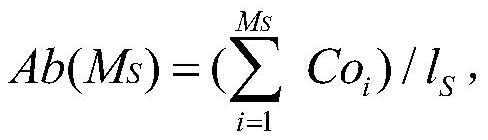Patents
Literature
61 results about "Pilus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A pilus (Latin for 'hair'; plural: pili) is a hair-like appendage found on the surface of many bacteria and archaea. The terms pilus and fimbria (Latin for 'fringe'; plural: fimbriae) can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term pilus for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation. All pili in the latter sense are primarily composed of pilin proteins, which are oligomeric.
Purification of bacterial antigens
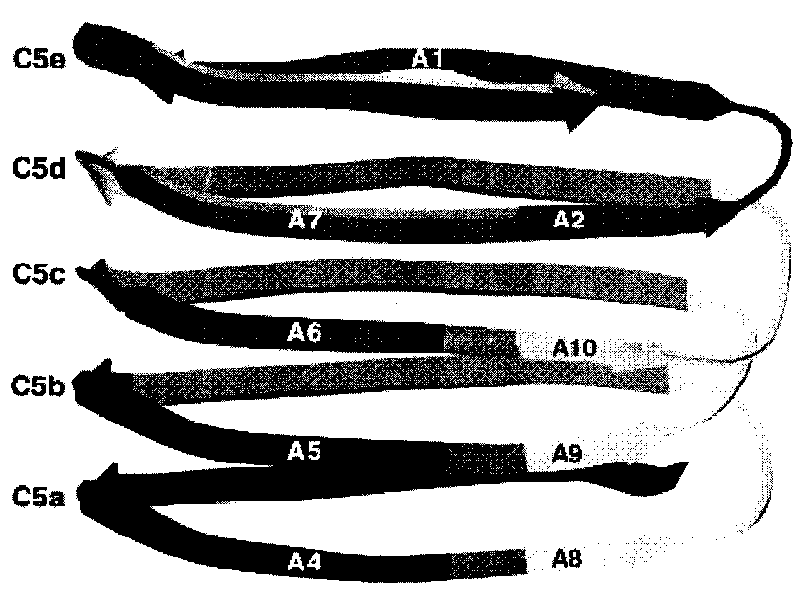
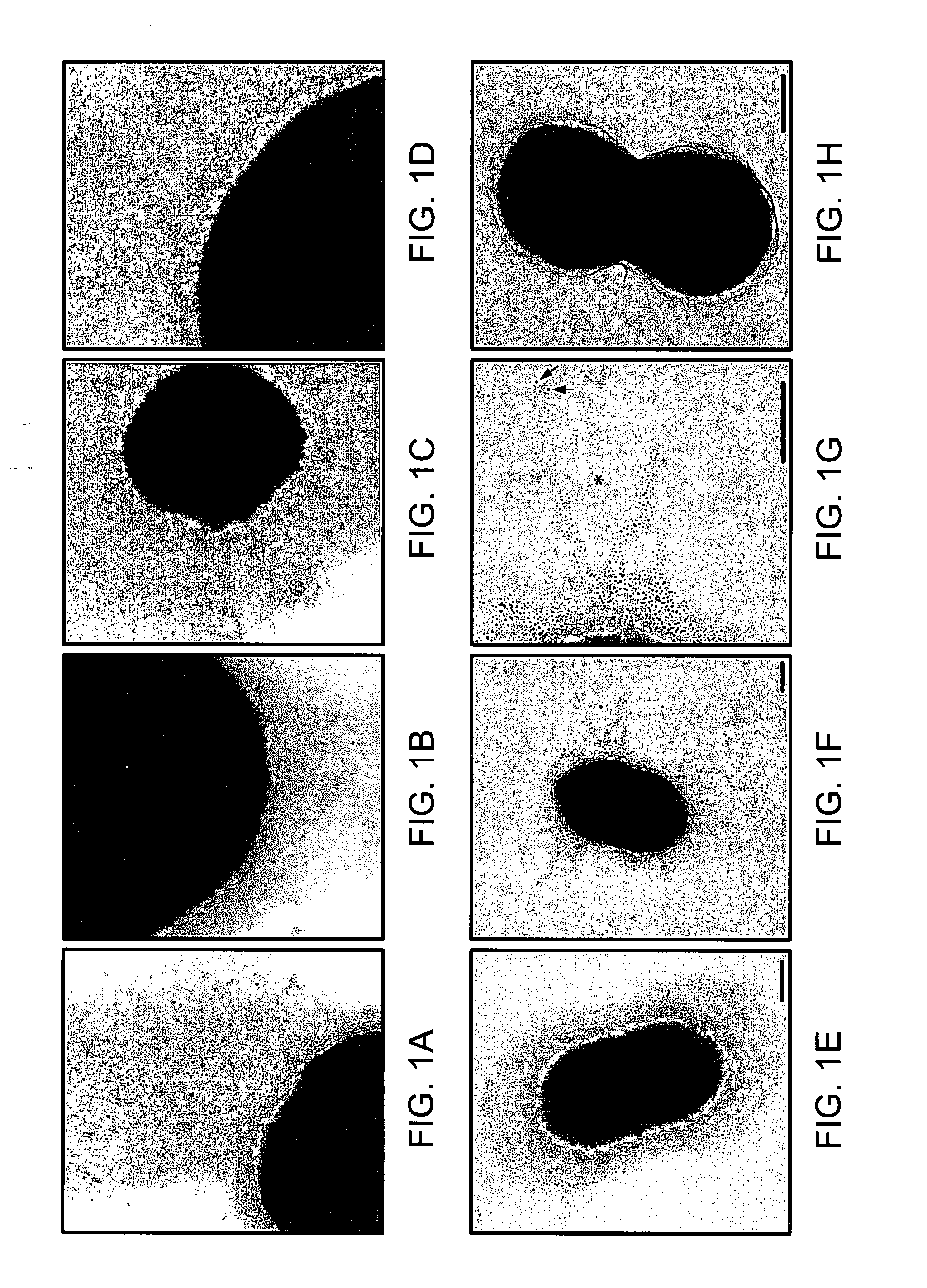
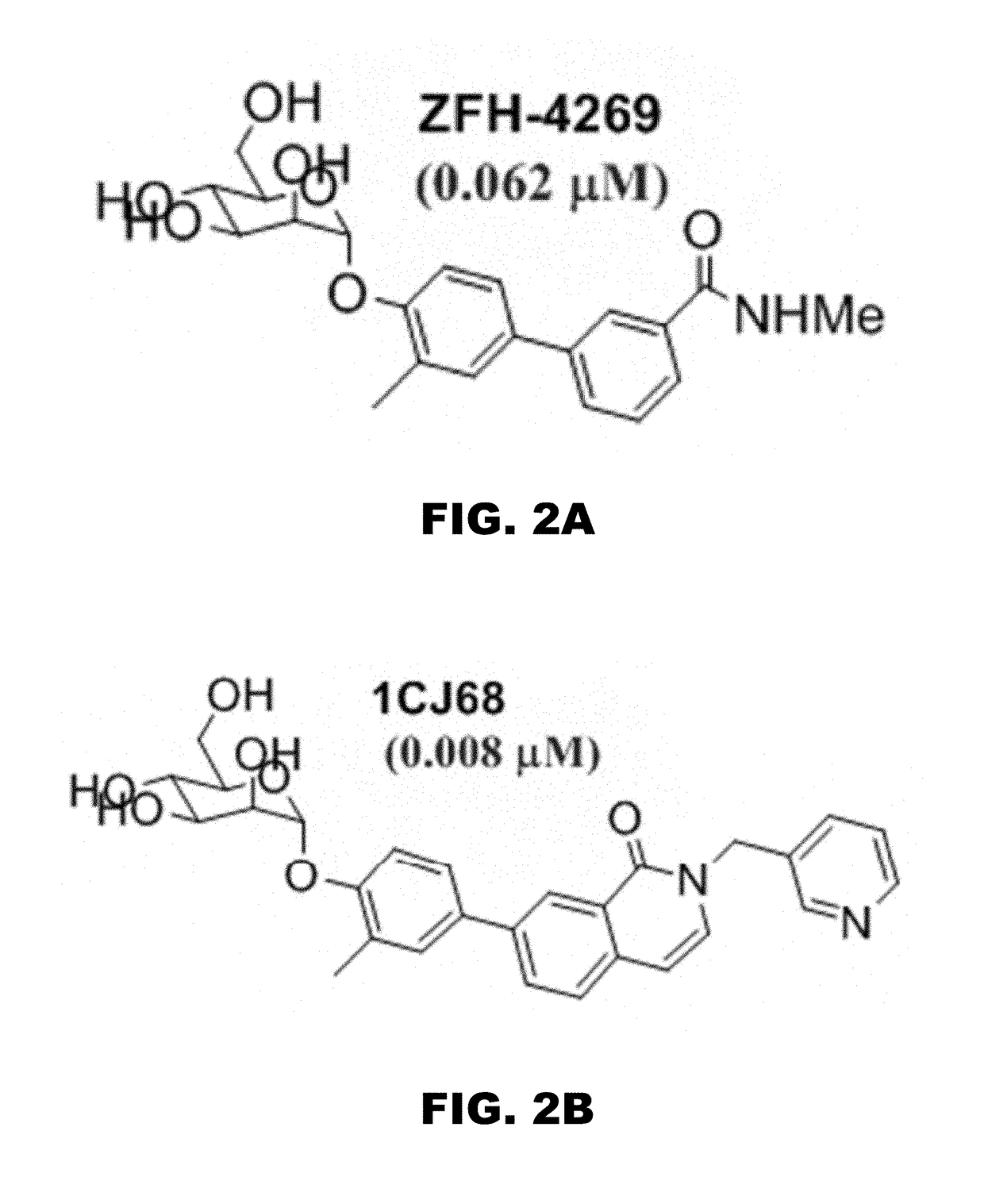
Presented are methods of isolation of pili and pilus-like structures from Gram-positive bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae and compositions that include such isolated pili. These compositions are useful as immunogenic compositions for the production of antibodies and immunostimulation. Also presented are methods of inhibiting Streptococcus pneumoniae, and methods of identifying inhibitors of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
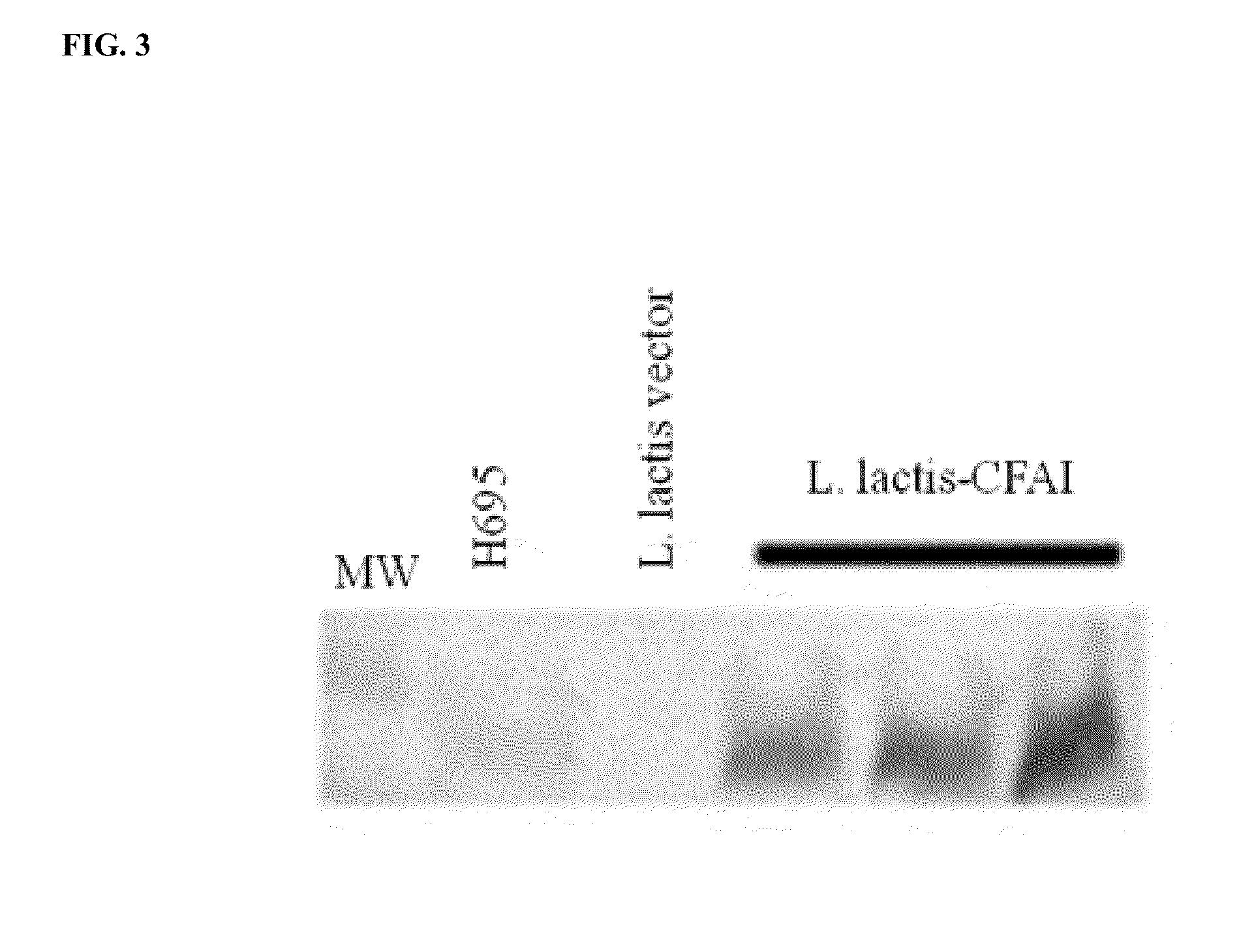
Recombinant lactococcus lactis expressing escherichia coli colonization factor antigen i (cfa/i) fimbriae and their methods of use
ActiveUS20140086950A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaFood additiveDisease
The present disclosure relates generally to therapeutic compositions comprising recombinant bacteria. Further, the disclosure elaborates upon methods of utilizing the taught therapeutic compositions to treat autoimmune and inflammatory disease. The present teachings also relate to the disclosed recombinant bacteria and methods of producing the recombinant bacteria utilized in the compositions and methods. Further taught herein are dietary supplements and food additive compositions comprising the taught recombinant bacteria.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
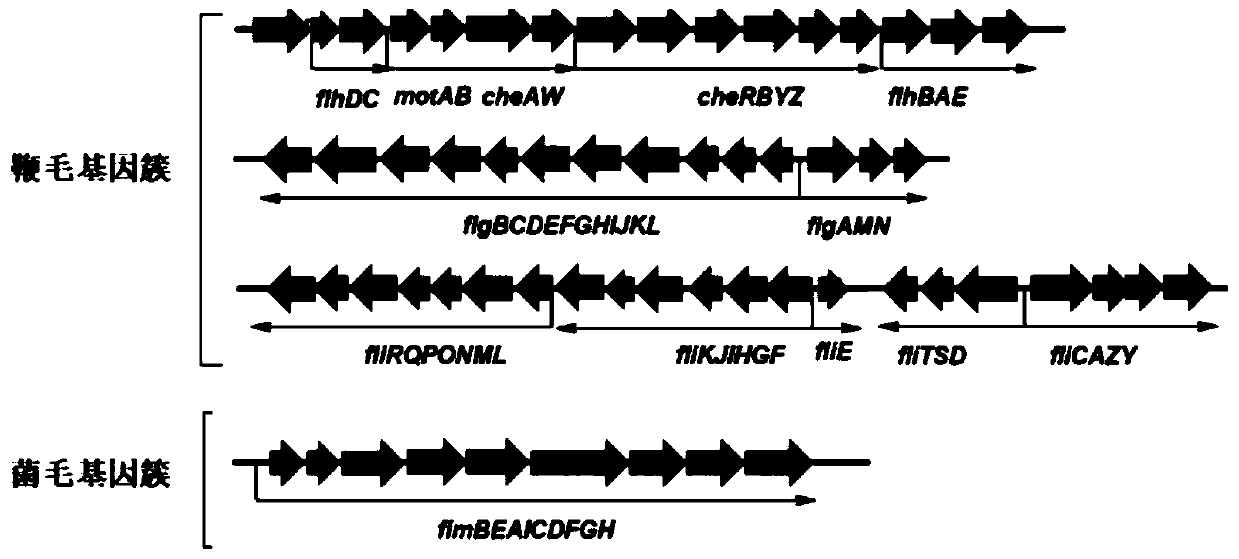
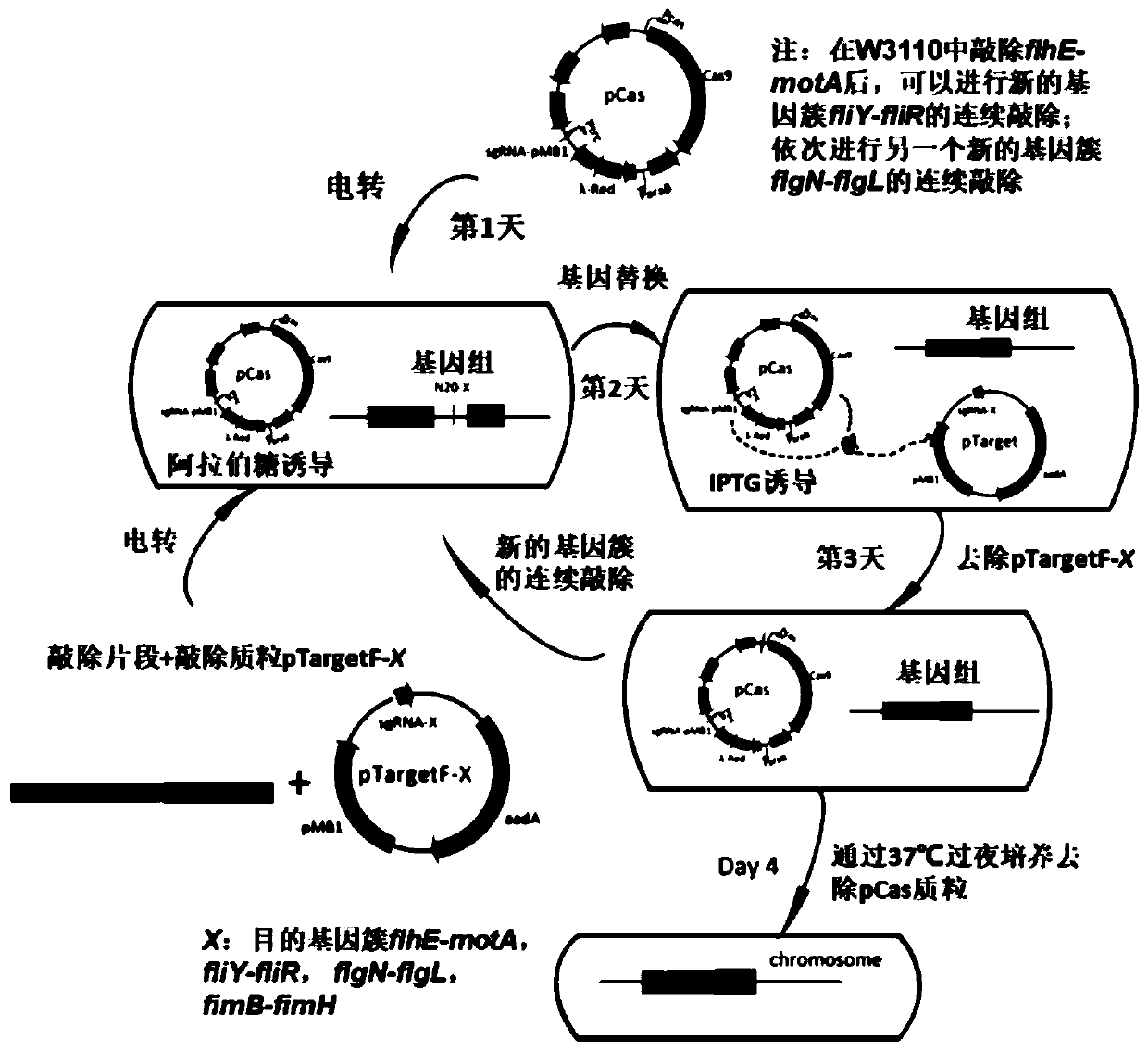
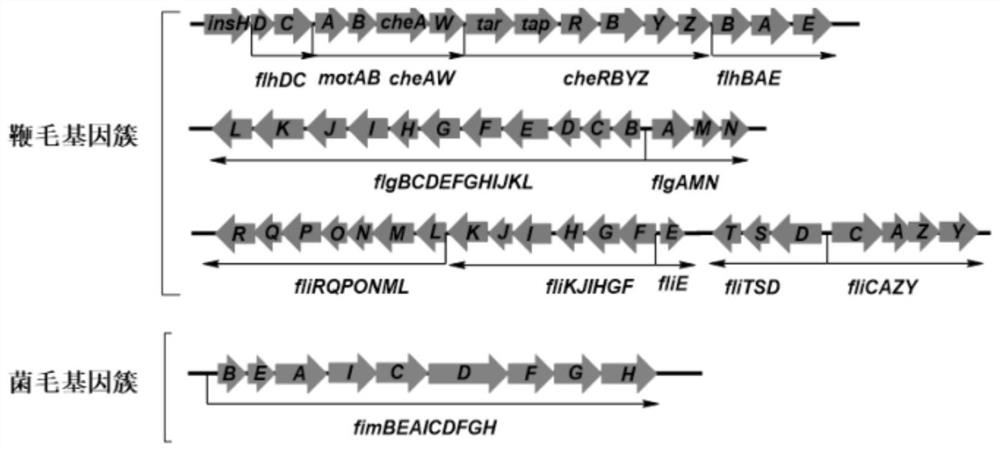
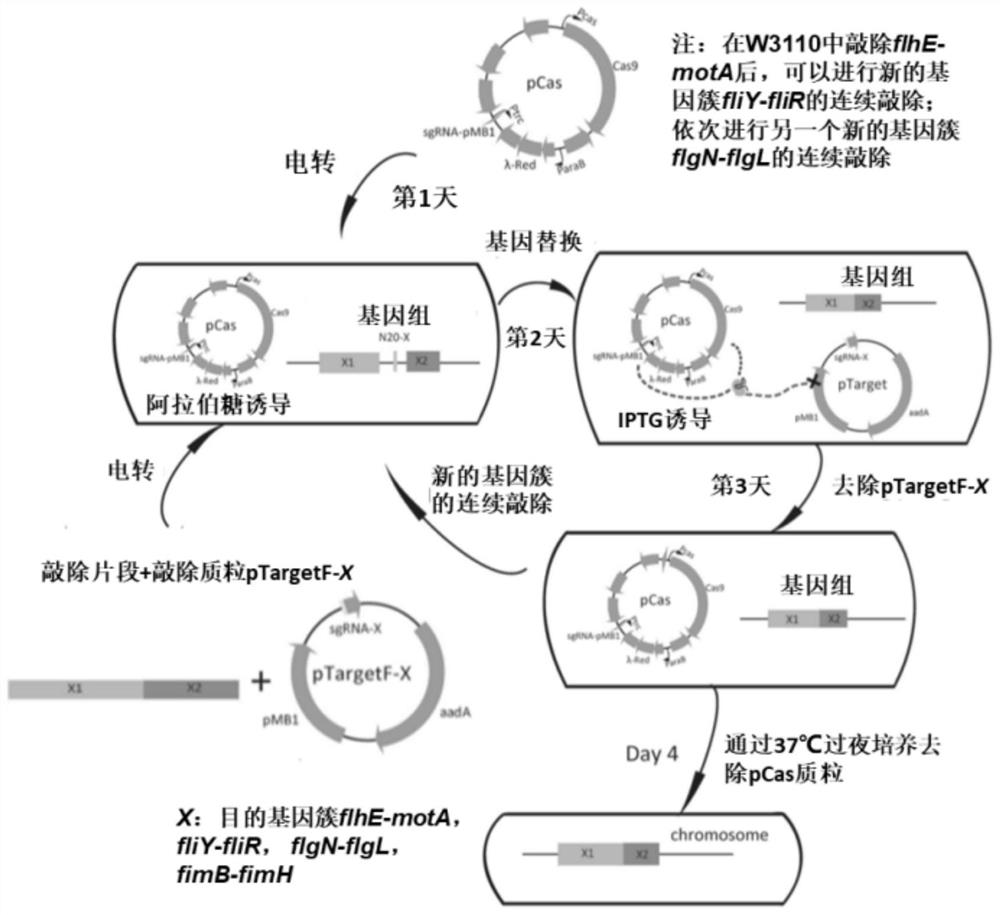
Method for efficiently synthesizing PHB by knocking out flagellum and pilus genes
ActiveCN110669709AGrowth is not affectedImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPilusGene cluster
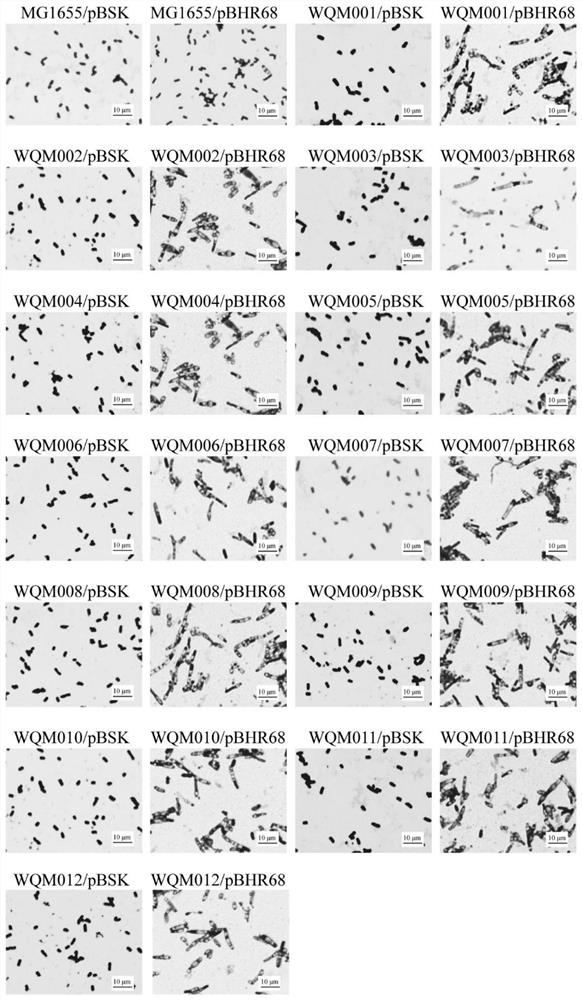
The invention discloses a method for efficiently synthesizing PHB by knocking out flagellum and pilus genes, which belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. According to the invention, three flagellum gene clusters flhE-motA, fliY-fliR and flgN-flgL on an escherichia coli genome are knocked out to obtain a flagellum simplified strain WJW010, and a fimbriae gene clusterfimB-fimH is knocked out to obtain a fimbriae simplified strain WJW011, the three genes synthesized by PHB can be transformed into strains WJW010 and WJW011, and the recombinant bacteria WJW010 / pBHR68 and the recombinant bacteria WJW011 / pBHR68 are obtained; pHB with the cell dry weight of 19.2% and 2.8% can be synthesized under the normal fermentation condition, and the volume yield of PHB is 9.6times and 1.4 times that of wild control bacteria W3110 / pBHR68 (2%).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A set of oligonucleotide probe for detecting intestinal hemorrhage type colibacillus and vibrio cholerae
InactiveCN1661113AAccurate detectionEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesDiseaseFood poisoning
A set of oligonucleotide probe for detecting the enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7 and cholera vibrio O139 is designed on the Shiga-like toxin generating gene stx1 or stx2 and the beta-glucuronidase gene uidA of said enterohemorrhagic E coli O157:H7 and the enterotoxin A subset (ctxA), toxicity coordinate pilus A subset (tcpA) and glucosyltransferase (LPS gt) genes of cholera vibrio O139, and has high sensibility and specificity. It can be used to detect the enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157:H7, cholera vibrio O139 and other pathogenic genes from the specimen.
