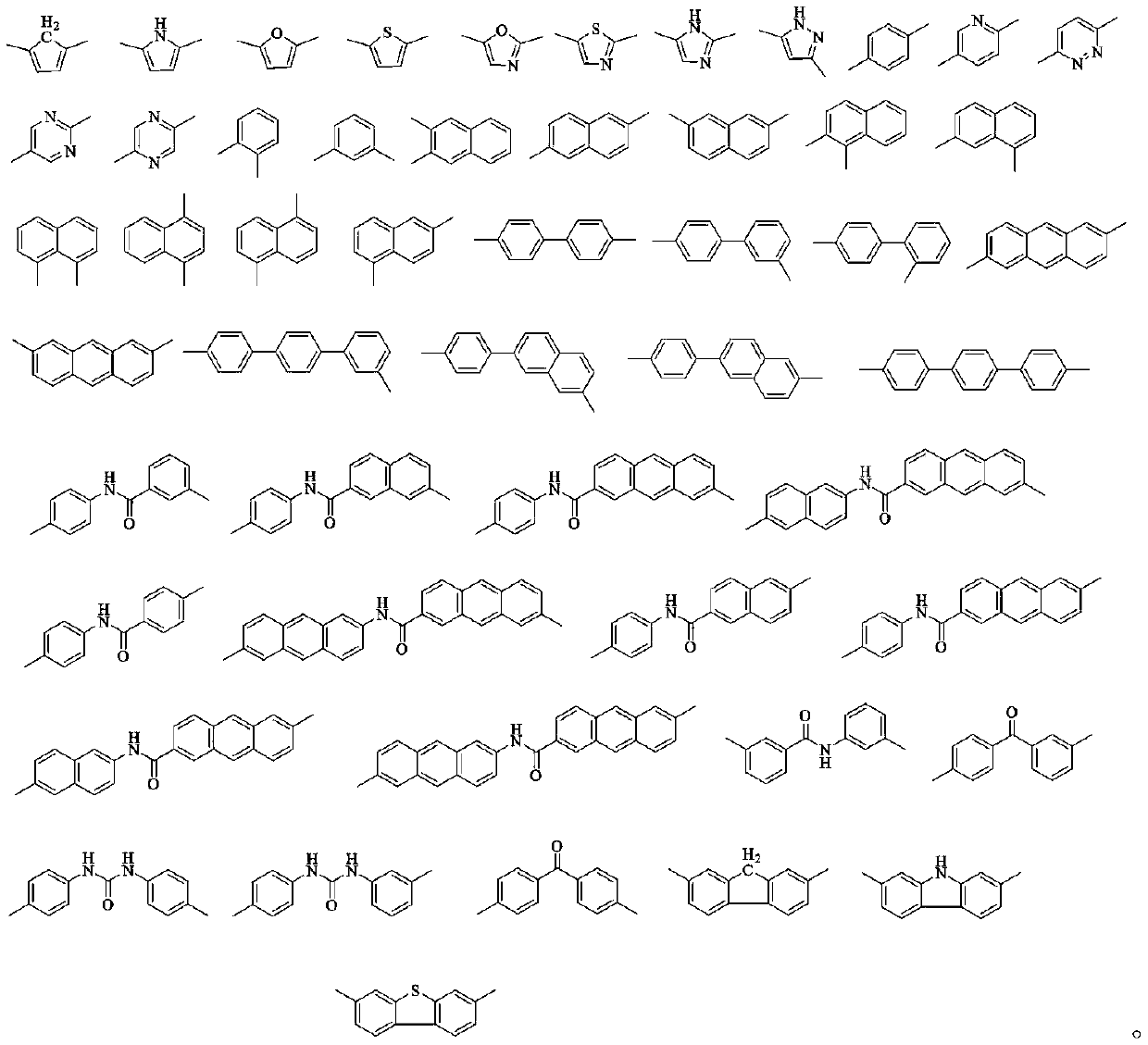Patents
Literature
117 results about "Acridone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
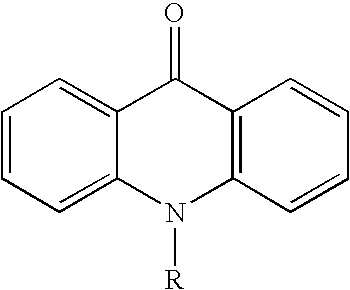
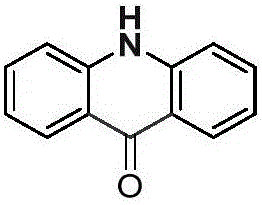
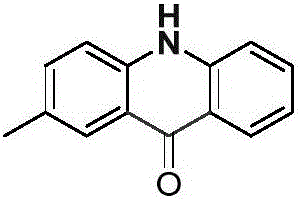
Acridone is an organic compound based on the acridine skeleton, with a carbonyl group at the 9 position. It may be synthesized by the self-condensation of N-phenylanthranilic acid.
Cyclin dependent kinase (CDK)4 inhibitors and their use for treating cancer
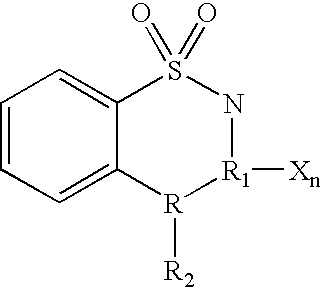
Certain derivatives of acridones and benzothiadiazines have been found to have anti-cancer properties by virtue of their specific inhibition of the cyclin D dependent kinase CDK4. These molecules inhibit CDK4 activity more than they inhibit the activity of other such kinases (e.g. CDC2 and CDK2). This specificity results in an improved therapeutic index when used as drugs to treat susceptible cancers.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
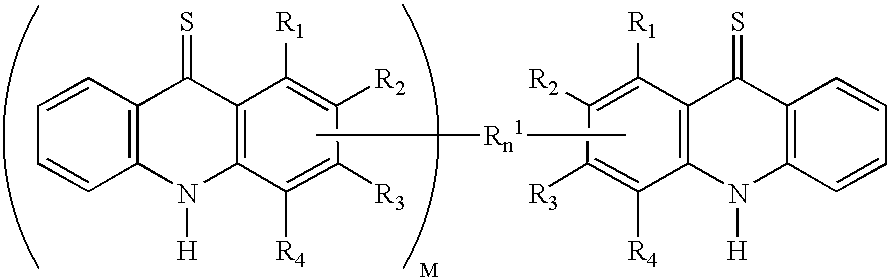
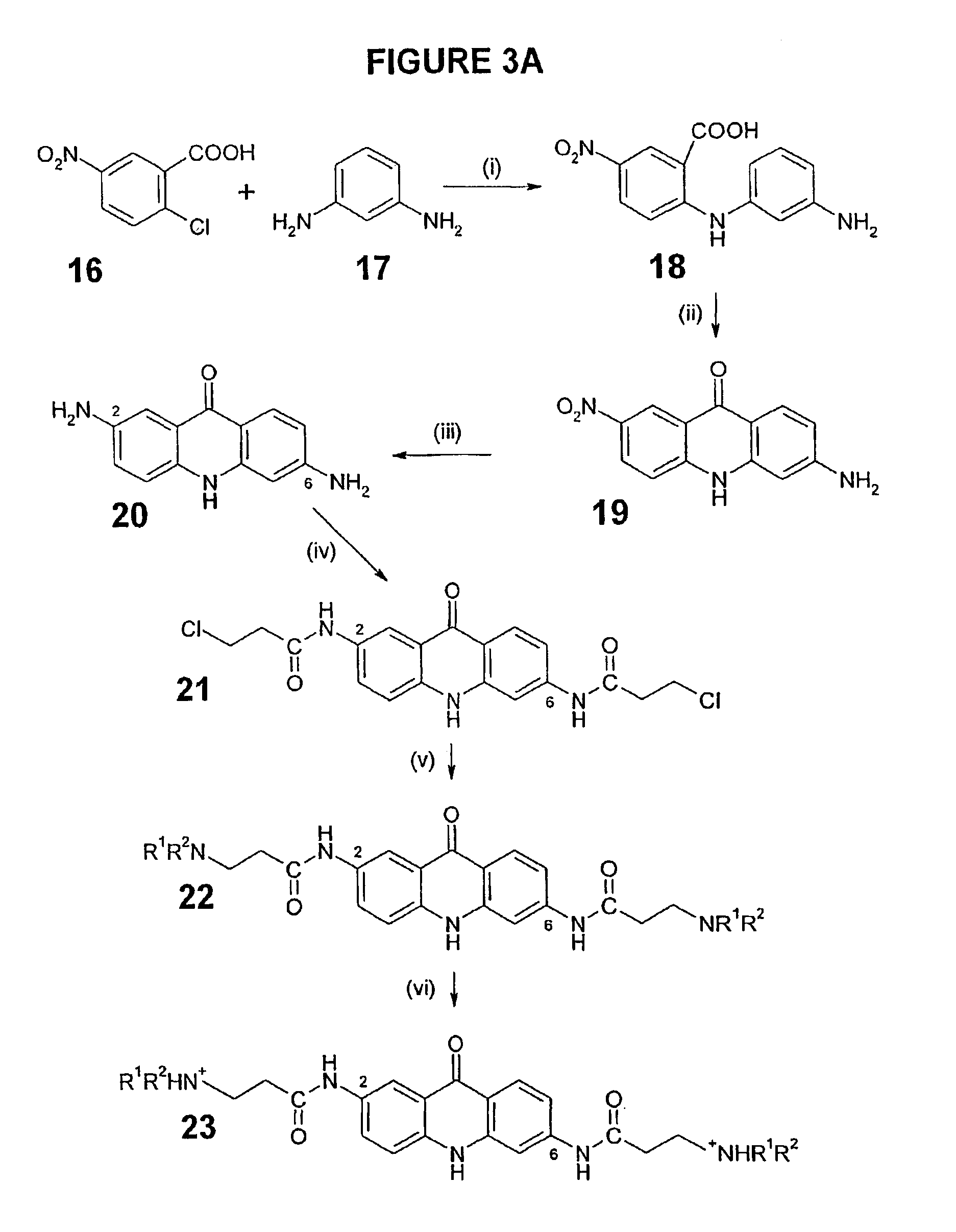
C8—linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids
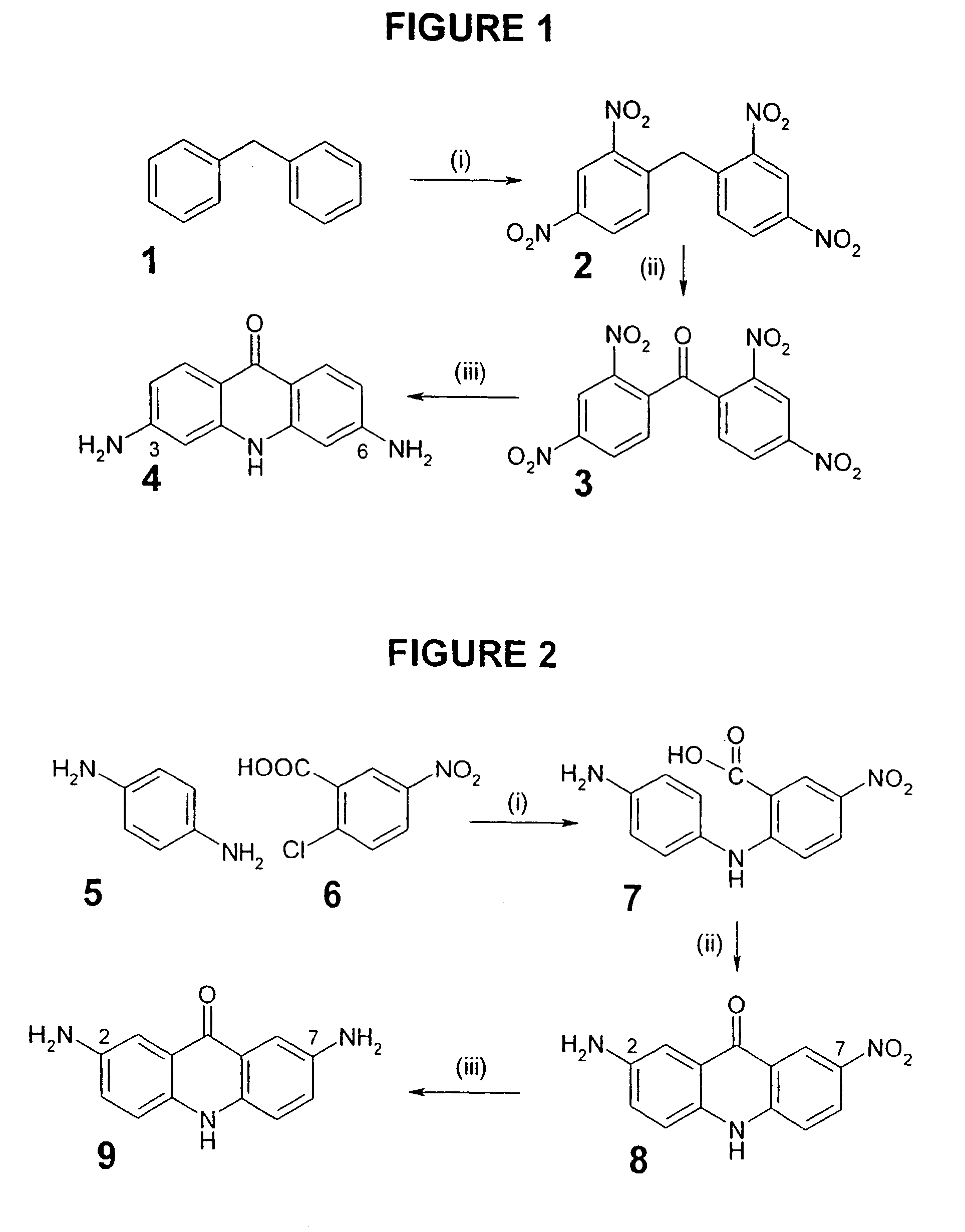
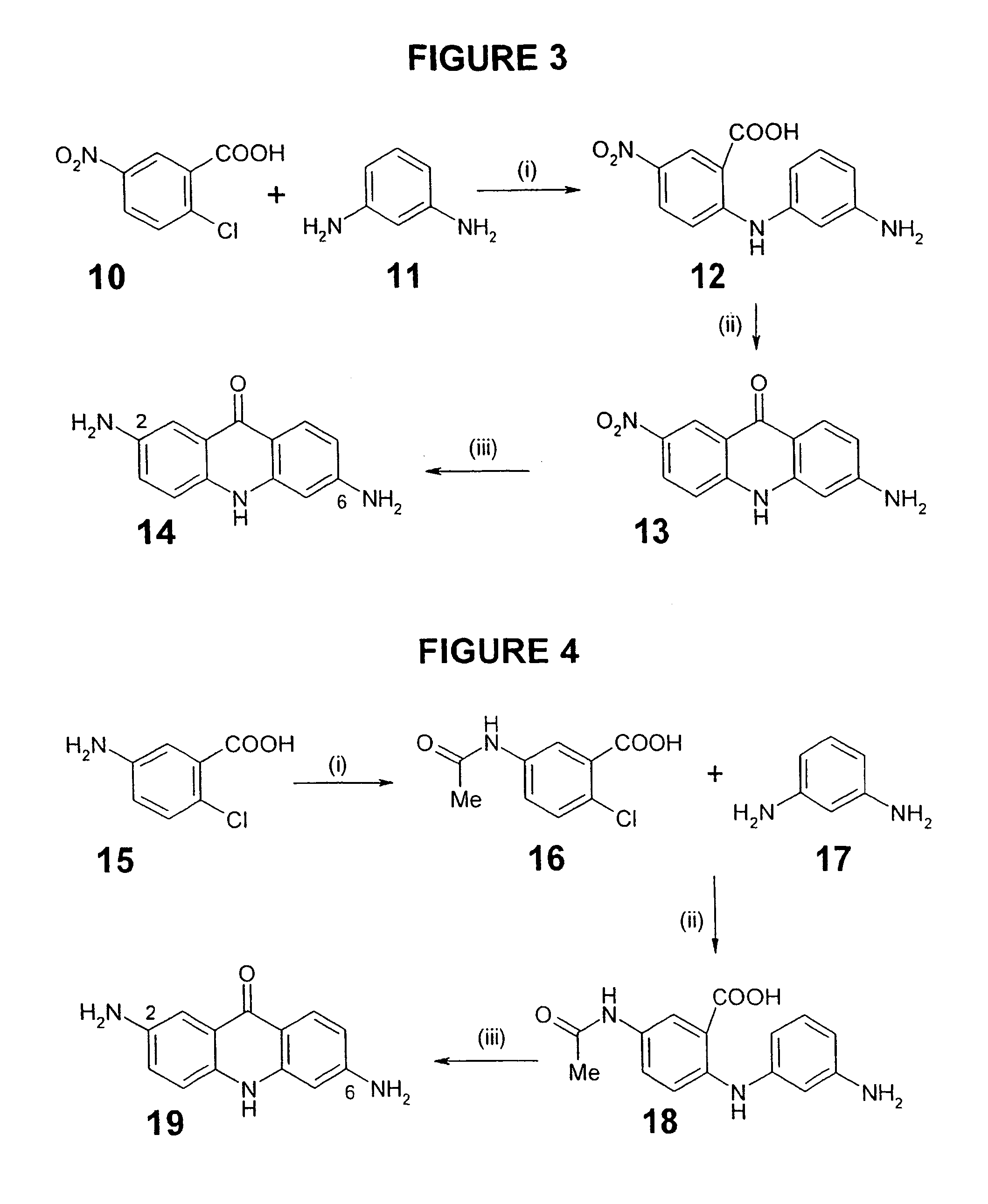
The present invention provides novel pyrrolo-[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine hybrids useful as anti-tumour agents and a process for the preparation thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for production of polymer-encapsulated pigments
The invention relates to a method for production of an aqueous dispersion of polymer-encapsulated pigments, characterised in that (a) an aqueous pigment dispersion, containing at least one organic pigment (P), selected from the group of azo, isoindolinone, isoindoline, anthanthrone, thioindigo, thiazinindigo, triarylcarbonium, quinophthalone, anthraquinone, dioxazine, phthalocyanine, quinacridone, quinacridonquinone, indanthrone, perylene, perinone, pyranthrone, diketopyrrolopyrrole, isoviolanthrone and azomethine pigments, at least one detergent (T), and water is prepared, (b) a monomer miniemulsion, stabilised by a hydrophobic organic compound with a water solubility at 20 DEG C of at most 5x10<-5> g / l, is prepared from a polymerisable monomer (M) and at least one detergent (T) in water, (c) a monomer pigment emulsion is prepared, whereby the aqueous dispersion from (a) and the monomer miniemulsion from (b) are mixed and homogenised and (d) the pigment-containing monomer from (c) is polymerised in the presence of a polymerisation initiator and / or by heat, whereupon an encapsulation of the pigment with the polymer thus formed occurs.
