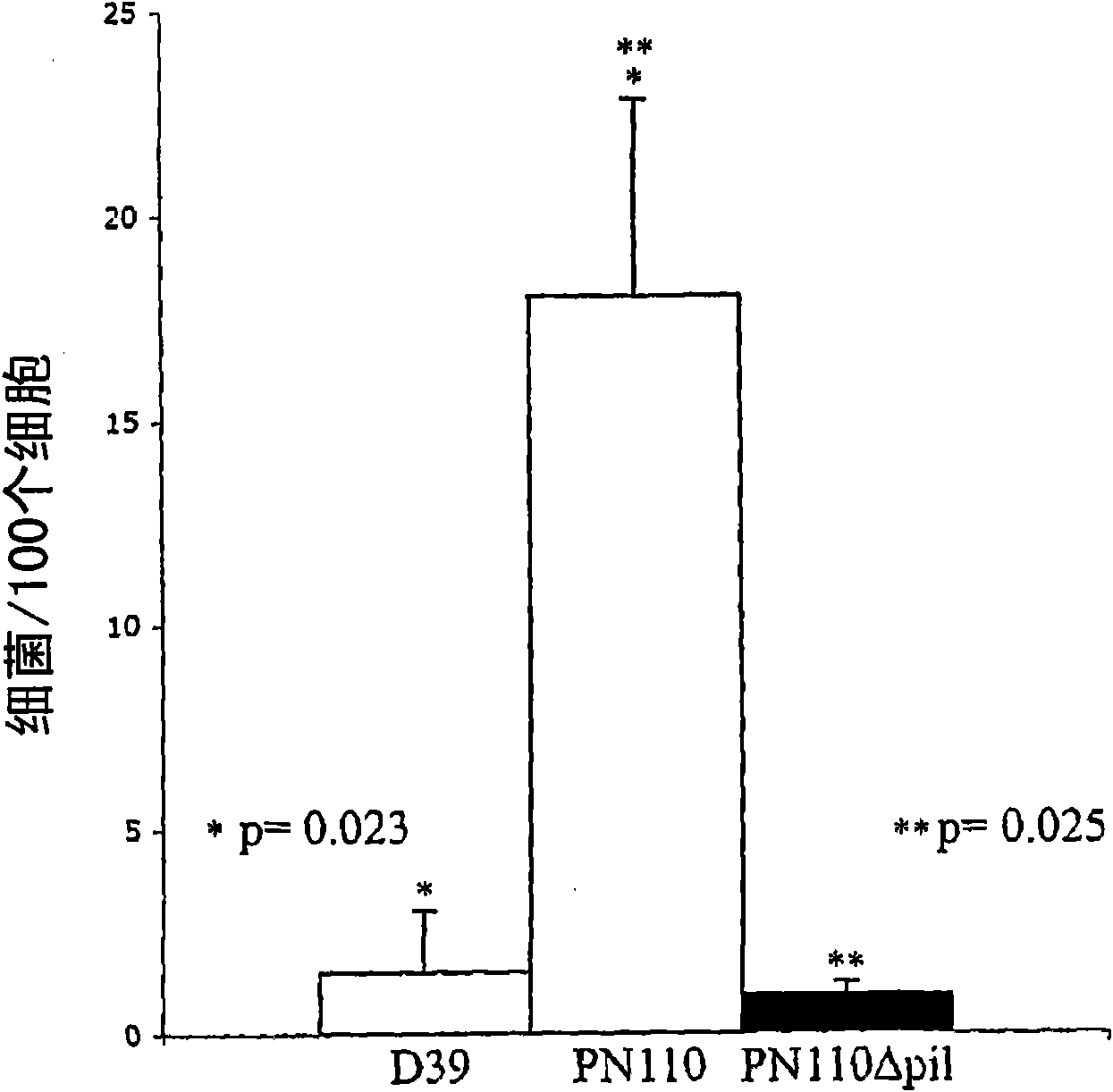
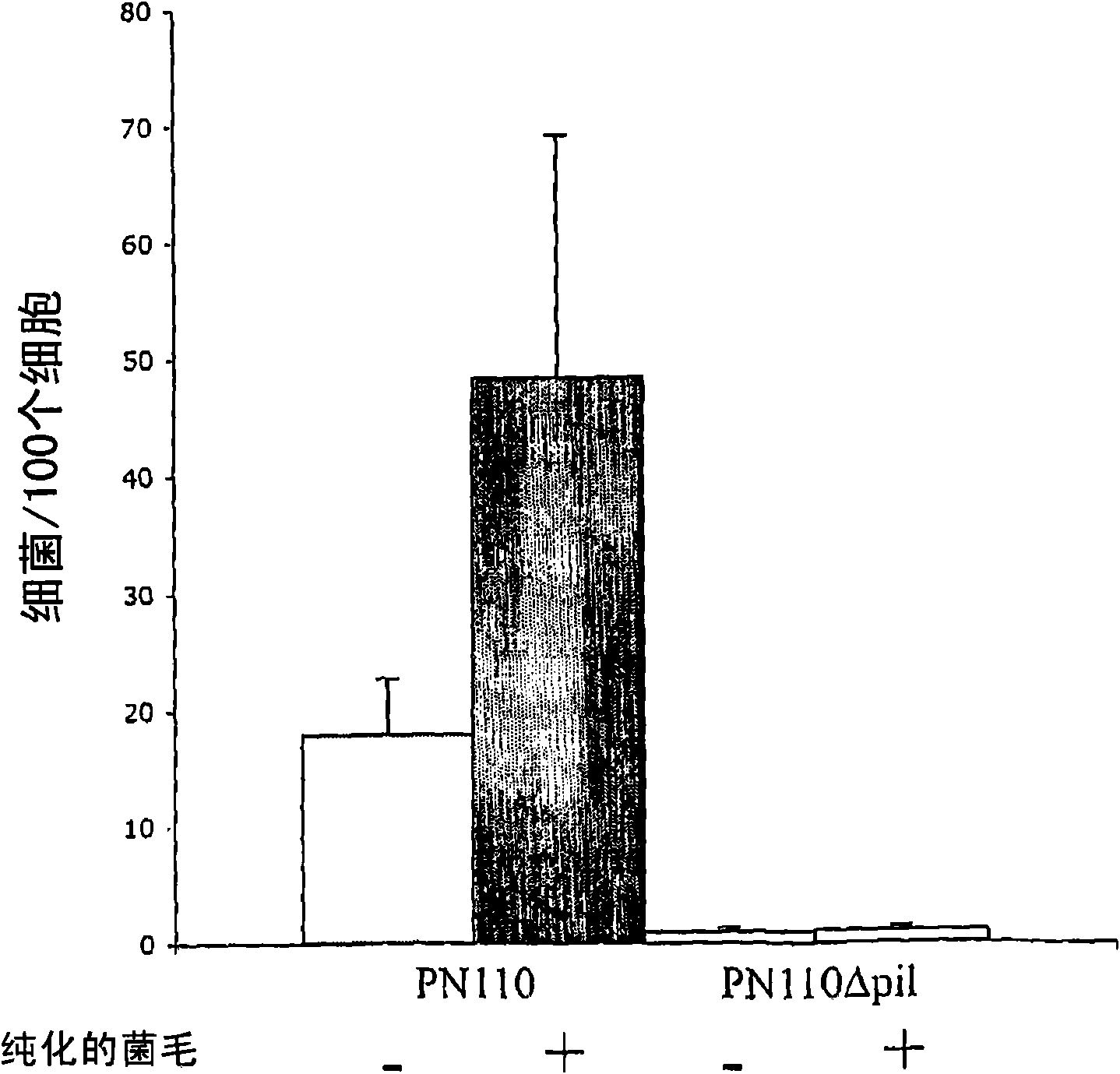
Streptococcus pneumoniae pilus antigens
A technology of Streptococcus pneumoniae and fimbriae, applied in the field of peptides, can solve problems such as unclear adhesion mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0224] In some aspects, methods for preparing antigen-adsorbed microparticles are provided. The method comprises: (a) providing an emulsion by dispersing a mixture comprising (i) water, (ii) a detergent, (iii) an organic solvent, and (iv) a biodegradable polymer selected from : Poly(alpha-hydroxy acids), polyhydroxybutyrates, polycaprolactones, polyorthoesters, polyanhydrides and polycyanoacrylates. The concentration of the polymer in the mixture is generally about 1%-30% relative to the organic solvent, and the weight ratio of soil release agent-polymer in the mixture is generally about 0.00001:1-0.1:1 (more typically about 0.0001 : 1-0.1: 1, about 0.001: 1-0.1: 1, or about 0.005: 1-0.1: 1); (b) removing the organic solvent in the emulsion; and (c) allowing the antigen to be adsorbed on the surface of the microparticle . In some embodiments, the concentration of the biodegradable polymer is about 3%-10% relative to the organic solvent.
[0225] In some embodiments, the mic...
