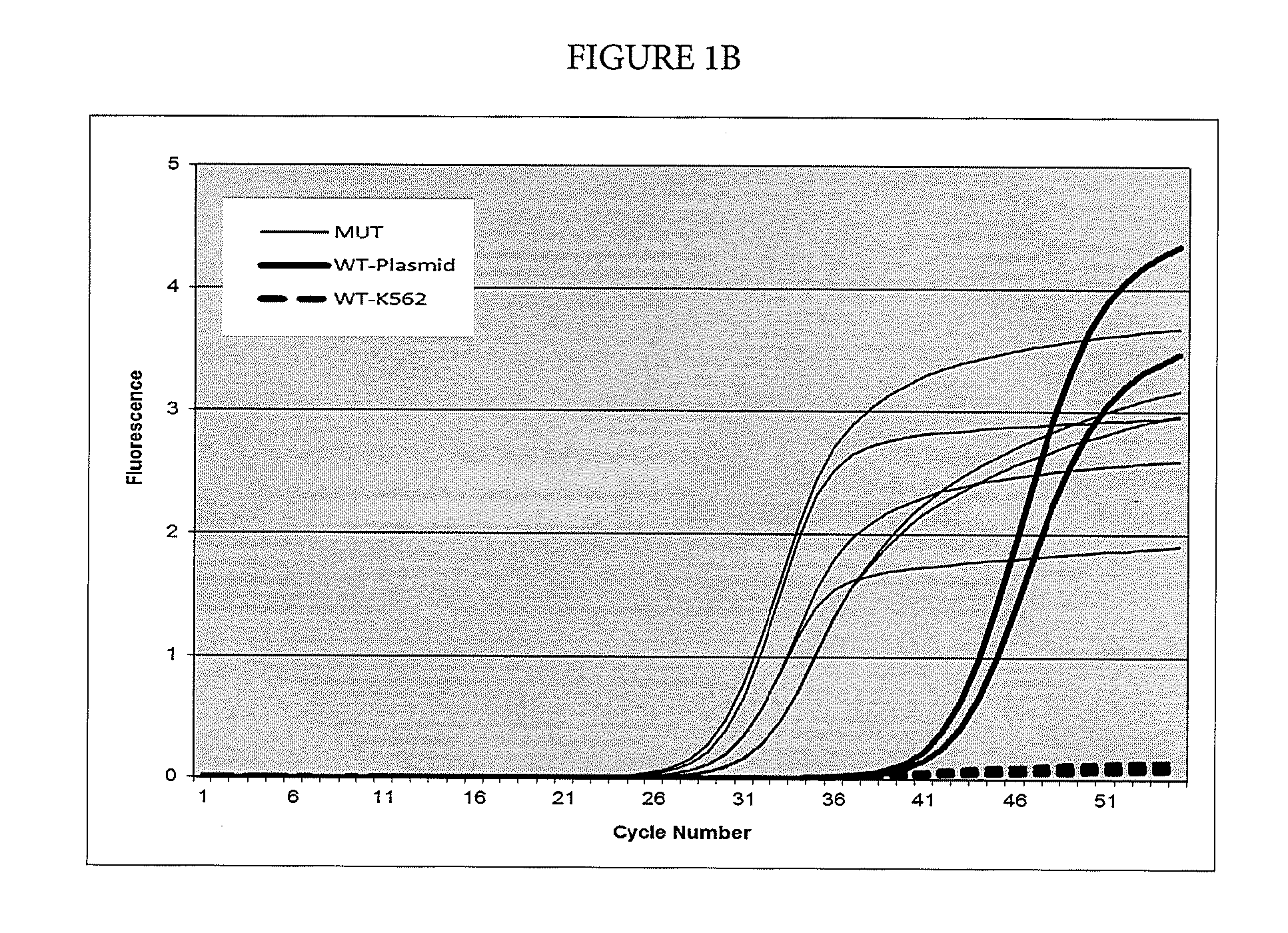
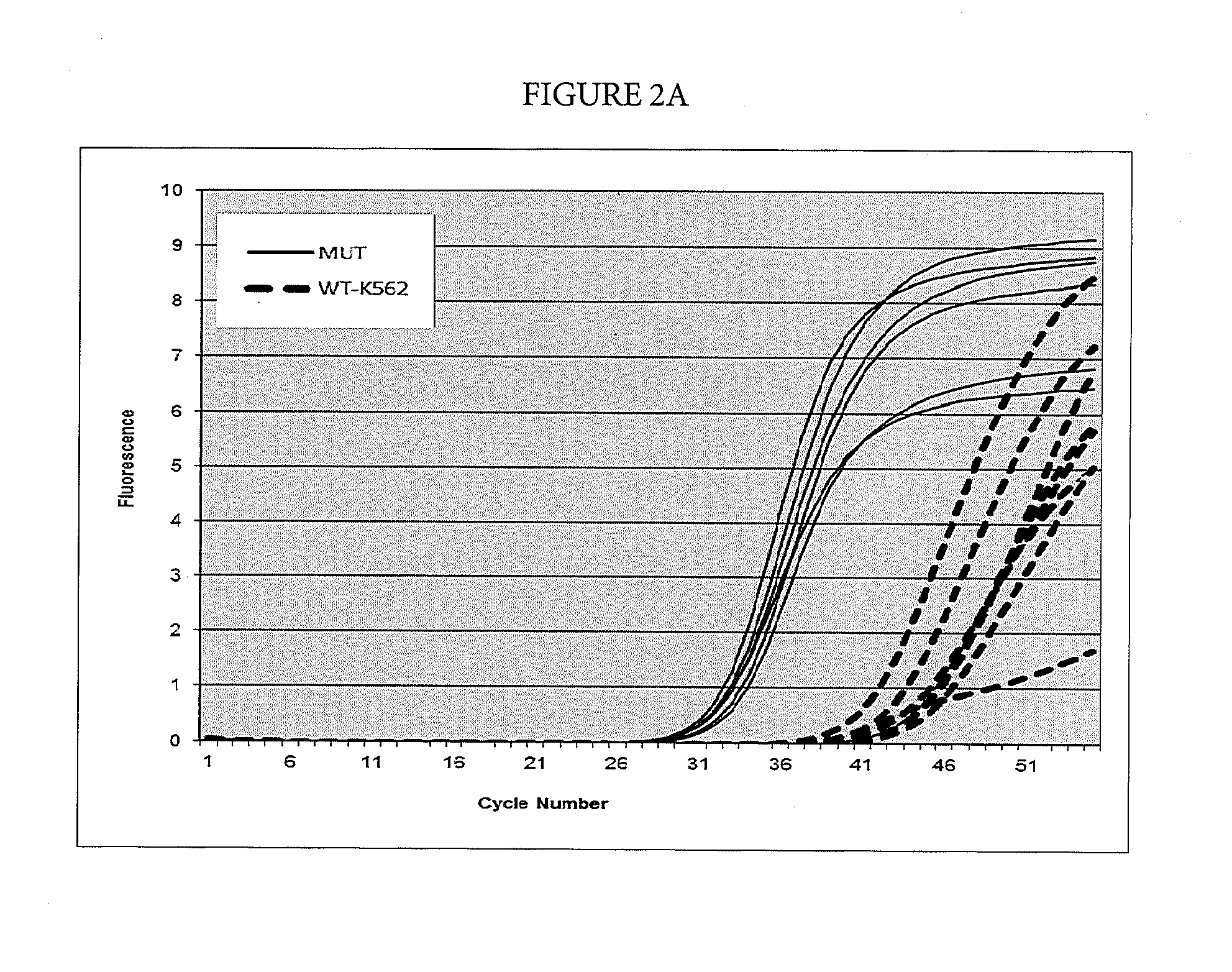
Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Reduce non-specific amplification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amplification using modified primers
InactiveUS20030044817A1Promote cloningExtension of timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
The present invention provides modified primers for use in the amplification of a nucleic acid sequence. Amplifications carried out using the modified primers result in less template-independent non-specific product (primer dimer) compared to amplifications carried out using unmodified primers.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Multiphase nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS9139870B2Reduce non-specific amplificationIncrease resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAnalyteImproved method
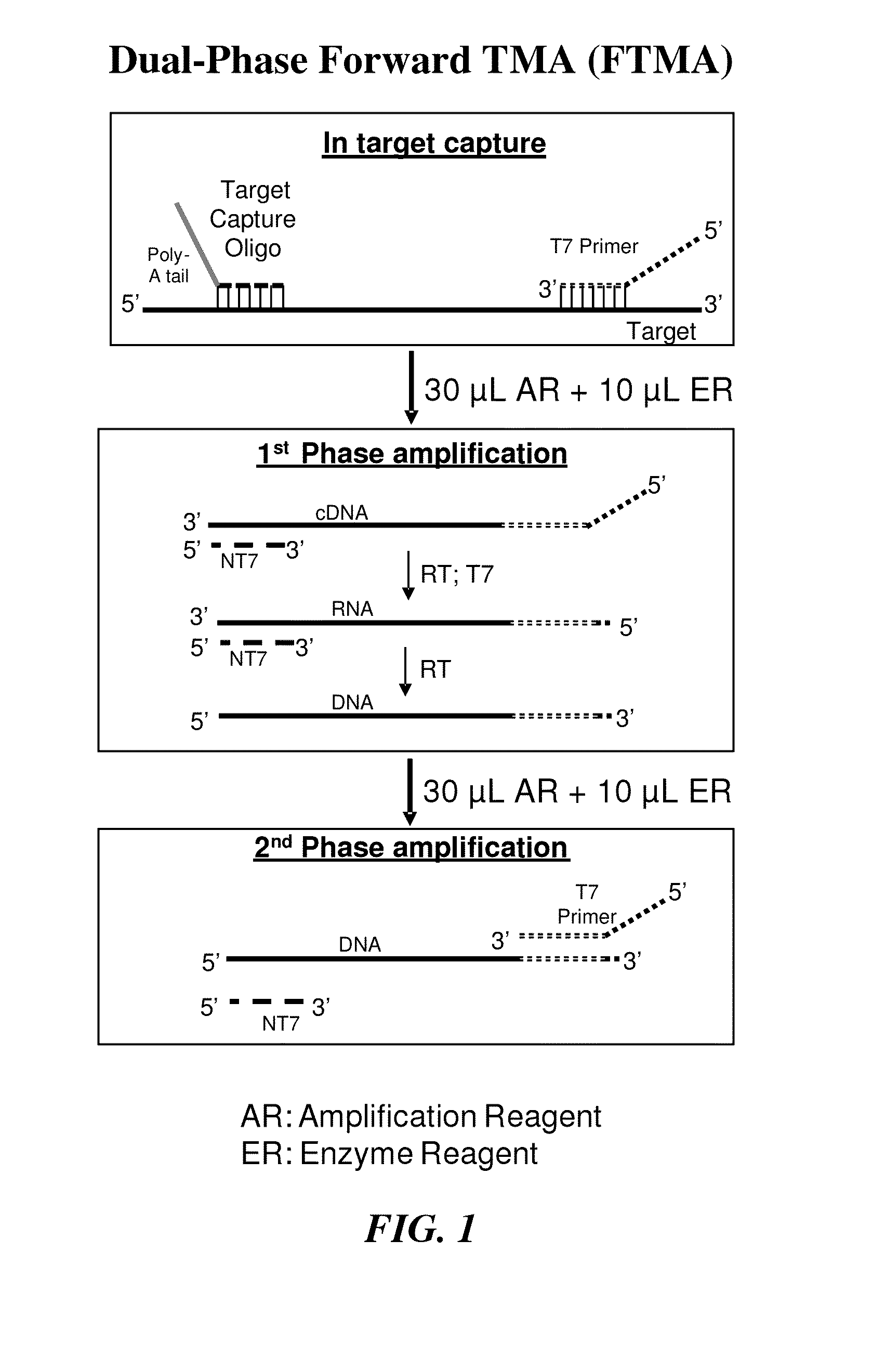
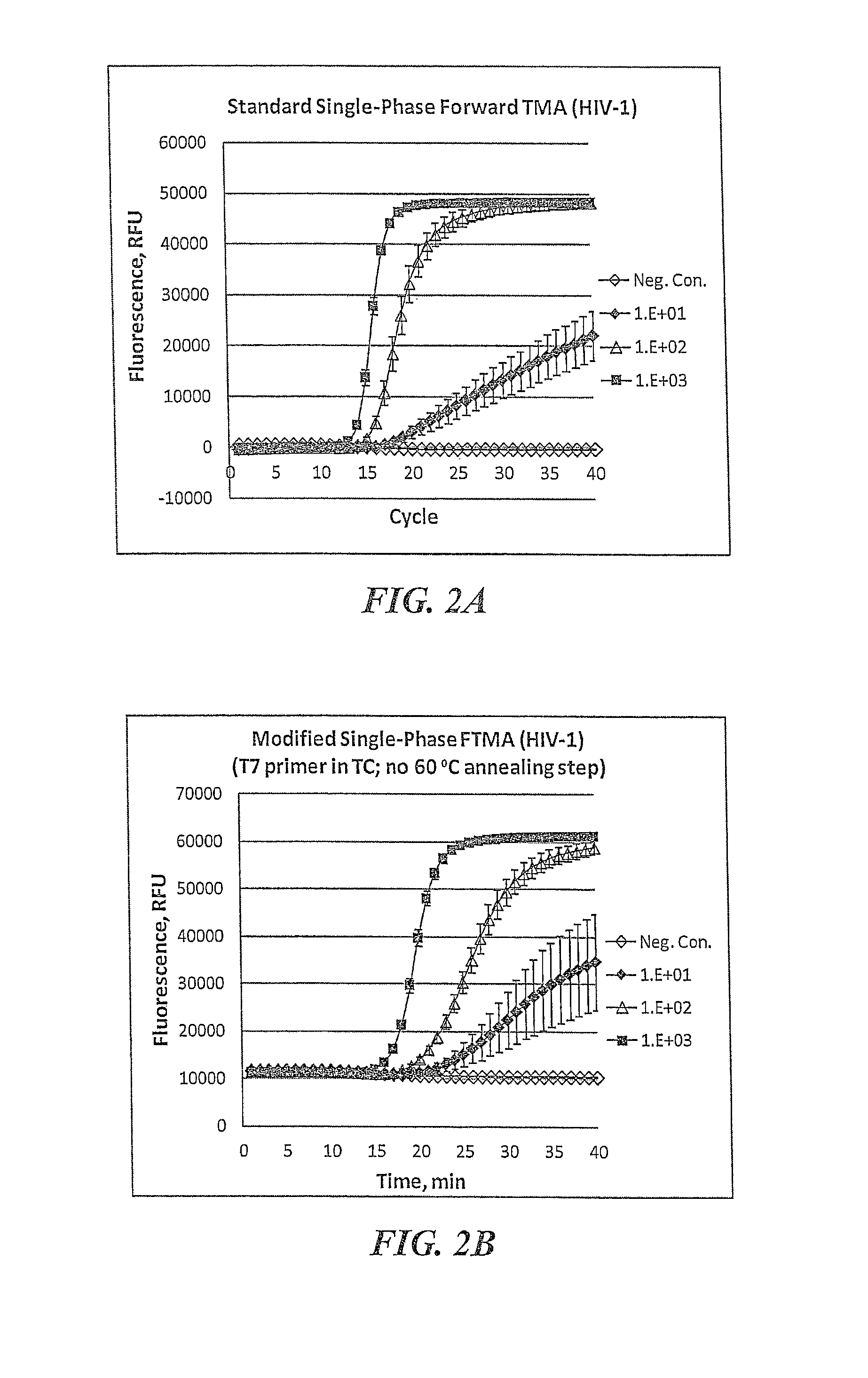
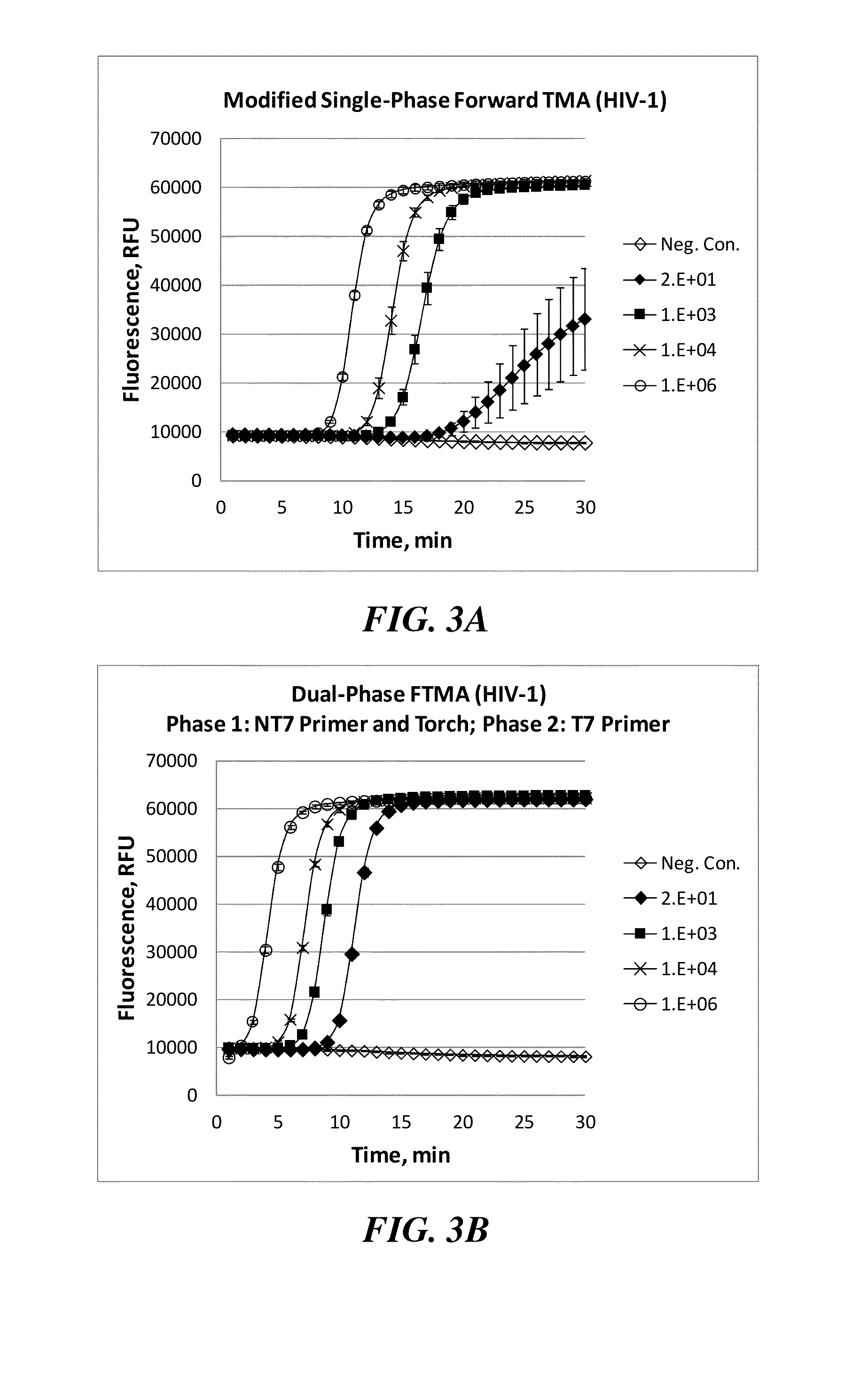
Improved methods for use in nucleic acid amplification, including multiplex amplification, where the amplification is carried out in two or more distinct phases are disclosed. The first phase amplification reaction preferably lacks one or more components required for exponential amplification. The lacking component is subsequently provided in a second, third or further phase(s) of amplification, resulting in a rapid exponential amplification reaction. The multiphase protocol results in faster and more sensitive detection and lower variability at low analyte concentrations. Compositions for carrying out the claimed methods are also disclosed.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
