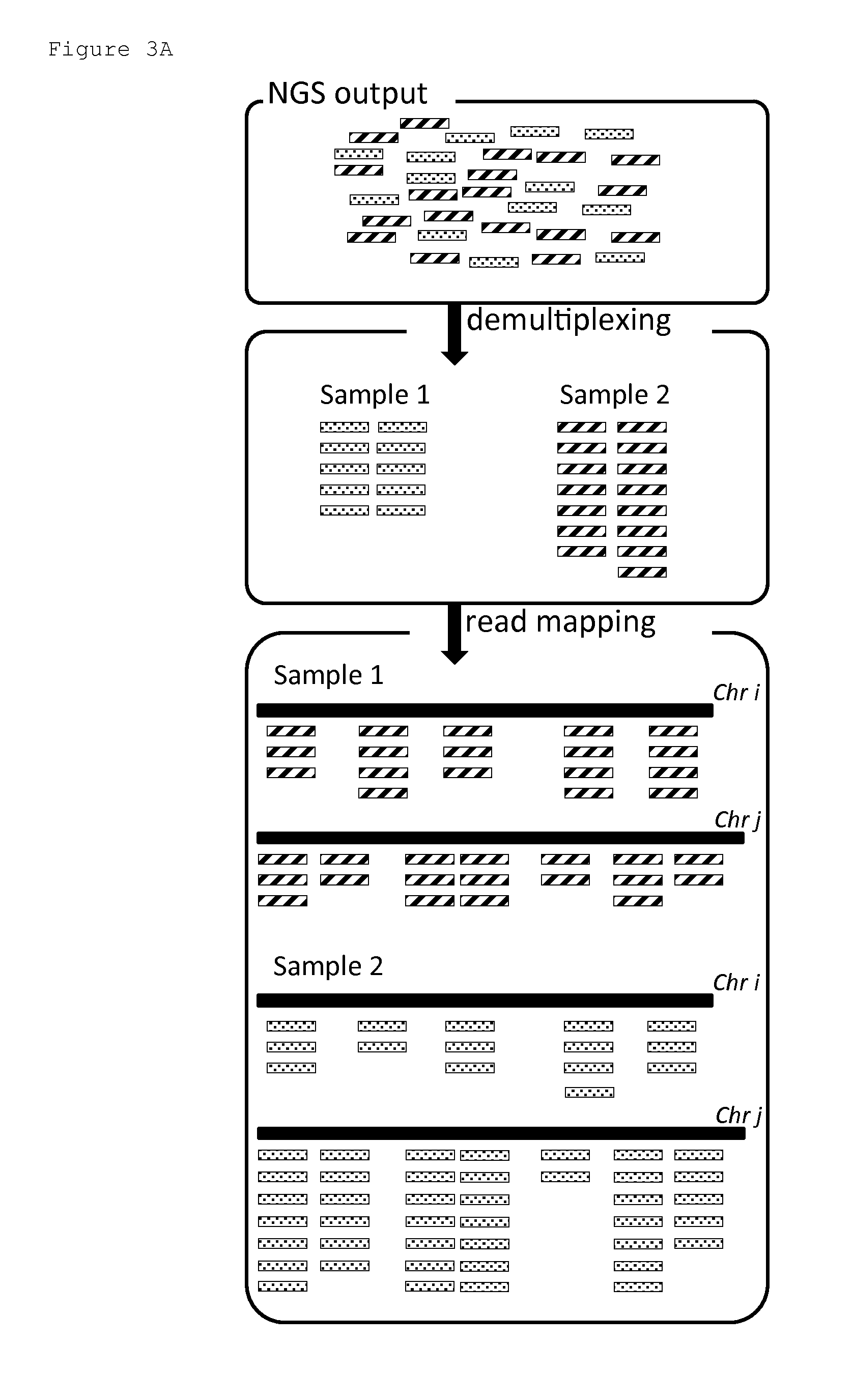
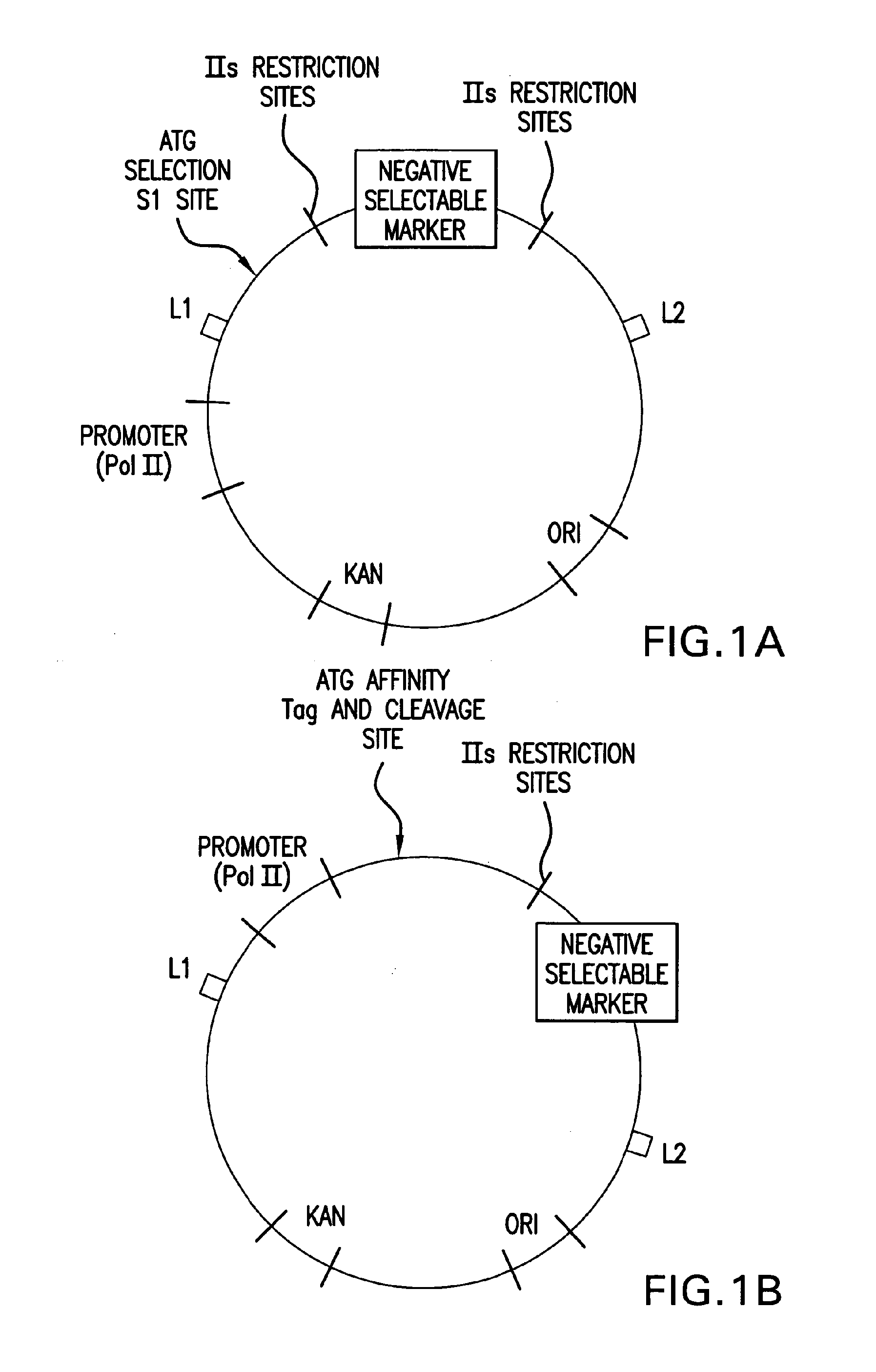
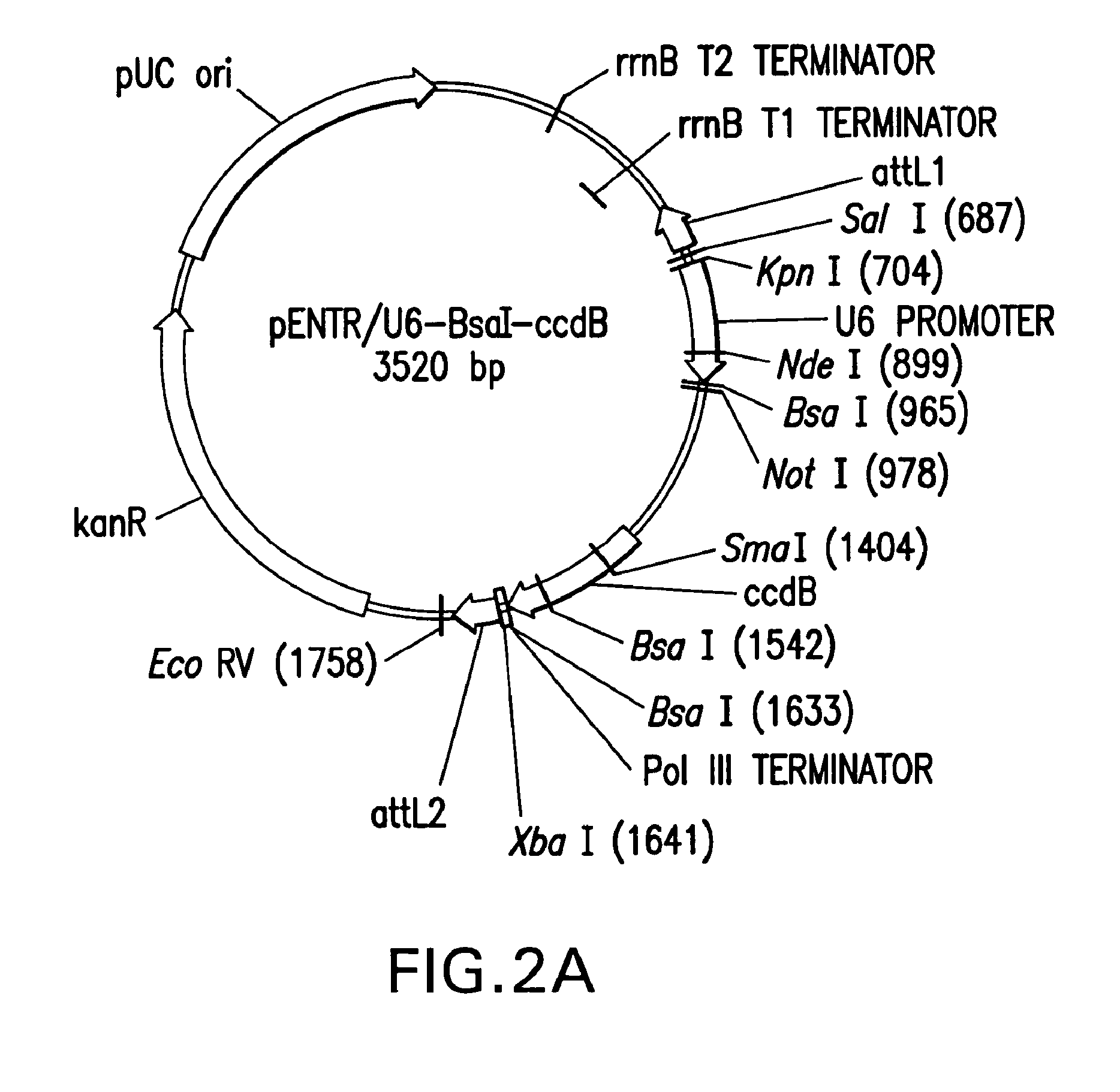
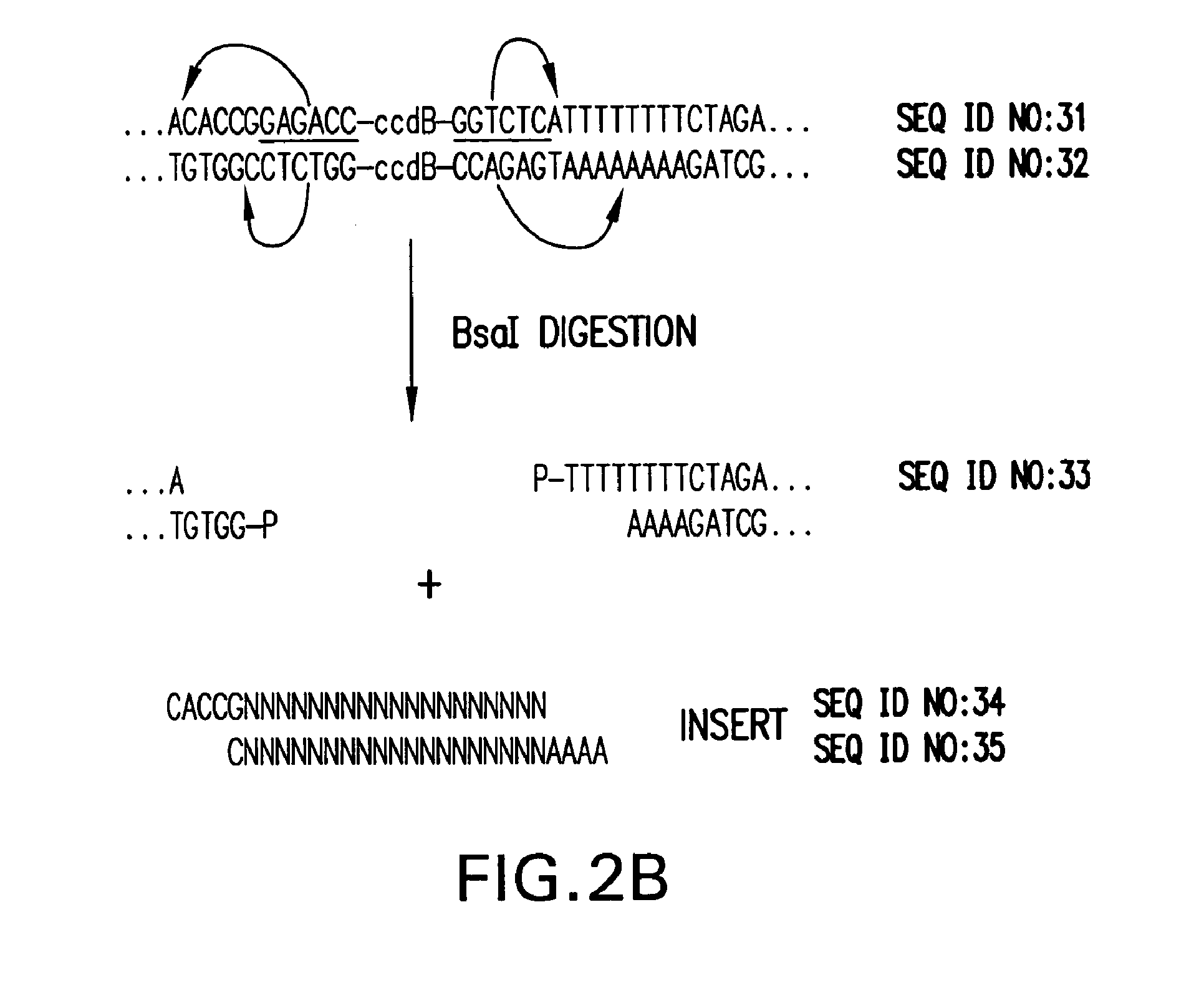
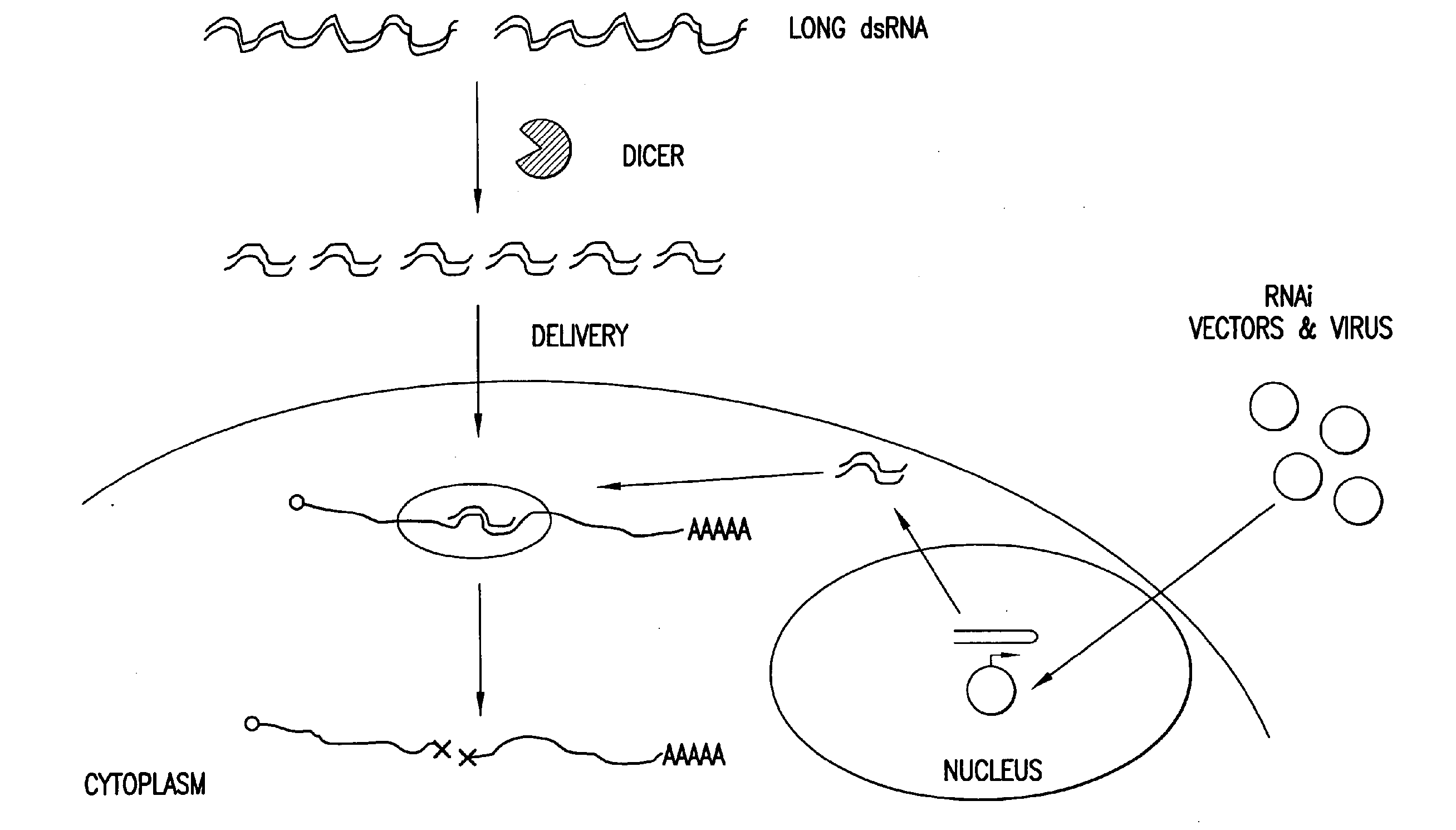
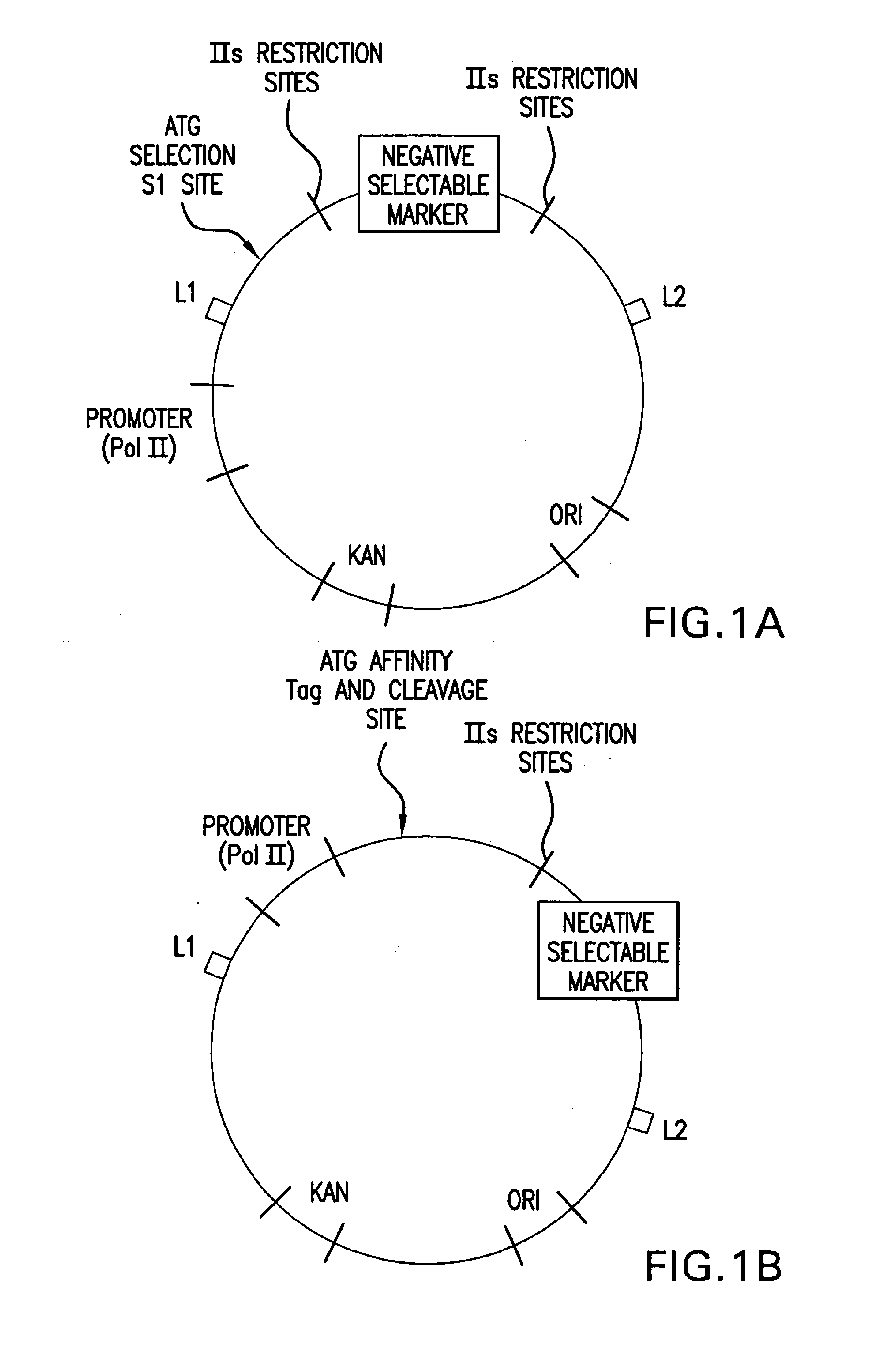
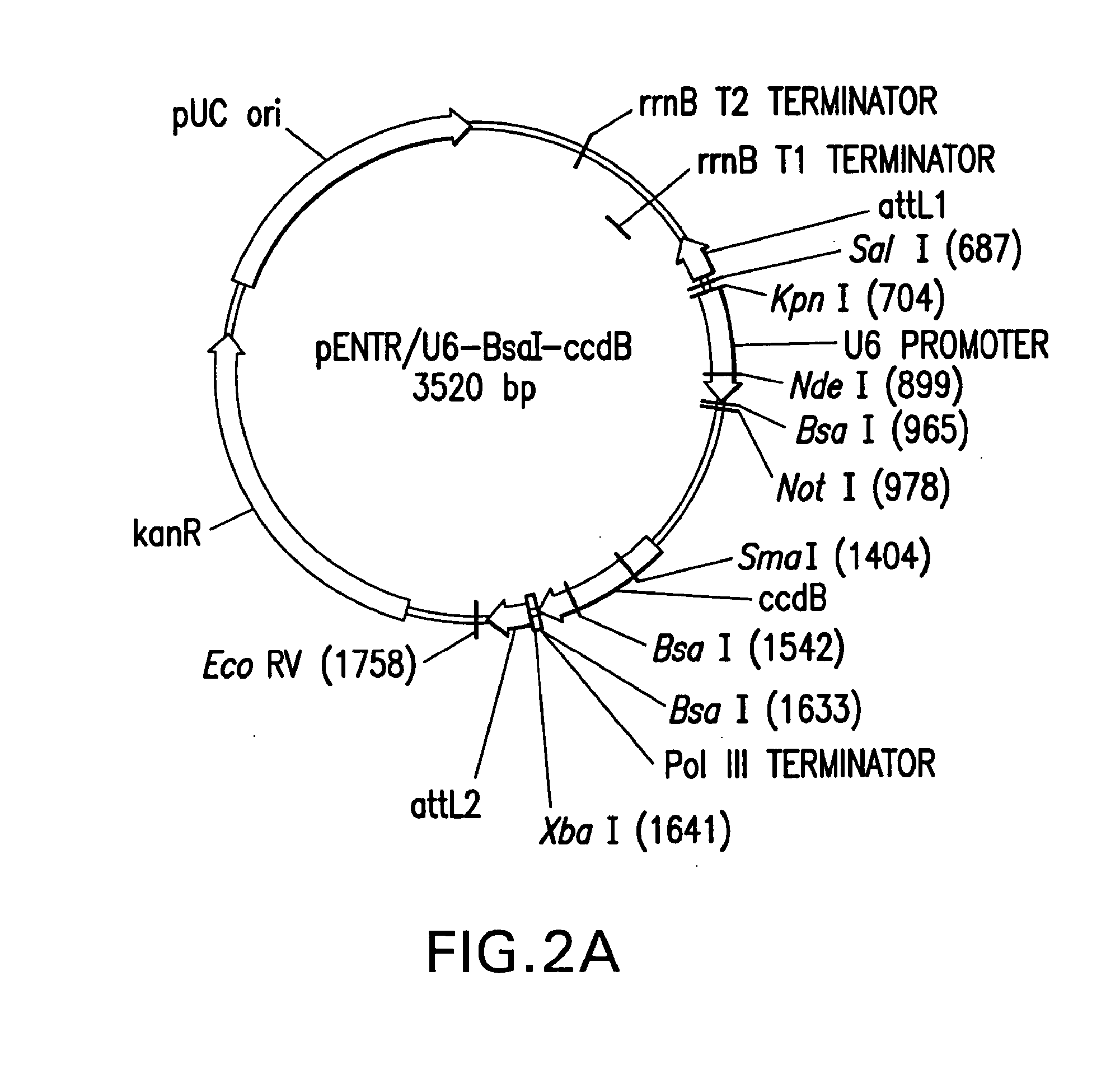
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Restriction Enzyme Recognition Site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
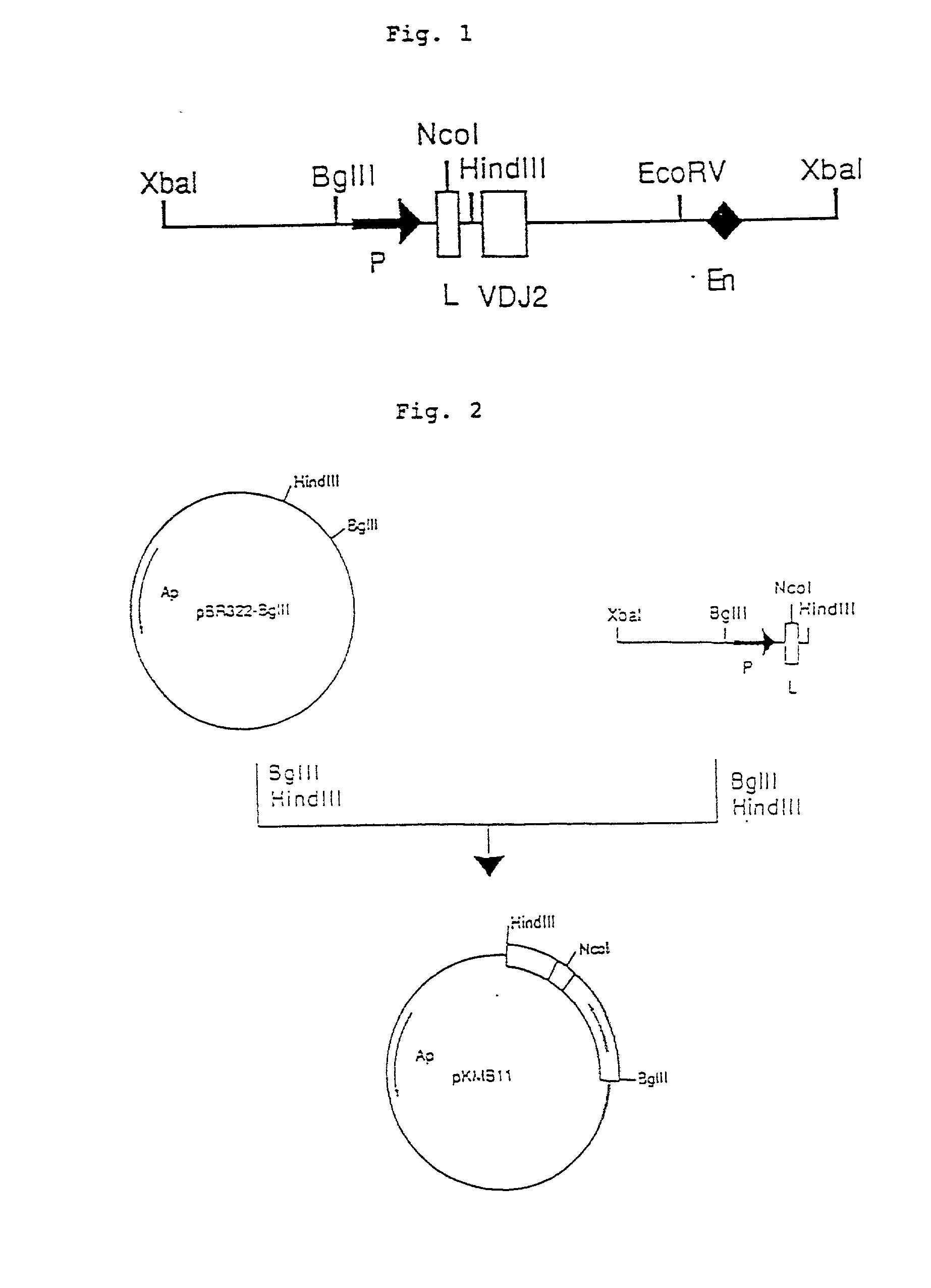
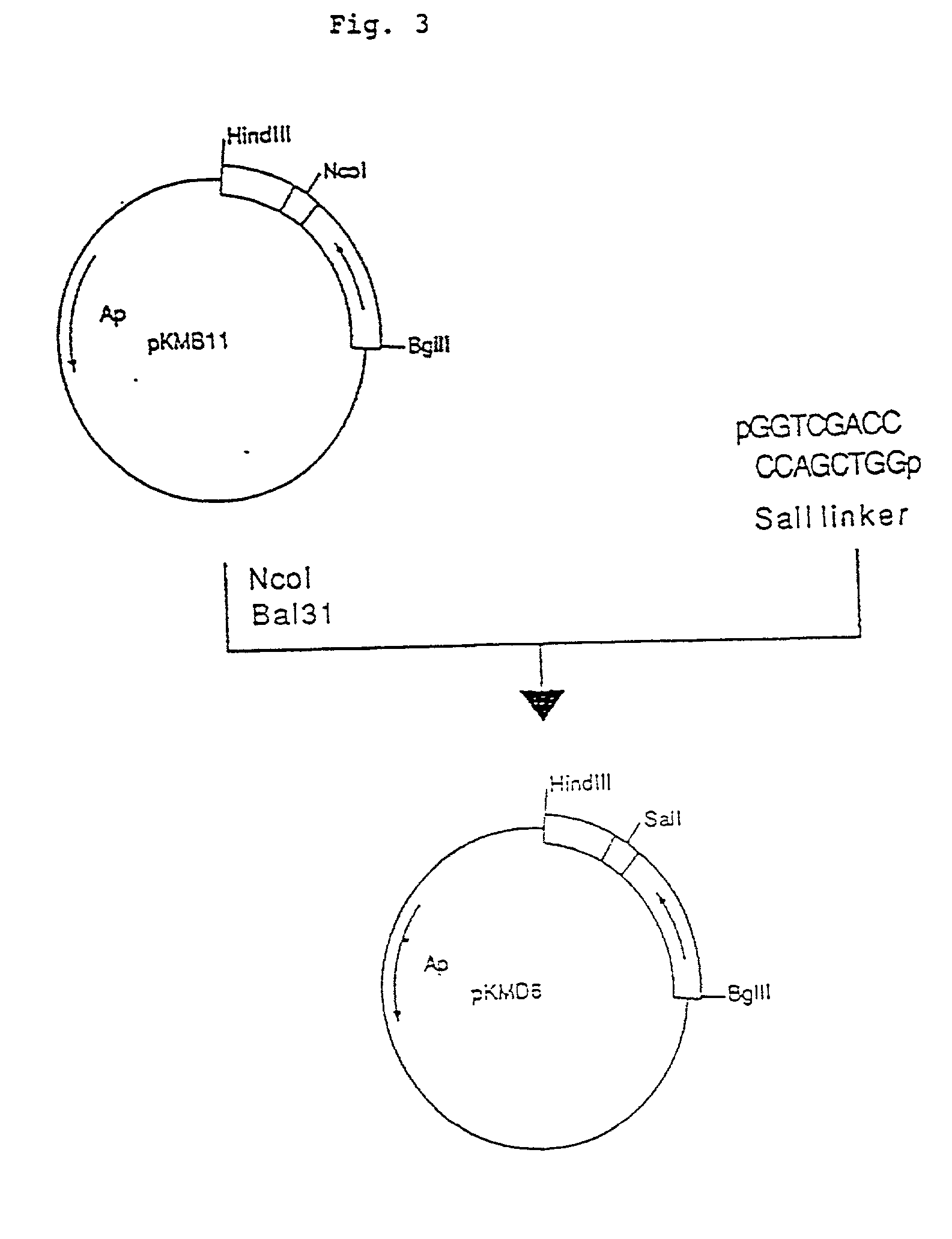
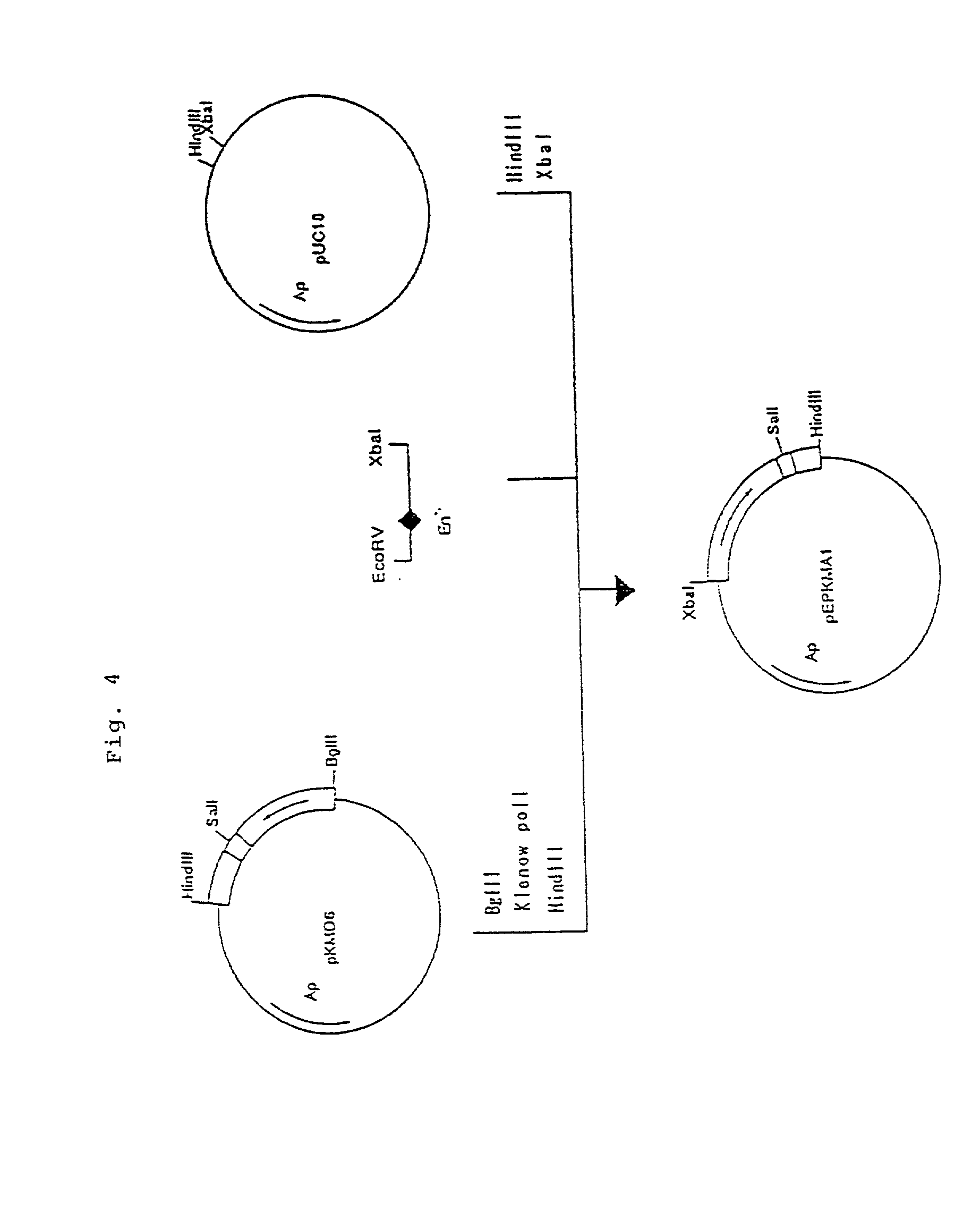
Process for producing humanized chimera antibody
InactiveUS20020026036A1Easy to produceEasy constructionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRestriction enzyme digestionSynthetic DNA
A process for the production of humanized chimera antibody, wherein the chimera antibody is produced easily without changing any of the amino acids of its mouse antibody variable region, which comprises the steps of: (1) constructing a cassette vector by inserting a cDNA coding for a heavy chain constant region of human antibody into an expression vector for animal cell use and establishing a cloning site in the upstream region of the heavy chain constant region of said cassette vector for inserting a cDNA which encodes a heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody; (2) digesting a cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody with restriction enzymes; (3) inserting said cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody into the cassette vector, using a synthetic DNA which comprises a base sequence corresponding to the 5'-end side of said heavy chain constant region of human antibody and a base sequence corresponding to the 3'-end side of said heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody and is possessed of the restriction enzyme recognition sites on both of its ends, thereby constructing a humanized chimera antibody heavy chain expression vector in