Patents
Literature
708 results about "Stoichiometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɪtri/ is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products, leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.
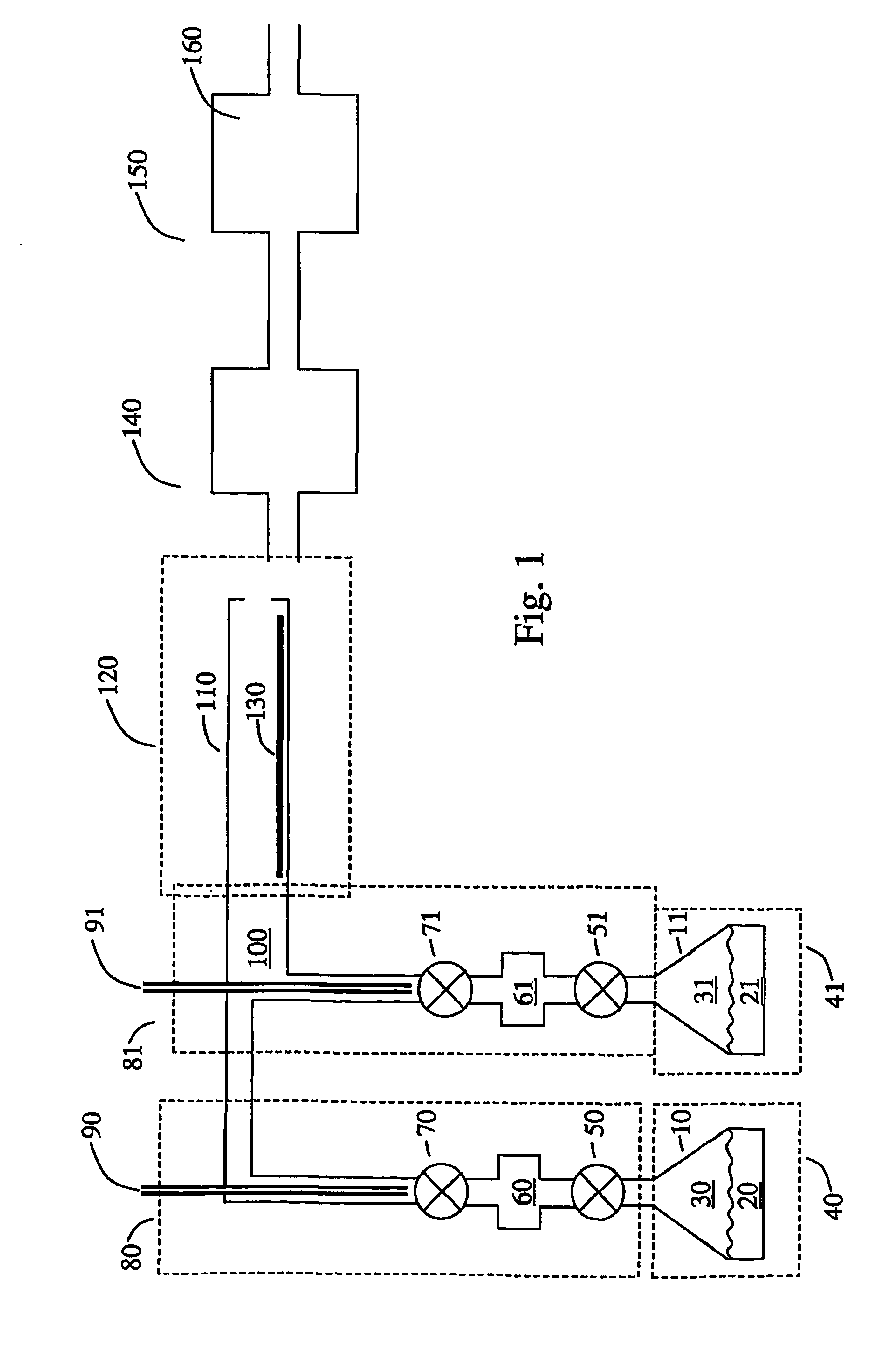
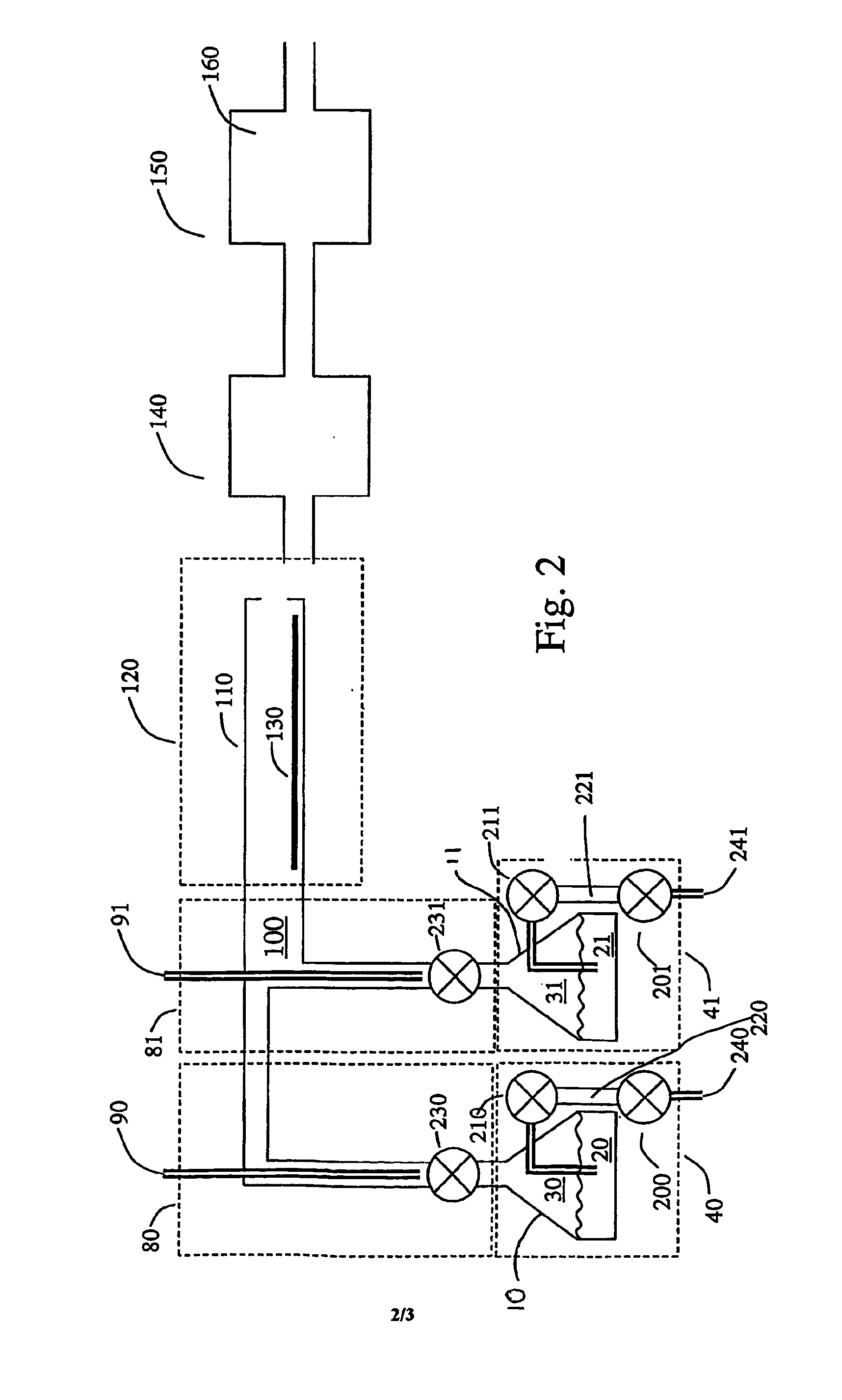
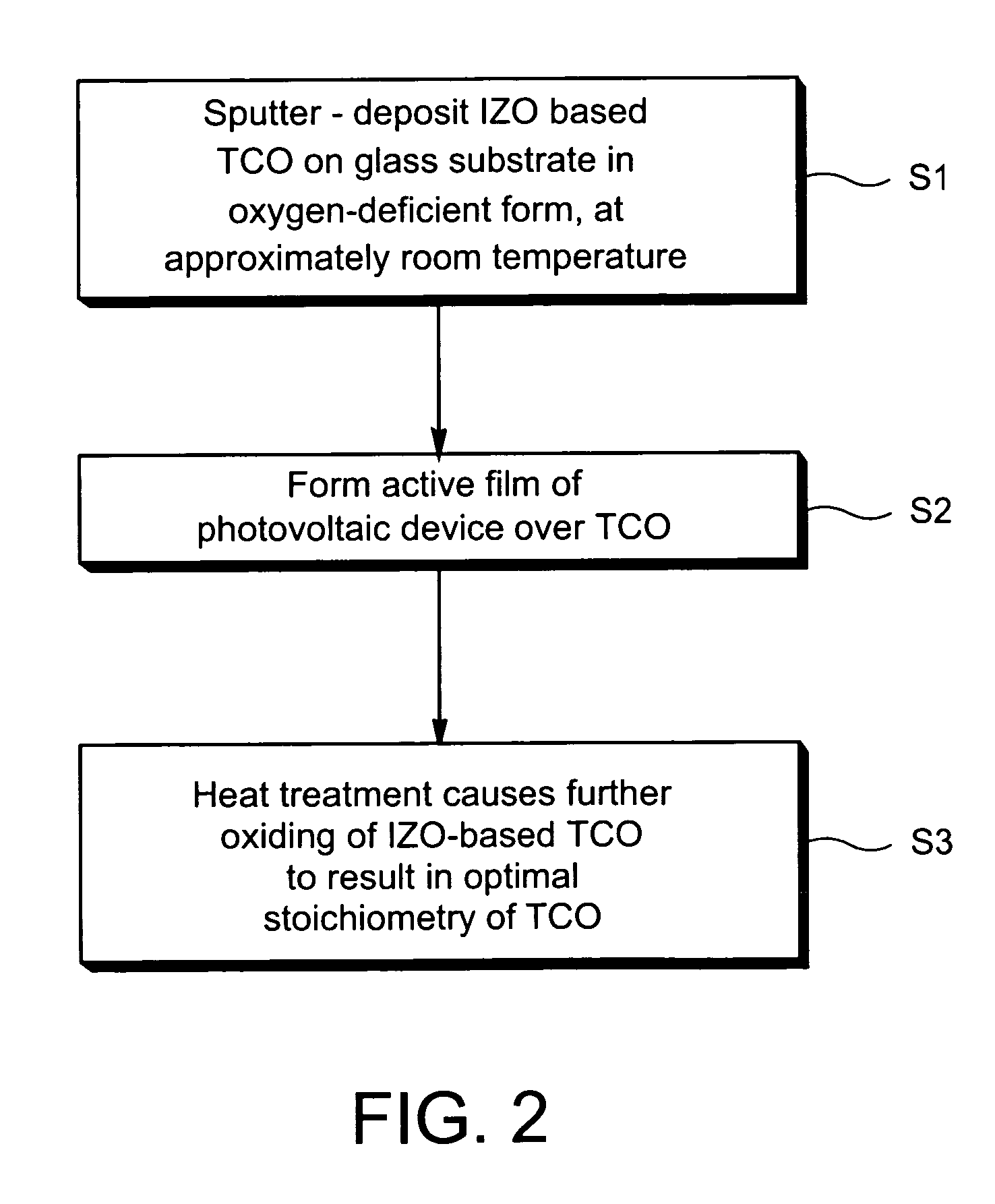
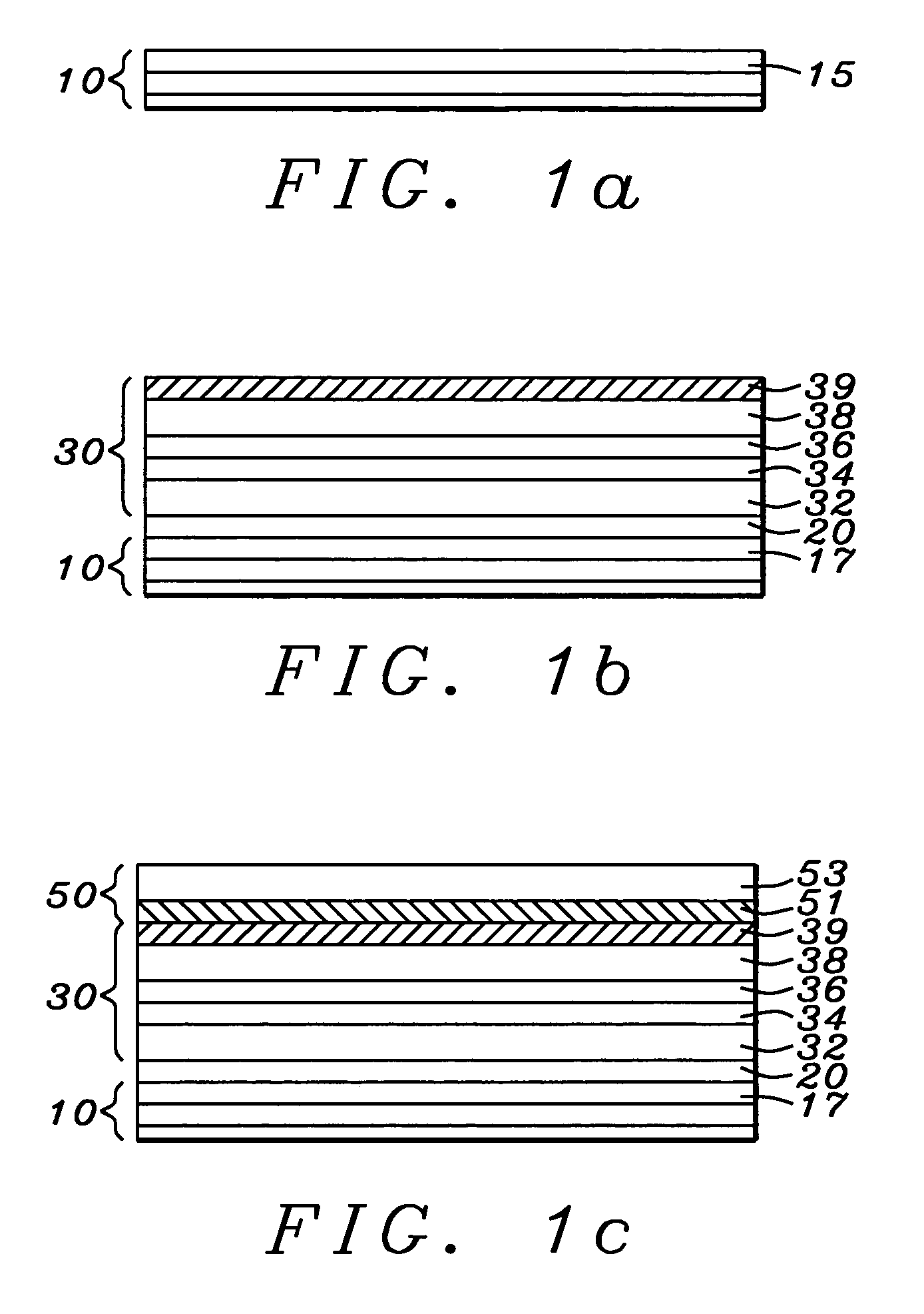
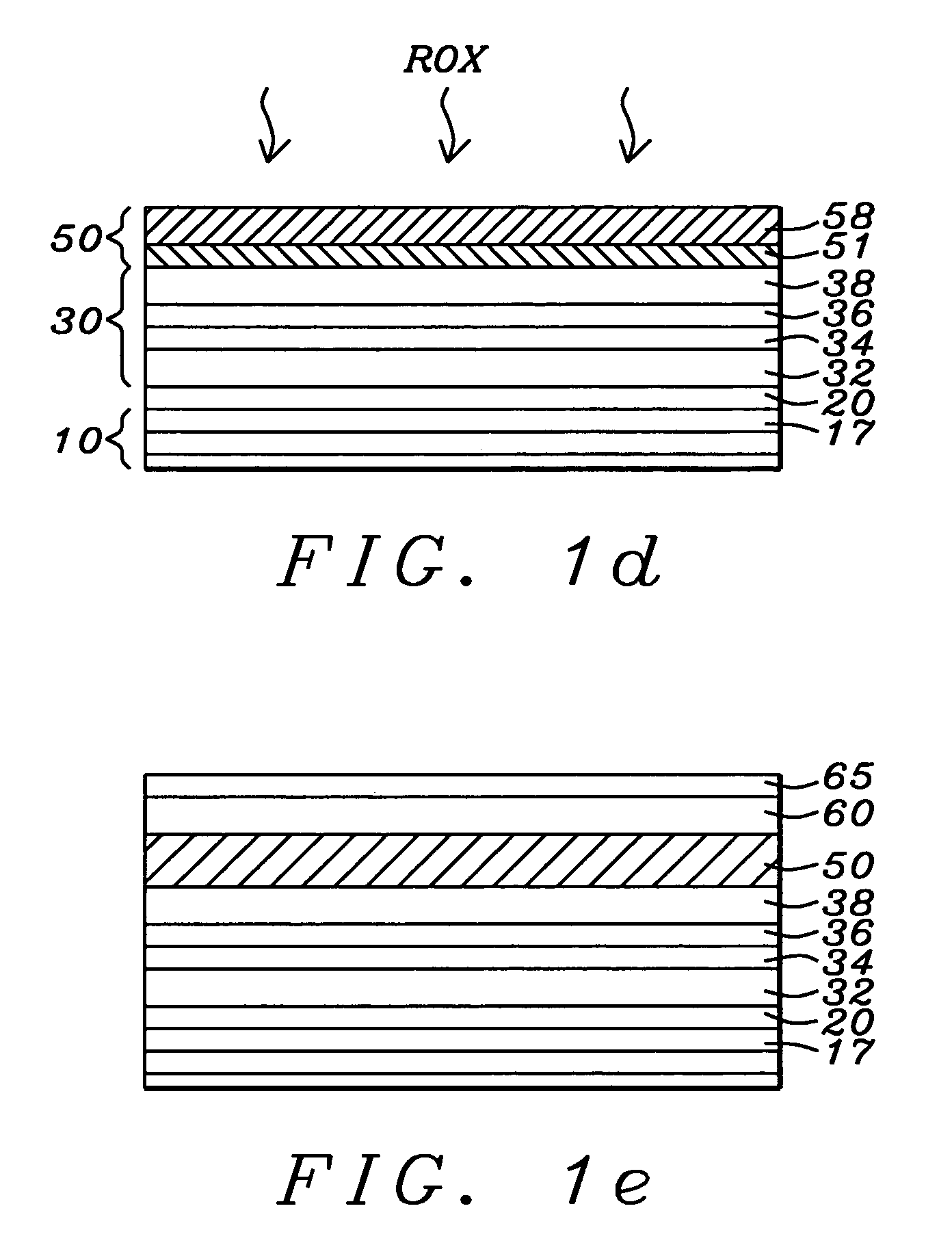
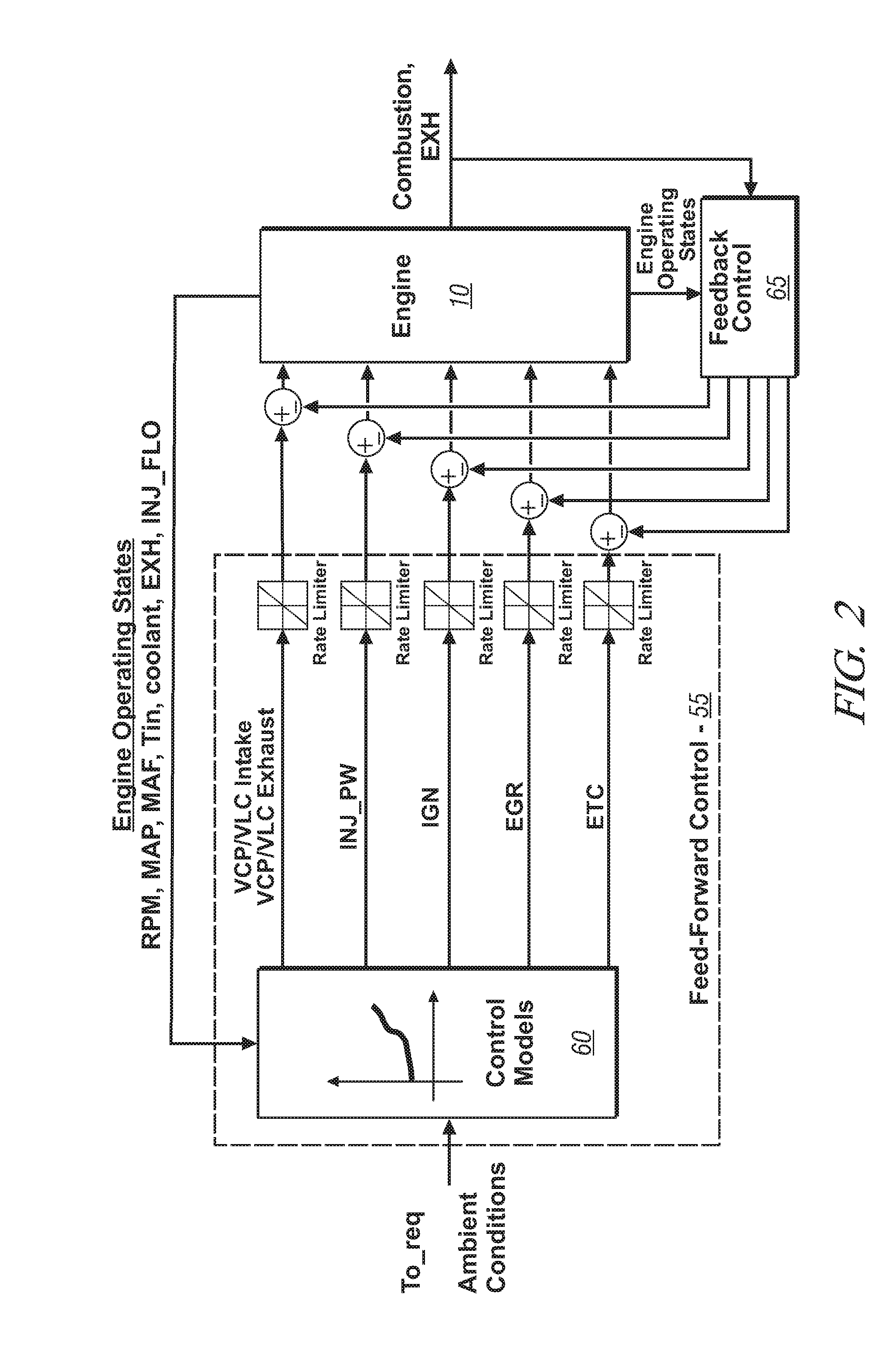
MODULATED DEPOSITION PROCESS FOR STRESS CONTROL IN THICK TiN FILMS
ActiveUS20100032842A1Liquid surface applicatorsIncorrect coupling preventionNitrogen plasmaDeposition process
A multi-layer TiN film with reduced tensile stress and discontinuous grain structure, and a method of fabricating the TiN film are disclosed. The TiN layers are formed by PVD or IMP in a nitrogen plasma. Tensile stress in a center layer of the film is reduced by increasing N2 gas flow to the nitrogen plasma, resulting in a Ti:N stoichiometry between 1:2.1 to 1:2.3. TiN films thicker than 40 nanometers without cracks are attained by the disclosed process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
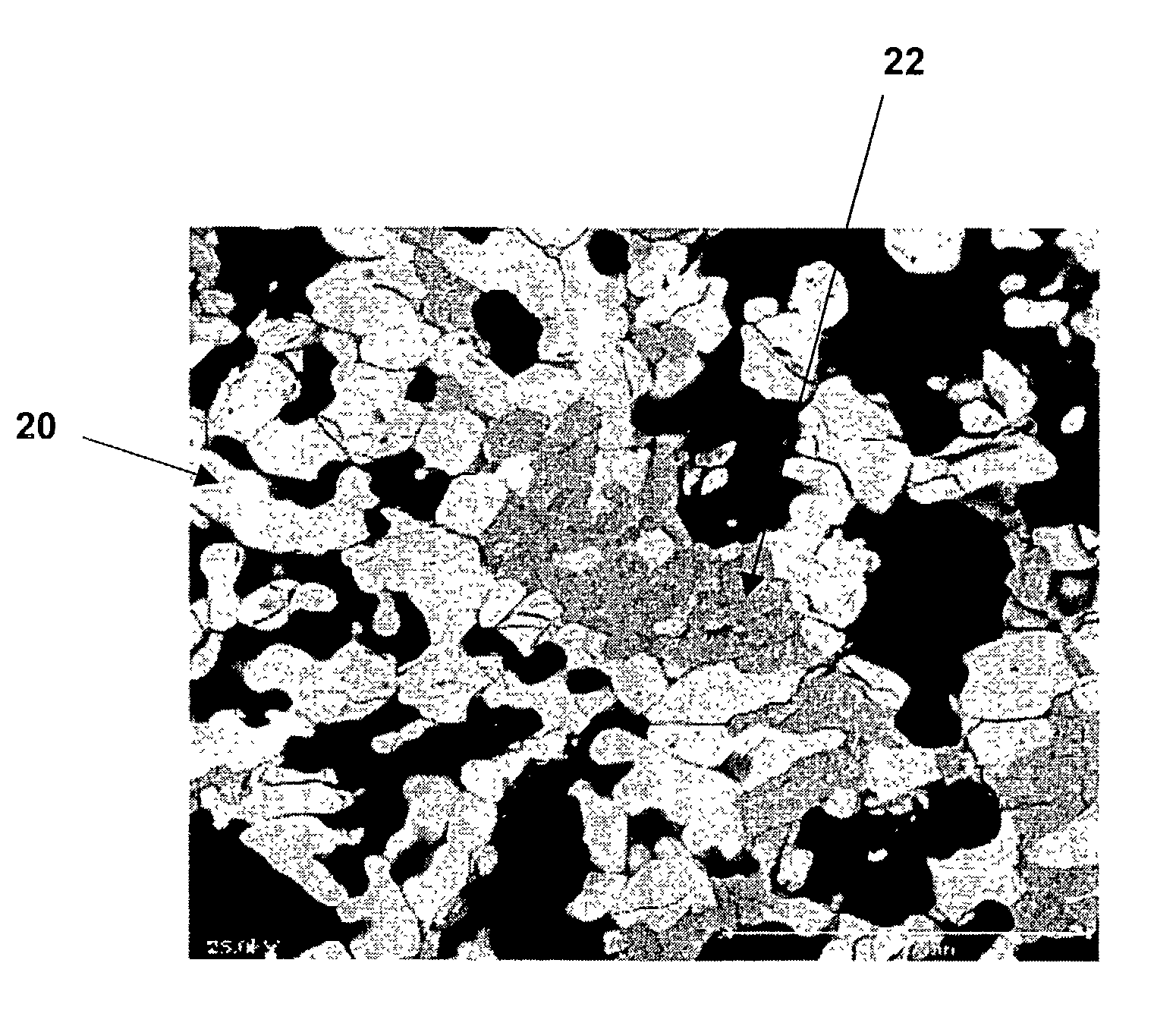
Coated nanoparticles and quantum dots for solution-based fabrication of photovoltaic cells
CIGS absorber layers fabricated using coated semiconducting nanoparticles and / or quantum dots are disclosed. Core nanoparticles and / or quantum dots containing one or more elements from group IB and / or IIIA and / or VIA may be coated with one or more layers containing elements group IB, IIIA or VIA. Using nanoparticles with a defined surface area, a layer thickness could be tuned to give the proper stoichiometric ratio, and / or crystal phase, and / or size, and / or shape. The coated nanoparticles could then be placed in a dispersant for use as an ink, paste, or paint. By appropriate coating of the core nanoparticles, the resulting coated nanoparticles can have the desired elements intermixed within the size scale of the nanoparticle, while the phase can be controlled by tuning the stochiometry, and the stoichiometry of the coated nanoparticle may be tuned by controlling the thickness of the coating(s).
