Telomerase activity detecting probe, reagent kit and method
A detection reagent and detection probe technology, applied in the field of molecular detection, can solve the problems of being fixed on a special support, low detection sensitivity, poor specificity, etc., and achieve low price, low reagent cost and broad application value. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
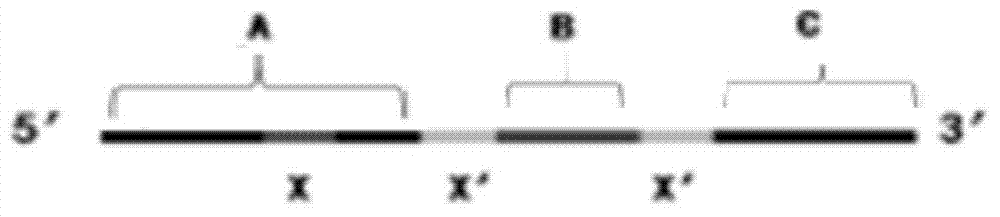
[0113] figure 1 A schematic diagram of the structure of the telomerase-binding primer provided in the embodiment of the present invention, the telomerase-binding primer includes A, B, and C in sequence. Wherein, the nucleotide sequence of A is a recognition site of a nicking endonuclease added to the nucleotide sequence of C, and the B has a DNase sequence, and the DNase sequence has a hemin-binding The poly-G nucleotide sequence of the site, the two ends of the DNase sequence have the recognition site of the nicking endonuclease (as shown by X' in the figure), the nucleotide sequence A, the distance A The 15-24 bases at the 5' end have a recognition site for a nicking endonuclease (as shown by X in the figure); the nucleotide sequence C has a sequence recognized by telomerase;
[0114] combine figure 1 , the present embodiment provides a primer for detecting telomerase activity, comprising the steps of:
