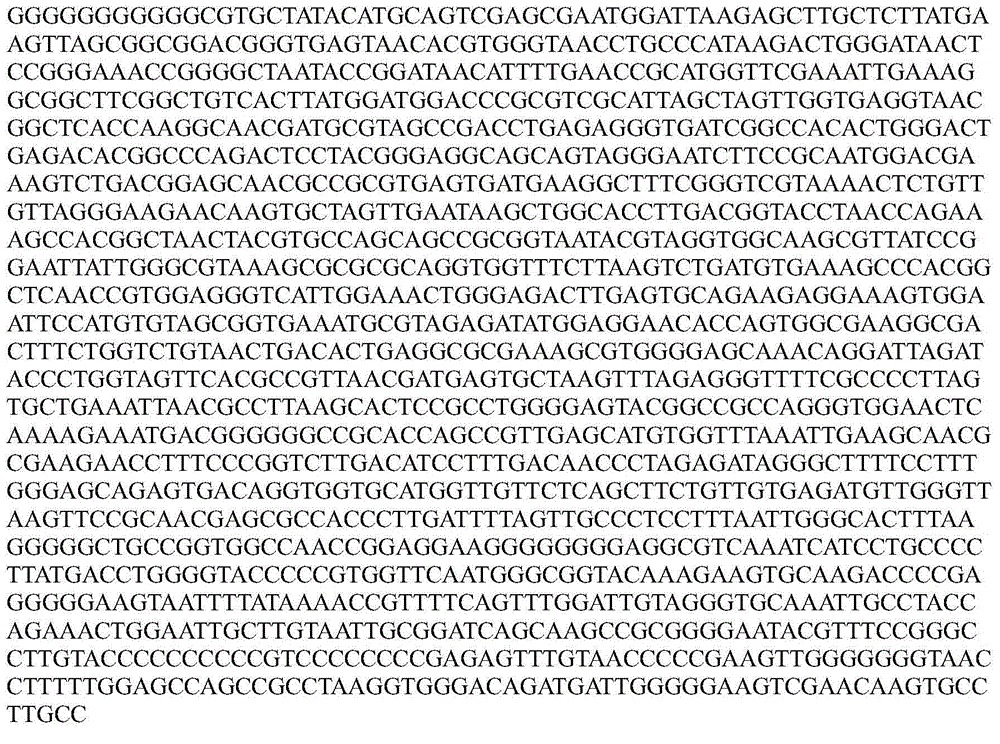Patents
Literature
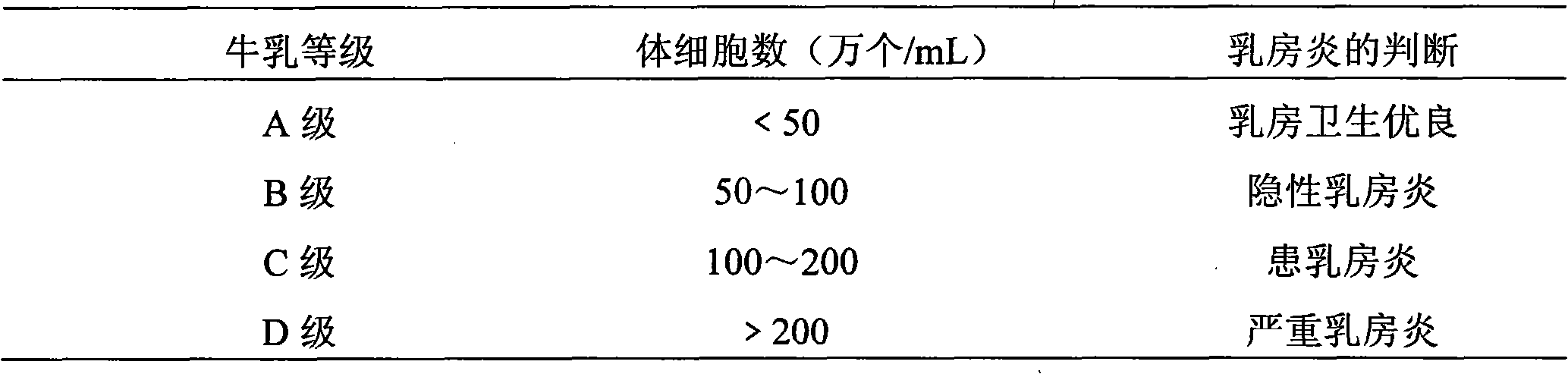
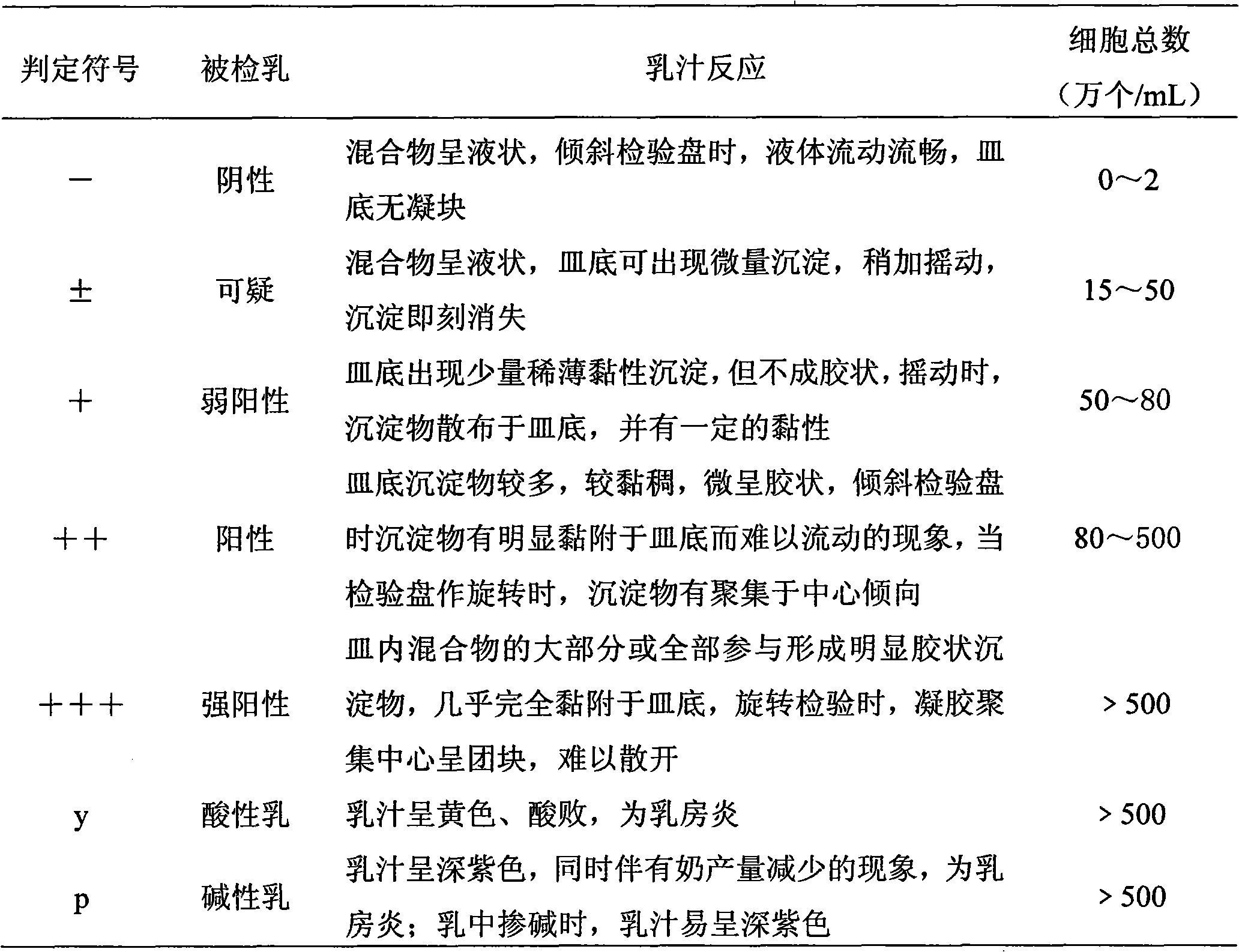
142 results about "Flagellum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
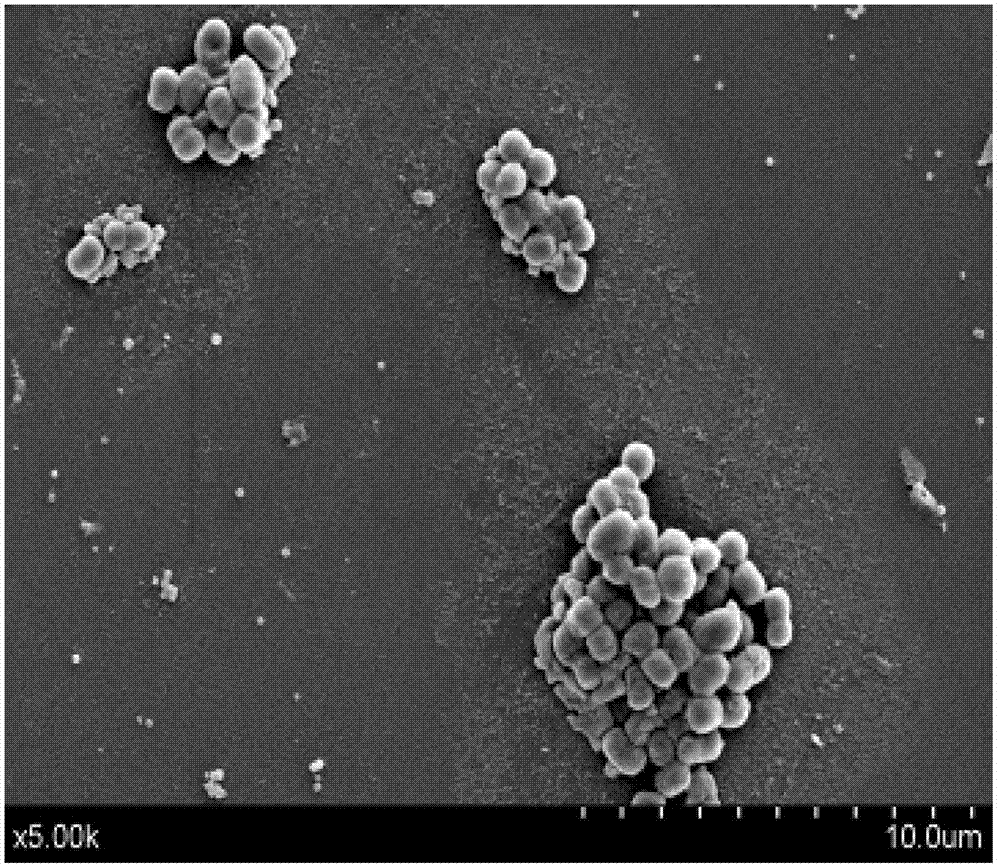
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain bacteria and eukaryotic cells termed as flagellates. A flagellate can have one or several flagella. The primary function of a flagellum is that of locomotion, but it also often functions as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. The similar structure in the archaea functions in the same way but is structurally different and has been termed the archaellum.