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Cobalt-molybdenum sulfide catalyst materials and methods for ethanol production from syngas
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the chemical conversion of syngas to alcohols. The invention includes catalyst compositions, methods of making the catalyst compositions, and methods of using the catalyst compositions. Certain embodiments teach compositions for catalyzing the conversion of syngas into products comprising at least one C1-C4 alcohol, such as ethanol. These compositions generally include cobalt, molybdenum, and sulfur. Preferred catalyst compositions for converting syngas into alcohols include cobalt associated with sulfide in certain preferred stoichiometries as described and taught herein.
Owner:ALBEMARLE CORP
Coated nanoparticles and quantum dots for solution-based fabrication of photovoltaic cells
CIGS absorber layers fabricated using coated semiconducting nanoparticles and / or quantum dots are disclosed. Core nanoparticles and / or quantum dots containing one or more elements from group IB and / or IIIA and / or VIA may be coated with one or more layers containing elements group IB, IIIA or VIA. Using nanoparticles with a defined surface area, a layer thickness could be tuned to give the proper stoichiometric ratio, and / or crystal phase, and / or size, and / or shape. The coated nanoparticles could then be placed in a dispersant for use as an ink, paste, or paint. By appropriate coating of the core nanoparticles, the resulting coated nanoparticles can have the desired elements intermixed within the size scale of the nanoparticle, while the phase can be controlled by tuning the stochiometry, and the stoichiometry of the coated nanoparticle may be tuned by controlling the thickness of the coating(s).
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
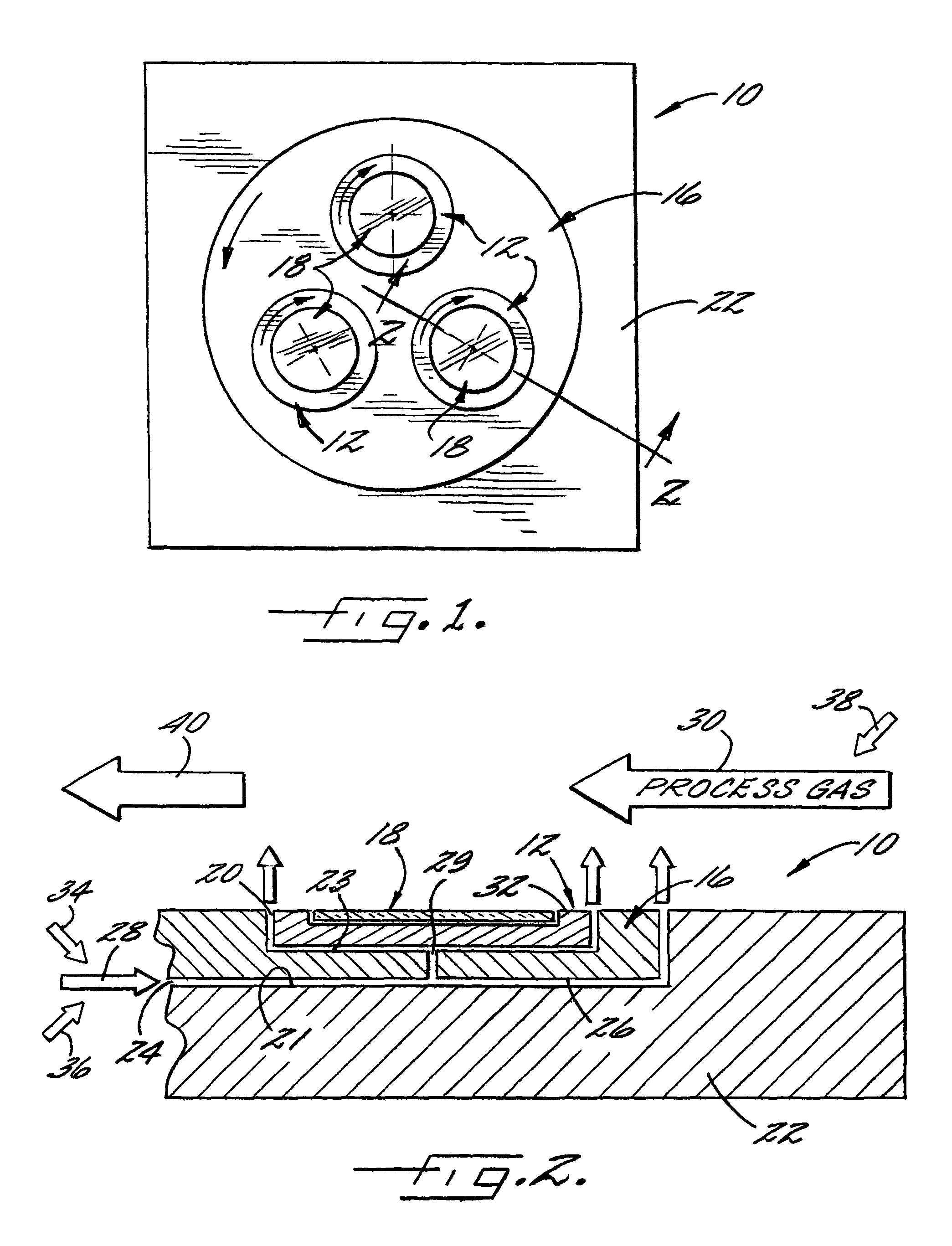
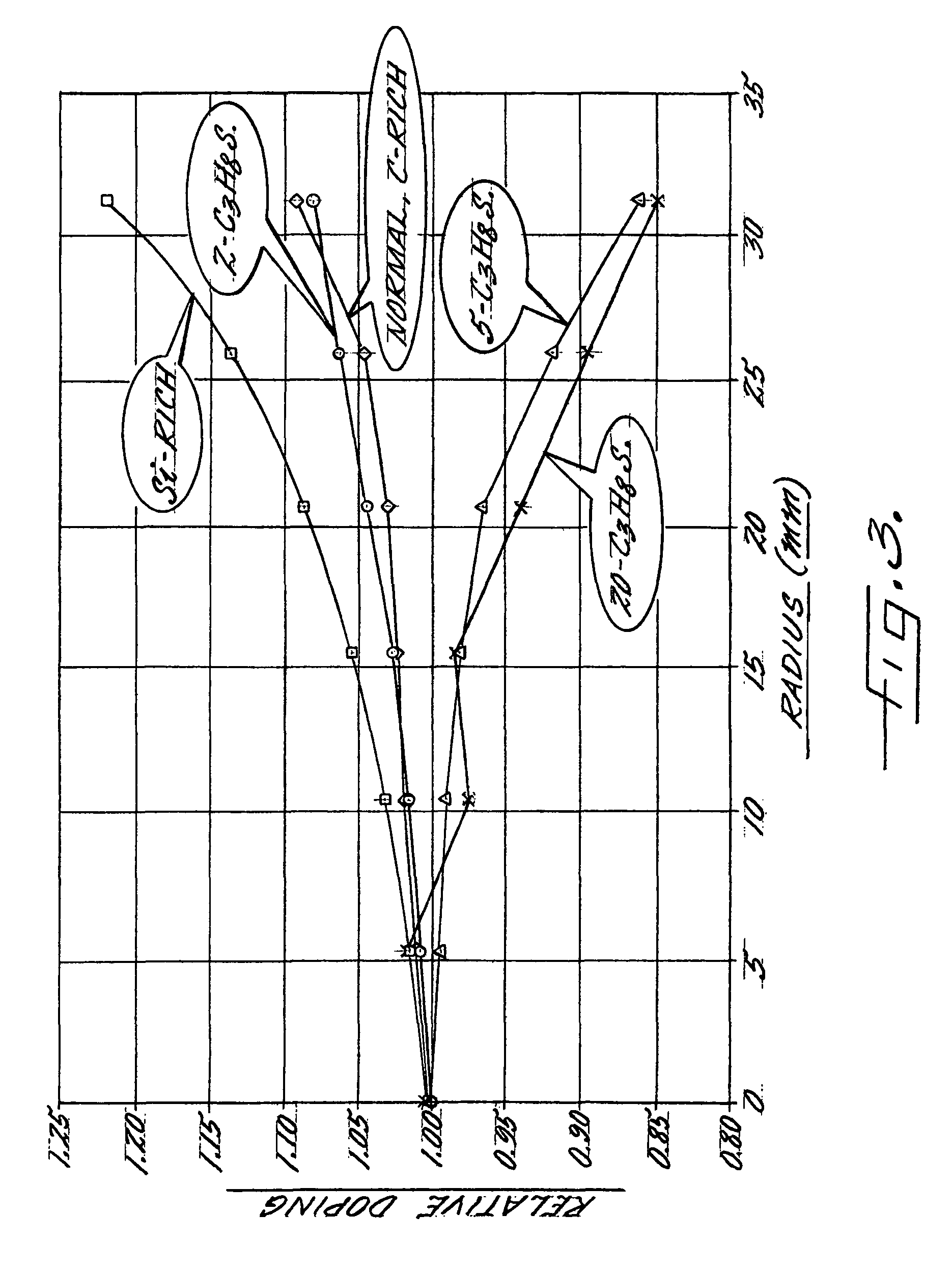
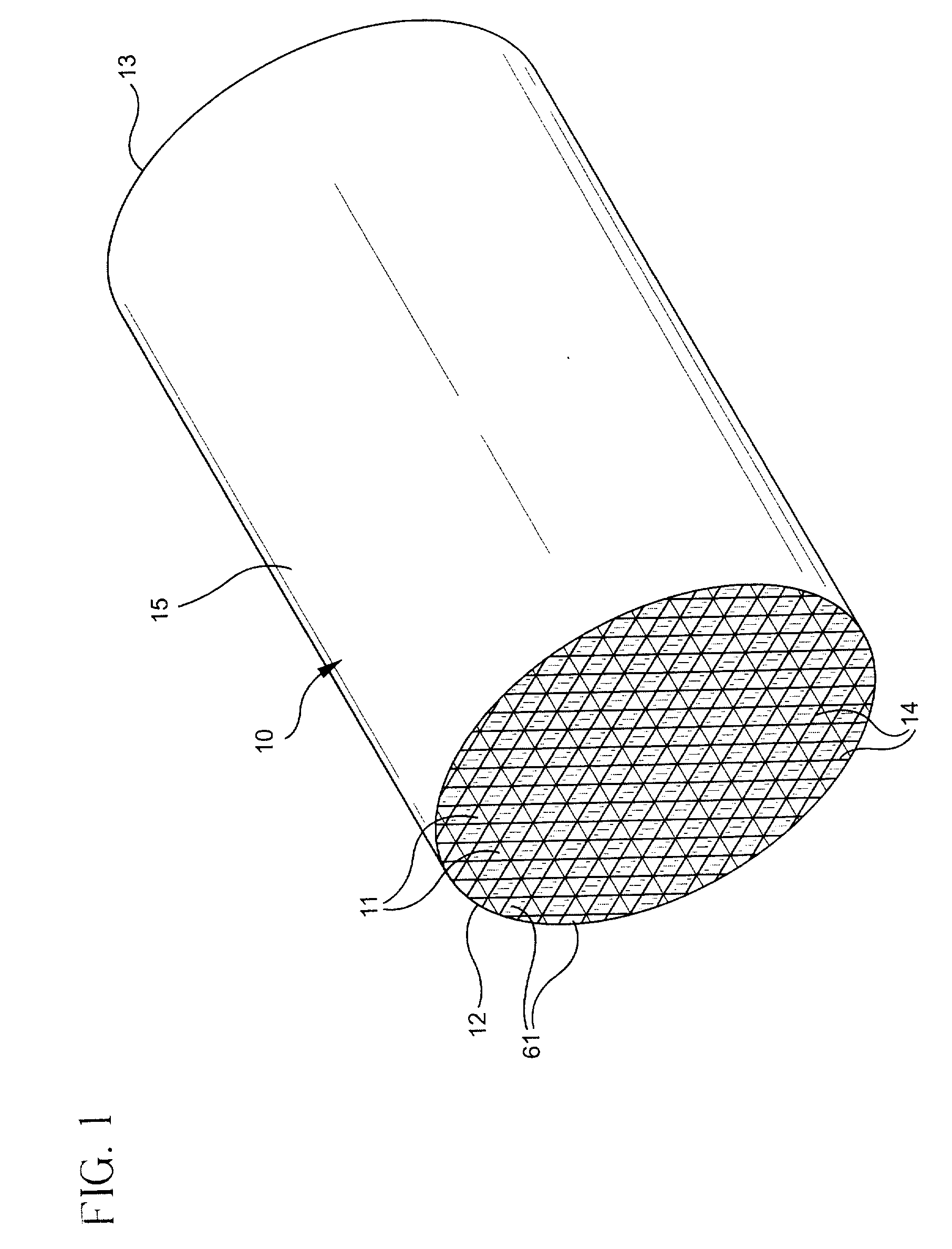
Directed reagents to improve material uniformity
A method for locally controlling the stoichiometry of an epitaxially deposited layer on a semiconductor substrate is provided. The method includes directing a first reactant gas and a doping gas across a top surface of a semiconductor substrate and directing a drive gas and a second reactant gas against the substrate separately from the first reactant gas in a manner that rotates the substrate while introducing the second reactant gas at an edge of the substrate to control each reactant separately, thereby compensating and controlling depletion effects and improving doping uniformity in resulting epitaxial layers on the substrate.
Owner:CREE INC
Single-source precursors for ternary chalcopyrite materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6992202B1Effective yieldFurnaces without endless coreMaterial nanotechnologyChalcopyriteQuantum dot
A single source precursor for depositing ternary I-III-VI2 chalcopyrite materials useful as semiconductors. The single source precursor has the I-III-VI2 stoichiometry “built into” a single precursor molecular structure which degrades on heating or pyrolysis to yield the desired I-III-VI2 ternary chalcopyrite. The single source precursors effectively degrade to yield the ternary chalcopyrite at low temperature, e.g. below 500° C., and are useful to deposit thin film ternary chalcopyrite layers via a spray CVD technique. The ternary single source precursors according to the invention can be used to provide nanocrystallite structures useful as quantum dots. A method of making the ternary single source precursors is also provided.
