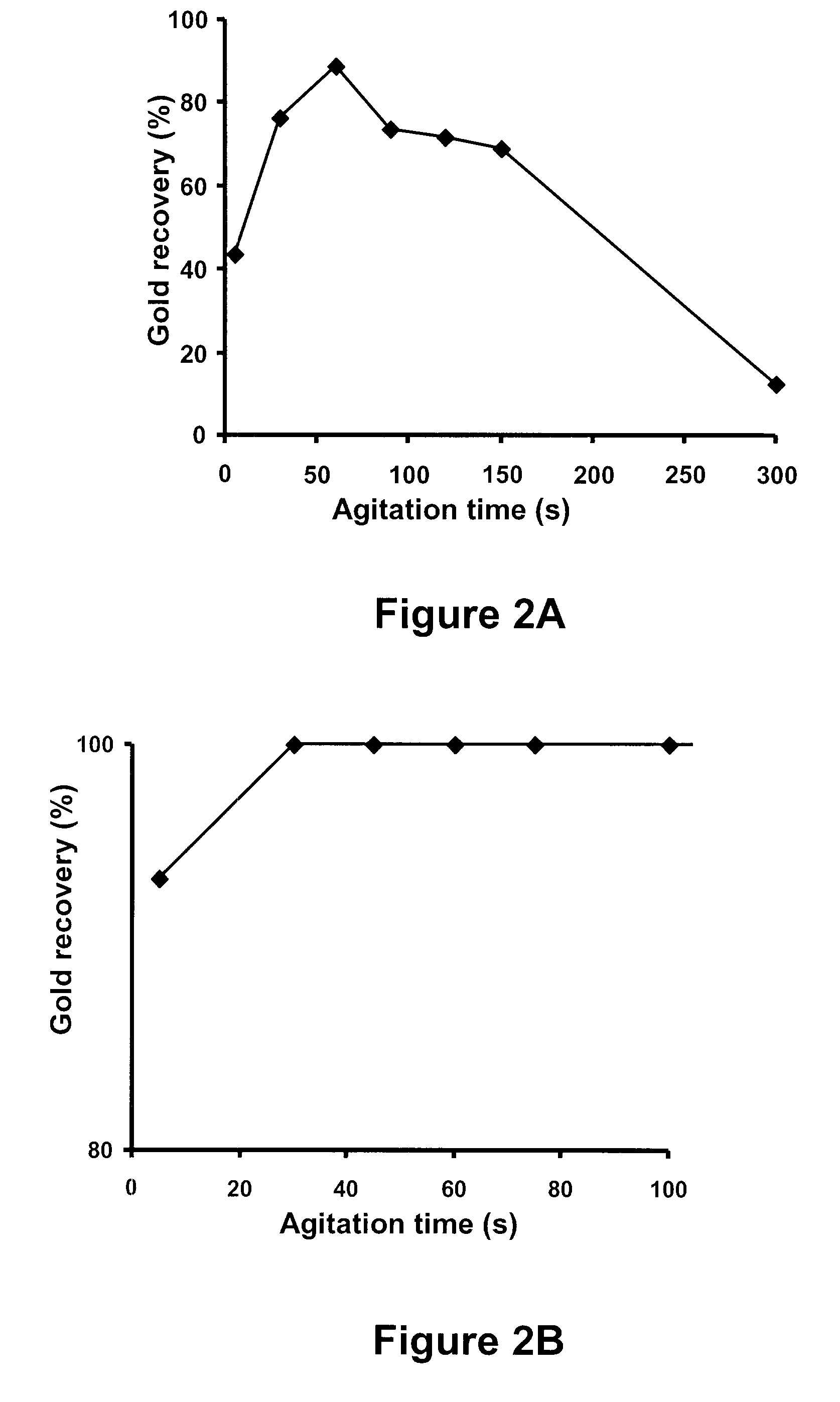
The invention relates to a method by which gold can be extracted form waste circuit boards. Secondary acid dipping can be used for pre-processing metal particles of waste circuit boards. A first leaching uses mixed acid solution of nitric acid and sulphuric acid to leach out base metals which mainly is copper and can be used for wrapping gold in circuit boards. The diluted nitric acid solution can be used for dissolving out base metals secondarily to create favorite condition for the following gold extracting. A little nitrogen oxides can be absorbed by water, and then non-cyanogen complexing agent thiourea can be used for selectively leaching out gold and silver; finally, base-metal ferrous powder can be used for displacing gold and silver form the leaching solution, thereby realizing the source recycling of gold and silver. With simple equipment and convenient operation, the method has great potential in industrial promotion. The invention recycles copper and silver when gold is extracted form waste circuit boards, thereby having considerable economic, social and environmental benefits.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Y molecular sieve high in silica alumina ratio and abundant in secondary holes and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN104843736ASimplify operation stepsLow cost of reagentsFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveSieve
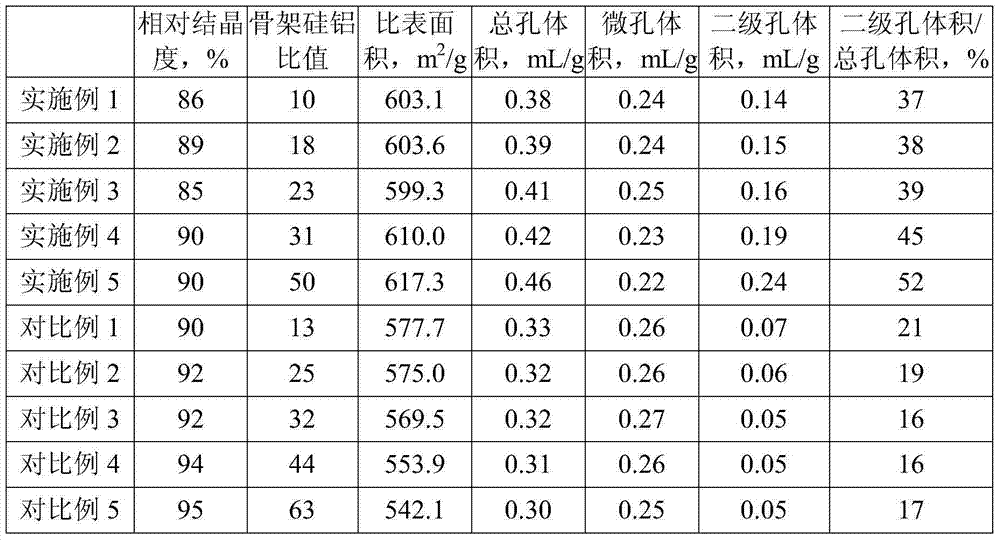
The invention provides a Y molecular sieve high in silica alumina ratio and abundant in secondary holes and a preparation method therefor. The preparation method comprises steps of: Y-type zeolite is processed for 1-5 hours at 300-600 DEG C to obtain dry Y-type zeolite, and calculated by SiO2 and Al2O3, the silica alumina mole ratio of the Y-type zeolite is (3-6):1;the temperature is lowered to 200-600 DEG C;in a waterless dry environment, dry air saturated by a dealuminated siliceous reinforcing agent is introduced to the dry Y-type zeolite to react for 0.5h-7h, or in a waterless dry environment, the temperature is raised to 500-700 DEG C at a constant speed, at the same time, the dry air saturated by a dealuminated siliceous reinforcing agent is introduced to the dry Y-type zeolite to react for 0.5h-7h, and a rough product is obtained; the rough product is subjected to alkali treatment for 10min-5h at 30-100 DEG C, solid-liquid mass ratio for the alkali treatment is (1-50):1, and a Y molecule sieve high in silica alumina ratio and abundant in secondary holes is obtained. The invention further provides the Y molecule sieve high in the silica alumina ratio and abundant in secondary holes, obtained by adopting the preparation method and has high silica aluminum ratio and abundant secondary hole structures.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Single molecule amplificaton and detection of DNA length
InactiveUS20080085521A1Lower the volumeLow cost of reagentsHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementStatistical analysisDNA
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Microfluidics devices and methods of diluting samples and reagents
InactiveUS7476361B2Low cost of reagentsShorten reaction timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMicroanalysis
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. These assays may be performed for a variety of purposes, including but not limited to screening of drug candidate compounds, life sciences research, and clinical and molecular diagnostics. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing any of a wide variety of microanalytical or microsynthetic processes are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
System for differentiating the lengths of nucleic acids of interest in a sample
ActiveUS20100129896A1Reliable resultsImprove reliabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyAmplicon
Systems for differentiating the lengths of nucleic acids of interest in a sample are provided. The system includes a microfluidic device, a detector, and a software system. The microfluidic device includes an amplification microchannel or microchamber containing a reaction mixture under conditions that provide one or more amplicons of the nucleic acid of interest. The detector is integral with or proximal to the microfluidic device and is configured to detect the amplicons as one or more signals from a homogenous mixture. The software system interprets one or more coincidentally detected signals to indicate lengths of one or more individual nucleic acid molecules of interest, thereby differentiating the lengths of the nucleic acids of interest.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Microorganism testing device