which said cDNA coding for the heavy chain constant region of human antibody and said cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody are linked together through said synthetic DNA; (4) constructing a cassette vector by inserting a cDNA coding for a light chain constant region of human antibody into an expression vector for animal cell use and establishing a cloning site in the upstream region of the light chain constant region of said cassette vector for inserting a cDNA which encodes a light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody; (5) digesting a cDNA coding for the light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody with restriction enzymes; (6) inserting said cDNA coding for a light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody into the cassette vector using a synthetic DNA which comprises a base sequence corresponding to the 5'-end side of said light chain constant region of human antibody and a base sequence corresponding to the 3'-end side of said light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody and is possessed of the restriction enzyme recognition sites on both of its ends, thereby constructing a humanized chimera antibody light chain expression vector in which said cDNA coding for the light chain constant region of human antibody and said cDNA coding for the light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody are linked together through said synthetic DNA; (7) introducing these expression vectors into host cells to obtain a transformant; and (8) culturing said transformant in an appropriate culture medium, thereby allowing the transformant to produce and accumulate a humanized chimera antibody, and collecting said humanized chimera antibody from the resulting culture broth.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Diagnostic Method
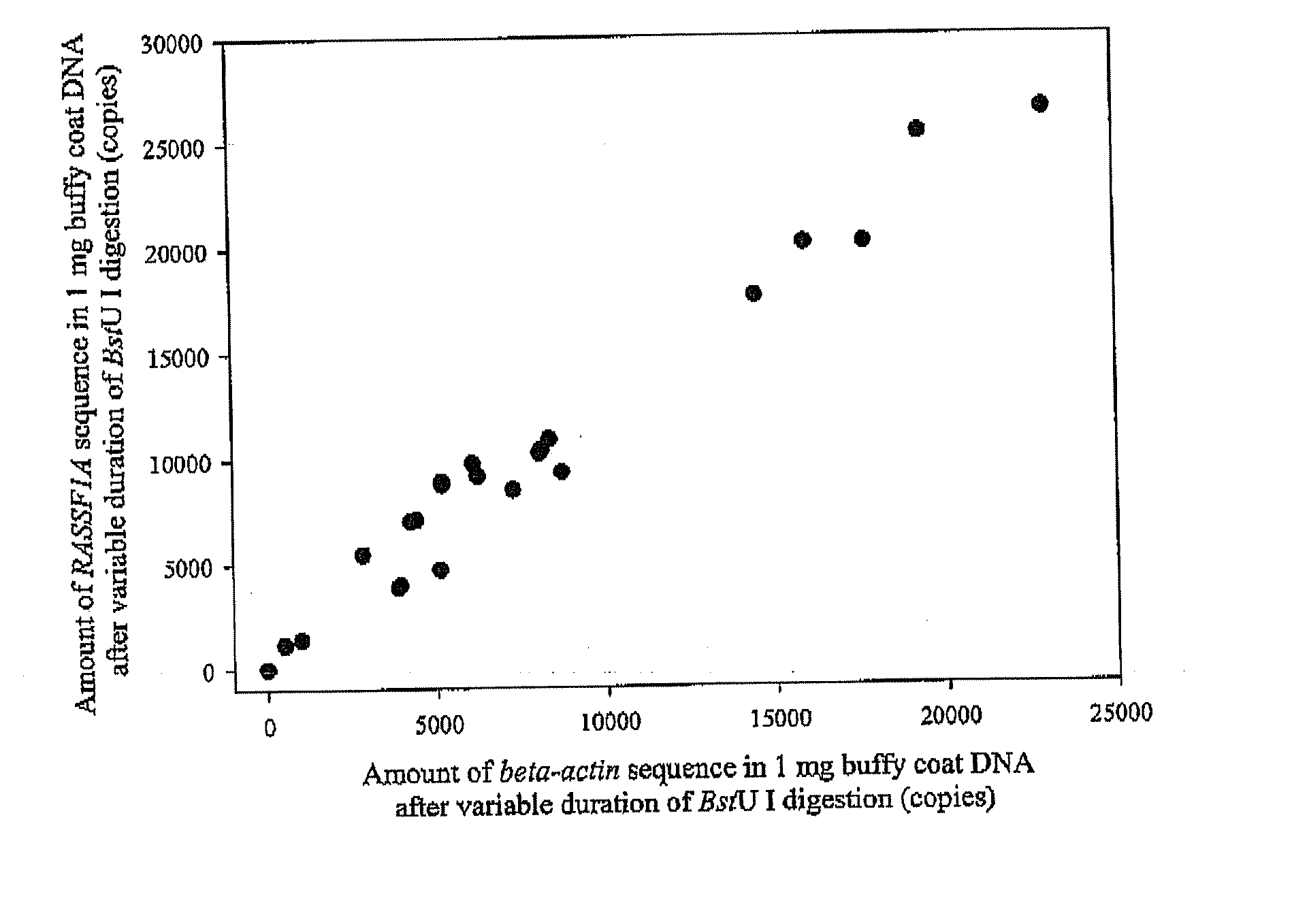
ActiveUS20080081338A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionA-DNA