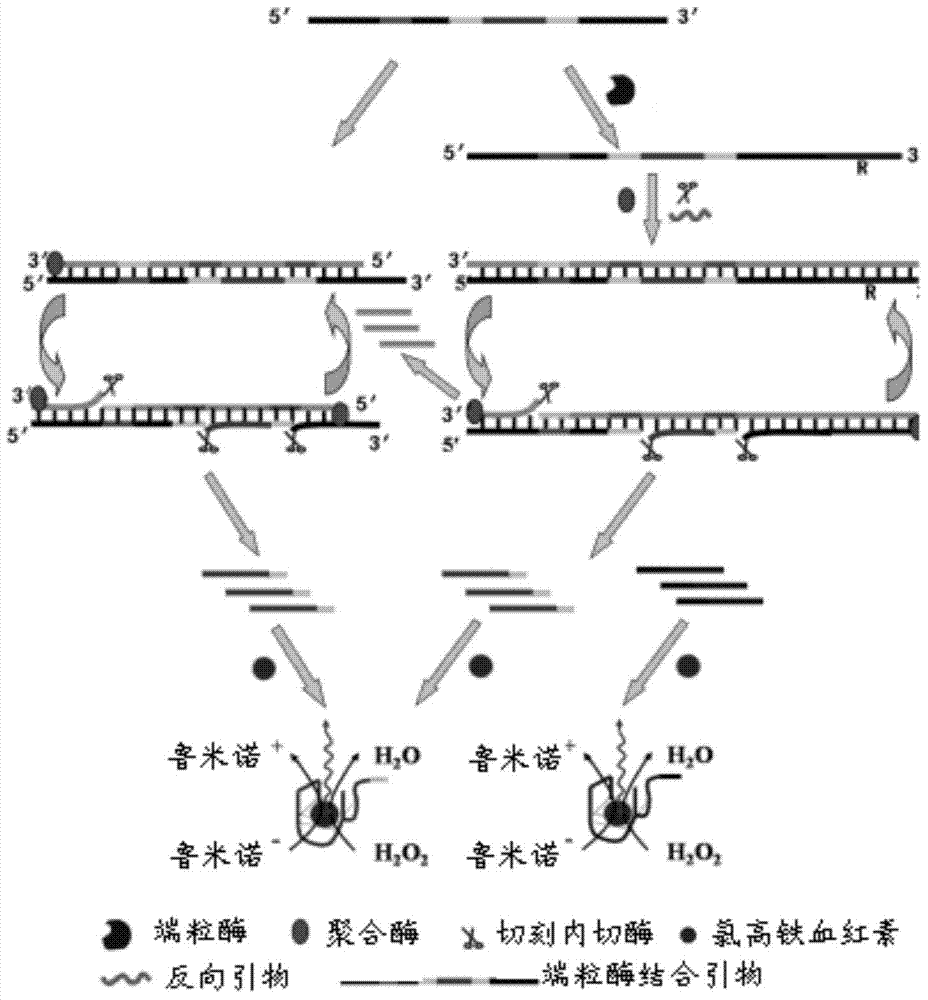
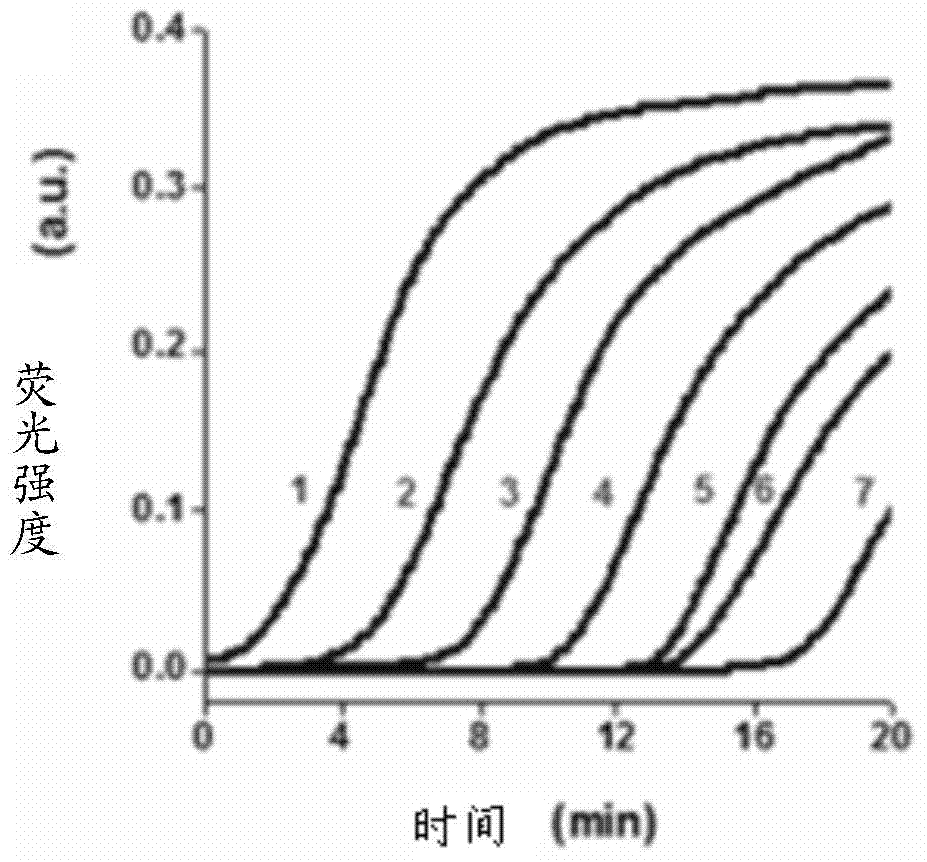
Telomerase activity detecting probe, reagent kit and method
InactiveCN103667513ALow cost of reagentsHigh sensitivity and specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNon specificEnzyme
The invention provides a telomerase activity detecting probe, a telomerase activity detecting reagent kit and a telomerase activity detecting method. The design of telomerase combination primers (TS) and reverse primers is simple, and TS only needs to comprise DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) enzyme sequences and restriction enzyme cutting sites of cutting enzyme and does not need any modification; the reverse primers only need to comprise sequences complemented with multiple-G sequences extending from telomerase, so the primers are easy to design, and the feasibility is high. The telomerase activity detecting method provided by the invention has the advantages that the reverse primers are only combined with TS primers extending from result telomerase, the nonspecific amplification is reduced, in addition, in the chemical luminous reaction, only amplified telomerase multiple-G sequences and DNA enzyme can be combined with hemin to form a tetramer, and chemical luminous signals are generated, so the telomerase activity detecting method provided by the invention has higher specificity and higher sensitivity. In addition, the telomerase activity detecting reagent kit provided by the invention has the advantages that the cost is low, the operation is simple, and the time is saved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
