Patents
Literature
93 results about "Negative coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radar device
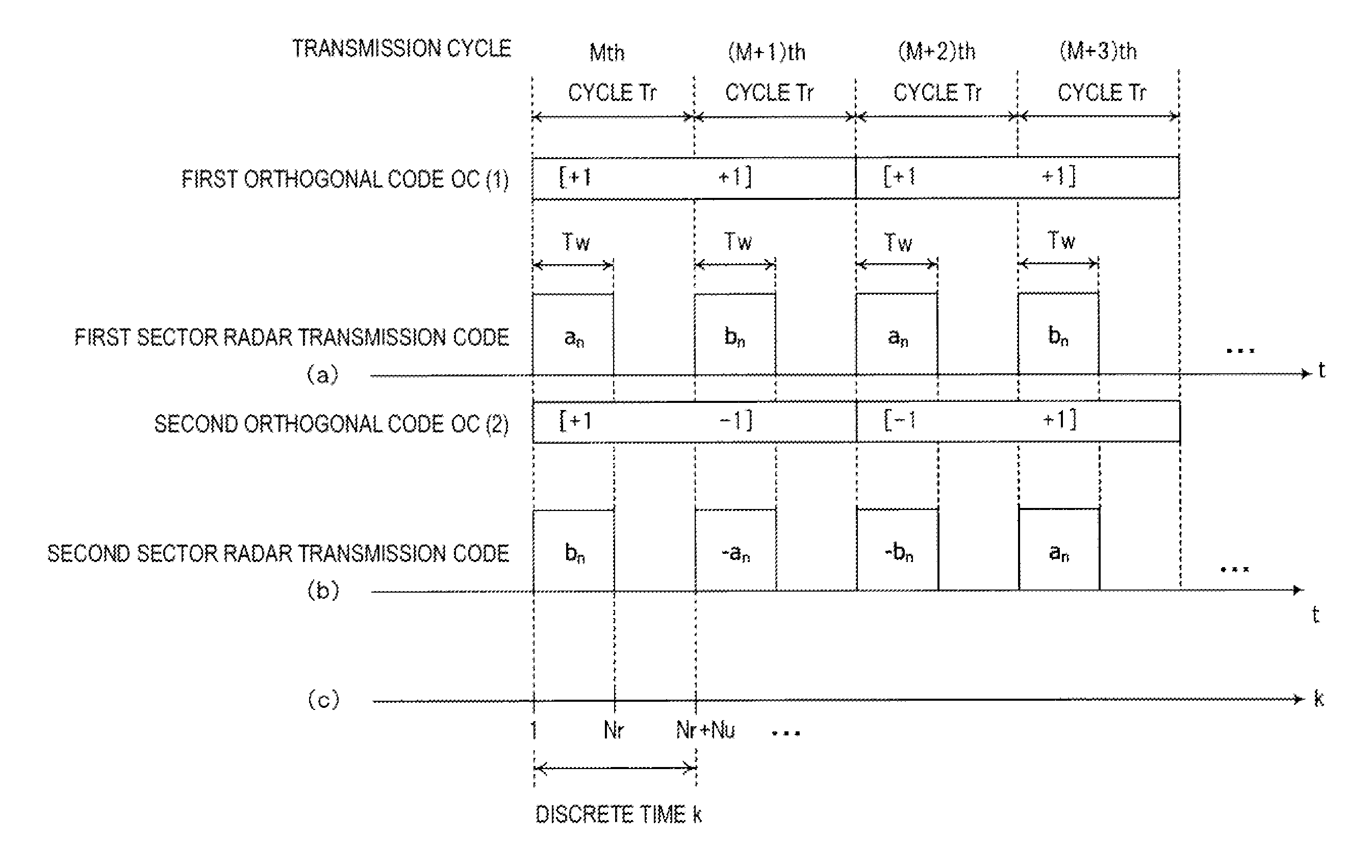
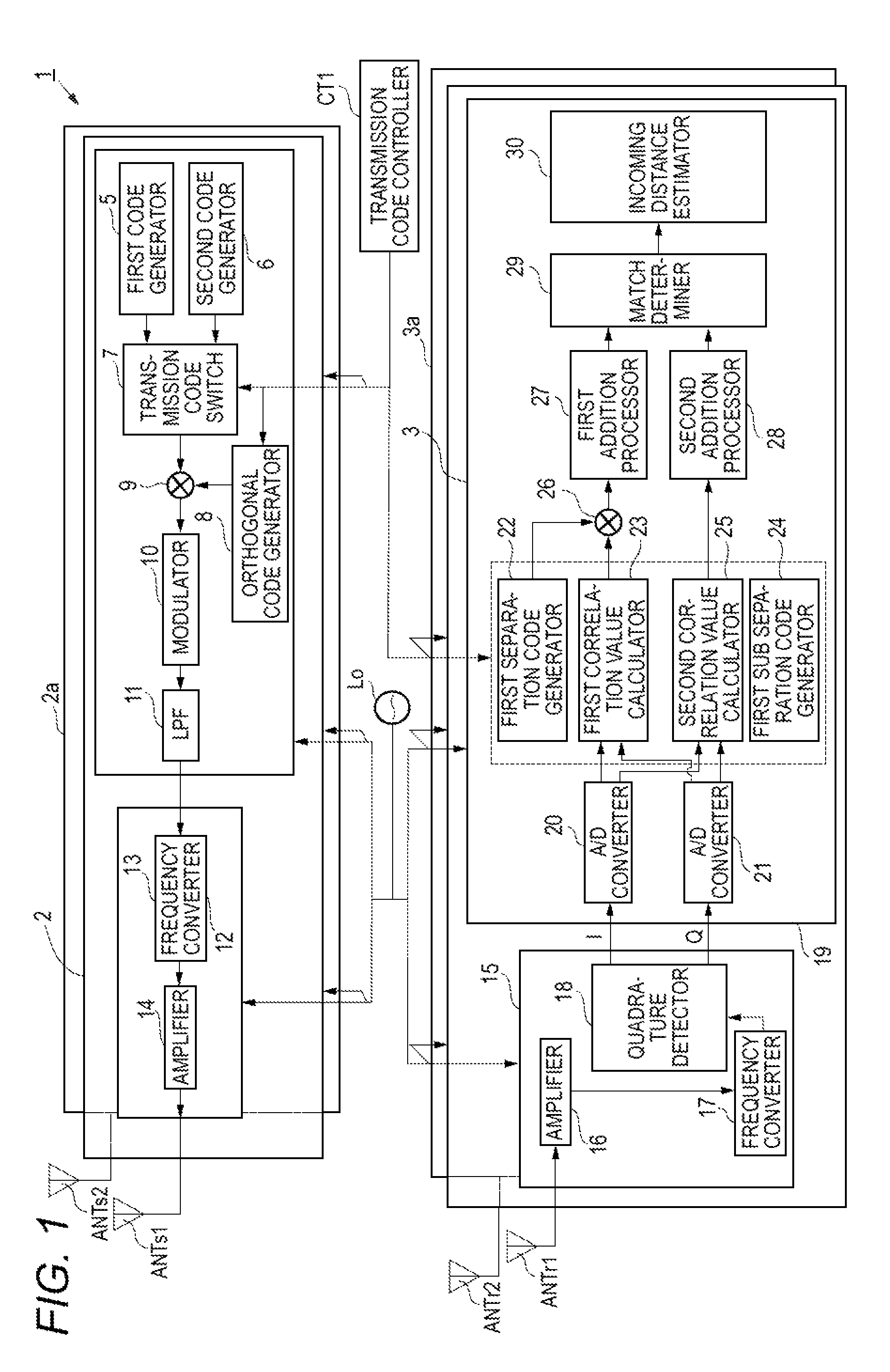
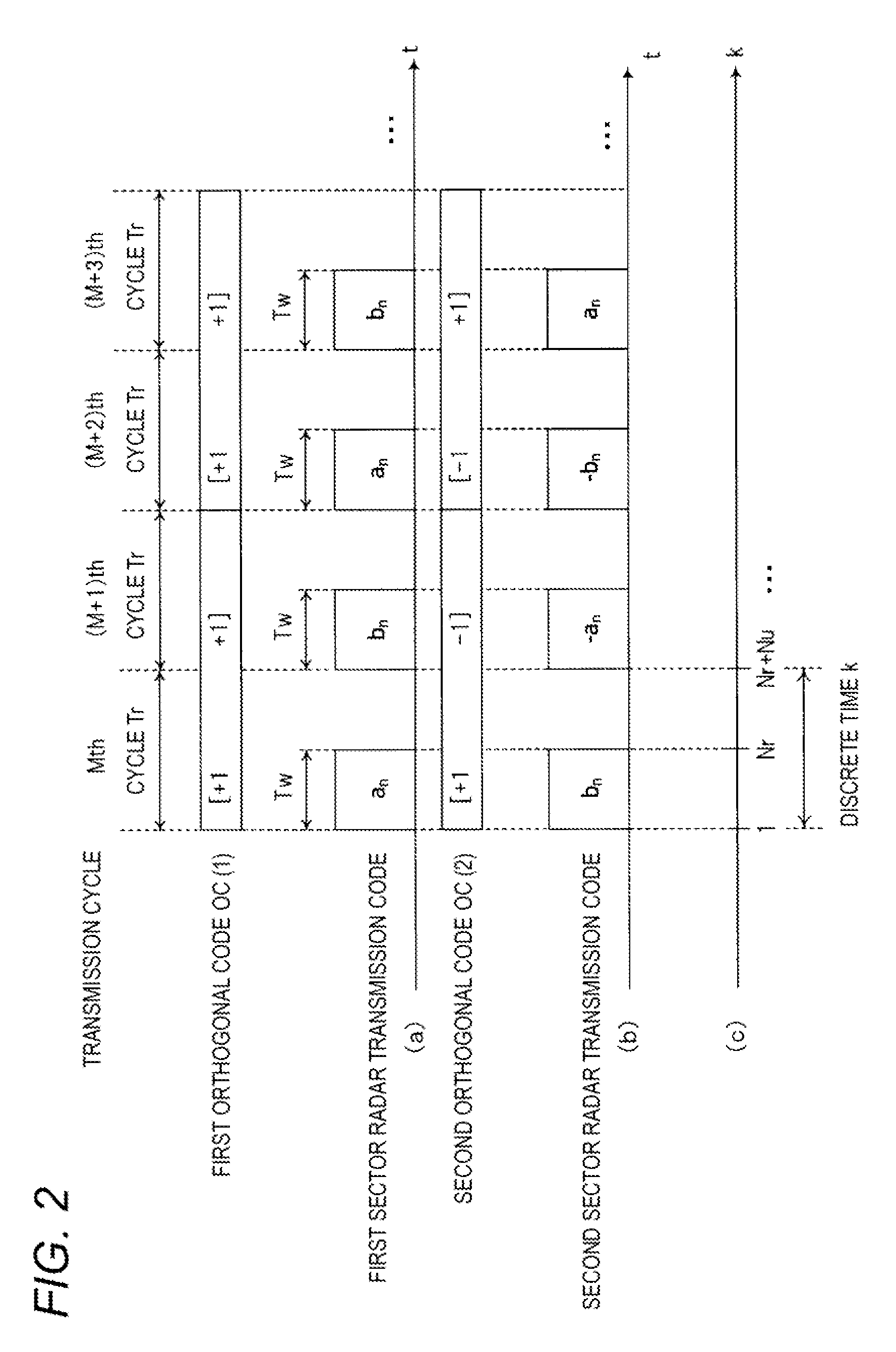
A radar device is provided, which includes a first sector radar and a second sector radar, each including a code generator that generates two code sequences, a multiplier that multiplies the two code sequences by a coefficient sequence, wherein the two coefficient sequences of the first and second sector radars, respectively, are orthogonal to each other, a transmission signal generator that modulates the orthogonalized two code sequences, and an RF transmitter that transmits the modulated signal including the two orthogonalized two code sequences. At least one of the two orthogonal coefficient sequences for the first and second sector radars, respectively, includes one or more negative coefficients. The two orthogonal coefficient sequences include coefficients, which are identical to each other, in a first transmission cycle, and include coefficients, which are different from each other, in a second transmission cycle different from the first transmission cycle.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Structure and method of thermal stress compensation
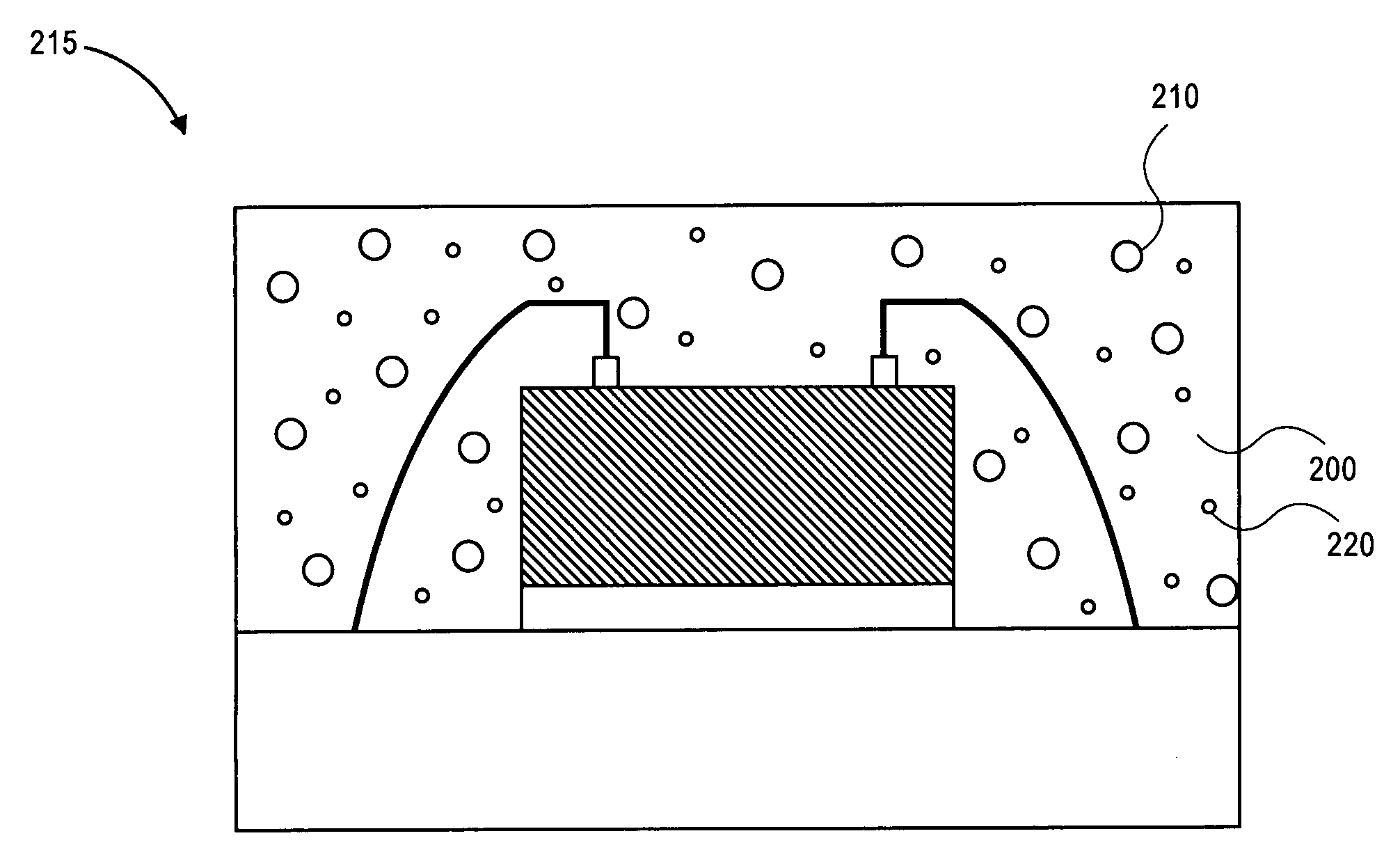
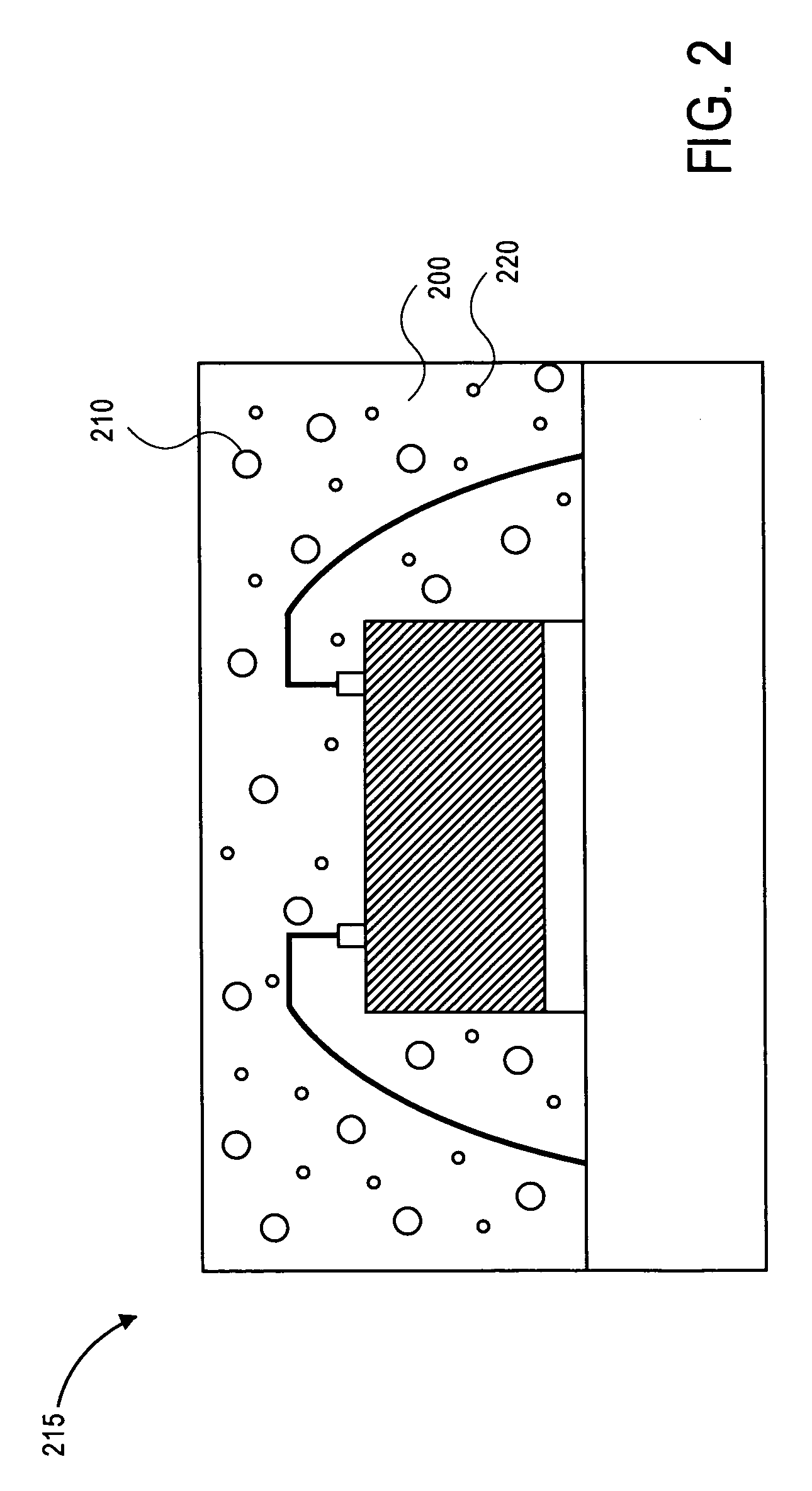
InactiveUS20060204776A1Reduce stress buildupThermometers using material expansion/contactionVacuum evaporation coatingNegative coefficientMaterials science
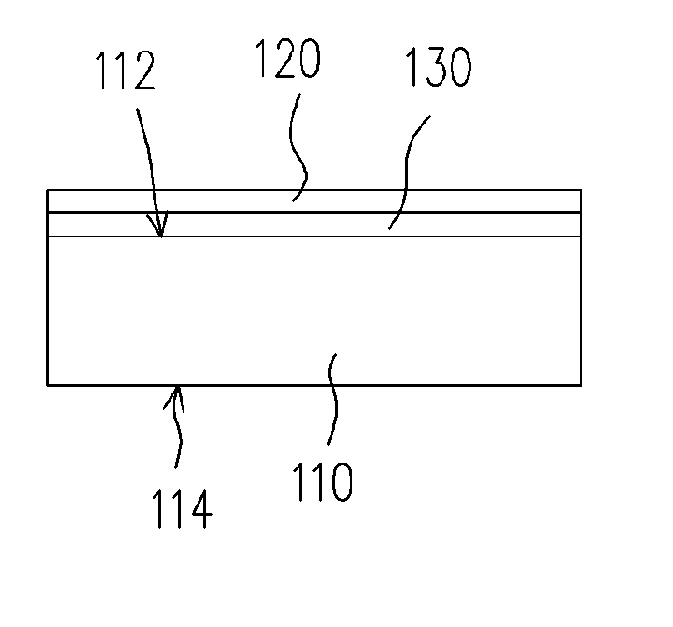
A structure of thermal stress compensation at least comprises a substrate, a first film and a second film. The substrate has a first positive coefficient of thermal expansion. The first film having a second positive coefficient of thermal expansion is over the substrate. The second film having a third negative coefficient of thermal expansion is over the substrate.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Very low thermal expansion composite
InactiveUS20050191515A1Low thermal expansionPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyNegative coefficientOpto electronic
Disclosed are composites having very low coefficients of thermal expansion and methods of preparing the composites. Also disclosed are composites having negative coefficients of thermal expansion. Applications of the composites to a wide variety of uses, such as electronic and optoelectronic devices are also disclosed.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
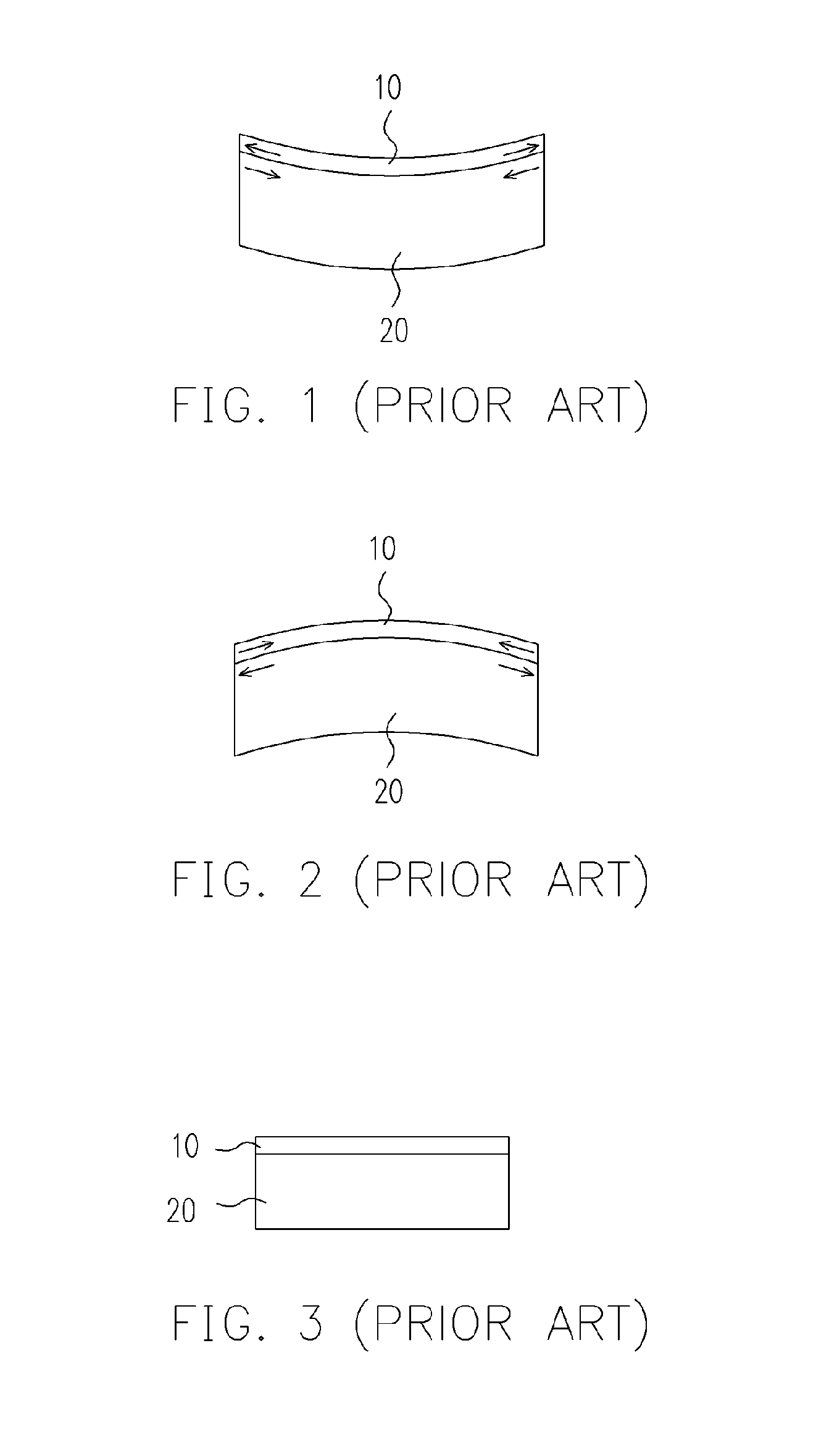
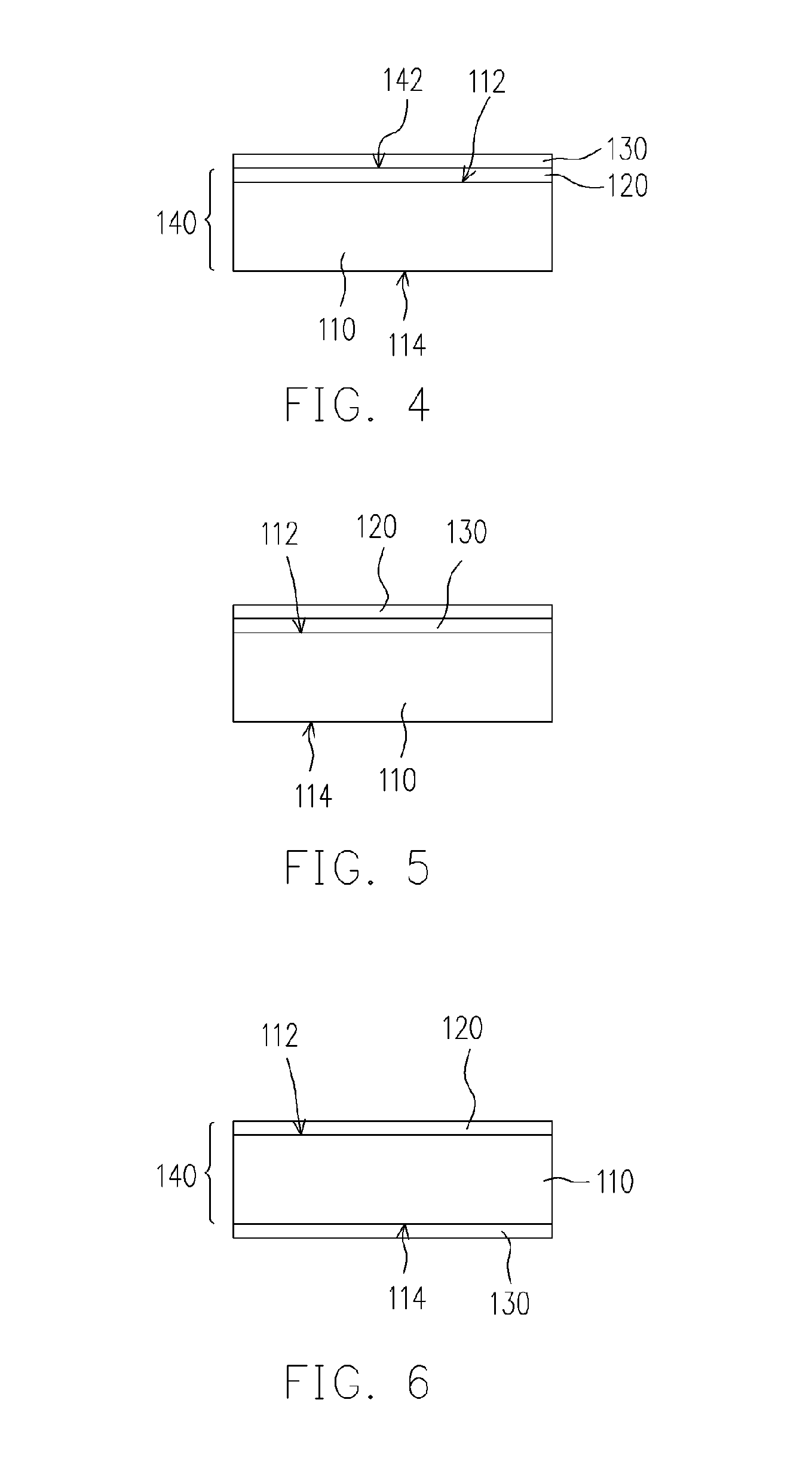
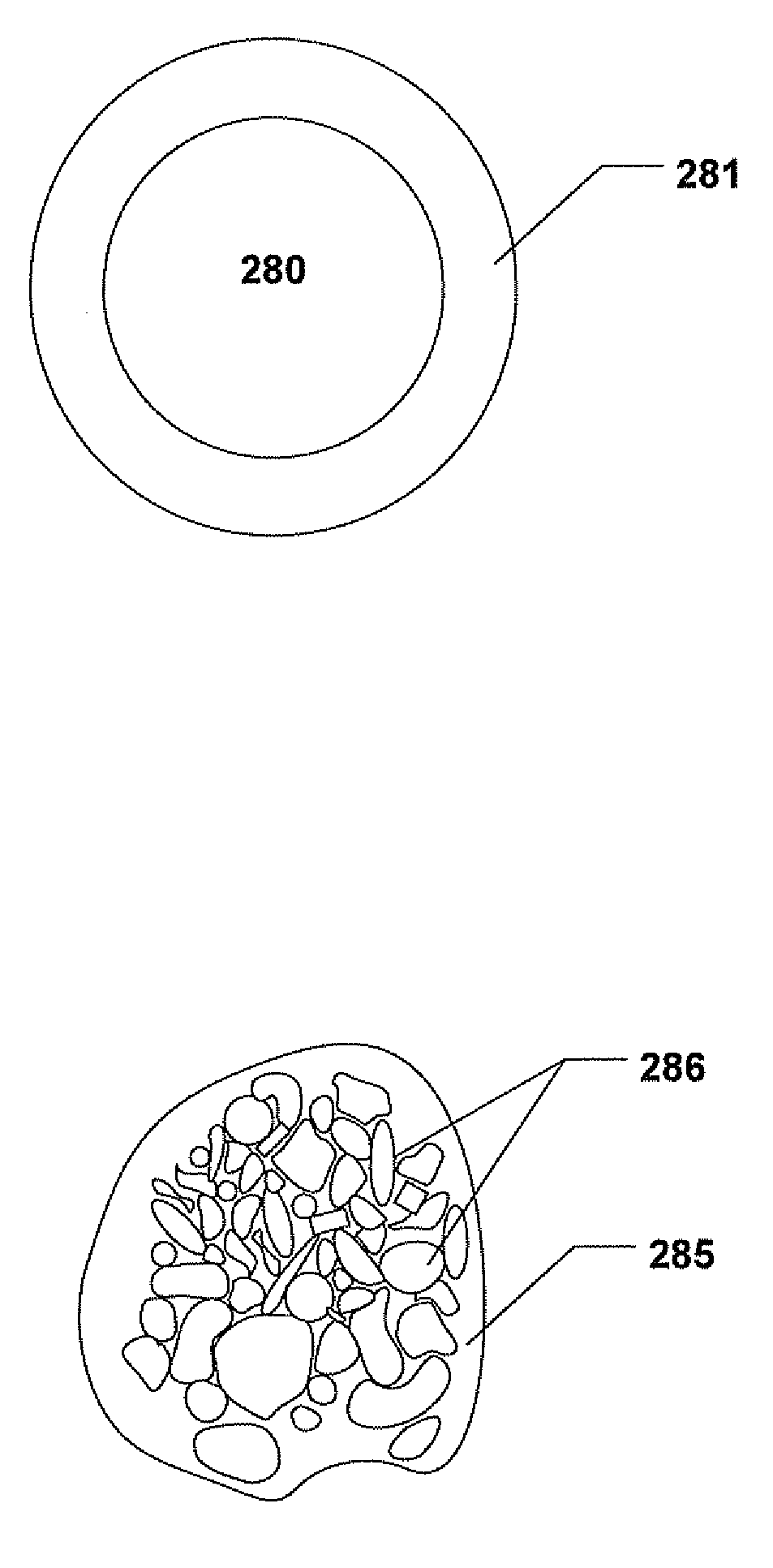
Abrasive article and method of forming
An abrasive article including a material including an abrasive material and a filler material having an average negative coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) within a range of temperatures between about 70K to about 1500K.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Braze System With Matched Coefficients Of Thermal Expansion
InactiveUS20080131723A1Reduce thermal stressPromote wettingExhaust apparatusFinal product manufactureParticulatesBraze alloy
A CTE modified braze composition that can be utilized to manufacture a strong, gastight joint where at least one of the joining members comprises a ceramic (e.g., a ceramic or a cermet). The braze composition is formulated so as to reduce the thermal stress that results from the mismatch of thermal expansion coefficients between a ceramic joining member and the braze or other joining members. The braze composition comprises a braze alloy in powder, paste or bulk form mixed with one or more particulate or fibrous fillers that exhibit a low (i.e., no more than 6 ppm / K) or negative coefficient of thermal expansion. The braze composition can be used to join members, at least one of which comprises ceramic, and to a composite member produced by joining the two or more members.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Negative thermal expansion material filler for low CTE composites
