Patents
Literature
91 results about "Beta-glucuronidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
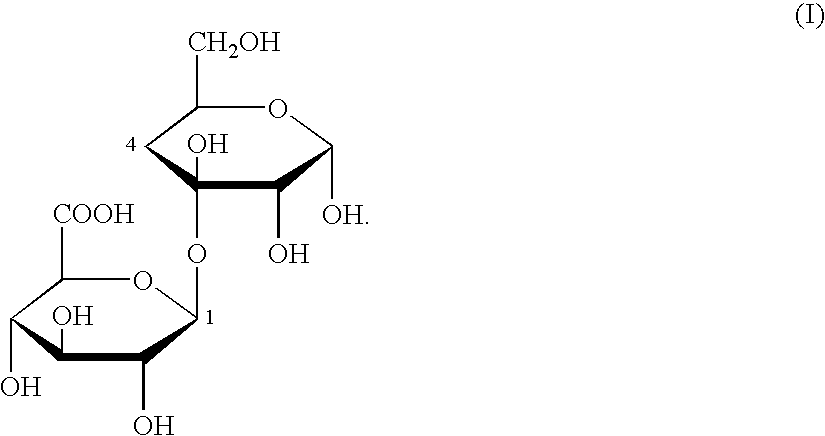
Beta-glucuronidases are members of the glycosidase family of enzymes that catalyze breakdown of complex carbohydrates. Human β-glucuronidase is a type of glucuronidase (a member of glycosidase Family 2) that catalyzes hydrolysis of β-D-glucuronic acid residues from the non-reducing end of mucopolysaccharides (also referred to as glycosaminoglycans) such as heparan sulfate. Human β-glucuronidase is located in the lysosome. In the gut, brush border β-glucuronidase converts conjugated bilirubin to the unconjugated form for reabsorption. Beta-glucuronidase is also present in breast milk, which contributes to neonatal jaundice. The protein is encoded by the GUSB gene in humans and by the uidA gene in bacteria.
Beta-glucuronidase with an attached short peptide of acidic amino acids
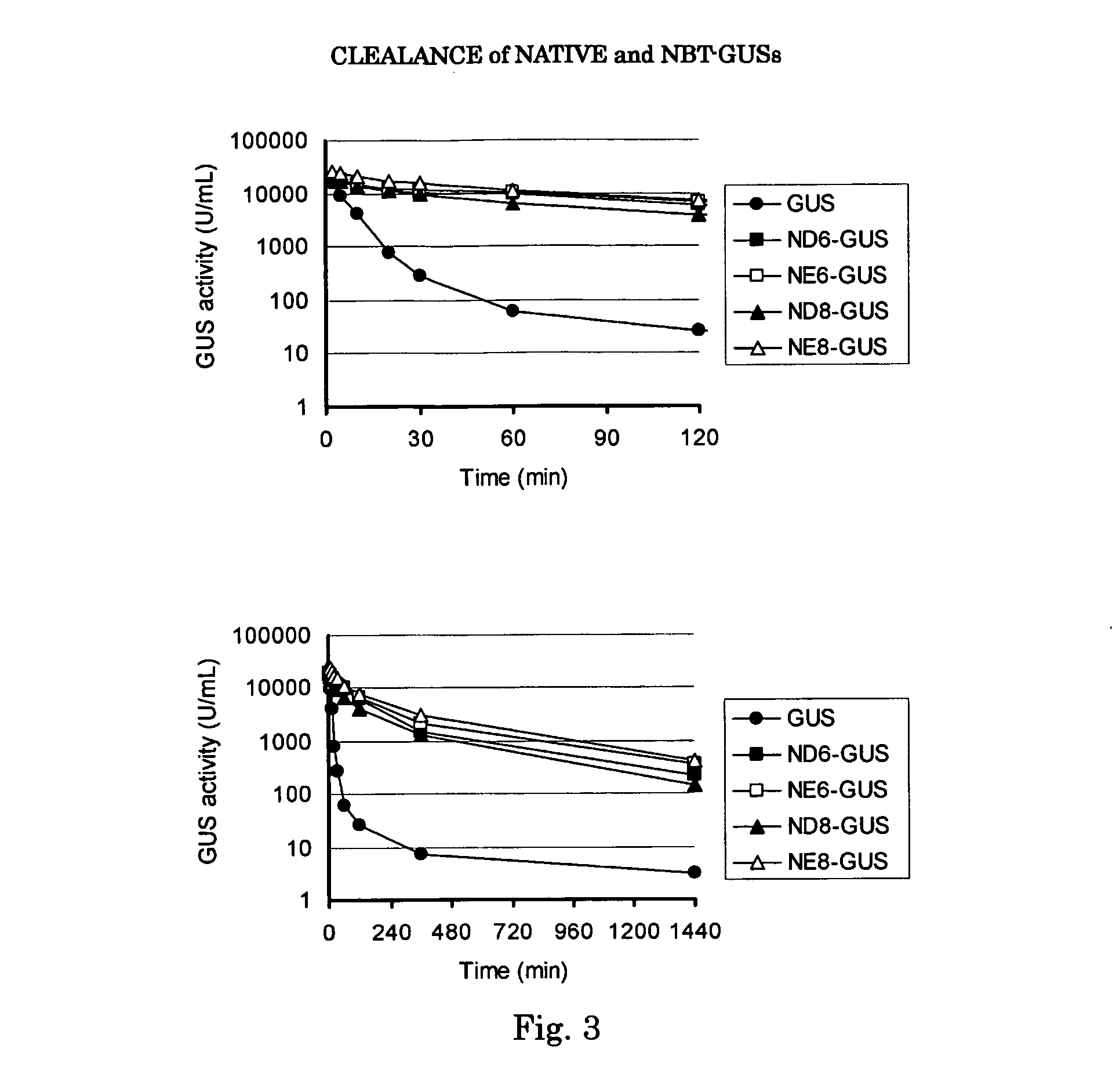
InactiveUS20070081986A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationBeta-glucuronidaseAcidic amino acids
Disclosed are a fusion protein comprising enzyme β-glucuronidase and short peptide consisting 4-15 acidic amino acids attached to the enzyme on its N-terminal side, pharmaceutical composition containing the fusion protein, and a method for treatment of type VII mucopolysaccharidosis using the fusion protein. Compared with the native enzyme, the fusion protein exhibits higher stability in the blood.
Owner:TOMATSU SHUNJI +5
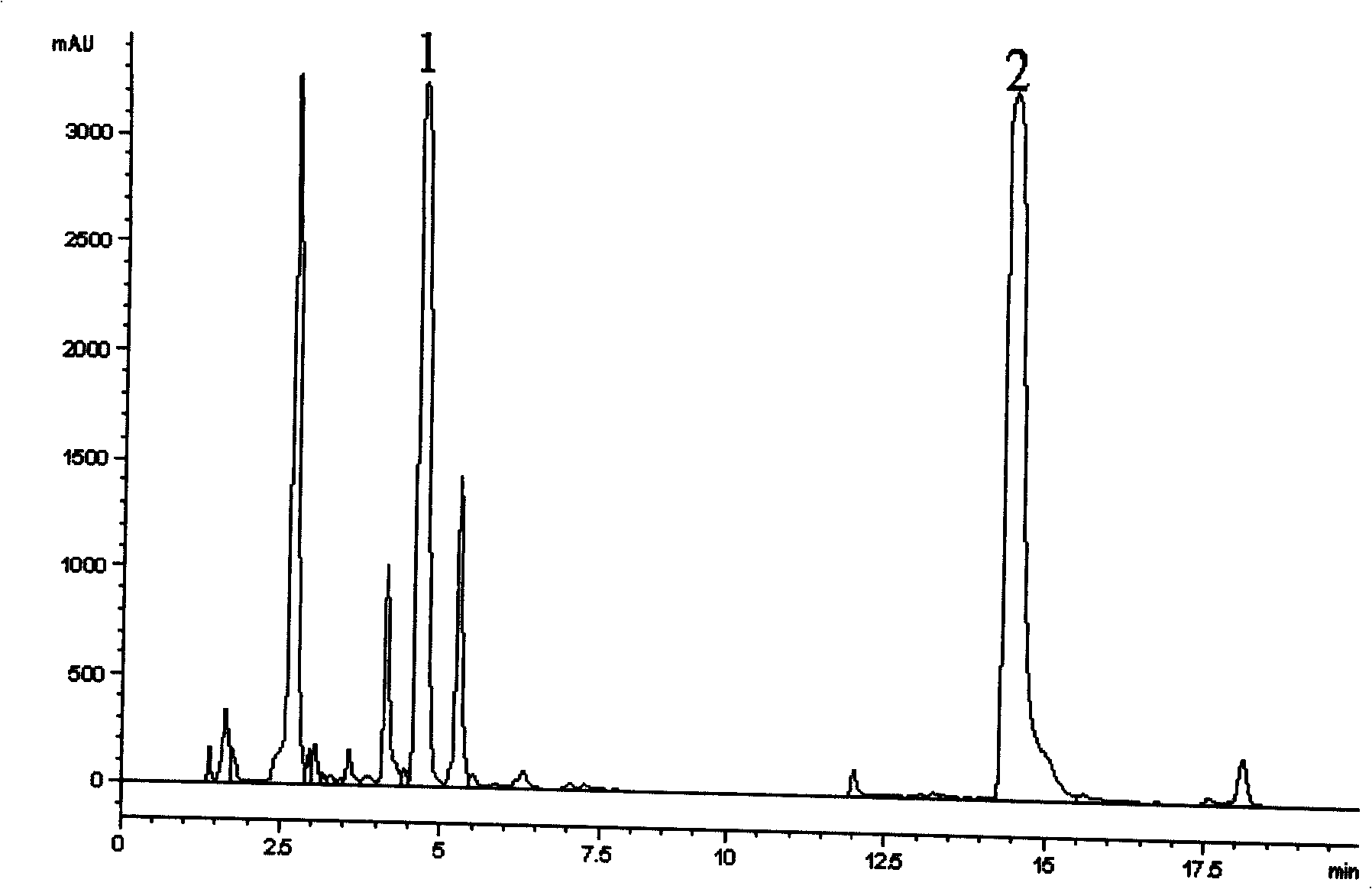
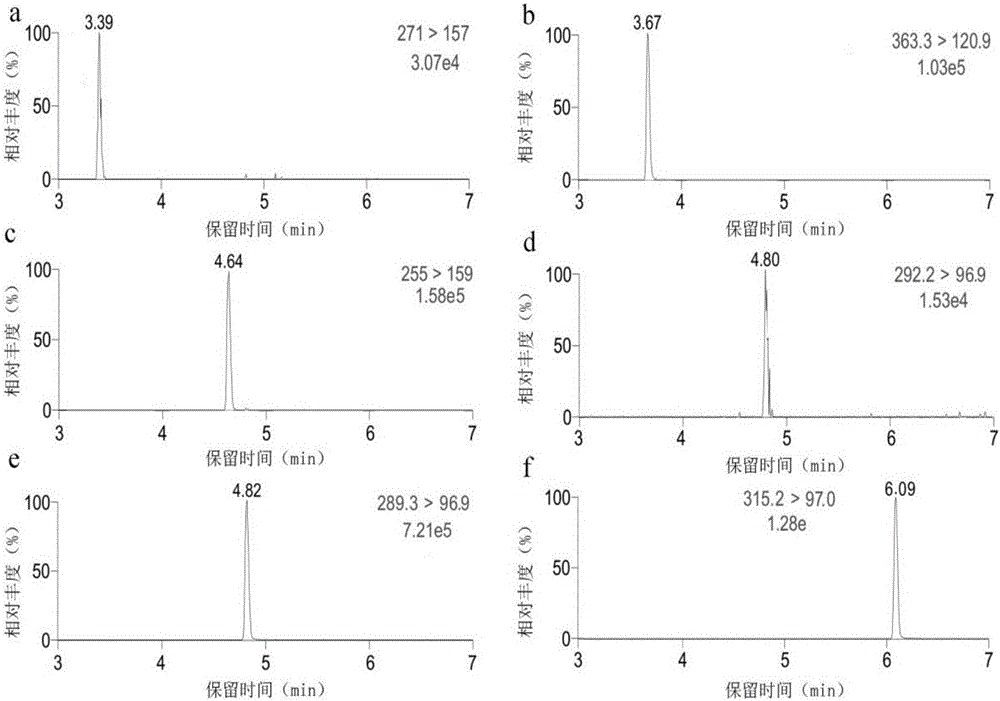
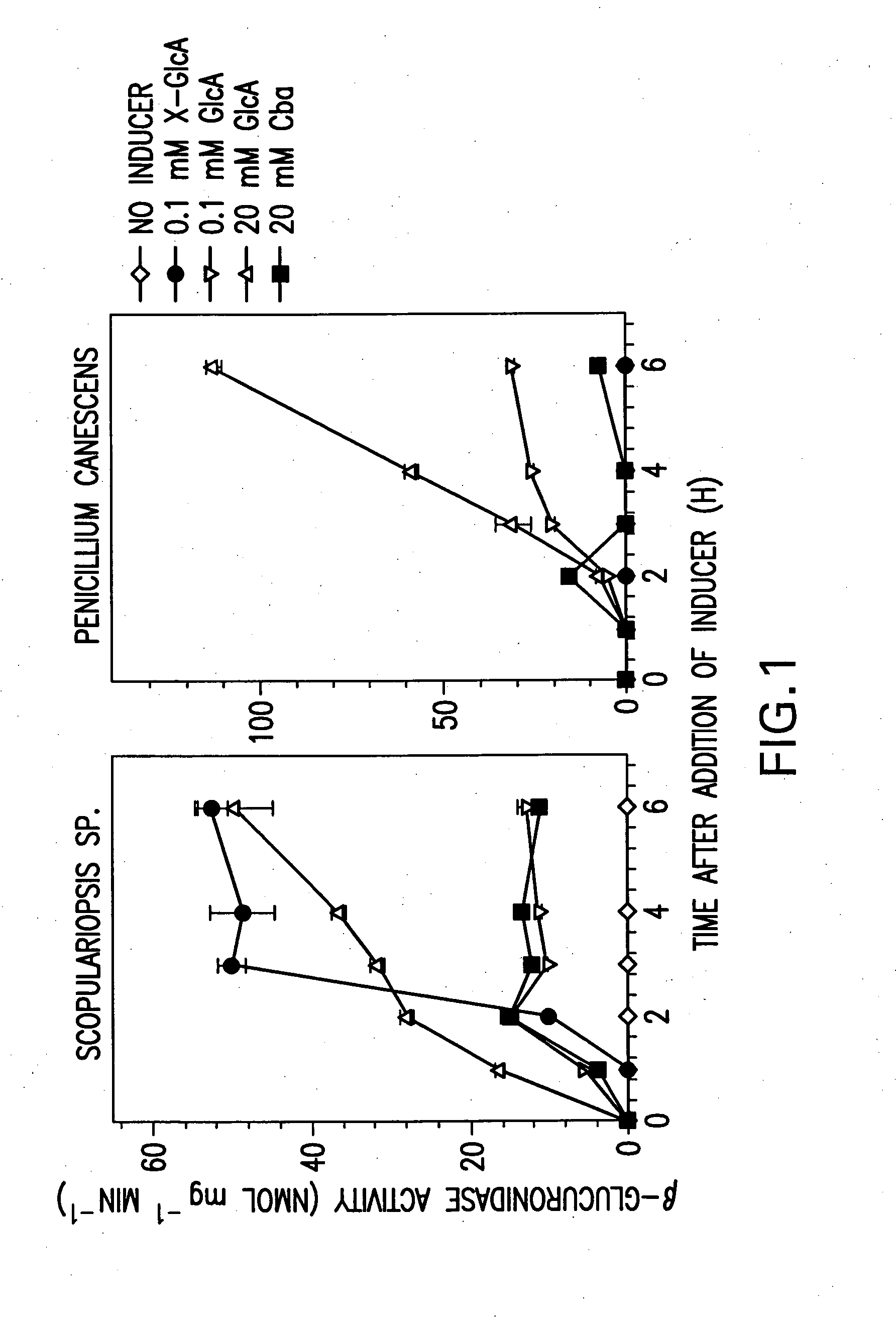
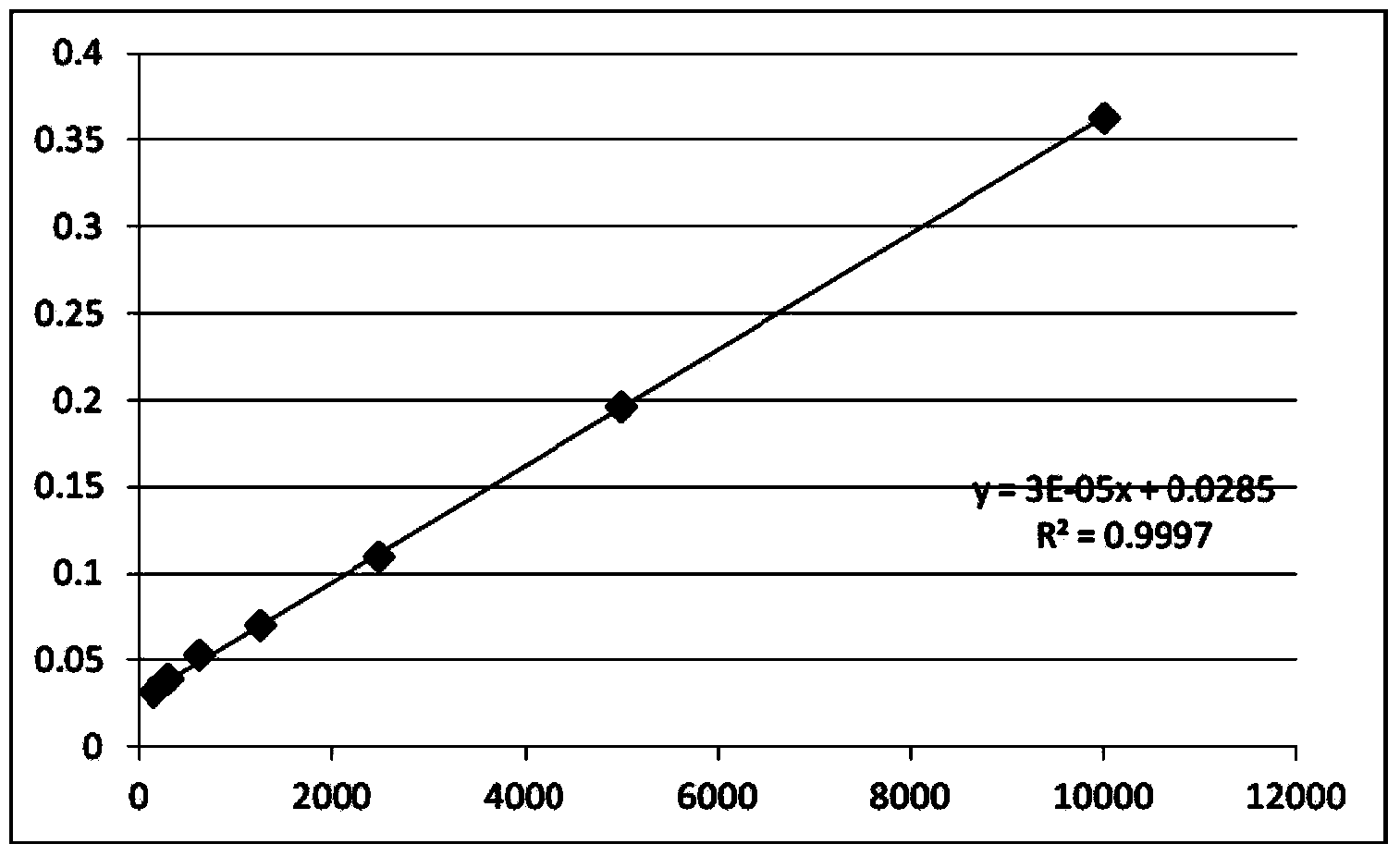
Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine
InactiveCN103063791AOptimizing enzymatic conditionsOptimizing Solid Phase Extraction ConditionsComponent separationChromatographic separationRotary evaporator
The invention discloses a method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine. The method comprises sequentially using beta-glucuronidase for enzymatic hydrolysis of samples, performing solid-phase extraction and purification, concentrating the samples with a vacuum rotary evaporator, and determining by using a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer, thereby rapidly, accurately and simultaneously detecting contents of 1-hydroxy pyrene (1-OHP), 3-hydroxy benzo [a] pyrene (3-OHB [a] P) and 3-hydroxy benzo [a] anthracene (3-OHB [a] A) in the urine. The method uses deuterated standards as quantitative analysis substances of internal standards and thus can reduce errors in a pretreatment process for the samples; uses a tandem mass spectrometer to relatively improve selectivity and accuracy of the method; and selects a method of preparing standards by matrices, wherein, compared with a method of preparing the standards by pure water, the method of preparing standards by matrices is relatively good in accuracy and can eliminate interference from matrix effects. Through selecting and optimizing chromatographic columns and gradient elution conditions, the method relatively improves a chromatogram separating process and shortens a chromatographic analysis time.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
Quality control product of AV/BV combined test kit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102864208AEasy to prepareEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTHydrogen peroxide
The invention provides a five-item quality control product of an AV / BV combined test kit and a preparation method thereof, belonging to quality control products for controlling the quality of kits used during female gynecological clinical detection. The quality control product comprises a vaginal discharge five-item positive quality control product and a vaginal discharge five-item negative quality control product, and the two types of quality control products are stored in the states of dry powder. The quality control product is used to carry out quality detection of a vaginitis test kit and can carry out quality control on five biochemical indexes including hydrogen peroxide, neuraminidase, leucocyte esterase, beta-glucuronidase and coagulase. By means of taking biological enzymes as active ingredients of the quality control product and preparing a dry powder quality control product by adopting a freezing-drying technology, the deactivation of a liquid quality control product in transportation and storage processes is avoided. The quality control product does not contain any human vaginal discharge, and does not cause infection to the environment and operators.