InactiveUS20080153153A1Measurement results are stableLow cost of reagentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid wasteMicroorganism
Pretreatment of residual food removal and bacteria dyeing, and measurement of the number of bacteria using the fluorescence flow cytometry method, are stably performed by easy operations.A measurement chip 10 includes: a specimen container 151; a reaction container 170 for mixing a specimen and a dyeing reagent into a liquid mixture; a bacteria detection portion 18 being irradiated with excitation light; a detection liquid waste container 163 into which liquid mixture which has passed the bacteria detection portion enters; a solution flow path 157 which connects the specimen container, the reaction container and the bacteria detection portion, and ventilation ports 1631 through 1633 which are connected to the specimen container, the reaction container and the detection liquid waste container, through a air flow path and is connected to a chip connecting tube. Bacteria are detected in the bacteria detection portion 18 by switching of the states of the specimen container, the reaction container, and the detection liquid waste container between a sealed state and a state open to the atmospheric pressure, by moving the specimen to the reaction container 170 to mix and stir the specimen and the dyeing reagent, and by moving of the liquid mixture to the detection liquid waste container 163.
Owner:HITACHI ENG & SERVICES CO LTD
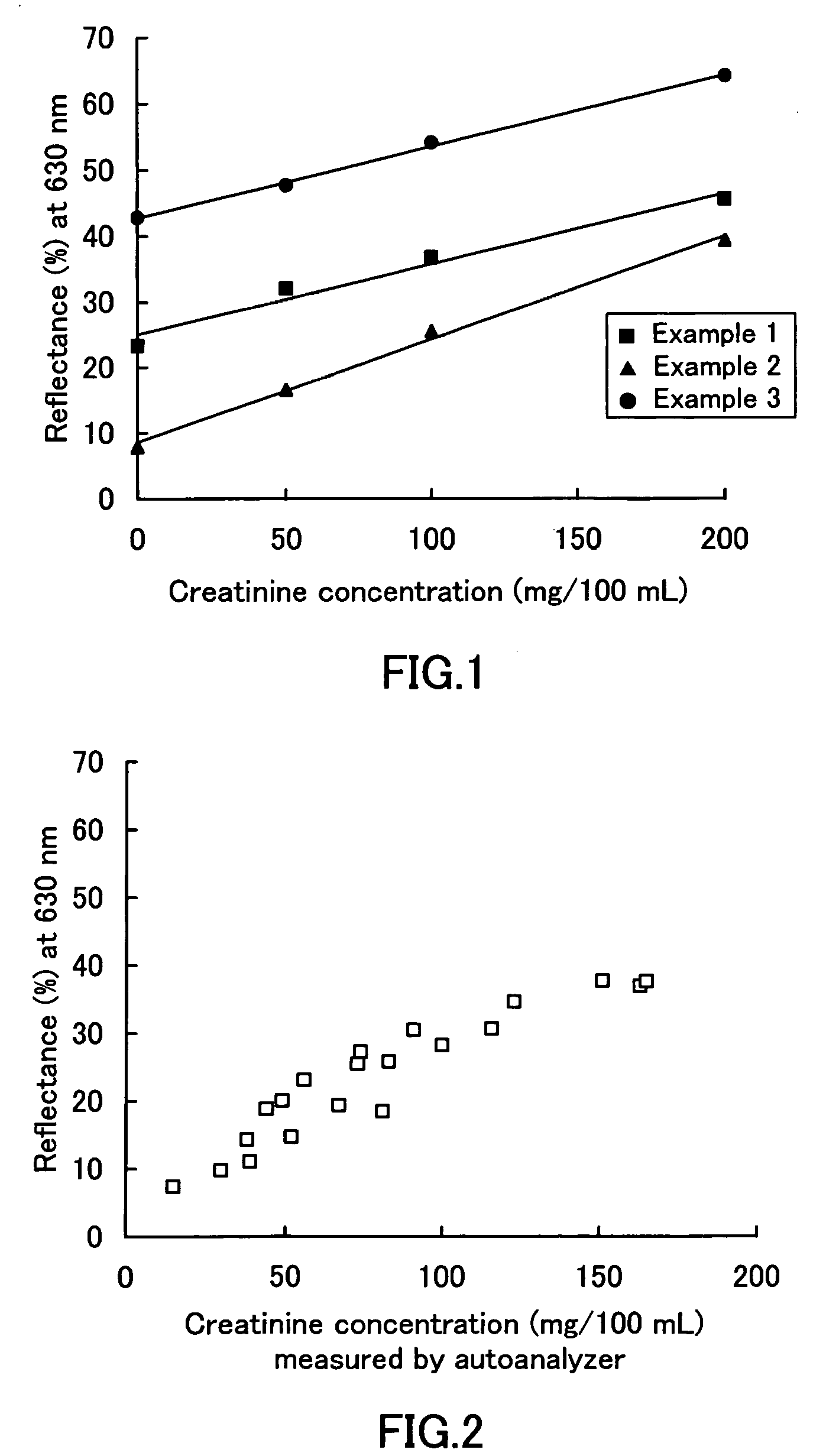
Test strip for creatinine determination
ActiveUS20050266574A1Delayed reaction timePerformed easily and quicklyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsCreatinine riseCreatinine Measurement
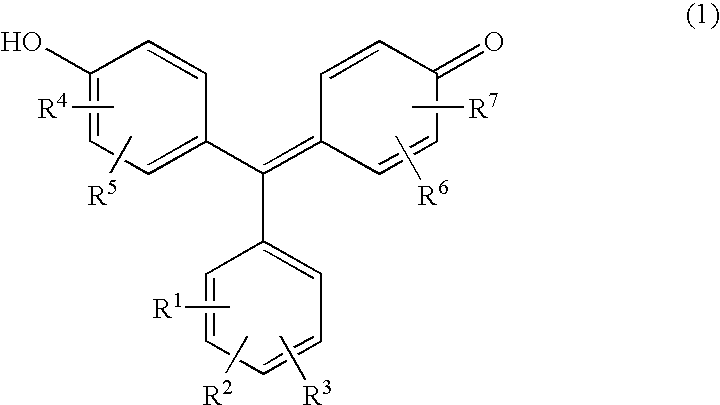
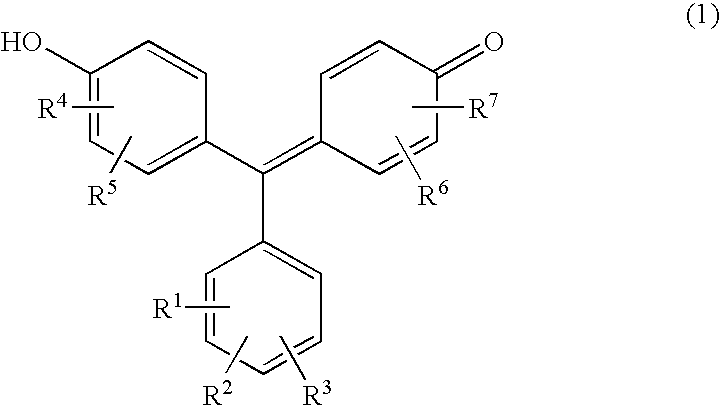
The present invention provides a novel test piece for creatinine measurement. The test piece includes a compound expressed by the following formula (1), a metal that forms a colored complex with the compound, and a buffer agent in a porous material. The amount of creatinine is determined by optically measuring a colored complex of the compound and the metal and evaluating the degree of inhibition of the colored complex formation by creatinine. In the formula (1), R1 represents H, SO3X, or COOX. R4 and R6 represent OH, SO3X, or COOX and may be either the same or different. R2, R3, R5, and R7 represent H, OH, Cl, Br, I, NO2, NO, or CH3 and may be either the same or different. Xs in the R1, R4, and R6 represent H, Na, K, or NH4 and may be either the same or different.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Method for making negative thermal expansion material zirconium tungstate
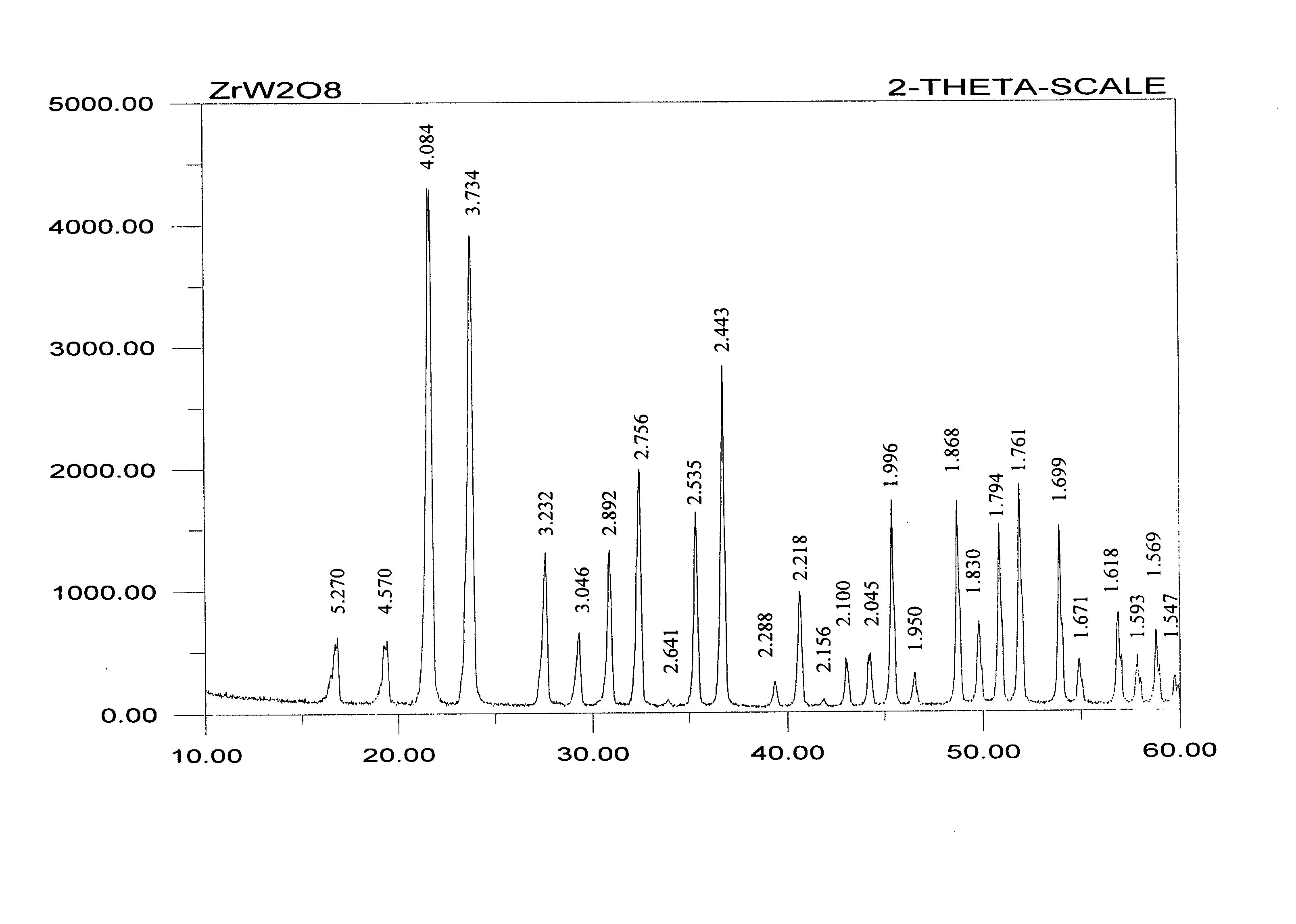
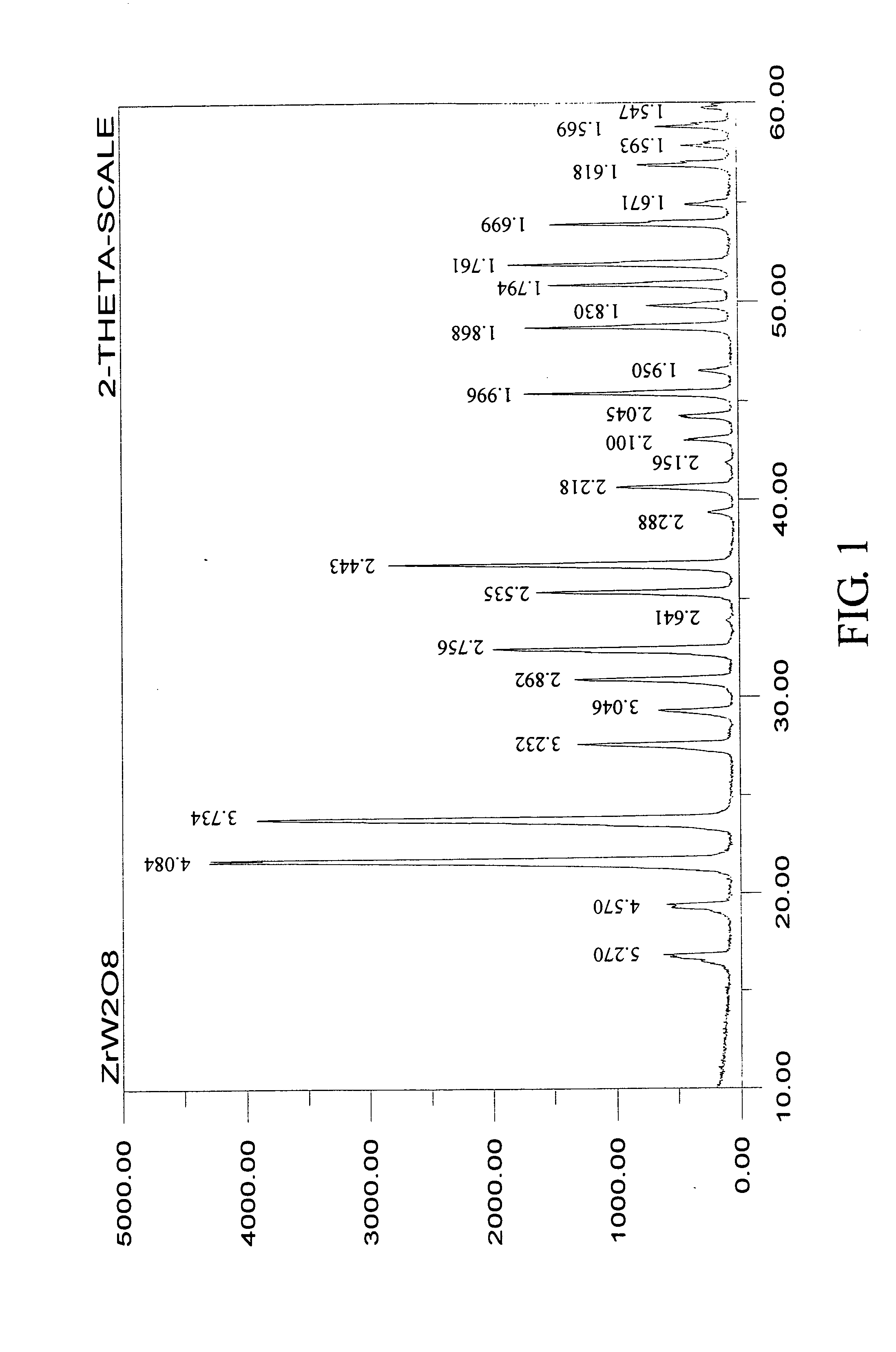
InactiveUS20050101133A1Low cost of reagentsSimple processFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthWater insolubleWater soluble
A method for making negative thermal expansion material zirconium tungstate (ZrW2O8) comprise: (a)forming a gel wrapped solid product comprising a water-soluble zirconium compound, preferably zirconium oxyhalides or zirconium oxynitrates and a water-insoluble tungsten compound, preferably tungsten powder or tungsten oxide powder; and (b)heating the gel wrapped solid product to a temperature sufficient to form ZrW2O8; the temperature required for forming zirconium tungstate should be at least about 1165° C.; the upper limit of the temperature should be about 1250° C., and preferably should be about 1180˜1200° C.; and the time needed for the formation of zirconium tungstate is less than about 5 hours; this method has the advantages on enhancing the selectivity of the reactants, simplifying production process, reducing the cost of reagent, and facilitating the mass production for making ZrW2O8.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Method for synchronous detection of sweet potato feathery mottle virus (SPFMV), sweet potato virus C (SPVC), sweet potato virus G (SPVG) and sweet potato virus 2 (SPV2)