Owner:OHIO AEROSPACE INST +1
Method for gas-solid contacting in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor
InactiveUS6894183B2Eliminate and drastically reduce bypassEffective contactThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingForming gasSolid particle
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
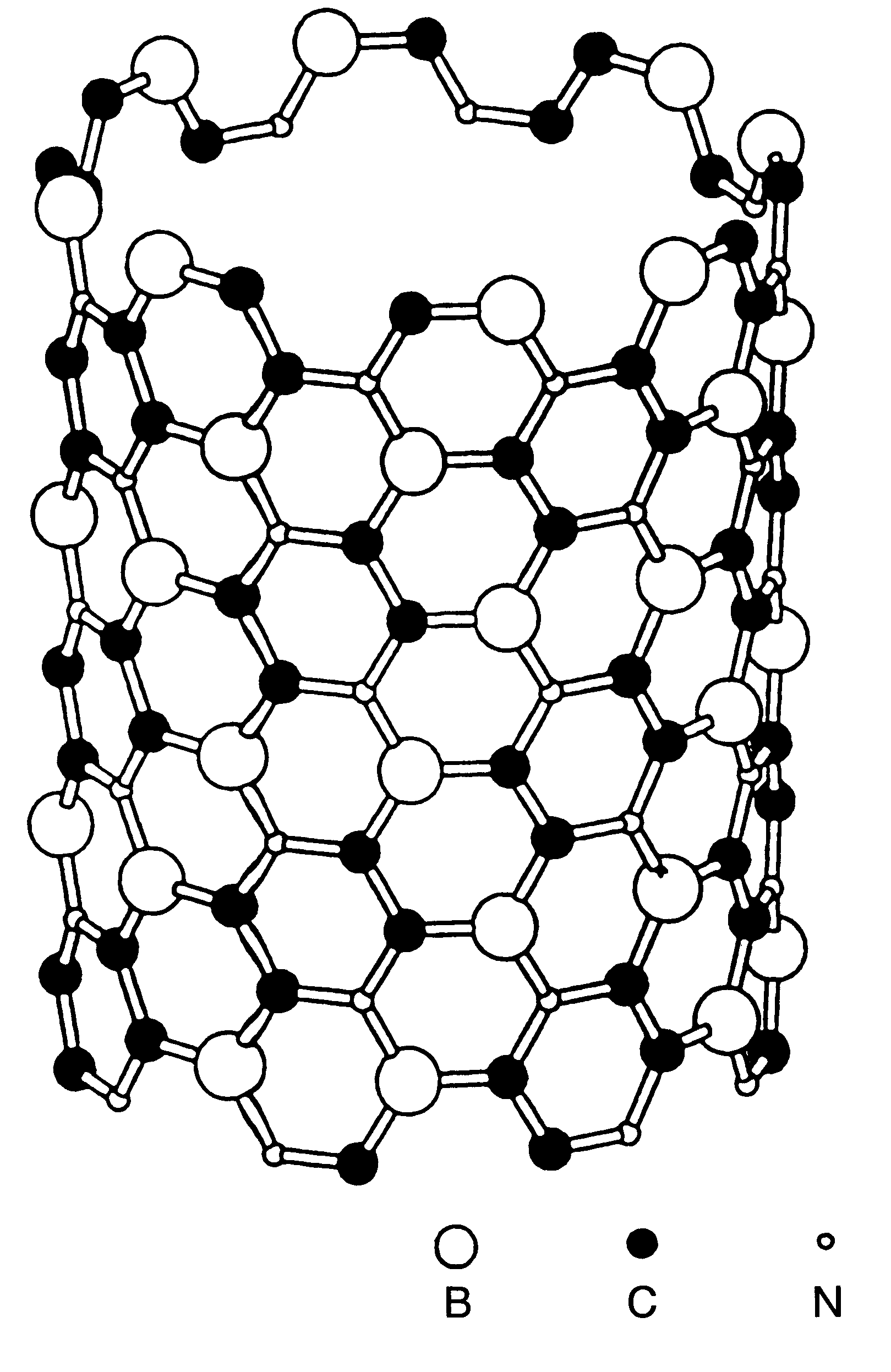
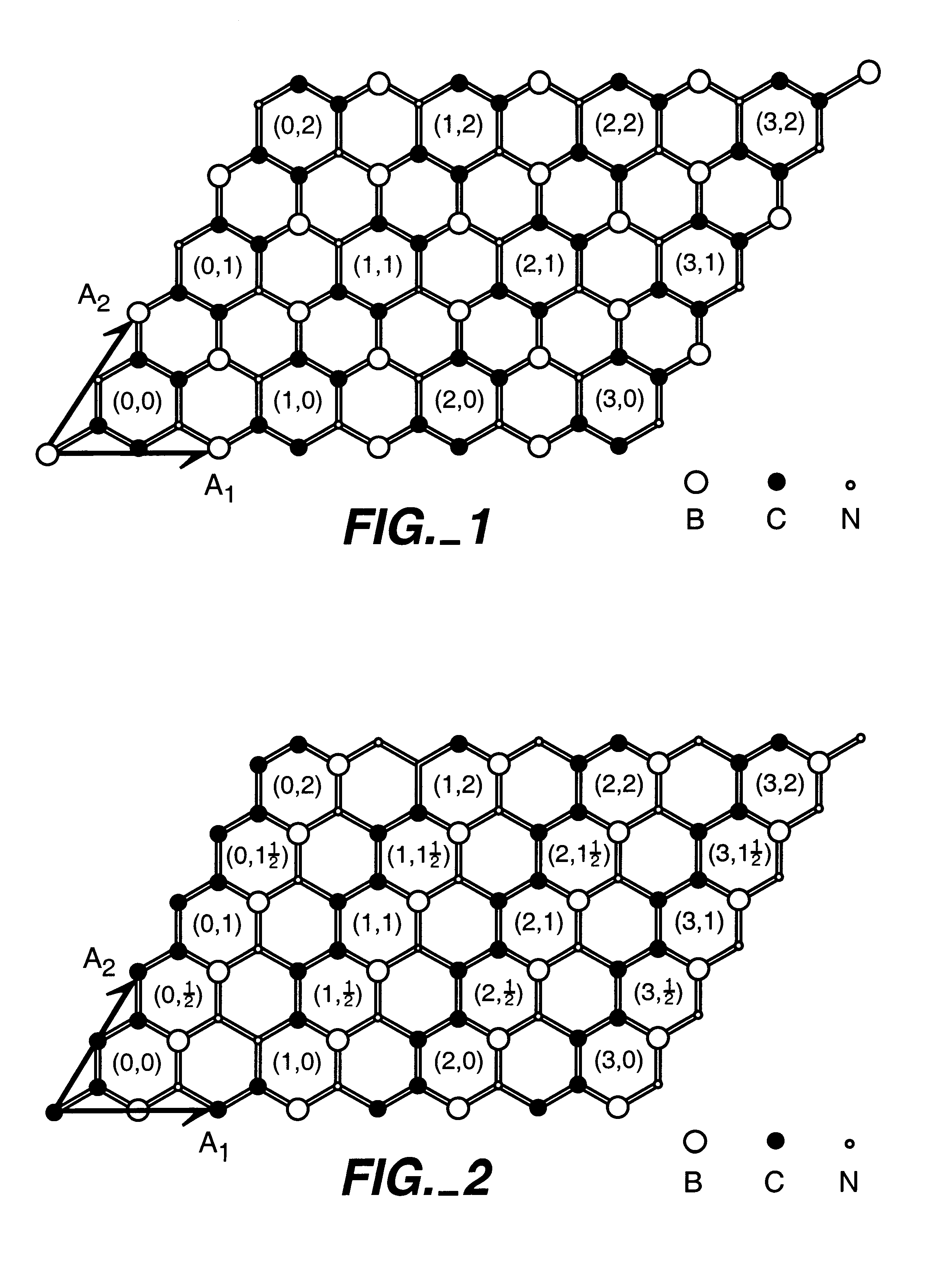
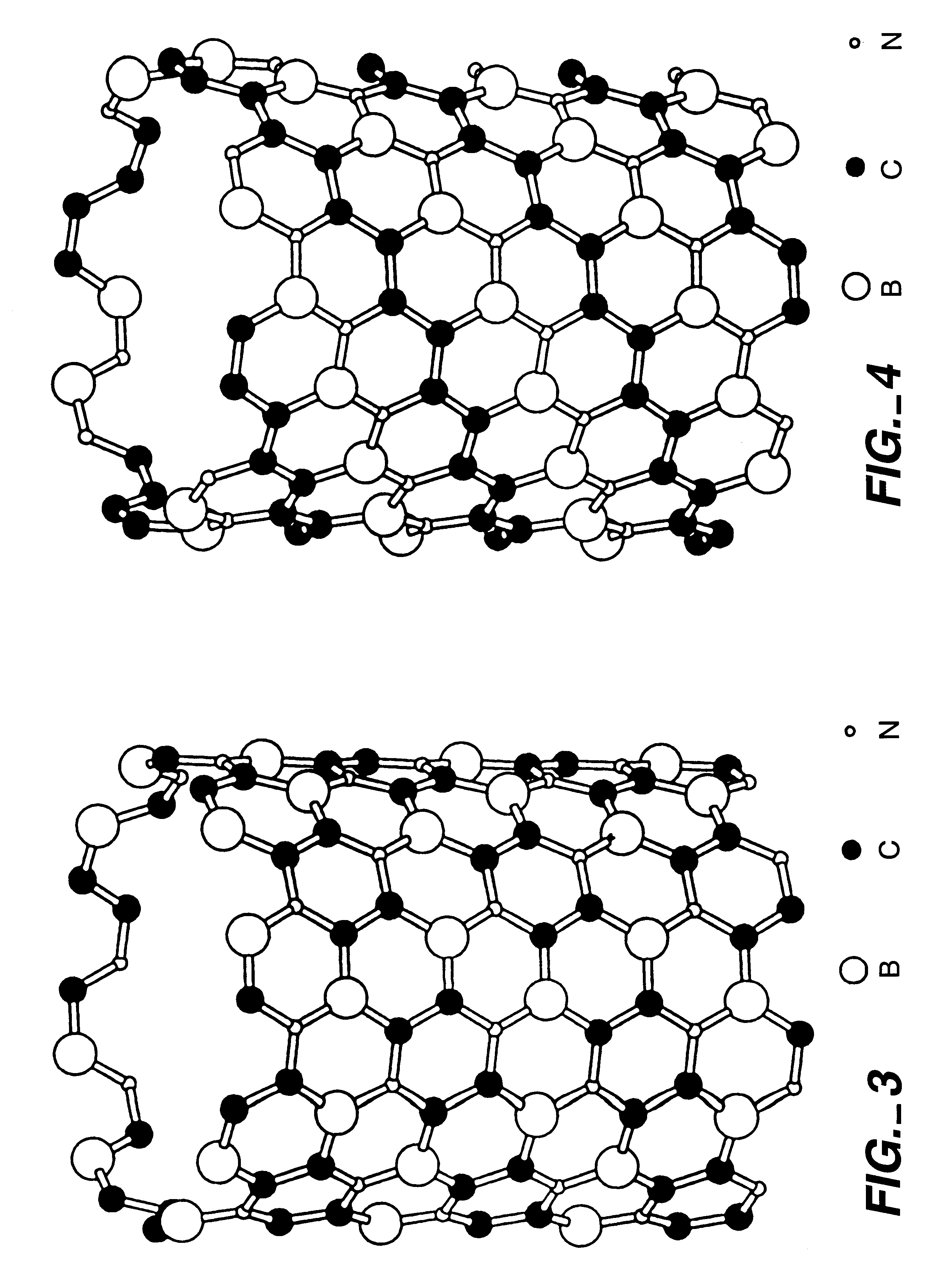
BX CY NZ nanotubes and nanoparticles
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Mullite-aluminum titanate diesel exhaust filter
InactiveUS6849181B2High porosityLarge apertureIron oxides/hydroxidesExhaust apparatusFiltrationMullite
The invention is directed at a mullite-aluminum titanate porous diesel particulate filter constituting a porous ceramic body containing, expressed in terms of weight percent of the total body, of 60-90%, preferably 70-80%, most preferably 70% iron-aluminum titanate solid solution having a stoichiometry of Al2(1−x)Fe2xTiO5, where x is 0-0.1, and 10-40%, preferably 20-30%, most preferably 30% mullite (3Al2O3.2SiO2), and consists essentially, expressed in terms of weigh percent on the oxide basis, of 3 to 15% SiO2, 55 to 65% Al2O3, 22 to 40% TiO2, and 0 to 10% Fe2O3, and being useful for filtration of diesel exhaust. The inventive diesel particulate filter exhibits high interconnected open porosity and large median pore size, in combination with high permeability when fired to a temperature of between 1650° to 1700° C., along with high thermal shock resistance and good filtration capability.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for making thin-film semiconductors based on I-III-VI2 compounds, for photovoltaic applications
InactiveUS7026258B2Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrochemistryChemical measurement
The invention concerns a method for making thin-film CIGS which consists in: electrochemically depositing on a substrate a layer of stoichiometry close to CuInSe2; then rapidly annealing said layer from a light source with pulses of sufficient power to recrystallize CIS. Advantageously, the electrodeposited elements are premixed. Thus, after the deposition step, a homogeneous matrix is obtained which can support sudden temperature increases during the rapid annealing.
Owner:ELECTRICITE DE FRANCE +1
Vapor deposition of metal oxides, silicates and phosphates, and silicon dioxide
InactiveUS6969539B2Good step coverageNarrow structureOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideAluminium silicatesAlkylphosphatePhosphate
Metal silicates or phosphates are deposited on a heated substrate by the reaction of vapors of alkoxysilanols or alkylphosphates along with reactive metal amides, alkyls or alkoxides. For example, vapors of tris-(ter-butoxy)silanol react with vapors of tetrakis(ethylmethylamido)hafnium to deposit hafnium silicate on surfaces heated to 300° C. The product film has a very uniform stoichiometry throughout the reactor. Similarly, vapors of diisopropylphosphate react with vapors of lithium bis(ethyldimethylsilyl)amide to deposit lithium phosphate films on substrates heated to 250° C. supplying the vapors in alternating pulse produces these same compositions with a very uniform distribution of thickness and excellent step coverage.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Mullite-aluminum titanate diesel exhaust filter
InactiveUS20040020846A1High interconnected porosityReduce back pressureIron oxides/hydroxidesExhaust apparatusFiltrationWhole body
The invention is directed at a mullite-aluminum titanate porous diesel particulate filter constituting a porous ceramic body containing, expressed in terms of weight percent of the total body, of 60-90%, preferably 70-80%, most preferably 70% iron-aluminum titanate solid solution having a stoichiometry of Al2(1-x)Fe2xTiO5, where x is 0-0.1, and 10-40%, preferably 20-30%, most preferably 30% mullite (3Al2O3.2SiO2), and consists essentially, expressed in terms of weigh percent on the oxide basis, of 3 to 15% SiO2, 55 to 65% Al2O3, 22 to 40% TiO2, and 0 to 10% Fe2O3, and being useful for filtration of diesel exhaust. The inventive diesel particulate filter exhibits high interconnected open porosity and large median pore size, in combination with high permeability when fired to a temperature of between 1650° to 1700° C., along with high thermal shock resistance and good filtration capability.
Owner:CORNING INC
Use of aluminum in perforating and stimulating a subterranean formation and other engineering applications
InactiveUS7393423B2More energy outputImprove mechanical propertiesExplosive chargesBlasting cartridgesMolten stateThermal energy
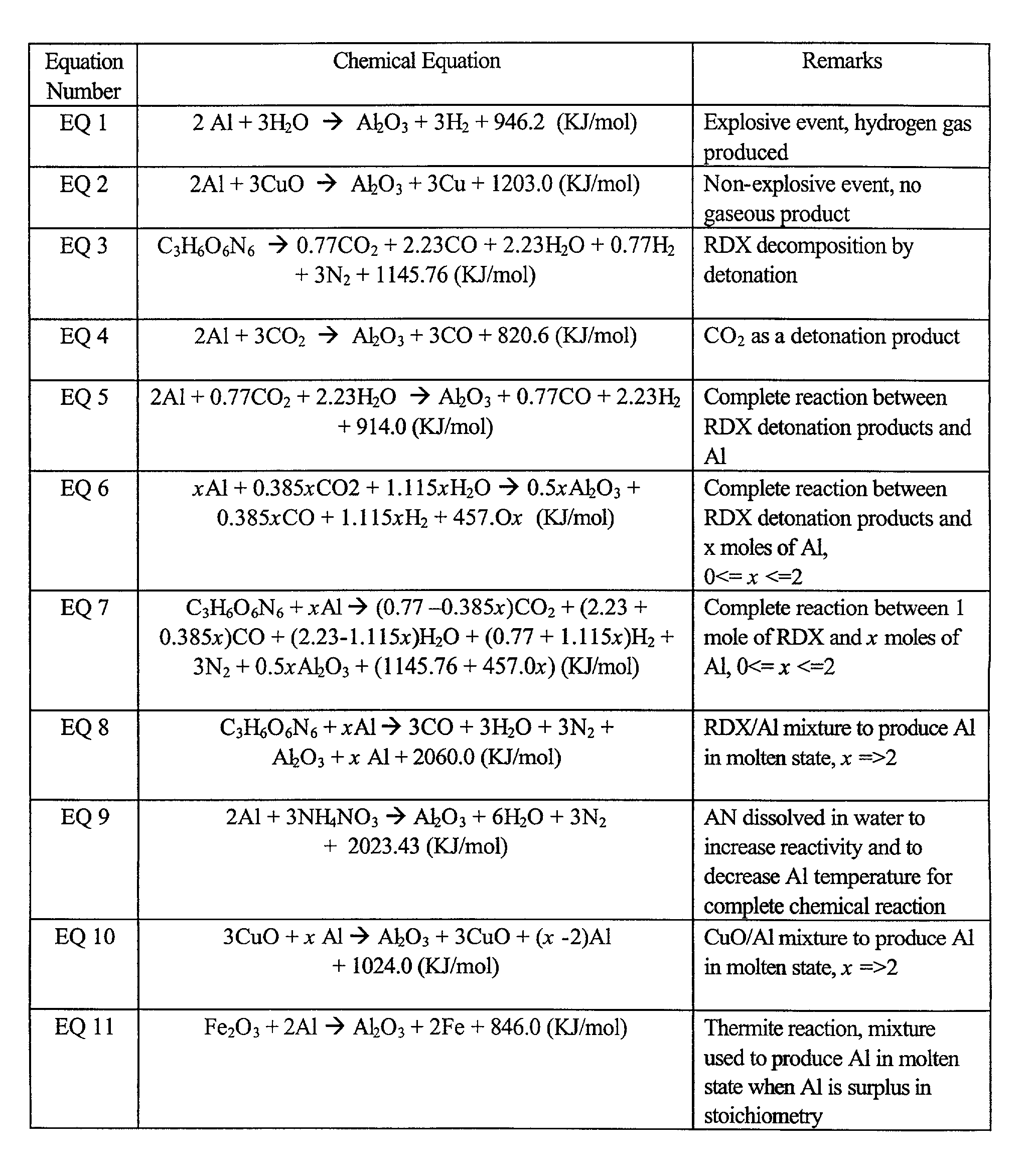
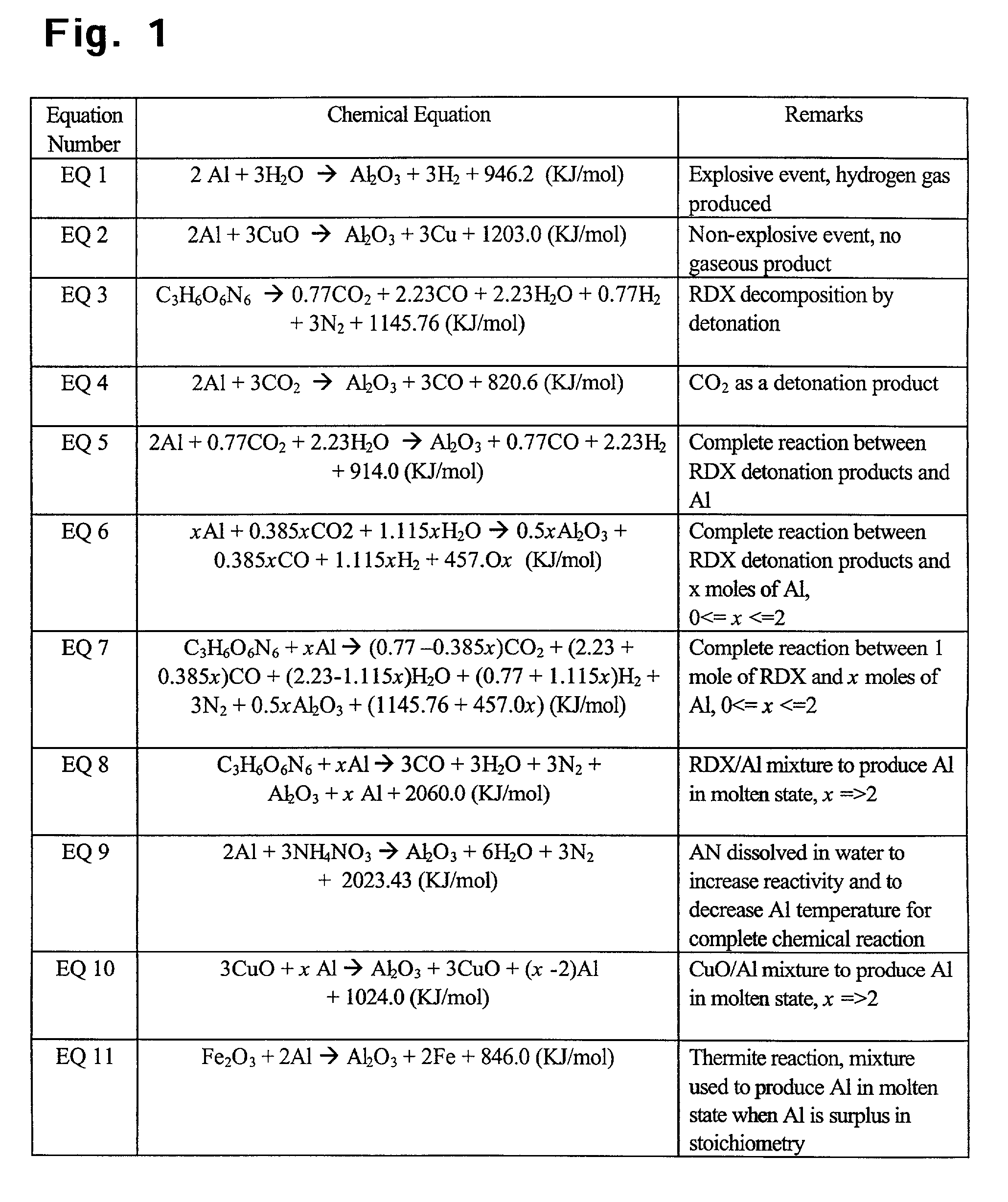
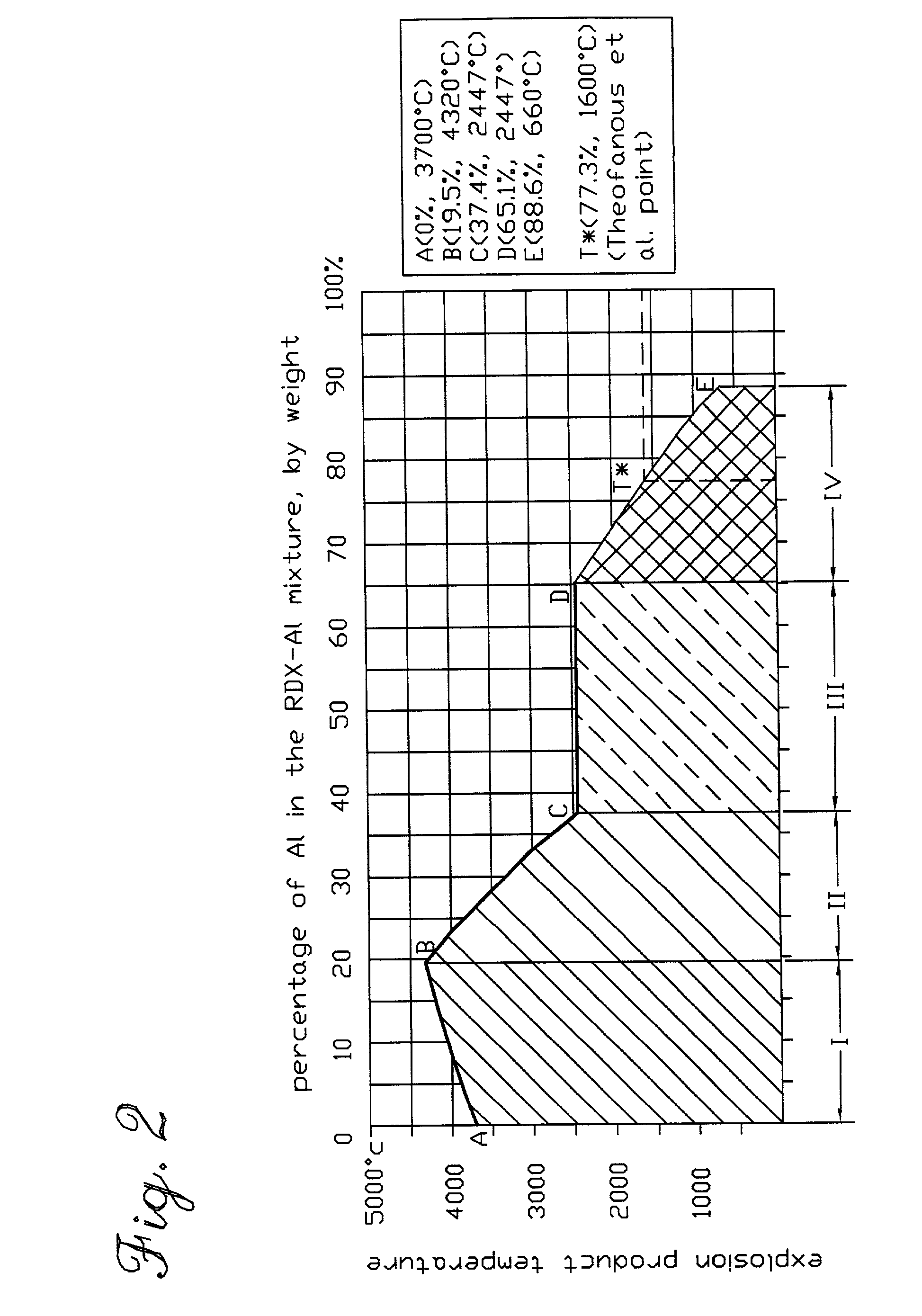
A chemical reaction between molten aluminum and an oxygen carrier such as water to do useful work is disclosed, and in particular two chemical methods to obtain aluminum in its molten state. One is to detonate a HE / Al mixture with surplus Al in stoichiometry, and the other is to use an oxidizer / Al mixture with surplus Al in stoichiometry. Additionally, there is a physical method of shocking and heating Al using high temperature reaction products. The produced Al in its liquid form is forced to react with an oxygen carrying liquid (e.g. water), giving off heat and releasing hydrogen gas or other gaseous material. A water solution of some oxygen-rich chemicals (e.g. ammonium nitrate) can be advantageously used in place of water. A shaped charge is also disclosed having a liner that contains aluminum, propelled by a high explosive such as RDX or its mixture with aluminum powder. Some aluminum in its molten state is projected into the perforation and forced to react with water that also enters the perforation, creating another explosion, fracturing the crushed zone of the perforation and initializing cracks. Another shaped charge is shown having a liner of energetic material such as a mixture of aluminum powder and a metal oxide. Upon detonation, the collapsed liner carries kinetic and thermal energy. Also shown are methods to build and to detonate or fire explosive devices in an oxygen carrying liquid (e.g. water) to perforate and stimulate a hydrocarbon-bearing formation.
