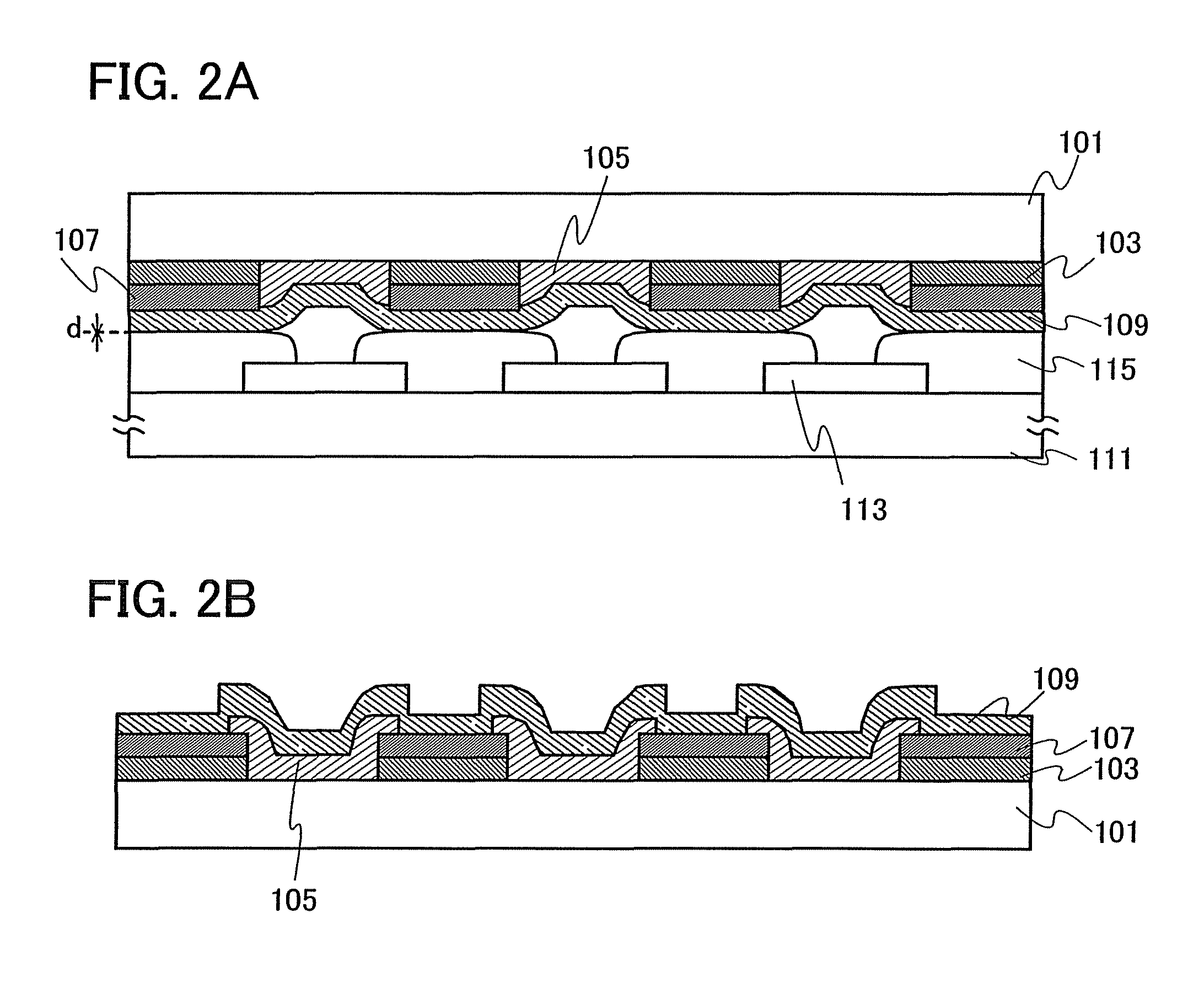
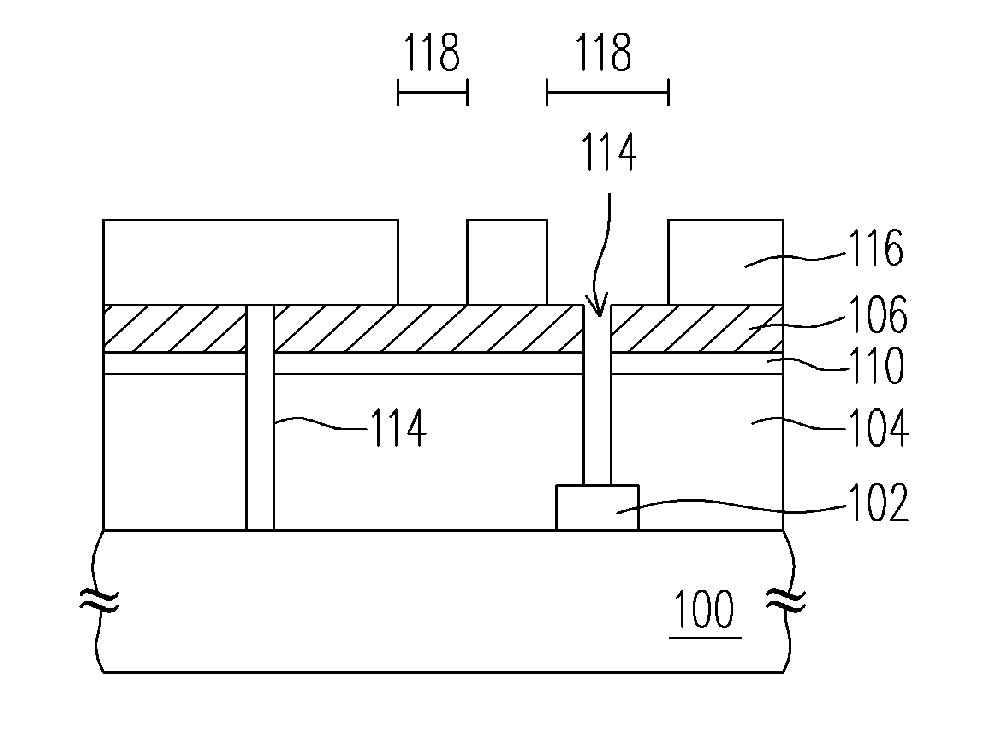