Owner:CLARIANT PROD DEUT GMBH
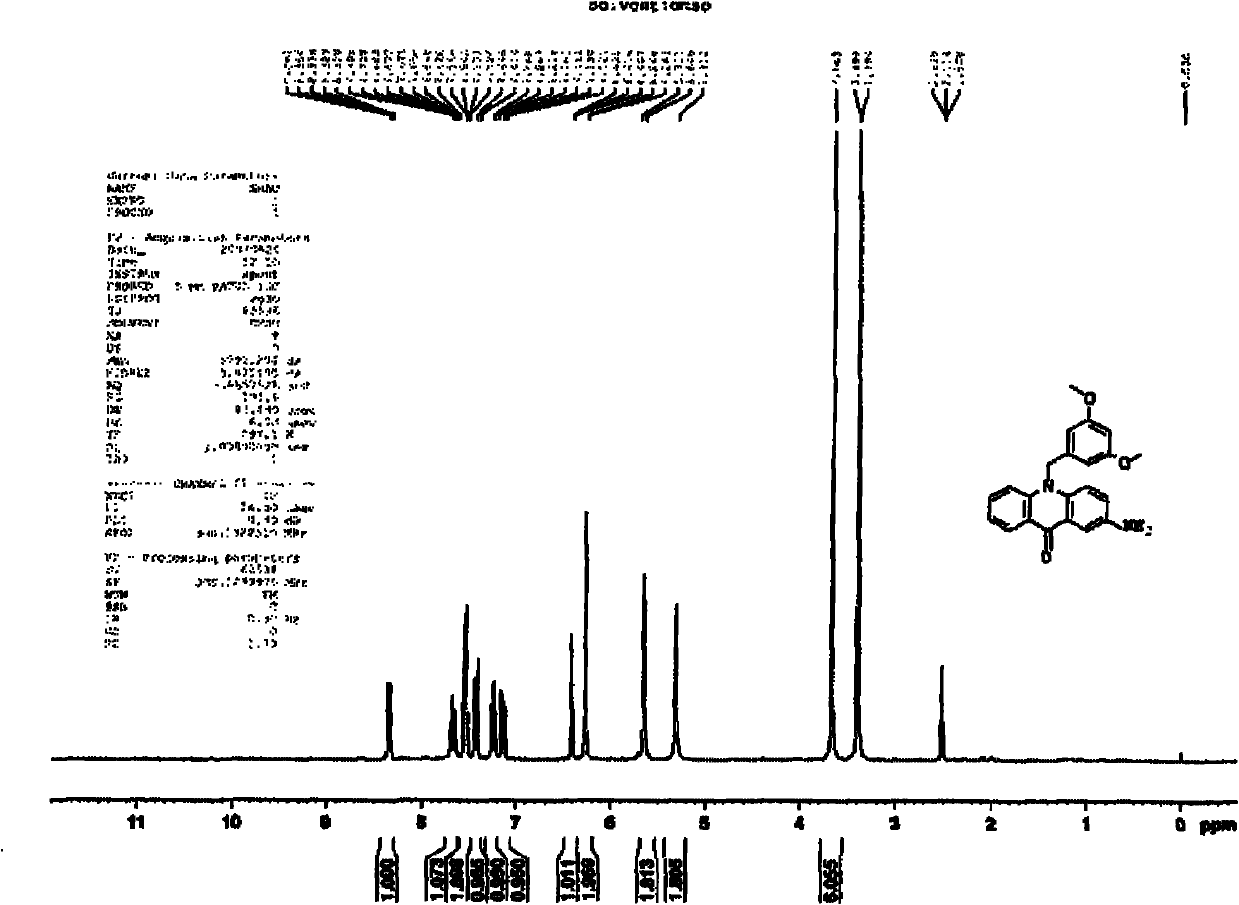
N-benzyl-acridone, derivatives of N-benzyl-acridone and preparation methods and application of N-benzyl-acridone and derivatives
ActiveCN102146056AGrowth inhibitionHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCancer cellAcridone
The invention discloses N-benzyl-acridone, derivatives of the N-benzyl-acridone and preparation methods and application of the N-benzyl-acridone and the derivatives. A structural formula of a compound is shown as a formula (I), wherein R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are all randomly selected from the following substituent groups: H, OH, NH2, Cl, F, Br, I, CN, NO2, CH3, OCH2Ph and O(CH2)nCH3; n in O(CH2)nCH3 is an integer in the range of 0 to 3; Z is randomly selected from the following substituent groups: CH2 and SO2; A is randomly selected form the following substituent groups: S, O and NH; R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11, R12 and R13 are all randomly selected from the following substituent groups: H, OH, NH2, Cl, F, Br, I, CN, NO2, CH3 and the following a and b; necessarily, only one substituent group of the R6, the R7, the R8, the R9, the R10, the R11, the R12 and the R13 is a or b; a represents NHCO(CH2)nR or CONH(CH2)nR, wherein n is an integer in the range of 0 to 3 and R represents tertiary amine; and b represents NHCOBNH2 or CONHBNH2, wherein B is an alkyl connection chain or an alkyl connection chain substituted heteroatom. A cell proliferation inhibition test result shows that the compound in the formula I can better inhibit cancer cell CCRF-CEM from growing, wherein part of compounds show higher activities than a parent compound (10-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl) acridone). (the formula I).
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
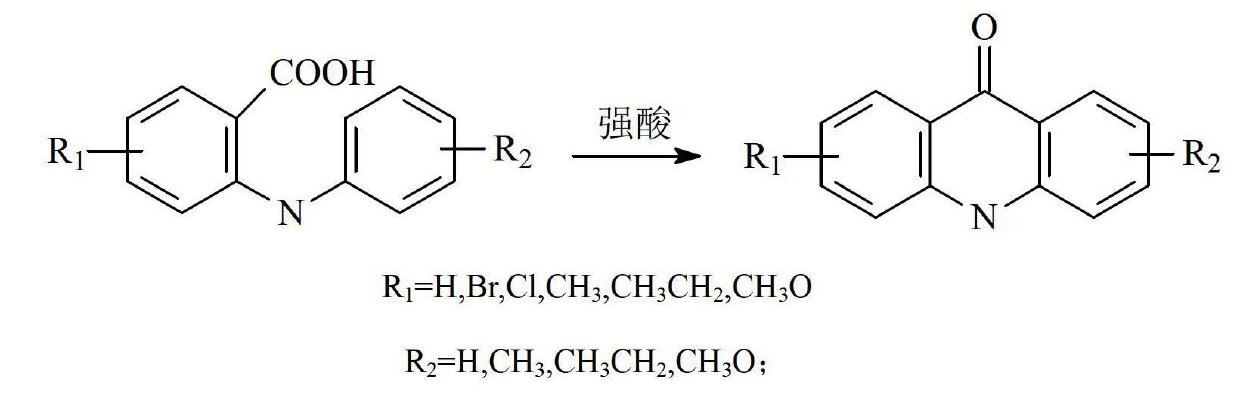
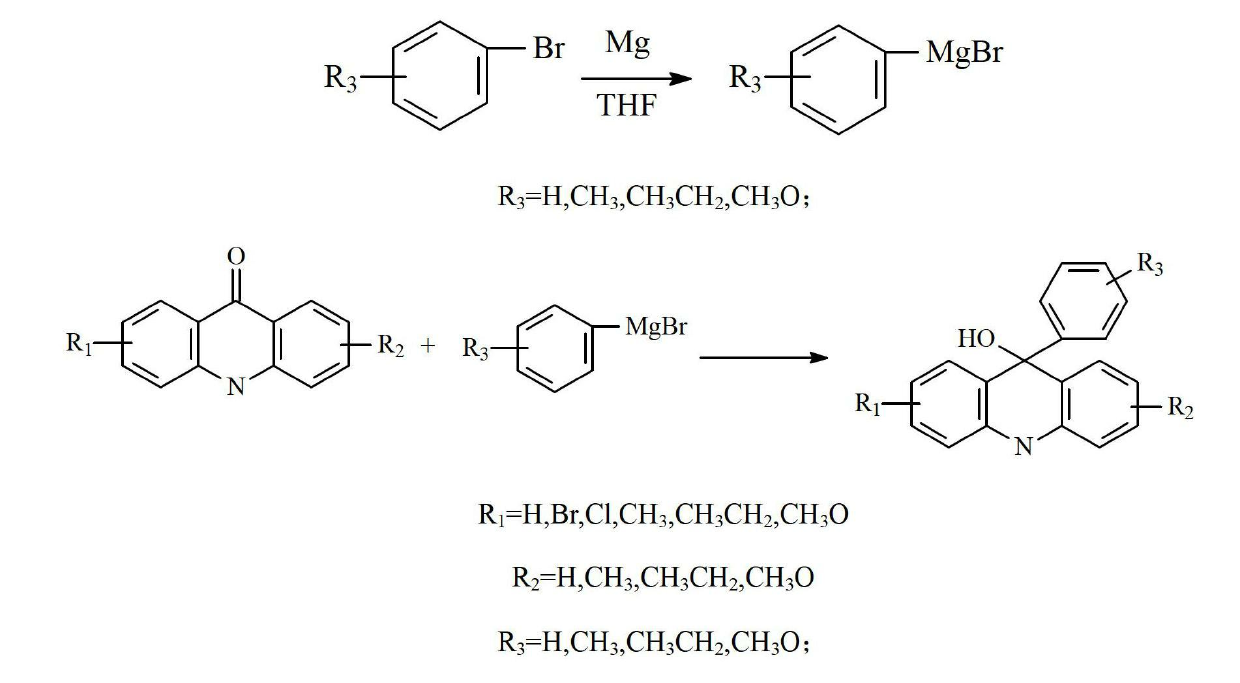
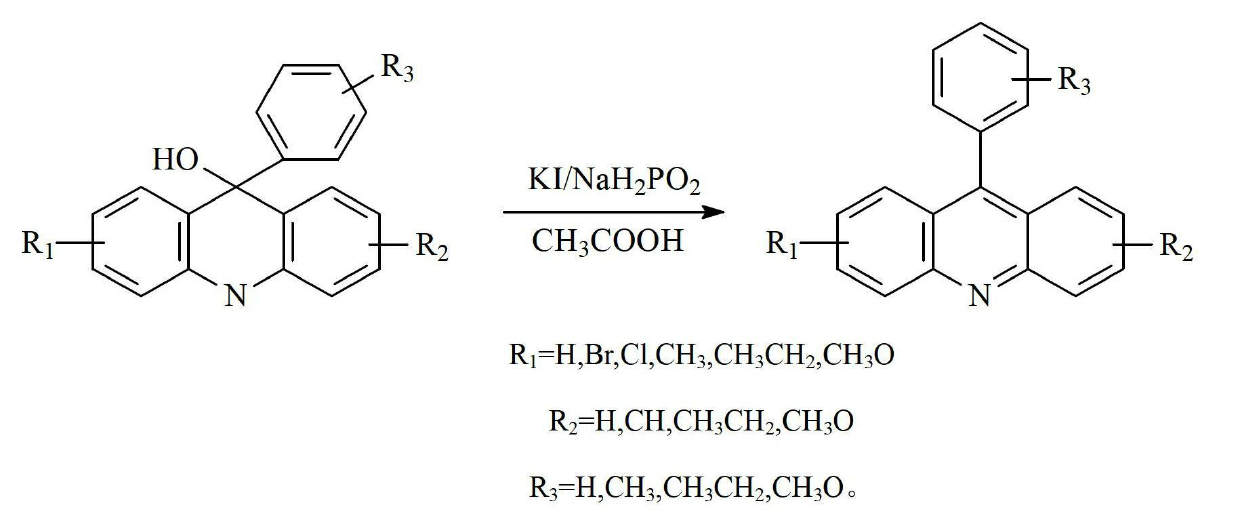
Preparation method of acridine compounds
ActiveCN102675203AReduce usageMild preparation conditionsOrganic chemistryGrignard reagent9-phenylacridine
The invention provides a preparation method of acridine compounds, and relates to the technical field of photoinitiator. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking substituted N-methyl anthranilic acid as initial raw material, generating substituted acridone under the condition of acid, carrying out reaction on substituted bromobenzene and magnesium to generate grignard reagent, carrying out reaction on substituted acridone and the grignard reagent to generate substituted 9-oxhydryl-9-phenylacridine, and reducing to obtain the substituted 9-phenylacridine compounds. Different from the conventional synthesis route, the preparation method of the acridine compounds provided by the invention has more operation steps compared with the conventional one-step method, thus being slightly lower in yield compared with the conventional synthesis route, however, the preparation condition is mild relatively, and the high-temperature and high-pressure reaction and the use of expensive heavy metal catalyst can be avoided, so that the preparation method is good in environment protection.