Owner:GEODYNAMICS
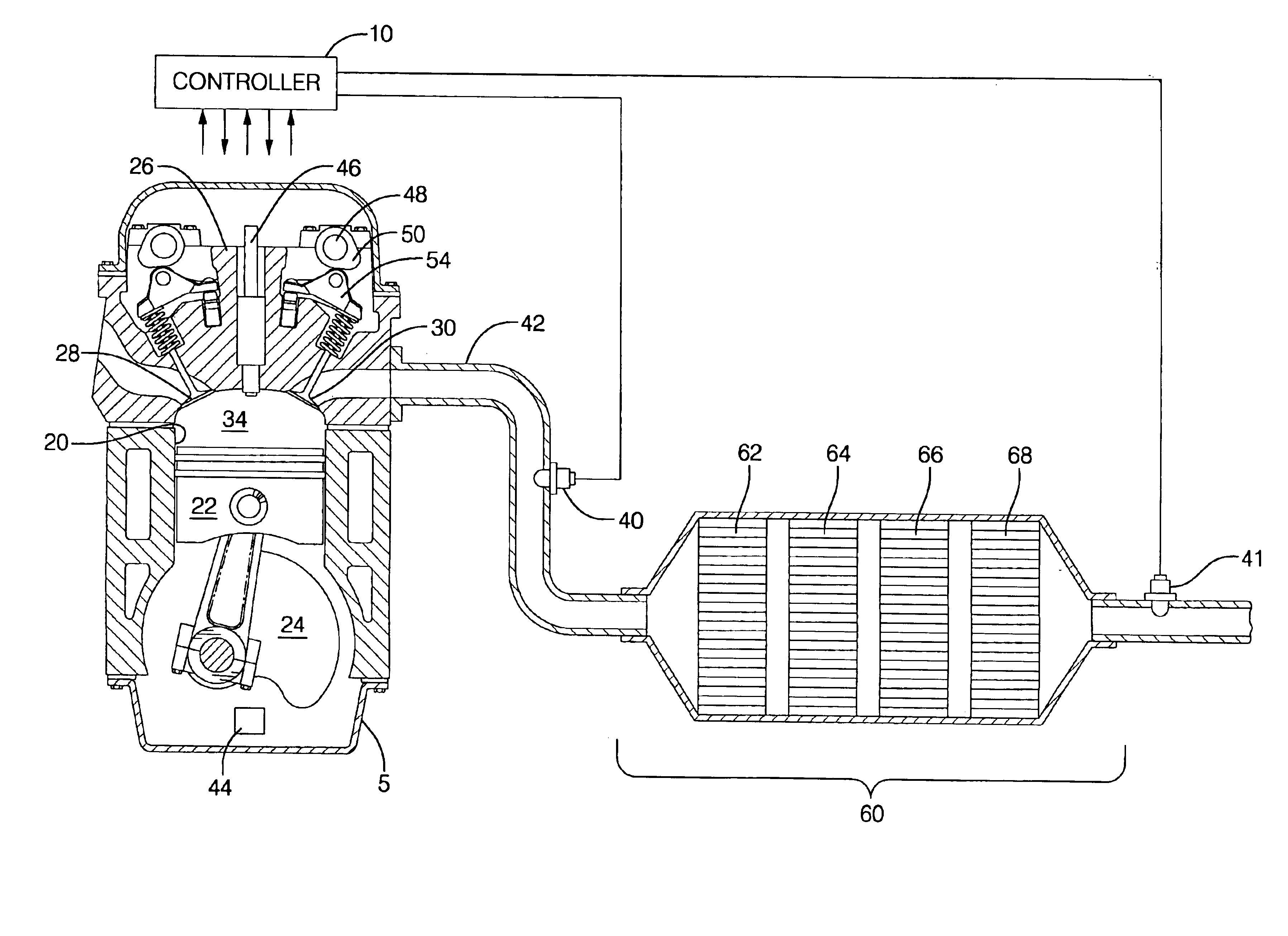
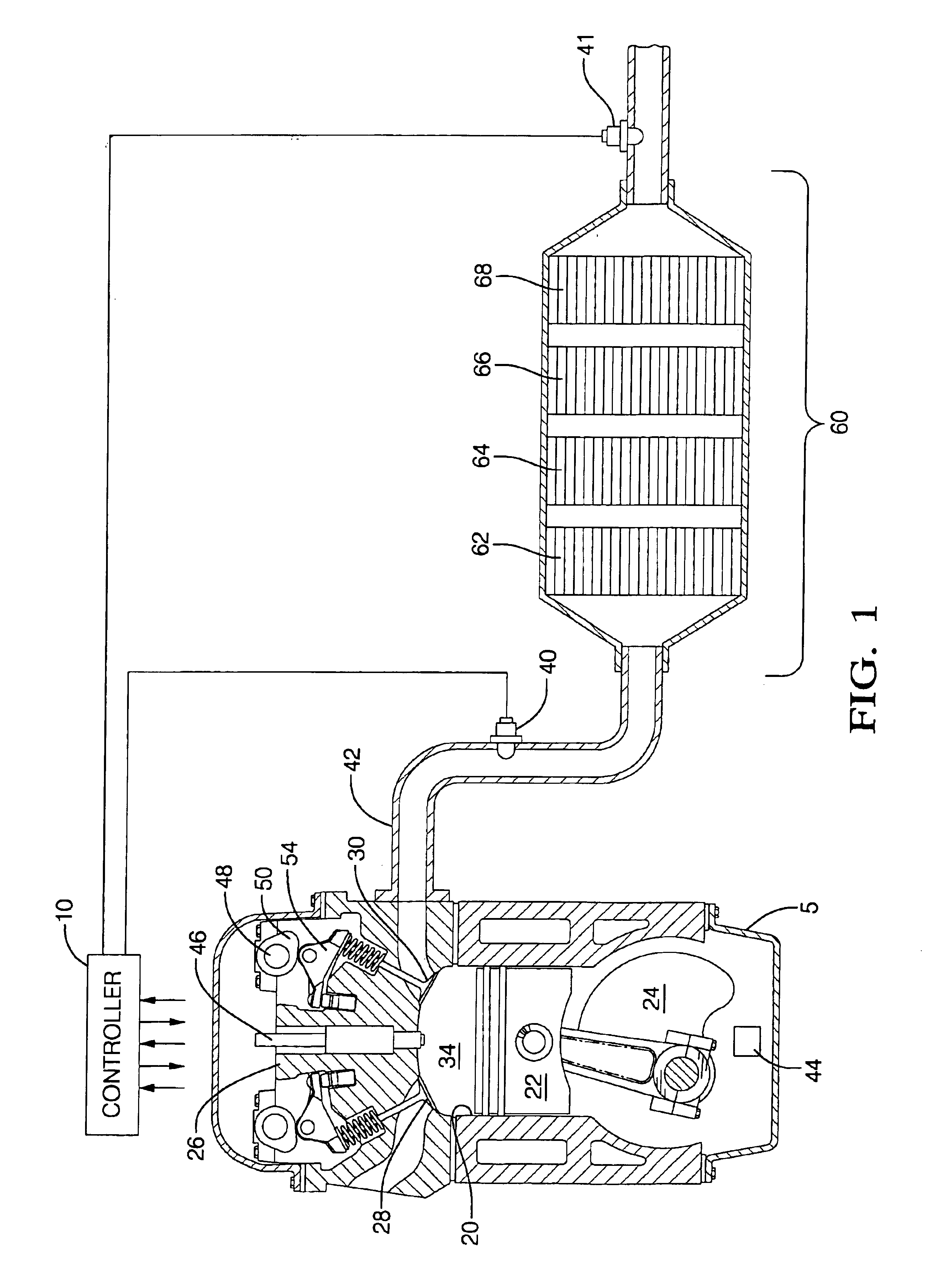
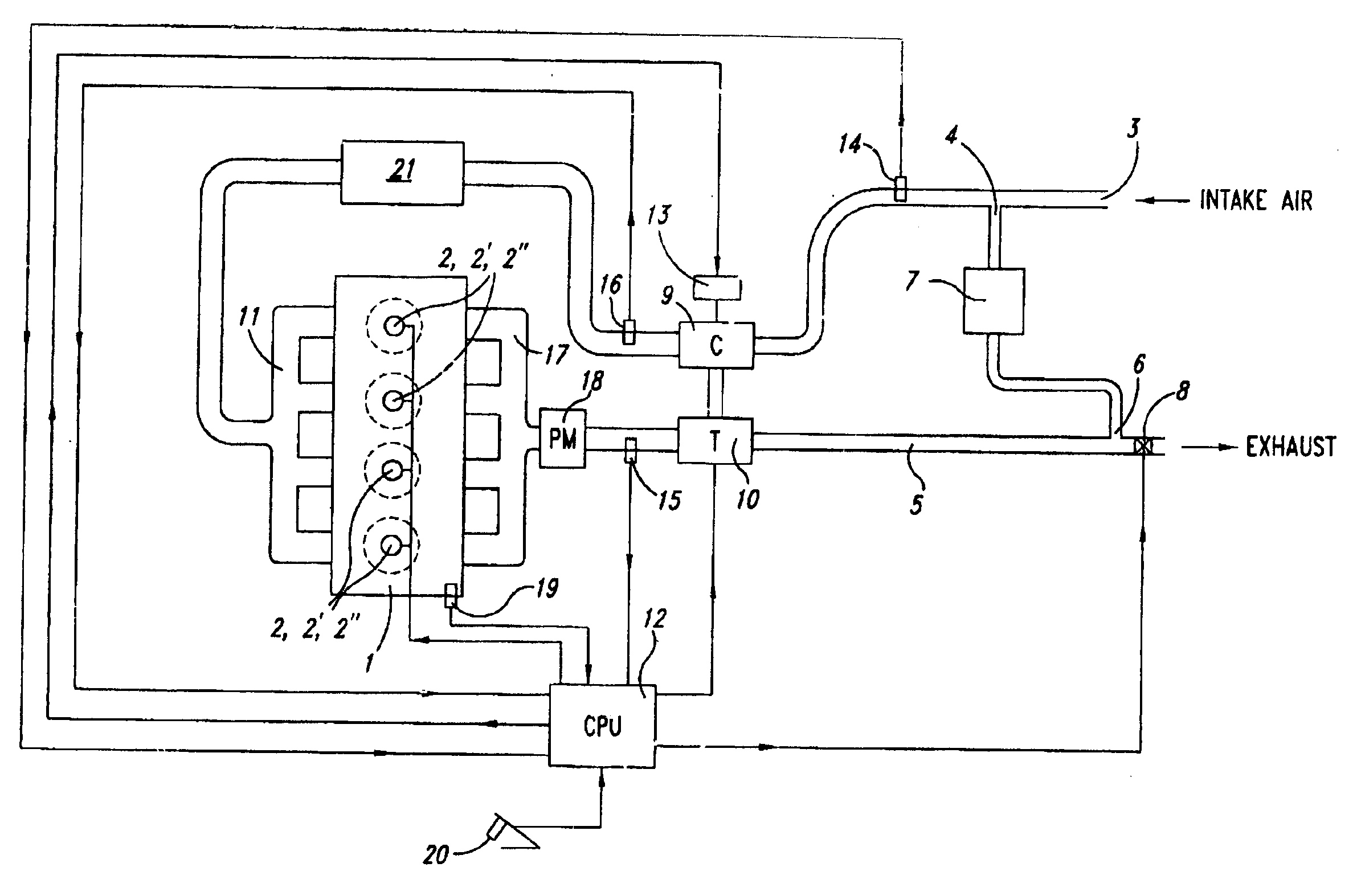
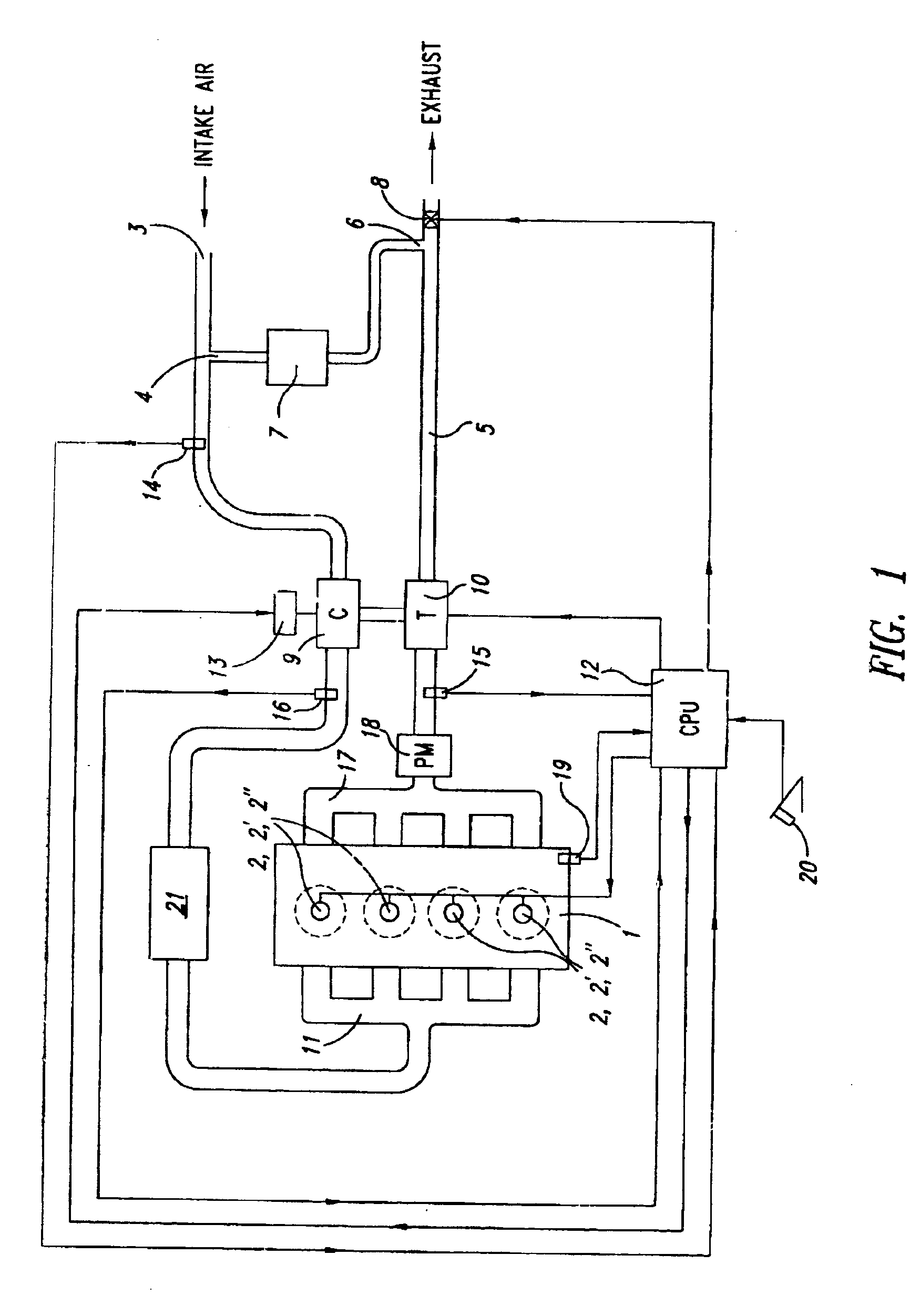
Engine cylinder deactivation to improve the performance of exhaust emission control systems
InactiveUS6904752B2Increase exhaust temperatureIncreases fuel chargeValve arrangementsAir-treating devicesParticulatesControl system
The invention provides a controller and cylinder deactivation system to regenerate an exhaust aftertreatment device for a multicylinder engine that operates primarily at an air / fuel ratio that is lean of stoichiometry. The invention uses the cylinder deactivation system to control temperature and air / fuel ratio of an exhaust gas feedstream going into an aftertreatment device. The invention also increases the amount of fuel delivered to each non-deactivated cylinder by an amount sufficient to maintain operating power of the engine. The regeneration action includes desorbing NOx from a NOx adsorber catalyst, desulfating the NOx adsorber catalyst, and purging a diesel particulate trap.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
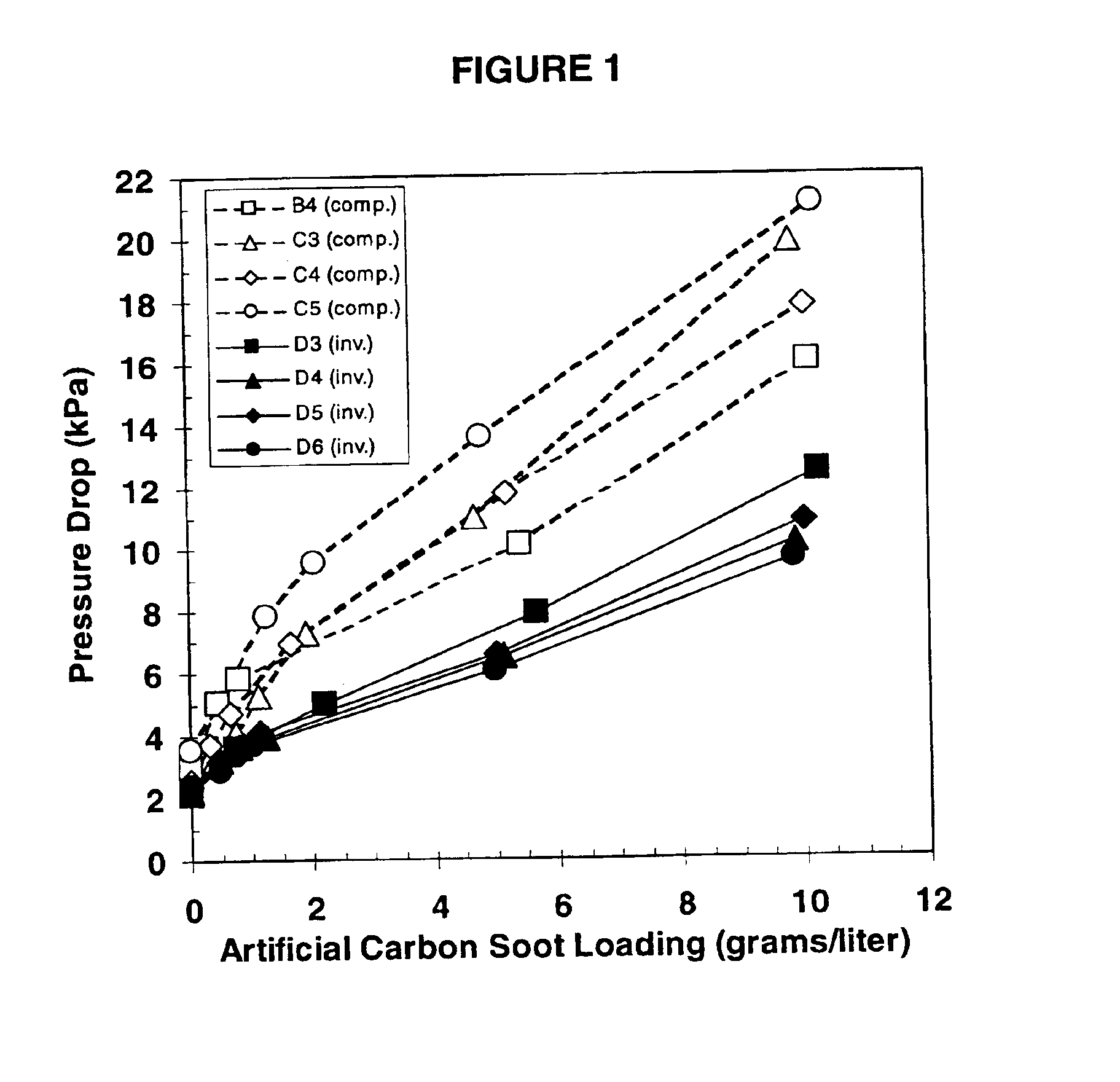
Cordierite body
InactiveUSRE38888E1Improve permeabilityReduce back pressureDispersed particle filtrationSilencing apparatusGramVolumetric Mass Density
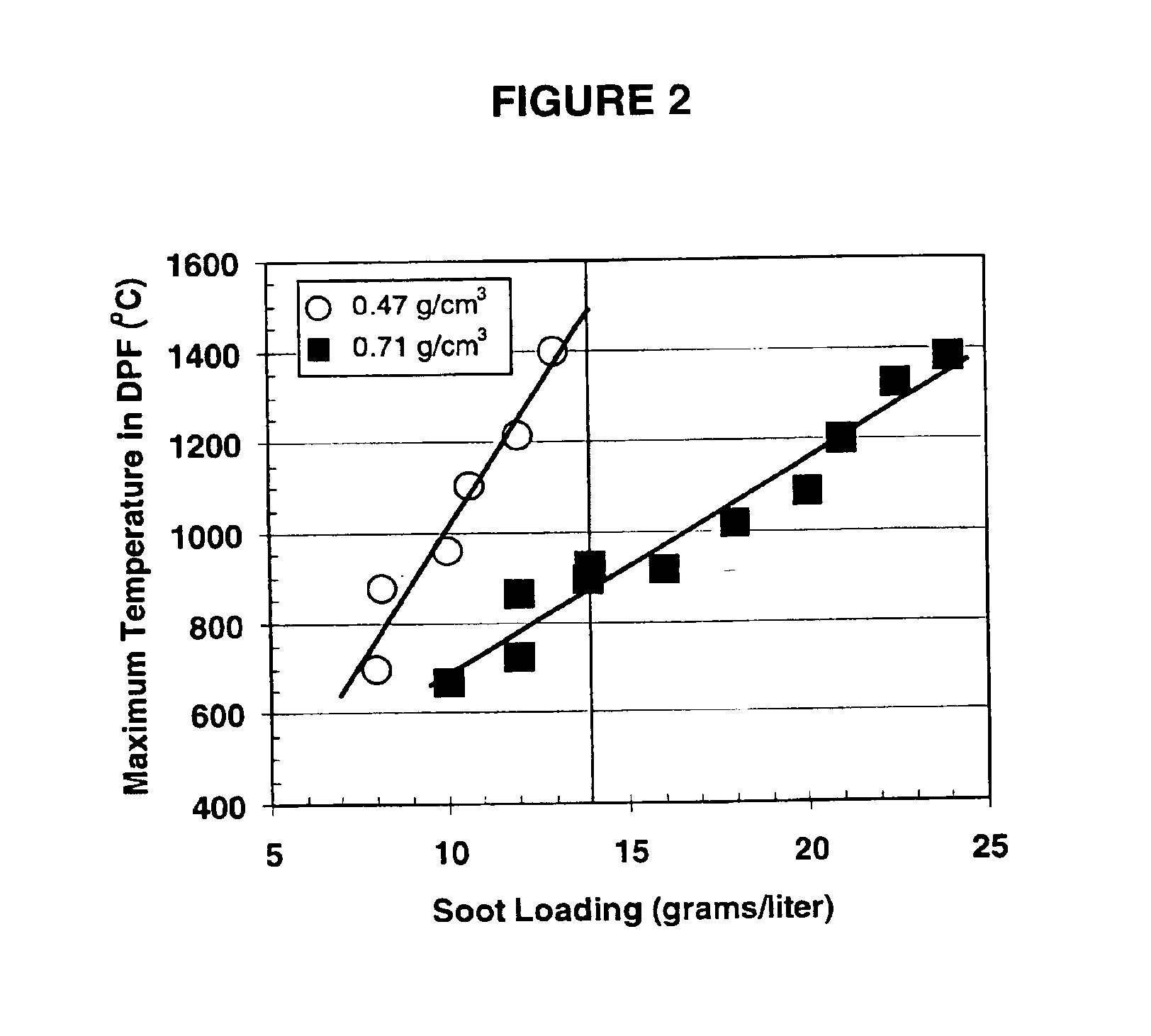
A ceramic comprising predominately a cordierite-type phase approximating the stoichiometry Mg2Al4Si5O18 and having a coefficient of thermal expansion (25-800° C.) of greater than 4×10−7 / ° C. and less than 13×10−7 / ° C. and a permeability and a pore size distribution which satisfy the relation 2.108 (permeability)+18.511 (total pore volume)+0.1863 (percentage of total pore volume comprised of pores between 4 and 40 micrometers)>24.6. The ceramic is suitable in the fabrication of cellular, wall-flow, diesel particulate filters having a pressure drop in kPa that at an artificial carbon soot loading of 5 grams / liter and a flow rate of 26 scfm is less than 8.9-0.035 (number of cells per square inch)+300 (cell wall thickness in inches), a bulk filter density of at least 0.60 g / cm3 and a volumetric heat capacity of at least 0.67 J cm−3 K−1 as measured at 500° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
Production Of Barium Titanate Compounds
InactiveUS20070202036A1High purityLow costMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline earth titanatesBarium titanateSpherical shaped
An ultrafine powder of barium titanate including solid solutions and doped compounds that meets up to specific characteristics is produced by method comprising two main steps. The first step is a reaction, typically in a Segmented Flow Tubular Reactor, between reactants to produce cubic-structure barium titanate composed of non-agglomerated ultrafine particles having a shape of given aspect ratio, usually a generally spherical shape, of low density corresponding at most to 90% of the intrinsic density, all particles being smaller than 1 micron and having a narrow particle size distribution and wherein the ratio of Ba:Ti including substitutents and dopants is very close to the ideal stoichiometry. This is followed by subjecting the powder produced in the first step to a second stage solvothermal post treatment typically in an autoclave at temperature less than 400° C. to convert the cubic-structure particles of low density to ultrafine tetragonal particles of increased density corresponding to at least 90% of the intrinsic density while maintaining the same aspect ratio, and maintaining the size of all particles below 1 micron, the narrow particle size distribution span, and the given ideal stoichiometry. The produced particles can have a non-spherical facetted shape such as cube-like.
Owner:JONGEN NATHALIE +1
Method for cutting single-wall carbon nanotubes through fluorination
InactiveUS7029646B2Shorten the lengthHigh voltageMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureFlat panel displayDerivatization
