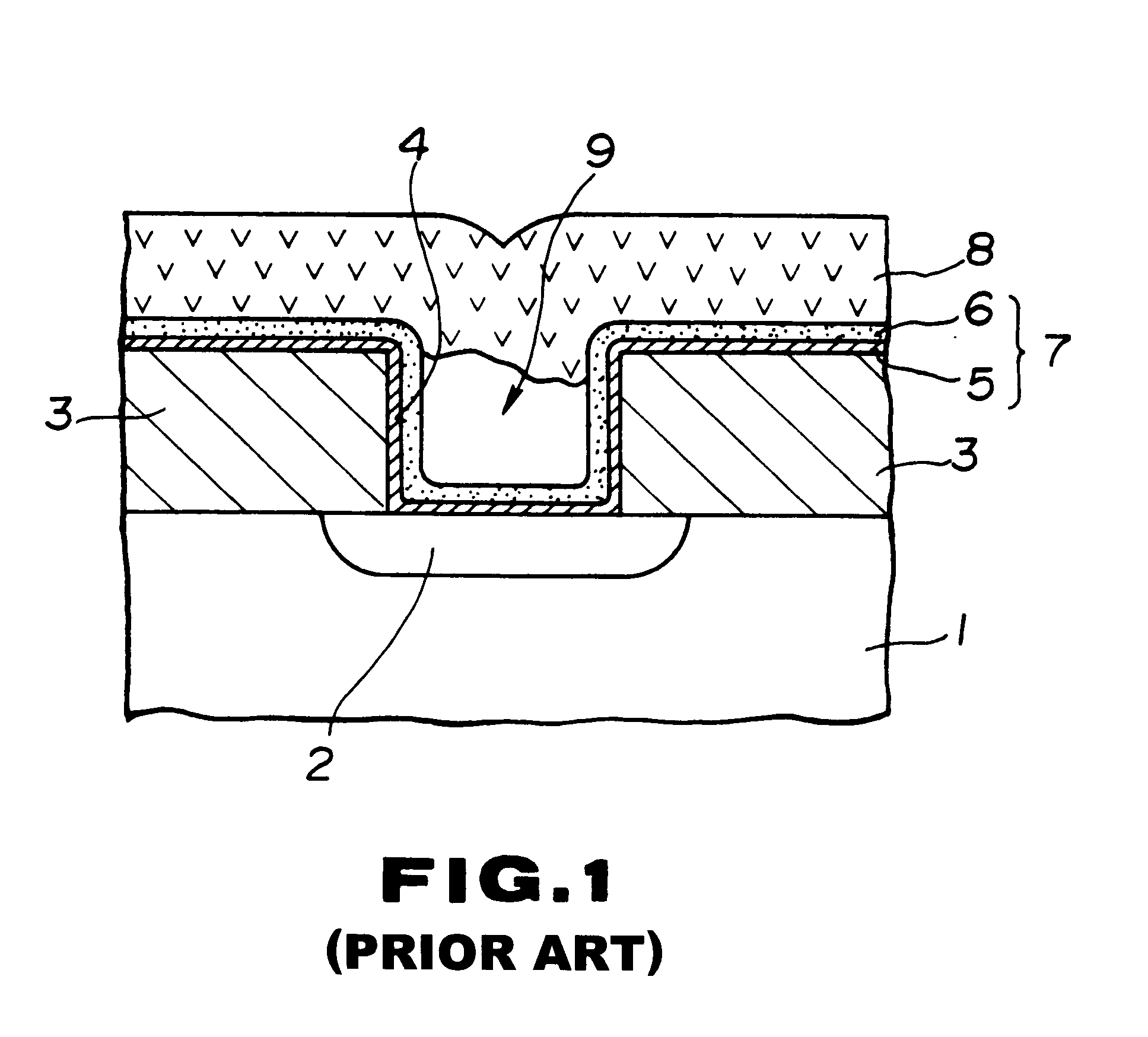
Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Low deposition rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
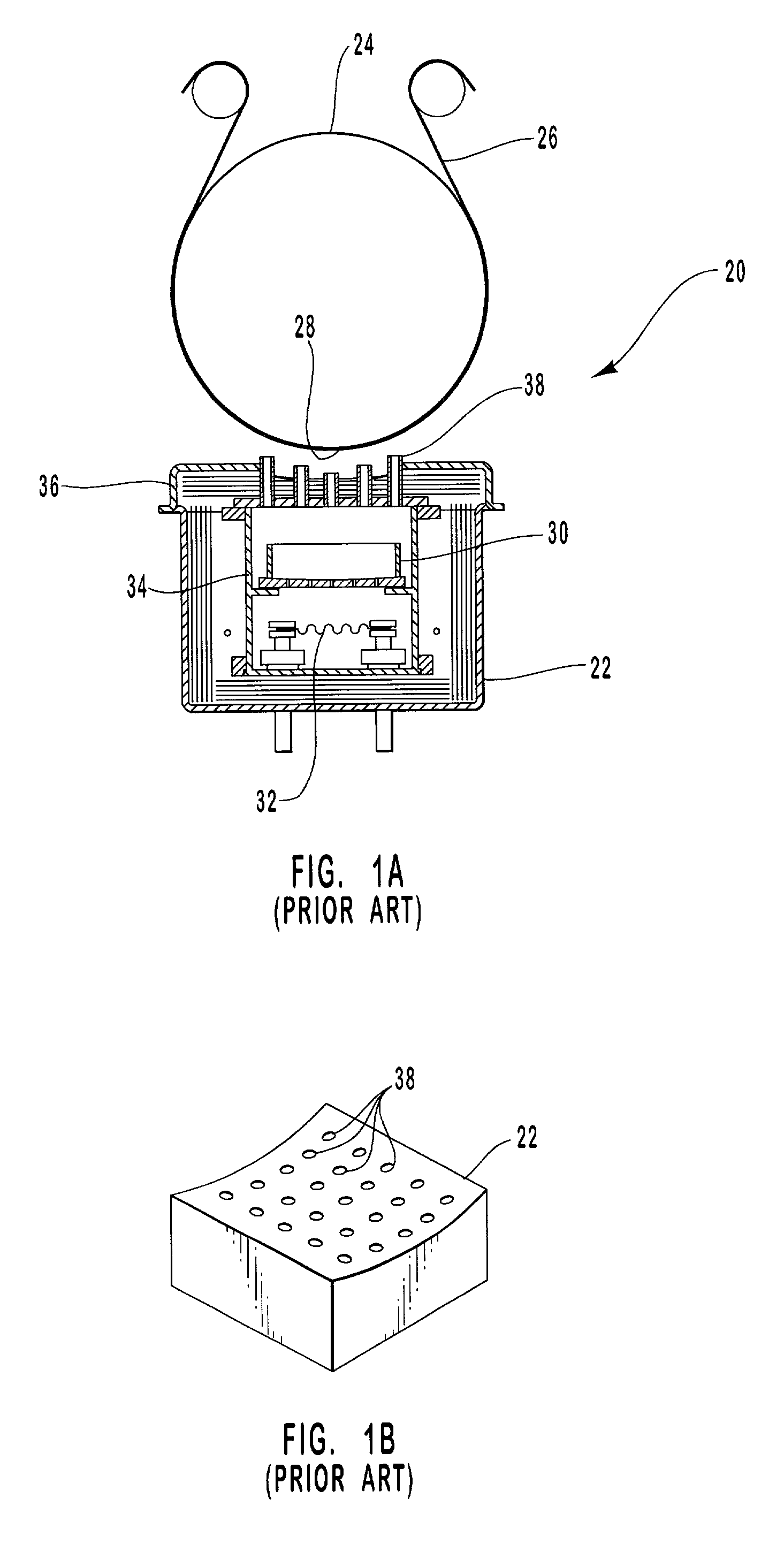
Linear aperture deposition apparatus and coating process
InactiveUS20010011524A1High and stable rateEasy to useVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesSource material
A linear aperture deposition apparatus and process are provided for coating substrates with sublimed or evaporated coating materials. The apparatus and process are particularly suited for producing flexible films having an optical interference coating with a very high surface thickness uniformity and which is substantially free of defects from particulate ejection of a source material. The apparatus includes a source box containing a source material, a heating element to sublime or evaporate the source material, and a chimney to direct the source material vapor from the source box to a substrate. A flow restricting baffle having a plurality of holes is positioned between the source material and the substrate to confine and direct the vapor flow, and an optional floating baffle is positioned on the surface of the source material to further restrict the vapor flow, thereby substantially eliminating source material spatter.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
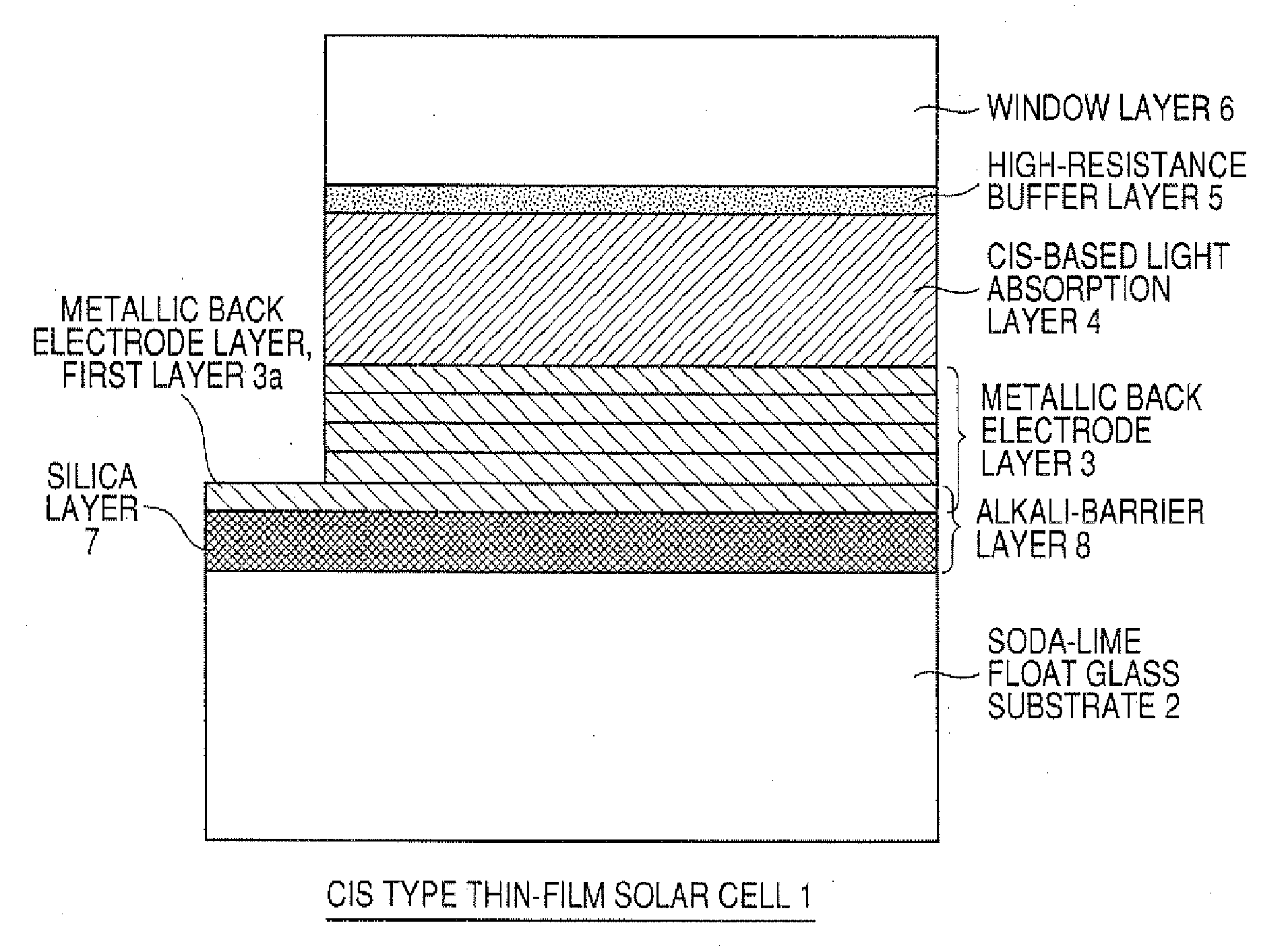
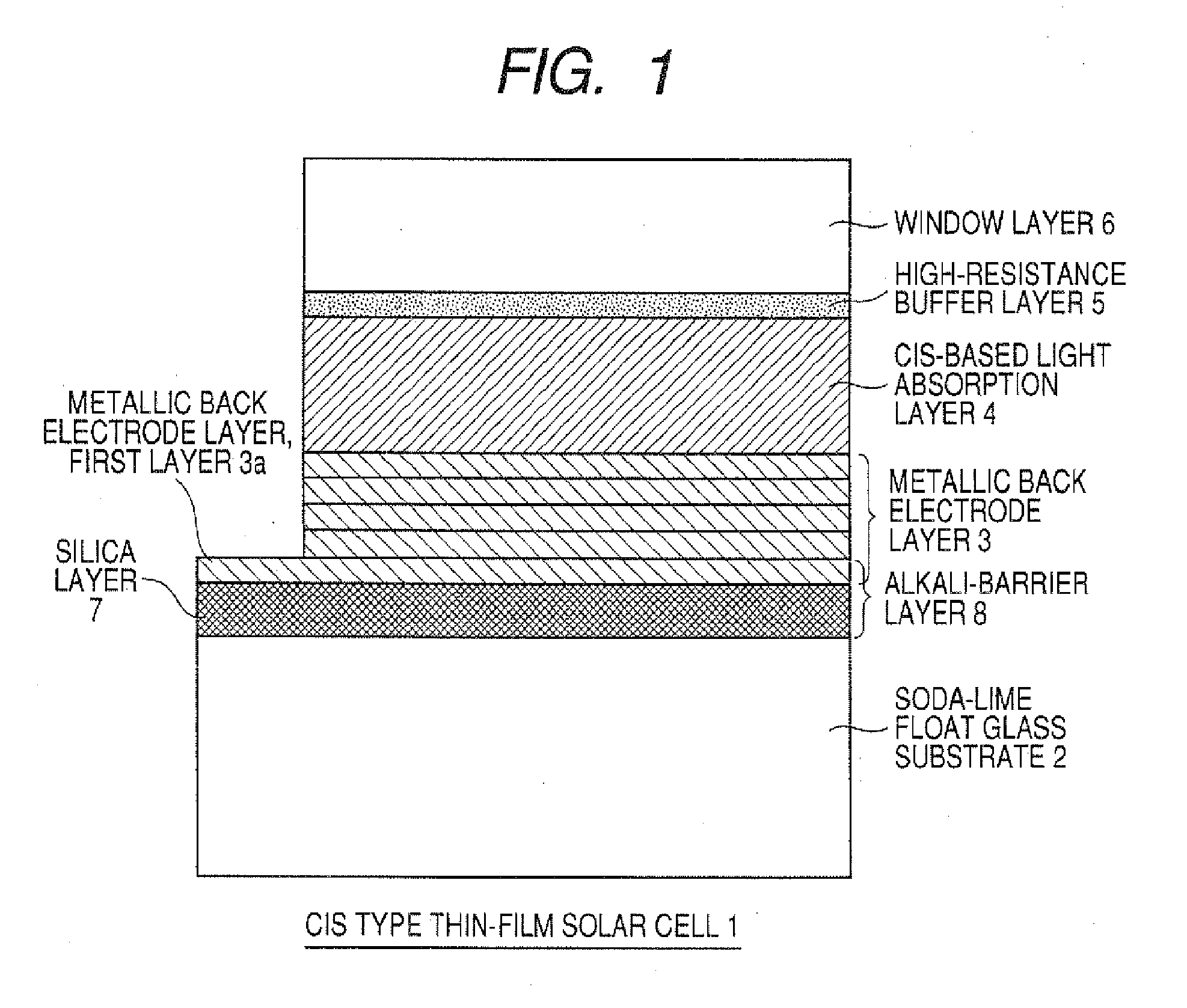
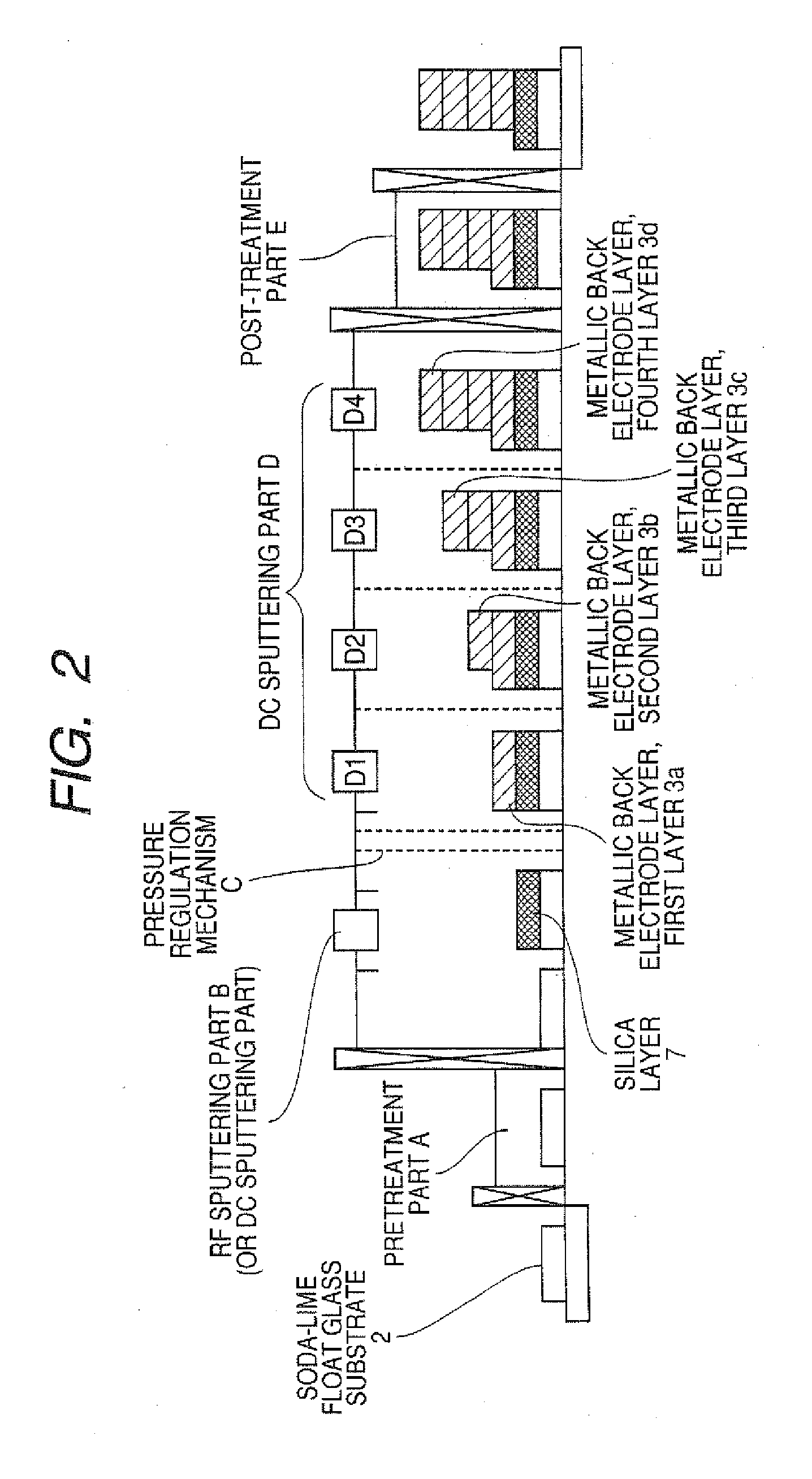
Cis Type Thin-Film Solar Cell and Process for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080271781A1Without reducing solar cell performanceLight layer can be preventedFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHigh resistanceAlkali free
This invention provides a CIS-based thin film solar battery and a process for producing the same in which the formation of an alkali barrier layer and a metal backside electrode layer is carried out at a low cost in a short time to prevent such an unfavorable phenomenon that a light absorbing layer is separated from the interface of the light absorbing layer and the metal backside electrode layer. The CIS-based thin film solar battery (1) comprises a glass substrate (2), an alkali-free layer (7) such as silica, a metal backside electrode layer (3) having a laminate structure, a p-type CIS-based light absorbing layer (4), a high-resistance buffer layer (5), and an n-type window layer (6) stacked in that order. The layer (7), either alone or together with a first layer (3a) in the layer (3), can function as an alkali barrier layer (8) that can prevent and control the thermal diffusion of an alkali component into the light absorbing layer during the formation of the layer (4) from the substrate (2). In the layer (3a), crystal grains are fine and has high density. After the formation of the layer (7) on the substrate by RF or DC sputtering, the layer (3) is continuously formed on the layer (7) by DC sputtering.