Owner:RADIOLOGY INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE SCI PLA
Construction method and application of faeG expressing gene engineering probiotic
InactiveCN102031262AEasy to manufactureImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaWestern blotDiarrhea
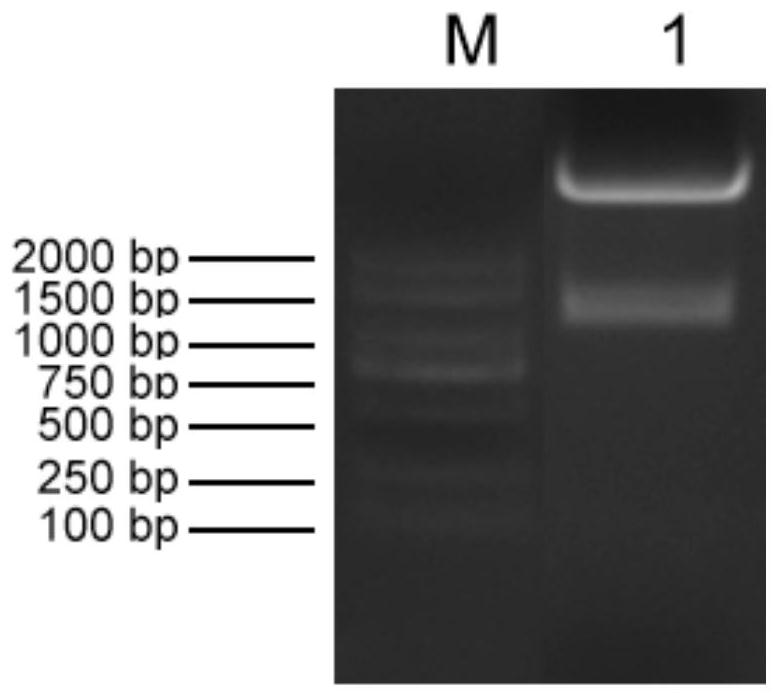
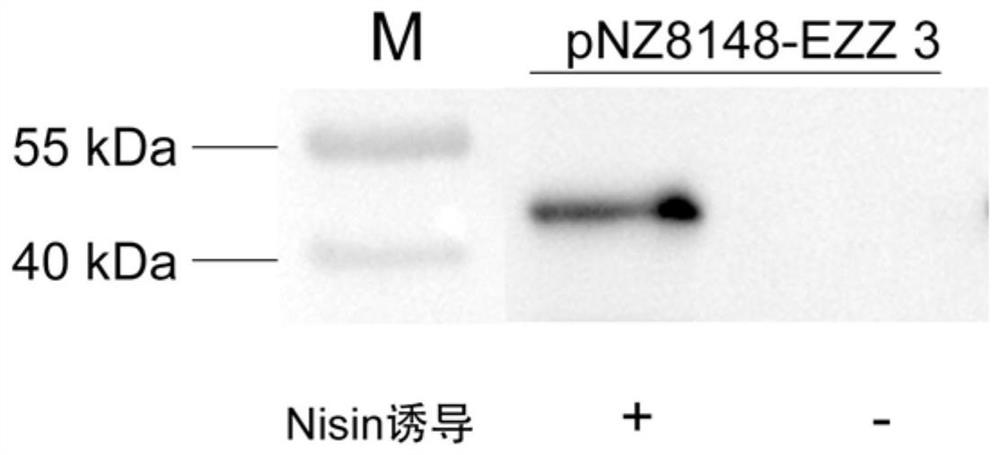
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a faeG expressing gene engineering probiotic. The method comprises the following steps of: according to the gene sequence and the expression vector plasmid characteristic of a disclosed F4 escherichia coli pilus adhesin faeG, designing a primer which contains a specific endonuclease site; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by taking deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of an enterotoxigenic escherichia coli plasmid as a template to obtain a faeG gene-containing segment, linking the segment with an expression vector plasmid pNZ8148 to obtain a recombinant plasmid pNZ8148-faeG, transferring the recombinant plasmid into lactobacillus or a galactococcus cell by using an electrotransformation method to obtain gene engineering probiotic which expresses enterotoxigenic escherichia coli pilus adhesin faeG, expressing under the induction of nisin and analyzing and proving a target gene by SDS-PAGE and Western blot so as to express correctly. A recombinant strain can be used for preventing colibacillus diarrhea of suckling pigs and weanling pigs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
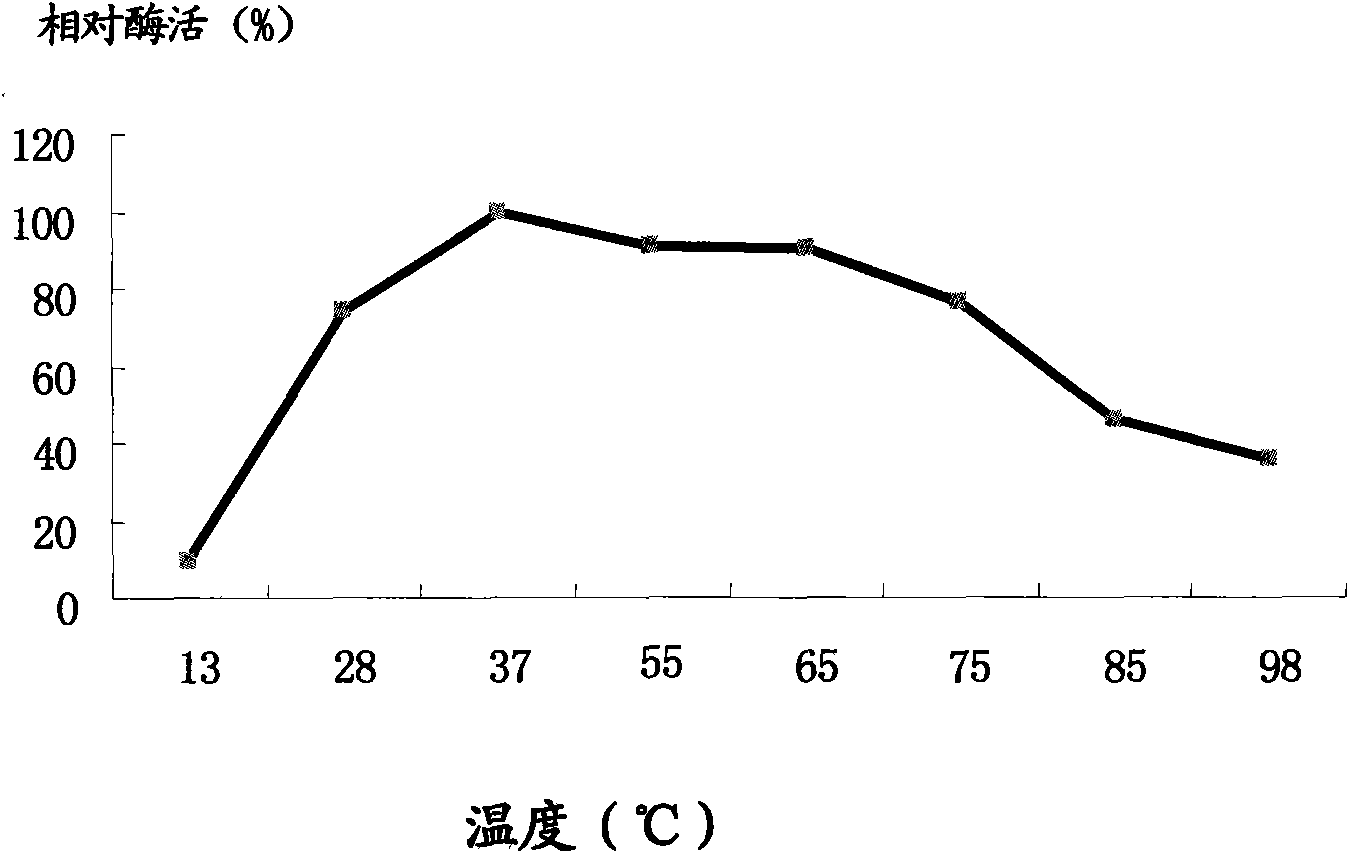
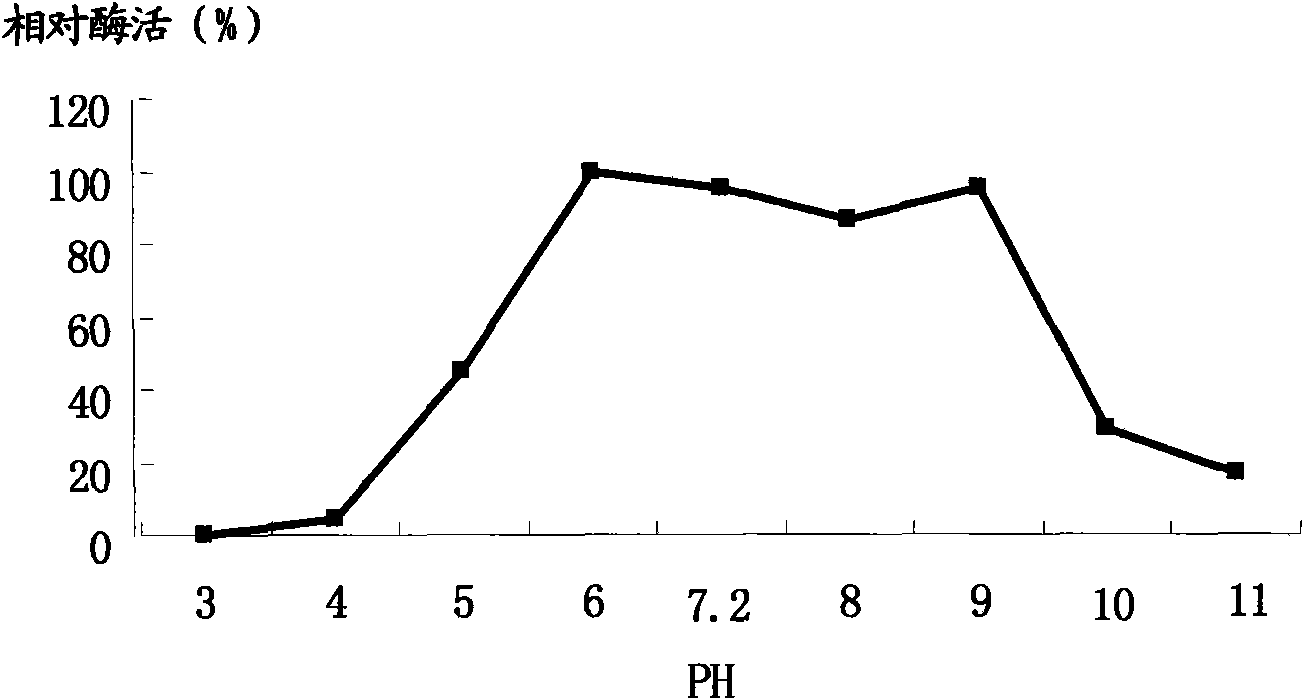
Method for preparing alpha-amylase by high-temperature laceyella sacchari RHA1 virus strain and purification method thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-temperature alpha-amylase by a heat resistant high-temperature laceyella sacchari RHA1 virus strain and a purification method thereof. The high-temperature laceyella sacchari RHA1 virus strain is white and transparent, has corrugations, dry surfaces, different positive colors and negative colors, ball shapes, laceyella sacchari gram-positive bacterium, no flagella or no pilus; and a large number of mycelium is produced when culturing liquid. The method for preparing the amylase by the high-temperature laceyella sacchari RHA1 comprises the following steps: carrying out ultrafilter concentration and ammonium sulfate precipitation on a fermentation supernatant through an ultrafilter envelope of 1KD to obtain crude enzyme liquid, and filtering by Superdex 75 10 / 300 gelatin to obtain pure heat resistant alpha-amylase. The molecular weight of the alpha-amylase obtained in the invention is only 11.9 KDa, and the alpha-amylase is a monomer protein and is an amylase with the minimal molecular weight reported recently. The alpha-amylase hydrolyzes amylose and soluble starch to obtain maltose and maltotriose, can resist high temperature and has wide action temperature range and application values in food processing, medicines, detergents and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
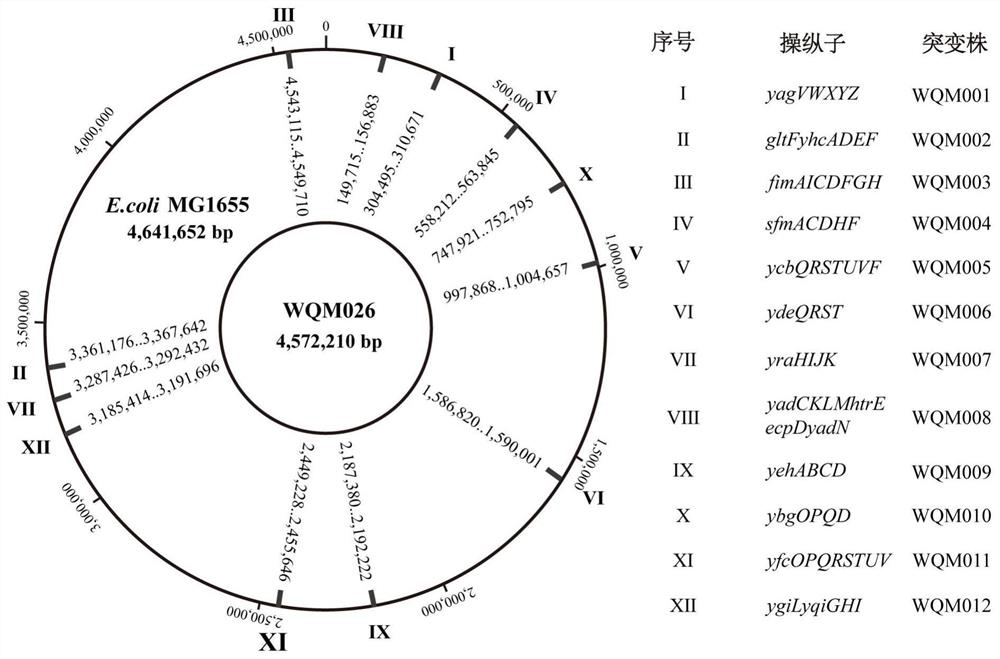
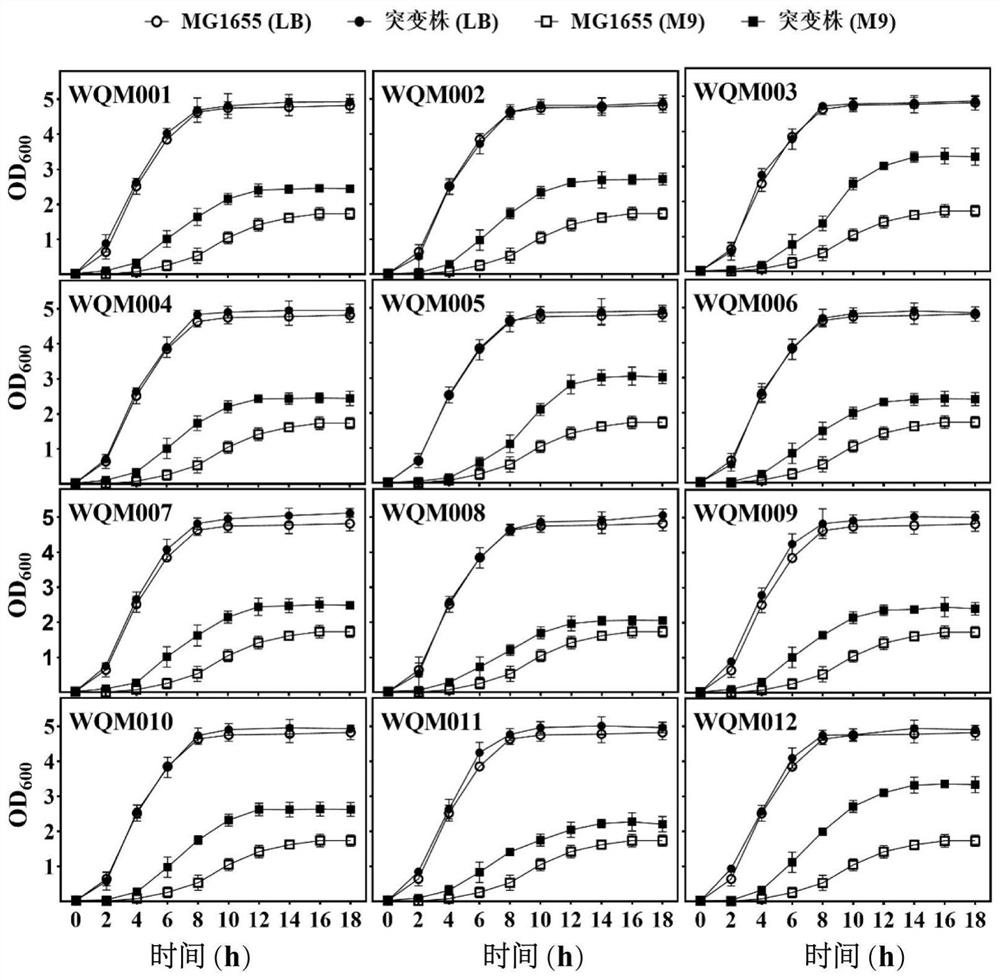
Construction and application of fimbriae-free escherichia coli capable of improving production efficiency
ActiveCN112680393AGrow fastEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPilus
The invention discloses construction and application of fimbriae-free escherichia coli capable of improving production efficiency, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. 64 genes of a fimbriae gene cluster on an escherichia coli genome are knocked out to obtain mutant bacteria WQM026, the strain grows faster in a nutrient-deficient culture medium, and the total amount of thalli is increased. The related genes synthesized by PHB and L-threonine are respectively transformed into the strain WQM026, and the obtained recombinant bacteria WQM026 / pBHR68 and WQM026 / pFW01-thrA*BC-rhtC can be used for respectively and efficiently synthesizing PHB and L-threonine. The synthesized PHB accounts for 87.87% of the dry weight of the cells and is 3.44 times that of wild type control bacteria. The yield of the L-threonine is 2.49 g / L and is 3.66 times that of wild type control bacteria.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Multiple PCR primer group for detecting five fimbrial genes of enterotoxigenic escherichia coli, kit and detection method
ActiveCN108588248AReliable detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEscherichia coliSpecific detection
The invention discloses a multiple PCR primer group for detecting five fimbrial genes of enterotoxigenic escherichia coli, a kit and a detection method. The enterotoxigenic escherichia coli causing diarrhea of young livestock is usually provided with F4, F5, F6, F18 and F41 fimbria and encoding genes thereof. A set of specific detection primer group is designed and synthesized by comparing and analyzing five fimbrial gene sequences, a multiple PCR detection method for detecting the five fimbrial genes for the enterotoxigenic escherichia coli is established, and a kit containing the specific primer group is assembled. When being used for detecting the five fimbrial genes of the enterotoxigenic escherichia coli, the kit has the advantages of high specificity, rapidness, simplicity, high sensitivity and the like, is suitable for rapidly detecting the fimbrial genes of escherichia coli separated from diarrhea samples of sick livestock, and is effective technological means of screening andauthenticating the serotype of the fimbria of the enterotoxigenic escherichia coli.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compounds and methods for treating bacterial infections
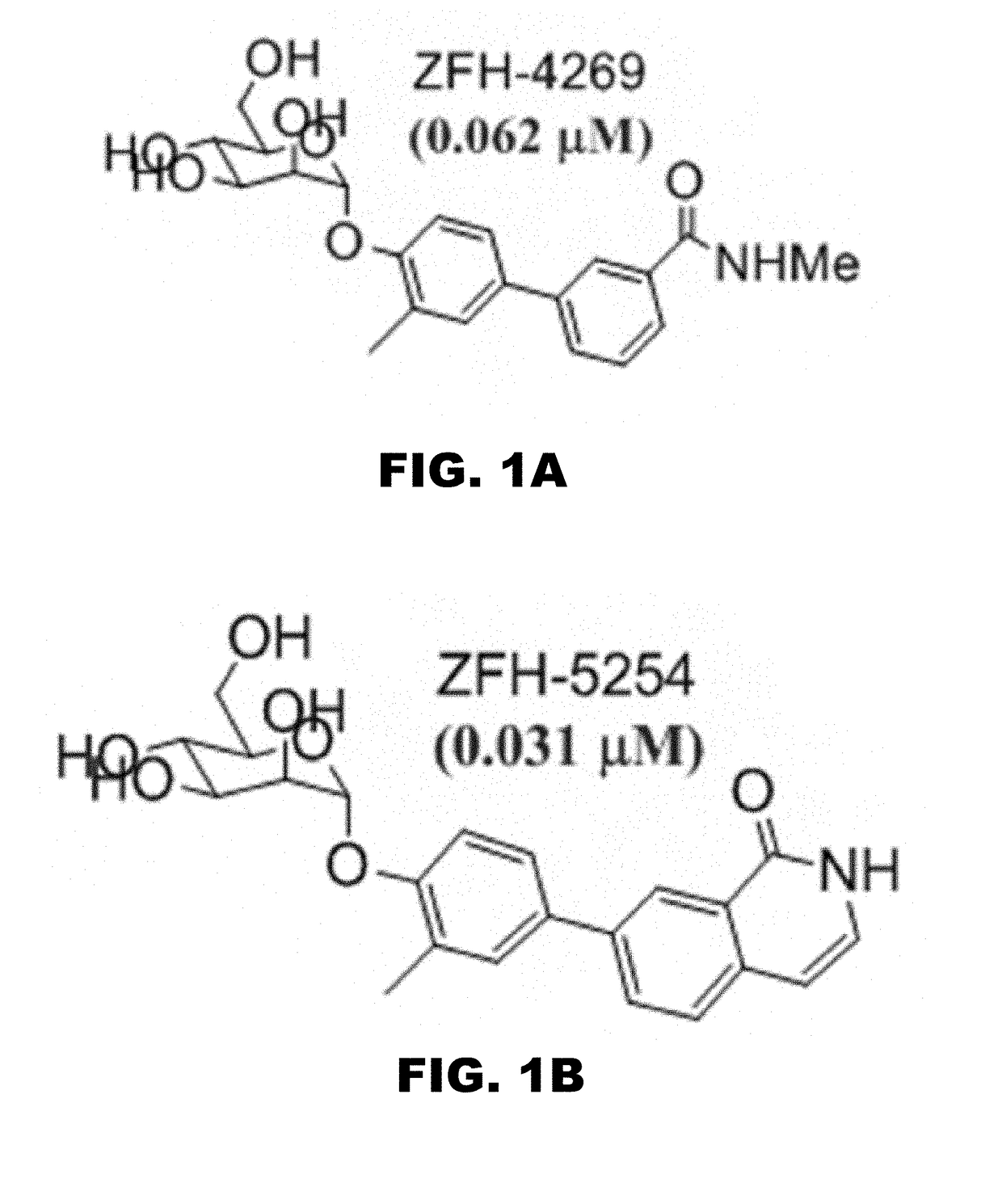
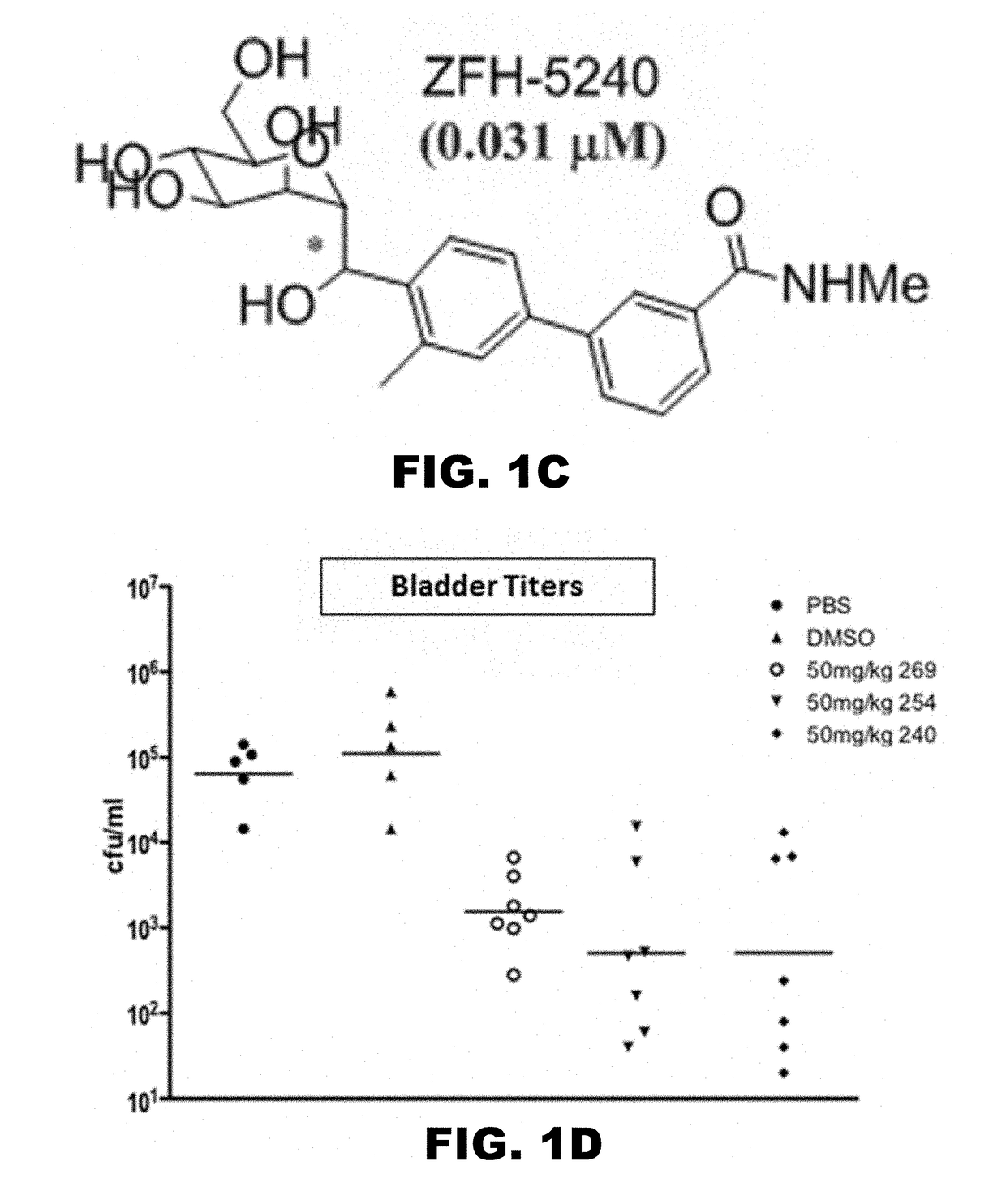
InactiveUS20180194792A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsUpper urinary tract infectionPilus
The present invention encompasses compounds and methods for treating and preventing bacterial infections specifically urinary tract infections and those caused by bacteria containing type 1 pili and FimH. The present invention also encompasses compounds and methods for treating inflammatory bowel disease specifically Crohn's Disease.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Making method of fermented bean curd
The invention relates to a making method of a fermented bean curd, in particular to a making technology of the fermented bean curd, which is simple to operate and convenient for home making, and the made fermented bean can be eaten after a short period and has unique flavor. The making method comprises the following steps of: 1, firstly washing a finished bean curd, and cutting into bean curd blocks with the square of about 3 centimeters and the thickness of about 6 millimeters; 2, soaking the cut and shaped bean curd blocks with 2% saline water, and placing into a steamer for steaming, shrinkage and sterilization; 3, placing the steamed bean curd blocks on a warm and lucifugal place for fermentation, wherein the temperature generally ranges from 20 DEG C to 25 DEG C, and white or yellow pilus (also called bean curd embryos) can grow on the surfaces of the bean curd blocks within fiver days; 4, filling the bean curd embryos with the white or yellow pilus growing on the surface into open tanks, splashing a saline water (with the proportion of 1:2) layer, a few peppercorn granules and rice wine or white wine on each bean curd embryo layer, and covering a seal; and fermenting again for 10 days to make the fermented bean curd. The prepared fermented bean curd has unique flavor and exquisite smell.
