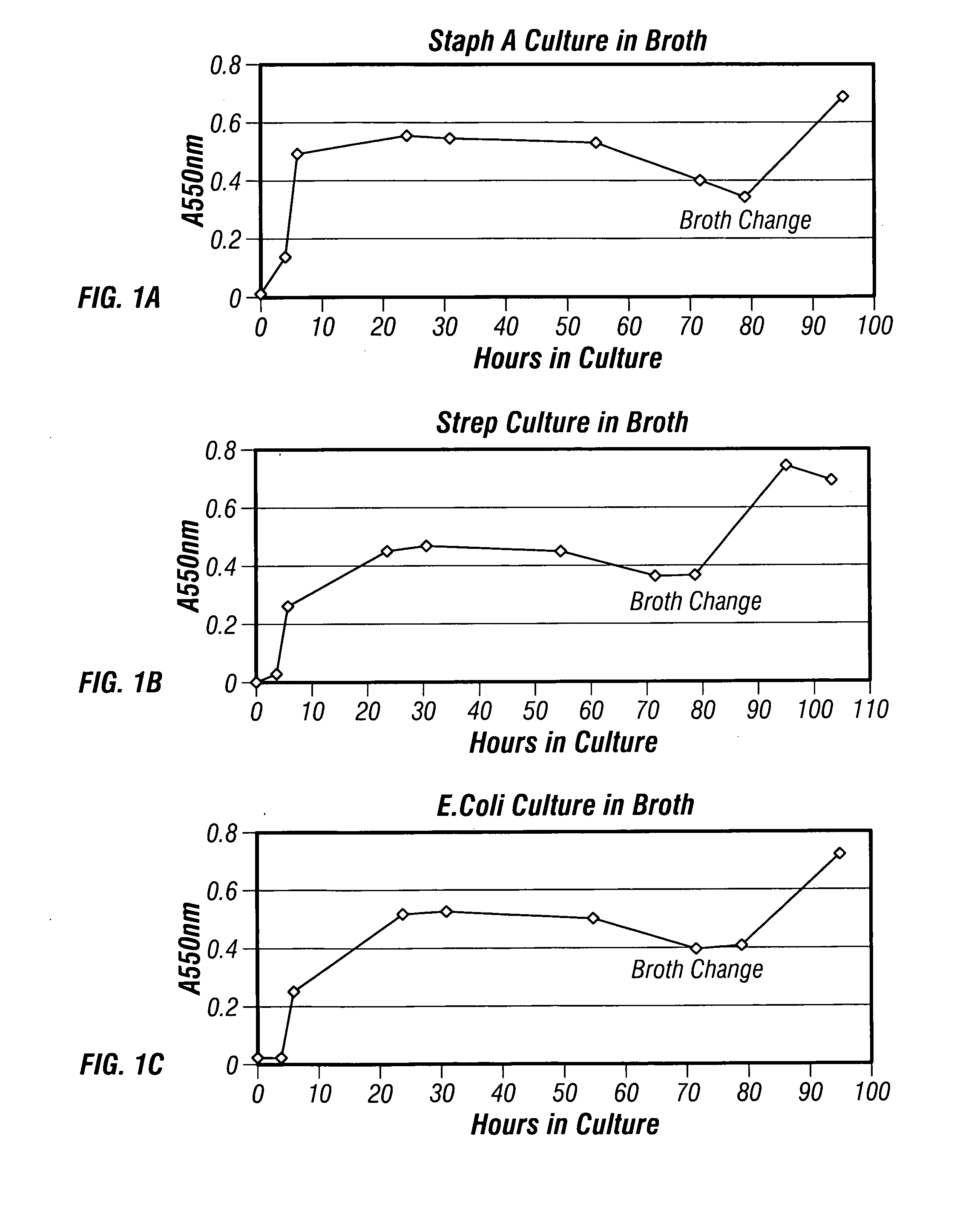
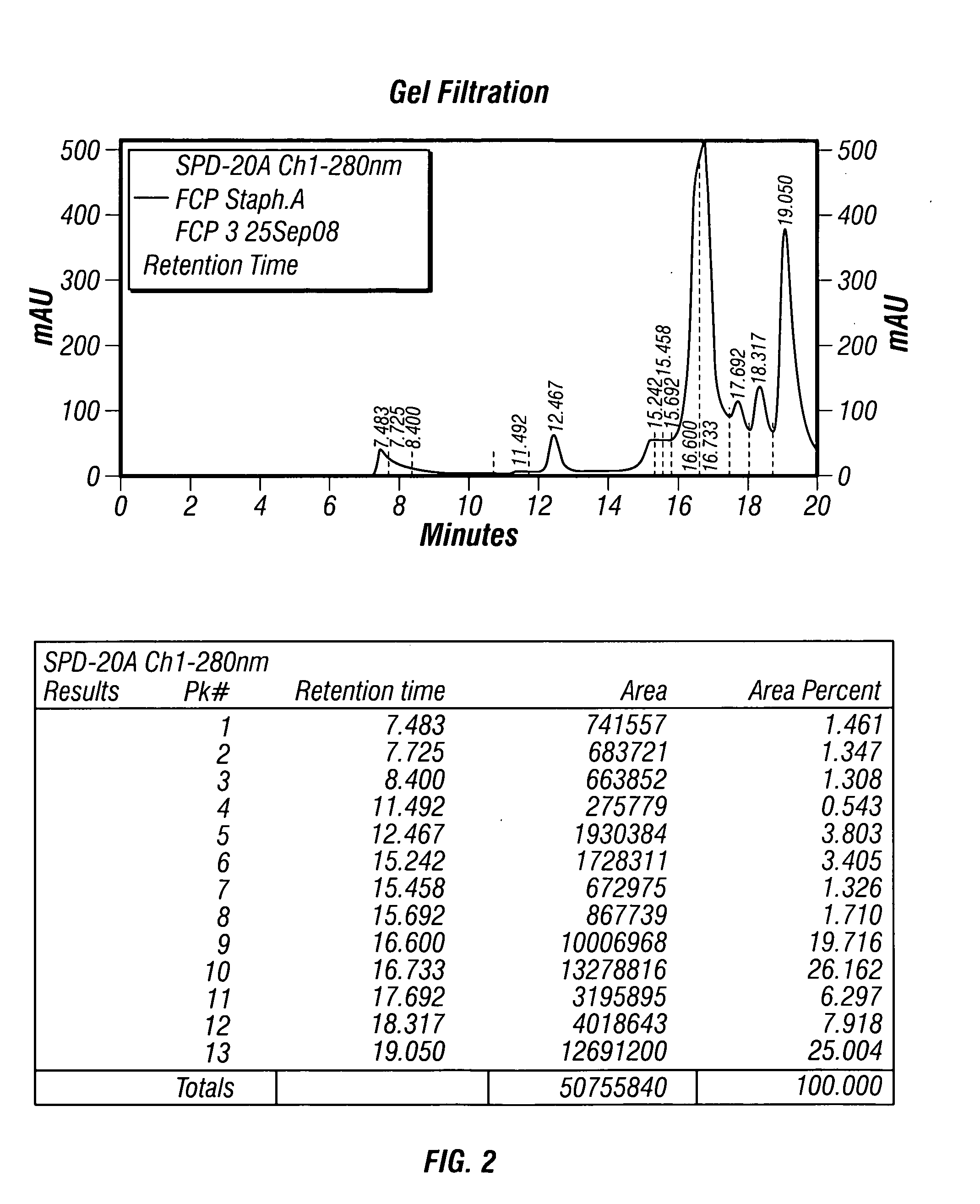
Patents
Literature
80 results about "Bacterial antigen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
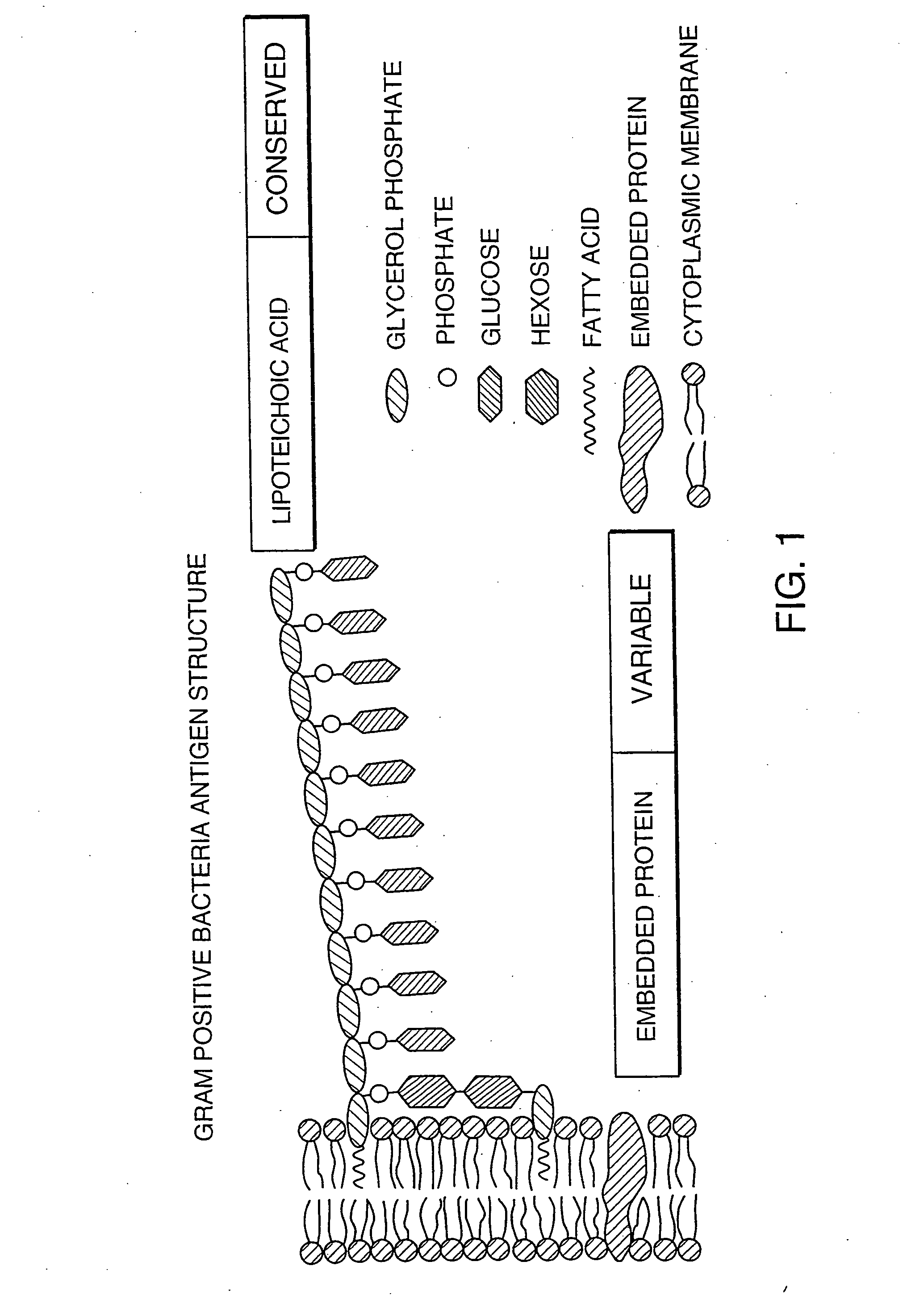
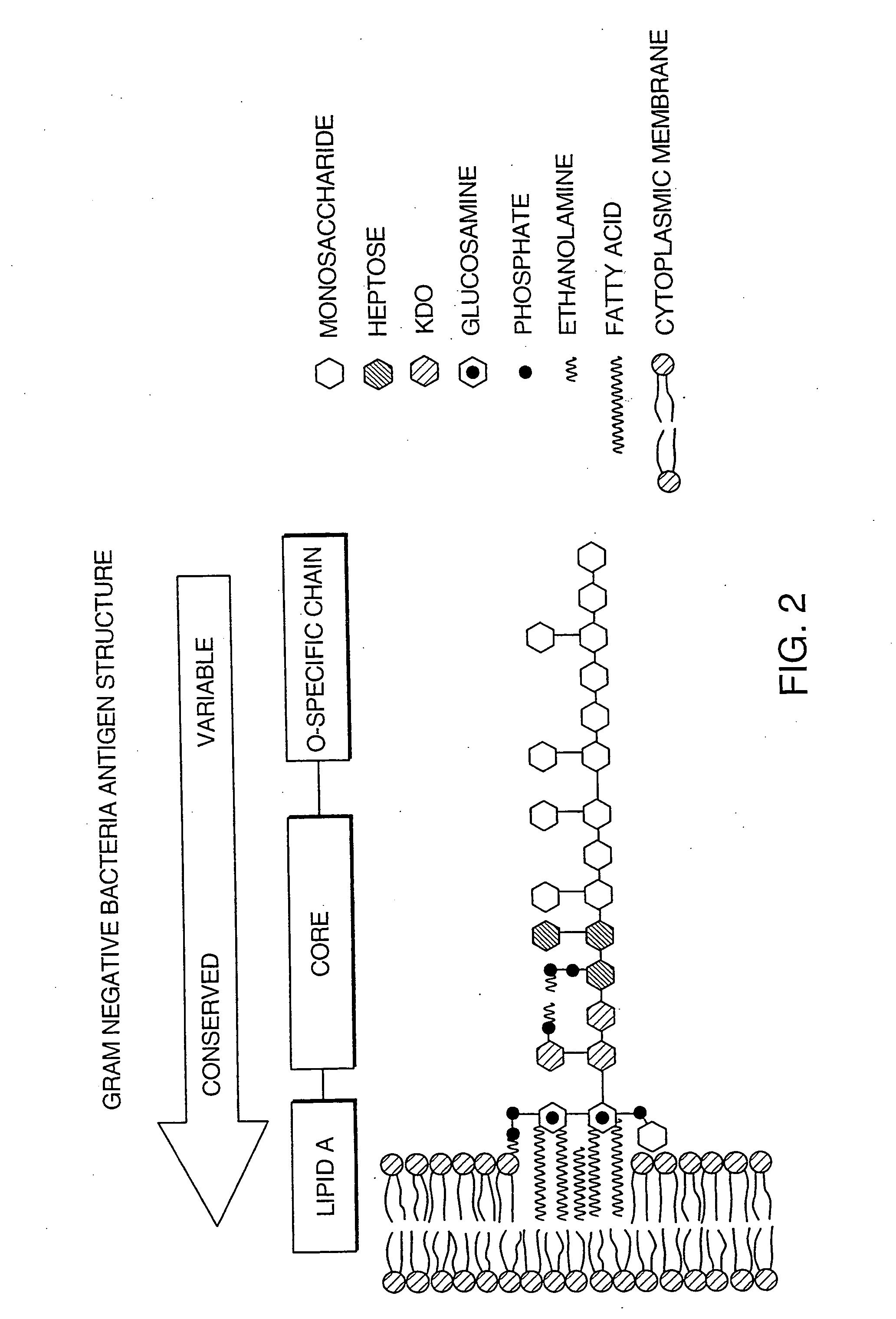
Substances elaborated by bacteria that have antigenic activity.
Affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies and methods of making and using them
The present invention describes a method for treating, removing or preventing a bacterial infection, which method comprises administering to a human suffering, suspected of suffering or at risk of suffering from Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infection, a Streptococcus infection, Escherichia coli (E. coli) infection, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) infection, Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) infection, Enterococcus faecium (E. faecium) infection and / or Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infection, an effective amount of human polyclonal antibodies affinity purified from a human blood sample with an antigenic preparation comprising cellular and / or secreted antigen(s) from bacterial cells selected from S. aureus, a Streptococcus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, E. faecium, C. difficile or a combination thereof, and optionally, wherein said affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies are purified (e.g., as made more concentrated as compared to the starting or unpurified material) relative to the same human polyclonal antibodies in the unpurified or non-affinity-purified human blood sample, e.g., intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) sample, and / or also optionally, wherein said affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies are specific for the bacterial antigens used in the affinity purification, and / or further optionally wherein the affinity purified human polyclonal antibodies are substantially free of human antibodies that specifically bind to non-bacterial antigens in the human blood sample. Pharmaceutical compositions for treating bacterial infections, comprising an effective amount of human polyclonal antibodies affinity purified from a human blood sample with an antigenic preparation comprising cellular and / or secreted antigen(s) from S. aureus, Streptococcus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, E. faecium, C. difficile or a combination thereof, are also provided.
Owner:SCANTIBODIES LAB
Use of alpha-toxin for treating and preventing staphylococcus infections
InactiveUS20090053235A1Low toxicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesAlpha-toxin
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Use of alpha-toxin for treating and preventing staphylococcus infections
InactiveUS20080131457A1Low toxicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesAlpha-toxin