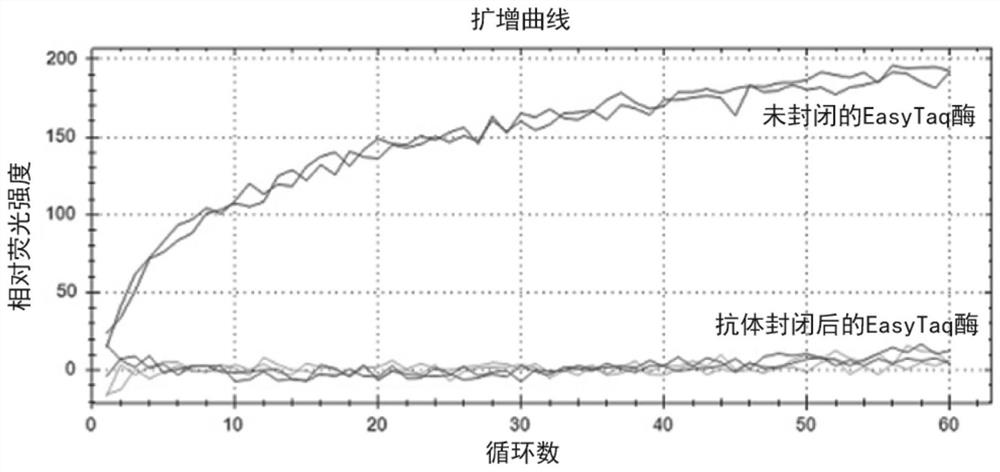
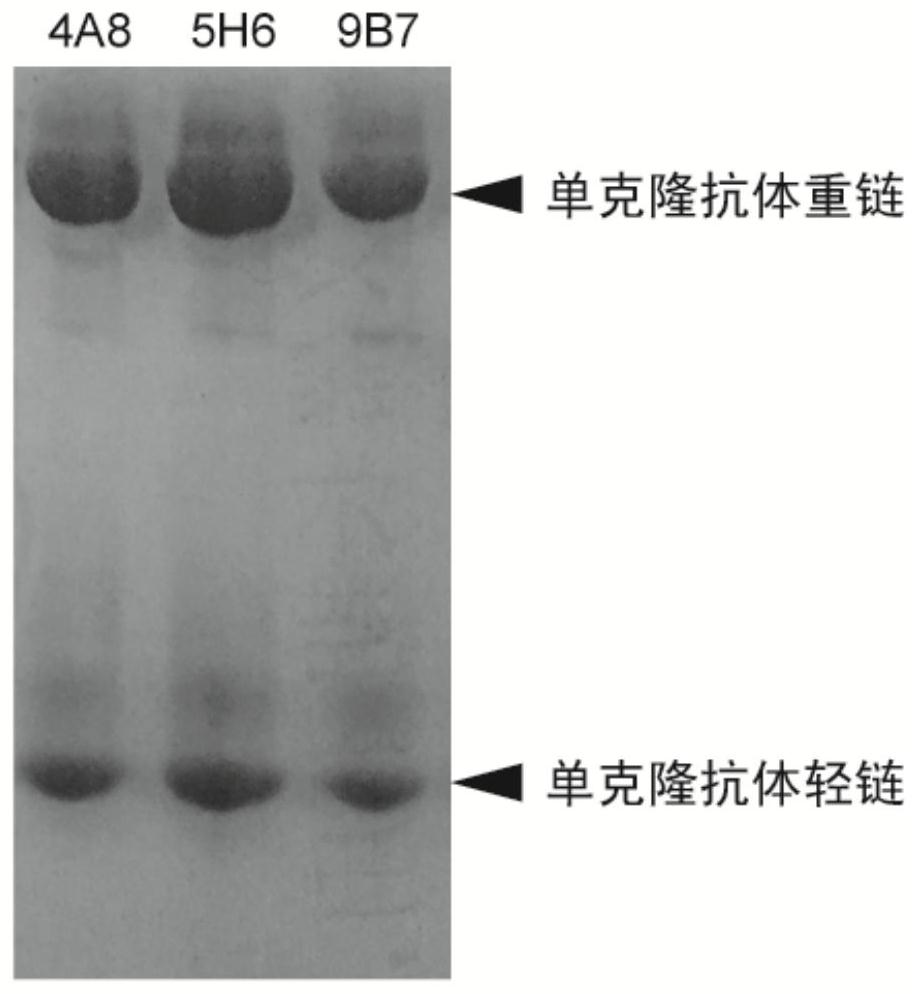
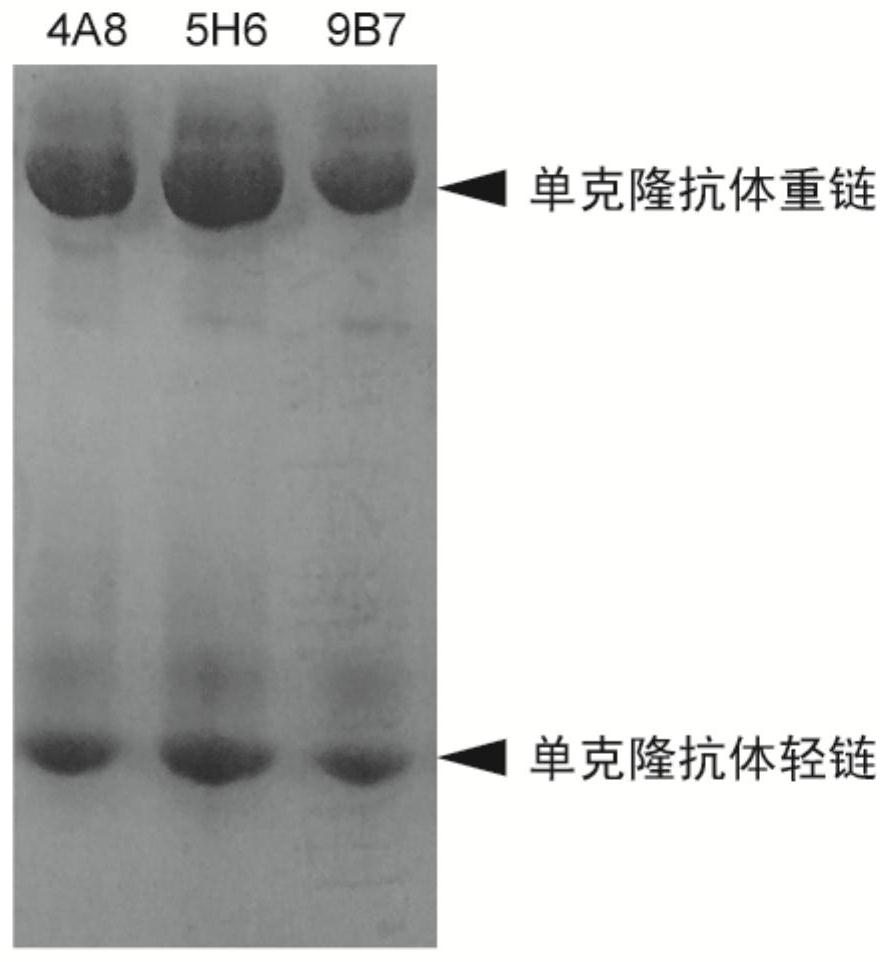
Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody combination as well as reaction system and application thereof
ActiveCN111808197AHigh activityGuaranteed thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAntiendomysial antibodiesEnzyme
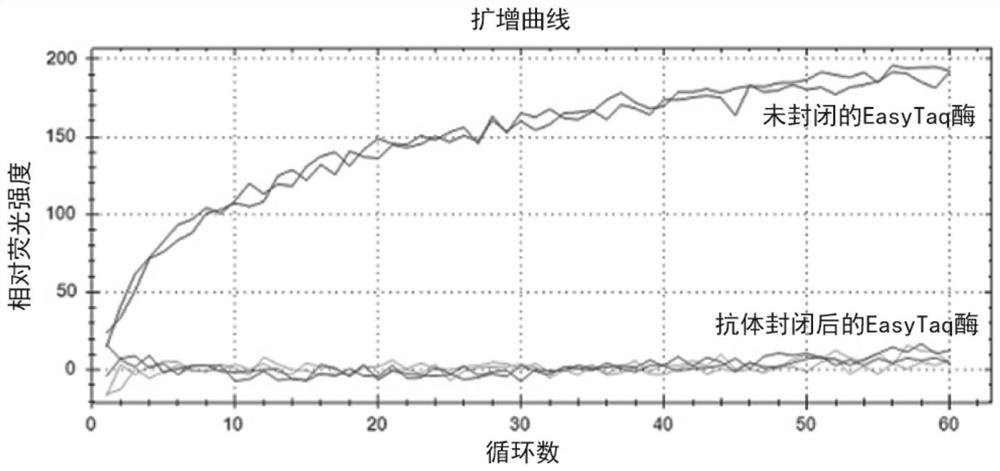
The invention discloses a Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody combination as well as a reaction system and application thereof. The invention firstly discloses the Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody combination. The combination comprises a monoclonal antibody 4A8 and a monoclonal antibody 9B7. The invention further discloses application of the antibody combination in reducing non-specific amplification of Taq DNA polymerase and / or ensuring thermal stability of Taq DNA polymerase, and a reaction system and a kit containing the antibody combination. The antibody combination and the optimized reaction solution can fully seal the active region of Taq DNA polymerase under the condition of low temperature, effectively reduce non-specific amplification and ensure the thermal stability of the enzyme, and can still effectively maintain the durability of the enzyme activity under the condition of higher amplification cycle number.