Peptide-based vaccine for influenza
A human synthetic peptide-based influenza vaccine for intranasal administration comprises a mixture of flagella containing at least four epitopes of influenza virus reactive with human cells, each expressed individually in Salmonella flagellin, said influenza virus epitopes being selected from the group consisting of: (i) one B-cell hemagglutinin (HA) epitope; (ii) one T-helper hemagglutinin (HA) or nucleo-protein (NP) epitope that can bind to many HLA molecules; and (iii) at least two cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) nucleoprotein (NP) or matrix protein (M) epitopes that are restricted to the most prevalent HLA molecules in different human populations.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Biocontrol bacteria strain preventing and curing plant disease
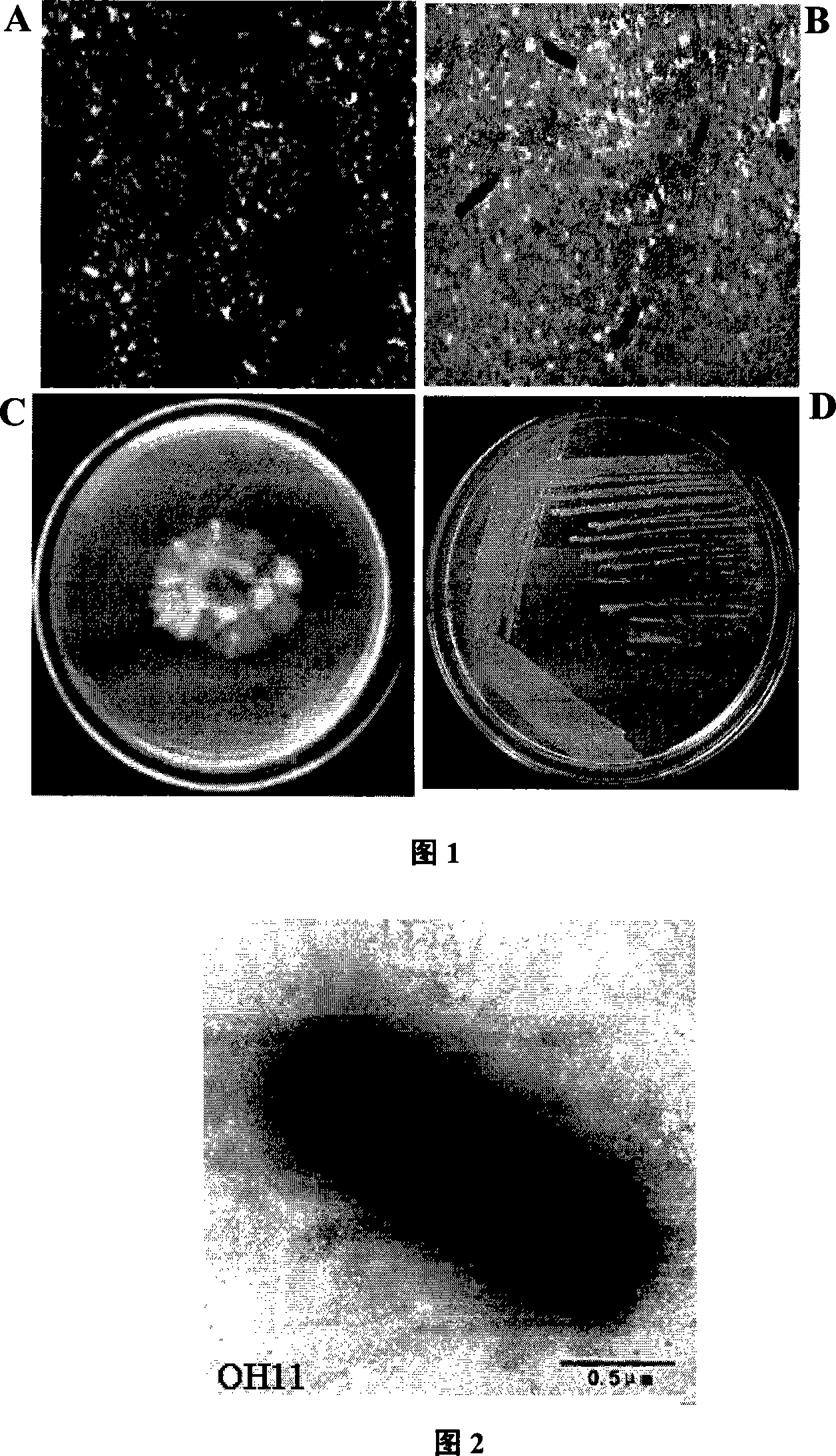
The invention provides a biocontrol bacterial strain for preventing and treating plant diseases and its bacterial agent, belonging to the field of biological control. The strains used are Gram-negative bacteria, identified as Lysobacter enzymogenes, and the strain code is OH11. Strain OH11 has no flagella but has slippage, can produce various extracellular hydrolytic enzymes including chitinase, β-1,3-glucanase and protease, and can effectively inhibit the growth of fungi and bacteria. The antibacterial zone diameters of strain OH11 against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Phytophthora capsici were both greater than 22.0 mm; the antagonism against potato ring rot was stronger, and the diameter of the inhibition zone reached 50 mm. The OH11 strain was inoculated into the seed tank, cultivated to the logarithmic growth phase, and the seed liquid was connected to the production tank for cultivation. The medium used in the production tank was the same as that of the seed tank. The liquid fermentation adopts aerobic submerged fermentation and fed-batch process, the dissolved oxygen is 15%-20%, the fermentation temperature is 30°C, the fermentation time is 72h, and the initial pH value is 7.5. After the fermentation is completed, the culture solution is taken out of the tank and directly packed into liquid dosage forms with plastic packaging barrels or packaging bottles, or subpackaged into solid dosage forms with peat adsorption packaging bags. The biocontrol strain OH11 can effectively control plant pathogenic fungi, bacteria, nematodes and other diseases, and the overall control effect is 50%-70%. In the greenhouse pot experiment, the control effects of OH11 on pepper blight and tomato bacterial wilt reached 83.6% and 86.4%, respectively. Strain OH11 has the characteristics of broad antibacterial spectrum, high activity, and environmental safety. In today's serious pesticide pollution, zymolysobacterium and its bacterial agent will be a good substitute.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof
The invention provides bacillus amyloliquefaciens SZ-60 which is characterized in that the collection number is CGMCC No.8277. The bacterial colony formed by the strain on a beef-extract peptone (NB) medium by virtue of single-cell reproduction is irregular with oyster white color, slight upheaval at the center and wet and semitransparent surface; the microscopy is of a rod shape, and the size is (0.3-0.4)*(3.2-3.3)microns; with flagella, G- and spores, the strain can grow on the beef-extract peptone (NB) medium containing 2-5% of NaCl; the formula of the beef-extract peptone (NB) medium contains 3.0g of beef extract, 10.0g of peptone, 5.0g of NaCl, 17g of agar and 1,000ml of water, and the pH is 6.8-7.2. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens realizes a remarkable antagonistic action on the main pathogenic bacteria causing ginseng root rot, epidemic diseases, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, cylindrocarpon destructans, black spot and damping off. The invention also provides an application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens SZ-60 in preventing plant fungal diseases, or application in preparing a microbial preparation for preventing plant fungal diseases.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Bdellovibrio strain for preventing and treating mastitis and applications thereof
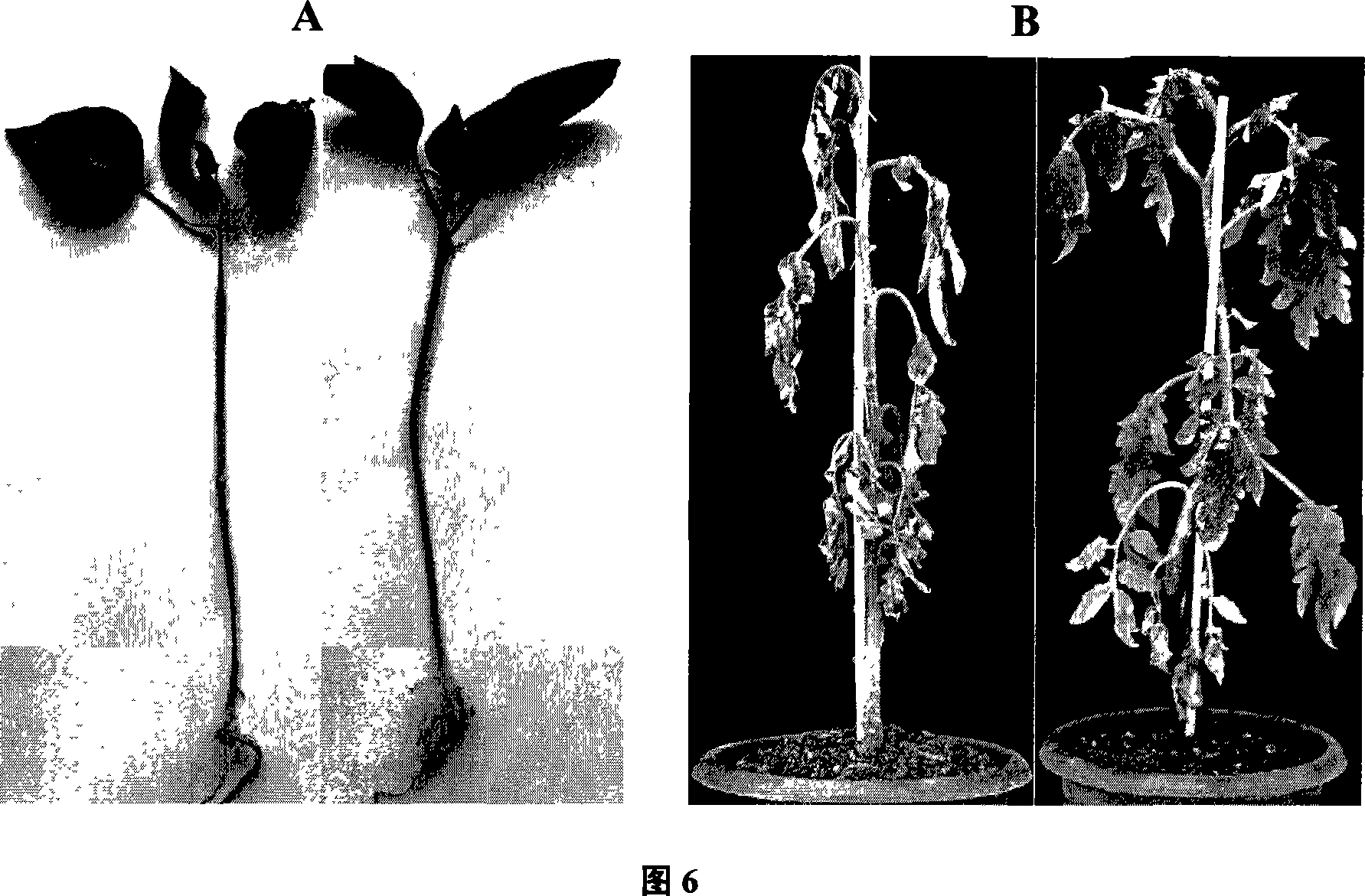
The invention discloses a Bdellovibrio strain for preventing and treating mastitis and applications thereof. A Bdellovibrio BDS01 is obtained by separation, and is unicellular, arced and 0.9-0.25 micrometer in size; the end of the Bdellovibrio BDS01 has flagellum which is 4 micrometers long. When cultured by a two-layer plating method at 28 DEG C for four days, the Bdellovibrio BDS01 can form transparent round plaques with the diameter of 1-2 mm. The microbial preparation prepared by using the Bdellovibrio BDS01 plastid has favorable effects for preventing cow mastitis. Compared with the telotroch, the plastid has the characteristics of convenient preparation and storage, strong environmental resistance, slightly slow sterilization action, longer sterilization action time, and the like, and does not have toxic or side effect on cows. Therefore, the microbial preparation containing the Bdellovibrio BDS01 plastid is suitable for large-size factory culture of cows, and a novel method forgreen processing and production of milk and for preventing and treating mastitis can be provided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel bacterial strain for highly effective degradation of chrysanthemum ester and organophosphorus pesticide and uses thereof