Owner:北京中生金域诊断技术股份有限公司
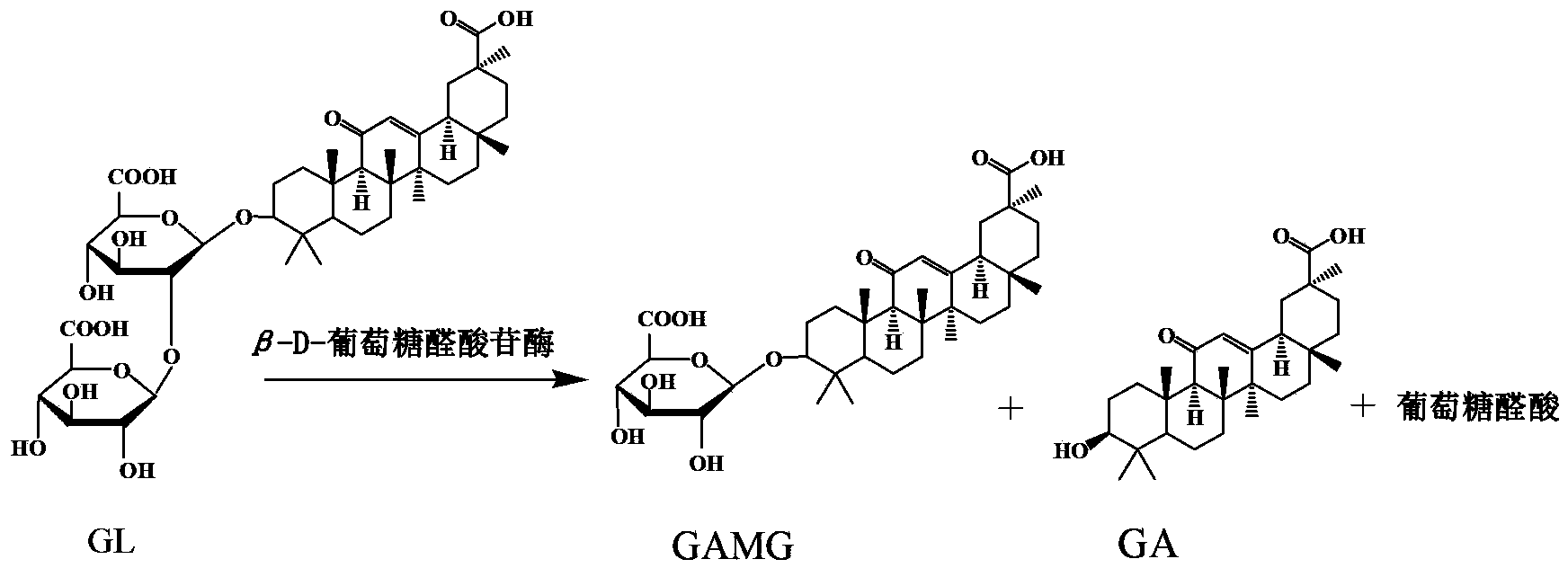
Method for preparing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide
ActiveCN103352062AHigh yieldImprove conversion rateHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesFood additiveGLYCYRRHIZA EXTRACT
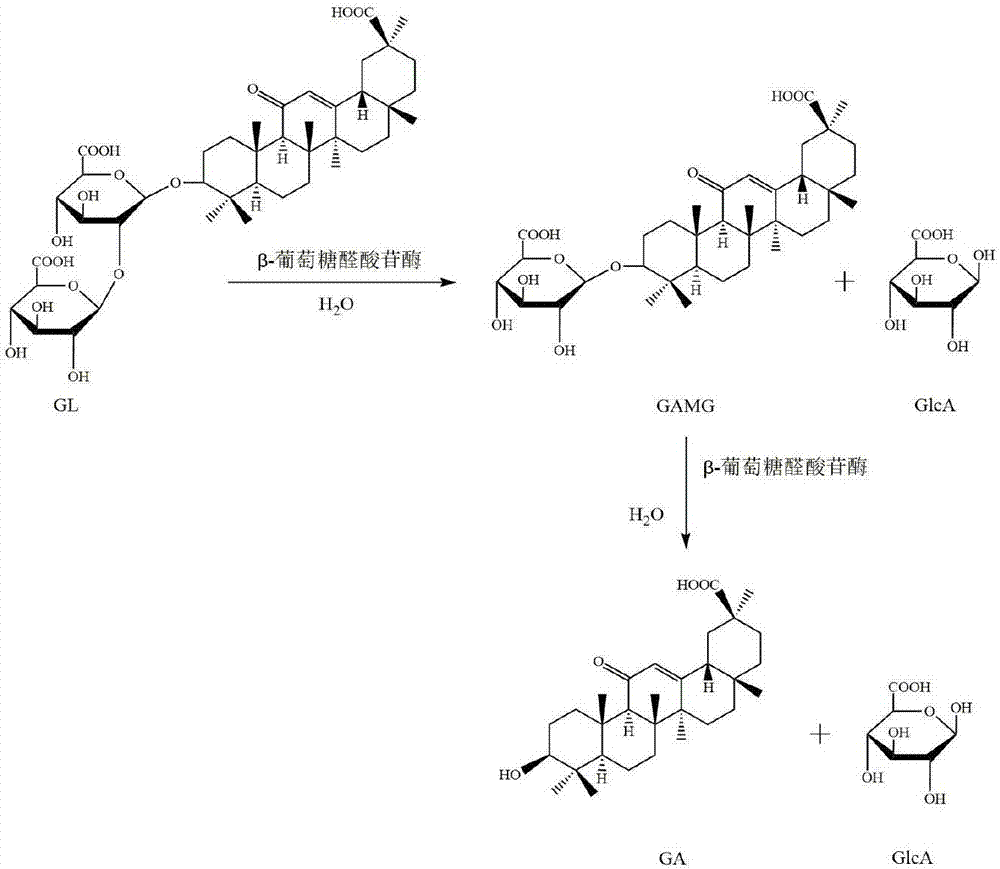
The invention relates to a method for preparing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide (GAMG), and belongs to the field of food additives. The method comprises the steps that accelerants of a liquorice total extract, or liquorice total polysaccharide and / or liquorice total flavone are added to a culture medium containing glycyrrhizic acid or salt of glycyrrhizic acid; Penicillium purpurogenum Li-3 is induced to generate beta-glucuronidase; the preservation number of Penicillium purpurogenum Li-3 is CGMCC No. 5446 (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Number 5446); enzyme production is 5-48h ahead compared with the condition that the accelerants are not added; the enzyme activity is increased by 0.5-5 times; a beta-glucuronidase crude enzyme preparation is prepared by thalli after the enzyme production or fermentation liquor containing the thalli; GAMG is generated by converting the liquorice total extract or glycyrrhizic acid and an analogue of glycyrrhizic acid in liquorice total triterpene; and GAMG in the fermentation liquor is separated and purified. The method improves the enzyme activity, avoids a complicated extraction and separation course by taking glycyrrhizic acid (or salt of glycyrrhizic acid) as carbon source glycyrrhizic acid (or salt of carbon source glycyrrhizic acid), and lowers the production cost.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
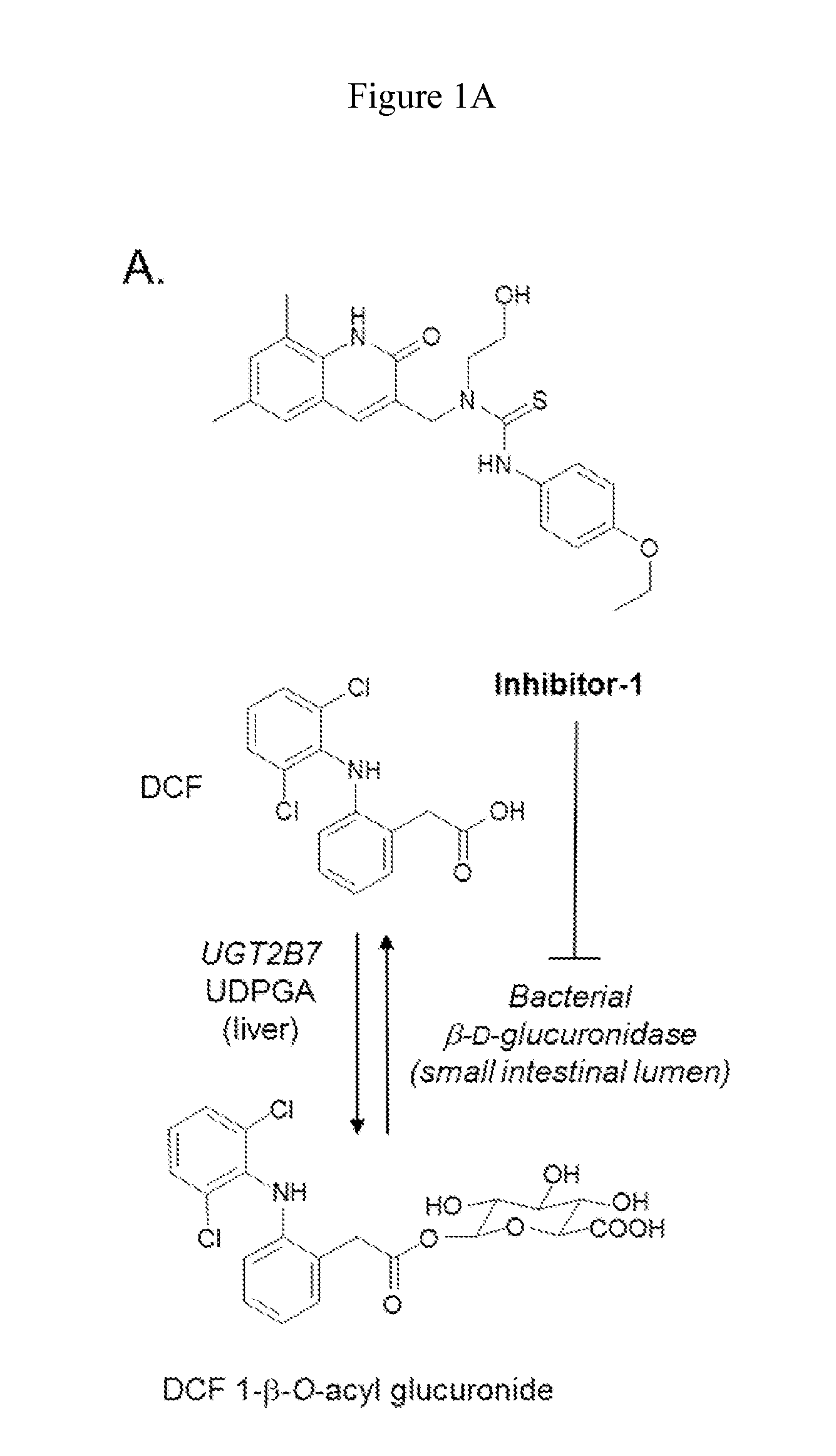
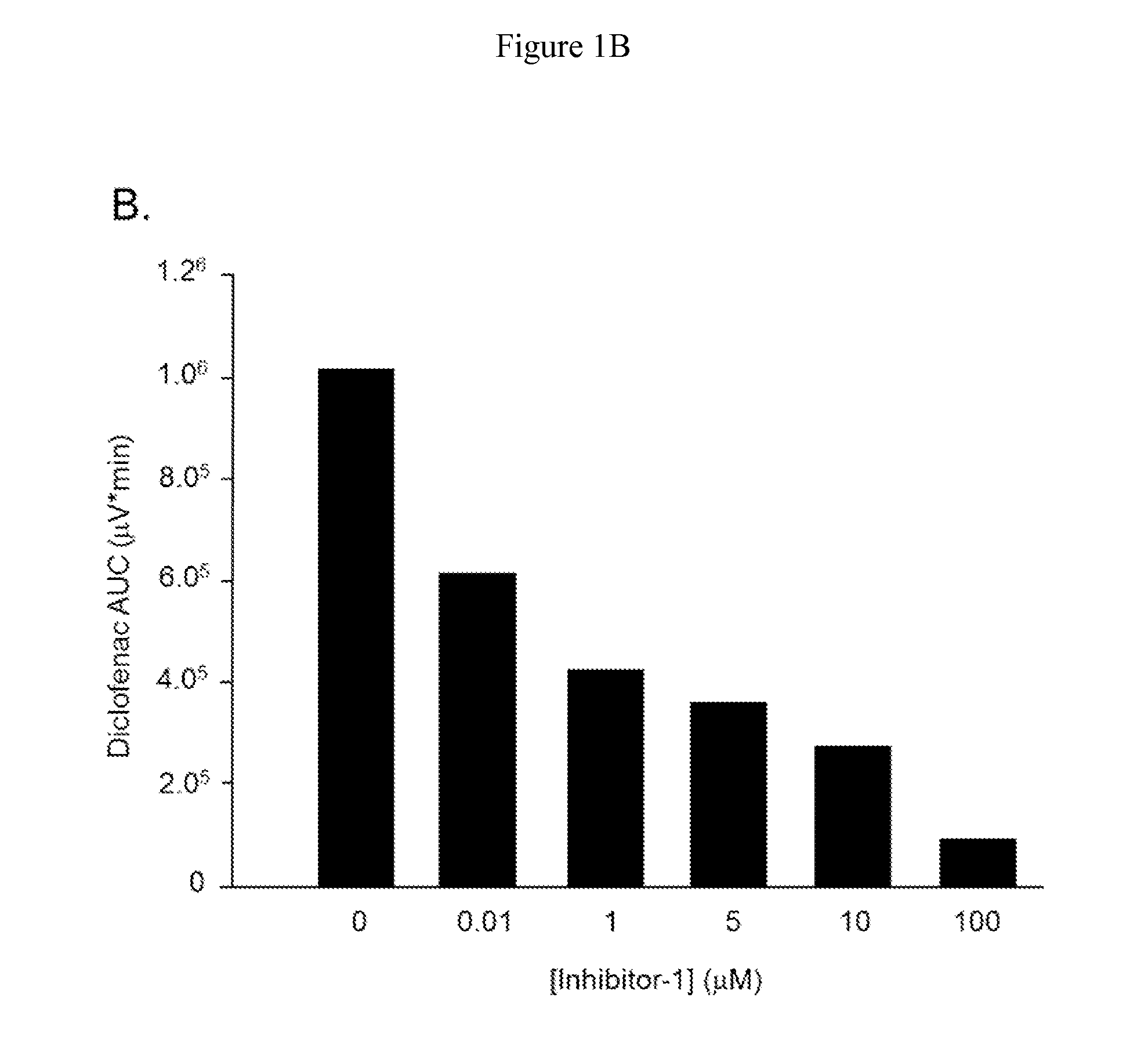
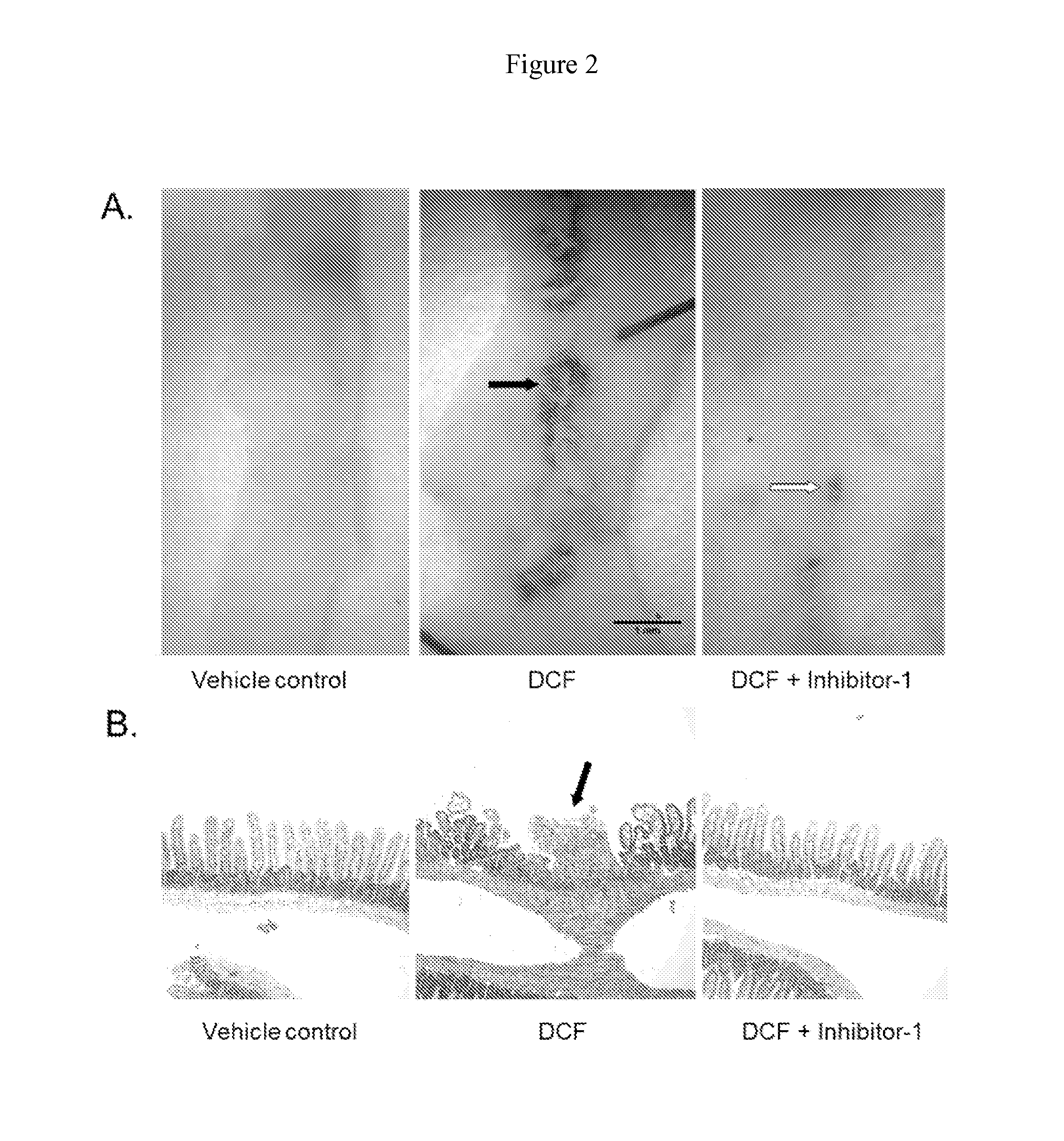
Methods of Treating Adverse Intestinal Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
InactiveUS20150011542A1Improve life expectancyIncreased future demandBiocideAntipyreticFenamic acidNon steroid anti inflammatory drug
Methods of treating adverse intestinal effects of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) in a subject by administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a selective bacterial beta-glucuronidase inhibitor. The adverse intestinal effects to be treated include the formation or growth of an intestinal ulcer, increased intestinal permeability, the loss of intestinal villi, bleeding of the intestinal mucosa, and an increased intestinal inflammatory response. The methods are useful for treating the adverse effects of any NSAID such as propionic acid derivatives, carboxylic acid derivatives, enolic acid derivatives, fenamic acid derivatives, sulphonanilidies, and selective COX-2 inhibitors. The bacterial beta-glucuronidase inhibitors are selective for the inhibition of bacterial beta-glucuronidase enzymes and do not inhibit mammalian beta-glucuronidase.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