InactiveUS20070135550A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolymer scienceBi modal
The present invention relates to a filler featuring a negative coefficient of thermal expansion and a bi-modal size distribution of filler particles. In an embodiment, the filler has micron and nanometer size filler particles. The present invention also relates to a composite having a polymer and a filler with nanometer size filler particles. Additionally, the present invention discloses a method of forming an electronic package with a composite having a polymer and a filler with nanometer size filler particles.
Owner:INTEL CORP
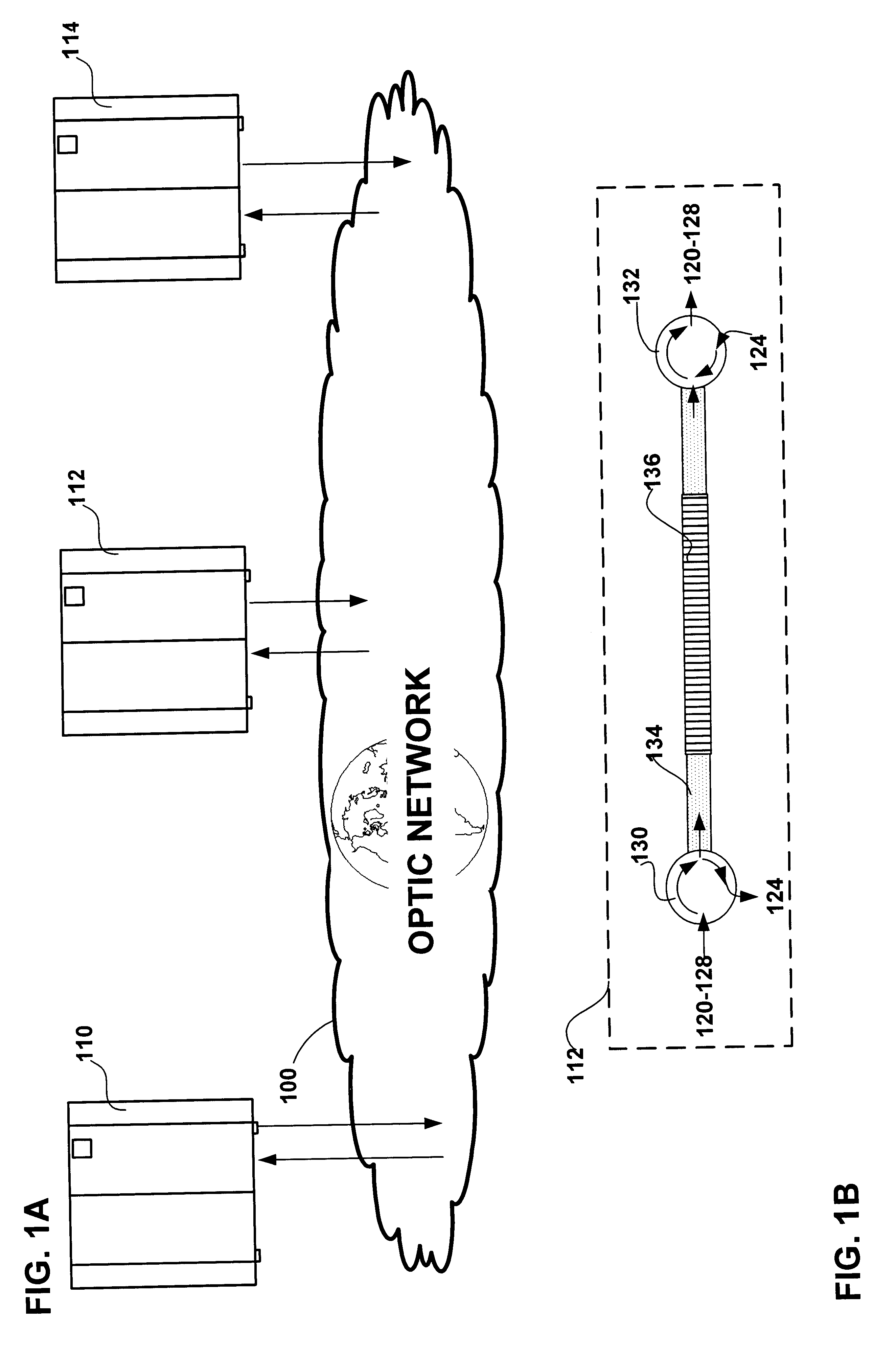
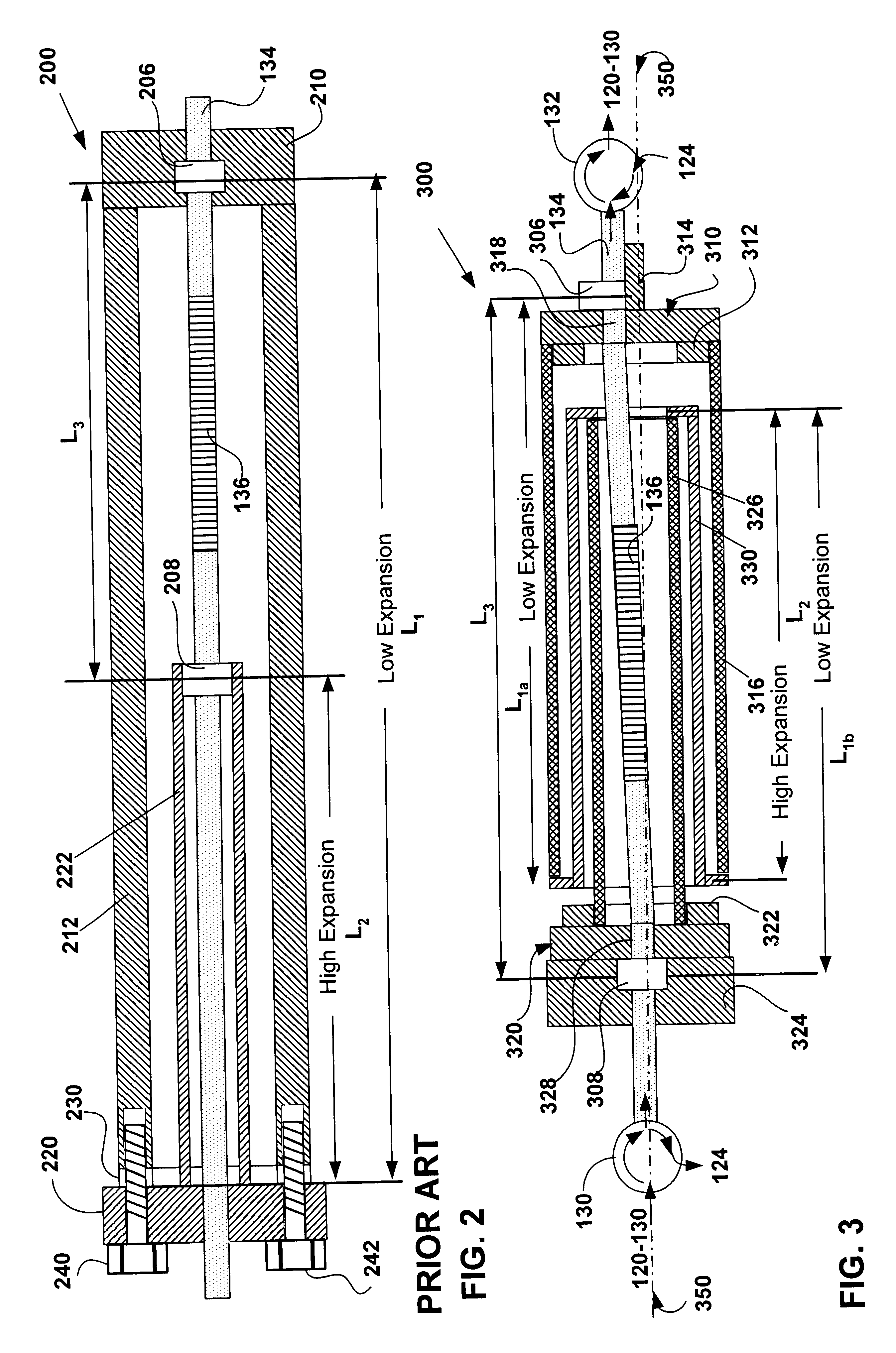
Method and apparatus for compensating an optical filter
A method and apparatus for compensating an optical filter is disclosed. The device substantially maintains the selected center wavelength in the optical filter across a range of operating temperatures. In an embodiment of the invention an optical filter is disclosed for filtering a selected channel among a plurality of multiplexed channels of an optical communication. The optical filter includes an optical fiber and an elongate housing. The optical fiber has a first side and a second side and a filter portion intermediate the first side and the second side, and the optical fiber for transmitting the multiplexed optical communication and the filter portion for filtering the selected channel. The elongate housing includes exposed end portions through which the optical fiber extends. The optical fiber is affixed at each exposed end portion. The exposed end portions exhibit between them a negative coefficient of thermal expansion sufficient to generate strains on the filter to substantially stabilize a filtered wavelength to substantially correspond with the selected channel during temperature variations. In an alternate embodiment of the invention the elongate housing is defined about a longitudinal axis and including a first anchor pad and a second anchor pad to which the filter portion is affixed. At least one of the anchor pads is at least initially movable in a plane intersecting the longitudinal axis to vary a strain on the filter portion to tune a center wavelength of the selected channel. In another embodiment of the invention an optical filter for filtering an optical signal is disclosed. In still another embodiment of the invention a method for compensating an optical filter is disclosed.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Composite material for turbine support structure
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus of image processing
InactiveUS20060002624A1Reduce noiseEnhanced edgeImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingEngineering
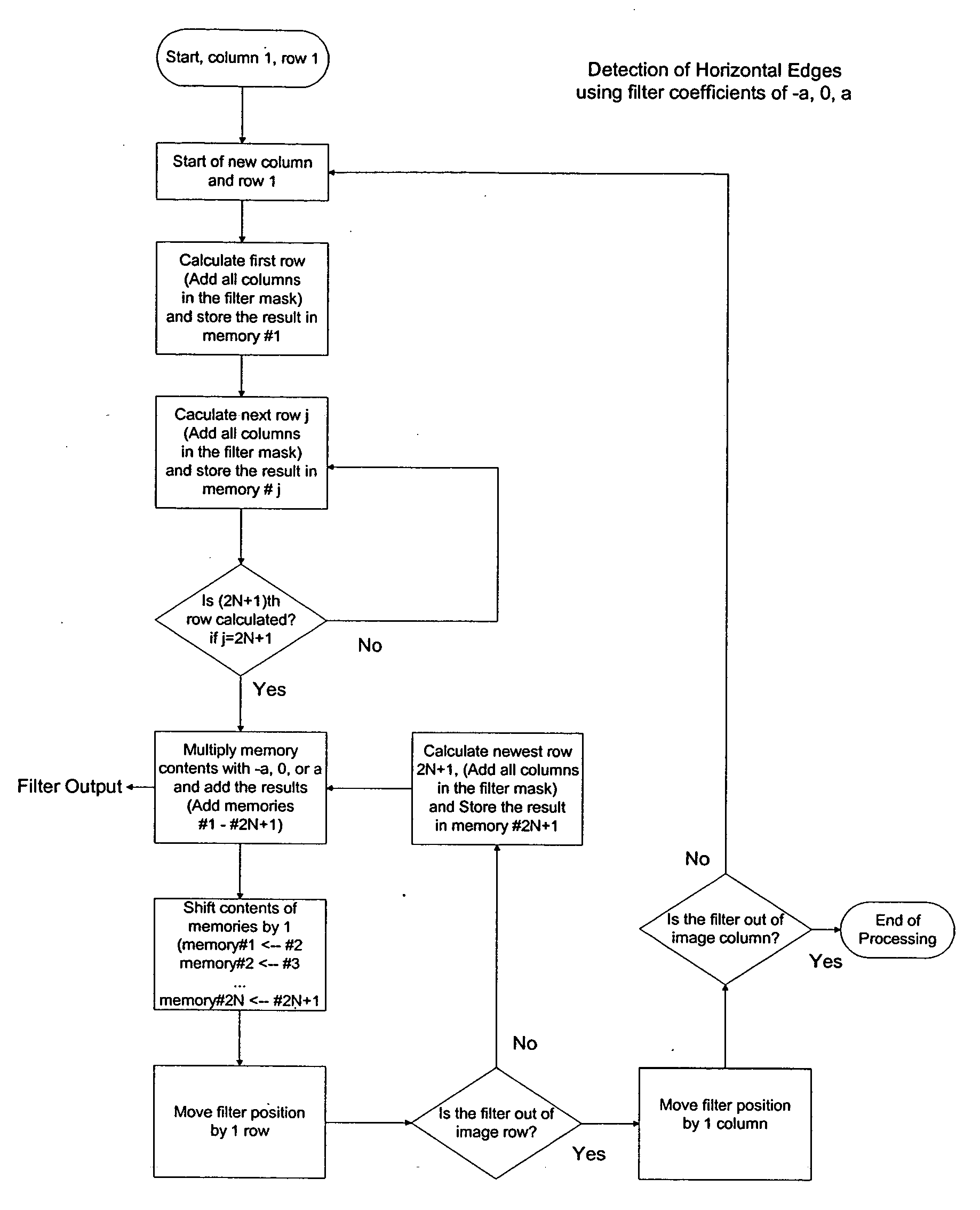
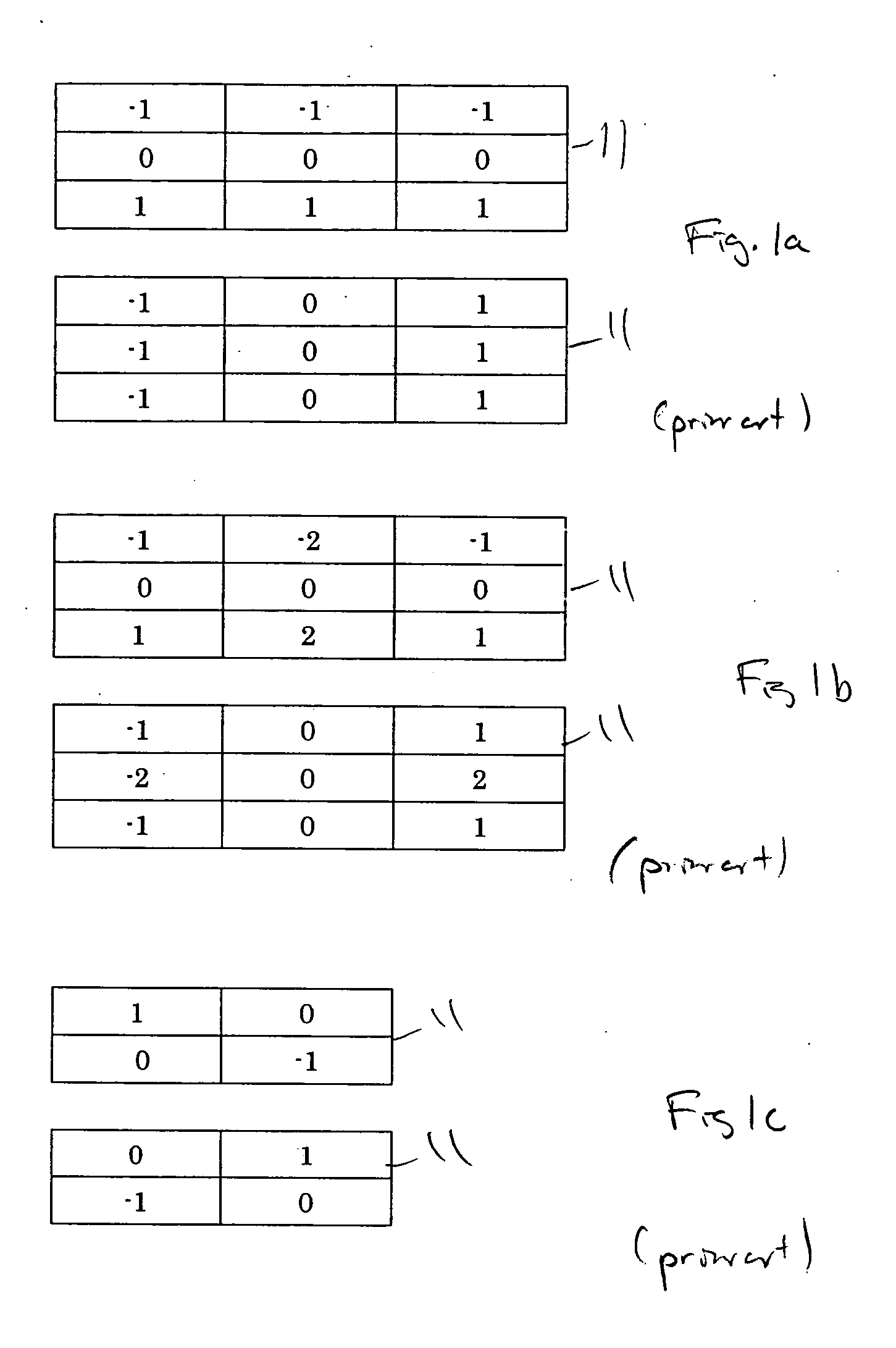
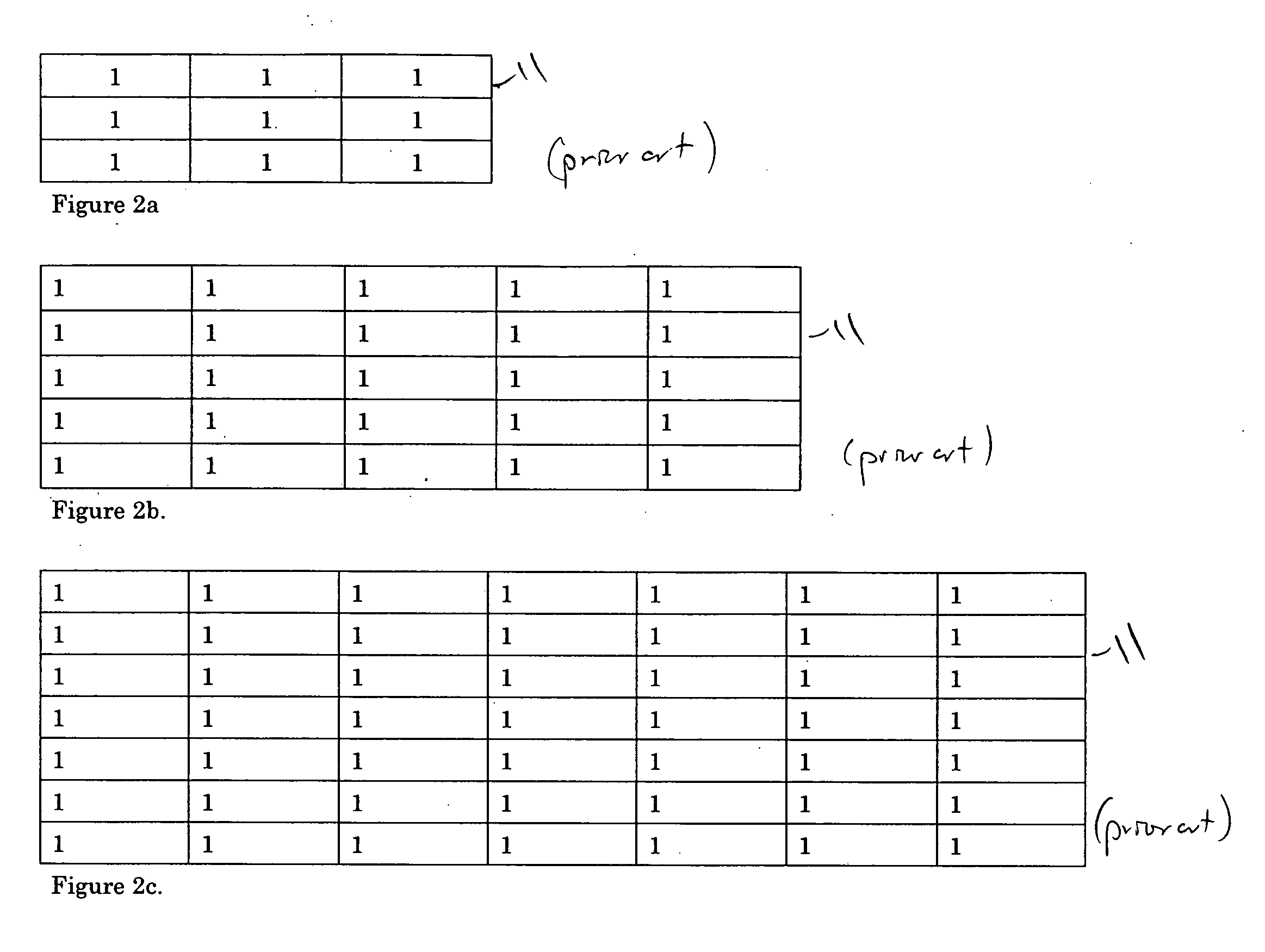
An edge detection filter comprising an array of filter coefficients having an odd number of rows and columns, a first set of zero coefficients extending along a direction traversing the array through a center position to form a first and second side, a second set of positive coefficients extending away from the direction on the first side, and a third set of negative coefficients extending away from the direction on the second side.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Thermally compensated fiber bragg grating mount
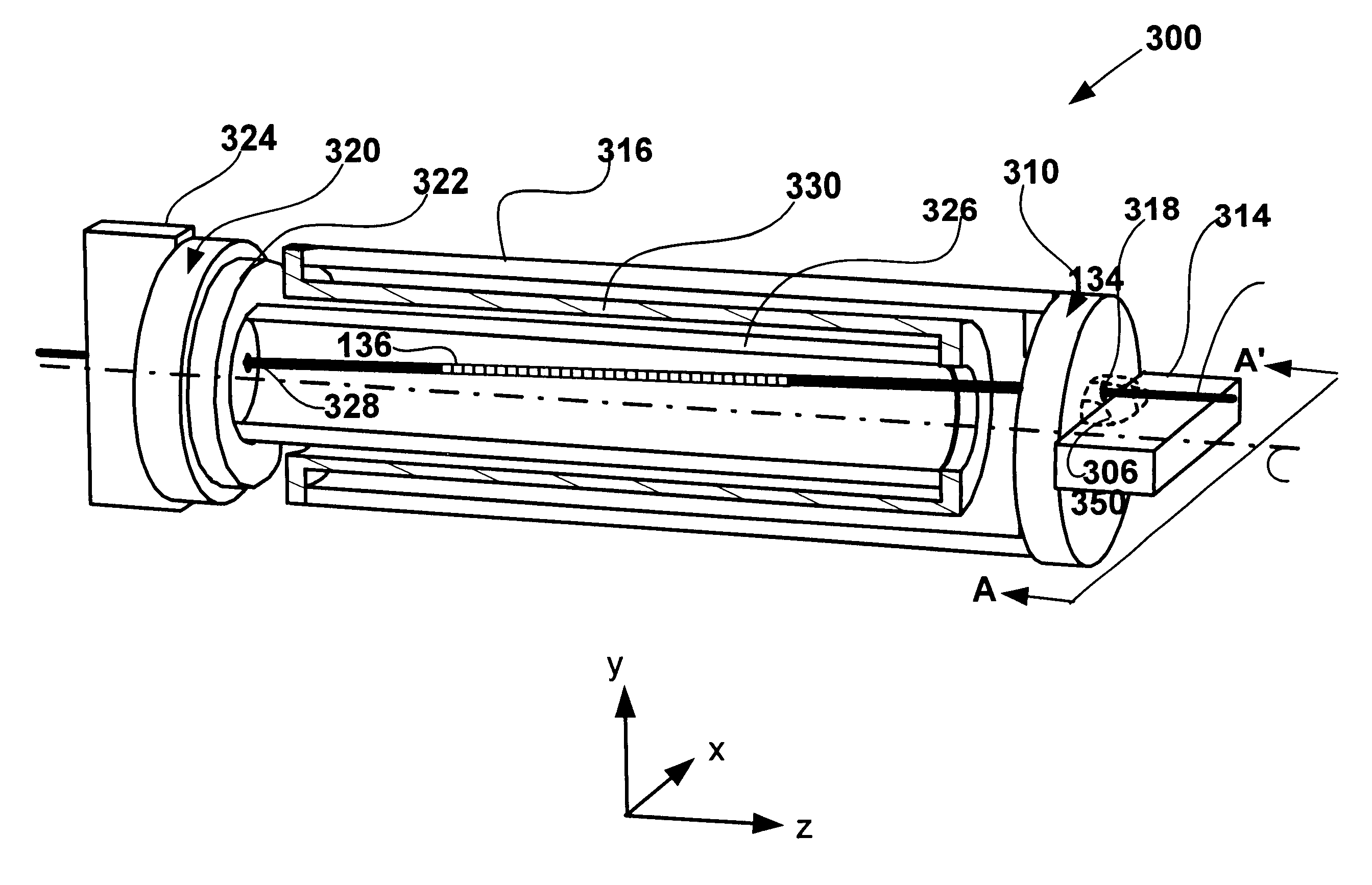