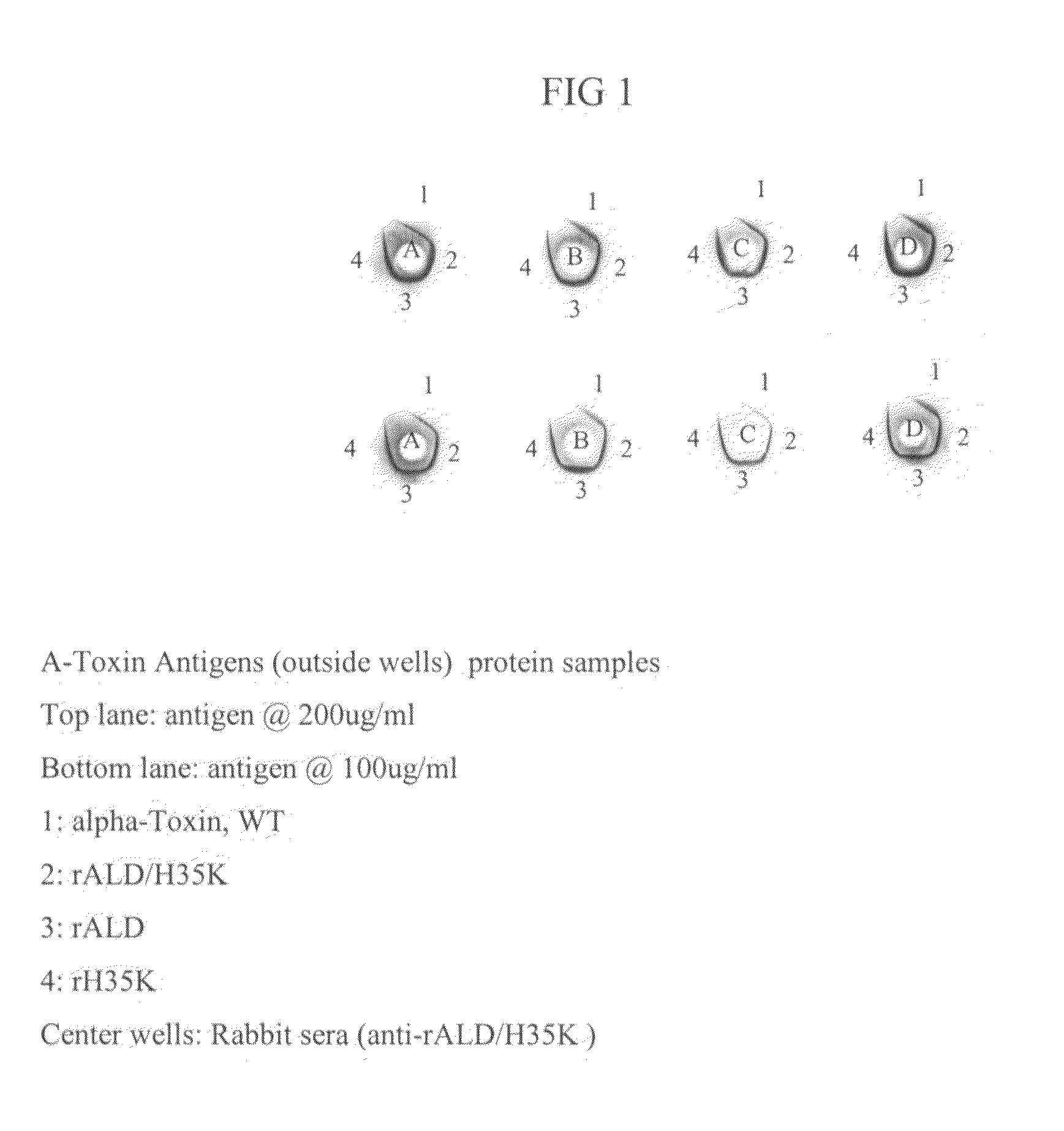
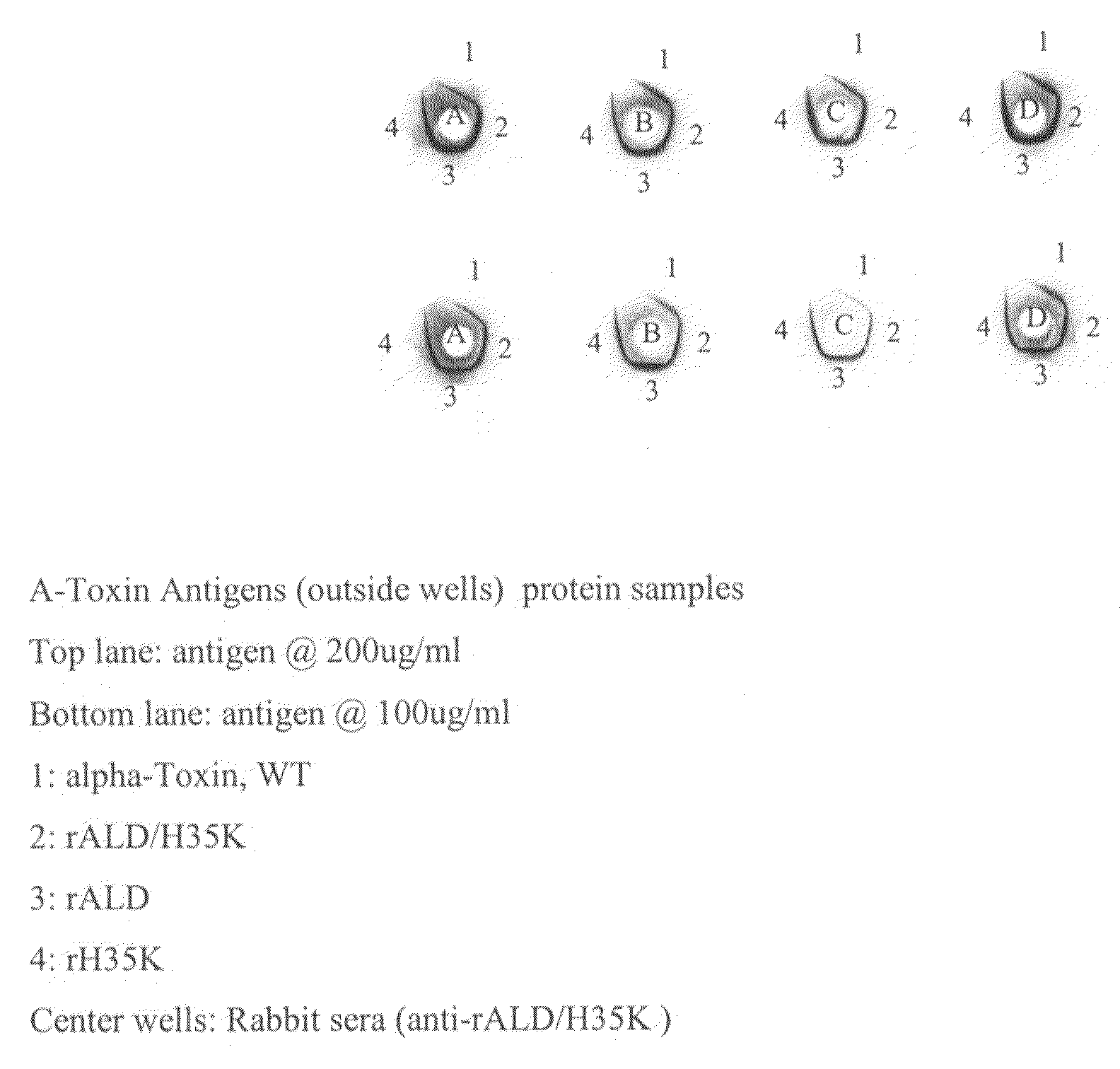
Vaccines comprising an S. aureus alpha-toxin antigen and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier are provided, and are useful for treating and preventing infections. The S. aureus alpha-toxin antigen may contain at least two alterations that reduce its toxicity and / or may be conjugated to or co-administered with another bacterial antigen. The vaccines may comprise one or more other bacterial antigens. Antibody compositions comprising antibodies to alpha-toxin and optionally one or more other bacterial antigens also are provided, and are useful for treating and preventing infections.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Purification of bacterial antigens
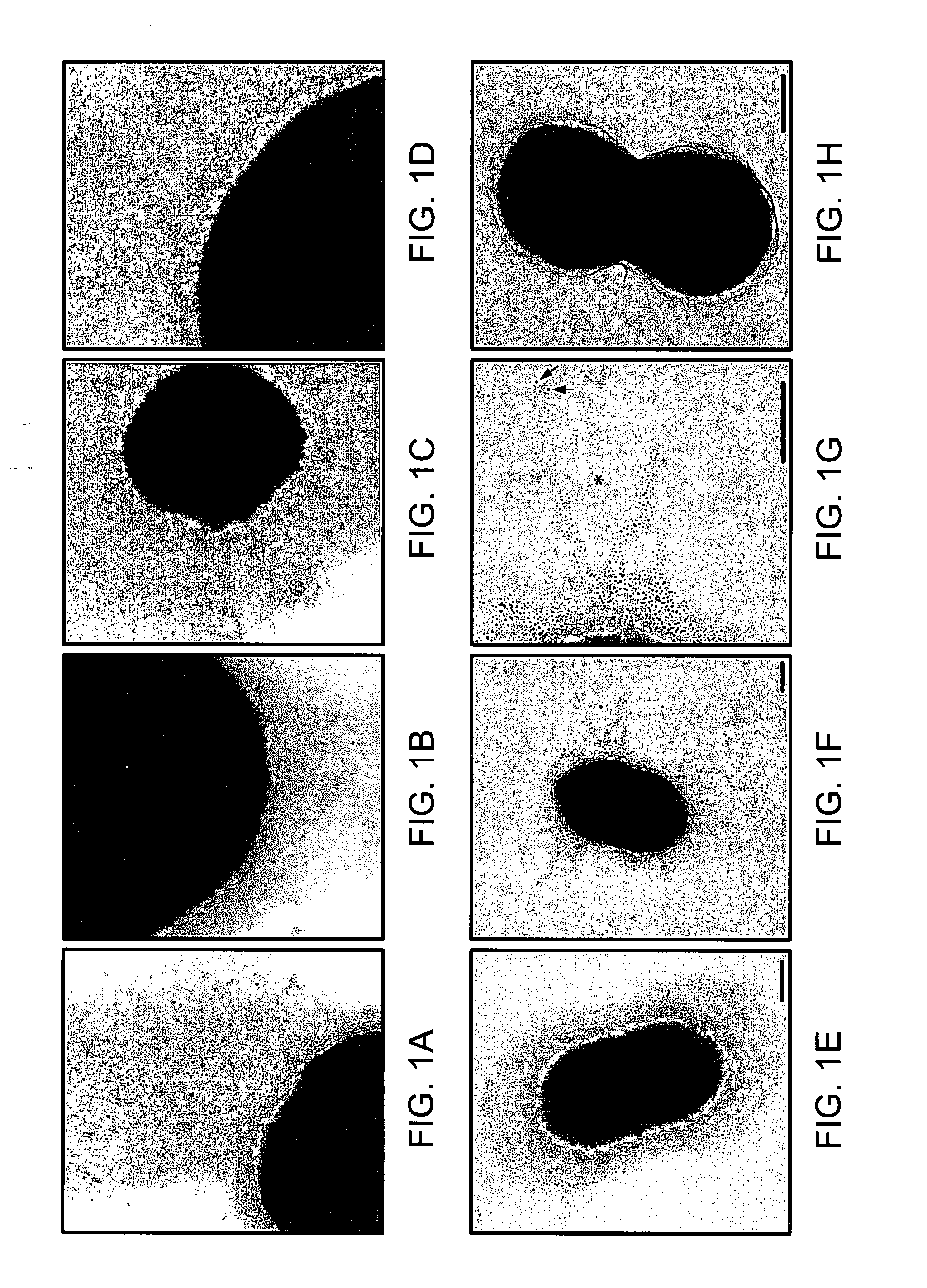
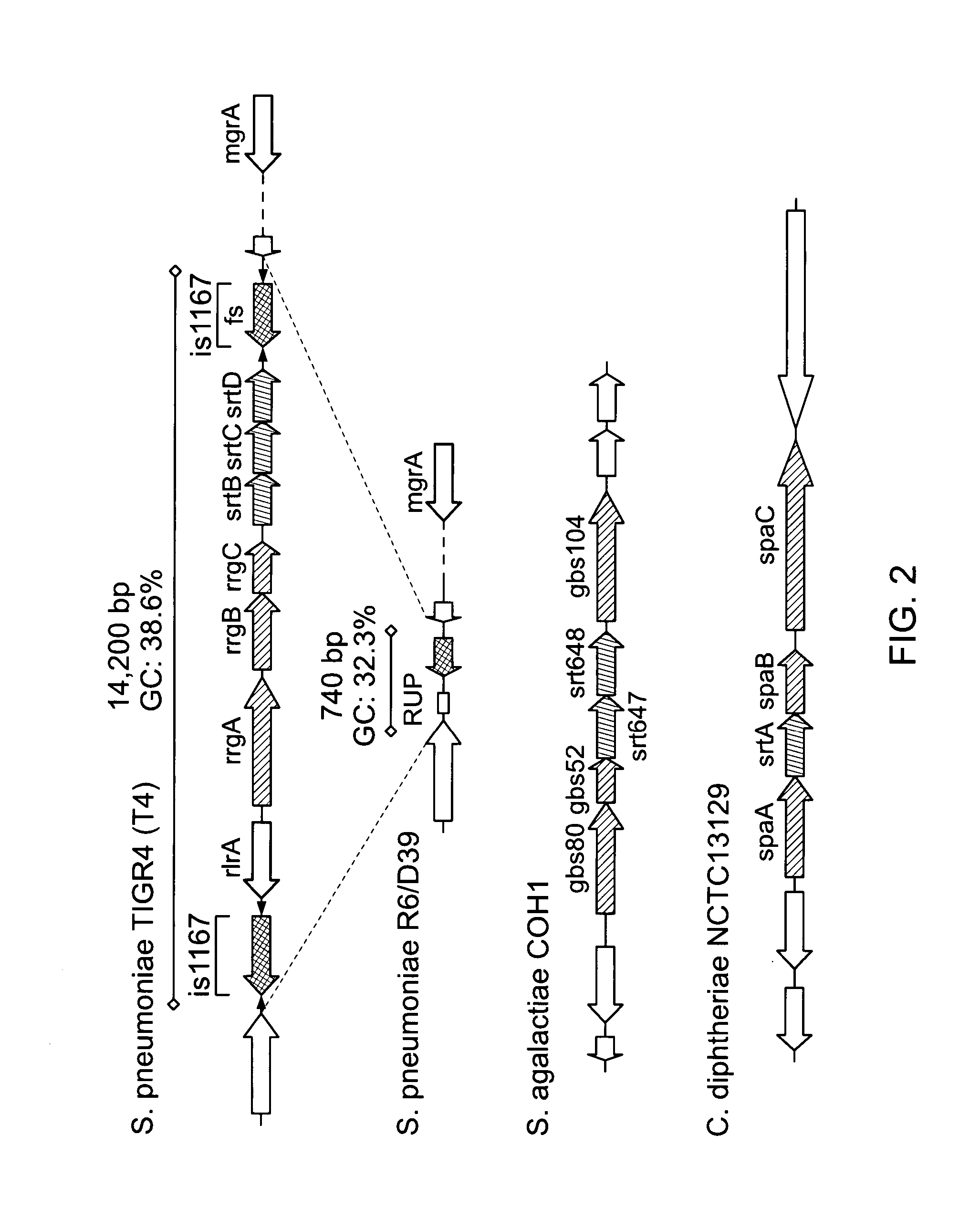
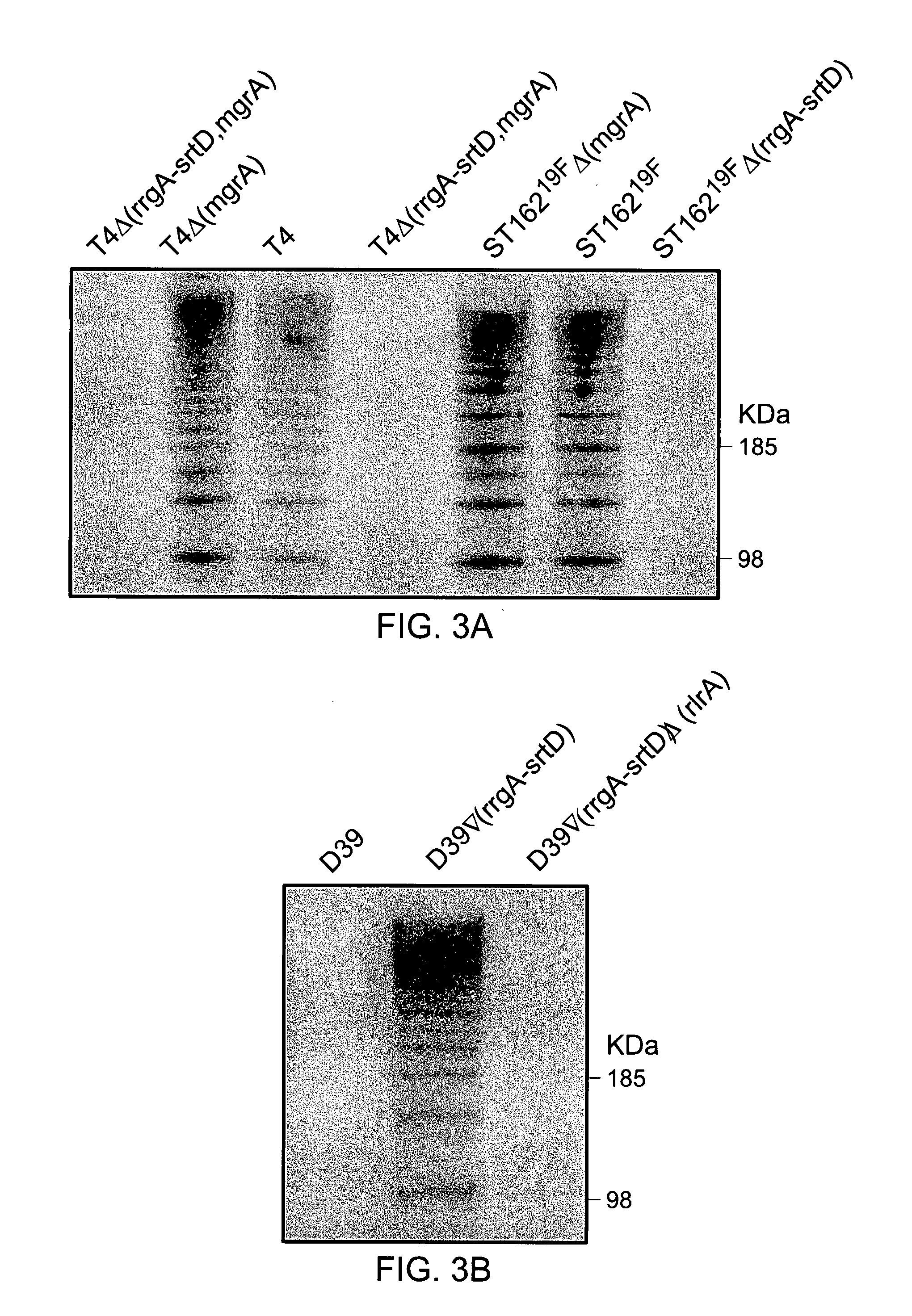
Presented are methods of isolation of pili and pilus-like structures from Gram-positive bacteria including Streptococcus pneumoniae and compositions that include such isolated pili. These compositions are useful as immunogenic compositions for the production of antibodies and immunostimulation. Also presented are methods of inhibiting Streptococcus pneumoniae, and methods of identifying inhibitors of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Modified bacterial surface layer proteins
InactiveUS20050233408A1Readily availableSure easyAntibacterial agentsFungiHeterologousProtein target
Modified bacterial surface layer (S-layer) proteins are disclosed where the modification is the insertion, at an internal location, of a heterologous polypeptide, or polypeptide of interest. The polypeptide is a binding or target protein, such as an antigen or antibody, or part thereof, in particular a bacterial antigen (e.g. from Clostridium tetani such as TTFC). The modified surface layer protein can then be expressed on the surface of the bacterial cell and used in a vaccine. Also disclosed are bacteria which have been modified to express a heterologous surface layer protein, but which do not as a wild-type possess an S-layer (such as L. casei), and modified bacteria which express only a modified surface layer protein (and not the wild-type S-layer protein). The wild type S-layer is completely replaced with the modified version where the polynucleotide encoding the modified version is integrated into the bacterial genome. The modified S-proteins can form crystalline arrays, sheets or layers that can be used to bind functional molecules (e.g. receptors) to solid surfaces (Au, silicon wafers) in biosensors.