Owner:芜湖启博知识产权运营有限公司
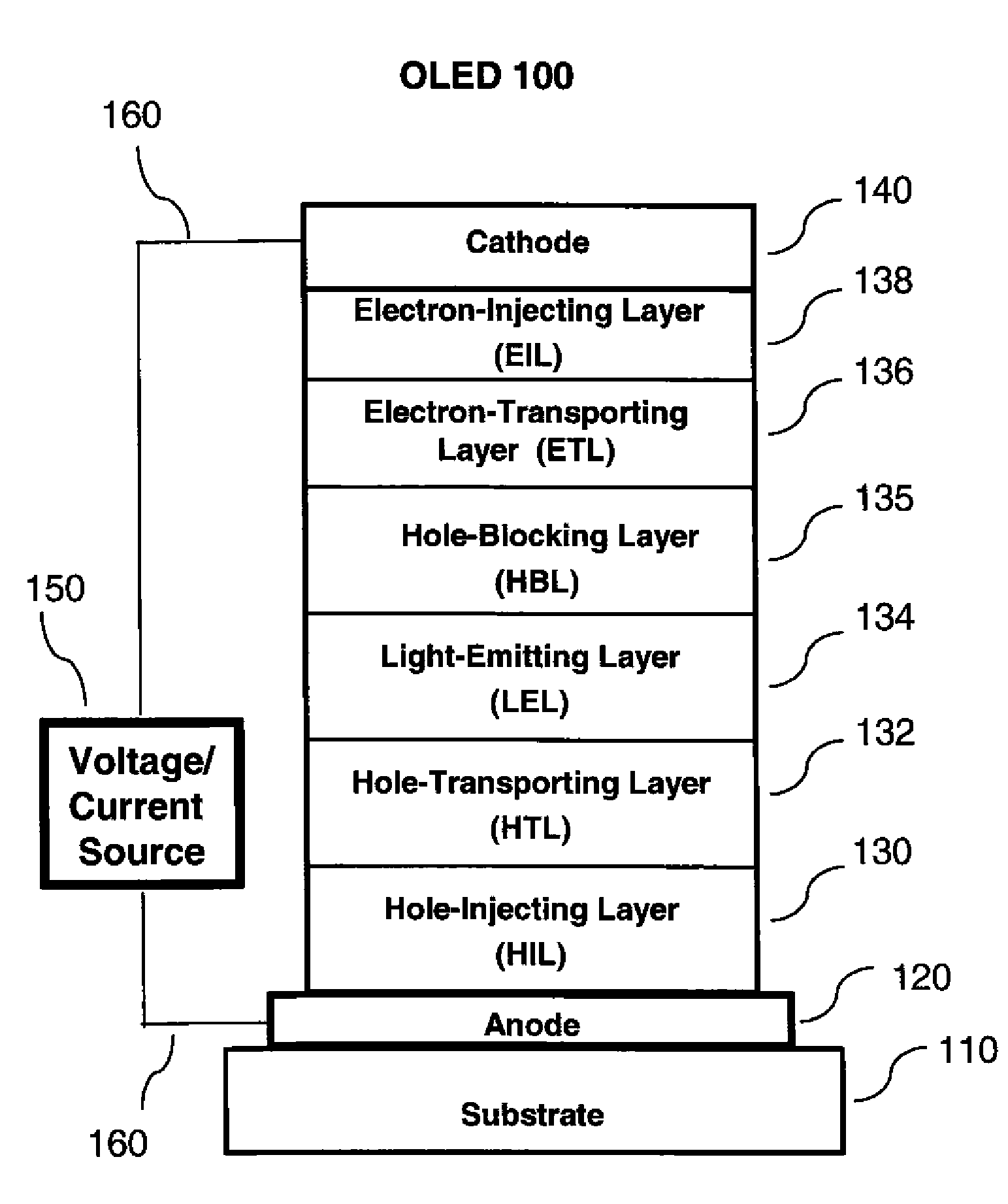
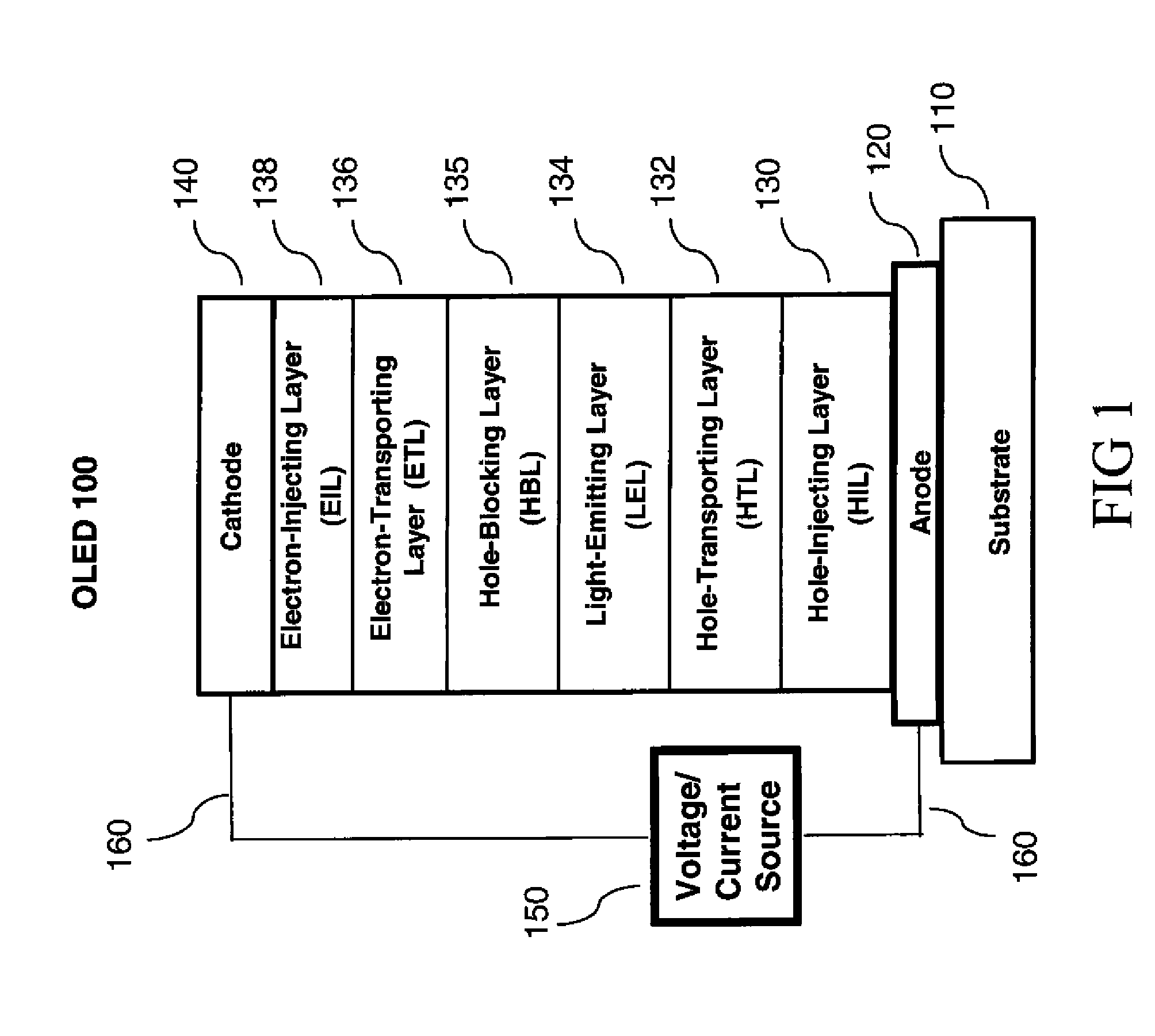
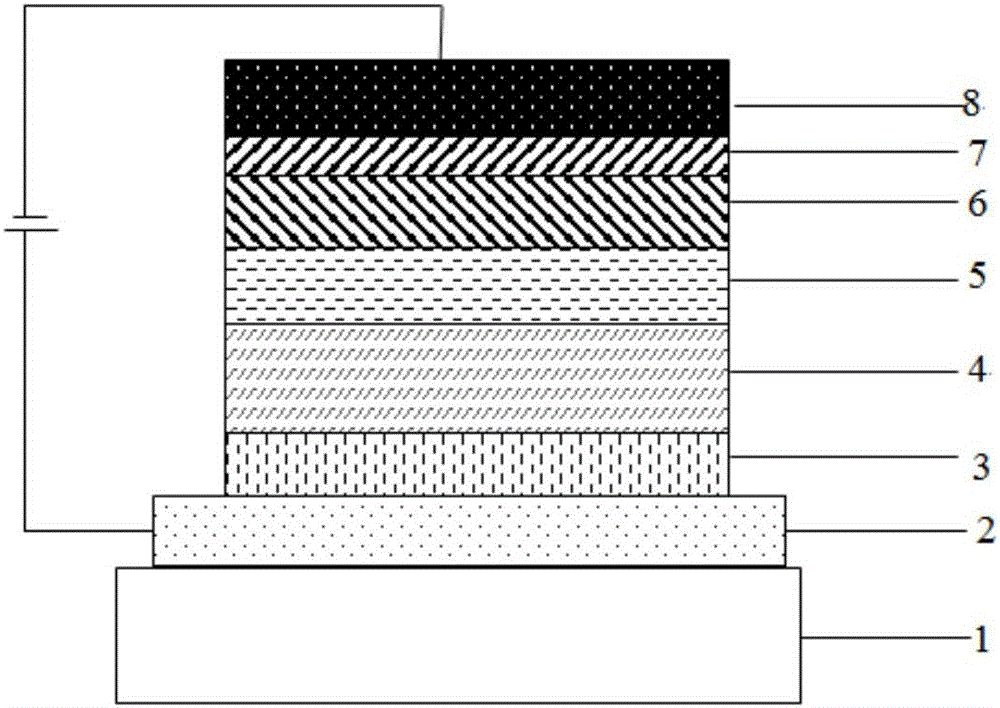
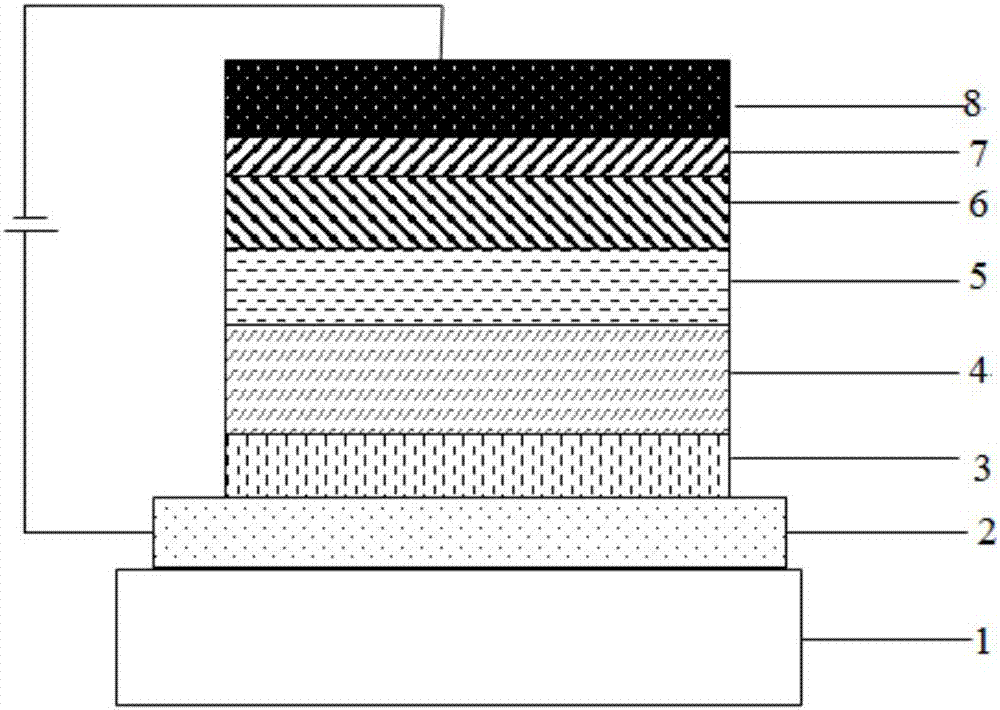
OLED device with substituted acridone compounds
ActiveUS20090153030A1Improve efficiencyHigh voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsAcridoneCarbazole
The invention provides an OLED device comprising a cathode, an anode, and having therebetween a layer containing an acridone compound including a diarylamine or carbazole substituent where the nitrogen of the acridone and the nitrogen of the diarylamine or carbazole are connected by an aromatic hydrocarbon linking group. OLED devices of the invention exhibit improved efficiency and drive voltage.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
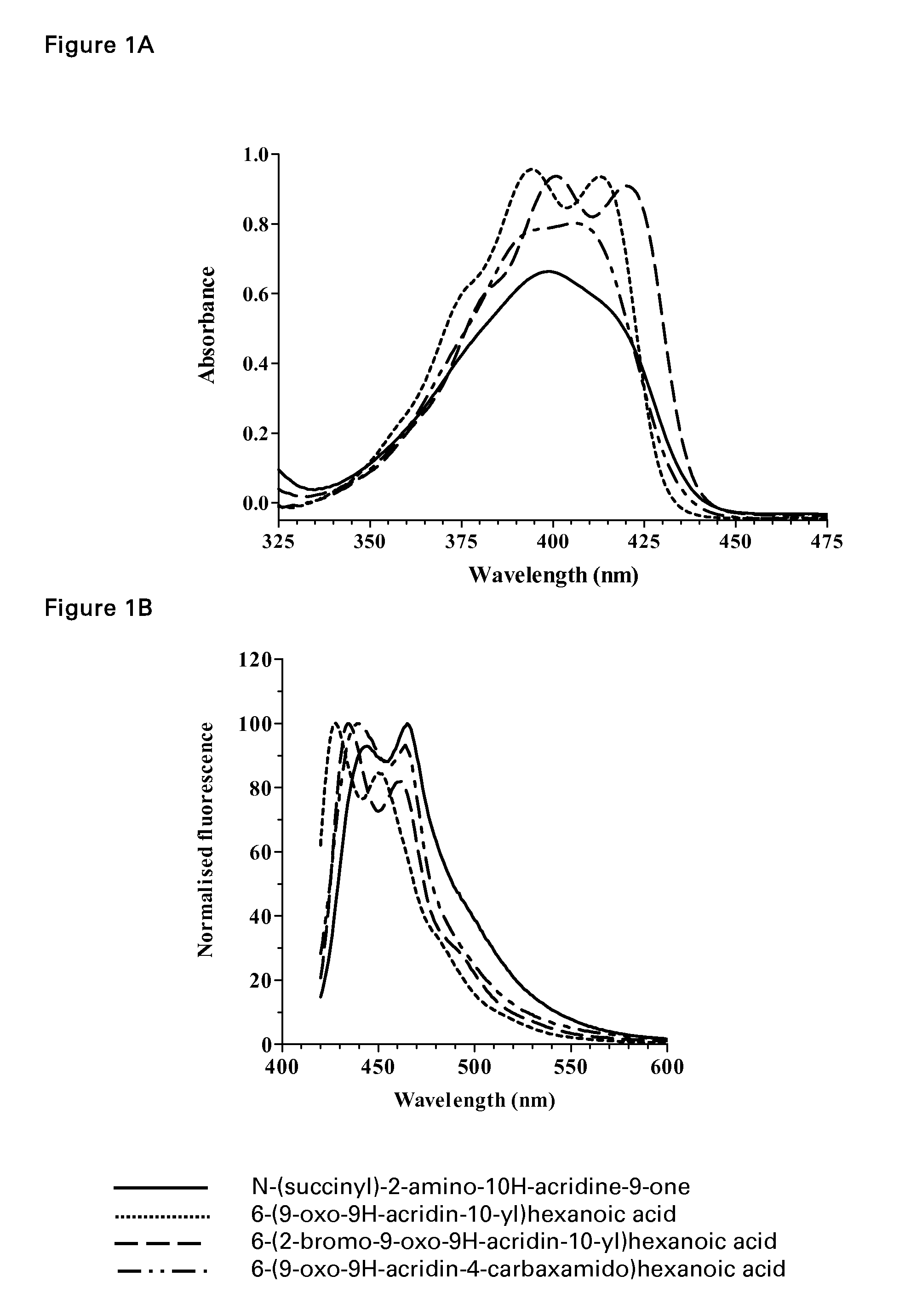
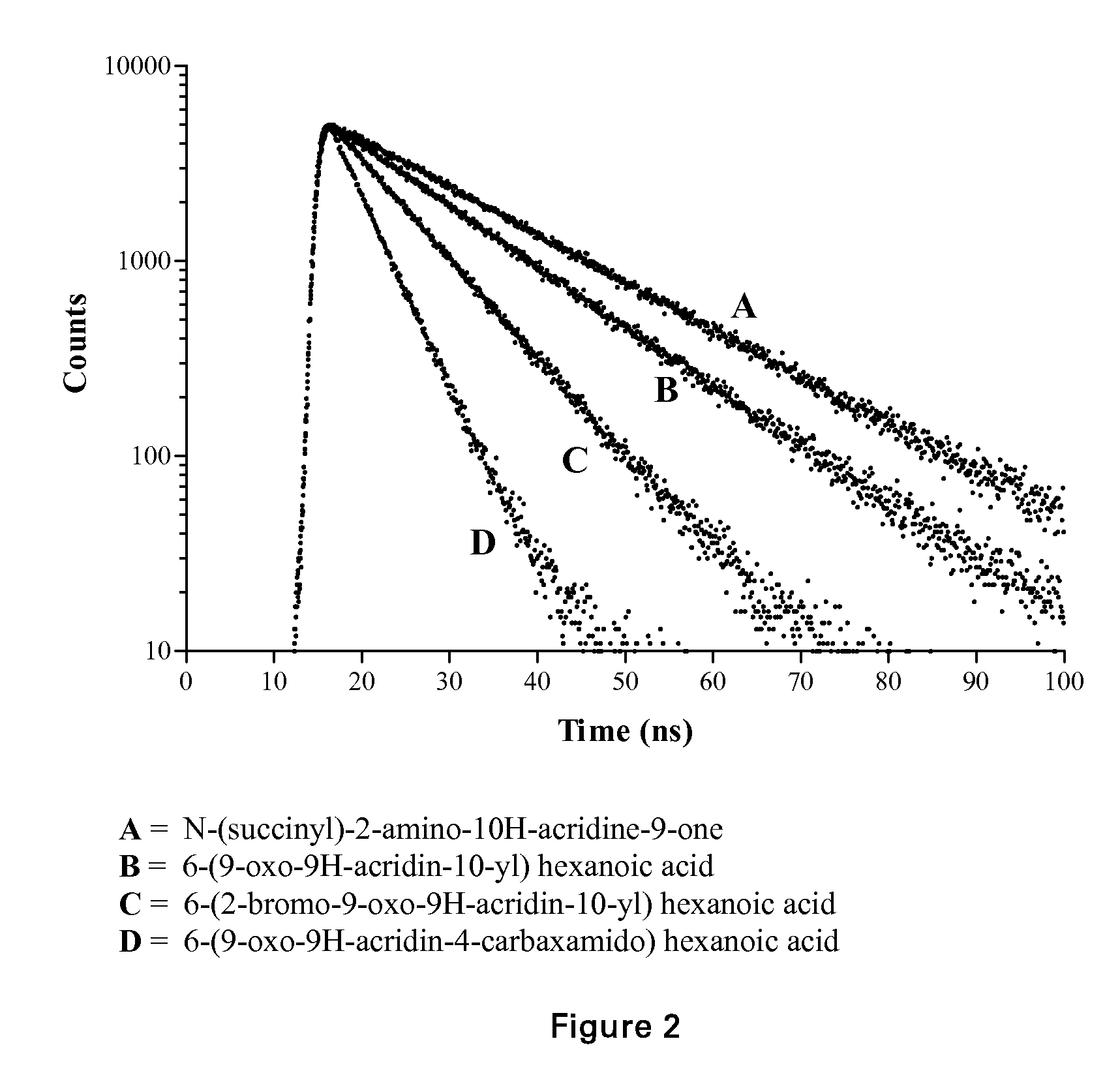
Acridone derivatives as labels for fluorescence detection of target materials
InactiveUS8034558B2Simple requirementsEasy to analyze and useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhosphateBiological materials
Owner:TTP LABTECH
Method for preparing 9-oxo-10(9H)-acridineacetic acid
ActiveCN103396362ASmooth responseResponse is smooth and easy to controlOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing 9-oxo-10(9H)-acridineacetic acid, and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) under the effects of a metal carbonate, a catalyst and a solvent, performing a condensation reaction on o-chlorobenzoic acid (a) and aniline (b) to prepare an intermediate c; (2) under the effects of toluene and p-toluenesulfonic acid, performing a cyclization reaction on the intermediate c by refluxing and dehydrating to prepare an intermediate d; (3) dissolving the intermediate d in dimethyl formamide , successively adding 60% NaH, KI and ethyl chloroacetate, reacting at room temperature to obtain a wet intermediate e; and (4) hydrolyzing the wet intermediate d with NaOH to obtain a crude product f, and refining the crude product f to obtain the 9-oxo-10(9H)-acridineacetic acid product. The method has the advantages of low cost consumption, small pollution during reaction, smooth and easy-controlling reaction and high product yield, and has better industrial application value.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU SIGMA CHEM
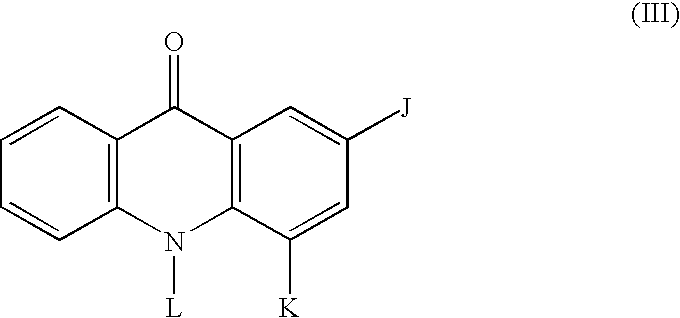
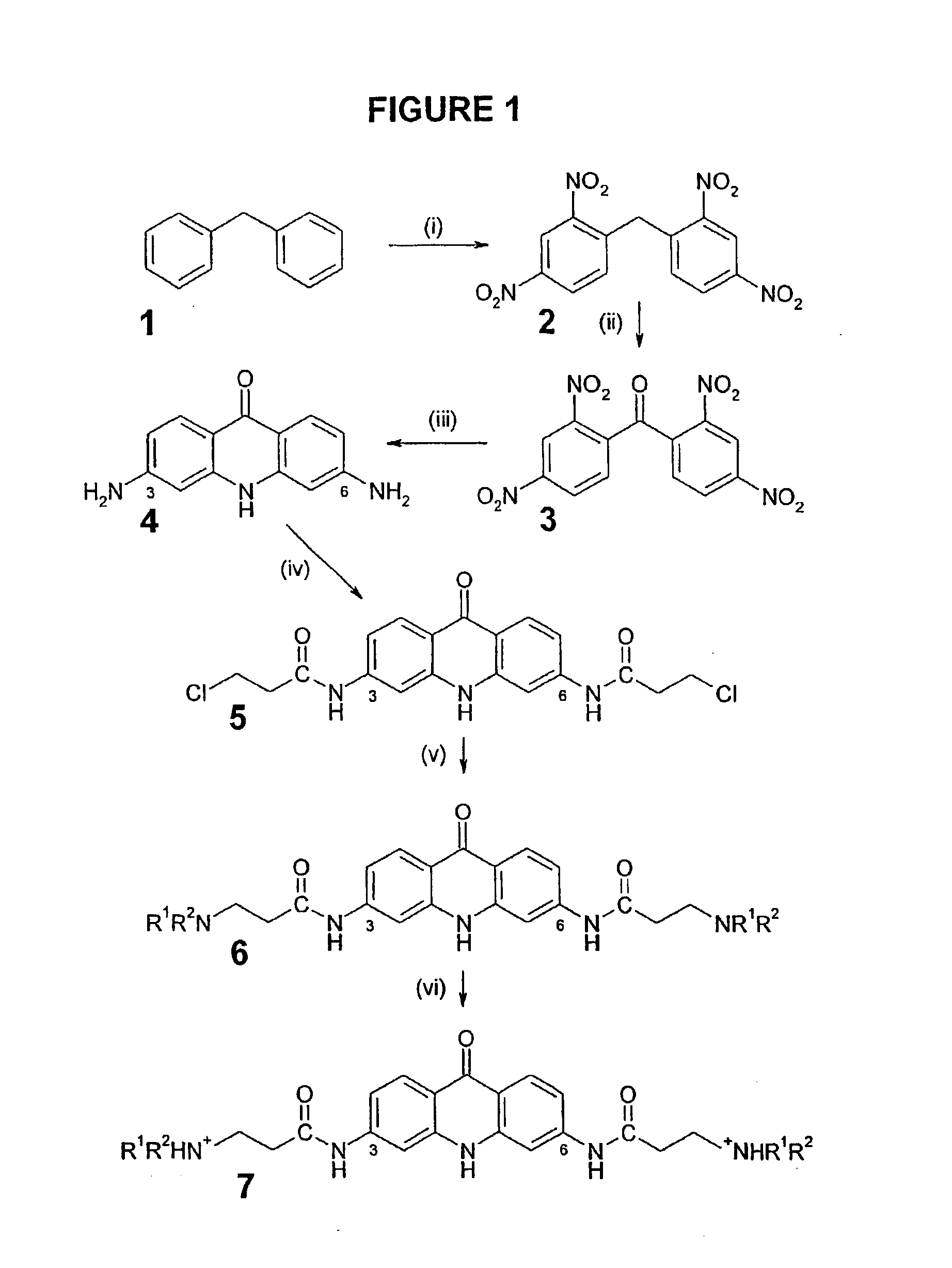
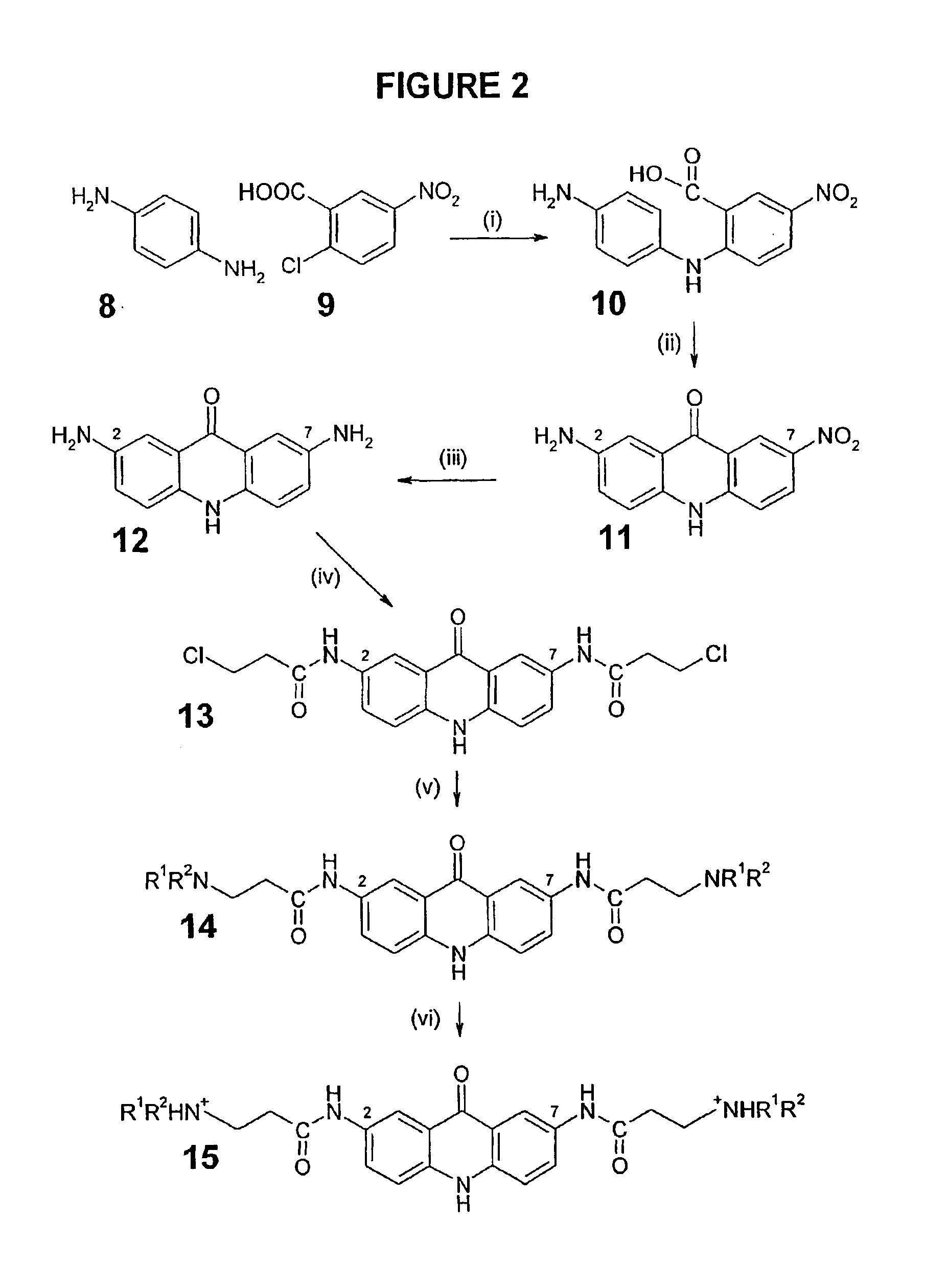
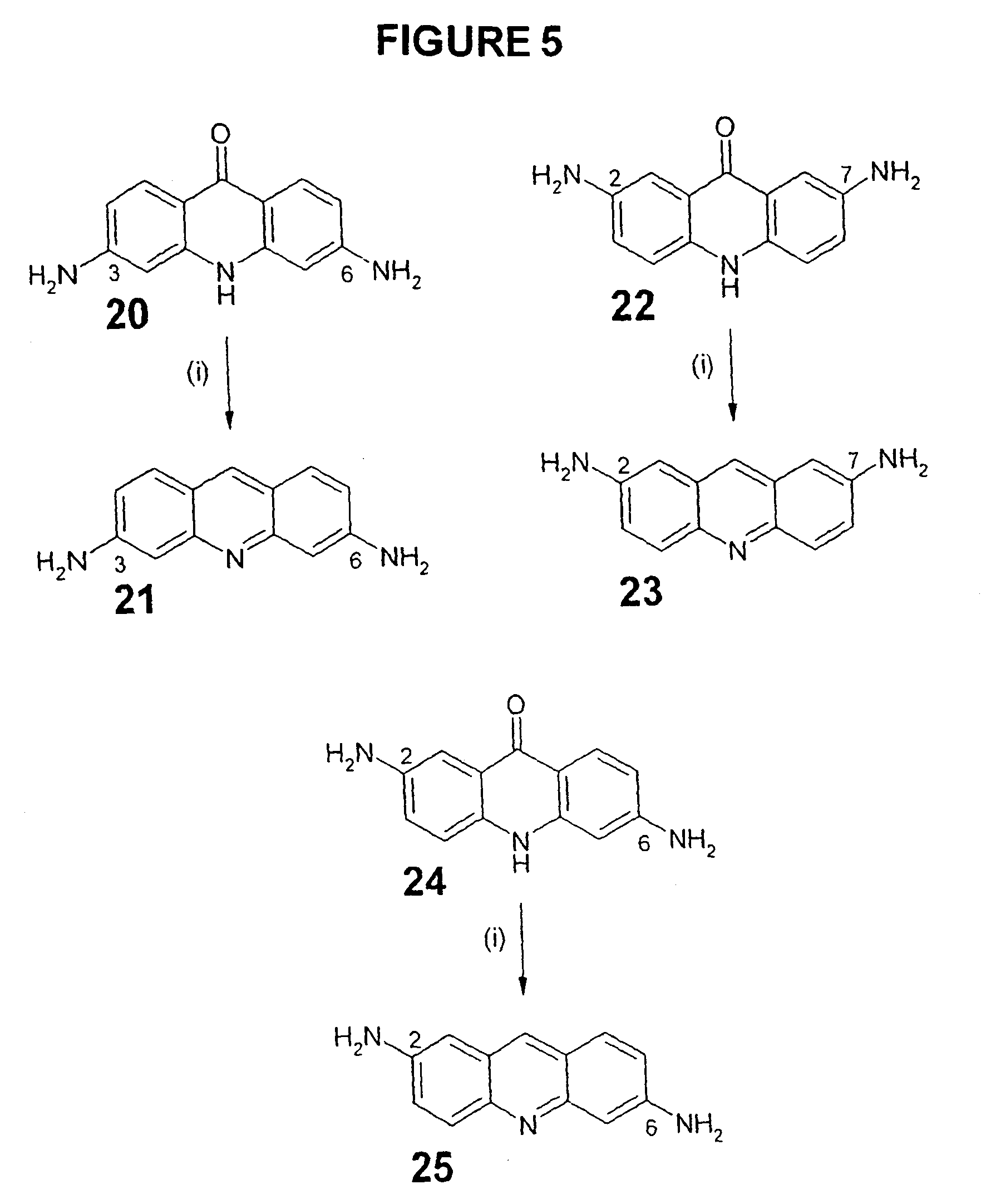
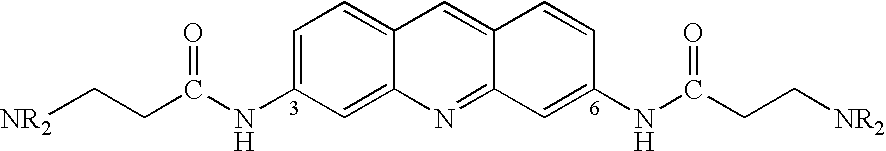
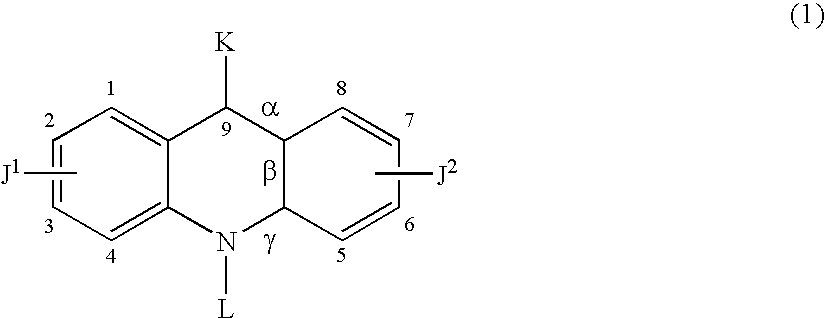
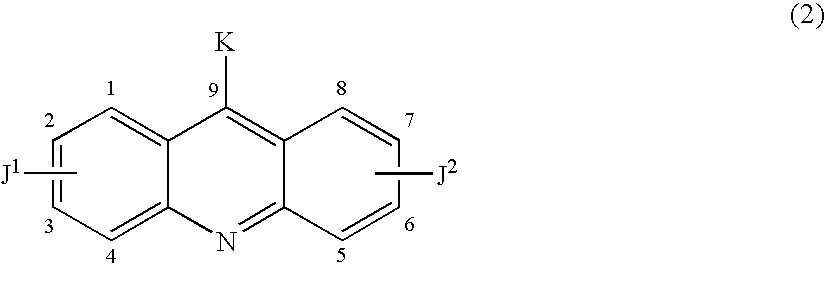
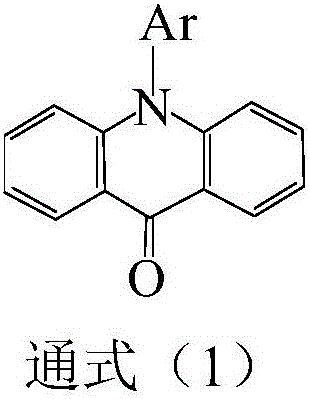
