Patents
Literature
75 results about "Zirconium tungstate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
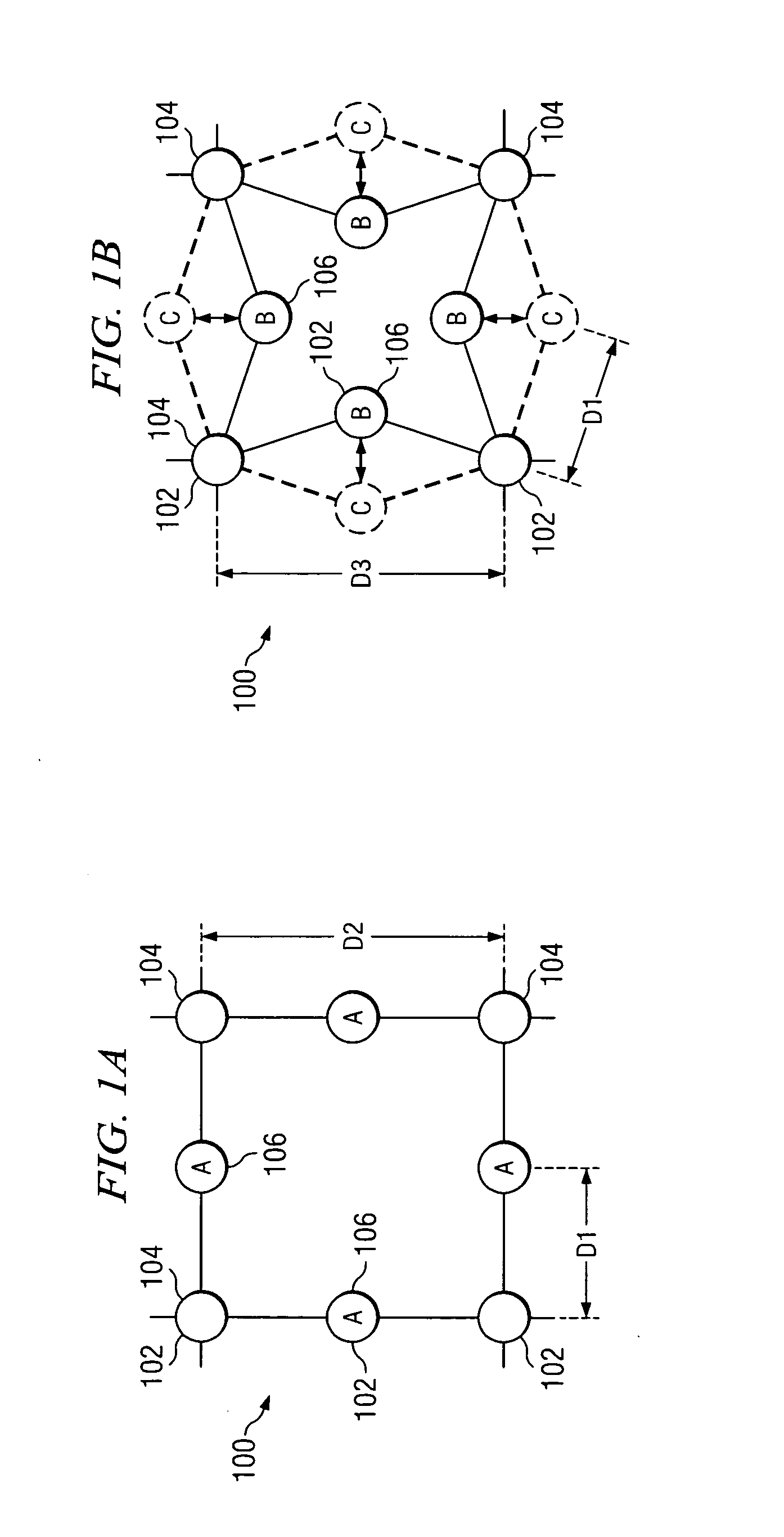
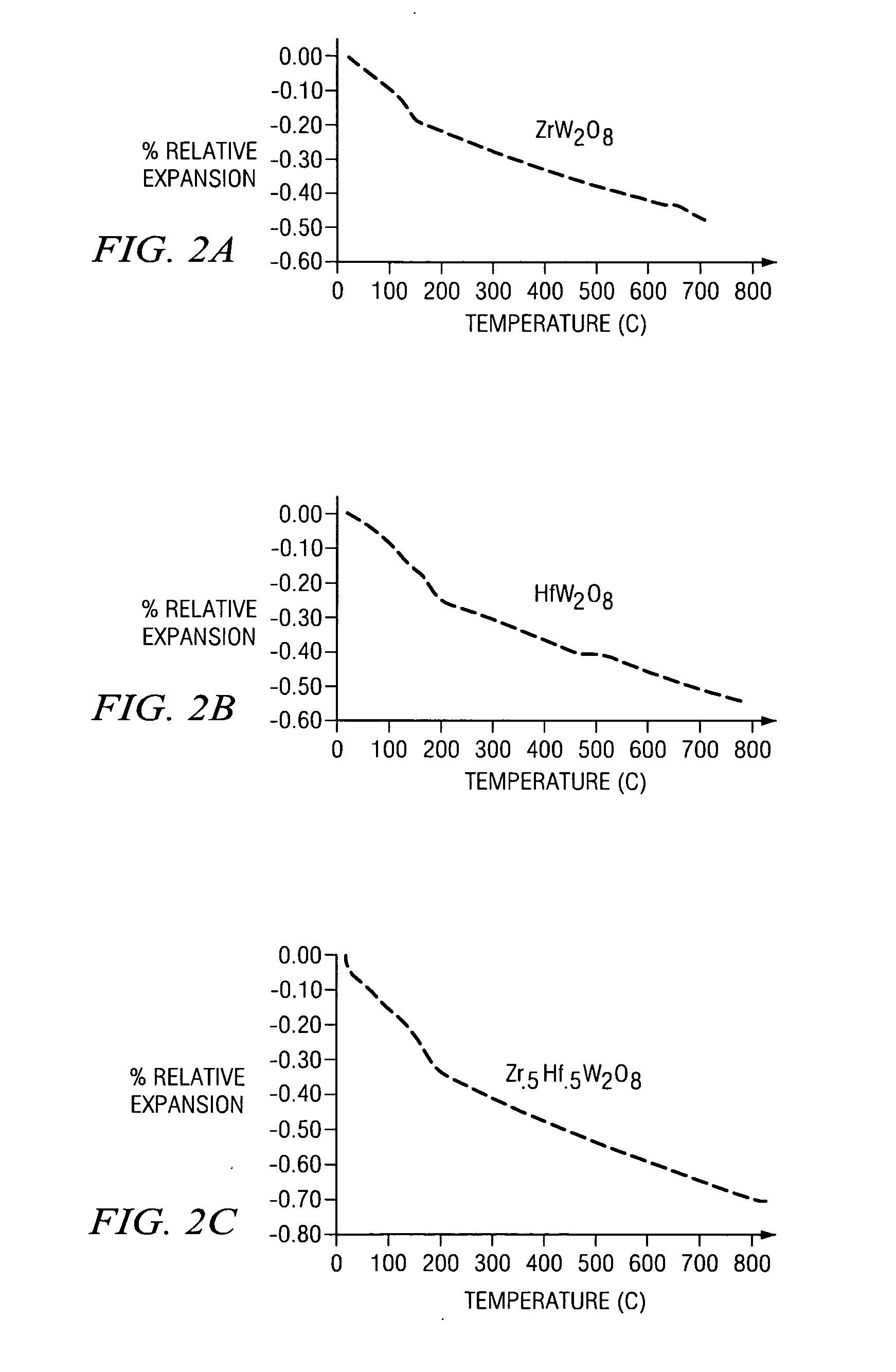
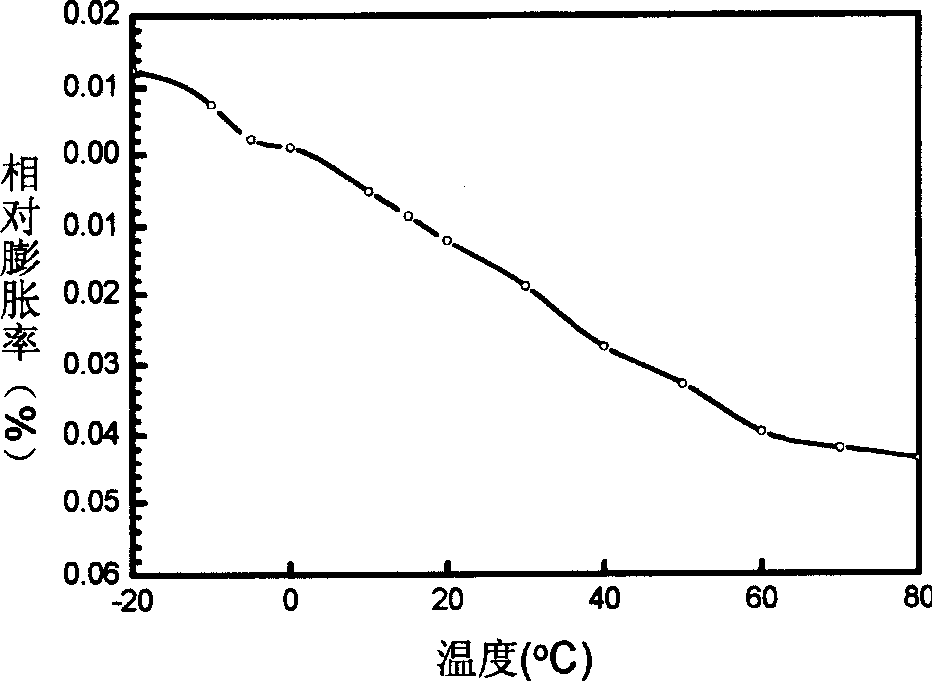
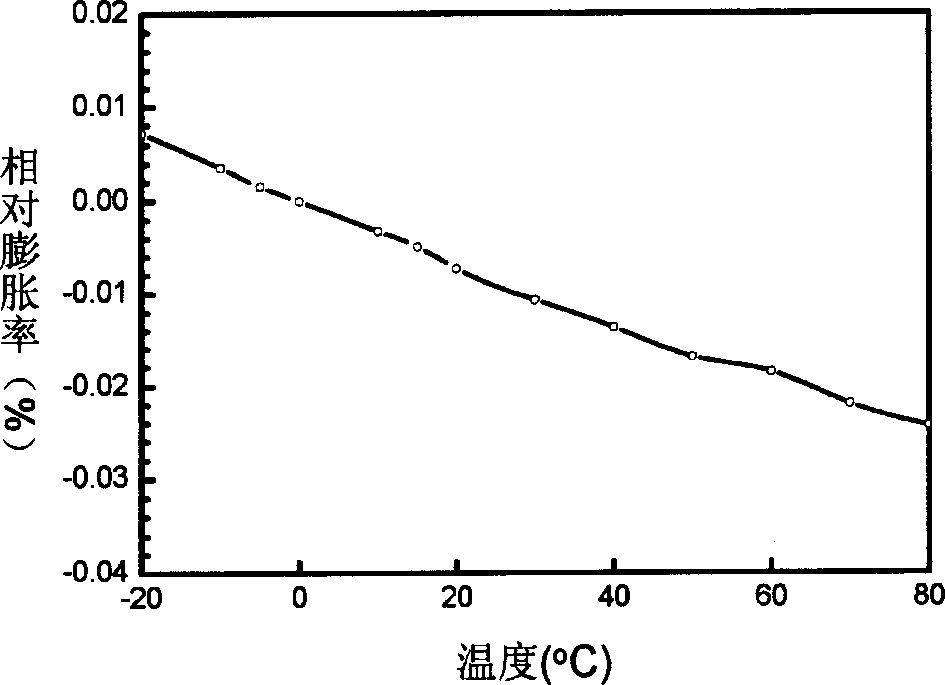
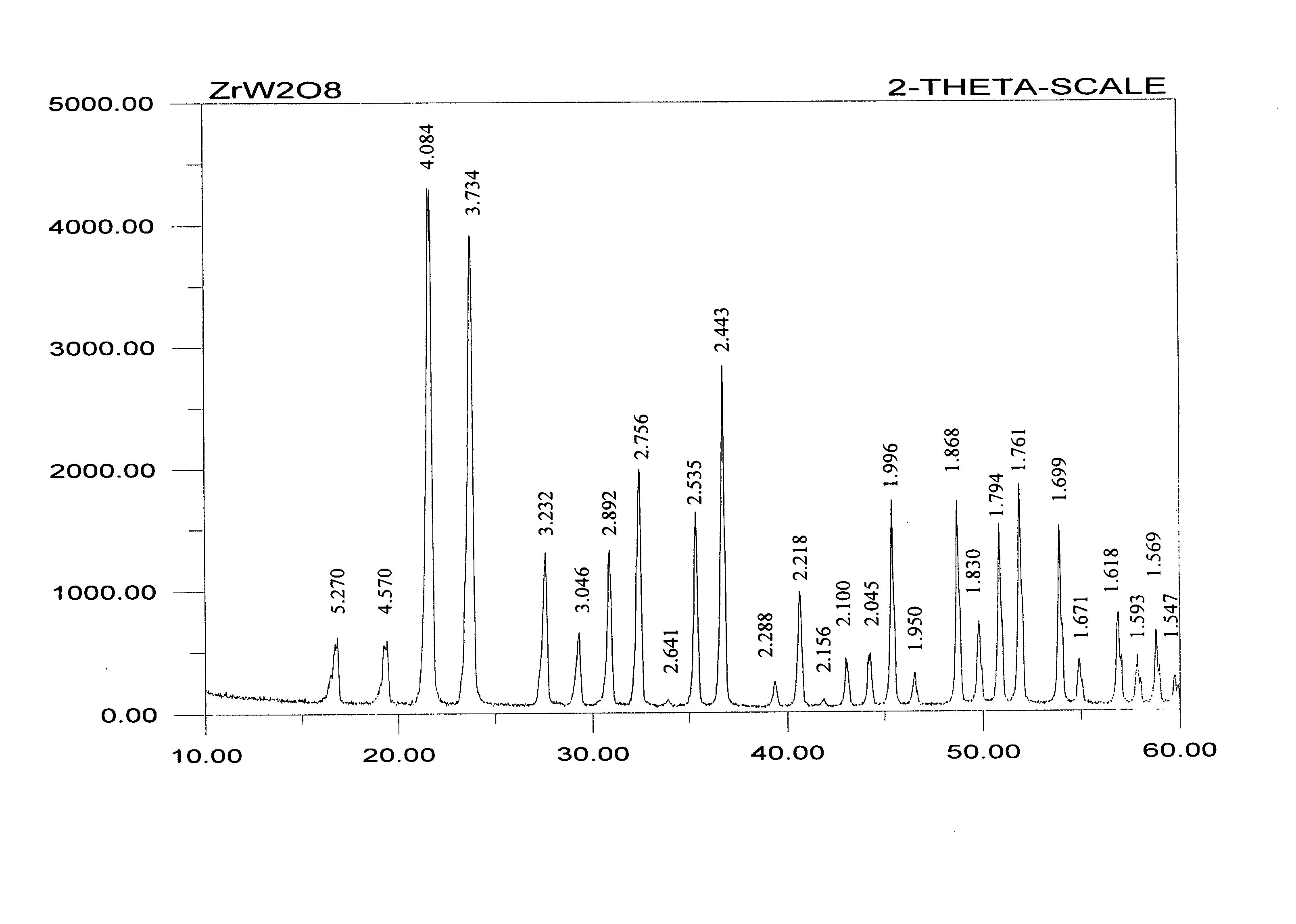
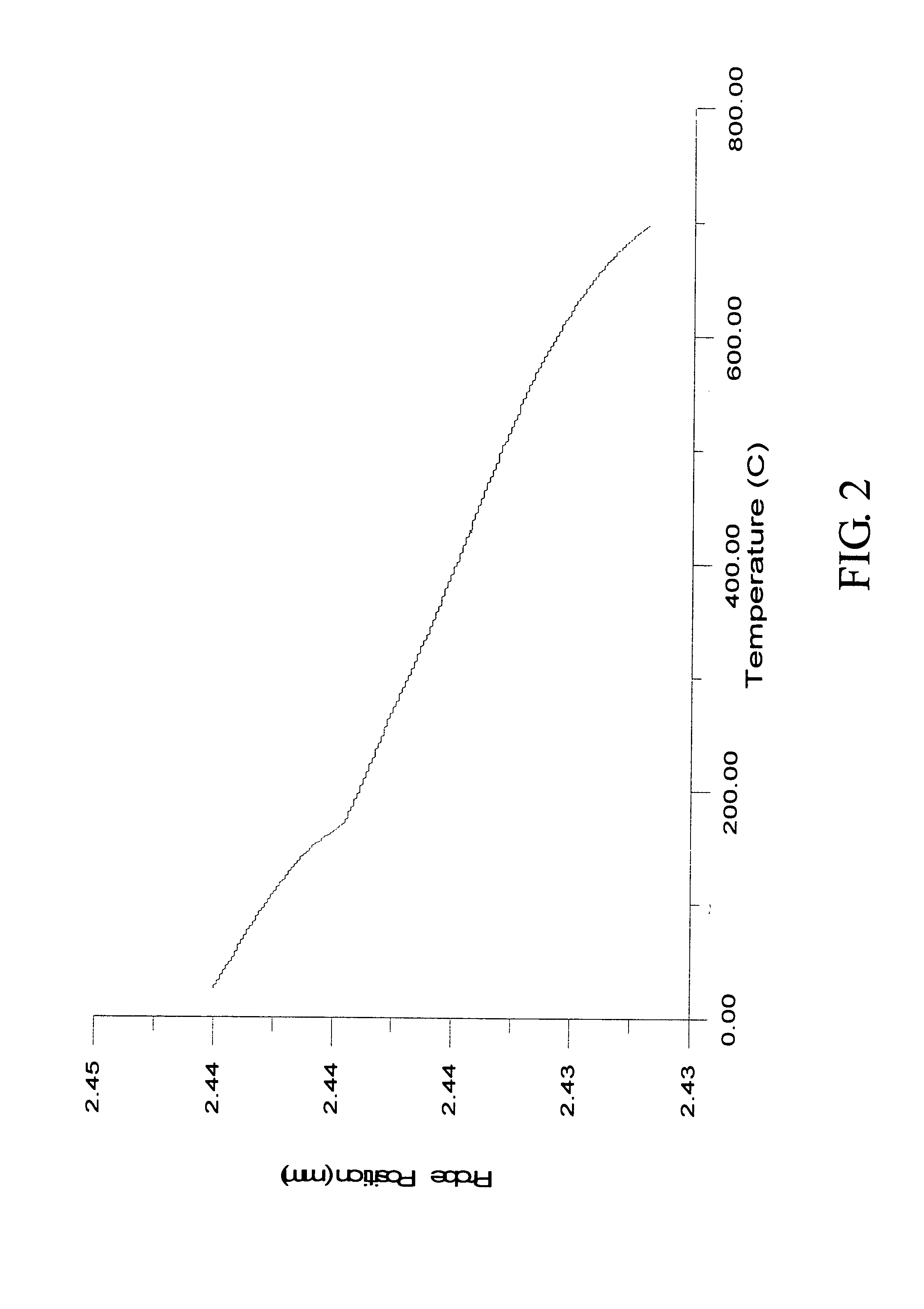
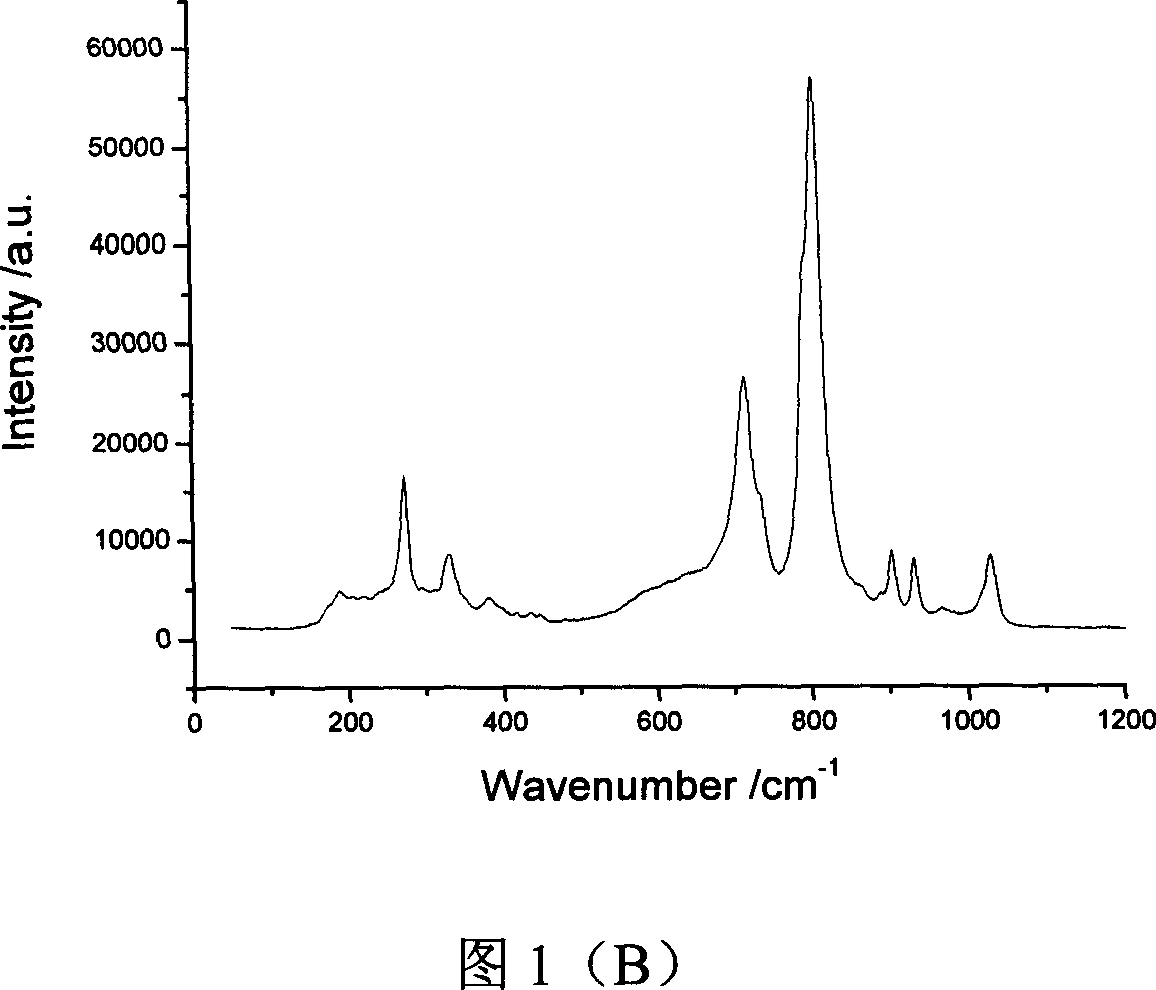
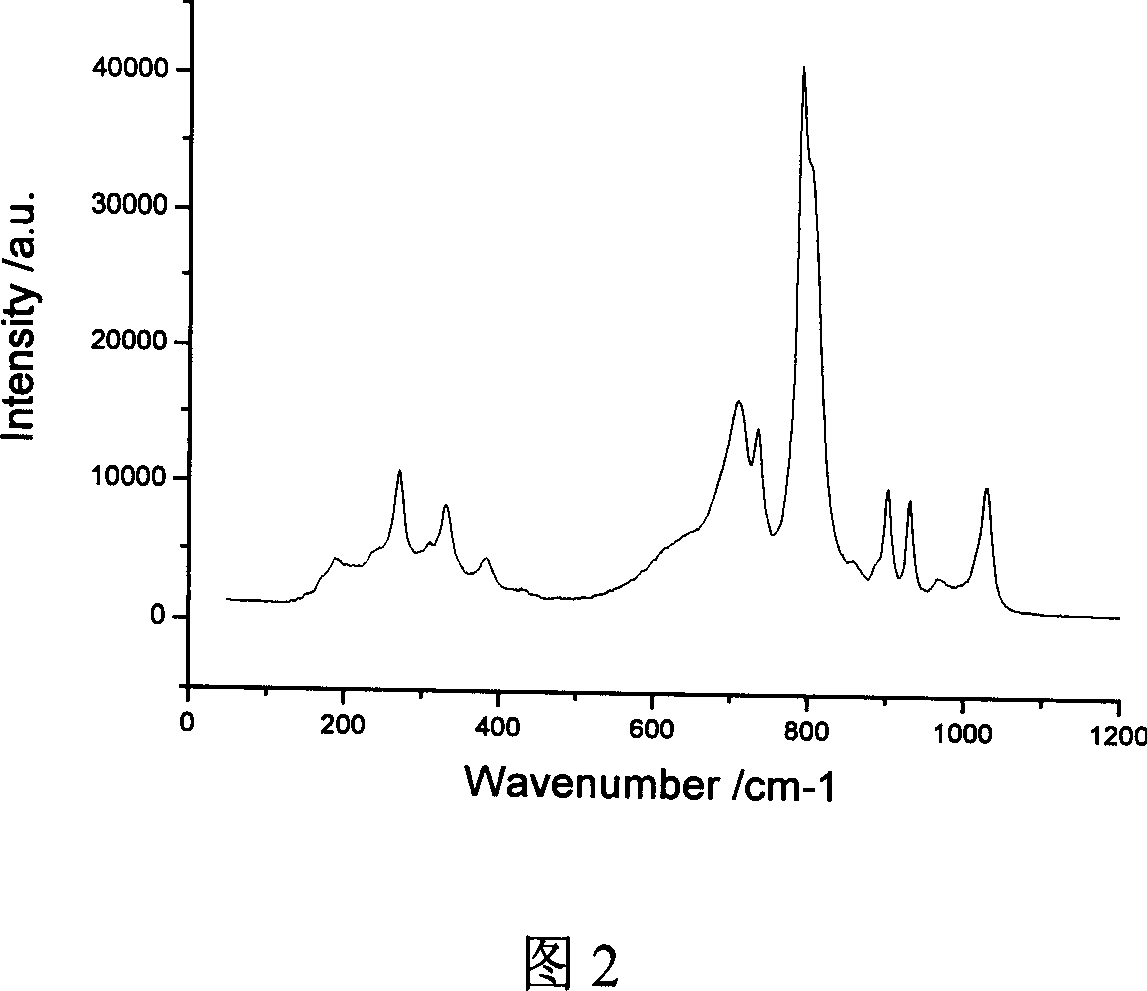