Owner:LACTRYS OCTROOI
Bacterial antigens and vaccine compositions
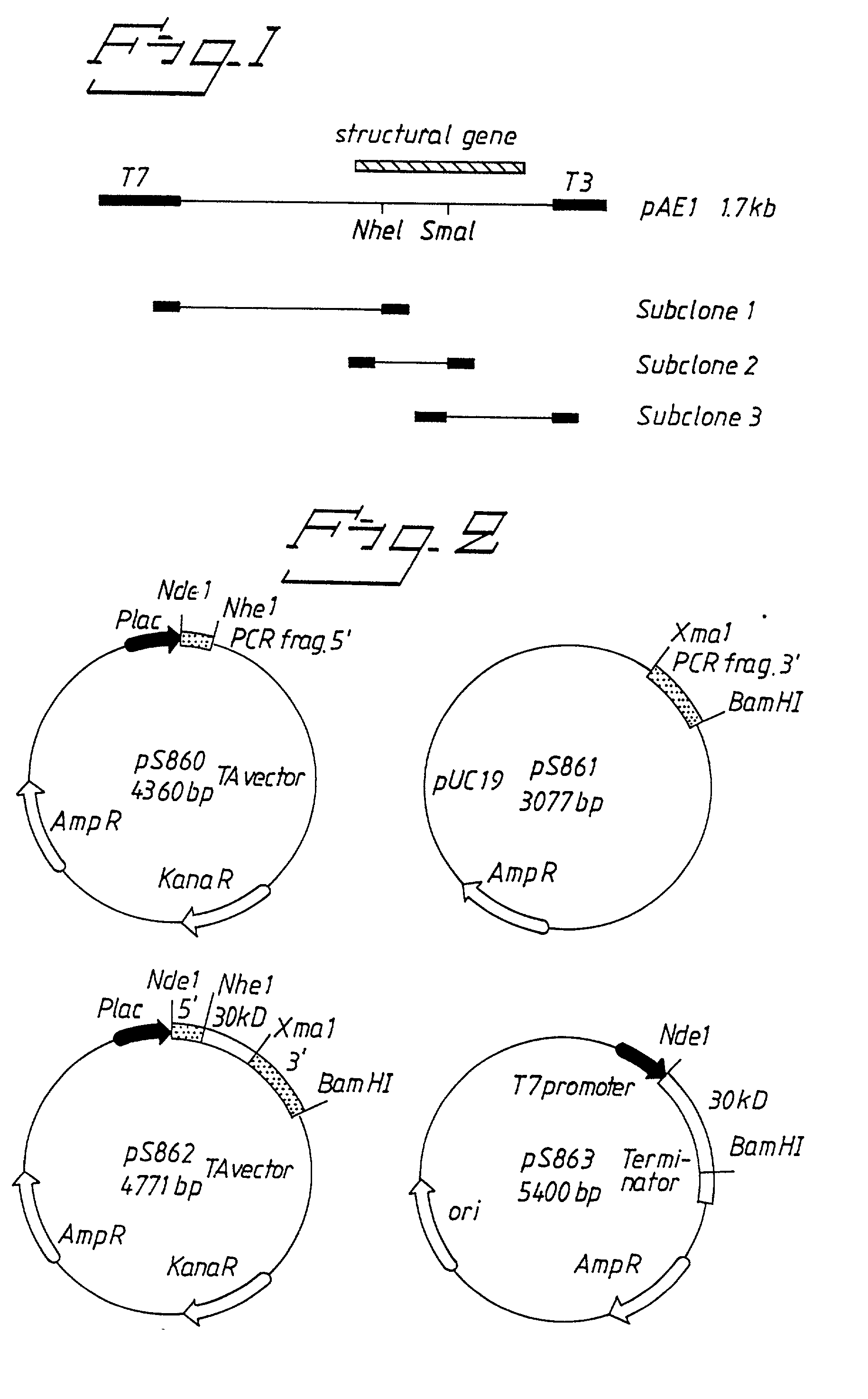
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00727 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 12, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 12, 1996 PCT Filed Jun. 3, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 38475 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 5, 1996The present invention relates to recombinant polypeptides which constitute Helicobacter pylori surface-exposed antigens with an approximate molecular weight of 29 kDa. The invention furthermore provides nucleic acid molecules coding for the said polypeptides, as well as vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The said recombinant polypeptides are useful for the diagnosis of H. pylori infections and for the manufacture of vaccine compositions which will elicit a protective immune response against such infections, said vaccine compositions being suitable for both therapeutic and prophylactic use.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Methods for producing enhanced antigenic Helicobacter sp.
InactiveUS6051416AEnhanced antigenic propertyIncrease proteinAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
Methods using in vitro processes are disclosed for inducing or enhancing expression of enteric bacterial antigens or virulence factors. The methods, therefore, produce antigenically enhanced enteric bacteria. Also methods for using the antigenically enhanced bacteria are also disclosed, as well as vaccines containing the enteric bacteria. Specifically a whole enteric bacterium or components thereof are provided by Helicobacter species. Also there are other enteric bacteria which are useful for the disclosed invention; such as Campylobacter jejuni.
Owner:BIOPORT R&D
Methods for Stimulating an Immune Response Using Bacterial Antigen Delivery System
InactiveUS20090324651A1Useful in treatment of cancerBiocideBacteriaAbnormal tissue growthTumor antigen
The invention relates to the use of the type III secretion system of bacteria to stimulate immune responses against tumor antigen(s) for treating antigen-loss variant tumors. Methods are provided for stimulating and / or increasing an immune response against tumor antigens. The invention also relates to the preparation of antigen presenting cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells using bacteria having a type III secretion system.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
ELISA kit for detecting salmonella antibody
InactiveCN106290918AImprove featuresGood repeatabilityDisease diagnosisBiological testingElisa kitGenus Orthobunyavirus
The invention discloses an ELISA kit for detecting a salmonella antibody. The kit comprises a solid-phase carrier coated with recombinant protein PagC, an enzyme-labeled antibody, salmonella negative serum and positive serum. The ELISA kit and method for detecting the salmonella antibody can be widely applied to salmonella, and application range is wide. The kit has high specificity and repeatability, the influence of temperature on reaction plates is small, and stability is high. Compared with an ELISA method with polysaccharide antigen as detection antigen, the method has the advantages that the occurrence rate of false positivity can be reduced to the maximum, and interference of other bacterial antigens in enterobacteriaceae on detection is avoided. Compared with a slide agglutination antigen detection method mostly adopted clinically, the method has the advantages that sensitivity and accuracy are higher, and detection throughput is increased greatly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Process for treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, tremors/parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, non-viral based cancers, alzheimers's disease, muscular dystrophy, attention deficit disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, complex regional pain syndrome, diabetes, neuropathic pain, spider arthritis, west nile virus, fibromyalgia, shingles, gout, migraine headaches, senile dementia, post polio syndrome, central virus deafness, asthma, chronic pain of unknown origin and hepatitis c
InactiveUS20100330117A1Improve walking abilityImprovement in their pain functionNervous disorderSsRNA viruses positive-senseProstate cancerGuillain-Barre syndrome
The present invention provides a composition and method for treating diseases associated with demyelination of the nerves, such as ALS, RA, Tremors / Parkinson's Disease, and MS, Alzheimer's disease, ALS, Guillain-Barre syndrome, atherosclerosis, schizophrenia, Tremors / Parkinsons's disease, senile dementia, Muscular Dystrophy, Attention Deficit Disorder, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, Diabetes, Neuropathic Pain, Spider Arthritis West Nile Virus, Fibromyalgia, Shingles, Gout, Migraine Headaches, Post Polio Syndrome, Central Virus Deafness, Asthma, Chronic Pain Of Unknown Origin and Hepatitis C and for treating non-viral based cancers. By administering measured doses of an immunity-provoking agent and a bacterial antigen activator, patients suffering from ALS, RA, MS, Tremors / Parkinson's Disease, and prostate cancer and others realized immediate beneficial results with no side effects.
Owner:HONOR CW M D LLC
Methods and compositions using peptide-pulsed dendritic cells for stimulating cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for tumor cells or virus-infected cells
InactiveUS20030032050A1Easy to synthesizePrevent proliferationBacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsDendritic cellT lymphocyte
A novel method of immunization, which can be used either prophylactically or therapeutically, is described. The method comprises coating of antigen presenting cells with a peptide and administering the peptide-coated cells to a mammalian subject to provoke an immune response. Useful peptides include peptides derived from viral or bacterial antigens or mutant oncogene or tumor suppressor gene products. Immunogens, constituted by the peptide-coated cells, are also described.
Owner:THE GOVT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF H & H SERVICES
Methods for detecting Campylobacter bacteria or antibodies to Campylobacter bacteria with an immunoassay
This invention relates generally to in vitro methods for inducing or enhancing expression of enteric bacterial antigens and / or virulence factors thereby producing antigenically enhanced enteric bacteria, to methods for using antigenically enhanced enteric bacteria and to vaccines comprising antigenically enhanced enteric bacteria. A Campylobacter bacterium having enhanced antigenic property is disclosed. A culture medium useful for culturing the Campylobacteria comprises 0.05% to 3% bile or 0.025% to 0.6% of one or more bile acids or salts. In addition a divalent cation chelator can also be included in the culture medium. The bacteria culture is in a growth phase at early log phase and between early log phase and stationary phase. The enhanced antigenic property is a higher level of an immunogenic antigen when compared to the antigenic property of the same bacteria grown on brain heart infusion broth. Also, antibodies to Campylobacter bacteria or Campylobacteria in samples are detected by immunoassays.
Owner:BIOPORT R&D
Papaya mosaic virus-based vaccines against salmonella typhi and other enterobacterial pathogens
An antigen-presenting system (APS) comprising one or more enterobacterial antigens in combination with a papaya mosaic virus (PapMV) or a virus like particle (VLP) derived from papaya mosaic virus isprovided. The PapMV or VLP included in the APS is capable of potentiating an immune response against said one or more enterobacterial antigens. The APS can be used, for example, as a vaccine against enterobacterial disease, such as typhoid fever. The one or more antigens comprised by the APS can be conjugated to a coat protein of the PapMV or PapMV VLP, or they may be non-conjugated (i.e. separatefrom the PapMV or PapMV VLP), or the APS can comprise both conjugated and non-conjugated antigens. Conjugation can be, for example, by genetic fusion with the coat protein, or binding via covalent, non-covalent or affinity means.