Owner:BEIJING TRANSGEN BIOTECH CO LTD
Multiplex fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) universal adapter for microsatellite detection, and detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN104178566ALow costSave moneyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceNucleotide
The invention discloses a multiplex fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) universal adapter for microsatellite detection, which comprises an adapter 1, an adapter 2, an adapter 3 and an adapter 4, wherein the nucleotide sequences of the adapters 1-4 are disclosed as SEQ ID:1-4. The universal adapter has the advantages of high PCR amplification efficiency and no interference, and can not interfere with microsatellite primers to be amplified. The invention also discloses a method for carrying out microsatellite multiplex fluorescence PCR detection by using the multiplex fluorescence PCR universal adapter for microsatellite detection. In the multiplex PCR process, primer screening and typing experiments can be performed only after the four or three fluorescence adapters are synthesized. The method has the advantages of simple steps, short experimental period and low experimental cost.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody combination, polymerase reaction system containing same and application of Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody combination
ActiveCN111662386AProtects TaqDNA polymerase activityGuaranteed thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against enzymesAntiendomysial antibodiesMonoclonal
Owner:BEIJING TRANSGEN BIOTECH CO LTD
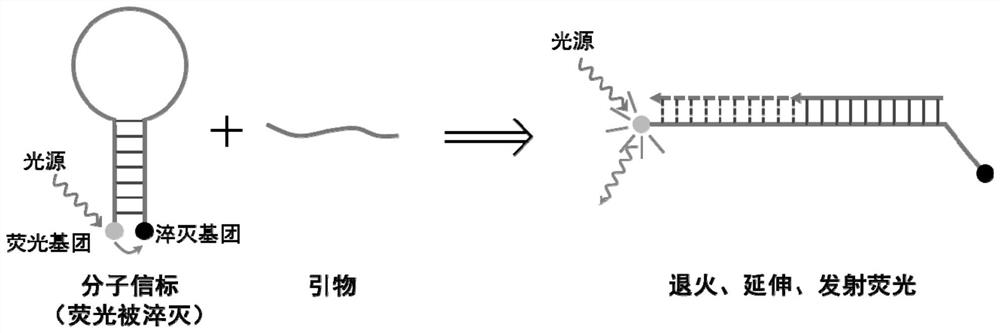
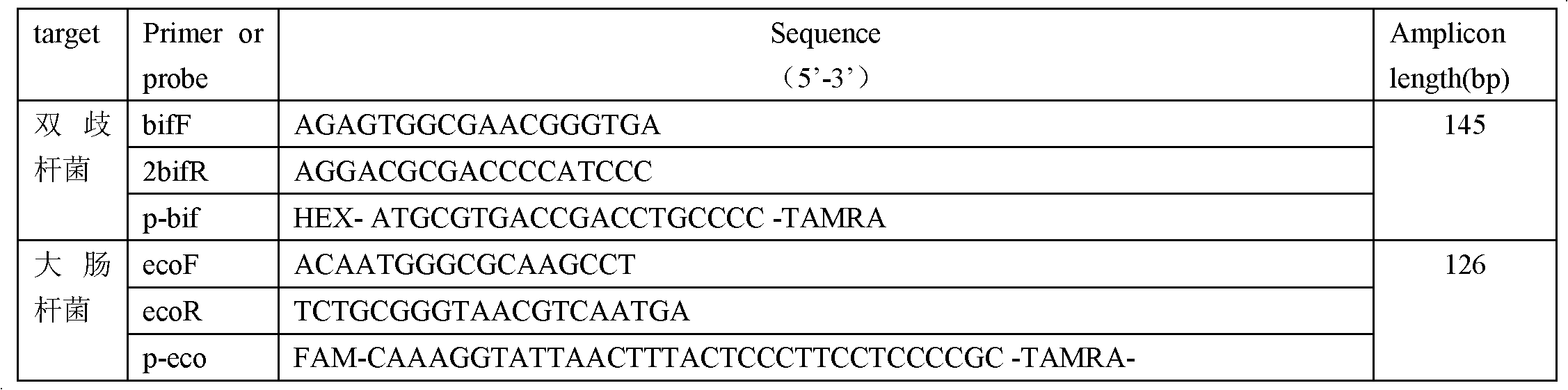
Method for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of bifidobacteria and Escherichia coli by using Taqman probes
InactiveCN102559912AKinetic Change MonitoringReveal diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPcr method
The invention discloses a method for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of bifidobacteria and Escherichia coli by using Taqman probes. The method comprises the following steps of: A) extracting bacterial genome DNA of the bifidobacteria and the Escherichia coli in a sample to be detected; B) synthesizing primers and the Taqman probes according to related sequences of the bifidobacteria and the Escherichia coli; and C) ensuring that the primers and the probes obtained in the step B) and other PCR reaction reagents form a reaction system for real-time quantitative PCR by the Taqman probes. The Taqman probes are labeled by double colors, by a double absolute quantitative PCR method, two kinds of intestinal bacteria in a sample can be accurately quantified at one time, the detection cost and detection time can be saved, and errors caused by repeated detection are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Universal multiple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method
InactiveCN102776172AImprove versatilityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGeneticsPcr method
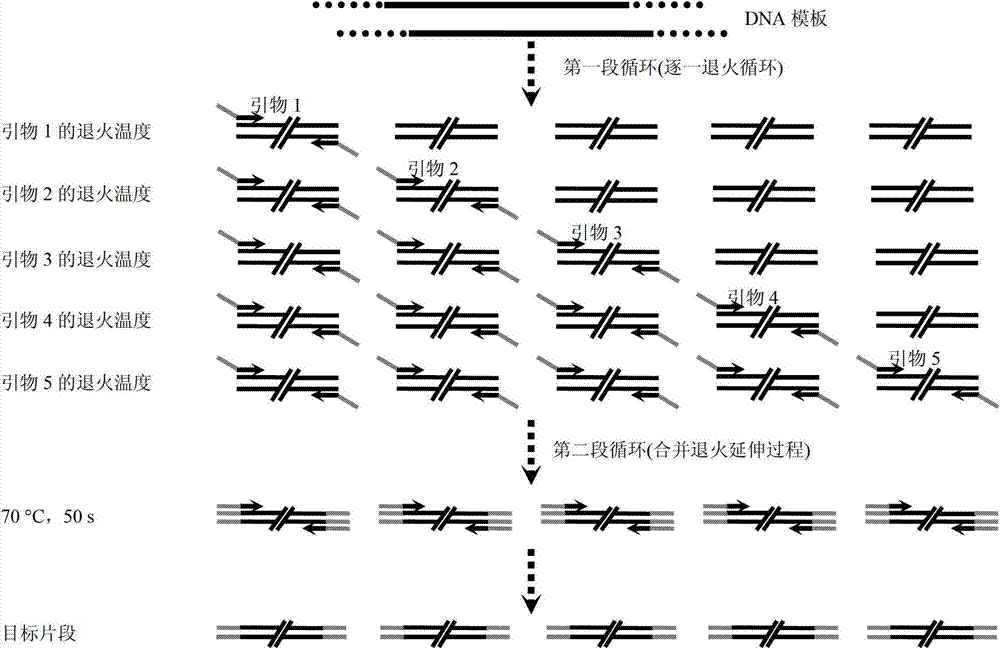
The invention relates to a universal multiple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. The universal multiple PCR method comprises the steps of: increasing a universal joint sequence to decrease difference of annealing temperature between primers, and increasing the annealing temperature (about 70 DEG C) of the jointed primers to be close to extension temperature; combining annealing and extensionphases; shortening PCR time; and improving the specificity and the yield of a PCR product by using two sections of circulation modes according to the gradual annealing circulation of primer annealingtemperatures from high to low. By using the universal multiple PCR method, the universality of multiple PCR can be remarkably improved, the universal multiple PCR method can be applied to many fields, such as seed purity identification, variety authenticity identification, polymorphism analysis, mutation analysis, quantitative analysis and species identification.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Micro-volume cell nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveCN108315389AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideCentrifugation
The invention provides a micro-volume cell nucleic acid amplification method which comprises the following steps: a) putting micro liquid droplets with a small amount of cells inside into a small-sizecontainer with an oil phase supplied in advance, and performing centrifugation to settle down the micro liquid droplets; b) putting cell lysis buffer droplets into the small-size container through micro-volume injection below the liquid level of the oil phase, performing centrifugation to settle down the cell lysis buffer droplets, and fusing the cell lysis buffer droplets with cell droplets so as to achieve splitting of cells and release of nucleic acid substances; c) adding splitting termination droplets through micro-volume injection, performing centrifugation, fusing the splitting termination droplets with the split cell droplets, and neutralizing or terminating the splitting reaction; d) adding one or more amplification reaction liquid through micro-volume injection, performing centrifugation fusion, and performing amplification on genomes, transcriptome or specific nucleotide sequences at an appropriate temperature. The micro-volume cell nucleic acid amplification method provided by the invention is simple in operation, low in cost and high in flux, and the reaction volume can be reduced to a nano liter grade.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
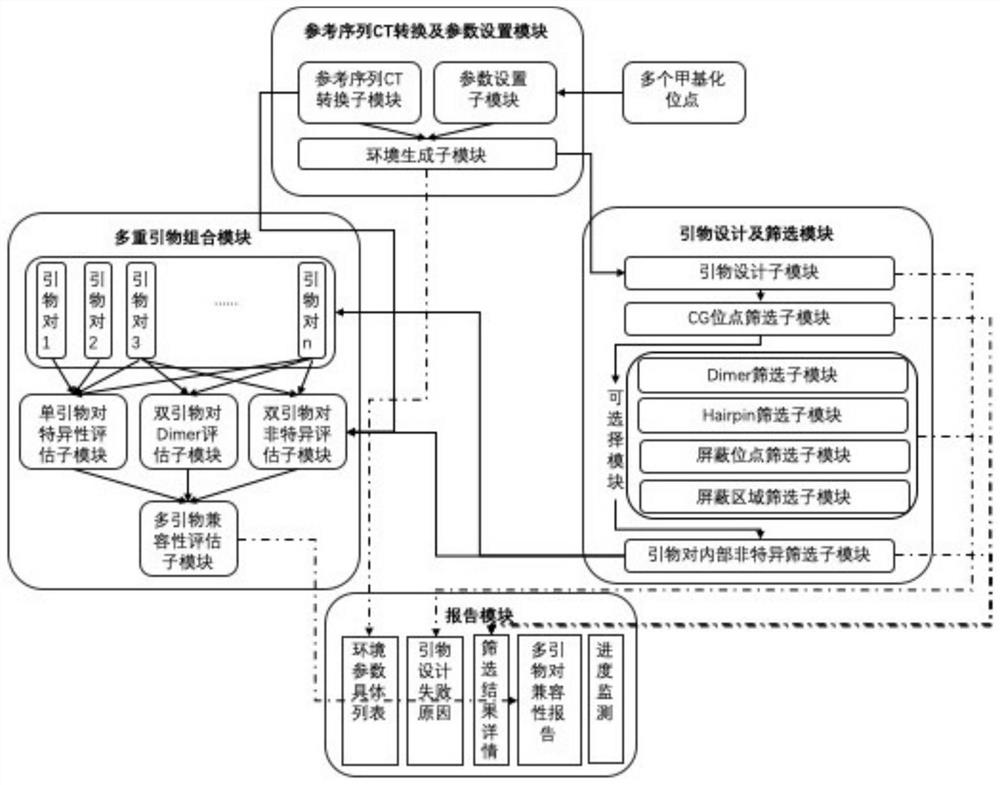
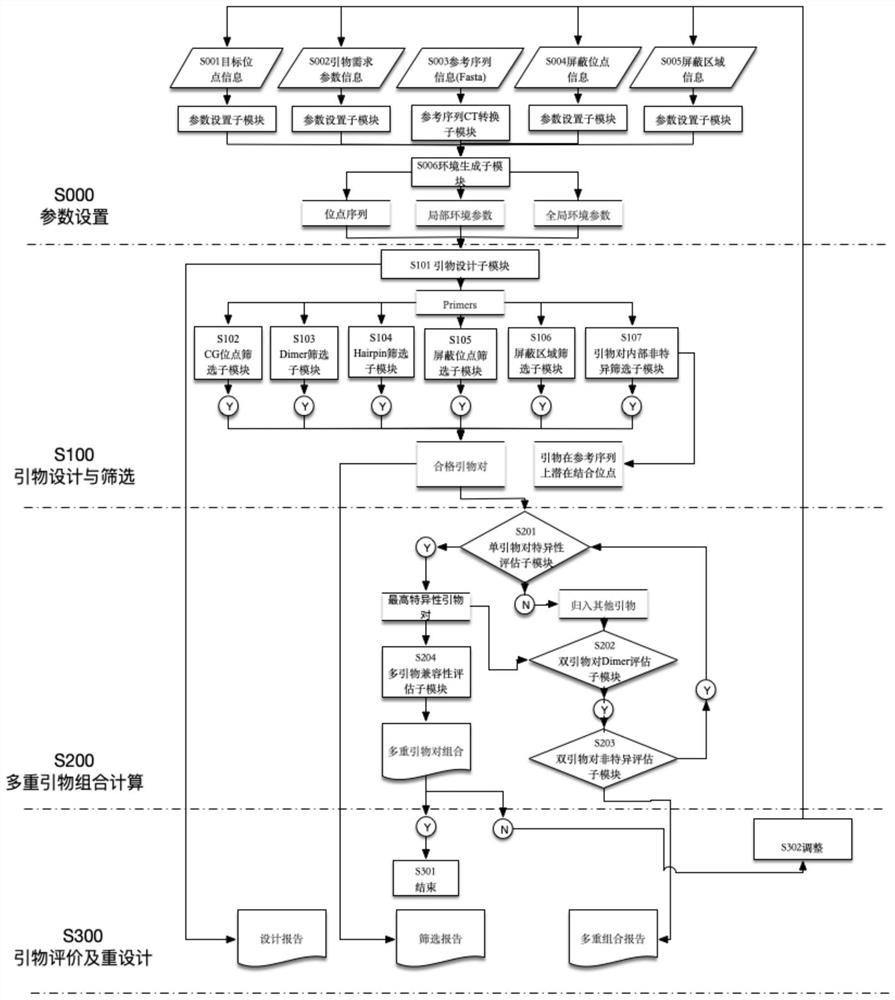
Multi-methylation specific PCR primer design method and system
PendingCN111653311AAvoiding the Problem of Differential AmplificationGuaranteed amplification efficiencyProteomicsGenomicsMethylation SiteMultiplex
The invention discloses a multi-methylation specific PCR primer design method and system. The method comprises the steps: setting parameters according to user requirements, designing and screening primers for a target methylation site, pairing the screened multiple methylation site primer pairs in pairs, checking the compatibility, selecting a maximum number of compatible multiple primer combinations, evaluating the designed multiple primer combinations, and determining whether the primers need to be redesigned. According to the invention, multi-methylation specific PCR primer design of a super-long sequence can be realized, secondary structures such as dimer / hairpin and the like between the interiors of a single pair of primers and between multiple pairs of primers can be effectively reduced, and non-specific amplification in a genome can be effectively reduced, the designed primers are high in specificity, the operability and accuracy of the multiplex methylation specific PCR experiment testing process are improved, and the working efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:WUHAN IGENEBOOK BIOTECH CO LTD
Zooplankton rrnL gene amplification primers and screening method, application and application method thereof
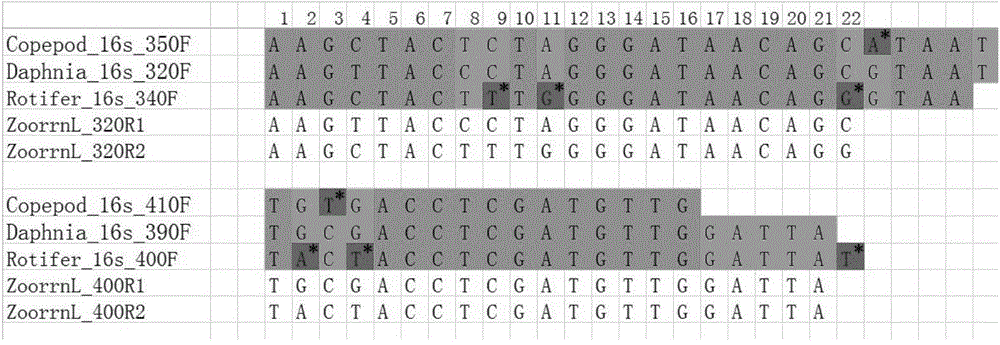
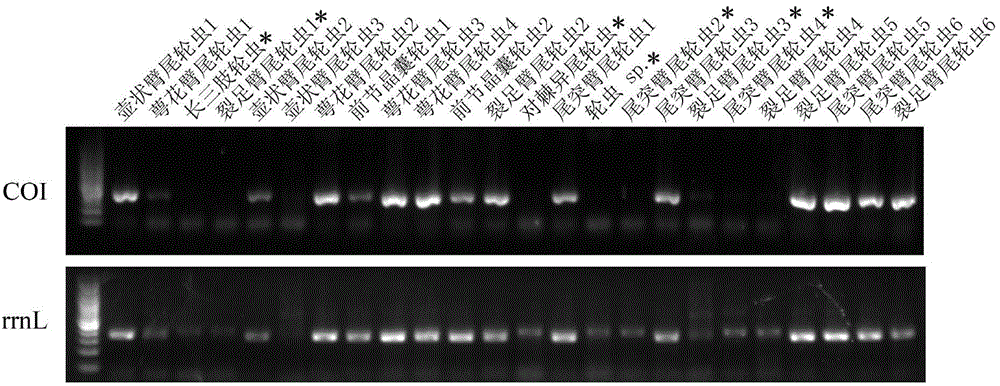
ActiveCN104404154AIncrease success rateReduce non-specific amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsSequence designZooplankton
The invention discloses zooplankton rrnL gene amplification primers and a screening method, application and an application method thereof, and belongs to the biotechnical field. According to common zooplankton rrnL gene sequences, 9 PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification primers are designed, comprising 5 upstream primers and 4 downstream primers; the primers have wide coverage and high amplification efficiency for zooplankton, and PCR products of the primers are compatible with a high-throughput sequencing platform; after the upstream primers and the downstream primers are combined in pairs, products with the lengths of 190-390 bp can be amplified; by a multi-primer combination method, nonspecific amplification can be reduced and the success rate of PCR can be improved; the PCR products can be widely used for performing species identification, biodiversity analysis and other researches through Barcode sequences.