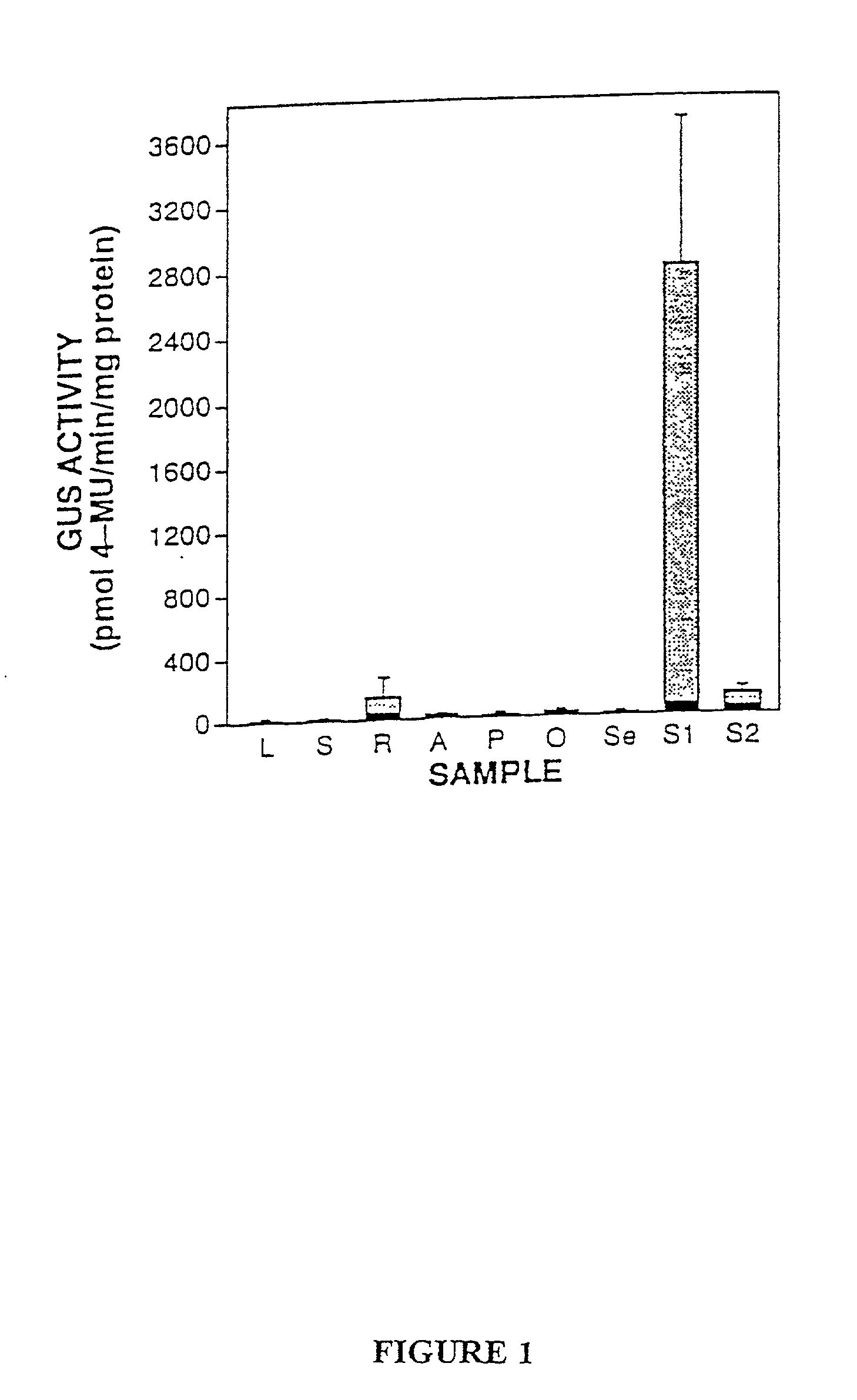
Cryptic regulatory elements obtained from plants
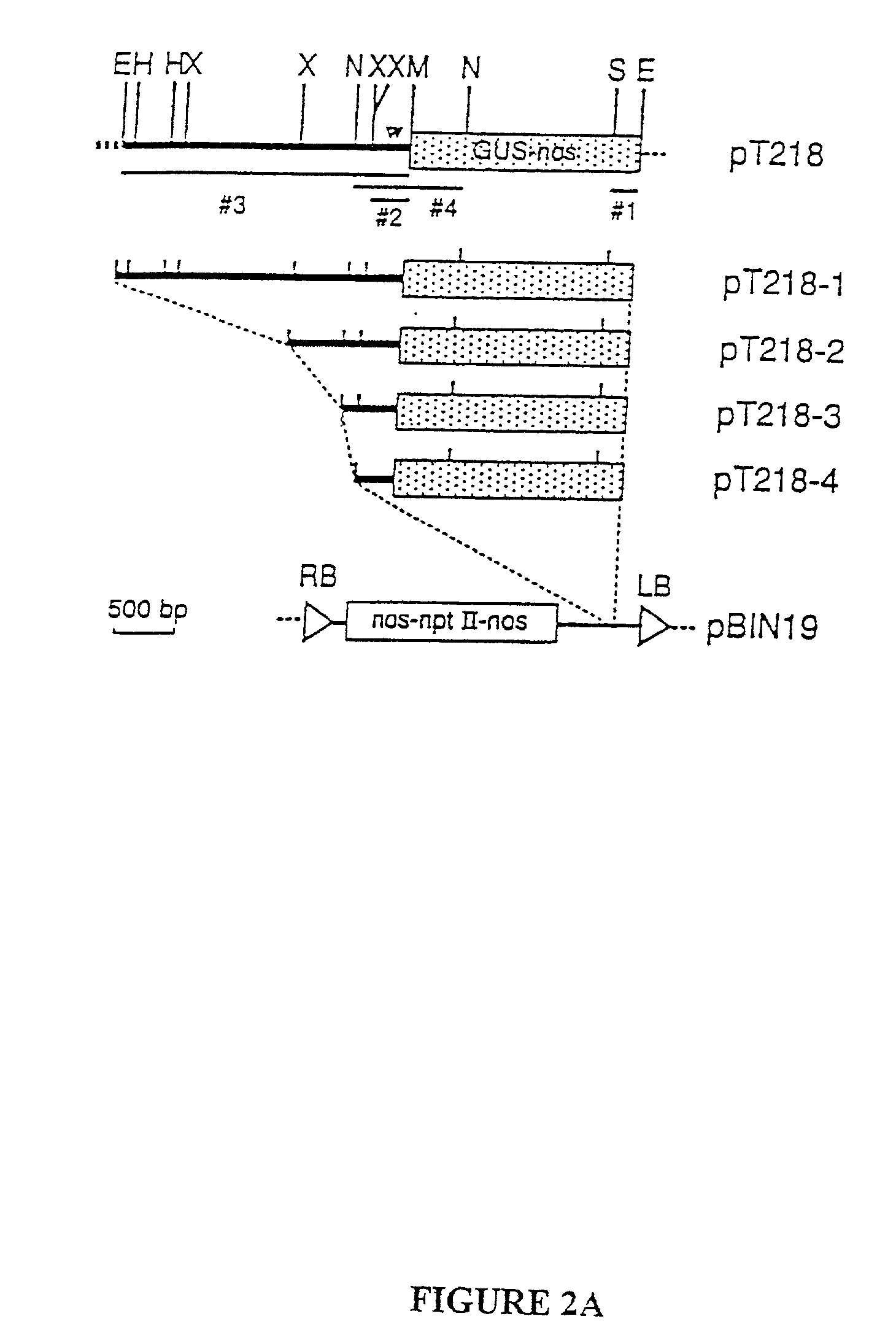
InactiveUS20010047091A1Reduce the amount requiredIncreased the amount of GUS specific activitySugar derivativesPlant peptidesNicotiana tabacumBeta-glucuronidase
T-DNA tagging with a promoterless beta-glucuronidase (GUS) gene generated transgenic Nicotiana tabacum plant that expressed GUS activity either only in developing seed coats, or constitutively. Cloning and deletion analysis of the GUS fusion revealed that the promoter responsible for seed coat specificity was located in the plant DNA proximal to the GUS gene. Analysis of the region demonstrated that the seed coat-specificity of GUS expression in this transgenic plant resulted from T-DNA insertion next to a cryptic promoter. This promoter is useful in controlling the expression of genes to the developing seed coat in plant seeds. Similarly, cloning and characterization of the cryptic constitutive promoter revealed the occurrence of several cryptic regulatory regions. These regions include promoter, negative regulatory elements, transcriptional enhancers, core promoter regions, and translational enhancers and other regulatory elements.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Method and kit for quantitatively measuring beta-glucuronidase in multiple samples by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELIASA) instrument
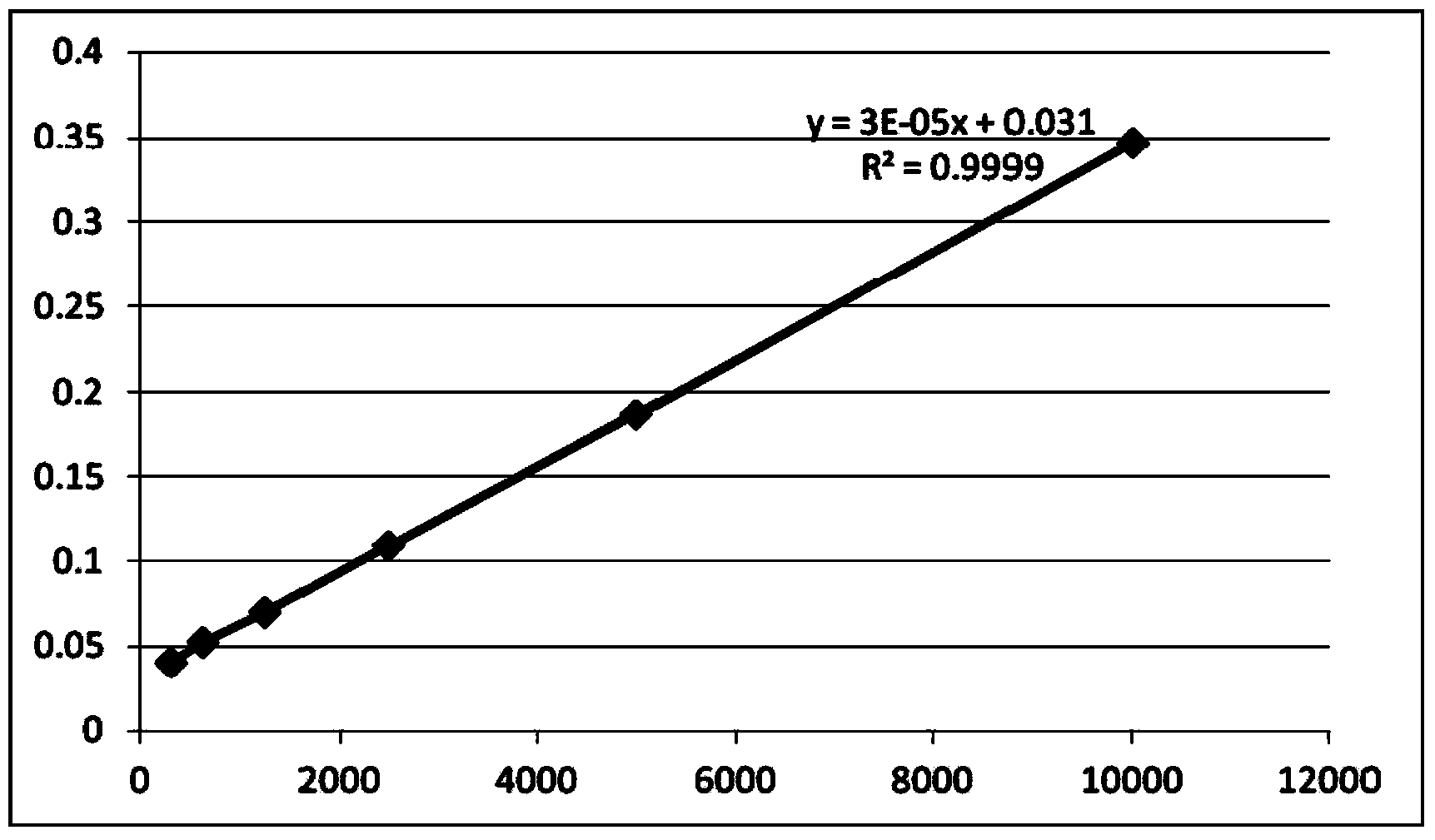
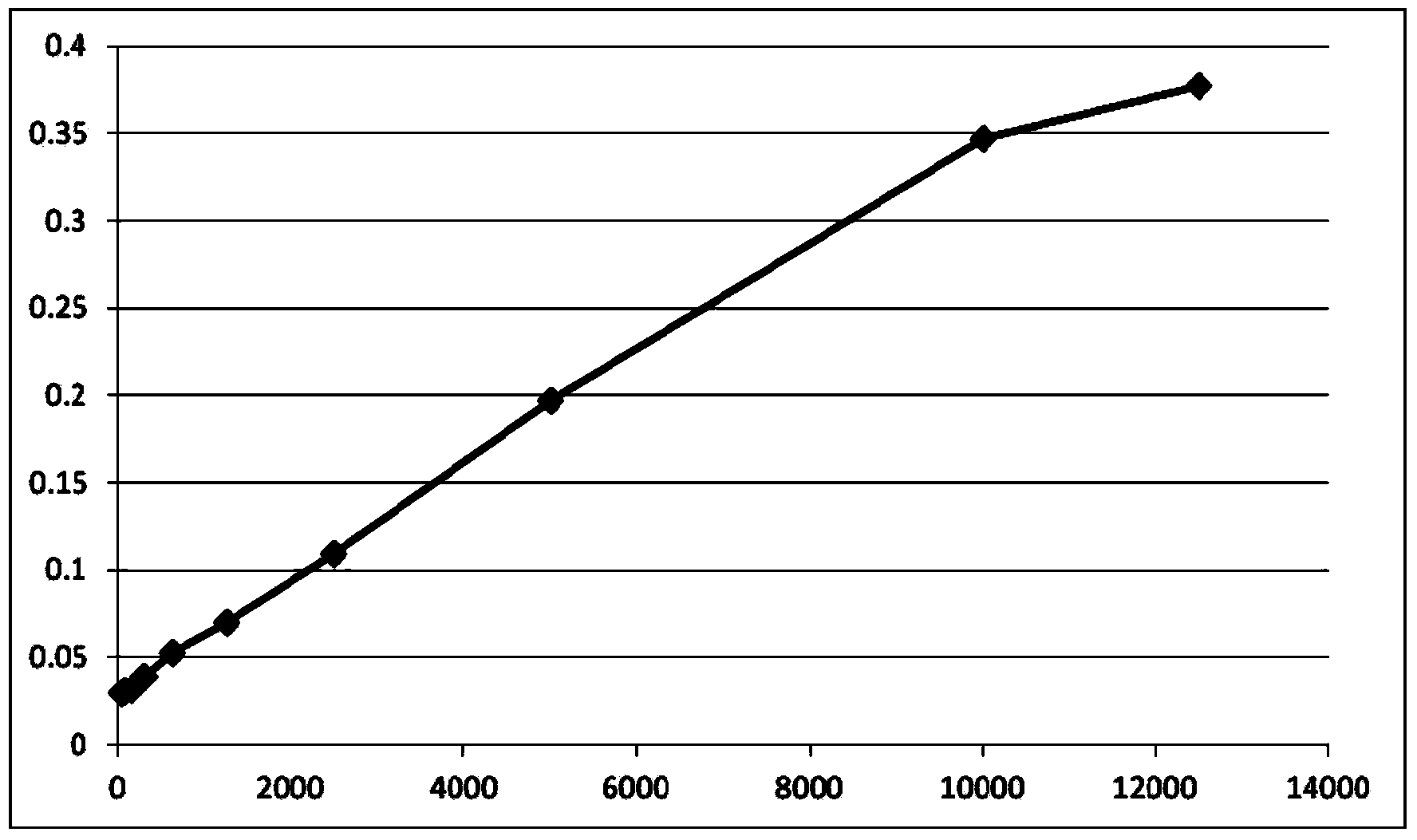
InactiveCN104034891AHigh sensitivityWide linear rangeColor/spectral properties measurementsPhenolphthaleinBeta-glucuronidase
The invention relates to a method and a kit for quantitatively measuring the beta-glucuronidase in multiple samples by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELIASA) instrument. The kit internally comprises beta-glucuronidase standard substance, working solution, phenolphthalein glucuronic acid reaction liquid, termination reaction reagent, a pH meter and the like. The method and the kit have the advantages that the concentration of the beta-glucuronidase in the multiple samples can be detected at the same time, and shorter detection time is consumed; the sensitivity is high, and the detection limit is 39.0625U / mL; the method is wide in linear range, the detection concentration is within the range of 39.0625-12500U / mL, and the three order of magnitudes are spanned; the accuracy is high; less reagent and fewer samples are used; the kit is convenient to operate; the samples can be fed once without being fed for a plurality of times; the cleaning step is omitted, so that the operation steps are reduced, cross contamination is prevented, and the result is guaranteed to be credible; the detected samples can be well stored so as to be repeatedly detected.