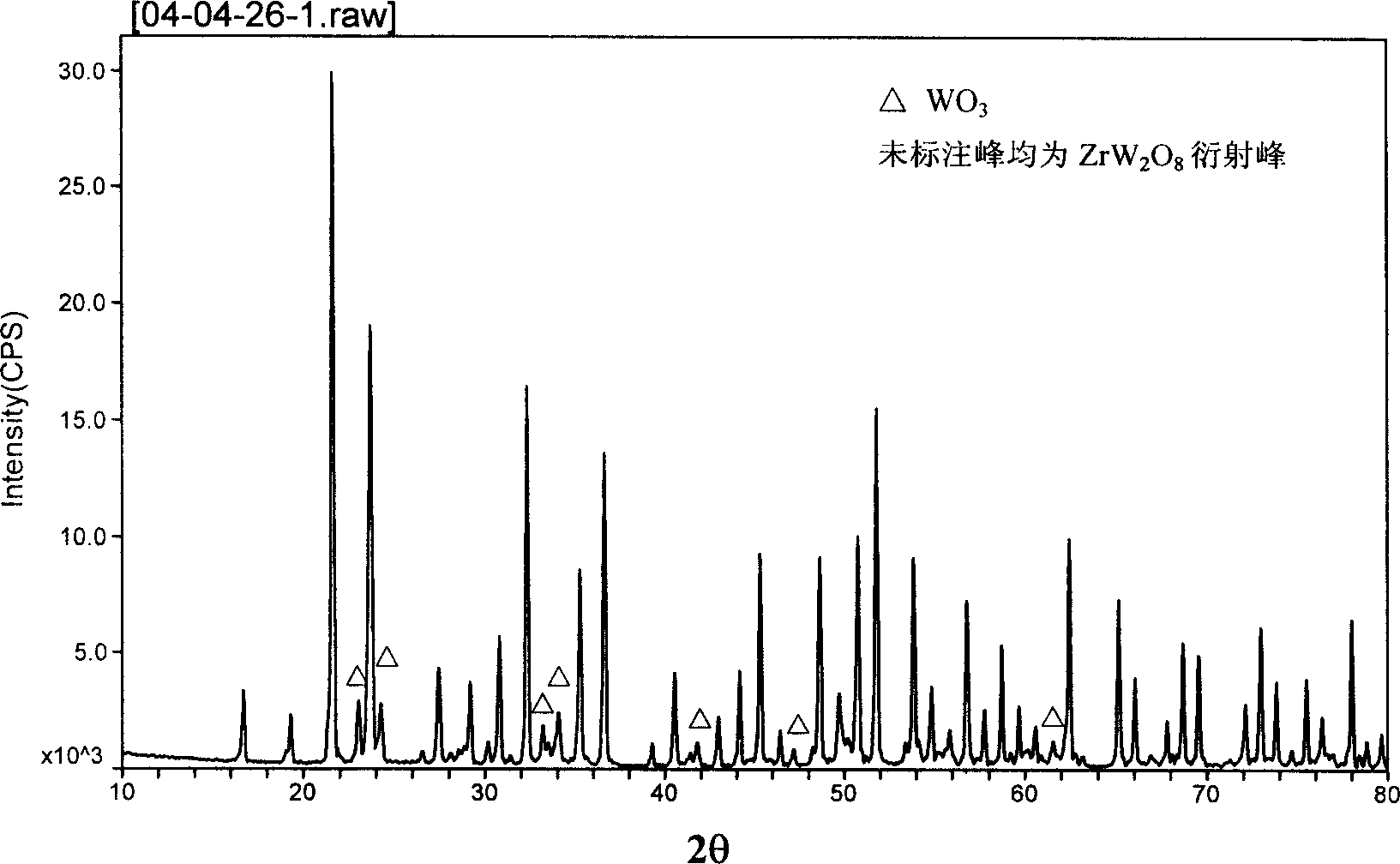
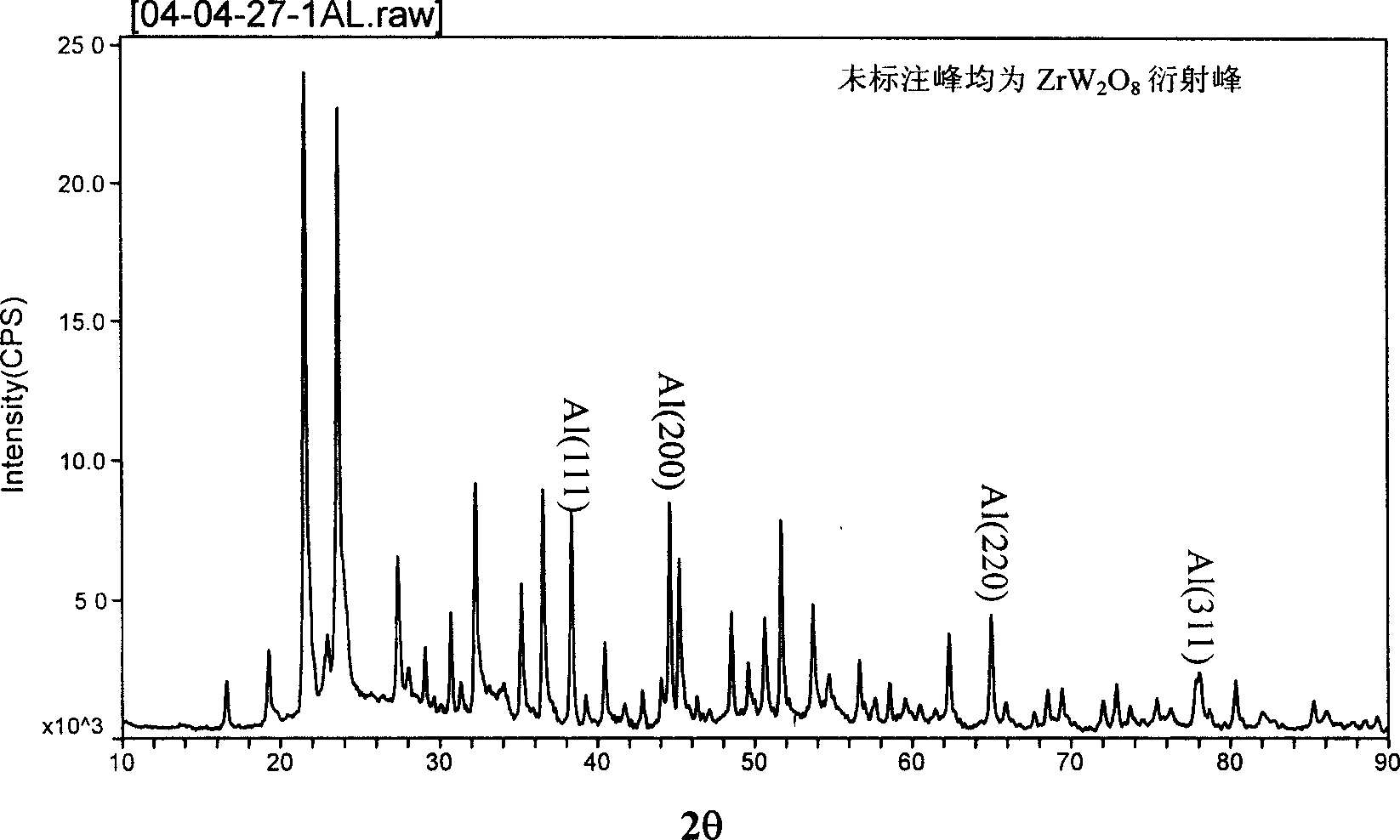
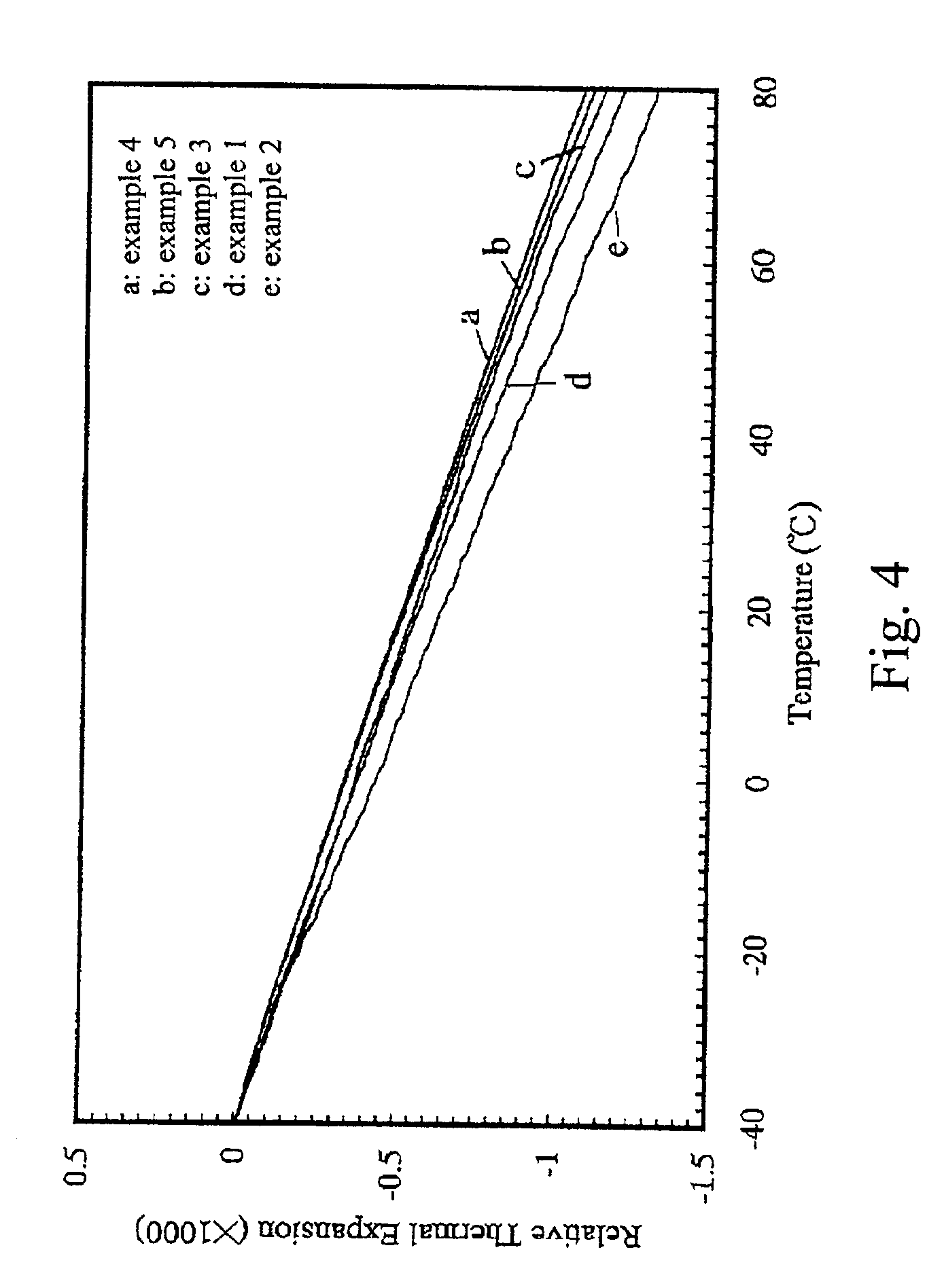
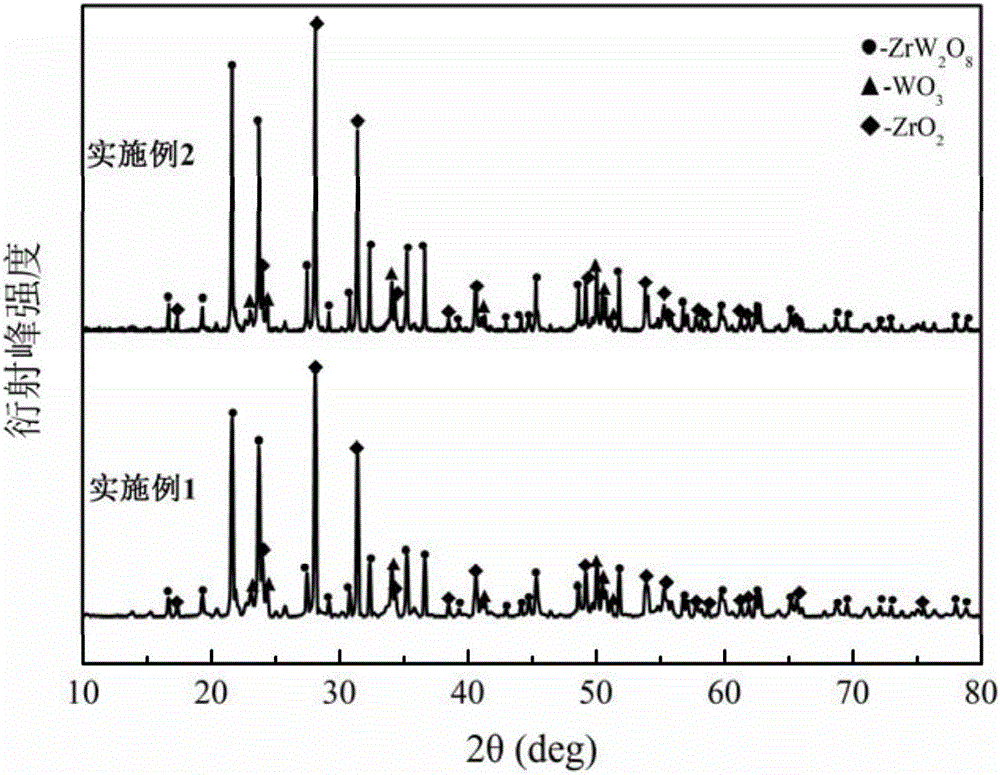
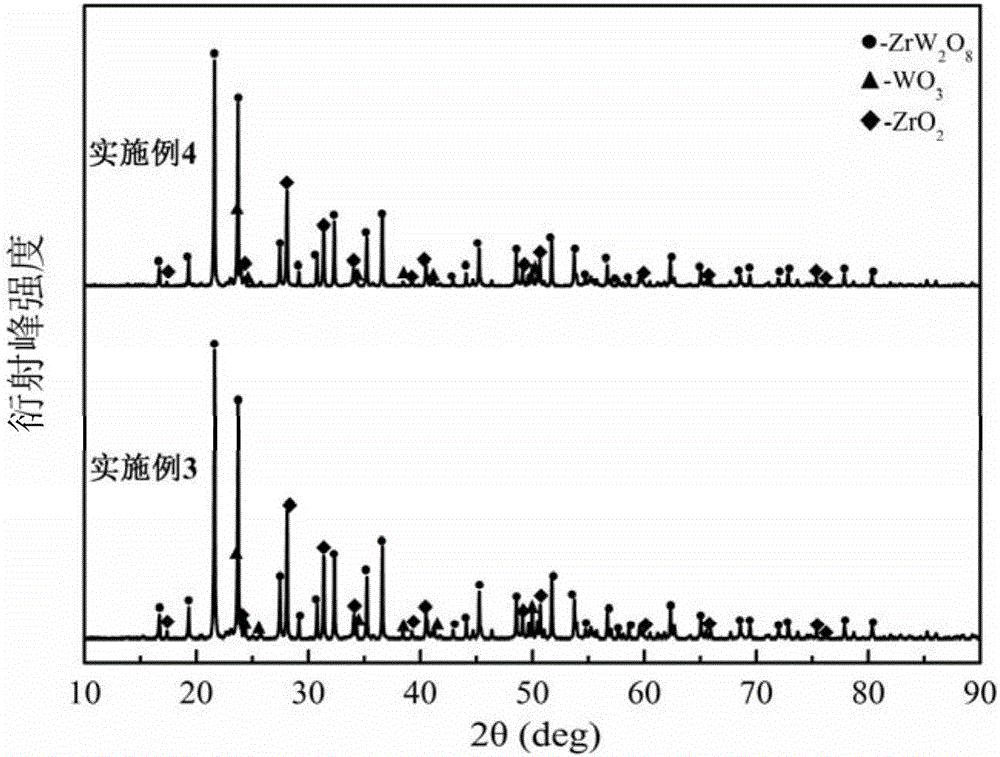
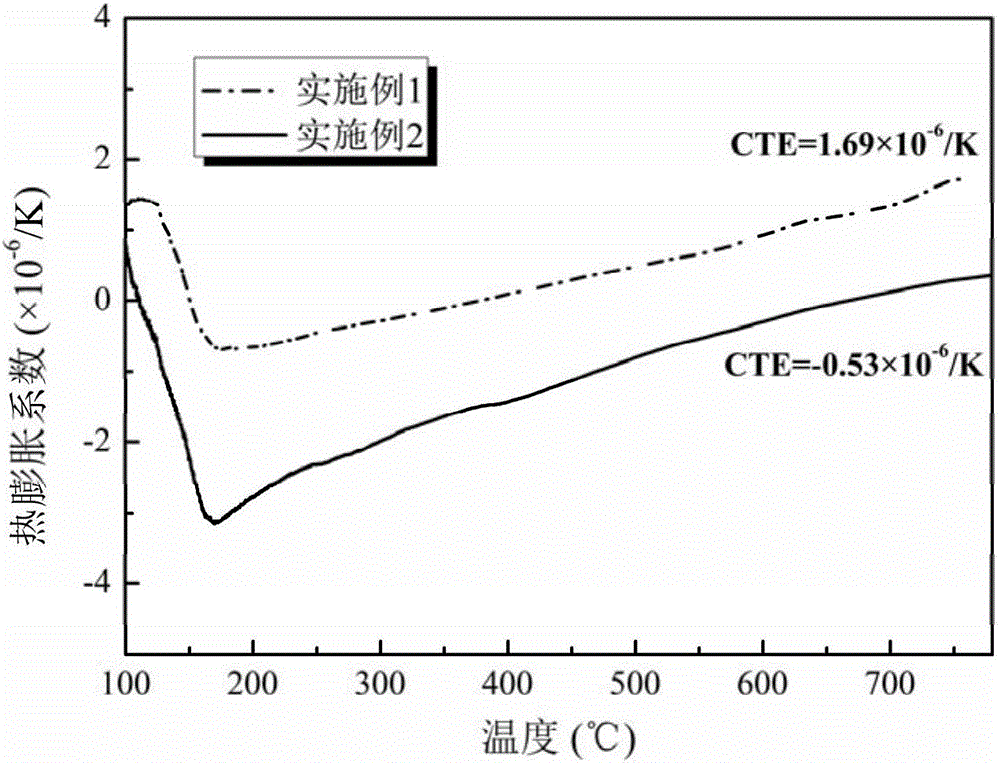
Zirconium tungstate (Zr(WO₄)₂) is a metal oxide with unusual properties. The phase formed at ambient pressure by reaction of ZrO₂ and WO₃ is a metastable cubic phase, which has negative thermal expansion characteristics, namely it shrinks over a wide range of temperatures when heated. In contrast to most other ceramics exhibiting negative CTE (coefficient of thermal expansion), the CTE of ZrW₂O₈ is isotropic and has a large negative magnitude (average CTE of -7.2x10⁻⁶K⁻¹) over a wide range of temperature (-273 °C to 777 °C). A number of other phases are formed at high pressures.