Therapeutic acridone and acridine compounds
The present invention pertains to acridone and acridine compounds of formula (I), wherein either: (a) K is ═O, L is —H, alpha single bond, beta is a double bond, gamma is a single bond (acridones); or, (b) K is a 9-substituent, L is absent, alpha is a double bond, beta is a single bond, gamma is a double bond (acridines); and wherein: J1 is a 2- or 3-substituent; J2 is a 6- or 7-substituent; J1 and J2 are each independently a group of the formula —NHCO(CH2)nNR1R2, wherein: n is an integer from 1 to 5; and, R1 and R2 are independently hydrogen, C1-7alkyl, C3-20heterocyclyl, or C5-20aryl, or R1 and R2, taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached, form a heterocyclic ring having from 3 to 8 ring atoms; and wherein, when K is a 9-substituent, K is a group of the formula —N(RN)Q, wherein: RN is an amino substituent and is hydrogen, C1-7alkyl, C3-20heterocyclyl, or C5-20aryl; and, Q is C1-7alkyl, C3-20heterocyclyl, or C5-20aryl, and is optionally substituted; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, amides, solvates, hydrates, and protected forms thereof. The present invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and the use of such compounds and compositions, both in vitro and in vivo, to inhibit telomerase, to regulate cell proliferation, and in the treatment of proliferative conditions, such as cancer.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
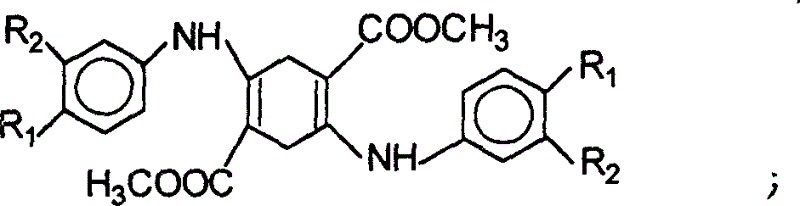
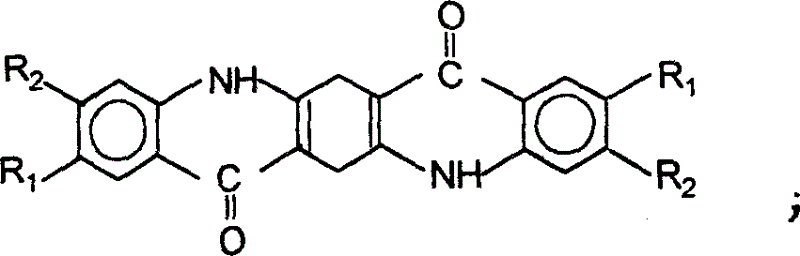
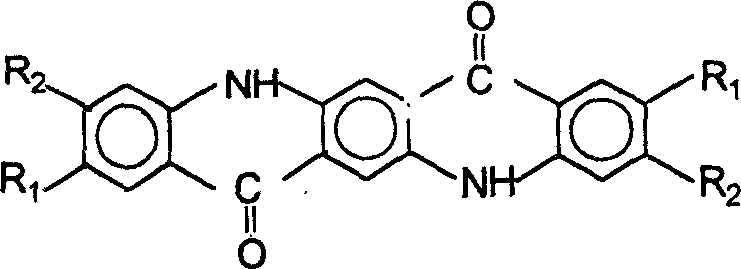
Process for preparation of quinacridone series pigments
InactiveCN1521218AAvoid generatingLow oxidation temperatureQuinacridonesReaction temperaturePhosphoric acid
The present invention discloses the preparation process of serial quinacridone dyes. The preparation process includes the first condensation of diacyl dimethyl succinate and aniline derivative in ethanol under the catalysis of hydrochloric acid to obtain 1, 4-(N-phenyl amino)-2, 5-dimethyl carboxylate; direct cyclization of 1, 4-(N-phenyl amino)-2, 5-dimethyl carboxylate under the action of phosphoric acid polymer to produce dihydroquinacridone; and final chemical oxidation or hydrogenating aromatization and cyclization under catalysis of Pt catalyst of dihydroquinacridone in the condition of being favorable to form aromatic nucleus to produce quinacridone. The process of the present invention has low reaction temperature and mild reaction condition, and the product has no deep colored impurity produced and no need of purification and crystal transformation in obtaining dye with required hue and crystal form.