Owner:北京洛奇医学检验实验室股份有限公司
Method for producing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide through intermittent feed supplement fermentation
ActiveCN102367463AOvercome the disadvantage of low selectivityReduce outputMicroorganism based processesFermentationDrug biotransformationCulture mediums
The invention relates to a method for producing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide (GAMG) through intermittent feed supplement fermentation, belonging to the technical field of biological transformation. The method specifically comprises the steps of: firstly, cultivating and inducing microorganisms capable of inducing to generate beta-glucuronidase in a seed culture medium and a fermentation culture medium containing glycyrrhizic acid to obtain corresponding beta-glucuronidase; and secondly, specifically splitting a terminal glucosidic bond in a glycyrrhizic acid molecular structure by using the beta-glucuronidase generated by the microorganisms through induction, generating the GAMG, and secreting the GAMG to a fermentation solution and intermittently replenishing glycyrrhizic acid and inorganic salts as a substrate for multiple times. Through replenishing the glycyrrhizic acid and the inorganic salts as the substrate, nutrient substances are replenished, thallus can grow in a proper environment and promote the synthesis of a target product; and after the fermentation is ended, the yield of the GAMG reaches 13-24g / L. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the fermentation yield of the GAMG can be effectively increased, the transformation period is prolonged, the equipment utilization rate is increased, and the product production cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
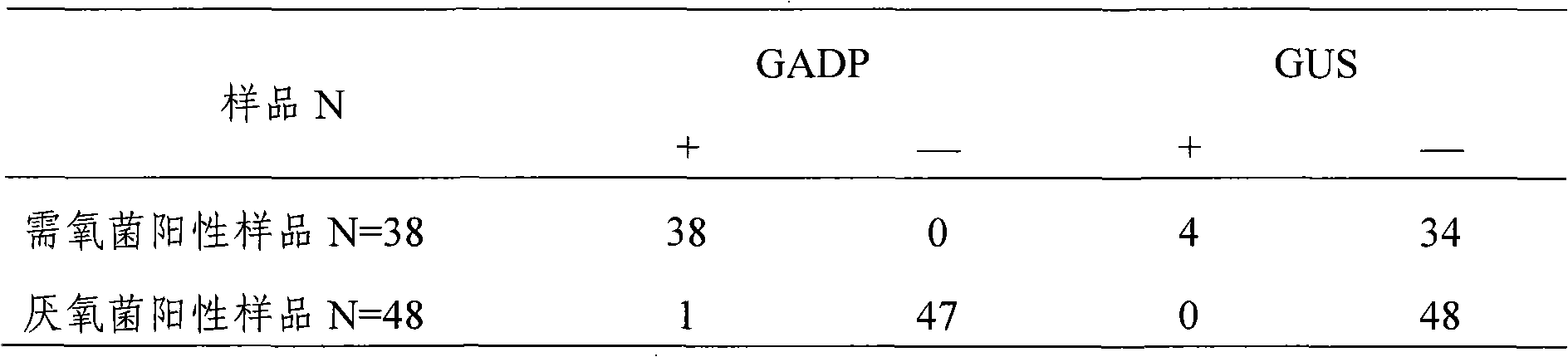
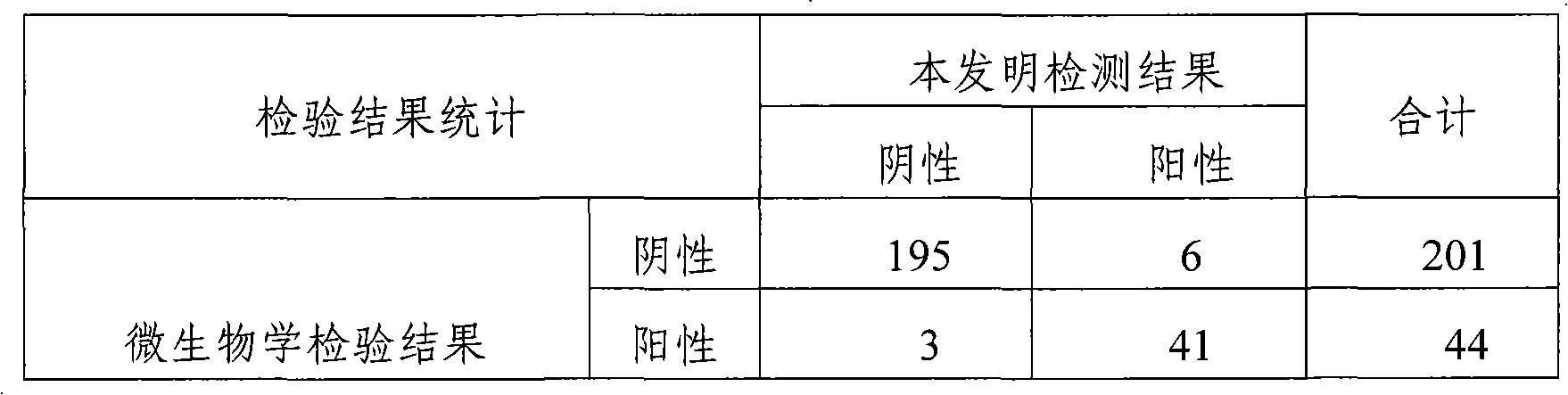
Kit for detecting aerobic bacteria in vaginal discharge and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101792792ANo training requiredSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention provides a kit for detecting aerobic bacteria in vaginal discharge, a dried kit comprises a reactor for detecting the enzyme activity of beta-glucuronidase and coagulase and color-developing agent, and a humidified kit comprises beta-glucuronidase substrate solution, coagulase substrate solution and color-developing agent. The invention also provides a preparation method of the kit. The kit in the invention directly identifies the aerobic flora, in particular to the aerobic floras such as staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, streptococcus group B, Escherichia coli and the like which can cause aerobic bacteria vaginalitis in vaginal discharge by detecting the activity of beta-glucuronidase and coagulase. The method has simple, convenient and rapid operation and high accuracy, and is suitable for convention application in clinics especially in hospital outpatient.
Owner:北京中生金域诊断技术股份有限公司
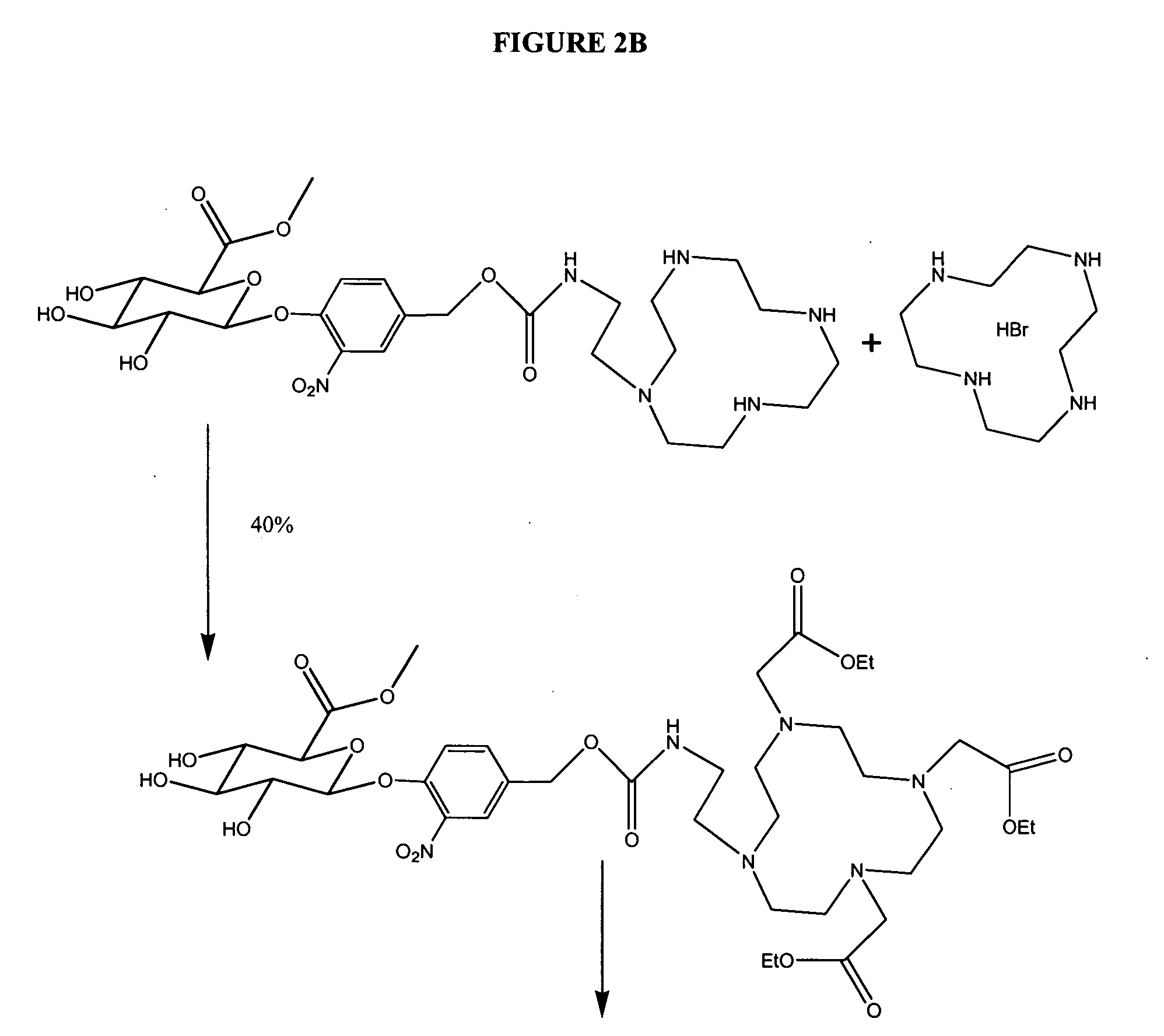
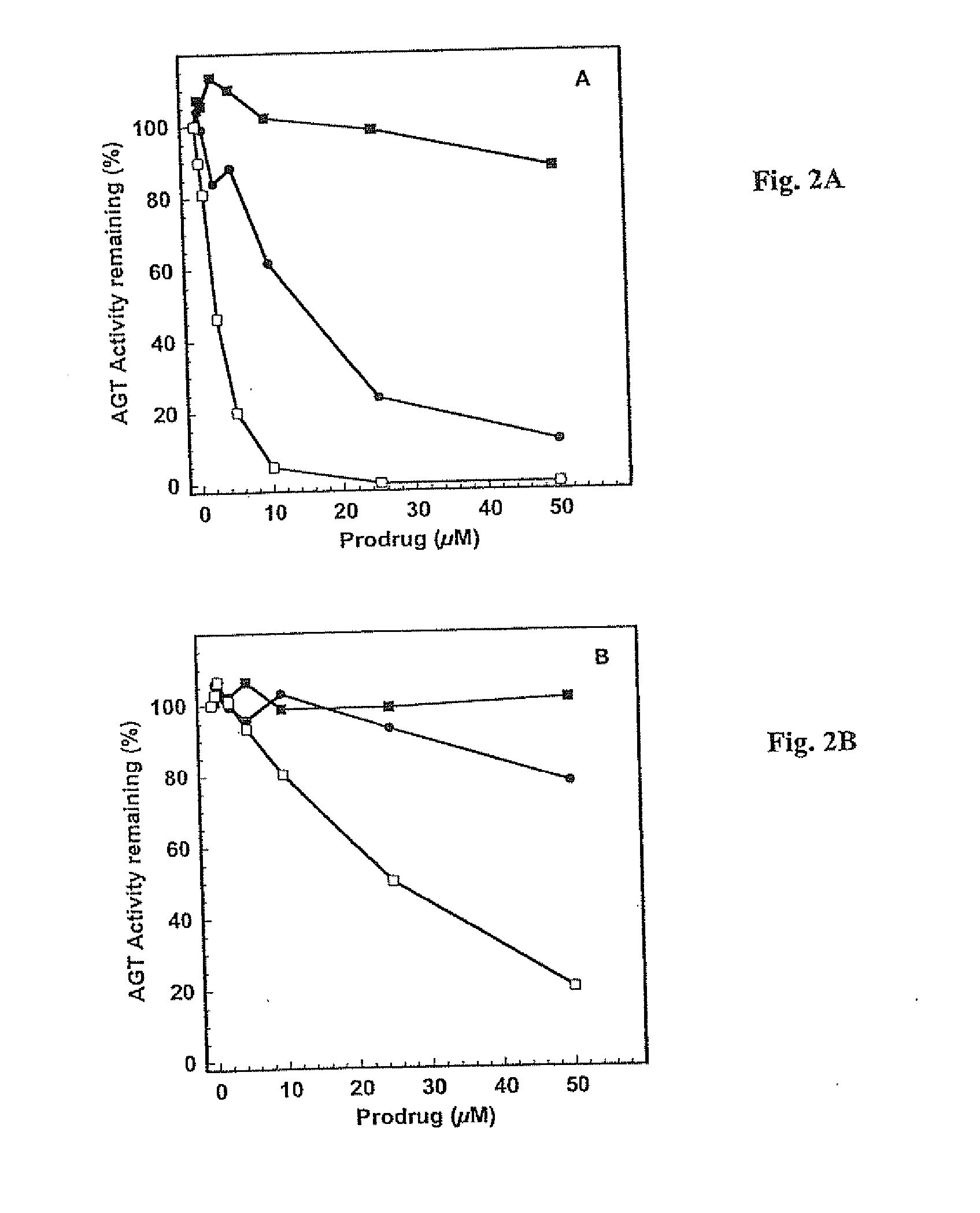
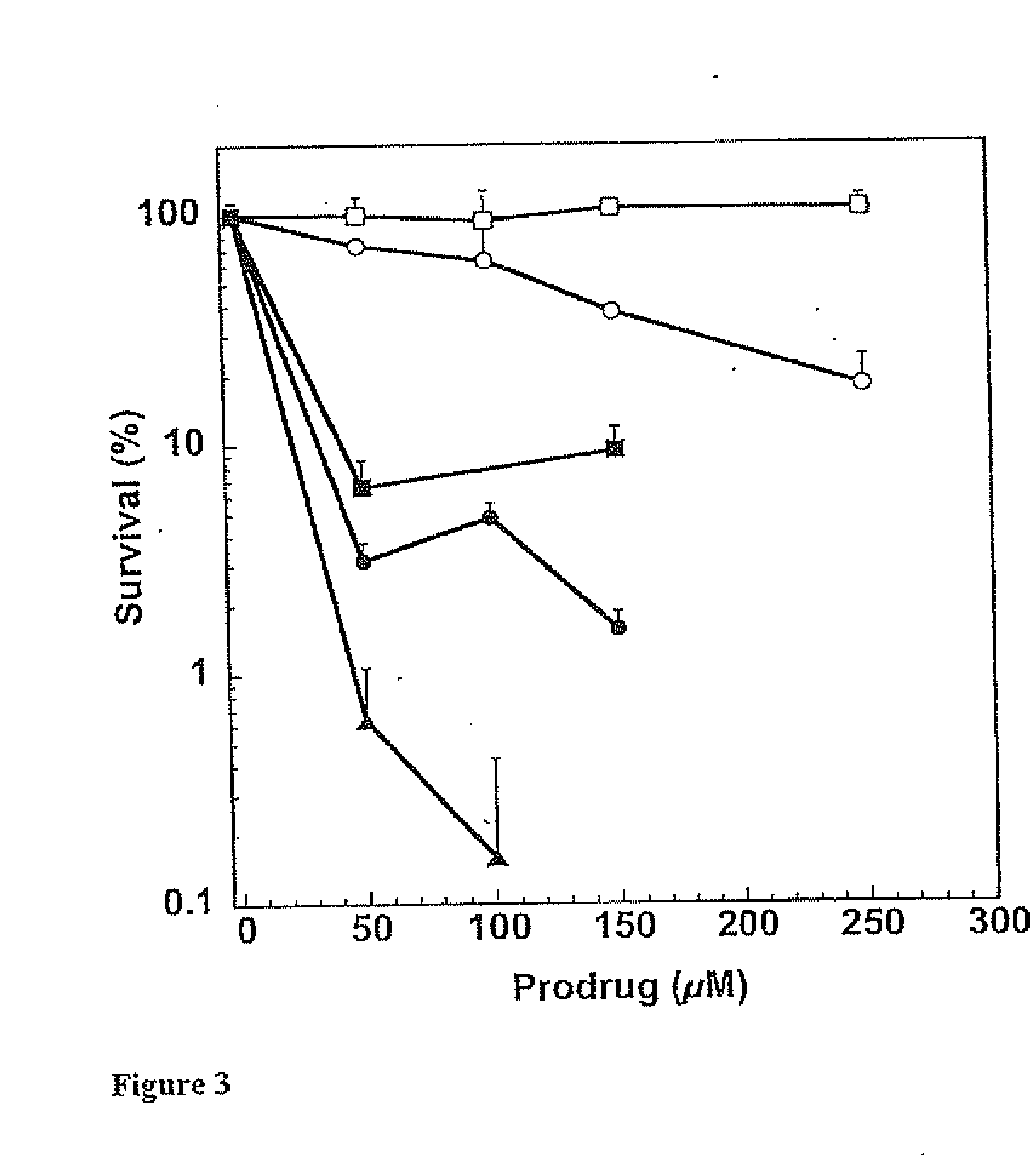
O6-alkylguanine-dna alkyltransferase inactivators and beta-glucuronidase cleavable prodrugs
Disclosed are prodrugs of inactivators of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT). The prodrugs are cleavable by the β-glucuronidase enzyme, which is either administered to the patient or produced by necrotic tumor cells. The prodrugs are represented by the formula A-B-C, wherein A is a glucuronosyl residue linked through its 1-oxygen to the phenyl ring of B; B is a benzyloxycarbonyl group, optionally ring-substituted with one or more electron withdrawing groups; and C is an inactivator of AGT, e.g., a substituted or unsubstituted O6-benzylguanine or O6-benzyl-2′-deoxyguanosine, Also disclosed are additional inactivators of AGT, pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inactivator or prodrug and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and a method of use of the inactivator or prodrug in enhancing the chemotherapeutic treatment of tumor cells in a mammal, e.g., a human, with an antineoplastic alkylating agent that causes cytotoxic lesions at the O6-position of guanine.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
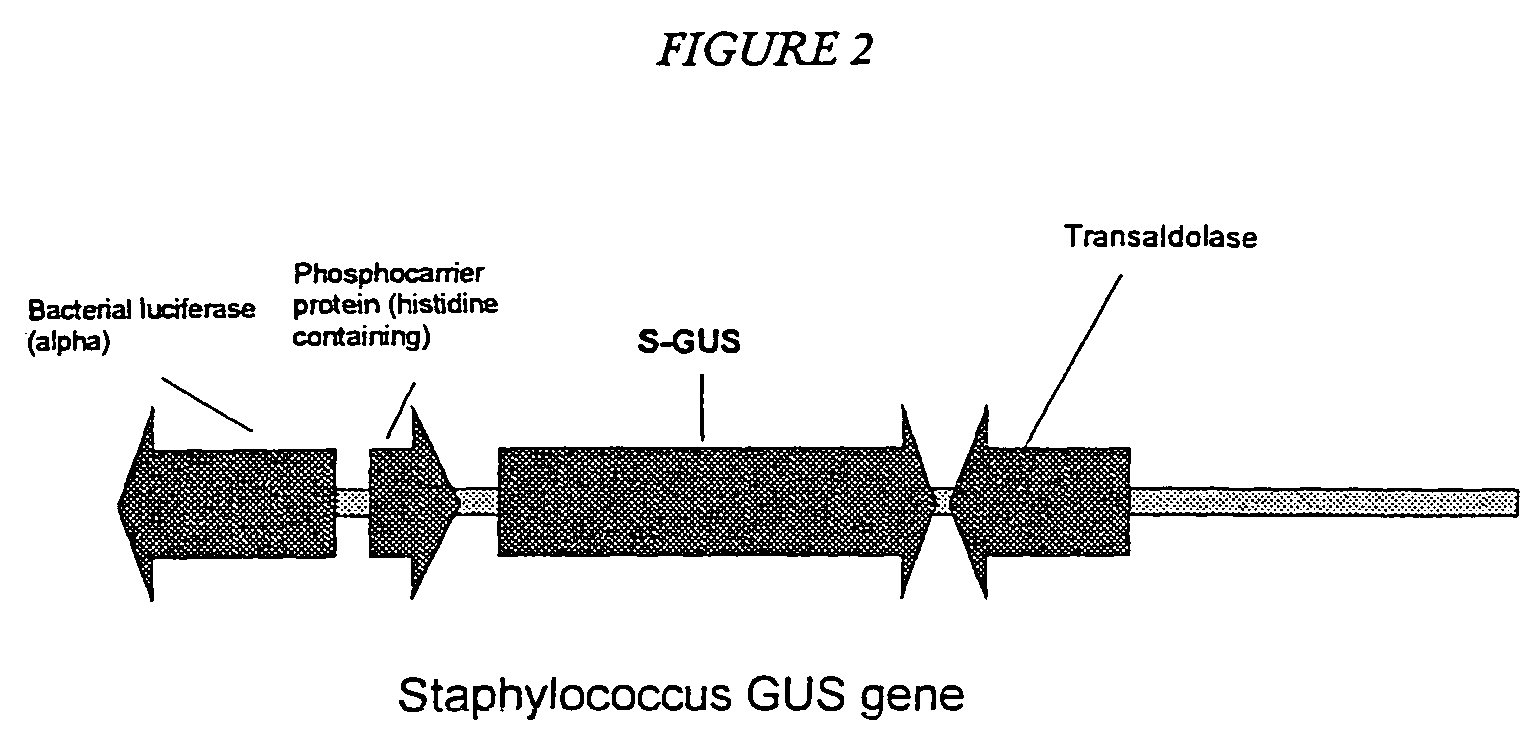
Mutant staphylococcus beta-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity
ActiveUS20160237415A1Improve enzymatic activityImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycosylasesBenzodiazepineOpiate
Mutated Staphylococcus sp. RLH1 β-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity and thermostability as compared to wild type enzyme are provided. The enzymes of the invention advantageously allow for accurate analysis of bodily samples for the presence of drugs in 30 minutes or less, as compared to the several hours needed using prior enzyme preparations. Methods of using the mutated enzymes for hydrolysis of glucuronide substrates, including opiates and benzodiazepines, are also provided.
