Papaya mosaic virus-based vaccines against salmonella typhi and other enterobacterial pathogens
A technology for Salmonella typhi and enterobacteria, which is applied in the field of vaccines based on plant virus particles and can solve problems such as inability to mediate virus attack
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0165] Preparation of APS
[0166] The present invention provides APS, which comprises PapMV or PapMV VLP derived from recombinant PapMV coat protein. The present invention also provides a recombinant PapMV VLP, which comprises one or more antigens or affinity parts fused to coat protein genes. These recombinant coat proteins can multimerize and assemble into VLPs. The method for gene fusion of an antigen or an affinity peptide for linking an antigen and coat protein is described below and in the examples. Methods of chemically cross-linking various molecules with proteins are well known in the art and can be used.
[0167] Papaya mosaic virus
[0168] PapMV is known in the art and is available under ATCC No. PV-204 TM Obtained, for example, from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). The virus can be stored in and purified from host plants (e.g., Carica papaya and Antirrhinum majus) according to standard procedures (see, for example, Erickson, JW & Bancroft, JB, 1978, Viro...
Embodiment I
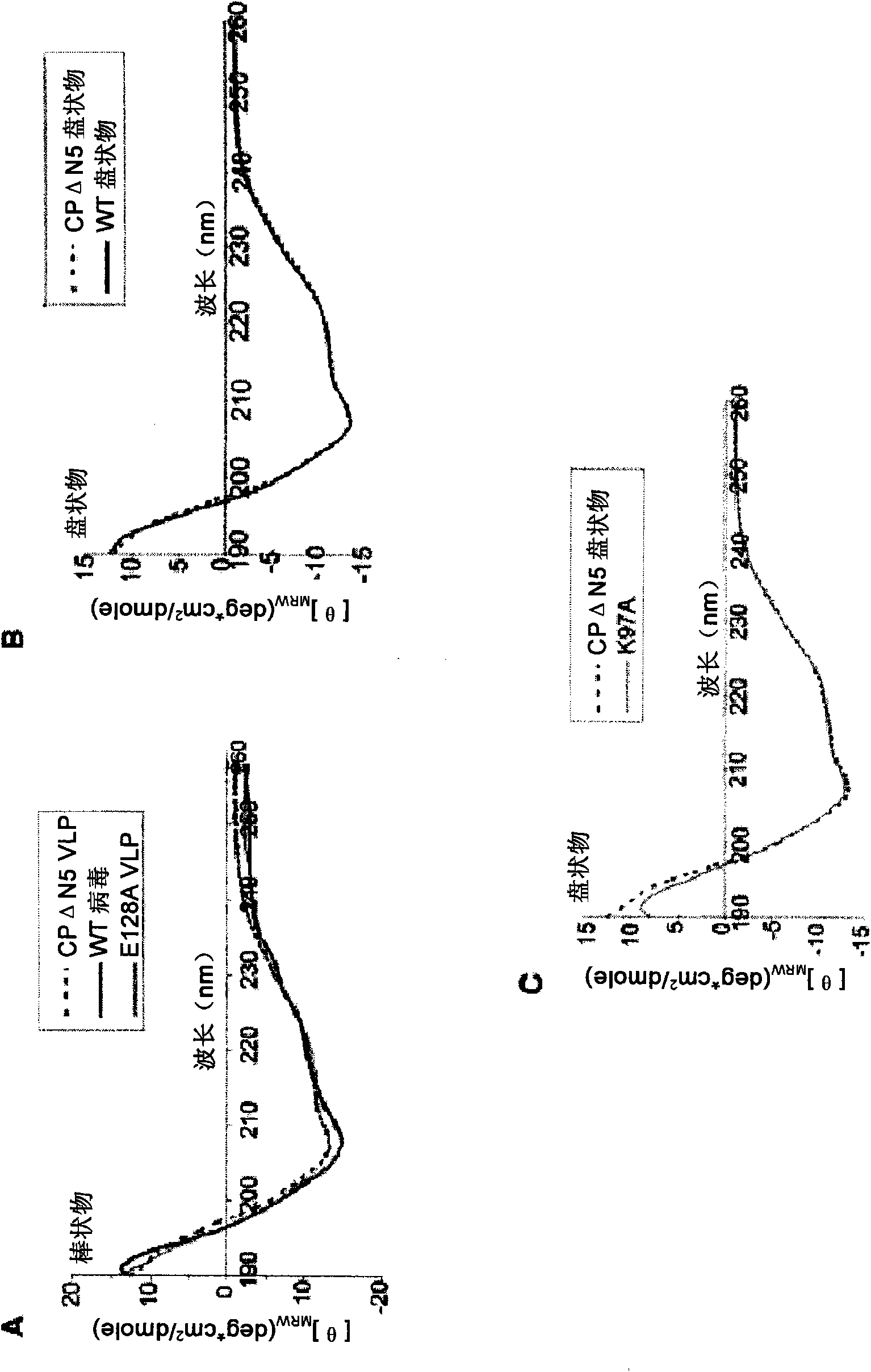
[0236] Example I: Effect of mutation on RNA binding and self-assembly of PapMV coat protein
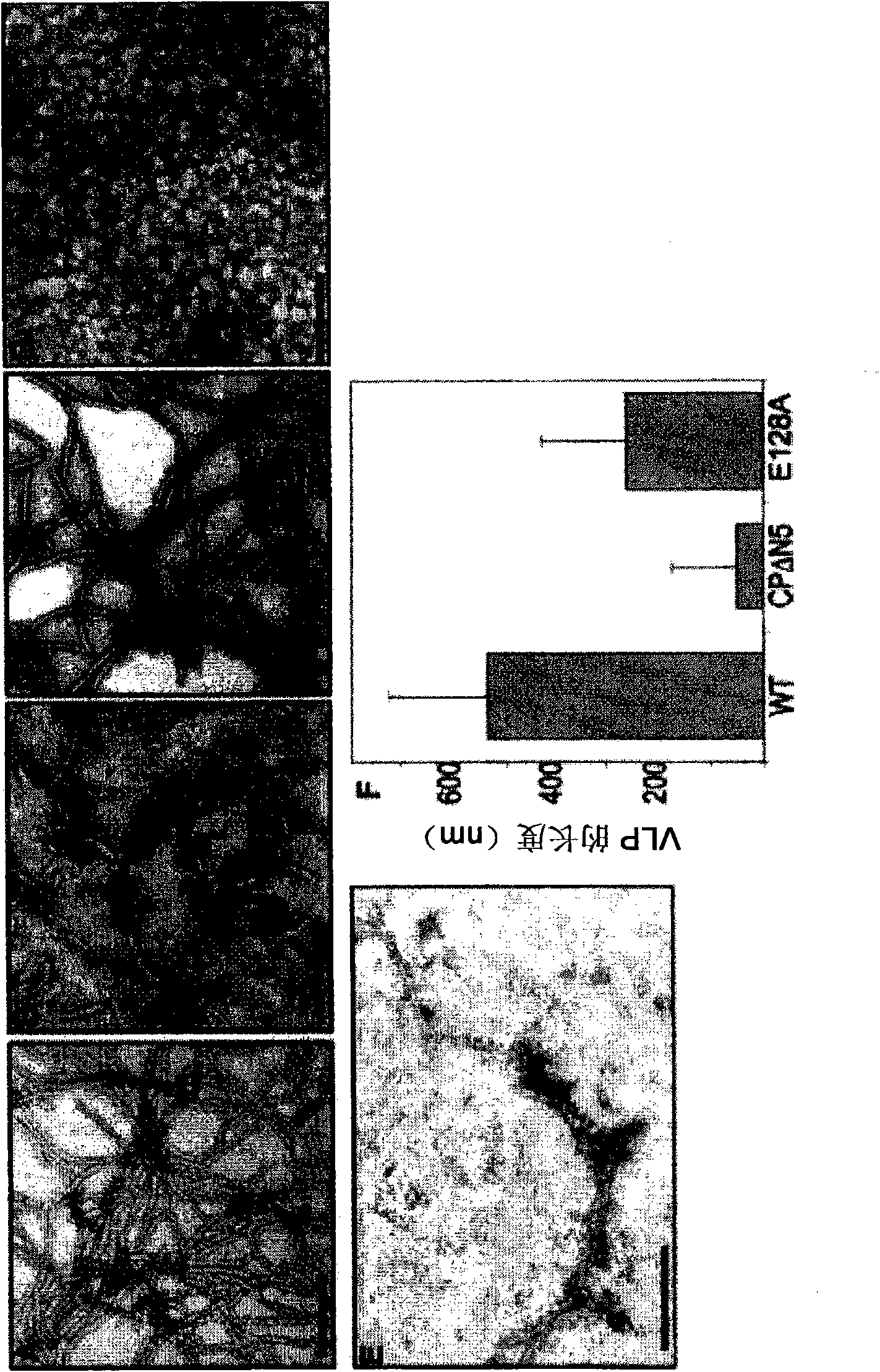