Owner:FOLIA BIOTECH +1
Method for preparing bacillus coli 0157:H7 antigen monoclonal antibody by subtractive immunization
InactiveCN101323642AEasy to getImprove immunityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEscherichia coliBALB/c
The invention discloses a method for preparing Escherichia coli O157:H7 antigen monoclonal antibody by using a subtractive immunization method. The method includes the steps that: (1) a BALB / c mouse is selected; (2) Escherichia coli, except Escherichia coli O157:H7, is used as toleragen for immunizing the BALB / c mouse and after the mouse is injected with the toleragen and then the abdominal cavity of the mouse is injected with cyclophosphamide to test the tolerance of the mouse; (3) the step (2) is repeated two weeks till the BALB / c mouse is tolerant toward the toleragen; (4) after the tolerance occurs in the BALB / c mouse, the Escherichia coli O157:H7 is used for immunizing the BALB / c mouse. The mouse which has low reaction titer with the toleragen while high reaction titer with the Escherichia coli O157:H7 is taken out and then the monoclonal antibody of the Escherichia coli O157:H7 is prepared according to the conventional hybridoma technique. Based on that antigen is not sublimated, the method of the invention is easier to obtain the monoclonal antibody of bacterial antigen so as to improve the immune effects and reduce the filtration workload of the monoclonal antibody.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
System for detecting bacteria in blood, blood products, and fluids of tissues
InactiveUS20100129836A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhole blood productMammal
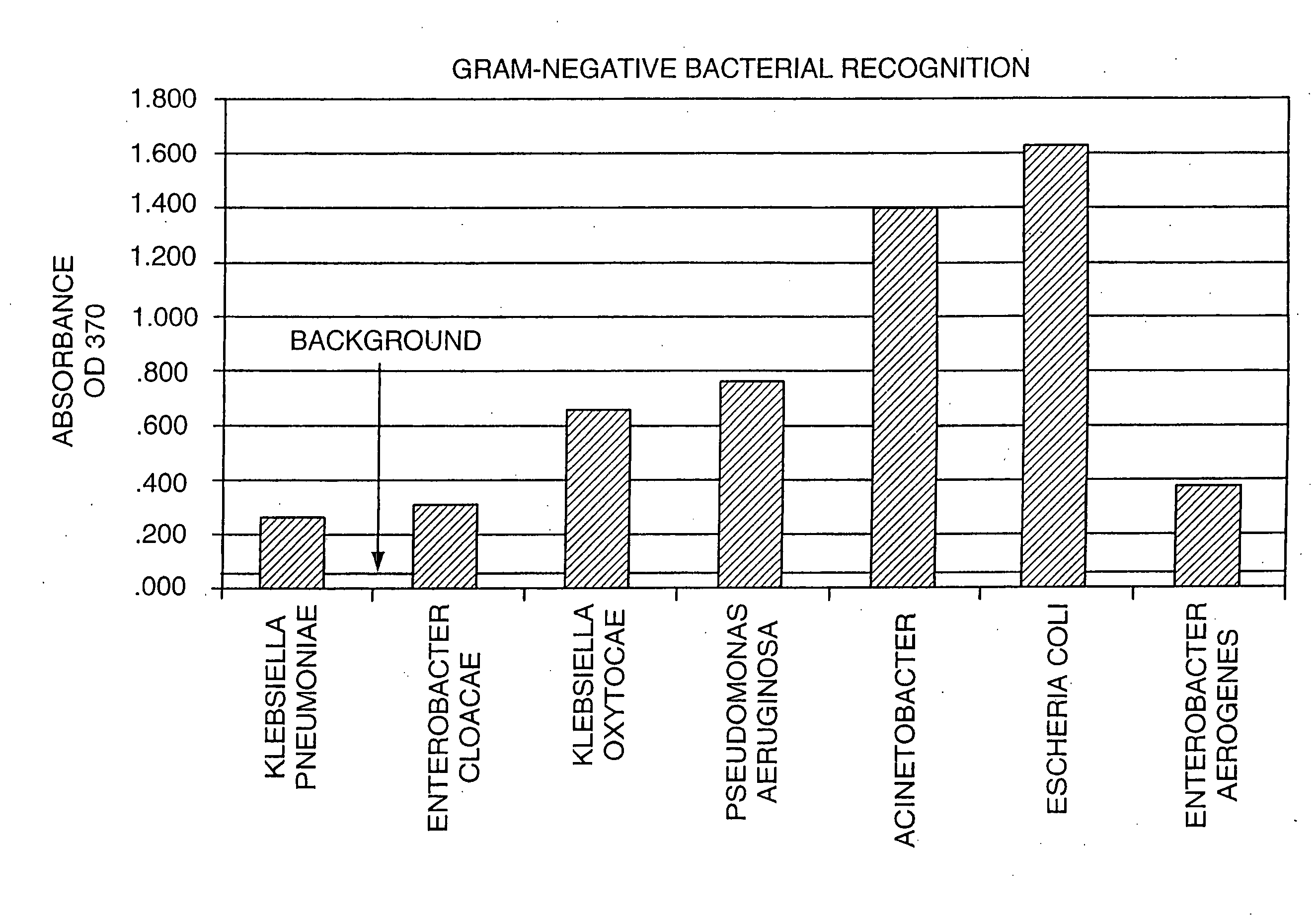
The invention provides methods for screening for the presence of a clinically relevant amount of bacteria in donor blood or a blood product from a donor mammal, particularly blood or a blood product that will be transferred from the donor mammal to a recipient mammal. The method comprises contacting a sample of the donor blood or a blood product with a set of binding agents that comprises binding agents that specifically bind to Gram-negative bacterial antigen and / or binding agents that specifically bind to Gram-positive bacterial antigen, and determining binding of the set of binding agents to the sample, wherein binding indicates the presence of a clinically relevant amount of Gram-positive bacteria and / or Gram-negative bacteria in the donor blood or blood product and no binding indicates the absence of a clinically relevant amount of Gram-positive bacteria and / or Gram-negative bacteria in the donor blood or blood product.The invention further provides methods and kits for screening for the presence of a clinically relevant amount of Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, or both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in a donor tissue by screening the fluid in which the donor tissue is stored.
Owner:VERAX BIOMEDICAL
Novel Neospora caninum Vaccine
InactiveUS20090208519A1Reduce severityPrevent and to decrease severityProtozoa antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsBALB/cBuprestis novemmaculata
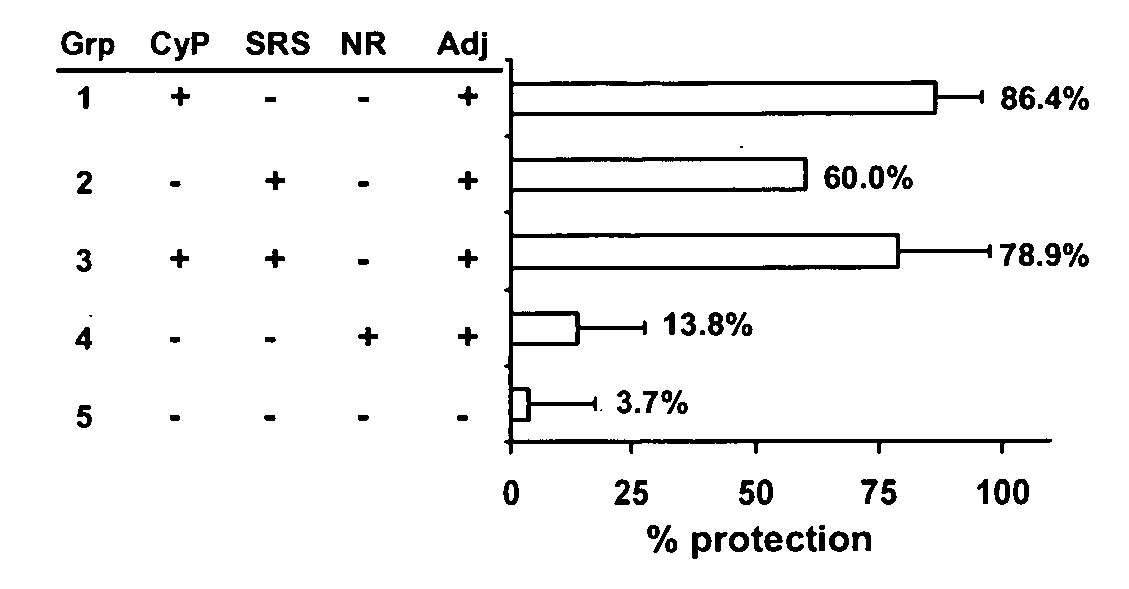
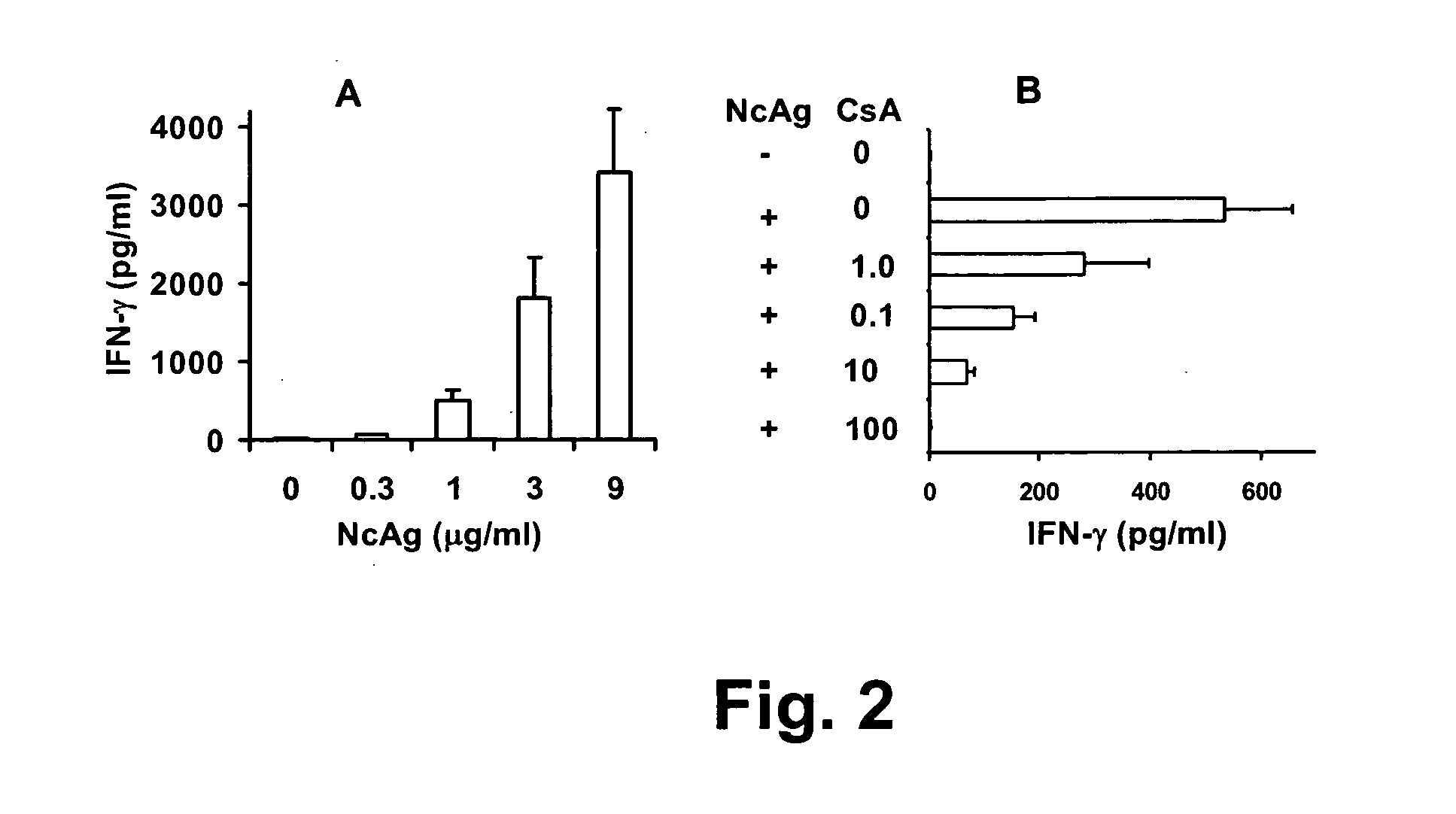