The invention pertains to the technical field of biologic degrading for chemical pesticide, and relates to a bacterial strain that can efficiently degrade Pyrethroid, Organophosphorus and vermectins pesticides and the application of the bacterial strain. The bacterial strain is an Acinetobacter sp. JCX22D bacterial strain, the biologic fature of the bacterial strain is Gram's negative, free from flagella, in form of short rod, is of esterase and lipase activity, free from oxidase activity, and can take use glucose and fructose. The bacterial strain is resistant to Ampicillin and low-concentration Spectinomycin and nalectin, and not resistant to rifamide. The degrading efficiency of the bacterial straine is more than 72% for high-efficiency cypermethrin, cyhalothrin, decamethrim, bifenthrin pesticid, is more than 70% for diazinon, parathion-methyl, phoxime and chlorpyrifos, and is 90% for vermectins. The bacterial strain can be used for biologically degrading above pesticides, and biologically recovering or cleaning any water body, soil and agricultural products that are polluted by pesticides.
Owner:许雷
Bacillus adhaerens and its use in preparing health food having thrombolysis property
InactiveCN1464046AHigh activityStrong thrombolytic effectBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsAcid-fastSolubility
Bacilliis natto NLSSc with the preservation number CGMCC No. 0724 is Gram staining positive, non-acid fast, straight or near straight, (0.6-0.8)x(1.5-2.0) micron sized and aerobic; has mesial and un-swelled spore with the spore number inside one sporange cell not more than one, meso diamino heptane diacid and glycin contained in the cell wall, no characteristic saccharum and peripheral flagellum; and can be grown well in five kinds of natural organic culture medium and can form relatively thick mycoderm and butter fat colored colony with smooth edge in soybean cake powder culture medium. Bacilliis natto can be cultured in culture medium with nitrogen source to obtain thrombus dissolving matter natto kinase and the cultured matter may be extracted to obtain powdered matter as the additive for thrombolytic health food.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus vallismortis and application thereof
The present invention provides Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4, which has the preservation number of CGMCC No.8273. According to the present invention, the strain grows on a beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium in a single cell reproduction growth manner to form bacterial colonies, and the bacterial colonies have characteristics of round shape, milk white color, slightly elevated center, and moist and transparent surface; microscopic examination results show that the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 has a rod shape, has flagella, has a size of 0.7-0.82*1.6-2.2 mum, presents the positive Gram staining effect, has spores, and can grow on a beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium containing 2-5% of NaCl, wherein the beef extract-peptone (NB) culture medium comprises: 3.0 g of a beef extract, 10.0 g of peptone, 5.0 g of NaCl, 17 g of agar and 1000 ml of water, and the pH value is 6.8-7.2; and the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 provides significant antagonism effects for pathogenic bacteria causing ginseng root rot, blight, sclerotinia sclerotiorum and botrytis cinerea. The present invention further provides an application of the Bacillus vallismortis SZ-4 in prevention and control of plant fungal diseases or preparation of microorganism preparations for prevention and control of plant fungal diseases.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
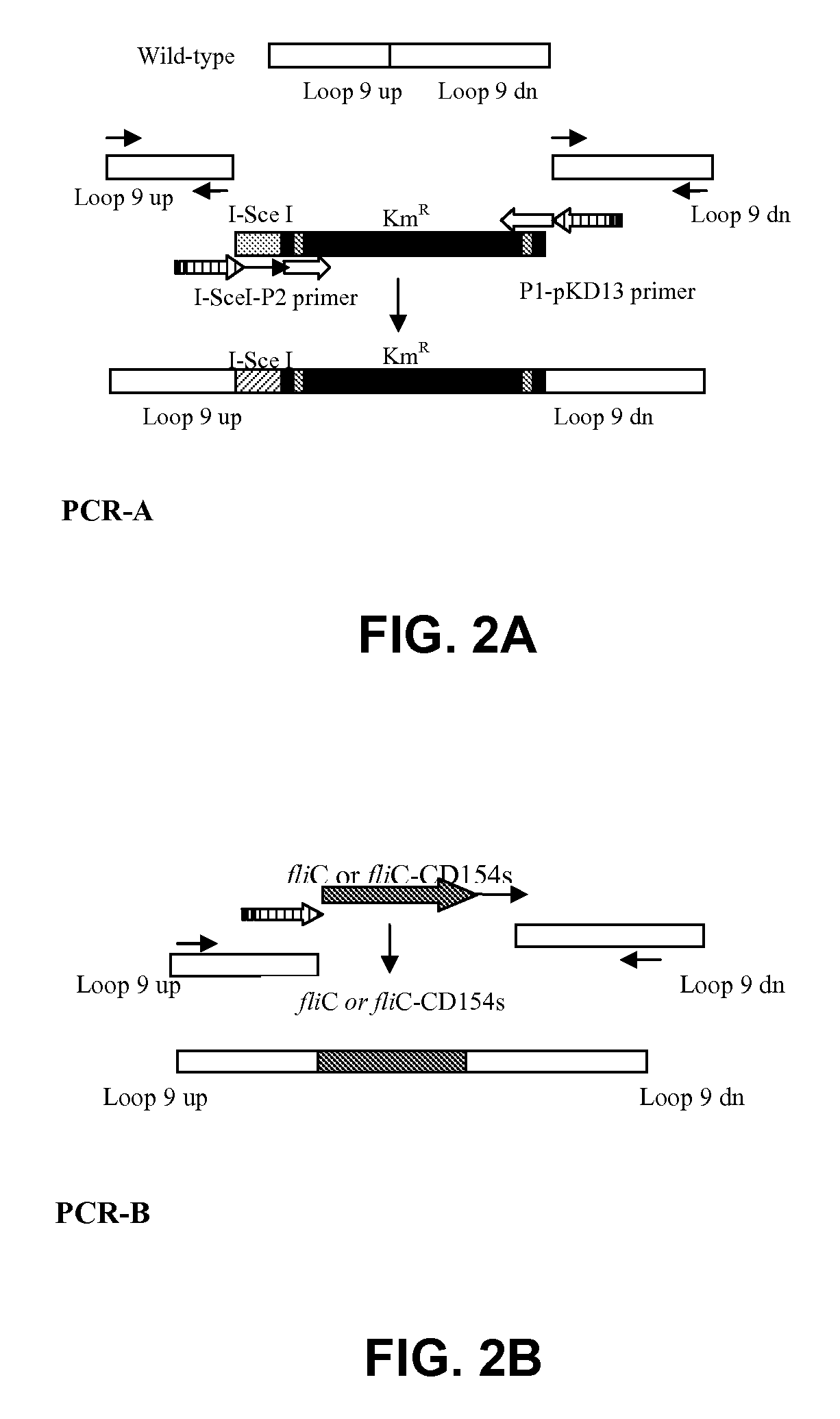
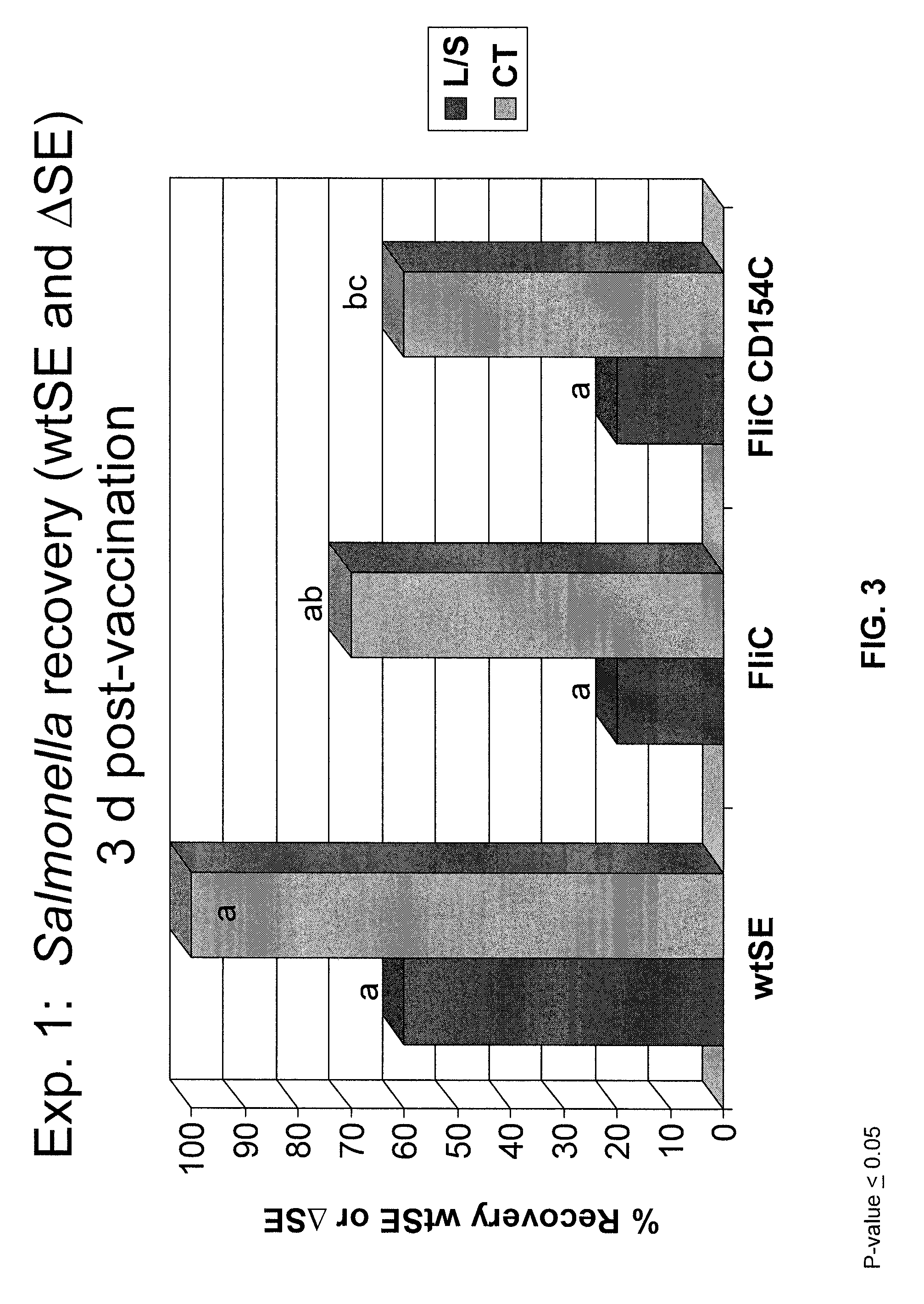
Compositions and methods of enhancing immune responses to flagellated bacterium
ActiveUS9125854B2Enhance immune responseReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSalmonella enteritidisImmunology
Vaccines comprising fliC and CD 154 polypeptides and Salmonella enteritidis vaccine vectors comprising fliC polypeptides are provided. Also provided arc methods of enhancing an immune response against flagellated bacteria and methods of reducing morbidity associated with infection with flagellated bacteria.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
Rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading nicosulfuron and applications thereof
ActiveCN106591168AResidue reductionReduce production and use costsBacteriaWater contaminantsAntibiotic YBiology
The invention discloses rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading nicosulfuron and applications thereof. The invention provides a strain namely rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading residual nicosulfuron in wastewater, and the identification shows that the strain belongs to Rhodococcus. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, CGMCC in February 9th, 2015; and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 10542. The main biological characteristics are as follows: the Gram staining reaction is negative; the bacterial colony is in an orange yellow color, is in a round shape, and is opaque, the surface of the bacterial colony is rough and dry; the cell is in a sphere shape or short bar shape, does not have any flagellum, is motionless, and does not generate any spore; the strain is aerobic and chemoheterotrophic and cannot liquefy gelatin and hydrolyze starch; the enzyme contact reaction is positive, the V.P. reaction is positive, the methyl red reaction is negative; the strain cannot degrade casein, cannot reduce nitrates; and the strain can produce acids from glucose, can utilize glucose, fructose, and citrates, cannot utilize mannose, arabinose, and raffinose, and can reduce more than 90% of antibiotics in water through direct application.
Owner:JIANGSU NANZI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH
Mucosal vaccine adjuvants containing bacterial flegellins as an active component
ActiveCN1909924ABacterial antigen ingredientsAntiinfectivesListerella paradoxaListeria monocytogenes
The present invention relates to mucosal vaccine adjuvants containing flagellins, the structural component of flagella, originated from Vibrio vulnificus, Salmonella typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes as an active component.
Owner:李浚行 +1
Bacterium of degrading residual of organophorus pespared agent of bacterium