Owner:SHOWA SHELL SEKIYU KK
Linear aperture deposition apparatus and coating process
InactiveUS20010005553A1Increase temperatureShorten the lengthSynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingParticulatesSource material
A linear aperture deposition apparatus and process are provided for coating substrates with sublimed or evaporated coating materials. The apparatus and process are particularly suited for producing flexible films having an optical interference coating with a very high surface thickness uniformity and which is substantially free of defects from particulate ejection of a source material. The apparatus includes a source box containing a source material, a heating element to sublime or evaporate the source material, and a chimney to direct the source material vapor from the source box to a substrate. A flow restricting baffle having a plurality of holes is positioned between the source material and the substrate to confine and direct the vapor flow, and an optional floating baffle is positioned on the surface of the source material to further restrict the vapor flow, thereby substantially eliminating source material spatter.
Owner:WITZMAN MATTHEW R +3
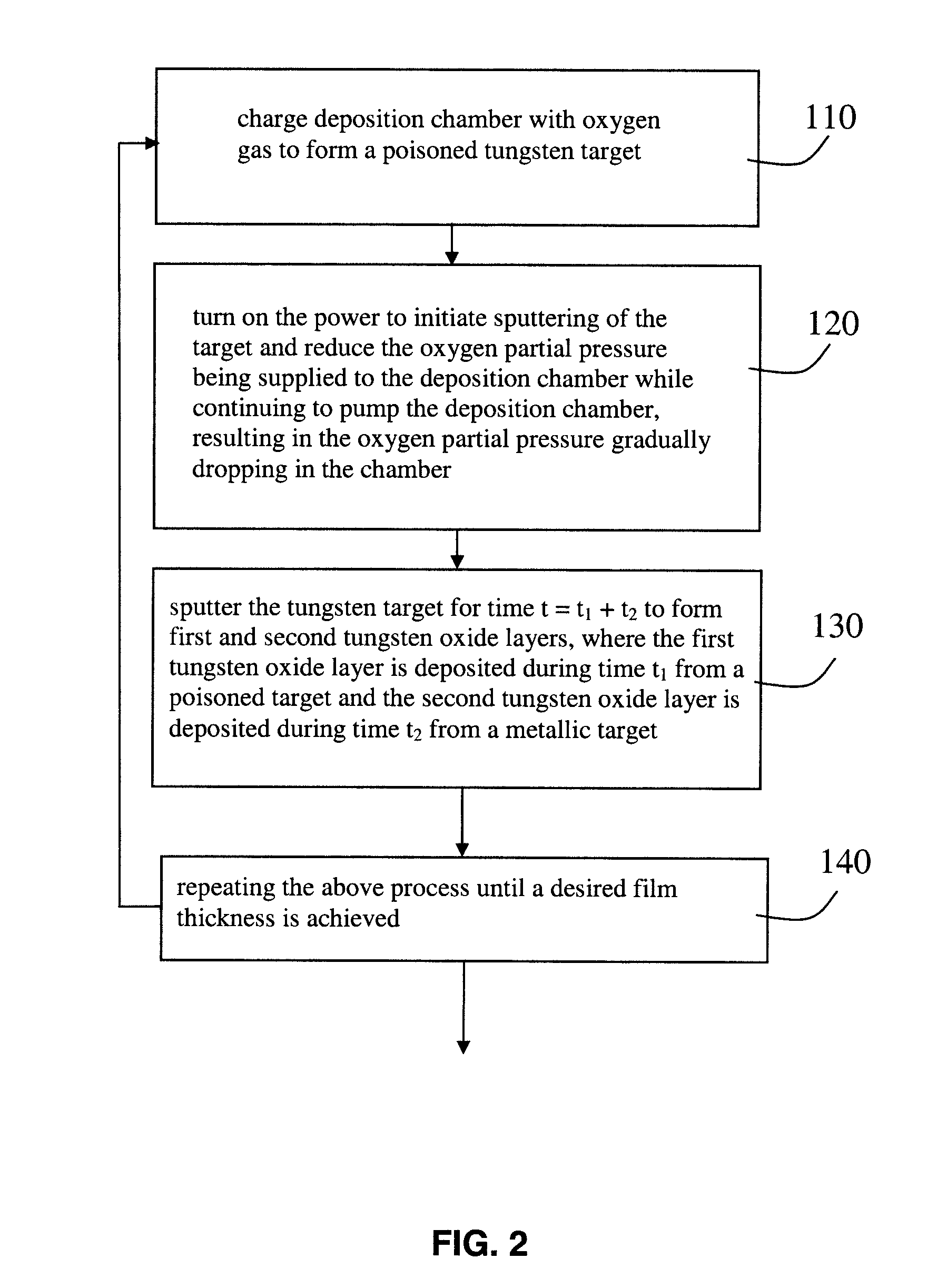
Electrochromic Tungsten Oxide Film Deposition
InactiveUS20120181167A1Reduce sheet resistanceIncrease deposition rateVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringMaterials science
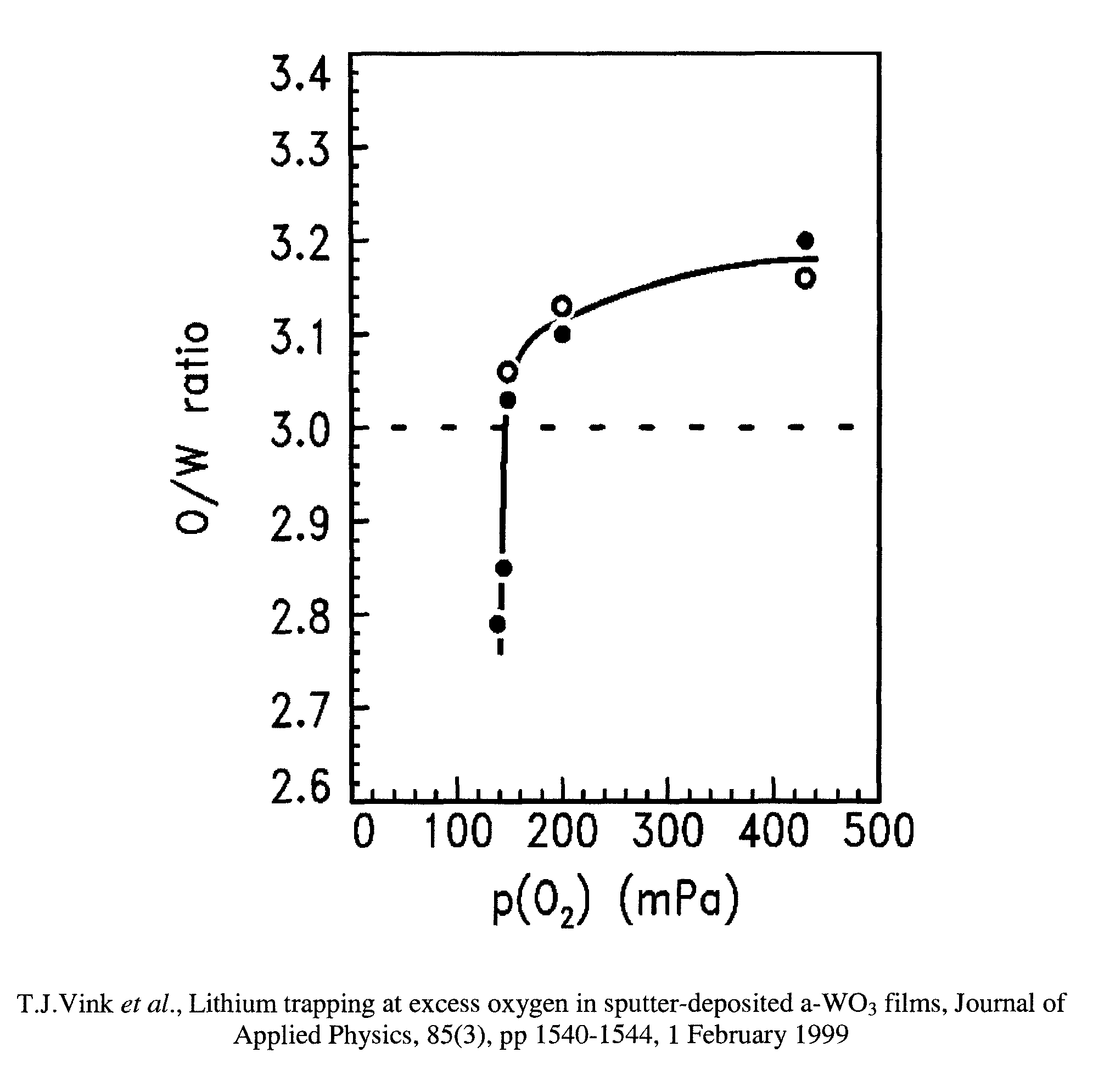
A deposition method for electrochromic WOx films involves cyclic deposition of very thin poisoned and metallic tungsten oxide layers to build up a film with a desired general stoichiometry with x in the range of 3>x>2.75. The method may include: charging a deposition chamber with oxygen gas to poison a tungsten metal target; initiating sputtering of the target while reducing the oxygen partial pressure being supplied to the chamber and pumping the chamber; sputtering target for time t1+t2 to form first and second tungsten oxide layers, where the first layer is deposited during time t1 from a poisoned target and the second layer is deposited during time t2 from a metallic target, and where the stoichiometry of the film comprising the first and second layers is a function of t1 and t2; and, repeating until a desired film thickness is achieved.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
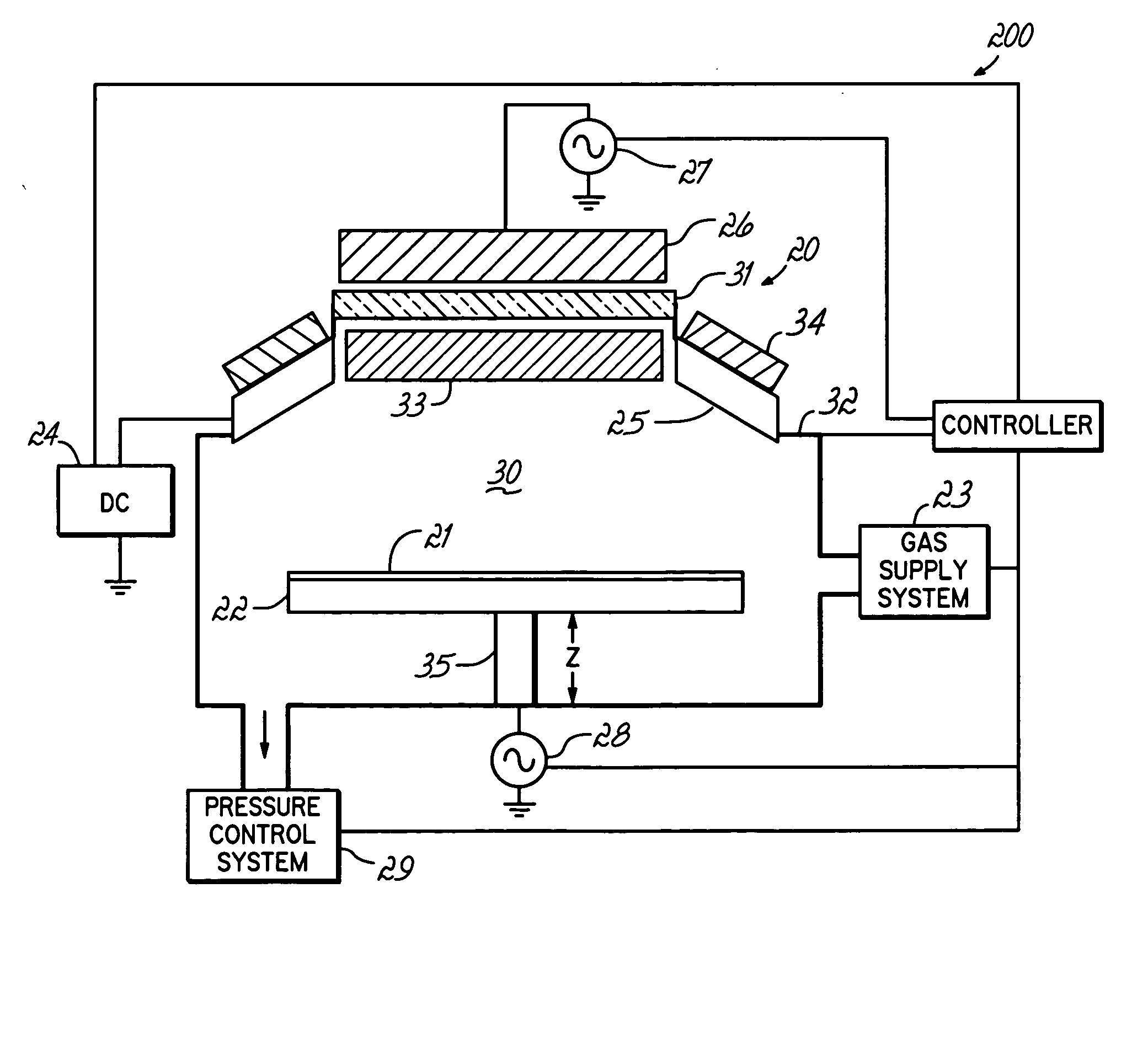
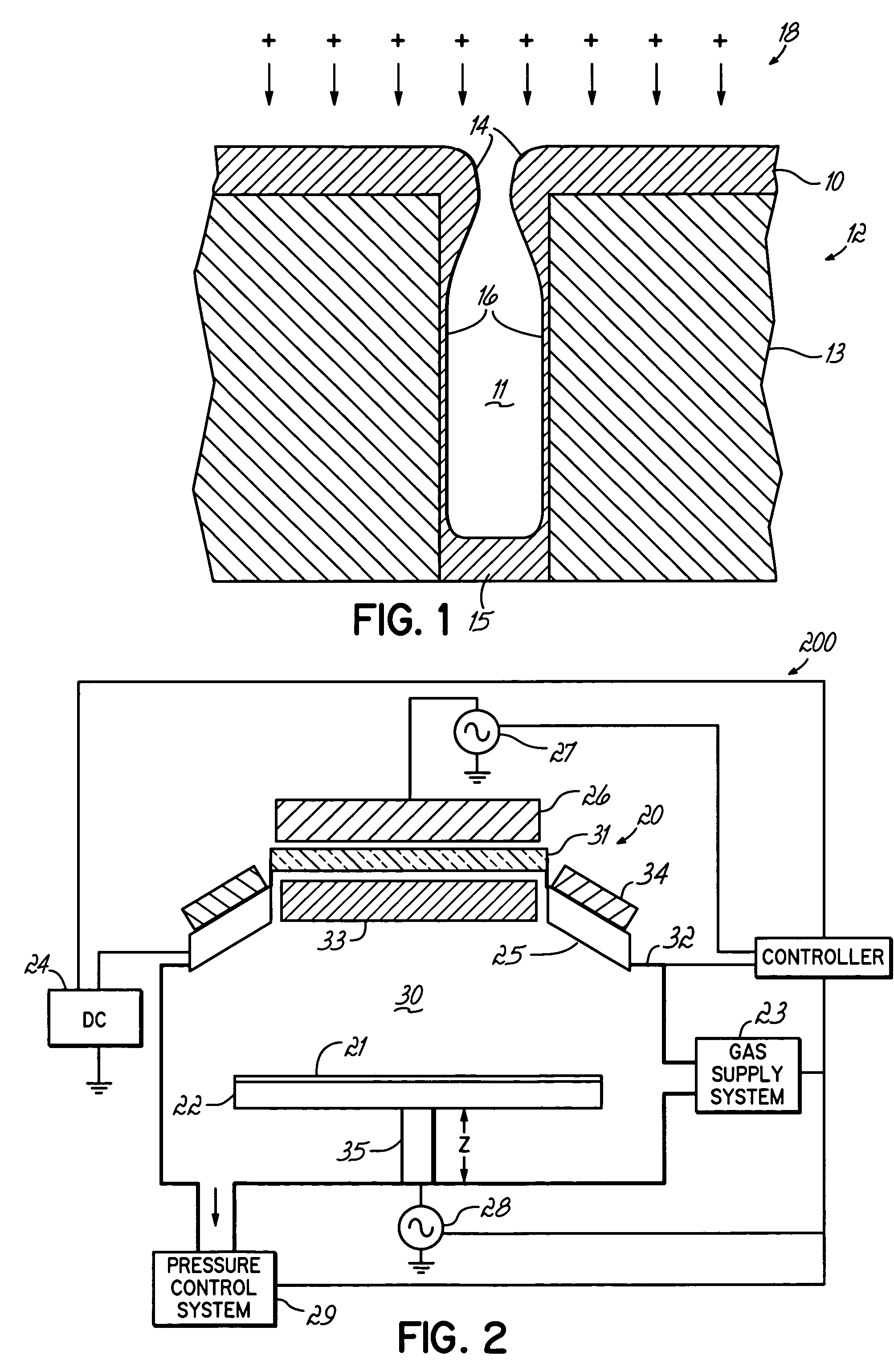
Ionized physical vapor deposition (iPVD) process
ActiveUS20050211545A1Low deposition rateEasy to adaptElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingIonizationSemiconductor
An iPVD system is programmed to deposit uniform material, such as barrier material, into high aspect ratio nano-size features on semiconductor substrates using a process which enhances the sidewall coverage compared to the field and bottom coverage(s) while minimizing or eliminating overhang within a vacuum chamber. The iPVD system is operated at low target power and high pressure >50 mT to sputter material from the target. RF energy is coupled into the chamber to form a high density plasma. A small RF bias (less than a few volts) can be applied to aid in enhancing the coverage, especially at the bottom.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
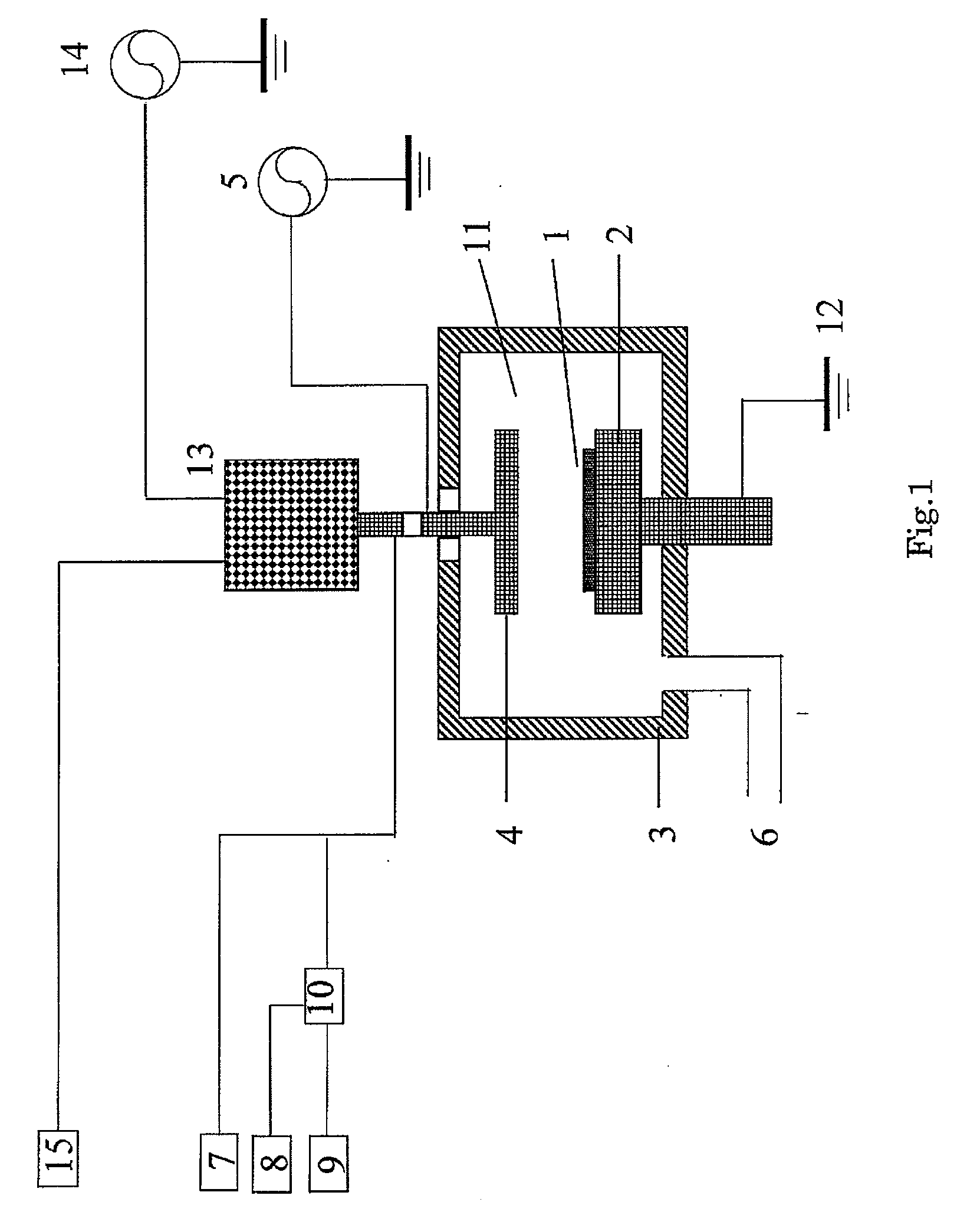
Two-step formation of hydrocarbon-based polymer film
InactiveUS20100104770A1Mechanical strengthHigh densityLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesPolymer thin filmsFlow ratio
A method of forming a surface-treated hydrocarbon-based polymer film includes: supplying a hydrocarbon gas as a source gas, and an inert gas, and applying RF power to generate a plasma and form a hydrocarbon-based principal film on a substrate; and without extinguishing a plasma, changing flow of the hydrocarbon gas and the inert gas by continuously decreasing a flow ratio of the hydrocarbon gas to the inert gas with time to treat a surface of the principal film on the substrate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Depositing rhuthenium films using ionized physical vapor deposition (IPVD)