InactiveCN102230027AClear detection effectLow cost of reagentsMicrobiological testing/measurementSweet potato virus GDiseased plant
The invention relates to method for a synchronous detection of sweet potato feathery mottle virus (SPFMV), sweet potato virus C (SPVC), sweet potato virus G (SPVG) and sweet potato virus 2 (SPV2), and belongs to the field of plant protection. The method comprises the following steps of respectively designing and synthesizing specific forward primers and a universal reverse primer of SPFMV, SPVC, SPVG and SPV2, extracting total RNA of tissue of a diseased plant through a cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) method, and carrying out one step quadruplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) magnification process to realize a synchronous detection of SPFMV, SPVC, SPVG and SPV2. Primers designed by the method have strong singularities and SPFMV, SPVC, SPVG and SPV2 share areverse primer thus an interaction of primers is reduced. In the invention, a CTAB method is utilized for extracting RNA from tissue of an RNA virus infected plant, thus a quality of RNA is guaranteed and a detection cost is reduced effectively; and the inverse transcription and the multiple PCR are completed in one step thus a detection time is saved. The method has the advantages of rapid detection speed, high efficiency, strong singularity, high sensitivity and low cost and can realize a synchronous detection of four kinds of sweet potato virus thus has wide application prospects.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Telomerase activity detecting probe, reagent kit and method
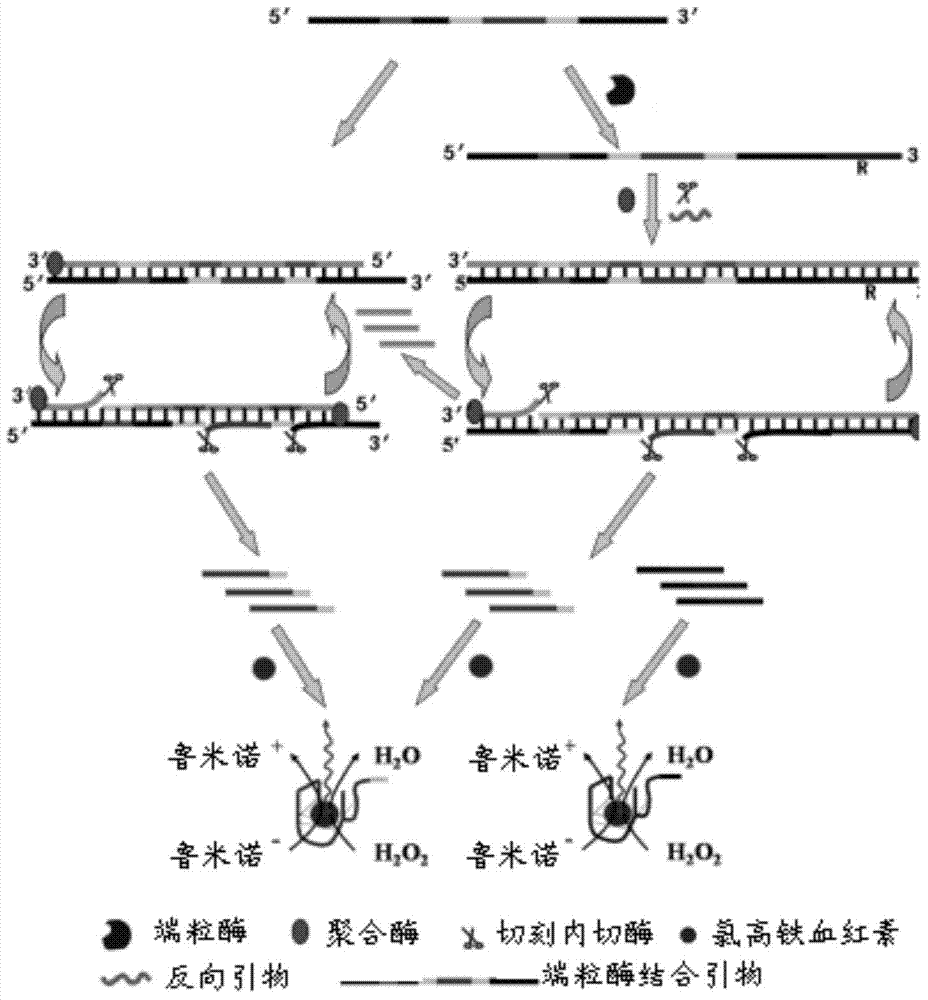
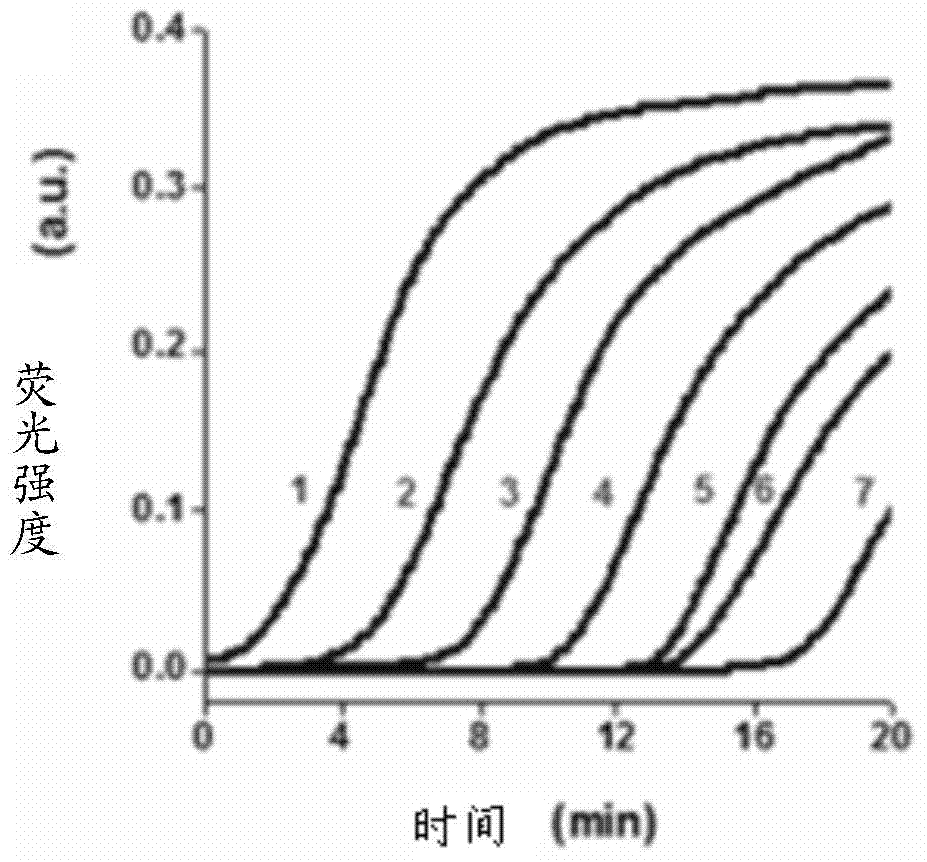
InactiveCN103667513ALow cost of reagentsHigh sensitivity and specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNon specificEnzyme
The invention provides a telomerase activity detecting probe, a telomerase activity detecting reagent kit and a telomerase activity detecting method. The design of telomerase combination primers (TS) and reverse primers is simple, and TS only needs to comprise DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) enzyme sequences and restriction enzyme cutting sites of cutting enzyme and does not need any modification; the reverse primers only need to comprise sequences complemented with multiple-G sequences extending from telomerase, so the primers are easy to design, and the feasibility is high. The telomerase activity detecting method provided by the invention has the advantages that the reverse primers are only combined with TS primers extending from result telomerase, the nonspecific amplification is reduced, in addition, in the chemical luminous reaction, only amplified telomerase multiple-G sequences and DNA enzyme can be combined with hemin to form a tetramer, and chemical luminous signals are generated, so the telomerase activity detecting method provided by the invention has higher specificity and higher sensitivity. In addition, the telomerase activity detecting reagent kit provided by the invention has the advantages that the cost is low, the operation is simple, and the time is saved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Stopped-flow chip
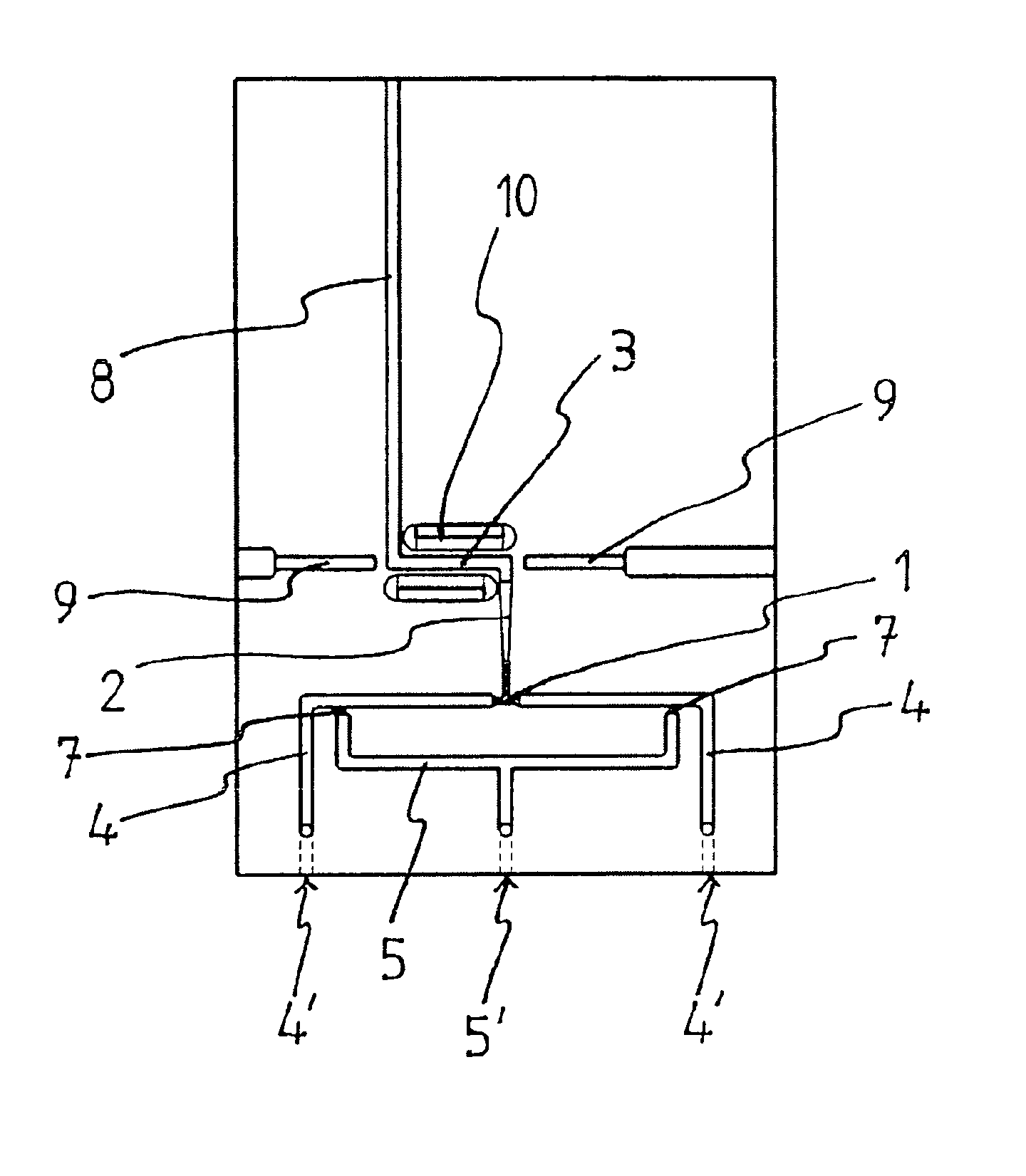
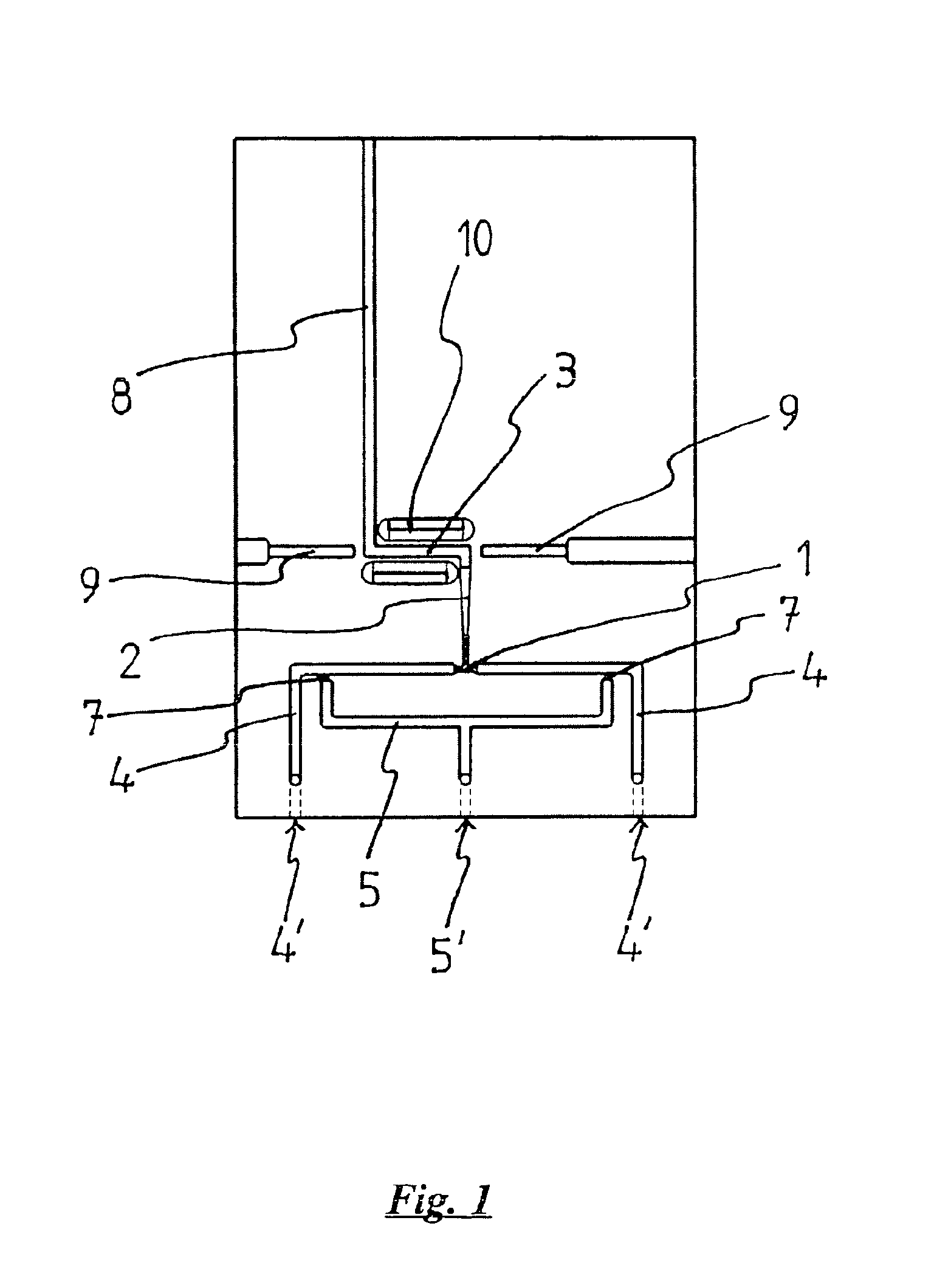
InactiveUS20110165025A1Less-expensive to produceLow level of sensitivityFlow mixersTransportation and packagingChemical reactionGuide tube
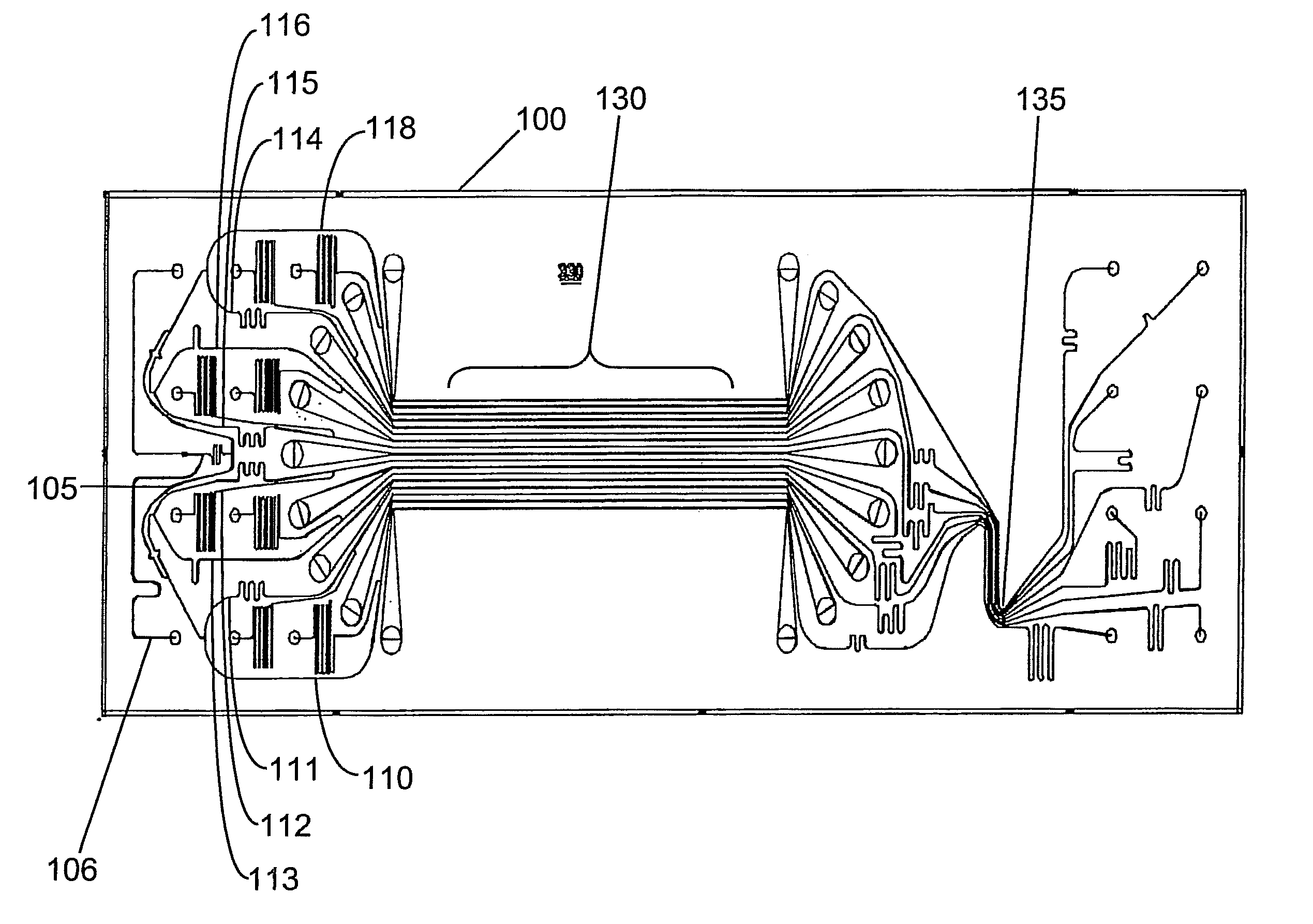
A chip for performing and measuring chemical reactions, interactions (bonds), and / or conformational changes, especially fast chemical reactions and processes. The chip includes a base plate, which is made of a polymer material that is transparent at least in the measuring zone, and having. fluid ducts parallel to the plane of the base plate and includes at least two reagent feeders leading into a mixer structure that has a number of inlets corresponding to the number of reagent feeders and an outlet leading into a mixing section, the outlet of the mixing section leads into a measuring section, the outlet of the measuring section is connected to a discharge section, the discharge section leads out of the base plate or into a reservoir that is arranged on the chip, and pressure conduits lead into the reagent feeders at a distance from the mixer structure.