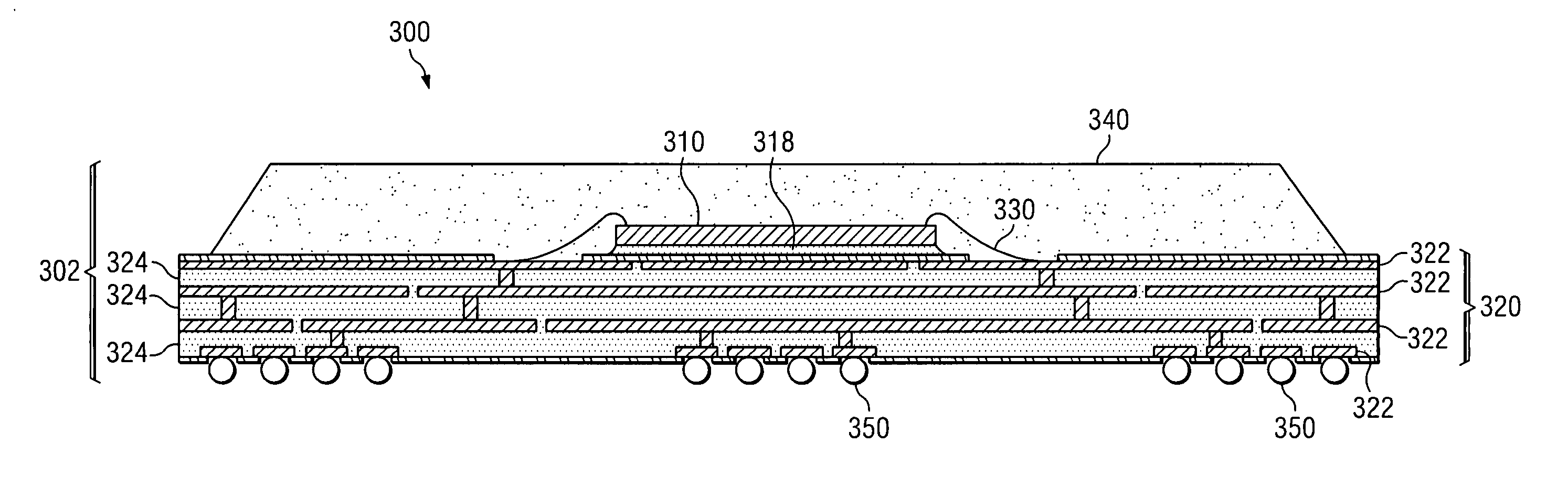
Low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) semiconductor packaging materials
InactiveUS20050110168A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTungstateSemiconductor package
A low-CTE packaging material for assembling a semiconductor die into a package and a method for assembling a semiconductor die into a package, in which the packaging material comprises a negative-CTE material. The low-CTE packaging material in accordance with the embodiments of the invention may be a die attach material, a lid attach material, or an encapsulant, such as a mold compound or glob-top material. Preferably, the negative-CTE material is a tungstate compound, such as zirconium tungstate, halfnium tungstate or a solution of zirconium and halfnium tungstate.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
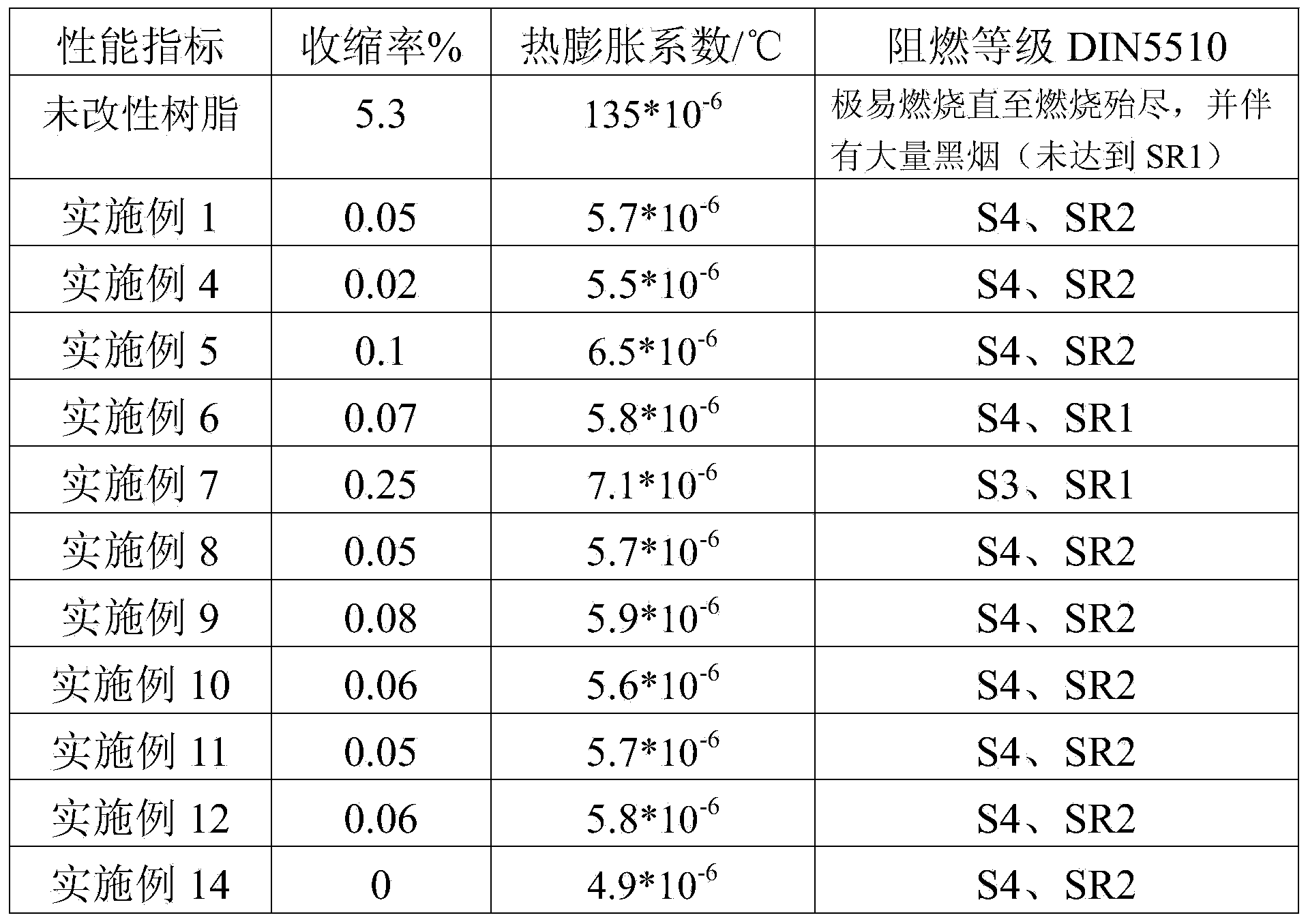
Novel electronic-grade polyimide film with low linear expansion coefficient and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of an electronic-grade polyimide film with low linear expansion coefficient. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that (1) the step-by-step condensation polymerization technology or the blending compounding technology is used for obtaining two or more polyamide acid glue solutions comprising rigid structures and soft structures at the same time and are different in rigidity and softness; (2) ultrafine inorganic whiskers, like zinc oxide whiskers, silicon carbide whiskers and zirconium tungstate whiskers, which are subjected to surface organic modification already and / or nanoparticle materials are smashed and cavitated through high-energy-density supersonic waves, and then the functional fillers are compounded with polybasic polyamide acid in an in-situ micro-nano mode; (3) the compounded glue solutions are subjected to filtration, vacuum defoamation, extrusion casting filming, chemical amidization or thermal amidization, infrared complete amidization, high-temperature thermal forming processing, corona processing and a reeling process, and therefore the electronic-grade polyimide film with the thickness being 7.5-125 micrometers, the linear expansion coefficient being 5-18ppm / DEG C, and good physical mechanical performance is obtained.
Owner:宏威高新材料有限公司 +1
Isotropic zero CTE reinforced composite materials
InactiveUS7105235B2Alter performance of antennaThin material handlingCeramicwareThermoplasticTungstate
A reinforced composite material, having isotropic thermal expansion properties and a low coefficient of thermal expansion over at least the temperature range of from about 0° C. to at least about 150° C., which composite material comprises in combination a first continuous phase comprising a three dimensional preformed bonded powder material reinforcement, including a bonding agent, and in which the bonded powder material is chosen from the group consisting of zirconium tungstate, hafnium tungstate, zirconium hafnium tungstate, and mixtures of zirconium tungstate and hafnium tungstate, and a second continuous phase matrix material chosen from the group consisting of aluminium, aluminium alloys in which aluminium is the major component, magnesium, magnesium alloys in which magnesium is the major component, titanium, titanium alloys in which titanium is the major component, engineering thermoplastics and engineering thermoplastics containing a conventional solid filler.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Method of preparing iolite honeycomb ceramic having relatively low thermel expansion coefficient
InactiveCN1785895AAdapt to the requirements of industrial productionSmall coefficient of thermal expansionExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusMicrowaveMetallic materials
The present invention relates to an improvement on preparation method of lower thermal expansion coefficient cordierite honeycomb ceramic which can be used as auto exhaust gas purifier carrier. Its process includes the following steps: synthesizing cordierite powder, synthesizing zirconium tungstate powder, mixing components, vacuum mixing mud, vacuum extruding, microwave forming, drying in drying oven, processing blank, high-temperature sintering and checking.
Owner:BEIJING AVIATION MATERIAL INST NO 1 GRP CORP CHINA AVIATION IND
Negative thermal-expansion coefficient adjustable laminated ceramic matrix composite and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1594207AAffect the intensity of useAffect the negative coefficient of expansionCeramic layered productsWater basedCeramic composite
The invention discloses a negative thermal-expansion coefficient adjustable laminated ceramic matrix composite and preparing method thereof consisting of, employing centrifugal casting and molding process, dispersing the negative expanding powder material whose component is cubic phase zirconium tungstate ZrW2O8 or doped and modified zirconium tungstate ZrW2O8 and near-zero expanding amorphous silicon oxide SiO2 powder into polyvinyl alcohol solution, so as to prepare zirconium tungstate powder slurry and silicon oxide powder slurry, employing a centrifugation deposition method to remove the water-based composition in the powder slurry, alternately depositing the zirconium tungstate powder and silicon oxide powder onto the filtration sheet, forming the blank of laminated composite material, finally proceeding high temperature sintering to obtain the compact laminated ceramic composite material.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for making negative thermal expansion material zirconium tungstate
InactiveUS20050101133A1Low cost of reagentsSimple processFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthWater insolubleWater soluble
A method for making negative thermal expansion material zirconium tungstate (ZrW2O8) comprise: (a)forming a gel wrapped solid product comprising a water-soluble zirconium compound, preferably zirconium oxyhalides or zirconium oxynitrates and a water-insoluble tungsten compound, preferably tungsten powder or tungsten oxide powder; and (b)heating the gel wrapped solid product to a temperature sufficient to form ZrW2O8; the temperature required for forming zirconium tungstate should be at least about 1165° C.; the upper limit of the temperature should be about 1250° C., and preferably should be about 1180˜1200° C.; and the time needed for the formation of zirconium tungstate is less than about 5 hours; this method has the advantages on enhancing the selectivity of the reactants, simplifying production process, reducing the cost of reagent, and facilitating the mass production for making ZrW2O8.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Thermally compensated fiber bragg grating mount
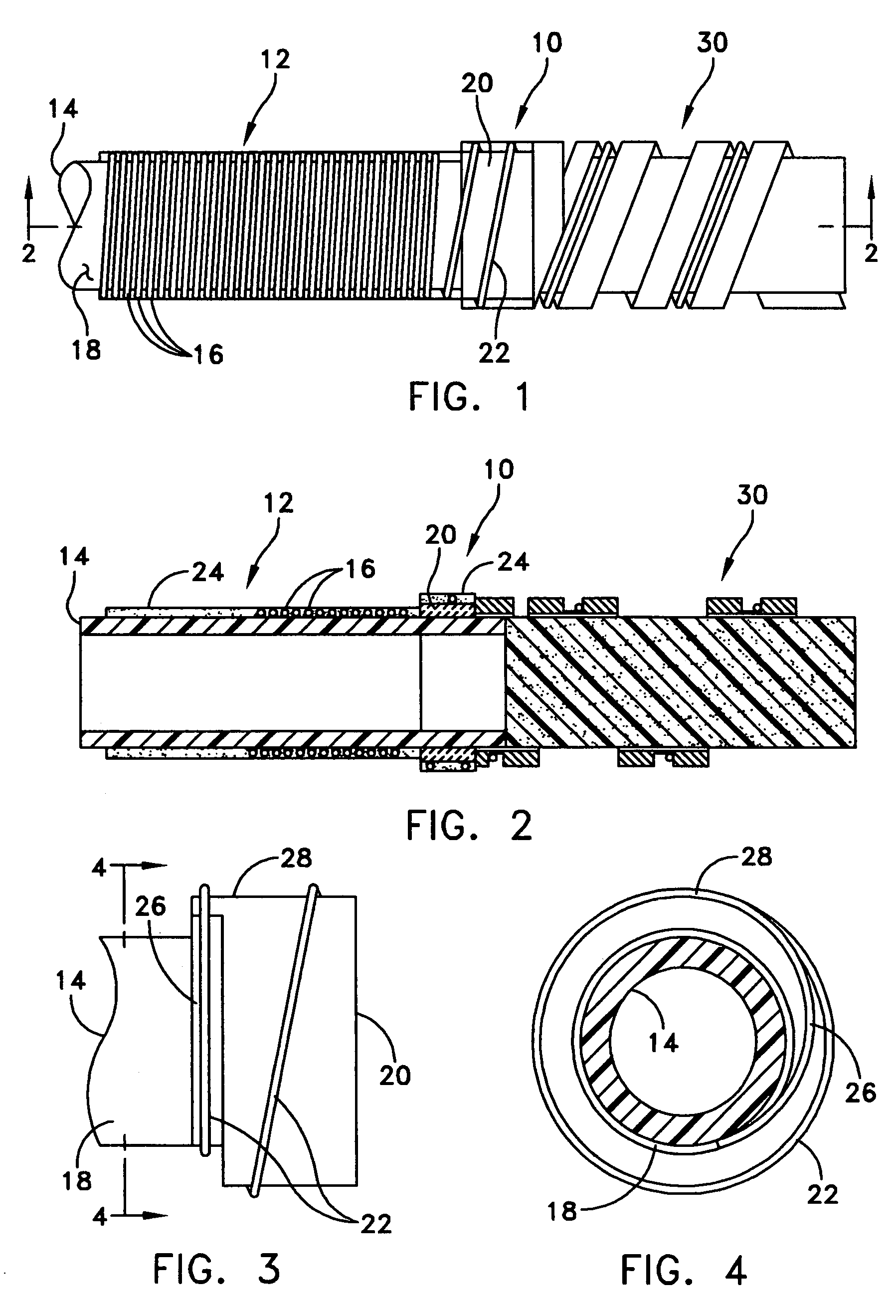
A thermally compensated fiber Bragg grating package is used with a fiber optic sensor. The package includes a Bragg grating mount connected at each end of a sensor mandrel. An optical fiber is wound around the sensor mandrel and a fiber portion having a Bragg grating therein is wound onto the mount. The mount is made of a rigid material having a negative coefficient of thermal expansion to minimize thermally induced spectral shifts. One example of the material includes zirconium tungstate. A coating material can be used to further adhere the optical fiber to the sensor mandrel and / or to the mount. The mount preferably includes a ramped groove to provide for a smooth transition from the sensor mandrel to the mount.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for preparing cesium tungstate of tungsten bronze structure
ActiveCN109368702AIncrease compaction densityDistortion activationTungsten compoundsAir atmosphereTungstate
The invention provides a method for preparing cesium tungstate of a tungsten bronze structure. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing cesium carbonate and tungsten oxide with deionized water so as to obtain a mixture A, adding a trace amount of sintering aids, and performing normal-temperature wet-method ball milling so as to obtain mixed slurry; (2) taking out the mixed slurry, drying, and carrying out thermal treatment on the dried material in a mixed atmosphere of H2 and N2 at 450-500 DEG C for 2-5 hours; (3) performing secondary sintering on the material obtained in step (2)so as to obtain a blue material, wherein the sintering conditions are that the sintering temperature is 800-1000 DEG C, the temperature keeping time is 1-4 hours, and an air atmosphere is provided; (4) carrying out ball milling and crushing on the blue material obtained in step (3), thereby obtaining blue cesium tungstate powder. By adopting the method, complex preparation processes in the prior art are simplified, the method is environmentally friendly, the cost is low, compared with a conventional solid-phase synthesis method, the method is simple to operate, and a process of one-time atmosphere protection sintering is avoided.
