Blood cell separation system
A blood cell and system technology, applied in analytical materials, biological material analysis, material inspection products, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
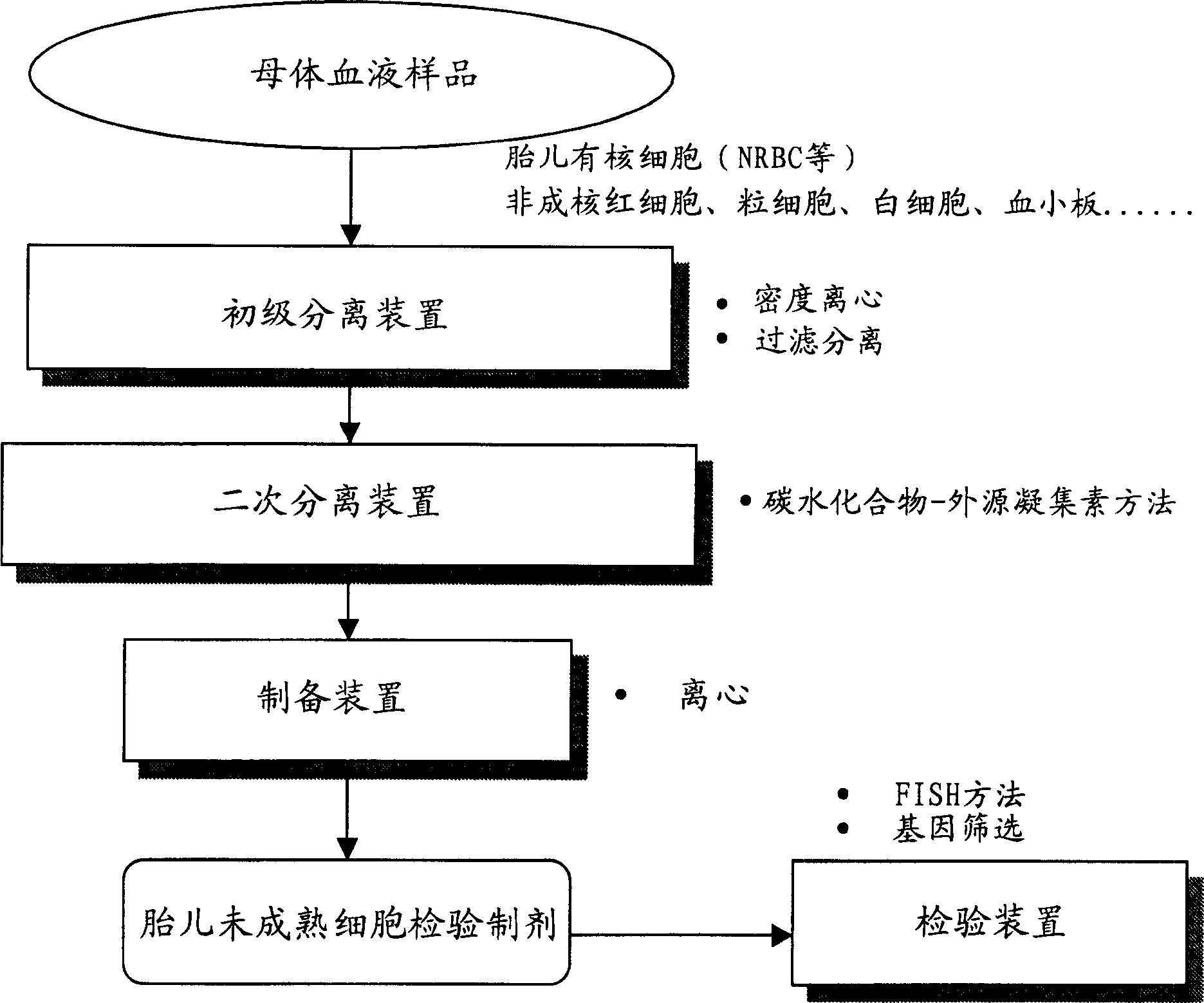
[0066] Example 1: Primary Separation Using Density Centrifugation
[0067] Histopaque (Sigma) was obtained and used as a density centrifugation reagent to which sodium diatrizoate was added and 6 types of density gradient fluids were prepared with specific gravity adjusted to 1.077-1.105. 7 cc of venous blood was obtained from pregnant women at 10-20 weeks of pregnancy, and then centrifuged in each density gradient fluid for 30 minutes (20° C., 1500 rpm). The collected cells surrounding the boundary between the density gradient fluid and the plasma fraction (upper layer) are recovered and centrifuged with a biological buffer to obtain a crude fraction free of most non-nucleated red blood cells and platelets.
[0068] Samples that were initially purified at various densities were subjected to secondary separations using the carbohydrate-lectin method. As a substrate, a plastic slide chamber (2-well, product of Nalgenunc) was used. The complex carbohydrate polymer coated on th...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2: Additional isolation by panning
[0072] Plastic slide chambers (4 wells, product of Nalgenunc) were treated with FCS or 0.01 wt% aqueous solution of complex glycopolymers (PV-glyco) (product of Netech). As complex glycopolymers, those containing glucose, maltose, gluconic acid, N-acetylglucosamine, mannose, lactose or melibiose structures are used.
[0073] The recovered postnatal cord blood was subjected to density gradient centrifugation using Histopaque (d, 1.095) according to standard methods, and cells agglutinated near the boundary between Histopaque and plasma were collected. The samples were resuspended in RPMI1640 supplemented with 10 wt% FCS, and seeded on the above-mentioned wells whose surface was coated with FCS or complex glycopolymer. After incubation at 37°C for 30 minutes, non-adhered cells were recovered in the form of a cell suspension fluid, and cells adhered to the wells were stained with Pappenheim's stain to identify their type. The ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3: Primary Separation Through Filtration Separation
[0081] Instead of the density centrifugation method in Example 1, a filter comprising a non-woven polyester fabric with an average pore size of 8 μm was used for primary separation. Maternal blood samples were diluted with biological buffer containing 1 wt% BSA and passed through the filter using natural dropwise addition. Next, pass the buffer only through the filter to wash the red blood cells remaining on the filter. Subsequently, the buffer was passed back through with a syringe pump, and non-adherent cells that did not pass through the filter were recovered. The fraction of cells that did not pass through the filter but did not strongly adhere to the filter was extracted as a primary fraction, which was subjected to secondary fractionation using the carbohydrate-lectin method. Table 4 shows the ratio (fold) of the results of primary separation samples obtained from the above filters to the results of s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com