Owner:JIANGSU YUANHONG FOOD
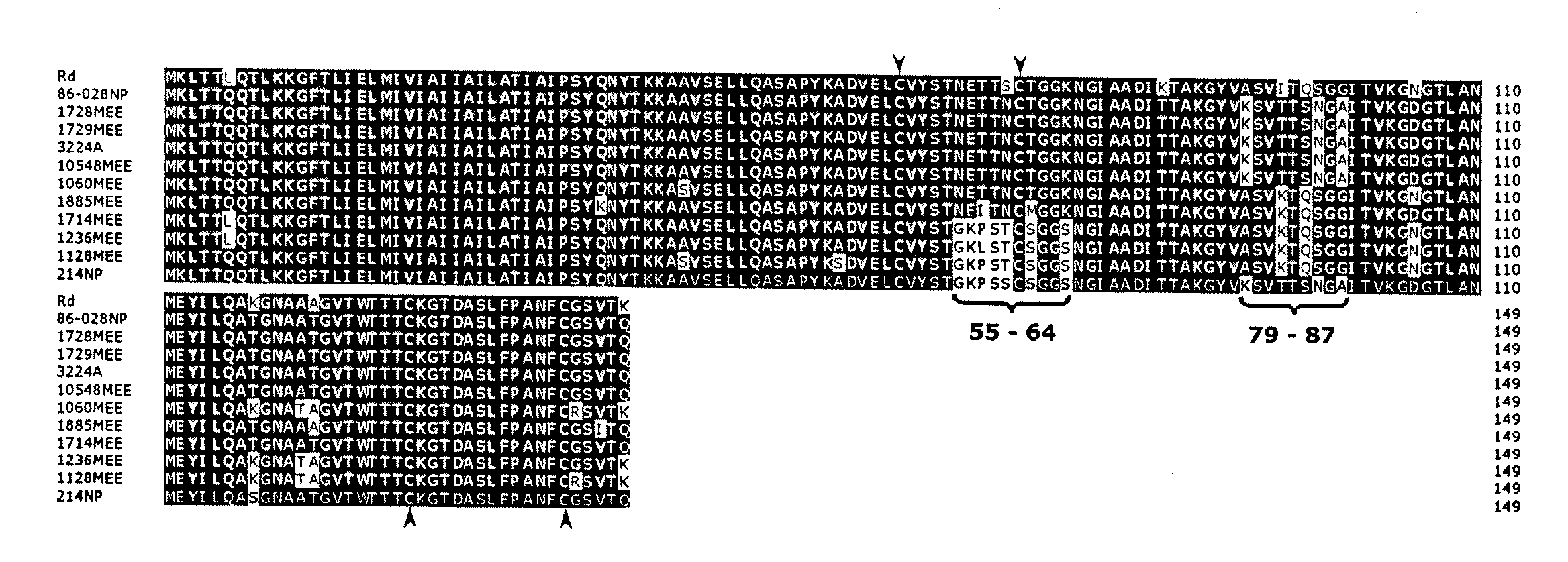
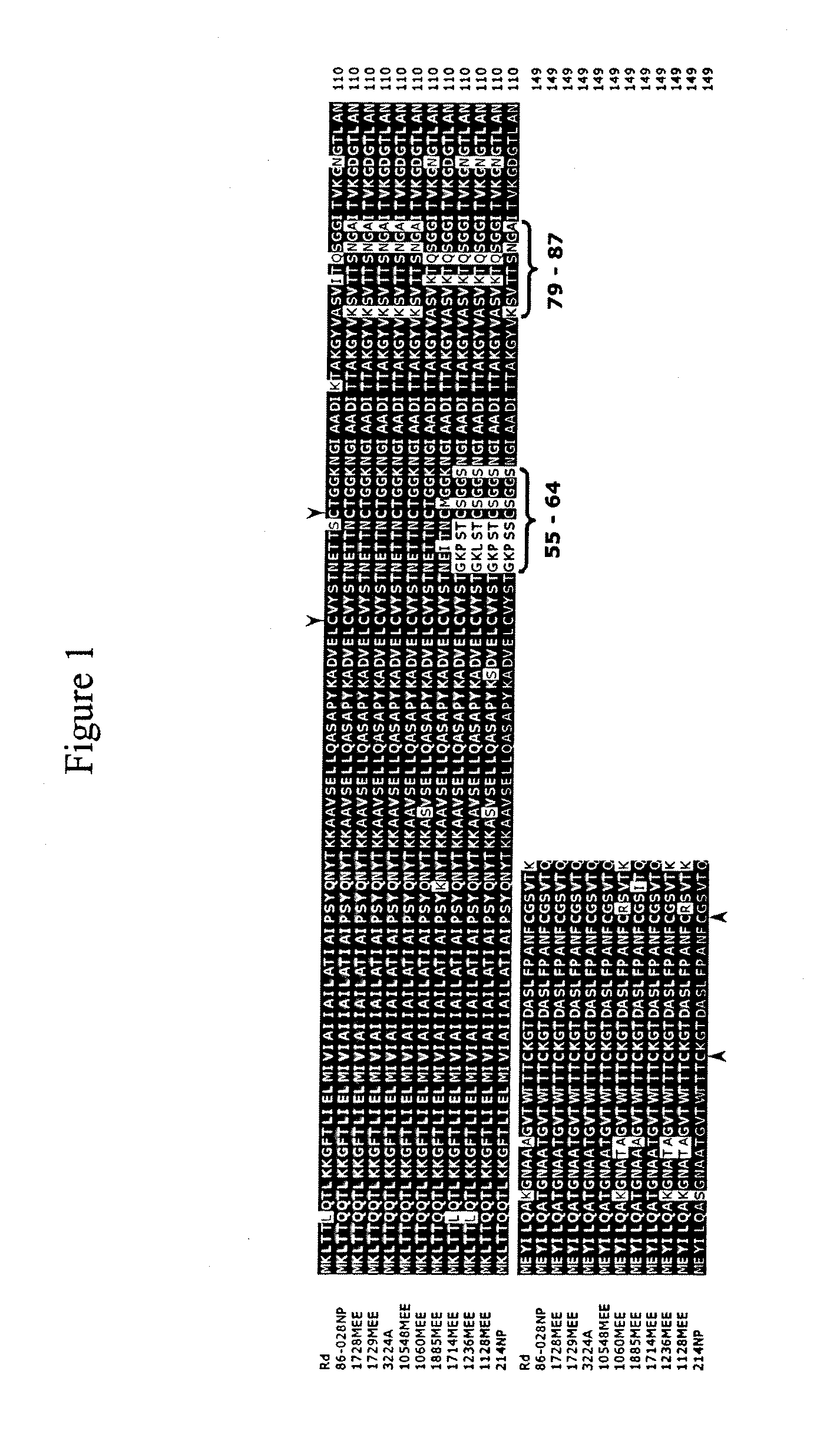
Haemophilus influenzae type IV pili
The invention described herein relates to a Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) regulon encoding type IV pili. In particular, the invention relates to type IV pili from nontypeable H. influenzae (NTHi) and from H. influenzae strains a, b, c, e and f. The invention provides isolated H. influenzae pilus polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides as well as polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides involved in the assembly / disassembly of the structure. The invention also relates to uses of these polynucleotides and / or polypeptides including methods for eliciting an immune response to H. influenzae and methods of treating and preventing H. influenzae related pathological conditions.
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
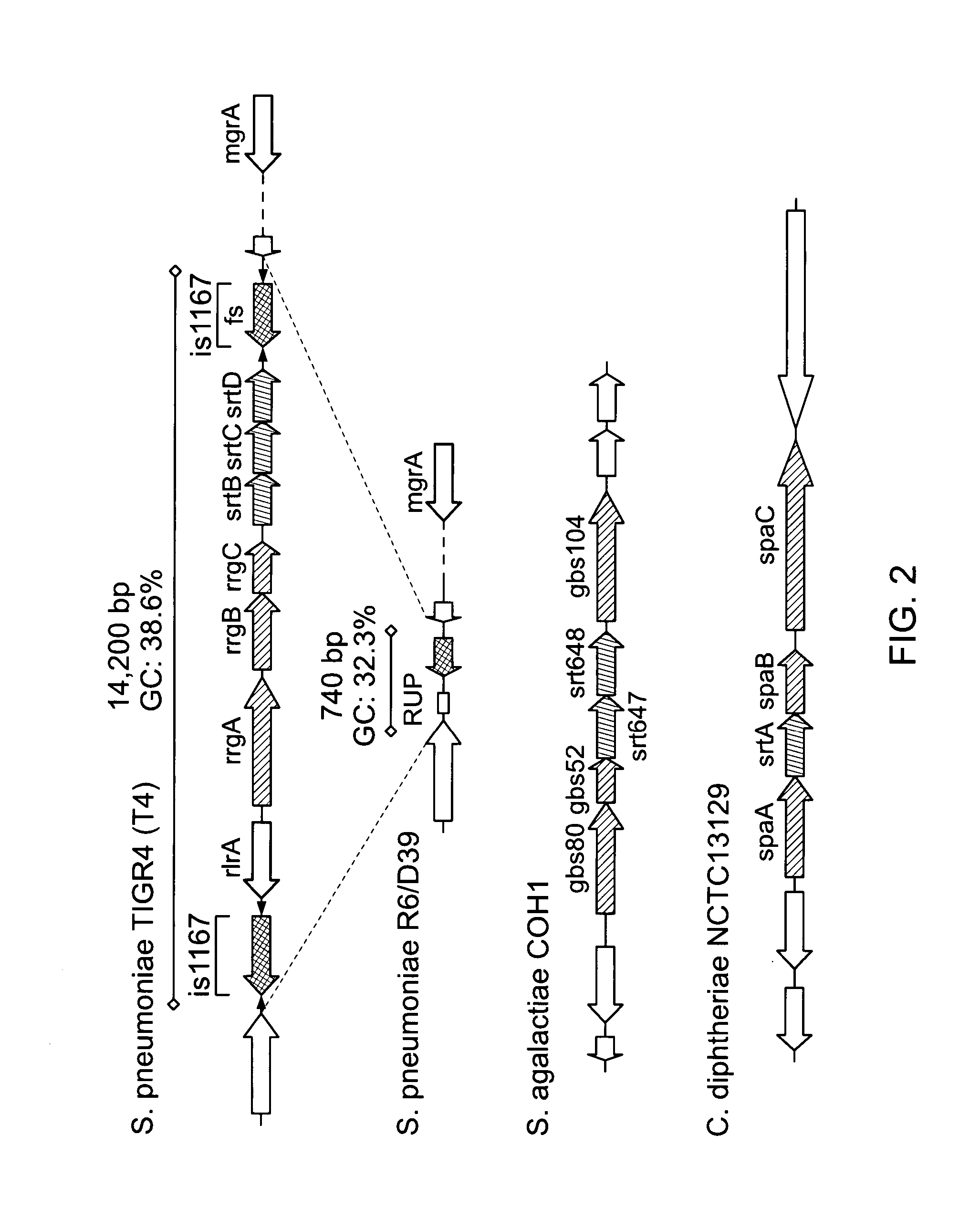
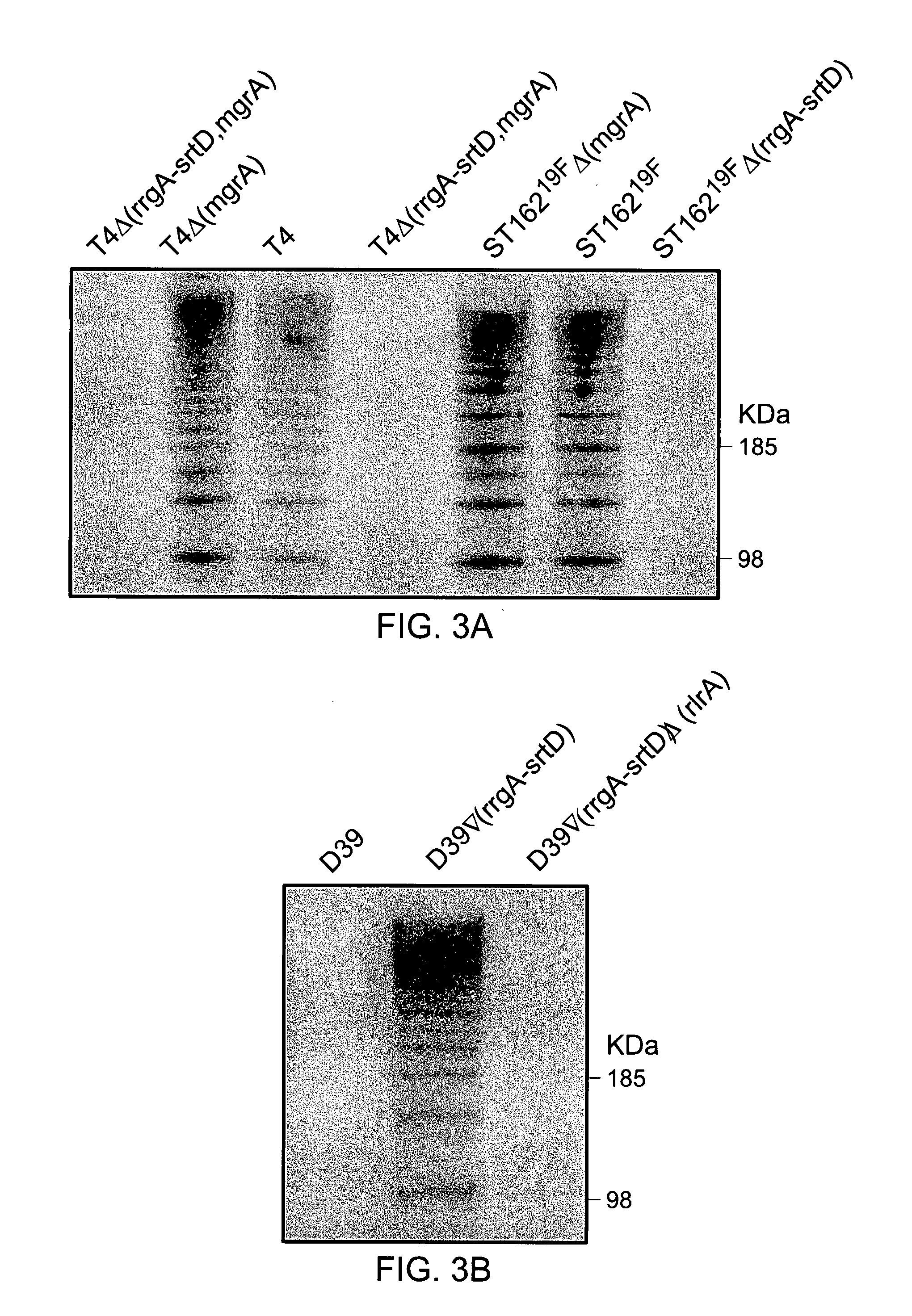
Streptococcus pneumoniae pilus antigens
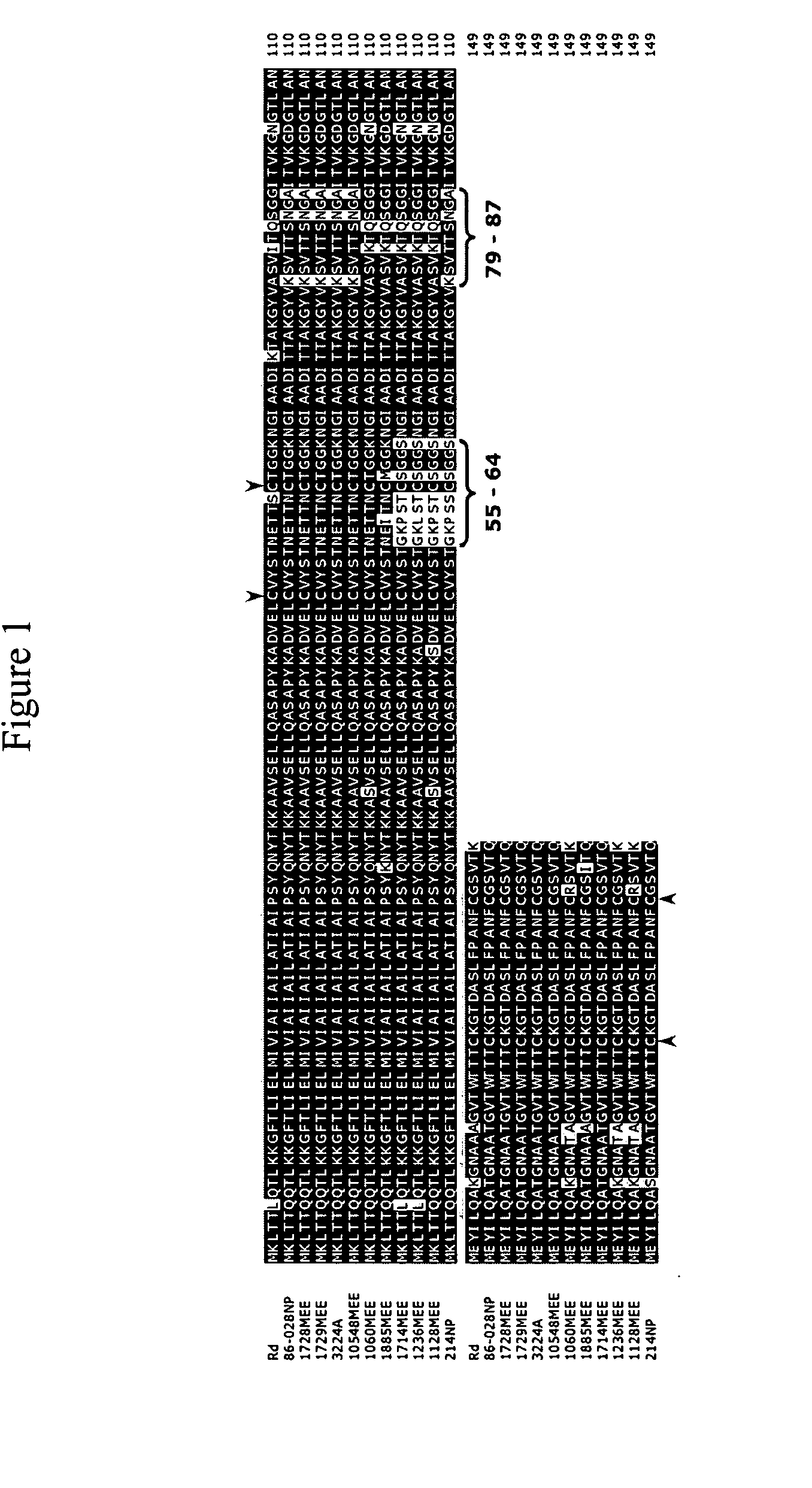
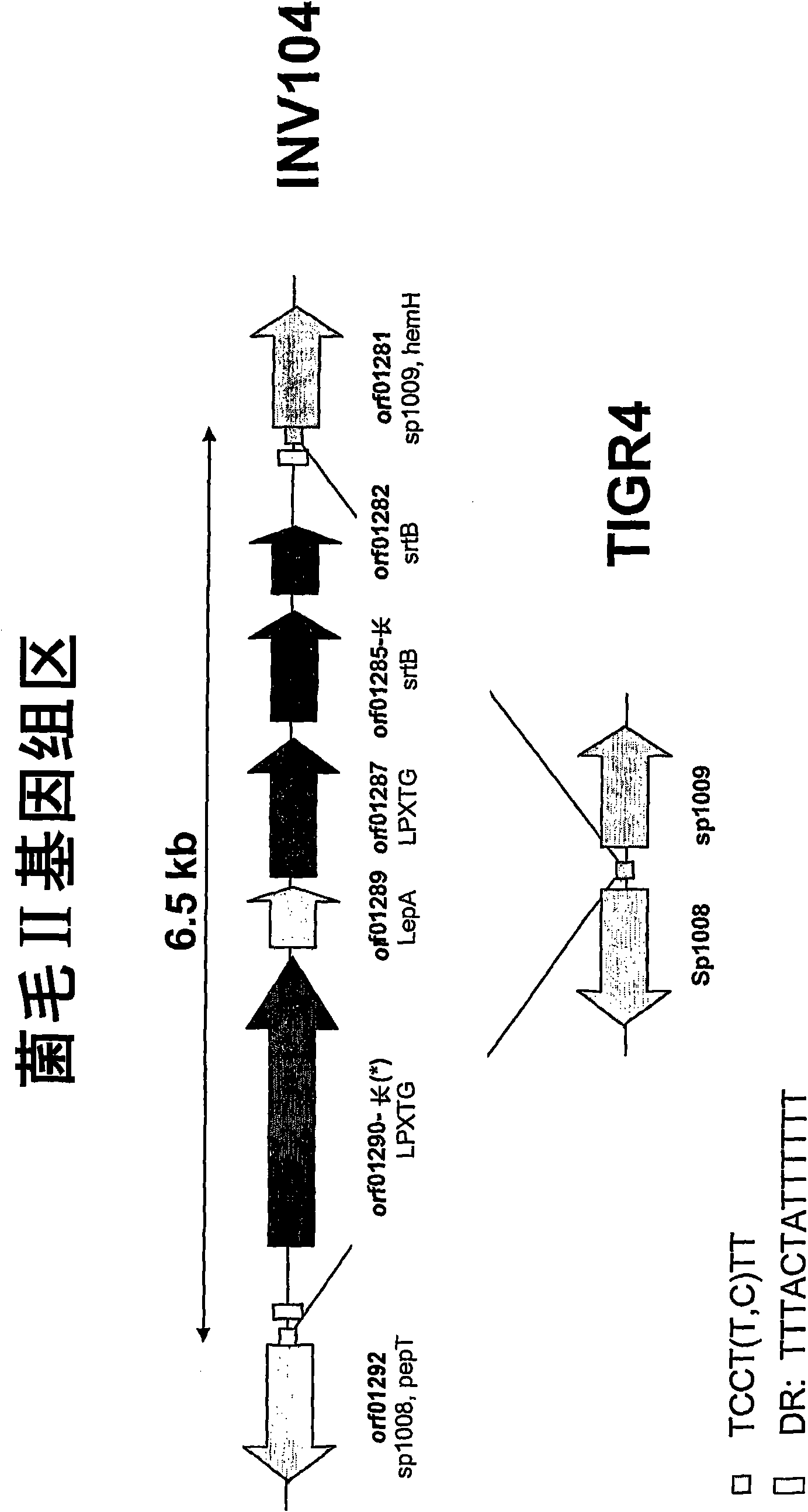
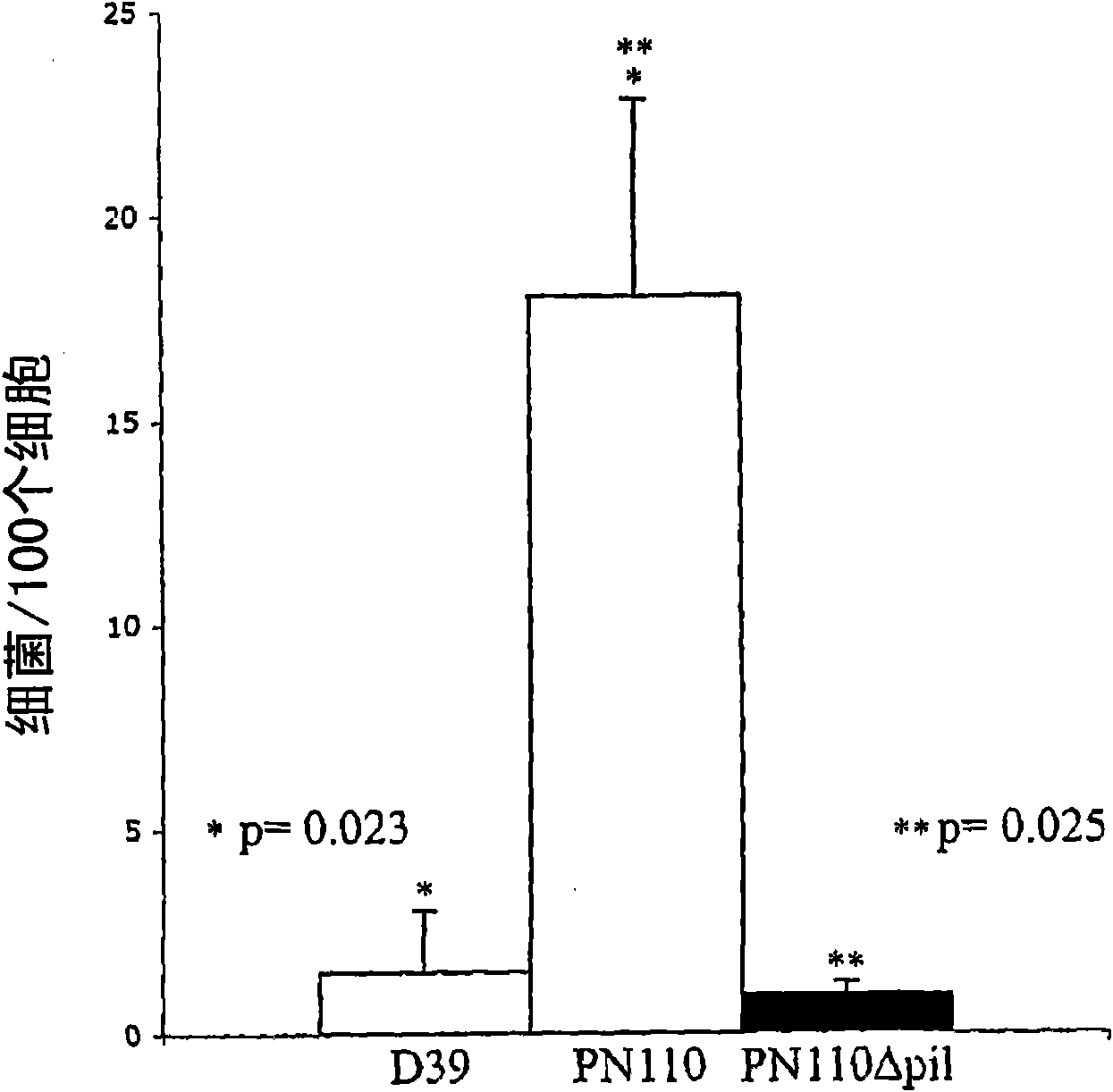
Polypeptides from Streptococcus pneumoniae are described. In some aspects the polypeptides include pili polypeptides from a second pili island (pilus II island (INVl 04B)) identified in Streptococcus pneumoniae isolate INVl 04. In other aspects the polypeptides include pili polypeptides and non-pilus polypeptides from Streptococcus pneumoniae strains 23F, INV200, and OXC141 that are absent from Streptococcus pneumoniae isolate INV104. The polypeptides, including fragments and