A thermally compensated fiber Bragg grating package is used with a fiber optic sensor. The package includes a Bragg grating mount connected at each end of a sensor mandrel. An optical fiber is wound around the sensor mandrel and a fiber portion having a Bragg grating therein is wound onto the mount. The mount is made of a rigid material having a negative coefficient of thermal expansion to minimize thermally induced spectral shifts. One example of the material includes zirconium tungstate. A coating material can be used to further adhere the optical fiber to the sensor mandrel and / or to the mount. The mount preferably includes a ramped groove to provide for a smooth transition from the sensor mandrel to the mount.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
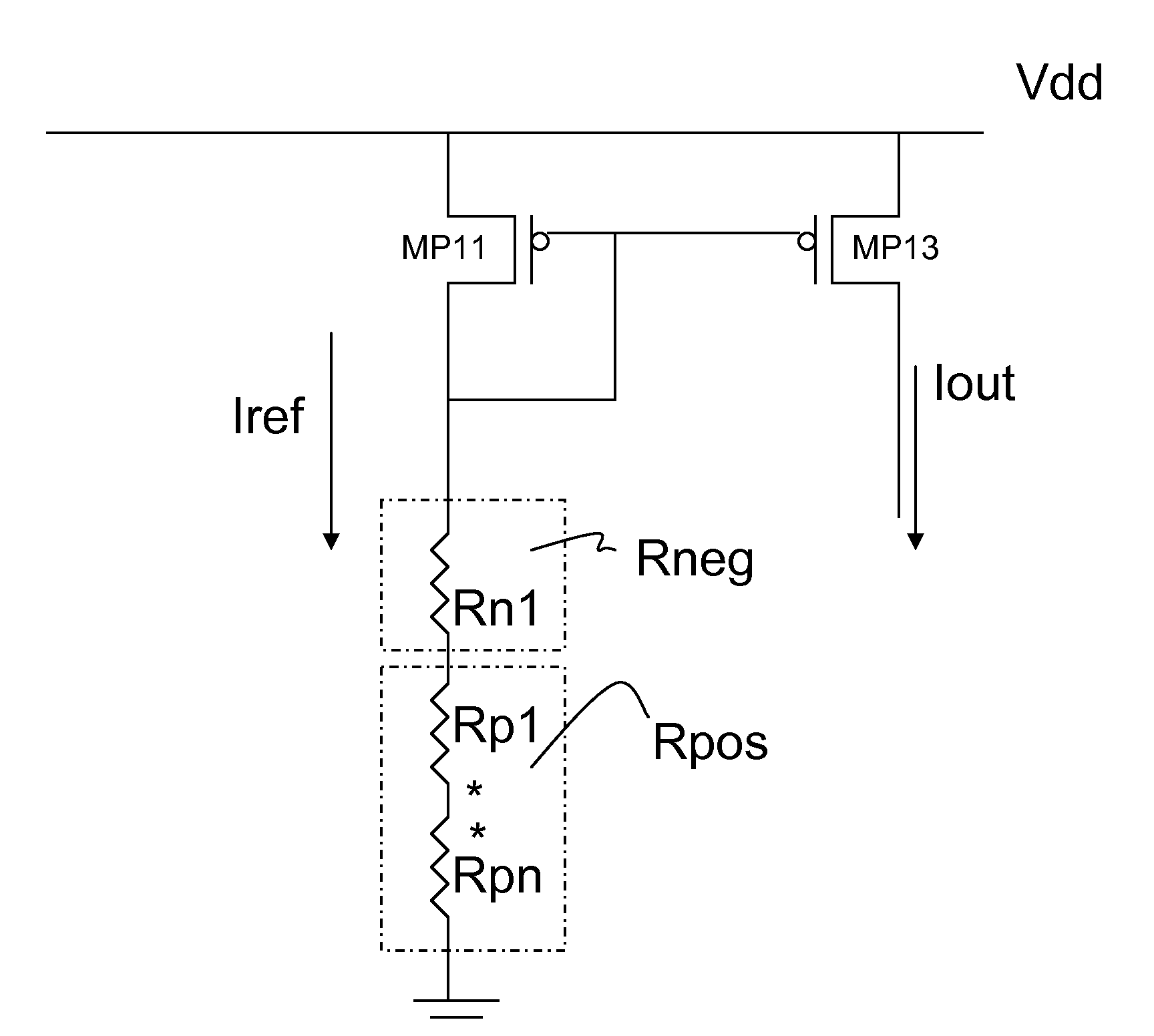
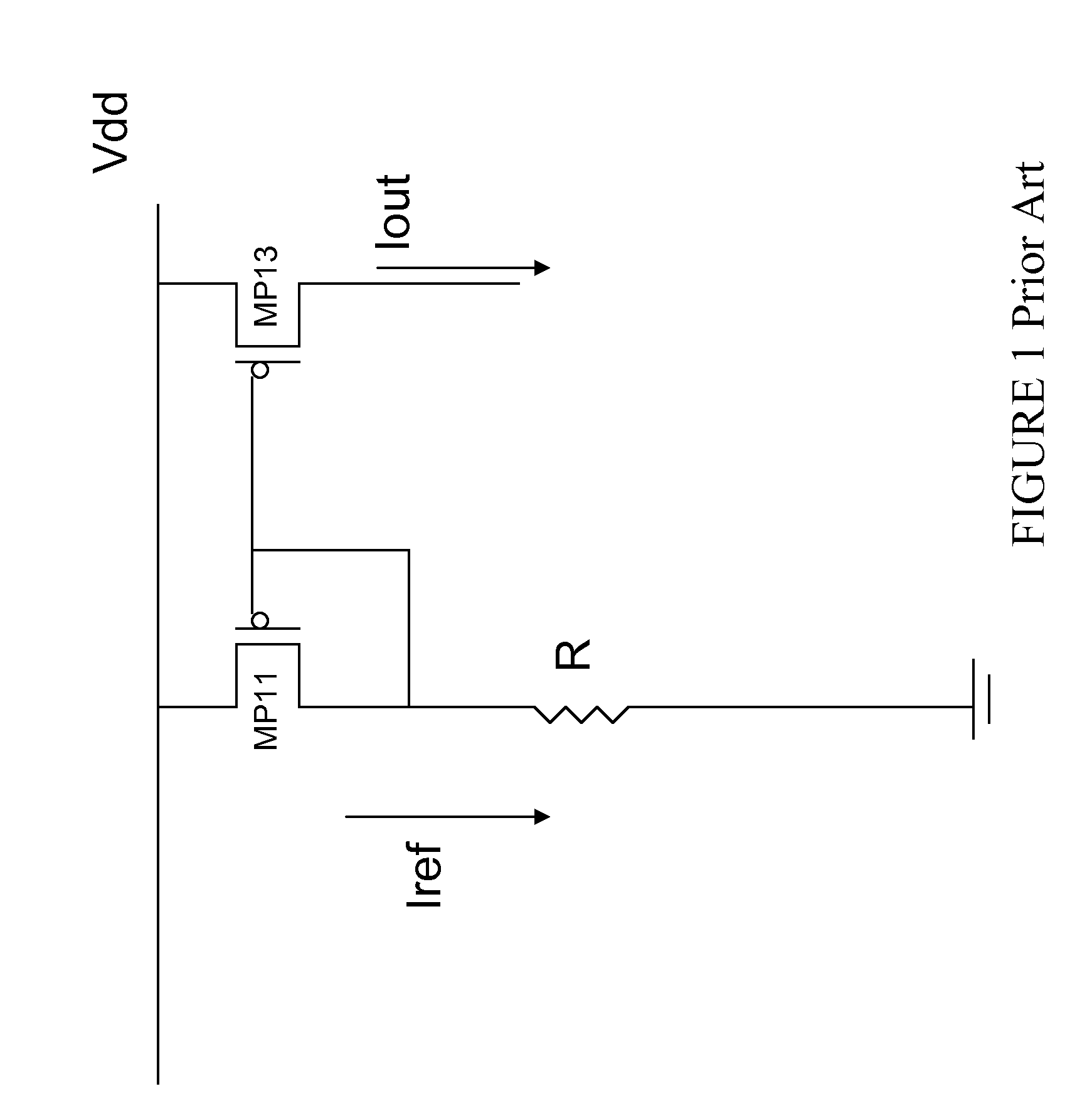
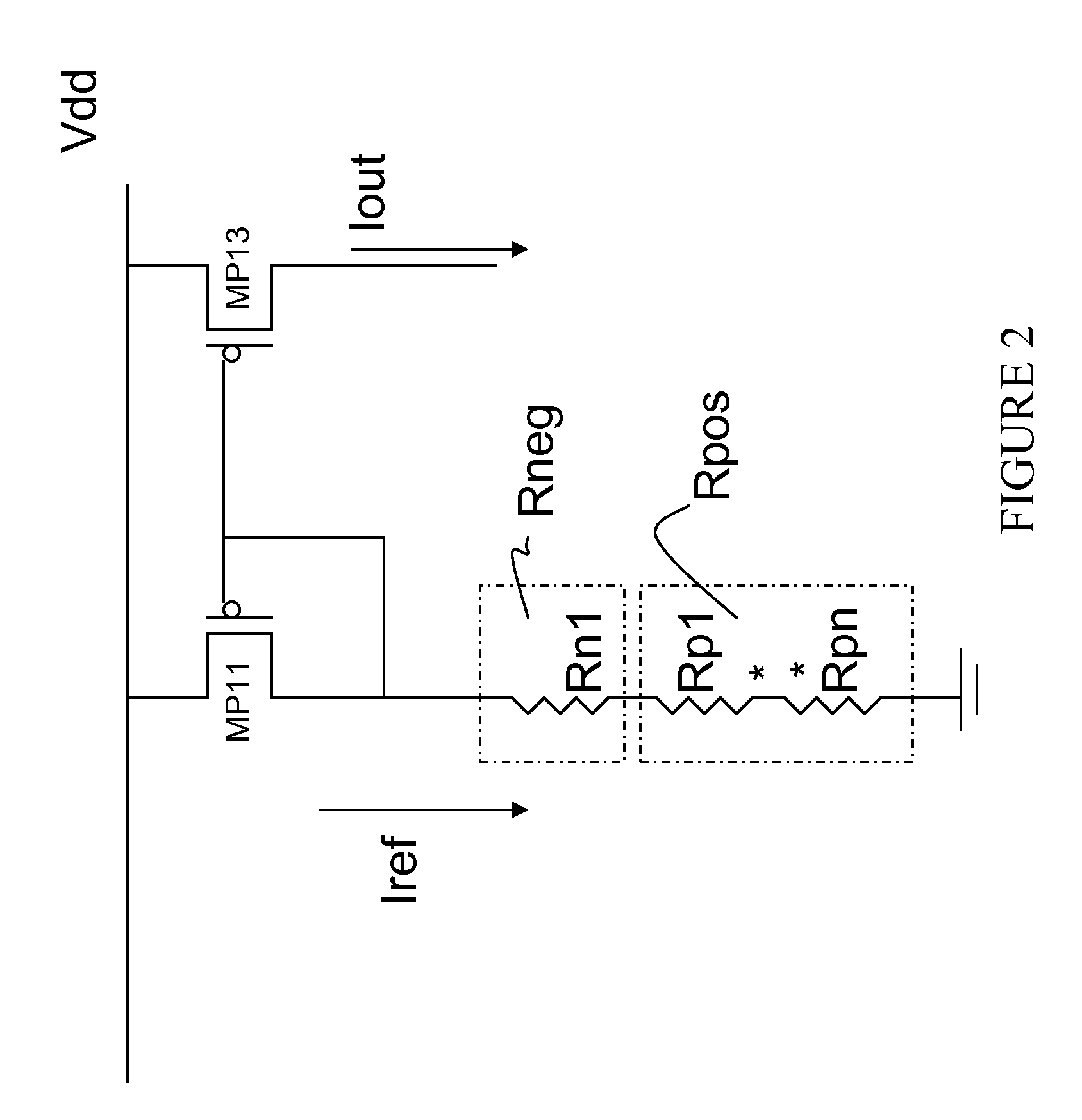
Circuit and Methods for Temperature Insensitive Current Reference
InactiveUS20100259315A1Less current is consumedSimple designElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceNegative temperature
Circuits and methods for providing a temperature insensitive reference current are disclosed. A voltage source is received having a temperature coefficient. A first resistive element having a positive temperature coefficient and a second resistive element having a negative temperature coefficient are series coupled to form a resistor ladder. The reference current is generated by coupling the voltage source across the resistor ladder. The temperature coefficients of the first and second resistive elements are chosen to cancel the temperature coefficient of the voltage source. In another embodiment a temperature compensated voltage source is coupled to a resistor ladder of a first resistive element and a second resistive element, and the first resistive element has a positive temperature coefficient and the second resistive element has a negative coefficient; these cancel to form a temperature insensitive reference current. A method for forming a temperature insensitive reference current from resistive elements is described.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Infrared image detail enhancing method based on second-generation wavelet
ActiveCN104036455AReduce computationFast operationImage enhancementDecompositionNegative coefficient
The invention provides an infrared image detail enhancing method based on second-generation wavelet. The method comprises the following steps: single-layer discrete two-dimensional wavelet decomposition is performed on an infrared image by use of a db1 second-generation wavelet integer lifting algorithm to obtain a low-frequency sub-band decomposition coefficient and three high-frequency sub-band decomposition coefficients respectively correspond to horizontal, vertical and diagonal directions; a corresponding threshold T of positive and negative coefficients of the three high-frequency sub-band decomposition coefficients is solved according to a formula; histogram equalization is performed in the positive and negative coefficients of the three high-frequency sub-band decomposition coefficients, and new coefficients of positive and negative parts of the three high-frequency sub-band decomposition coefficients are calculated; and finally, wavelet reconstruction is performed on the low-frequency sub-band decomposition coefficient and the three new high-frequency sub-band coefficients to obtain a detail-enhanced infrared image. According to the invention, details can be enhanced to the maximum extent on the premise of effectively suppressing noise, and the defect that noise is amplified after image enhancement existing in common algorithms like homomorphic filtering and histogram equalization is overcome.