Owner:ANHUI SHENGHONG ELECTRONICS
Synthesis method of zirconium tungstate with minus thermal-expansion coefficient
InactiveCN1923705AAvoid pollutionNo pollution in the processZirconium compoundsTungsten compoundsSolid reactionMetal
The invention discloses a zirconium tungstate synthesizing method of negative heat-bulking coefficient material in the inorganic non-metal material synthetic technological domain, which comprises the following steps: blending ZrO2 and WO3 evenly with molar rate at 1:2-2.2; grinding the composite material for 60-120 min; sintering at 1280-1450 deg.c for 5-600min; cooling in the water rapidly.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Preparation of zirconium tungstate ceramic body products thereby and optical fiber grating temperature compensator
A process for preparing zirconium tungstate (ZrW2O8) ceramics includes the reacting between the superfine Zr compound and W compound particles and sintering, and features that the powdered monocrystal of ZrW2O8 is used as the crystal seeds in said reaction for simplifying process, shortening period and lowering sinter temp and cost. A modified ZrW2O8 ceramics with regulated thermal expandability is prepared by generating the second phase in the ZrW2O8 ceramics and can be used for the temp compensator of fibre Bragg garting (FBG).
Owner:BROPTICS TECHNOLOGY LTD
Preparation method of aluminium base zirconium tungstate particle composite material
InactiveCN1718815AHigh bonding strengthAchieve compositeParticle compositionUltimate tensile strength
A process for preparing Al-based ZrW2O8 (or SiCp=ZrW2O8) particle composition with high compactness and strength and near zero expansibility includes such steps as prefabricating the blank of ZrW2O8 (or SiCp=ZrW2O8) particles, preheating it, penetrating the molten Al in the gaps between said particles, and quick solidifying.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing low-temperature lead-free near zero expansion microcrystalline ceramic coating
The invention relates to a method for preparing a low-temperature lead-free near zero expansion microcrystalline ceramic coating, belonging to the technical field of specific and functional ceramic. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly performing dry mixing on one or two of low temperature clinker 2, spodumene melt or eucryptite melt in an arbitrary proportion, one or two or three of low temperature clinker I, zirconium tungstate powder, an additive I or an additive 2 in an arbitrary proportion and a nucleating agent; melting the mixture in a Muffle furnace, and preserving the temperature of between 950 and 1,200 DEG C for 0.5 to 1h; pouring the molten glass fluid on a preheated stainless steel plate; continuously heating the molten glass fluid to 750 DEG C in the Muffle furnace at the temperature of between 560 and 650 DEG C, and preserving the temperature for 1 to 4h; naturally cooling the glass fluid to room temperature, crushing to obtain composite ceramic powder; adding a plasticizing agent and deionized water into the composite ceramic powder to prepare slurry; and coating the slurry on the surface of a matrix to sinter at the temperature of between 600 and 650 DEG C to obtain a composite inorganic microcrystalline ceramic coating. The method is scientific and reasonable, simple and practicable, and is convenient to implement; and the prepared coating material is water proof, is lead free, can be used at low temperature, and has near zero linear expansion coefficient.
Owner:ZHONGCAI HIGH NEW MATERIAL +1
Cerium doping zirconium tungstate negative heat expansion conductive ceramic powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101186500APrevent volatilizationHigh purityNon-metal conductorsCe elementZirconium tungstate
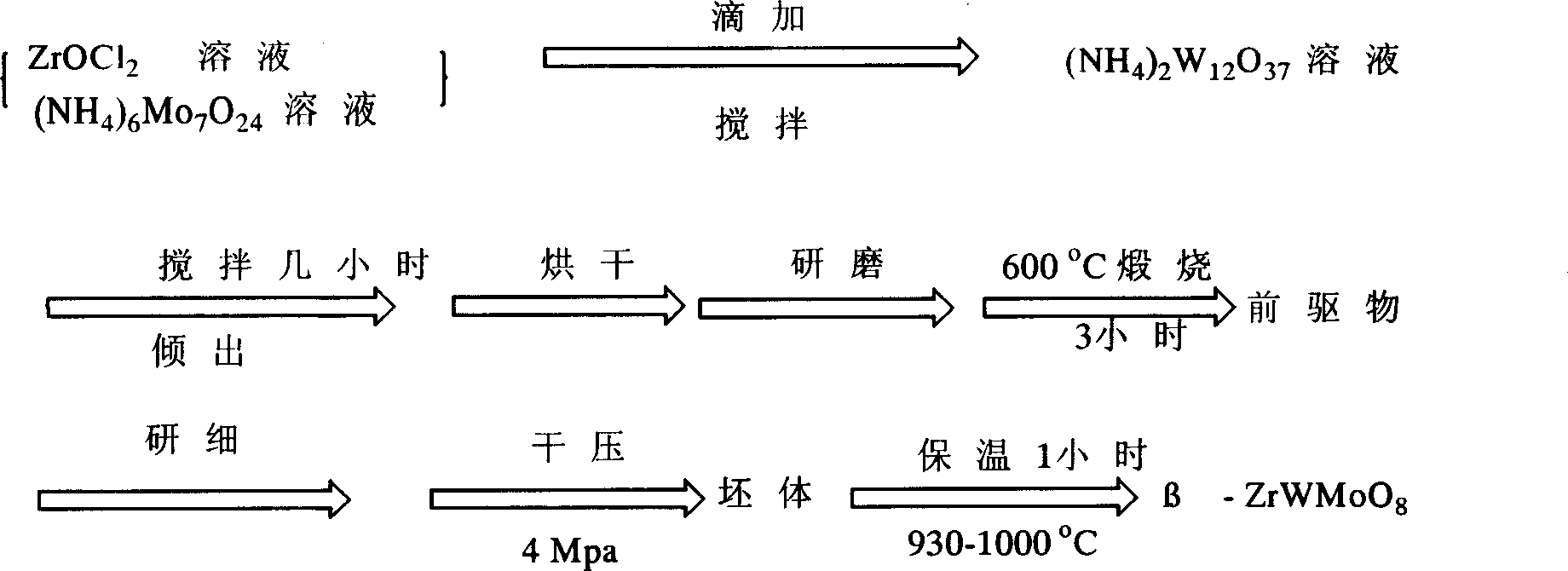
The invention provides a negative-thermal expansion and conductive ceramic powder body of Ce-doped zirconium tungstate and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises the component: Zr1-xCexW2O8 (wherein, the x is more than zero and less than or equal to 0.02); the preparation adopts the components ZrOCl2.8H2, 5(NH4)2O.12WO3.5H2O and (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6 as precursors, and uses a hydrothermal synthetic method. The negative-thermal expansion and conductive ceramic powder body of Ce-doped zirconium tungstate of the invention has not only negative thermal expansion, but also conductivity under the temperature of 350 to 700 DEG C. Compared with the traditional sintering method, the hydrothermal synthetic method avoids high-temperature sintering process, thus saving energy and simplifying synthetic technique.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing porous zirconium/aluminum tungstate composite material by spark plasma sintering
The invention discloses a method for preparing a porous zirconium / aluminum tungstate composite material by spark plasma sintering, relates to a preparation method for a porous zirconium / aluminum tungstate composite material, and aims to solve the problems of large fluctuation of a thermal expansion curve of a conventional aluminum-base zirconium tungstate particle composite material and high thermal expansion value. The method comprises the following steps: 1, weighing 50 to 60 percent of zirconium tungstate powder and 40 to 50 percent of aluminum powder in volume fraction; 2, performing ball-milling mixing to obtain a ball-milled mixed material; 3, performing drying and sieving to obtain mixed powder; 4, performing spark plasma sintering to obtain the porous zirconium / aluminum tungstate composite material. The method has the advantages that 1, the crystal completeness of zirconium tungstate is guaranteed, and direct interface reaction between the zirconium tungstate and aluminum is effectively inhibited; 2, a sintering aid is not added; 3, generation of a gamma phase is greatly reduced; 4, the porosity is higher while the axial pressure is lower, and the thermal expansion value is smaller while the content of the gamma phase is lower. The method is mainly used for preparing the porous zirconium / aluminum tungstate composite material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Novel method for preparing zirconium tungstate powder