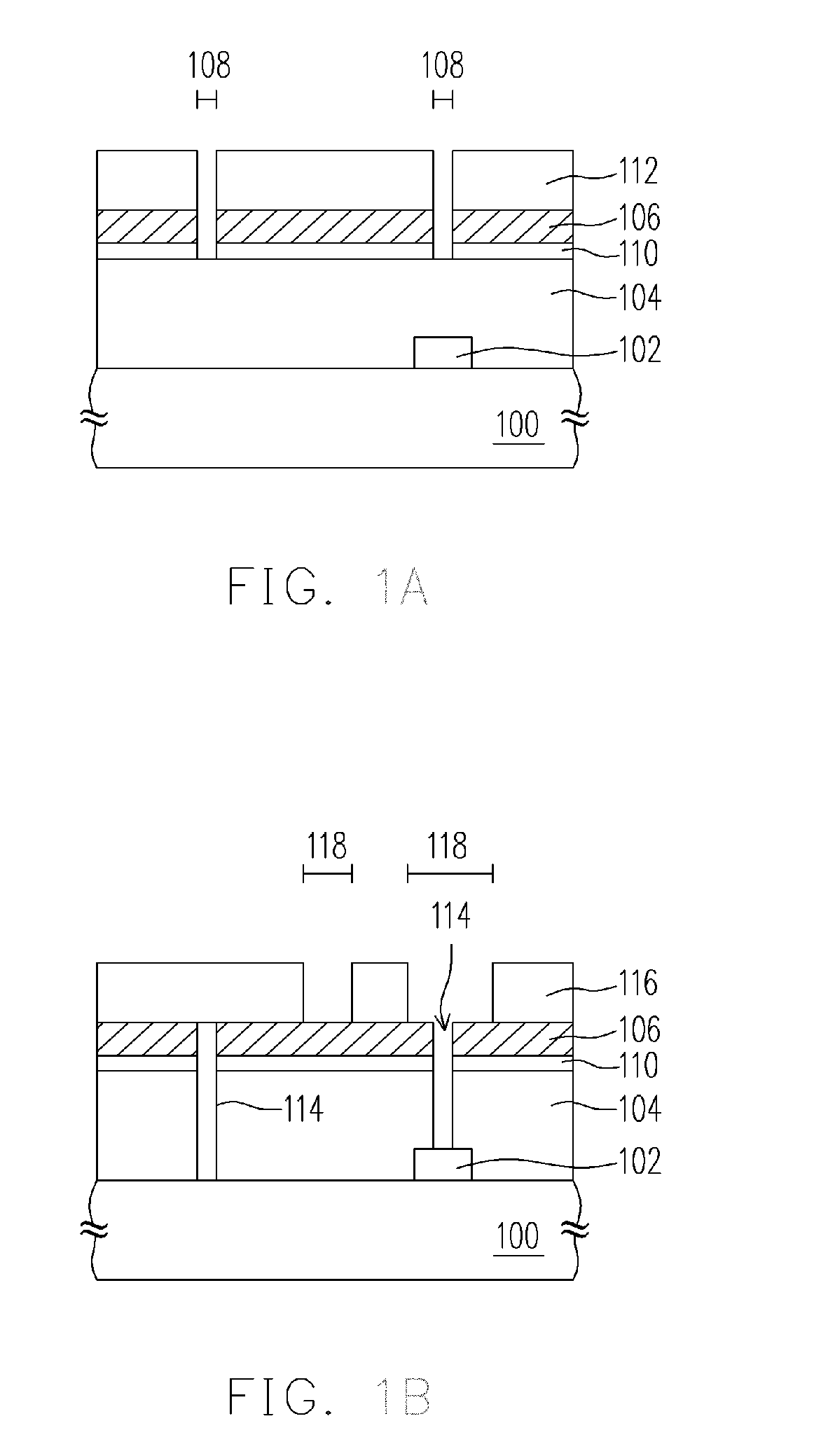