variants thereof, may be used in immunogenic compositions for prophylactic or therapeutic immunization against Streptococcus pneumoniae. The polypeptides are also disclosed to be used in compositions useful for the production of antibodies and immunostimulants. Also presented are methods of inhibiting Streptococcus pneumoniae, methods of treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection, methods of identifying inhibitors of Streptococcus pneumoniae and methods for diagnosing / detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae infection.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Process for preparing chicken colibacillus pilus monoclonal antibody
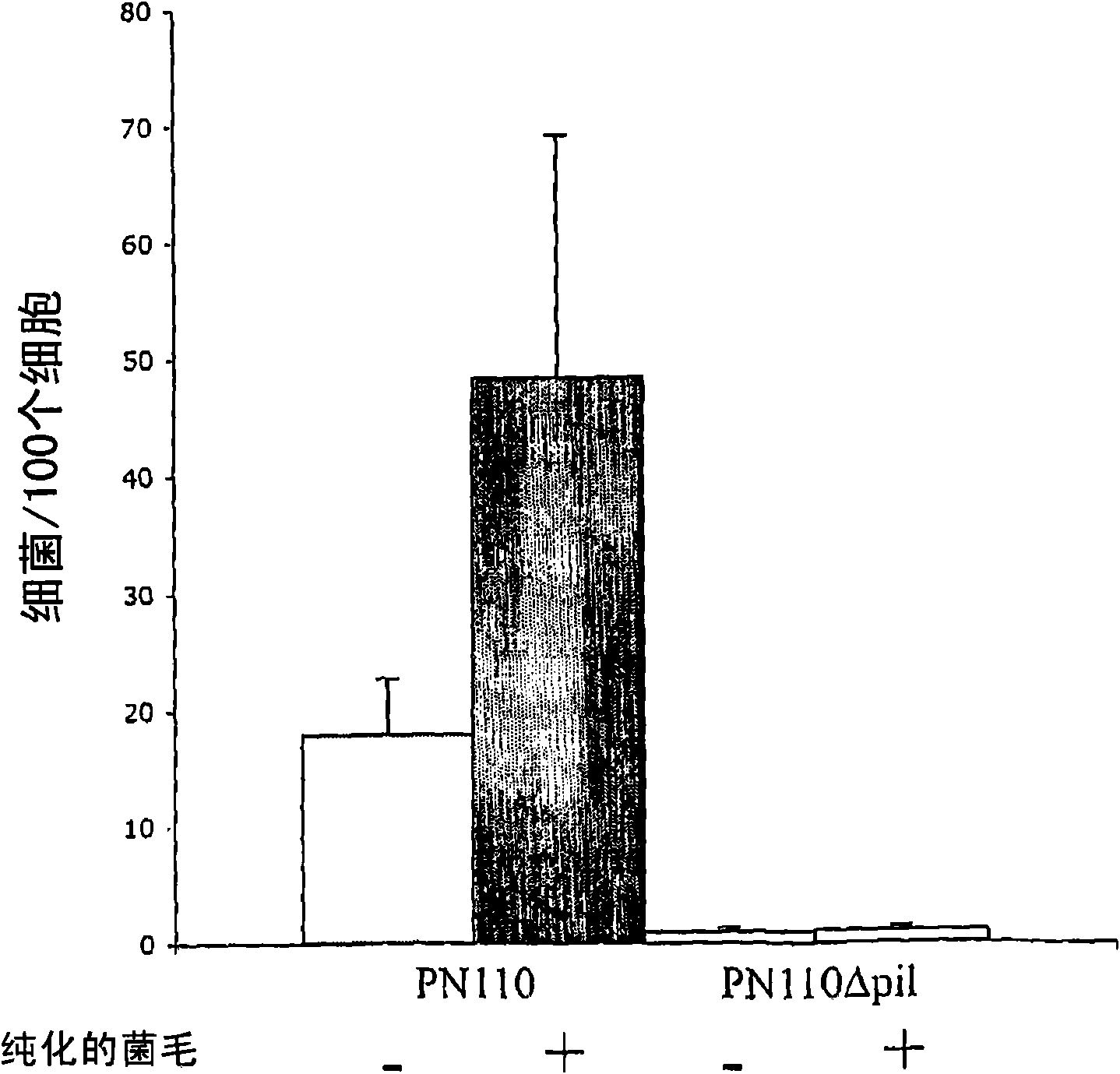
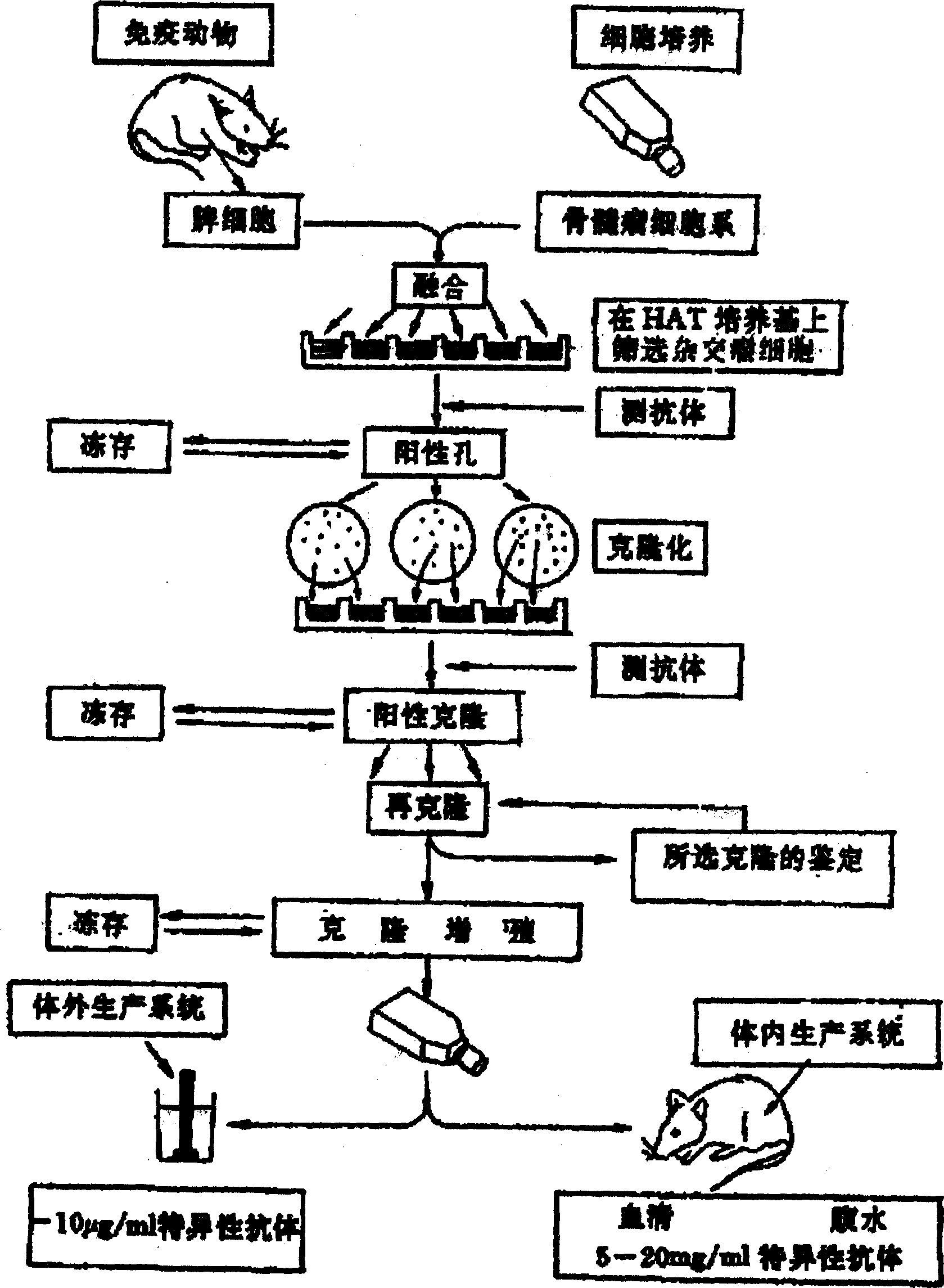
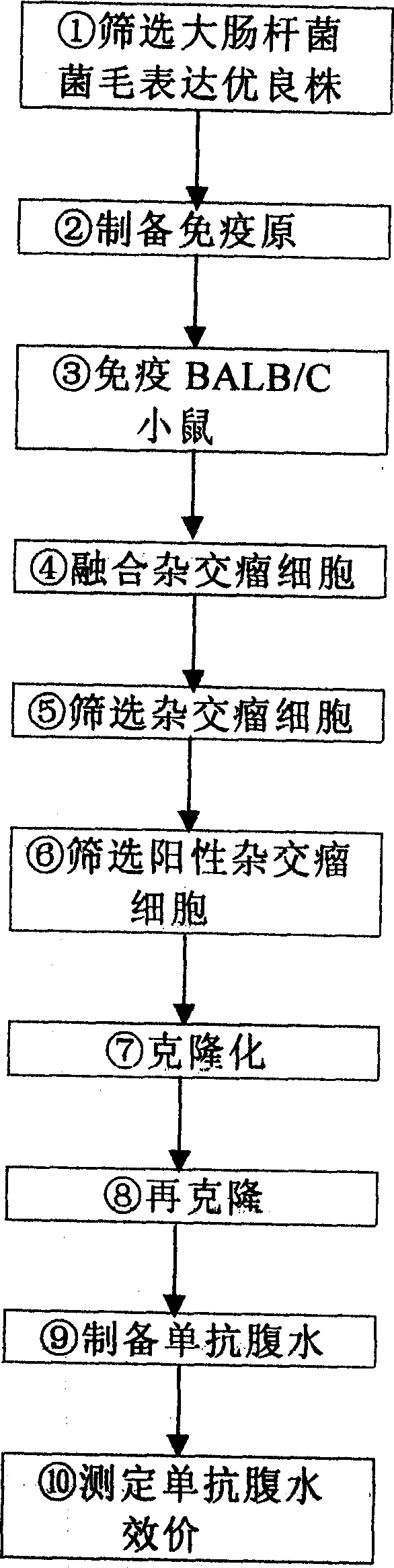
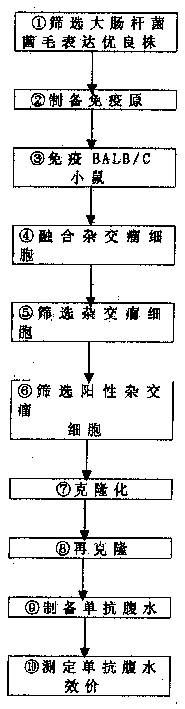
A method of preparing monoclonal antibody against pillis of bacillus coli. It comprises: 1) screening good strains of bacillus coli; 2) preparing immunogens;3) immunizing BALB / C mice;4)fusing hybridoma cells; 5) screening hybridoma cells; 6) screening positive hybridoma cells;7) clonizing;8) clonizing again;9) inducing ascitic fluid containing monoclonal antibody; 10) measuring valence of monoclonal antibody in ascitic fluid. The monoclonal antibody has a high valence, could discriminate F1,P and other pillis, which could be used to determine pathogenic bacillus coli strains.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
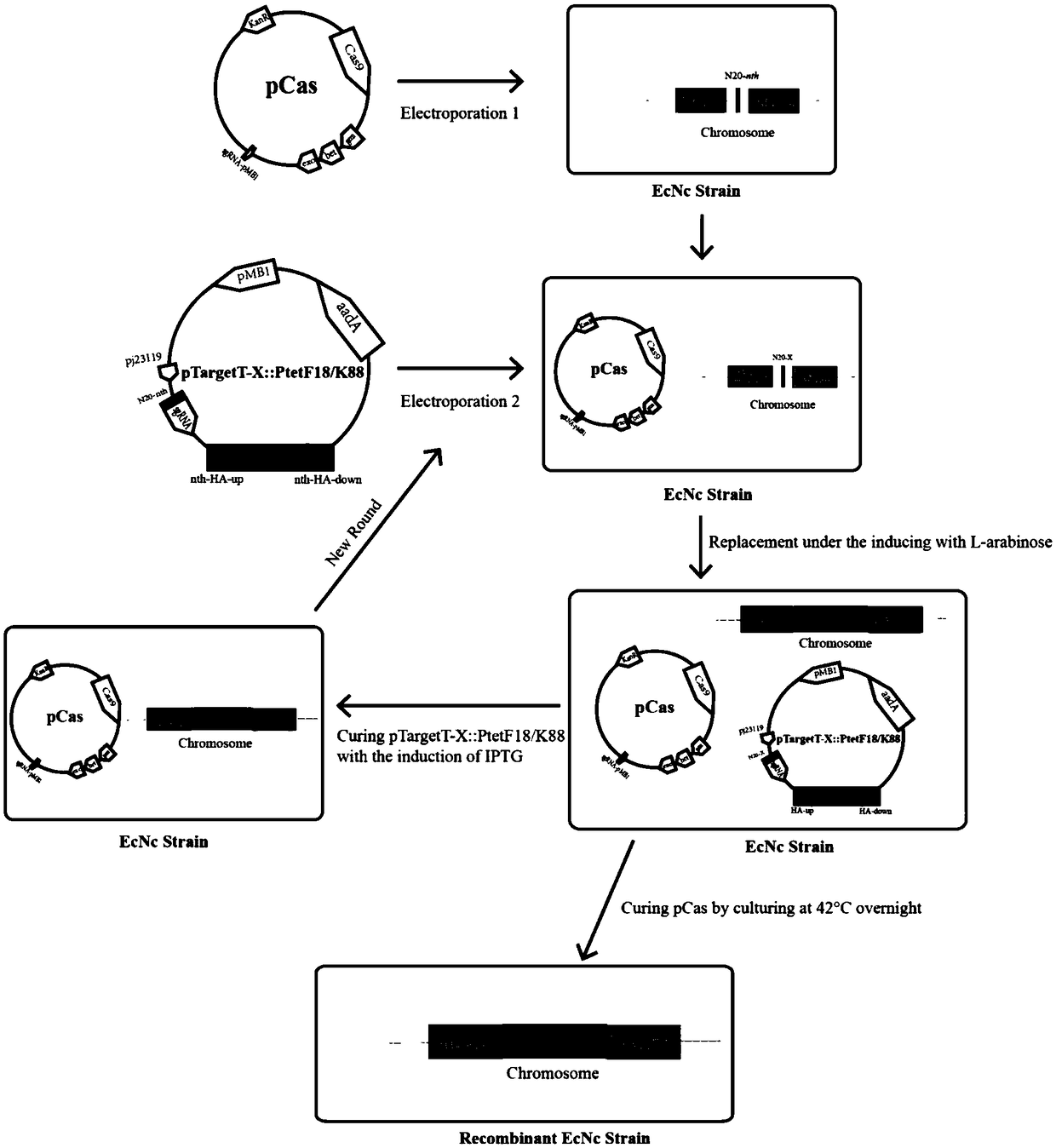
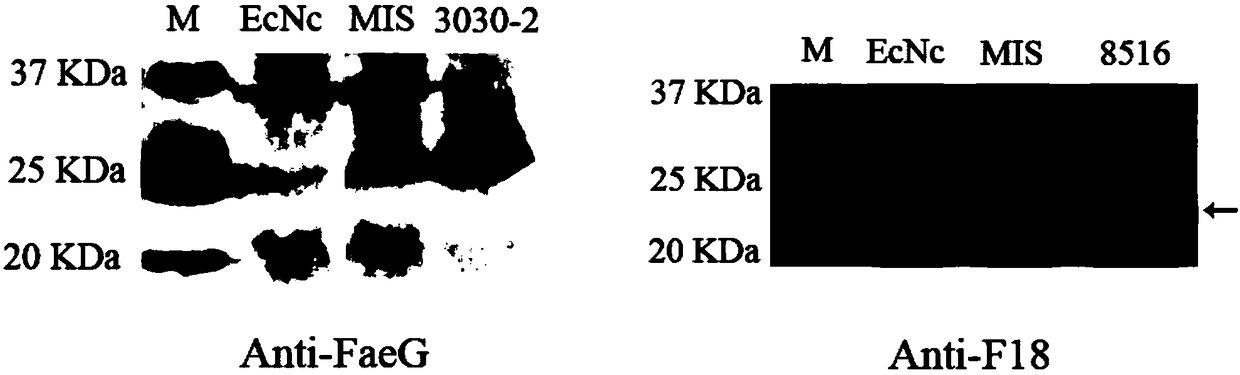
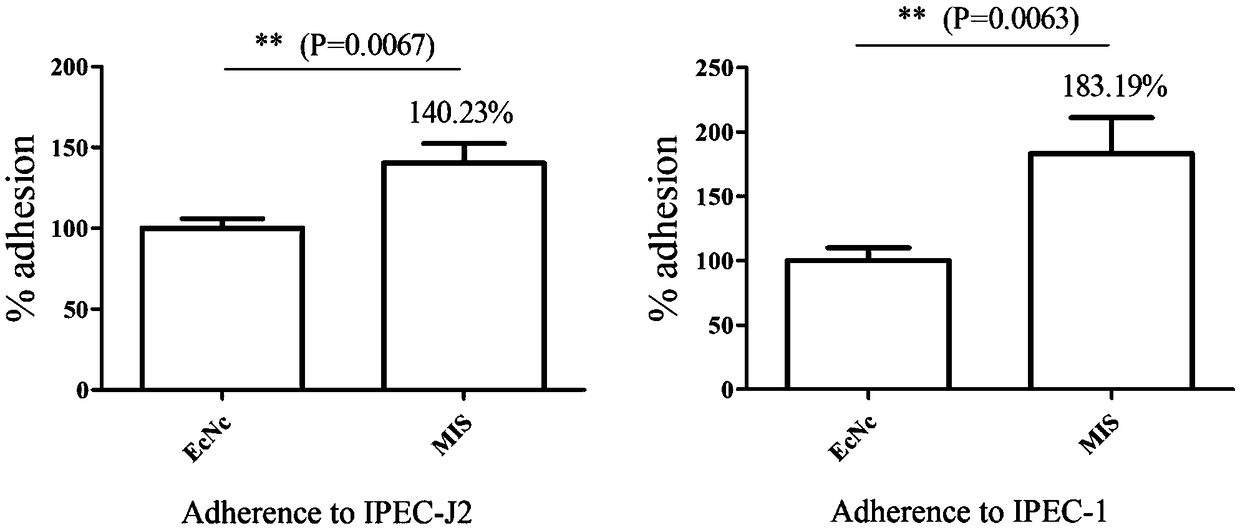