InactiveUS7588667B2Low deposition rateHigh densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh densityRuthenium
An iPVD system is programmed to deposit a barrier and / or seed layer using a Ru-containing material into high aspect ratio nano-size features on semiconductor substrates using a process which enhances the sidewall coverage compared to the field and bottom coverage(s) while minimizing or eliminating overhang within an IPVD processing chamber. In the preferred embodiment, an IPVD apparatus having a frusto-conical ruthenium target equipped with a high density ICP source is provided.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method and apparatus for depositing antireflective coating
InactiveUS7070657B1Low deposition rateEasy to controlLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesRefractive index
This invention provides a stable process for depositing an antireflective layer. Helium gas is used to lower the deposition rate of plasma-enhanced silane oxide, silane oxynitride, and silane nitride processes. Helium is also used to stabilize the process, so that different films can be deposited. The invention also provides conditions under which process parameters can be controlled to produce antireflective layers with varying optimum refractive index, absorptive index, and thickness for obtaining the desired optical behavior.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Fabrication system, light-emitting device and fabricating method of organic compound-containing layer
InactiveUS7378133B2Reduction factorLow thermal expansionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsGas phase
The present invention provides a vapor deposition system for a film forming systems that promote an efficiency of utilizing an EL material and is excellent in uniformity or throughput of forming an EL layer and a vapor deposition method. According to the present invention, vapor deposition is carried out in a deposition chamber by moving an evaporation source holder 903 on which six containers 911 filled with an evaporation material are set at a certain pitch with respect to the substrate. The evaporation holder 903 is transported from an installation chamber 905 by a transport mechanism 902b. A heater is provided in a turntable 907. Throughput can be improved by heating the evaporation holder 903 in advance of transporting containers into the evaporation holder 903.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Effective delivery of nanoparticles and micrometer-sized pharmaceutical aerosols to the lung through enhanced condensational growth
ActiveUS20110056492A1Efficient deliveryEffectively penetrate the lungsPowder deliveryBiocideHigh humidityMedicine
Methods and devices for inhalation therapy to deliver and embed (deposit) particles less than about 1 μm in diameter in the lung. High humidity treatment of the lungs causes condensational growth in particle size upon entering the lungs. Increased particle size is conducive to particle embedment (deposition) in deep lung tissue or at a specific targeted lung region.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition for a solid oxide fuel cell
InactiveUS20080029026A1Easy to set upLarge film growth rateBurnersLiquid surface applicatorsThin layerSpray nozzle