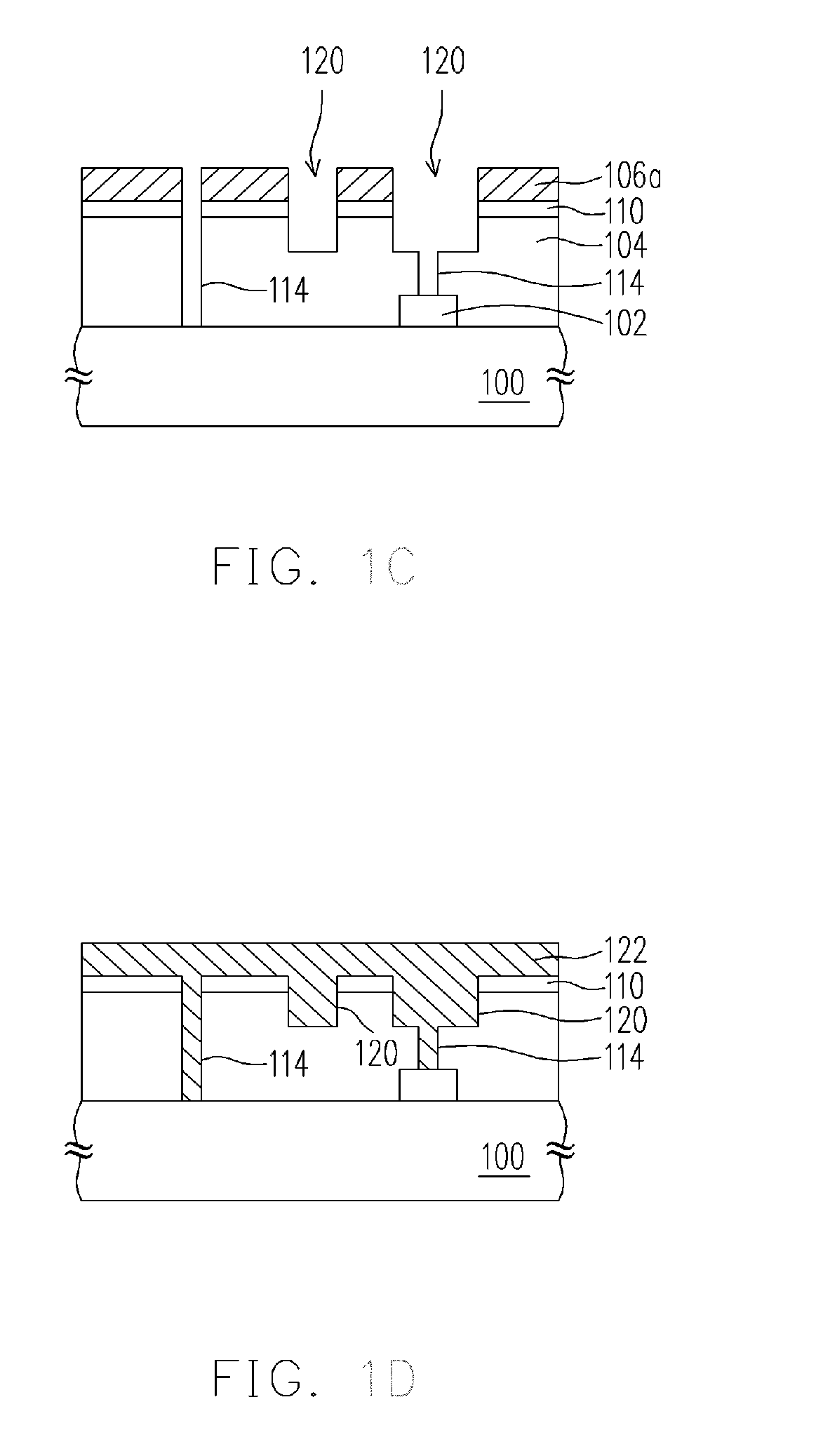
Patents
Literature
78results about