Owner:IMM INST FUR MIKROTECHNIK GMBH
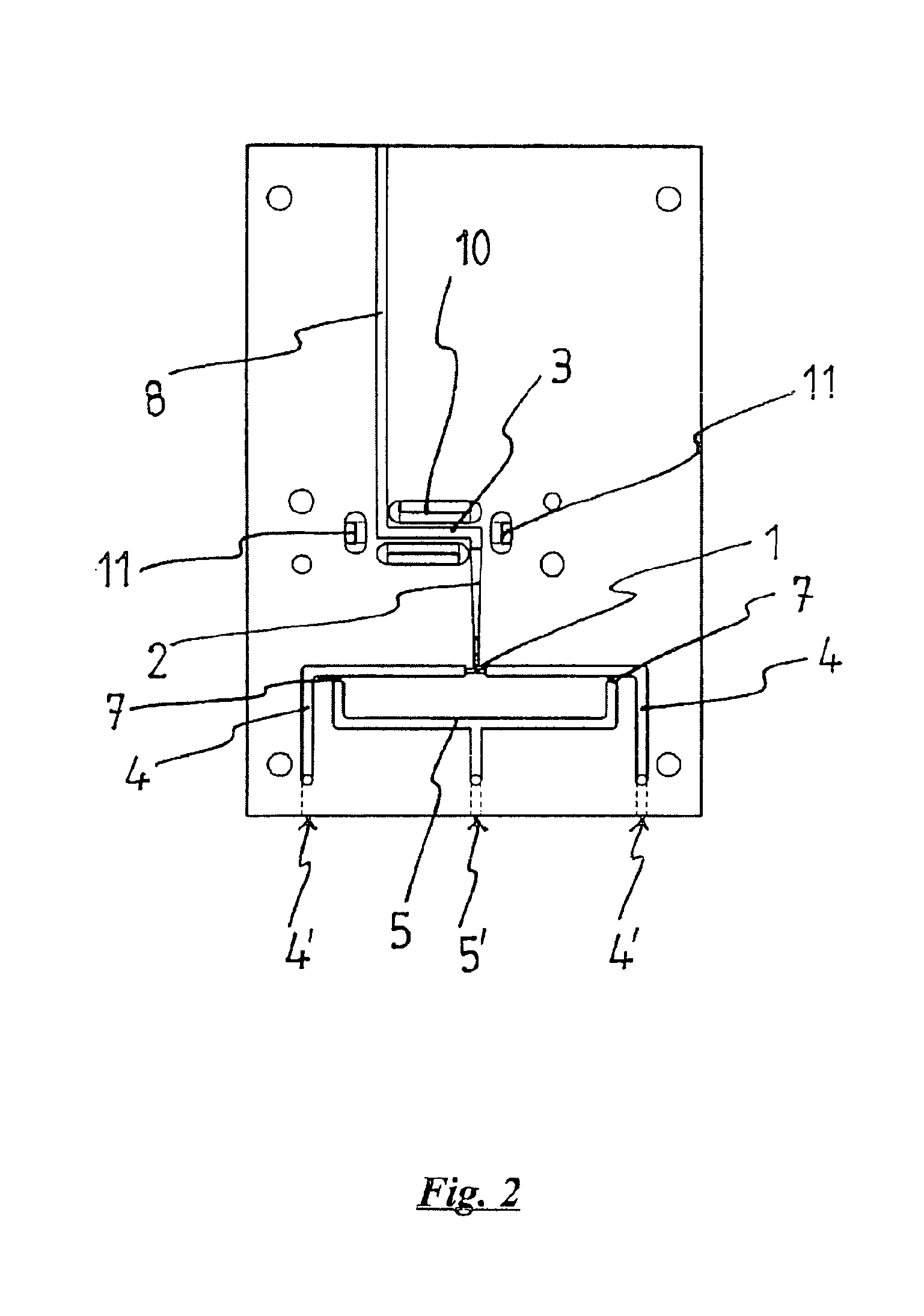
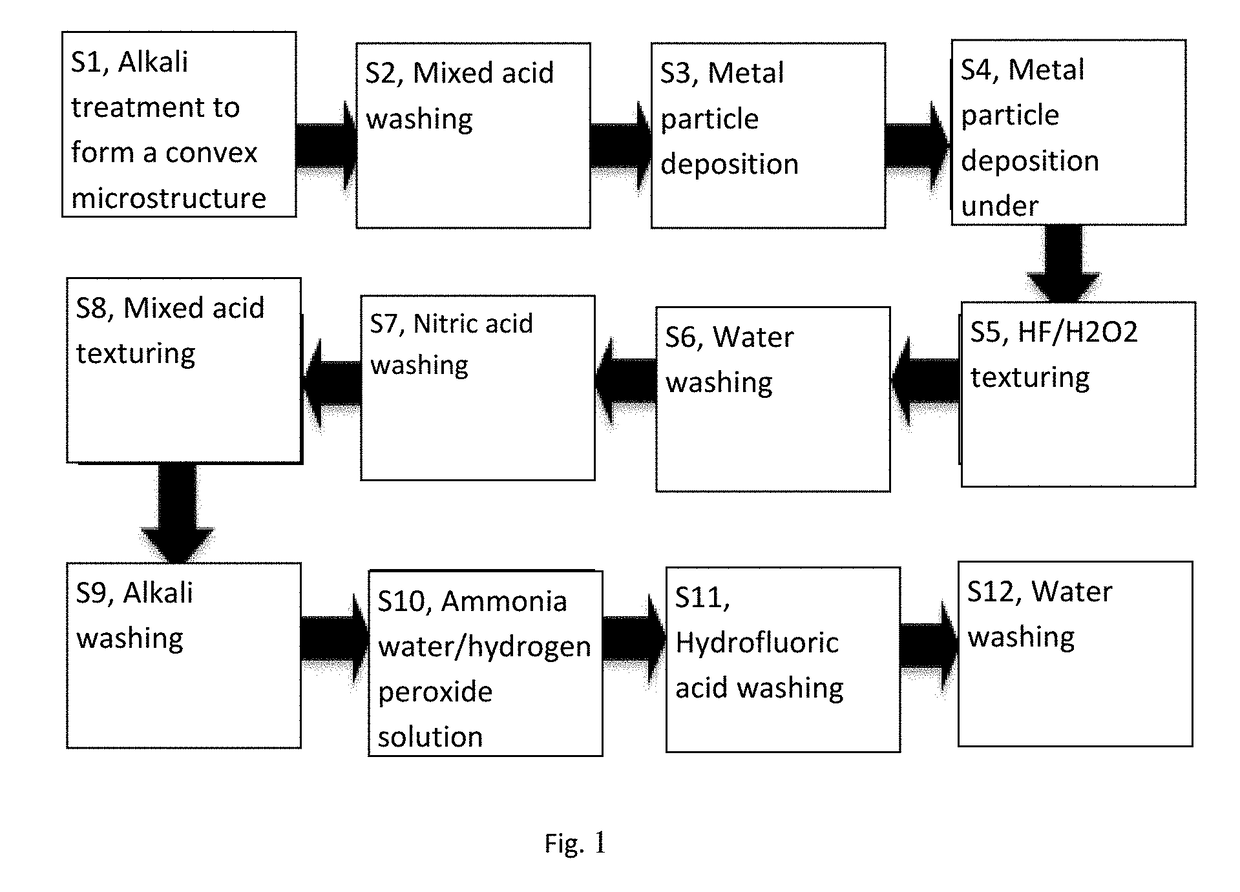
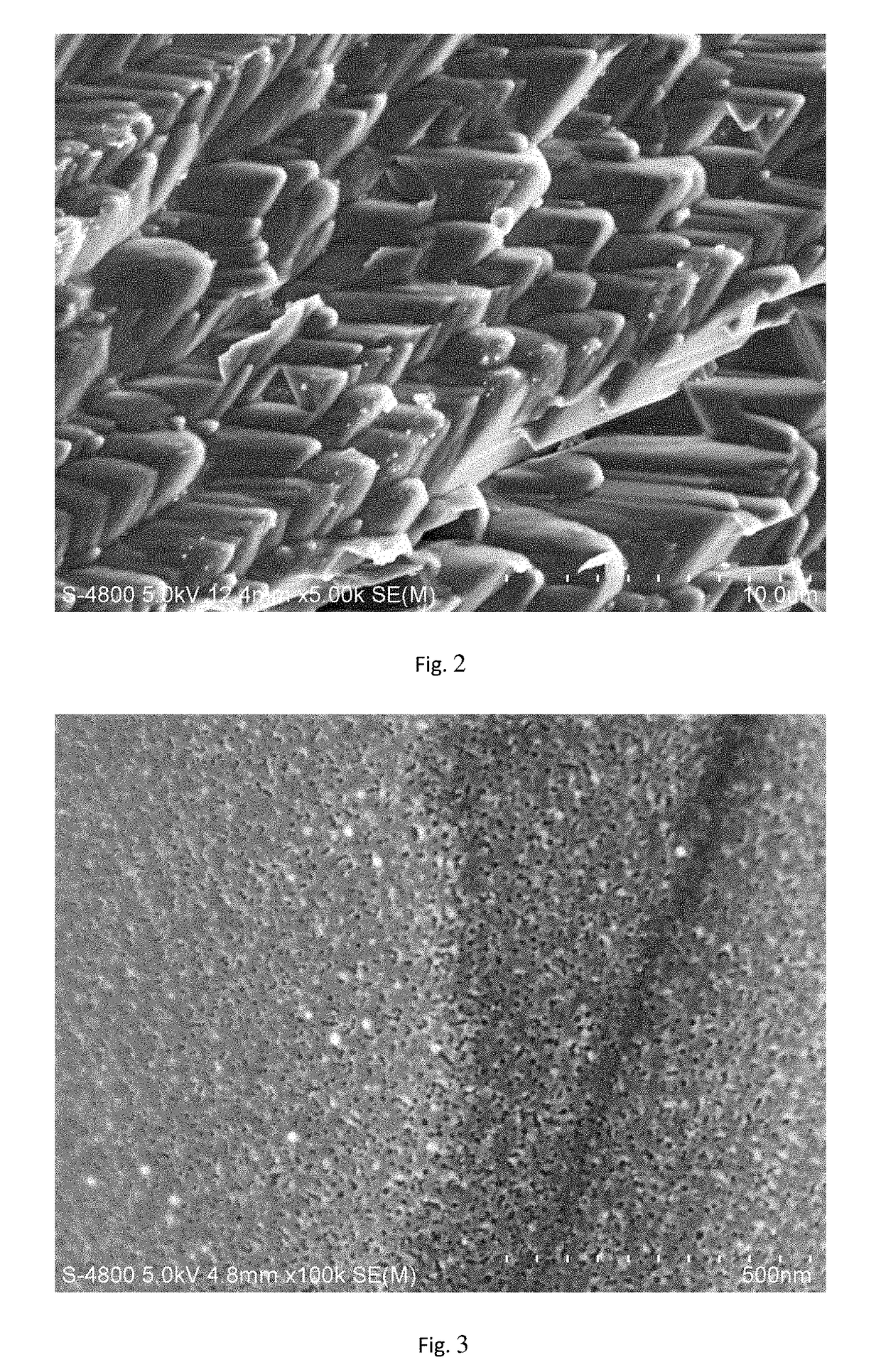
Texturing Method for Diamond Wire Cut Polycrystalline Silicon Slice
ActiveUS20190067496A1Improve conversion efficiencyLight structurePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHydrofluoric acidInorganic ions
It discloses a texturing method for a diamond wire cut polycrystalline silicon slice, including the following steps: firstly, immersing the diamond wire cut polycrystalline silicon slice into a mixed aqueous solution of an alkali solution and an alkali reaction control agent, removing a damaged layer on a surface of the silicon slice, and then immersing the silicon slice into a hydrofluoric acid solution containing inorganic ions and organic molecules for reaction; secondly, pretreating the polycrystalline silicon surface by a mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and hydrogen peroxide, adding a pore-forming regulator at the same time, and finally texturing the surface of the silicon slice by a mixed acid solution of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Coagulation analyzer and coagulation analysis method
PendingCN107315094AUse less frequentlyLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingAnalysis methodComputer science
The invention discloses a coagulation analyzer and a coagulation analysis method, which belong to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments. The coagulation analyzer comprises an optical coagulation analysis module, a sample interference analysis module, a magnetic coagulation analysis module and a test transfer module; according to the coagulation analyzer, the sample interference analysis module is utilized for judging whether an interfering substance in a sample influences a coagulation detection result of the optical coagulation analysis module or not; if not, the optical coagulation analysis module is utilized for carrying out coagulation analysis and reporting a detection result; if yes, the test transfer module is utilized for transferring a test to the magnetic coagulation analysis module for carrying out coagulation analysis and reporting a detection result.
Owner:SHENZHEN THISTORY BIO MEDICAL CO LTD
Detection method of quinolone drugs, detection reagent kit and application
ActiveCN101672792AEasy to operateLow cost of reagentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationAmmonium sulfateQuinolone
The invention discloses a detection method of quinolone drugs, a detection reagent kit and the application; in the method, methylene dichloride and hydrochloric acid are adopted to carry out pretreatment to a sample, ferric ammonium sulfate solution or ferric chloride solution is used for color reaction, according to the color development result, the detection of the quinolone drugs is realized. In the invention, mass samples to be detected are sieved preliminarily by fluorescence viewing under an ultraviolet lamp, the operation is simple and suspected positive samples can be rapidly sorted out, and then high specificity and high sensitivity color development reaction is utilized, so as to lead the detection accurate rate to reach 99 percent. The pretreatment method can eliminate effect ofcomplex and various interfering substances in the sample to be detected, and the concentration of the objective compound in the sample to be detected is improved, thereby being beneficial to observation to color reaction results in a latter period by a naked eye. The detection reagent kit in the invention can be used for detecting quinolone drugs which are mixed in cosmetics, health-care foods, disinfection products or Chinese patent drugs, and detecting the quinolone drugs and identification of the preparation.
Owner:广东省药品检验所
Medicine for treating inflammation of female reproductive system and preparation and quality control method thereof
InactiveCN101822743AAvoid time costLow cost of reagentsComponent separationAntipyreticSugar Coated TabletDisease
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine for treating inflammation of a female reproductive system and a preparation method thereof as well as a quality control method thereof. The medicine is prepared by the following raw materials in part by weight: 200 to 300 parts of Picria fel-terrae, 350 to 450 parts of herba elephantopi, 350 to 450 parts of Caulis Spatholobi, 350 to 450 parts of Radix zanthoxyli, 350 to 450 parts of membranaceous beautyleaf root, 350 to 450 parts of persimmon leaf and 350 to 450 parts of Thlaspi. The preparation method of the medicine is characterized in that medicinal extracts are used as medicine after being made into dry powder. The medicine is preferably made into sugar coated tablets. At the same time, a quality control method for content measurement and discrimination of the medicine is provided. The general effective rate of the medicine is verified by the clinical test result to be 97.96 percent, and the general effective rate of reference drug is 96.05 percent. After the treatment with the medicine, the disease and the primary symptom are remarkably improved. The medicine has good effect on treating the vaginitis and has slight adverse reaction.