Probiotics cloned strain of integrated four-cope F18 pili operon gene and two-copy F4 pili operon gene and construction method
ActiveCN109468256AImprove adhesionReduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to probiotics cloned strain of integrated four-cope F18 pili operon gene and two-copy F4 pili operon gene and a construction method. The method comprises the following steps: constructing pTargetT-X::PtetF18 and pTargetT-X::PtetF4 recombinant plasmid; and obtaining nonresistant four-cope F18 pili gene and two-copy F4 pili geneintegration cloned strain through construction of the probiotics cloned strain of the four-copy functional F18 pili operon gene and the two-copy F4 pili operon gene. The probiotics cloned strain has the benefits that recombinant bacteria can effectively improve the adhesion property to pig intestinal passage epithelial cell; mice subjected to oral immunization can produce immune serum, namely anti-F18 pili IgG antibody and anti-F4 pili IgG antibody; and serum of the mice subjected to oral immunization can obviously reduce adhesion to pig intestinal passage cell line IPEC-J2 by F18+ strain andF4+ strain.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Mannose-sensitive hemagglutination) pilus strain
The invention relates to a klebsiella pneumoniae mannose-sensitive hemagglutination pilus strain which is characterized by comprising mannose-sensitive hemagglutination pilus. The invention also relates to the cultivation, treatment, application and using method of the klebsiella pneumoniae mannose-sensitive hemagglutination pilus strain. The invention also relates to a medical product prepared by the klebsiella pneumoniae mannose-sensitive hemagglutination pilus strain.