Embodiment 1
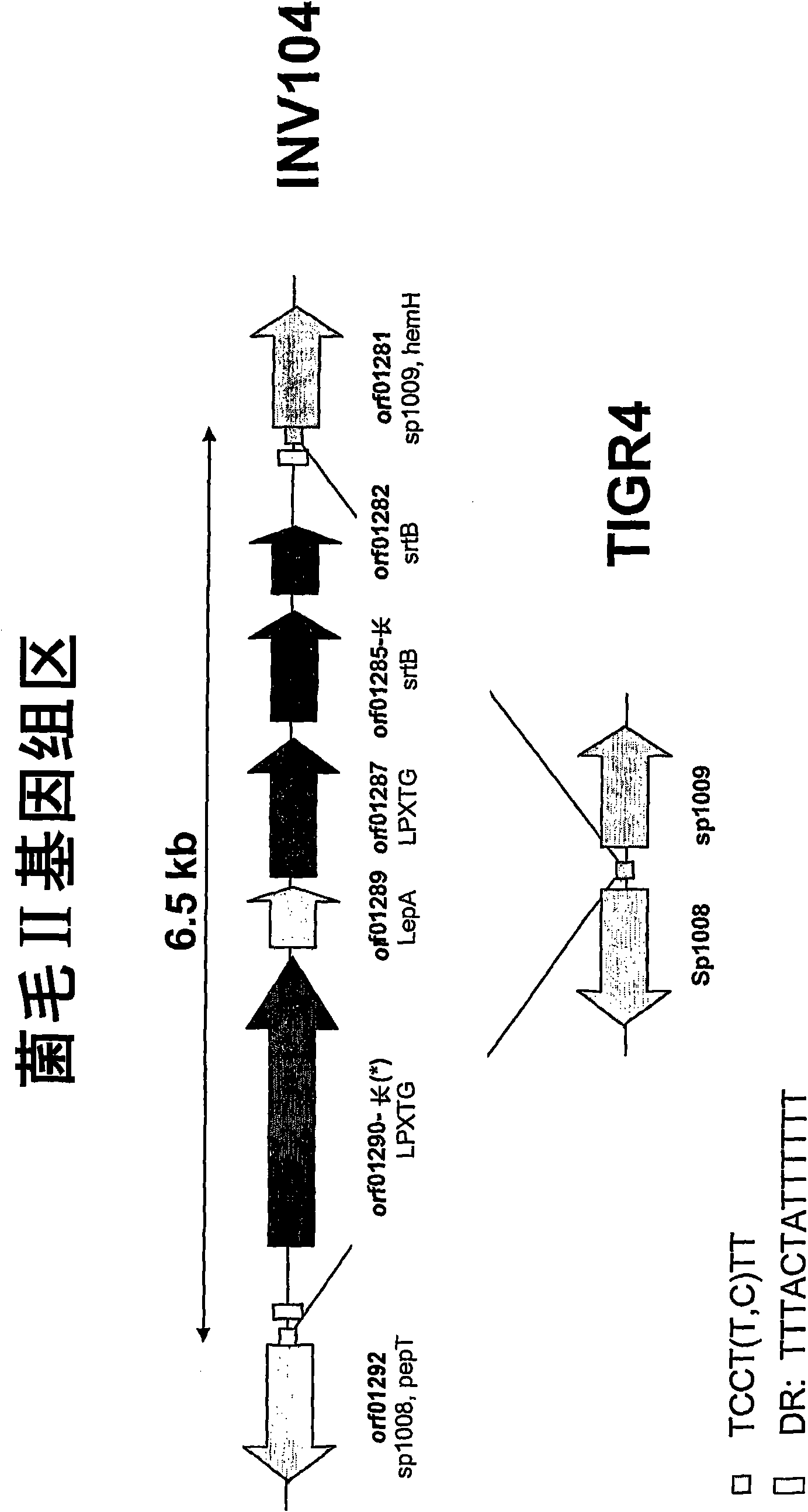
[0496] Example 1: Detection of pili II islands (INV104B) in genomic DNA
[0497] The presence of S. pneumoniae pili II islands (INV104B) shown in Table 1 was determined on purified genomic DNA or directly on bacteria (colony PCR). Table 2 lists the four oligonucleotides used for amplification.
[0498] Table 2 PCR oligonucleotides
[0499] logo
direction
sequence
1008 Forward
5’→3’
GCTGGATCGAGTTTGAAACCAGAA (SEQ ID
NO: 24)
1009 reverse
3’→5’
TAAGGATCACCAAAGTCCAAGGCA (SEQ ID
NO: 25)
Int - reverse
3’→5’
TTTCAGTGTATGTTTTAGTGCTTCA (SEQ ID
NO: 26)
Int - Forward
5’→3’
ATGGCTTCAGGGGCTATGTTCGGTG (SEQ ID
NO: 27)
[0500] Three diagnostic PCRs were performed on each of the strains listed in Table 1 using the following PCR oligonucleotide combinations: 1008 forward-1009 reverse; 1008 forward-int reverse; and int forward-1009 reverse. 1008 forward-int reverse and in...
Embodiment 2
[0503] Example 2: Sequences of 23F, INV200 and OXC141
[0504] 1. Sequence download and assembly
[0505] The initial sequences of the four S. pneumoniae strains were downloaded from the Sanger website (see World Wide Web "sanger.ac.uk / Projects / Microbes / ”). The Sanger sequences consisted of varying numbers of non-contiguous contigs. Details of the downloaded sequences are listed in Table 3:
[0506] Table 3. Download sequence
[0507] strain
ST
number of contigs
total bp
23F
23F
81
21
2225211
INV104B
1
227
68
1986609
NV200
14
9
167
2022487
[0508] strain
ST
number of contigs
total bp
OXC141
3
180
120
1962139
[0509] To identify the likely sequence of the contig, this sequence was aligned with the complete TIGR4 sequence using MUMmer3.19 to form a single pseudomolecule. To separate the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com