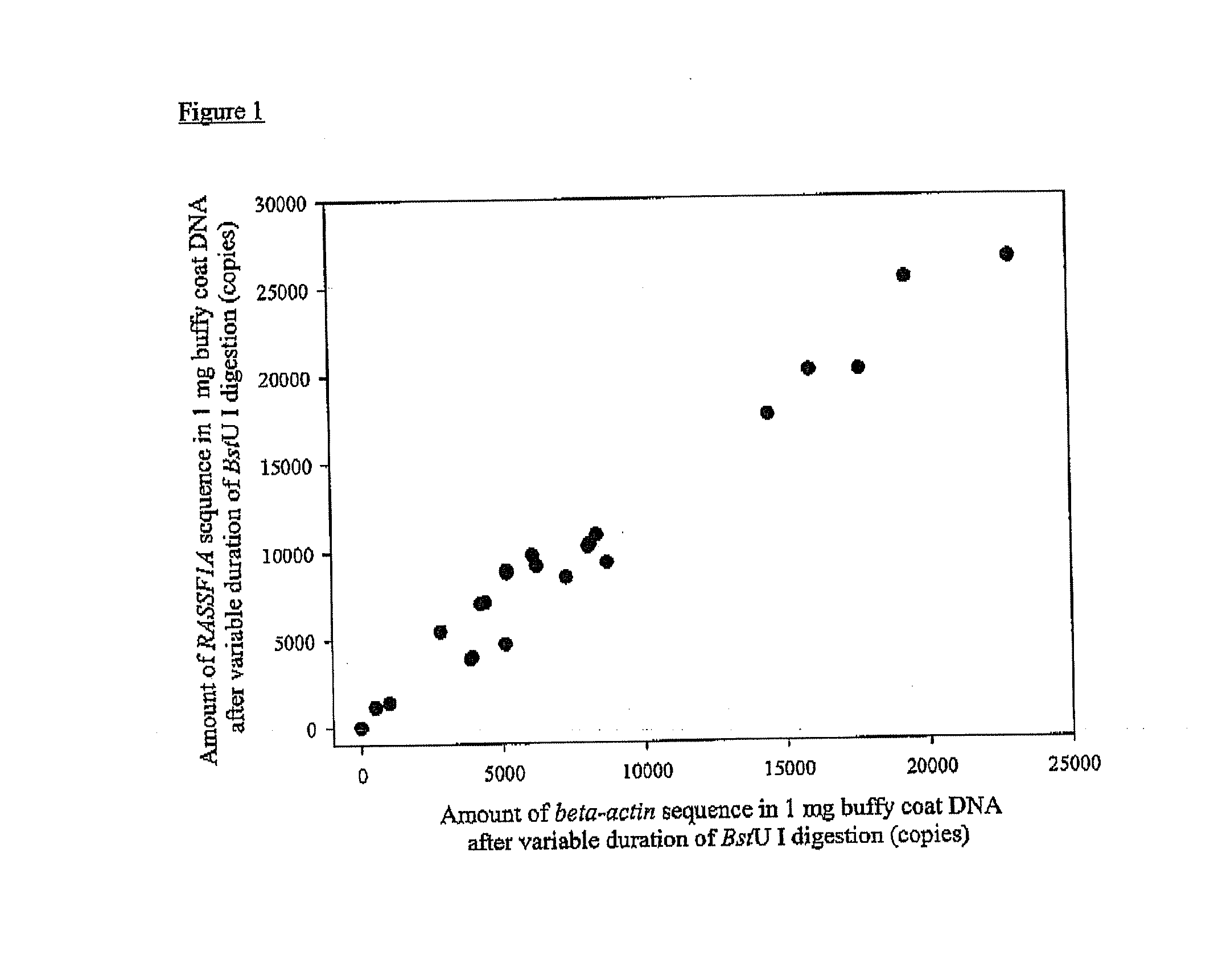
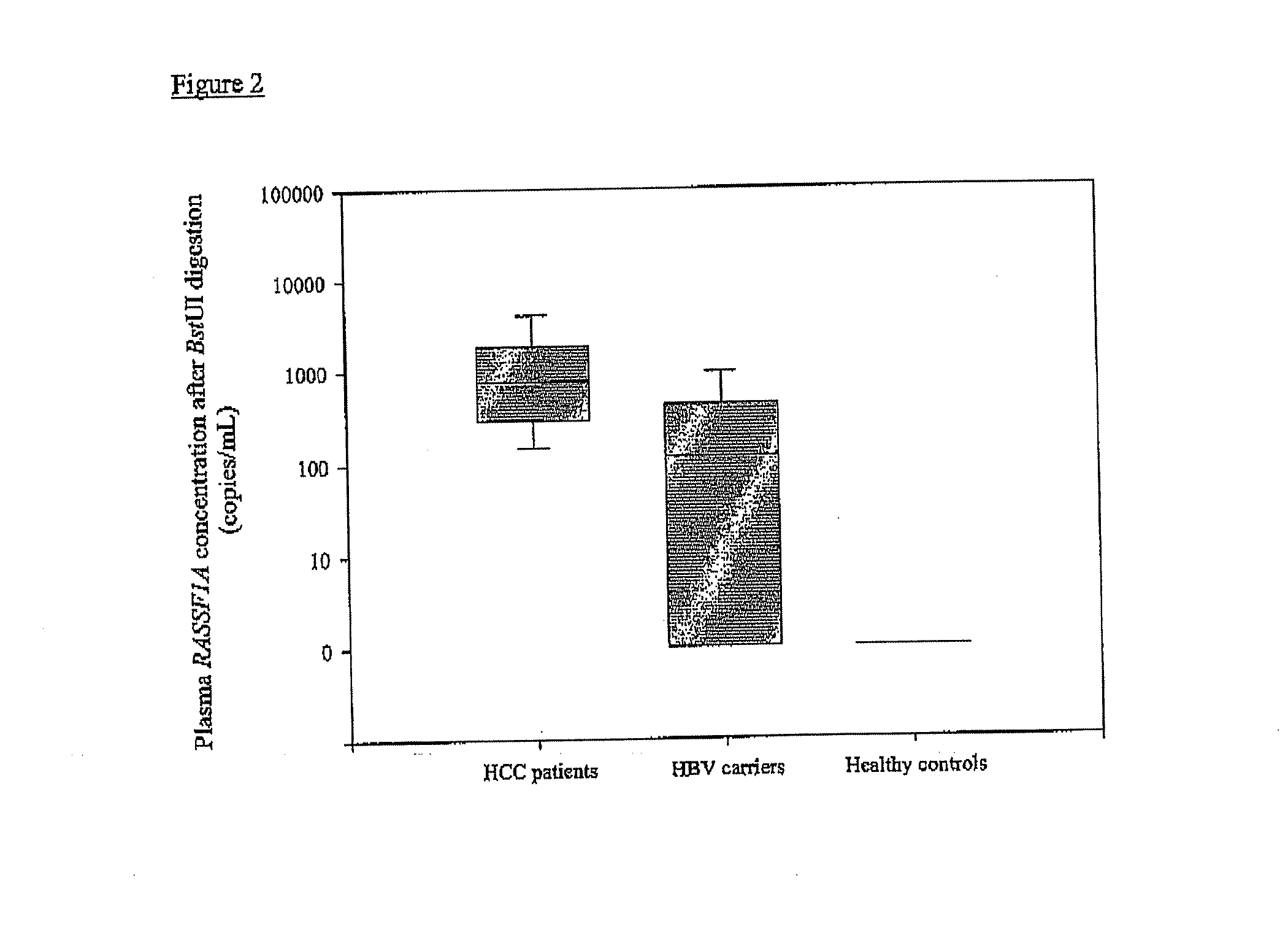
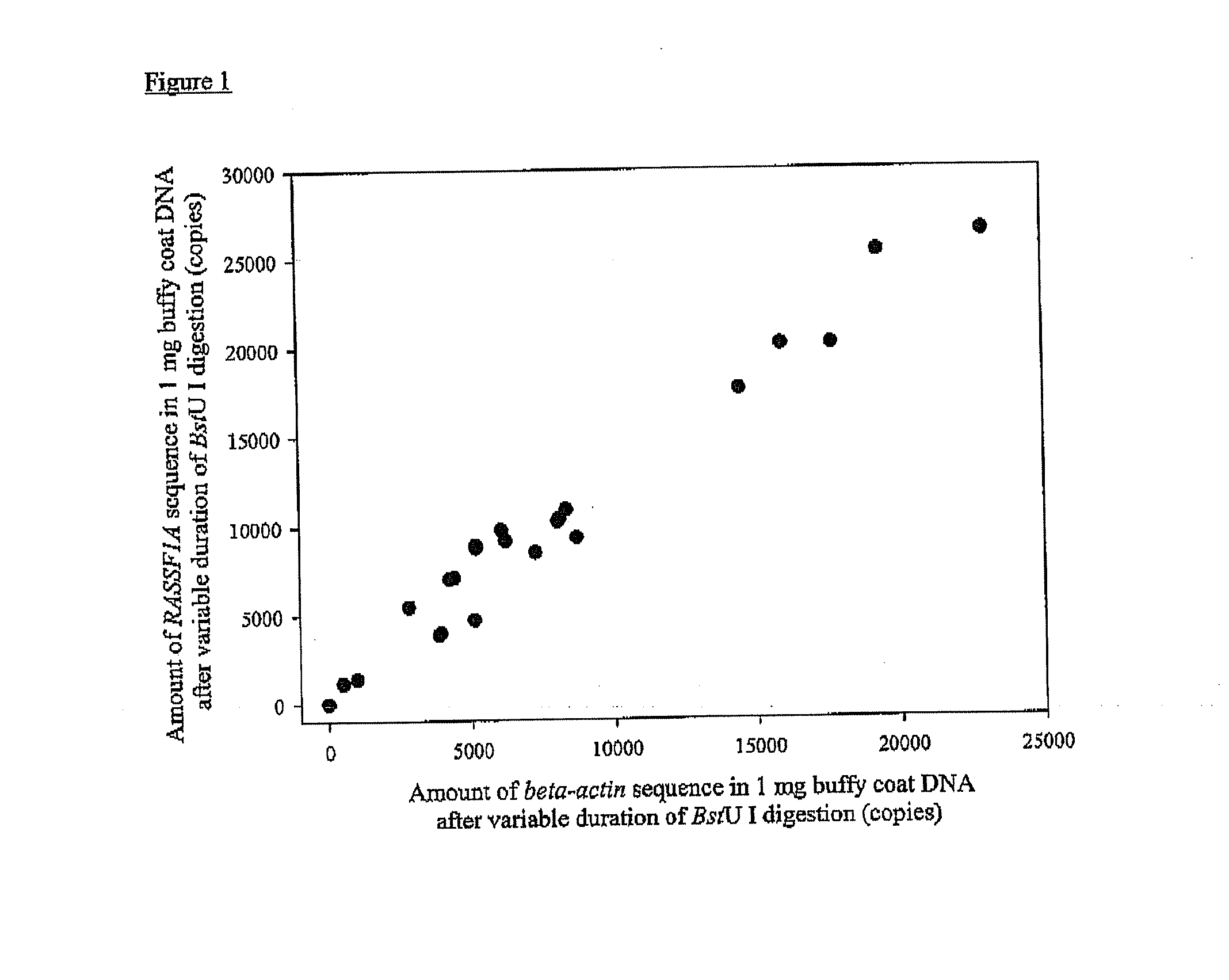
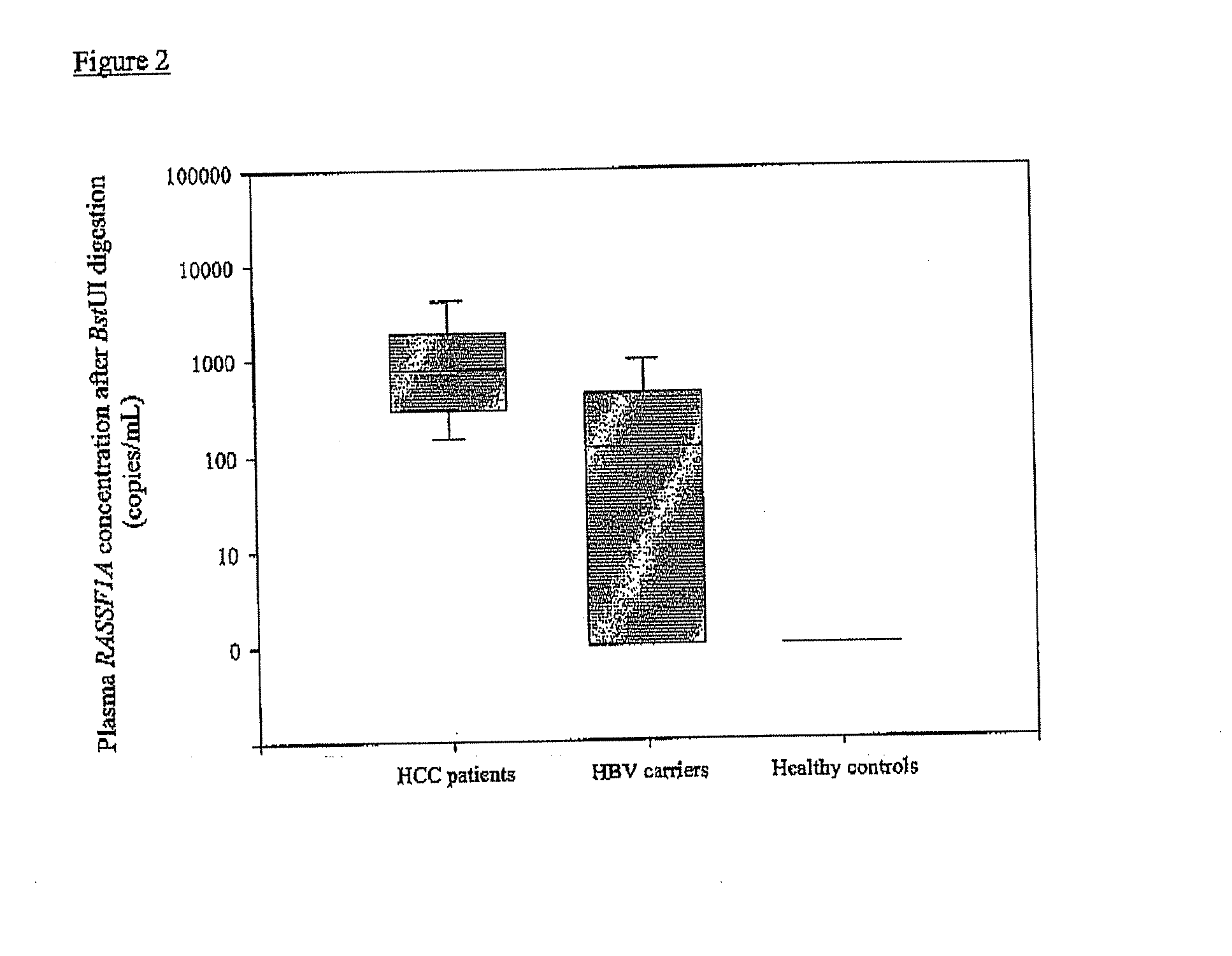
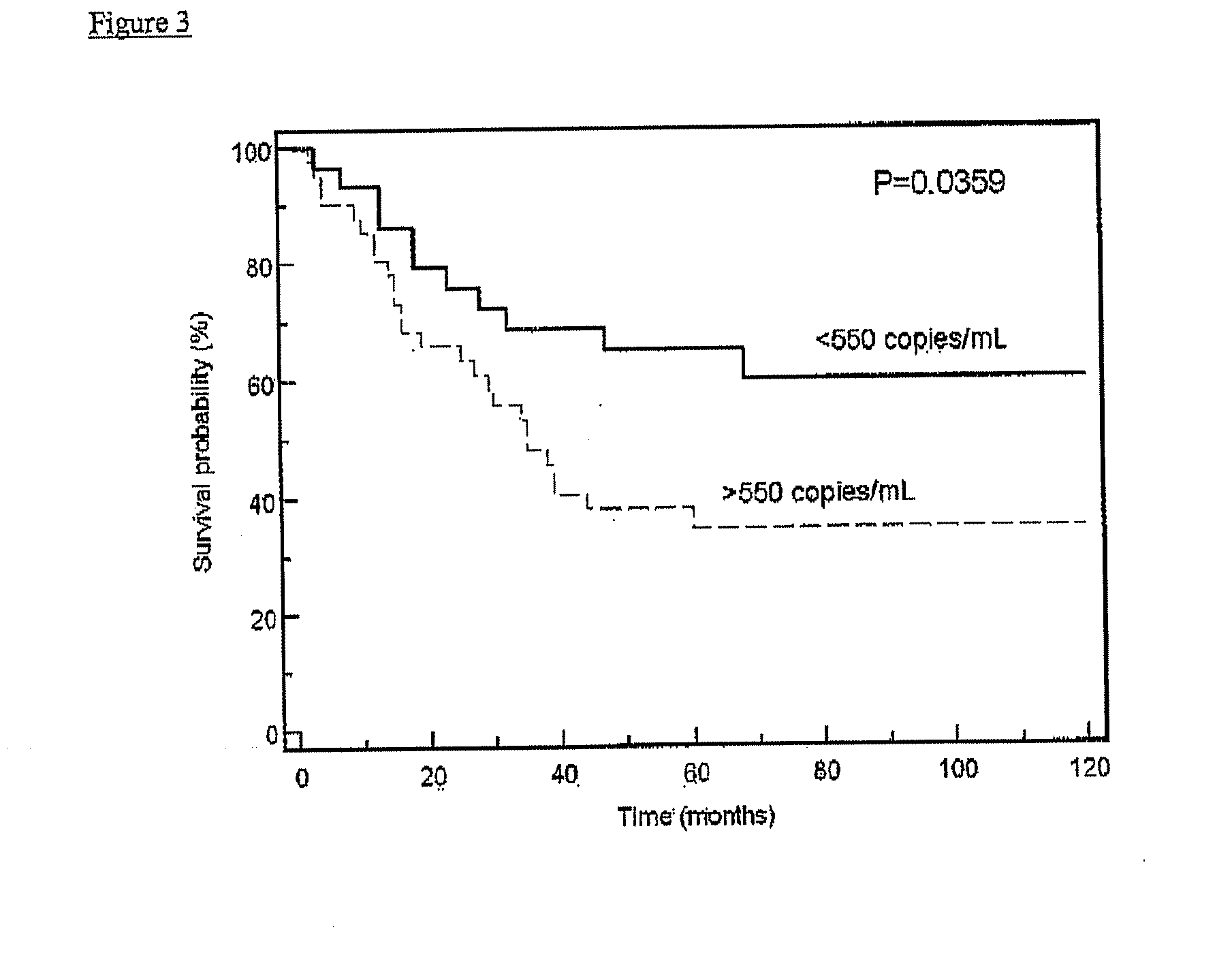
The present invention concerns a method for the detection or monitoring of cancer using a biological sample selected from blood, plasma, serum, saliva, urine from an individual, said method comprising: (a) obtaining DNA from the said biological sample; (b) digesting the DNA sample with one or more methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes; (c) quantifying or detecting a DNA sequence of interest after step (b), wherein the target sequence of interest contains at least two methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme recognition sites; and (d) comparing the level of the DNA sequence from the individual to a normal standard, to detect, prognosticate or monitor cancer.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods for multipart, modular and scarless assembly of DNA molecules
InactiveUS20140038240A1Accurate and cost-effective engineeringHydrolasesFermentationModularityRestriction Enzyme Recognition Site
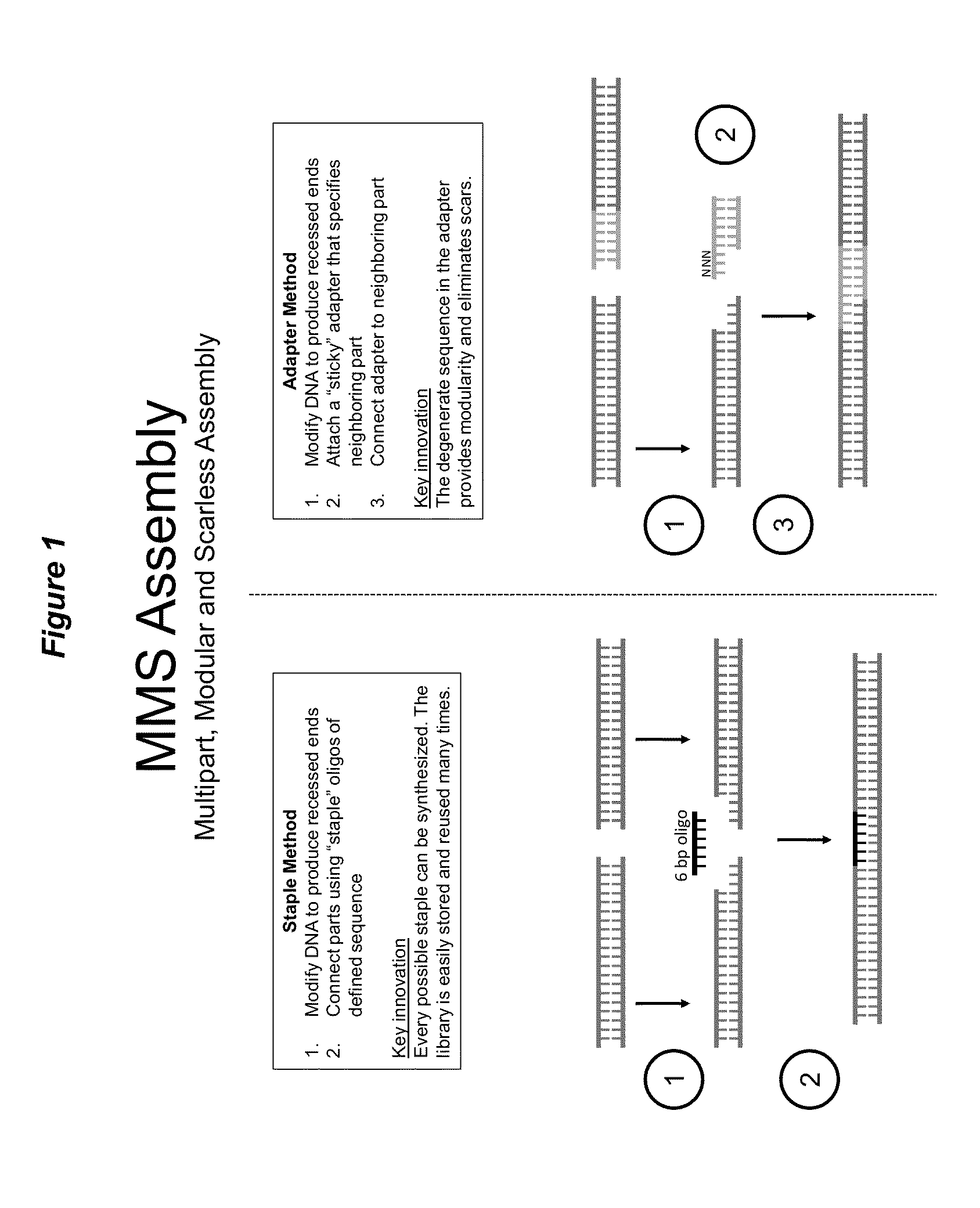
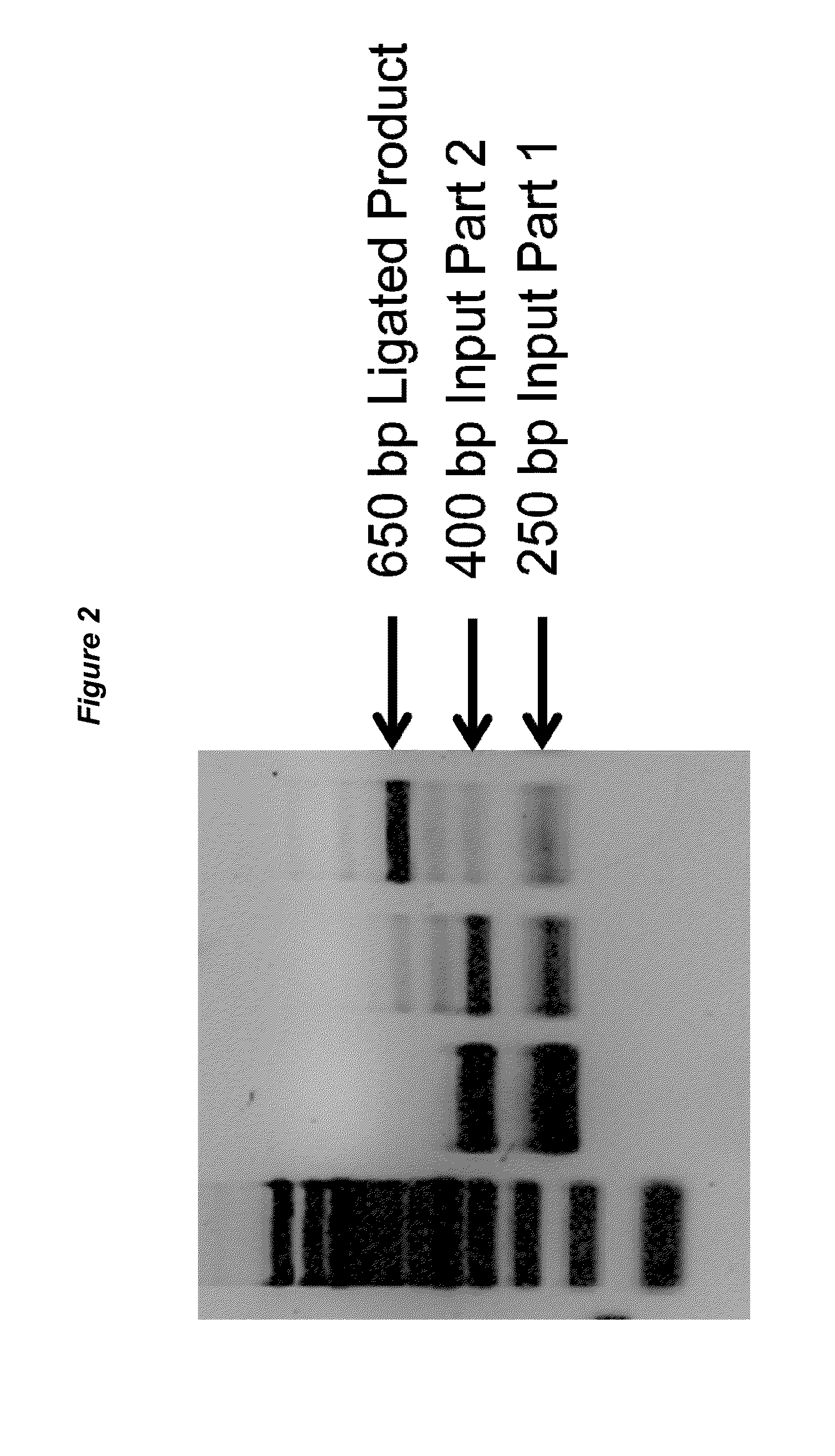
The present invention consists of methods for joining DNA molecules (parts) together to form larger DNA molecules (assemblies) of specified sequence and organization. The invention exhibits three necessary characteristics. Firstly, the invention enables 2 or more parts to be joined in a single reaction. Secondly, the seam between joined parts is scarless, producing no residual sequence dependencies like restriction enzyme recognition sites. Thirdly, parts are modular and can easily be reused in novel assemblies without modification. Prior technologies have exhibited no more than two of the three necessary characteristics, limiting their utility in synthesizing and editing DNA molecules of arbitrary sequence.