How to "Accurate layering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
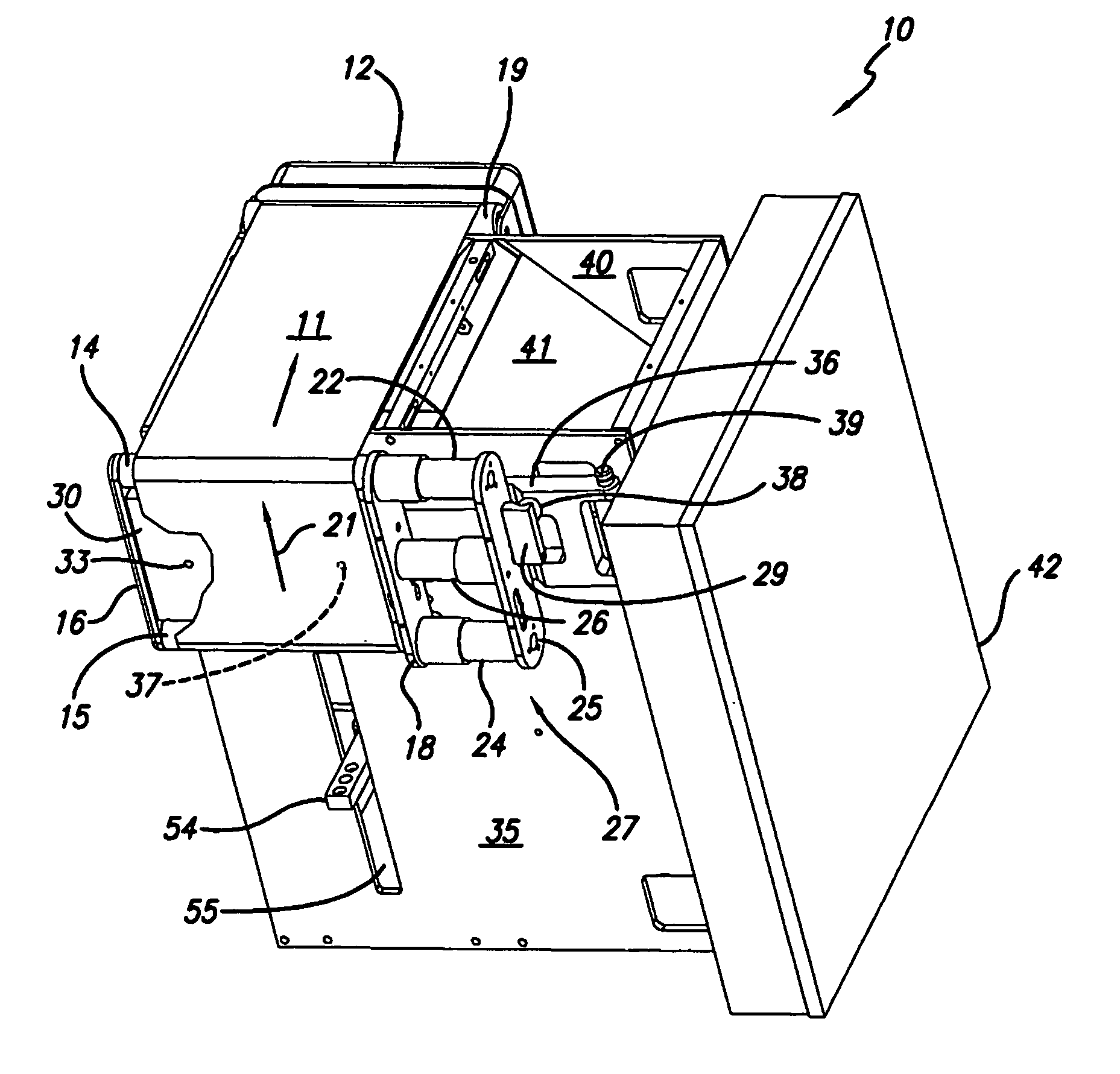