A method for cutting single-wall carbon nanotubes involves partially fluorinating single-wall carbon nanotubes and pyrolyzing the partially fluorinated nanotubes in an inert atmosphere or vacuum up to about 1000° C. The nanotubes are optionally purified before cutting. The partial fluorination involves fluorinating the nanotubes to a carbon-fluorine stoichiometry of CFx, where x is up to about 0.3. The invention also relates to the derivatization of fluorinated and cut single-wall carbon nanotubes. The single-wall carbon nanotubes can be cut to any length depending on the fluorination and pyrolysis conditions. Short nanotubes are useful in various applications, such as field emitters for flat panel displays and as “seeds” for further nanotube growth.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Low emission diesel combustion system with low charge-air oxygen concentration levels and high fuel injection pressures
InactiveUS6857263B2Cost effectiveLower Level RequirementsLiquid coolingEngine sealsLow loadMass ratio
This invention sets forth a commercially viable diesel combustion system that meets environmentally acceptable levels of NOx emissions (i.e. 0.2 g / bhp-hr or lower across a full map of engine speeds and loads) without the need for use of NOx aftertreatments, and simultaneously maintains engine-out PM emissions relatively close (e.g. with smoke levels at or below 3 BSN) to environmentally acceptable PM post-aftertreatment levels. The invention achieves these results by operating within a unique combination of parameters. These parameters comprise: (1) charge-air oxygen concentration below 16%, preferably between 10% and 15%, more preferably between 11% and 14%, and most preferably between 12% and 13.5% for virtually all engine operating conditions (but not necessarily at no-load or low load conditions), (2) fuel injection pressures at or exceeding 1800 bar, preferably exceeding 2100 bar, more preferably exceeding 2300 bar, and most preferably exceeding 2500 bar, at most engine speeds and loads, and (3) charge-air mass / fuel mass ratio between 25:1 and 45:1 for medium and high loads. Furthermore, the system is preferably run continuously slightly lean of stoichiometry, providing just enough excess oxygen to facilitate completeness of combustion and to maintain an exhaust oxygen level sufficient for continuous trap regeneration at a balance point in operation.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
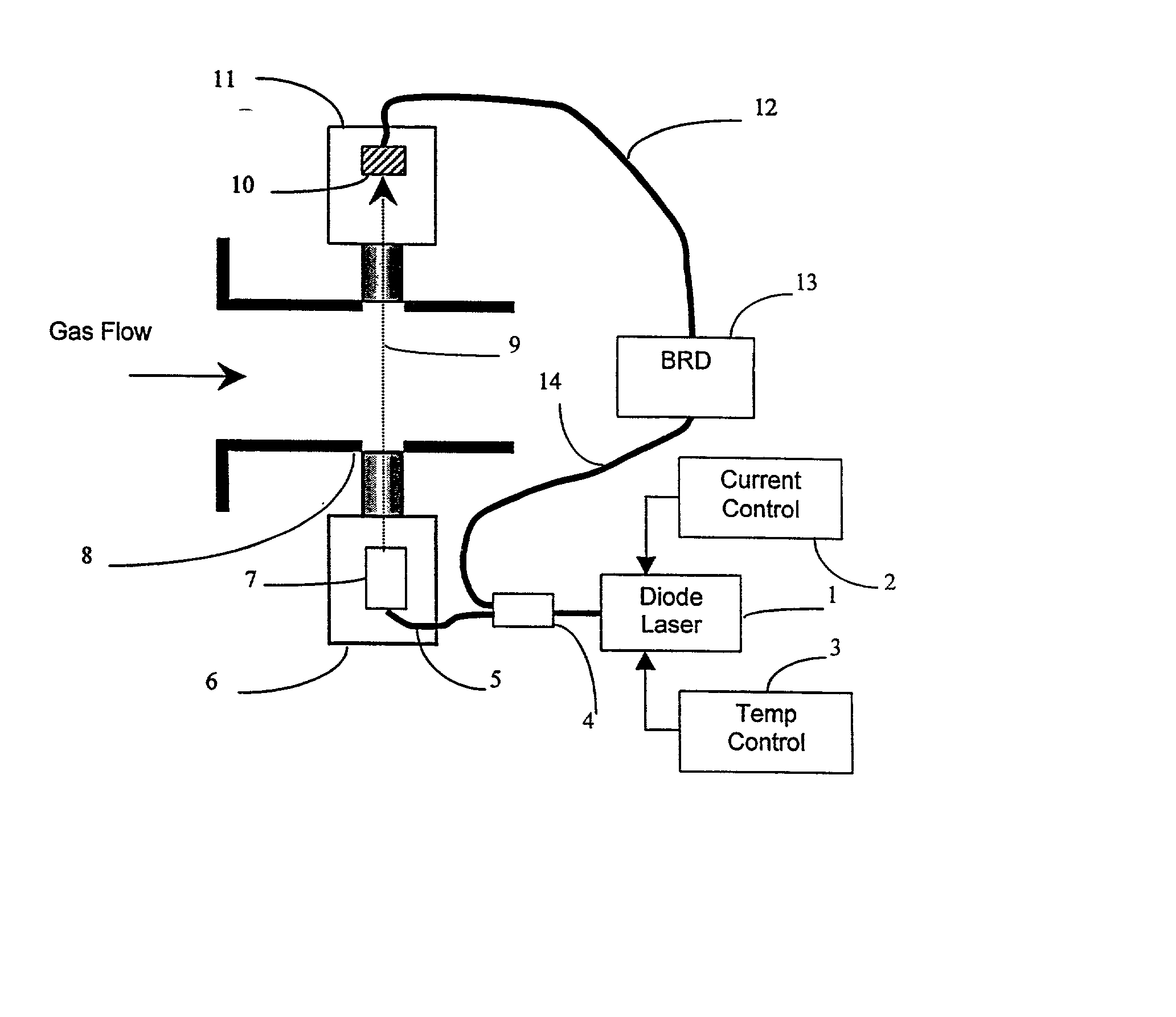
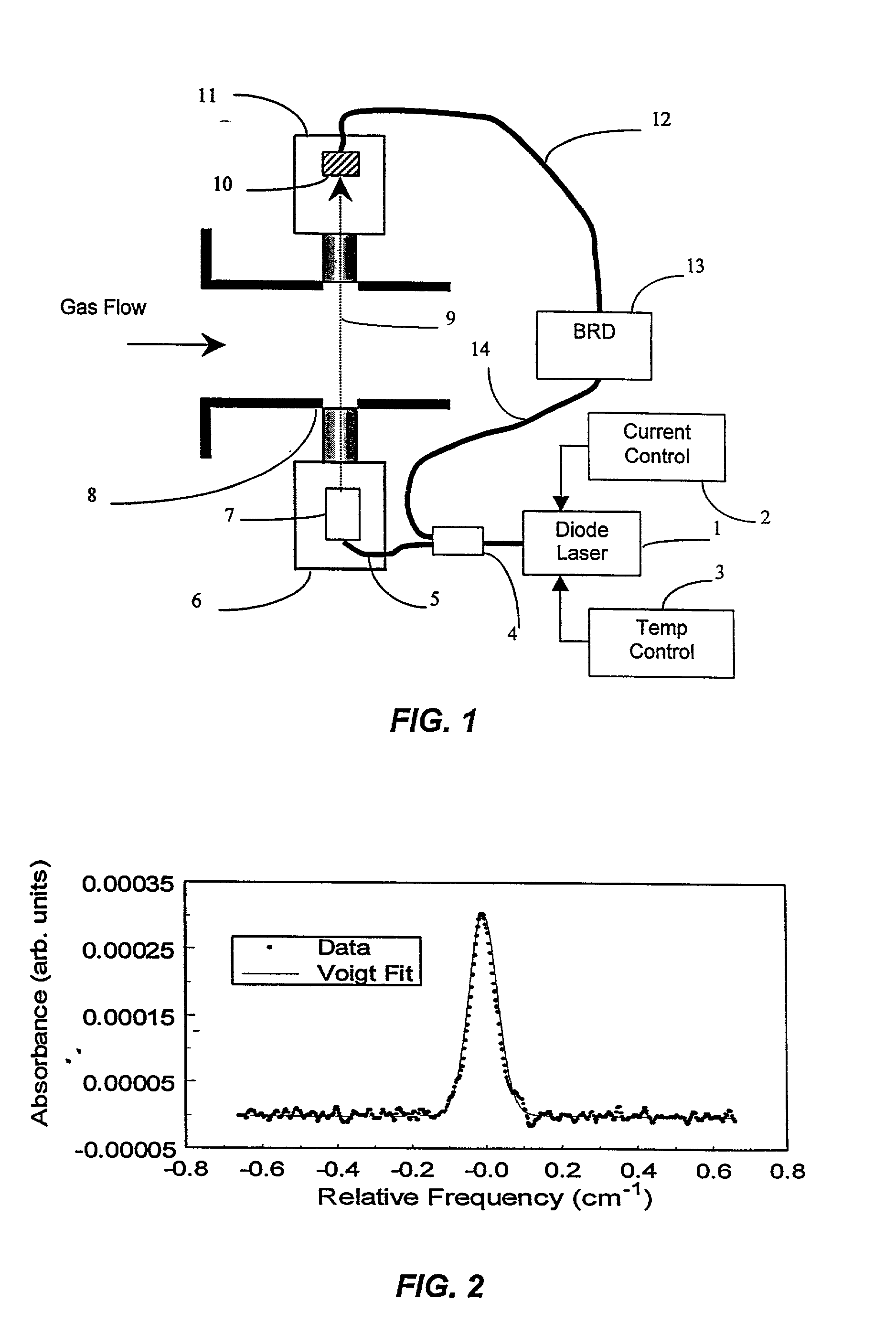
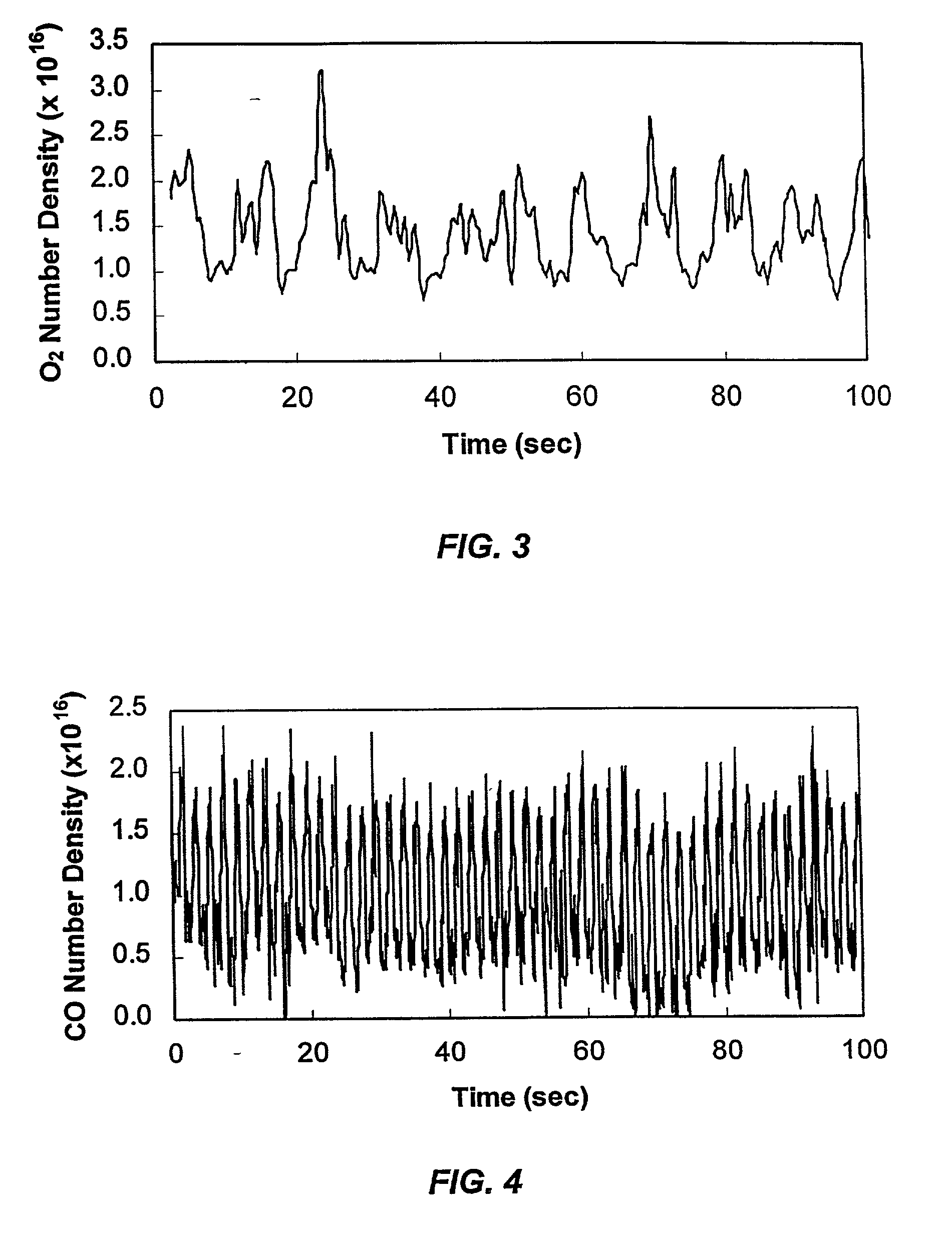
Method for continuously monitoring chemical species and temperature in hot process gases
InactiveUS20020031737A1Minimizing dilution effectInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsColor/spectral properties measurementsAir entrainmentOrganic fuel
Methods and apparatus are presented using tunable diode lasers for monitoring and / or controlling a high temperature process using an oxidizer containing O2 and organic fuel. Real-time monitoring of key species such as O2, CO, and H2O allow determination of the global or local stoichiometry, gas temperature, particulate concentration, and air entrainment levels into the process. Coupling the measured information with a control system provides a means for optimizing and controlling the process.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Body-contacted semiconductor structures and methods of fabricating such body-contacted semiconductor structures
InactiveUS20080044959A1Improves cell data retention timeEliminate the effects ofSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceFloating body effect
A semiconductor structure for a dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell array that includes a plurality of vertical memory cells built on a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) wafer and a body contact in the buried dielectric layer of the SOI wafer. The body contact electrically couples a semiconductor body with a channel region of the access device of one vertical memory cell and a semiconductor substrate of the SOI wafer. The body contact provides a current leakage path that reduces the impact of floating body effects upon the vertical memory cell. The body contact may be formed by an ion implantation process that modifies the stoichiometry of a region of the buried dielectric layer so that the modified region becomes electrically conductive with a relatively high resistance.