Owner:INTEGRATED MICRO CHROMATOGRAPHY SYST INC
A set of oligonucleotide probe for detecting intestinal hemorrhage type colibacillus and vibrio cholerae
InactiveCN1661113AAccurate detectionEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesDiseaseFood poisoning
A set of oligonucleotide probe for detecting the enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7 and cholera vibrio O139 is designed on the Shiga-like toxin generating gene stx1 or stx2 and the beta-glucuronidase gene uidA of said enterohemorrhagic E coli O157:H7 and the enterotoxin A subset (ctxA), toxicity coordinate pilus A subset (tcpA) and glucosyltransferase (LPS gt) genes of cholera vibrio O139, and has high sensibility and specificity. It can be used to detect the enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7, cholera vibrio O139 and other pathogenic genes from the specimen.
Owner:RADIOLOGY INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE SCI PLA
Microbial beta-glucuronidase genes, gene products and uses thereof
InactiveUS7087420B1Improve thermal stabilityImprove turnover rateGlycosylasesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Beta-glucuronidase as well as gene and applications thereof
ActiveCN106978407AEfficient expressionHigh expressionFungiFermentationPichia pastorisBeta-glucuronidase
The invention discloses beta-glucuronidase, as well as a gene, an expression vector and a transformant of beta-glucuronidase, and applications in preparing glycyrrhetinic acid monoglucuronide (GAMG). The gene sequence of the beta-glucuronidase is shown as SEQ ID No.1. After the gene is bonded to the expression vector, the obtained product is transformed into pichia pastoris, and thus a pichia pastoris engineering strain is obtained. When the beta-glucuronidase recombinase expressed by the engineering strain is used for preparing GAMG, the result shows that the enzyme has the advantages that the specificity of the substrate is high, no by-product, namely, glycyrrhetinic acid is generated, and the yield of GAMG is about 95%, which proves that beta-glucuronidase and the gene of the beta-glucuronidase have good application prospects in production of GAMG.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Ethylene responsive factor gene OsERF3 and application of promoter thereof in regulating and controlling development of rice roots
InactiveCN103525856AIncrease productionAlleviate food shortagesVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsYeastBeta-glucuronidase
The invention discloses application of an ethylene responsive factor gene OsERF3 in regulating and controlling the development of rice roots. By using a yeast two-hybrid method, an ethylene responsive factor OsERF3 interacted with a published OsWOX11 protein is obtained by screening. By using an overexpression and small artificial interference RNA method, transformed rice corresponding to a gene is obtained, and a situation that the length of a main root and the number of crown roots of a plant subjected to gene overexpression are obviously increased in comparison with those of wild compared plants, and the length increasing of the main root is caused by the length increasing of cells in a maturation zone of a root tip, the length of the main root and the number of crown roots of a plant subjected to small artificial interference RNA transgenosis are obviously reduced in comparison with those of wild compared plants, and the length reducing of the main root is caused by the length reducing of cells in a meristematic zone and a maturation zone. Results show that the gene has a function of promoting the development of rice roots. A result of fusing the promoter of the gene with a report gene beta-glucuronidase shows that the gene is expressed in a meristematic zone of a root tip.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Aerobic and bacterial vaginosis combined determination kit
The invention discloses an aerobic and bacterial vaginosis combined determination kit and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises a color-developing agent and a reaction device, wherein the reaction device comprises a hydrogen oxide reaction pad, a neuraminidase reaction pad, a leucocyte esterase reaction pad, a beta-glucuronidase reaction pad and a coagulase reaction pad. Sample liquid is sucked by using straw, one drop of the sample liquid is dropwise added on each of the hydrogen oxide reaction pad, the neuraminidase reaction pad, the leucocyte esterase reaction pad, the beta-glucuronidase reaction pad and the coagulase reaction pad of the reaction device, the volume of each drop of the sample liquid is 30 mu l, after the reaction device is put into a water bath at a temperature of 36-38 DEG C or a dry bath at a temperature of 48 DEG C to carry out color developing for 15 minutes, one drop of color-developing liquid A is added on the neuraminidase reaction pad, one drop of color-developing liquid B is added on the coagulase reaction pad, and 30 seconds later, a result is shown. Thus, an effect of simultaneously detecting hydrogen oxide, neuraminidase, leucocyte esterase, beta-glucuronidase and coagulase to diagnose aerobic and bacterial vaginosis can be achieved.