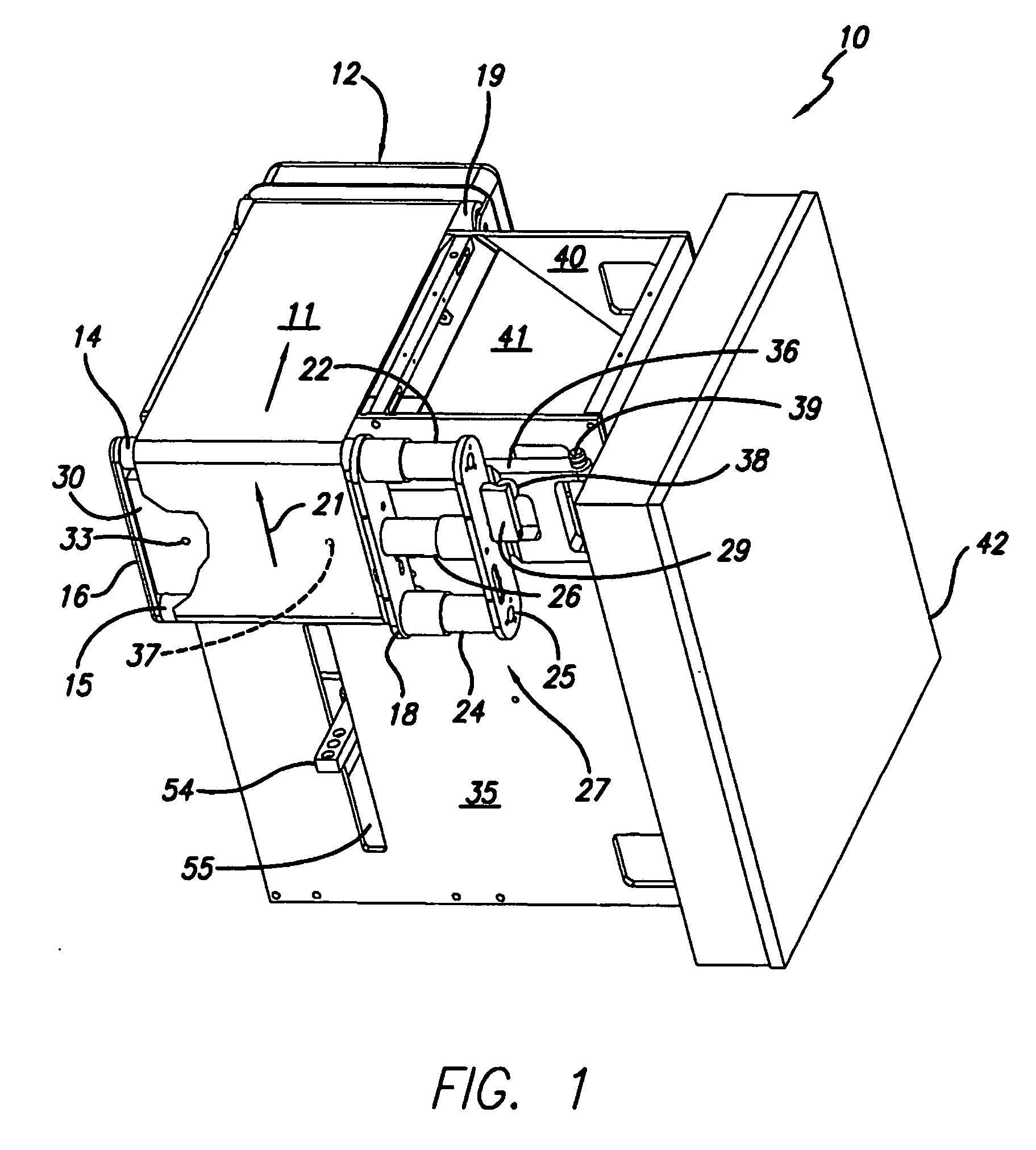
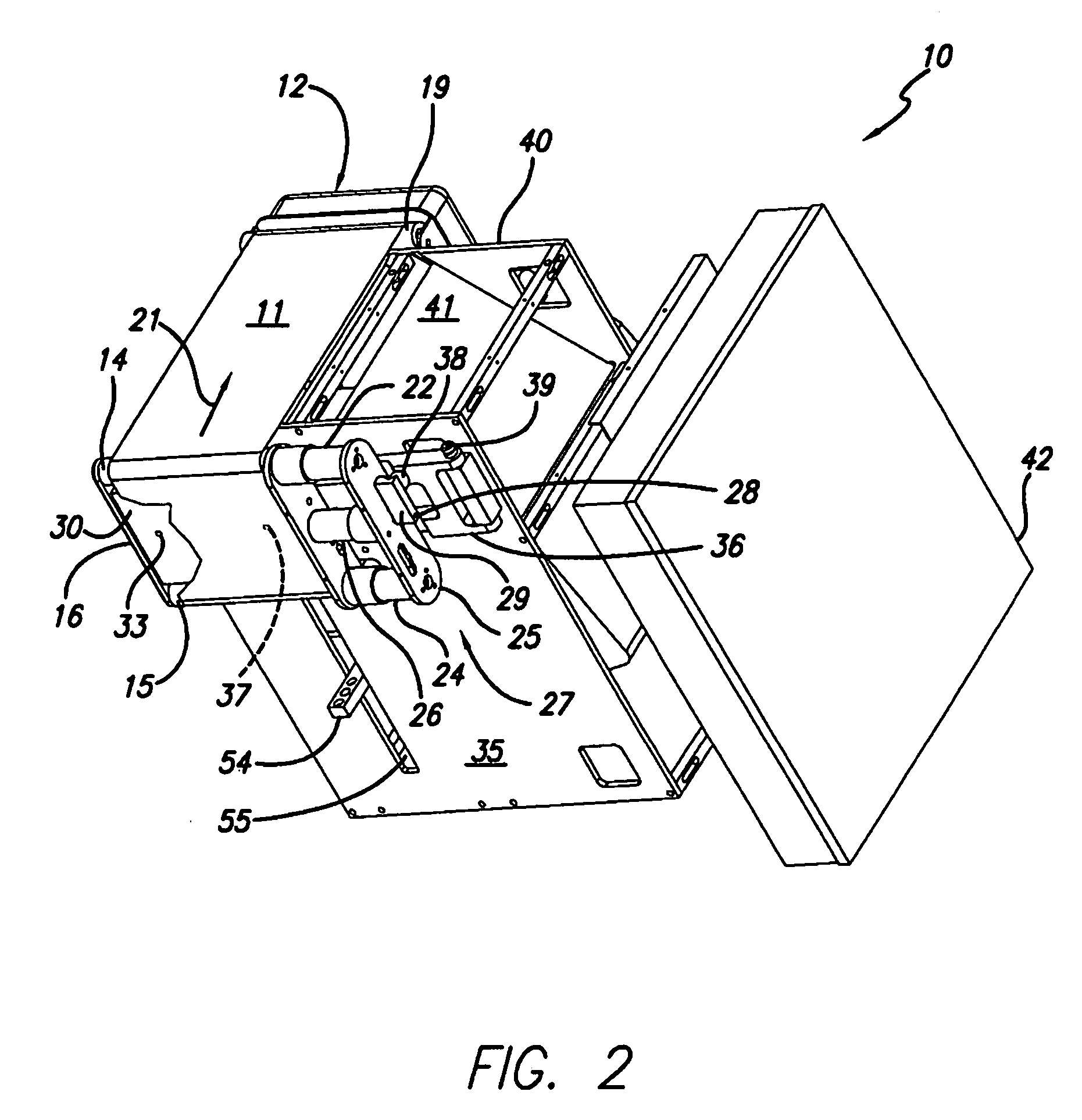