Owner:CHANGZHOU MICROINTELLIGENCE CO LTD
Light-emitting diode fixture with an improved thermal control system
ActiveUS20140009064A1Planar light sourcesLighting heating/cooling arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
A light-emitting diode fixture comprises spaced-apart first and second housing portions. There is a cooling device disposed within the first housing portion. The cooling device is in fluid communication with the second housing portion. First and second printed circuit boards are disposed within the second housing portion. A light-emitting diode and a negative coefficient thermistor array are mounted on the first printed circuit board. The light-emitting diode and the negative coefficient thermistor array are each thermally coupled to a heat sink. A rectifier is mounted on the second printed circuit board. The rectifier is electrically connected in series with the negative coefficient thermistor array and the cooling device. Current used to power the cooling device flows from the rectifier through the negative coefficient thermistor array to the cooling device.
Owner:MP DESIGN
Power storage device
ActiveUS20100136461A1Improve performanceLower the volumeSubstation/switching arrangement detailsPrimary cellsFuel cellsEngineering
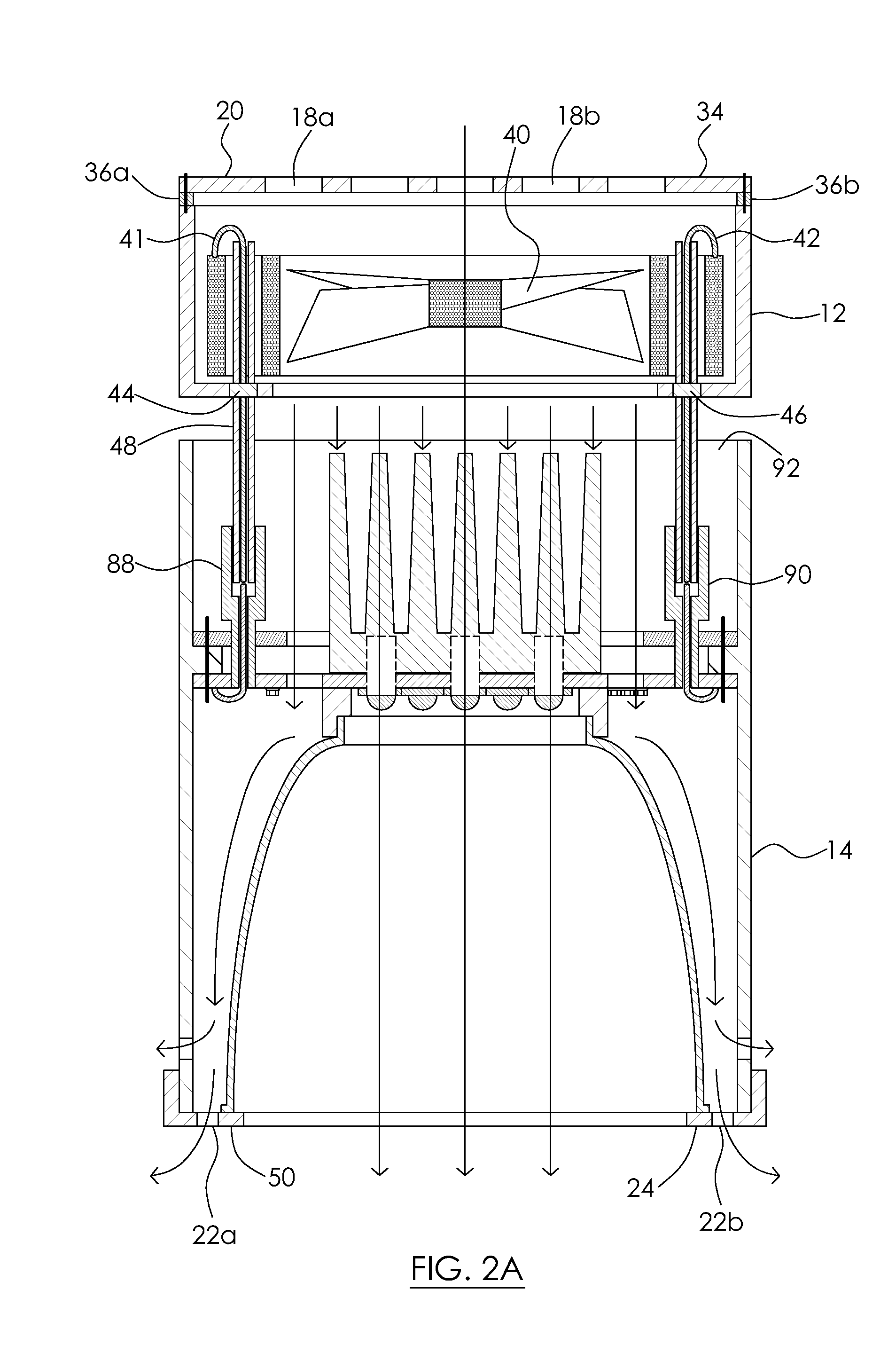
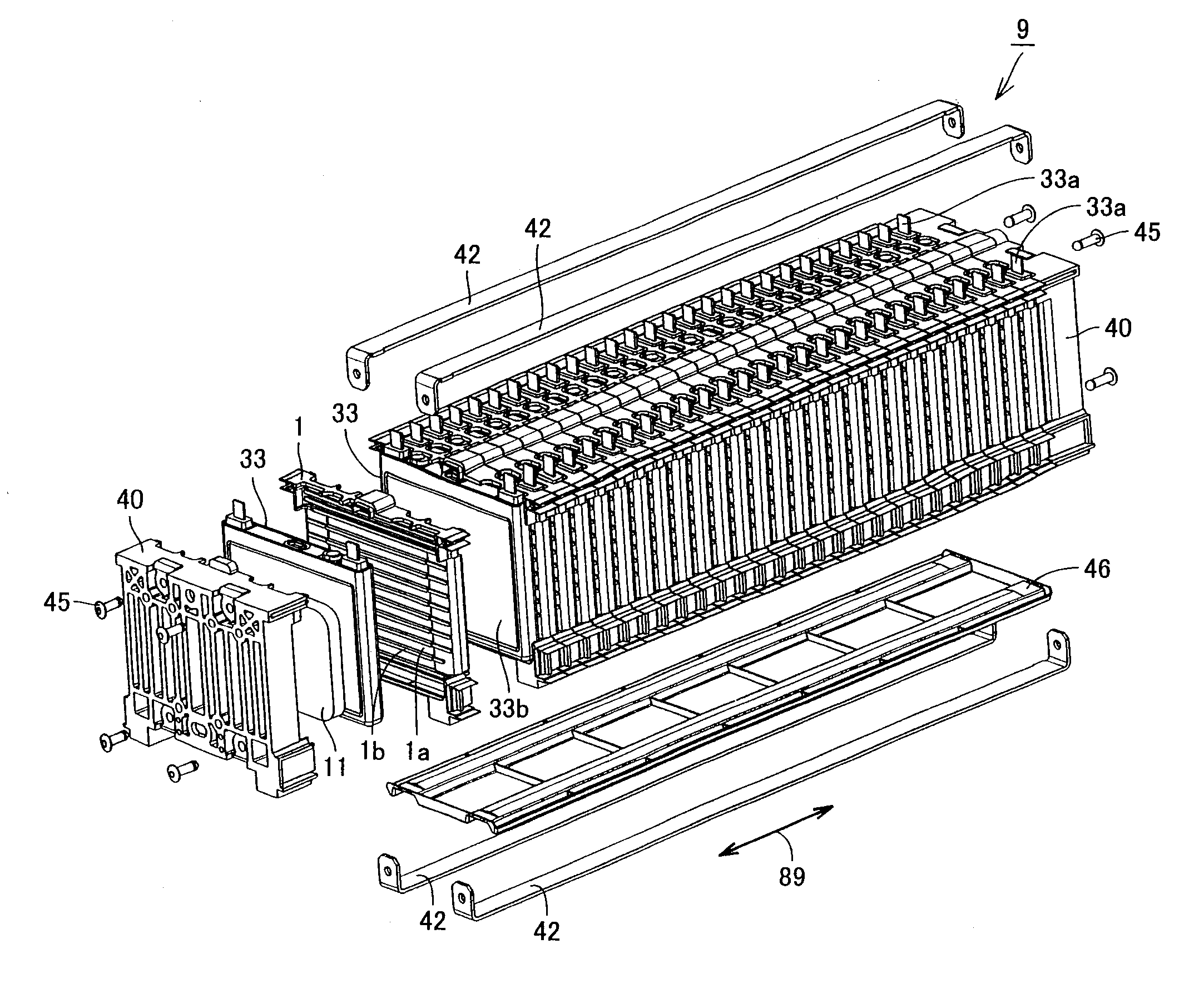
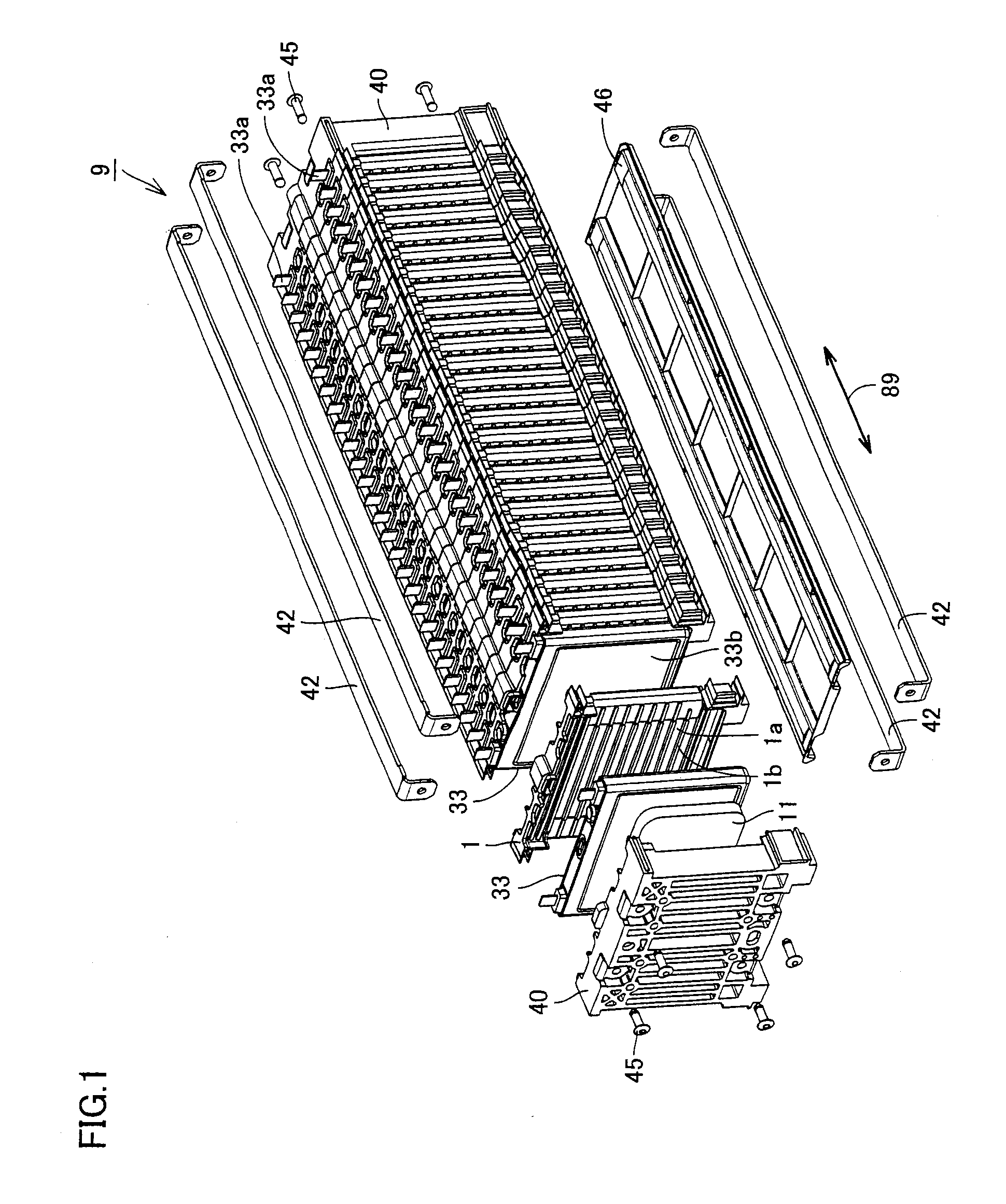
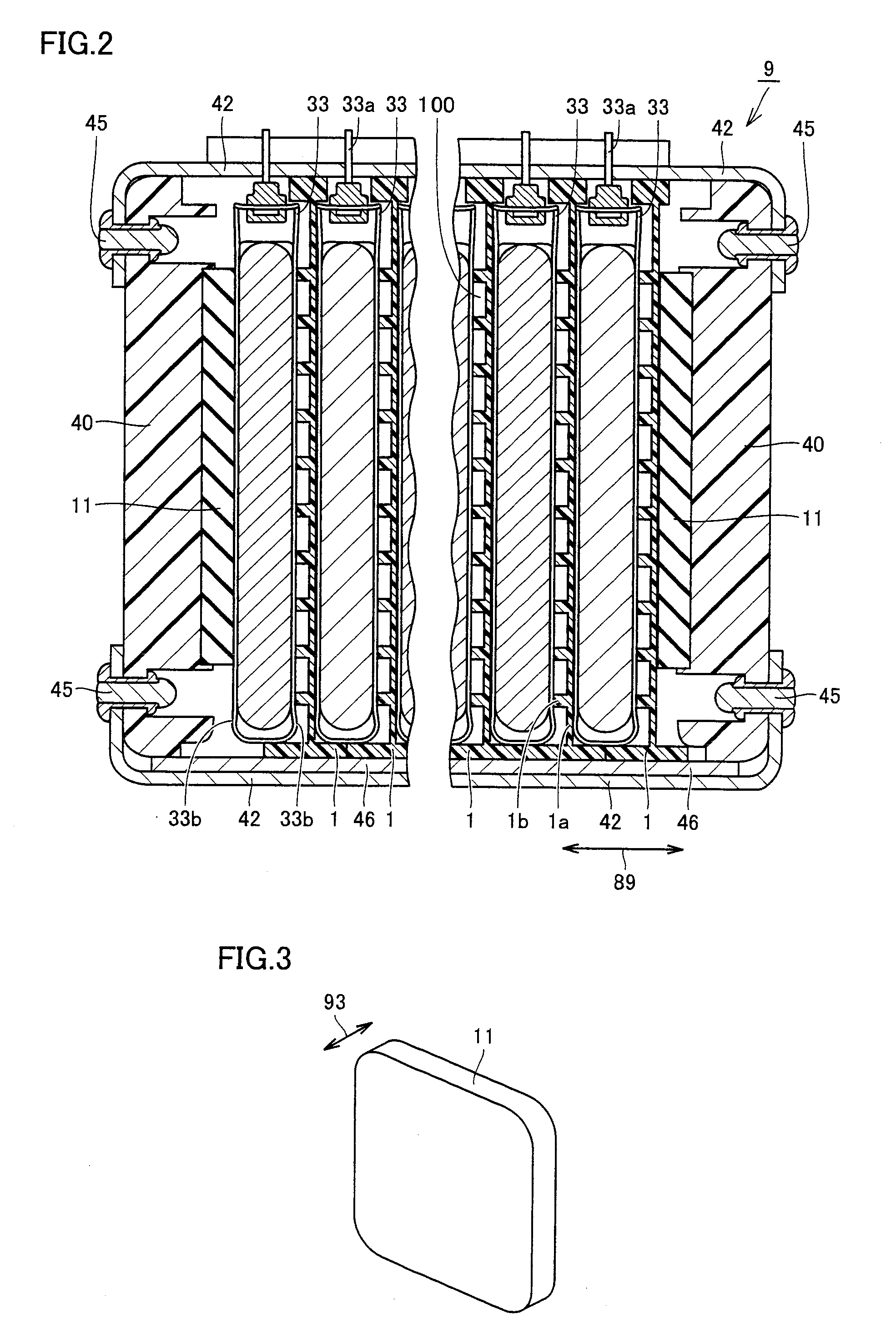
A power storage device includes a fuel cell (33), a battery holder (1) and an end plate (40) for sandwiching and binding the fuel cell, and an interposed member (11) disposed between the end plate (40) and the fuel cell (33). The battery holder (1) and the end plate (40) are made of resin, and have a positive coefficient of thermal expansion at a temperature lower than a predetermined temperature. The interposed member (11) is formed to have a substantially negative coefficient of thermal expansion at a temperature lower than the predetermined temperature.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
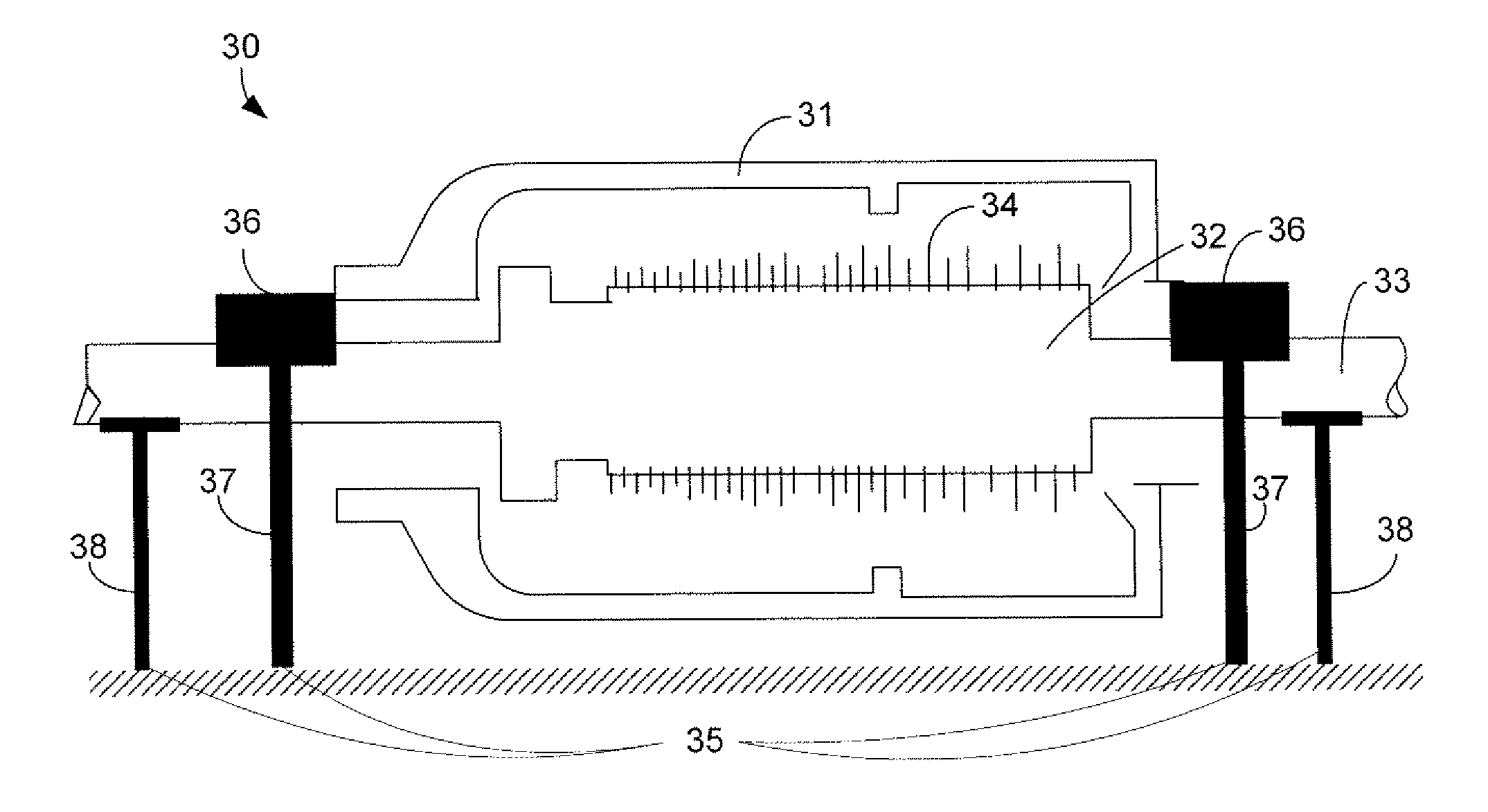
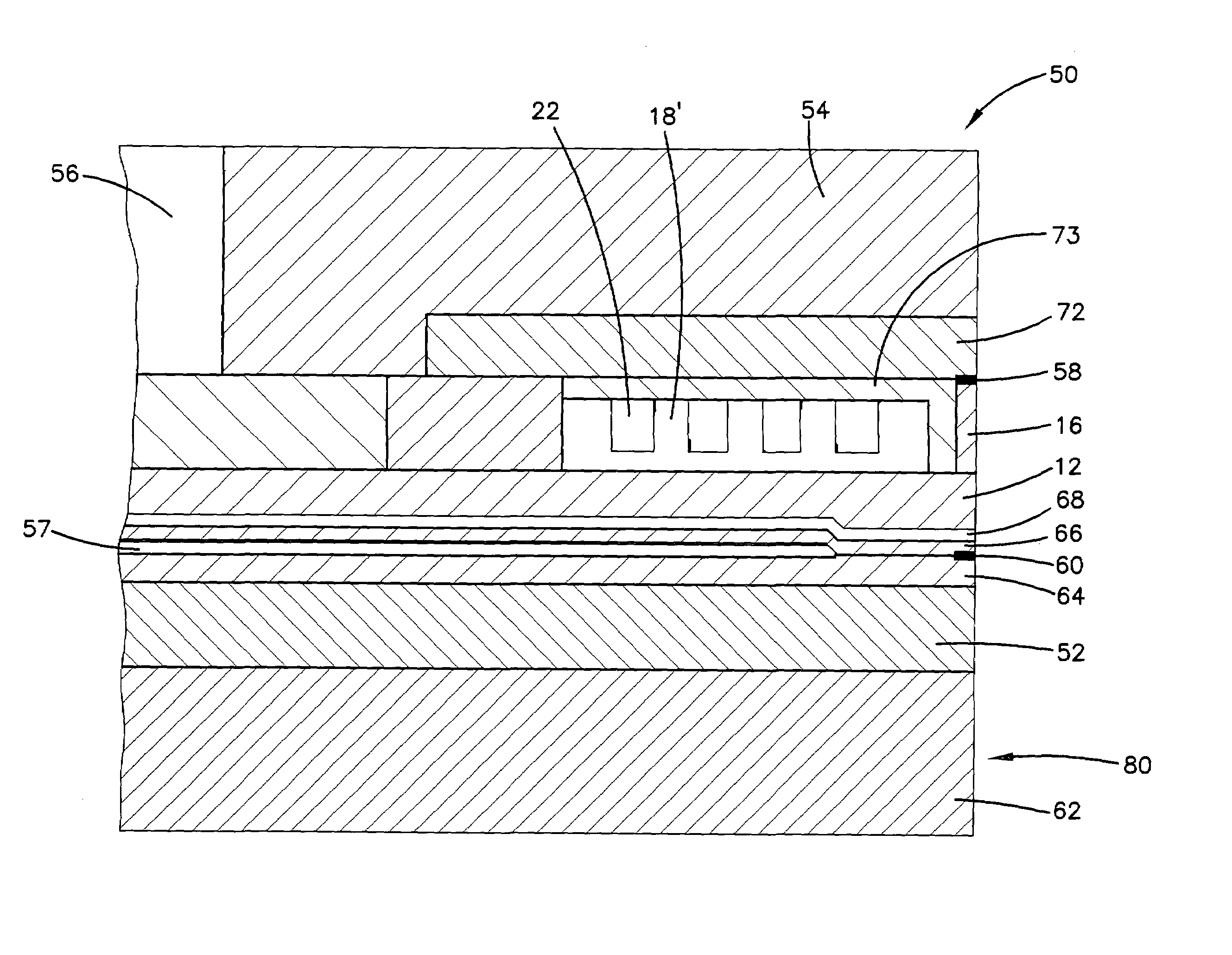
Negative thermal expansion dielectrics for thermal pole tip protrusion compensation
InactiveUS7102853B2Low deposition rateEasy to controlConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsDielectricTransducer
A slider having a magnetic read / write head and including, a base coat, a reader element having a transducer, a writer element, the writer element including at least one conductive coil, the coil being electrically insulated by a composition which has a negative coefficient of thermal expansion, and an overcoat.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
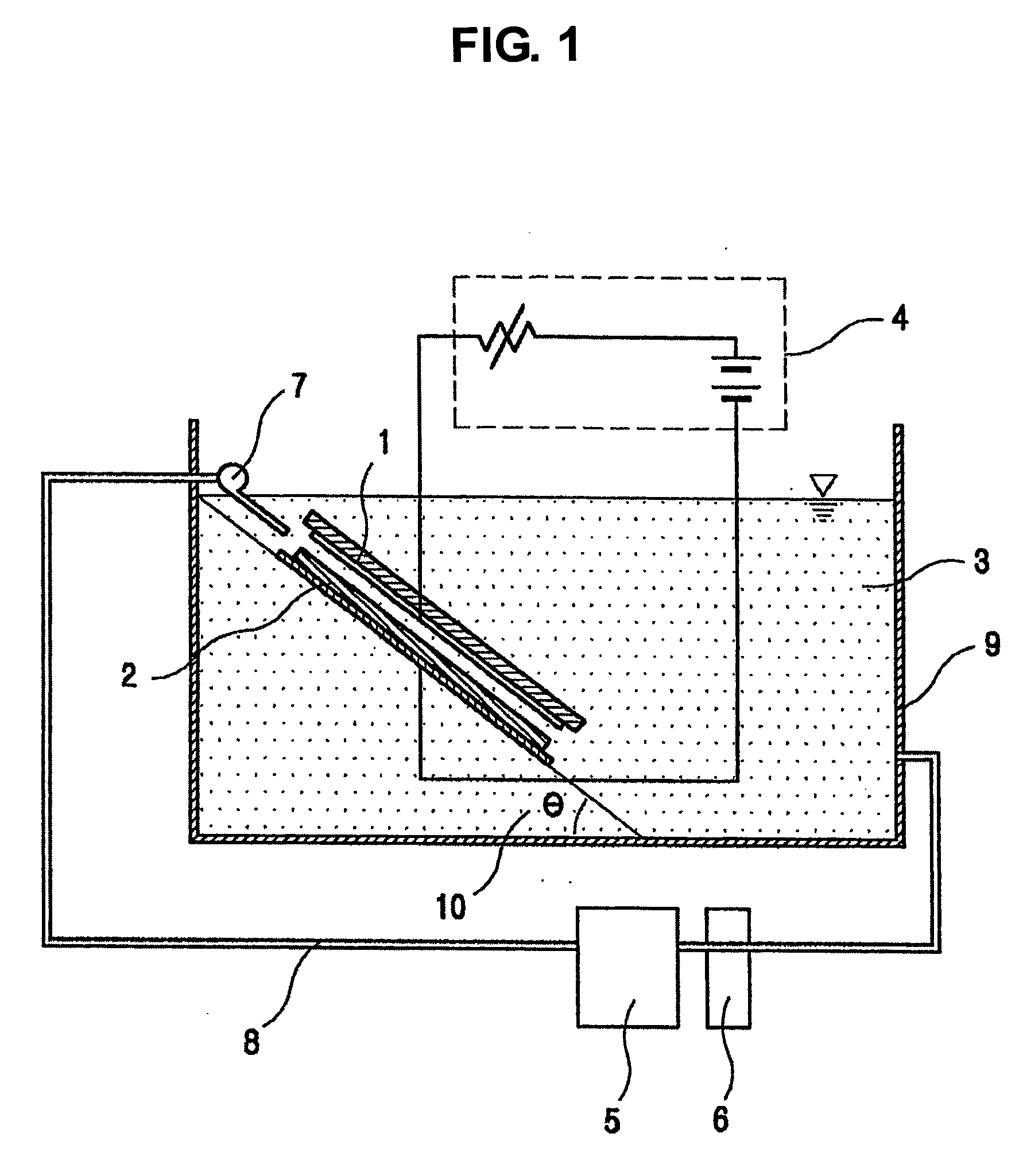
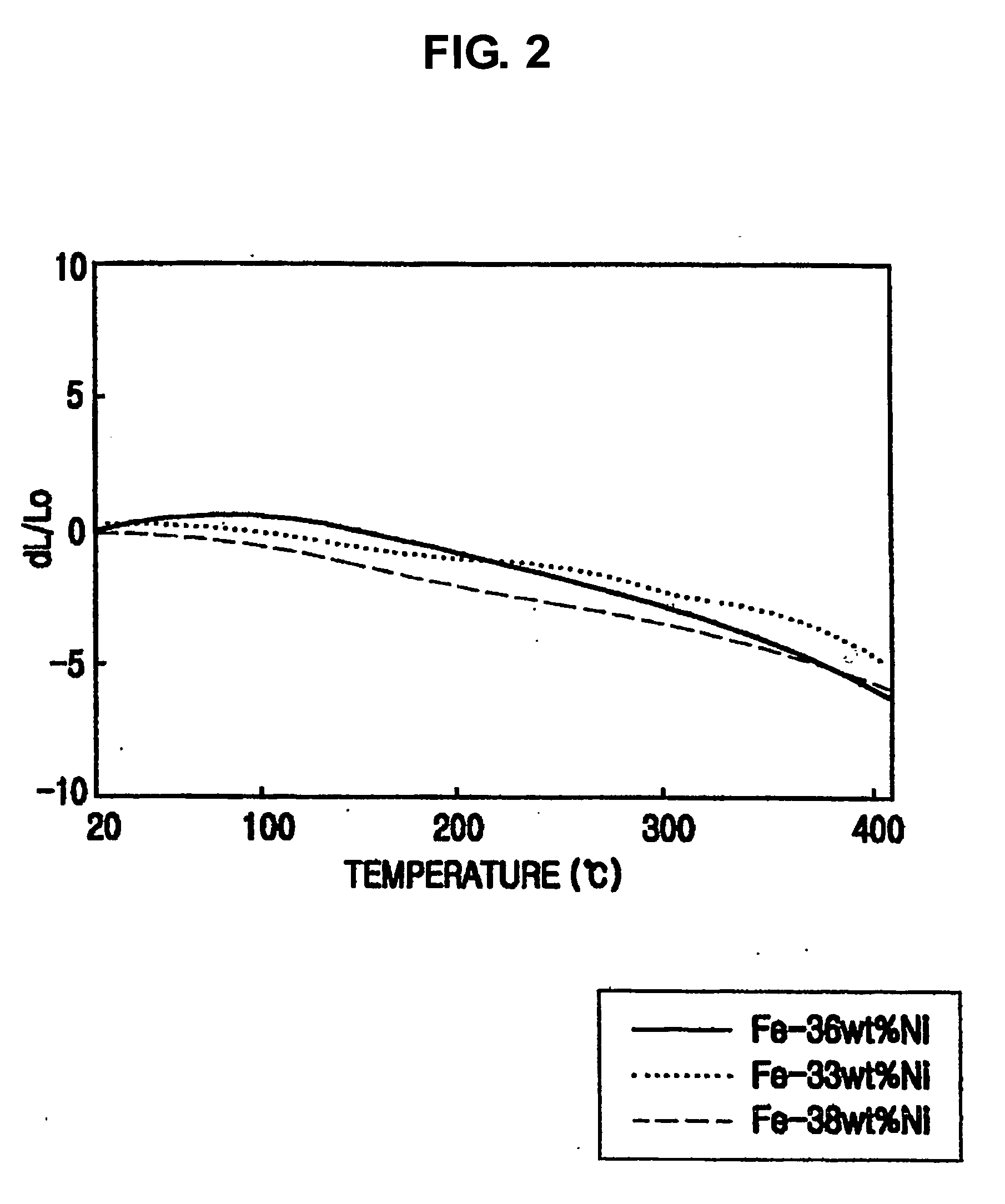
Nano invar alloys and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060037671A1Improve mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyPhotography auxillary processesInvar alloySulfate
The present invention relates to an electrolyte for producing a novel Fe—Ni alloy having an Ni content in a range of 33 to 42 wt %, specifically a nanocrystalline invar alloy having a grain size of 5 to 15 nm, by electroplating, and preparation conditions thereof. The electrolyte comprises, on the basis of 1 L of water, 32 to 53 g of ferrous sulfate or ferrous chloride, a mixture thereof; 97 g of nickel sulfate, nickel chloride, nickel sulfamate or a mixture thereof; 20 to 30 g of boric acid; 1 to 3 g of sodium saccharin; 0.1 to 0.3 g of sodium lauryl sulfate; and 20 to 40 g of sodium chloride. The Fe—Ni alloy sheet of the present invention exhibits excellent mechanical property compared to the conventional Fe—Ni alloy and a new property, i.e., a negative coefficient of thermal expansion at a given temperature range.
Owner:NANO INVAR
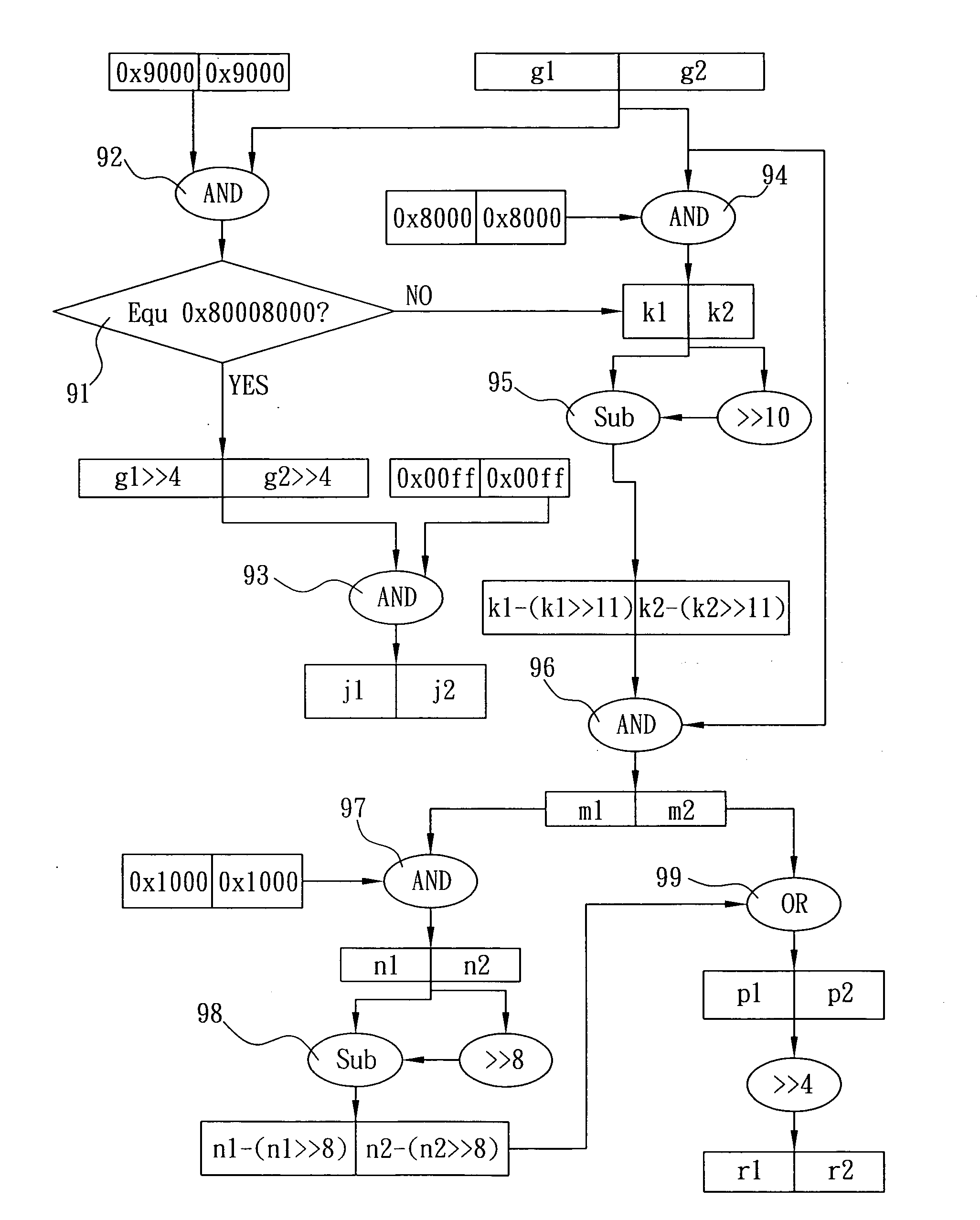
Method of parallelly filtering input data words to obtain final output data words containing packed half-pel pixels
ActiveUS20080123974A1Efficiently filter data streamIncreased complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionData stream
The present invention is to provide a parallel filtering method, which is implemented to an interpolation filter and comprises the steps of separating coefficients of the interpolation filter into two sets comprising the positive and negative coefficients respectively for parallelly filtering a plurality of input data pixels packed into data words inputted to the interpolation filter concurrently to obtain a first result data word, and clipping and shifting the first result data word to obtain a final output data word containing packed half-pel pixels for parallelly and efficiently filtering data stream of video without increasing the complexity, cost, size and power consumption of circuitry of an electronic video apparatus.