[0237] According to the method listed in the literature Tremblay, MH. et al., 2006, FEBS J., 273:14-25, a series of mutants were prepared using PapMV coat protein (CP ΔN5; as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3), the PapMV The coat protein has an alanine inserted at position 2, and its N-terminal 5 amino acids are deleted from the WT sequence. According to the alignment of the amino acid sequence of 19 potato X virus CP between amino acids 90 to 169 of PapMV CP (which shows that in most potato X viruses, the amino acid corresponding to the 128th position of PapMV CP is A, but in PapMV In E) and the report that the charged residues R104, K133, K137 and R161 may be involved in the interaction with genomic RNA and play an important role in the assembly and packaging of the viral genome (Abouhaidar, & Lai, 1989, J. Gen. Virol. 70, 1871-5), the following mutants were prepared: E128A; K97A; R104K105R108 / A;...
Embodiment II
[0267] Example II: Preparation and modification of PapMV gp100 and PapMV Flu VLP
[0268] Cloning of PapMV CP gene
[0269] The CPΔN5PapMV coat protein (CP) gene was used in the following examples and prepared according to the method described in the document Tremblay, M-H. et al., 2006, FEBS J., 273:14-25. In short, the following oligonucleotide primers were used to amplify the CP gene from isolated viral RNA by RT-PCR.
[0270] Forward CPΔN5 primer:
[0271] 5′AGTC CCATGG ATCCAACGTCCAATCTTCTG-3'[SEQ IDNO:27]
[0272] Reverse CPΔN5 primer:
[0273] 5′-ATGC GGATCC TTACTAATGGTGATGGTGATGGTGTTCGGGGGGTGGAAG-3'[SEQ ID NO:28]
[0274] The PCR product was digested with NcoI and BamHI, and inserted into the vector pET-3d to prepare a CPΔN5PapMV VLP clone, in which the N-terminal 5 amino acids were deleted from the WT sequence. PapMV VLP also has an inserted alanine at position 2 of the recombinant protein. The amino acid sequence of CPΔN5PapMV VLP clone is as follows figure 1 C[SEQ ID NO: ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com