Owner:PIVOT BIO
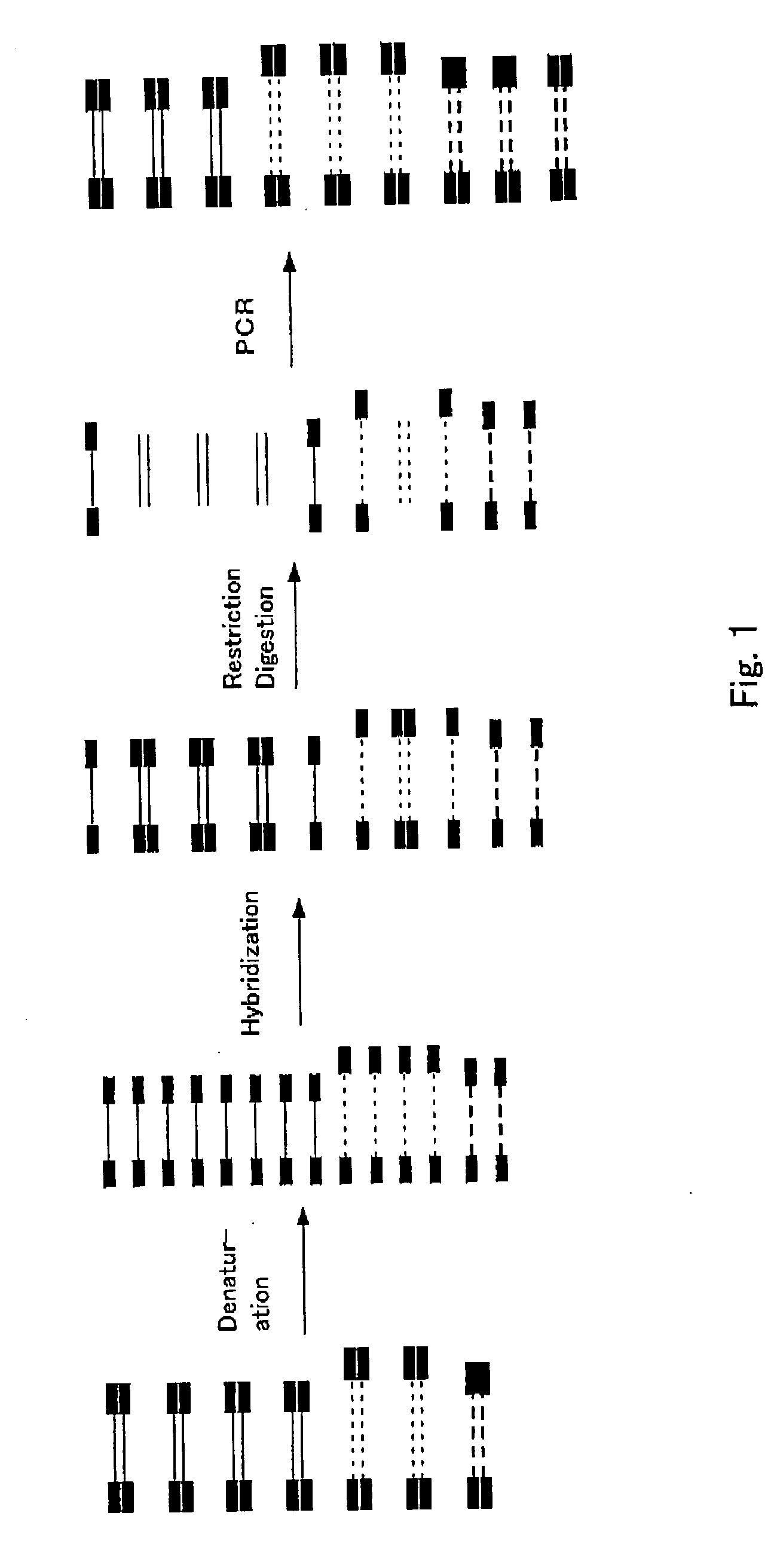
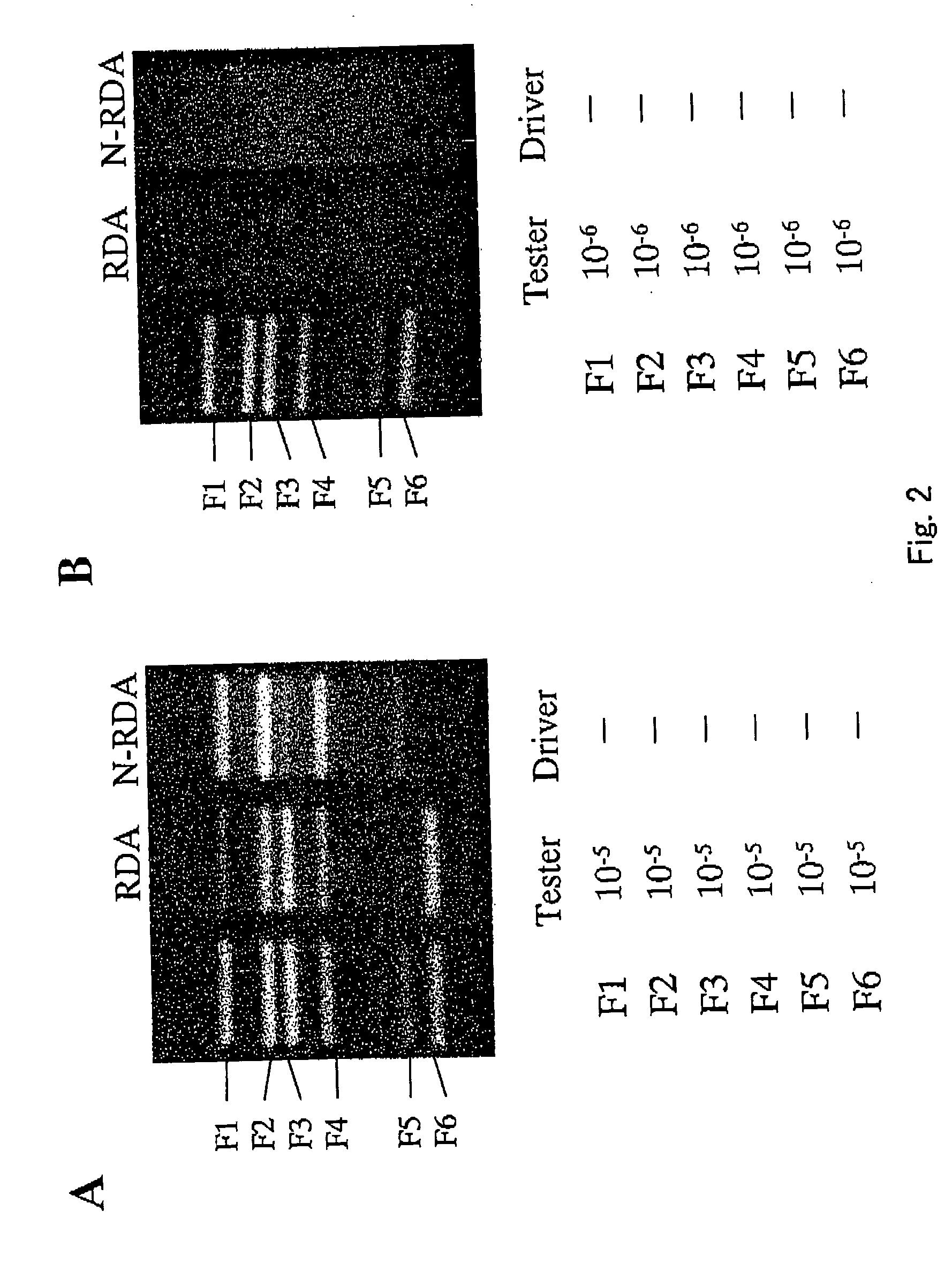
Method of uniformizing dna fragment contents and subtraction method
A method of normalizing contents of DNA fragments in a sample among respective DNA fragments, comprising: preparing DNA fragments in which adaptors each comprising an oligodeoxyribonucleotide are attached to both ends of each DNA fragment in the sample to form restriction enzyme recognition sites that do not exist in the DNA fragments in the sample, and at least a part between the restriction enzyme recognition sites at both ends, including the restriction enzyme recognition sites, is double-stranded; denaturing the prepared double-stranded DNA fragments; hybridizing the denatured DNA fragments under a condition that a part of the DNA fragments remains single-stranded; cleaving the hybridized double-stranded DNA fragments with a restriction enzyme having a cleavage site exclusively in the adaptors; and performing PCR using the obtained DNA fragments as templates and using a primer having a nucleotide sequence complementary to a nucleotide sequence of the adaptors before the cleavage; and a subtraction method comprising performing normalization by the method.
Owner:EISAI CO LTD
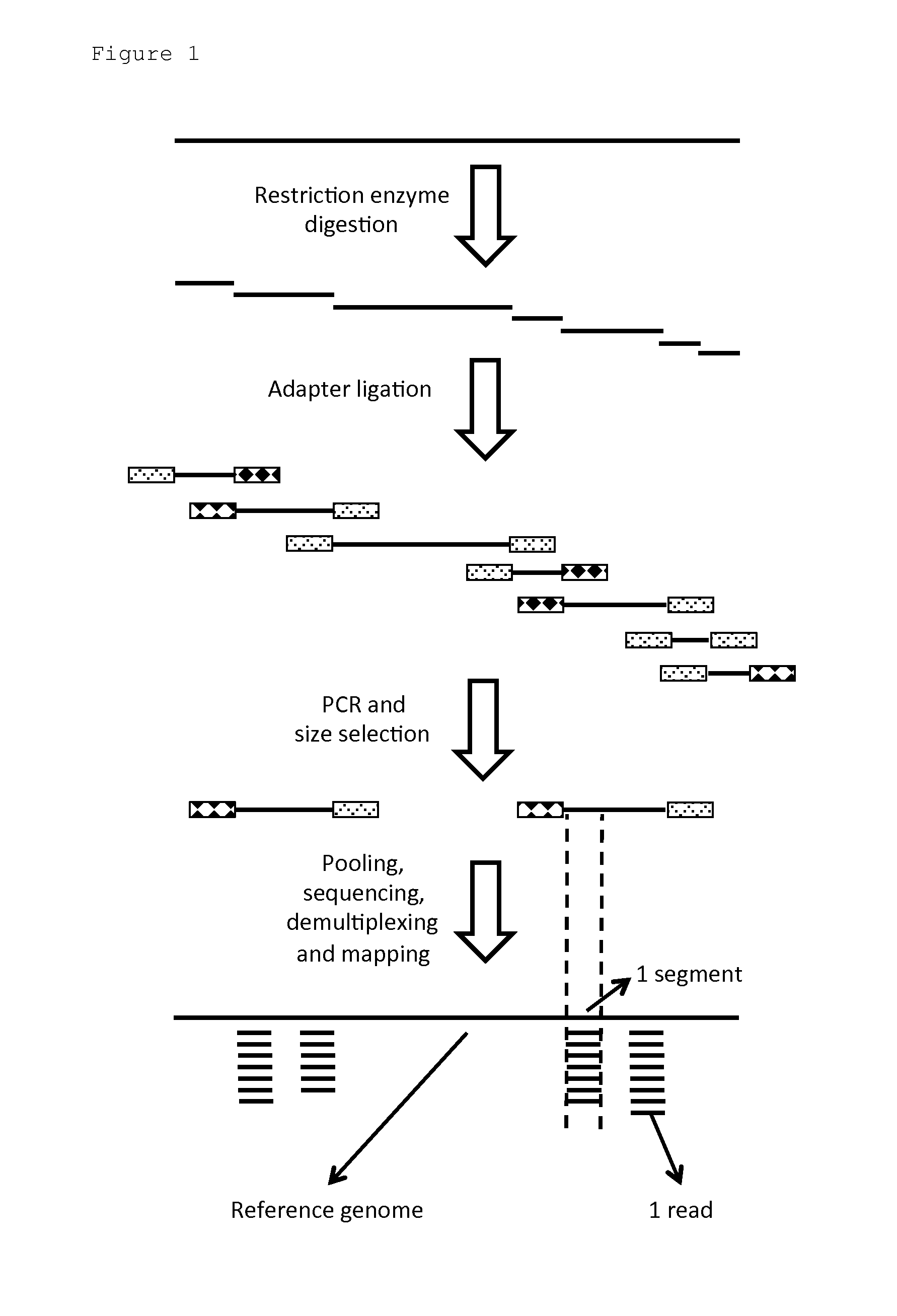
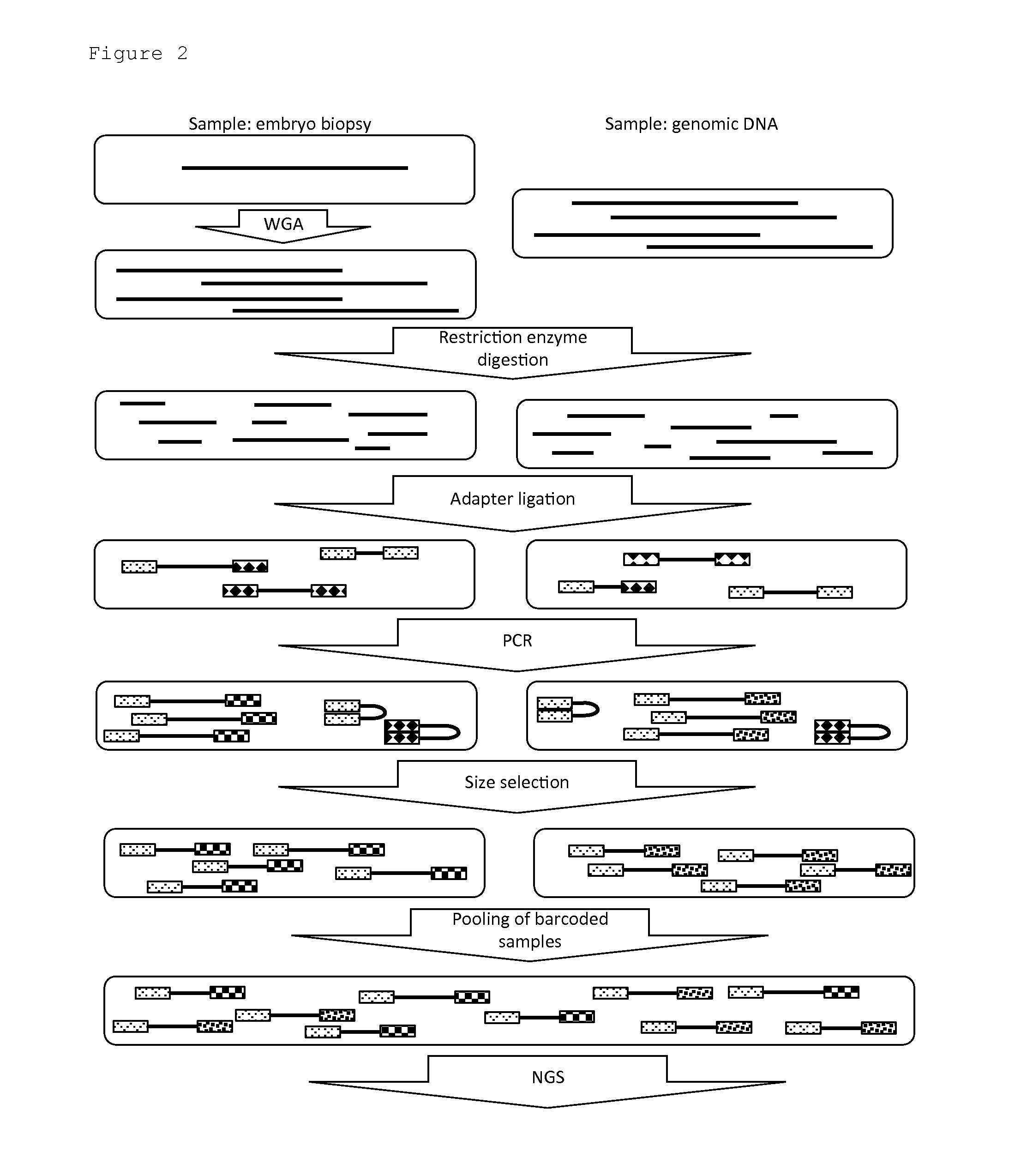
Genetic analysis method
InactiveUS20160275239A1Easy and quick interpretationImprove computing efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsRestriction Enzyme Recognition SiteAnalysis method
A method of target DNA genome analysis is provided. The method comprises the steps of: —obtaining non-overlapping segments of target DNA stretches with segment boundaries defined by the presence of particular restriction enzyme recognition sites, whereby the assembly of said non-overlapping segments compose a reduced representation library of said target DNA genome; —obtaining for said segments, raw metrics from a sequencing process applied on said reduced representation library; —clustering non-overlapping, nearby segments with similar raw metrics to provide master segments; —providing metrics describing the master segments, —making a final discrete DNA call based on the master segments and its metrics.
Owner:AGILENT TECH BELGIUM NV
Methods and compositions for seamless cloning of nucleic acid molecules
ActiveUS8338091B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSubcloningRestriction Enzyme Recognition Site
The present invention is in the fields of biotechnology and molecular biology. More particularly, the present invention relates to cloning or subcloning one or more nucleic acid molecules comprising one or more type IIs restriction enzyme recognition sites. The present invention also embodies cloning such nucleic acid molecules using recombinational cloning methods such as those employing recombination sites and recombination proteins. The present invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules (including RNA and iRNA), as well as proteins, expressed from host cells produced using the methods of the present invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) multi-site directed mutation method
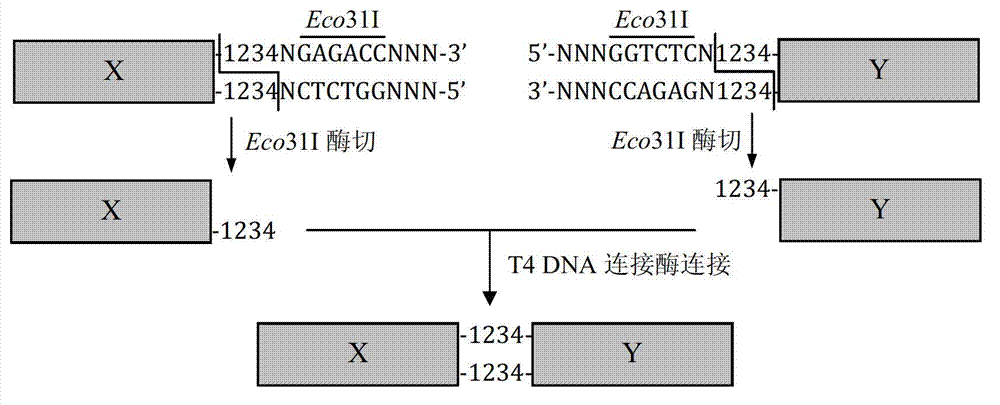
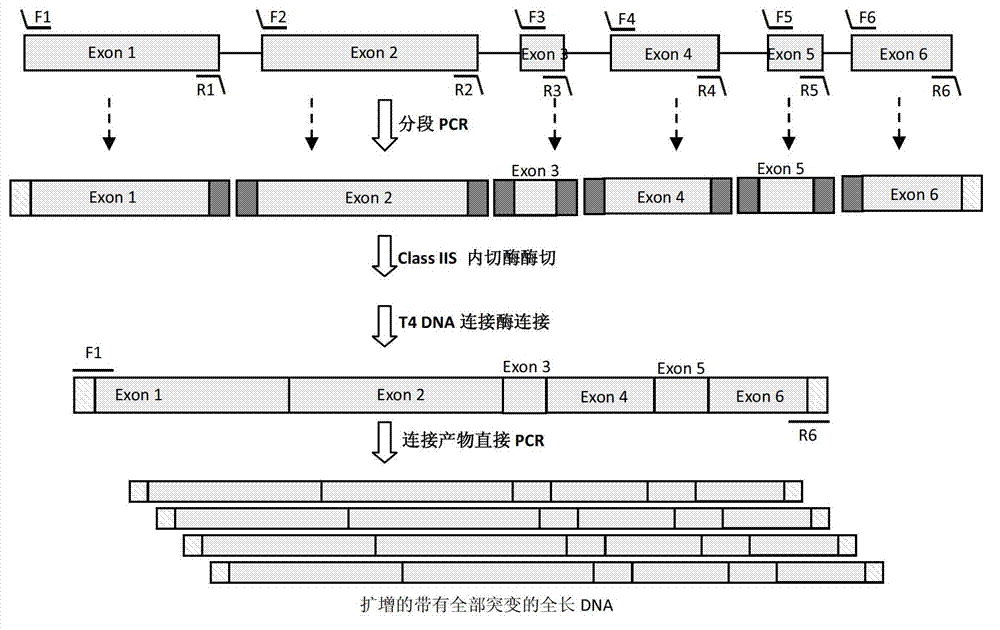
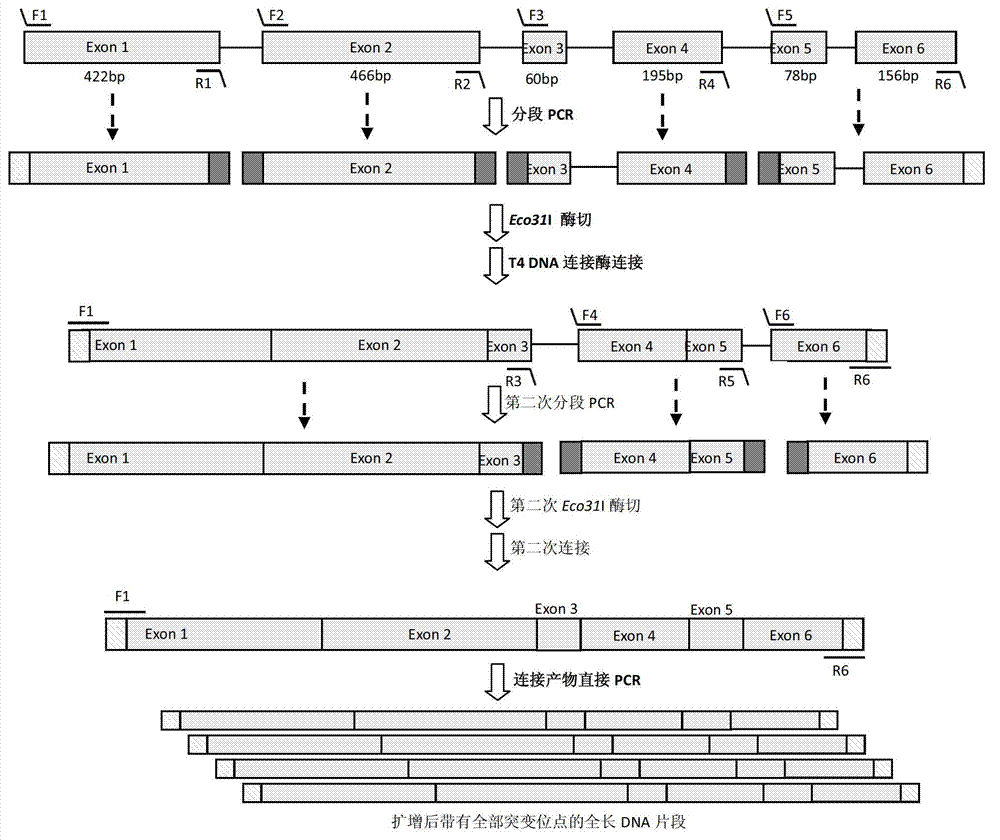
The invention provides a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) multi-site directed mutation method which comprises the following steps: designing Class IIS-containing restriction enzyme recognition site and cleavage site according to DNA mutation sites, performing segmented polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, digestion and connecting reaction to obtain a connecting product, directly performing PCR amplification by using the connecting product, and realizing DNA multi-site mutation. The DNA multi-site directed mutation can be rapidly and efficiently realized simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
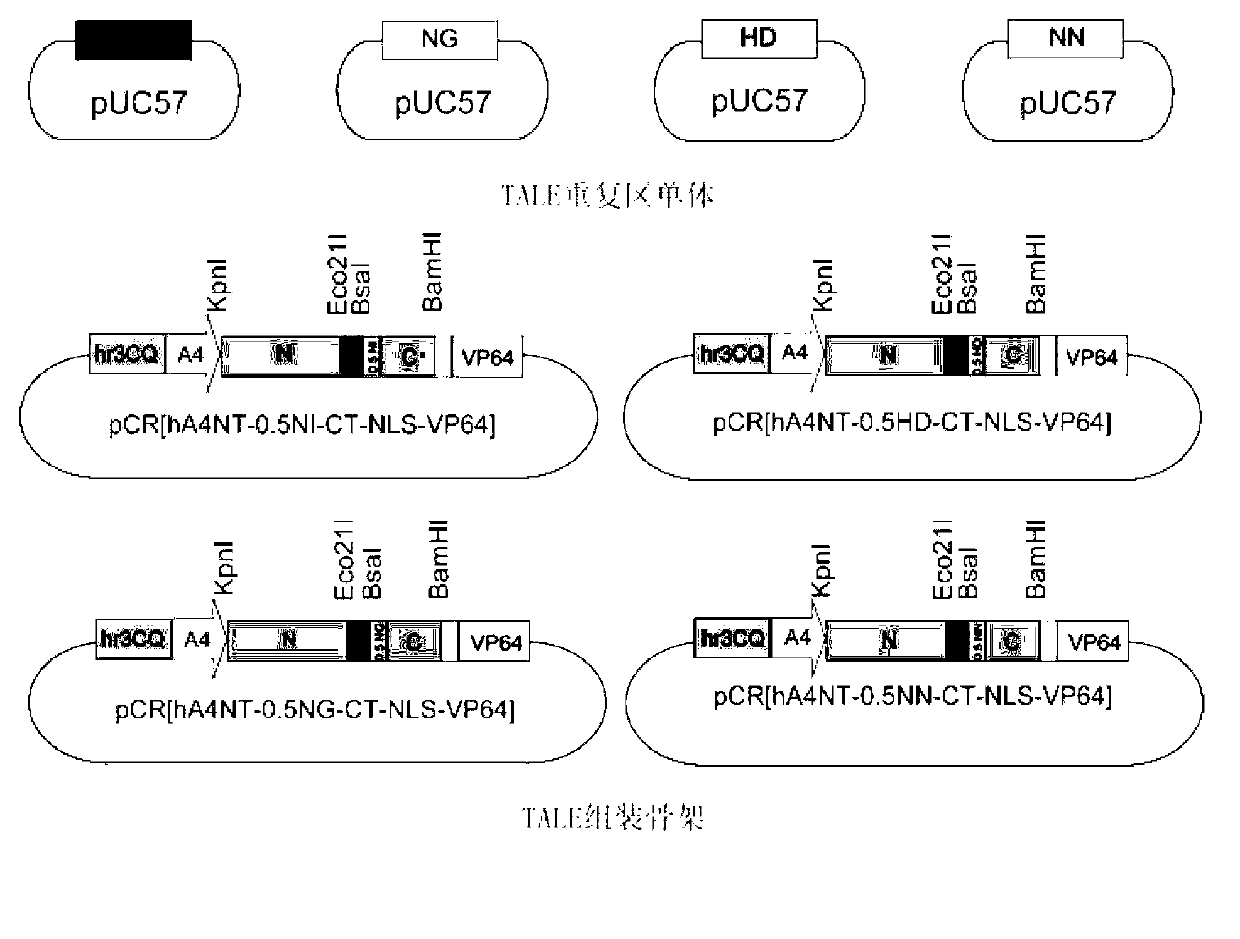
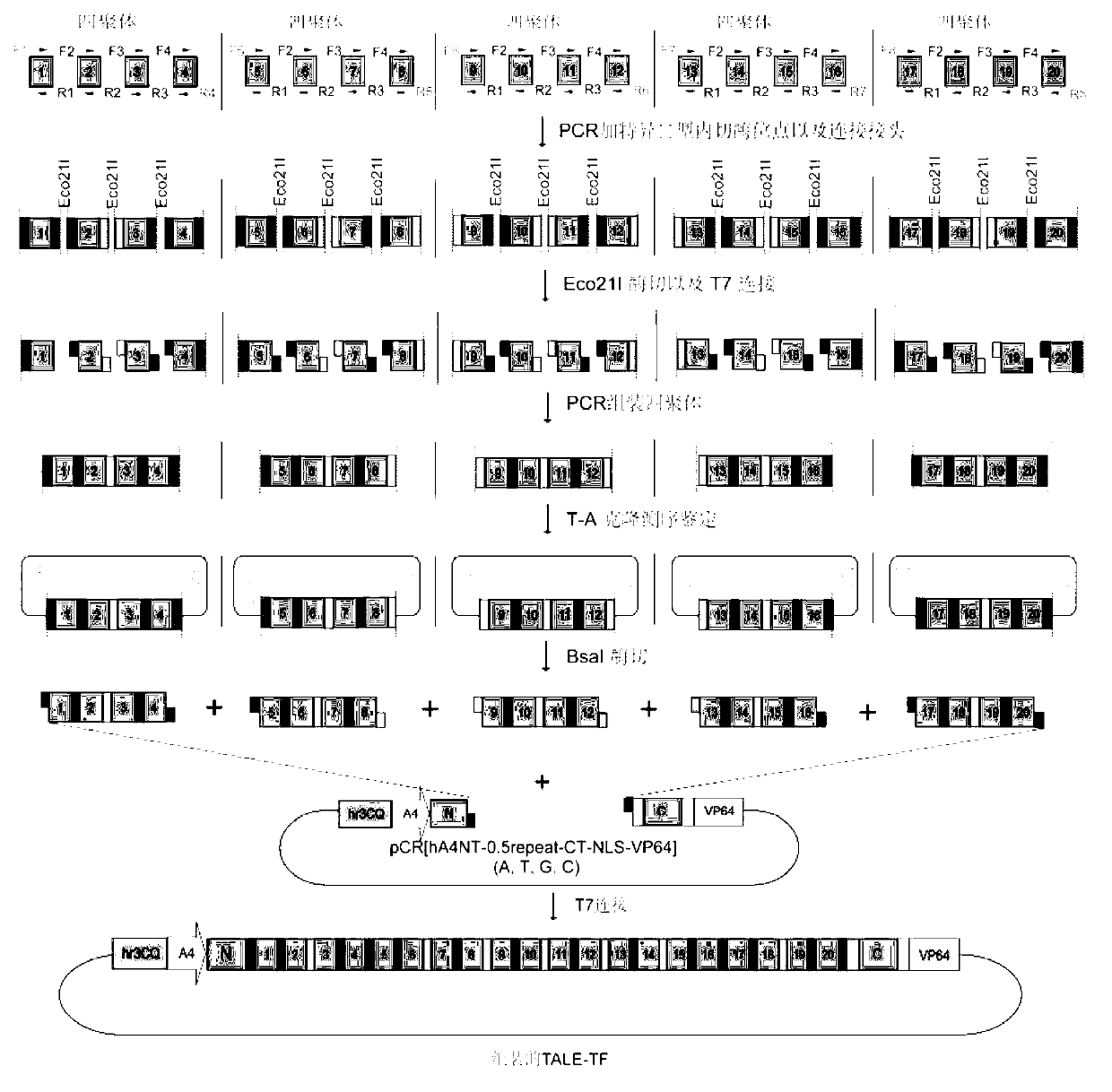
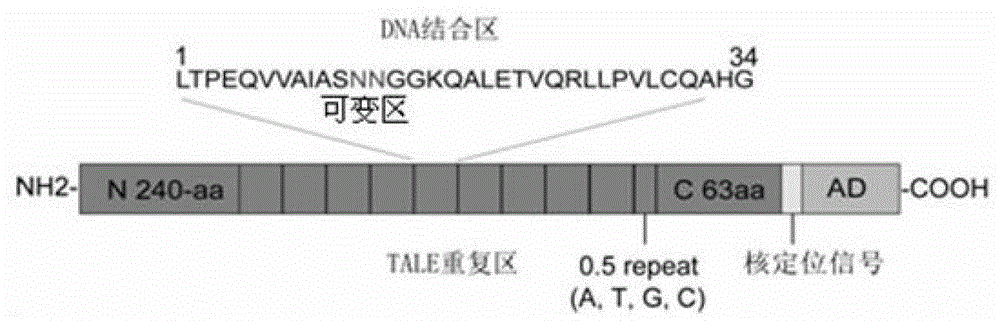
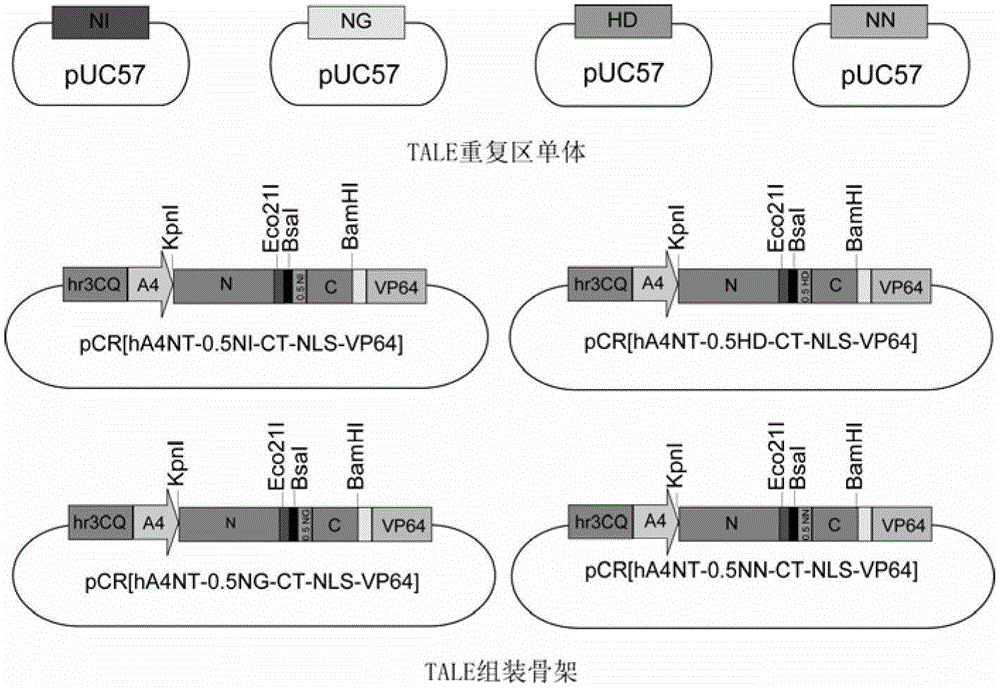
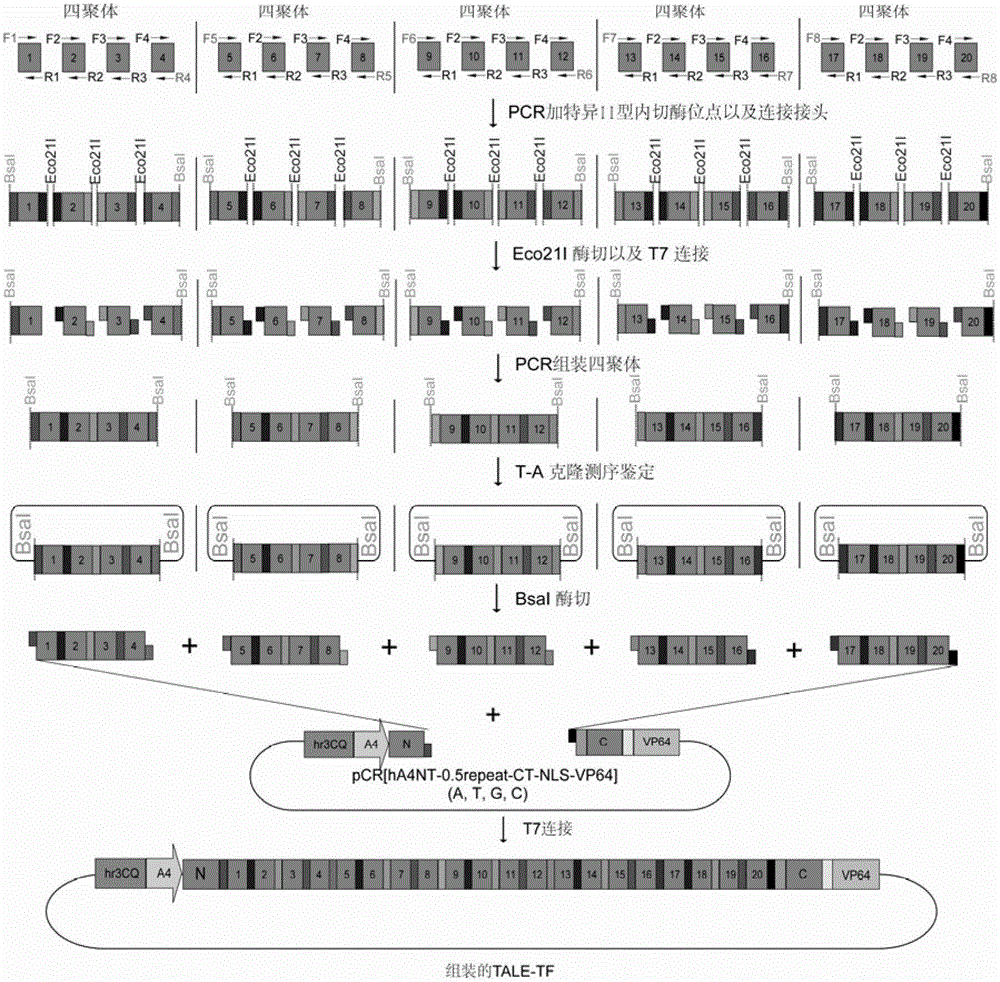
Efficient assembling method of transcription activator-like effectors (TALE) repeating region for editing silkworm genome and framework carrier thereof
ActiveCN103131695AEasy to editEasy to transformVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationRestriction Enzyme Recognition SiteGenome