Neospora caninum is the causal agent of bovine neosporosis which results in high levels of abortion. The present study determined the protective efficacy of two Neospora antigens—Neospora cyclophilin (NcCyP) and NcSRS2. The ability of native NcCyP to upregulate mouse IFNγ was also confirmed in this study. Recombinant NcCyP or NcSRS2 were tested either alone or in combination and formulated with adjuvant ImmuMax-SR and CpG. Female BALB / c mice (n=15) of 10-12 weeks of age were immunized s.c. twice in a 2-week interval with vaccines containing either NcCyP alone, NcSRS2 alone, NcCyP plus NcSRS2, or non-recombinant bacterial antigen (NR) in 2 separate trials. All mice were challenge-infected 3 weeks following the booster immunization and necropsied 3 weeks after the challenge infection. Brain and serum were collected and Nc-specific DNA sequence in brain tissue and antibodies in serum were analyzed by PCR or ELISA / Western blotting. Results showed that mice vaccinated with rNcCyP, rNcSRS2, or both rNcCyP and rNcSRS2 responded with high levels of NcCyP or NcSRS2 specific antibodies. Overall, mice received vaccines formulated with either rNcCyP or rNcCyP and rNcSRS2 had a higher (p<0.01) percent protection when compared to the mock- or non-vaccinated mice. The groups immunized with rNcSRS2 alone exhibited slightly lower levels of protection, which was higher (p<0.05) than that of the non-vaccinated group but did not differ (p=0.06) from that of the mock-vaccinated group. The results of the present study indicate that NcCyP is a highly efficacious vaccine candidate which may be useful in protection against Neospora infection.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Borrelia burgdorferi bacterial antigen diagnosic test using polymeric bait containing capture particles
InactiveUS20130085076A1Improve abilitiesReliable, rapid, inexpensive and non-invasiveLibrary screeningImmunoassaysDiagnostic testSeroconversion
The invention relates to both a sensitive method for the capture and detection of low-abundance Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb) bacterial antigens allowing for the diagnosis of Lyme Disease using standard immunoassays. Furthermore, this invention allows the antigen to be identified in a sample of urine, serum, or other biological fluids isolated from humans and animals. The invention provides a method to capture, concentrate, separate and specifically quantify the abundance of Bb antigens using immunoassays. The detection of Bb Outer Surface Protein A is presented as an example of the disclosed invention. High sensitivity levels, low cost and easily collected biofluids allow this technology to reach patients in clinics as well as POC applications for the early detection of Lyme disease prior to seroconversion. A kit containing necessary reagents and the method for diagnosis, monitoring or assessing lyme disease using an immunoassay such as an ELISA, western blot or RPPMA is disclosed.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC +1
Anti-bacterial antibodies
InactiveUS8142780B2Efficient infectionFacilitate immune system-mediated clearanceAntibacterial agentsAntibody ingredientsMonoclonal antibodyAntigen binding
A pharmaceutical composition includes a purified antibody and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The antibody can be a monoclonal antibody having both an antigen-binding portion that binds at least one bacterial antigen and a constant region that does not bind staphylococcal protein A.
Owner:STROX BIOPHARMLS
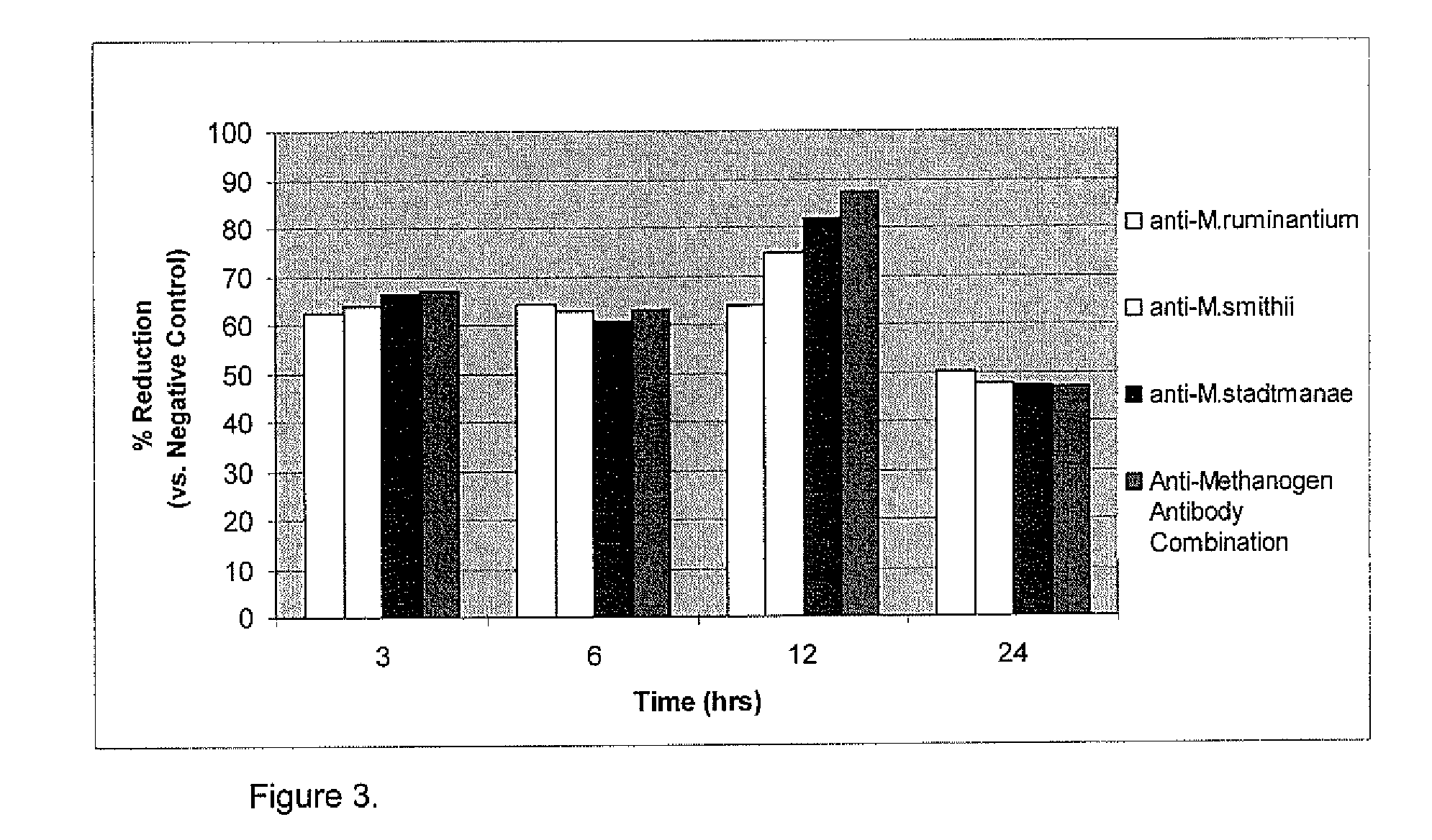
Use of avian anti-methanogen antibodies for reduction of methane production
InactiveUS7820171B2Reduce gas productionReducing methane gasPowder deliveryDigestive systemAdjuvantControl animal
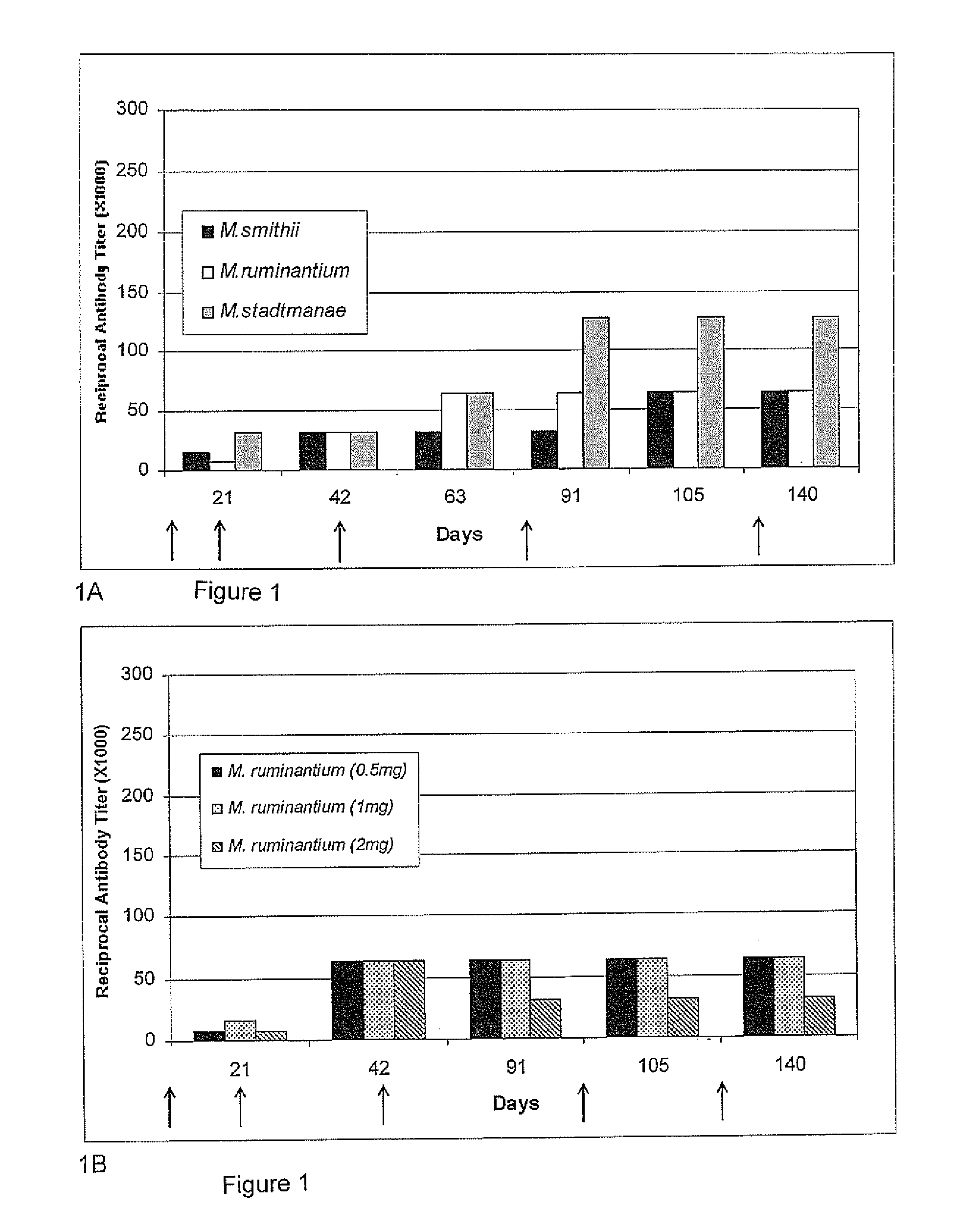