InactiveCN1563356AWill not affect the use effectEasy to useBacteriaPesticide residuePseudomonas putida
A bacterial strain for eliminating organophosphorous residue is Granis staining reaction negative bacteria DLL-1 identified as pseudomonas putida. Its biological feature is G- with thallus being short bar shape, tail end being oval and single end being grown thickly with flagellum. The Genbank landing number of 16S rDNA for the bacterial strian is AF 447394.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus licheniformis capable of producing beta-mannanase
InactiveCN102071156ASolve the problem of low enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses bacillus licheniformis capable of producing beta-mannanase, which relates to bacillus licheniformis. The invention solves the low enzymatic activity problem of the conventional production of beta-mannanase by fungi. The bacillus licheniformis capable of producing beta-mannanase belongs to a new bacillus licheniformis variety, and was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan University in Wuhan on November 29th, 2009, with a collection number of CGTTC No.M209288; the bacillus licheniformis capable of producing beta-mannanase is Gram-positive and anaerobic bacillus, is 0.5 to 0.8-micrometer wide, 1.5 to 2.0-micrometer long and does not have flagella and mesic elliptic spores. The beta-mannanase produced by the bacillus licheniformis is acidic mannanase, as is proved by a test. The molecular weight of the beta-mannanase is about 38kD. The beta-mannanase has higher high temperature resistance activity, and the highest activity of the beta-mannanase is 5168U / mL.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
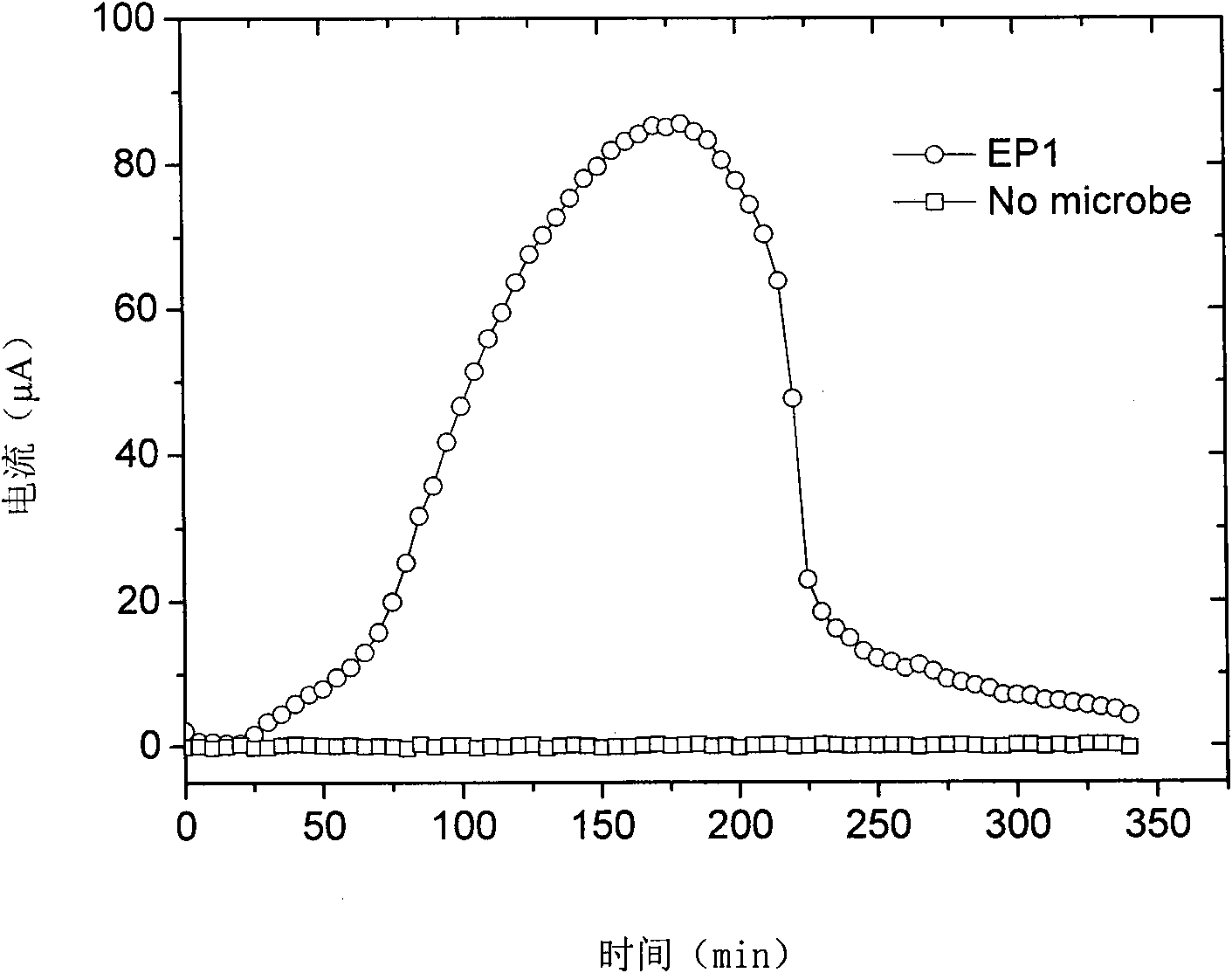
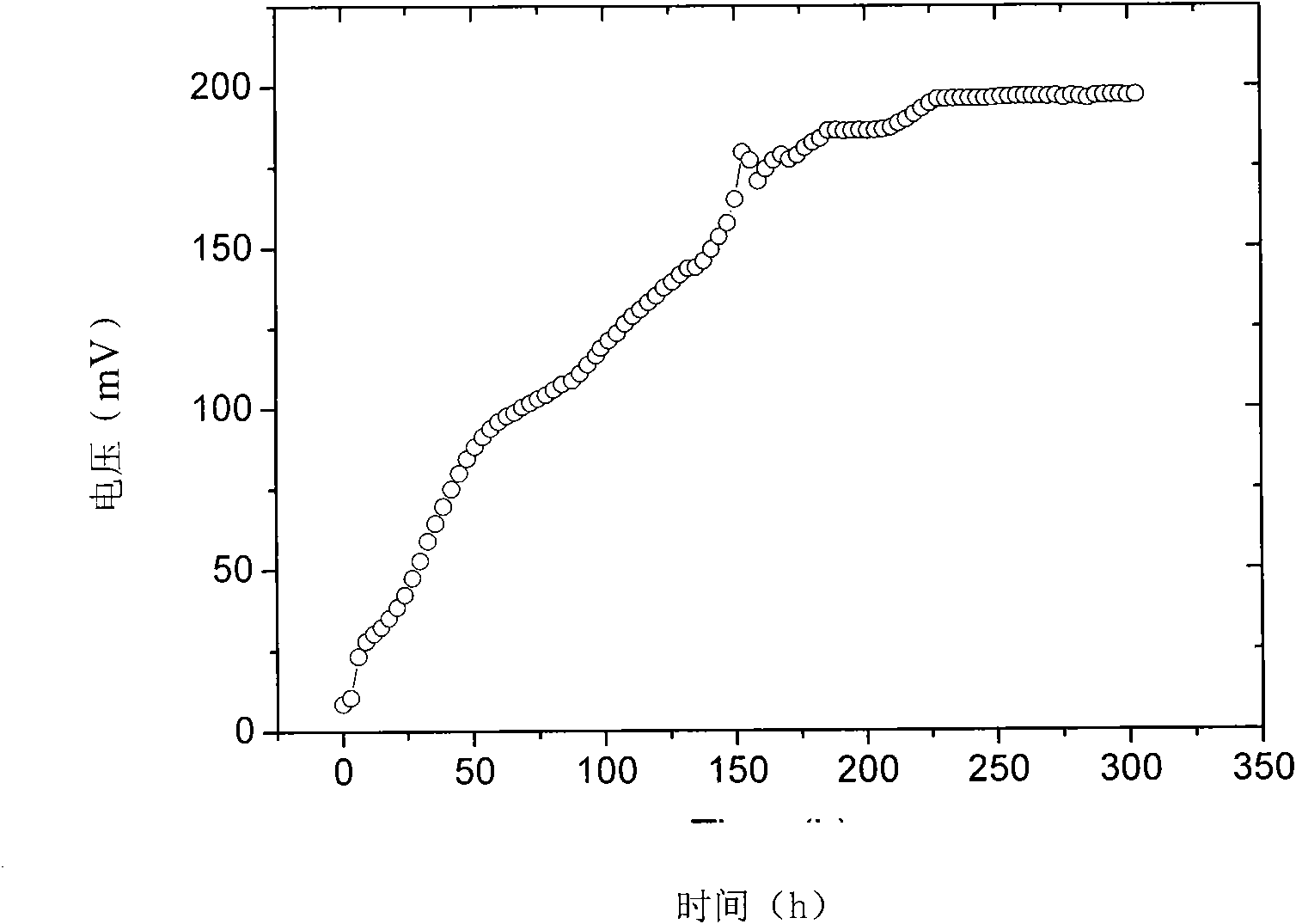
Shewanella and application thereof in microbiological fuel cell
InactiveCN101880638AHas electricity-generating propertiesWide salt ion concentration toleranceBacteriaCell electrodesGram stain negativeMicroorganism
The invention discloses shewanella and application thereof in a microbiological fuel cell, and relates to the technical field of biology. The shewanella is Shewanella marisflavi EP1 which is preserved in 'China Center for Type Culture Collection' in January 2009 with the preservation number of CCTCC M 209016. The shewanella is characterized in that: the shewanella is gram-negative; the thalli are rod-shaped and straight; two ends are circular; the diameter is 0.3 to 1.0 micro; the length is 2.5 to 6.0 micros; the thalli can singly exist or are arranged in pair or in a short-chain shape; and the thalli have autogenetic flagella and can move. The shewanella is separated from offshore ocean sediments, has wide salt ion concentration tolerance activity, and can generate power in electrode liquid at the concentration of up to 8 percent. Therefore, the internal resistance of the microbiological fuel cell is effectively reduced.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
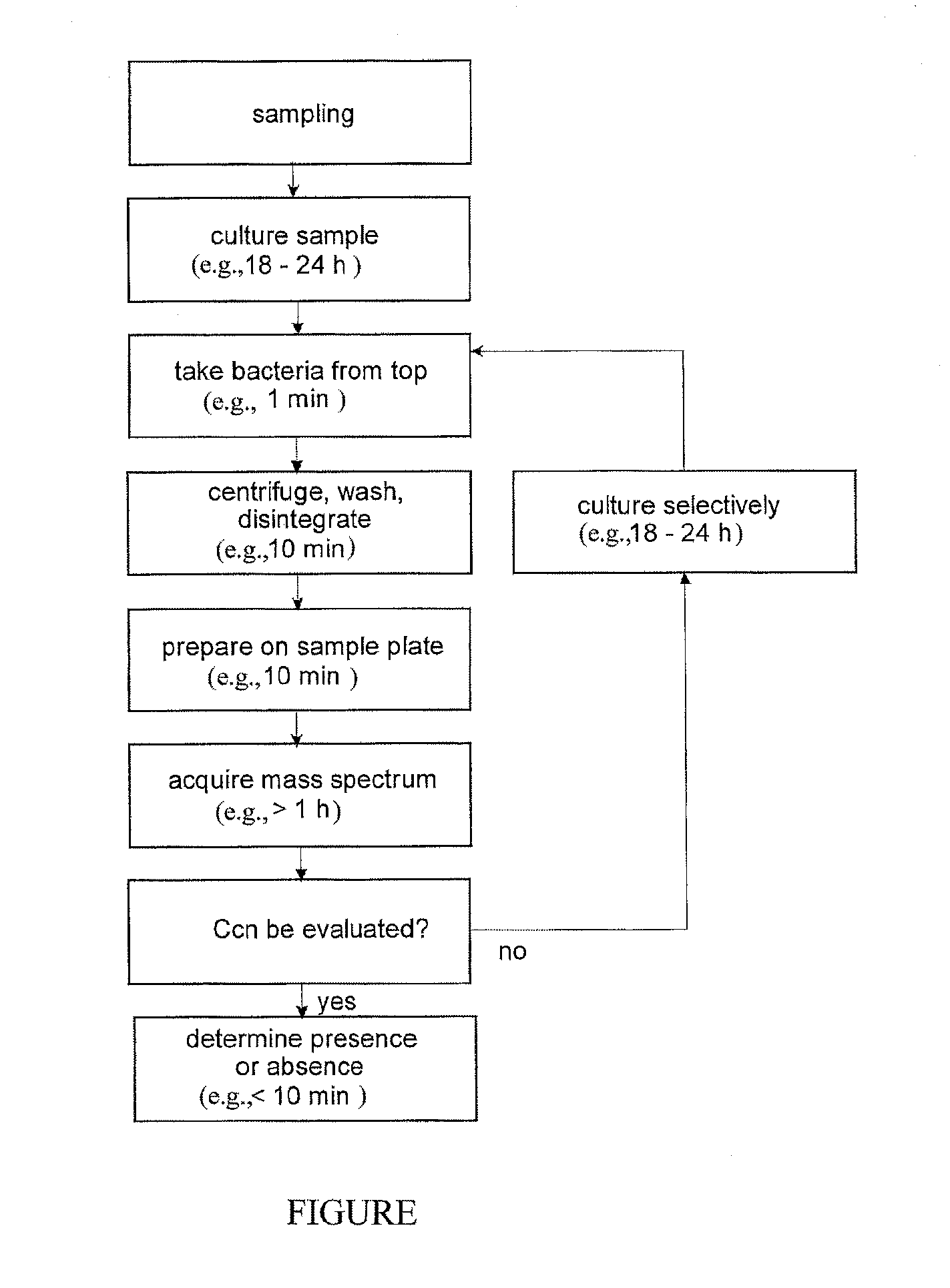
Mass spectrometric rapid detection of salmonella
ActiveUS20120107864A1Microbiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisMicroorganismFeces
The invention relates to the detection of specified, flagellated bacteria, particularly Salmonella, in food and stool. A single culturing period of about 12 to 24 hours in a liquid nutrient medium without agitation is combined with a position-selective sampling of the flagellated microbes from the liquid of the culture, after which a mass spectrometric detection method is used which recognizes the target bacteria in mixtures. A second culture step is only necessary in exceptional cases. A species-selective or genus-selective culture medium is advantageous. Positional selection becomes possible because these bacteria use their flagella to counteract sedimentation by chemotaxis, and they collect near the surface. This provides a low-cost detection method that is several days faster than conventional methods
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
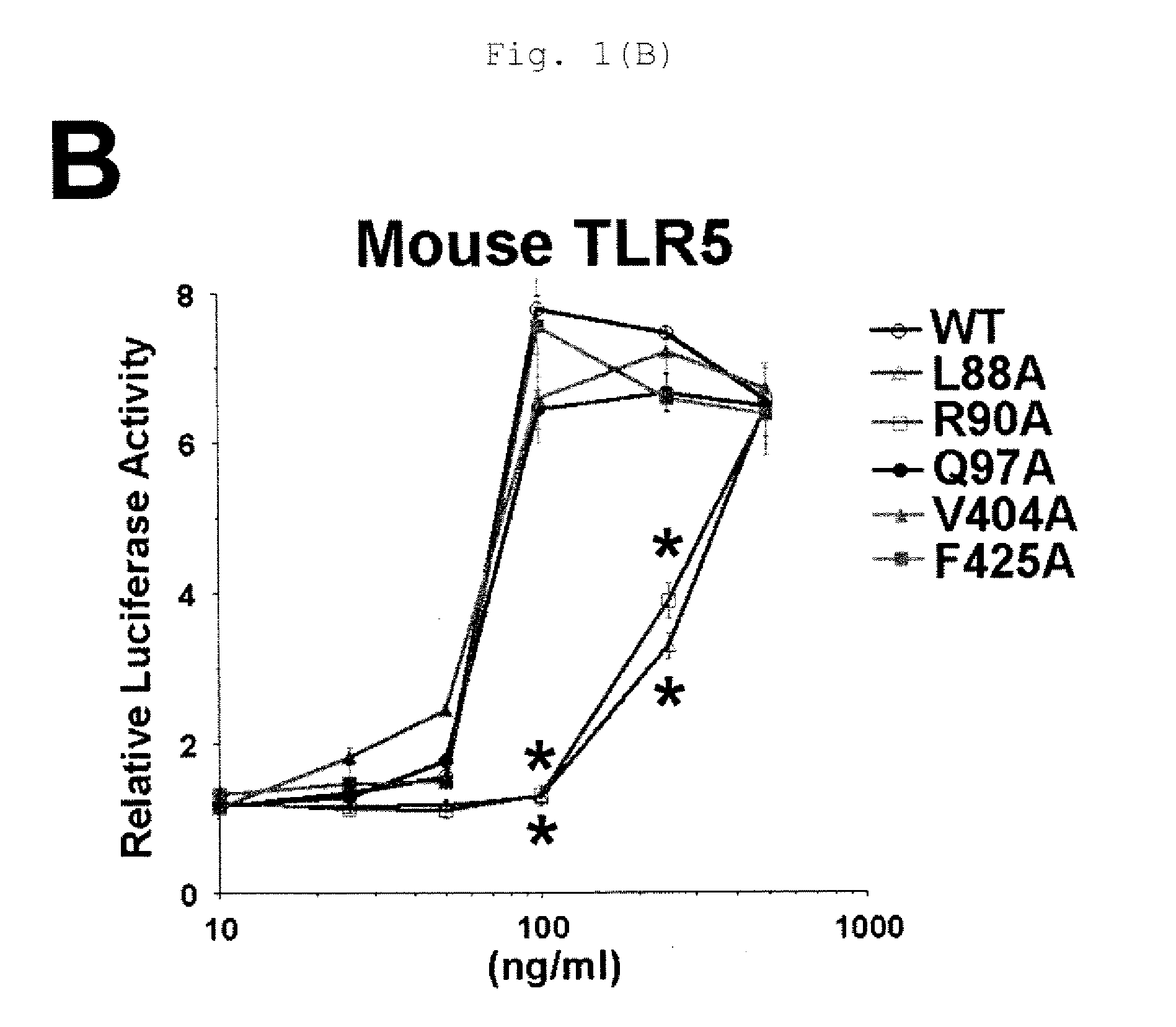
Flagellin mutant vaccine
InactiveUS20100015170A1Protected growthEffectively eliminating flagellated bacteriaAntibacterial agentsBacteriaToll-like receptorWild type
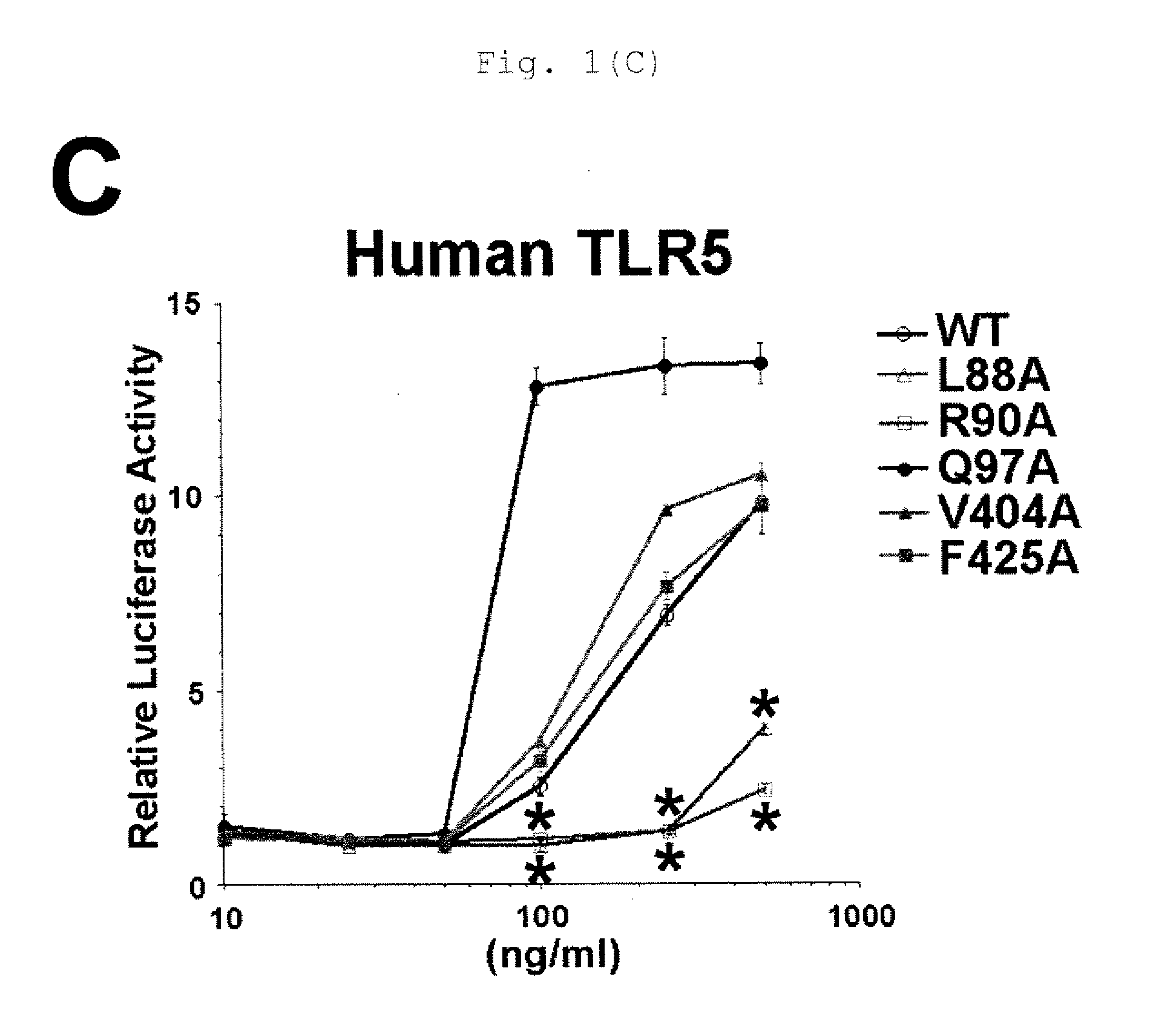
The present invention provides a vaccine which effectively induces protective immune response particularly against flagellated pathogens (such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa).A flagellin mutant into which a mutation has been introduced at least at one site in the Toll-like receptor 5 activation domain of a corresponding wild-type flagellin to thereby attenuate the ability to activate Toll-like receptor 5. A vaccine targeting the flagellin mutant.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA CITY UNIV
Oil-degradation oil-and-salt tolerance bacterial strain, and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN103205378AGood oil and salt resistanceFast growthBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEscherichia coliScreening method
The invention relates to an oil-degradation oil-and-salt tolerance bacterial strain which is named as SY-1. The systematic name of the SY-1 is Escherichia coli, the file number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center No.7075, the file date is December 31, 2012, the file address is the Micro-organism Study of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, No.1 Beichen west road, Chaoyang district, Beijing city, and the file unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The oil-degradation oil-and-salt tolerance bacterial strain is good in oil and salt tolerance, is Gram-negative bacterium shaped in short rhabditiform and with flagellum and no spores and active, is in citrate and glucose ammonium salt positive property and can generate catalase without gelatinase. The bacterial strain is fast in growth, can grow in oil used as unique carbon source, and has the advantages of oil degradation.