Owner:IBM CORP
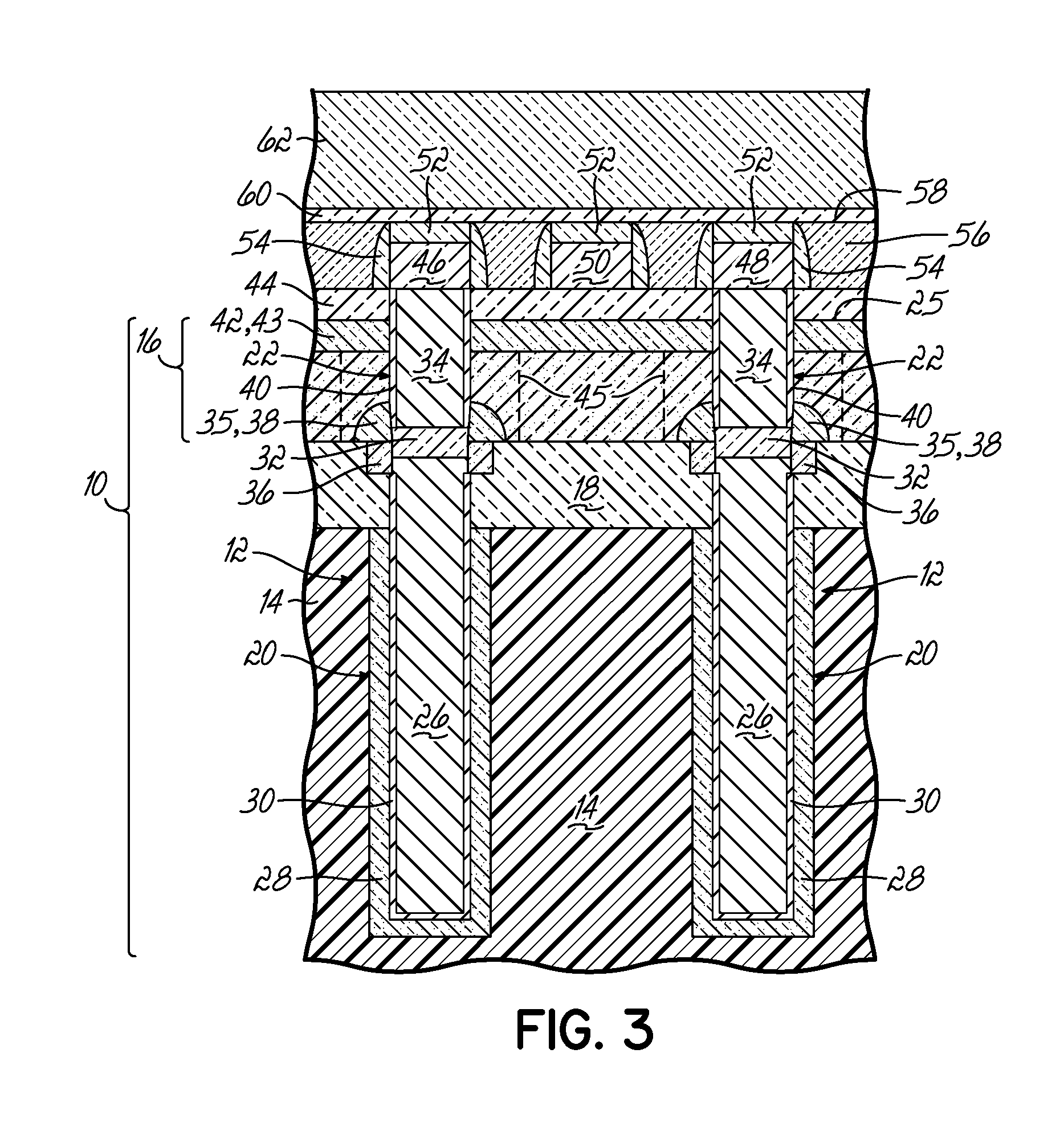
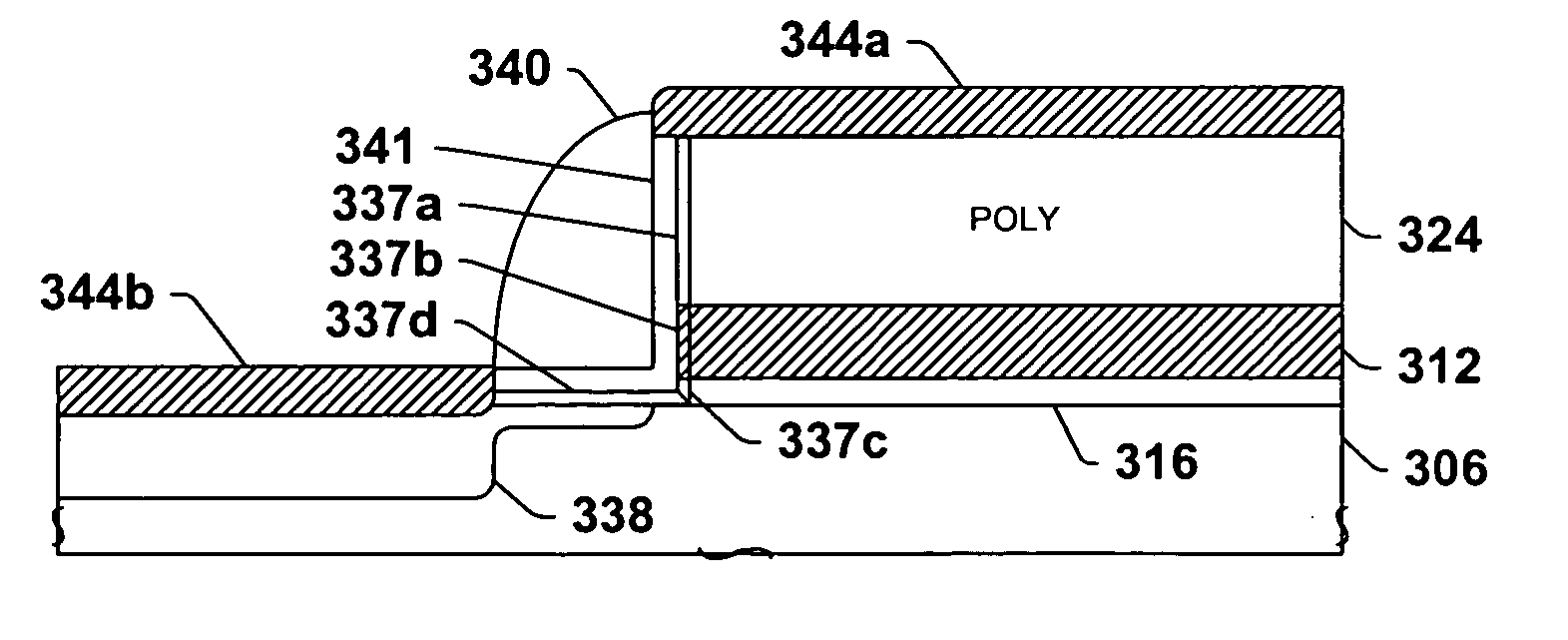
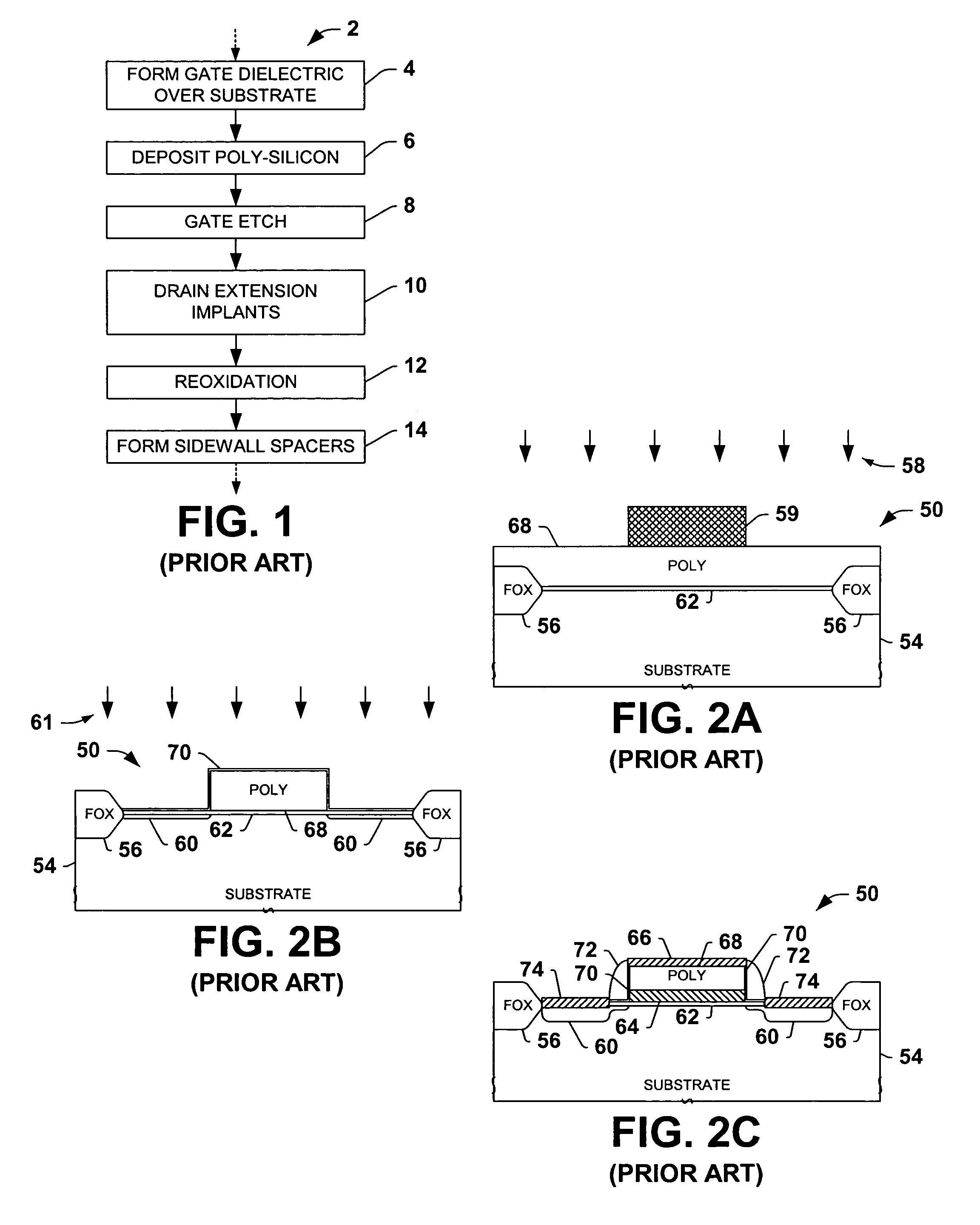
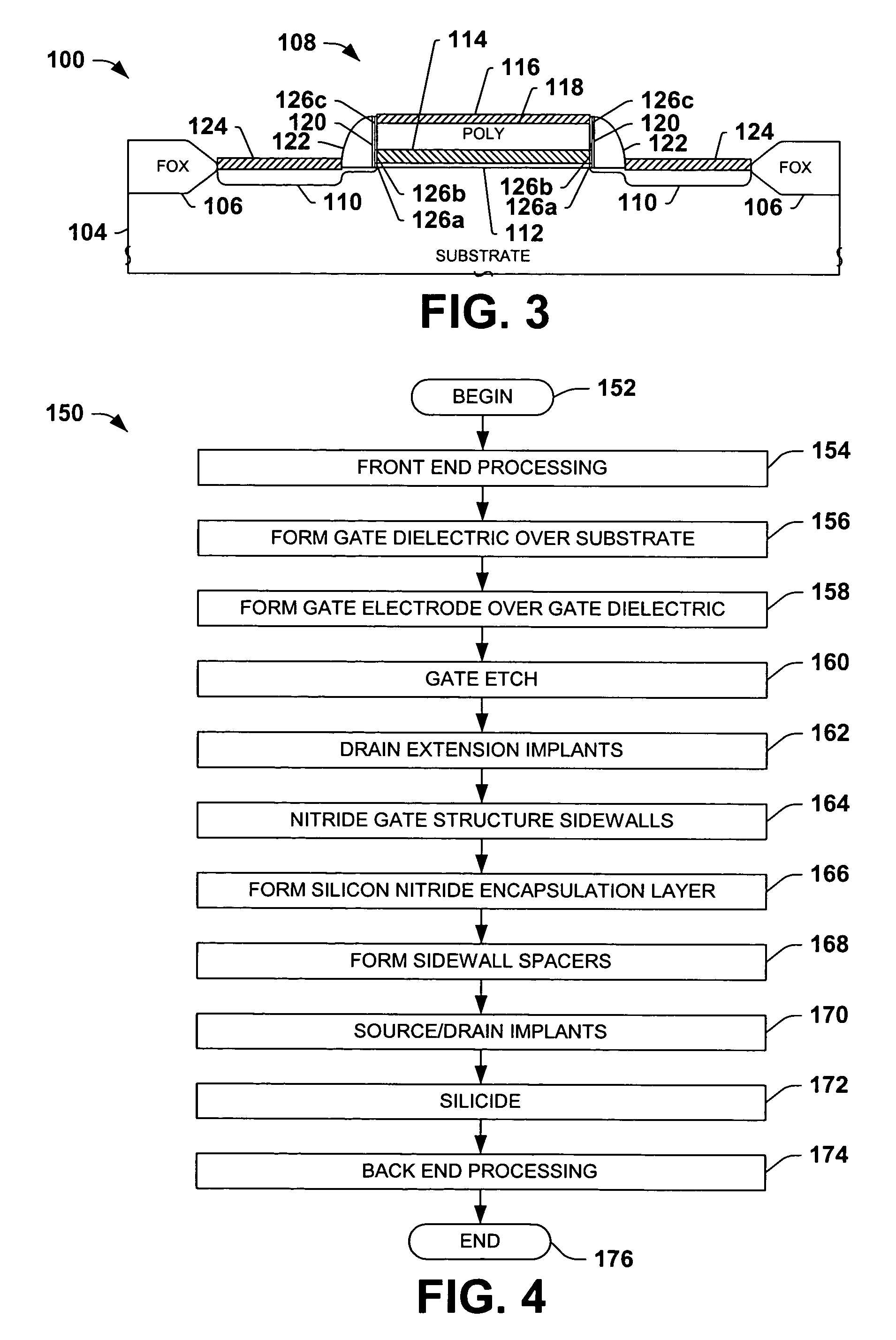
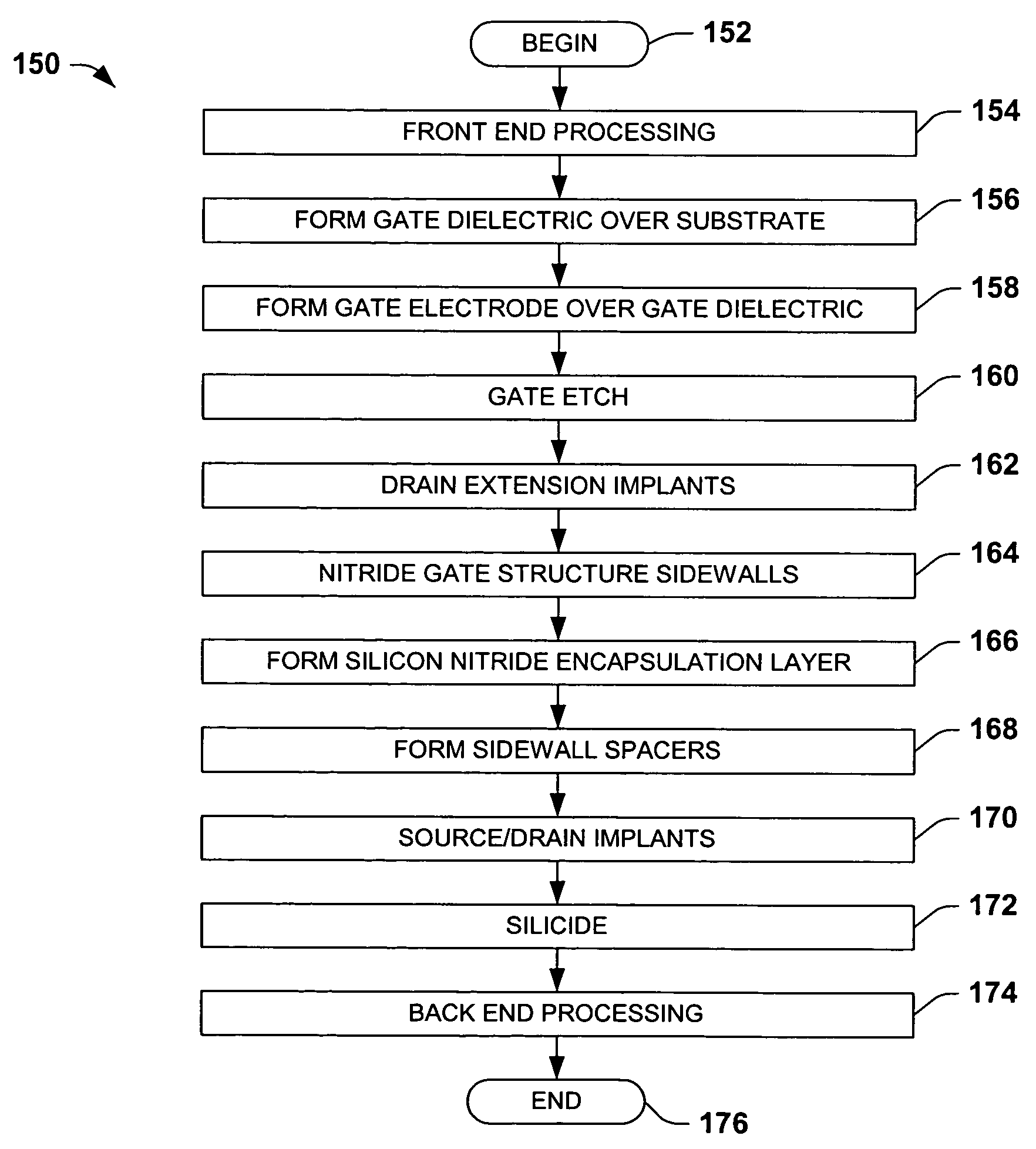
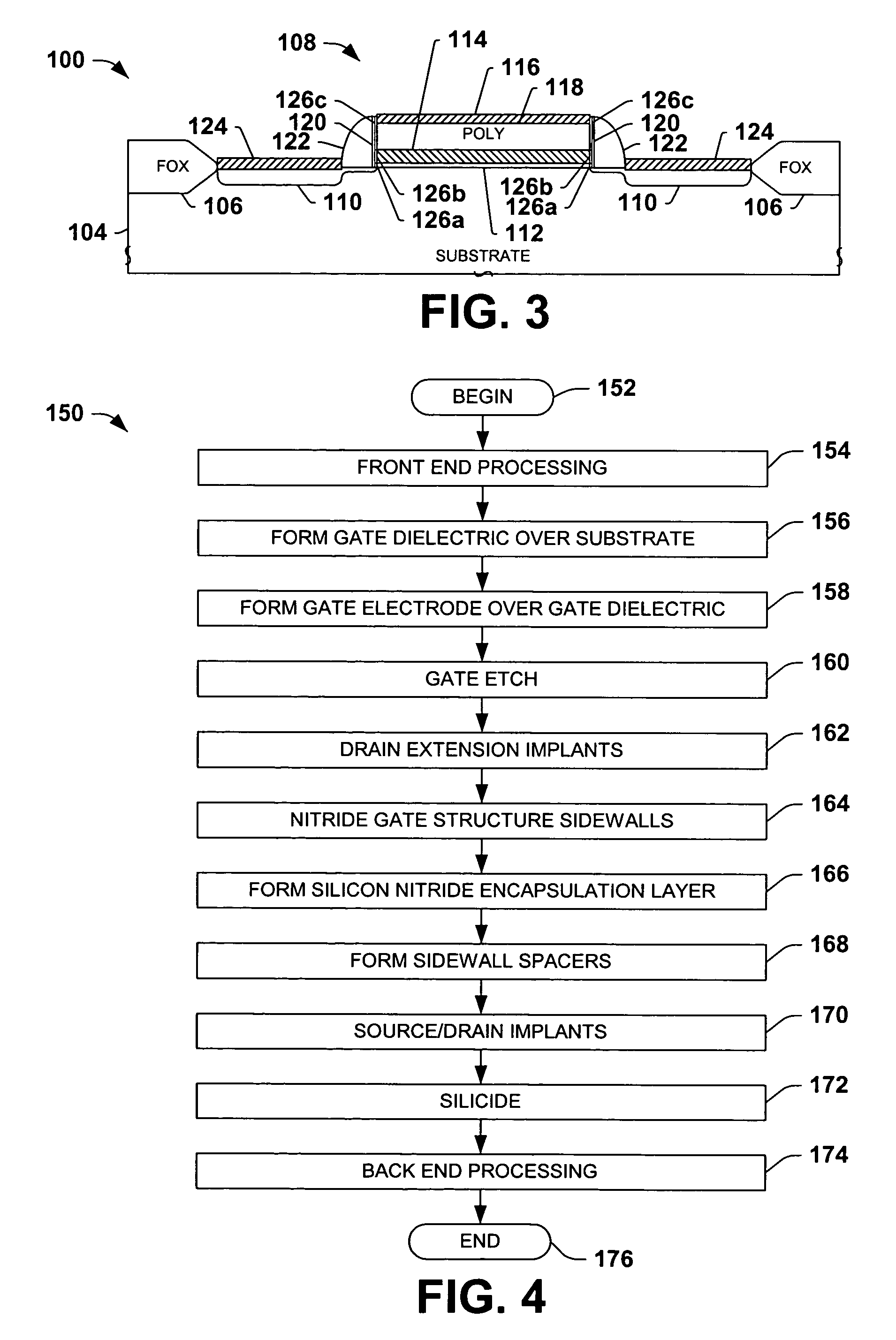
Encapsulated MOS transistor gate structures and methods for making the same
InactiveUS7015534B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyEngineering
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Encapsulated MOS transistor gate structures and methods for making the same
ActiveUS20050079696A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyEngineering
Transistor gate structures, encapsulation structures, and fabrication techniques are provided, in which sidewalls of patterned gate structures are conditioned by nitriding the sidewalls of the gate structure, and a silicon nitride encapsulation layer is formed to protect the conditioned sidewalls during manufacturing processing. The conditioning and encapsulation avoid oxidation of gate stack layers, particularly metal gate layers, and also facilitate repairing or restoring stoichiometry of metal and other gate layers that may be damaged or altered during gate patterning.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
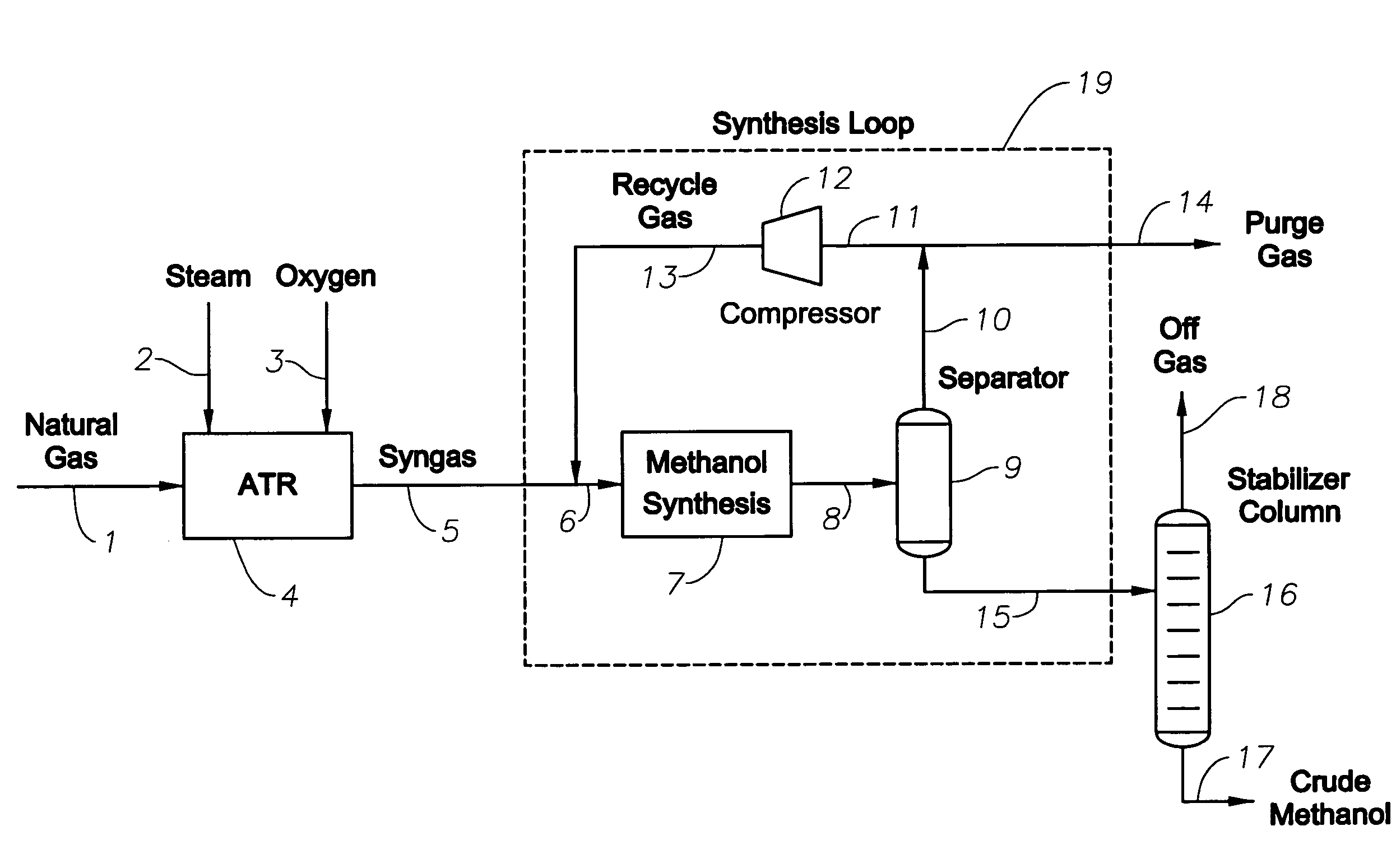
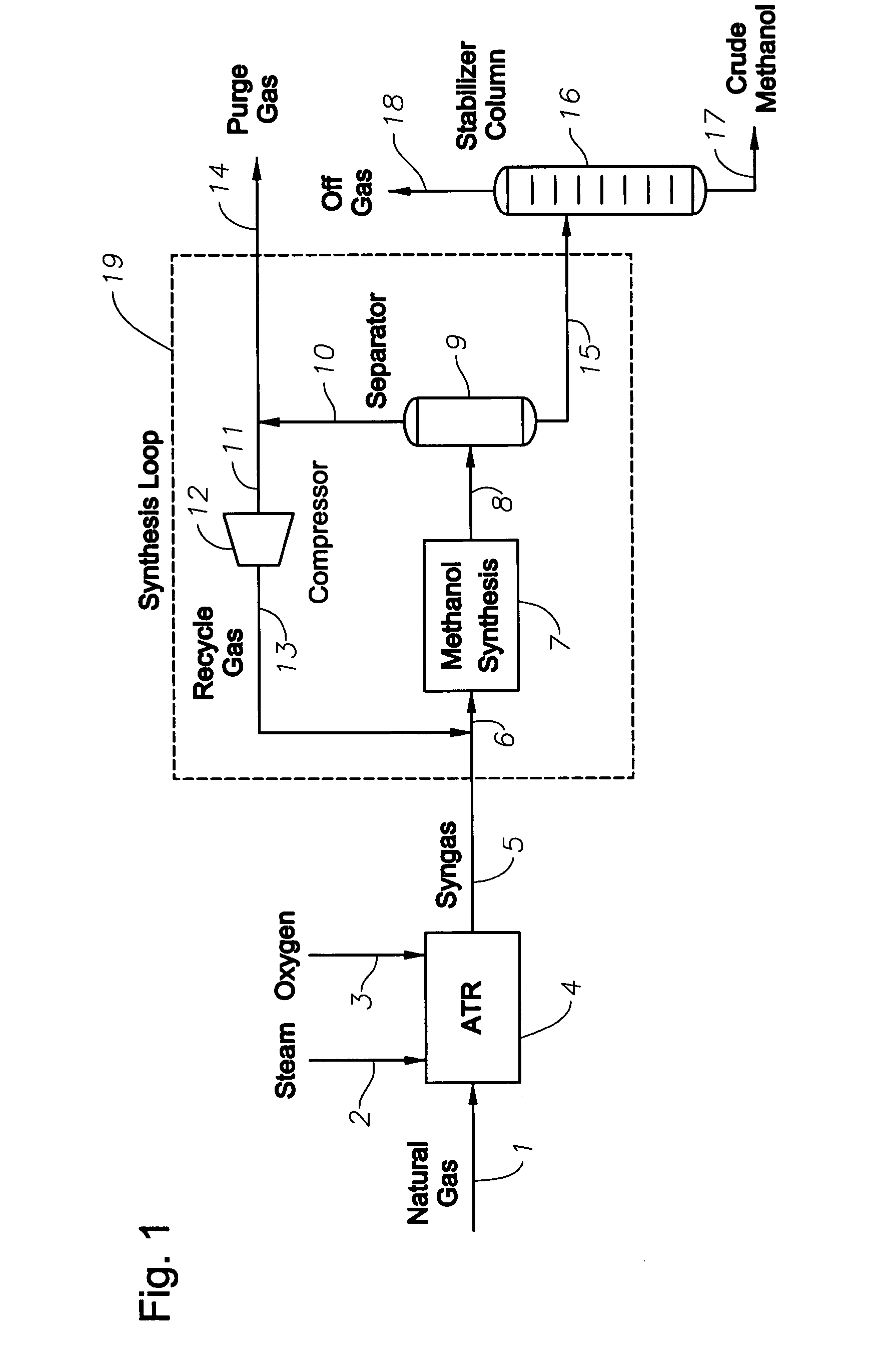
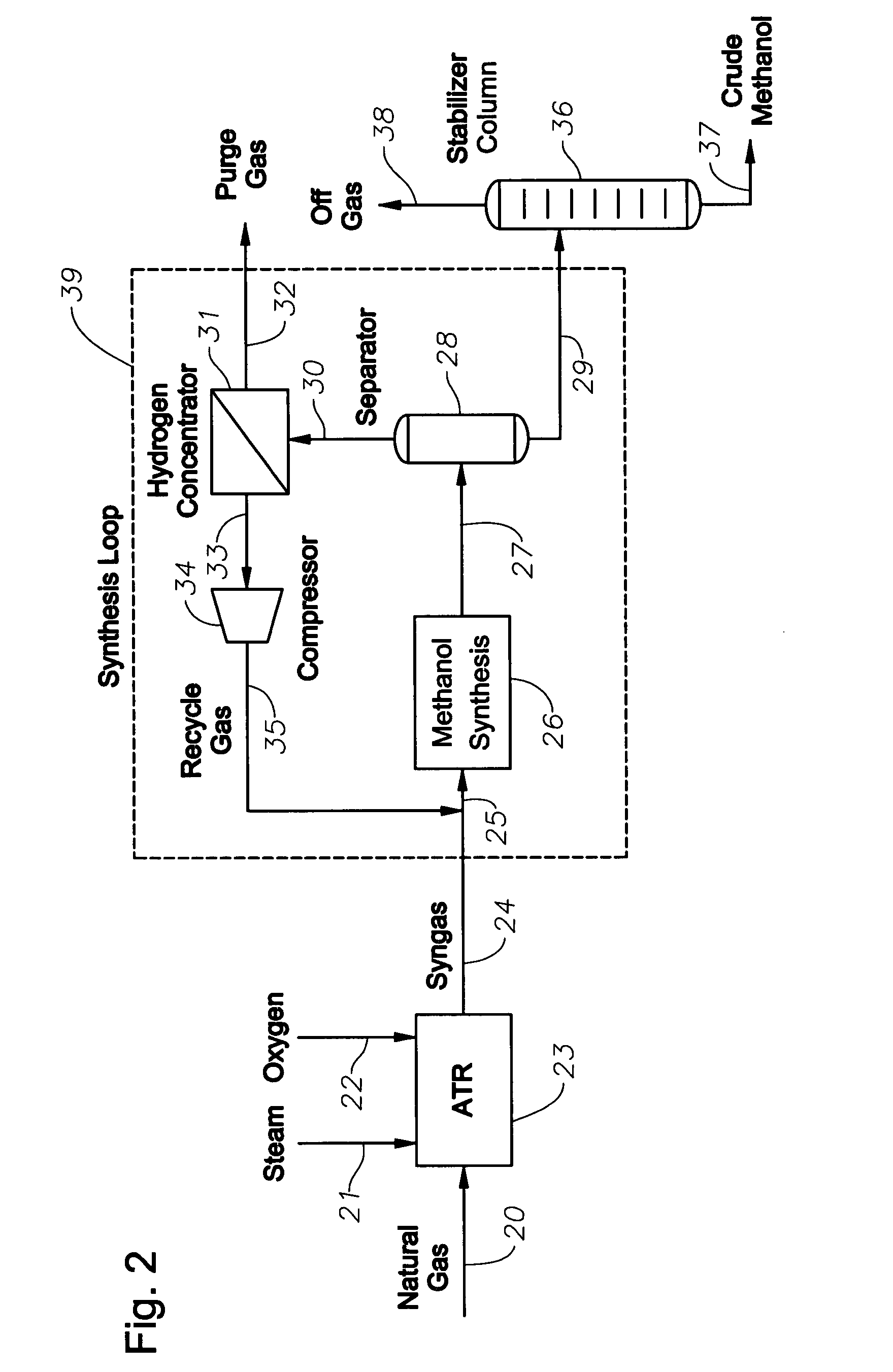
Synthesis gas production and use
InactiveUS20070282018A1Low costEfficiently utilizing hydrogenHydrogenOrganic compound preparationSyngasProduct gas
A method of producing synthesis gas for methanol synthesis that comprises the steps of: (a) obtaining a hydrogen stream that has greater than 5 mol % methane from an external process; (b) feeding into a reforming reactor: (i) a feed gas that comprises methane, (ii) water in a specified amount, (iii) oxygen in a specified amount, and (iv) the hydrogen stream in a specified amount; (c) reacting the feed gas, water, oxygen and the hydrogen stream in the reactor; and (d) withdrawing from the reactor the synthesis gas that is at a specific temperature, has less than 3 mol % methane, and has a stoichiometric number of from 1.9 to 2.3.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
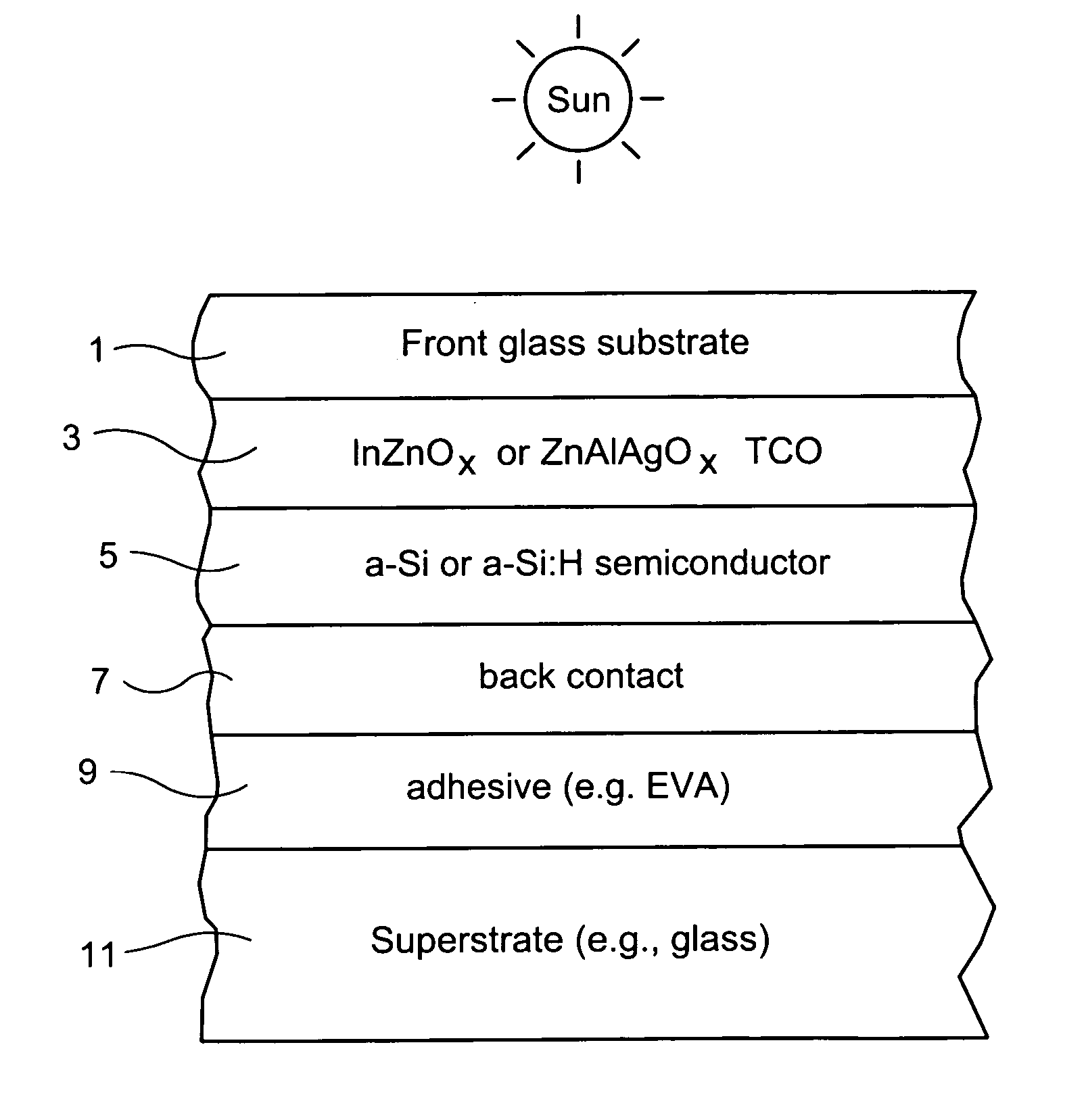
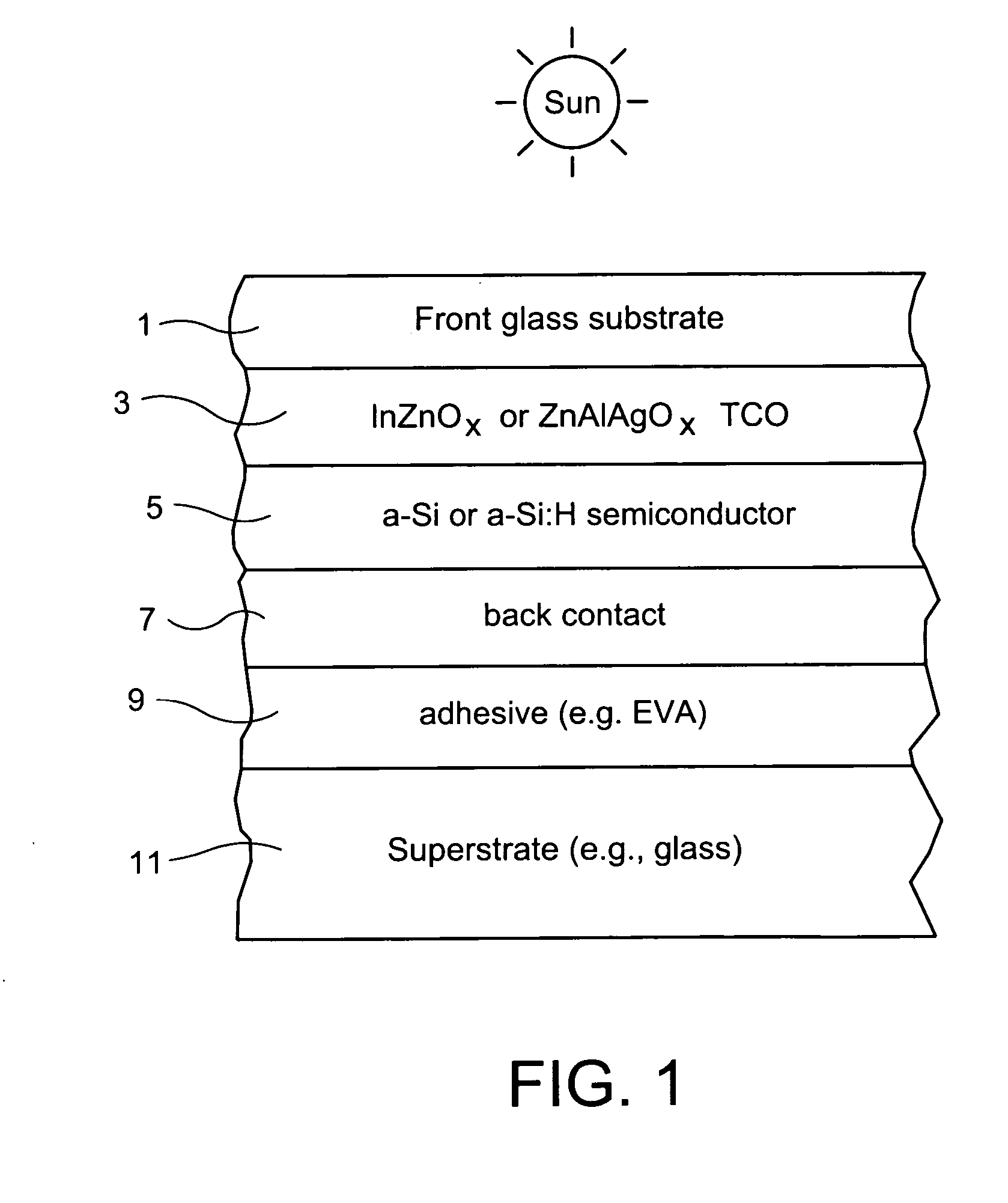
Indium zinc oxide based front contact for photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20070193624A1Low resistivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesCooking & bakingIndium zinc oxide