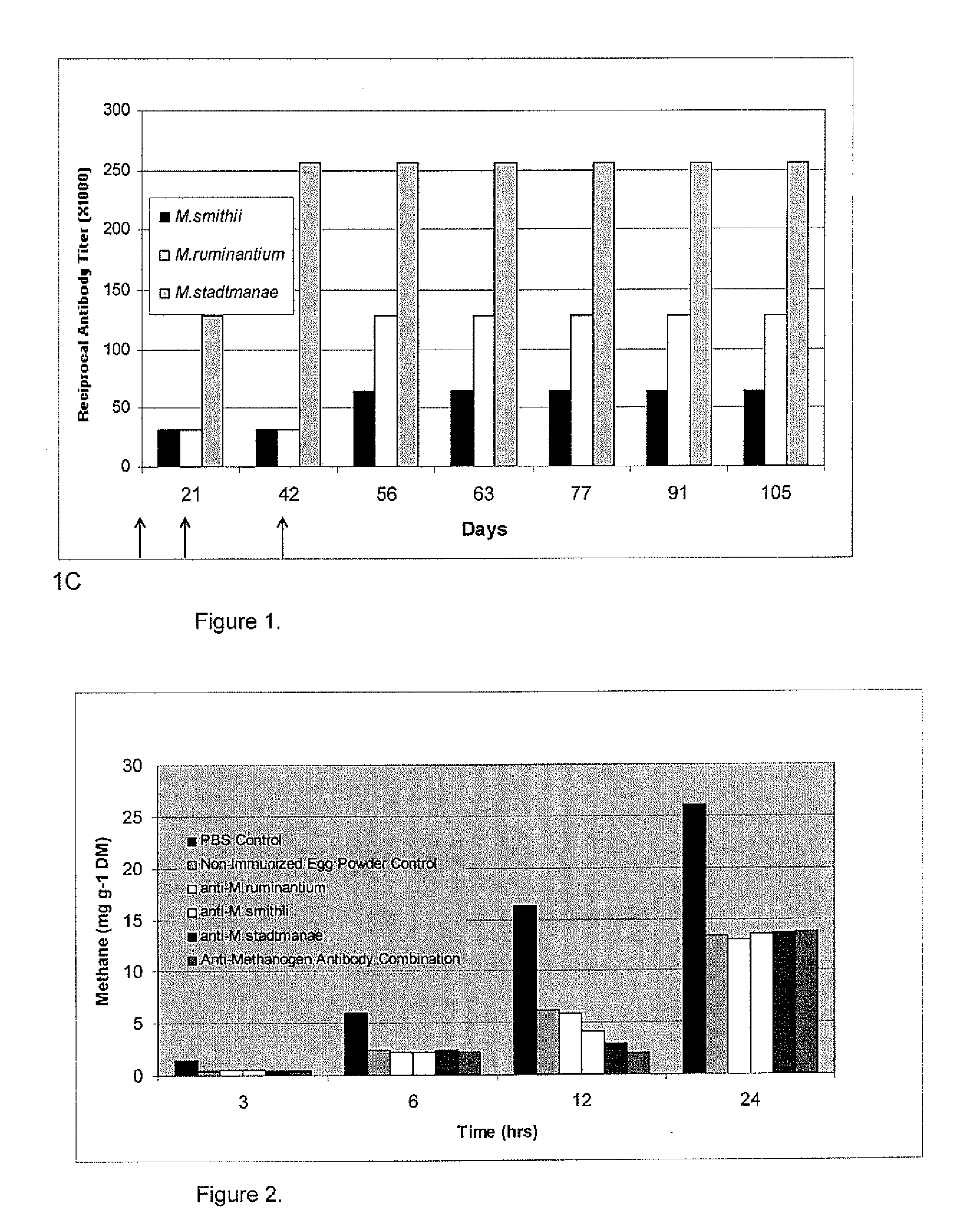
Herein, it is shown that strong specific anti-methanogen avian antibodies can be produced when chickens are immunized with an optimal dose of methane producing bacterial antigen (methanogen) formulated with an appropriate adjuvant. The antibodies can in turn be used to reduce methane gas production from an animal by administering an effective amount of the anti-methanogen antibodies to the animal, thereby reducing methane gas evolved by the animal compared to an untreated or mock treated control animal of similar age and condition.
Owner:MAITI PRADIP
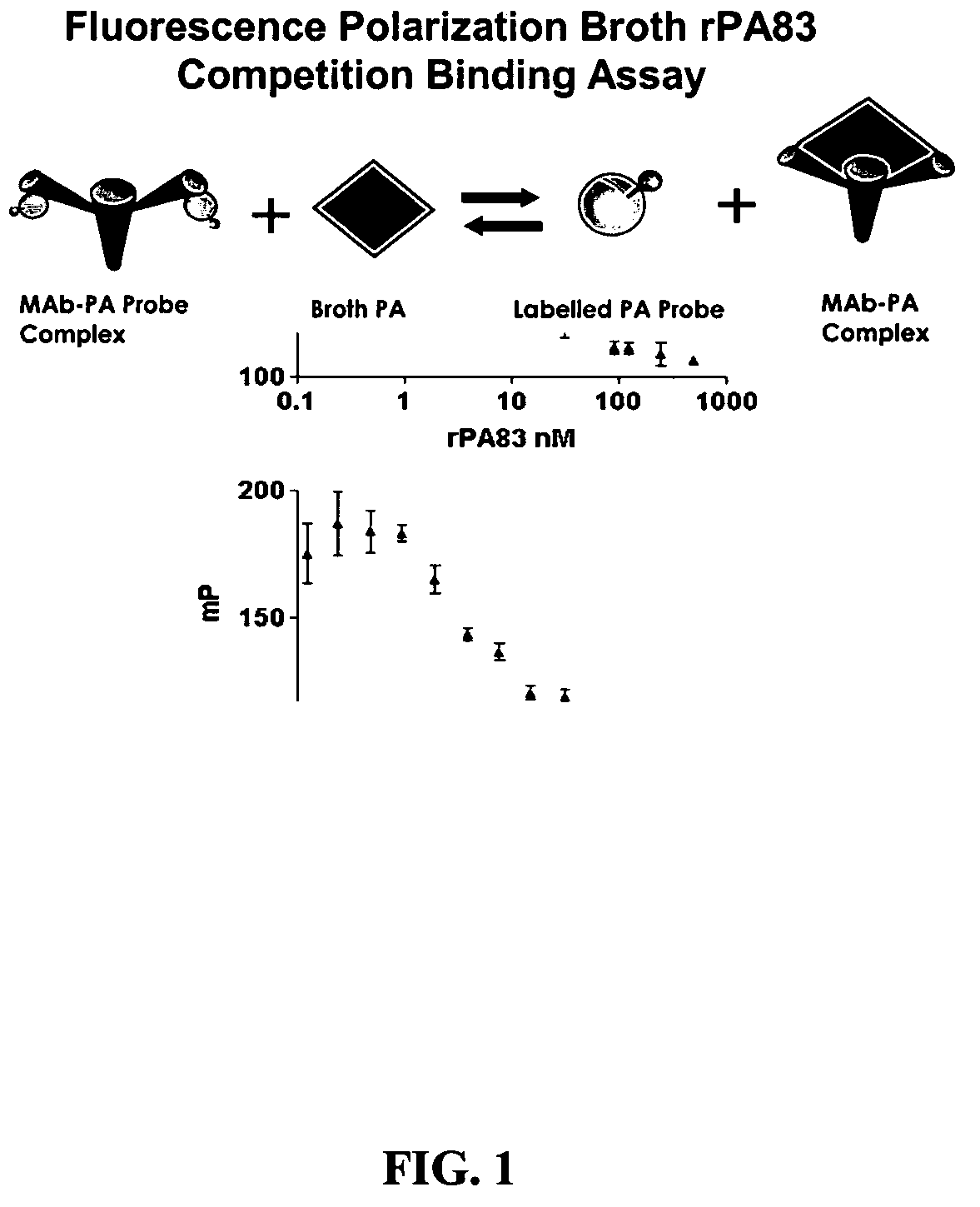
Rapid immunoassay of anthrax protective antigen in vaccine cultures and bodily fluids by fluorescence polarization
The inventive subject matter relates to a competitive method for estimating the concentration in a sample of a Bacillus anthracis protein or antibody thereof selected from the group consisting of protective antigen (PA), lethal factor (LF) and edema factor (EF). The method may employ the use of Fluorescence Polarization, FLT or FRET. The competitive methods are capable of detecting a target protein within 5 minutes within the range of 0.1 to 10.0 nM. The methods provide for the rapid detection and quantitation of bacteria, bacterial antigen or antibody in culture media or broth of growing cultures of bacteria, including B. anthracis by fluorescent methods.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Modified bacterial surface layer proteins
InactiveUS20100172938A1Mitigate and avoid degradationSure easyAntibacterial agentsFungiHeterologousProtein target
Modified bacterial surface layer (S-layer) proteins are disclosed where the modification is the insertion, at an internal location, of a heterologous polypeptide, or polypeptide of interest. The polypeptide is a binding or target protein, such as an antigen or antibody, or part thereof, in particular a bacterial antigen (e.g. from Clostridium tetani such as TTFC). The modified surface layer protein can then be expressed on the surface of the bacterial cell and used in a vaccine. Also disclosed are bacteria which have been modified to express a heterologous surface layer protein, but which do not as a wild-type possess an S-layer (such as L. casei), and modified bacteria which express only a modified surface layer protein (and not the wild-type S-layer protein). The wild type S-layer is completely replaced with the modified version where the polynucleotide encoding the modified version is integrated into the bacterial genome. The modified S-proteins can form crystalline arrays, sheets or layers that can be used to bind functional molecules (e.g. receptors) to solid surfaces (Au, silicon wafers) in biosensors.
Owner:LACTRYS OCTROOI
Recombinant phages
The present invention relates to bacteriophages for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of bacterial infections, especially mucosal bacterial infections such as Heliobacter pylori infections, in particular, it relates to modified filamentous bacteriophages, e.g. M13 phages, for such use, which bacteriophages present at the surface a recombinant protein comprising (i) a first component derived from a bacteriophage surface protein; and (ii) a second component comprising variable region sequences of an antibody to provide a bacterial antigen binding site, said second component rendering said bacteriophage capable of binding to and thereby inhibiting growth of bacterial cells involved in the etiology of said infection.