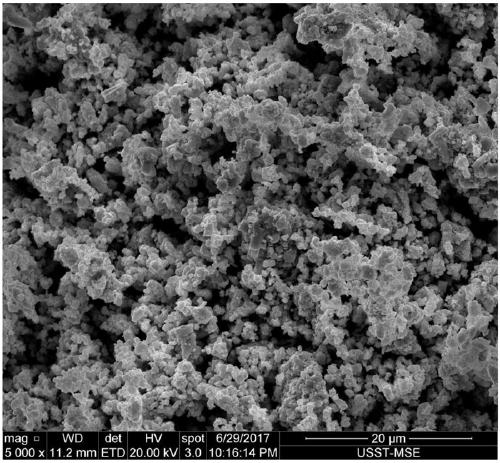
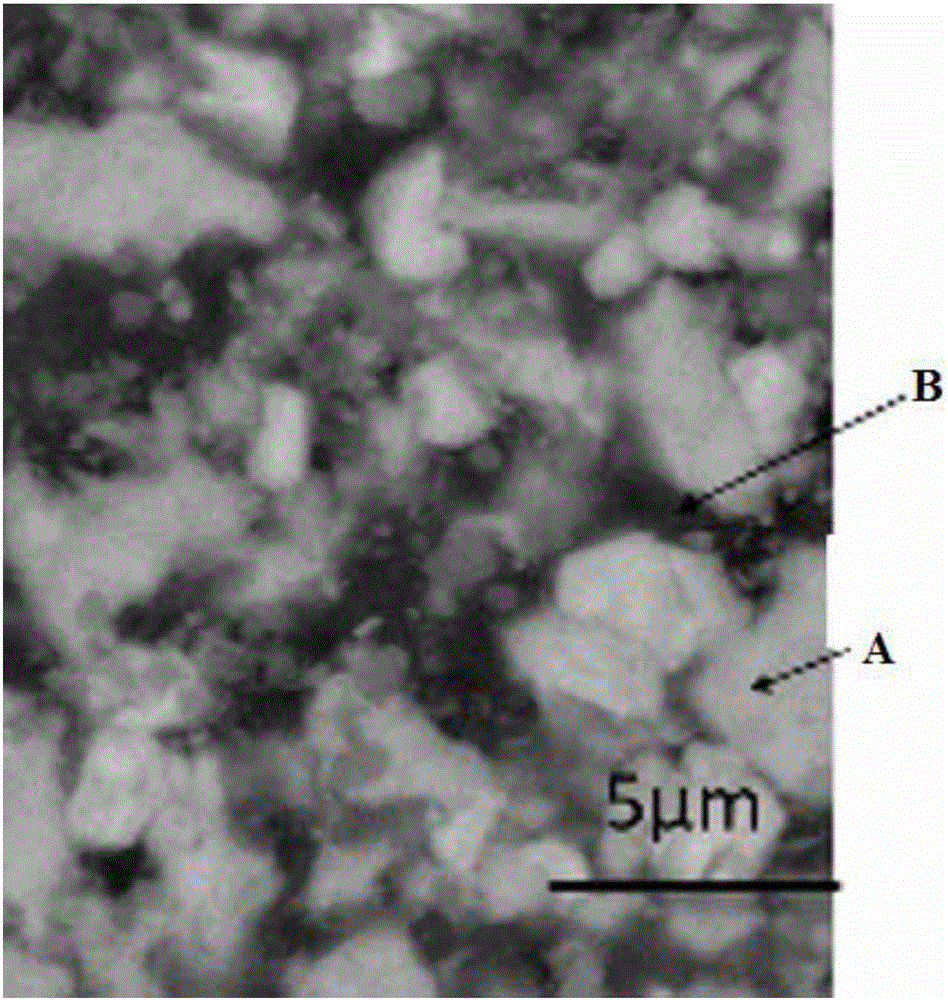
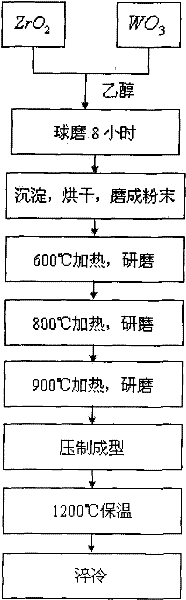
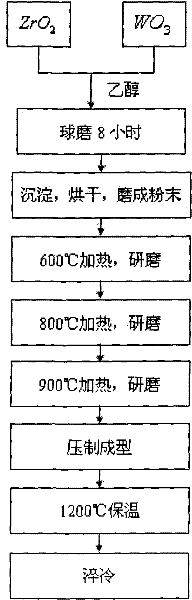
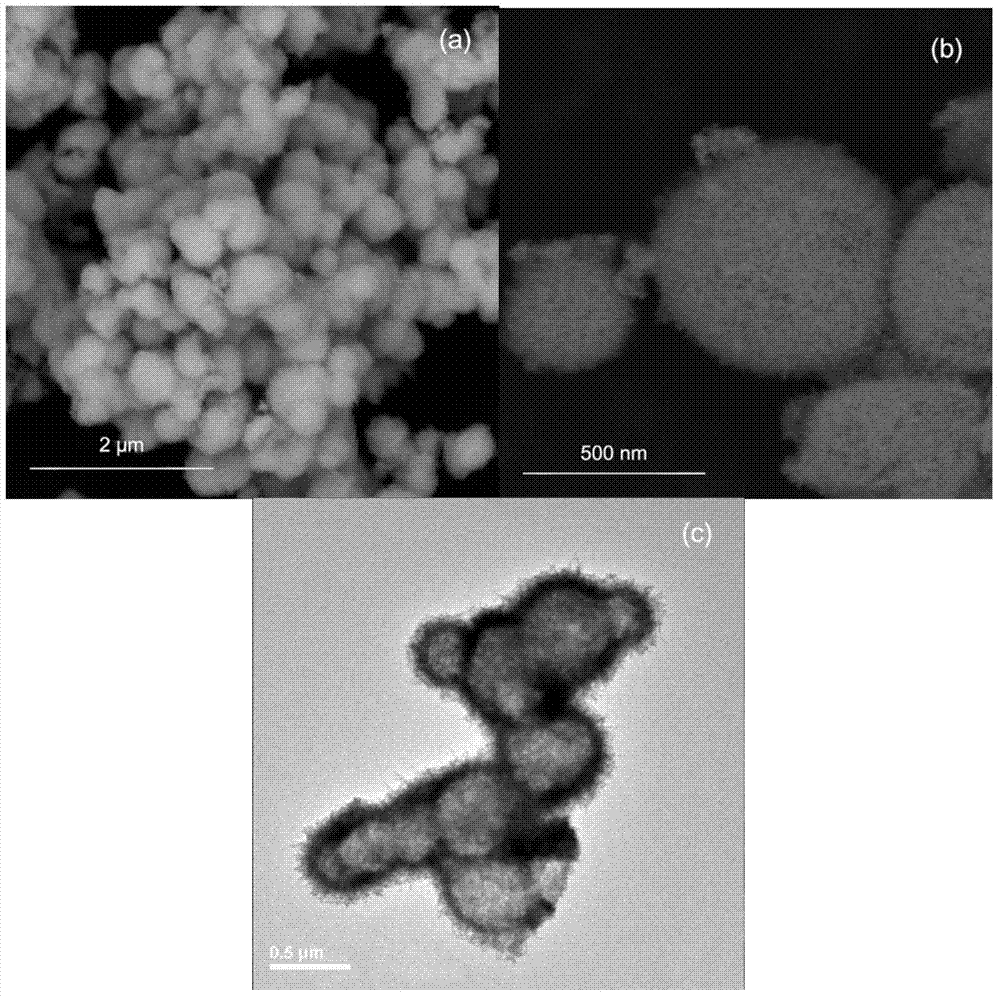
The invention relates to a novel method for preparing zirconium tungstate powder, which is characterized by comprising the following process steps of: weighing in a stoichiometric ratio of ZrO2 to WO3 of 1:2, putting the ZrO2 and WO3 into a resin ball mill, adding absolute ethanol serving as a solvent, performing ball milling in a ball mill for 8 hours, standing for sedimentation, removing an upper-layer clear solvent, drying in an oven, putting powder into a quartz crucible, heating at 600DEG C for 4 hours, taking out, and cooling in the air; grinding for 40 minutes; regulating the temperature to be 800DEG C, heating for 8 hours, cooling together with a furnace, taking out, and grinding for 40 minutes; heating at 900DEG C for 12 hours, cooling together with a furnace, taking out, and grinding for 40 minutes; and putting ZrO2 and WO3 mixed powder into a mold with the diameter of 60mm, pressing under the pressure of 125MPa into a round sheet, and keeping the temperature of 1,220DEG C for 3 hours. Compared with the prior art, the novel method has the advantages that: the grain size is 0.5-1mu m, the purity is high, and the average coefficient of linear expansion is -5.33*10<-6> / K in a section of 20-700DEG C.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAHAN NEW MATERIAL TECH
Isotropic zero CTE reinforced composite materials
InactiveUS20050223846A1Alter performance of antennaThin material handlingCeramicwareThermoplasticTungstate
A reinforced composite material, having isotropic thermal expansion properties and a low coefficient of thermal expansion over at least the temperature range of from about 0° C. to at least about 150° C., which composite material comprises in combination a first continuous phase comprising a three dimensional preformed bonded powder material reinforcement, including a bonding agent, and in which the bonded powder material is chosen from the group consisting of zirconium tungstate, hafnium tungstate, zirconium hafnium tungstate, and mixtures of zirconium tungstate and hafnium tungstate, and a second continuous phase matrix material chosen from the group consisting of aluminium, aluminium alloys in which aluminium is the major component, magnesium, magnesium alloys in which magnesium is the major component, titanium, titanium alloys in which titanium is the major component, engineering thermoplastics and engineering thermoplastics containing a conventional solid filler.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES
2-substituted cubic-phase zirconium tungstate solid solution temperature-sensitive dispersion compensation porcelain body and preparing method therefor
This invention relates to one kind of disubstituted cube zirconium tungstate solid solution temperature sensitive dispersion compensation thermal shrinking ceramic body and its preparation method. Binding sol-gel method and high temperature solid phase method are used in this invention to make solid solution ceramic, its chemical formula is (Zr1-xAx)(W2-yMoy)O8-delta, and A equals to Yb,Er,Dy,Eu,Ce,Ga,Mn,Cu,Zn etc. X equals to 0-0.1, y equals to 0-1.3, delta equals to 0-0.1. The ceramic body with basic structure cube phase ZrW208 has linear thermal shrinking character of isotropy, good damp resistance character, its thermal lag character is low, thermoshock resistance is good, which can be used as no heat source temperature sensitive dispersion compensation compact ceramic basal body of Prague optical grating of adjustable minus thermal expansion coefficient.Its preparation technique is simple, manufacturing condition is easy to control, and material thermal shrinking and other physical property can be controlled by adjusting its components.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
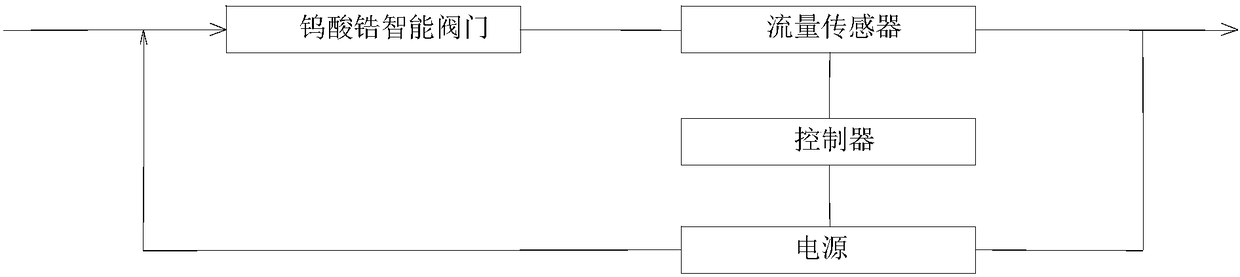
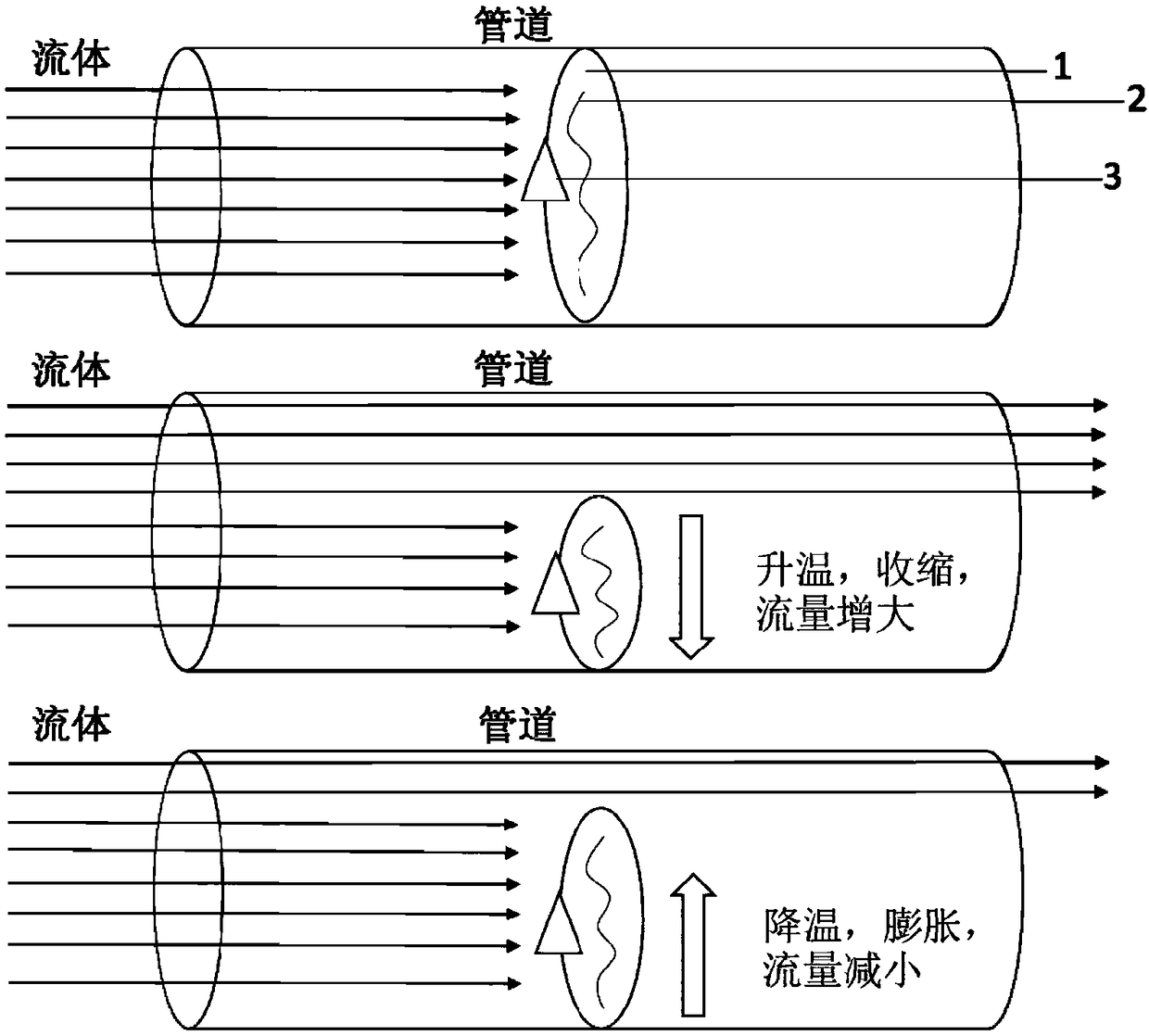
Intelligent valve made of zirconium tungstate negative thermal expansion material
PendingCN108167469APrecise TuningHigh temperature resistantDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringTemperature resistance
The invention discloses an intelligent valve made of a zirconium tungstate negative thermal expansion material. The intelligent valve is made of the composite material formed by combining zirconium tungstate and graphene. An electric heating wire is arranged in the valve, and the valve is connected to a control circuit. The valve is prepared through a 3D printing technology. A flow sensor is installed in the pipeline, and a controller is arranged and connected with the flow sensor. When the flow in a pipeline reaches a lower threshold, a variable voltage power source supplies electricity to the valve made of the intelligent material, the valve structure is heated, the material structure is driven to generate a heat-shrinkable effect, a channel is opened, and the flow is increased. The novel material serve as the core structure of the valve, the zirconium tungstate negative thermal expansion material and a graphene ultralight material are combined to achieve high temperature resistance,high conductivity and good mechanical properties, the effect of accurately regulating the flow in the pipeline can be achieved, and thus the intelligent valve can be applied to flow control of the pipeline under various environments and has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
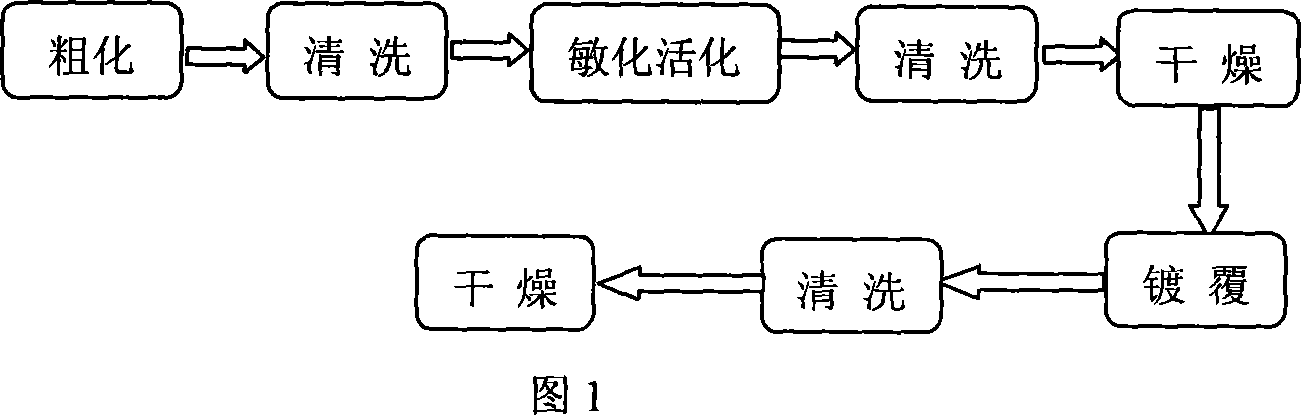
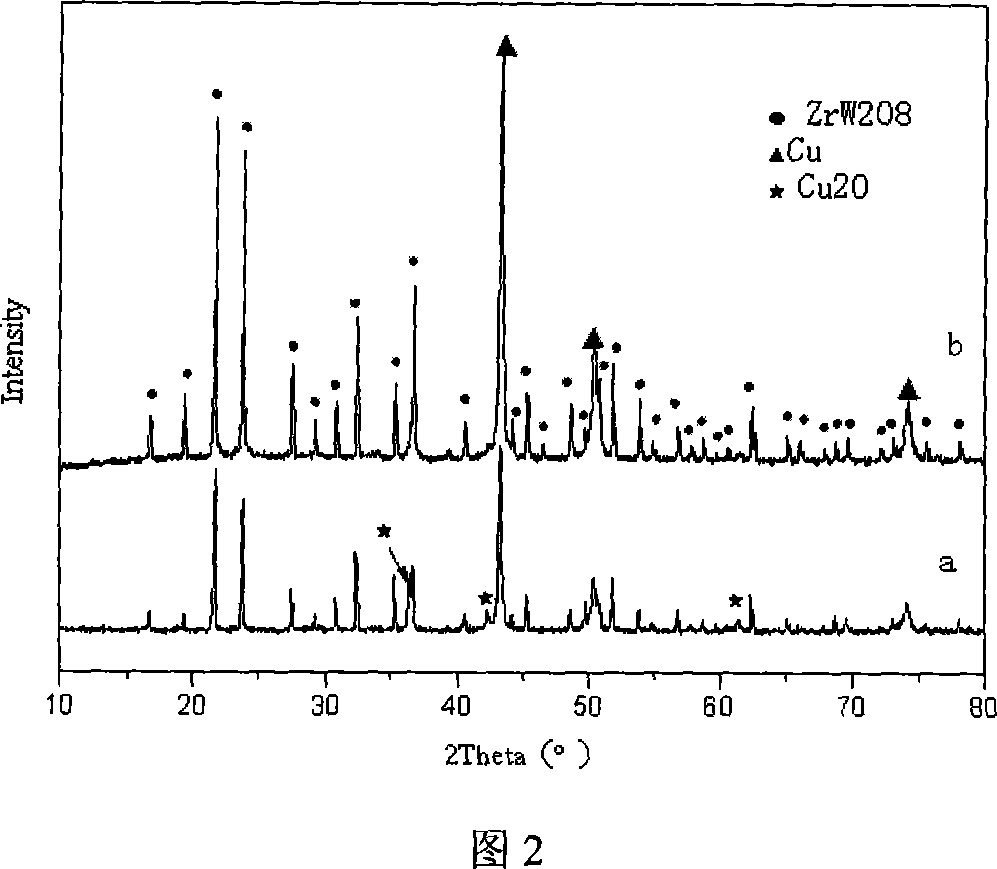
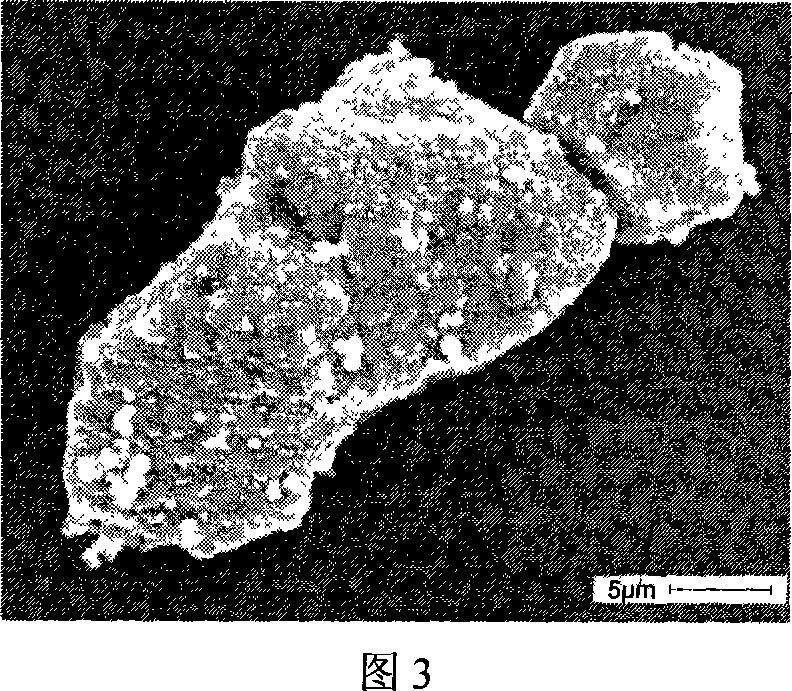
Method for promoting preprocessing of copper-clad zirconium tungstate composite powder
InactiveCN101067201AEasy to synthesizeSynthesis fastLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingVery large scale integrated circuitsPretreatment method