The invention discloses an efficient assembling method of a transcription activator-like effectors (TALE) repeating region for editing a silkworm genome. The efficient assembling method specifically comprises the steps of firstly numbering random sequences containing X basic groups sequentially and dividing the random sequences into Y groups according to numbers, wherein each group contains 1-4 basic groups; designing a primer pair for amplifying TALE repeating units, and then utilizing the designed primer pair to perform polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification with four types of regulatory volume decrease (RVD) repeating units as templates so as to obtain a PCR product library, wherein the primer pair contains II type restriction enzyme recognition sites and specific joints connected with adjacent TALE repeating units in a seamless mode; numbering and grouping target sequences with X basic groups by means of the same method, taking out PCR products with the same numbers as the target sequences and identifying corresponding basic groups from the PCR product library, mixing the PCR products in the same groups, performing GoldenGate connection, and then performing the GoldenGate connection of connection products again to obtain the TALE repeating region containing X repeating units. By utilizing the method, a large amount of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is not required to be synthesized, and the cost is low. The efficient assembling method can be used for preparing the TALE repeating region for editing the silkworm genome.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
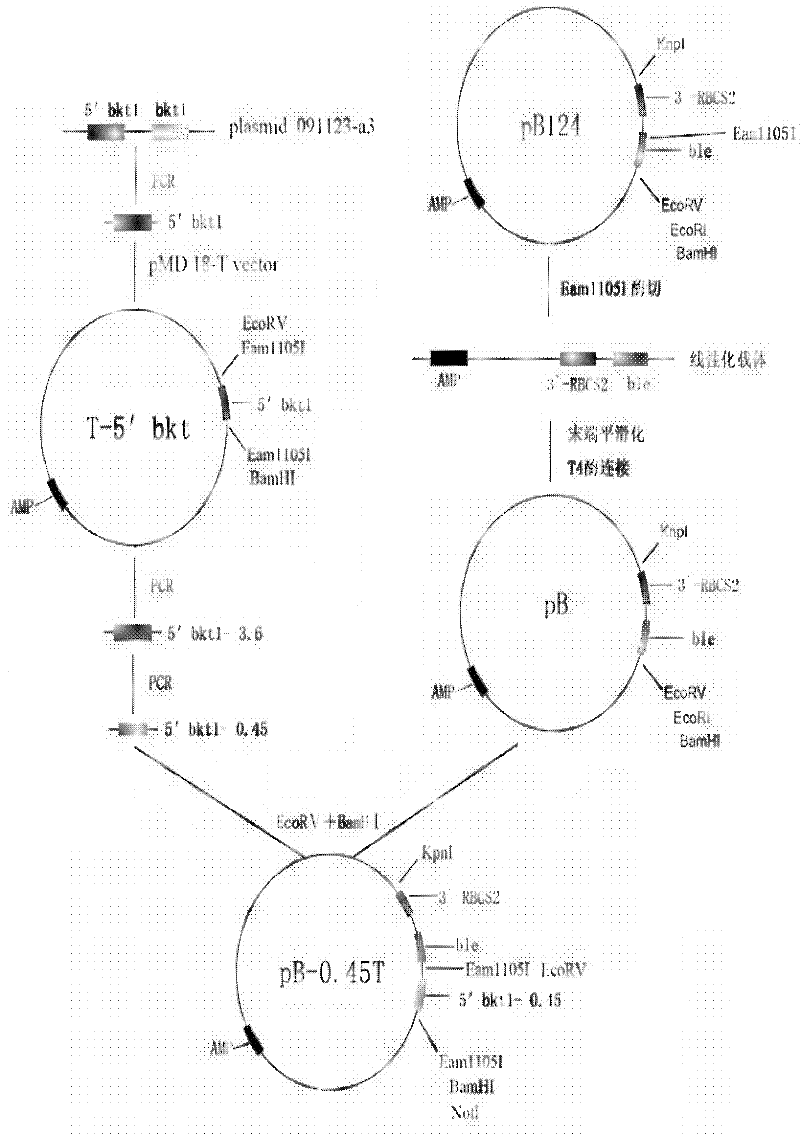
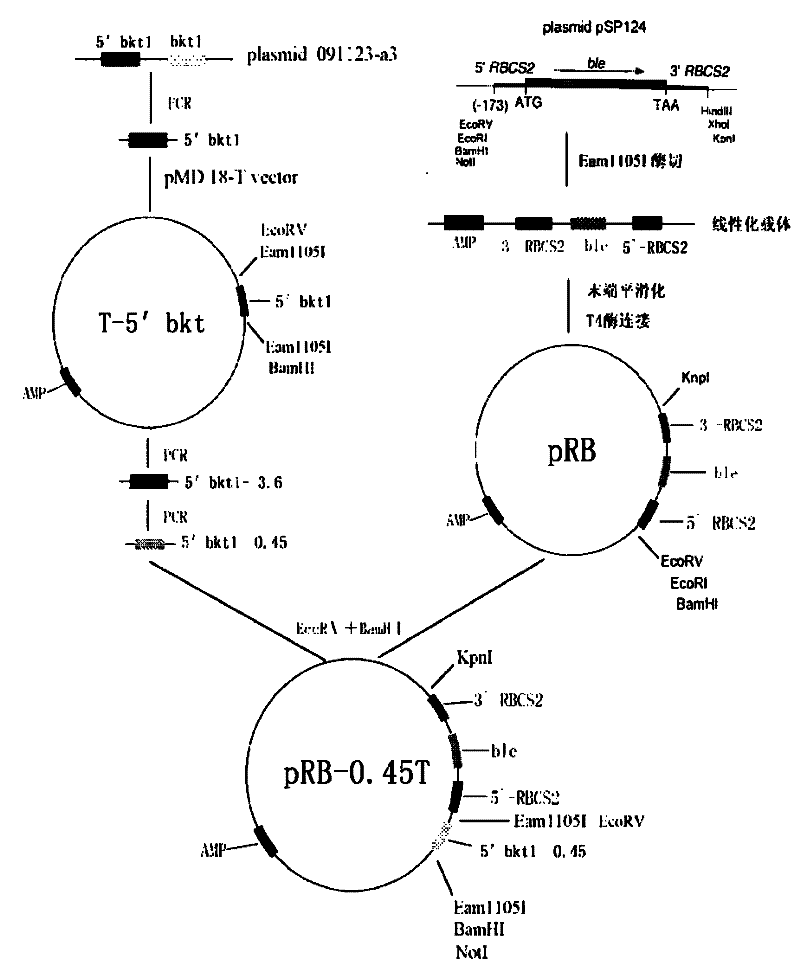
Preparation method of T vector capable of cloning microalgae promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN102399811AMature construction technologySimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEnzyme digestionAgricultural science
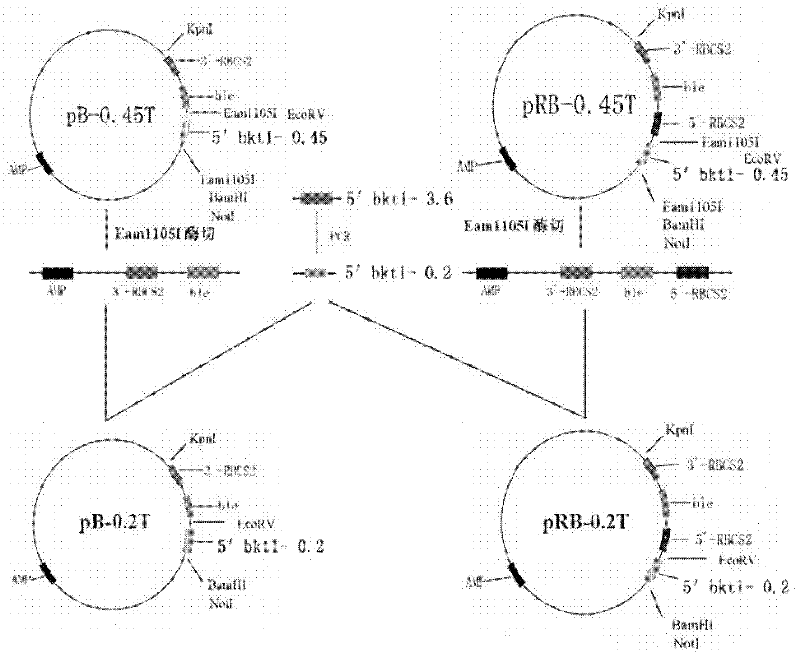
The invention discloses a preparation method of a T vector capable of cloning a microalgae promoter and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a spacer sequence by undergoing a PCR (polymerase chain reaction), and introducing a restriction enzyme recognition site; connecting the spacer sequence to a pSP124 vector with a mutated Eam1105I site, and constructing a pre-T vector respectively; introducing a ble gene to be served as a screening gene; performing enzyme digestion, electrophoretic separation and rubber cutting recovering to obtain a T vector, connecting a microalgae promoter fragment to an Eam1105I enzyme digestion site; and connecting the microalgae promoter to obtain a complete expression cassette, wherein the expression cassette consists of a promoter, an expression gene and a terminator. The invention further discloses application of the T vector capable of cloning the microalgae promoter to detecting the function of the microalgae promoter. The method is easy, and the technology is mature and reliable. The microalgae promoter is cloned rapidly by using the vector, and the function of the promoter is verified in chlamydomonas reinhardtii; and the T vector becomes a beneficial tool for research personnel of microalgae gene engineering.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
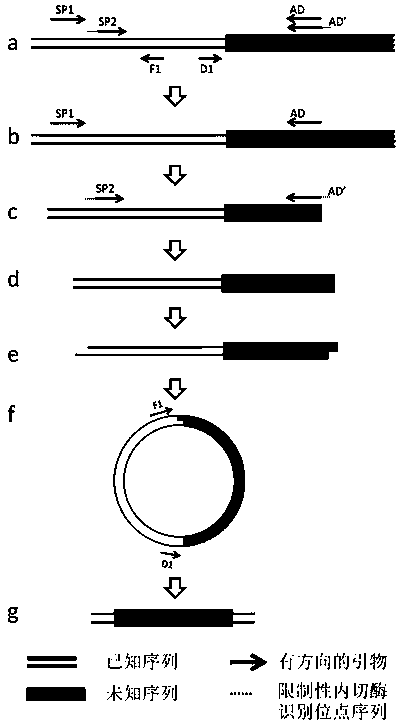
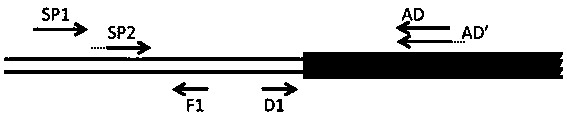
A method of acquiring an unknown flanking sequence of a known sequence
ActiveCN105400771AReduce non-specific amplificationEasy to operateDNA preparationRestriction Enzyme Recognition SiteGenome
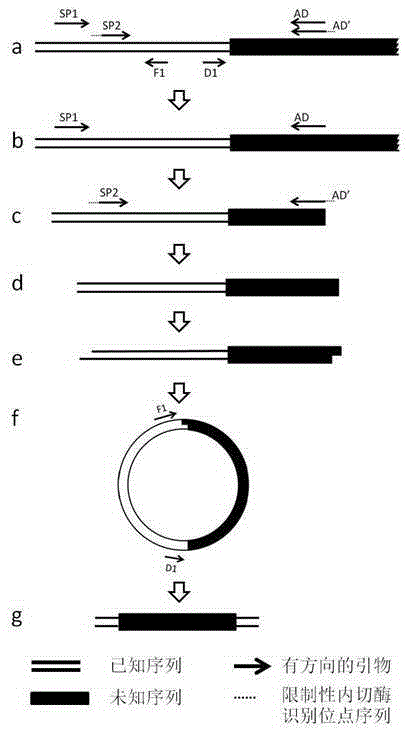
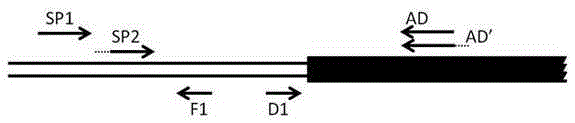
A method of acquiring an unknown flanking sequence of a known sequence is disclosed. The method includes 1) designing two specific primers according to the known sequence which are labeled as SP1 and SP2, with the SP2 carrying a restriction enzyme recognition site, and designing a pair of reverse PCR primers which are F1 and D1 between the SP2 and a border sequence, 2) amplifying to obtain a PCR product 1 by adopting genome DNA as a template and by using any one degenerate primer and the specific SP1 primer, 3) amplifying to obtain a PCR product 2 by adopting the PCR product 1 as a template and by using the specific SP2 primer and a degenerate primer, with the degenerate primer in the step 3) being same with the degenerate primer in the step 2), but comprising a restriction enzyme recognition site, and 4) subjecting the PCR product 2 to digestion, adding T4 ligase, cyclizing, and amplifying by adopting the cyclized product as a template and by using the F1 primer and the D1 primer to obtain a PCR product 3, thus acquiring the flanking sequence. The method is advantaged by simple and easy operation, a low cost, a high success rate, short time, and the like.