Owner:航天圣诺(北京)环保科技有限公司
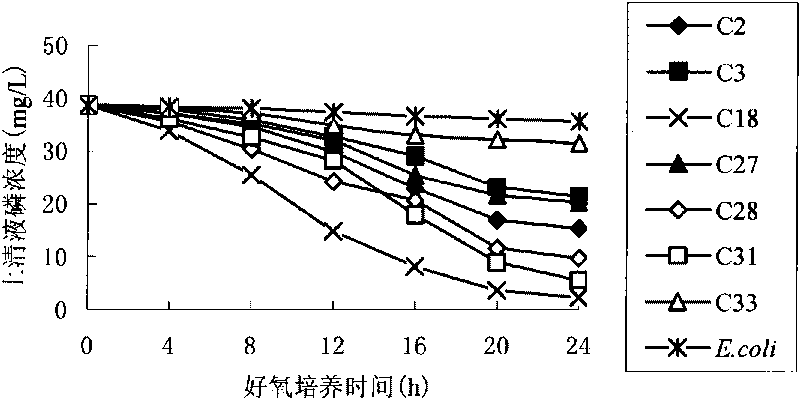
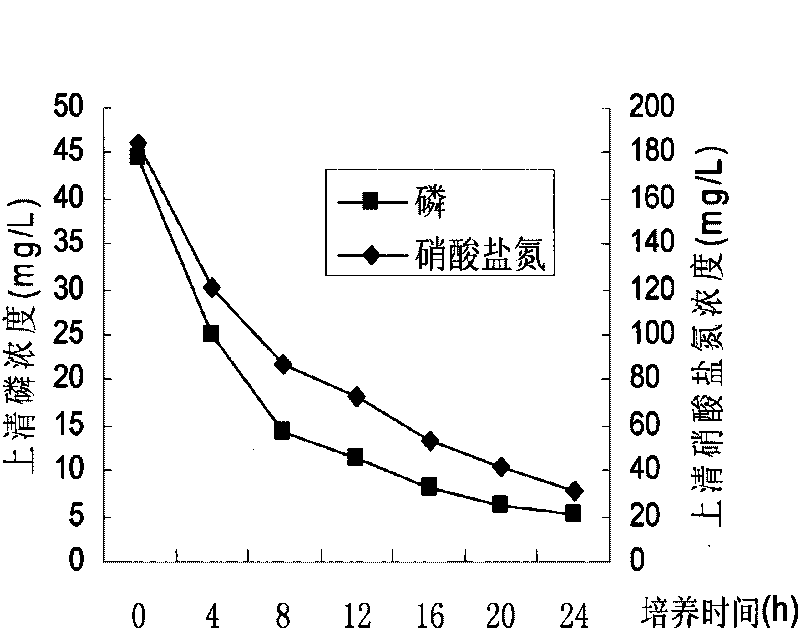
High-efficiency denitrification and dephosphorization bacterial strain C18
InactiveCN101735973AGood nitrogen and phosphorus removal capacityReduce processing costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological propertyIndole test
The invention provides a high-efficiency denitrification and dephosphorization bacteria strain C18, which belongs to the technical field of waste water biochemical treatment process. The bacterial strain C18 is gram-negative bacteria, which is identified as a pseudomonas (pseudomonas grimontii). The main biological characteristic of the bacterial strain is G-; thalli is of short rod shape; the size is about 0.9*0.6 mu m; a flagellum is grown on a partial side; V-P test is positive; indole test is positive; and the bacterial strain can hydrolyze starch. After 24 hours anaerobic cultivation, the bacterial strain C18 has a dephophorization rate of 88.3 percent and a denitrogenation rate of 83.4 percent, and can be used in the waste water biochemical treatment process so as to reduce the content of the nitrogen and the phosphorus in the waste water greatly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Polysaccharide conjugate vaccine and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a polysaccharide conjugate vaccine, which comprises a chemical conjugate consisting of a bacterial polysaccharide and a vector protein, wherein the vector protein is a bacterial slime invasion-associated protein, such as a bacillus coli heat-labile toxin B subunit, a campylobacter jejuni flagellum secretion protein A1, a campylobacter jejuni flagellum secretion protein A2, a pneumococcus surface protein and a pneumococcus surface adhesin. The invention further relates to a preparation method for the polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. According to the invention, the mucosa delivery of the polysaccharide conjugate vaccine can be realized on the premise of not adding any other extrinsic protein; and due to the adoption of an immune route, the vaccine is more efficient, convenient and safe to use.
Owner:BEIJING BIOLOGICAL PROD INST CO LTD
Detection kit for helicobacter pylori virulence protein antibody and detection method by using the same
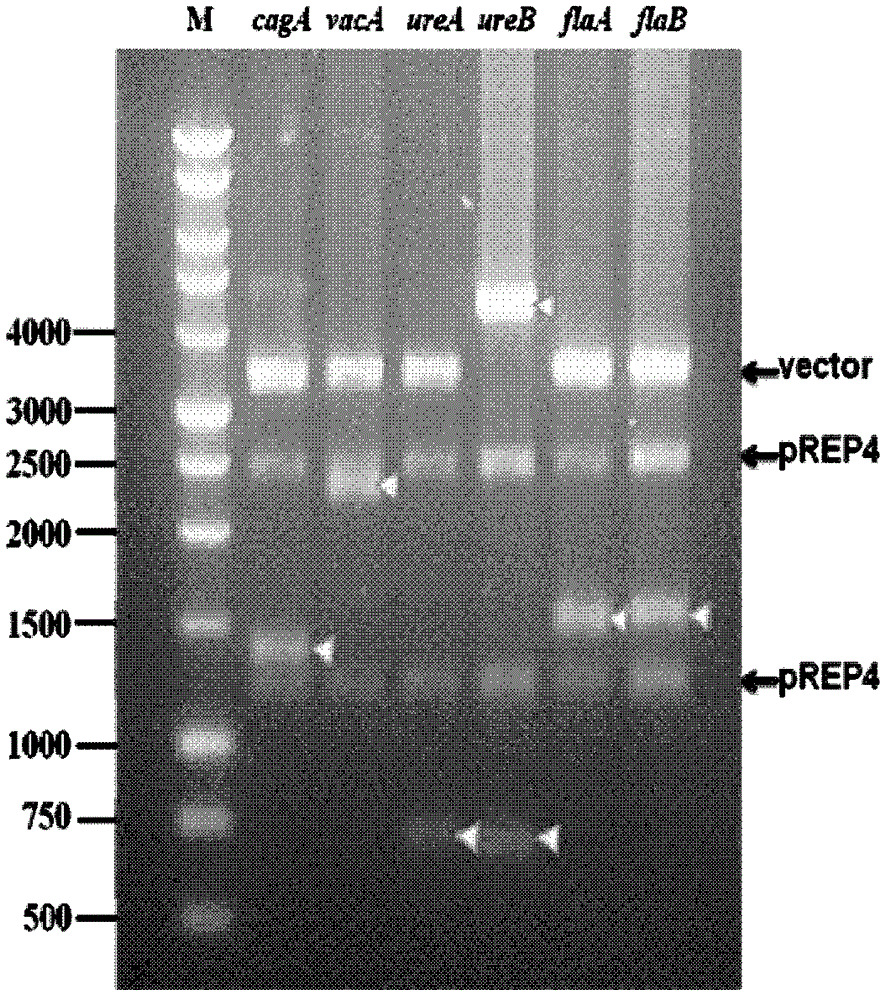
InactiveCN102721815AStrong specificityDifferentiate between strong and weak virulenceBiological testingAntigenPositive control
The invention relates to a detection kit for helicobacter pylori virulence protein antibody and a detection method by using the same. The kit comprises a microwell plate, an enzyme-labeled secondary antibody, a negative control serum, a positive control serum, a substrate, a stop buffer and a washing liquor, wherein the microwell plate is coated with purified recombinant helicobacter pylori virulence proteins, the substrate is a solution containing 1% m / m 3, 3', 5, 5'-tetramethyl benzidine and 30% v / v hydrogen peroxide, and the recombinant helicobacter pylori virulence proteins are cytotoxin-associated protein CagA, vacuolating toxin protein VacA, flagellum protein subunit A, flagellum protein subunit B, urease subunit A, and urease subunit B. According to the invention, six purified helicobacter pylori virulence proteins are used as antigens which itself have high conservatism and specificity and are related to the symptom of a patient, so the kit has characteristics of high specificity, identification capacity for helicobacter pylori clinical strain virulence strength, and semi-quantitative detection capacity.
Owner:TIANJIN TIANFOLUO BIOLOGICAL TECH
Engineered immunostimulatory bacterial strains and uses thereof
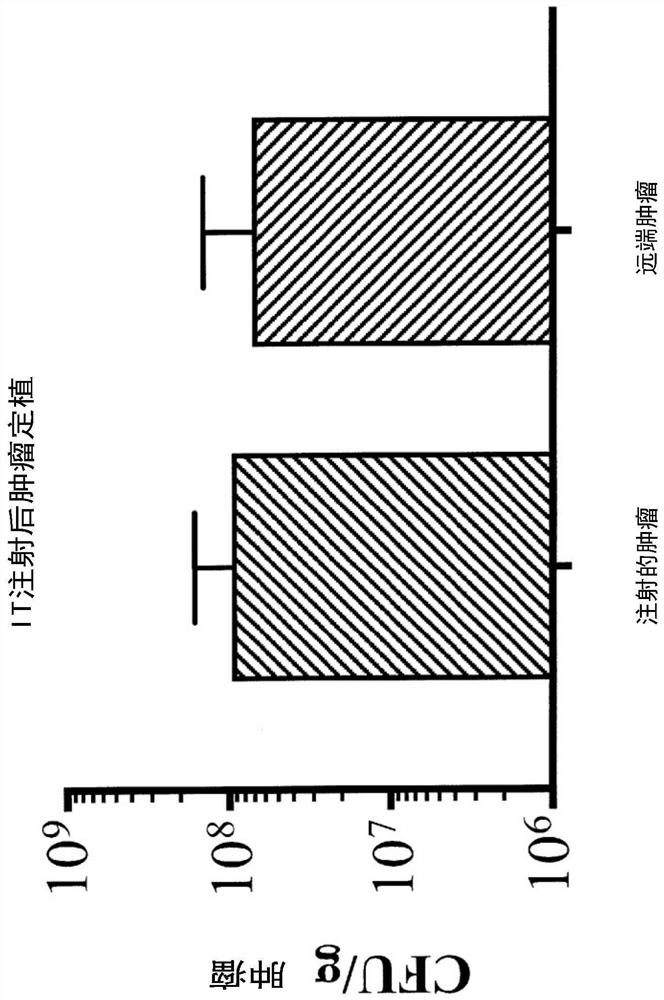
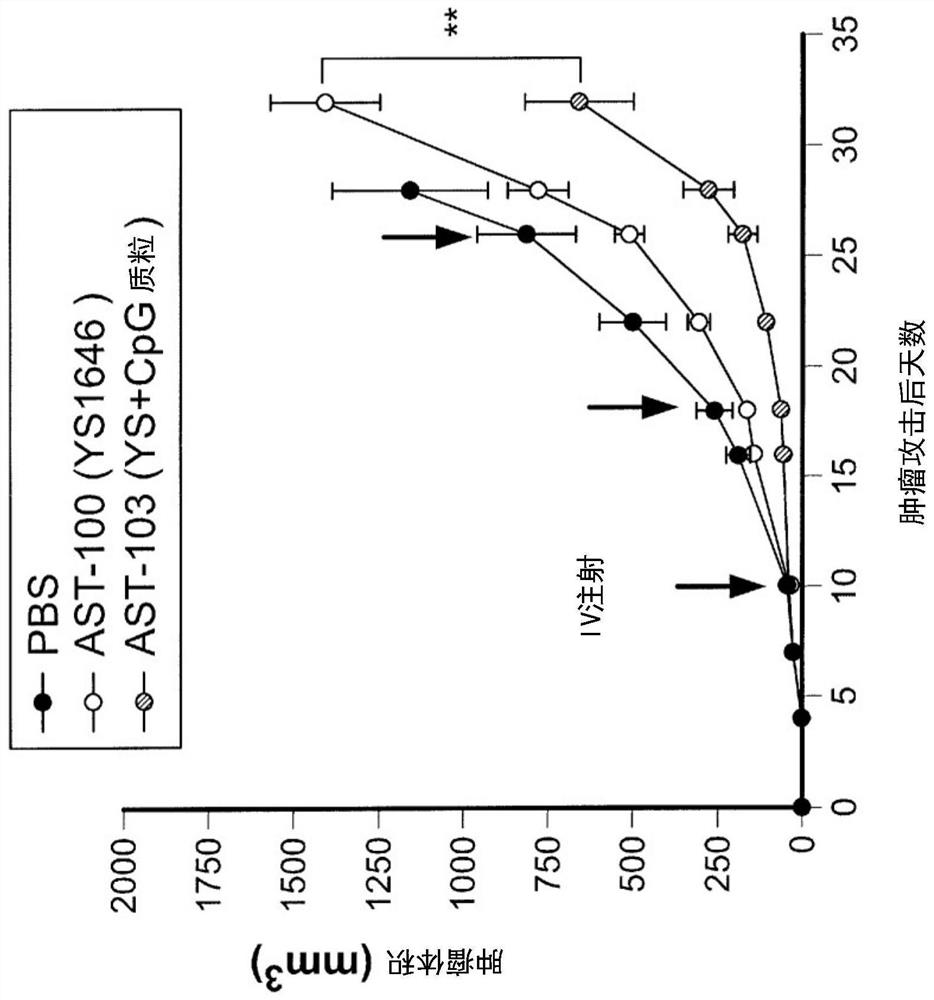
Provided are delivery immunostimulatory bacteria that have enhanced colonization of tumors, the tumor microenvironment and / or tumor-resident immune cells, and enhanced anti-tumor activity. The immunostimulatory bacteria are modified by deletion of genes encoding the flagella or modification of the genes so that functional flagella are not produced, and / or are modified by deletion of pagP or modification of pagP to produce inactive PagP product. As a result, the immunostimulatory bacteria are flagellin- and / or pagP -. The immunostimulatory bacteria optionally have additional genomic modifications so that the bacteria are adenosine or purine auxotrophs. The bacteria optionally are one or more of asd -, purI - and msbB -. The immunostimulatory bacteria, such as Salmonella species, are modified to encode immunostimulatory proteins that confer anti-tumor activity in the tumor microenvironment, and / or are modified so that the bacteria preferentially infect immune cells in the tumor microenvironment or tumor-resident immune cells and / or induce less cell death in immune cells than in other cells. Also provided are methods of inhibiting the growth or reducing the volume of a solid tumor by administering the immunostimulatory bacteria.