The present invention relates to powder coating technology, and is especially pre-treatment process for promoting cladding of zirconium tungstate (ZrW2O8) powder with copper. The micron level ZrW2O8 powder is surface roughened, sensitized and activated before it is clad chemically with copper powder under the irradiation of ultrasonic wave. The present invention makes it possible to clad ZrW2O8 powder easily with compact copper layer to prepare composite powder, and has simple technological process and high cladding effect, and the composite powder may be used in be used in producing substrate of SLSI and electronic device.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
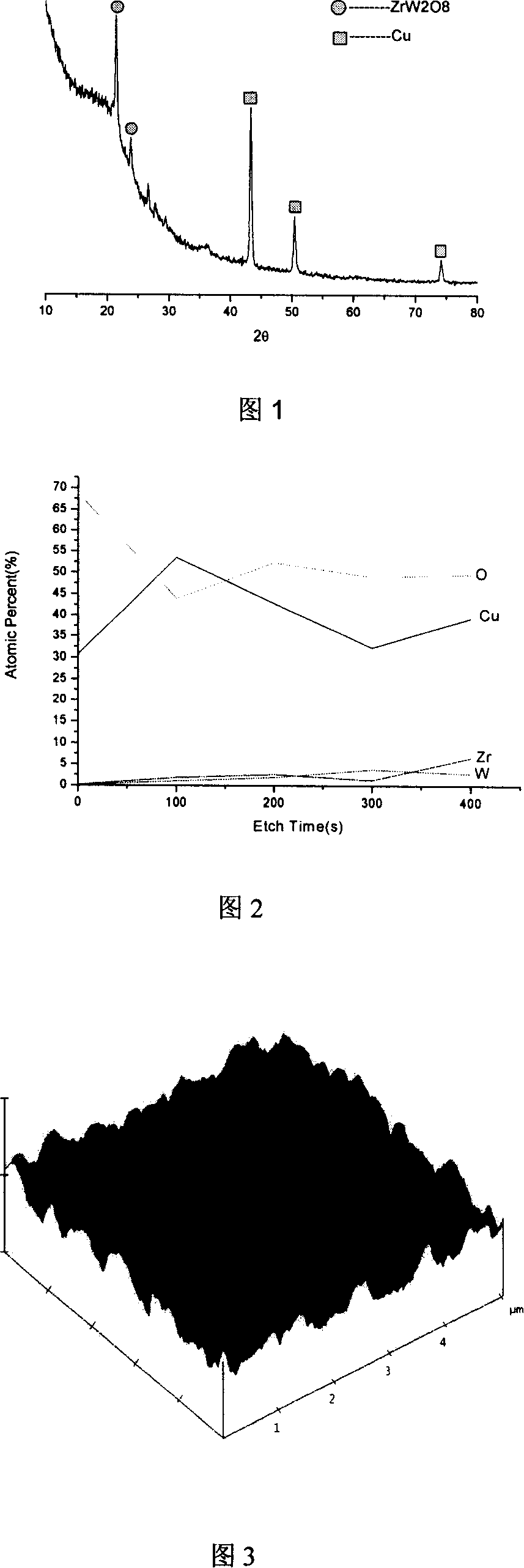
Method for preparing zirconium wolframic acid-copper gradient composite film
A process for preparing zirconium tungstate-copper gradient composite films relates to the technical field of composite film preparation, and comprises: preparing magnetic-control sputtering targets firstly; then conducting surface activation treatment on a mono-crystal Si substrate with the conventional technology; placing the composite oxide target, copper target and the silicon slice respectively into a main sputtering room and a sample-introducing room; vacuumizing the main sputtering room and the sample introducing room; pre-sputtering on the oxide target for clearing away impurities on the surface; adjusting the volume ratio of argon to oxygen to be between zero and one, the distance between the base material and the target to be 5 to 15cm, and the sputtering power to be 130 to be 250W for striking sputtering; setting the sputtering power of the composite oxide plated target to be 200 to 280W and of the Cu target to be 50 to 70W; for every hour, increasing the sputtering power of the Cu target by 10 to 20W while decreasing the sputtering power of the composite oxide target by 20 to 50W; taking the sample out from the main sputtering room after sputtering; conducting heat treatment on the film. Thereby a ZrW2O8 / Cu gradient composite film is obtained. The present invention has the advantages of simple process, easy implementation, short synthesis time and low post heat-treatment temperature.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Hydrothermal synthesis method of nano-scale zirconium tungstate hollow spheres
ActiveCN104495939AUniform particle sizeGood negative expansion performanceMaterial nanotechnologyTungsten compoundsAmmonium metatungstateHydrothermal synthesis
The invention discloses a hydrothermal synthesis method of nano-scale zirconium tungstate hollow spheres, wherein the hydrothermal synthesis method comprises the following steps: according to the stoichiometric ratio of ZrW2O8, respectively weighing zirconium oxychloride and ammonium metatungstate, and respectively preparing a zirconium oxychloride aqueous solution and an ammonium metatungstate aqueous solution; adding the zirconium oxychloride aqueous solution while stirring the ammonium metatungstate aqueous solution, stirring and preheating at the temperature of 60-70 DEG C, then adding a hydrochloric acid solution, stirring and heating at the temperature of 80-100 DEG C, and thus obtaining a zirconium tungstate precursor suspension liquid; and carrying out a hydrothermal reaction on the zirconium tungstate precursor suspension liquid at the temperature of 170-190 DEG C, then cooling, collecting a precipitate, washing to remove Cl<->, drying the precipitate, calcining at the temperature of 800-1000 DEG C, and thus obtaining the product. The negative-thermal-expansion zirconium tungstate nano hollow spheres are prepared at the low temperature by adopting the hydrothermal synthesis reaction, nano-scale regular particles are obtained, the density of zirconium tungstate is reduced, and the nano-scale zirconium tungstate hollow spheres have a great application potential in the field of aeronautics and astronautics.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Niobium-zirconium tungstate composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102492885AImprove high temperature strengthLower sintering temperatureNiobiumRoom temperature
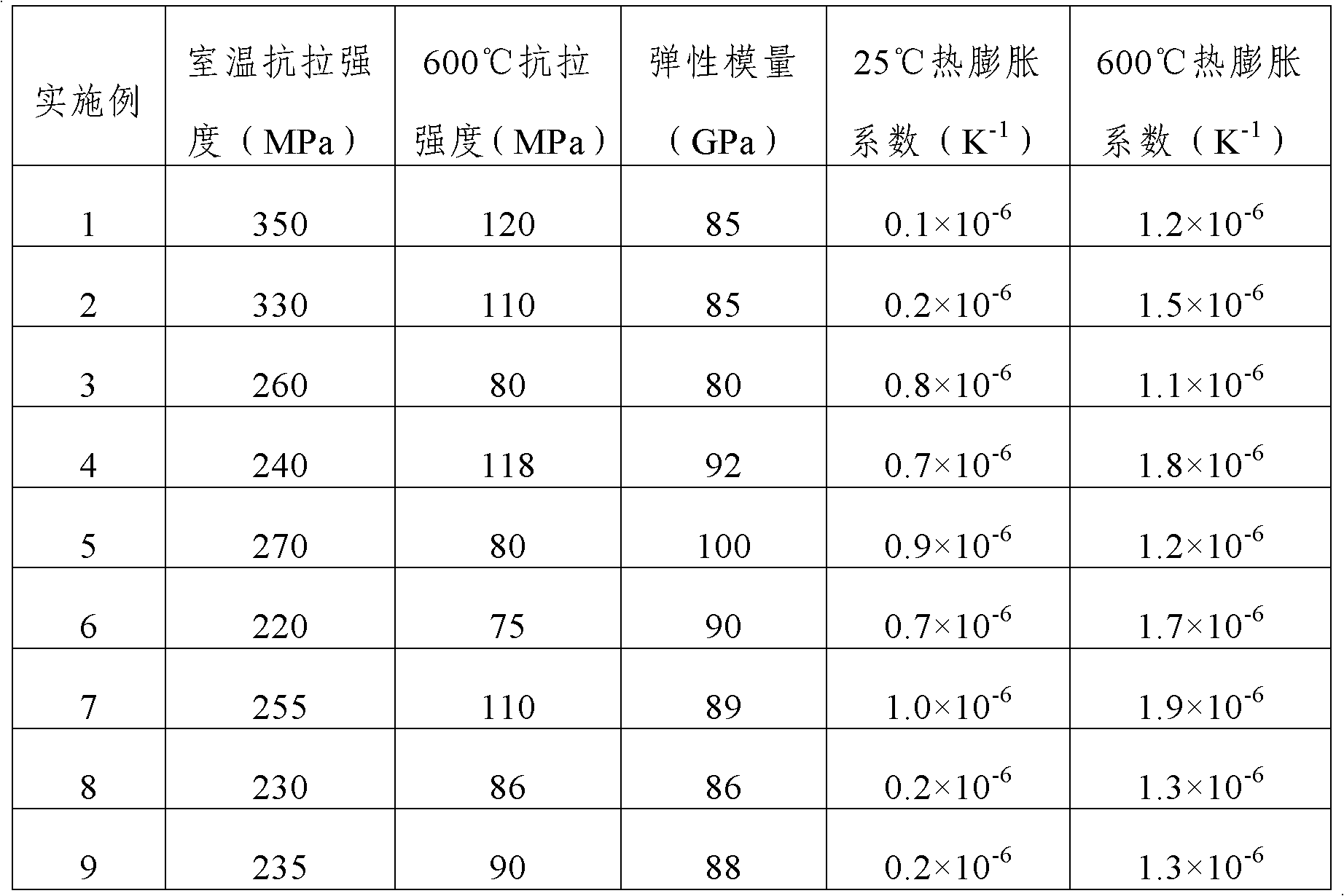
The invention discloses a niobium-zirconium tungstate composite material which is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 35-75% of zirconium tungstate, 1-10% of chromium and 20-60% of niobium. The mass purity of the zirconium tungstate is not less than 97%, and the mass purity of the chromium is not less than 99%. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the composite material. The chromium powder is introduced into the niobium-zirconium tungstate composite material system to enhance the high-temperature strength of the material; mechanical alloying is utilized to lower the sintering temperature of the niobium-zirconium tungstate composite material, thereby avoiding separation of the ceramic phase and the base; and the tensile strength of the preparedniobium-zirconium tungstate composite material at room temperature is 220-350MPa, the tensile strength at 600 DEG C is 75-120MPa, the thermal expansion coefficient at 25-600 DEG C is 0.1-1.9*10<-6>K<-1>, and the elastic modulus is less than or equal to 100GPa.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Process for preparation of zirconium tungstate ceramic body, zirconium tungstate ceramic body prepared thereby, and temperature compensated fiber bragg grating device
InactiveUS6936235B2Uniform microstructureSimple procedureCladded optical fibreTungsten oxides/hydroxidesFiberGrating
The present invention discloses a process for the preparation of zirconium tungstate (ZrW2O8) ceramic body, comprising a reactive sintering step to react and sinter powders of the raw materials comprising a Zr-containing compound and a W-containing compound to form a zirconium tungstate ceramic body. The addition of zirconium tungstate powders as the seeds in the process can effectively reduce the steps, shorten the preparation time, lower the sintering temperature and duration, save the cost, and provide the zirconium tungstate ceramic body with uniform microstructure. Also, a process for the preparation of modified zirconium tungstate ceramic body is disclosed, by forming a second phase in the zirconium tungstate ceramic body to tune the thermal expansion coefficient of the zirconium tungstate ceramic body. The present invention also relates to the use of the modified zirconium tungstate ceramic body to provide a temperature compensated fiber bragg grating (FBG) device.