Owner:SANMING UNIV
Rapid analysis of variations in a genome
InactiveUS20050260656A1Increase delayMaximize efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionOligonucleotide Primer
The invention provides a method useful for determining the sequence of large numbers of loci of interest on a single or multiple chromosomes. The method utilizes an oligonucleotide primer that contains a recognition site for a restriction enzyme such that digestion with the restriction enzyme generates a 5′ overhang containing the locus of interest. The 5′ overhang is used as a template to incorporate nucleotides, which can be detected. The method is especially amenable to the analysis of large numbers of sequences, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms, from one sample of nucleic acid.
Owner:RAVGEN INC
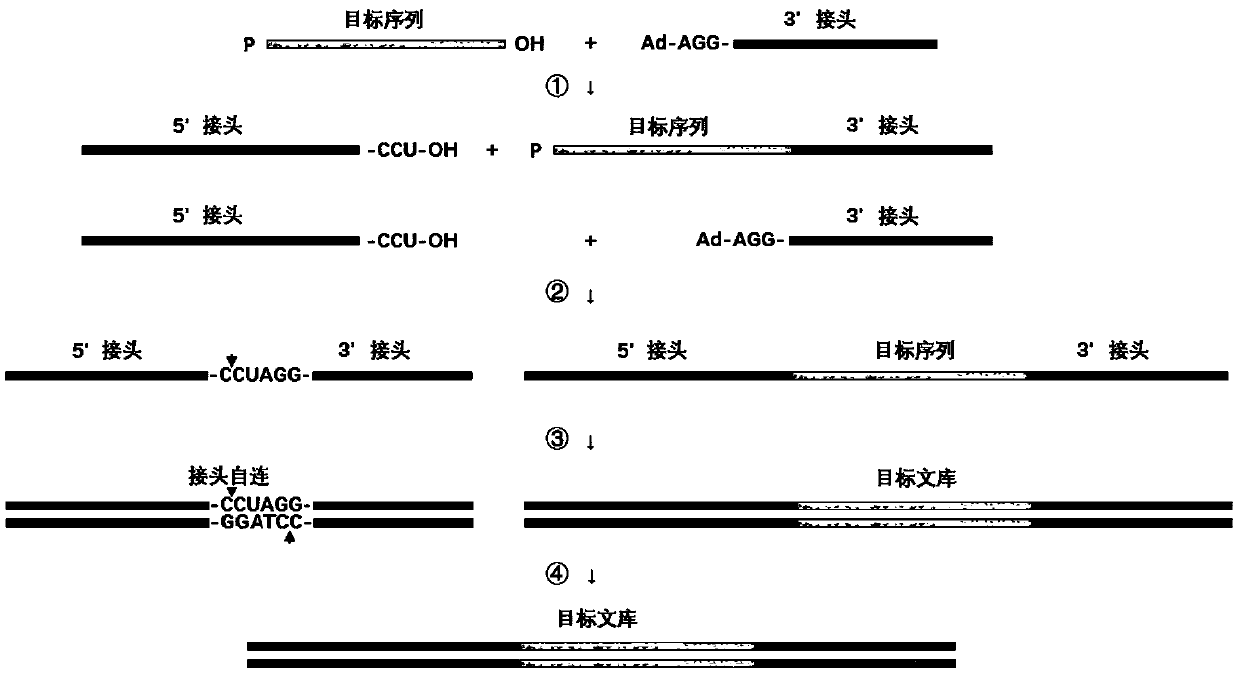
Linker composition and application thereof
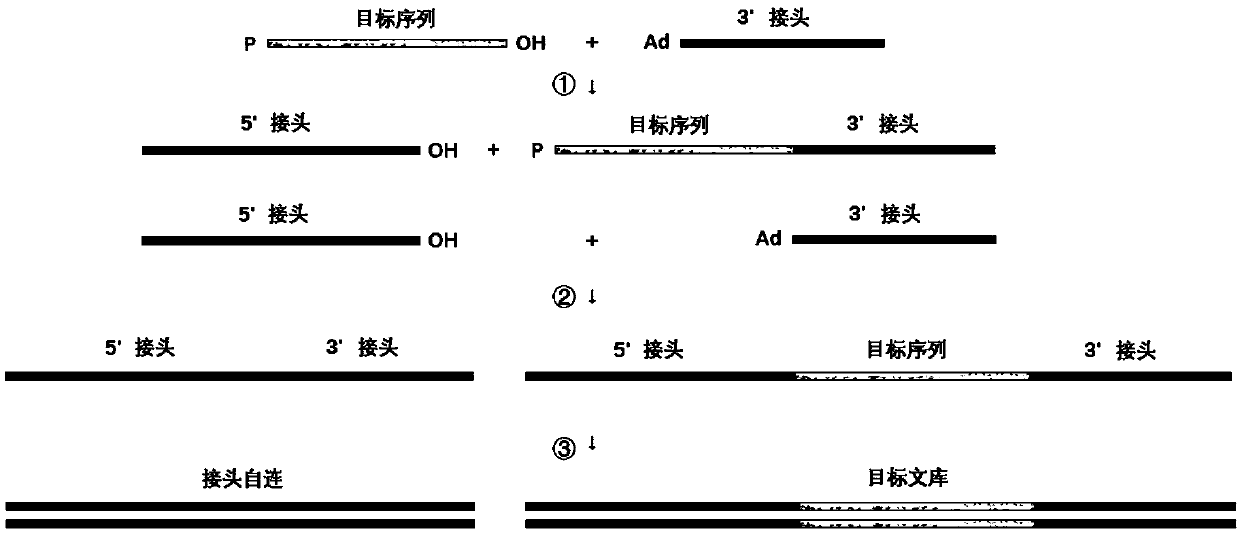
ActiveCN110499362AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCombinatorial chemistryRestriction Enzyme Recognition Site
The present invention provides a linker composition. The linker composition comprises a first linker and a second linker, wherein a 3' end sequence of the first linker and a 5' end sequence of the second linker form restriction enzyme recognition sites during self-ligation of the first linker and the second linker. The linker composition according to embodiments can be specifically cleaved and degraded by restriction enzymes during the self-ligation. Therefore, when the linker composition is applied to library construction, the self-ligated linker cannot enter downstream experiments under a function of the restriction enzymes. The linker composition effectively improves utilization of sequencing data.
Owner:WUHAN BGI CLINICAL LAB CO LTD
Methods of making and using vaccines utilizing minicircle DNA expression vectors for production of foot-and-mouth-disease virus proteins and virus-like particles
This application is directed generally to minicircle DNA vectors for the vaccination of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD). The transgene expression cassette in the minicircle DNA vector includes: a eukaryotic translation initiation nucleotide sequence, a mutant nucleotide sequence that encodes a foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) capsid polyprotein precursor that contains at least one mutation to eliminate a restriction enzyme recognition site, a nucleotide sequence that encodes a protease that cleaves the FMDV capsid polyprotein precursor into a plurality of FMDV capsid proteins and a translational regulatory element to regulate the expression of the protease. The minicircle DNA vectors can be transfected directly into the cell of a mammalian host. When transfected into the mammalian host cell, virus-like particles can be produced intrinsically to stimulate the mammalian host's immune system to develop adaptive immunity toward foot-and-mouth disease.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF HOMELAND SECURITY
Diagnostic method
The present invention concerns a method for the detection or monitoring of cancer using a biological sample selected from blood, plasma, serum, saliva, urine from an individual, said method comprising:(a) obtaining DNA from the said biological sample;(b) digesting the DNA sample with one or more methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes;(c) quantifying or detecting a DNA sequence of interest after step (b), wherein the target sequence of interest contains at least two methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme recognition sites; and(d) comparing the level of the DNA sequence from the individual to a normal standard, to detect, prognosticate or monitor cancer.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
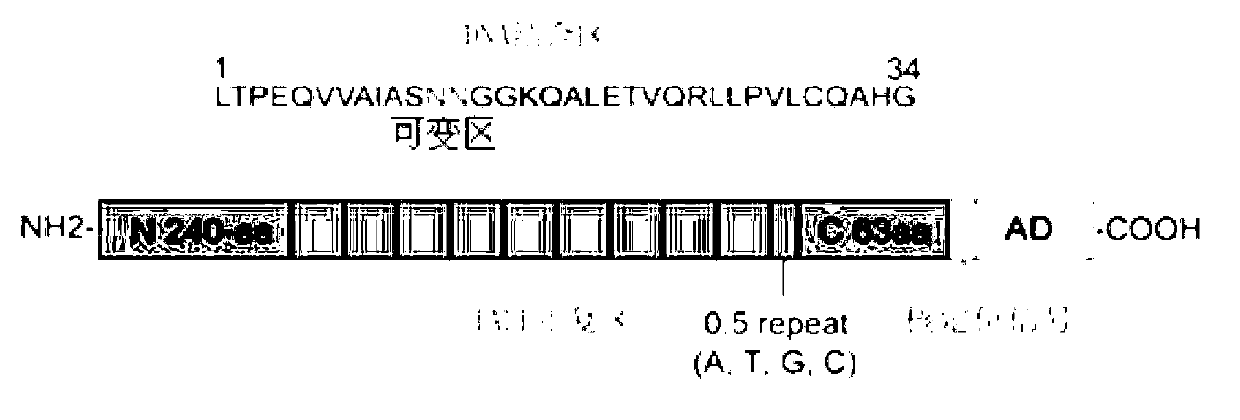
High-sweetness sweet protein gene and synthesis method thereof
The invention discloses a high-sweetness sweet protein gene and a synthesis method thereof. Codons preferred by yeast are adopted to design a gene sequence by knocking out the fist amino acid at an amino terminal, turning 29-bit aspartic acid Asp into lysine Lys, turning 41-bit glutamic acid Glu into lysine Lys, designing four pairs of primers according to the characteristics of pGAPZ alphaA multiple clone sites and the restriction enzyme property of a Brazzein gene, inducing an Xbak restriction enzyme recognition site at an upstream primer, inducing an Xhol restriction enzyme recognition site at a downstream primer and adopting an SOE-PCR method to obtain a Brazzein gene product with the full length of 188bp. The sweetness of modified sweet protein is 2 to 6 times of the sweetness of the original Brazzein gene.
Owner:刘松财 +1
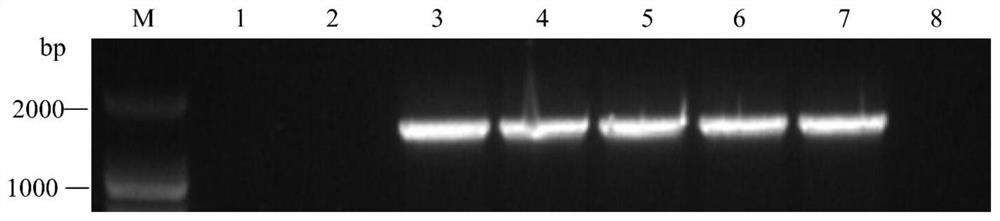
Strawberry vein banding virus vector, construction method thereof and application of strawberry vein banding virus vector in foreign protein expression
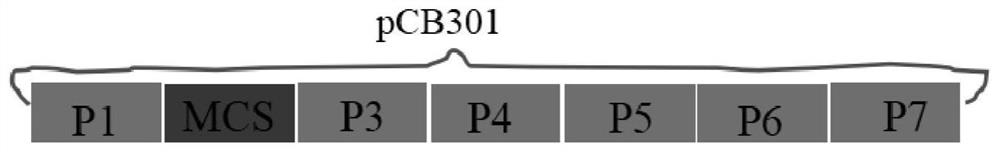
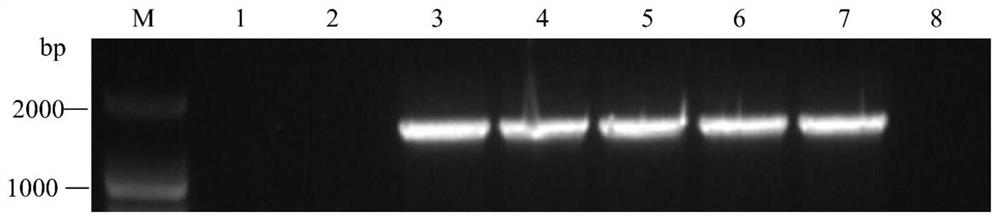
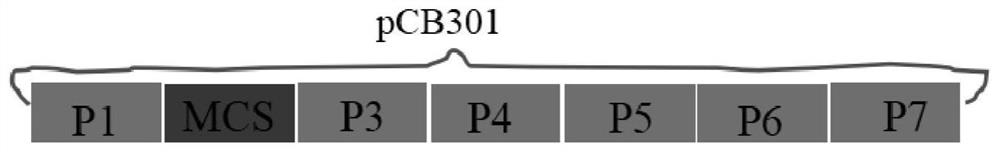
ActiveCN113512561AStable and efficient infectionEfficient expressionAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionFragariaPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a strawberry vein banding virus vector as well as a construction method and application thereof in foreign protein expression, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The strawberry vein banding virus vector is pSVBVSY-P1-MCS or pSVBVSY-P4-MCS, and the strawberry vein banding virus vector is pSVBVSY-P1-MCS; the sequence of the pSVBVSY-P1-MCS is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the sequence of the pSVBVSY-P4-MCS is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing strawberry vein banding virus infectious clone; (2) constructing a multi-cloning-site fragment; (3) constructing a strawberry vein banding virus vector, in particular, inserting a gene sequence with Pml I and BamH I restriction enzyme recognition sites between P1 and P2 or between P4 and P5 of strawberry vein banding virus infectious clone in a homologous recombination mode. The vector constructed by the invention is subjected to vacuum filtration inoculation through an agrobacterium infiltration method and stably and efficiently infects forest strawberries, and meanwhile, foreign proteins can be efficiently expressed on the forest strawberries.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
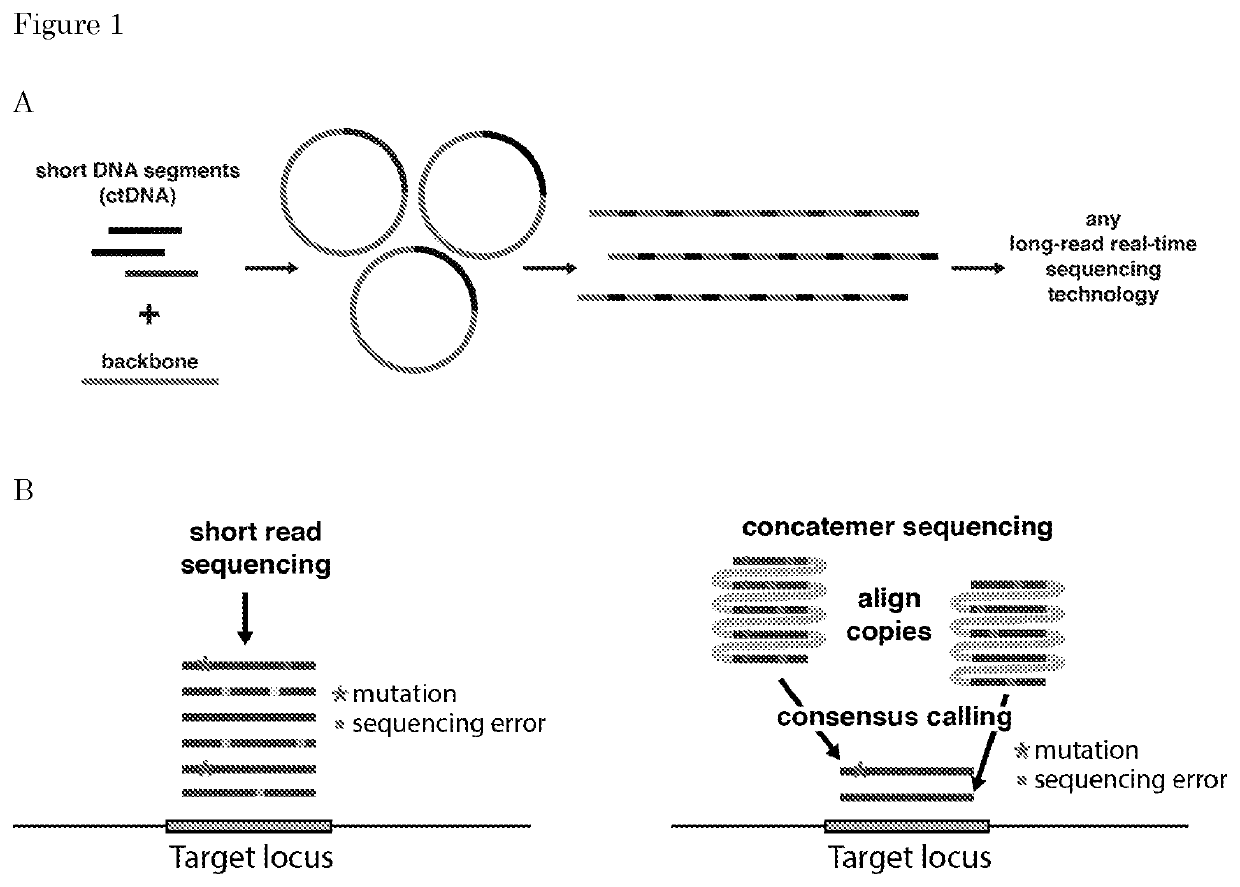
Methods for preparing nucleic acid molecules for sequencing
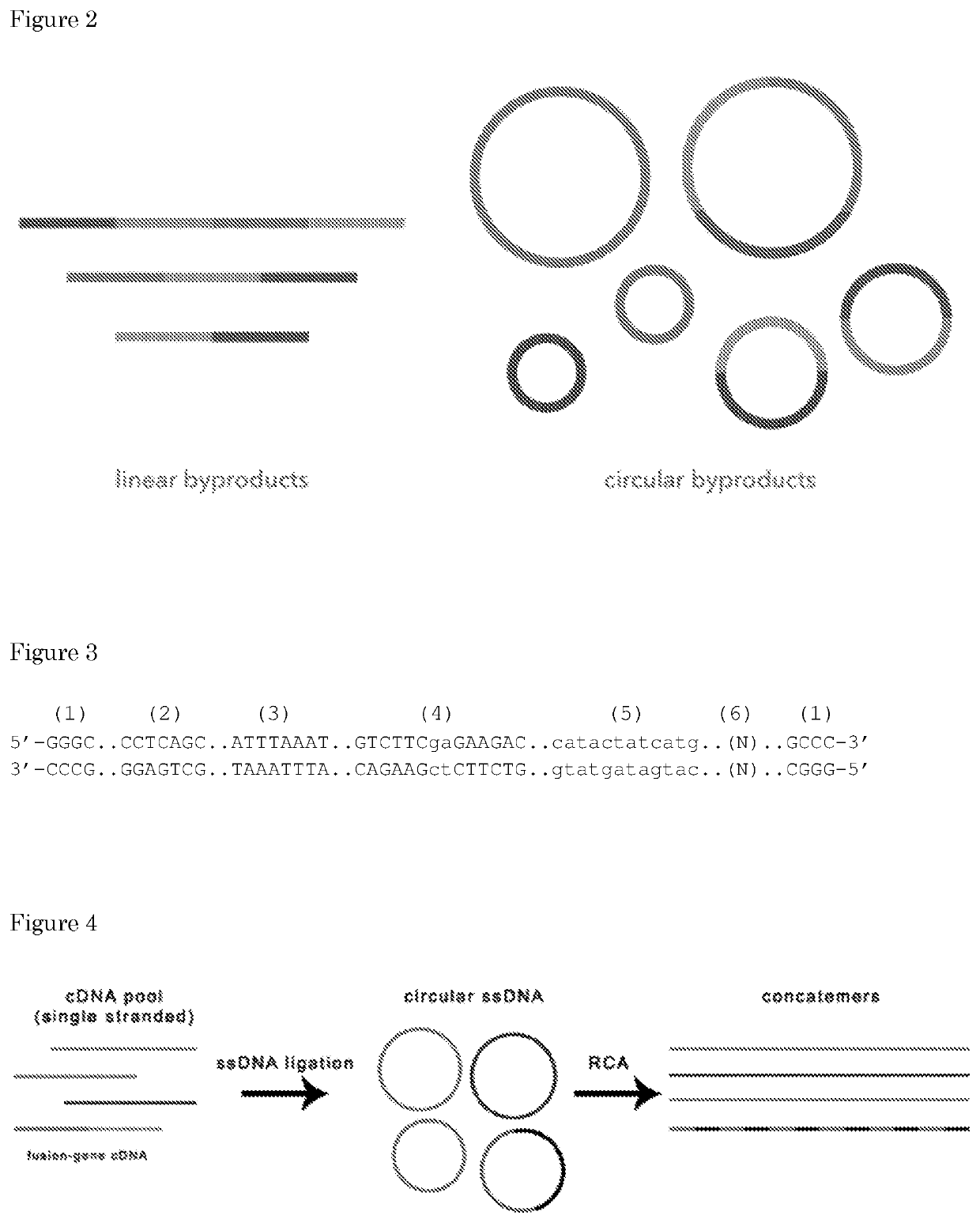
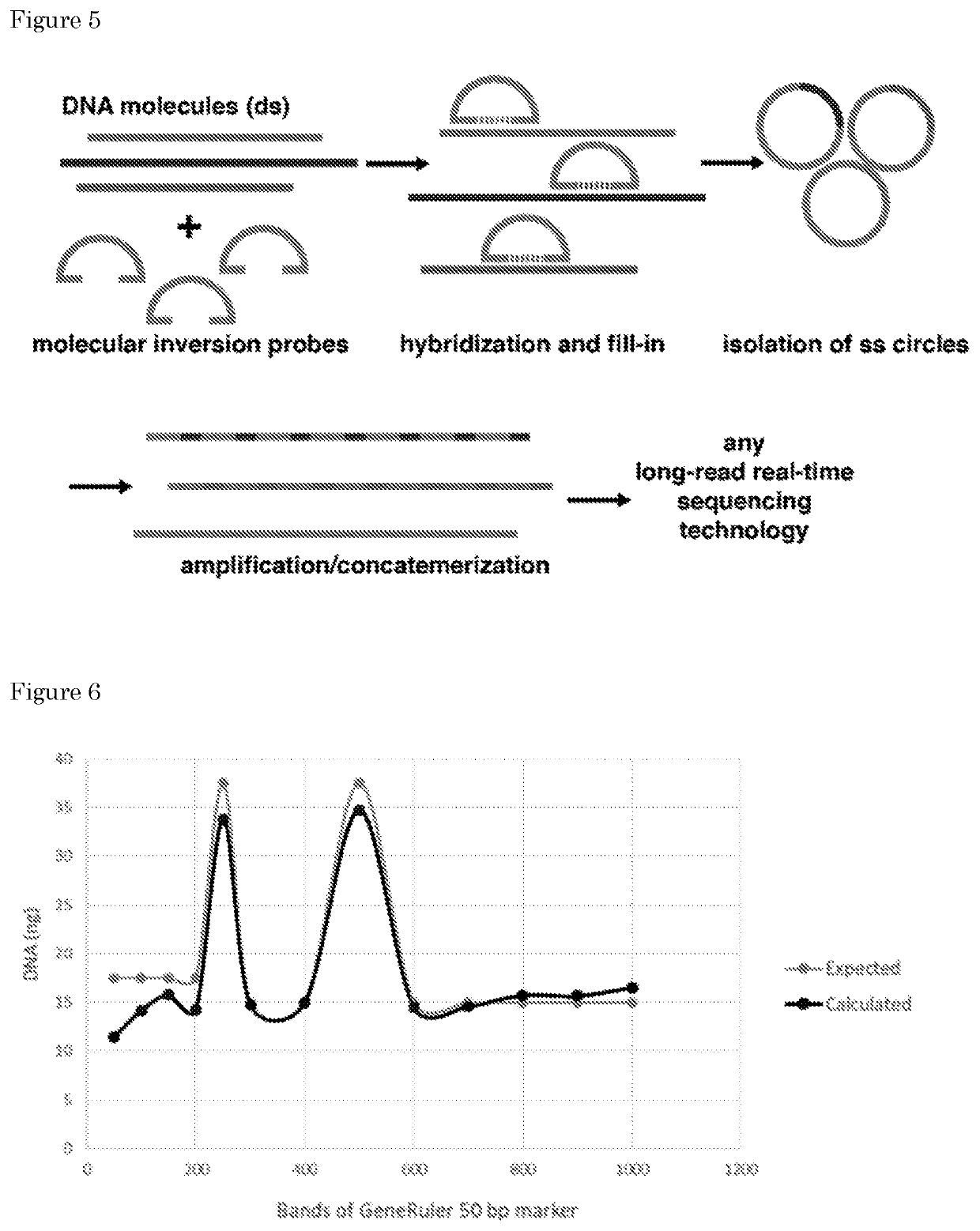
The invention relates to means and methods for preparing double stranded target DNA molecules for sequencing. In embodiments double stranded backbone DNA molecules comprising 5' and 3' ends are provided that are ligation compatible with 5' and 3' ends of said target DNA; form a first restriction enzyme recognition site when self-ligated; in a form that enables self-ligation. Methods may comprise providing, if not already present, said target DNA with 5' and 3' ends that are in a form that prevents self-ligation and that are ligation compatible with said backbone DNA 5' and 3' ends. Methods mayfurther comprise ligating said target DNA to said backbone DNA in the presence of a ligase and a first restriction enzyme that cuts said first restriction enzyme recognition site, thereby producing at least one DNA circle comprising a backbone DNA molecule and a target DNA molecule. Linear DNA may be removed at this time and subsequently a concatemer DNA molecule comprising an ordered array of copies of said at least one DNA circle through rolling circle amplification is produced that can be sequenced.