Owner:南京易基诺环保科技有限公司
Quantitative fluorescent PCR inspection for hepatitis-B virus drug-tolerant gene mutation
ActiveCN1896278ARaise the annealing temperatureTroubleshooting Nonspecific Amplification ProblemsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceLamivudine resistanceGene mutation
The present invention relates to the real-time quantitative PCR assay for the Lamivudine resistance mutation of hepatitis b virus. The mutations related with Lamivudine resistance locate in the rtL180M and rtM204V / I mutations of DNA polymerase. This method utilizes the character that the primer cannot elongate correctly during the PCR process with mismatches in the 3'-end, designs the mutation site in the 3'-end of the real-time quantitative PCR primer, chooses proper primer concentrations and Touch-down PCR process, and couples the melting point curve of PCR product containing SyBrGreen I. The existence of mutation in the Lamivudine site can be determined with the real-time quantitative PCR signals and the melting point curve. This invention can detect the DNA mutations in the clinical hepatitis b virus specimens rapidly and accurately, and is also suitable for the detection of other gene mutations.
Owner:SHANDONG MEDICAL BIO TECH RES CENT
Primer group, kit and library construction method for detecting five bloodstream infection pathogens,
PendingCN110964840AStrong specificityReduce non-specific amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPathogenStaphyloccocus aureus
The invention discloses a primer group, a kit and a library construction method for detecting five bloodstream infection pathogens. The primer group comprises primer pairs used for detecting staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, acinetobacter baumannii, klebsiella pneumonia and enterococcus faecium. The primer group disclosed by the invention is high in specificity, a situation of non-specificamplification is effectively reduced, and the culture level of bacteria can be directly authenticated through specific primer amplification. When the primer group disclosed by the invention is adoptedto detect the bloodstream infection pathogens, a blood culture operation is not required, pathogens in a blood sample can be directly detected, the shortest time for obtaining a detection result is 48 h, and a detection period is greatly shortened.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司 +1
Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN114736301AGood sealingConvenient and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesMonoclonal antibody agentEnzyme
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibodies, and discloses a Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody and application thereof. The Taq DNA polymerase monoclonal antibody has a good sealing effect on Taq DNA polymerase, can well seal the activity of the Taq DNA polymerase under the conditions of 37 DEG C and 55 DEG C, deactivates and releases the activity of the Taq DNA polymerase under the condition of PCR denaturation at 94 DEG C, and reduces non-specific amplification at low temperature; meanwhile, the hot start enzyme containing the Taq DNA monoclonal antibody has better amplification efficiency and sensitivity, and the detection sensitivity is about 1.5 copies and is higher than the sensitivity in the prior art; and the detection effect is not influenced after the hot start enzyme containing the TaqDNA monoclonal antibody is repeatedly frozen and thawed or stored at 37 DEG C for 7 days, and the hot start enzyme has good stability and has important significance for deviating from normal storage conditions for a short time in the processes of use, transportation and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG HECIN SCI INC
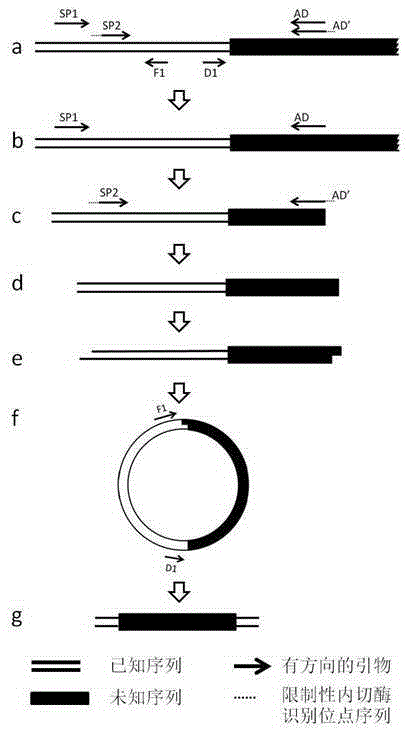
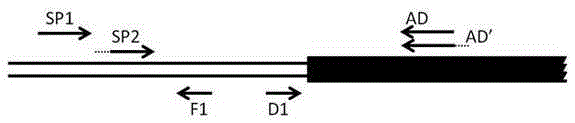
A method of acquiring an unknown flanking sequence of a known sequence
ActiveCN105400771AReduce non-specific amplificationEasy to operateDNA preparationRestriction Enzyme Recognition SiteGenome
A method of acquiring an unknown flanking sequence of a known sequence is disclosed. The method includes 1) designing two specific primers according to the known sequence which are labeled as SP1 and SP2, with the SP2 carrying a restriction enzyme recognition site, and designing a pair of reverse PCR primers which are F1 and D1 between the SP2 and a border sequence, 2) amplifying to obtain a PCR product 1 by adopting genome DNA as a template and by using any one degenerate primer and the specific SP1 primer, 3) amplifying to obtain a PCR product 2 by adopting the PCR product 1 as a template and by using the specific SP2 primer and a degenerate primer, with the degenerate primer in the step 3) being same with the degenerate primer in the step 2), but comprising a restriction enzyme recognition site, and 4) subjecting the PCR product 2 to digestion, adding T4 ligase, cyclizing, and amplifying by adopting the cyclized product as a template and by using the F1 primer and the D1 primer to obtain a PCR product 3, thus acquiring the flanking sequence. The method is advantaged by simple and easy operation, a low cost, a high success rate, short time, and the like.
Owner:SANMING UNIV
Universal shell type fluorescent reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection method of bird flu virus and detection kit
InactiveCN102071264AIncreased sensitivityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBird fluBinding site