Owner:ARCSOFT
Negative coefficient of thermal expansion particles and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20050100743A1Eliminate and reduce problemSimple and inexpensive methodLiquid surface applicatorsConductive materialNegative coefficientMaterials science
A negative coefficient of thermal expansion particle includes a first bilayer having a first bilayer inner layer and a first bilayer outer layer, and a second bilayer having a second bilayer inner layer and a second bilayer outer layer. The first and second bilayers are joined together along perimeters of the first and second bilayer outer layers and first and second bilayer inner layers, respectively. The first bilayer inner layer and the second bilayer inner layer are made of a first material and the first bilayer outer layer and the second bilayer outer layer are made of a second material. The first material has a greater coefficient of thermal expansion than that of the second material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Fiber composite over-wrap for a cryogenic structure
InactiveUS7541078B1Envelopes/bags making machineryContainer filling methodsCarbon compositesNegative coefficient
A structure has an inner, load bearing member and a surrounding, concentric over-wrap. The inner member is composed of a carbon composite and the over-wrap is composed of a non-carbon composite. The inner member has a negative coefficient of thermal expansion and the over-wrap has a positive coefficient of thermal expansion that is an order of magnitude greater than that of the inner member. When subjected to cryogenic temperatures, the over-wrap will shrink and apply a compressive force against the inner member, to resist the creation of microcracks in the inner member.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
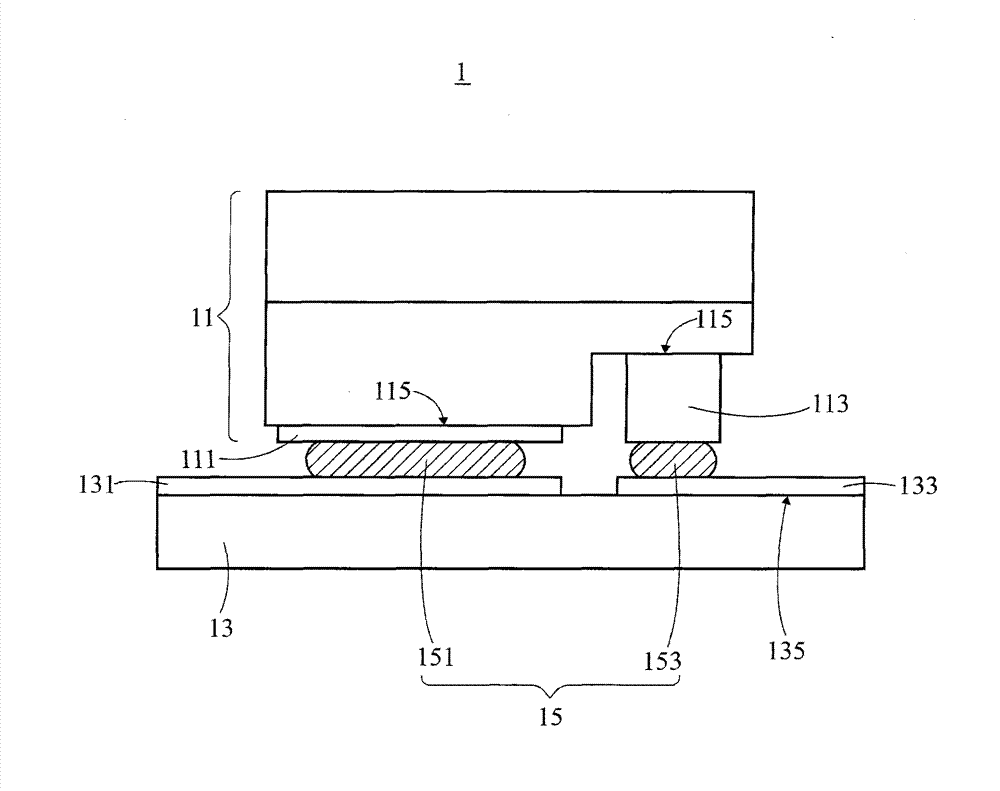
Package structure and manufacturing method for the same
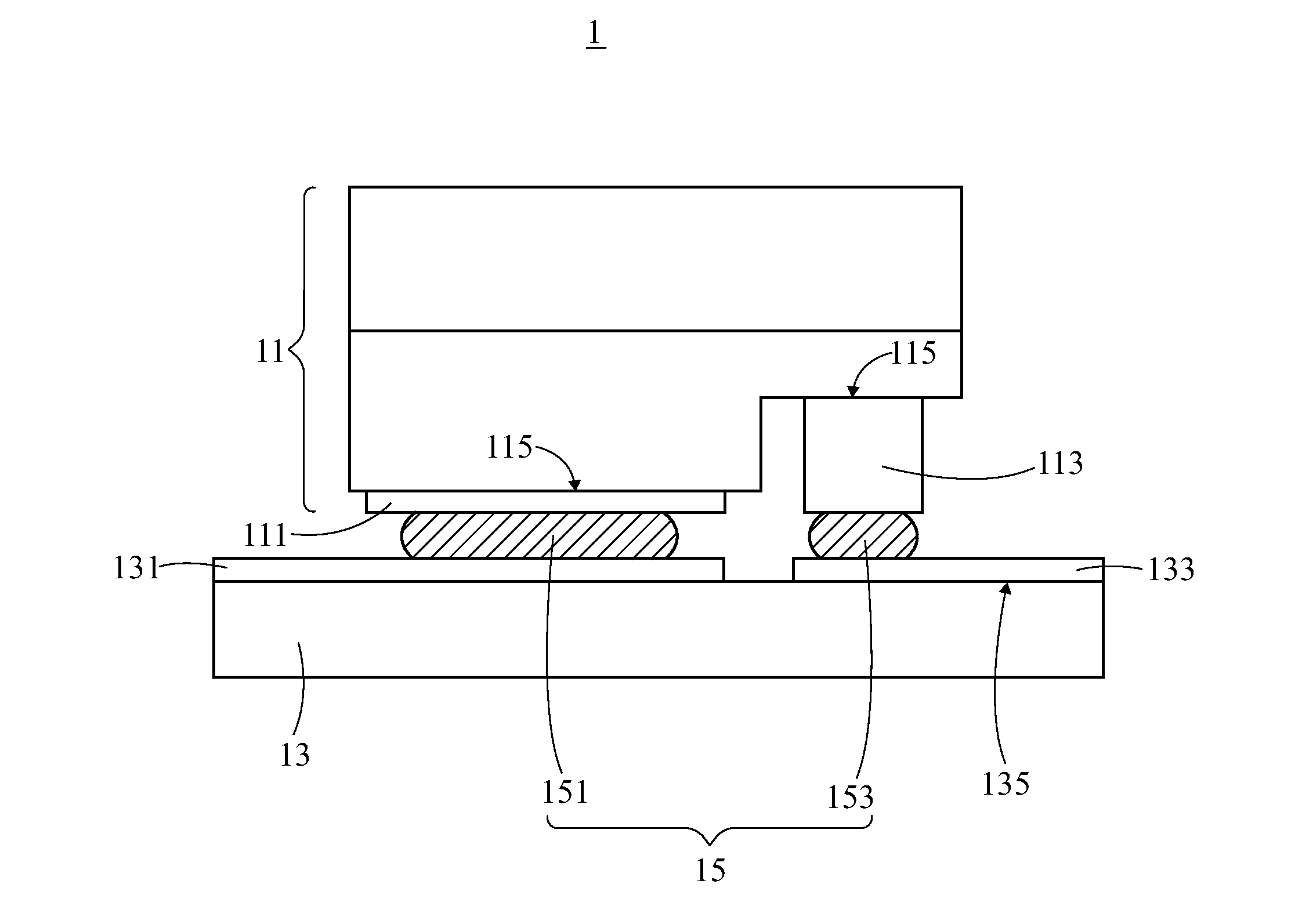
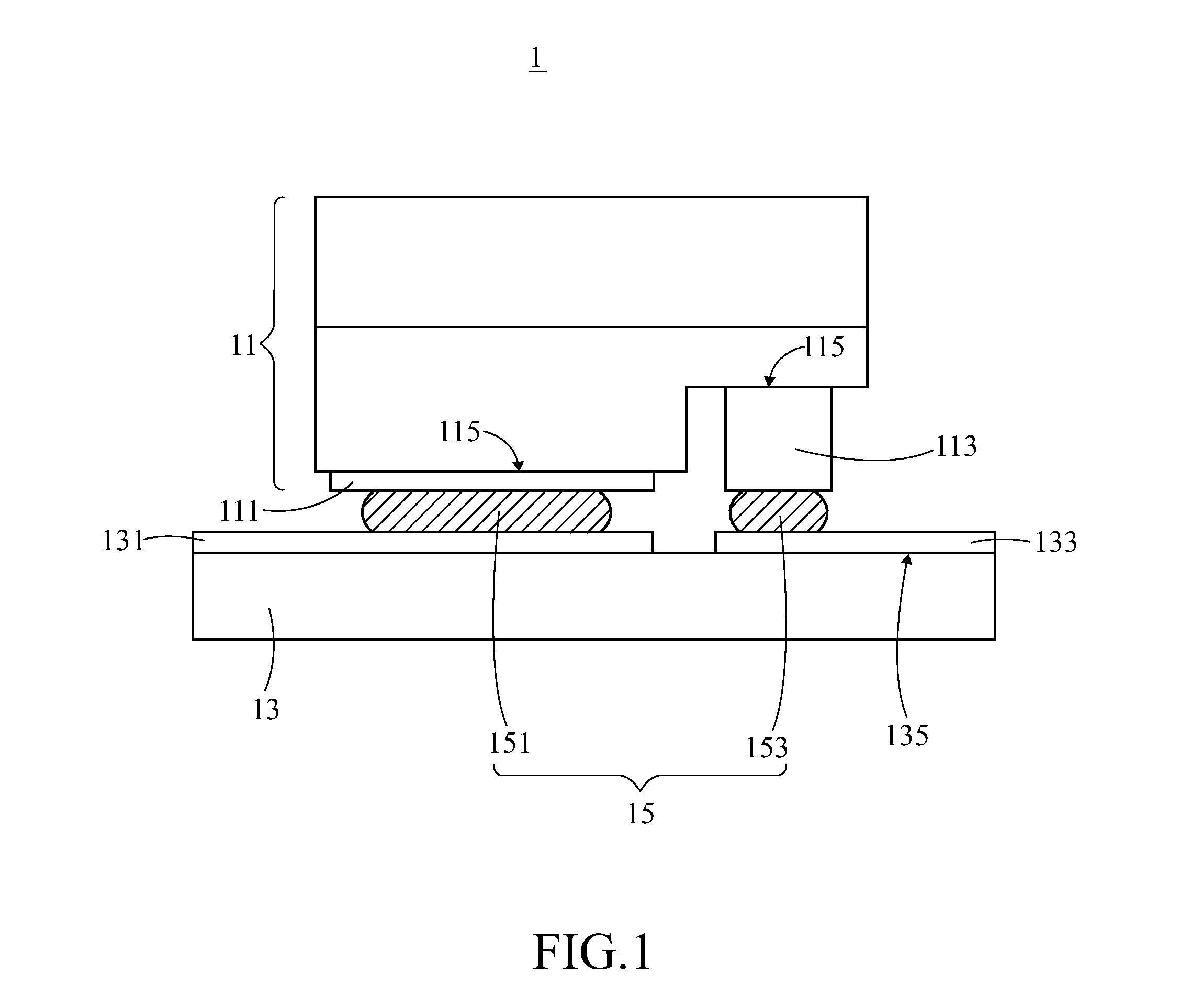
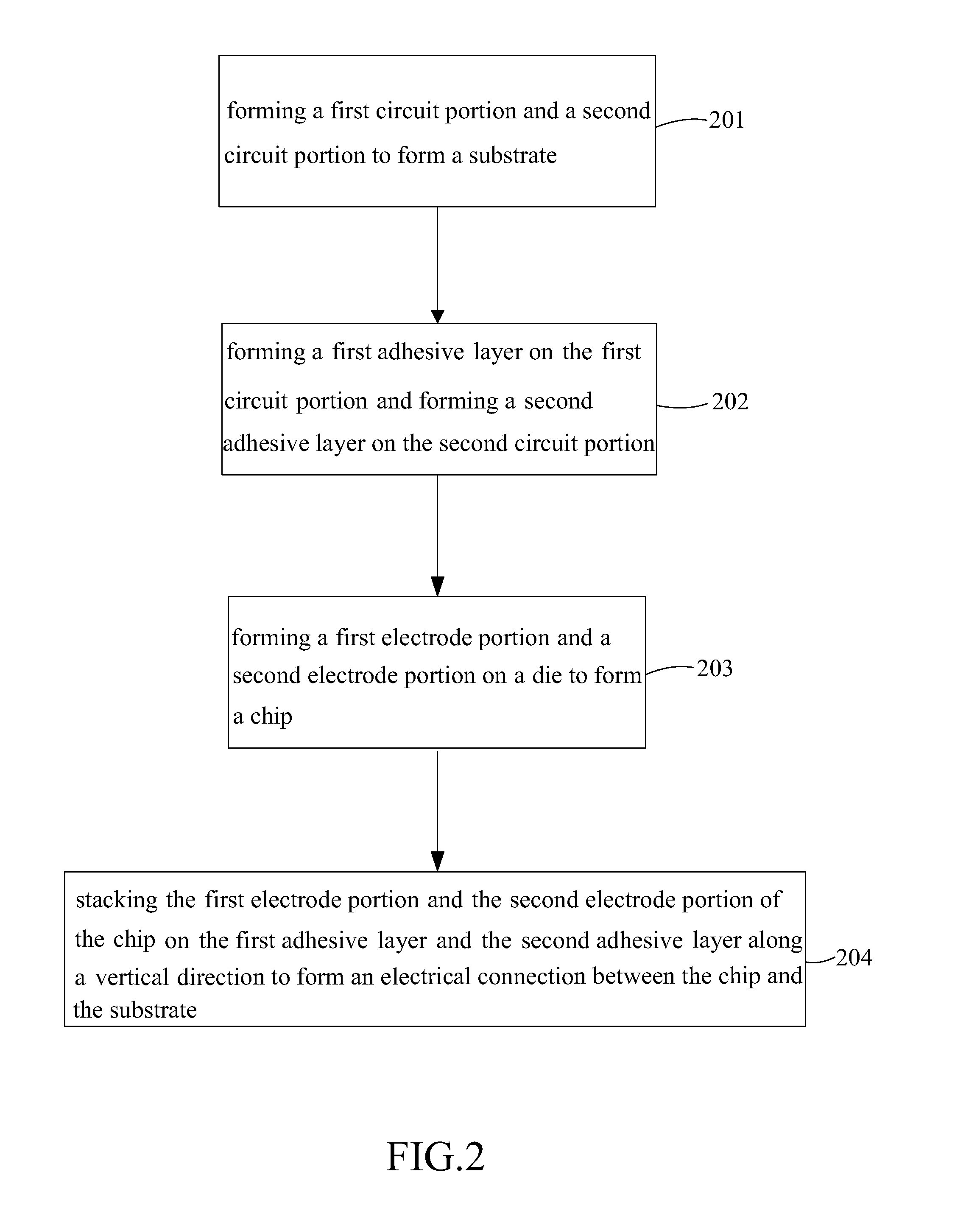
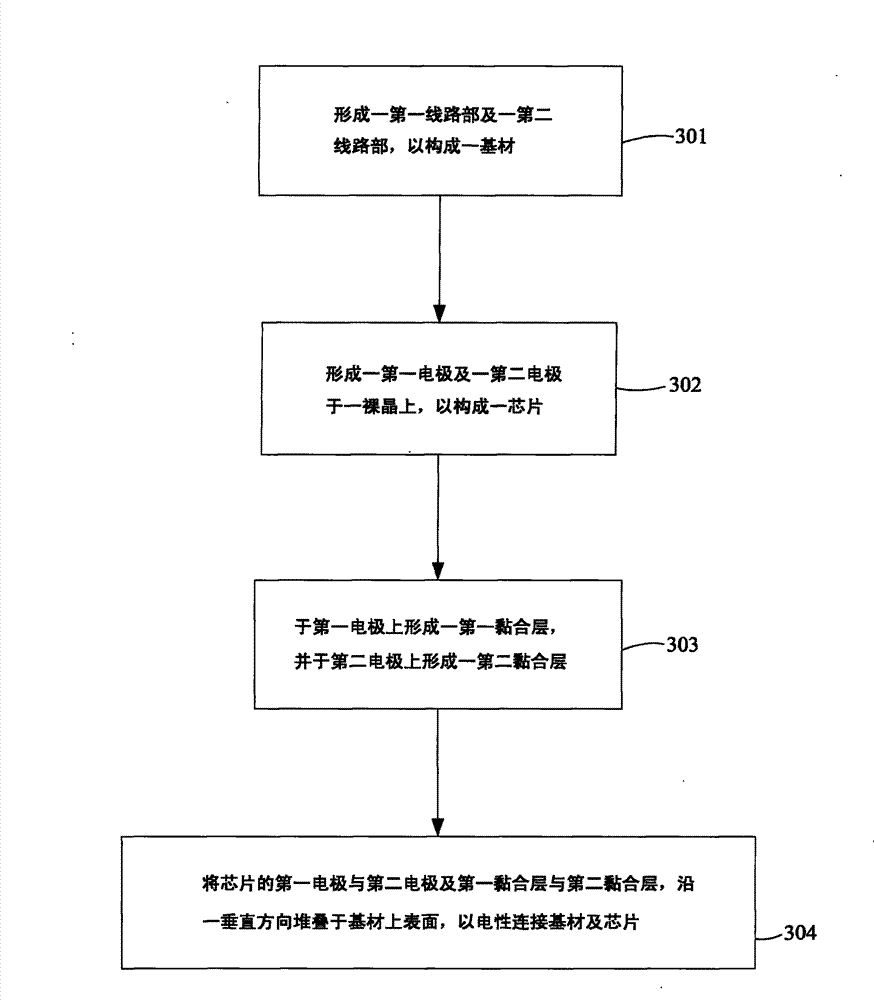
InactiveUS20130105852A1Avoid alignmentAlignment shiftSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound (substance)Electrical connection
A package structure and a manufacturing method for the same are provided. The package structure includes a chip, a substrate and at least one adhesive layer. The chip has at least one electrode portion. The substrate has at least one circuit portion. The adhesive layer is disposed between the electrode portion and the circuit portion to form an electrical connection therebetween. The adhesive layer is a material, which comprises a metal compound, with a Negative Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (Negative CTE). Because of the material with a Negative CTE, the alignment shift can be avoided after the chip and the substrate are adhered together.
Owner:WALSIN LIHWA
Microwave photon filter construction capable of implementing negative coefficient
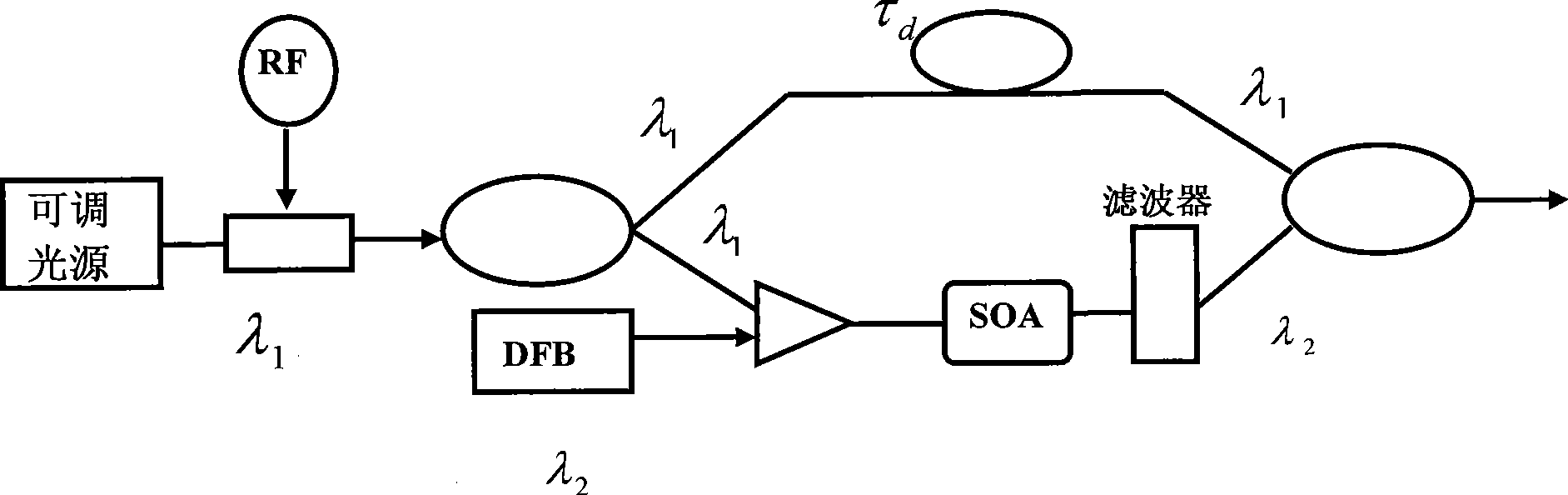
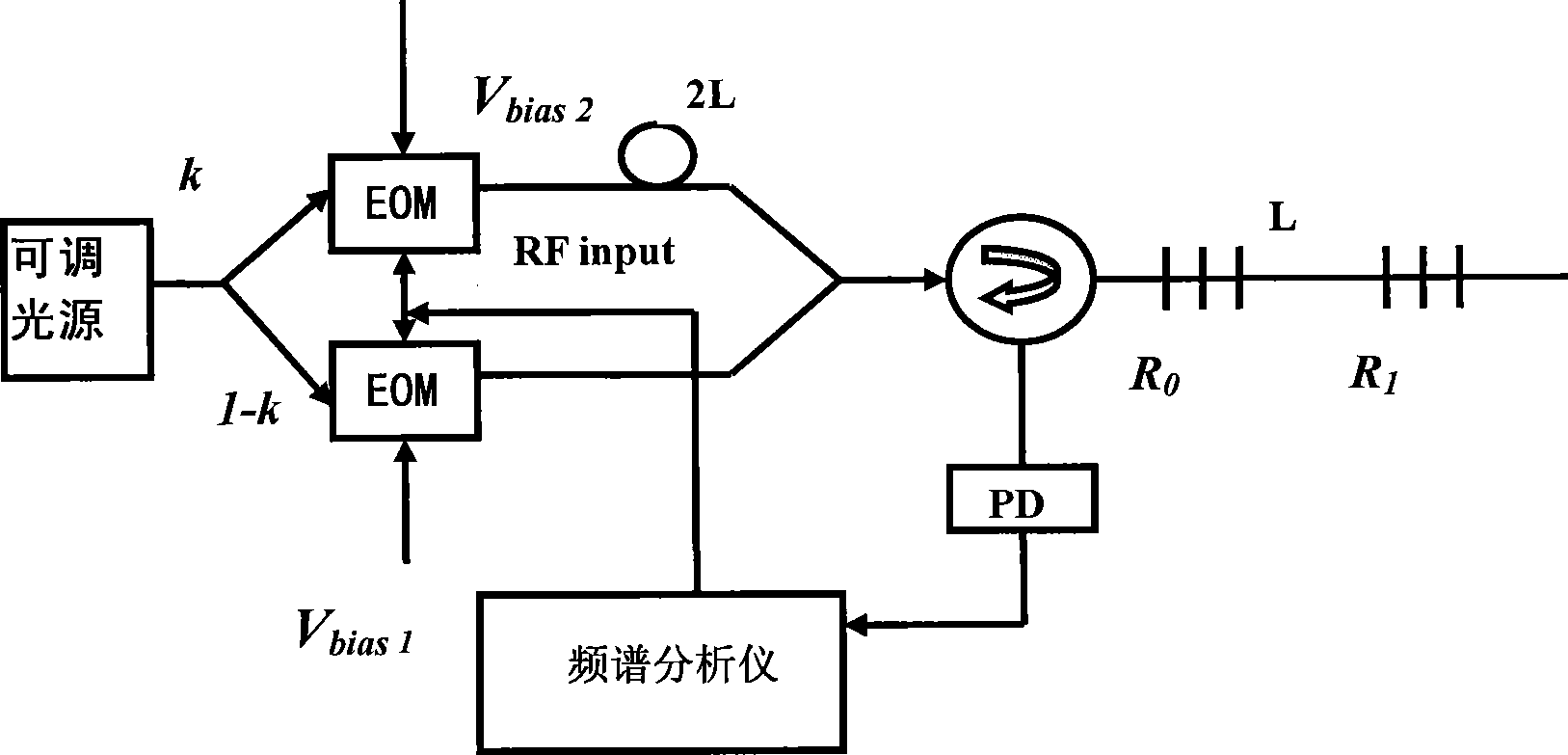
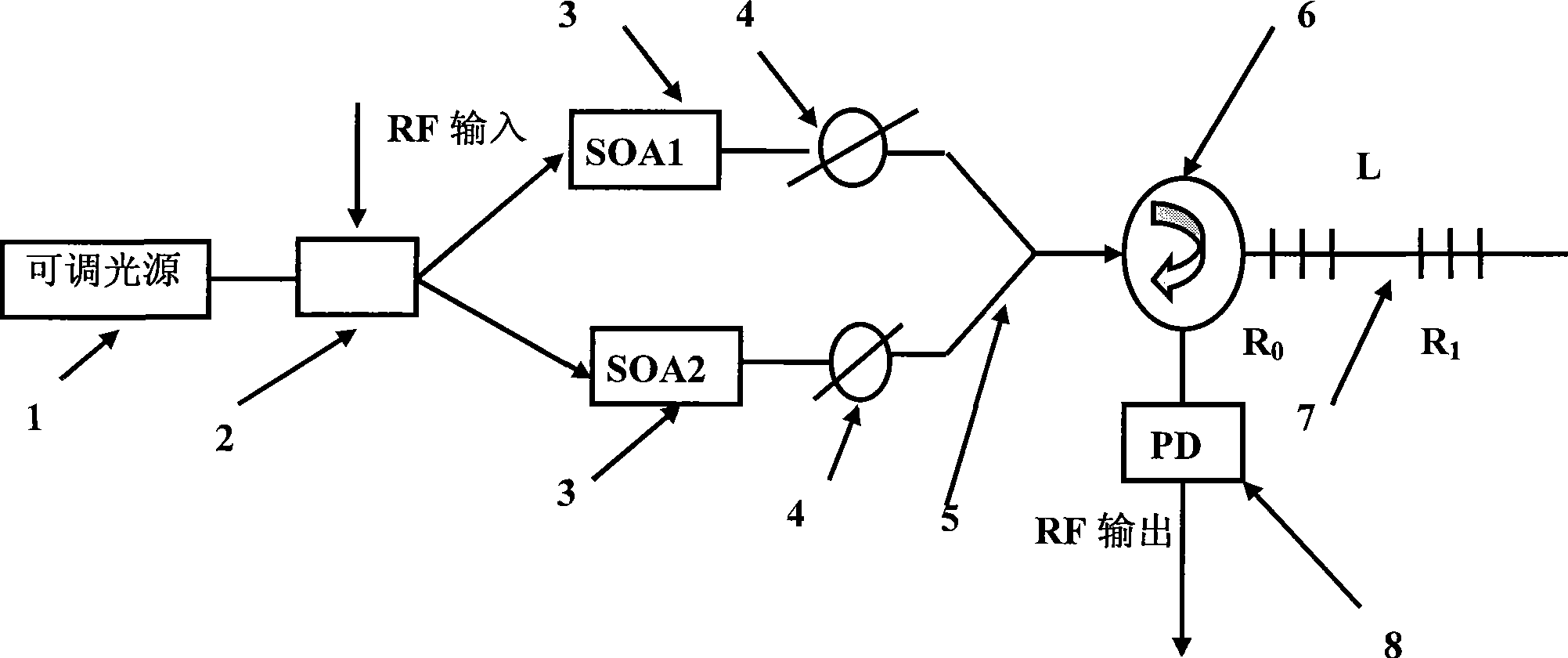
InactiveCN101436904AHigh extinction ratioCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionGratingBeam splitter
The invention relates to a microwave photon filter structure which can achieve a negative coefficient and belongs to the field of high-capacity microwave photon communication. The structure consists of a tunable light source (1), a 3db beam splitter (2), a semiconductor amplifier SOA (3), an attenuator or an amplifier (4), a coupler (5), a circulator (6), a Bragg grating (7) and an optoelectronic detector (8). The microwave photon filter structure has the advantages that the characteristic of achieving the negative coefficient of the microwave photon filter is achieved, and finally a light signal passing through a photodiode is converted into a radio frequency signal so that the function of filtering the radio frequency signal in an optical domain is realized directly.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
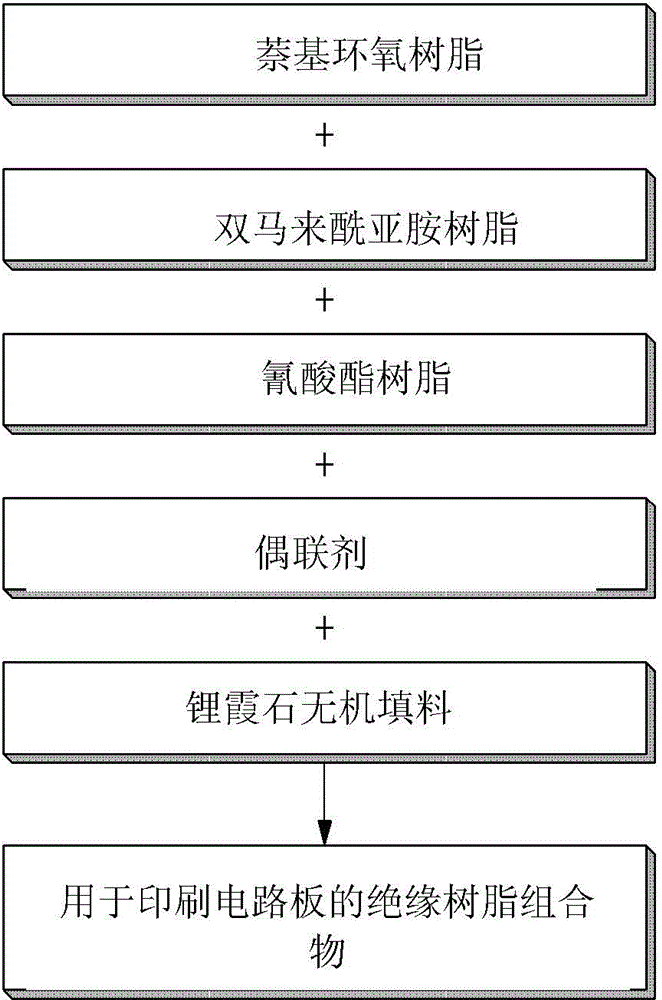
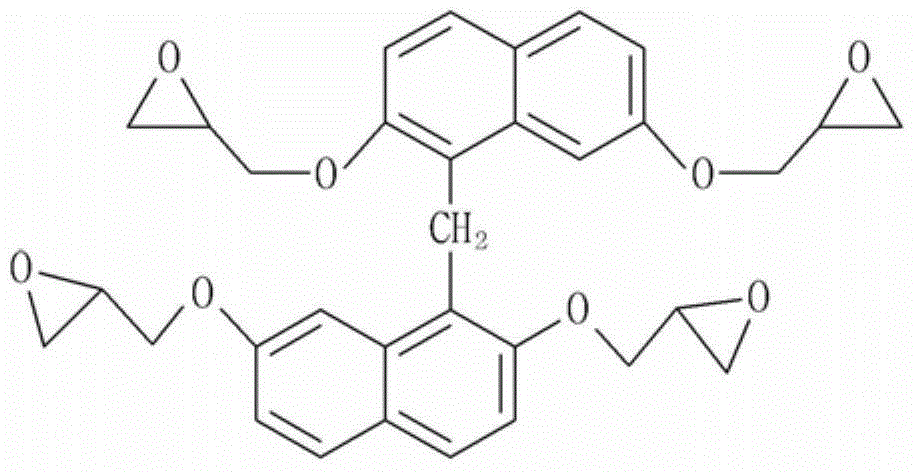
Insulating resin composition for printed circuit board and products manufactured by using the same
InactiveCN104559055APlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsCopperNegative coefficient