Owner:阿克蒂姆治疗有限公司
Tolumonas osonensis bacterial strain with electrogenesis characteristic, and applications thereof in microbial fuel cells
InactiveCN103509735AHas electricity-generating propertiesHigh electroactivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSodium acetateSludge
The invention relates to Tolumonas osonensis P2-A-1 bacterial strain with electrogenesis characteristic. The bacterial strain is obtained by steps of enriching, separating, purifying and screening from sludge of sewage treatment plant; belongs to Tolumonas osonensis species, Tolumonas genus; and is named as Tolumonas osonensis P2-A-1. The bacterial strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, on May, 2013, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.7562. The bacterial strain possesses following characteristics: short rod-liked mycelial morphology; 2.4 to 3.6 [mu]m in length, and 0.9 [mu]m in width; the bacterial strain is distributed separately or in pairs, possesses no flagellum, is capable of growing with or without oxygen; no bacterial spore is produced; gram negative; at a temperature of 22 DEG C, after 48h of culturing on tryptone soybean broth plating medium, white bacterial colonies are formed, are round in shape, are easy to be stirred up, and are nontransparent, the edge is smooth, and diameter is 2 to 4mm; the bacterial strain is capable of using a plurality of substrates such as glucose and sodium acetate. The bacterial is used for electrogenesis in microbial fuel cells, electrogenesis capacity is relatively high, and power density reaches 509mW / m<2>. The electrogenesis capacity of T.osonensisa, and applications of T.osonensisa in microbial fuel cells are disclosed for the first time.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
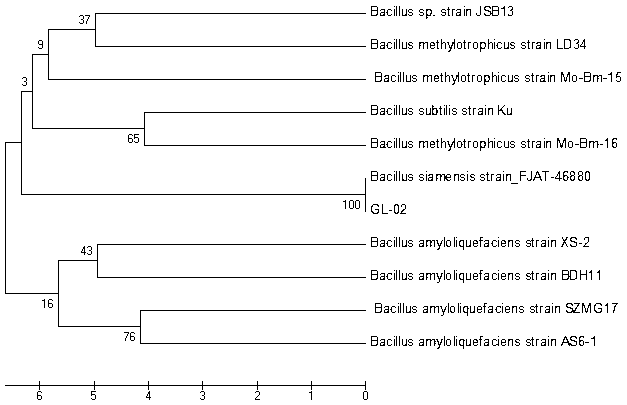
Bacillus siamensis and application thereof
ActiveCN109468243ABroad antibacterial spectrumEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaMicroscopic examPlant disease
The invention provides bacillus siamensis GL-02, the preservation number of which is CGMCC No.16068. A single colony formed by the strain propagating and growing on a beef extract peptone (NB) culturemedium is round, milky white, slightly bulgy in center, and moist and transparent on surface; through microscopic examination, the single colony is rod-shaped, flagellated, 0.7-0.8*1.6-2.2[mu]m in size, and G+,with spores. The single colony can grow on a beef extract peptone culture medium containing 2-5% NaCl. The formula of the beef extract peptone (NB) culture medium comprises 3g of beef extract, 10g of peptone, 12g of agar, and 1L of water, and the pH value is 6.8-7.0. The bacillus siamensis GL-02 has a significant antagonistic effect on pathogens causing corn stalk rot, bipolaris maydisand curvularia leaf spot. The invention also provides application of bacillus siamensis GL-02 in controlling plant fungal diseases, or application in preparing microbial preparations for controlling plant fungal diseases.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria and bactericide thereof
InactiveCN101974453ASolve usabilityEfficient solutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWrinkle skinGram
The invention discloses pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria and a bactericide thereof, belonging to the field of biological high-tech. The adopted strain ZS-S-01 is identified as Stenotrophomonas sp. with the preservation number of CCTCC M 2010095, wherein, the Genbank registry number of the 16S rDNA of the strain is HM016874. The main biological characteristics are as follows: the strain is Gram-negative and has multiple polar flagellum and cells in a short rod shape; and the bacterial colony is milky white and slight yellowish, thicker and non-transparent, the diameter is 0.5mm-1mm, the edge is regular and orderly, the middle part is slightly protruding, and the surface is smooth and bright without wrinkles. The bactericide of the invention has the advantages of low production cost, convenient use and good degradation effect, thus being applicable to the national fruit and vegetable production and export bases or places with green food brand marks at a large area. The bactericide is of great significance to promoting production of nuisance-free vegetables and green food.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pseudomonas and application thereof to degrading macromolecular synthetic plastics