The invention discloses a high-efficiency high-sensitivity universal shell type fluorescent reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection method of bird flu virus and a detection kit. The detection method is a method in which two sets of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers (one pair of outer primers and one pair of inner primers) are utilized to carry out two rounds of PCR amplification, namely, the products of the outer primers subjected to the PCR amplification are used as templates of the inner primers to be subjected to the PCR amplification, the bonding sites of the inner primers and the template DNAs are positioned at the inner sides of the DNA fragments amplified by the outer primers, and shell type PCR is extremely effective for reducing or eliminating nonspecific amplification and improving sensitivity. Compared with the fact that the temperate with an extremely low concentration (one or multiple copies) is difficult to detect by using the common detection method, the efficiency and fidelity of amplification can be greatly improved by using the detection method in the invention; and the detection method disclosed by the invention is significantly effective for the amplification of extremely trace target genes in environmental samples, is extraordinarily beneficial to the amplification of the trace temperate of the bird flu virus in a fish farming water body, and can fully meeting the requirements of the sensitivity and specificity of the bird flu virus detection in fishpond farming water.
Owner:中华人民共和国珠海出入境检验检疫局
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection kit for BDV (Borna Disease Virus) p24 segment
ActiveCN101967525AReduces the risk of contamination causing false positivesImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBorna disease virusFluorescence
The invention provides a fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit with simple and convenient usage and high sensitivity and specificity, which can optimize and improve the amplification efficiency of the PCR, reduce the contamination rate of the PCR, exactly and fast detect the BDV nucleic acid of a sample. In the invention, the real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit for a BDV p24 segment comprises 10* reverse transcription reaction liquid, an AMV (Avian Myeloblastosis Virus) reverse transcriptase, 2* fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction liquid, a Taq polymerase, a standard substance and the negative control, wherein the fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction liquid is optimized reaction liquid. The invention can shorten the reaction time and reduce the possibility of the PCR contamination, and can also remarkably improve the quantitative accuracy and the amplification efficiency.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Locked nucleic acid modified LAMP primer composition and application thereof
InactiveCN107338289AImprove stabilityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLocked nucleic acidBiology
The invention discloses a locked nucleic acid modified LAMP primer composition. In the LAMP primer composition, the locked nucleic acid modification position is at least one of three basic groups on the outmost side of the end 3' of an FIP primer and a BIP primer. The invention further relates to an LAMP reaction system comprising the LAMP primer composition. The system comprises formamide and hot start Taq. The invention further relates to an amplification method adopting the LAMP primer composition, and the amplification temperature is 58-72 DEG C. For solving the LAMP non-specific amplification problem, by adopting the technical scheme, while the amplification efficiency is improved slightly, non-specific amplification is greatly lowered, the stability and specificity of the LAMP reaction system are greatly improved, and the great significance in further improvement and clinic application of the LAMP technology is achieved.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +3
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nano PCR differential diagnosis kit and detection method thereof
InactiveCN105200163ARapid identificationImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHighly pathogenicRespiratory syndrome virus
The invention discloses a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nano PCR differential diagnosis kit and a detection method thereof. The kit comprises 5*reverse transcription buffering liquid, dNTP Mixture, reverse transcription inverse transcriptase, RNA enzyme inhibitor and reverse transcription primers. The method is characterized in that the kit further comprises 2*NanoPCR Mix, upstream primers and downstream primers, wherein the sequence of the upstream primers is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the sequence of the downstream primers is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The kit can be used for detecting porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and distinguishing strain types (typical strains or highly pathogenic strains). The invention further provides a method for conducting porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus detection through the kit, the detecting porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus can be detected rapidly and specifically, the strain types are distinguished, the detection efficiency of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus is greatly improved, and the specific amplification output of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus is greatly increased.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