Owner:秦皇岛润青制药有限公司
Precious metal recovery from solution
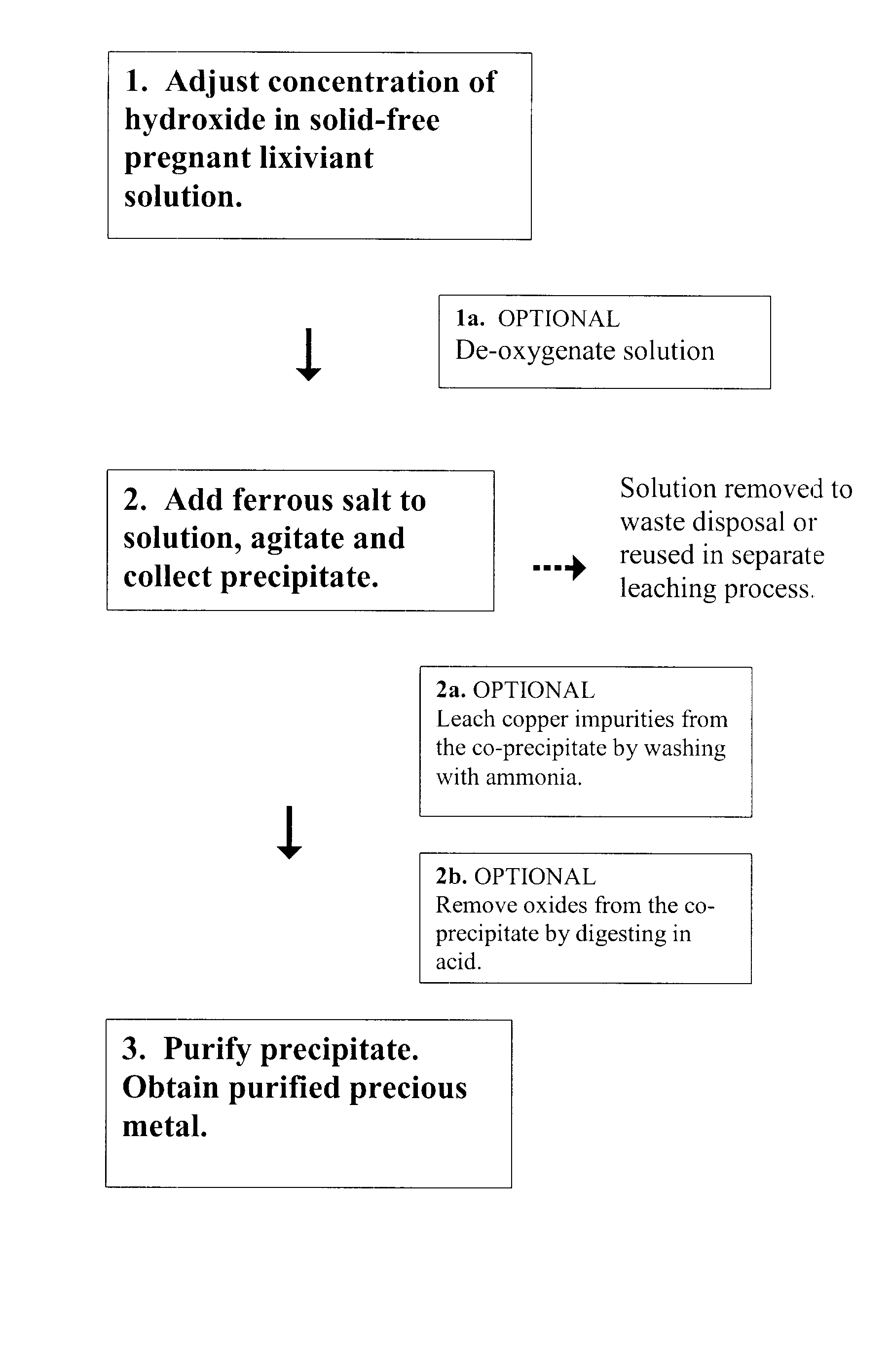
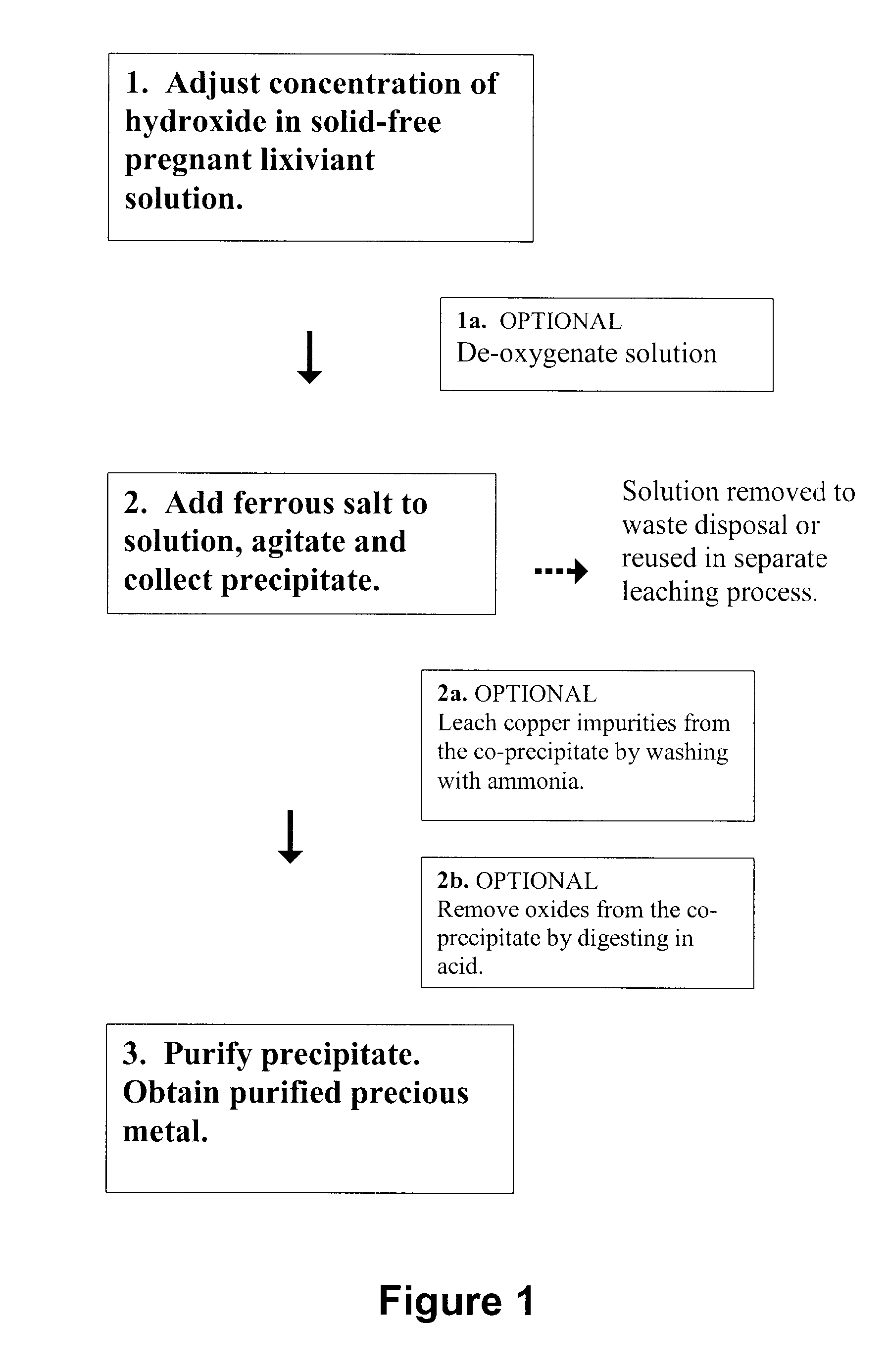
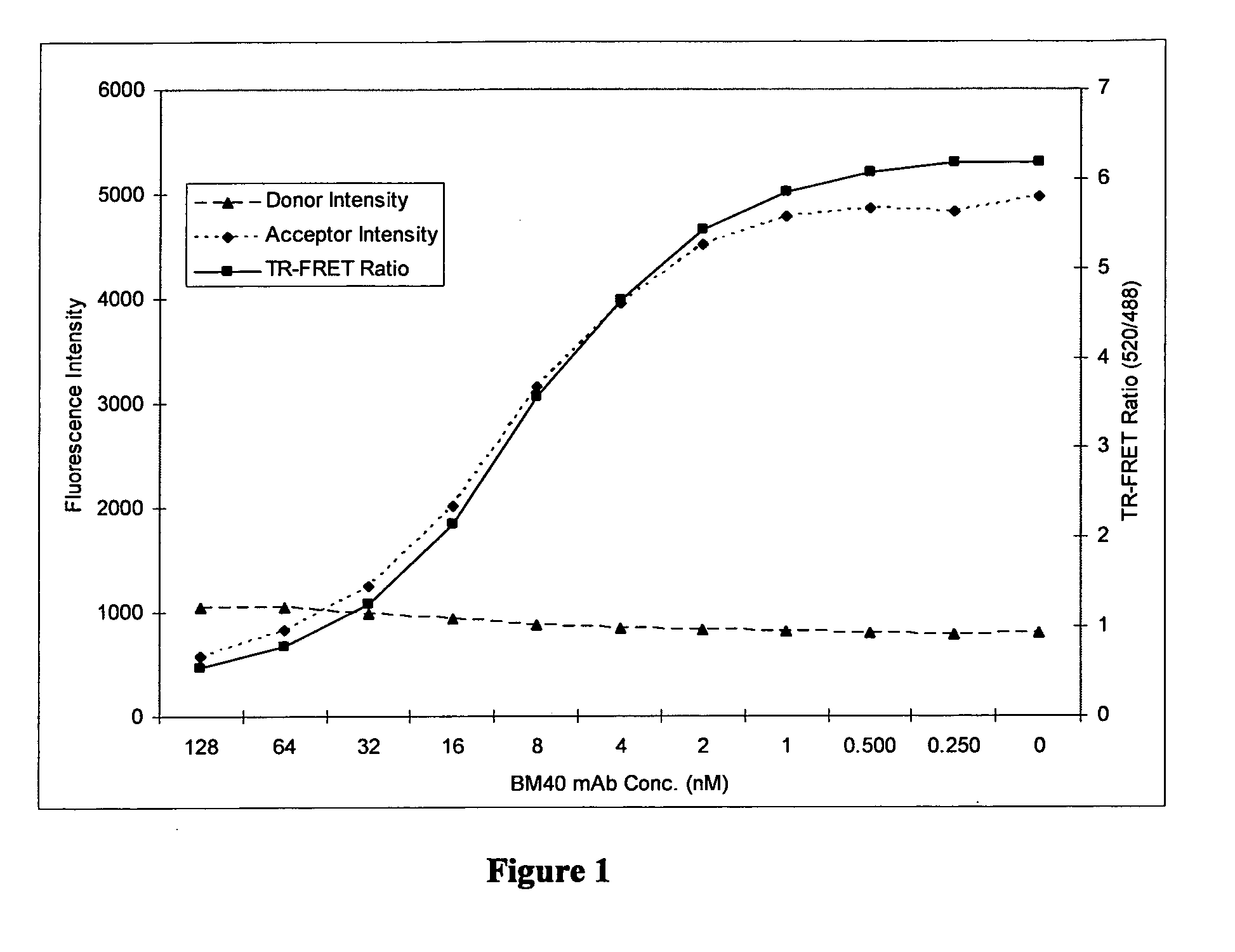
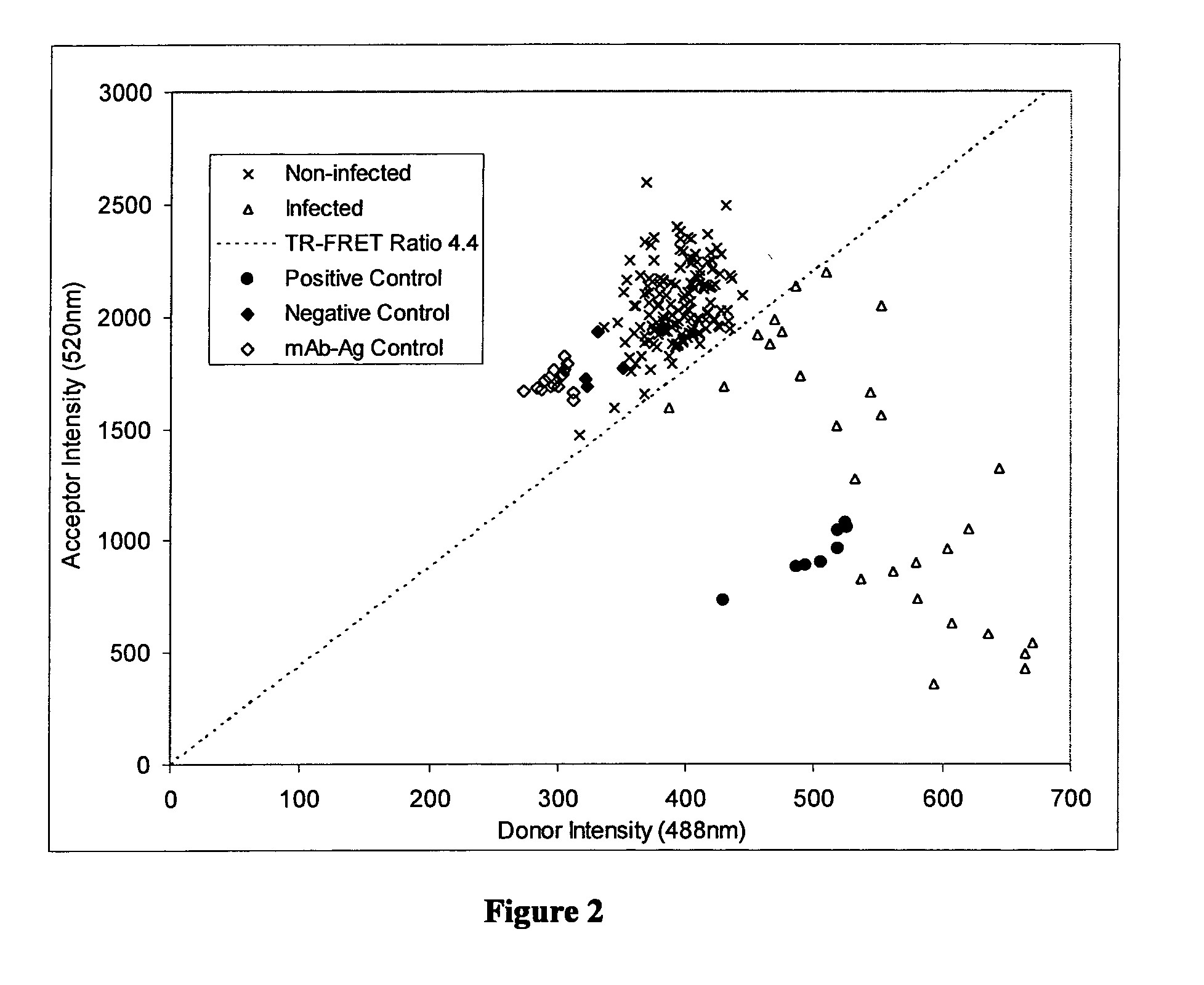
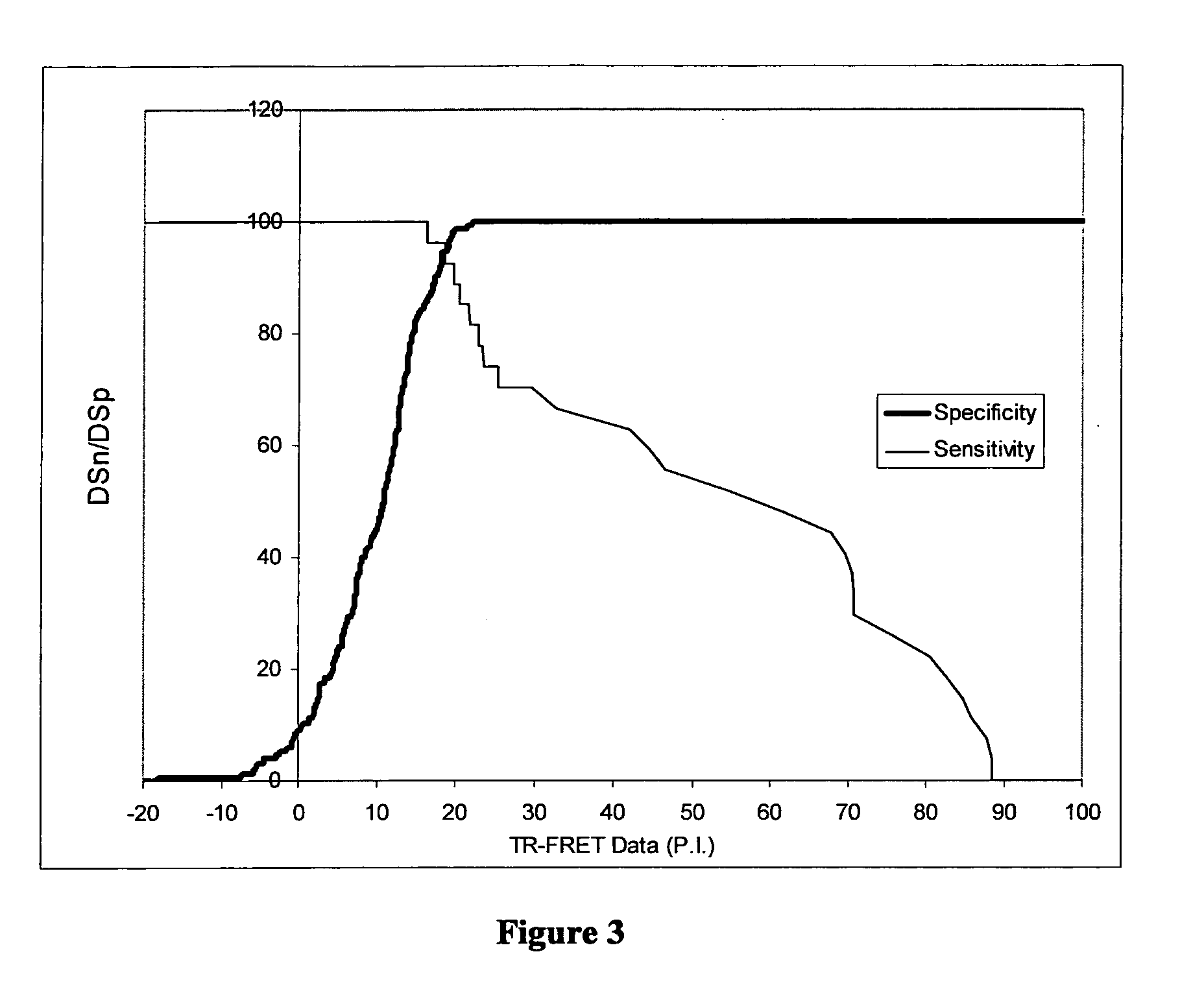
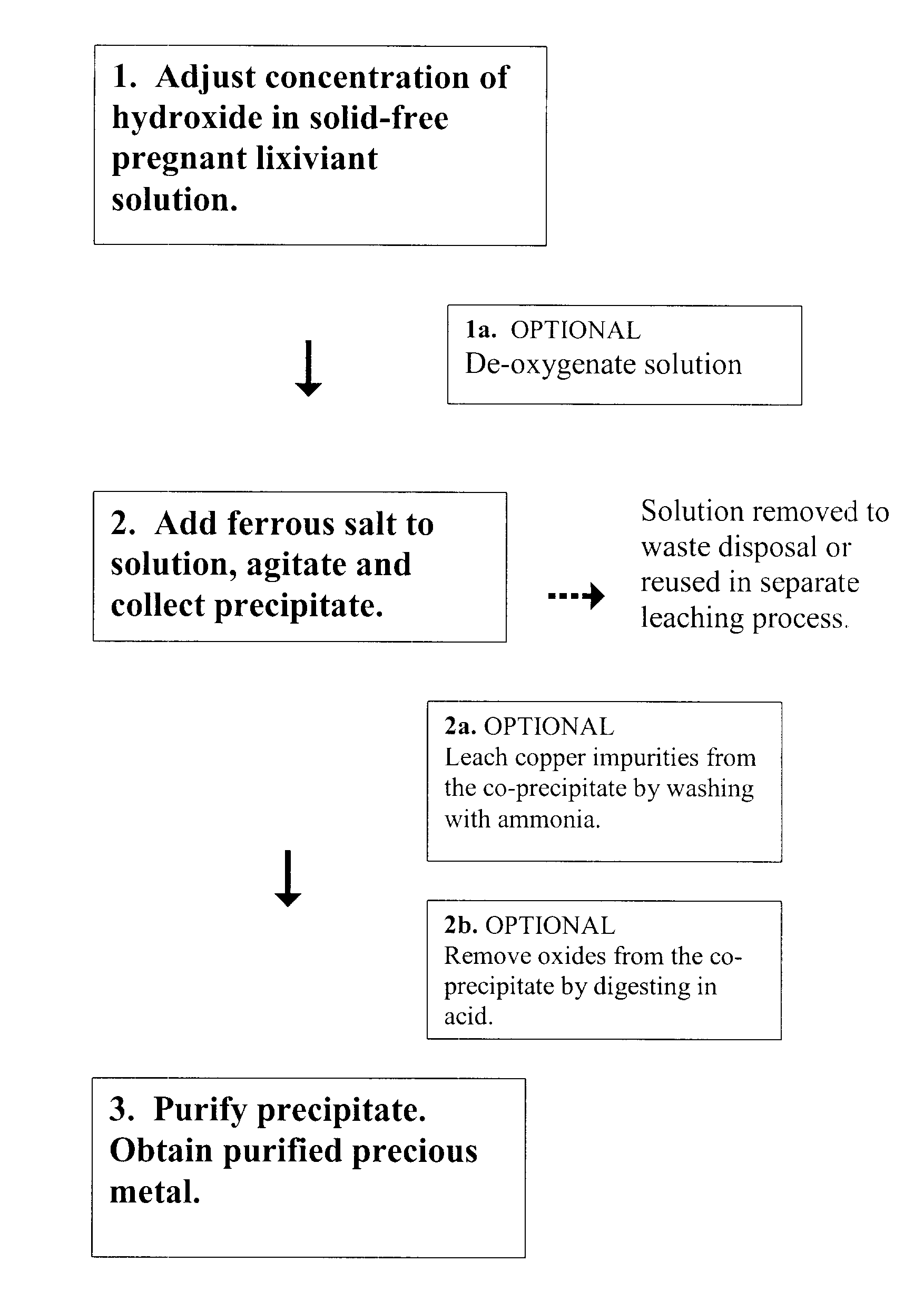
InactiveUS7972413B2Easy to separateLow cost of reagentsPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementFerric oxide hydrateAqueous solution
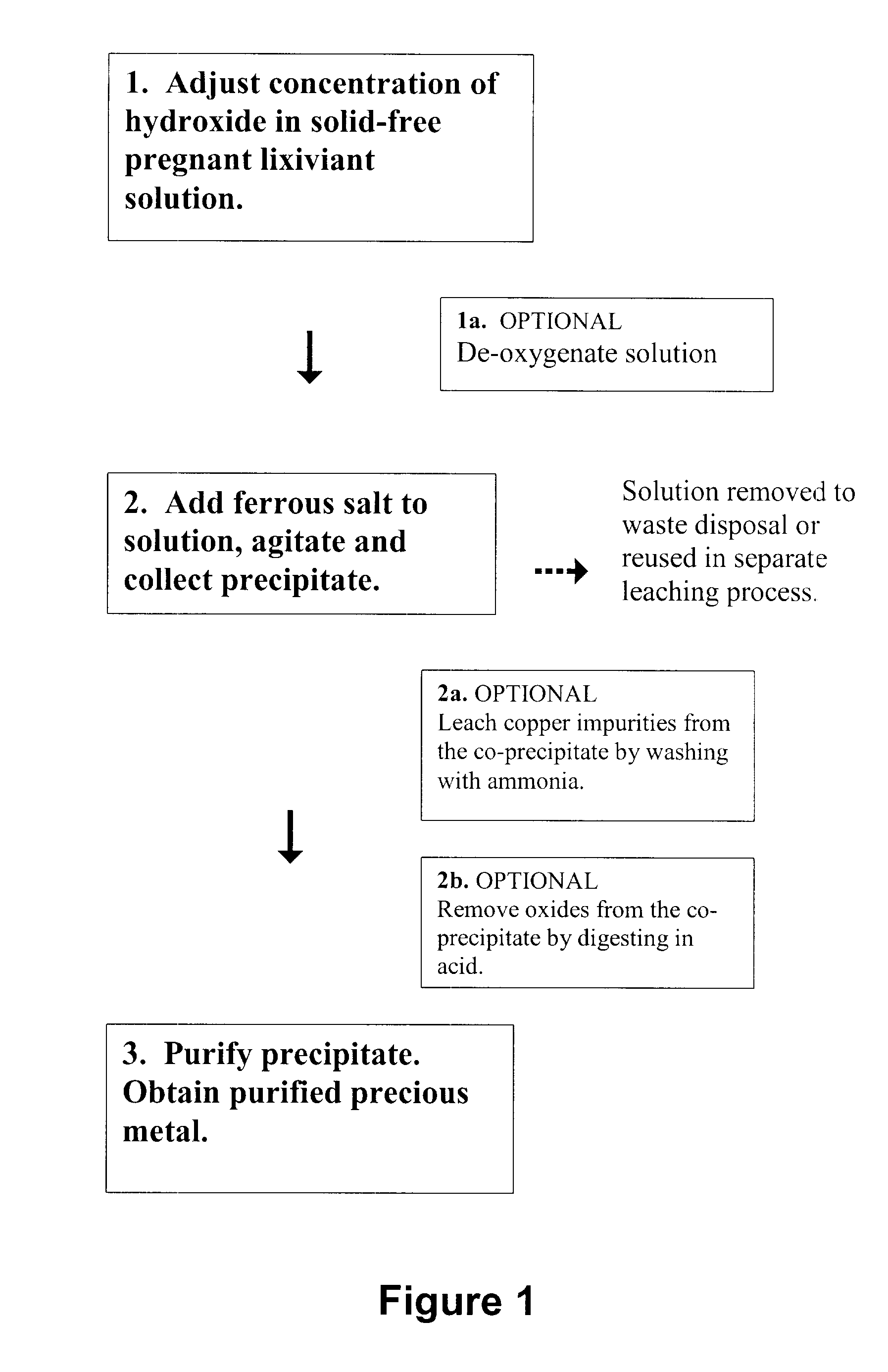
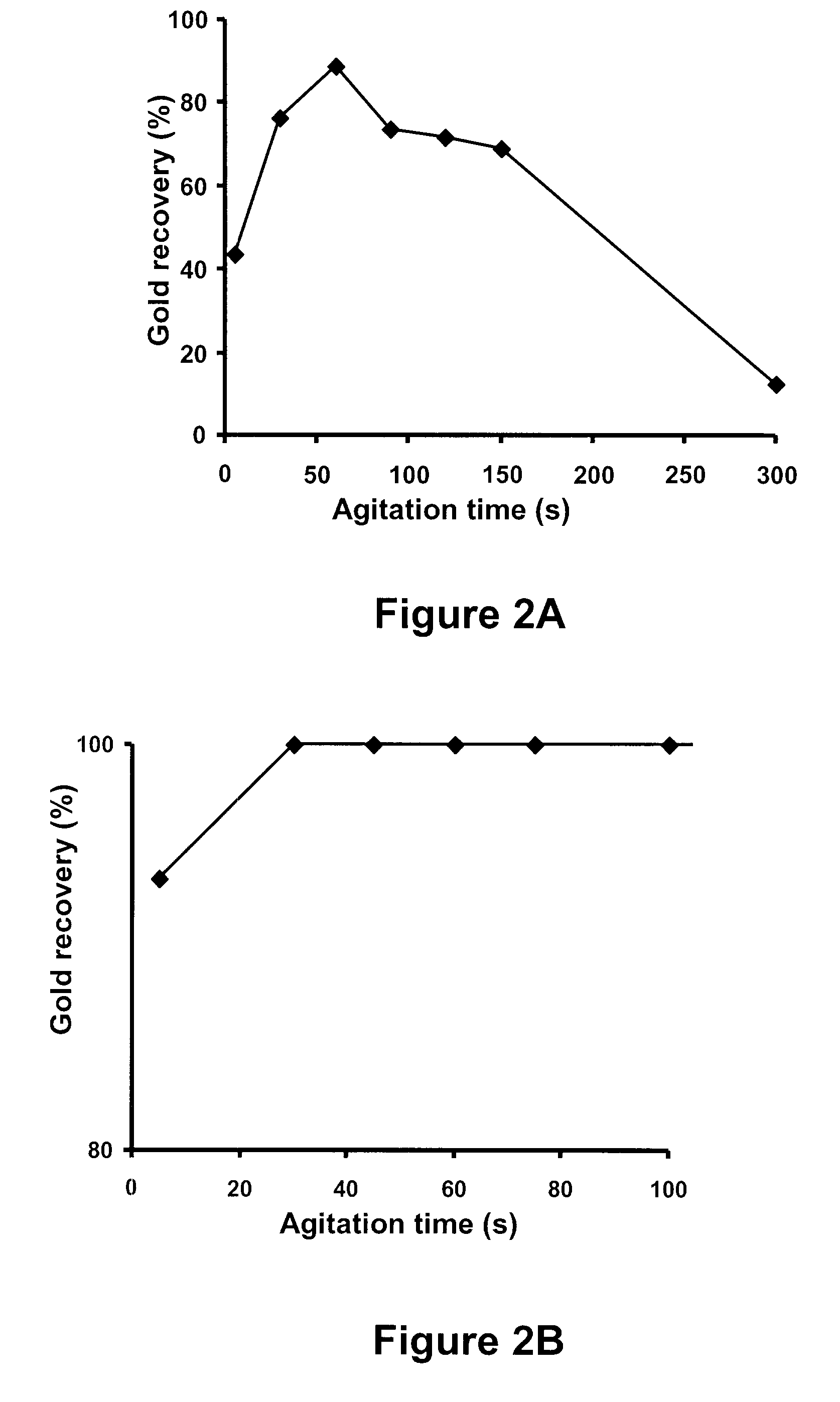
A method for recovering precious metals such as gold and silver from aqueous solution as solid is described The method includes mixing an aqueous solution (e.g, thiosulfate or thiocyanate lixiviant) containing precious metals with ferrous ions in the presence of an effective amount of hydroxide ions. The precious metal ions are reduced and co-precipitate with iron hydroxides and / or hydrated iron oxides The co-precipitate is collected and purified. De-oxygenation of the reaction solution is optional. The recover / method is fast, complete and clean.
Owner:METAL ASIA INT
Method for simultaneously separating three main components of bovine milk casein
ActiveCN107840883ARealize industrial preparationSimple processPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesBiotechnologyIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously separating three main components of bovine milk casein, and aims to provide a method for separating the three main monomer components of casein, which adopts the bovine milk casein as a raw material, adopts a DEAE ion exchange column as separating equipment, and can simultaneously obtain alpha-casein, beta-casein and kappa-casein through one-timeseparation. According to the method provided by the invention, the three casein monomer components can be obtained through one-step separation, separation steps are less, a separation process is simple and easy to operate, a separation condition is mild and easy to implement, the separating equipment is simple and easy, the dosage of chemical reagents is less during a separation process, not onlyis the separation cost of the casein monomers reduced, but also the environment pollution is reduced, and the