InactiveCN102181378AHas degradative propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlastic wastePseudomonas
The invention belongs to the fields of microbial biotechnology and environmental biotechnology, particularly relates to pseudomonas and application thereof to degrading some macromolecular synthetic plastics. The pseudomonas is Pseudomonas sp. DS1001; a colony of the pseudomonas is circular and yellow white and has a smooth surface and a tidy edge; the thallus is in the shape of a short rod and is gram negative, has flagellum and does not have spore or capsule; a macromolecular compound such as polylactic acid (PLA), poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB), polycaprolactone (PCL) and the like can be used as a unique carbon source for growth; and the pseudomonas has a high-efficiency degradation effect on the compounds. The pseudomonas can be applied to treatment and biological recycling of plastic wastes taking the macromolecular material as a main component.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sedum rhizosphere lead-resistant strain pseudomonas as well as screening method and application thereof
InactiveCN104974960AIncreased tolerance to heavy metal leadBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationHigh resistanceScreening method
The invention relates to sedum rhizosphere lead-resistant strain pseudomonas sp JPb5, in particular to a lead-resistant strain pseudomonas sp JPb5 separated from sedum rhizosphere. The lead-resistant strain pseudomonas sp JPb5 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the preservation number of CGMCC No.10087 on December 1, 2014. The lead-resistant strain pseudomonas sp JPb5 is gram-negative bacteria or aerobasilus, and has flagella and capsules. The strain has relatively high resistance to heavy metal lead, and has practical significance and important engineering application value on the aspect of remediation of heavy metal lead contaminated soil through combination of plants and microorganisms.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES CORPORATION +1
Sedum rhizosphere cadmium-resistant bacillus sp. strain, screening method and application thereof
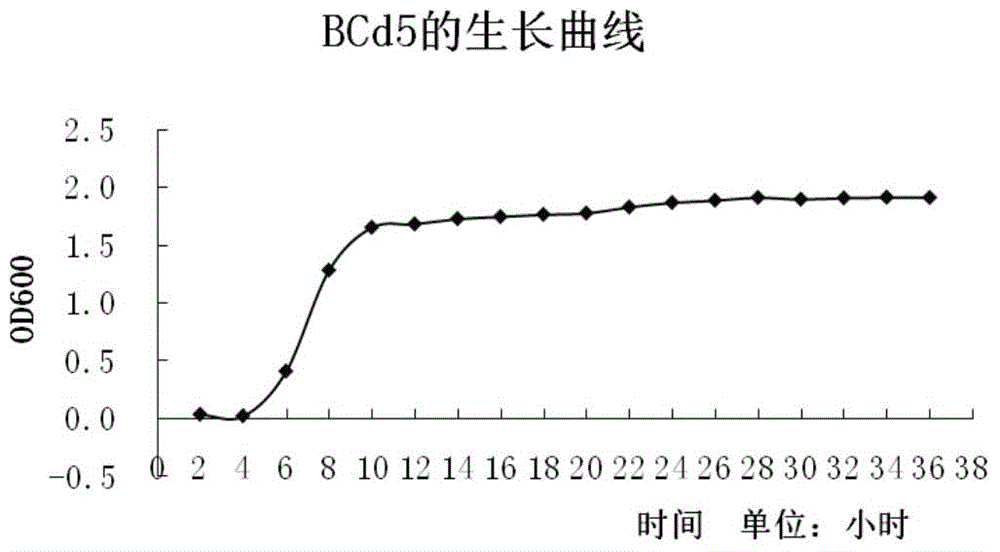
InactiveCN105018375AIncreased resistance to heavy metal cadmiumBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationHigh resistanceScreening method
The invention relates to a sedum rhizosphere cadmium-resistant bacillus sp. BCd5 strain and its screening method. The invention specifically relates to a sedum rhizosphere cadmium-resistant bacillus sp. BCd5 strain which has been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on December 1st, 2014 with the preservation number being CGMCC NO. 10077. 16S rDMA gene sequence of the strain is as shown in the Figure 1. The strain is a Gram-negative bacterium, aerobasilus having flagellum and capsule. The strain has high resistance to cadmium and has practical significance and important engineering application value in plant-microbial remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES CORPORATION +1
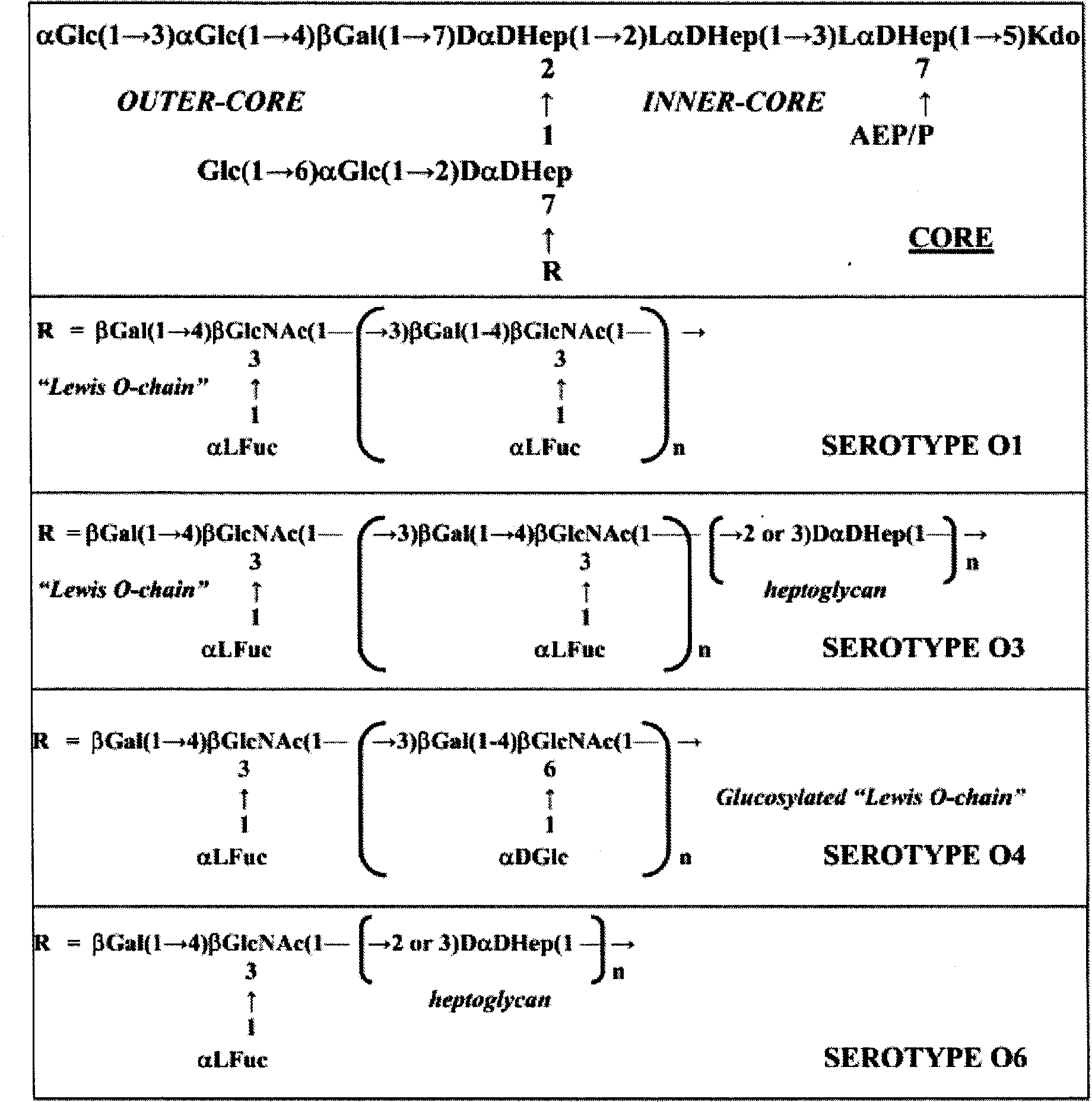
Helicobacter pylori serotype classification method and helicobacter pylori biochip construction method
InactiveCN104357552AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisVirulent characteristicsClassification methods
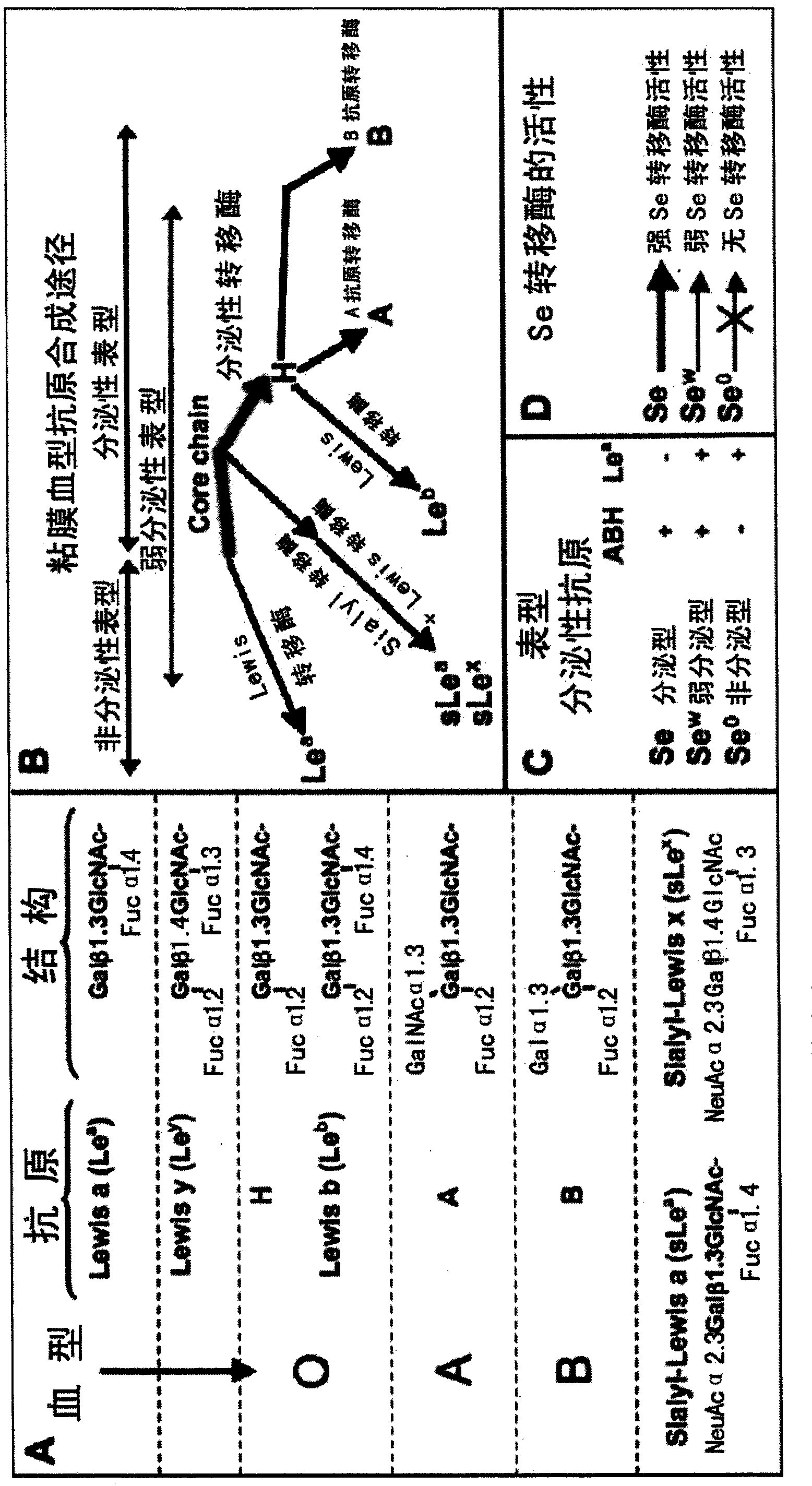
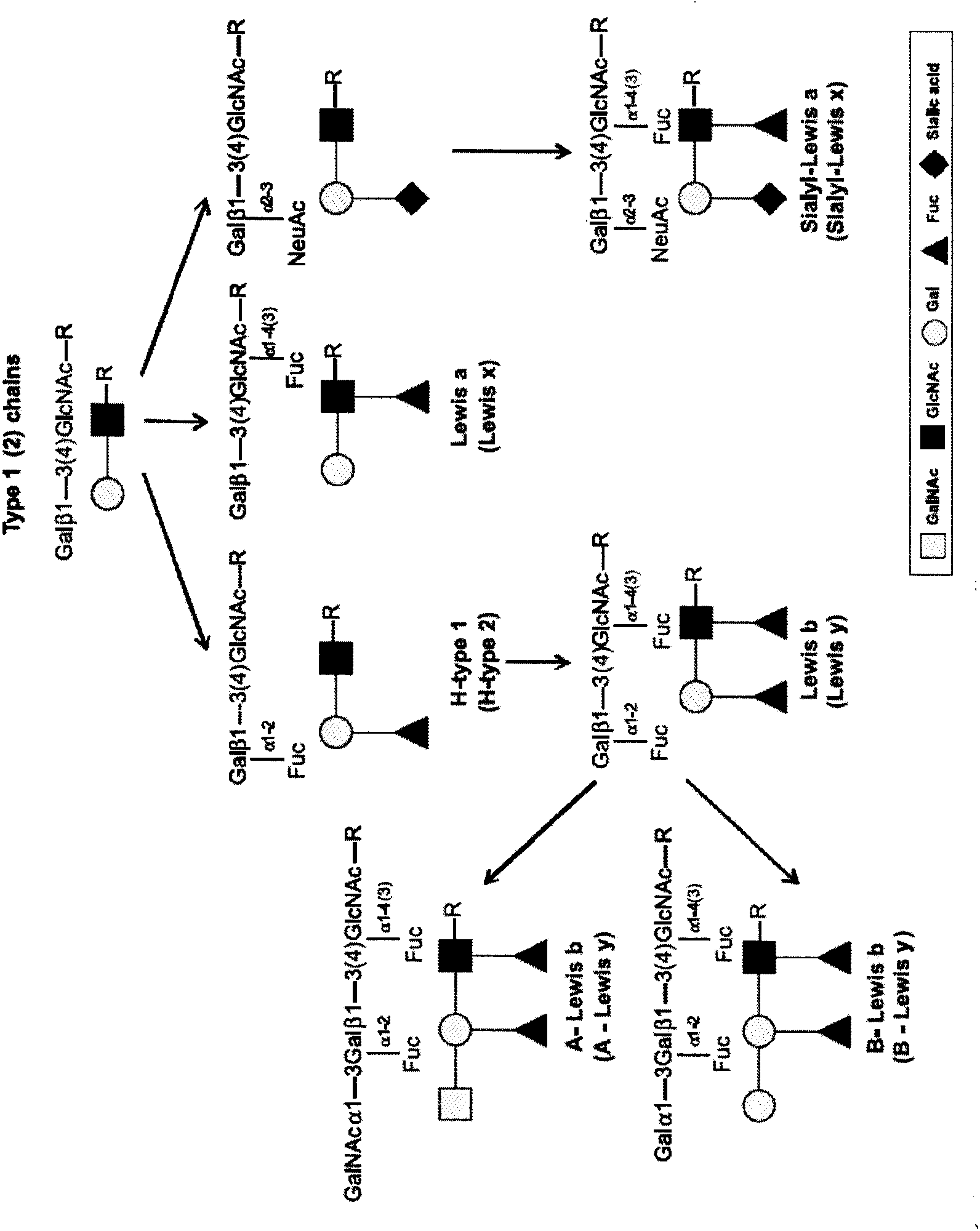
The invention discloses a helicobacter pylori serotype classification method and a helicobacter pylori biochip construction method. According to the methods, helicobacter pylori is extracted from a patient with helicobacter pylori; the extracted helicobacter pylori has PCR (polymerase chain reaction) of cagA and vacA and is sequenced; after sequencing for helicobacter pylori virulence genes cagA and vacA is finished, a regional virulence epidemic strain is screened out based on gene combination and is named; lipopolysaccharide and flagellum of the helicobacter pylori virulence epidemic strain are extracted and subjected to structural analysis, and serotype naming is performed according to virulence genes, the structure of the flagellum, the Lewis blood type structure of lipopolysaccharide and repeated oligosaccharide structure; and lipopolysaccharide and flagellum of the named strain are extracted to construct the biochip. The helicobacter pylori serotype classification method and the helicobacter pylori biochip construction method can greatly simplify detection means, has the characteristics of high accuracy, high throughput and high repeatability, and can meet requirements of clinical diagnosis, specific treatment and epidemiological investigation for helicobacter pylori.