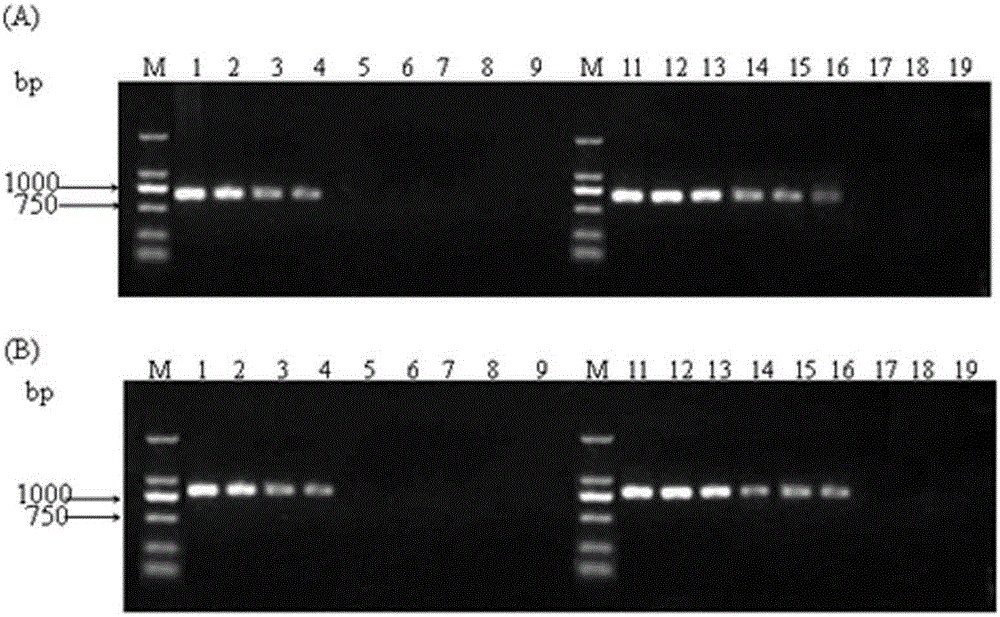
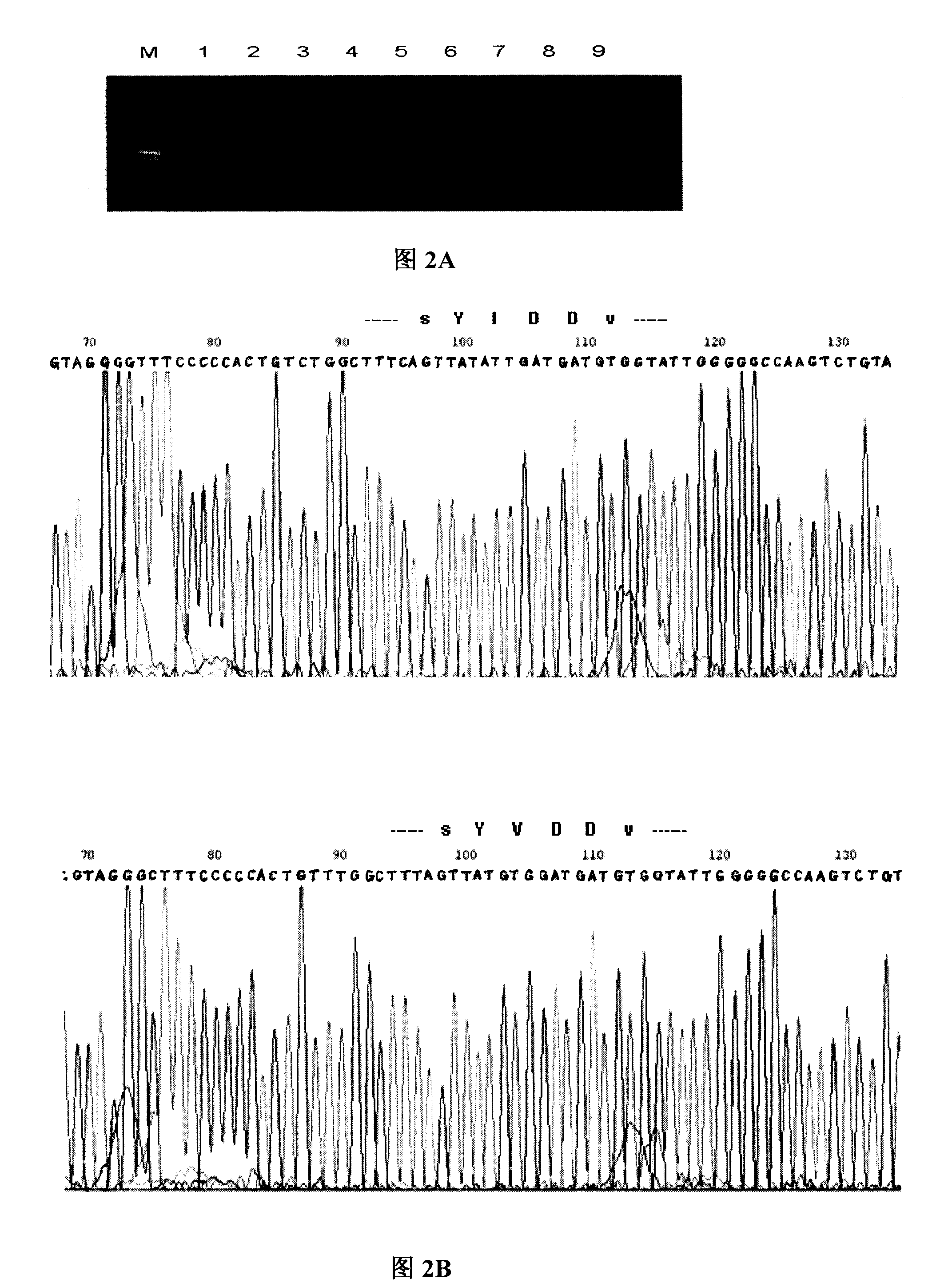
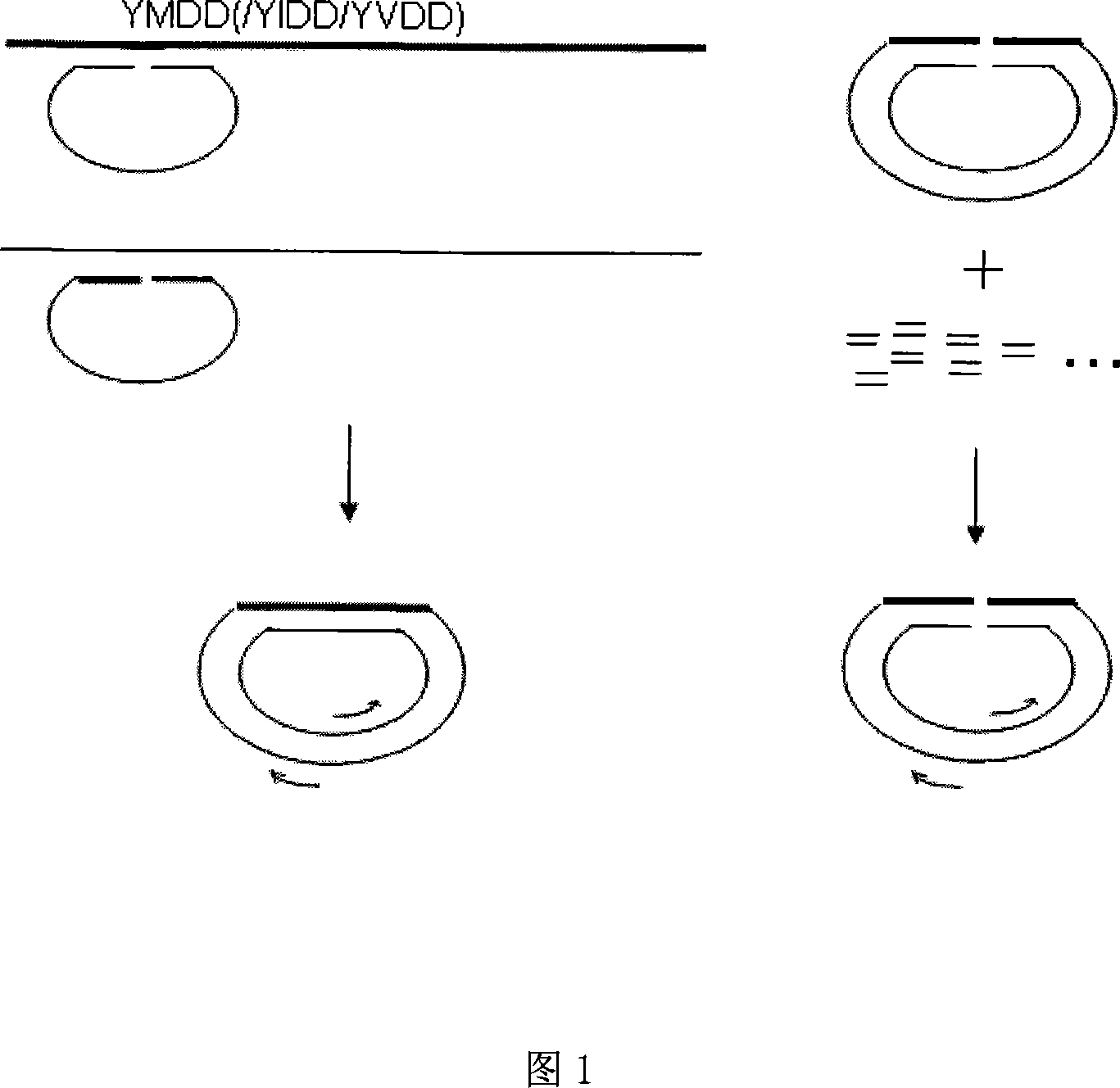
Displacement amplification method for detecting hepatitis B viruse P gene YMDD variation
InactiveCN101250581AReduce sensitivityReduce non-specific amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationFluorescenceInduction system
The invention relates to a displacement amplification process which is used to detect hepatitis b virus P gene YMDD variation, which is characterized in that detected HBV P gene YMDD motif and variation YIDD, wherein YVDD sequence is displaced into indication DNA through hybridization-ligase reaction, and then is reversely amplified into an induction system. The YMDD hybrid sequence is separated into left half and right half and is added on the front end and the tail end of a section of induction DNA, is hybridized with P gene YMDD region sequence after added with front and tail induction DNA, make the front end and tail end are in accordance with each other, and the hybrid gap is connected with ligase. The reverse amplification induction DNA adopts right middle sequence of induction DNA as primer, reversely amplifies the covalence connection of the front end and the tail end to induct DNA, wherein base groups on the two sides of the gap are connected through matching with dependency, thereby being suitable to one nucleotide mutagenic gene analysis. Detection can be displaced into several inducted PCR, thereby avoiding the recontamination of one set of system amplification products. Detected RNA can be displaced into induction DNA to be directly detected through hybridization-connection reaction, or is suitable to the real-time quantitative analysis of detected gene through combining with SYBR Green dye or fluorescent molecular probe.
Owner:北京万达因生物医学技术有限责任公司
Suppression of non-specific amplification with high-homology oligonucleotides
ActiveUS9260714B2Reduce non-specific amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisHigh homologySuppressor
The invention comprises suppressor oligonucleotides for reducing amplification of a non-target nucleic acid sequences; the method of designing and using such oligonucleotides, as well as kits and reaction mixtures.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
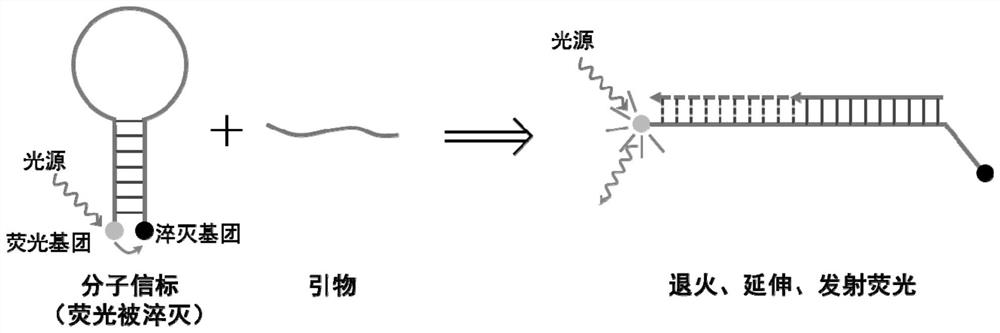
Multiple nucleic acid detection system as well as preparation method and application thereof
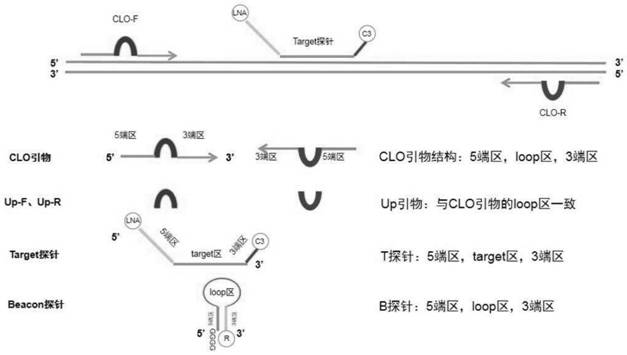
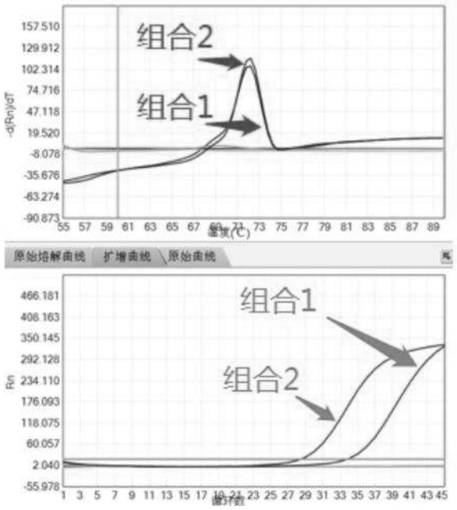
PendingCN114134219AReduce non-specific amplificationHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
The invention relates to a multiple nucleic acid detection system, which comprises an amplification primer group and a detection probe group aiming at a target nucleic acid sequence, the detection system comprises a Target probe modified by LNA and a Beacon probe for achieving a fluorescence quenching effect through 1-8 continuous G basic groups, and meanwhile, based on the proposal of the multiple nucleic acid detection system, the inventor combines a touchdown PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) program to detect the target nucleic acid sequence. The invention further provides a multiple nucleic acid detection method which can further reduce non-specific amplification in PCR reaction and improve detection sensitivity. Therefore, the limitation of traditional real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR typing is overcome, single-tube multi-typing is realized through special signal and melting curve analysis, and accurate qualitative detection of each target gene in at most 20 to-be-detected target nucleic acid sequences in a sample can be realized with a simpler reaction system and lower detection cost.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JINQIRUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Suppression of Non-Specific Amplification with High-Homology Oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20130177946A1Reduce non-specific amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh homologySuppressor
The invention comprises suppressor oligonucleotides for reducing amplification of a non-target nucleic acid sequences; the method of designing and using such oligonucleotides, as well as kits and reaction mixtures.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Composition for polymerase reaction
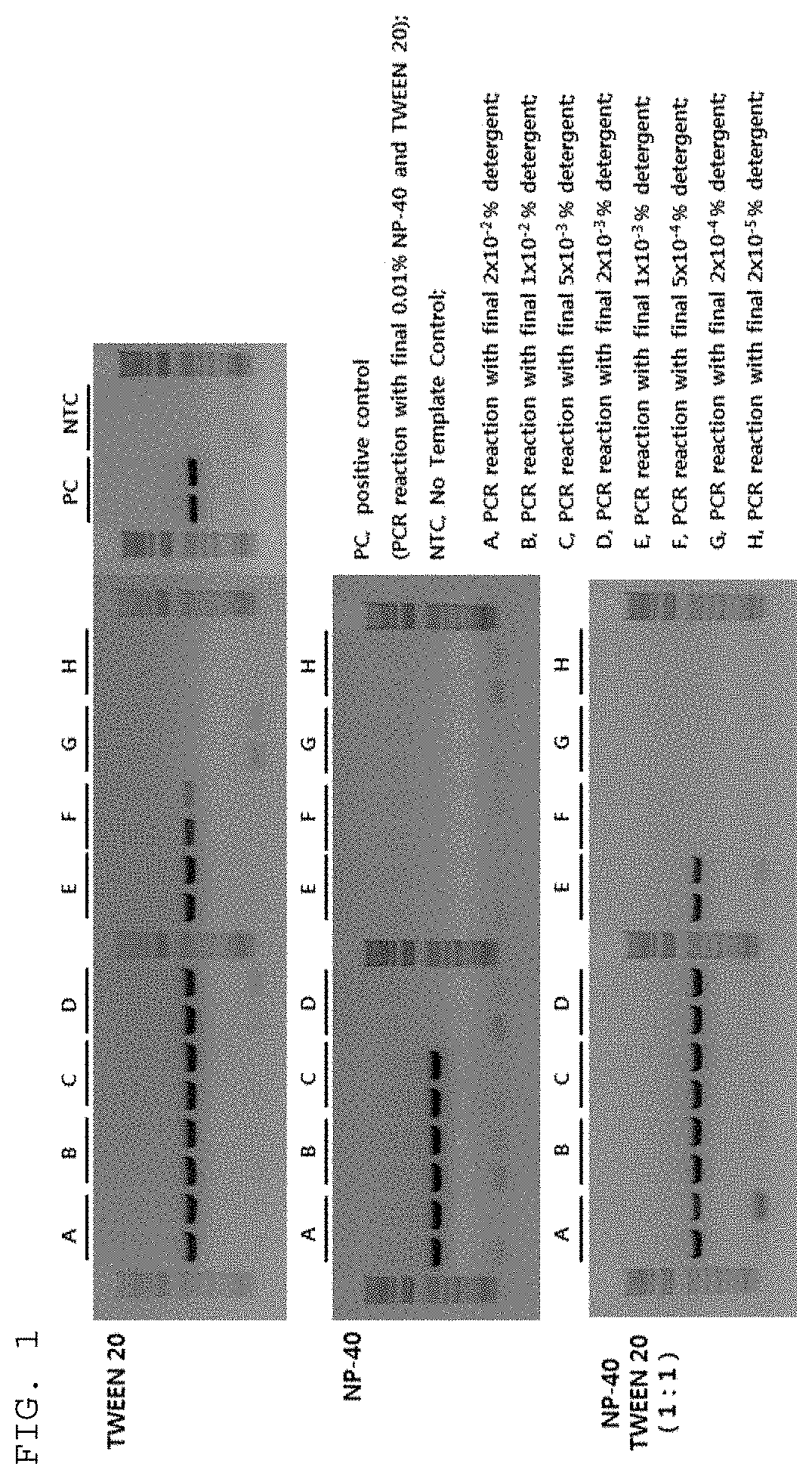
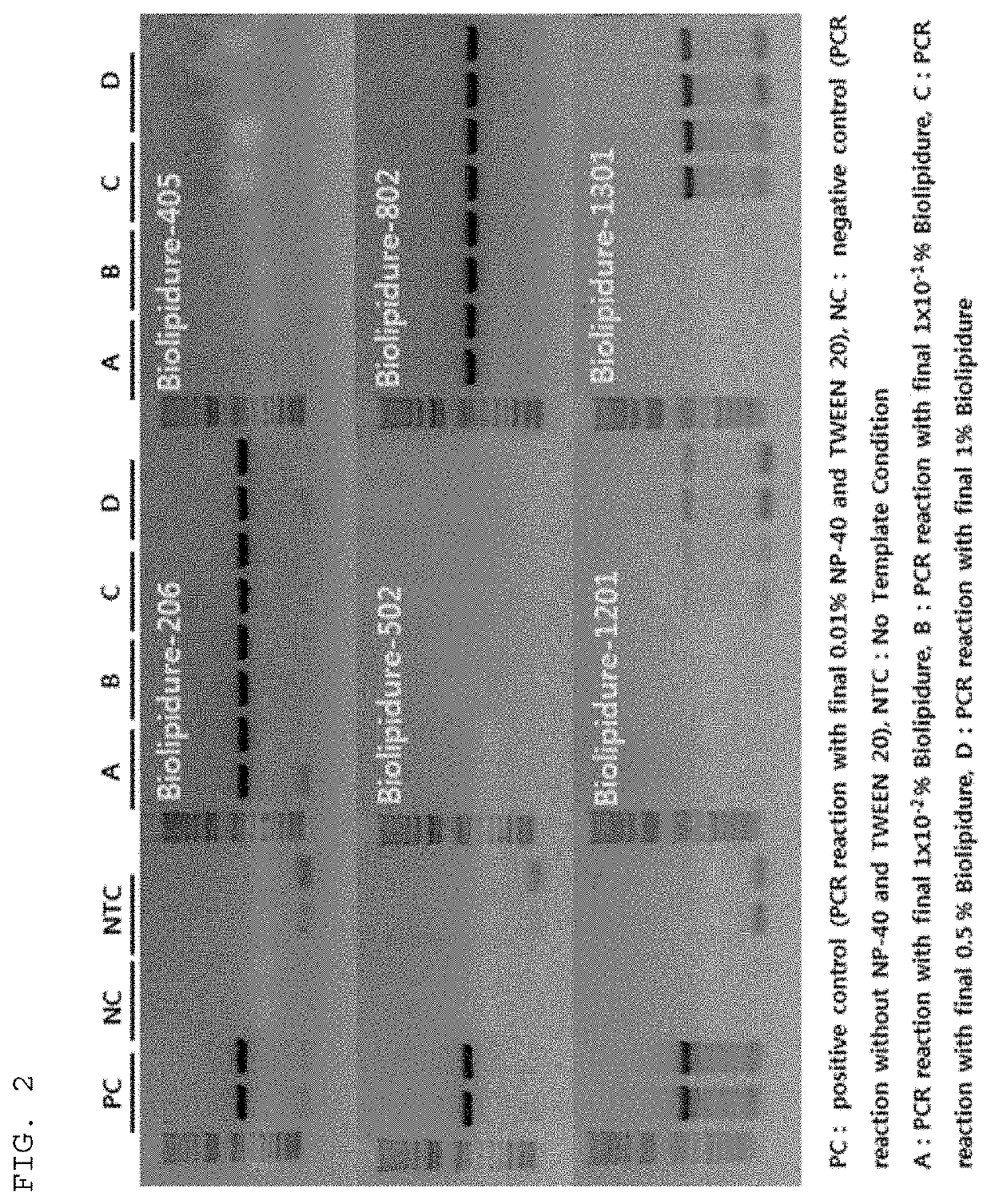
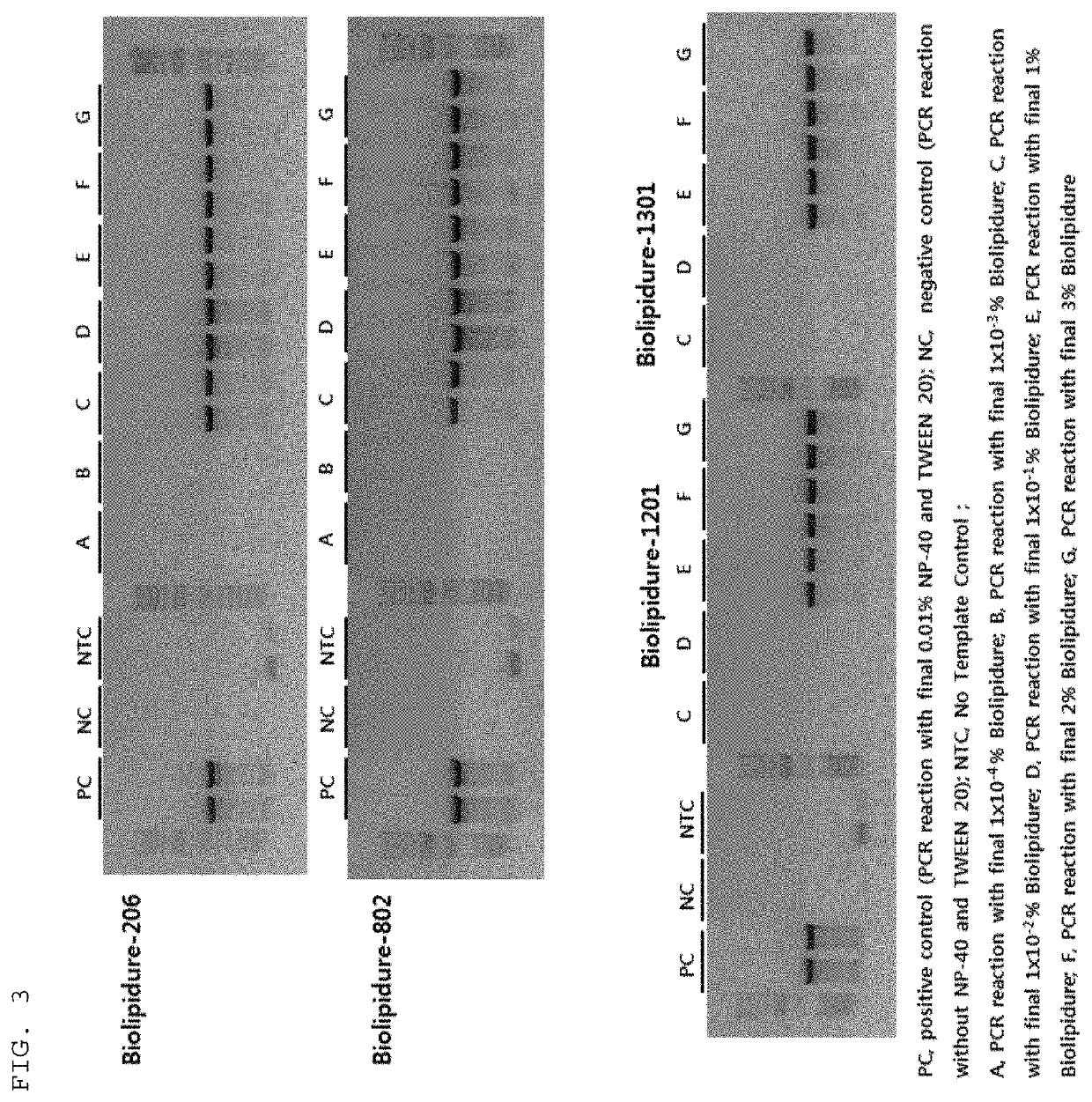
ActiveUS20190360021A1Reduce non-specific amplificationImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswares2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine2-methylpropene
Provided are a composition for a polymerase reaction, containing a nucleic acid polymerase and a 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC)-containing zwitterionic copolymer detergent, a tube for a polymerase reaction, and a kit for a polymerase reaction. The stability of the composition for a polymerase reaction can be improved and the reliability of the results of polymerase reaction such as nucleic acid polymerization or amplification can be improved.