Owner:余世春 +1
Photosensitive resin composition, method for preparing the same, and dry film resist comprising the same
InactiveUS20090136872A1High sensitivityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPolymer scienceAcridone
The present invention relates to a photosensitive resin composition, a preparation method thereof, and a dry film resist comprising the same. More particularly, the photosensitive resin composition of the present invention is directed to a photosensitive resin composition including a) an alkali-soluble acrylate resin, b) a cross-linking monomer having at least two ethylenic double bonds, and c) a phosphinoxide based photopolymerization initiator and an acridon based photopolymerization initiator.According to the photosensitive resin composition and the dry film resist, it is easy to finely pattern using a laser direct image (LDI) with high density and the dry film has excellent sensitivity, resolution, and adhesiveness to the substrate.
Owner:DONGJIN SEMICHEM CO LTD
Aromatic ketones and uses thereof
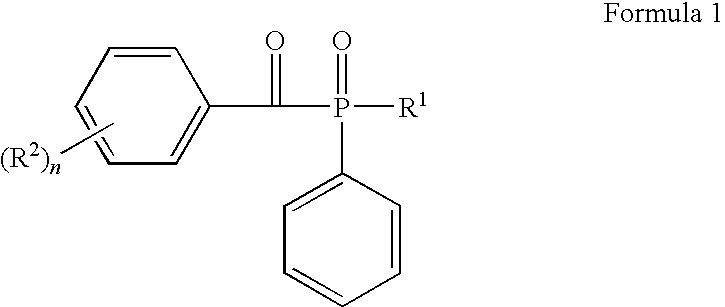
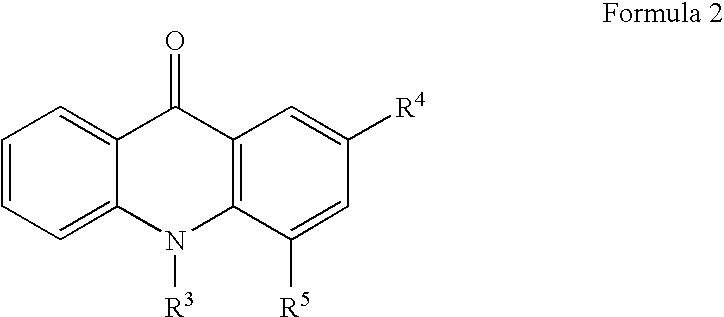
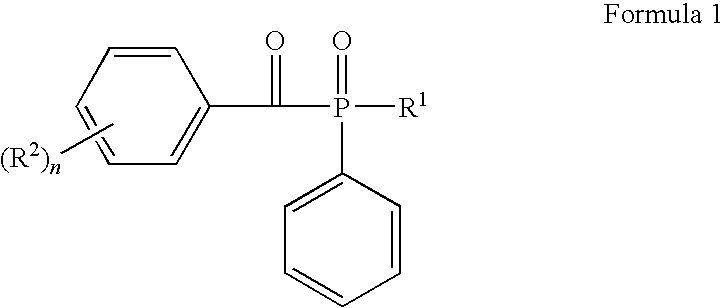
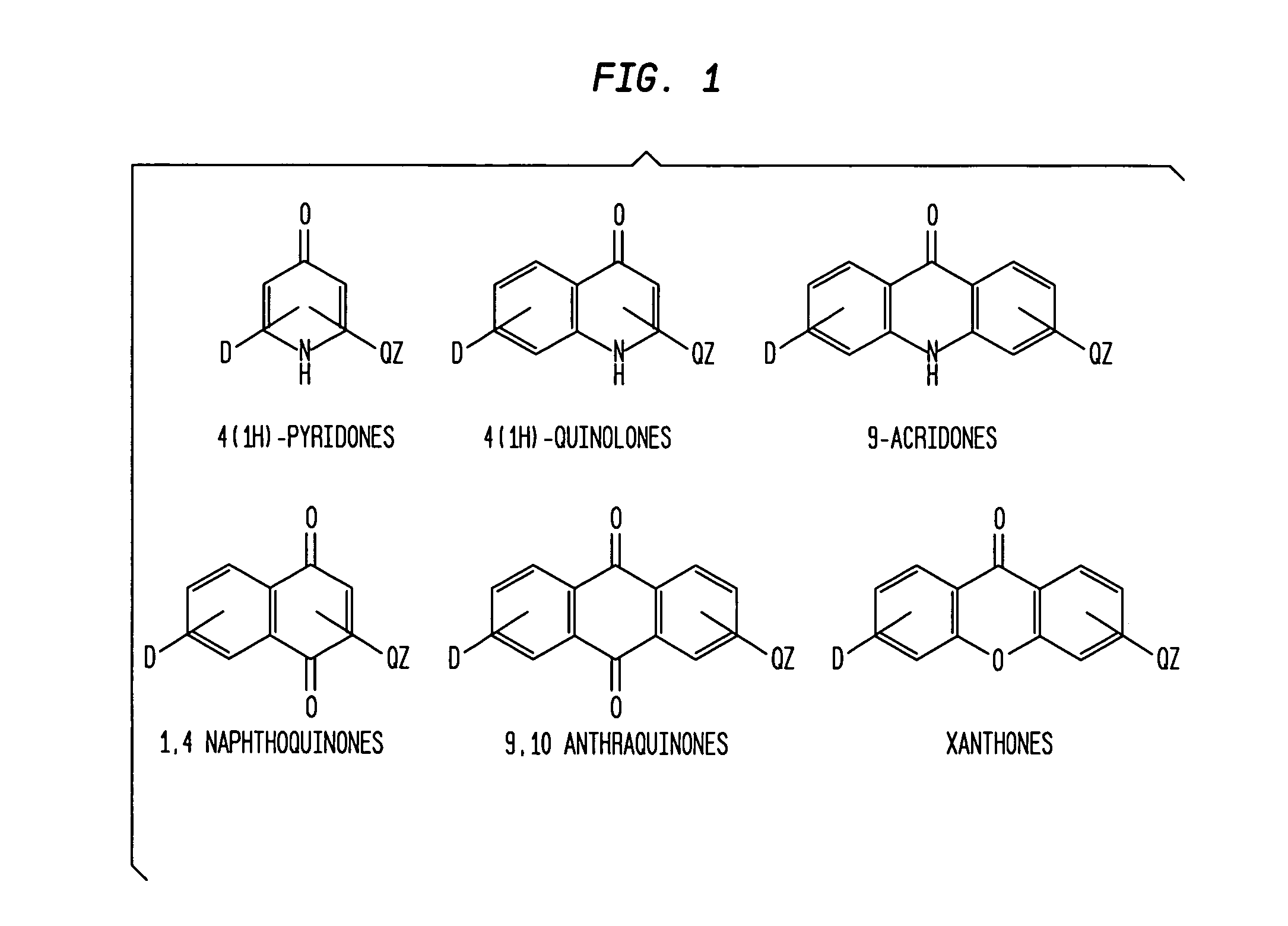
InactiveUS7829578B1Improves antimalarial potencyEnhanced anti-parasiticBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseXanthone
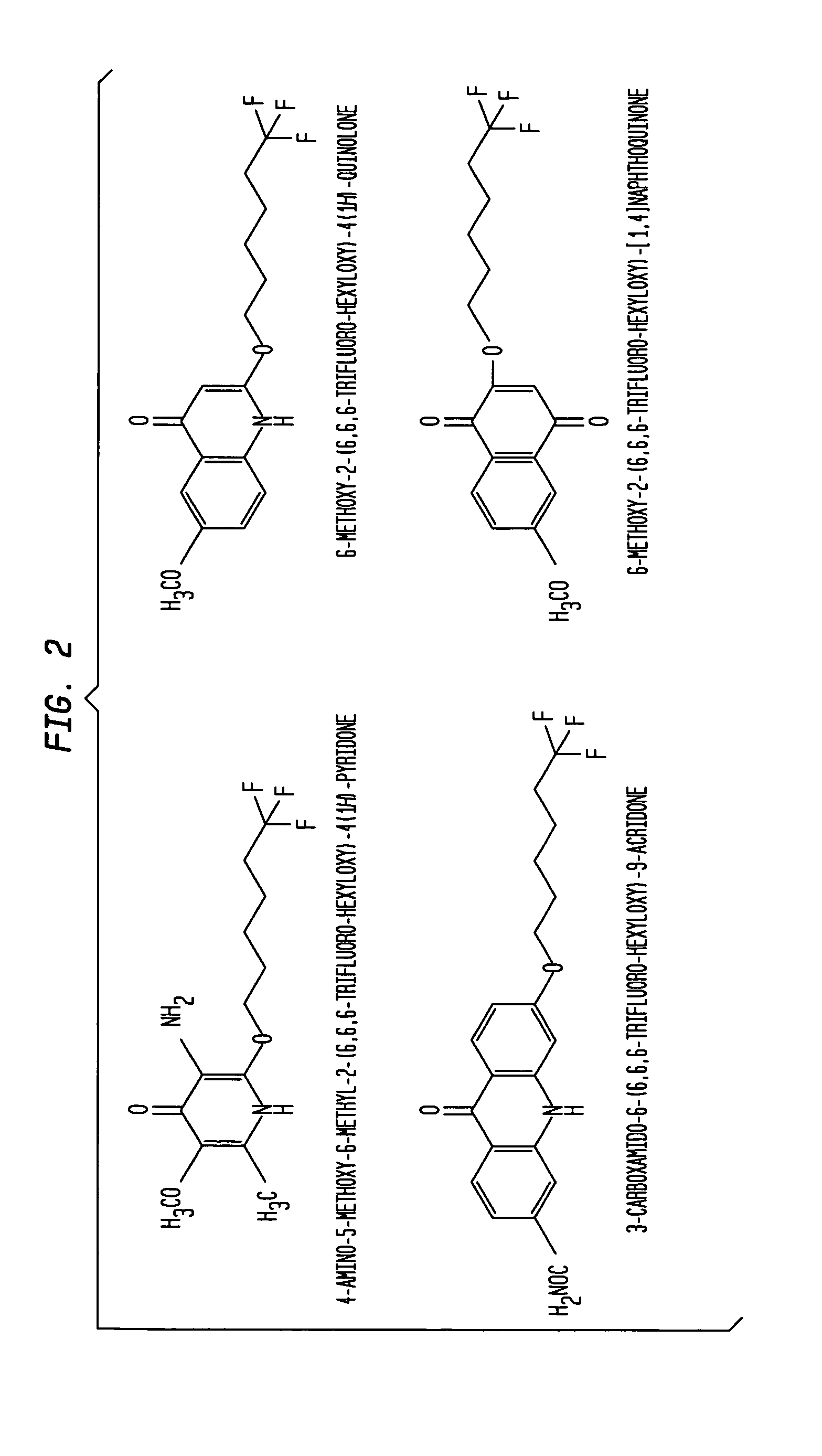
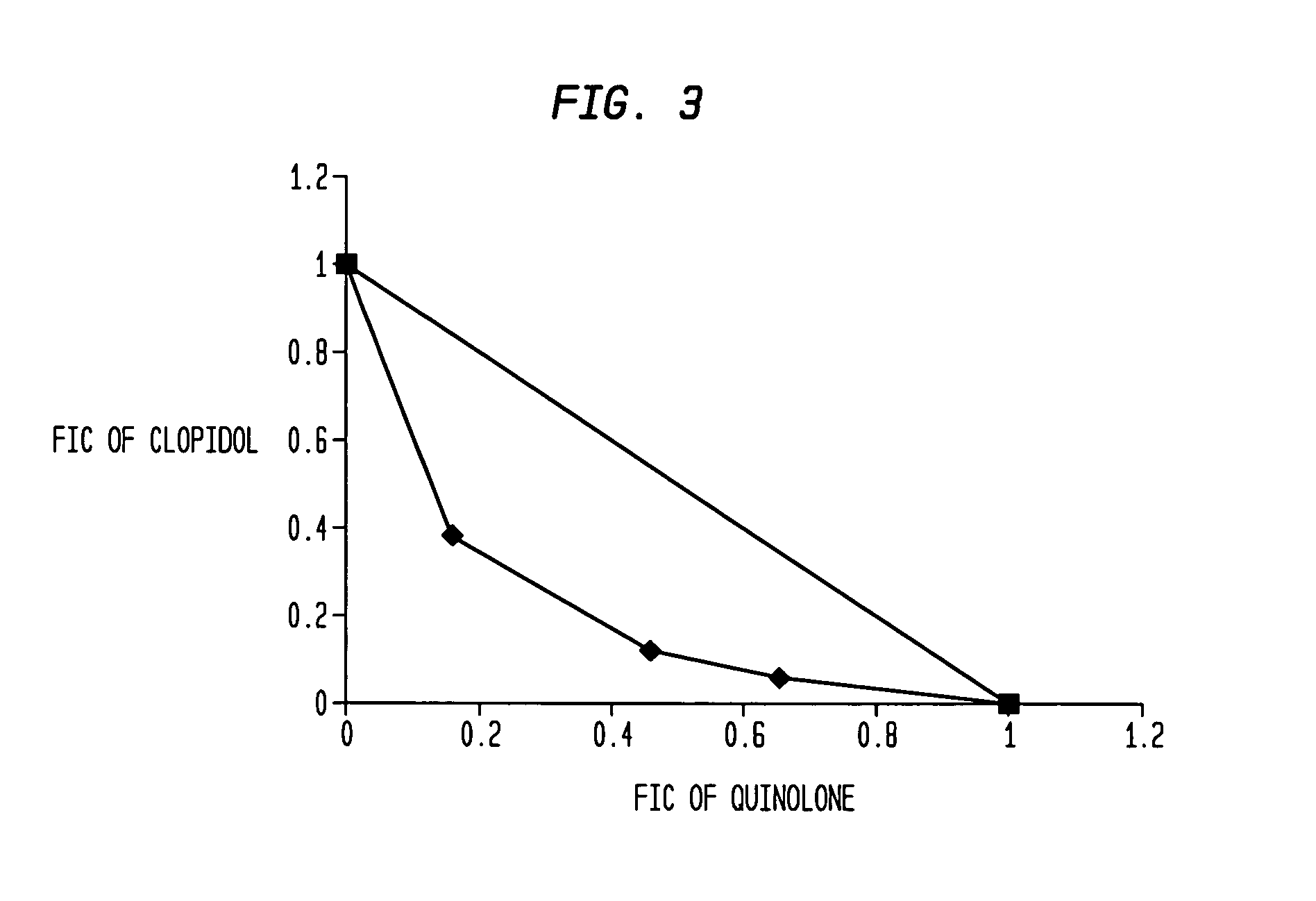
Aromatic ketones having an extended fluoro-alkyl or fluoro-alkoxy moiety are disclosed. In particular aspects, the compounds comprise substituted 9-acridone, 9-xanthone, 4(1H)-quinolone, 4(1H) pyridone, 1,4-naphthoquinone, 9,10-anthraquinone derivatives. These preparations possess potent pharmacological activity for inhibiting malaria and mosquito-borne (Plasmodium) diseases. The haloalkyl / alkoxy aromatic compounds possess significant pharmacological activity, with IC50 values in the nanomolar and sub-nanomolar range, and reduced toxicity against host derived cells and tissues. Methods of using the fluoro-alkyl / alkoxy aromatic compounds in the treatment of malaria and other human and animal diseases are also disclosed. Agricultural uses of the fluoro-alkyl / alkoxy aromatic compounds, such as in control of fungal diseases and in the production of important commercial crops (apples, etc.), are also presented.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Therapeutic acridone and acridine compounds
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Therapeutic acridone and acridine compounds
The present invention pertains to acridone and acridine compounds of formula (I), wherein either: (a) K is ═O, L is —H, alpha is a single bond, beta is a double bond, gamma is a single bond (acridones): or, (b) K is a 9-substituent. L is absent, alpha is a double bond, beta is a single bond, gamma is a double bond and wherein: J1 is a 2- or 3-substituent; J2 is a 6- or 7-substituent; J1 and J2 are each independently a group of the formula —NHCO(CH2)nNR1R2, wherein: n is an integer from 1 to 5; and, R1 and R2 are independently hydrogen, C1-7alkyl, C3-20heterocyclyl, or C5-20aryl, or R1 and R2, taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached, form a heterocyclic ring having from 3 to 8 ring atoms; and wherein, when K is a 9-substituent, K is a group of the formula —N(RN)Q, wherein: RN is an amino substituent and is hydrogen. C1-7alkyl, C3-20heterocyclyl, or C5-20aryl; and, Q is C1-7alkyl, C3-20heterocyclyl, or C5-20aryl, and is optionally substituted; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, amides, solvates, hydrates and protected forms thereof. The present invention also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, and the use of such compounds and compositions, both in vitro and in vivo to inhibit telomerase, to regulate cell proliferation, and in the treatment of proliferative conditions, such as cancer.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
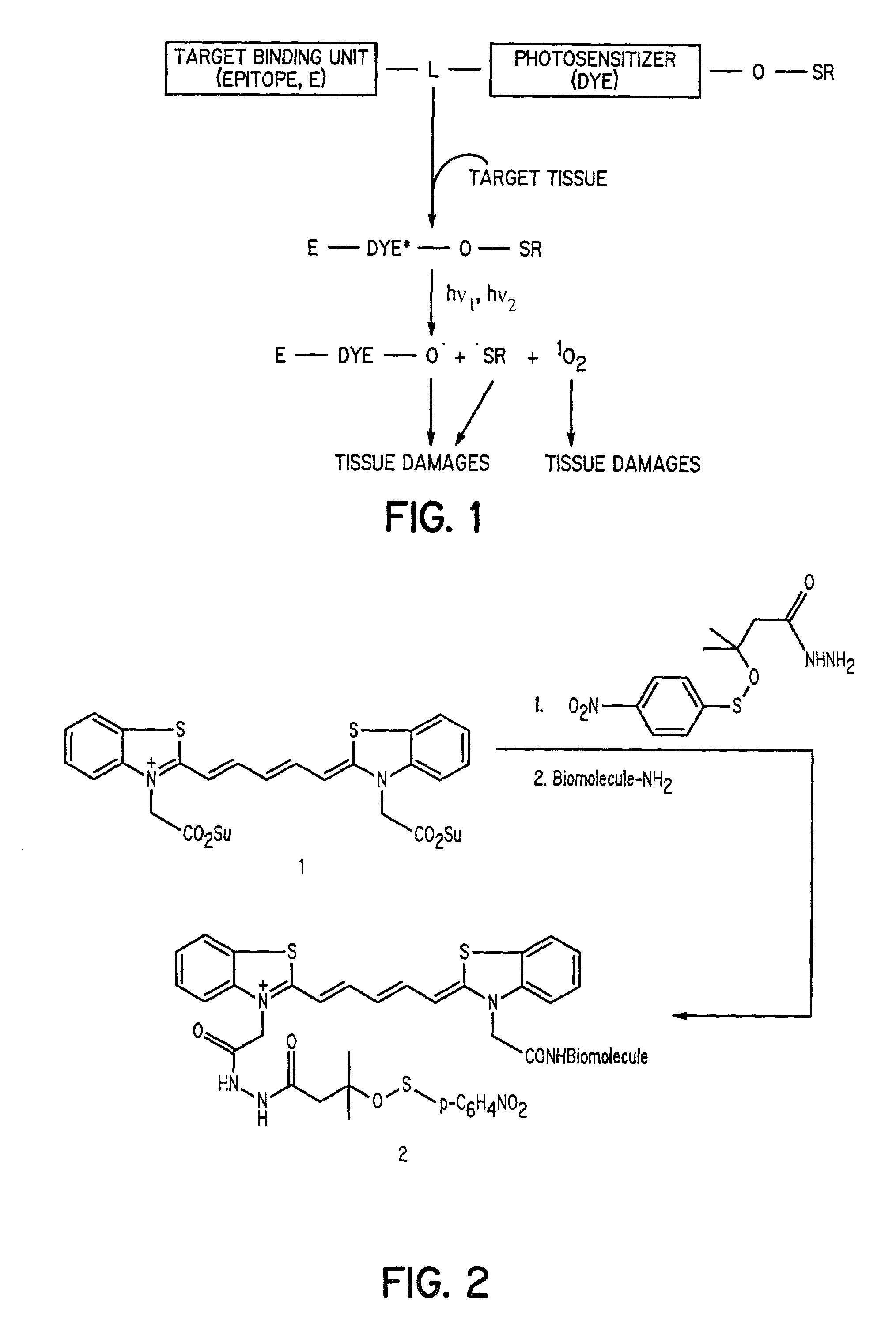
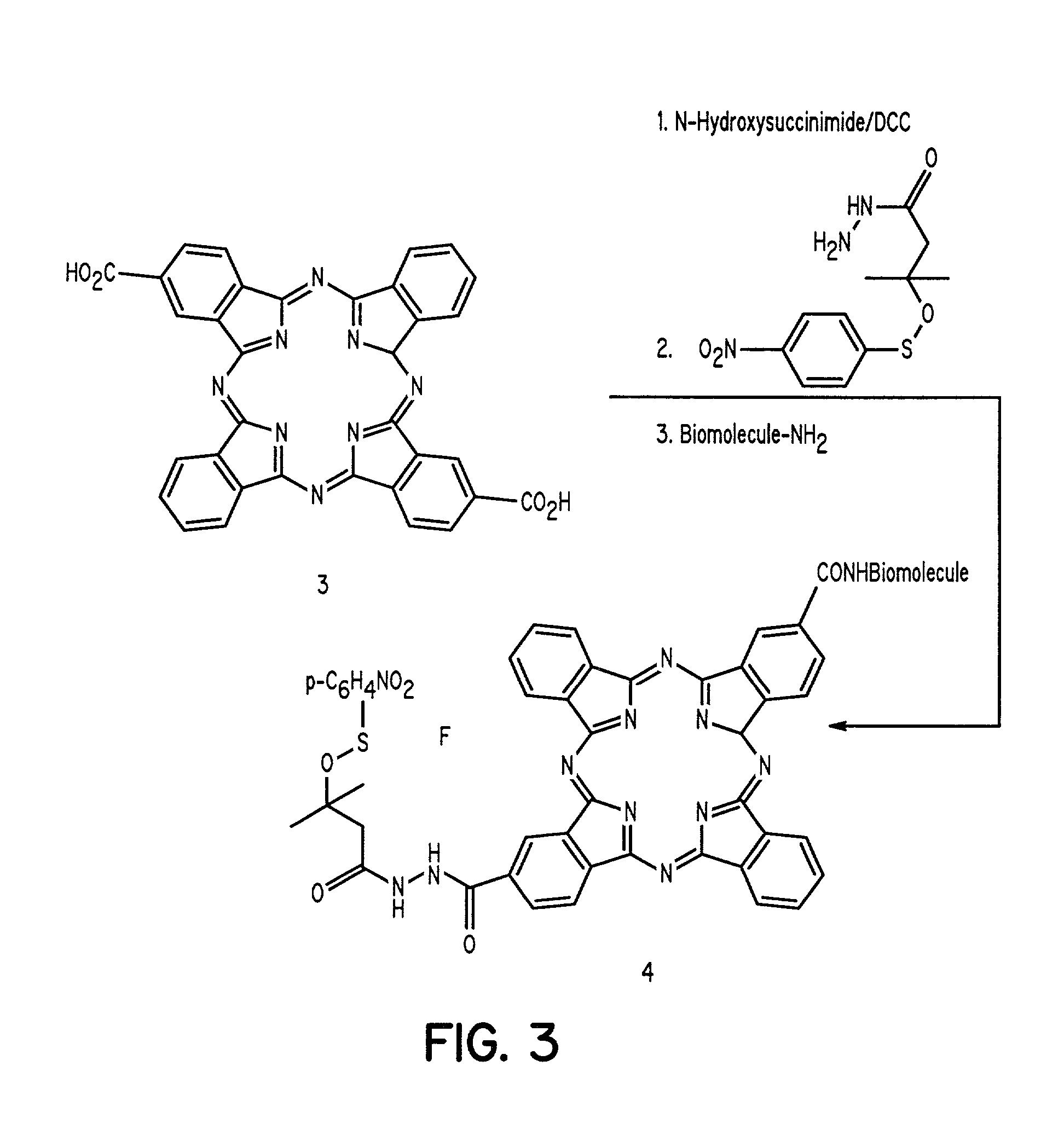
Cyanine-sulfenates for dual phototherapy