Owner:浙江亚培生物技术有限公司
Method for fixing beta-glucuronidase by alginate-calcium carbonate hybrid gel
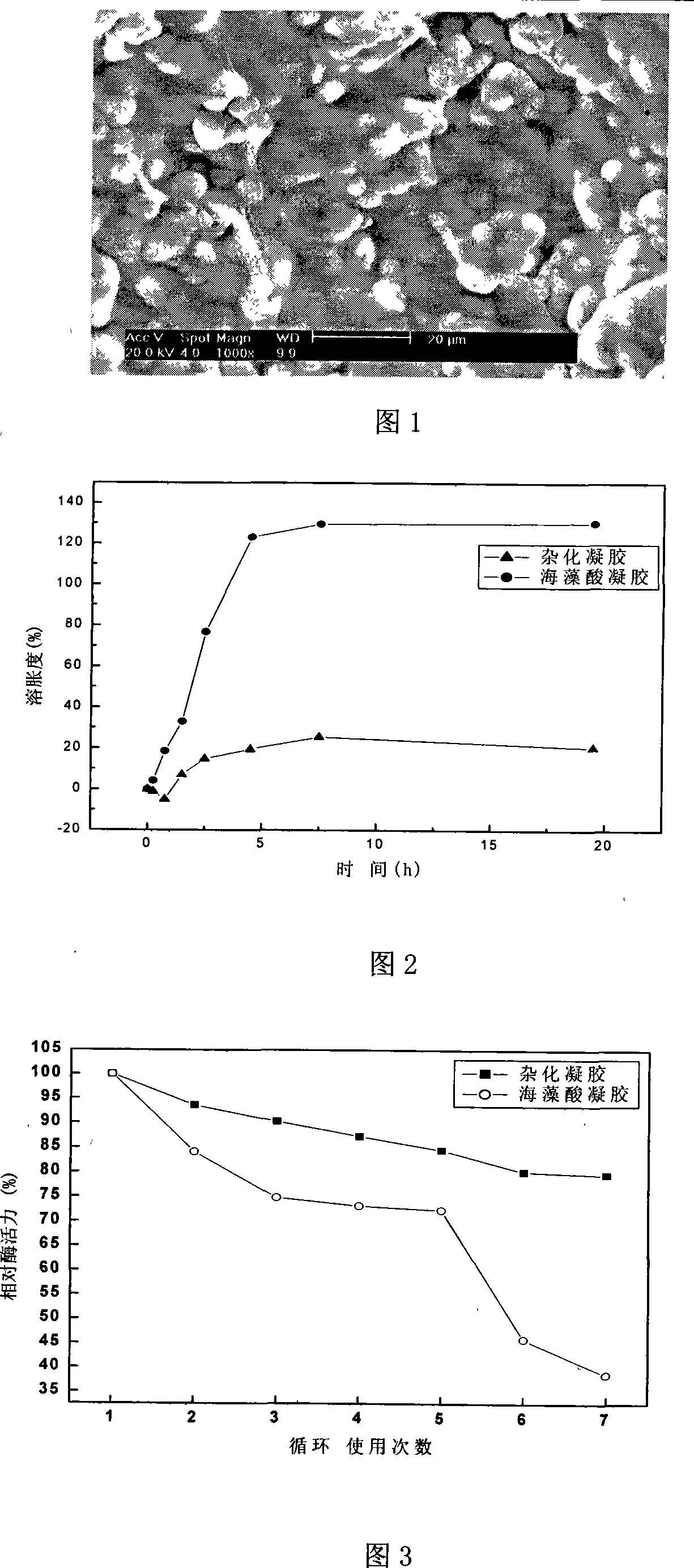
InactiveCN101205532AEasy to fixReduce leak rateHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierSwelling capacityLow leakage
The invention relates to a method for using alginic acid-calcium carbonate hybrid gel to immobilize beta-glucuronidase, wherein, calcium carbonate powdered precipitation is generated by mixing and stirring sodium carbonate solution and calcium chloride solution at room temperature, and then kept, washed by water and acetones and dried, and micron mesoporous calcium carbonate particles are obtained which are added into trihydroxymethyl aminomethane-hydrochloric acid (Tirs-HCl) buffer of beta-glucuronidase or aqueous solution thereof for absorption, and calcium carbonate particles absorbing glucuronidase are obtained after centrifugal separation, then uniformly mixed with sodium alginate solution and added into calcium chloride solution by dropping for aging. The invention has the advantages of mild preparation conditions, simple and easy preparation technologies, good immobilization ability of obtained hybrid vectors on enzymes, low leakage rate of immobilized beta-glucuronidase, low swelling capacity and good reusage stability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
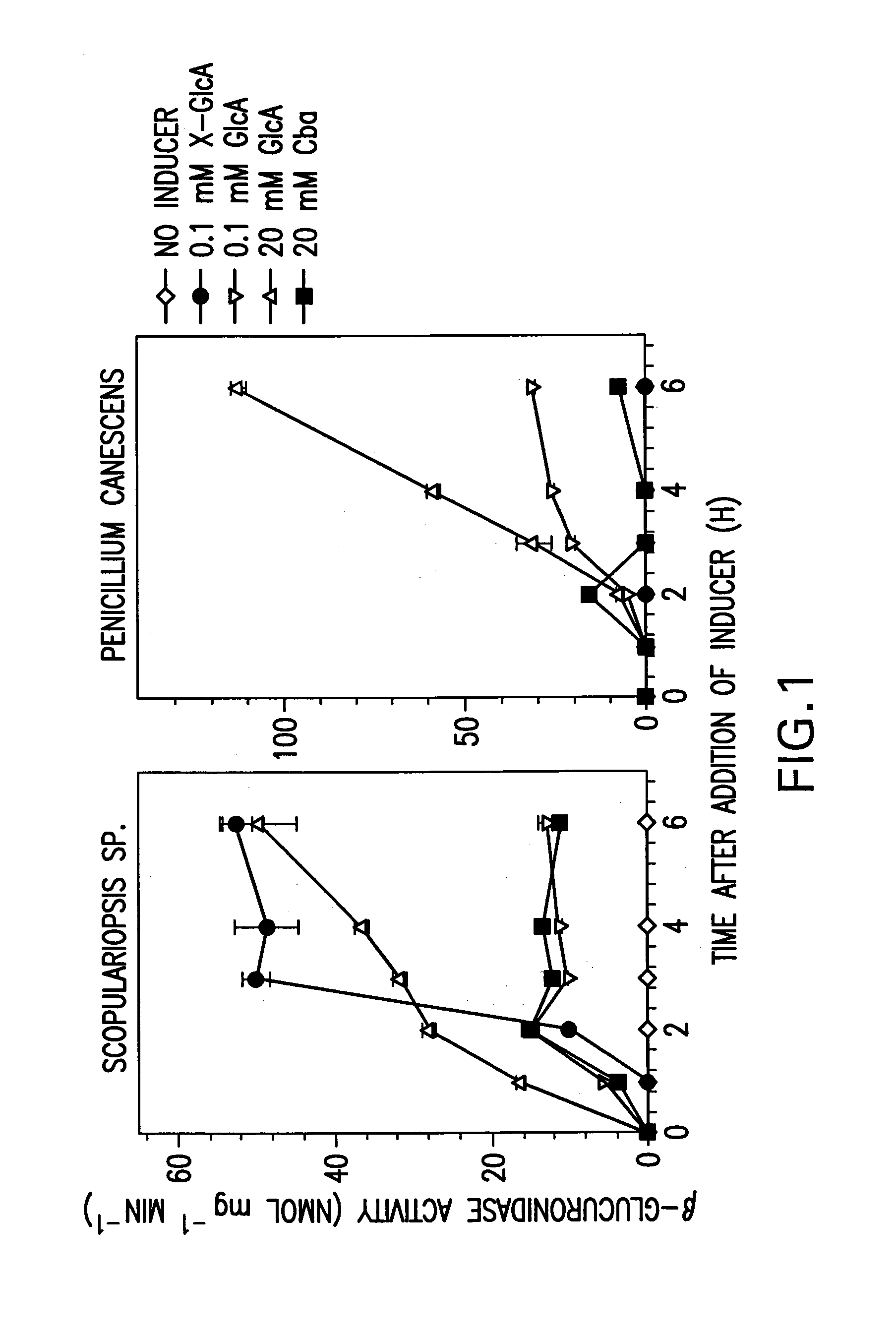
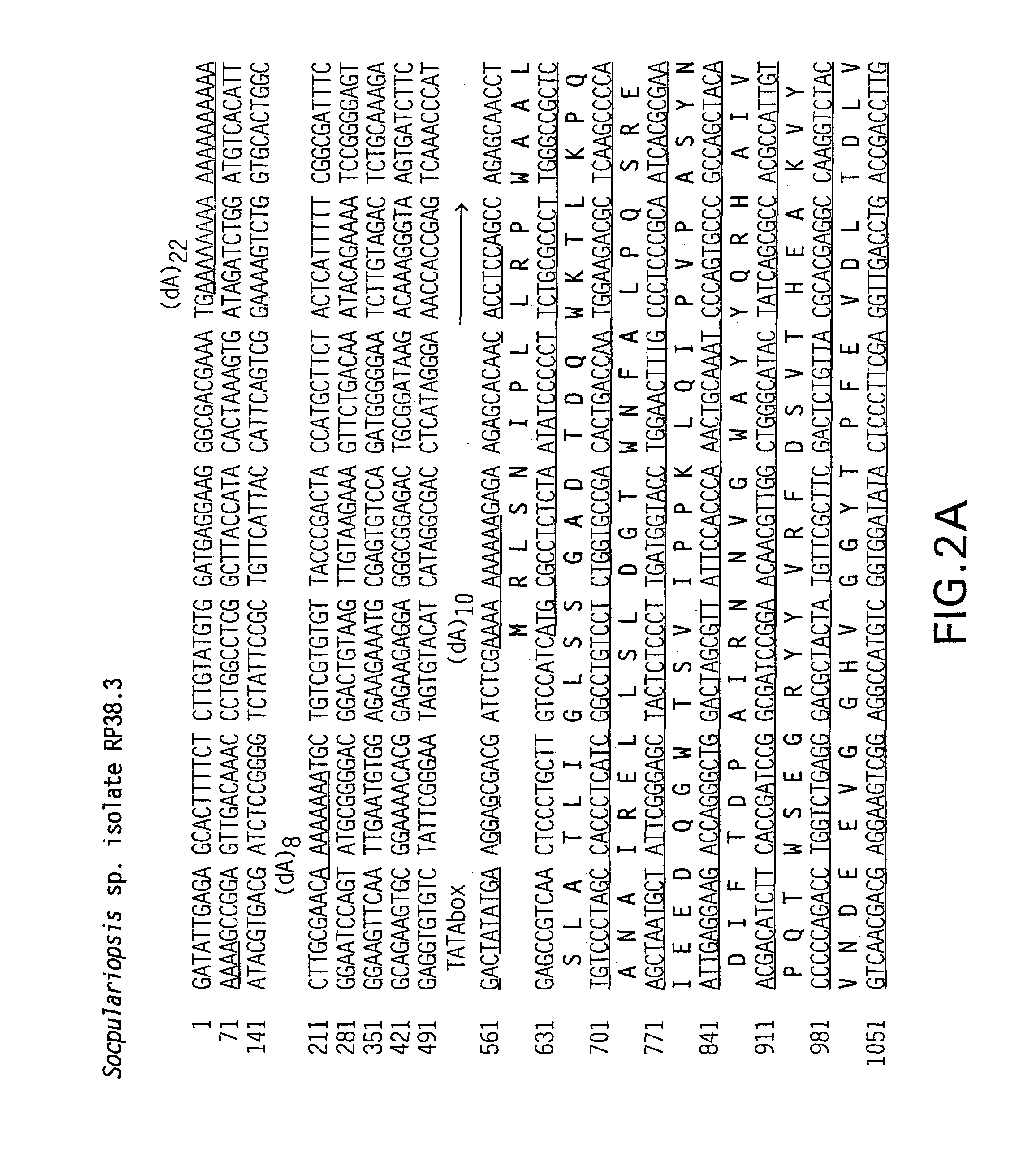
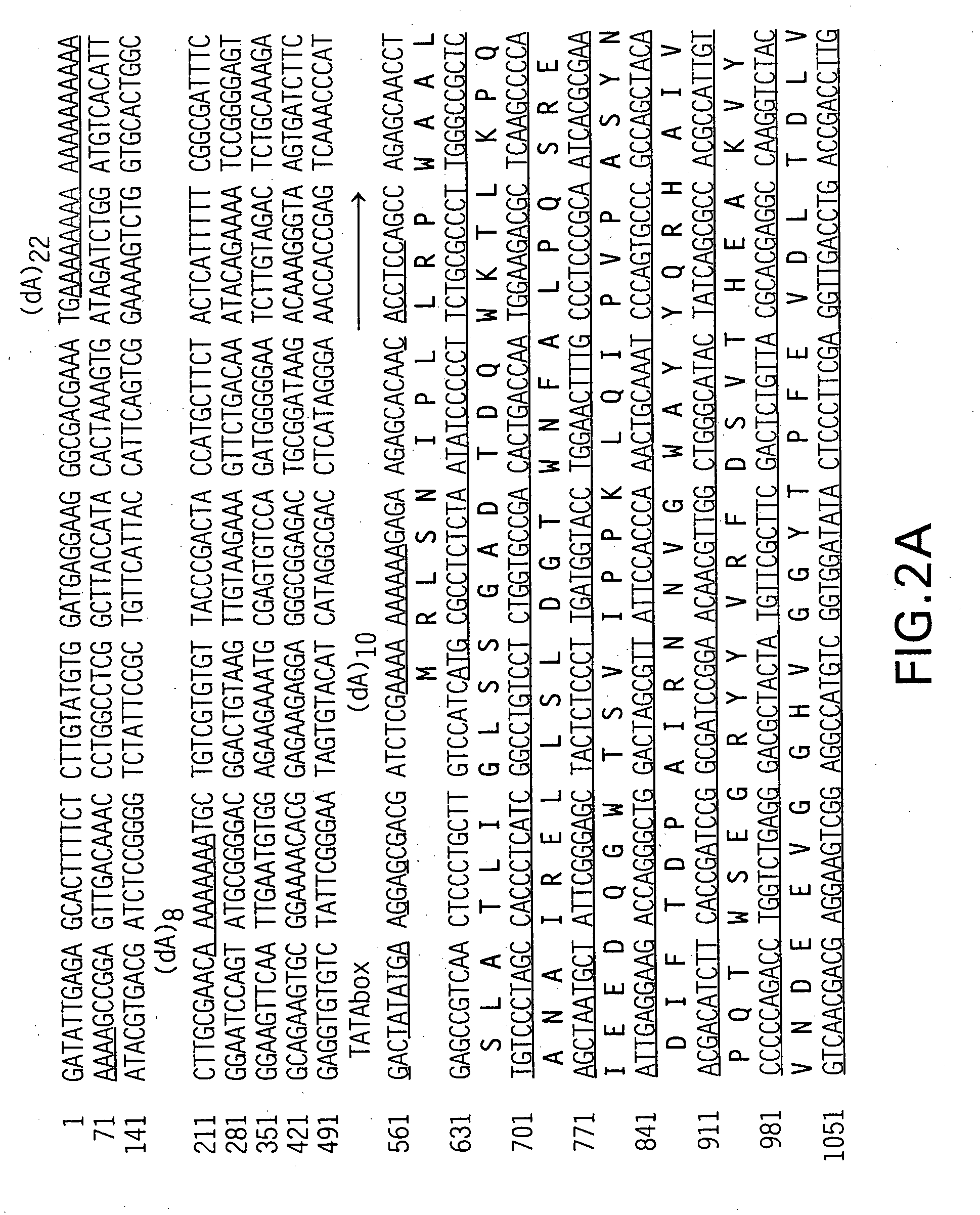
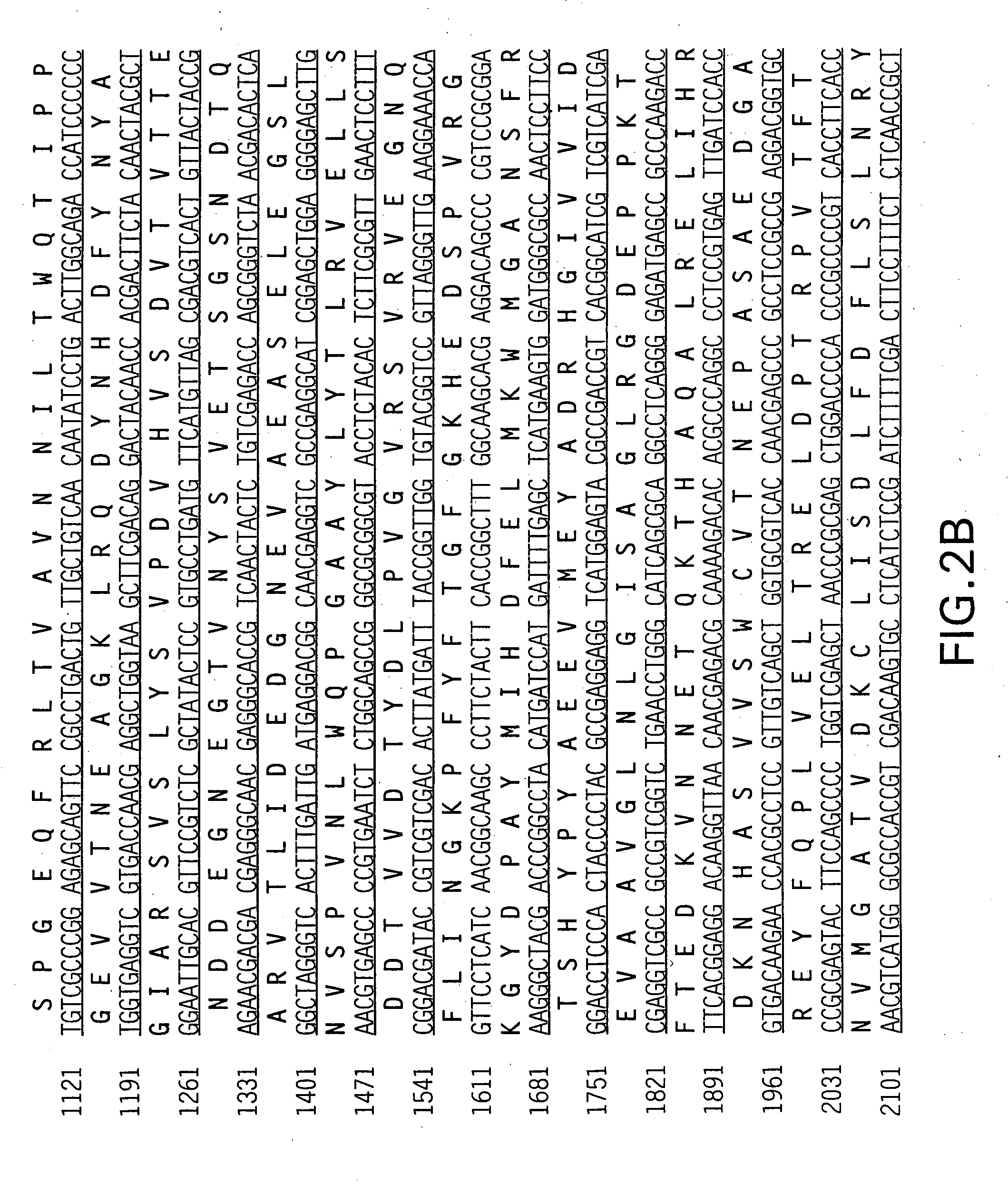
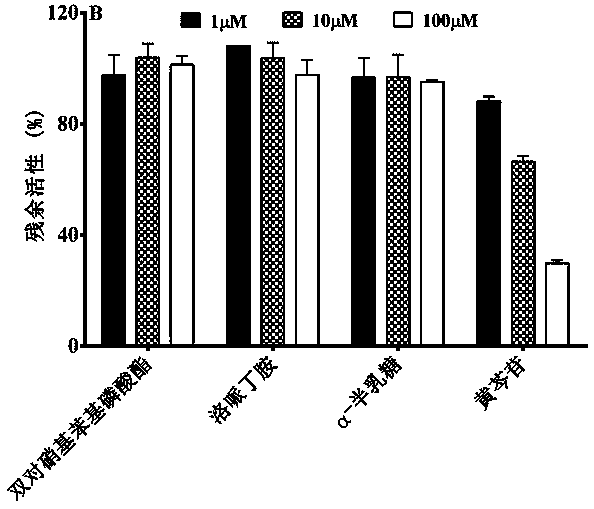
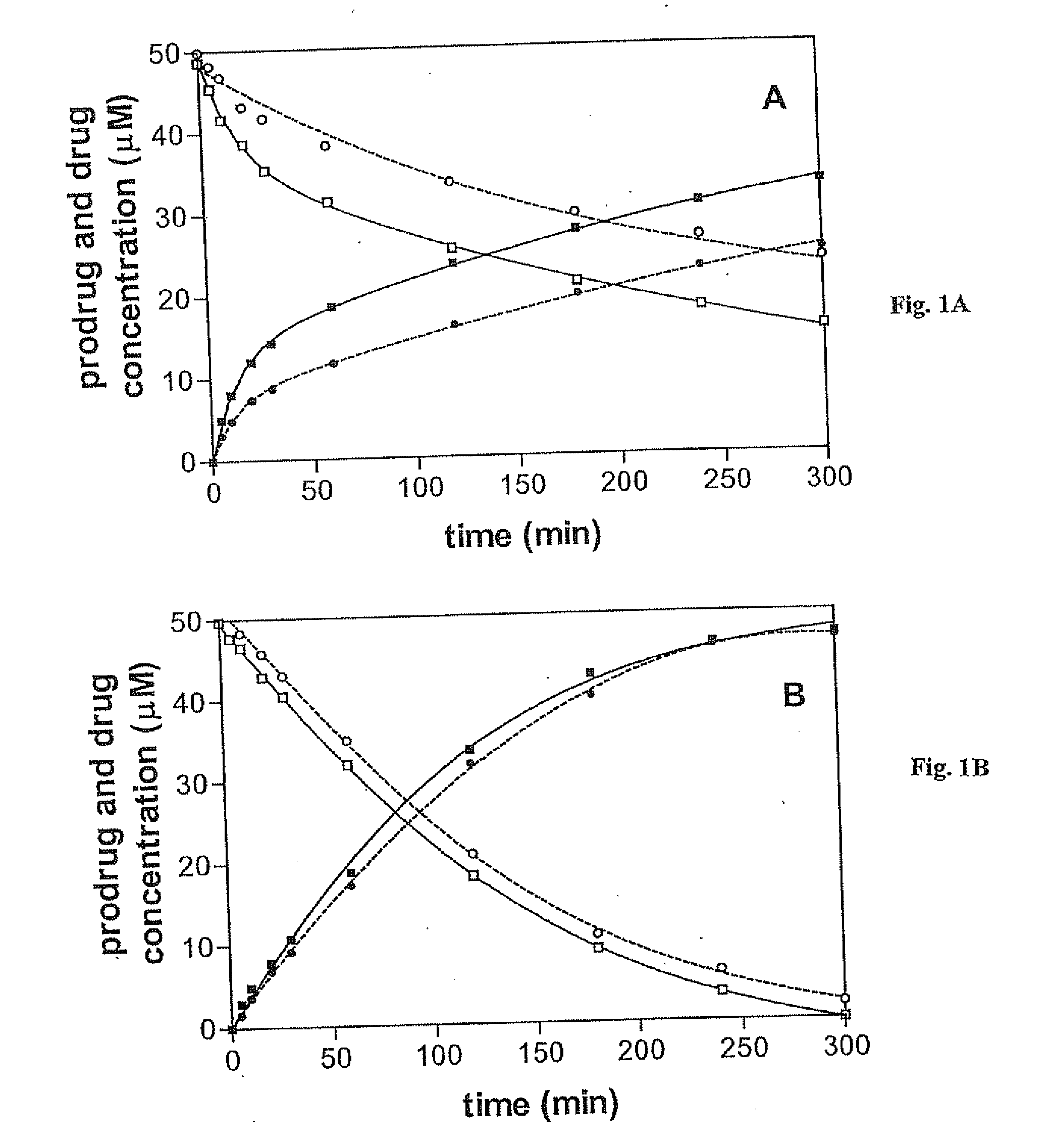
[Beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability
The invention discloses a [beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. [Beta]-glucuronidase, which is derived from talaromyces pinophilum Li-93 (preservation number is CGMCC No.11765), undergoes site-specific mutagenesis, so that the mutation of valine on the 212th site, threonine on the 220th site, cysteine on the 238th site and valine onthe 348th site, which are coded by the [beta]-glucuronidase, into arginine is promoted; and 23 amino acids at the N terminal of the enzyme ([beta]-glucuronidase) are cut off, and a recombinant plasmidof mutant gene is transformed in pichia pastoris GS115 and is expressed, so that the [beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability is obtained. According to the [beta]-glucuronidase mutant provided by the invention, half-life periods under 55 DEG C and 70 DEG C are prolonged by 81min and 25min in comparison with wild type, namely 3 times and 2.3 times as much as that of the wild type.A process of pyrolytic conversion GL is established on the basis of the mutant. The [beta]-glucuronidase mutant provided by the invention has a broad industrial application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for preparing recombinant heat-proof beta-glucuronic acid enzyme
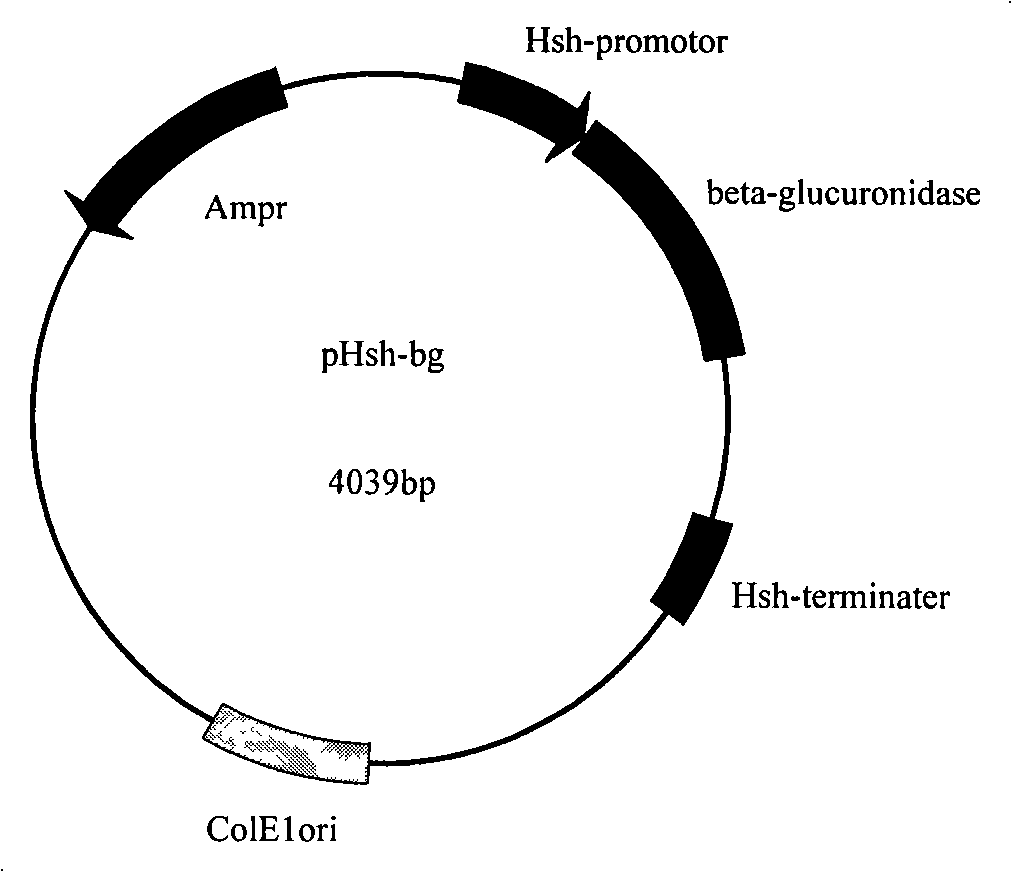
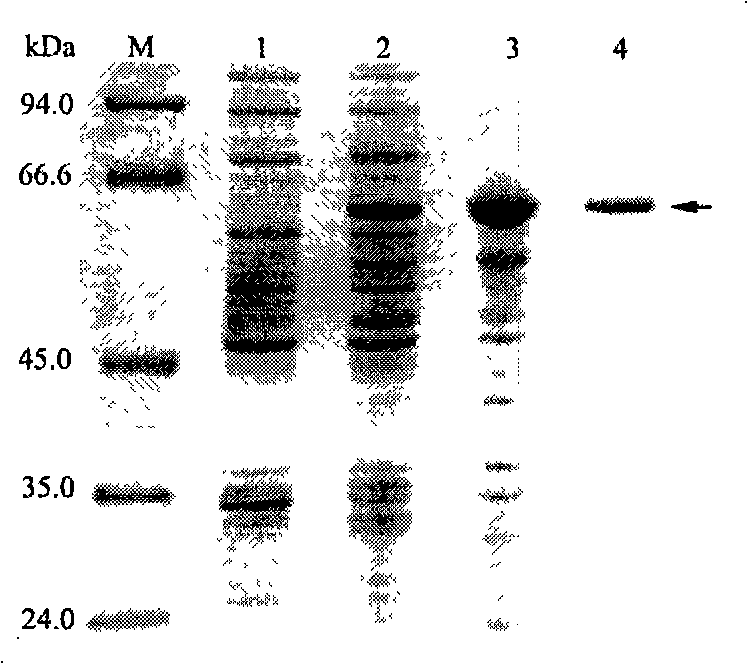
InactiveCN101250539AImprove expression levelEasy to purifyEnzymesFermentationEscherichia coliGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a method for preparing recombinant extremely heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase, which comprises flowing steps: inserting heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase genes into an expression vector pHsh, transforming escherichia coli to obtain expression plasmids of heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase, then, mutating genes, changing a secondary structure of mRNA, obtaining optimized expression plasmids of the heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase, then, transforming the expression plasmids of the heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase or the optimized expression plasmids of the heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase into the escherichia coli, obtaining genetic engineering bacteria, enabling the beta-glucuronidase to obtain over-expression through hot-shock inducement, finally, collecting cells, breaking wall, centrifuging, then, obtaining crude enzyme, further purifying, then, and obtaining pure enzyme. The method of the invention uses the expression vector pHsh to express the genes of the heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase on high level for the first time and applies the recombinant heat-resistant beta-glucuronidase in preparing glycyrrhetinic acid for the first time.