Owner:FOURTH HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV +2
Hylotelephium erythrostictum rhizosphere cadmium-resistant Cupriavidus sp., and screening method and applications thereof
InactiveCN106337026AIncreased resistance to heavy metal cadmiumBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationHigh resistanceScreening method
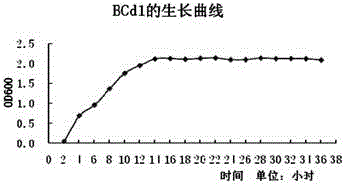
The invention relates to hylotelephium erythrostictum rhizosphere cadmium-resistant Cupriavidus sp. BCd1, and a screening method and applications thereof, and more specifically relates to the cadmium-resistant Cupriavidus sp. BCd1 obtained via separation from hylotelephium erythrostictum rhizosphere. The hylotelephium erythrostictum rhizosphere cadmium-resistant Cupriavidus sp. BCd1 is stored in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 1th December 2014, and preservation number is CGMCC No.10080. The 16S rDNA gene sequence is represented by graph 1. The hylotelephium erythrostictum rhizosphere cadmium-resistant Cupriavidus sp. BCd1 is Gram negative, belongs to aerobic coccobacillus, possesses flagellum and capsule, possesses relatively high resistance on heavy metal cadmium, and possesses practical significance and high engineering value in plant-microorganism combined remediation of cadmium heavy metal polluted soil.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES CORPORATION +1
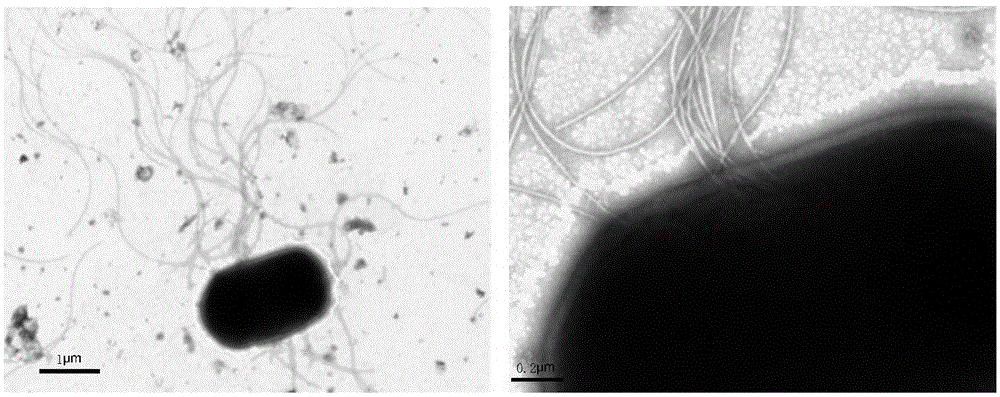
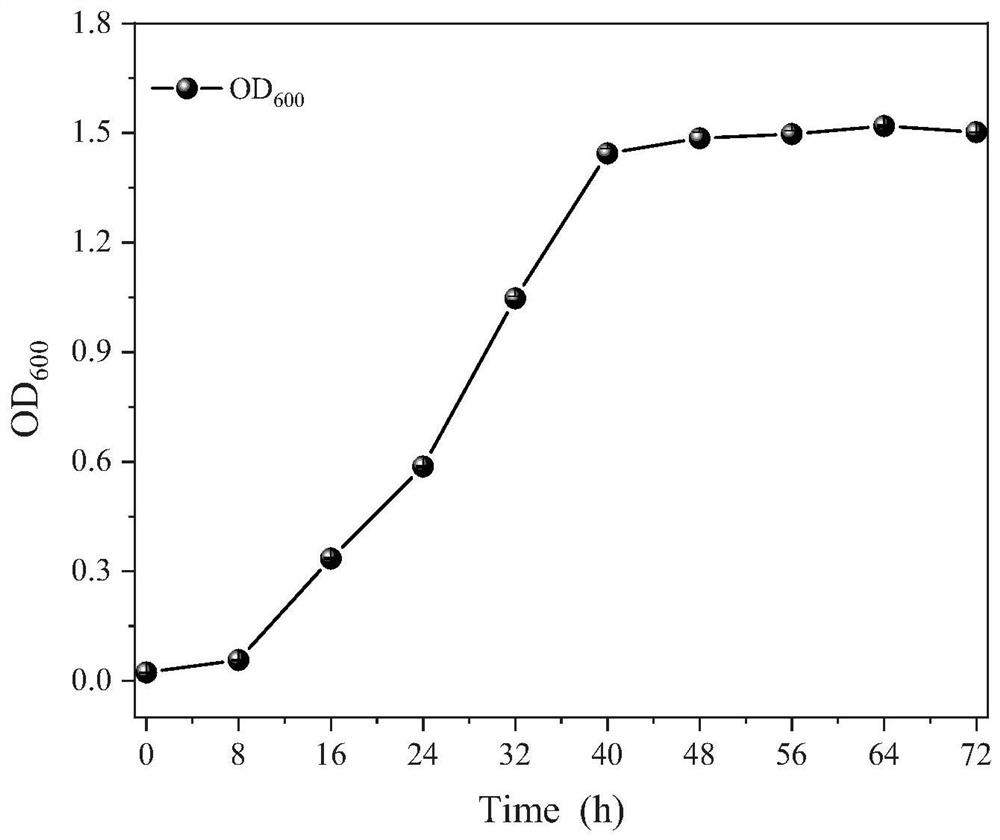
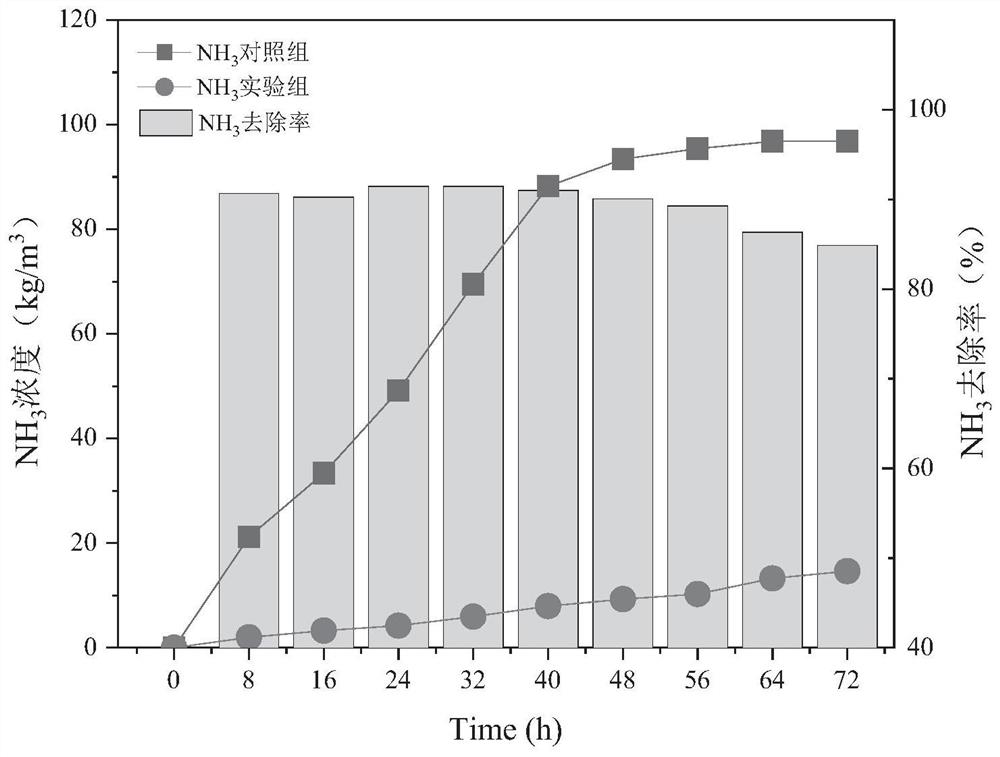
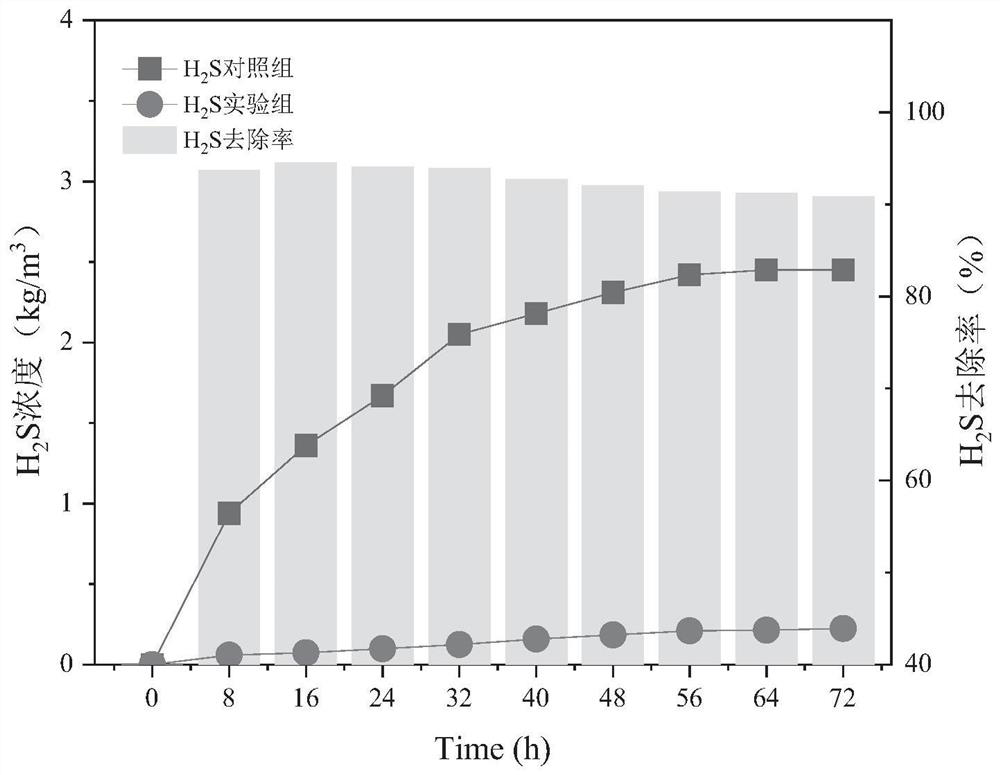
Efficient deodorizing bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN111676150AImprove deodorization abilityBacteriaSpecific water treatment objectivesBiotechnologyLivestock manure
The invention discloses efficient deodorizing bacteria and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of bioengineering and environmental engineering. The efficient deodorizing bacteriaare named HCSW-2, are identified to belong to Lactobacillus plantarum, and are preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date is August 14th, 2019, andthe preservation number is CGMCC No.18384. The efficient deodorizing bacteria are Gram negative bacteria, and are facultative anaerobic, a growth temperature range is 10-42 DEG C, the thallus lengthis 1.5-5.0 [mu]m, the width is 0.5-1 [mu]m, the efficient deodorizing bacteria are in shapes of ball rods or lines, one ends of thalli have flagella, and no spores exist. The strain HCSW-2 has excellent deodorizing efficacy after being subjected to activation culture, and can be used for enhanced biological deodorization in landfill or compost treatment processes of solid waste of livestock manure, excess sludge, garbage and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU HAICHENG BIOTECH CO LTD
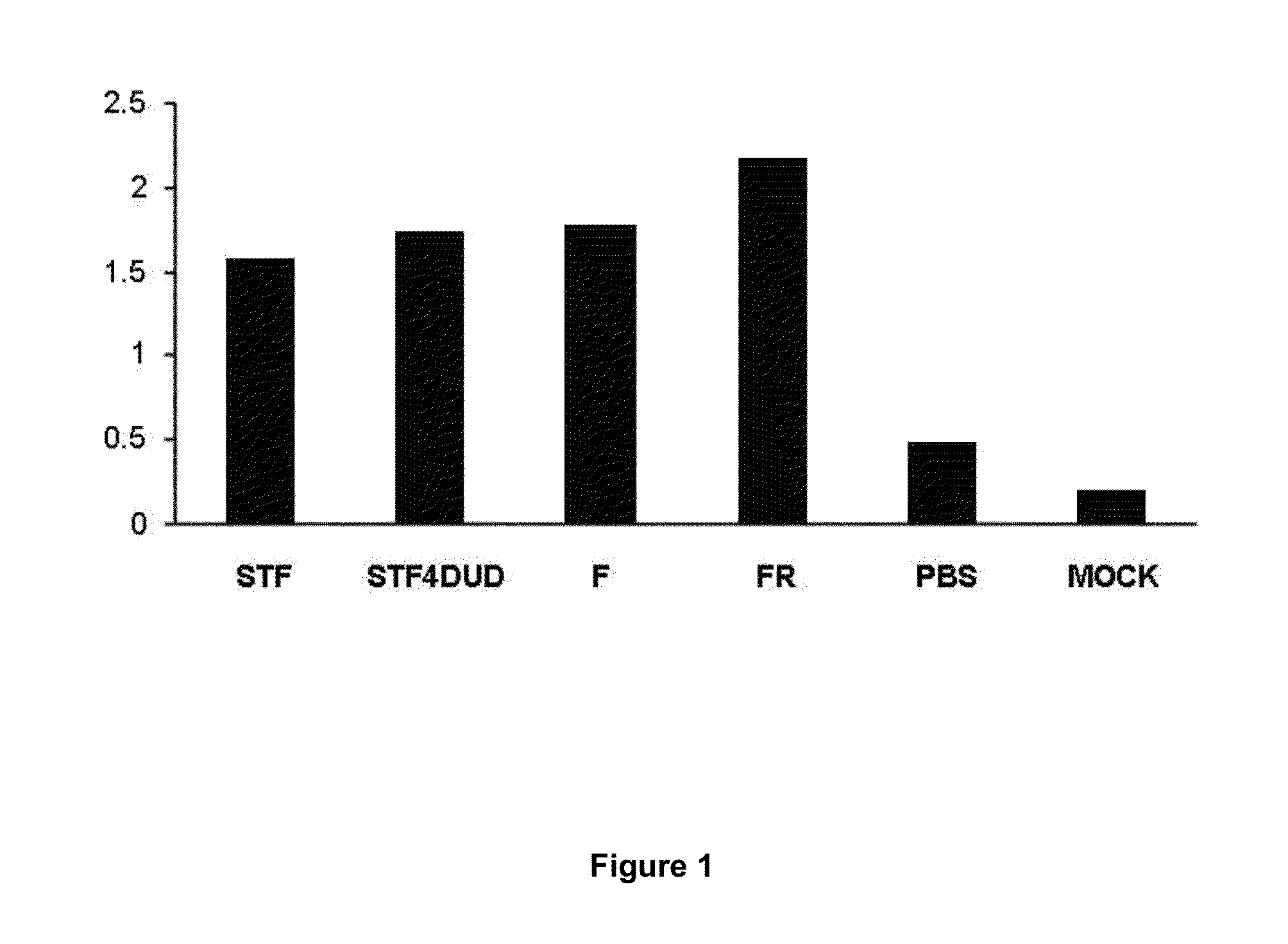
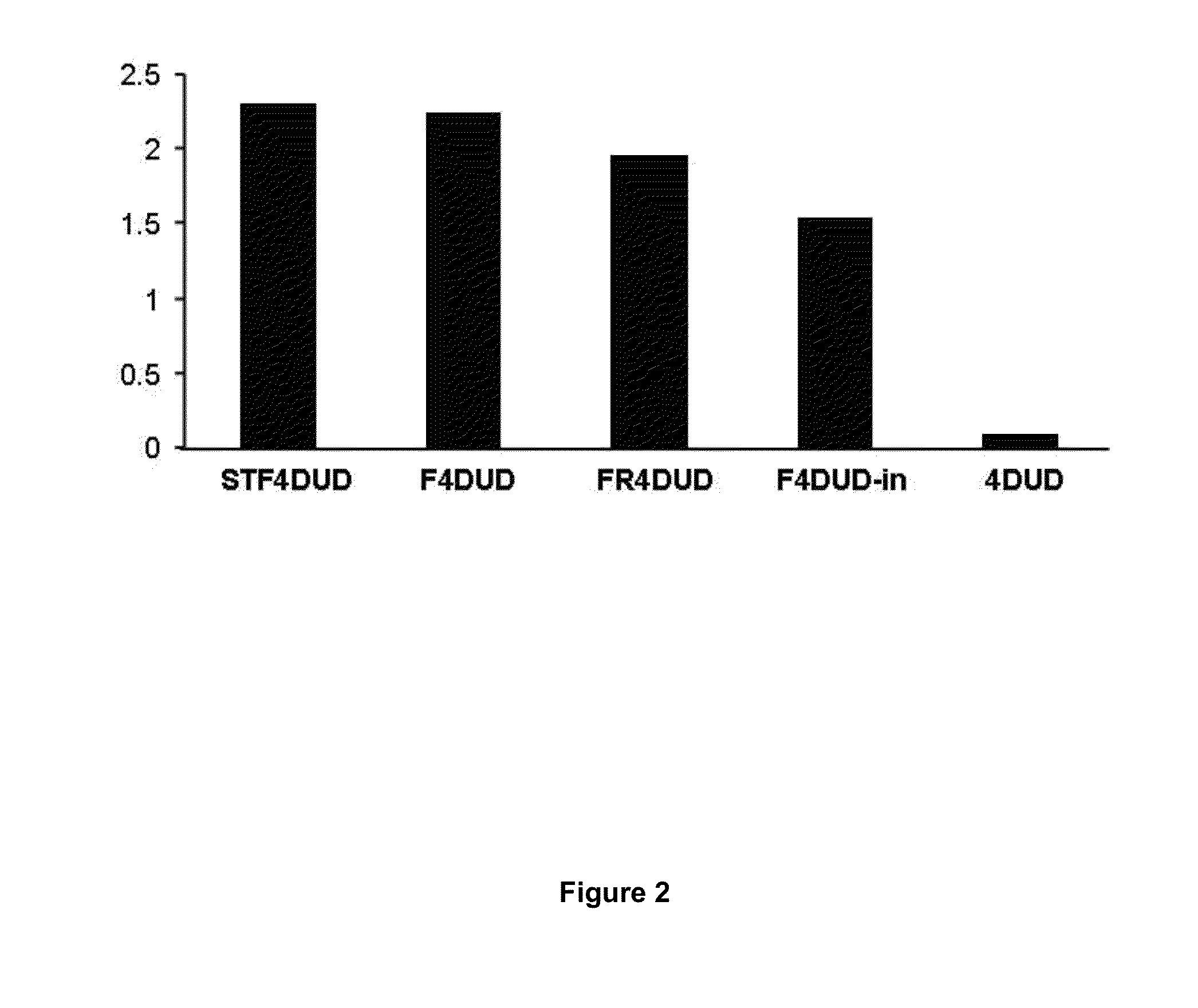
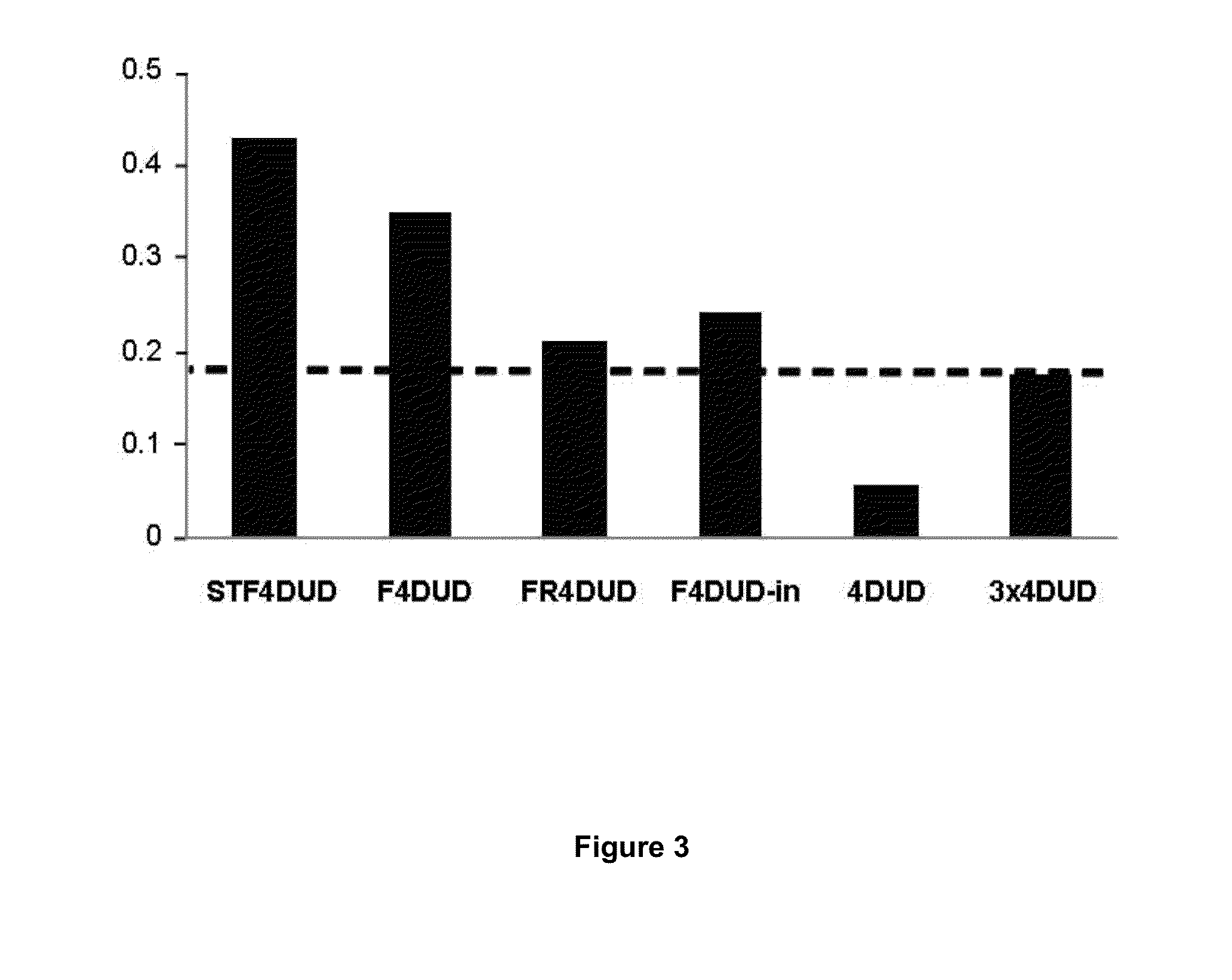
Use of flagellins from the genus marinobacter as vaccination adjuvants
Use of flagellins from the genus Marinobacter as vaccine adjuvants. This invention is based on the use of two recombinant flagellins, F and FR, from the species Marinobacter algicola (DG893T strain), as vaccine adjuvants capable of developing a specific immune response, against peptides or proteins fused to said flagellins, or administered unfused jointly with the flagellins. This invention also describes new combined vaccination strategies, based on the two Marinobacter algicola flagellins and the Salmonella typhimurium flagellin.
Owner:INST NAT DE INVESTIGACION Y TECH AGRARIA Y ALIMENTARIA INIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com