Dye-sulfenate derivatives and their bioconjugates for dual phototherapy of tumors and other lesions. The compounds comprise sulfenates having the formula, t,0080where E is selected from the group consisting of somatostatin receptor binding molecules, heat sensitive bacterioendotoxin receptor binding molecules, neurotensin receptor binding molecules, bombesin receptor binding molecules, cholecystekinin receptor binding molecules, steroid receptor binding molecules, and carbohydrate receptor binding molecules, and dihydoxyindolecarboxylic acid; L and X are independently selected from the group consisting of —(R5)NOC—, —(R5)NOCCH2O—, —(R5)NOCCH2CH2O—, —OCN(R5)—, —HNC(═S)NH—, and HNC(═O)NH—; DYE is an aromatic or a heteroaromatic radical derived from the group consisting of cyanines, indocyanines, phthalocyanines, rhodamines, phenoxazines, phenothiazines, phenoselenazines, fluoresceins, porphyrins, benzoporphyrins, squaraines, corrins, croconiums, azo dyes, methine dyes, indolenium dyes, crellins, and hypocrellins; R1 to R5 are independently selected from the group comprising hydrogen, C1-C10 alkyl, C5-C10 aryl, C1-C10 polyhydroxyalkyl, and C1-C10 polyalkoxyalkyl; and Ar is an aromatic or heteroaromatic radical derived from the group consisting of benzenes, naphthalenes, naphthoquinones, diphenylmethanes, fluorenes, anthracenes, anthraquinones, phenanthrenes, tetracenes, naphthacenediones, pyridines, quinolines, isoquinolines, indoles, isoindoles, pyrroles, imidiazoles, oxazoles, thiazoles, pyrazoles, pyrazines, purines, benzimidazoles, furans, benzofurans, dibenzofurans, carbazoles, acridines, acridones, phenanthridines, thiophenes, benzothiophenes, dibenzothiophenes, xanthenes, xanthones, flavones, coumarins, and anthacylines. The compounds are designed to produce both Type 1 and Type 2 phototherapeutic effects at once using a dual wavelength light source that will produce singlet oxygen and free radicals at the lesion of interest.
Owner:MEDIBEACON
Method for synthesizing acridone derivatives by means of palladium-copper co-catalysis
ActiveCN106187890AEasy to prepareAtom economy is highOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAcridoneOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing acridone derivatives by means of palladium-copper co-catalysis. The method comprises the steps that on the condition that palladium chloride, copper pivalate and di-tert-butyl peroxide or oxygen co-exist, diphenylamine compounds including symmetric diphenylamine and asymmetric diphenylamine are dissolved in an anhydrous organic solvent, all the materials are mixed to be uniform, a reaction is conducted for 20 h to 30 h under the condition of 80 DEG C to 120 DEG C in a carbon monoxide atmosphere, separation and purification are conducted, and the acridone derivatives can be obtained. According to the method for synthesizing the acridone derivatives by means of palladium-copper co-catalysis, the preparation method is simple, the diphenylamine compounds which are simple and easy to obtain are used as the raw materials, and the acridone derivatives are directly constructed through C-H / C-H oxidative carbonylation; the preparation condition is mild, and the target product can be obtained in a high-selectivity mode at 80 DEG C to 120 DEG C; the acridone derivatives have good substrate applicability, the range of substrates is greatly expanded, and the acridone derivatives have a great application prospect in biological medicine and materials and the like.
Owner:SUQIAN XINYA TECH
Application of high-specificity fluorescent probe for detecting human serum albumin
ActiveCN106841128AHas fluorescent propertiesSensitive detectionOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceMetaboliteAcridone
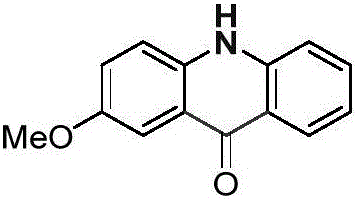
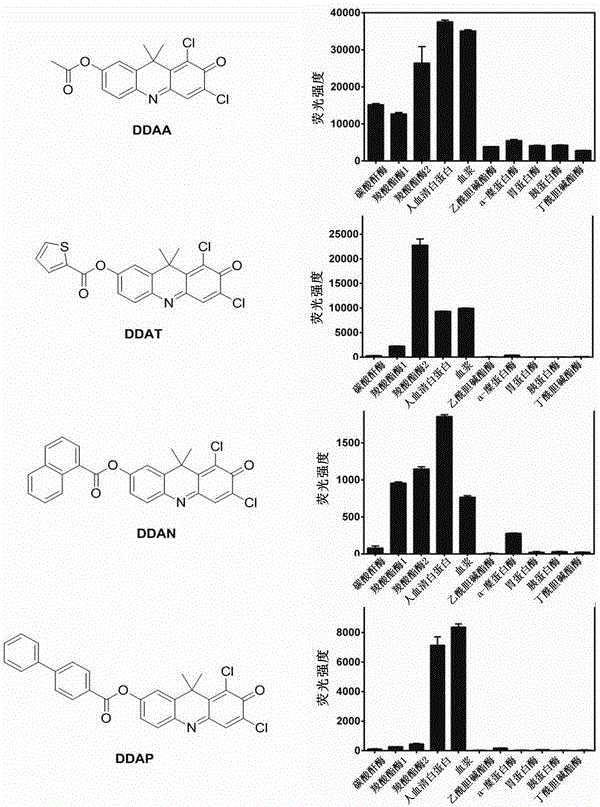
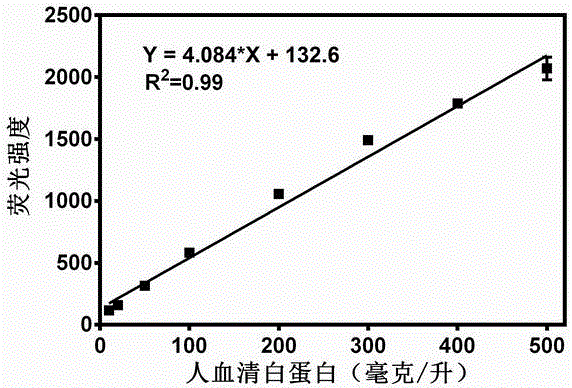
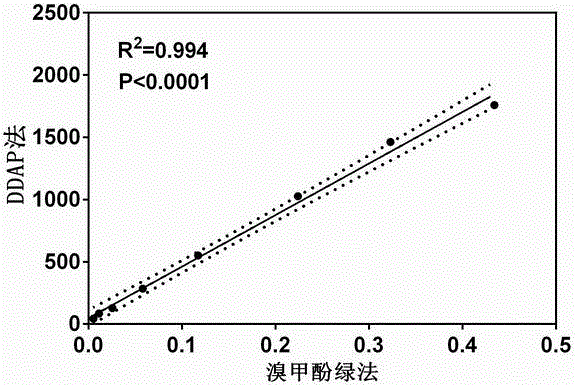
The invention relates to application of a high-specificity fluorescent probe for detecting human serum albumin, and belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering. The high-specificity fluorescent probe is a 1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxyl-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone compound ester derivative, and is used for detecting the existence of HAS (human serum albumin) in different biological samples and the quantitative measuring of activity. The enzyme activity measuring process specifically comprises the following steps of selecting hydrolysis reaction of the 1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxyl-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone compound ester derivative as probe reaction, and selecting proper primer concentration to detect the generation amount of a hydrolyzing metabolite (1,3-dichloro-7-hydroxyl-9,9-dimethyl-2(9H)-acridone) in unit time within the online reaction zones, so as to measure the actual activity of the HAS in each biological sample. The high-specificity fluorescent probe can be used for quantitatively evaluating the activity of the HAS in different biological samples.