This invention relates to a photovoltaic device including a front contact and / or a method of making the same. In certain example embodiments, the transparent conductive oxide (TCO) front contact is of indium zinc oxide (IZO). In other example embodiments, the IZO may have other element(s) such as silver (Ag) added thereto so that the front contact may be of or include zinc aluminum silver oxide (ZnAlAgO) for example. Moreover, in certain example embodiments the front contact (e.g., IZO or ZnAlAgO) may be sputter-deposited in an oxygen deficient form (substoichiometric); so that subsequent heat treatment or baking used in the photovoltaic device manufacturing (e.g., for subsequent layer formation) results in an optimal stoichiometry which may or may not be substoichiometric in the final product.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Modeling changes in the state-of-charge open circuit voltage curve by using regressed parameters in a reduced order physics based model
A method for modeling changes in the state of charge vs. open circuit voltage (SOC-OCV) curve for a lithium-ion battery cell as it ages. During battery pack charging, voltage and current data are gathered for a battery cell. A set of state equations are used to determine the stoichiometry and state of charge of the cathode half-cell based on the charging current profile over time. The voltage and current data, along with the stoichiometry and state of charge of the cathode half-cell, are then used to estimate maximum and minimum solid concentration values at the anode, using an error function parameter regression / optimization. With stoichiometric conditions at both the cathode and anode calculated, the cell's capacity and a new SOC-OCV curve can be determined.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
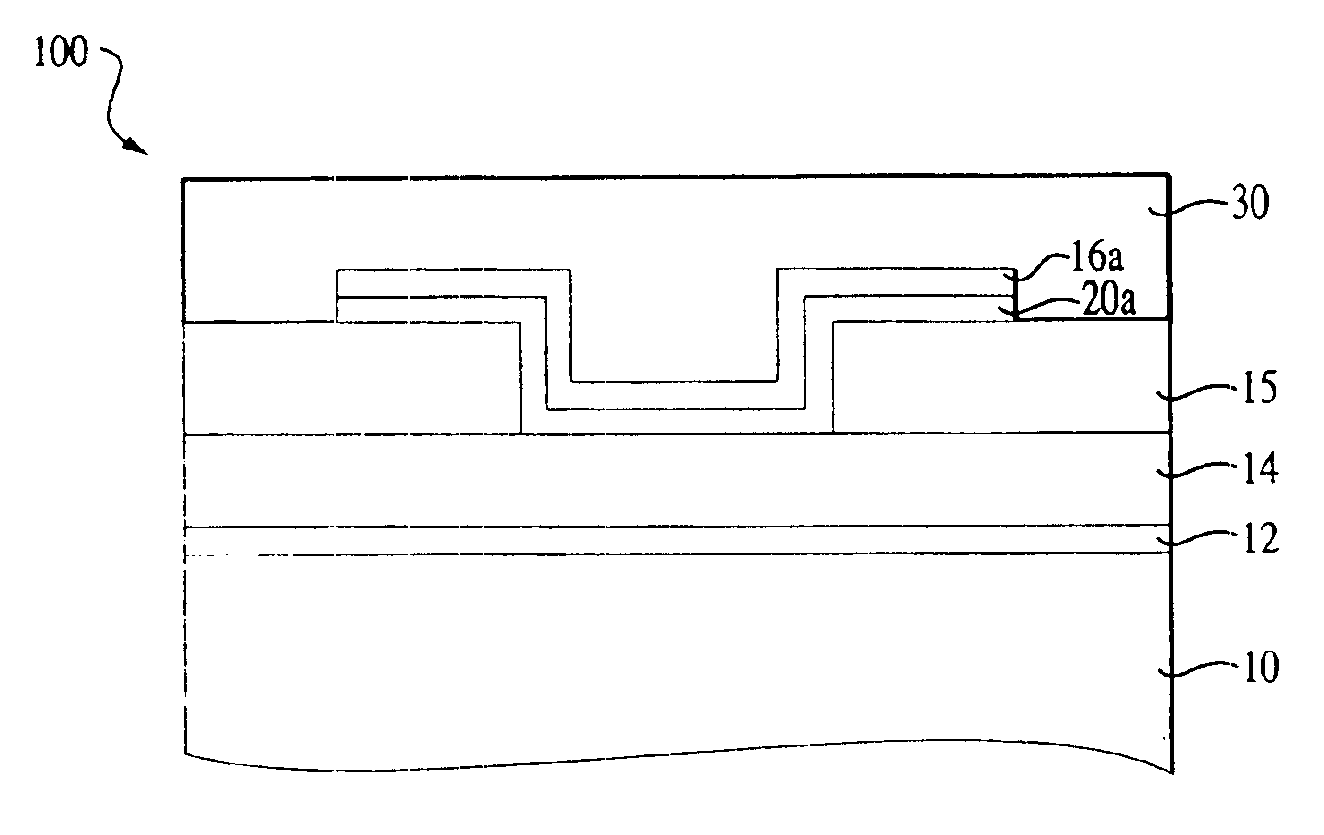
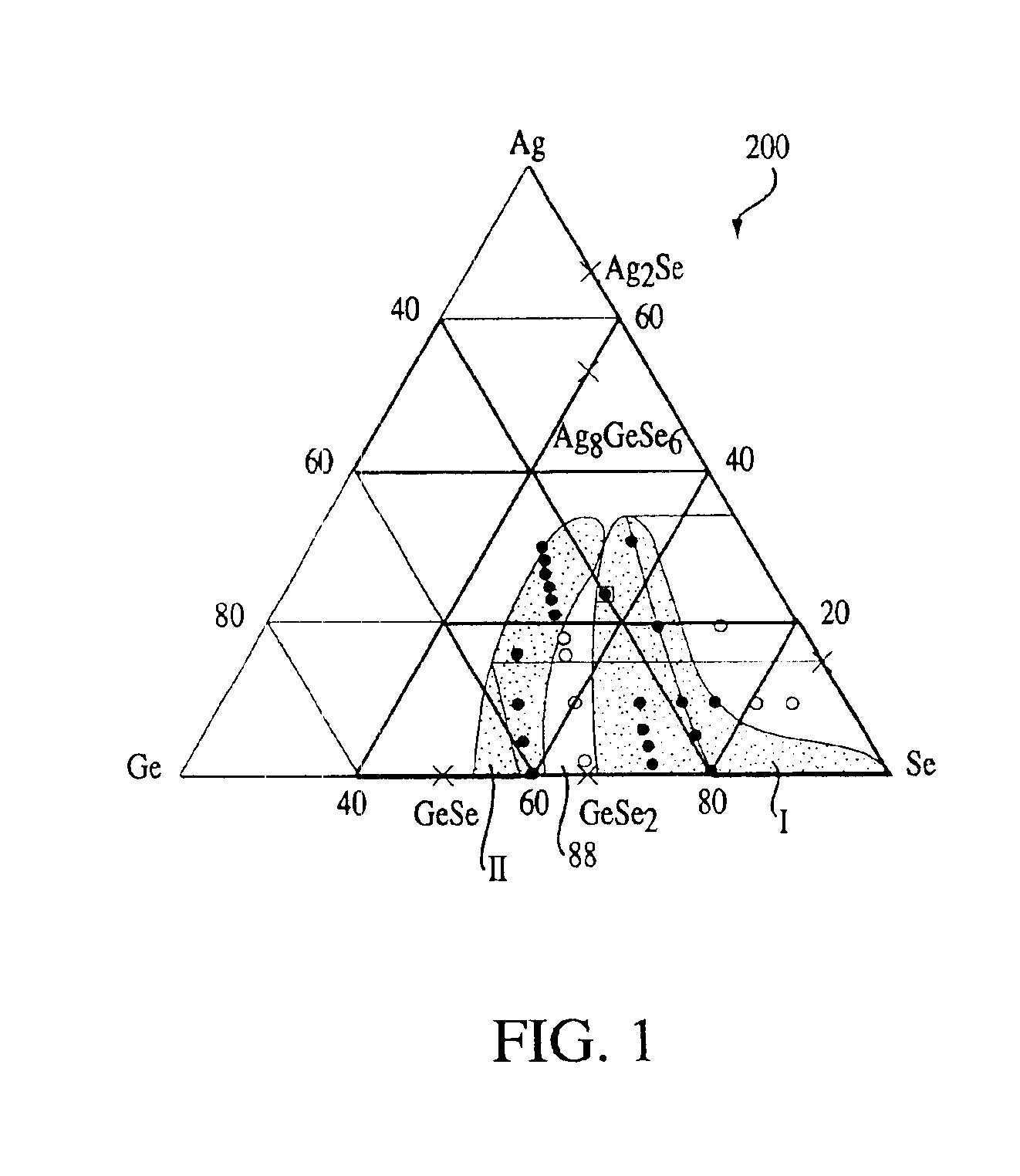
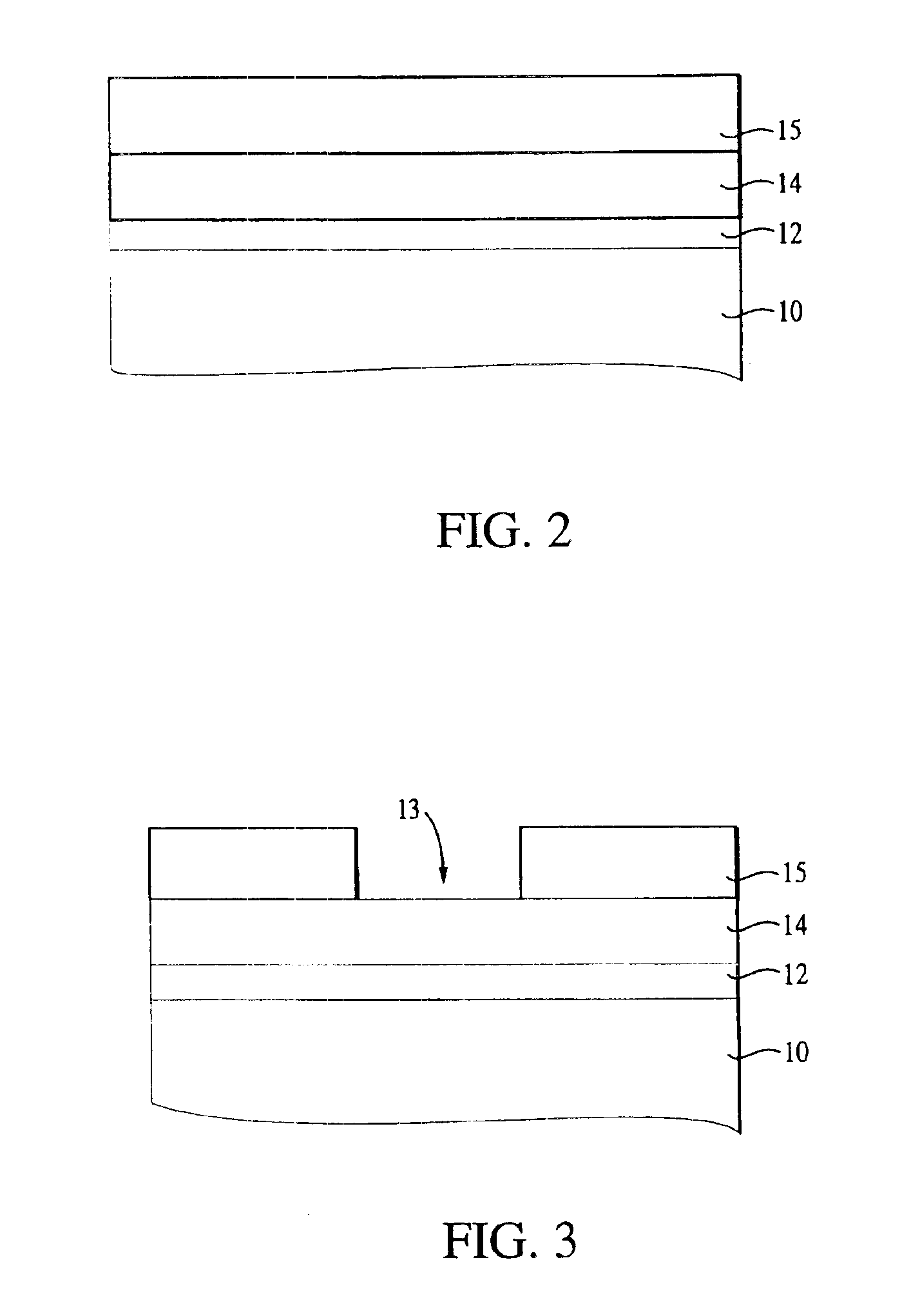
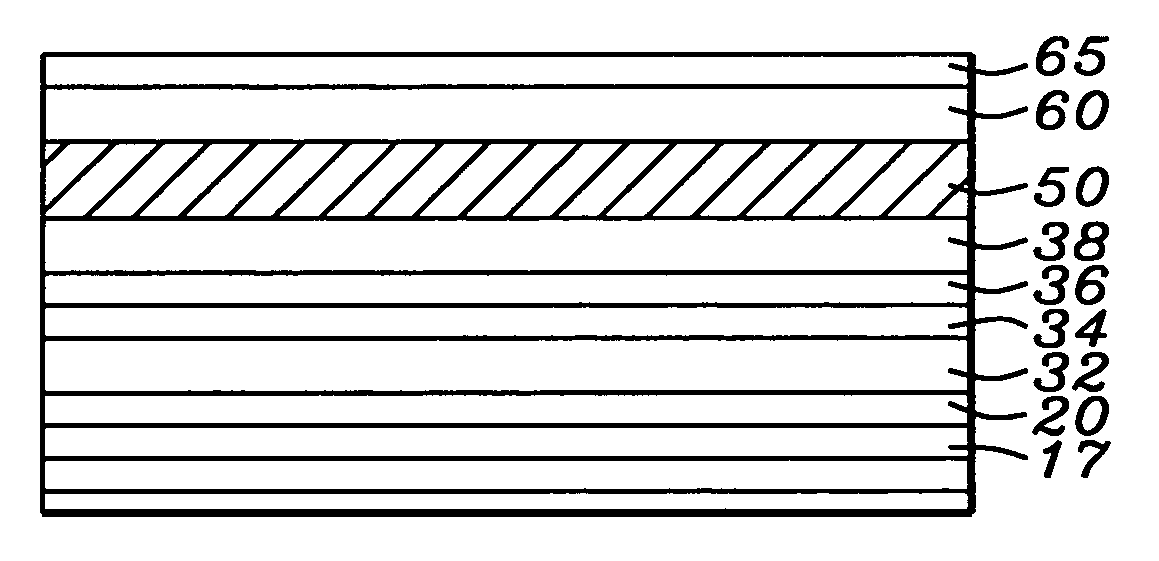
Stoichiometry for chalcogenide glasses useful for memory devices and method of formation
InactiveUS6888155B2High glass transition temperatureRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVitrificationChalcogenide glass
A method of forming resistance changing elements with improved operational characteristics for use in memory devices and the resulting structures are disclosed. A chalcogenide glass having the formula (Gex1Se1-x1)1-y1Agy1, wherein 18≦x1≦28, or the formula (Gex2Se1-x2)1-y2Agy2, wherein 39≦x2≦42, and wherein in both the silver is in a concentration which maintains the germanium selenide glass in the glass forming region is used in a memory cell. The glass may also have a glass transition temperature (Tg) near or higher than typical temperatures used for fabricating and packaging memory devices containing the memory cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Oxidation structure/method to fabricate a high-performance magnetic tunneling junction MRAM
ActiveUS6974708B2Improve homogeneityEnhance layeringMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesRandom access memoryMagnetization