Owner:BEIJING WONDER BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR THE TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF Ebp PILUS-RELATED DISEASES
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
AIDS live carrier multipartial vaccine and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101716350AStable structureStructural ConservationBacteriaGenetic material ingredientsEpitopePilus
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
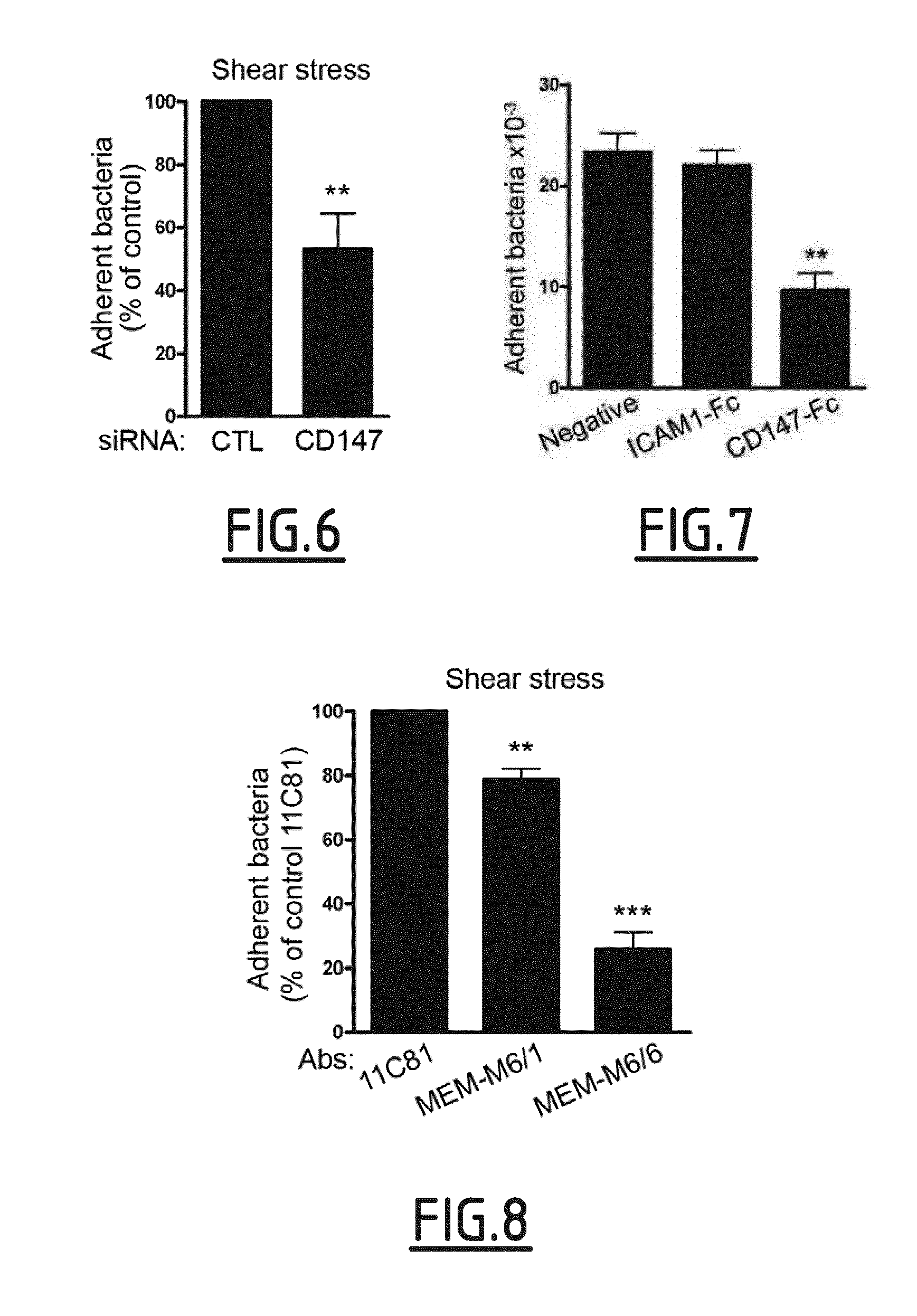
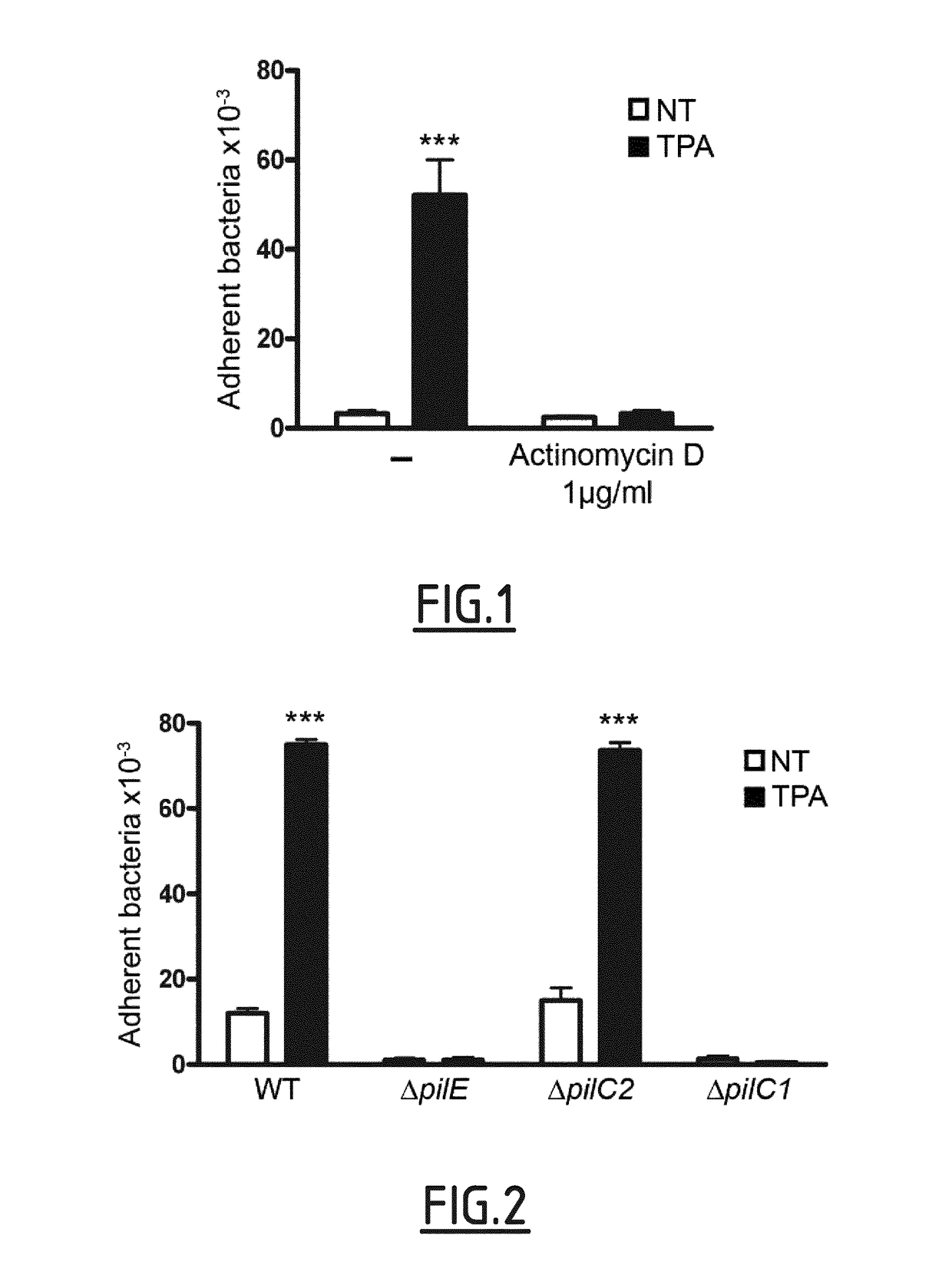
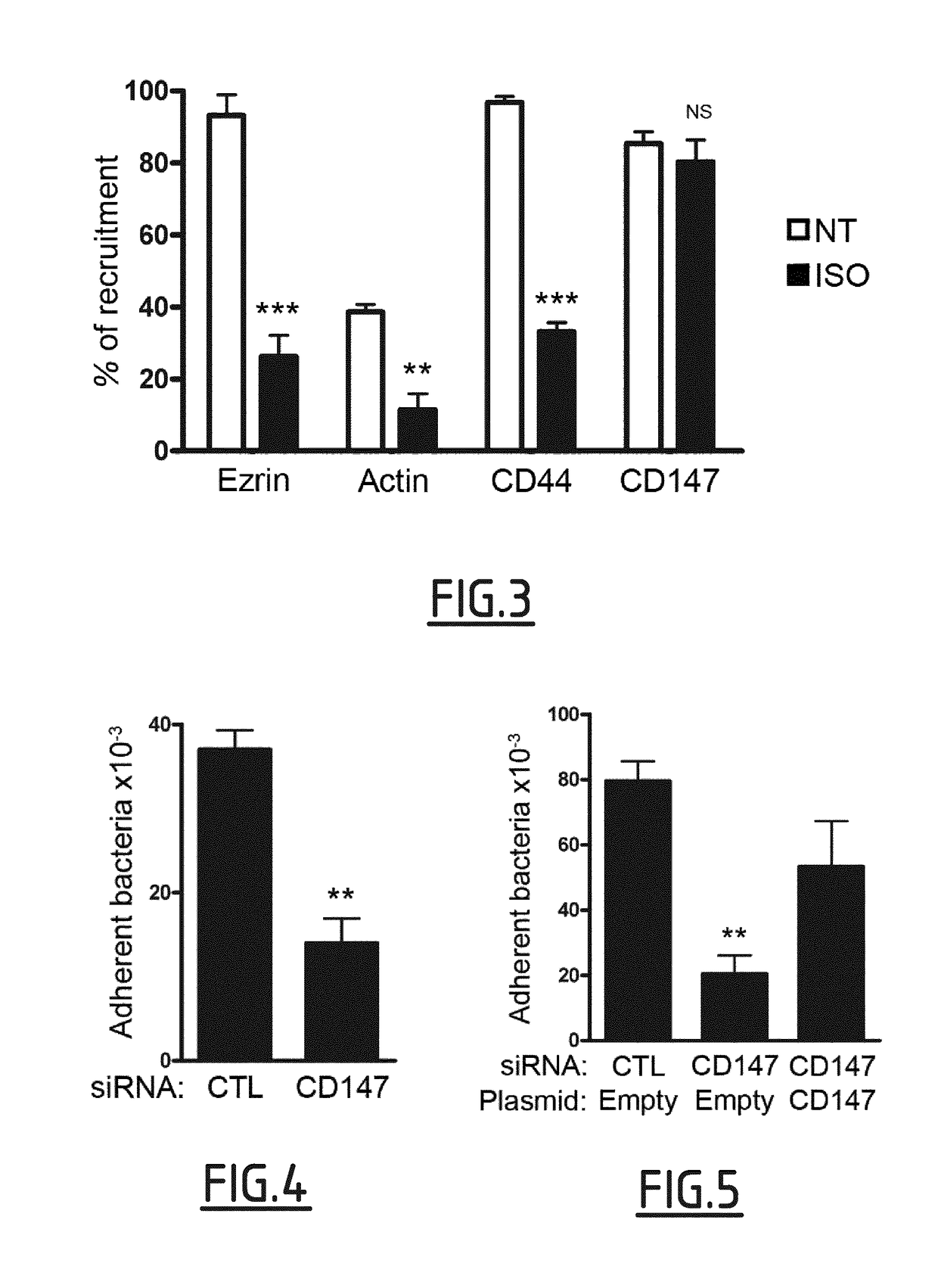
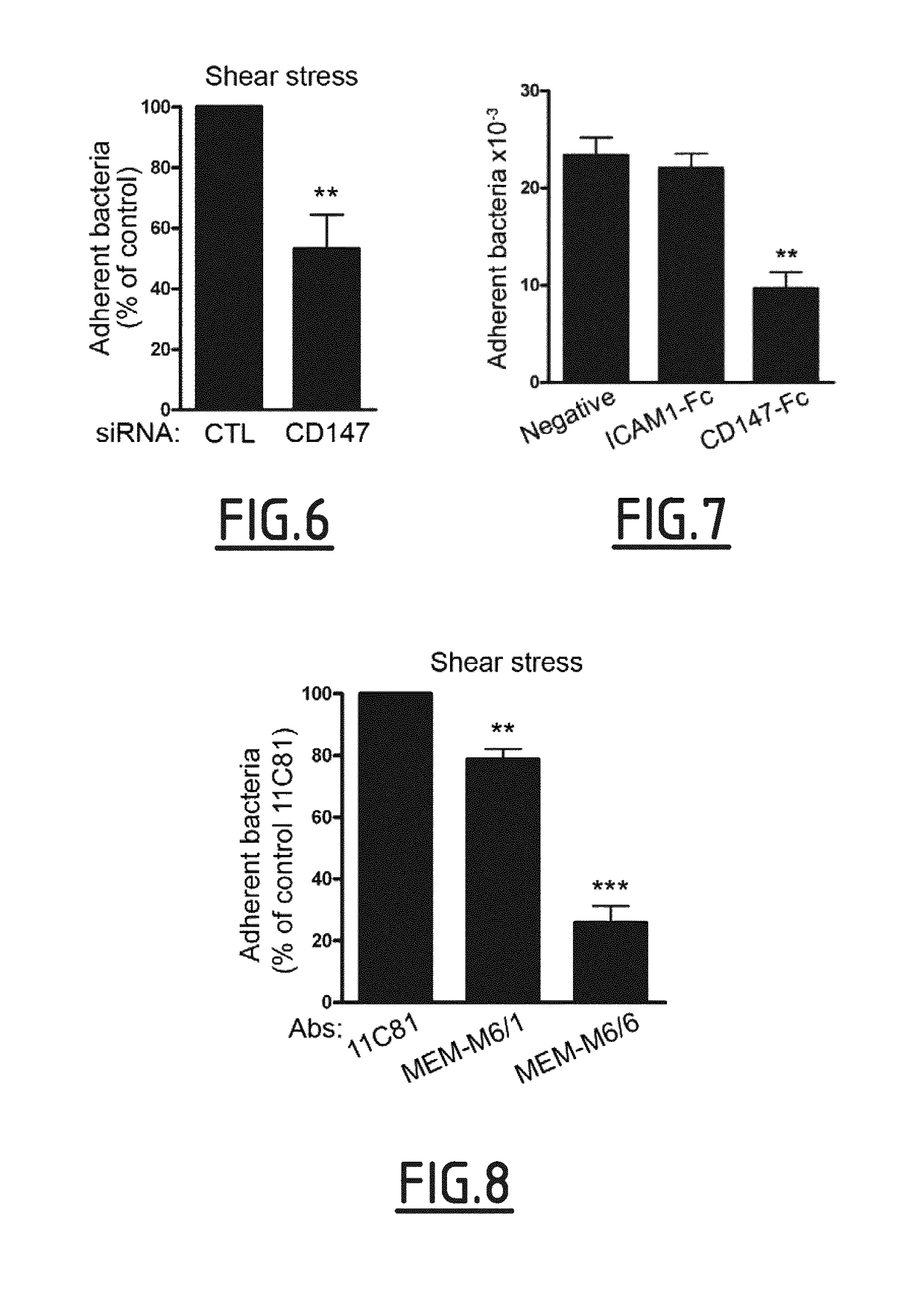
Cd147 as receptor for pilus-mediated adhesion of meningococci to vascular endothelia
InactiveUS20150110806A1Inhibiting meningococcal bacteraemiaAntibacterial agentsCompound screeningVascular endotheliumPilus
The present invention concerns the use of an inhibitor of an interaction between type IV pilus-associated protein and CD147 for preventing or treating meningoccal bacteraemia and / or infection. The present invention also relates to the combined use of such inhibitor and of an anti-bacterial compound, such as one used to prevent or treat a meningococcal infection. The invention also relates to a method for the prevention and / or treatment of meningococcal bacteraemia and / or infection, and to a method for screening inhibitors of the interaction between type IV pilus-associated protein and CD147.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
A method for efficiently synthesizing PHB by knocking out flagella and pilus genes
ActiveCN110669709BGrowth is not affectedImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPilusGene cluster
The invention discloses a method for efficiently synthesizing PHB by knocking out flagellum and pilus genes, which belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. According to the invention, three flagellum gene clusters flhE-motA, fliY-fliR and flgN-flgL on an escherichia coli genome are knocked out to obtain a flagellum simplified strain WJW010, and a fimbriae gene clusterfimB-fimH is knocked out to obtain a fimbriae simplified strain WJW011, the three genes synthesized by PHB can be transformed into strains WJW010 and WJW011, and the recombinant bacteria WJW010 / pBHR68 and the recombinant bacteria WJW011 / pBHR68 are obtained; pHB with the cell dry weight of 19.2% and 2.8% can be synthesized under the normal fermentation condition, and the volume yield of PHB is 9.6times and 1.4 times that of wild control bacteria W3110 / pBHR68 (2%).