Owner:南京仙奕基因科技有限公司
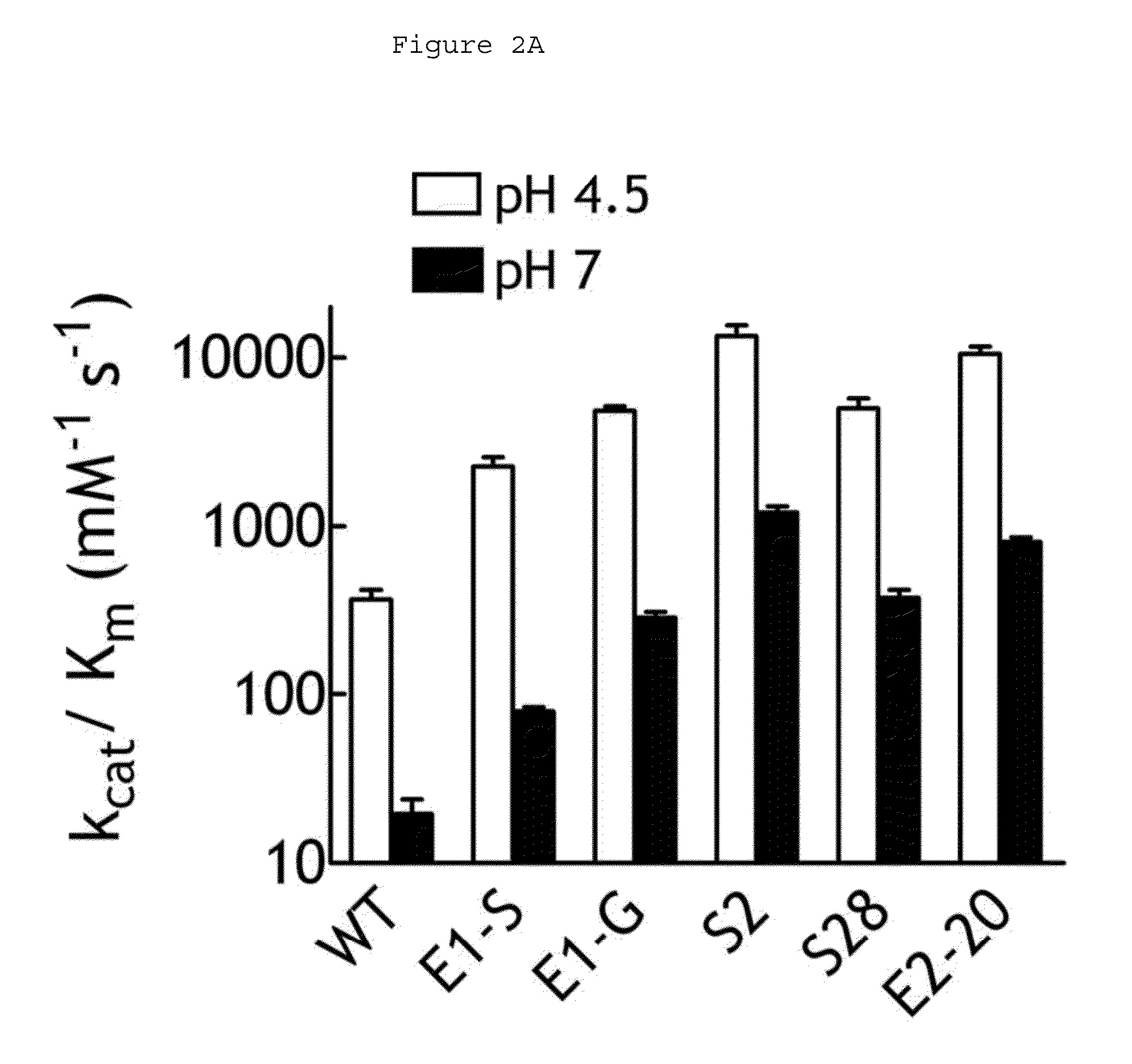
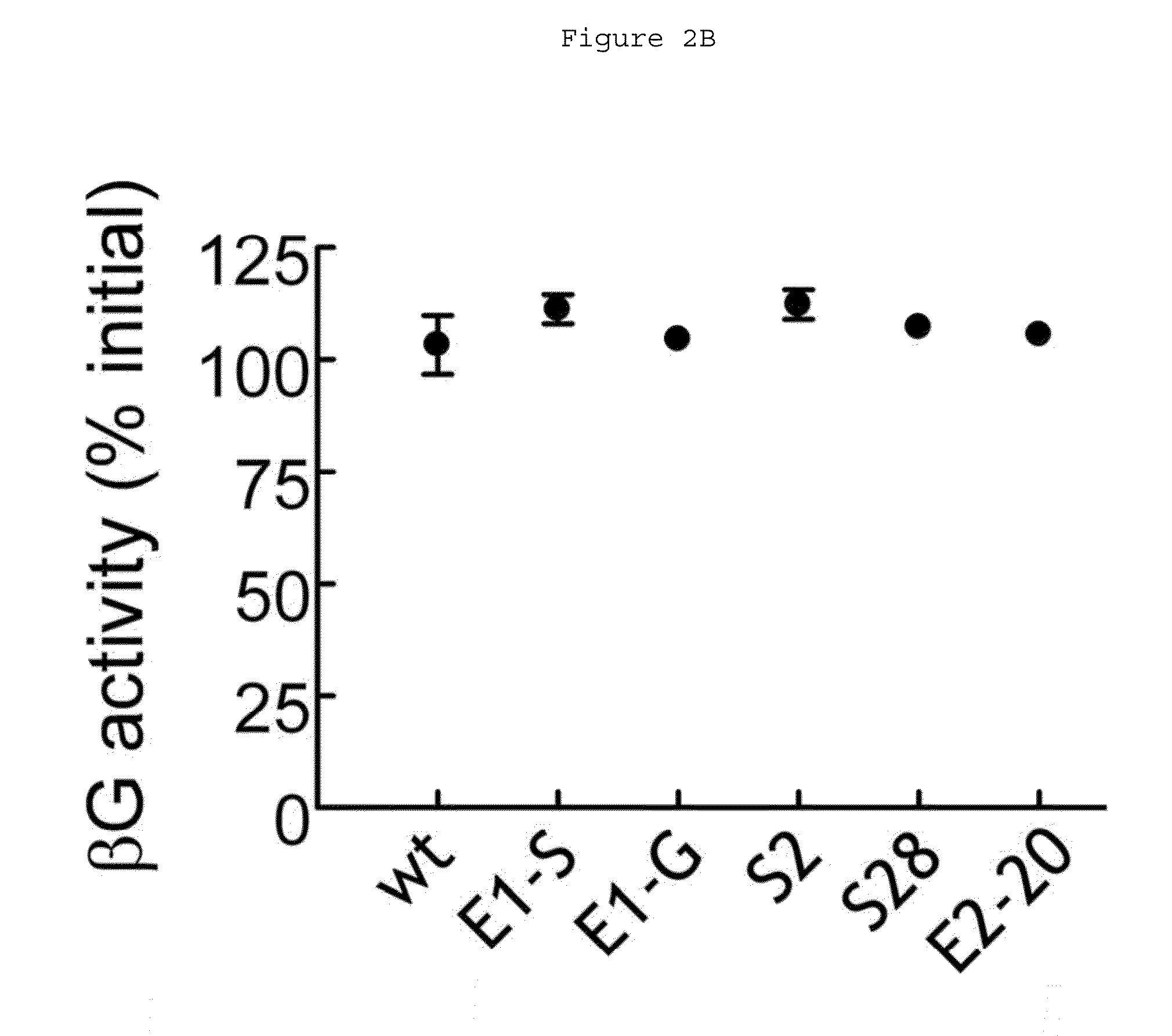
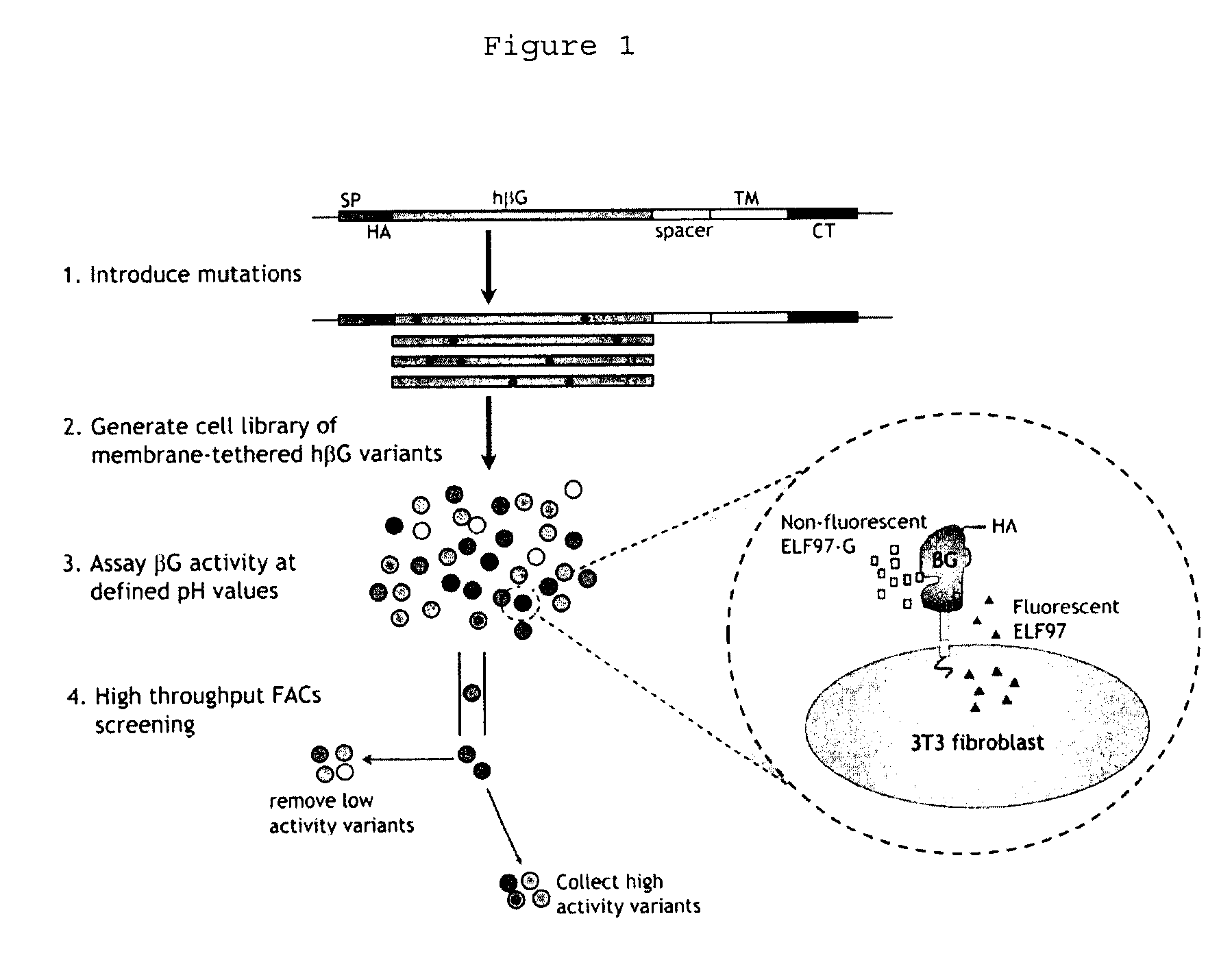
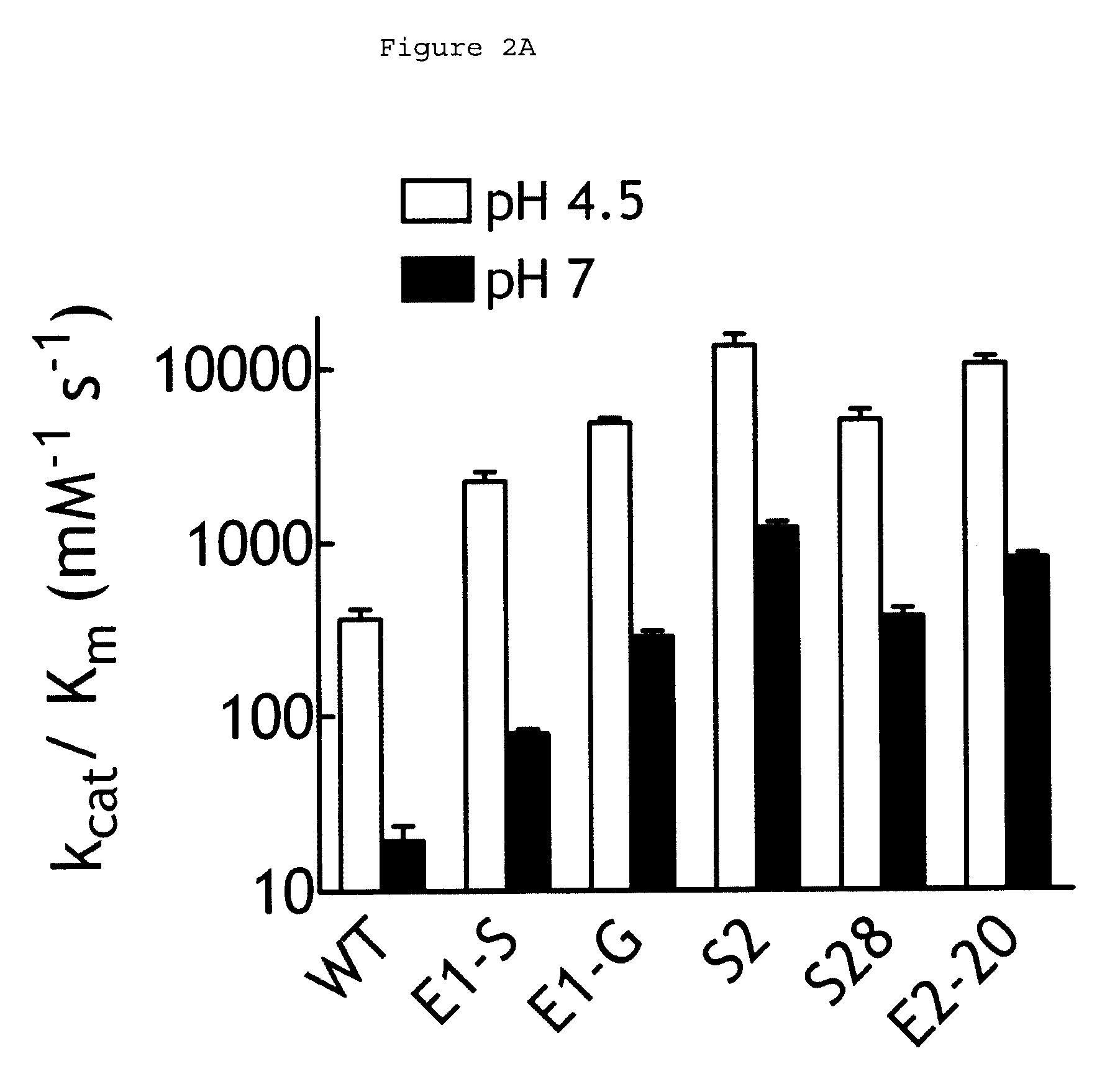
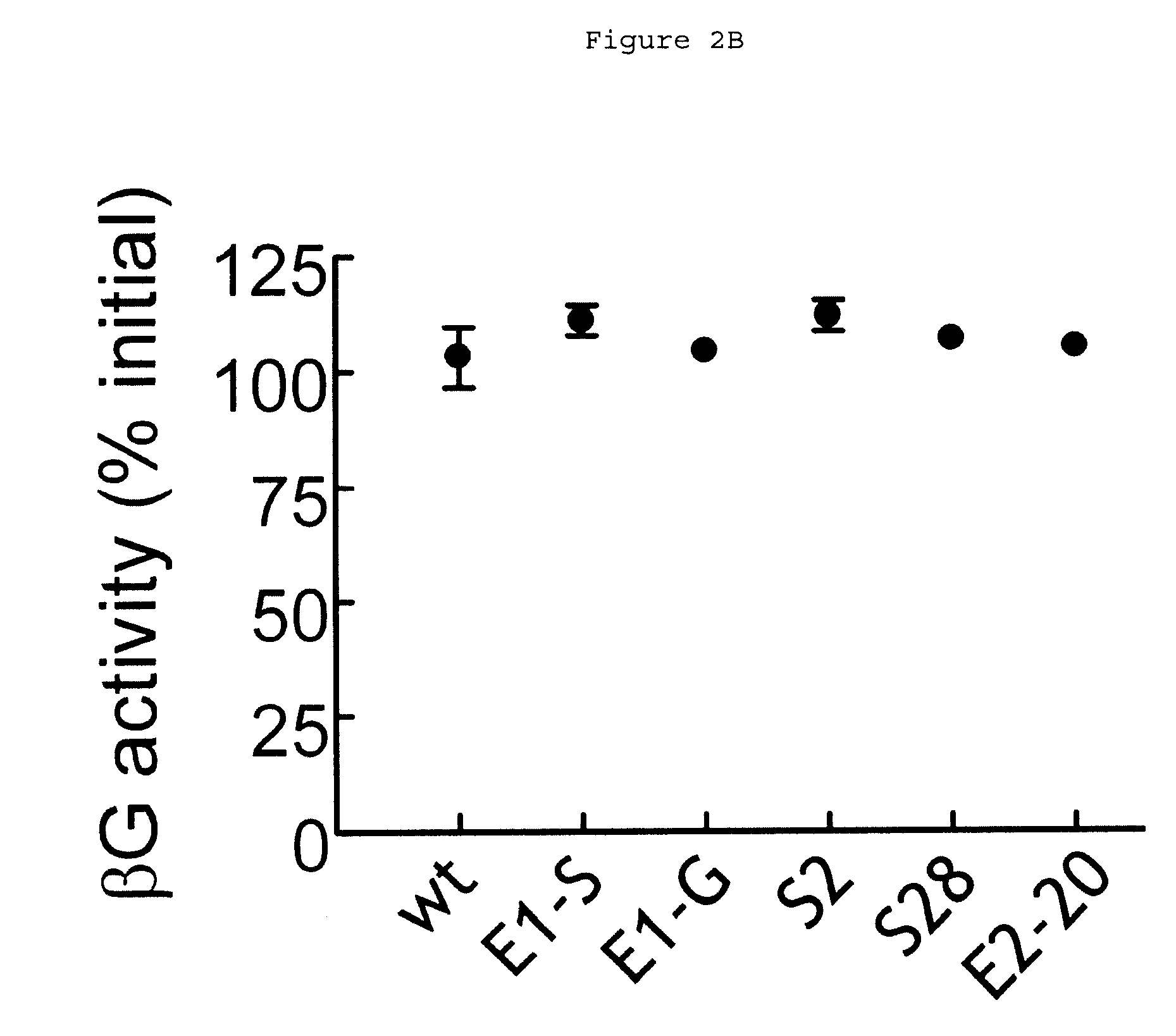
Human beta-glucuronidase mutants with elevated enzymatic activity under physiological conditions and method for identifying such
A number of human beta-glucuronidase variants having higher enzymatic activity at physiological pH as compared with wild-type beta-glucuronidase and uses thereof in prodrug therapy. Also disclosed herein is a method for identifying enzyme variants having elevated enzymatic activity using a mammalian surface display system.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
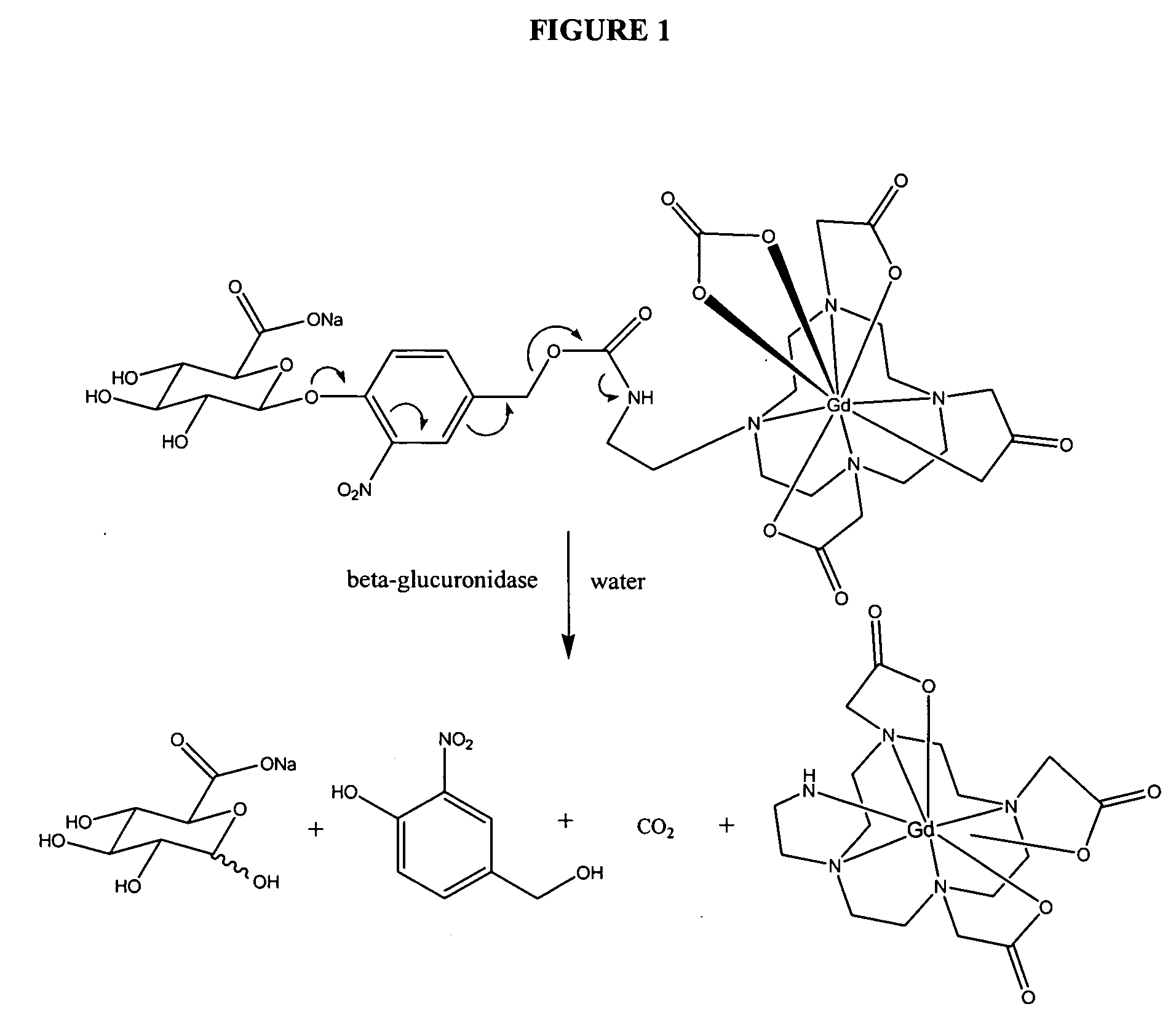
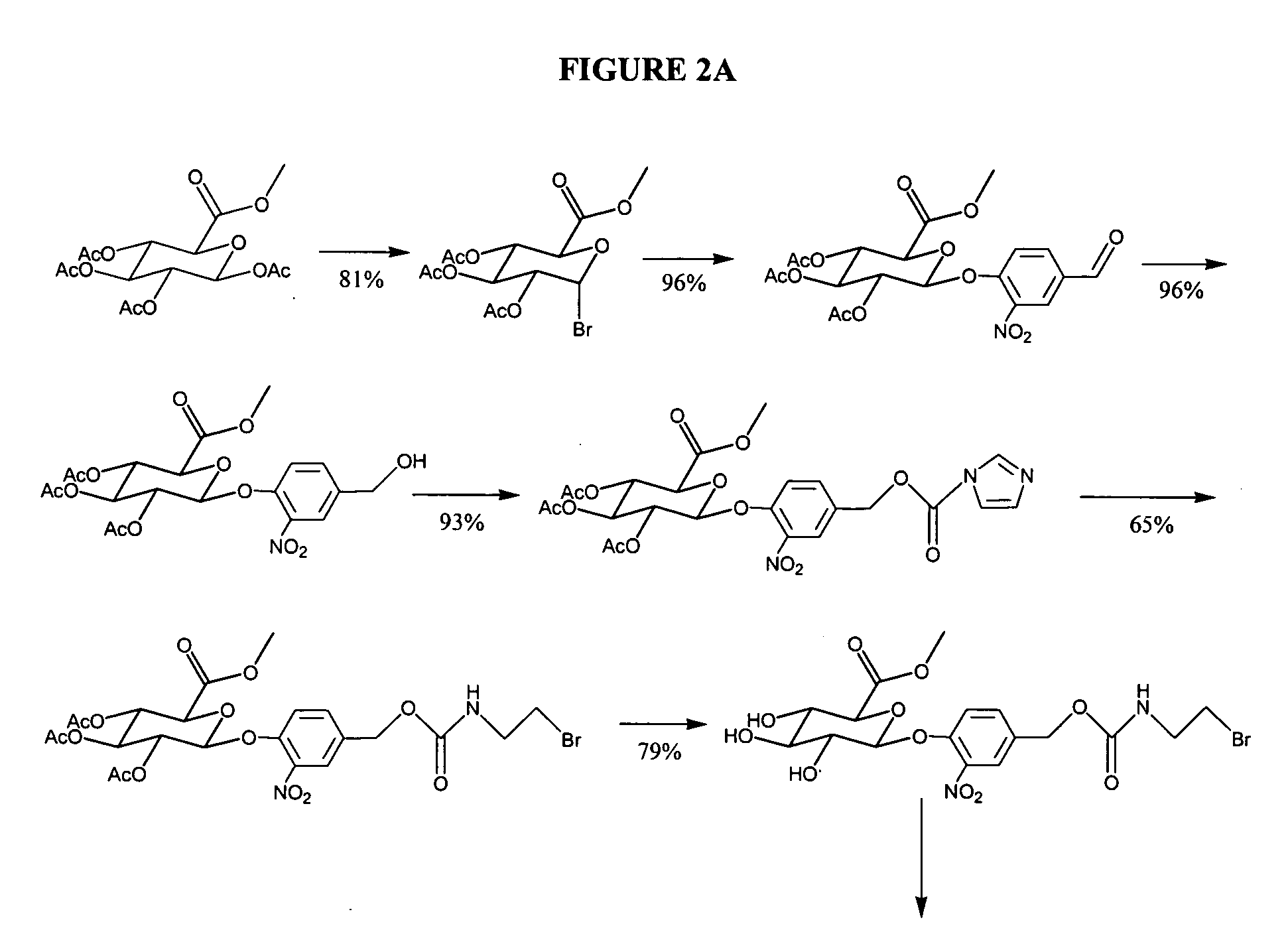
Self-immolative magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents sensitive to beta-glucuronidase
InactiveUS20060088475A1Diagnostic recording/measuringPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGreek letter betaMRI contrast agent
The present invention relates to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent. In particular, the present invention provides MRI contrast agents that are sensitive to the enzyme beta-glucoronidase. The MRI contrast agents provide compositions and methods for non-invasive diagnostic imaging of tissues, including necrotic tumors.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Fungal beta-glucuronidase genes and gene products
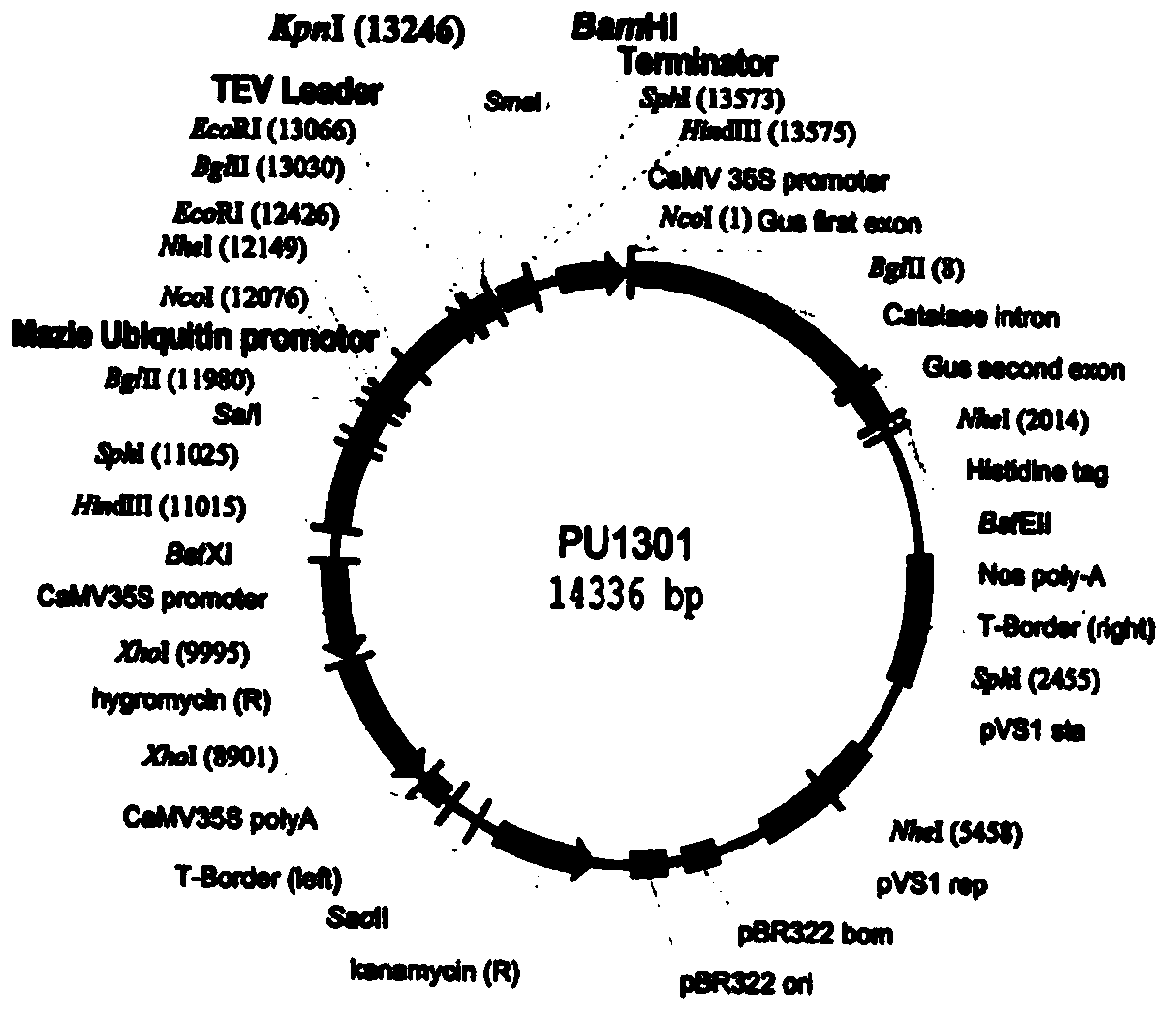
Nucleic acid molecules encoding fungal β-glucuronidases are provided. Gene products, expression vectors and host cells suitable for expressing β-glucuronidase are also provided. In addition, uses of the β-glucuronidase as a visual and as a selectable marker for transformation are also described.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Mutant beta-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity
ActiveUS20160090582A1Improve enzymatic activityImprove thermal stabilityFermentationGlycosylasesBenzodiazepineOpiate
Mutated β-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity and thermostability as compared to wild type enzyme are provided. The enzymes of the invention advantageously allow for accurate analysis of bodily samples for the presence of drugs in 30 minutes or less, as compared to the several hours needed using prior enzyme preparations. Methods of using the mutated enzymes for hydrolysis of glucuronide substrates, including opiates and benzodiazepines, are also provided.
Owner:INTEGRATED MICRO CHROMATOGRAPHY SYST INC
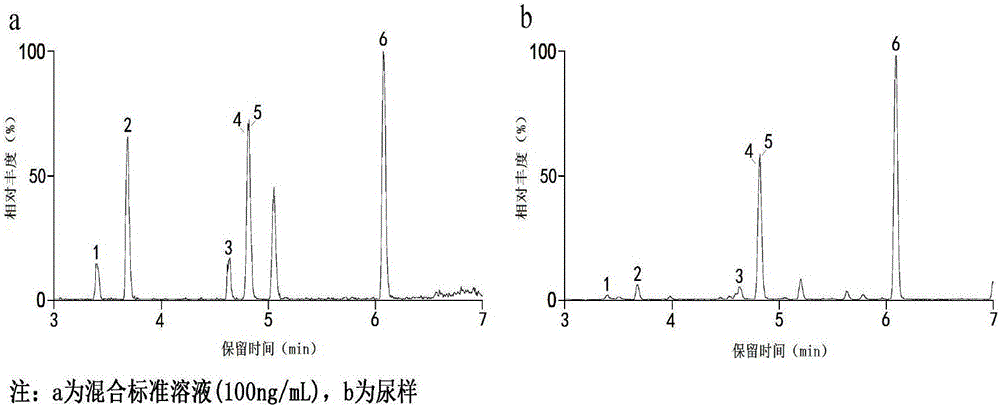
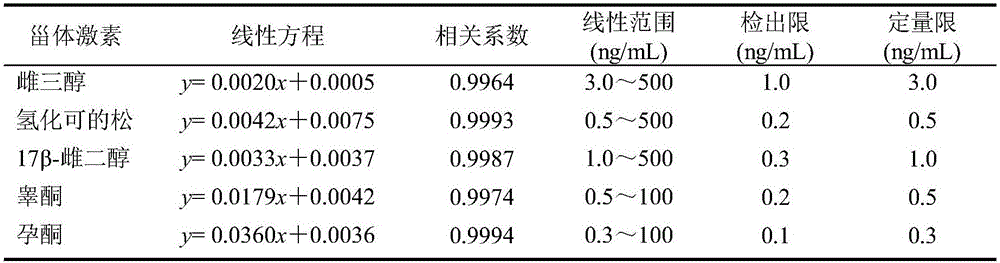
Method for rapidly detecting steroid hormones in urea through UPLC-MS/MS technology
InactiveCN106198786AMeet the requirements of simultaneous detectionWide detection rangeComponent separation17beta estradiolEstriol
The invention relates to a method for rapidly detecting steroid hormones in urea through an UPLC-MS / MS technology, and belongs to the field of analysis chemistry and medical science. The concentrations of estriol, hydrocortisone, 17beta-estradiol, testosterone and progesterone in human urea are simultaneously detected through the UPLC-MS / MS technology by adopting a beta-glucuronidase enzymatic hydrolysis technology, the detection limit is 0.1-1.0 ng / mL, and the quantitation limit is 0.3-3.0 ng / mL. The method is fast, sensitive and accurate, can meet requirement of simultaneous detection of above five steroid hormones in urea, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:WUXI NO 4 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Mutant Staphylococcus beta-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity
ActiveUS9719075B2Improve enzymatic activityImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycosylasesBenzodiazepineBeta-glucuronidase
Mutated Staphylococcus sp. RLH1 β-glucuronidase enzymes with enhanced enzymatic activity and thermostability as compared to wild type enzyme are provided. The enzymes of the invention advantageously allow for accurate analysis of bodily samples for the presence of drugs in 30 minutes or less, as compared to the several hours needed using prior enzyme preparations. Methods of using the mutated enzymes for hydrolysis of glucuronide substrates, including opiates and benzodiazepines, are also provided.
Owner:INTEGRATED MICRO CHROMATOGRAPHY SYST INC
Human beta-glucuronidase mutants with elevated enzymatic activity under physiological conditions and method for identifying such
ActiveUS20100129367A1Improve enzymatic activityIncrease enzyme activityCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsSurface displayNPPase activity
A number of human beta-glucuronidase variants having higher enzymatic activity at physiological pH as compared with wild-type beta-glucuronidase and uses thereof in prodrug therapy. Also disclosed herein is a method for identifying enzyme variants having elevated enzymatic activity using a mammalian surface display system.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Promoter for expressing specificity of plant tissue and later development and application thereof