An MTJ (magnetic tunneling junction) MRAM (magnetic random access memory) has a tunneling barrier layer of substantially uniform and homogeneous Al2O3 stoichiometry. The barrier layer is formed by depositing Al on a CoFe layer or a CoFe—NiFe bilayer having an oxygen surfactant layer formed thereon, then oxidizing the Al by radical oxidation. The underlying surfactant layer contributes oxygen to the bottom surface of the Al, forming an initial amorphous Al2O3 layer. This layer produces small, uniform grains in the remaining Al layer, which promotes a uniform oxidation of the Al between its upper and lower surfaces by the subsequent radical oxidation. A final annealing process to set a pinned layer magnetization enhances the homogeneous oxidation of the layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD +1
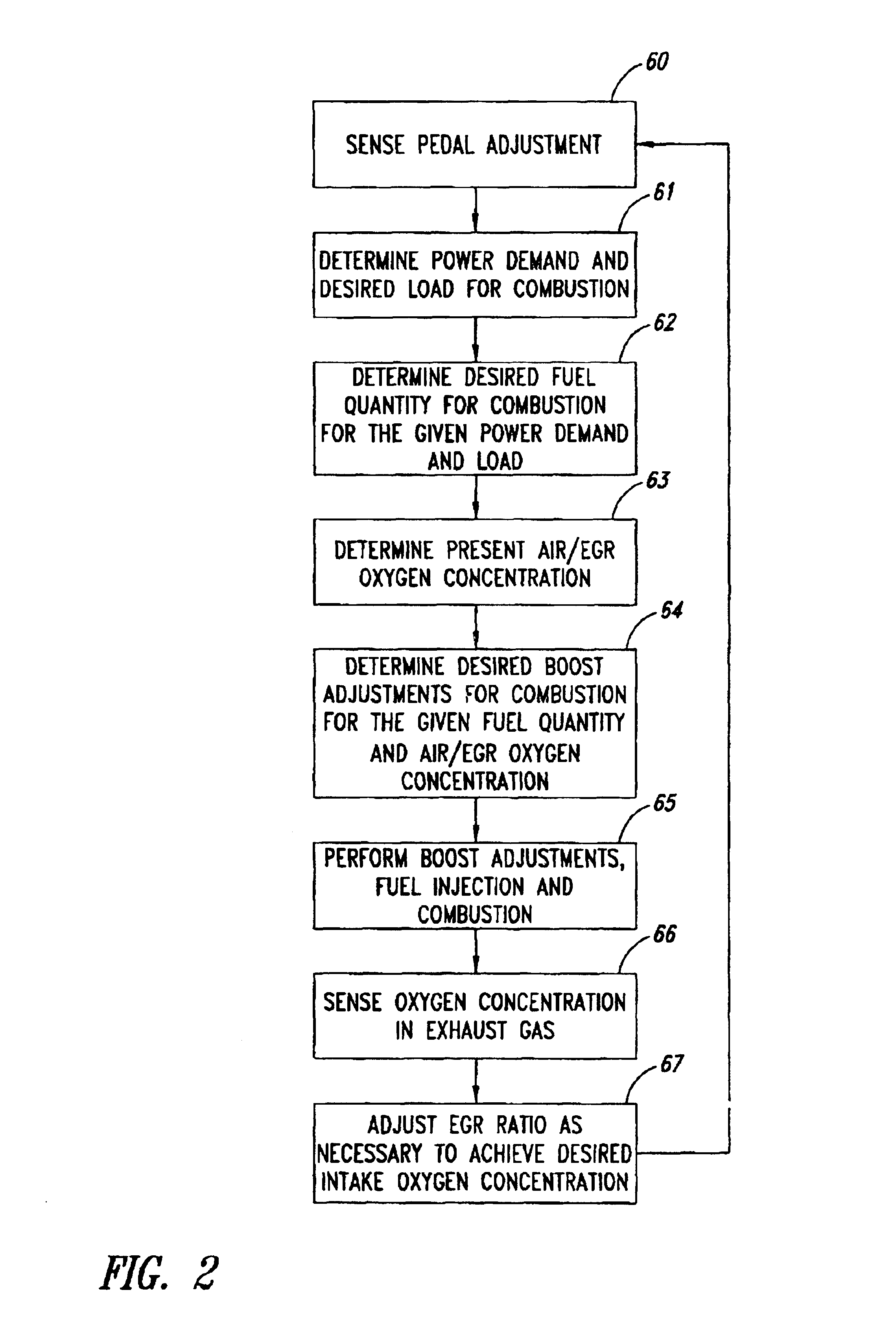
Method and apparatus to control operation of a homogeneous charge compression-ignition engine
InactiveUS7360523B2Weakening rangeReduce environmental stressValve arrangementsElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionAmbient pressure
The invention provides a method for operating a multi-cylinder, spark-ignition, direct-injection, four-stroke internal-combustion engine adapted to operate in a controlled auto-ignition mode selectively operative at stoichiometry and lean of stoichiometry. The method comprises adapting an engine valve actuation system to control engine valve opening and closing, and monitoring engine operating conditions and ambient barometric pressure. The engine is operated unthrottled and the engine valve actuation system is controlled to effect a negative valve overlap period when the engine operating conditions are within predetermined ranges. A mass of fuel is injected during the negative valve overlap period. The magnitude of the negative valve overlap period is decreased with decreasing ambient pressure and increased with increasing ambient pressure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Monazite-based thermal barrier coatings
Monazites and xenotimes are rare-earth phosphates showing a combination of properties expected to be suitable for thermal barrier coatings. For example, lanthanum phosphate (La-monazite) can be used to form thermal barrier coatings to protect superalloy and ceramic parts exposed to high temperature and damage by sulfur, vanadium, phosphorus and other contaminants. The monazite or xenotime coatings can be applied using any of the common application methods including EB-PVD, laser ablation and plasma spraying. The stoichiometry of the coatings can be modulated according to the stoichiometry of specially prepared starting target (source) material. The most effective coatings appear to be largely crystalline and show a columnar structure with feather-like microstructure. For La-monazite, effective coatings between 10 and 500 micrometers in thickness can be deposited on substrates having temperatures between about 750° C. and about 950° C.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com