Disclosed herein are an insulating resin composition for a printed circuit board, and an insulating film, a prepreg, a copper clad laminate, or a printed circuit board manufactured by using the same. More specifically, the insulating resin composition contains an eucryptite inorganic filler having a negative coefficient of thermal expansion, such that a glass transition temperature and a coefficient of thermal expansion may be improved, and warpage of the insulating film, the prepreg, the copper clad laminate, or the printed circuit board manufactured by using the insulating resin composition for a printed circuit board may be minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
MEMS structure and optical modulator having temperature compensation layer
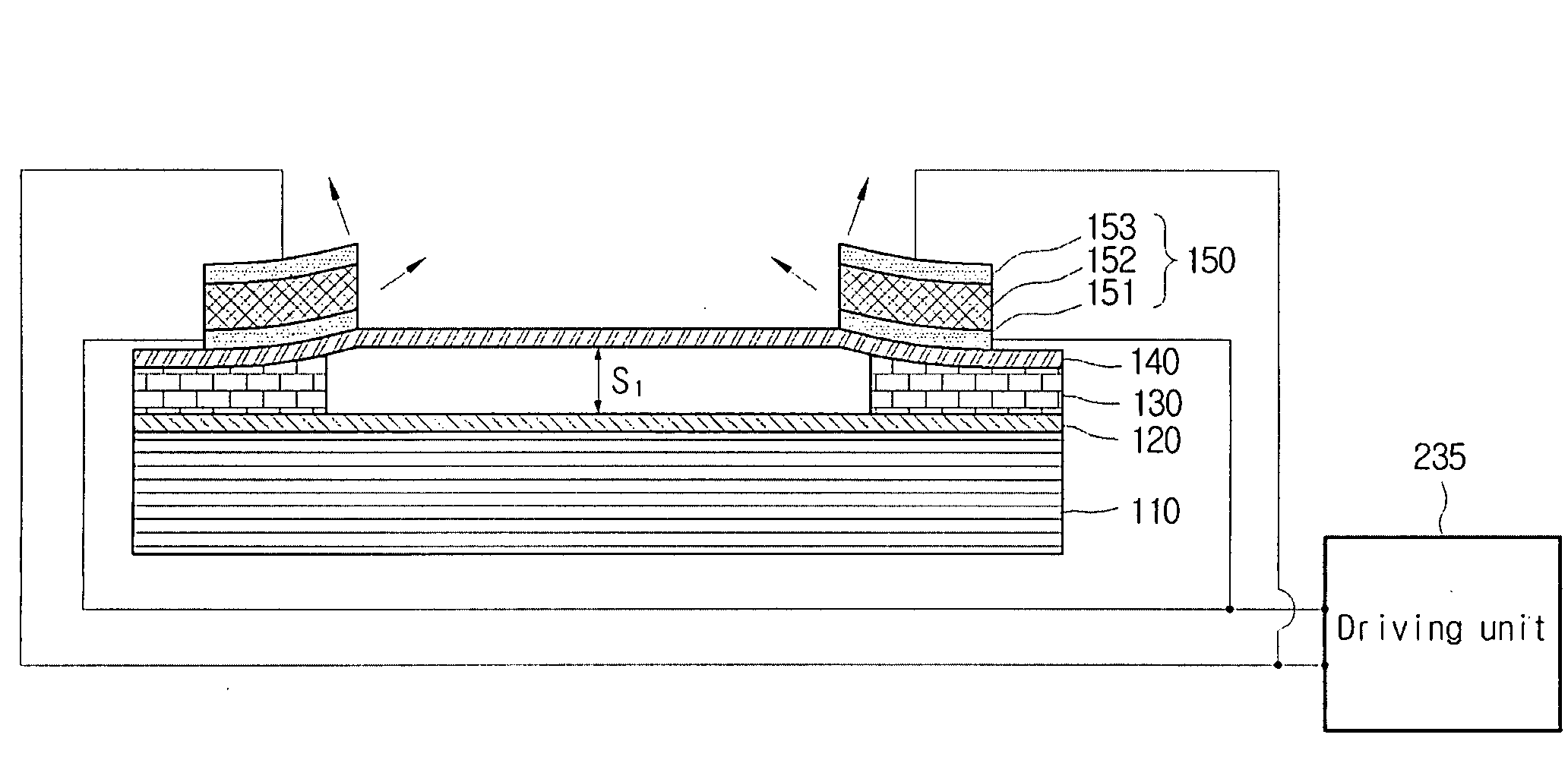
An optical modulator can be provided that includes a substrate; an insulation layer positioned on the substrate; a ribbon layer such that its center portion is spaced apart from the insulation layer; a piezoelectric actuator positioned on either end of the ribbon layer that provides the driving force which moves the center portion of the ribbon layer vertically; and a temperature compensation layer, which is made of a thermally contracting material having a negative coefficient of expansion, and which is formed on at least one position of an upper portion of the piezoelectric actuator, a lower portion of the piezoelectric actuator, and a lower surface of the ribbon layer corresponding to a position of the piezoelectric actuator. In the optical modulator, the problem of thermal deformation due to rises in temperature can be resolved, whereby the accuracy and reliability of operation of the component can be increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Superconductive nanocomposite
InactiveUS20110021360A1Low densityReadily apparentMagnetic/electric field screeningThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The superconductive nanocomposite is a composition formed by nanoparticles of a high temperature superconductor blended with a polymer matrix containing natural rubber and polyethylene. The high temperature superconductor is preferably a bismuth-based superconductor (BSCCO) having a particle size of about 21 nm, but may be any other high temperature or Type II ceramic, metal oxide superconductor. The superconductor nanoparticles comprise about 15% of the weight of natural rubber in the composition. The polyethylene is preferably low density polyethylene and may comprise between 0% up to about 40% of the weight of natural rubber in the composition. The nanocomposite may be prepared by blending the components and roll milling the rubber. Depending upon the percentage of polyethylene present in the matrix, the nanocomposite has useful applications as a double thermistor (both positive and negative coefficients of electrical resistivity), for antistatic charge dissipation, and for electromagnetic shielding in the microwave region.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Inorganic filler, and insulating resin composition, insulating film, prepreg and printed circuit board including the same
InactiveUS20150027763A1Reduce diffusePresent inventionPrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit manufactureNegative coefficientPrinted circuit board
An inorganic filler has a negative coefficient of thermal expansion, and a shell thereon that decreases diffusion of ions contained in the inorganic filler to outside of the shell and organic filler.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Materials for electronic devices
InactiveUS20050151270A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNegative coefficientMaterials science
Improved materials for use in the fabrication of electronic devices and devices made therewith are described. The materials comprise fillers having a negative coefficient of thermal expansion.
Owner:INTEL CORP
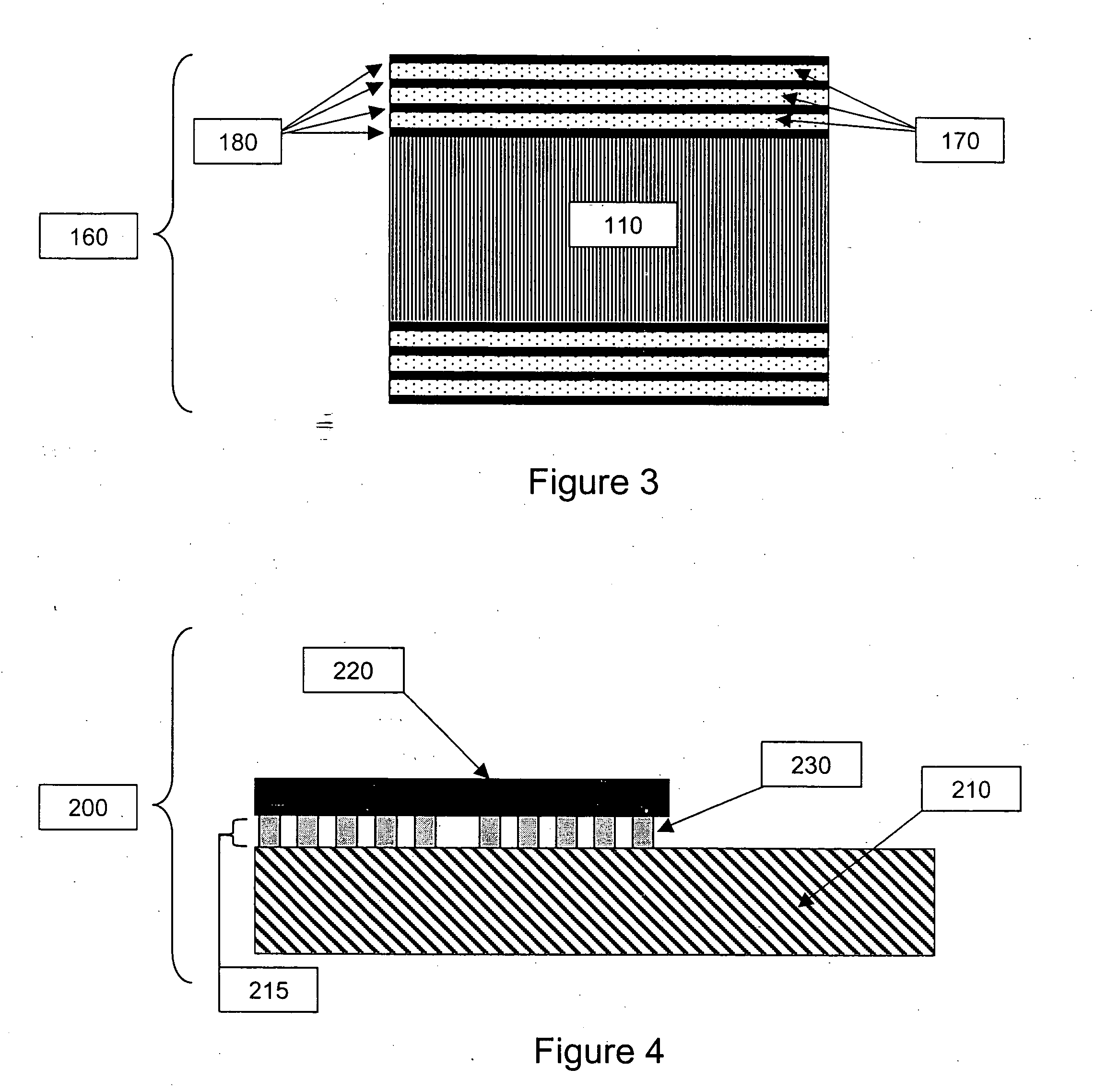
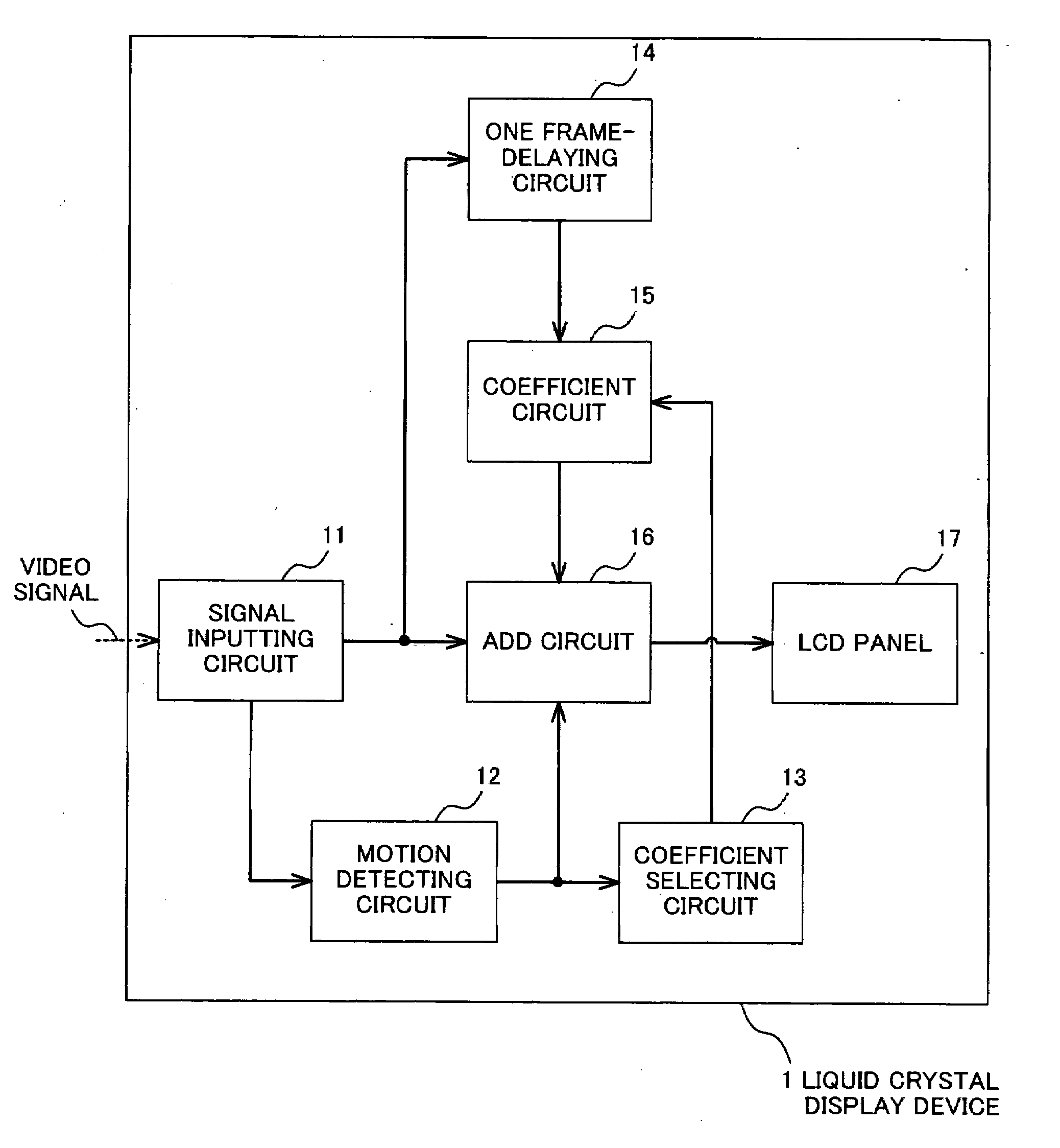
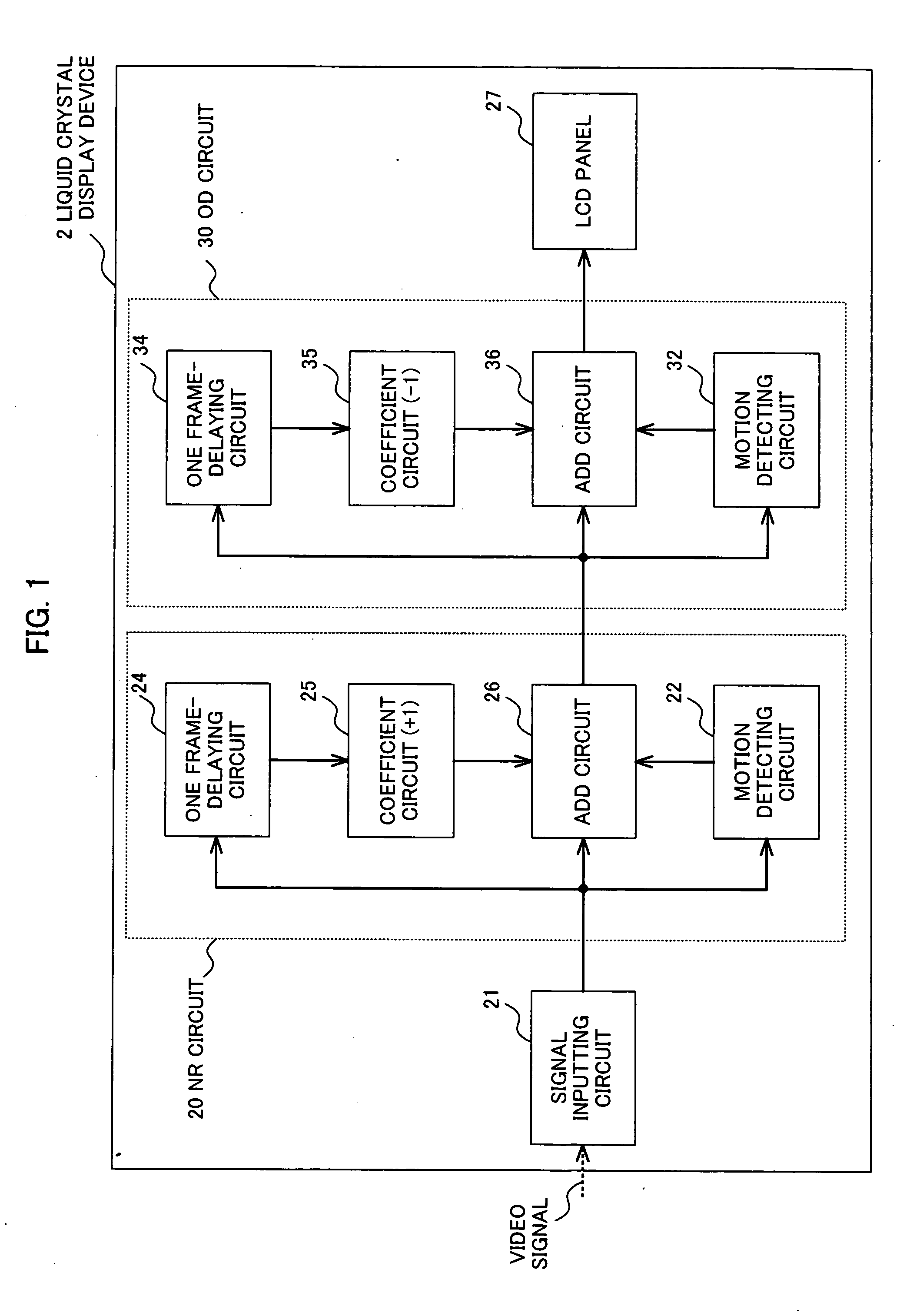
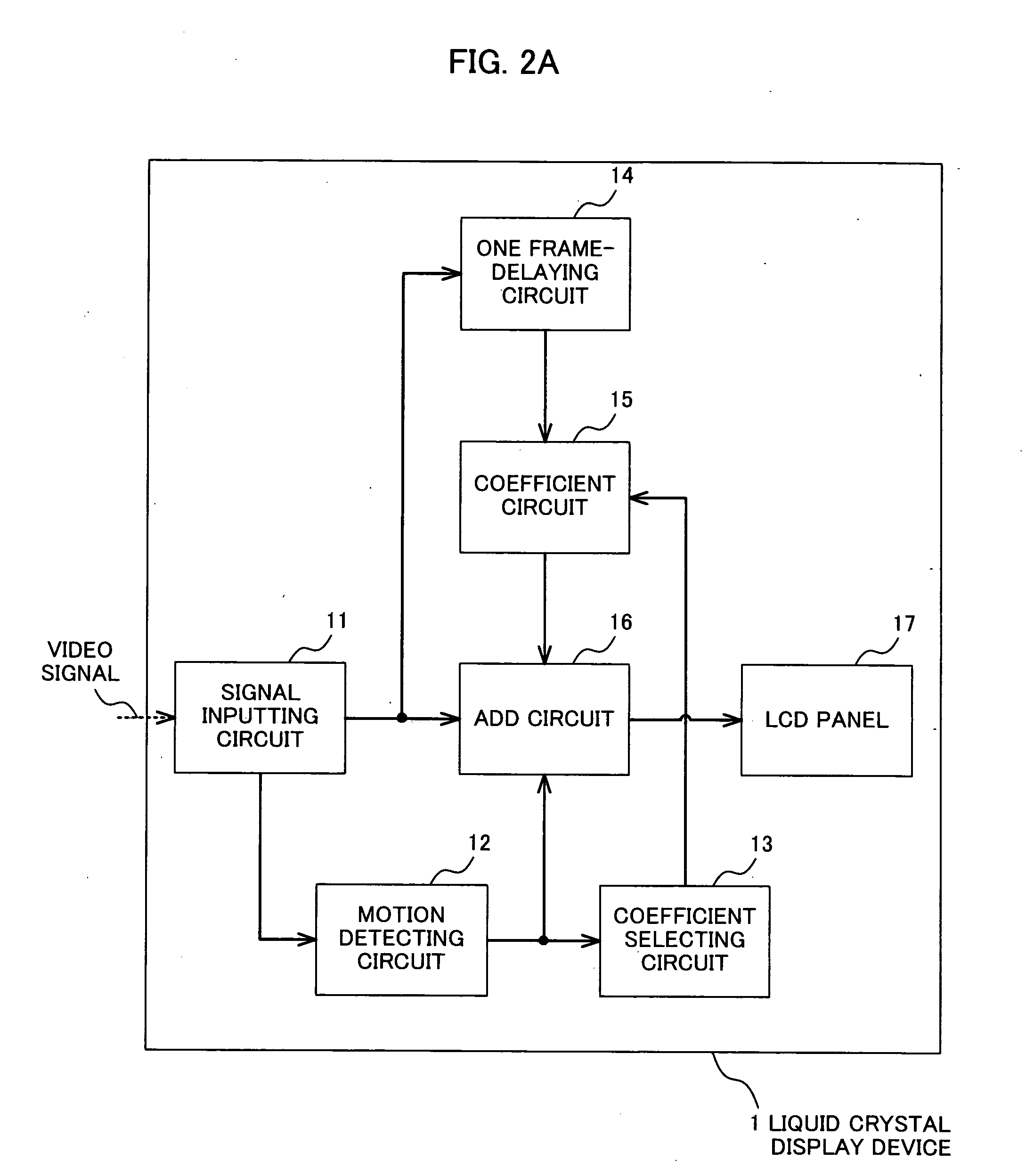
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20080001872A1Television system detailsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayNoise reduction