A method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition (ESD) for fabricating a thin-layer yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) electrolyte on a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anode substrate constructed of nickel-YSZ cermet. By reducing the thickness of the electrolyte, and thereby reducing the cell internal IR drop, an intermediate temperature SOFC (ITSOFC) can operate at 600-800° C. A collar positioned at a distance from a discharge end of a spray nozzle enhances a spray pattern of a precursor including the electrolyte material and thus provides a very thin electrolyte layer.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Process for producing electrophotographic photosensitive member, and electrophotographic photosensitive member and electrophotographic apparatus making use of the same
InactiveUS7033717B2Improve image qualityEasy to handleElectrographic process apparatusAbnormal growthsHigh frequency power
An electrophotographic photosensitive member production process is provided having the steps of placing a cylindrical substrate having a conductive surface in a first film-forming chamber, and decomposing a source gas with high-frequency power to deposit on the cylindrical substrate a first layer formed of a non-single-crystal material, taking out of the first film-forming chamber the cylindrical substrate with the first layer deposited thereon, and placing the cylindrical substrate with the first layer deposited thereon in a second film-forming chamber, and decomposing a source gas with a high-frequency power to deposit on the first layer a second layer having an upper-part blocking layer formed of a non-single-crystal material. Even where abnormal growth portions called spherical protuberances are present on the photosensitive member surface, they can be made not to appear on images, and image defects can vastly be remedied.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition for a solid oxide fuel cell
InactiveUS20050095369A1Easy to set upLarge film growth rateElectric shock equipmentsFinal product manufactureThin layerSpray nozzle
A method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition (ESD) for fabricating a thin-layer yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) electrolyte on a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anode substrate constructed of nickel-YSZ cermet. By reducing the thickness of the electrolyte, and thereby reducing the cell internal IR drop, an intermediate temperature SOFC (ITSOFC) can operate at 600-800° C. A collar positioned at a distance from a discharge end of a spray nozzle enhances a spray pattern of a precursor including the electrolyte material and thus provides a very thin electrolyte layer.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Aluminum metallization by a barrier metal process
InactiveUS6197686B1Improve featuresImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSputteringRough surface
A metallization method for filling an Al-based material in a contact hole having a barrier metal structure, in which high barrier characteristics and high step coverage may be achieved simultaneously, is proposed. The present invention is based on two concepts. The first concept is to provide a Ti / TiON / Ti three-layer barrier metal structure and to deposit a layer of the Al-based material by high temperature sputtering. Sufficient barrier characteristics may be provided by the intermediate TiON layer of the three-layer structure. The interface between the Al-based layer and the barrier metal layer is the Ti layer having excellent wetting characteristics with respect to the Al-based layer so that the contact hole can be filled uniformly without forming voids. The second concept is to set the substrate heating temperature during high temperature sputtering to 450 to 550° C. and to set the deposition rate to 0.6 mum / minute or less. In this manner, moderate Al migration and sufficiently long reaction time may be assured even on a Ti layer which partially reflects the rough surface morphology of the TiON layer for further improving reliability in filling.