InactiveCN101831424AMitigating the impact of agronomic traitsIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant tissueOrgan Specificity
The invention relates to a promoter for the specificity expression and the later development expression of a plant tissue and application thereof, belonging to the biotechnology field. In the invention, a promoter sequence of a cotton cyclopropane fatty acid synthase with the length of 2.6kb is obtained. Place analysis proves that the promoter sequence contains a CAAT box, a TATA box, a cupric ion induced expression element, a pathogenicbacteria induced expression element, a dry response element, a cold stress response element, and the like as well as some root specificity expression elements and floral organ specificity elements. After GUS (beta-Glucuronidase) is dyed, a traditional gene is specially expressed at a later development stage by the promoter, and the expression parts are only restricted at a stem base part, a root and an anther.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Fungal beta-glucuronidase genes and gene products
Nucleic acid molecules encoding fungal β-glucuronidases are provided. Gene products, expression vectors and host cells suitable for expressing β-glucuronidase are also provided. In addition, uses of the β-glucuronidase as a visual and as a selectable marker for transformation are also described.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Method for extracting bilirubin from ox bile by using fermentation process
ActiveCN104774885AReduce the possibilityHigh activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBile JuiceAntioxidant
The invention provides a method for extracting bilirubin from ox bile by using a fermentation process. The method mainly comprises the following four steps: fermenting ox bile, sterilizing an ox bile fermentation solution, forming bilirubin, extracting and refining bilirubin. By virtue of the method, high-yield beta-glucuronidase and ox-bile-resistant clostridium perfringens are added into the animal ox bile and fermented; a mercaptoalcohol reducing agent is added, so that the effects of improving the activity of beta-glucuronidase and ox-bile-resistant clostridium perfringens and resisting oxidants are implemented; the overall process is greatly optimized under the control of the special condition; the production efficiency is improved; the cost is reduced; the yield of the finally prepared bilirubin is 0.010-0.014%; and the purify of the bilirubin reaches over 92%.
Owner:WUHAN JIANMIN DAPENG PHARMA
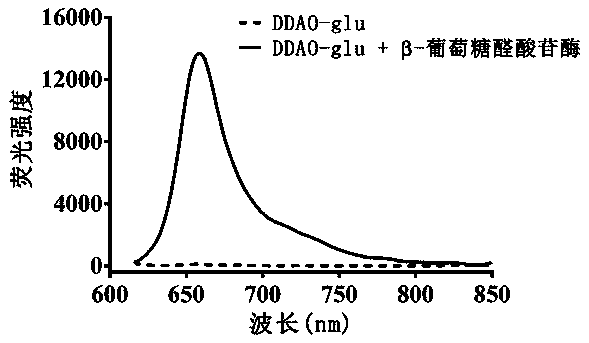
Fluorescence probe based on beta-glucuronidase of acridone and application of fluorescence probe
InactiveCN107915764ANot easy to interfereAdvantages of in vitro activitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescence probe based on beta-glucuronidase of acridone and application of the fluorescence probe, belonging to the technical field of biological medicines. The fluorescence probe can be used for determining the enzyme activities of beta-glucuronidase in biological systems of different sources. HC-glu is taken as a specific probe reaction substrate, beta-glucuronidasehydrolysis reaction is taken as a probe reaction by virtue of a beta-glucuronidase in-vitro reaction system, and the activity of beta-glucuronidase in each biological sample is determined by quantitatively detecting the generation amount of an aglycone metabolite in a unit time. The fluorescence probe can be applied to the qualitative and quantitative determination of the activities in beta-glucuronidase of different individual sources of human and animal tissue samples, different species of cells and cell preparation objects and various plants and microorganisms, and the evaluation of the drug treatment capacity of beta-glucuronidase and the development and screening of a beta-glucuronidase inhibitor can be realized.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ddef151-5fe8-4064-a572-cbb073af4b27/HDA00002539623800011.PNG)
![Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ddef151-5fe8-4064-a572-cbb073af4b27/HDA00002539623800012.PNG)
![Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine Method of simultaneously determining contents of 1-OHP ,3-OHB[a]P and 3-OHB[a]A in urine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/1ddef151-5fe8-4064-a572-cbb073af4b27/HDA00002539623800021.PNG)












![[Beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability [Beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/654d9337-b917-4872-ae7f-e64c3bd6778d/DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.png)
![[Beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability [Beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/654d9337-b917-4872-ae7f-e64c3bd6778d/HDA0001557441410000011.png)
![[Beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability [Beta]-glucuronidase mutant with improved thermostability](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/654d9337-b917-4872-ae7f-e64c3bd6778d/BDA0001557441400000021.png)