[0115] (1) In vitro synthesis of telomerase-binding primer (TS), t...
Embodiment 2
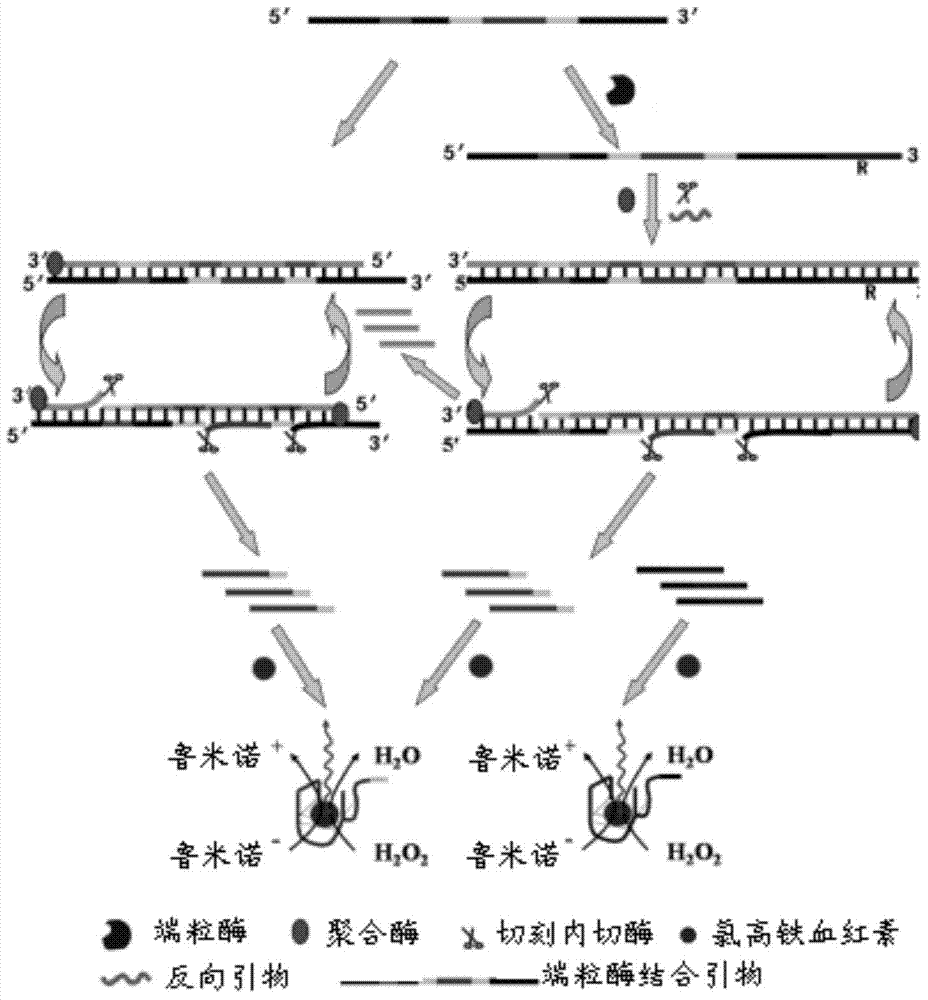
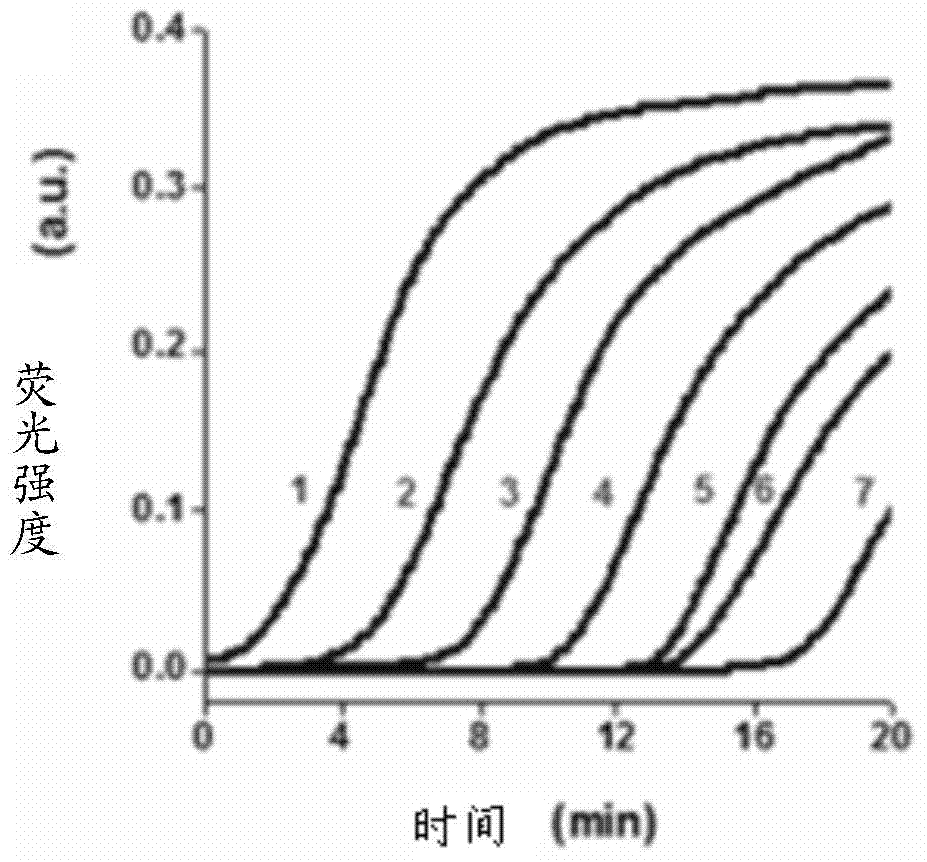
[0129] This embodiment provides a flow chart of a method for detecting telomerase activity, such as figure 2 shown. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that this detection method can be roughly divided into three steps. The first step: the telomerase-binding primer (TS) with a nicking endonuclease site. A poly-G sequence (TTAGGG) is continuously added to the 3′ end. Step 2: The reverse primer is complementary to the extension product of telomerase - the poly-G sequence (TTAGGG), which is copied and extended under the action of the polymerase. After forming a double strand, the new amplification template and the nicking endonuclease are digested Site formation; the new amplification template is cleaved by a nicking endonuclease, and then the polymerase uses the newly formed amplification template as a template for strand displacement (SDA) replication, thereby generating a telomerase product-polyG sequence (TTAGGG ), DNase and a primer (trigger) that initiates the following ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com