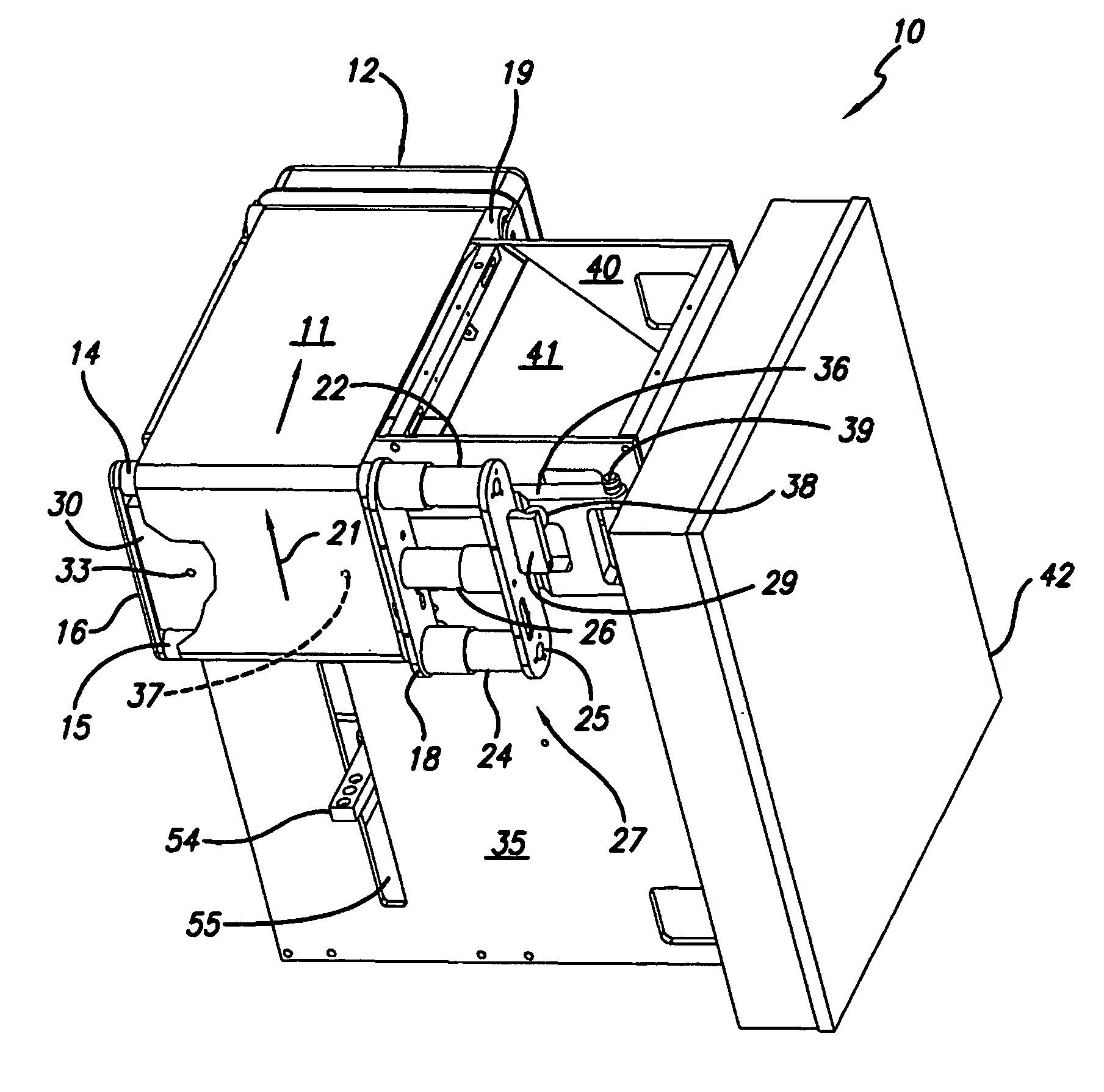