method meets a new concept on low carbon and environment protection; the average yield for separating the casein monomers is high, the average yield of the alpha-casein can reach 75 percent or more, the average yield of the beta-casein can reach 80 percent or more, and the average yield of the kappa-casein can reach 85 percent or more; the obtained three casein monomers have high purity which can reach to 95 percent or more; the method not only can meet the requirement on preparing the three high-purity casein monomer components in a laboratory, but also can be used for industrially preparing the main monomers of the casein, and is wide in application range.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
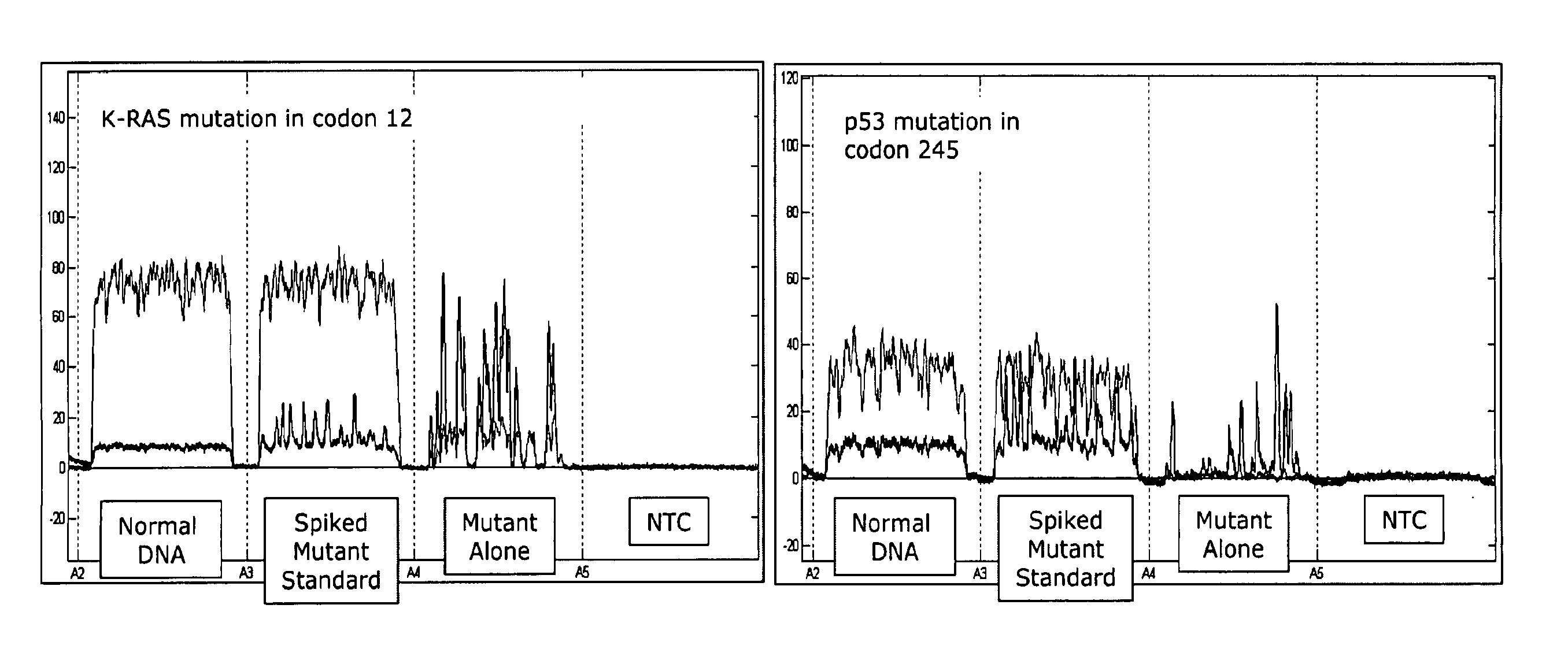
Detection method
InactiveUS20110039256A1Early detectionEnabling diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisWavelengthReagent
A method for detecting the presence of a diagnostic moiety indicative of exposure to an infectious organism in a biological sample taken from a human or animal, said method comprising; (a) adding to said sample a first fluorescently labelled reagent which binds said diagnostic moiety, and a second fluorescently labelled reagent which either binds said diagnostic moiety in addition to said first fluorescently labelled reagent, or which binds the first fluorescently labelled reagent or a complex comprising the first fluorescently labelled reagent in competition to the said diagnostic moiety, wherein a label on one of the first or second fluorescently labelled reagent acts as a fluorescent energy donor compound and wherein the other of the first or second fluorescently labelled reagent acts as a fluorescent energy acceptor compound which is able to accept fluorescent energy from said donor compound; (b) exciting the fluorescent energy donor compound by illuminating with light of a wavelength which is absorbed by said fluorescent energy donor compound; (c) measuring fluorescent signal emitted by said fluorescent energy acceptor compound as a result of its absorption of the fluorescent energy from the donor compound after a time delay; and (d) relating the results to the presence or absence of diagnostic moiety in said sample.