Owner:M ANG RDH SVEN
Antigenic polypeptides of chlamydia-related bacteria for diagnosis and vaccine
InactiveUS20110250222A1Avoiding false-positivesAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseDiagnostic test
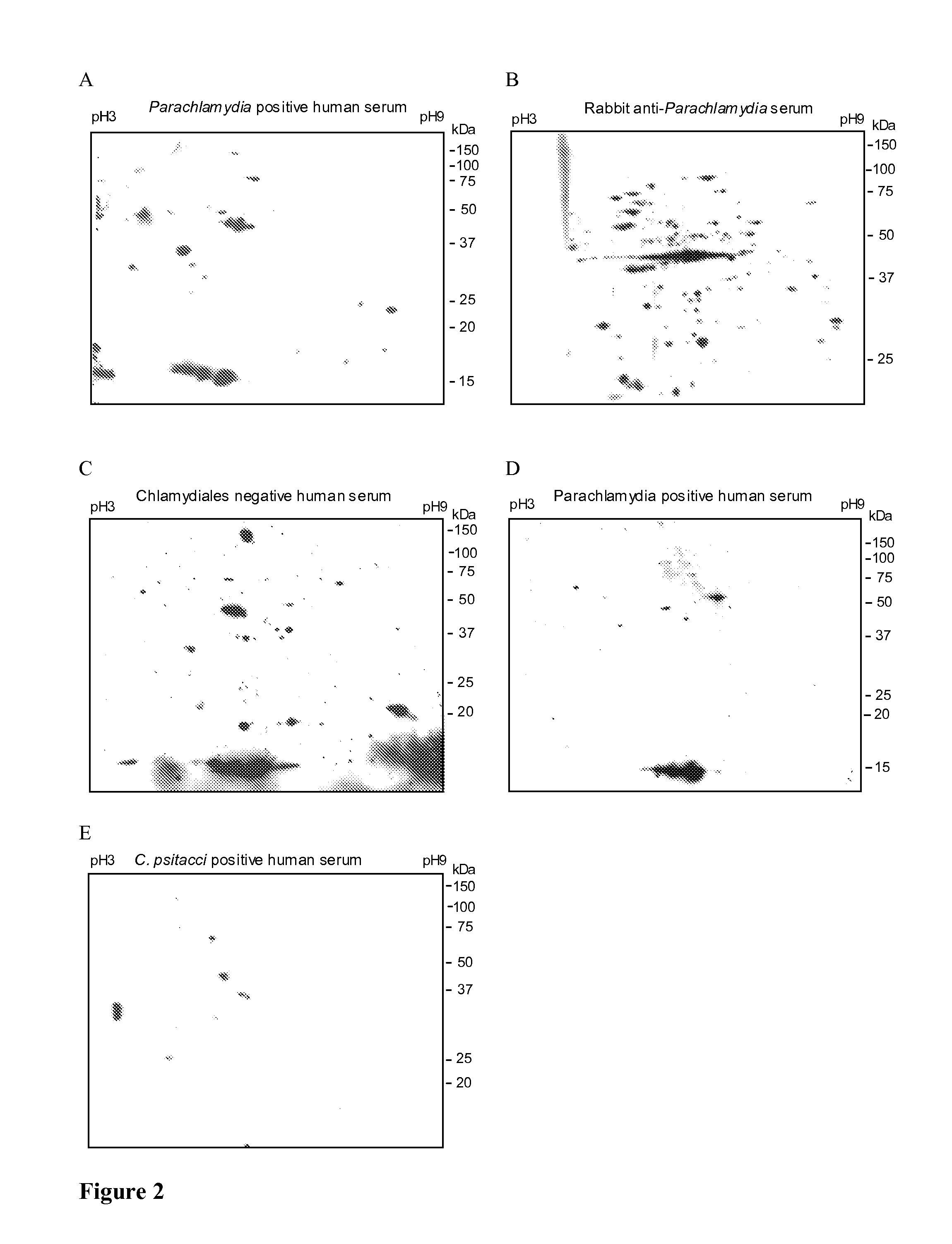
The present invention relates to the disclosed transgenic peptides for use in the diagnosis of an infection by intracellular Chlamydia-like bacteria. The invention also relates to a serological diagnostic test. The transgenic peptides are selected from the proteome of Parachlamydia acanthamoebae properties of binding to antibodies of infected human and animals. The test may give further insight in the role of this microorganism in pulmonary diseases and possibly in miscarriage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
Preparation method and application of bacillus cereus monoclonal antibody
InactiveCN105237634AHigh potencyStrong specificityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMaterial analysisCapture antibodyBacillus cereus
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a bacillus cereus monoclonal antibody. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing bacterial antigen through fixation of bacillus cereus by incubation treatment of paraform; 2, injecting the bacterial antigen so as to avoid emulsification; 3, performing short spacing impulse injection so as to quickly promote immunization; 4, planting solid tumors so as to rejuvenate tumor cells; 5, performing chemical induction and fusion; 6, performing semifluid selection so as to obtain monoclonal hybridoma; 7, performing cooperation of negative screening and positive screening so as to obtain a specific antibody; and 8, using a polyclonal antibody as a capture antibody and using a monoclonal antibody as a detection antibody to establish dual-antibody sandwich ELISA.
Owner:FUDEAN OF BEIJING TECH +1
Nucleotide with specificity to o-antigen of type-12 shigella shigae and colibacillus 0152
The present invention includes nucleotide with specificity to O-antigen of Shigella dysenteriae 12 and Escharichia coli O152; the whole nucleotide sequence of gene cluster of Shigella dysenteriae 12 to control the synthesis of O-antigen; the structure of O-antigen gene cluster, oligoneotide of glycosyltransferase gene and oligosaccharide unit processing gene original from O-antigen of Shigella dysenteriae 12; and method of obtaining bacterial O-antigen gene cluster. PCR proves the specificity to O-antigen of shigella dysenteriae 12 and Escherichia coli O152 of the present invention. The method of detecting and identifying Shigella dysenteriae 12 and Escherichia coli O152 in body and in environment with the oligoneotide of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine recombinant protein SBP, and preparation method and applications thereof
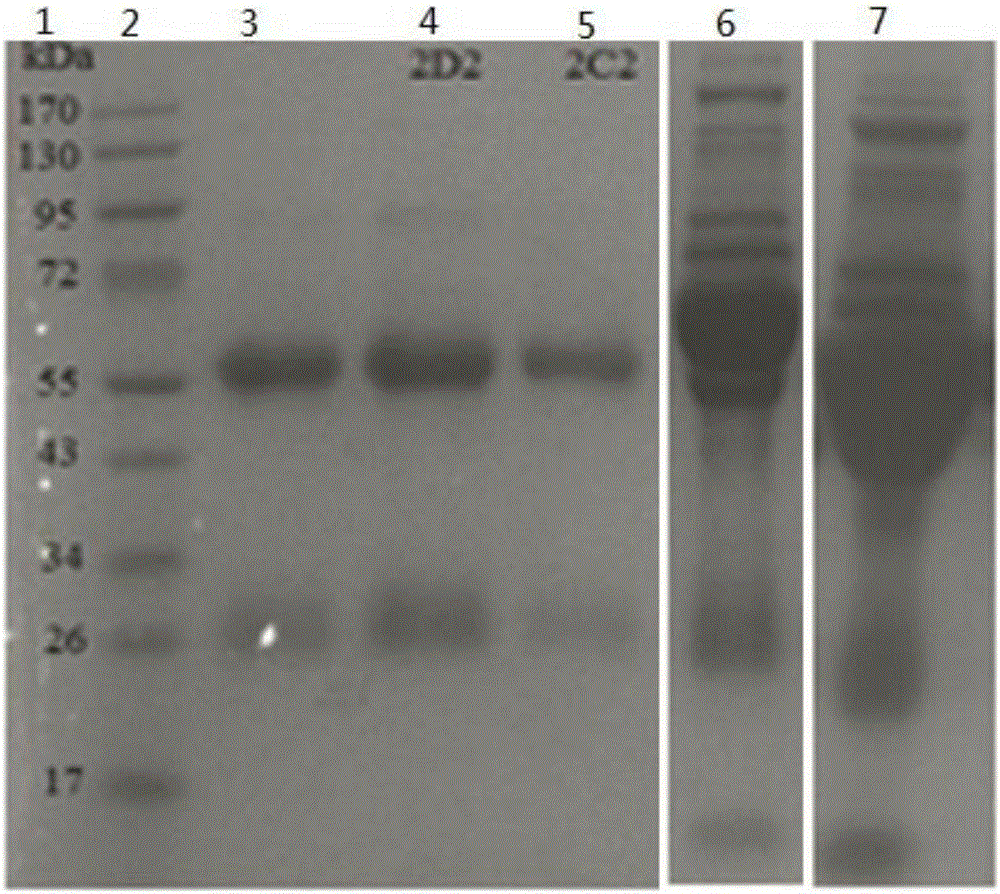
ActiveCN109293750AHas immune protectionGood immune protectionAntibacterial agentsDepsipeptidesImmunogenicityTGE VACCINE
The invention belongs to the technical field of bacterial antigen, and discloses a pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine recombinant protein SBP, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO:1; the amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO:2; a recombinant expression carrier contains a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO:1. According to the preparation method, pGEX-6p-1carrieris adopted in construction of a recombinant expression plasmid for expression of recombinant protein SBP; pGEX is an expression fusion protein carrier constructed by Smith and Johnson in 1987, and the main characteristic is that the carrier is grafted with glutathione-S-transferase (GST) with a molecular weight of 26kDa; the expressed fusion protein contains a GST label; and the label is a protein purification label. Compared with other fusion carriers, the pGEX carrier is capable of maintaining the space conformation and the immunogenicity of the purified protein as far as possible.
Owner:重庆艾力彼生物科技有限公司
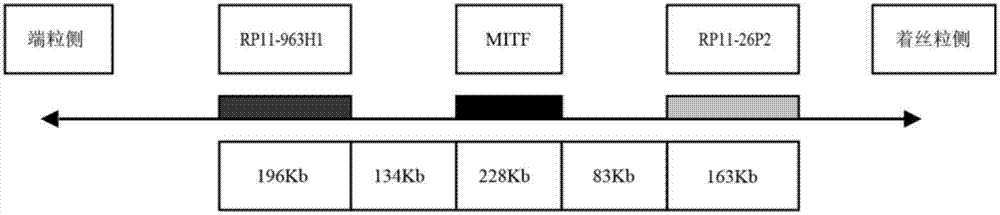
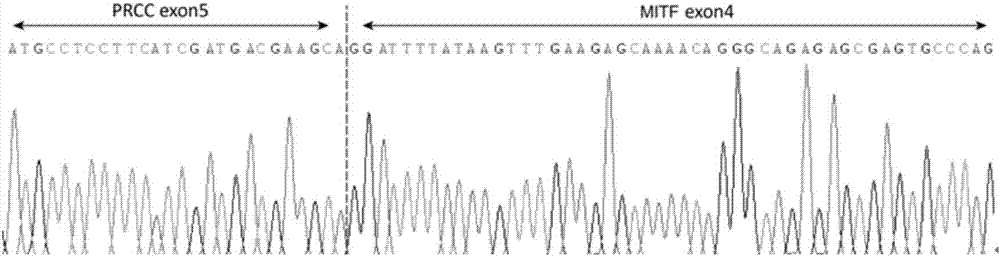
Separating probe combination for diagnosing MITF (Microphthalmia-associated Transcription Factor) translocation kidney cancer and application of separating probe combination
ActiveCN107299152AEasy to detectEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBac cloneKidney cancer
The invention discloses a separating probe combination for diagnosing MITF (Microphthalmia-associated Transcription Factor) translocation kidney cancer and application of the separating probe combination. The separating probe combination for diagnosing the MITF translocation kidney cancer consists of a BAC (Bacterial Antigen Complex) cloning probe RP11-26P2 and a BAC cloning probe RP11-963H1. According to the separating probe combination disclosed by the invention, a fluorescence labeled DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) combination combined at two ends of an MITF gene is designed according to the characteristics of the MITF translocation kidney cancer; in-situ hybridization, detection fusion and signal separation are carried out on the basis of paraffin embedded tissue sections, so that the accuracy rate of diagnosing tumors can be greatly increased. The probe combination for detecting the MITF translocation kidney cancer, provided by the invention, has the advantages of convenience,` quickness, reliability and high success rate, can be used for preparing a diagnosis kit for the MITF translocation kidney cancer, and provides a novel tool for quickly and accurately diagnosing the MITF translocation kidney cancer.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Use of alpha-toxin for treating and preventing staphylococcus infections
InactiveUS20150165015A1Low toxicitySerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBacteroidesAlpha-toxin
Vaccines comprising an S. aureus alpha-toxin antigen and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier are provided, and are useful for treating and preventing infections. The S. aureus alpha-toxin antigen may contain at least two alterations that reduce its toxicity and / or may be conjugated to or co-administered with another bacterial antigen. The vaccines may comprise one or more other bacterial antigens. Antibody compositions comprising antibodies to alpha-toxin and optionally one or more other bacterial antigens also are provided, and are useful for treating and preventing infections.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Bacterial antigens and vaccine compositions
Owner:BOLIN INGRID +1
Haemophilus parasuis test paper strip and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104251905AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysisPolyvinyl chlorideEngineering
The invention discloses a haemophilus parasuis type 5 colloidal gold formed kit and a preparation method thereof. The test paper strip comprises a sample pad, a colloidal gold pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and an absorbent pad which are orderly connected and fixed on a PVC (polyvinyl chloride) plate, and also comprises a detection line and a quality control line, the sample pad comprises a water absorbent material, the colloidal gold pad is coated with antigen, the detection line and the quality control line are located on the nitrocellulose membrane and are separated from each other, the antigen coating the colloidal gold pad is haemophilus parasuis OPPA (oligopeptide binding protein A) fusion protein, the detection line is haemophilus parasuis type 5 antigen, and the quality control line is haemophilus parasuis whole bacterial antigen polyclonal antibody IgG. The test paper strip has the advantages of good specificity, strong sensitivity and repeatability.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com