Owner:SONY CORP
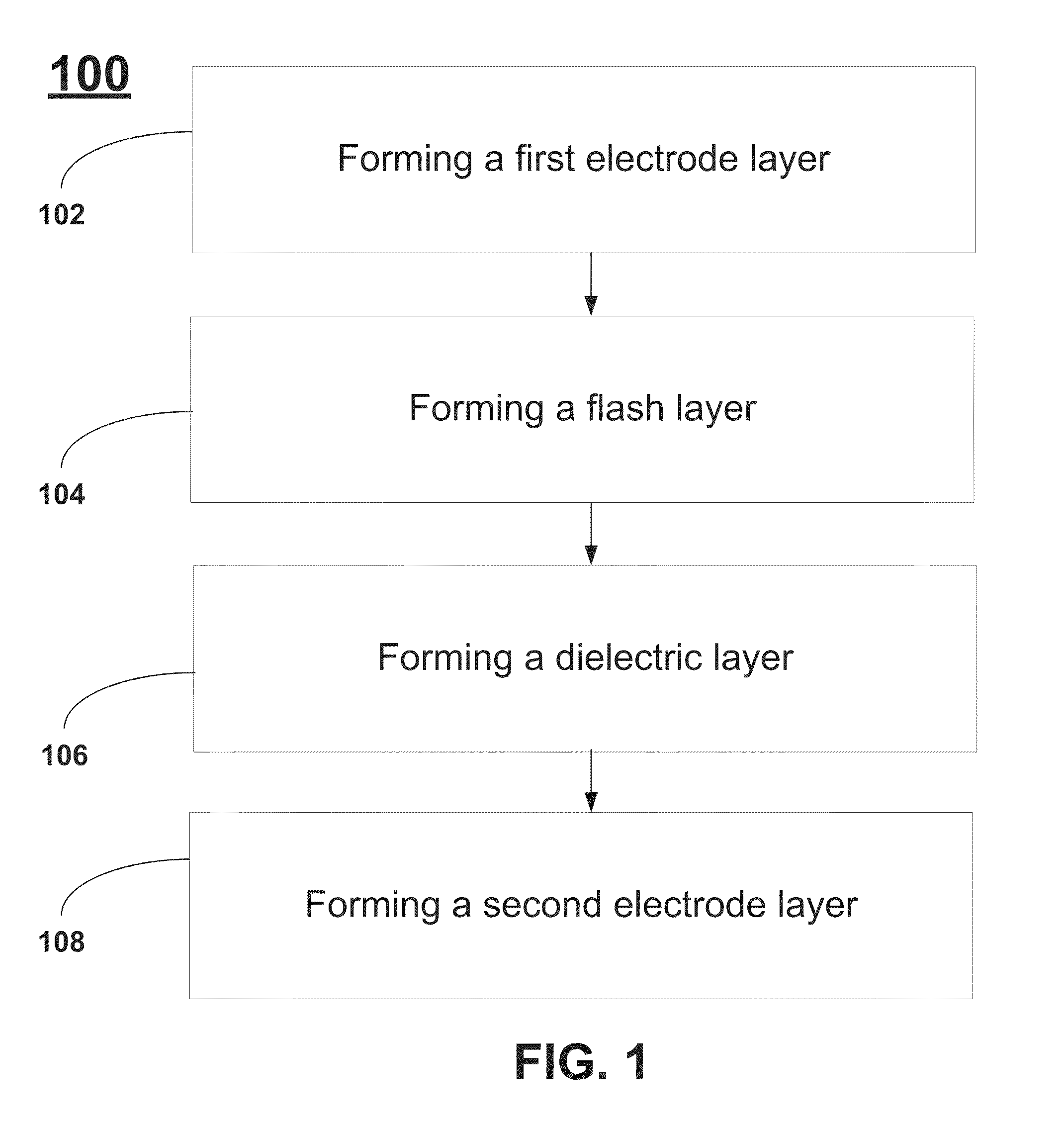
Methods for Reproducible Flash Layer Deposition
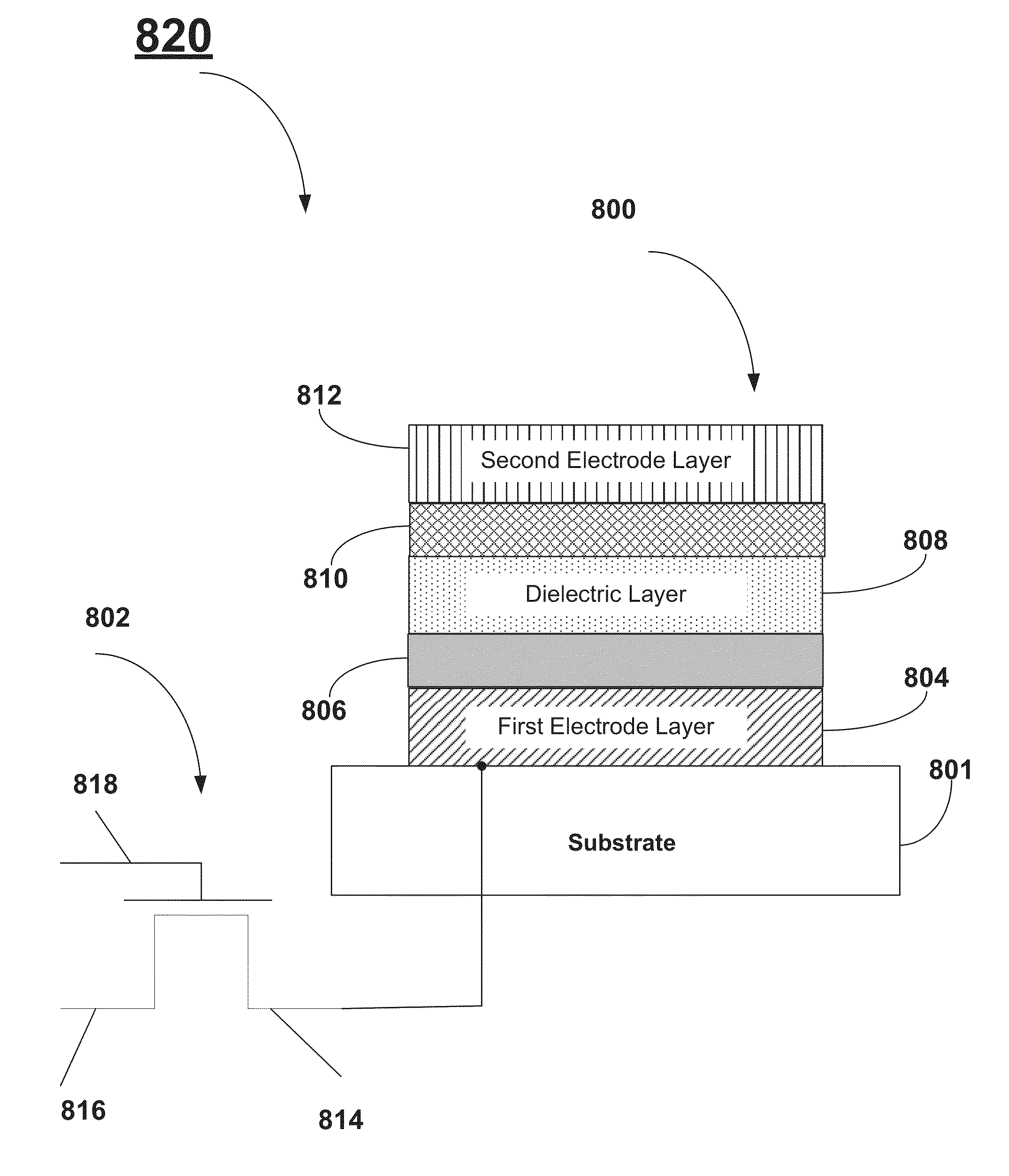
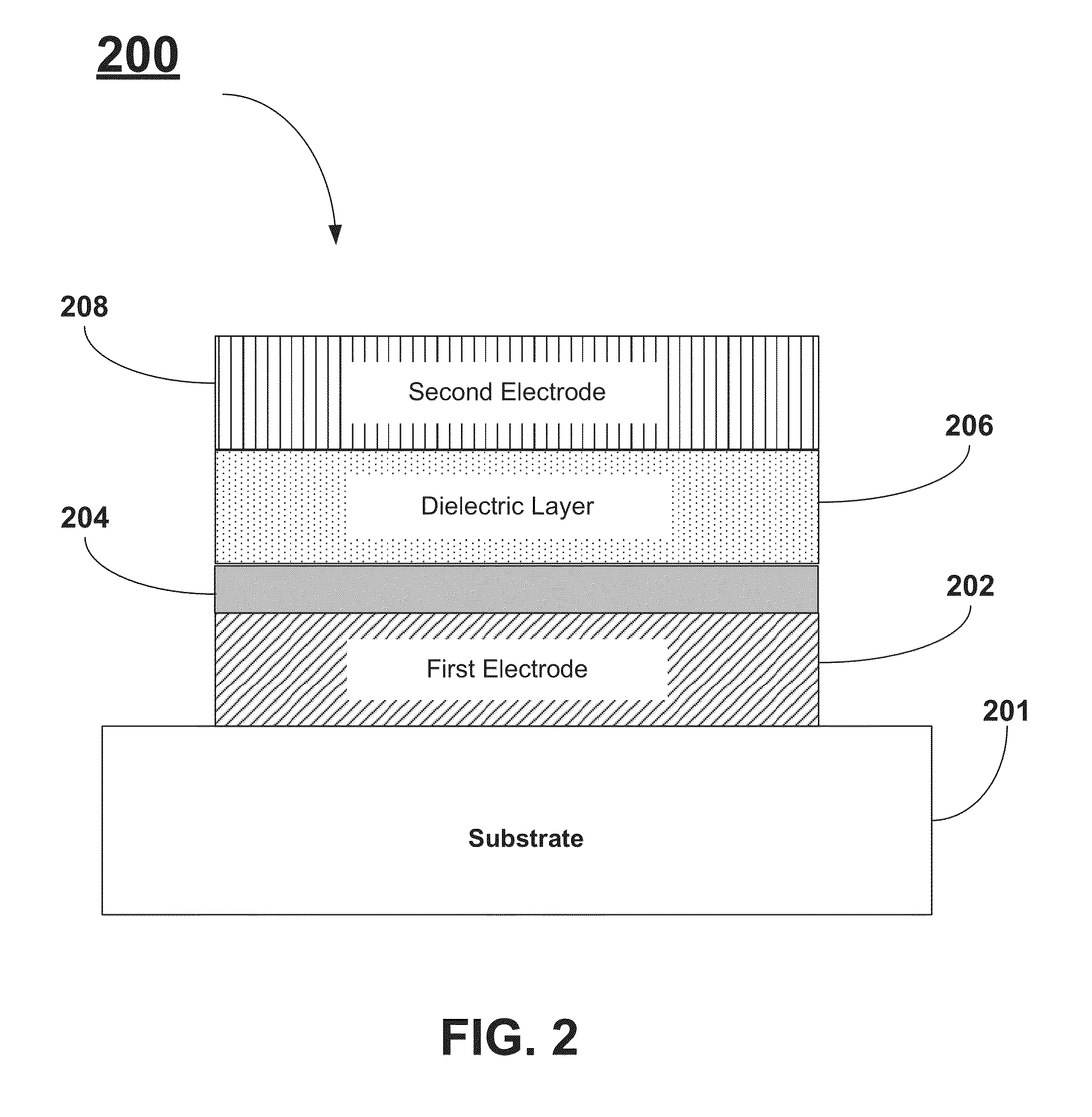
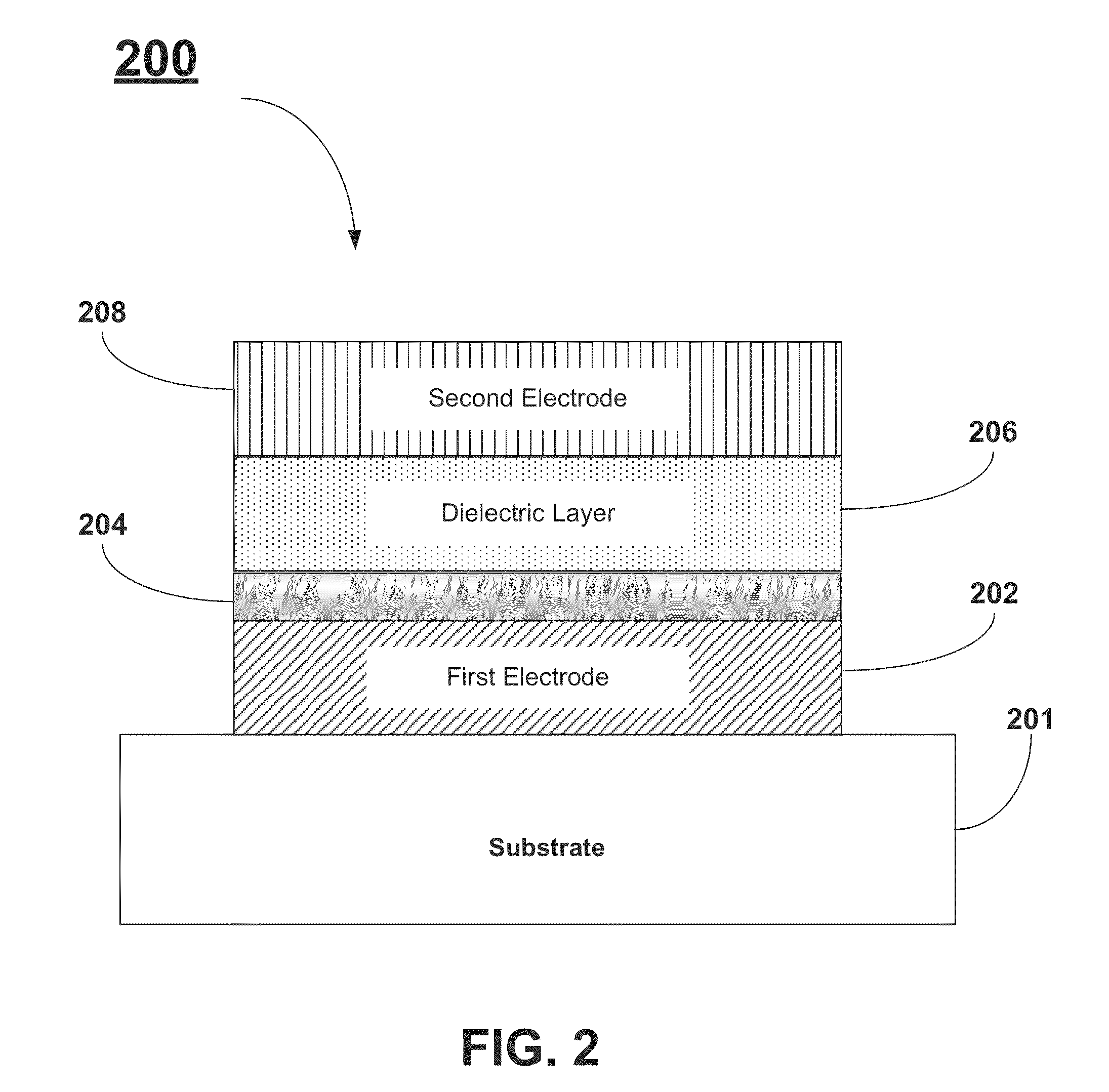
InactiveUS20140183695A1Reduce leakage currentIncrease K valueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal-insulator-metalOxygen
A method for reducing the leakage current in DRAM Metal-Insulator-Metal capacitors includes forming a flash layer between the dielectric layer and the first electrode layer. A method for reducing the leakage current in DRAM Metal-Insulator-Metal capacitors includes forming a capping layer between the dielectric layer and the second electrode layer. The flash layer and the capping layer can be formed using an atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique. The precursor materials used for forming the flash layer and the capping layer are selected such they include at least one metal-oxygen bond. Additionally, the precursor materials are selected to also include “bulky” ligands.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition for a solid oxide fuel cell
InactiveUS7252851B2Satisfactory rateEasy to controlElectric shock equipmentsCell electrodesSpray nozzleThin layer
A method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition (ESD) for fabricating a thin-layer yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) electrolyte on a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anode substrate constructed of nickel-YSZ cermet. By reducing the thickness of the electrolyte, and thereby reducing the cell internal IR drop, an intermediate temperature SOFC (ITSOFC) can operate at 600–800° C. A collar positioned at a distance from a discharge end of a spray nozzle enhances a spray pattern of a precursor including the electrolyte material and thus provides a very thin electrolyte layer.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Ionized physical vapor deposition (iPVD) process
InactiveUS7901545B2Easy to adaptHigh ionizationElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesHigh densityEngineering
An iPVD system is programmed to deposit uniform material, such as barrier material, into high aspect ratio nano-size features on semiconductor substrates using a process which enhances the sidewall coverage compared to the field and bottom coverage(s) while minimizing or eliminating overhang within a vacuum chamber. The iPVD system is operated at low target power and high pressure >50 mT to sputter material from the target. RF energy is coupled into the chamber to form a high density plasma. A small RF bias (less than a few volts) can be applied to aid in enhancing the coverage, especially at the bottom.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
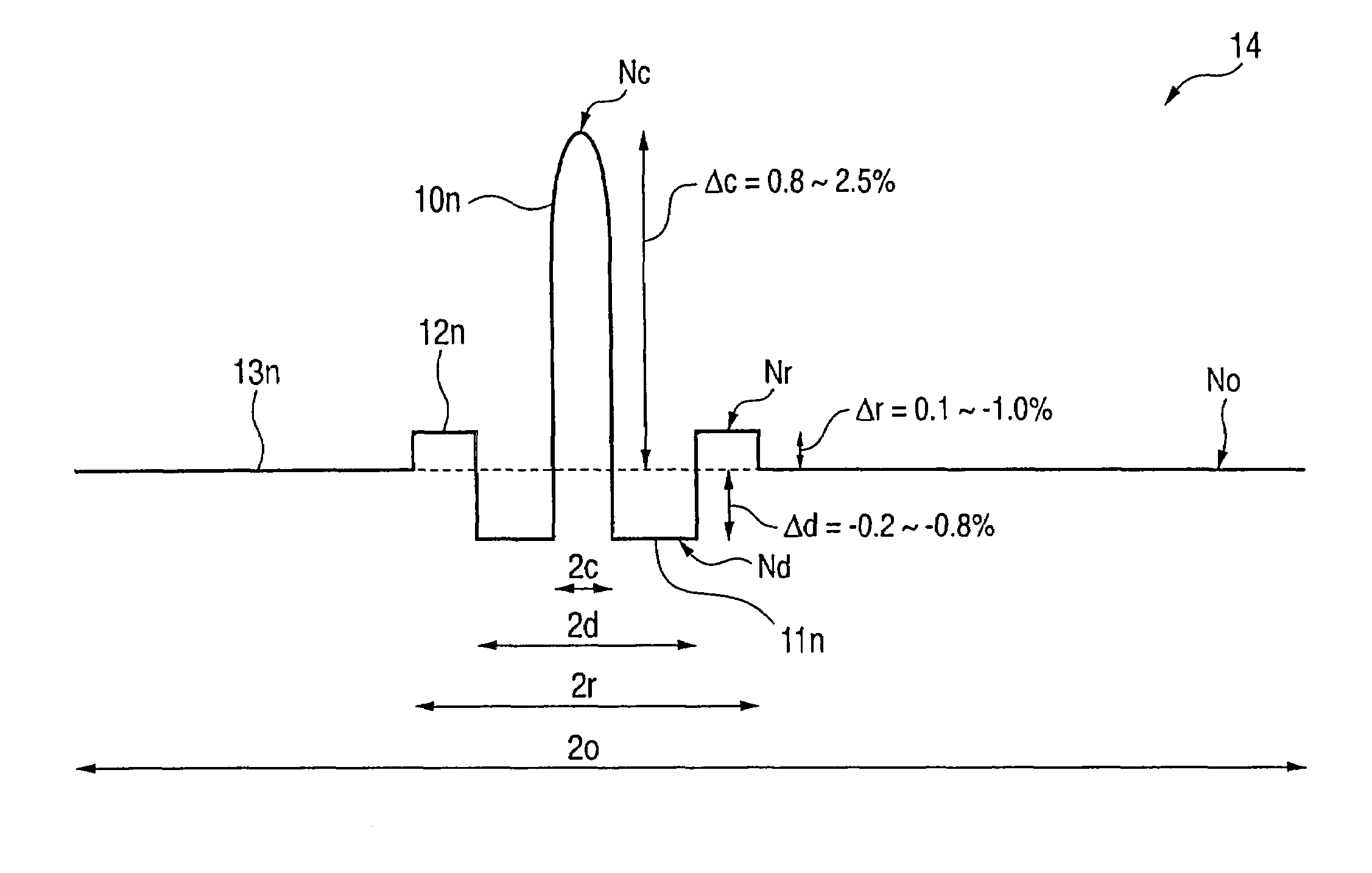
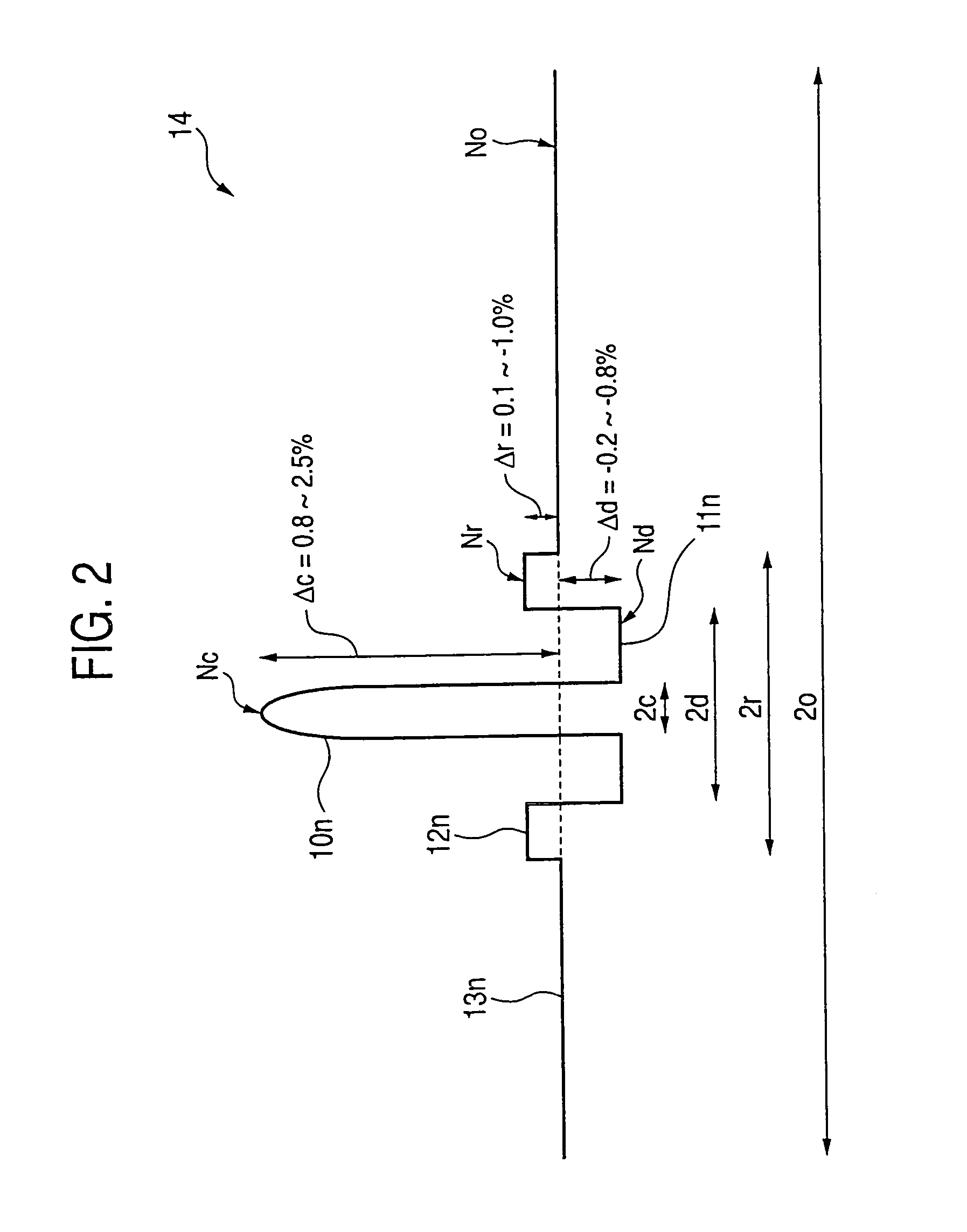
Optical fiber preform producing method, optical fiber production method, and optical fiber
InactiveUS7068901B2Improve accuracyLow deposition rateGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingRefractive indexVitreous Bodies
An optical fiber preform comprises a central core portion having a maximal value Nc of refractive index in the center, and outside the central core portion, comprising at least a depressed portion having a minimal value Nd of refractive index, a ring portion having a maximal value Nr of refractive index and an outside cladding layer having a maximal value No of refractive index. The optical fiber preform satisfies a relation of Nc≧Nr>No>Nd among the values of refractive index. A method of the optical fiber preform comprises fabricating a glass rod by inserting a rod containing at least the central core portion into a pipe containing at least the depressed portion and integrating them, fabricating a glass pipe having the ring portion, and fabricating a vitreous body by integrating the glass rod and the glass pipe by collapsing after inserting the glass rod into the glass pipe.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Methods for reproducible flash layer deposition
InactiveUS9012298B2Increased k-valueReduce leakage currentFixed capacitor electrodesSolid-state devicesMetal-insulator-metalOxygen
A method for reducing the leakage current in DRAM Metal-Insulator-Metal capacitors includes forming a flash layer between the dielectric layer and the first electrode layer. A method for reducing the leakage current in DRAM Metal-Insulator-Metal capacitors includes forming a capping layer between the dielectric layer and the second electrode layer. The flash layer and the capping layer can be formed using an atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique. The precursor materials used for forming the flash layer and the capping layer are selected such they include at least one metal-oxygen bond. Additionally, the precursor materials are selected to also include “bulky” ligands.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR +1