Owner:BROPTICS TECHNOLOGY LTD
Method for preparing near-zero thermal expansion ZrO2/ZrW2O8 composite material
ActiveCN106565236ASimple and fast operationLittle influence from external factorsAuxillary shaping apparatusDecompositionPolyvinyl alcohol
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Intermediate transfer members containing thermoplastic mixtures
ActiveUS20130009103A1Conductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialThermosetting polymerZirconium tungstate
An intermediate transfer member that includes a mixture of a thermoplastic polymer, a zirconium tungstate, an optional polysiloxane, and an optional conductive filler.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for preparing zirconium tungstate film
InactiveCN101550548AUniform thicknessSimple preparation processSolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingPolymer scienceNitrate
A method preparing zirconium tungstate film belongs to the field of film preparing. The invention settles the problems of complex operation and high cost existing in prior method for preparing zirconium tungstate film. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: 1. mixing zirconyl nitrate and dissolvent for obtaining a solution A; 2. mixing complexing agent, dissolvent and ammonium metatungstate for obtaining a solution B; 3. mixing A and B for preparing colloidal sol; 4. preparing a wet film through spin coating, and then presintering the wet film; 5. preparing amorphous film of zirconium tungstate; and 6. obtaining the zirconium tungstate film after crystallizing the amorphous film of zirconium tungstate. The method for preparing zirconium tungstate film according to the invention has the advantages of simple preparing process and low cost. The obtained film has the advantages of smooth and compact surface, uniform thickness and uniform crystalline size.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for decreasing thermal expansion coefficient of concrete
InactiveCN108892448ASmall coefficient of thermal expansionProof of thermal expansion coefficientTemperature controlTemperature stress
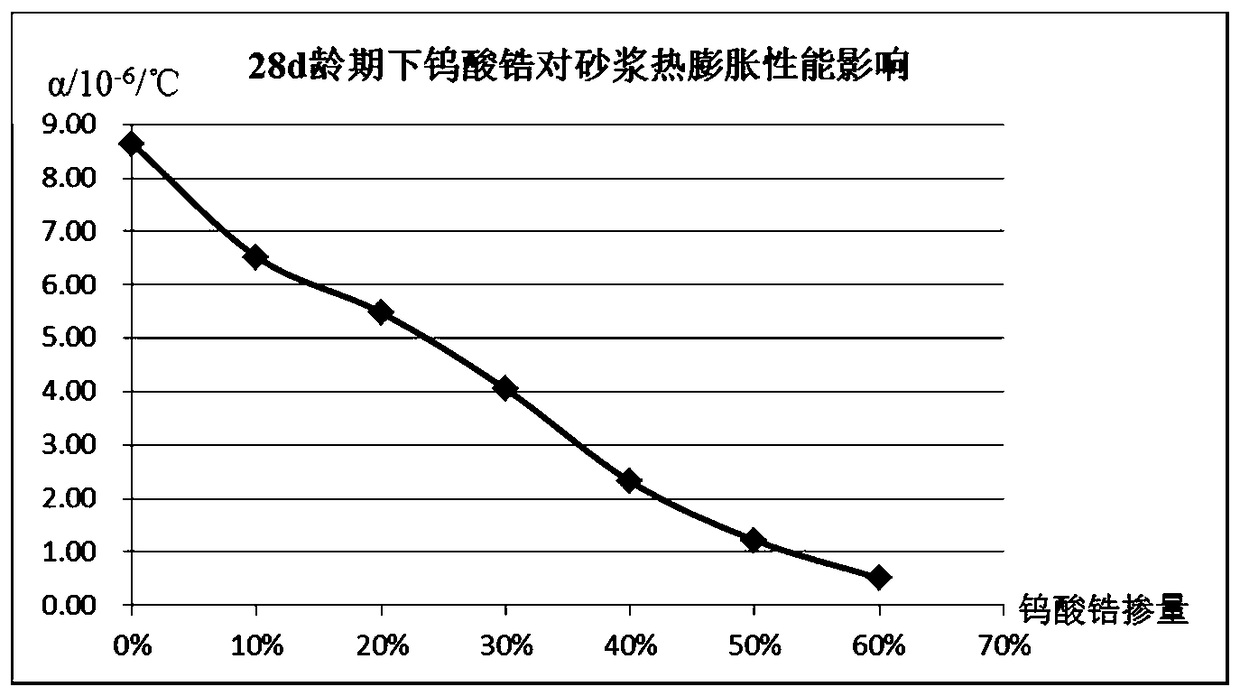
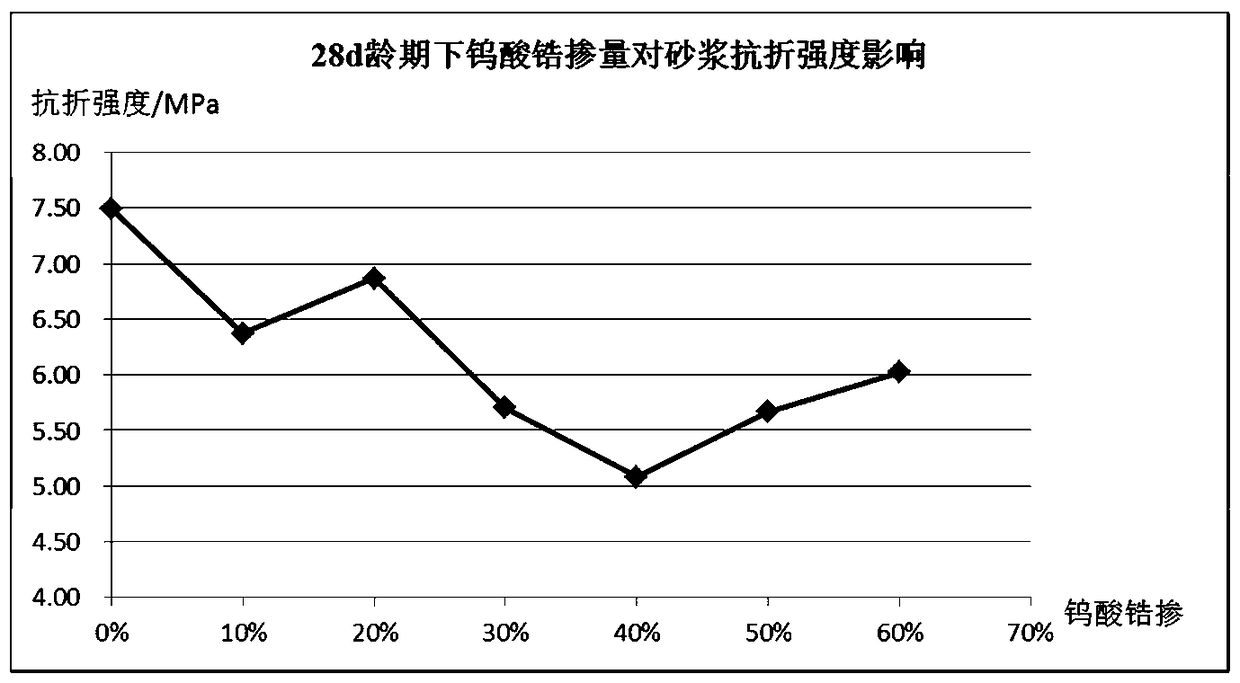
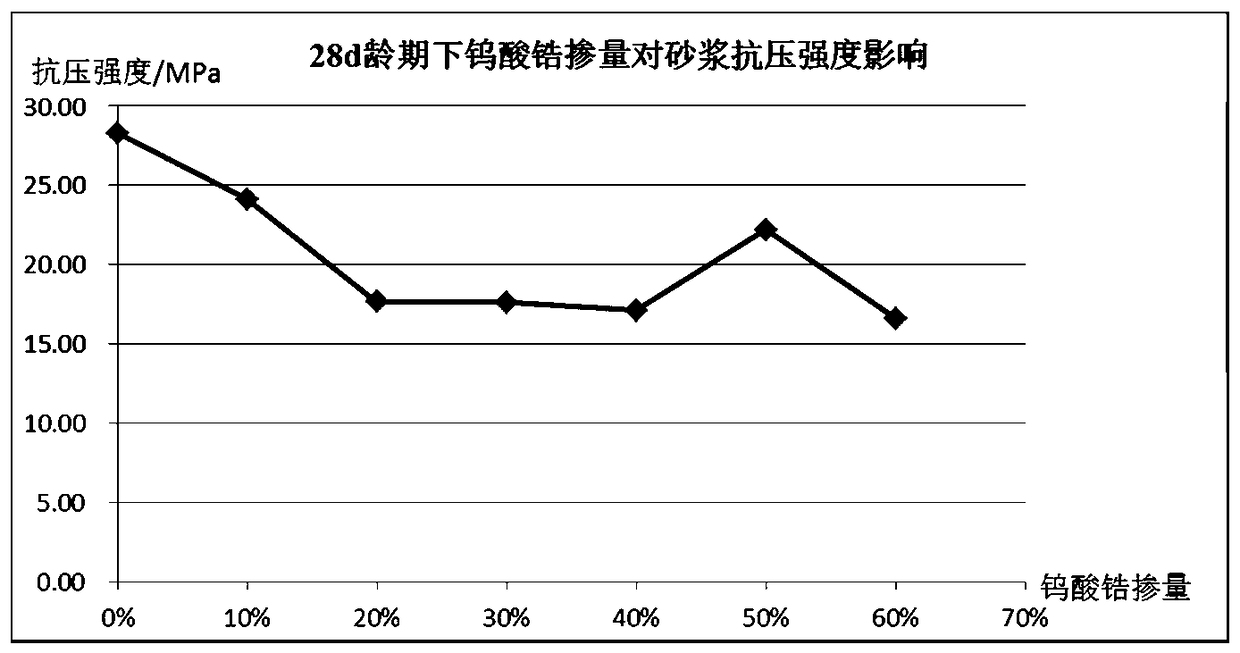
The invention discloses a preparation method for decreasing the thermal expansion coefficient of concrete. According to the novel preparation method, the effect is good, the thermal expansion coefficient of the concrete can be decreased, and the preparation method can meet the strength requirements of the concrete. According to the technical scheme, a negative thermal expansion material with hot contraction and cold expansion properties is added into the concrete, so that swelling deformation caused due to the heating of the concrete can be effectively counteracted or partially counteracted, and the thermal expansion coefficient of the concrete is decreased. According to the preparation method, a proper amount of zirconium tungstate (ZrWO2) with the negative thermal expansion property is doped into the concrete, so that a new temperature control research thought is provided for solving the problem that the concrete usually cracks in the early period due to the poor temperature stress in large-volume concrete structural construction.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Aging-resistant aluminum oxide-nylon heat conducting composite material for LED lamps and preparation method of composite material
InactiveCN106009646AImprove light aging resistanceImprove impact resistanceCarbon fibersShock resistance
Provided is an aging-resistant aluminum oxide-nylon heat conducting composite material for LED lamps. The composite material is prepared from, by weight, 200 parts of nylon 6, 8-10 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 30-40 parts of aluminum oxide, 5-8 parts of zirconium tungstate, 20-30 parts of carbon fibers, 50-60 parts of acetone, 80-100 parts of 60%-70% nitric acid, 70-80 parts of a 1%-3% silane coupling agent water solution, 8-10 parts of acetic acid, 15-20 parts of isophorone diisocyanate, 20-25 parts of pentaerythritol triacrylate, 0.4-1 part of a catalyst, 0.4-2 parts of a polymerization inhibitor, 3-5 parts of gelatin, 150-170 parts of tetrahydrofuran, 80-100 parts of toluene and an appropriate amount of deionized water. According to the composite material, nano-zinc oxide is adopted, and therefore the light aging resistance, the shock resistance and the toughness of plastic are improved; surface modification is conducted on the carbon fibers, aluminum oxide is coated with high polymers, and therefore the compatibility of the carbon fibers, aluminum oxide and the nylon 6 is enhanced.
Owner:BENGBU GAOHUA ELECTRONICS
A method for preparing acetonitrile by catalyzing zirconium-tungsten mesoporous molecular sieves
ActiveCN104447404BReduce consumptionImprove stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsPreparation by ammonia-carboxylic acid reactionMolecular sieveAcetic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing acetonitrile by applying a zirconium tungsten mesoporous molecular sieve catalyst. The method comprises the following steps that raw material acetic acid and ammonia are preheated after being vaporized respectively, the molar ratio of the acetic acid to the ammonia is 1:2.5-7, the acetic acid and the ammonia enter a mixer to be mixed, and then enter a static bed containing the zirconium tungsten mesoporous molecular sieve catalyst to carry out a catalytic reaction, the reaction temperature ranges from 360 DEG C to 450 DEG C, and reaction gas is absorbed by water to obtain an acetonitrile product; the zirconium tungsten mesoporous molecular sieve catalyst is formed by loading ZrO2 and WO3 on a mesoporous molecular sieve. According to the method, the acetic acid and the ammonia are used as raw materials, by means of the static bed reactor, under the effect of the zirconium tungsten mesoporous molecular sieve catalyst, an ammonification method is used for synthesizing the acetonitrile, the zirconium tungsten mesoporous molecular sieve catalyst is good in stability, the selectivity conversion rate is high, and the product yield is high.
Owner:NANTONG LIYANG CHEM CO LTD
Composite material for shell of toilet of high-speed train and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104072682AGuaranteed precisionControlling the coefficient of thermal expansionFiberCombustion
The invention discloses a composite material for a shell of a toilet of a high-speed train and a preparation method thereof. The shell is formed by compounding modified unsaturated polyester resin and reinforced fibers by virtue of a hand lay-up moulding technology or a compression moulding technology, wherein the modified unsaturated polyester resin is obtained by modifying unsaturated polyester resin by virtue of a diluter, zirconium tungstate, aluminium hydroxide and bentonite, then adding an accelerator and an initiating agent and uniformly stirring. The composite material for the shell of the toilet of the high-speed train has the beneficial effects that shrinking percentage of a product during curing is reduced, and accuracy of dimension is guaranteed; thermal expansion coefficient of resin matrix can be effectively regulated and controlled to be close to that of the reinforce fibers, internal thermal stress is reduced and even eliminated, and service life of the product is effectively prolonged; flame retardant property of the shell of the toilet is improved, the amount of smoke produced during combustion is reduced, and product cost is further reduced.
Owner:CRRC WIND POWER(SHANDONG) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com