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A strain of Corynebacterium glutamicum overexpressing adenosine triphosphate and its construction method and application
The invention discloses a Corynebacterium glutamicum overexpressing adenosine triphosphatase, wherein the gene sequence of the adenosine triphosphatase is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. As that adenosine triphosphatase ATPase is overexpress in Corynebacterium glutamicum, the invention provides energy for the intermediate convert protein VirB11, causes the pili to fall off to form a type IV secretion pathway, increases the amount of extracellular DNA secretion, improves the initial adhesion ability of the bacteria, and improves the stability of the biofilm structure.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Recombinant lactococcus lactis for secretory expression of swine-derived anti-enterotoxigenic escherichia coli K88 pilus single-chain antibody and preparation method of recombinant lactococcus lactis
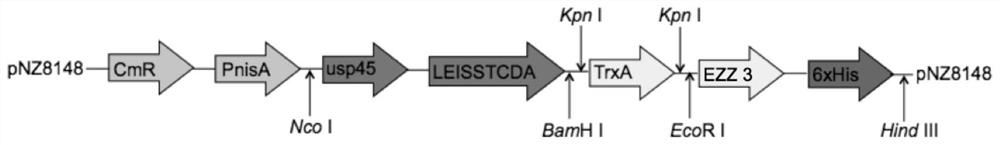
ActiveCN112011497AAvoid direct oral exposure to gastric acidAvoid the effects of proteasesPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaSingle-Chain AntibodiesAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to recombinant lactococcus lactis for secretory expression of a swine-derived anti-enterotoxigenic escherichia coli K88 pilus single-chain antibody and a preparation method of the recombinant lactococcus lactis, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The recombinant lactococcus lactis carries a fusion sequence for secretory and expression of an anti-enterotoxigenic escherichia coli K88 pilus single-chain antibody. The fusion sequence has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and a single-chain antibody sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, wherein the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 is a sequence containing a secretion signal peptide USP45, a secretion enhancing signal peptide LEISSTCDA and a thioredoxin gene. The molecular weight of the obtained secreted single-chain antibody for resisting enterotoxigenic escherichia coli K88 pilus is about 45kDa, and the secreted single-chain antibody can specifically recognize enterotoxigenic escherichia coli,block bacterial infection and protect piglets against enterotoxigenic escherichia coli diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
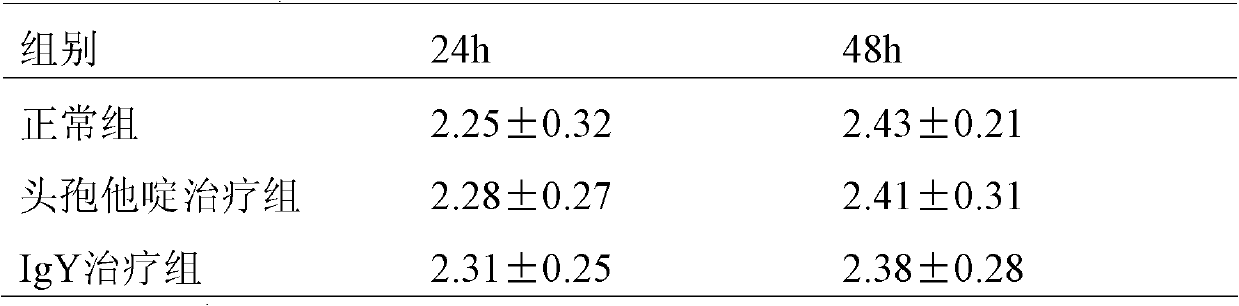
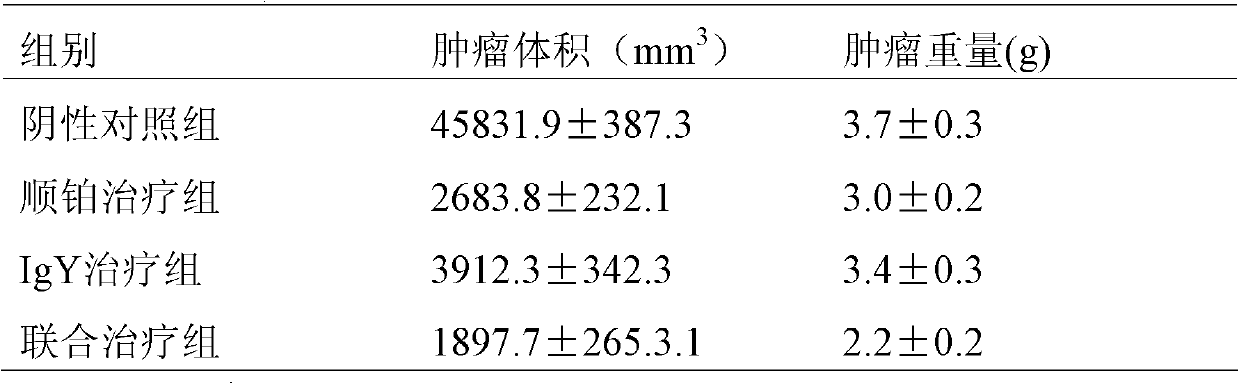
Anti-calf escherichia coli F41 pilus antigen hyperimmune egg yolk antibody IgY preparation method and application
PendingCN109912712AAvoid treatmentEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsEgg immunoglobulinsAntigenPilus
The invention relates to the technical field of agriculture, in particular to an anti-calf escherichia coli F41 pilus antigen hyperimmune egg yolk antibody IgY preparation method and application. Themethod includes steps: (1) pathogenic bacterium separation and identification; (2) pilus gene identification and screening; (3) pilus antigen extraction and purification; (4) egg yolk sterile separation; (5) antibody purification. Clear thinking is realized, by adoption of calf escherichia coli F41 pilus as an antigen for immunization of egg-laying hens, the egg-laying hens generate an anti-pilusantibody, hyperimmune eggs are collected, egg yolks are separated, and an antibody extracted from the egg yolks is a hyperimmune egg yolk antibody (IgY), and the hyperimmune egg yolk antibody is applied to treatment and prevention of colibacillosis of calves.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV FOR THE NATITIES
An IgY for a PA-MSHA bacterial strain, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102770452AGood adjuvant therapyHigh activityAntibacterial agentsEgg immunoglobulinsYolkBacterial strain
The invention relates to an IgY for a mannose-sensitive hemagglutination pilus strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA-MSHA) and a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the preparation method comprises the steps of: (S1) preparing an antigen of the PA-MSHA bacterial strain; (S2) immunizing egg-laying poultry by injecting said PA-MSHA antigen, and checking immunized eggs laid by the immunized poultry; and (S3) taking out yolk of the immunized eggs to extract the IgY for the PA-MSHA bacterial strain. According to the invention, PA-MSHA is used to immunize egg-laying poultry, and the IgY for the PA-MSHA bacterial strain is then extracted from the poultry eggs. The IgY for the PA-MSHA bacterial strain can be further made into health-care and biological products to prevent and cure broad-spectrum opportunistic infection floras such as escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, pneumococcus, deformation coccus, and helicobacter pylori, and to play a role of auxiliary treatment effect in various cancers such as breast cancer, liver cancer, lymph cancer, lung cancer, bladder cancer and leukemia, especially suitable for active and passive immunotherapy for cancers.
Owner:SHENZHEN BROSTIGER BIO PHARMA
Haemophilus influenzae type IV pili
ActiveUS20090041774A1Improve efficiencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHaemophilusPilus
The invention described herein relates to a Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) regulon encoding type IV pili. In particular, the invention relates to type IV pili from nontypeable H. influenzae (NTHi) and from H. influenzae strains a, b, c, e and f. The invention provides isolated H. influenzae pilus polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides as well as polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides involved in the assembly / disassembly of the structure. The invention also relates to uses of these polynucleotides and / or polypeptides including methods for eliciting an immune response to H. influenzae and methods of treating and preventing H. influenzae related pathological conditions.
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
CD147 as receptor for pilus-mediated adhesion of Meningococci to vascular endothelia
InactiveUS10000545B2Inhibiting meningococcal bacteraemiaAntibacterial agentsCompound screeningVascular endotheliumReceptor
The present invention concerns the use of an inhibitor of an interaction between type IV pilus-associated protein and CD147 for preventing or treating meningoccal bacteraemia and / or infection. The present invention also relates to the combined use of such inhibitor and of an anti-bacterial compound, such as one used to prevent or treat a meningococcal infection. The invention also relates to a method for the prevention and / or treatment of meningococcal bacteraemia and / or infection, and to a method for screening inhibitors of the interaction between type IV pilus-associated protein and CD147.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
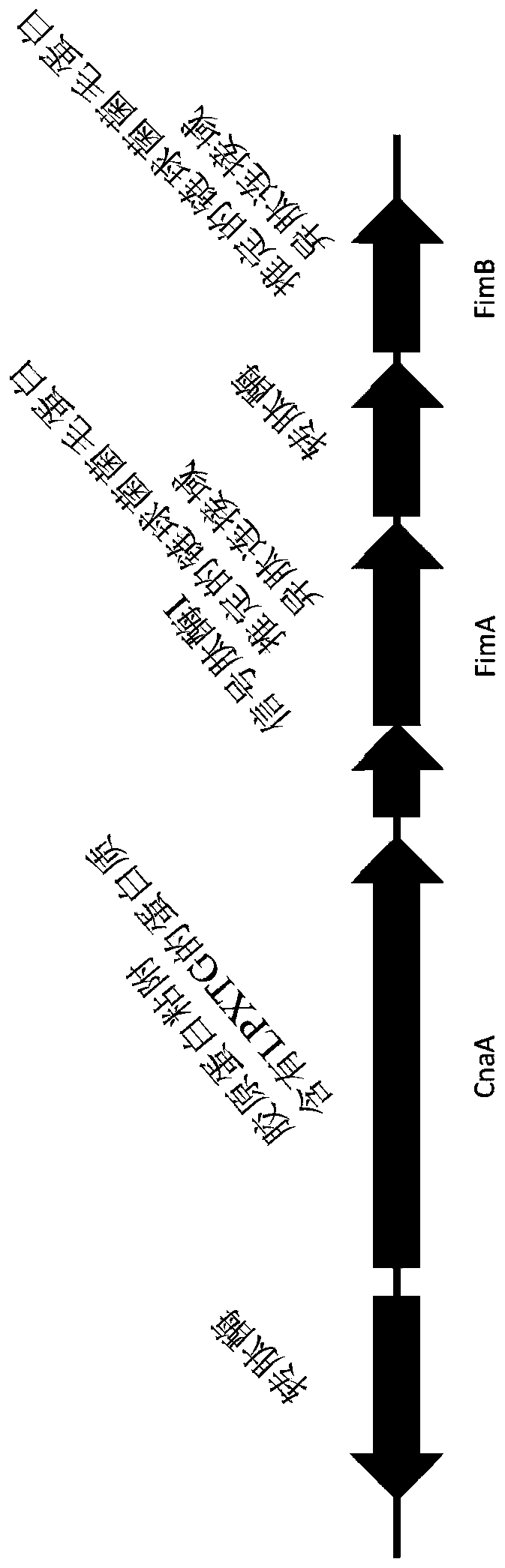
Vaccine against necrotic enteritis in poultry
An immunogenic polypeptide selected from an isolated Clostridium perfringens pilus polypeptide, a variant of the pilus polypeptide; a fragment of the pilus polypeptide; and a fragment of the variant,is useful for the preparation of a vaccine for the treatment or prevention of enteric necrosis in poultry. The isolated Clostridium perfringens pilus polypeptide includes an assembled pilus or the pilus subunits CnaA, FimA and / or FimB.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Inhibitor for urinary tract infection pathogen urinary tract pathogenic escherichia coli
ActiveCN114246868AAvoid stickingAbility to inhibit invasionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENUpper urinary tract infection
The invention discloses an inhibitor for urinary tract infection pathogen urinary tract pathogenic escherichia coli. The dictamnine can inhibit the adhesion and invasion ability of the urinary tract pathogenic Escherichia coli to urinary tract epithelial cells, inhibit the expression of urinary tract pathogenic Escherichia coli pili genes, inhibit the expression of cell adhesion receptor genes, and influence the pili form of the urinary tract pathogenic Escherichia coli. The dictamnine can be used as an effective and indirect antibacterial potential medicine for treating urinary tract infection.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Inhibitors of f18+ e coli binding
The present invention relates to blood group A / B / H determinant on Type 1 Core glycosphingolipids chains as recognition point for the FedF protein of F18-fimbriated Enterotoxigenic and verotoxinogenic Escherichia coli and the use of compounds comprising such determinants for the treatment of F18′ E. coli infections in pigs and in screening methods.
Owner:UNIV GENT
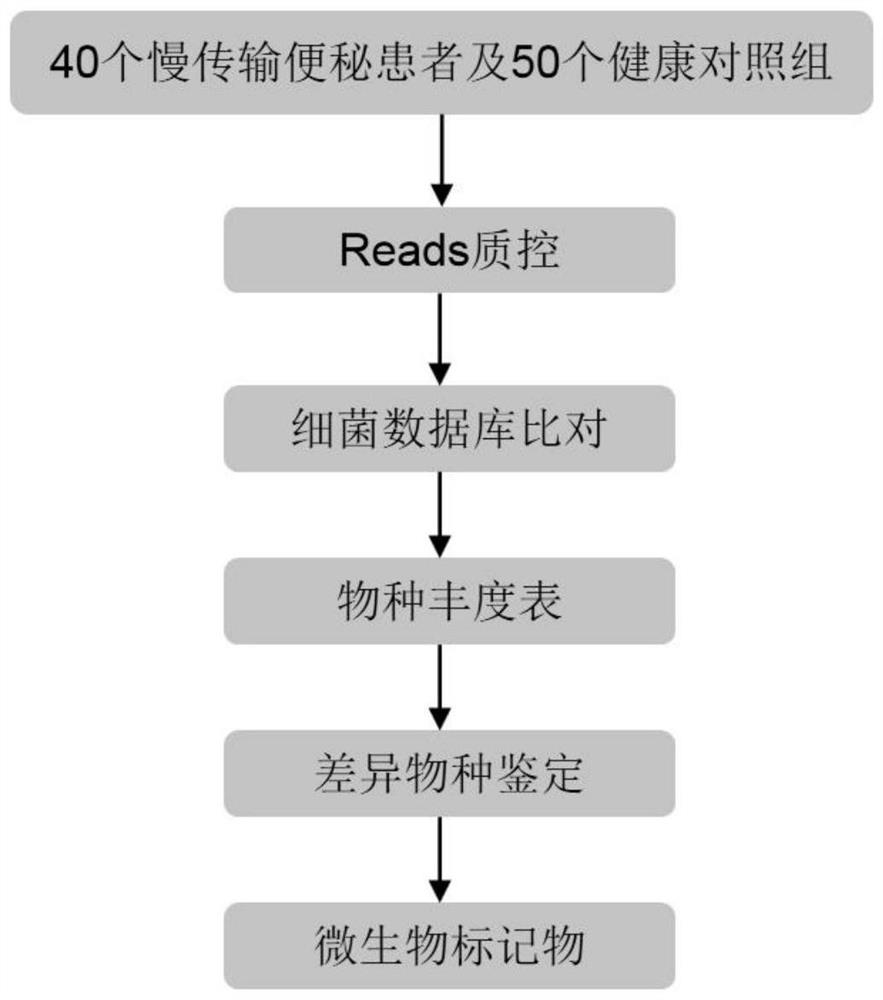
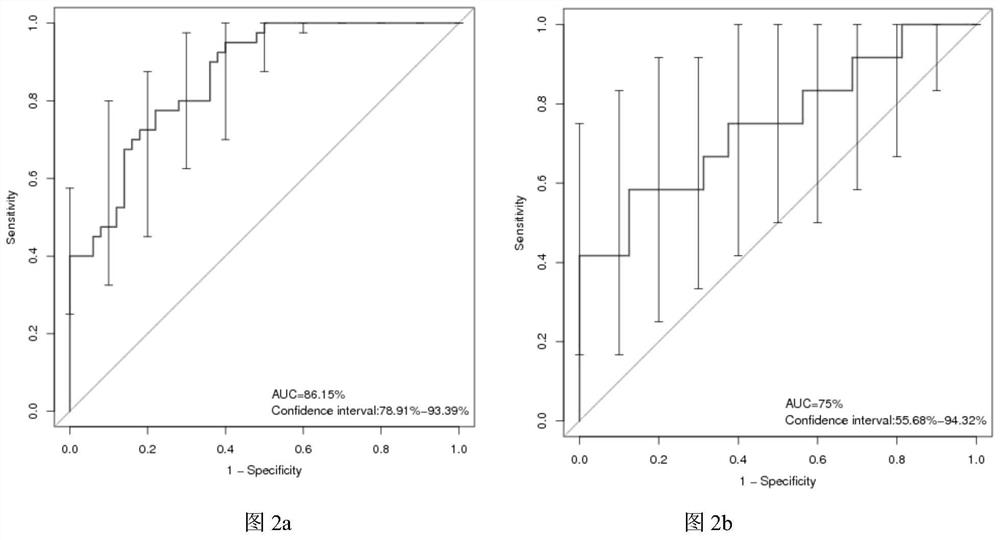
Slow-transit constipation marking microorganism and application thereof
PendingCN114410809APrevent slow transit constipationRelief of clinical symptomsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a slow transit constipation marking microorganism and application thereof, and further provides a kit according to the marking microorganism, which comprises a reagent suitable for detecting at least one strain in the marking microorganism, the invention relates to a method for preparing a microbial marker, which is characterized in that the microbial marker comprises the following strains: clostridium harzianum, Lachnospiraceae bacteria 3157 FAA CT1, a new species, Erysipastoris bacteria, Erysipastoris bacteria 2244A, Gordoniapastoris, Akkermansia muciniphila and clostridium symbiosum, and the microbial marker comprises the following strains: the clostridium harzianum, the Lachnospiraceae bacteria 3157 FAA CT1, the new species, the Erysipastoris bacteria 2244A, the Gordoniapastoris bacteria 2244A, the Akkermansia muciniphila and the clostridium symbiosum. The abundance of the microorganism provided by the invention is remarkably different in healthy people and patients with slow transit constipation, and the microorganism can be used as a marker for detecting and / or treating slow transit constipation.
Owner:上海金翌生物科技有限公司
Multiplex PCR primer set, kit and detection method for detecting 5 pili genes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
ActiveCN108588248BReliable detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMultiplexInfant animal
The invention discloses a multiplex PCR primer set, a kit and a detection method for detecting five pili genes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. The enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli that causes diarrhea in young animals often carries F4, F5, F6, F18 and F41 pili and their coding genes. The present invention designs and synthesizes a set of The primer set was specifically detected, and a multiplex PCR detection method was established for detecting five pili genes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, and a kit containing the specific primer set was assembled. Using the kit of the present invention to detect 5 pili genes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli has the advantages of strong specificity, quickness, simplicity, and good sensitivity, and is suitable for rapidly detecting the pili genes of Escherichia coli isolated from diarrhea samples of sick animals. An effective technique for screening and identifying serotypes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli pili.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com