Electrochromic tungsten oxide film deposition
InactiveUS8894827B2Highly undesirableReduce sheet resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringTungsten(IV) oxide
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20120001335A1Small sizeImprove productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMixed gas
Provided is a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having favorable electric characteristics with a high yield. A groove and / or a contact hole reaching a semiconductor region or a conductive region is formed in an insulating film covering the semiconductor region or the conductive region; a first conductive film is formed in the groove and / or the contact hole; the first conductive film is exposed to plasma generated from a mixed gas of an oxidizing gas and a halogen-based gas and to an atmosphere containing water to be fluidized partially or entirely; and a second conductive film is formed over the first conductive film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Additive manufacturing device, additive manufacturing method, and profile rod therefor
ActiveUS20200307069A1Improve layered meltingRemove restrictionsManufacturing enclosures3D object support structures3d printFiber
A method of using solid profile rods instead of the usual filament coils for additive manufacturing methods such as 3D printing for industrial applications such as aircraft manufacturing, and to enable a more rapid production of fiber-composite components. The additive manufacturing device, or the 3D printer which generates the component layer by layer, respectively, comprises a material magazine in which a plurality of profile rods are stored. The profile rods are pre-tailored and are adapted to the component layer by layer. The profile rods, when printing, are successively retrieved from the material magazine and, by way of an infeed installation, guided to the nozzle of the additive manufacturing installation and subsequently applied to the printing bed so as to form the component layer by layer.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Multi-layer dielectric and method of forming same
InactiveUS6940171B2Low deposition rateSolve the real problemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDopantSemiconductor materials
A multiple dielectric device and its method of manufacture overlaying a semiconductor material, including a substrate, an opening relative to the substrate, the opening having an aspect ratio greater than about two, a first dielectric layer in the opening, wherein a portion of the opening not filled with the first dielectric layer has an aspect ratio of not greater than about two, and a second dielectric layer over said first dielectric layer. The deposition rates of the first and second dielectric layers may be achieved through changes in process settings, such as temperature, reactor chamber pressure, dopant concentration, flow rate, and a spacing between the shower head and the assembly. The dielectric layer of present invention provides a first layer dielectric having a low deposition rate as a first step, and an efficiently formed second dielectric layer as a second completing step.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Effective delivery of nanoparticles and micrometer-sized pharmaceutical aerosols to the lung through enhanced condensational growth
ActiveUS8479728B2Efficient deliveryEffectively penetrate the lungsPowder deliveryBiocideHigh humidityMedicine
Methods and devices for inhalation therapy to deliver and embed (deposit) particles less than about 1 μm in diameter in the lung. High humidity treatment of the lungs causes condensational growth in particle size upon entering the lungs. Increased particle size is conducive to particle embedment (deposition) in deep lung tissue or at a specific targeted lung region.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition for a solid oxide fuel cell
InactiveUS8166911B2Satisfactory rateEasy to controlBurnersLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzleThin layer
A method and apparatus for electrostatic spray deposition (ESD) for fabricating a thin-layer yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) electrolyte on a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anode substrate constructed of nickel-YSZ cermet. By reducing the thickness of the electrolyte, and thereby reducing the cell internal IR drop, an intermediate temperature SOFC (ITSOFC) can operate at 600-800° C. A collar positioned at a distance from a discharge end of a spray nozzle enhances a spray pattern of a precursor including the electrolyte material and thus provides a very thin electrolyte layer.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Plating bath composition and method for electroless plating of palladium