A liquid crystal display device (1) according to the invention adds a former image and a latter image which are continuous. When an image corresponding to a received video signal is a still image, an effect of noise reduction is provided by multiplying the former image by a positive coefficient. On the other hand, when an image corresponding to the received video signal is a moving image, a difference between the former image and the latter image is obtained by multiplying the former image by a negative coefficient, thereby providing an effect of overdrive.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Air flow detection circuit of digital air flow meter
ActiveCN101551262AAccurate measurementElectrical controlVolume/mass flow measurementLinear amplificationEngineering
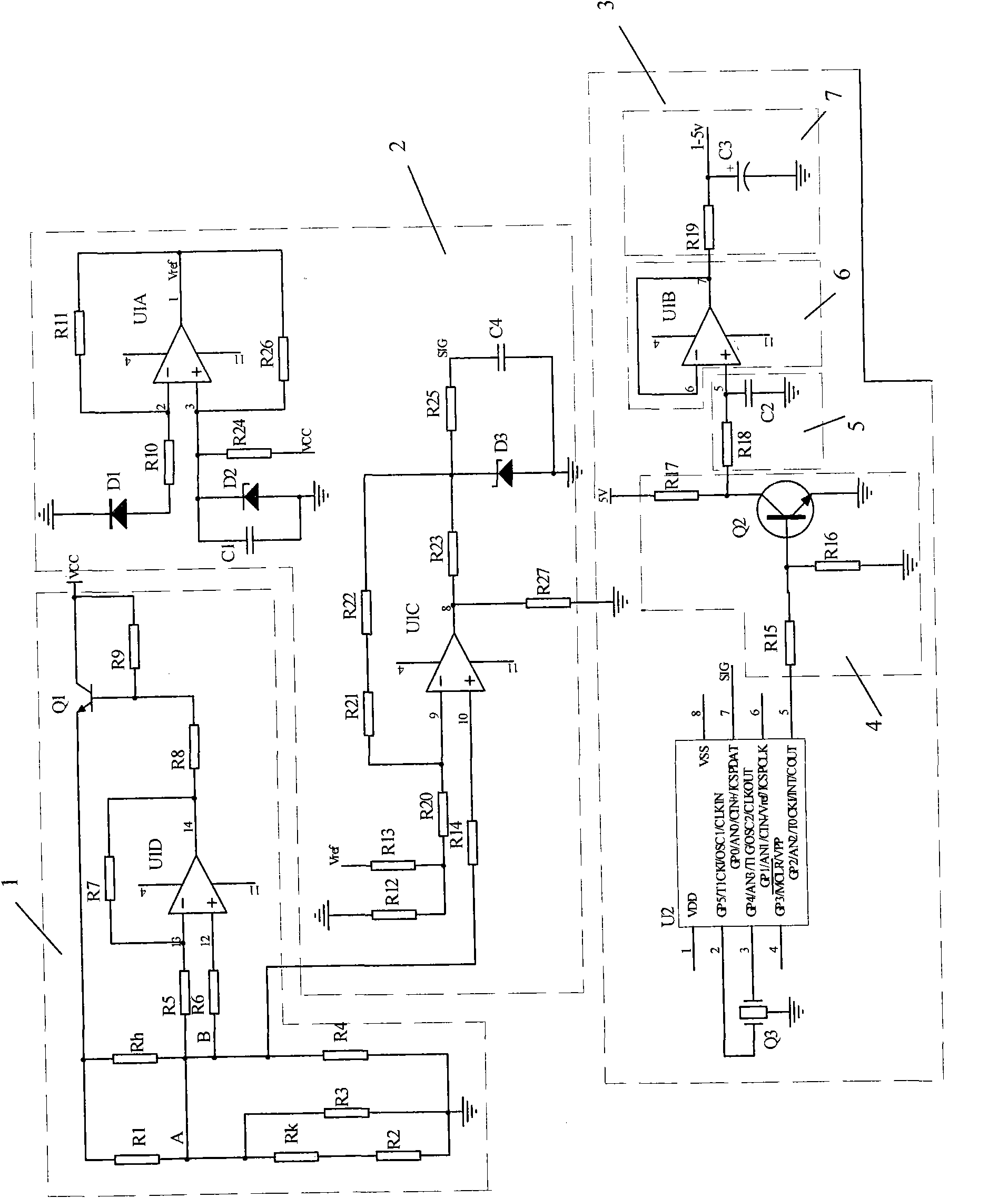
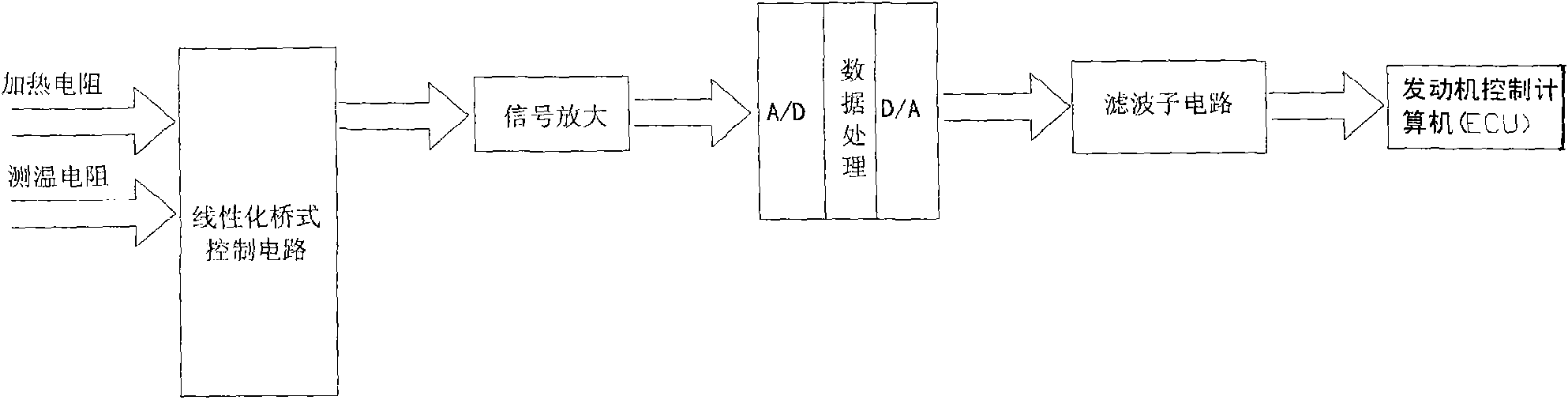
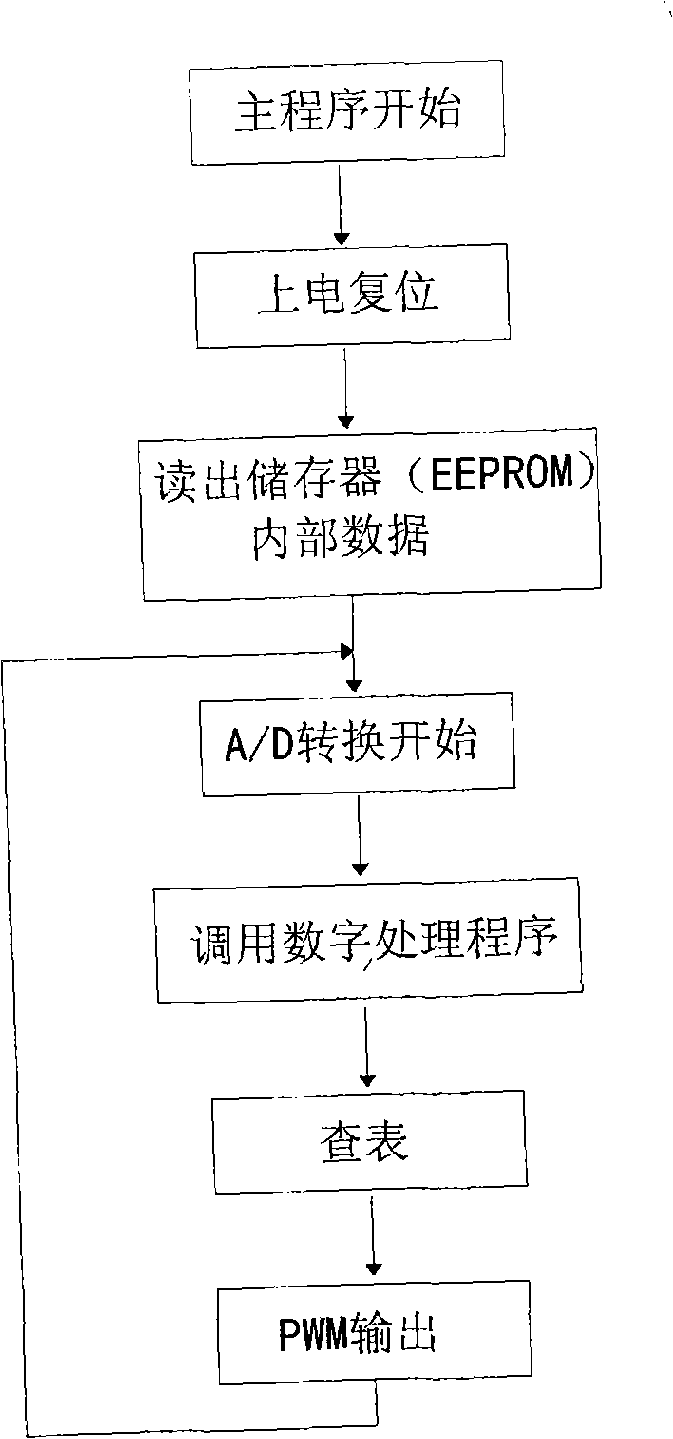
The invention disclose an air flow detection circuit of digital air flow meter, wherein the bridge branched circuit (1) is a linearization bridge branched circuit, wherein a speed measurement resistance R4 is the film strain gauge and a temperature measurement resistance RK is a negative coefficient thermistor and the temperature measurement PK is in series connection with the resistance R2 and then the temperature measurement resistance RK is in parallel connection with the resistance R2 and R3; the linear amplification branched circuit (2) is electrically connected with a data treatment and filter branched circuit (3) and the data treatment and filter branched circuit converses the air flow signal output by the linear amplification branched circuit into the digital signal and the ideal output value is obtained by a program and the output of the digital signal by controlling the duty ratio of the pulse width modulation, finally the analog quantity obtained by a low pass filtering sub-circuit is output and sent to a motor control computer. Therefore the air flow into the electric eruption motor in flash is accurately and rightly measured. The air flow detection circuit has features of automatic convenient operation, quick signal transfer speed and high working efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENKO AUTO SPARE PARTS
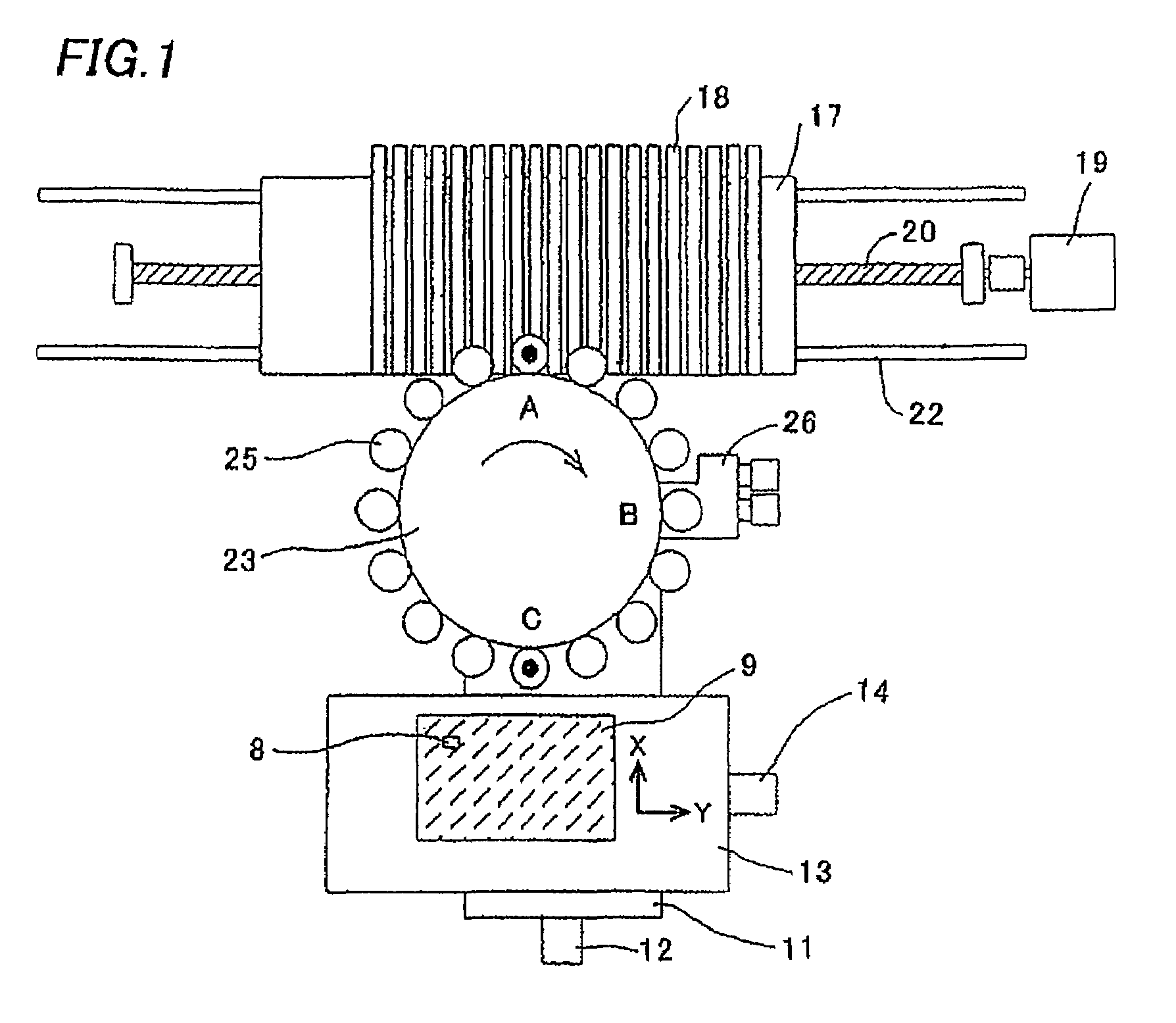
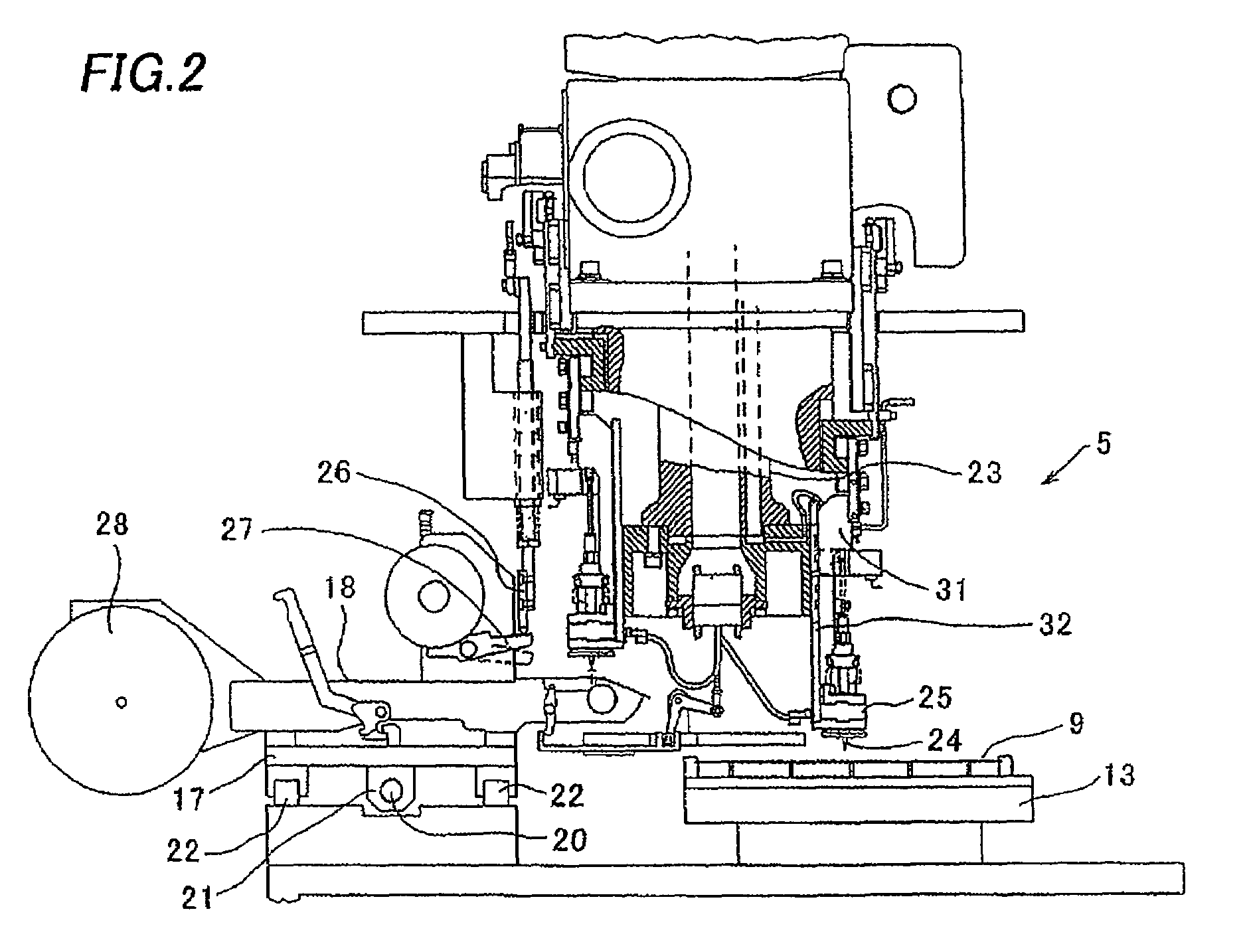
Electronic component mounting method and electronic component mounting apparatus
ActiveUS7533459B2Printed circuit assemblingAutomatic control devicesCounting NumberNegative coefficient
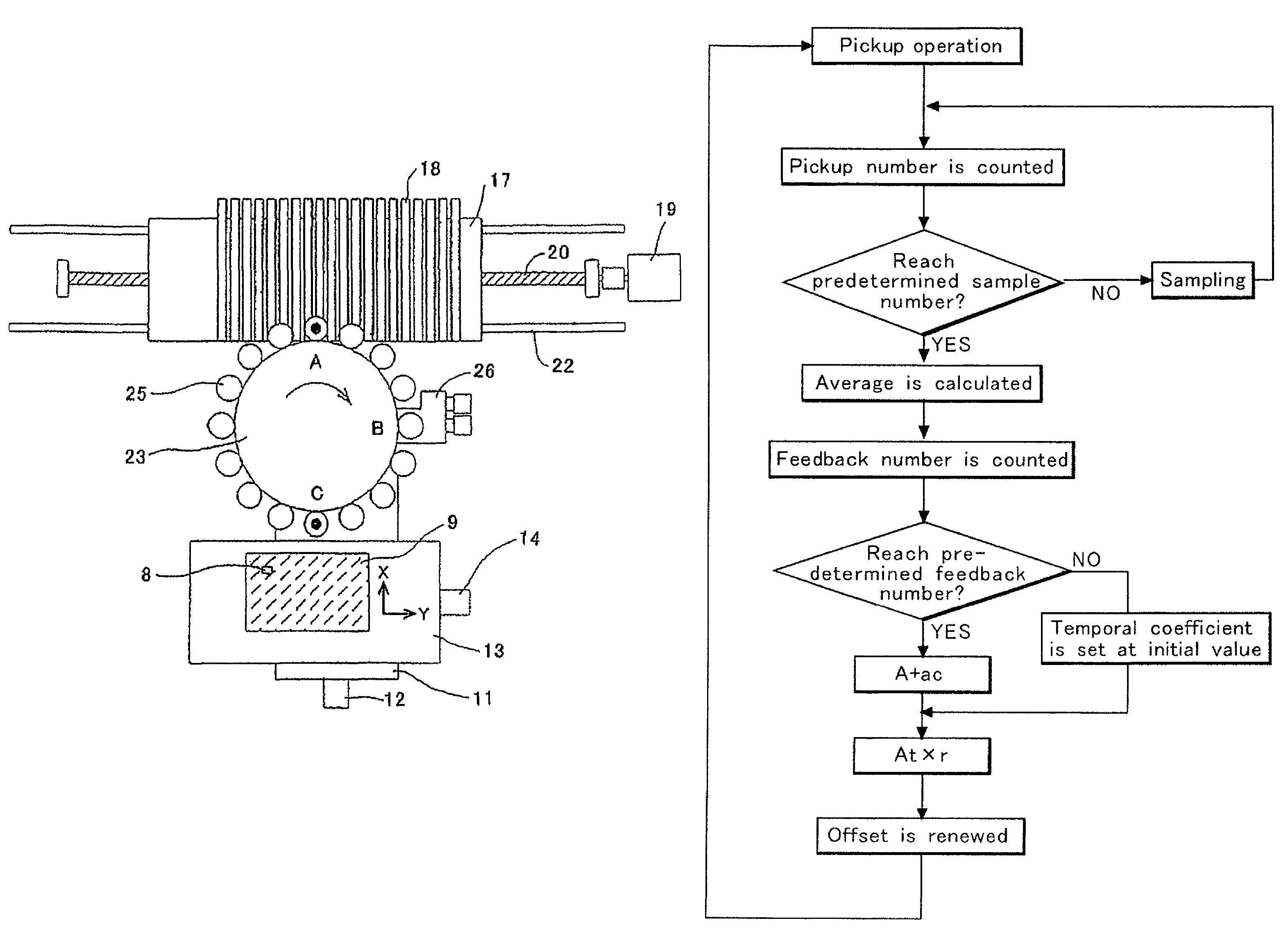
The invention is directed to increased stabilization of a pickup operation by reducing a reaction against disturbance by reducing a feedback value when a pickup rate is improved. A positional shifting amount of an electronic component on a suction nozzle before the electronic component is mounted on a printed board is stored in a RAM each time the component is picked up at a component feeding unit until a pickup count number reaches a predetermined pickup number, and a CPU calculates an average of the positional shifting amounts. When the pickup count number reaches the predetermined pickup number, the CPU obtains a temporary coefficient by adding an initial value to a value obtained by multiplying a negative coefficient by the pickup count number, and calculates a feedback value by multiplying the temporary coefficient by the average. The calculated feedback value is added to an offset value of a component pickup position to modify the offset value, and uses the offset value in the next pickup operation at the component feeding unit.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Package structure and manufacturing method for the same
InactiveCN103094463AAvoid affecting signal transmissionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical connectionEngineering
A package structure and a manufacturing method for the same are provided. The package structure includes a chip, a substrate and at least one adhesive layer. The chip has at least one electrode portion. The substrate has at least one circuit portion. The adhesive layer is disposed between the electrode portion and the circuit portion to form an electrical connection therebetween. The adhesive layer is a material, which comprises a metal compound, with a Negative Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (Negative CTE). Because of the material with a Negative CTE, the alignment shift can be avoided after the chip and the substrate are adhered together.
Owner:WALSIN LIHWA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com