Owner:王铮
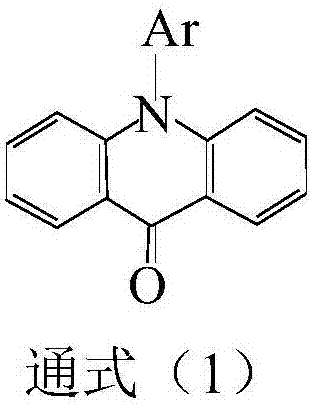
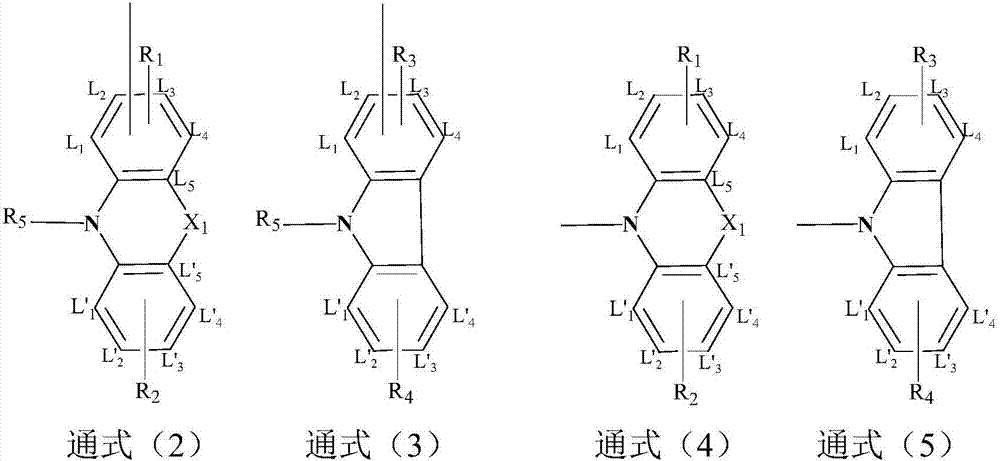
Compound with acridone as core and application of compound to organic electroluminescent device
ActiveCN106467511AImprove thermal stabilityGood film formingOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyAcridone
The invention discloses a compound with acridone as the core and application of the compound to an organic electroluminescent device. The compound has acridone as the core, is not easy to crystallize between molecules and is not easy to aggregate, and has good film forming ability. When the compound is used as a luminescent layer material of an OLED luminescent device, current efficiency, power efficiency and external quantum efficiency of the device are all greatly improved. Meanwhile, life of the device is obviously prolonged.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
C8 - linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids
The present invention provides novel pyrrolo-[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine hybrids useful as anti-tumour agents and a process for the preparation thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Acridone derivatives as labels for fluorescence detection of target materials
InactiveUS20120015373A1Simple requirementsEasily discriminatedOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhosphateFluorescence
Disclosed are methods for assay of an analyte employing acridone dyes having the structure:Z1 and Z2 represent atoms necessary to complete one ring, two fused ring, three fused ring aromatic or heteroaromatic systems, each ring having five or six atoms selected from carbon atoms and optionally no more than two atoms selected from oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur; R2, R3, R4 and R5 are selected from hydrogen, halogen, amide, hydroxyl, cyano, nitro, mono- or di-nitro-substituted benzyl, amino, mono- or di-C1-C4 alkyl-substituted amino, sulphydryl, carbonyl, carboxyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, acrylate, vinyl, styryl, aryl, heteroaryl, C1-C20 alkyl, aralkyl, sulphonate, sulphonic acid, quaternary ammonium, the groups -E-F and —(CH2—)nY; R1 is selected from hydrogen, mono- or di-nitro-substituted benzyl, C1-C20 alkyl, aralkyl, the groups -E-F and —(CH2—)nY; where E is a spacer group, F is a target bonding group; Y is selected from sulphonate, sulphate, phosphonate, phosphate, quaternary ammonium and carboxyl.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Fluorescence probe based on beta-glucuronidase of acridone and application of fluorescence probe
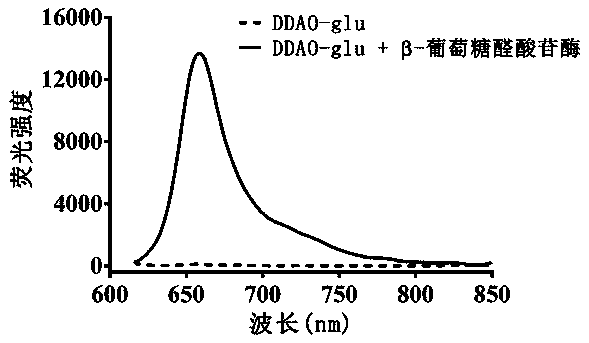
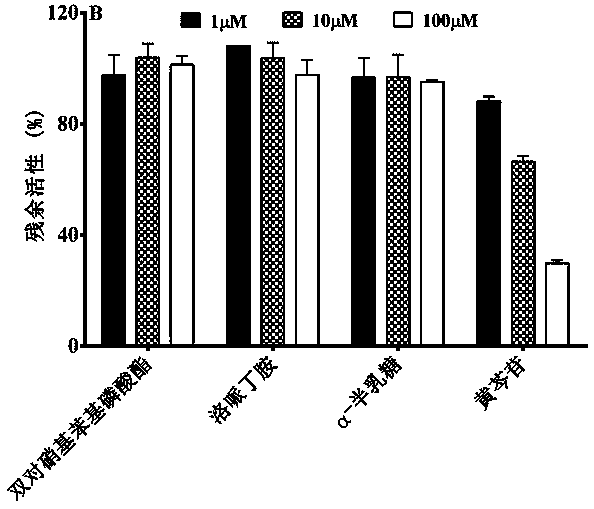
InactiveCN107915764ANot easy to interfereAdvantages of in vitro activitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescence probe based on beta-glucuronidase of acridone and application of the fluorescence probe, belonging to the technical field of biological medicines. The fluorescence probe can be used for determining the enzyme activities of beta-glucuronidase in biological systems of different sources. HC-glu is taken as a specific probe reaction substrate, beta-glucuronidasehydrolysis reaction is taken as a probe reaction by virtue of a beta-glucuronidase in-vitro reaction system, and the activity of beta-glucuronidase in each biological sample is determined by quantitatively detecting the generation amount of an aglycone metabolite in a unit time. The fluorescence probe can be applied to the qualitative and quantitative determination of the activities in beta-glucuronidase of different individual sources of human and animal tissue samples, different species of cells and cell preparation objects and various plants and microorganisms, and the evaluation of the drug treatment capacity of beta-glucuronidase and the development and screening of a beta-glucuronidase inhibitor can be realized.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Compound taking acridone as core and application of compound to organic electroluminescent device
InactiveCN107057682ADestroy crystallinityInhibit aggregationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyAcridone
The invention discloses a compound taking acridone as the core and application of the compound to an organic electroluminescent device. The compound takes acridone as the core, and therefore, has the characteristics that the probabilities of crystallization and clustering between molecules are low and the film-forming property is favorable. When the compound serves as a luminescent layer material of the organic electroluminescent device, the current efficiency, the power efficiency and the external quantum efficiency of the organic electroluminescent device are greatly improved; and meanwhile, the service life of the organic electroluminescent device can be remarkably prolonged.
Owner:VALIANT CO LTD
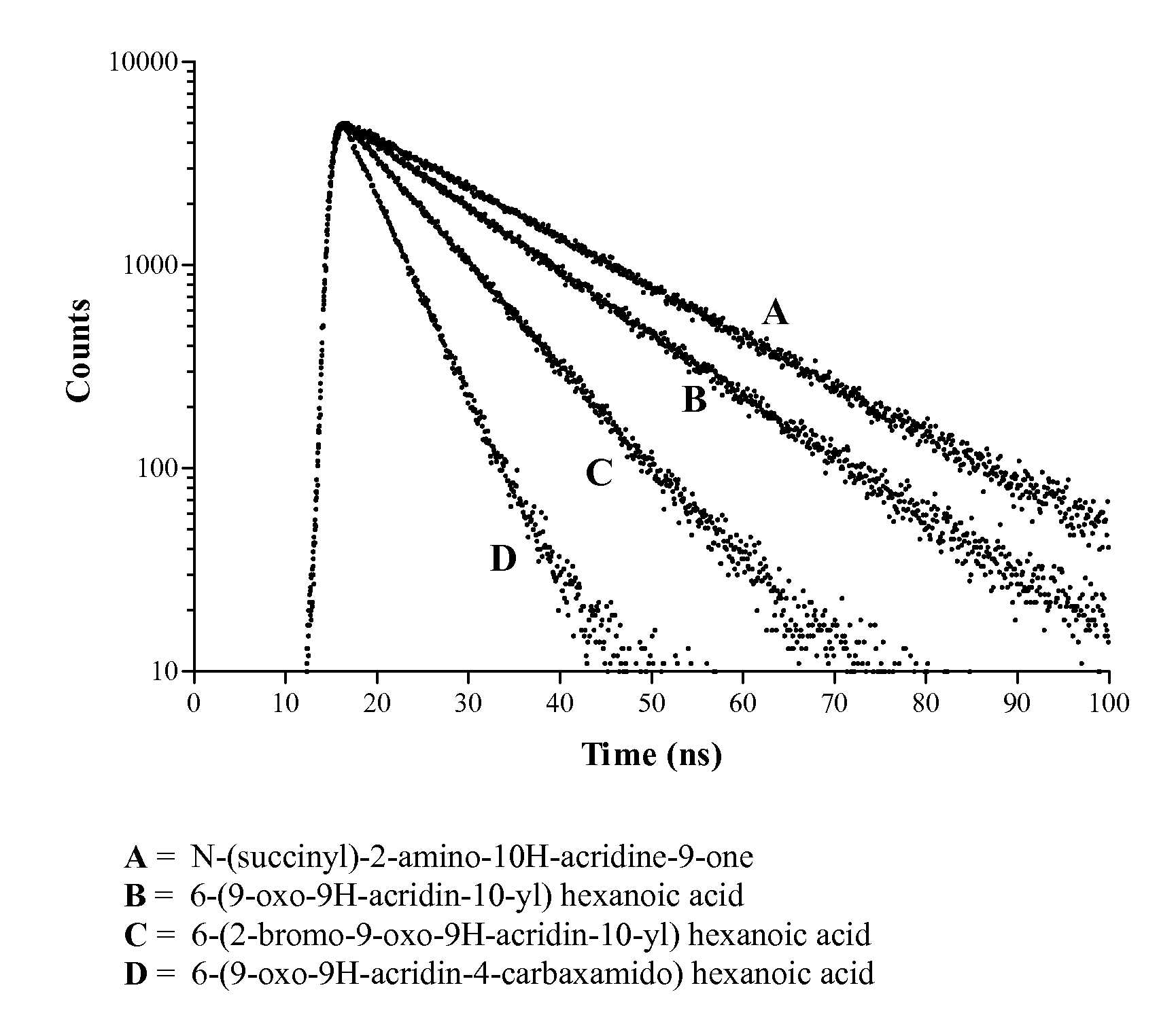
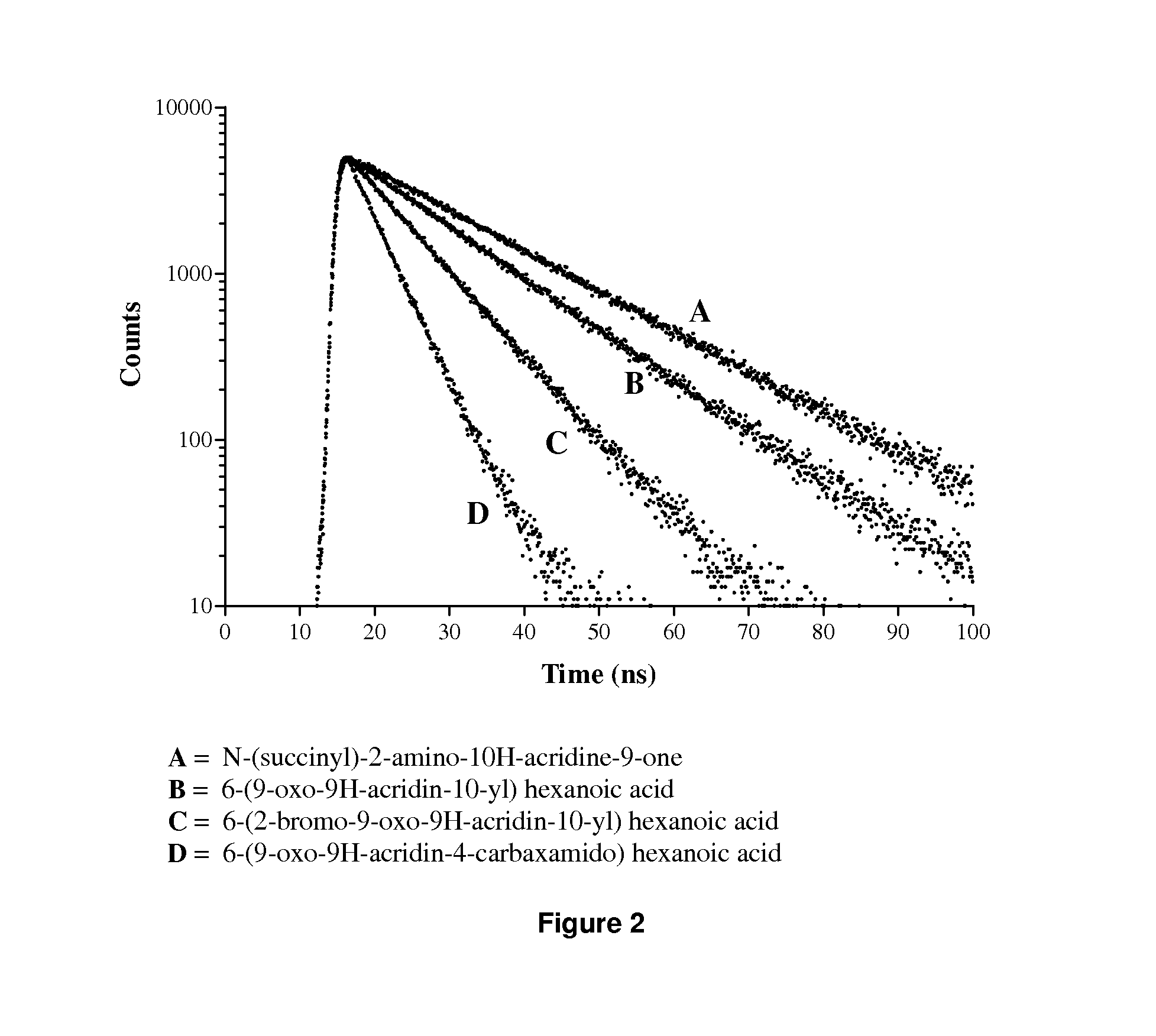
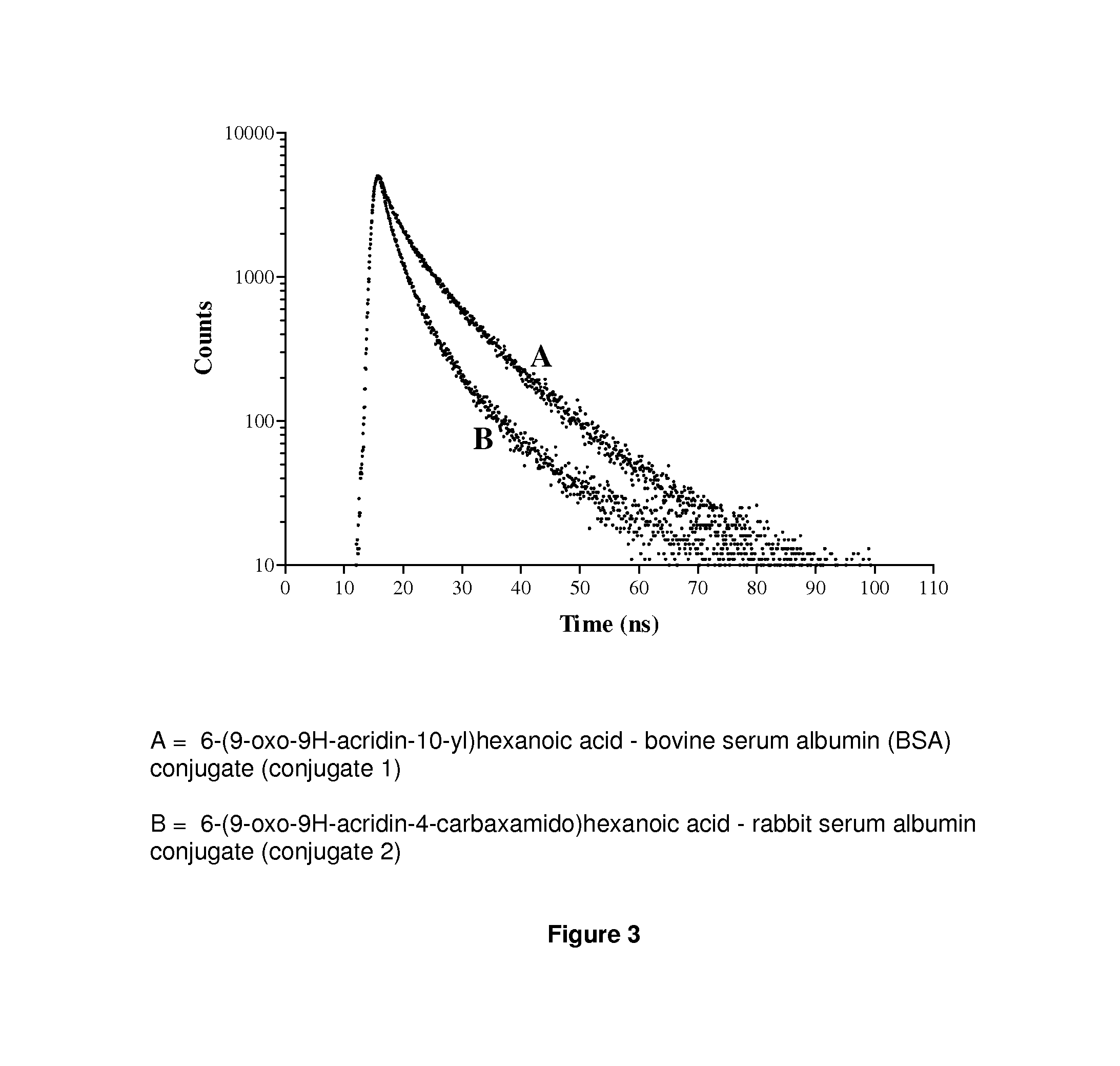
Site-specific labelling of proteins using acridone and quinacridone lifetime dyes
The present invention provides reagents and methods that afford direct attachment of a fluorescent acridone or quinacridone dye to either the N-terminus or C-terminus of a synthetic or recombinant peptide or protein, and their derivatives, in a site-specific manner, coupled with purification of the resultant labelled molecule.