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
Methods and compositions for seamless cloning of nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20110046201A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSubcloningRestriction Enzyme Recognition Site
The present invention is in the fields of biotechnology and molecular biology. More particularly, the present invention relates to cloning or subcloning one or more nucleic acid molecules comprising one or more type IIs restriction enzyme recognition sites. The present invention also embodies cloning such nucleic acid molecules using recombinational cloning methods such as those employing recombination sites and recombination proteins. The present invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules (including RNA and iRNA), as well as proteins, expressed from host cells produced using the methods of the present invention.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
A strawberry vein virus vector and its construction method and application in foreign protein expression
ActiveCN113512561BStable and efficient infectionEfficient expressionAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionFragariaPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a strawberry vein virus vector, its construction method and its application in exogenous protein expression, belonging to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. Strawberry vein virus vector pSVBV SY ‑P1‑MCS or pSVBV SY ‑P4‑MCS; pSVBV SY The sequence of ‑P1‑MCS is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, pSVBV SY The sequence of ‑P4‑MCS is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Its construction method is as follows: (1) construction of strawberry vein virus infectious clone: (2) construction of multiple cloning site fragments: (3) construction of strawberry vein virus vector, specifically, will have Pml I The gene sequence of the BamH I restriction endonuclease recognition site is inserted between P1 and P2 or between P4 and P5 preparations of the Strawberry Vein Virus infective clone by means of homologous recombination. The vector constructed by the invention is vacuum-filtered and inoculated through the Agrobacterium infiltration method, and stably and efficiently infects the forest strawberry, and can also efficiently express the foreign protein on the forest strawberry.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of high-throughput screening tool for enabling Escherichia coli to obtain effective NHEJ system in Escherichia coli gene editing
PendingCN114277047APromotes non-homologous end joiningImprove efficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention provides application of a high-throughput screening tool for enabling escherichia coli to obtain an effective NHEJ system in escherichia coli gene editing. The high-throughput screening tool for enabling the Escherichia coli to obtain the effective NHEJ system comprises a pDual-Cas9-Parental plasmid vector and a high-throughput screening vector, wherein the pDual-Cas9-Parental plasmid vector contains a DNA helicase gene, a replicon, an antibiotic resistance gene, a nuclease gene, an araC gene, an arabinose promoter and an IIs type restriction enzyme recognition site; and the pDual-sgRNA-lacZ plasmid vector contains an sgRNA sequence of a targeted lacZ gene, a strong promoter for constitutive expression, a replicon and an antibiotic resistance gene. The NHEJ system obtained through screening has good connection efficiency in escherichia coli, efficient gene editing can be carried out, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
Efficient assembling method of transcription activator-like effectors (TALE) repeating region for editing silkworm genome and framework carrier thereof
ActiveCN103131695BEasy to editEasy to transformVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationBase JRestriction Enzyme Recognition Site
The invention discloses an efficient assembling method of a transcription activator-like effectors (TALE) repeating region for editing a silkworm genome. The efficient assembling method specifically comprises the steps of firstly numbering random sequences containing X basic groups sequentially and dividing the random sequences into Y groups according to numbers, wherein each group contains 1-4 basic groups; designing a primer pair for amplifying TALE repeating units, and then utilizing the designed primer pair to perform polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification with four types of regulatory volume decrease (RVD) repeating units as templates so as to obtain a PCR product library, wherein the primer pair contains II type restriction enzyme recognition sites and specific joints connected with adjacent TALE repeating units in a seamless mode; numbering and grouping target sequences with X basic groups by means of the same method, taking out PCR products with the same numbers as the target sequences and identifying corresponding basic groups from the PCR product library, mixing the PCR products in the same groups, performing GoldenGate connection, and then performing the GoldenGate connection of connection products again to obtain the TALE repeating region containing X repeating units. By utilizing the method, a large amount of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is not required to be synthesized, and the cost is low. The efficient assembling method can be used for preparing the TALE repeating region for editing the silkworm genome.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
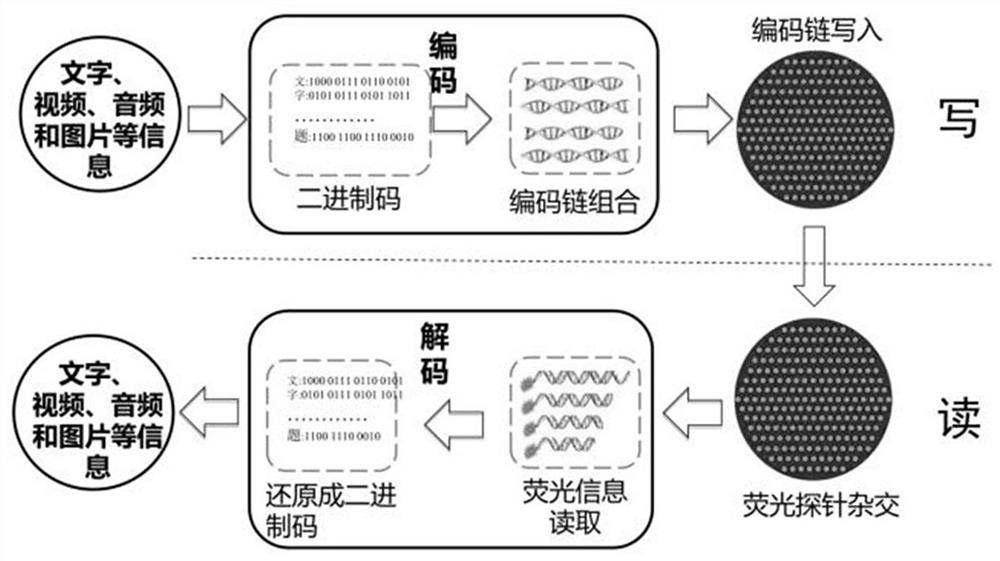
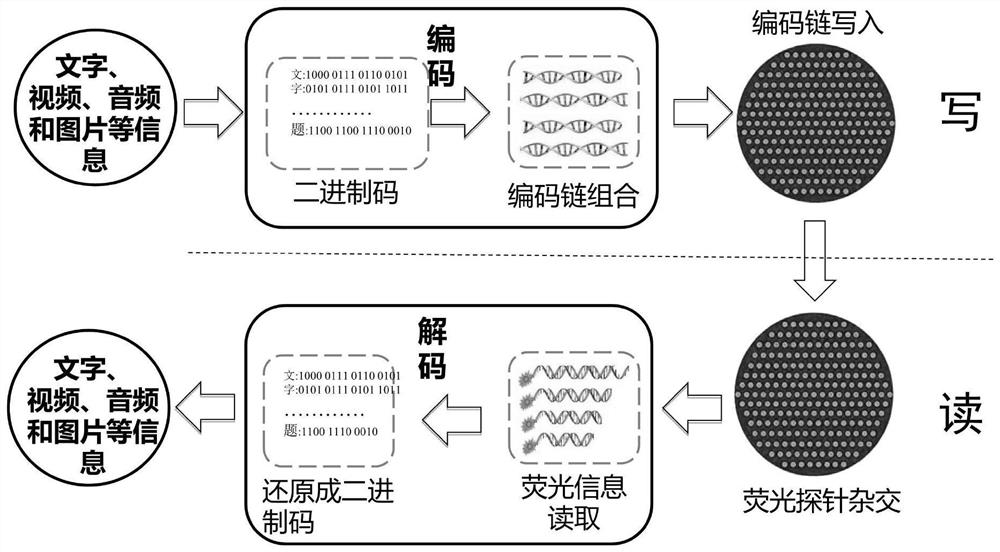
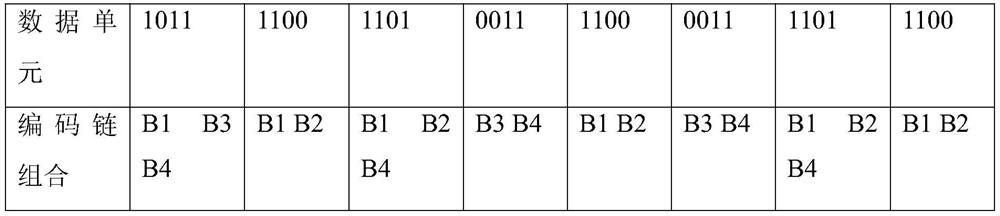
DNA hybridization information storage encryption method based on addition and removal of coding chain hairpin structure
ActiveCN113539379ARealize hard encryption functionAvoid accessDigital data protectionHybridisationComputer hardwareA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA storage encryption method based on specific removal of a hairpin structure of a coding chain. The DNA storage encryption method comprises a set of combination of a DNA coding chain with a hairpin structure and a restriction enzyme recognition site and a restriction enzyme, wherein the specific restriction enzyme can cut off the hairpin structure of the specific coding chain, so that the coding region is exposed and activated. In the information reading process, if a DNA coding chain is not correctly activated, the information cannot be effectively read due to the fact that hybridization is hindered by a hairpin structure. When the method is implemented, a sender selects one group from a code chain combination for data writing, sends a storage disk to a receiver, and sends a secret key (namely correct incision enzyme information) by using another confidential way. After receiving the secret key, the receiver can correctly process and activate the coding chain, but cannot activate the coding chain due to wrong processing, and even may cause self-destruction of the memory disk. Hard encryption of the DNA hybrid storage technology is realized, and application of the storage technology is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
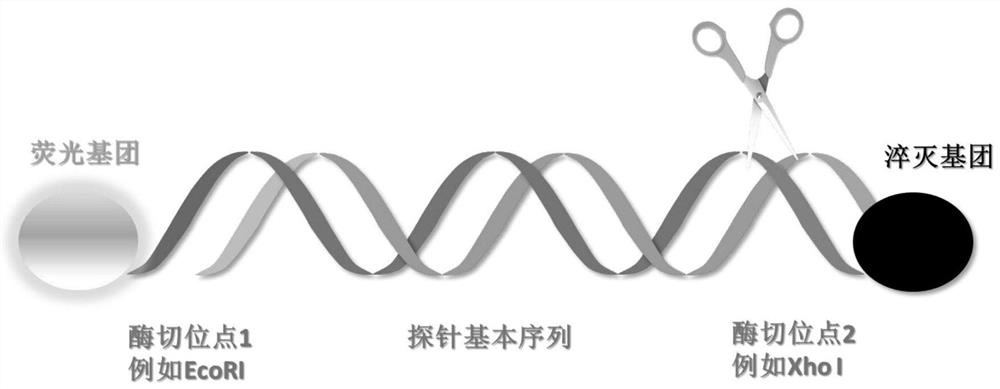
DNA hybridization information storage encryption method based on probe blocking and unblocking
ActiveCN113539363AImplement hard encryptionImprove securityDigital data protectionSequence analysisFluorophoreA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA hybridization information storage encryption method based on probe blocking and unblocking, and belongs to the technical field of DNA storage. The DNA hybridization information storage encryption method based on probe blocking and unblocking comprises a set of DNA oligonucleotide probe combination with a fluorophore, a quenching group and restriction enzyme recognition sites and a set of restriction enzyme combination, wherein the specific restriction enzyme can cut off a quenching group of the specific probe, so the probe is activated; in the DNA hybridization process of DNA hybridization storage information reading, if a probe which is not correctly activated is directly used, due to the existence of a quenching group, an effective fluorescence detection signal cannot be obtained after hybridization, and the storage information cannot be read. Hard encryption of the DNA hybridization information storage technology is achieved, the safety of the DNA hybridization information storage technology can be effectively improved, and application of the technology in the fields of military, government affairs and commercial encryption storage is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
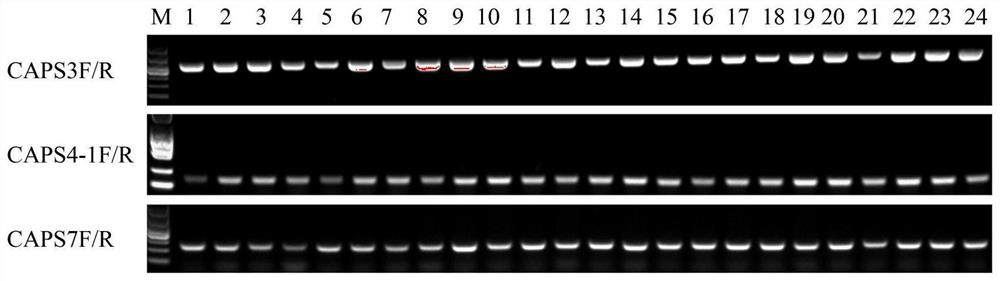
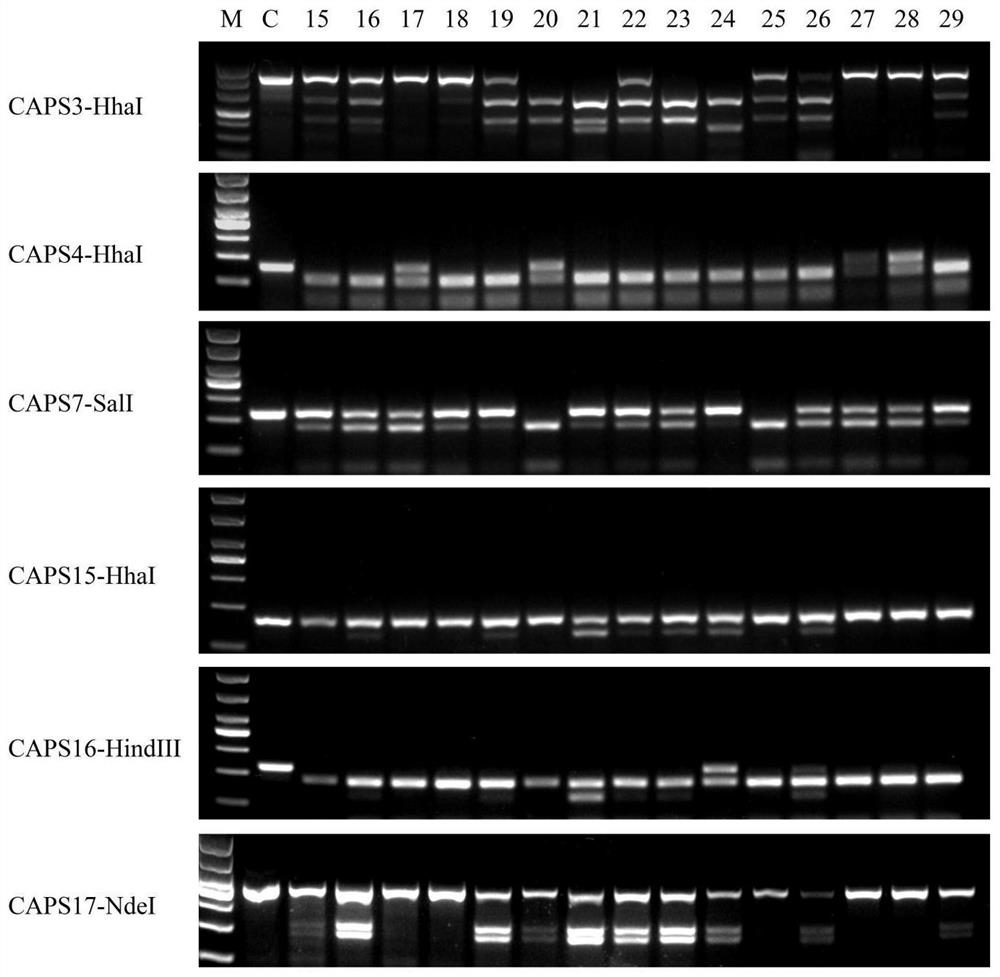
CAPS molecular marker for identifying oncidium varieties, screening method and application
ActiveCN113549616AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a CAPS molecular marker for identifying oncidium varieties. The marker comprises sequences shown as SEQIDNO.1-SEQIDNO.12. A screening method of the sequences comprises the following steps of obtaining SNP sites based on transcriptome data of six oncidium varieties, searching for SNP sites capable of causing change of restriction enzyme recognition sites, and designing a CAPS primer pair according to different SNP sites; extracting genome DNA of oncidium; carrying out PCR amplification on genome DNA of different oncidium varieties by using CAPS primers to obtain a target fragment; and performing enzyme digestion on the target fragment by using a restriction enzyme, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis detection and enzyme digestion product polymorphism analysis on an enzyme digestion product, if the enzyme digestion product polymorphism exists between the varieties, taking the SNP site as the CAPS marker for identifying the oncidium varieties. The molecular marker can be used for identifying the oncidium varieties.
Owner:CROP RES INST OF FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods for preparing nucleic acid molecules for sequencing
Means and methods for preparing double stranded target DNA molecules for sequencing. In embodiments double stranded backbone DNA molecules comprising 5′ and 3′ ends are provided that are: ligation compatible with 5′ and 3′ ends of the target DNA; form a first restriction enzyme recognition site when self-ligated; in a form that enables self-ligation. Methods may comprise providing, if not already present, the target DNA with 5′ and 3′ ends that are in a form that prevents self-ligation and that are ligation compatible with the backbone DNA 5′ and 3′ ends. Methods may further comprise ligating the target DNA to the backbone DNA in the presence of a ligase and a first restriction enzyme that cuts the first restriction enzyme recognition site, thereby producing at least one DNA circle comprising a backbone DNA molecule and a target DNA molecule. Linear DNA may be removed at this time and subsequently a concatemer DNA molecule comprising an ordered array of copies of the at least one DNA circle through rolling circle amplification is produced that can be sequenced.