Owner:THE SEC OF STATE FOR ENVIRONMENT FOOD & RURAL AFFAIRS ACTING THROUGH THE ANIMAL HEALTH & VETERINARY LAB AGENCY
Precious Metal Recovery from Solution
InactiveUS20100025259A1Easy to separateLow cost of reagentsPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementFerric oxide hydrateFerric hydroxide oxide
A method for recovering precious metals such as gold and silver from aqueous solution as solid is described The method includes mixing an aqueous solution (e.g, thiosulfate or thiocyanate lixiviant) containing precious metals with ferrous ions in the presence of an effective amount of hydroxide ions. The precious metal ions are reduced and co-precipitate with iron hydroxides and / or hydrated iron oxides The co-precipitate is collected and purified. De-oxygenation of the reaction solution is optional. The recover / method is fast, complete and clean.
Owner:METAL ASIA INT
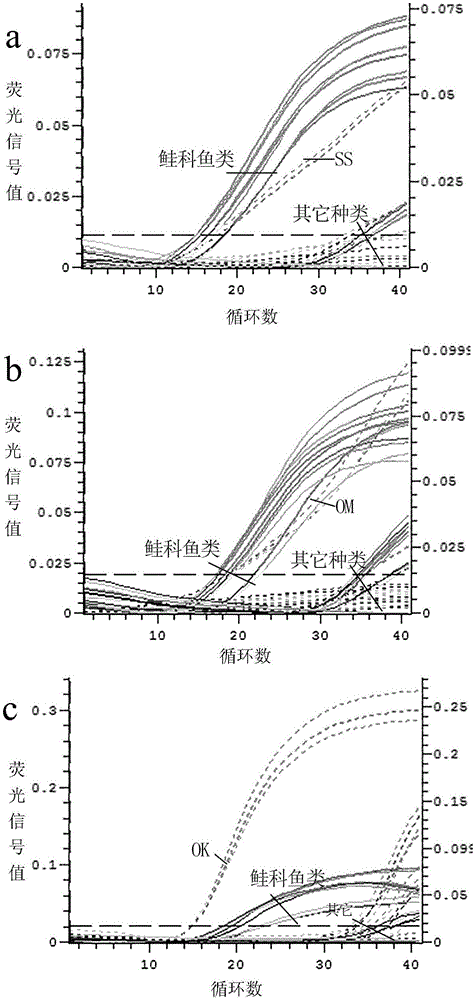
Dual fluorescent quantitative PCR method for species identification of salmons and highly processed products of salmons
InactiveCN105039329ALow cost of reagentsShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpecies identificationDog Salmon
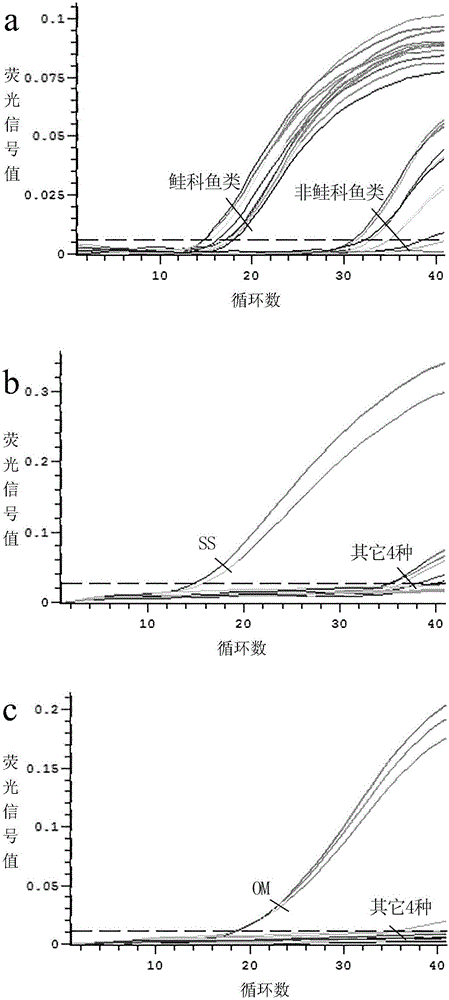
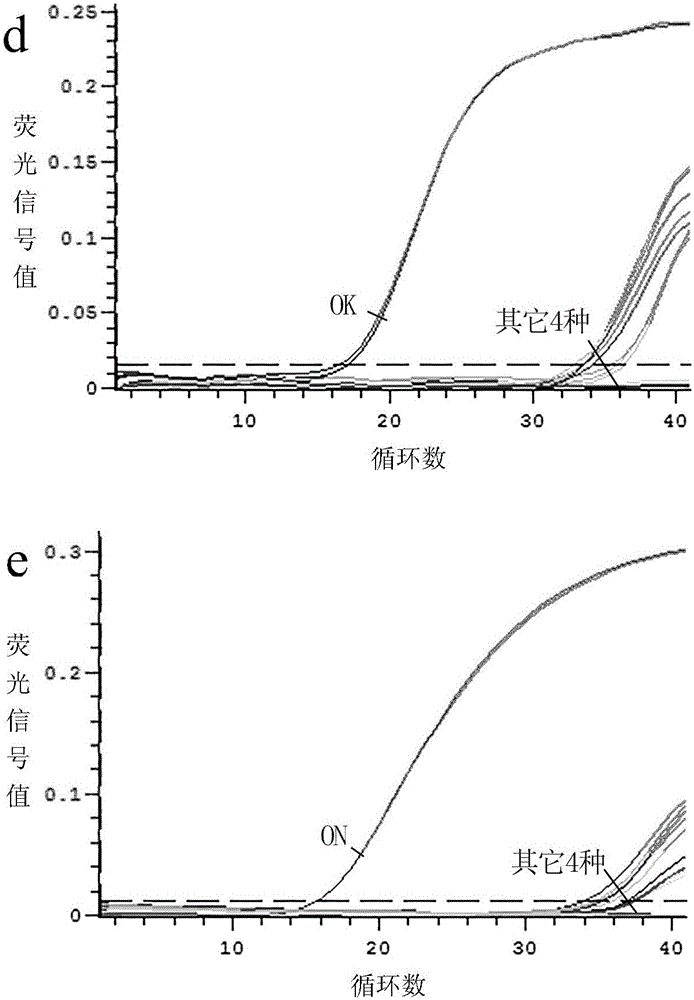
The invention provides a dual fluorescent quantitative PCR method for species identification of salmons and highly processed products of the salmons, and discloses a method for detecting the species of the salmons and the highly processed products of the salmons through dual fluorescent quantitative PCR. The method includes the following steps that firstly, specific identification primers and probes of salmonidae and four kinds of common salmons are designed, wherein the four kinds of common salmons include atlantic salmons, rainbow trouts, dog salmons and sockeye salmons; secondly, genome DNA in a salmon sample to be detected is extracted; thirdly, a dual fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification system is set; fourthly, judgment is made according to real-time fluorescent PCR detection results. The effective method is provided for quick detection of species identification of the salmons and the highly processed products of the salmons, and a technological guarantee is provided for aquatic product and food import and export.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Eukaryotic cell nucleic acid extraction method
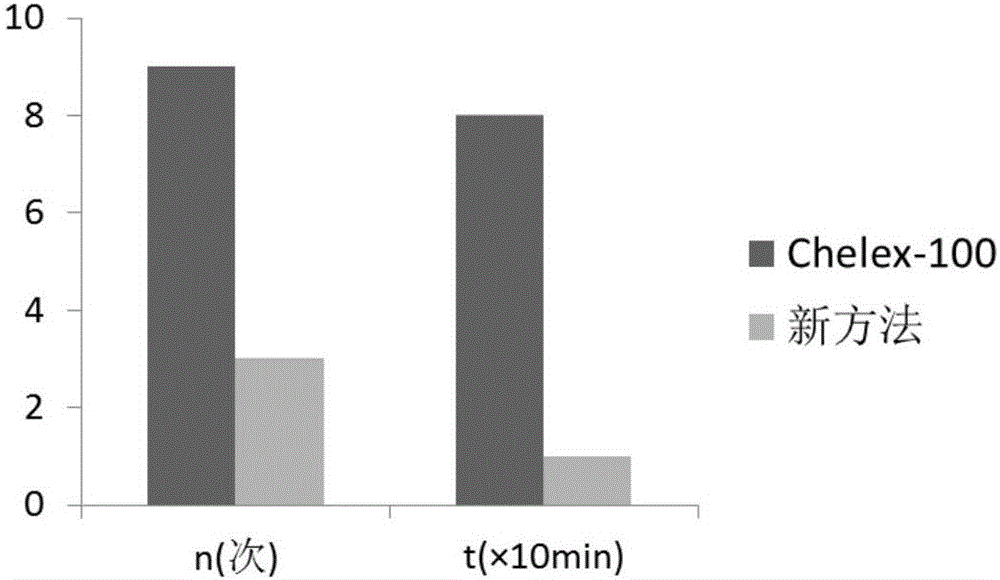
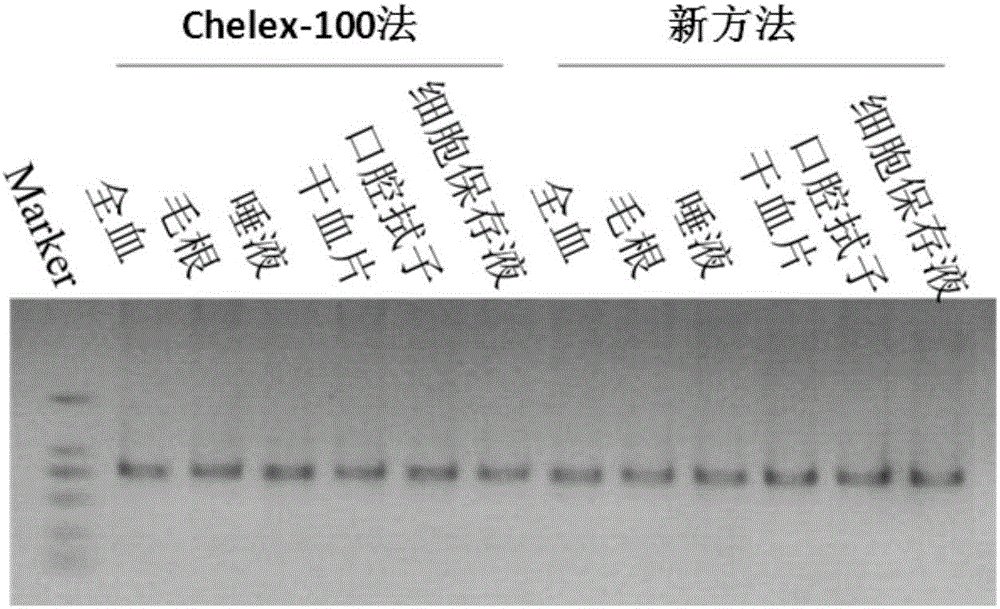
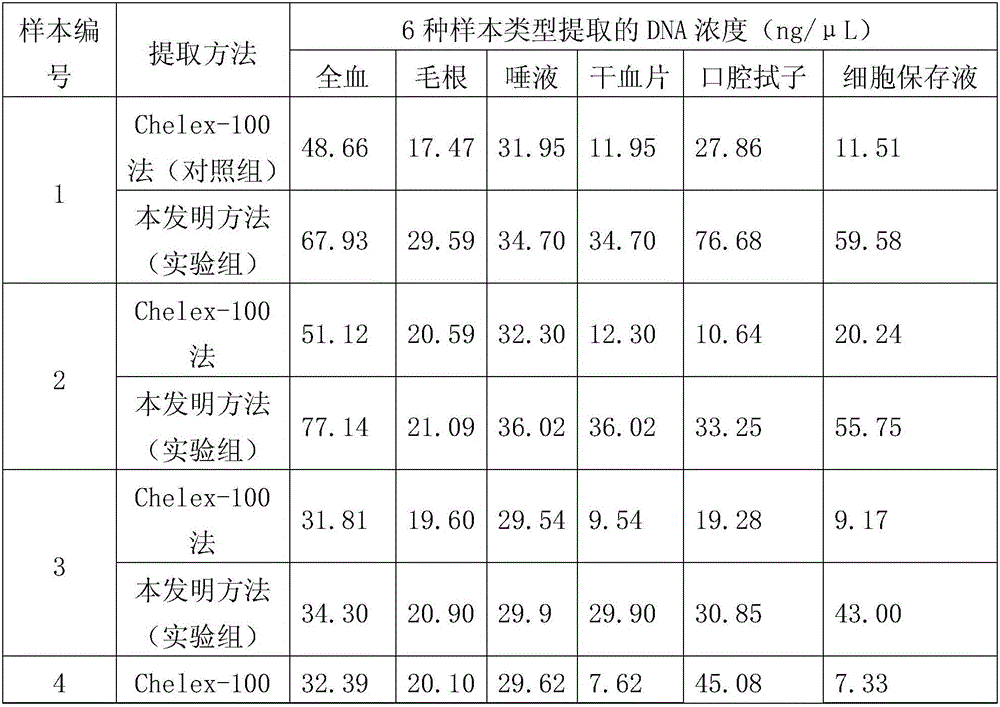
InactiveCN106350512AQuick extractionReduce pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationCell membraneRapid dna
The invention discloses a eukaryotic cell nucleic acid extraction method and provides a nucleic acid extraction method which comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing a to-be-tested sample with alkaline liquid, and performing reaction at a high temperature, thereby obtaining nucleic acid. Experiments prove that compared with an existing DNA extraction method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that operation steps such as repeated cleaning, warm bath and centrifugation are removed; through creating an alkaline high-temperature liquid environment around the sample, membrane rupture and protein degeneration of eukaryotic cells are accelerated, the extraction efficiency of eukaryon genome DNA is greatly improved, and rapid DNA extraction is realized. The nucleic acid extraction method has no special requirements on aspects of sample types and laboratory conditions, is wide in application range and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Methods of chemotype evolution