Owner:NANOHELIX
Nucleic acid ligand and application thereof
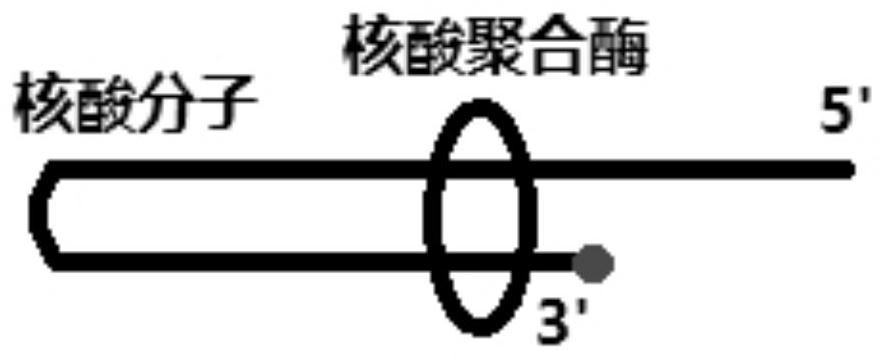
PendingCN113897366AReduce non-specific amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical treatment enzyme inactivationEnzymePolymerase
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and particularly discloses a nucleic acid ligand (nucleic acid polymerase substrate analogue) and application thereof. The nucleic acid ligand is a single nucleic acid molecule or a nucleic acid molecule analogue which forms complementary pairing in a molecule, or a single or two nucleic acid molecules or nucleic acid molecule analogues which form complementary pairing among molecules; and a 3' terminal of the nucleic acid ligand has modification for inhibiting extension of the 3' terminal of the nucleic acid ligand. According to the nucleic acid ligand provided by the invention, when an amplification reaction mixture is kept at or below a certain temperature, the enzyme activity of nucleic acid polymerase is inhibited by the nucleic acid ligand, and no residual enzyme activity exists. When the reaction mixture is heated, the nucleic acid polymerase is separated from the nucleic acid ligand, activity is exerted, and a primer extension product is formed, so that the effect of inhibiting non-specific amplifications is achieved. The nucleic acid ligand is applicable to all polymerases and can be widely applied to the field of nucleic acid amplification, so that the non-specific amplifications are reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU NUHIGH BIOTECH
Polymerase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN114574465AHigh synthesis efficiencyHigh detection sensitivityTransferasesAgainst vector-borne diseasesReverse transcriptaseBinding peptide
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a ZO5 DNA polymerase mutant and application thereof. According to the specific technical scheme, the ZO5 DNA polymerase mutant is obtained through mutation on the basis of ZO5 wild type polymerase, and the amino acid sequence of the ZO5 wild type polymerase is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; the mutation sites comprise E628K, I709L, E744R and A745R, and the mutation sites comprise E628K, I709L, E744R and The polymerase mutant provided by the invention can enlarge the ability of various activities including reverse transcriptase, and can catalyze reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification by using an RNA template. The polymerase mutant fused with the binding peptide has strong anti-interference capability, such as interference of chocolate, peanut butter, milk, seafood, meat or egg, chocolate, pepper, blood, urine, humic acid, bile, tannin, melanin, indigo dye, plant materials and the like; and the time required by LAMP can be effectively shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGQI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
Amplification method for 3'-RACE adaptor primer and 3'-end unknown gene sequences
InactiveCN107760678AStrong targetingAvoid lostMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNucleotideThymine
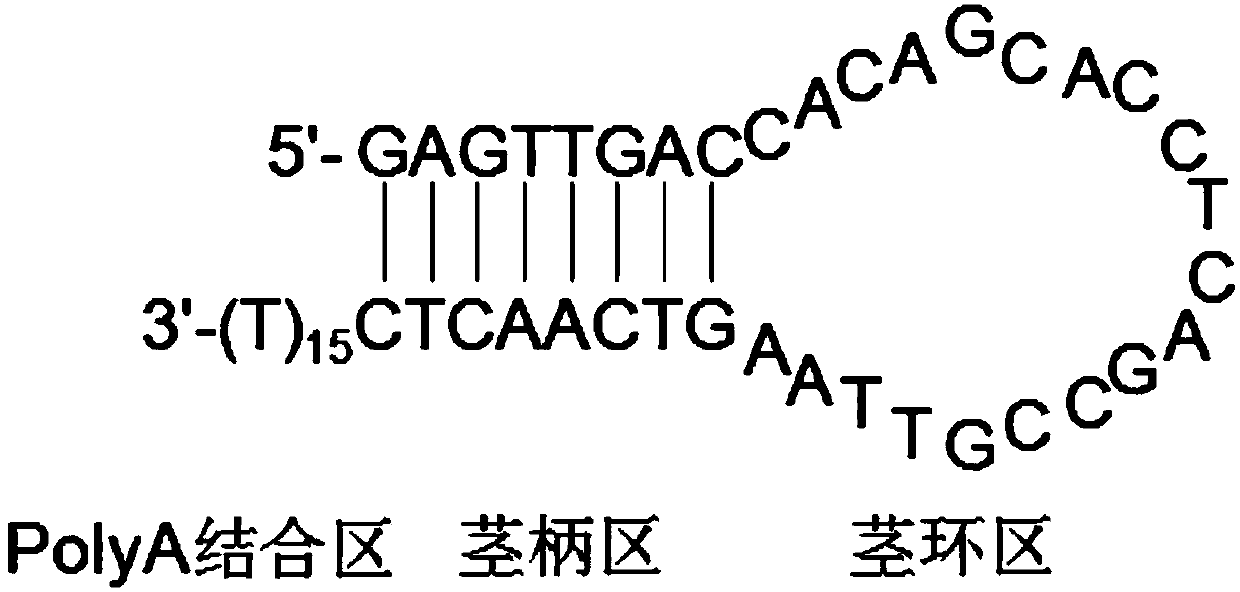
The invention discloses an amplification method for 3'-RACE adaptor primer and 3'-end unknown gene sequences. The 3'-RACE adaptor primer is of a stem-loop structure composed of a stem handle region, astem-loop region and a PolyA binding region; the stem handle region and the stem-loop region have a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1; and 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 continuous thymine are designed in the PolyA binding region. Two fragments of the stem handle region of the 3'-RACE adaptor primer have complementary sequence base so as to form a handle of the stem loop. Due to base stacking atthe handle, the stability of the primer is increased, and the reverse transcription efficiency is improved. A stem-loop configuration is formed due to a double-chain structure and self-complementaryproperty, so that hybridization between a reverse transcription primer and a target RNA template can be avoided, and background interference is reduced. More G / C bases are particularly inserted into the stem-loop region of the 3'-RACE adaptor primer, so that the annealing temperature is increased, and the non-specific PCR amplification is reduced.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
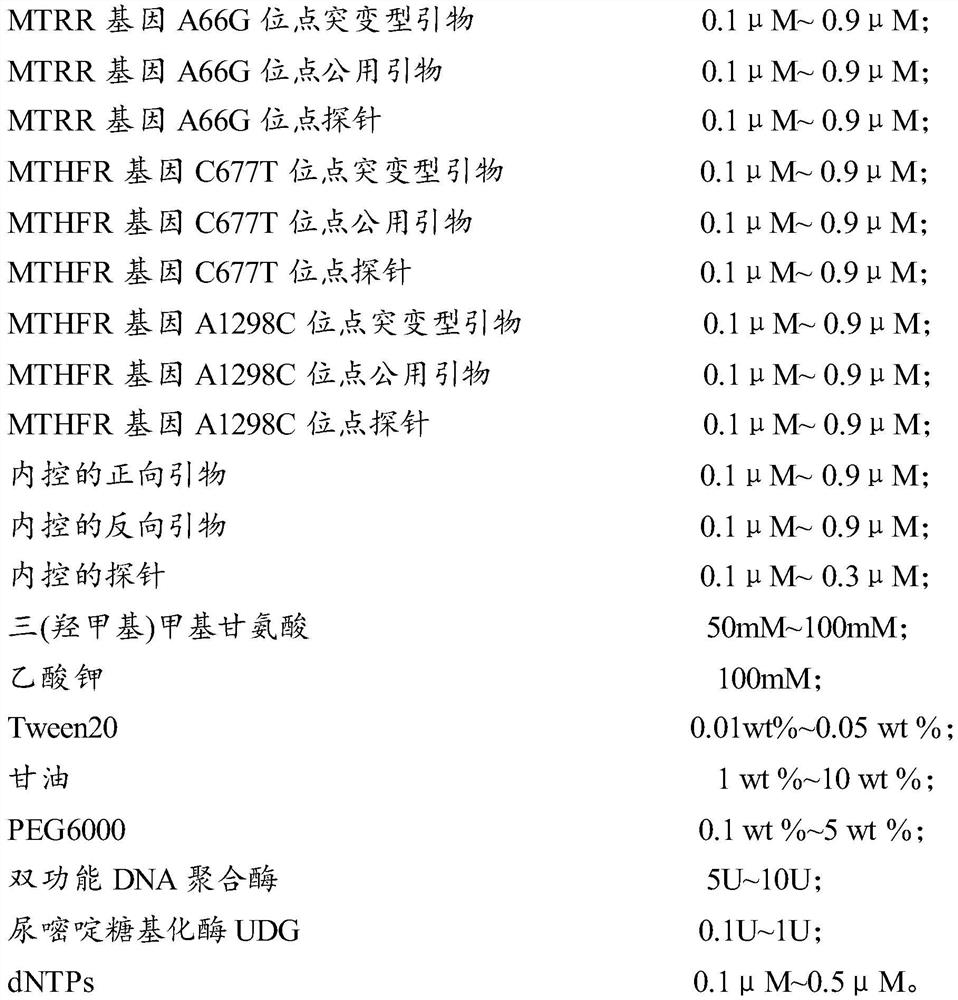
Kit for simultaneously detecting human MTHFR and MTRR genes
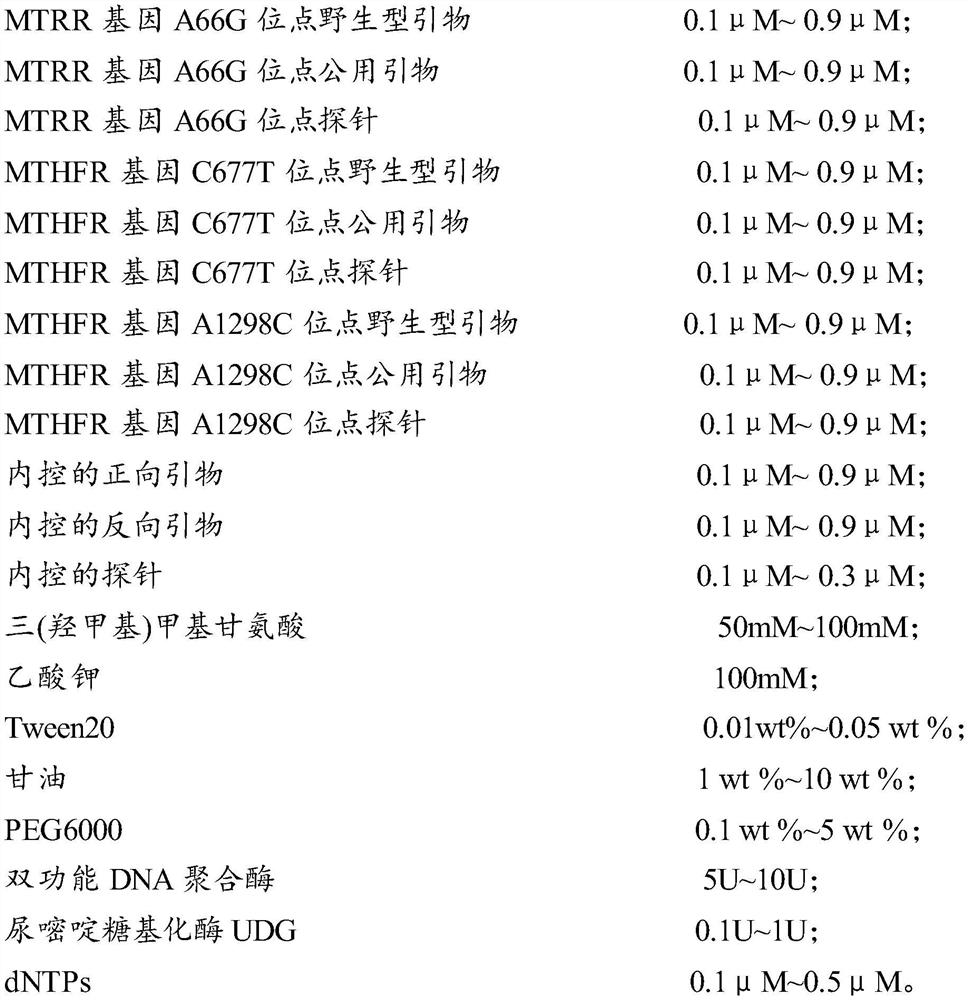
PendingCN111876482AStrong specificityCheap manufacturingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGlycerolPotentiator
The invention relates to the technical field of gene detection, in particular to a kit for simultaneously detecting human MTHFR and MTRR genes. The primer provided by the invention has good specificity, and the kit provided by the invention can simultaneously obtain detection results of three sites of C677T, A1298C and A66G in primary detection, so that sample preparation is saved, manual operation and secondary repeated detection are avoided, and the detection efficiency is greatly improved. By adding PCR protective agents namely Tween20 and glycerol, the denaturation of bifunctional DNA polymerase is effectively prevented, the enzyme stability and activity are improved, and the long-term stable preservation of an amplification reagent at 2-8 DEG C is realized. By adding a reinforcing agent PEG6000, the melting point and melting temperature of DNA are functionally reduced, non-specific amplification is reduced, the amplification efficiency is improved, and the detection of a sample iscompleted within 50 minutes.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Primer pair, probe and kit for detecting SLCO1B1 521T)C gene polymorphism
InactiveCN108977523AReduce design difficultyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSLCO1B1Fluorescence
The invention discloses a primer pair, a probe and a kit for detecting SLCO1B1 521T)C gene polymorphism. The kit comprises a primer and a fluorescence probe; the primer is designed for SLCO1B1 521T locus and has a base sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, wherein a 5'-base of the base sequence is equipped with an amino-modified group; the fluorescence probe is designed for SLCO1B1 521T locus and has the base sequence shown as SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No.4, wherein one basic group in the base sequence is equipped with the amino-modified group. Compared with the prior art, the kit disclosed by the invention adopts the amino modified primer and probe, further limits the detection time and is capable of obviously shortening the time required by detection, reducing non-specific amplification, detecting SNPs and point mutation, reducing design difficulty and detection cost without influence on diagnosis accuracy, realizing a method for detecting mutation without opening a single reaction tube, extremely avoiding aerosol pollution, bringing convenience to clinic application and reducing the error caused by operation.
Owner:东莞博盛生物科技有限公司
Application of single primer amplification library building technology in detection of fragmented rare DNA molecular mutation and kit
PendingCN114807324AReduce non-specific amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationNucleotideCirculating tumor DNA
The invention discloses application of a single-primer amplification library building technology in detection of fragmented rare DNA molecular mutation.The single-primer amplification library building technology comprises the following steps that target DNA is linearly amplified through a specific primer, a linear amplification product is obtained, and the 3'terminal nucleotide of the specific primer contains a bicolor functional group; linker connection is conducted on the linear amplification product, a linker connection product is obtained, and a linker connection system comprises single-chain ligase and a single-chain linker. The invention also discloses a kit / reagent for high-sensitivity detection of rare DNA molecular mutation. According to the method, rare mutant molecules with extremely low abundance in a sample can be detected with high sensitivity, and circulating tumor DNA molecules in a blood sample of an early-stage cancer patient can be detected at the same time.
Owner:APOGENOMICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com