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
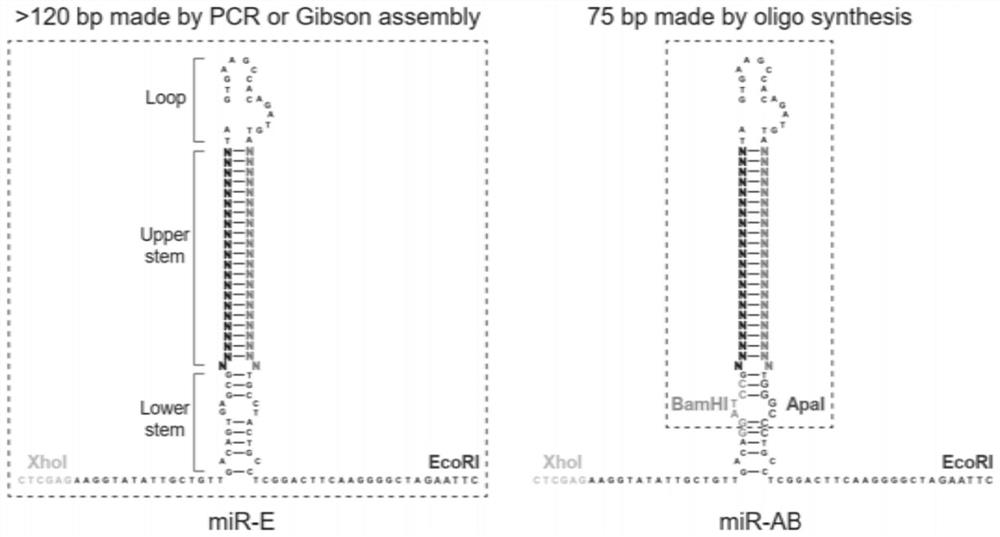
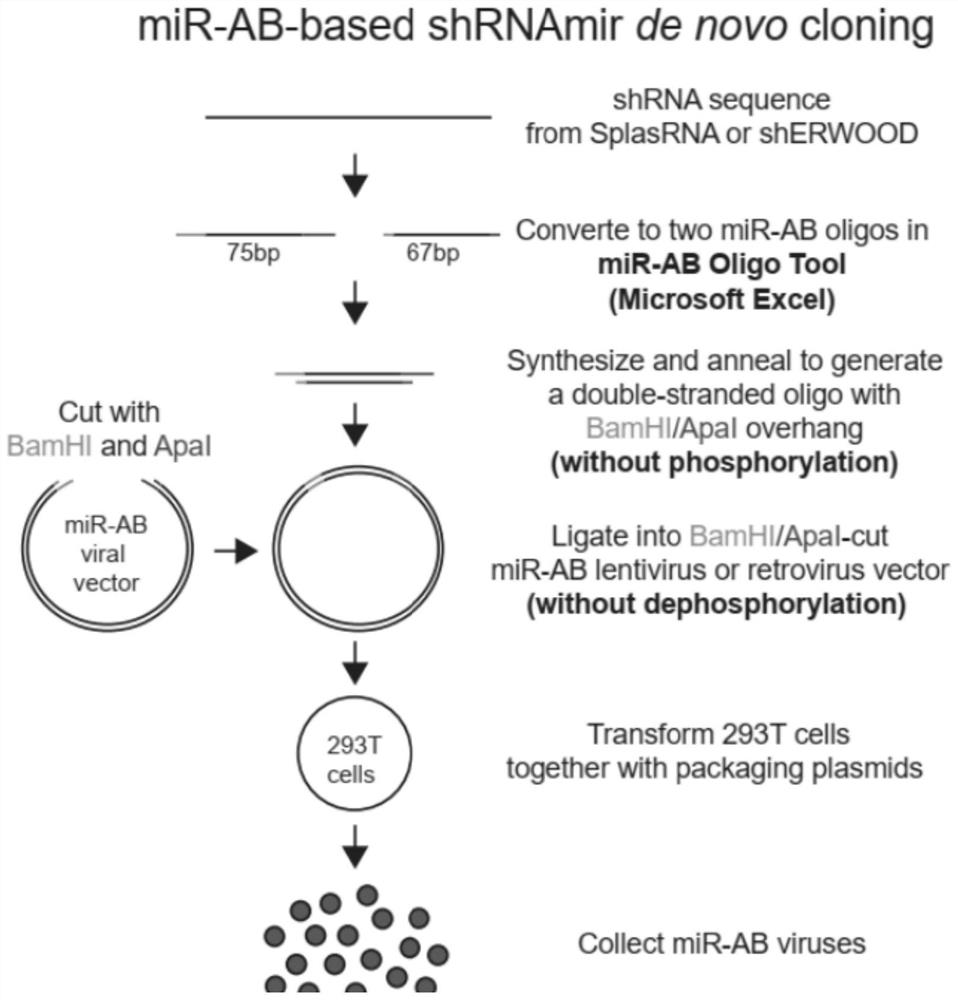
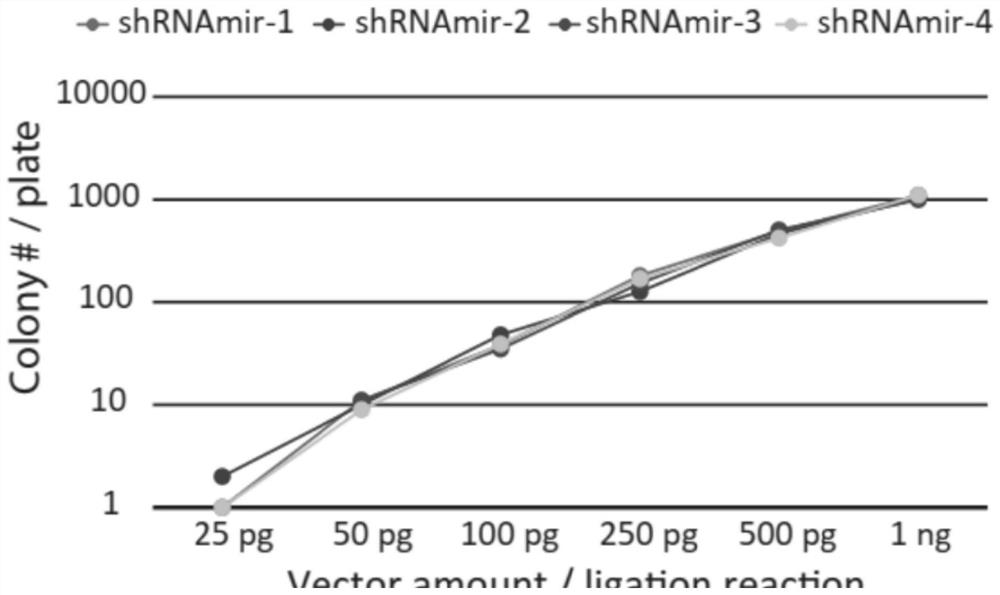
Pri-miRNA improved sequence and vector for expressing same
PendingCN114277030AEnsure high efficiencyGuaranteed accuracyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionChemical synthesisNucleotide
The invention relates to the technical field of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference, in particular to a pril-miRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) improved sequence based on human miR-30 (Micro Ribonucleic Acid) and a vector for expressing the sequence, and BamHI and Apal restriction endonuclease recognition sites are introduced into a stem part of the pril-miRNA improved sequence. According to the invention, a sequence of pril-miRNA, namely a frame of shRNAmir, is modified, two ends of a gene-specific shRNA sequence of a stem part of the pril-miRNA are improved on the premise of not influencing biological processing of the pril-miRNA, and a part of the original sequence is replaced by BamHI and ApaI restriction enzyme recognition sites, namely, only the shRNA sequence is arranged between the recognition sites of the two restriction enzymes, namely BamHI and ApaI, so that only the shRNA sequence is arranged between the recognition sites of the two restriction enzymes; therefore, it is guaranteed that only a very short gene specific shRNA sequence is cloned in the cloning process, the latter can be synthesized by using a DNA oligonucleotide chemical synthesis technology, the problem that a pril-miRNA basic sequence is cloned in is effectively avoided, and high efficiency and accuracy of cloning are guaranteed.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
High-throughput screening tool for enabling escherichia coli to obtain effective NHEJ system and application of high-throughput screening tool
PendingCN114164225AShort timeImprove screening efficiencyHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention provides a high-throughput screening tool for enabling escherichia coli to obtain an effective NHEJ system and an application of the high-throughput screening tool. The high-throughput screening tool comprises a pDual-Cas9-Parental plasmid vector, a plasmid vector and a screening vector, wherein the pDual-Cas9-Parental plasmid vector contains a DNA helicase gene, a replicon, an antibiotic resistance gene, a nuclease gene, an araC gene, an arabinose promoter and an IIs type restriction enzyme recognition site; and the pDual-sgRNA-lacZ plasmid vector contains an sgRNA sequence of a targeted lacZ gene, a strong promoter for constitutive expression, a replicon and an antibiotic resistance gene. The high-throughput screening tool can perform rapid and high-throughput screening on effective Ku + ligD combinations in escherichia coli, multiple Ku + ligD combination results can be obtained through one screening experiment, the time is short, the screening efficiency is high, and conditions are created for gene editing research of escherichia coli.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
A Method of Obtaining Unknown Sequences Flanking Known Sequences
ActiveCN105400771BReduce non-specific amplificationEasy to operateDNA preparationRestriction Enzyme Recognition SiteBiology
A method of acquiring an unknown flanking sequence of a known sequence is disclosed. The method includes 1) designing two specific primers according to the known sequence which are labeled as SP1 and SP2, with the SP2 carrying a restriction enzyme recognition site, and designing a pair of reverse PCR primers which are F1 and D1 between the SP2 and a border sequence, 2) amplifying to obtain a PCR product 1 by adopting genome DNA as a template and by using any one degenerate primer and the specific SP1 primer, 3) amplifying to obtain a PCR product 2 by adopting the PCR product 1 as a template and by using the specific SP2 primer and a degenerate primer, with the degenerate primer in the step 3) being same with the degenerate primer in the step 2), but comprising a restriction enzyme recognition site, and 4) subjecting the PCR product 2 to digestion, adding T4 ligase, cyclizing, and amplifying by adopting the cyclized product as a template and by using the F1 primer and the D1 primer to obtain a PCR product 3, thus acquiring the flanking sequence. The method is advantaged by simple and easy operation, a low cost, a high success rate, short time, and the like.
Owner:SANMING UNIV
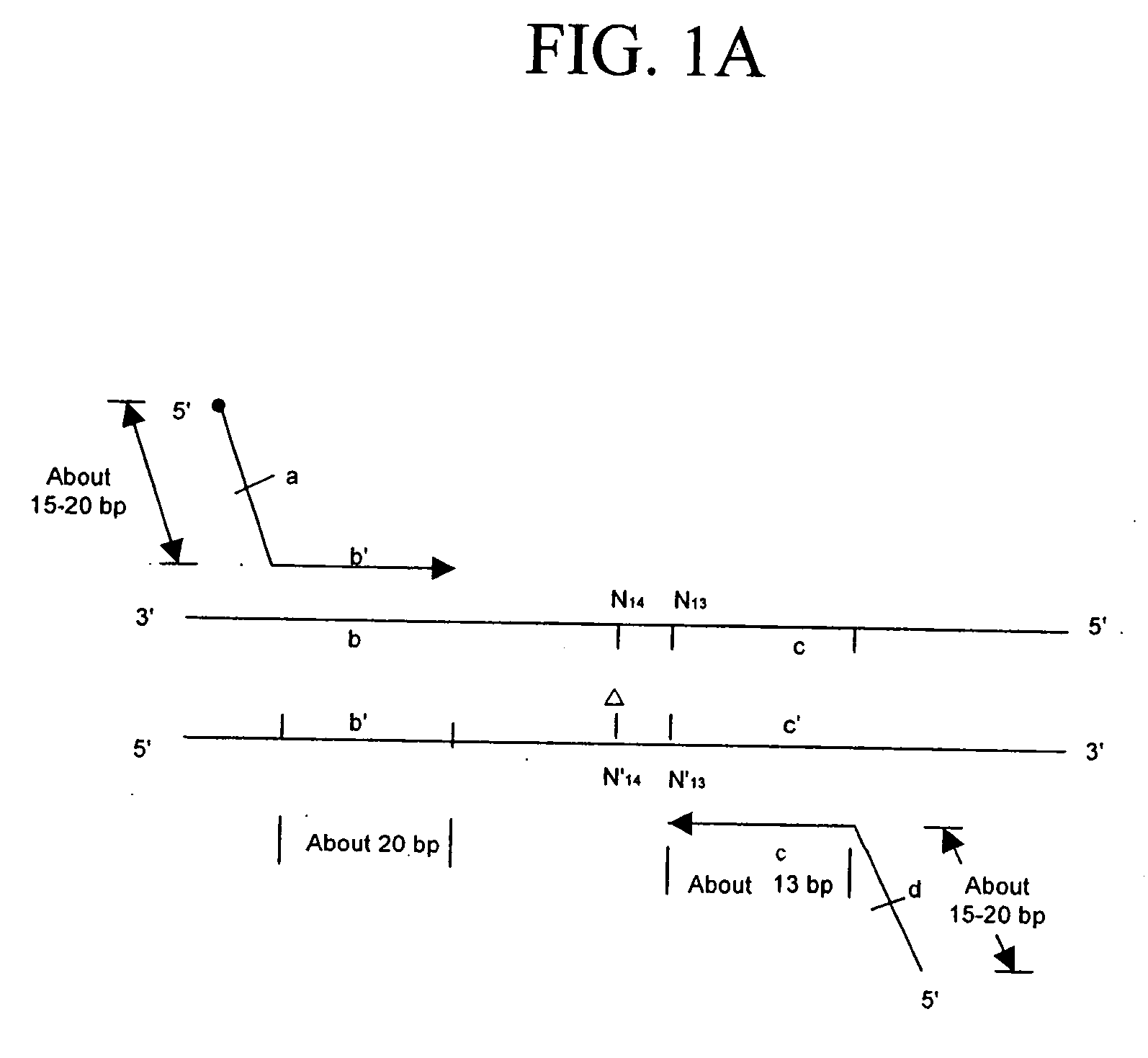
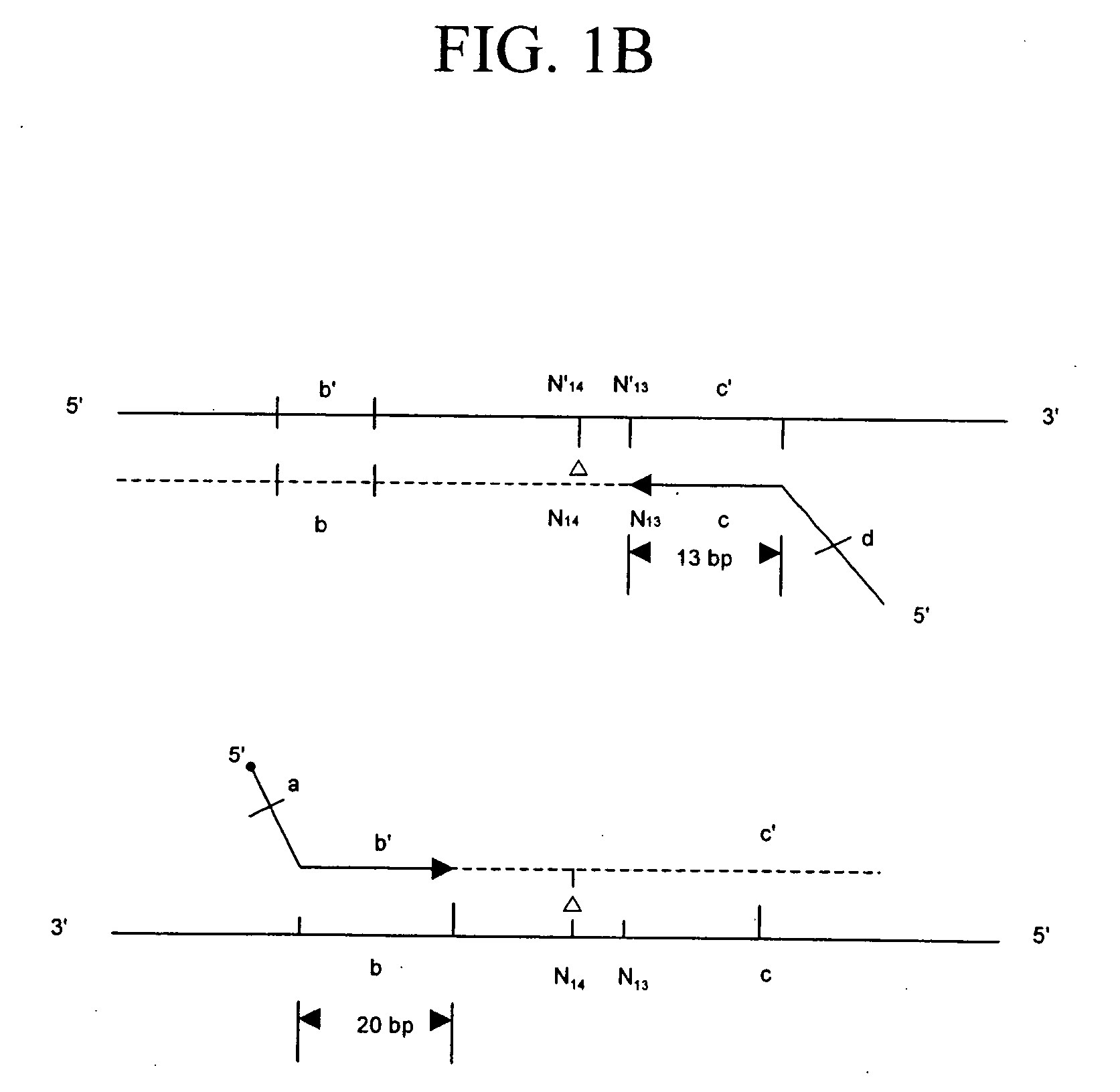
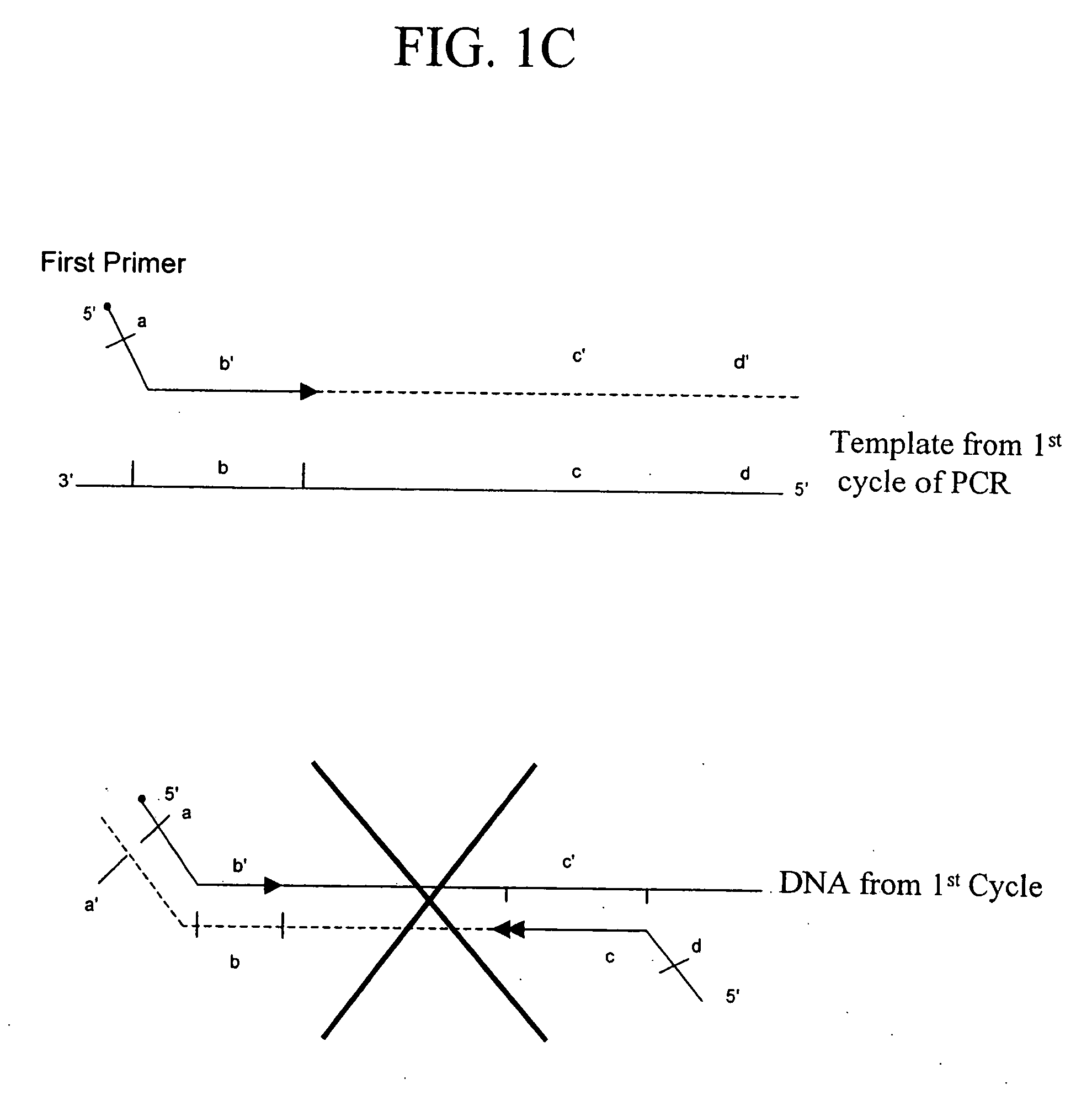
Methods for rapid production of double-stranded target DNA
InactiveUS9206473B2Increase synthesisIncrease volumeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA constructSingle strand
A method of rapidly producing a double-stranded target DNA is disclosed. The method includes the step of producing multiple single stranded primary DNA constructs having (a) partially overlapping and complementary internal regions that together define the target DNA, and (b) flanking regions on either side of the internal regions containing a PCR primer recognition site and a restriction enzyme recognition site. The primary DNA constructs are amplified to form a pool of double-stranded primary constructs, and a restriction enzyme is used to cleave off the flanking regions. The target double-stranded DNA is then assembled from the cleaved fragments. Hundreds of thousands of oligonucleotides can be synthesized and quickly and efficiently assembled into many different individual double-stranded DNA target sequences using this method.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
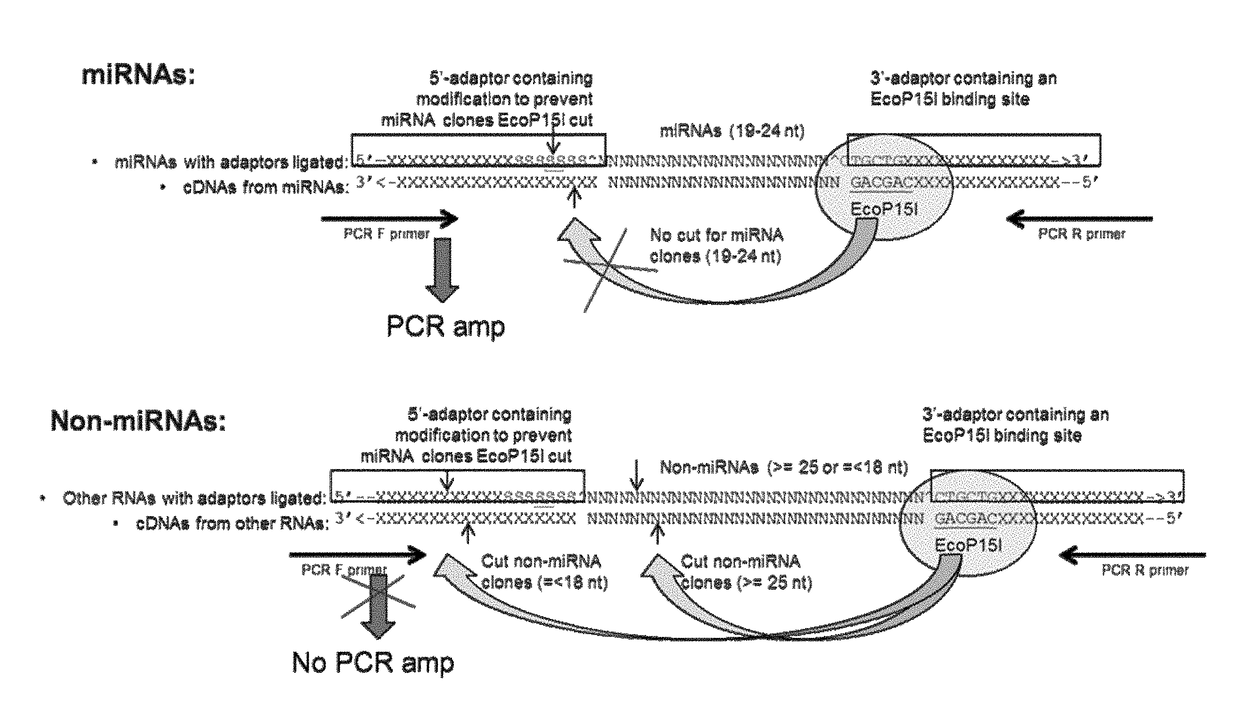
miRNA TRANSCRIPTOME METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS
Methods, polynucleotides, kits, and reaction mixtures are disclosed for the enriching of short polynucleotide molecules that have a length within a desired target length range. A Type IIS or Type III restriction enzyme is used to cleave polynucleotides at cleavage sites located at a distance from the restriction enzyme recognition sites. For example, a mixture of polynucleotides can be formed by inserting DNA molecules between a recognition site for the restriction enzyme and a region of non-naturally-occurring nucleotides that block cleavage by the restriction enzymes. If a polynucleotide contains a DNA molecule with a length within a target range, then the cleavage site will be within the blocking region, and cleavage will not occur. Polynucleotides containing DNA molecules with lengths outside the target range can be cleaved. By selectively enriching, through PCR or other means, polynucleotides that are intact, a concentrated population of polynucleotides of a target length can be formed.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com