ActiveUS20110118126A1Low cost of reagentsBig spaceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein targetCombinatorial chemistry
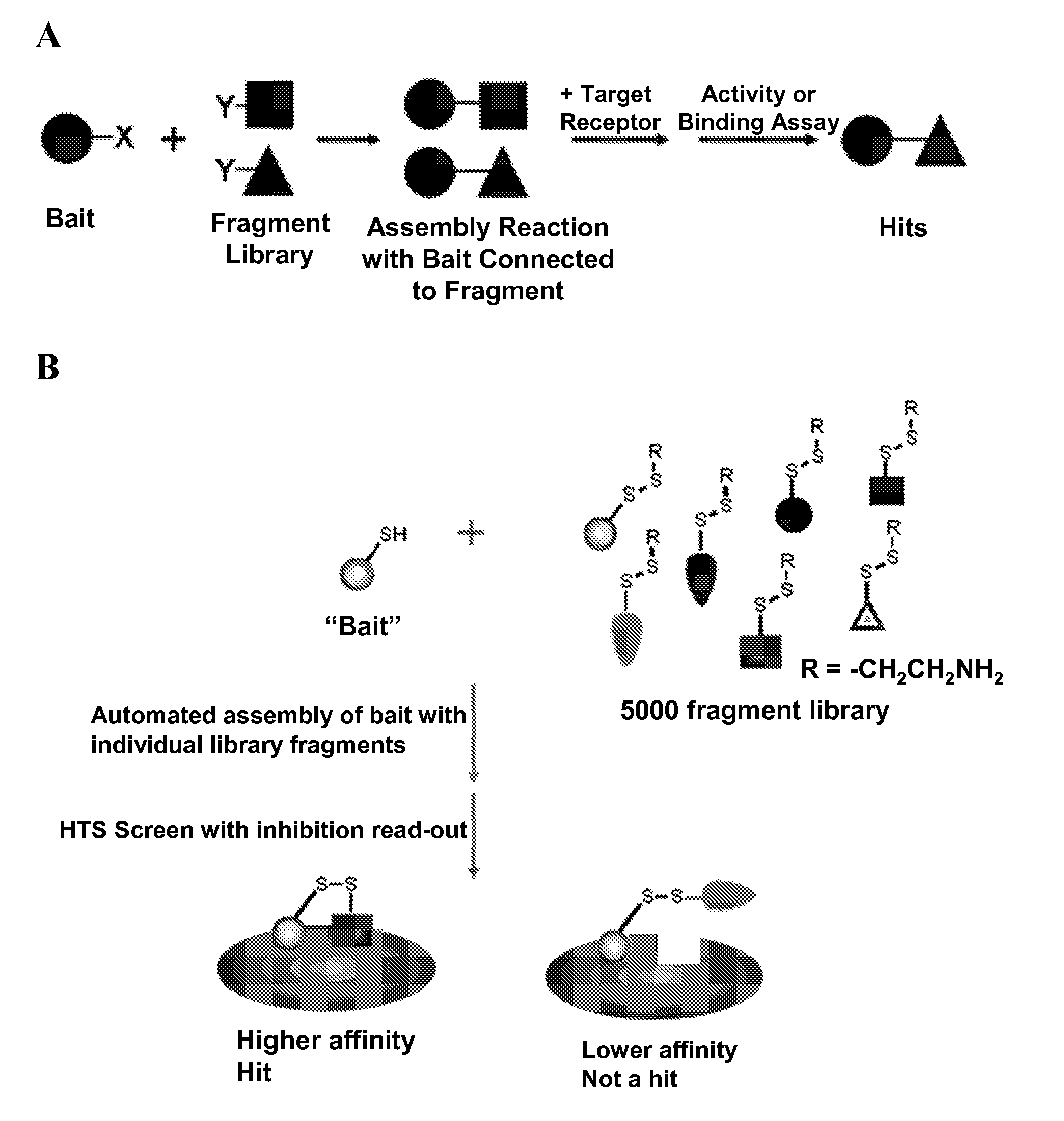
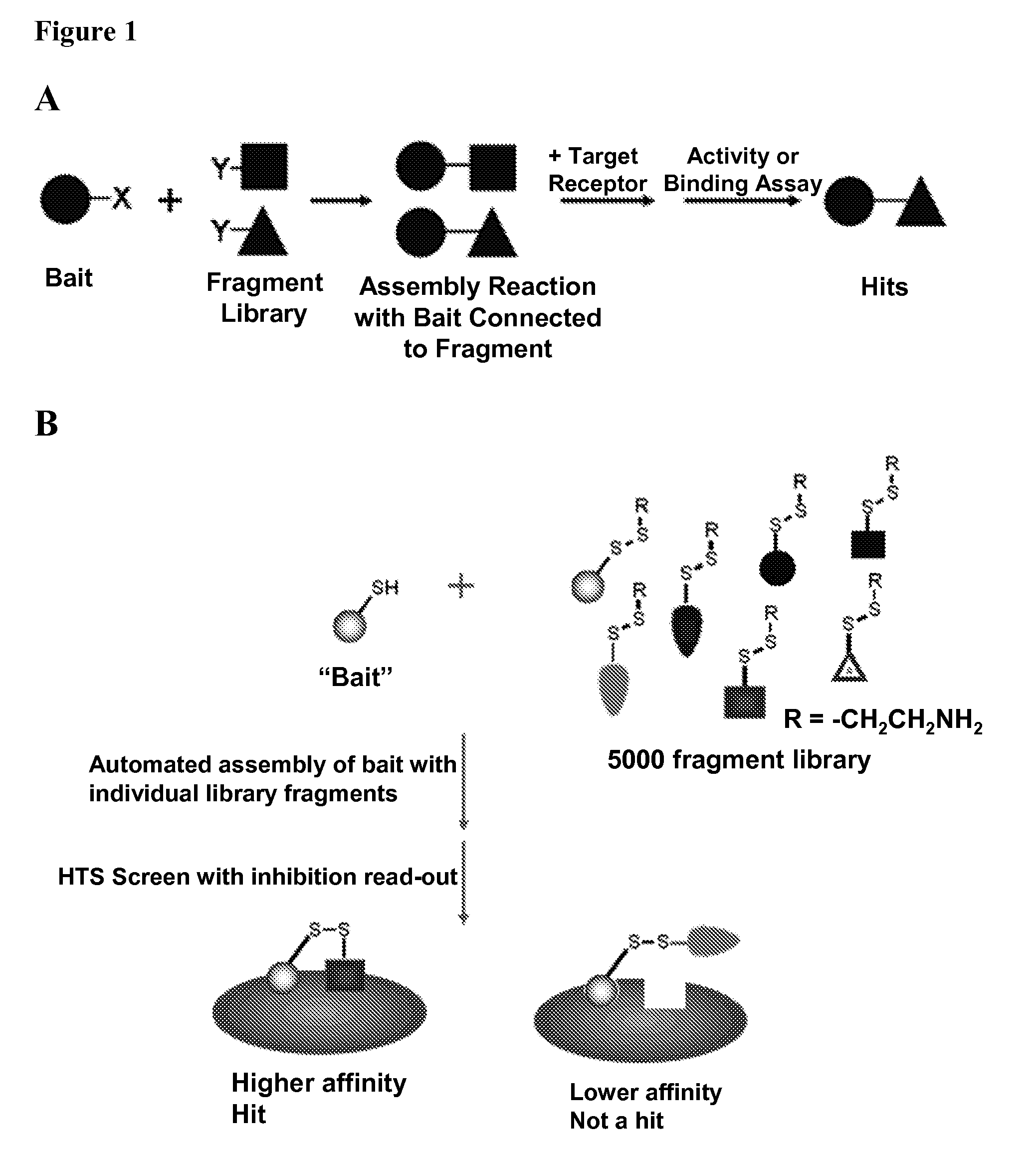
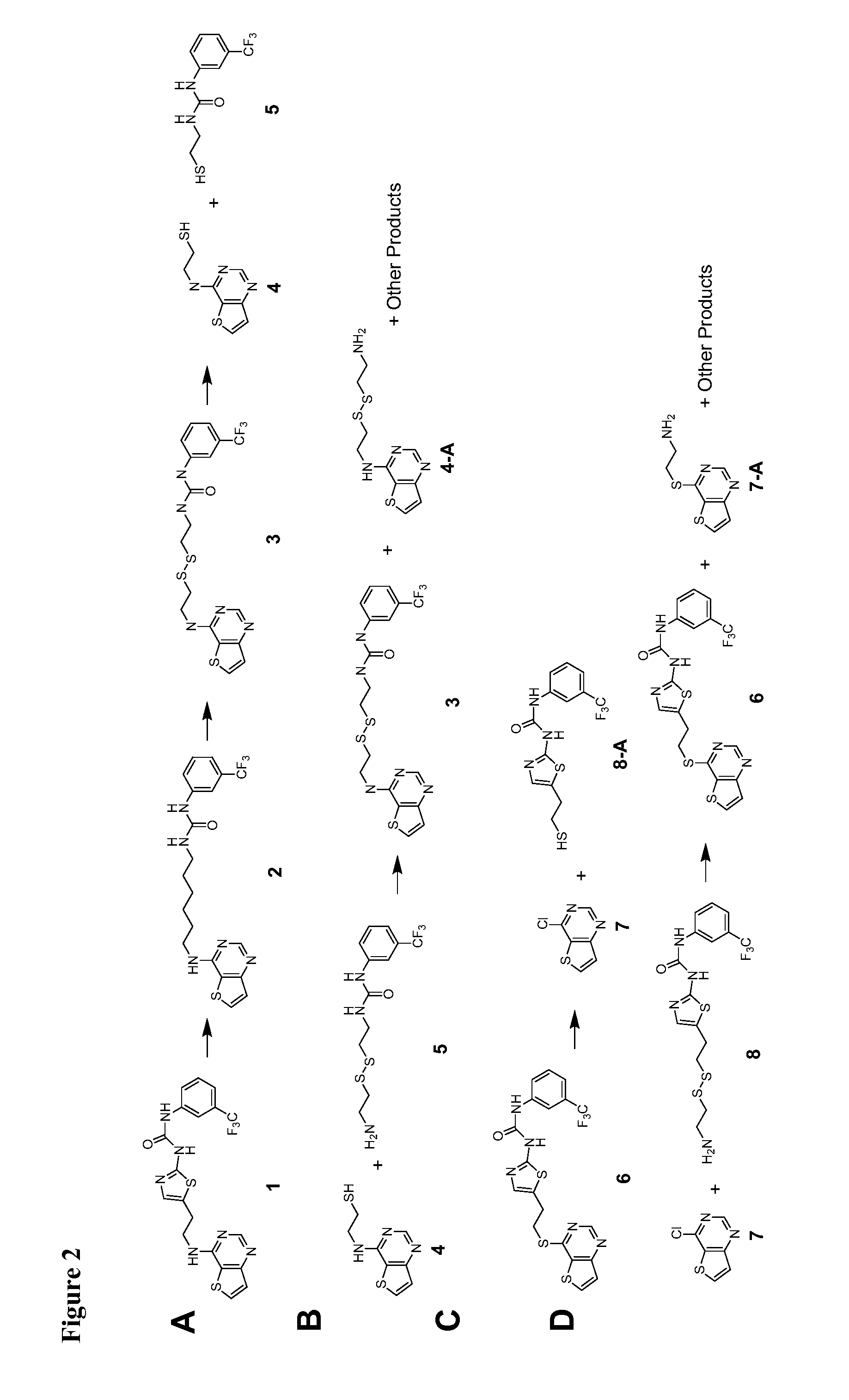
Herein is described a method to rapidly screen a large chemical space for a compound that binds to a target protein through an iterative fragment assembly approach that can be performed at low reagent cost and without requiring purification of the assembled product. The method employs a library of test ligands each of which comprise a ‘bait’ molecule, which is known from prior art or prior screening to have some intrinsic affinity for the target protein, and a test moiety.
Owner:CARMOT THERAPEUTICS INC
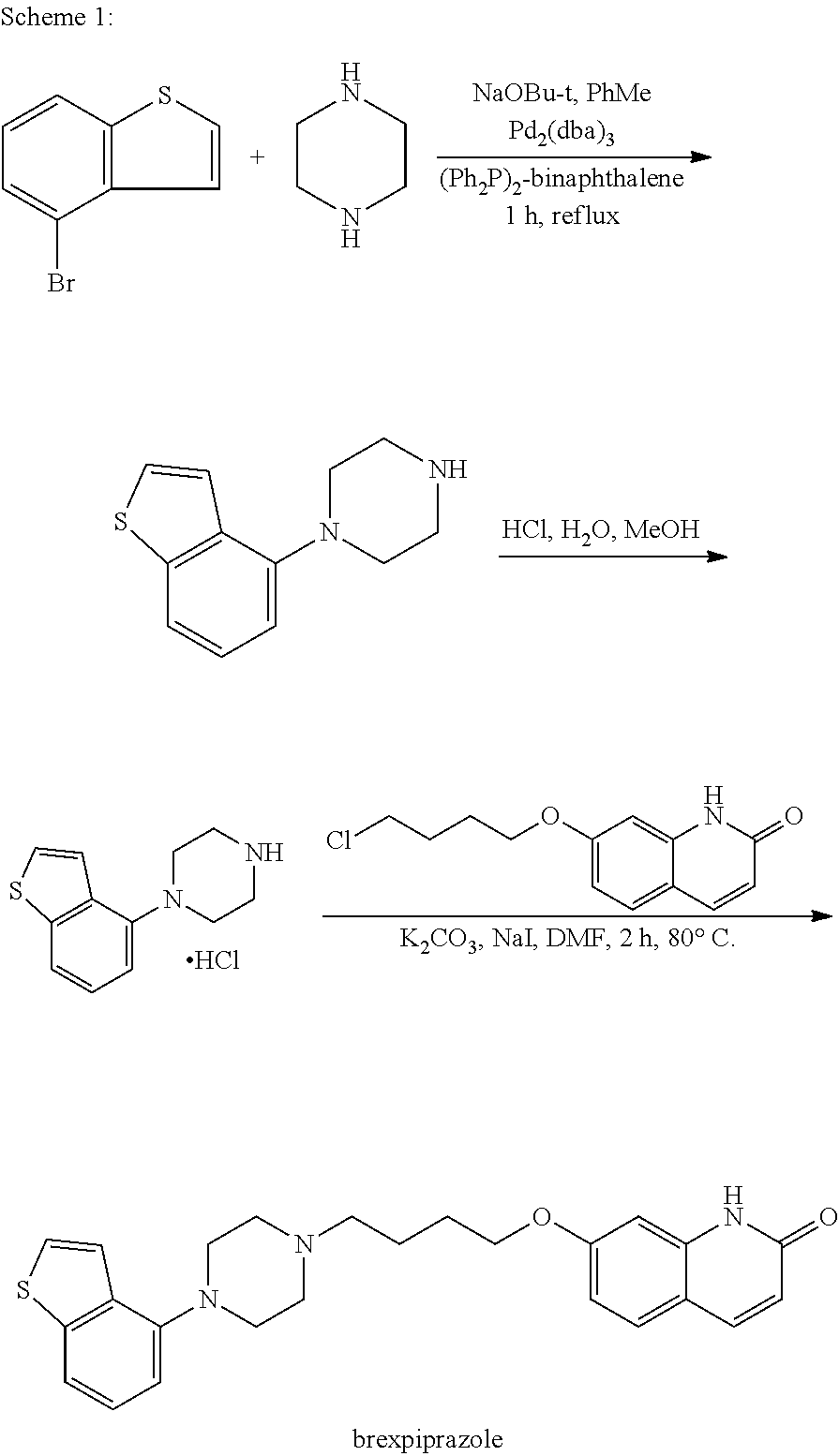
Methods for preparing brexpiprazole, key intermediates thereof and salts thereof
InactiveUS20160272624A1Easy to operateImprove yield and product qualityOrganic chemistryBrexpiprazoleCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention relates to the methods for preparing brexpiprazole, the analogs, key intermediates, and salts thereof, specifically, the present invention relates to a new method for preparing brexpiprazole, the analogs, key intermediates, and salts thereof, and the key intermediates, and salts thereof provided during the preparation. The preparation method has a mild reaction condition, stable intermediate, easy operation, and uses cheap and easy-to-get reagents, thus it saves the synthesis cost, shortens the production cycle, improves the yield and product quality, and is suitable for mass production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Novel coronavirus RPA test strip detection kit
PendingCN111635962AHigh sensitivityLow cost of reagentsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesVirus detectionMolecular biology
The invention discloses a novel coronavirus RPA test strip detection kit, and belongs to the field of virus detection. The kit disclosed by the invention comprises primers with sequences shown as SEQID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and a probe with a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.3. The kit provided by the invention does not need to depend on a high-cost (fluorescent quantitative) PCR instrument, can realize high-sensitivity and specific rapid detection at reagent cost of 50% lower than that of a conventional RPA detection kit, and is suitable for novel coronavirus detection in various occasions.
Owner:CHENGDU HAIZHIYUAN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Cleaning fluid
InactiveCN104017665AImprove cleaning effectLow cost of reagentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsDetergent compounding agentsEnvironmental chemistryAlkali hydroxide
The invention discloses cleaning fluid which comprises an anionic surfactant, a non-ionic surfactant, an alkali metal hydroxide, plantrennet and a buffer agent for stabilizing the pH value to be greater than 12.0. When being used, the cleaning fluid disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of low protein substance residue rate, low fat substance residue rate, good in-batch repeatability of clinical projects, low cross contamination, low reactant deposition and the like, and meanwhile the testing result of a biochemical analyzer is not affected; a liquid path system and a reaction cup of the biochemical analyzer are not corroded in the washing process; meanwhile, all components of the cleaning fluid disclosed by the invention can be biologically degraded, no potential pollution to the environment is caused, and the requirements of environmental protection are met.
Owner:NANTONG YONGKANG DETECTION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com