Owner:AMERSHAM BIOSCIENCES UK LTD
Preparation method and application of hybridization indicator 5,7-binitro-2-sulfo-acridone
InactiveCN104316705AHigh selectivityGood water solubilityBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorRelated gene
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a hybridization indicator 5,7-binitro-2-sulfo-acridone and provides a preparation method of an electrochemical biosensor based on a triple signal amplification technology of film modified electrode, exonuclease III auxiliary target sequence circulation and DNA long-range self-assembly by using the 5,7-binitro-2-sulfo-acridone as an indicator. The 5,7-binitro-2-sulfo-acridone is used for detecting extra-high sensitivity and high specificity of a gene relative to a target sequence c-erbB-2 relative to lung cancer. As the linear range of the electrochemical biosensor is 2 aM-50 fM, detection limit reaches 0.5 am, and sequences which are completely complementary and mismatched to each other can be better recognized, so that ultralow content of target sequence in an actual lung cancer serum sample can be clinically detected.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method of acridone N-alkylation derivative
ActiveCN104592115AMild reaction conditionsOperational securityOrganic chemistryAlkyl transferAcridone
The invention discloses a preparation method of acridone N-alkylation derivative, which comprises the following steps: adding an alkaline ion liquid and acridone into a three-neck flask provided with a condensation reflux unit at room temperature, stirring uniformly, adding halide, stirring to react at 20-50 DEG C for 6-12 hours, standing at room temperature, filtering, washing the filter cake with methanol, and drying to obtain the acridone N-alkylation derivative product. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, high yield and recyclable ion liquid, is safe and convenient to operate, and has favorable industrialized application value.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU SIGMA CHEM
12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN104610271AHigh activityProfit absorptionOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsAcridineKetone
The invention discloses 12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone and a synthesis method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of dihydroketoacridine derivatives. The method comprises the steps of uniformly mixing 3,4-methylenedioxy aniline, 2-fluorobenzaldehyde, 2-hydroxyl-1,4-naphthaquinone, a catalyst and toluene sulfonic acid, performing heating and stirring, controlling the temperature to be 115-130 DEG C, and performing a reaction for 3-5h. Fluorine atom and methylenedioxy structures are introduced into 12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone, so that 12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone has higher activity, and more facilitates absorption. The synthesis method has the characteristics that the synthesis method is simple to operate, high in yield, green and environment-friendly, and raw materials are easy to obtain.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
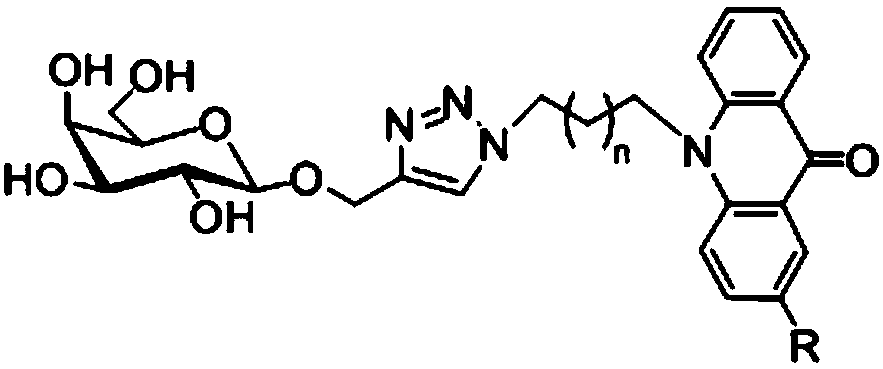
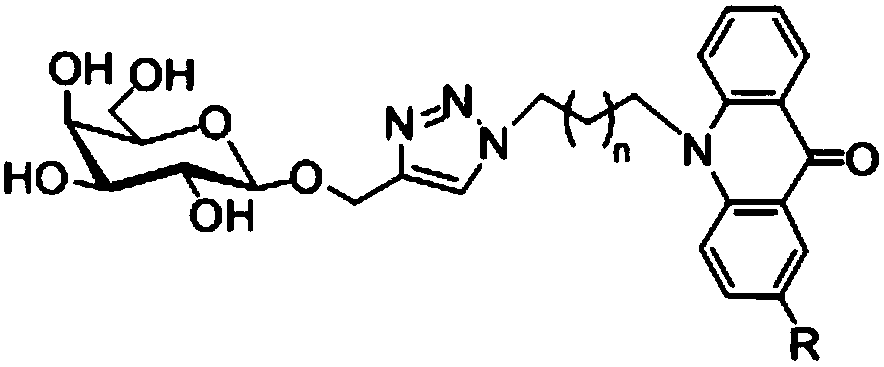
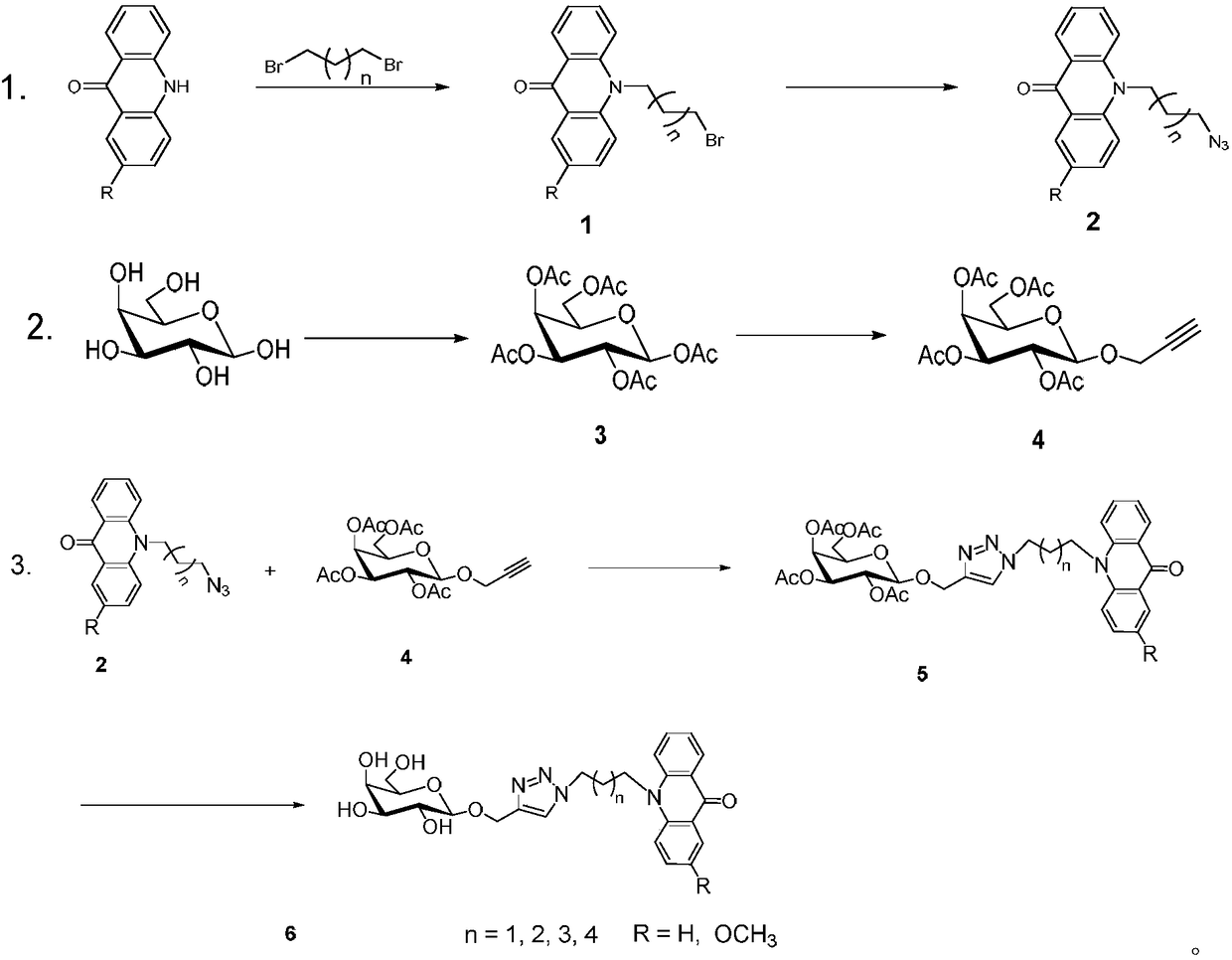
Acridone derivative containing galactose, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109336940AImprove biological activityHigh anticancer activitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAcridoneDrugs synthesis
The invention discloses acridone derivative containing galactose, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of drug synthesis. The acridone derivative has the technical scheme points that the specific structure of acridone derivative is as follows. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the acridone derivative containing galactose, and application of the acridone derivative containing galactose to preparation of anti-cancer drugs. The method has the advantages that the method is simple to operate and wild in reaction conditions, ensures that adopted reagents are all industrial common reagents, is suitable for large-scale industrial preparation, pollution-free in synthesis steps, and less in by-products; the formed acridone derivativehas excellent biological activity and anti-cancer activity, and has good commercial application value.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Acridone derivatives and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN103694173AOperableHigh fluorescence intensityOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsAcridineChemical synthesis
The invention discloses novel compounds containing an acridone structure, and particularly relates to acridone derivatives and a synthesis method thereof, belonging to the technical field of organic chemical synthesis. The structure of the acridone derivatives is shown in the specification, wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from H, methoxy, C1-10 alkyl and C1-10 haloalkyl. The compounds have higher fluorescence and can be used for organic luminescent materials.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU SIGMA CHEM
Material with antibacterial performance, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111253576ARestricted movementSmall free volumeBiocideOrganic chemistryThermal dilatationAcridine
The invention discloses a material with antibacterial performance, a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the material is polyimide and is formed by polymerizing a diamine monomer containing an acridone structure and a dianhydride monomer. According to the invention, acridone with a planar rigid structure and a polar group are creatively introduced into a polyimide main chain, wherein the planar rigid acridone structure is beneficial to regular stacking of molecular chains and induction of polymer crystallization, and the polar group can enhance the hydrogen-bond interaction ofthe molecular chains and promote the tight stacking of the molecular chains, so that polyimide has excellent barrier property, high glass-transition temperature and thermal stability and low thermal expansion coefficient; and the polyimide contains an acridone structure and a polar group, so that the polyimide is endowed with a certain antibacterial property.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
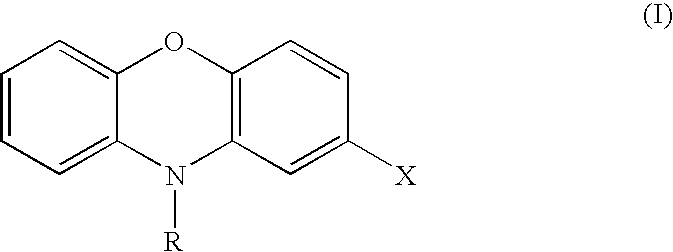
Substituted phenoxazines and acridones as inhibitors of AKT
InactiveUS20060241108A1Inhibit cell growthOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseCoronary artery disease
The invention provides compositions and methods that modulate the activity of AKT family kinase proteins, including AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3 (also referred to as PKBα, PKBβand PKBγ). Specifically, the invention provides a number of phenoxazine and acridone compounds that inhibit AKT phosphorylation and kinase activity. The invention provides compositions for and methods of modulating AKT activity, inhibiting cell growth, treating cancer, treating transplant rejection, and treating coronary artery disease based upon the phenoxazine and acridone compounds of the invention.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![C8—linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids C8—linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9137b741-81bb-4108-b21a-567f2cb25f70/US07056913-20060606-D00001.png)
![C8—linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids C8—linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9137b741-81bb-4108-b21a-567f2cb25f70/US07056913-20060606-C00001.png)
![C8—linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids C8—linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9137b741-81bb-4108-b21a-567f2cb25f70/US07056913-20060606-C00002.png)

![C8 - linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids C8 - linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/c9be3835-11ea-49c0-b2e7-74b04aaa0bb3/US20050222132A1-20051006-P00001.png)
![C8 - linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids C8 - linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/c9be3835-11ea-49c0-b2e7-74b04aaa0bb3/US20050222132A1-20051006-C00001.png)
![C8 - linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids C8 - linked pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-acridone/acridine hybrids](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/c9be3835-11ea-49c0-b2e7-74b04aaa0bb3/US20050222132A1-20051006-C00002.png)


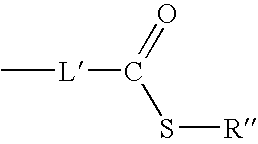
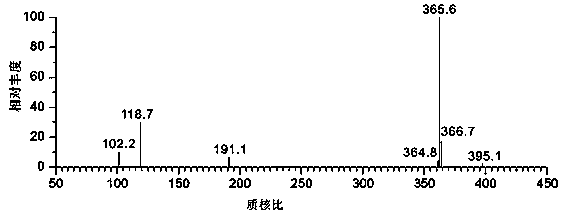
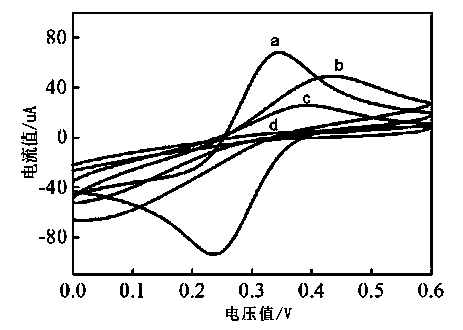
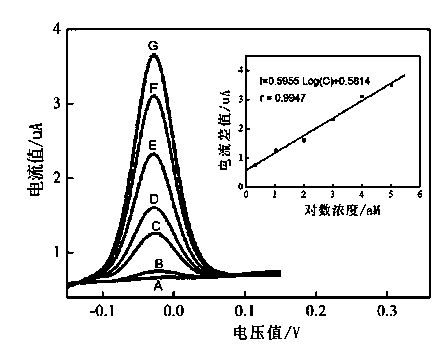
![12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone and synthesis method thereof 12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone and synthesis method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b61ecf96-9fcc-4ae3-ae15-bd62743e13ee/DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.PNG)
![12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone and synthesis method thereof 12-(2-fluorophenyl)-benzo [h][1,3] methylenedioxy [4,5-b] acridine-10,11-diketone and synthesis method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b61ecf96-9fcc-4ae3-ae15-bd62743e13ee/DEST_PATH_IMAGE003.PNG)