ActiveUS10385458B2Extended service lifeIncrease deposition rateLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingLife timePalladium ion
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Surface modification device based on electrophoresis-assisted micro-nano particle melting and self-assembly
InactiveUS20190040542A1Improve bindingLow deposition rateMaterial nanotechnologyCellsMicro structureMolten state
A surface modification device based on electrophoresis-assisted micro-nano particle melting and self-assembly, includes a working table, a particle and solution mixing and circulating container, a processing recess, a solution conveying apparatus, an electrophoresis-assisted apparatus, a vacuum heating apparatus and an integrated control cabinet. Sacrifice particles with a relatively low melting point are in a molten state. The molten particles cover or are adhered to another type of modified particles and the surface of the metal workpiece, so that the binding force between the metal workpiece and micro-nano particles is enhanced. By taking advantage of characteristics of the modified particles, hydrophilic and hydrophobic micro structures are obtained on the metal surface. The electrophoresis-assisted apparatus may greatly improve the deposition efficiency of extremely fine particles in a solution. The deposition rate and the deposition thickness may be adjusted by adjusting the intensity of an electric field.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing electrophotographic photosensitive member, and electrophotographic photosensitive member and electrophotographic apparatus making use of the same
InactiveUS20050153223A1Increase deposition rateSuperior film quality uniformityElectrographic process apparatusAbnormal growthsHigh frequency power
An electrophotographic photosensitive member production process is provided having the steps of placing a cylindrical substrate having a conductive surface in a first film-forming chamber, and decomposing a source gas with high-frequency power to deposit on the cylindrical substrate a first layer formed of a non-single-crystal material, taking out of the first film-forming chamber the cylindrical substrate with the first layer deposited thereon, and placing the cylindrical substrate with the first layer deposited thereon in a second film-forming chamber, and decomposing a source gas with a high-frequency power to deposit on the first layer a second layer having an upper-part blocking layer formed of a non-single-crystal material. Even where abnormal growth portions called spherical protuberances are present on the photosensitive member surface, they can be made not to appear on images, and image defects can vastly be remedied.
Owner:CANON KK
Lubricant
InactiveUS20130150270A1Reduce frictionLess fuel consumptionMoulding toolsAdditivesEngineeringLubrication
A solid lubricant composition which can be used for lubrication of railway wheel to rail contact points. The composition can be adjusted to create lubricants having targeted coefficient of friction properties for optimal performance at the specific sites of application whether on the wheel flange or wheel tread areas. The compound is preferably composed of powder and liquid elements and extruded directly into a finished solid lubricant stick.
Owner:ABBOTT JOSHUA
A kind of environment-friendly and easily decomposable vegetable oil-based lubricating oil and its production process
ActiveCN104745280BMeet actual use needsProduce pollutionLubricant compositionVegetable oilSunflower oil
The invention discloses an environmentally friendly and easily decomposable vegetable oil-based lubricating oil and a production process thereof, belonging to the field of lubricating oil. The lubricating oil of the present invention adopts vegetable oil as the base oil, and the mass ratio of the base oil and the additive is 7:3, wherein the base oil includes high oleic sunflower oil and castor oil, and the quality of the high oleic sunflower oil and castor oil is The ratio is 6:4. Among them, high oleic sunflower oil, with an oleic acid content of up to 90%, has extremely high antioxidant properties, while castor oil has an ideal viscosity. The two are used in a ratio. As an ideal vegetable oil, no special processing is required. Advantageous characteristics of conventional mineral oils as base oils. In addition, through the auxiliary modification of additives, no special processing is required, and it can be put into use after simple proportioning and high-temperature smelting. The production cost is low and it is easy to popularize.
Owner:HANERGY (QINGDAO) LUBRICATION TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com