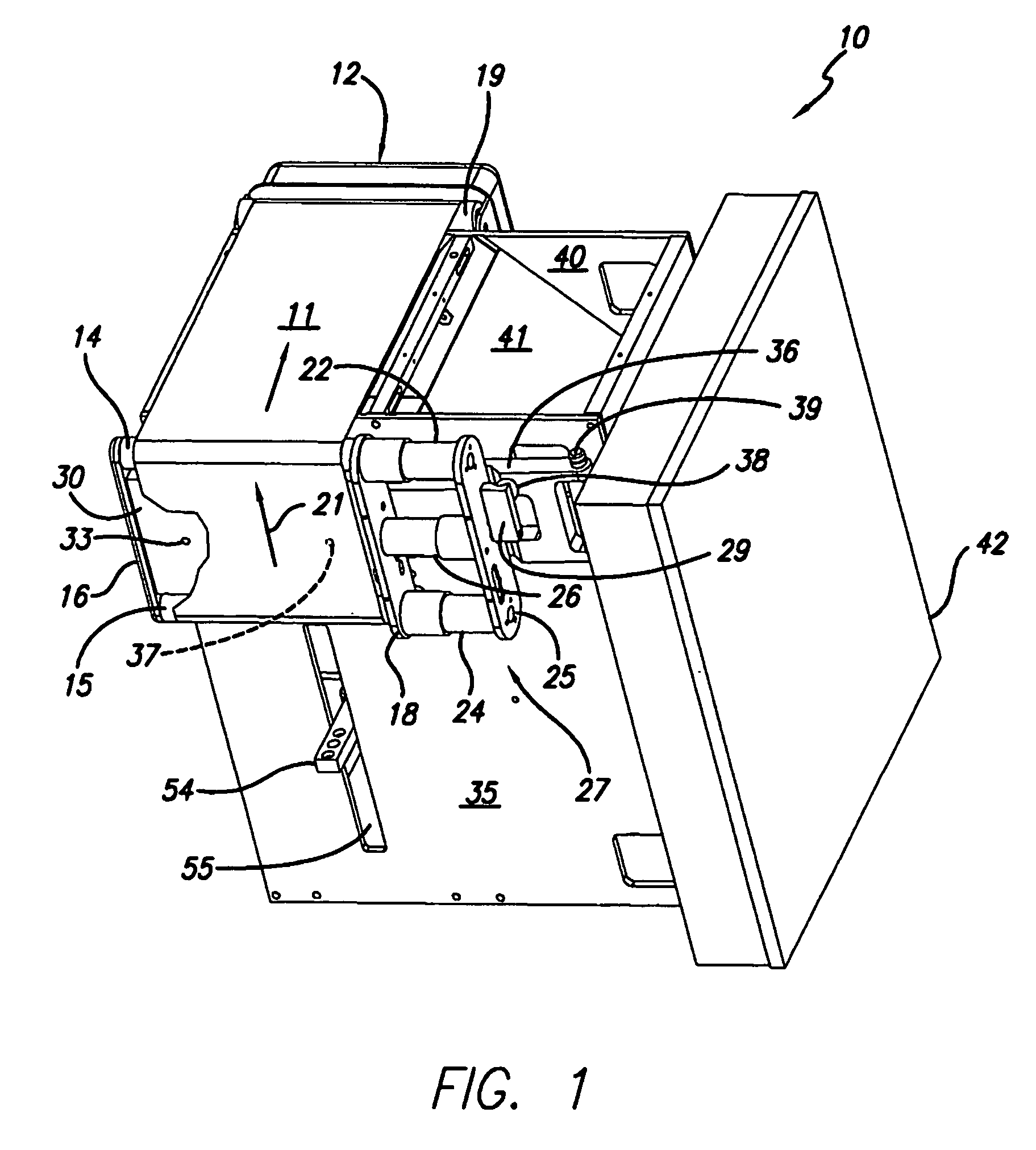
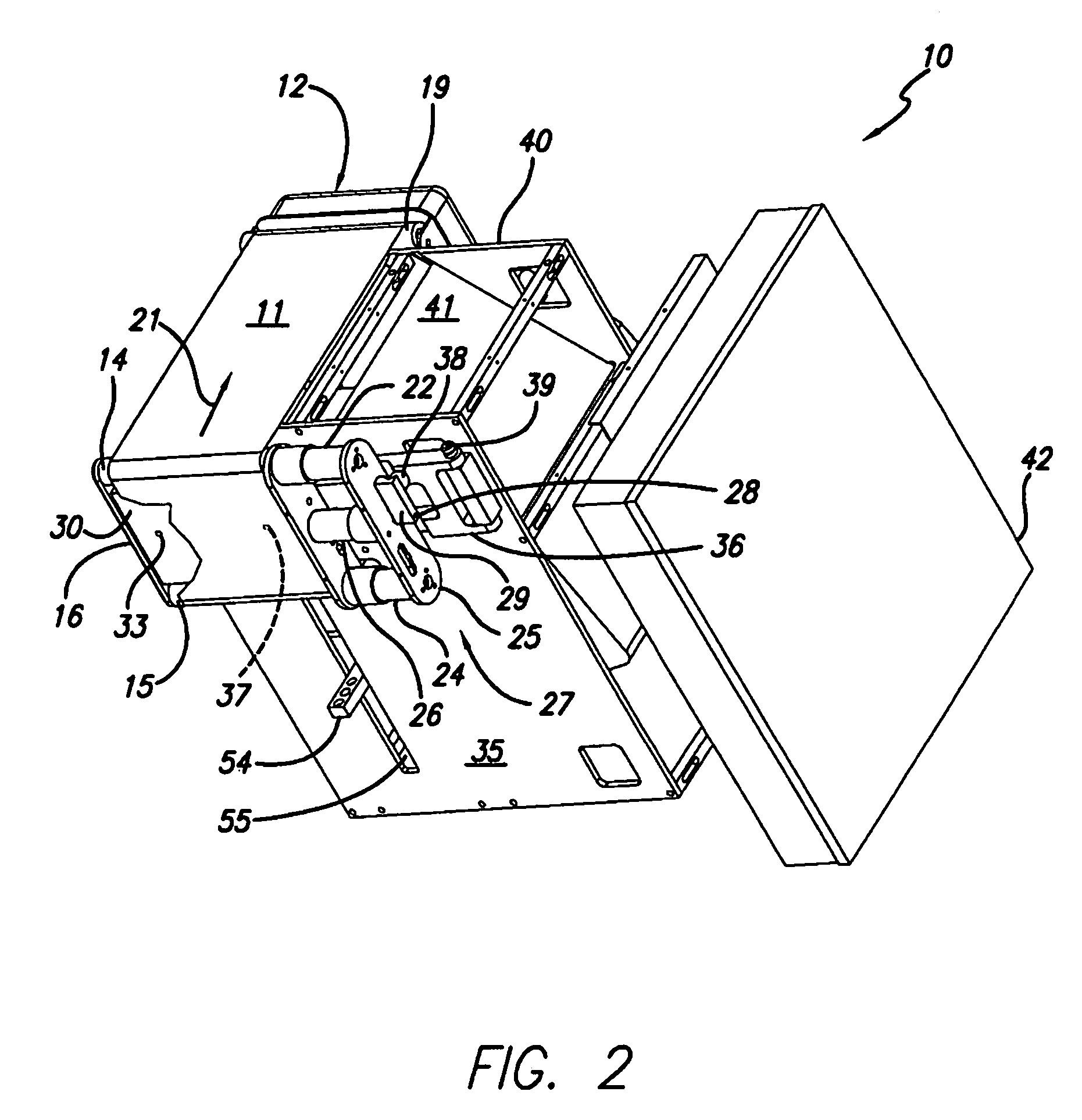
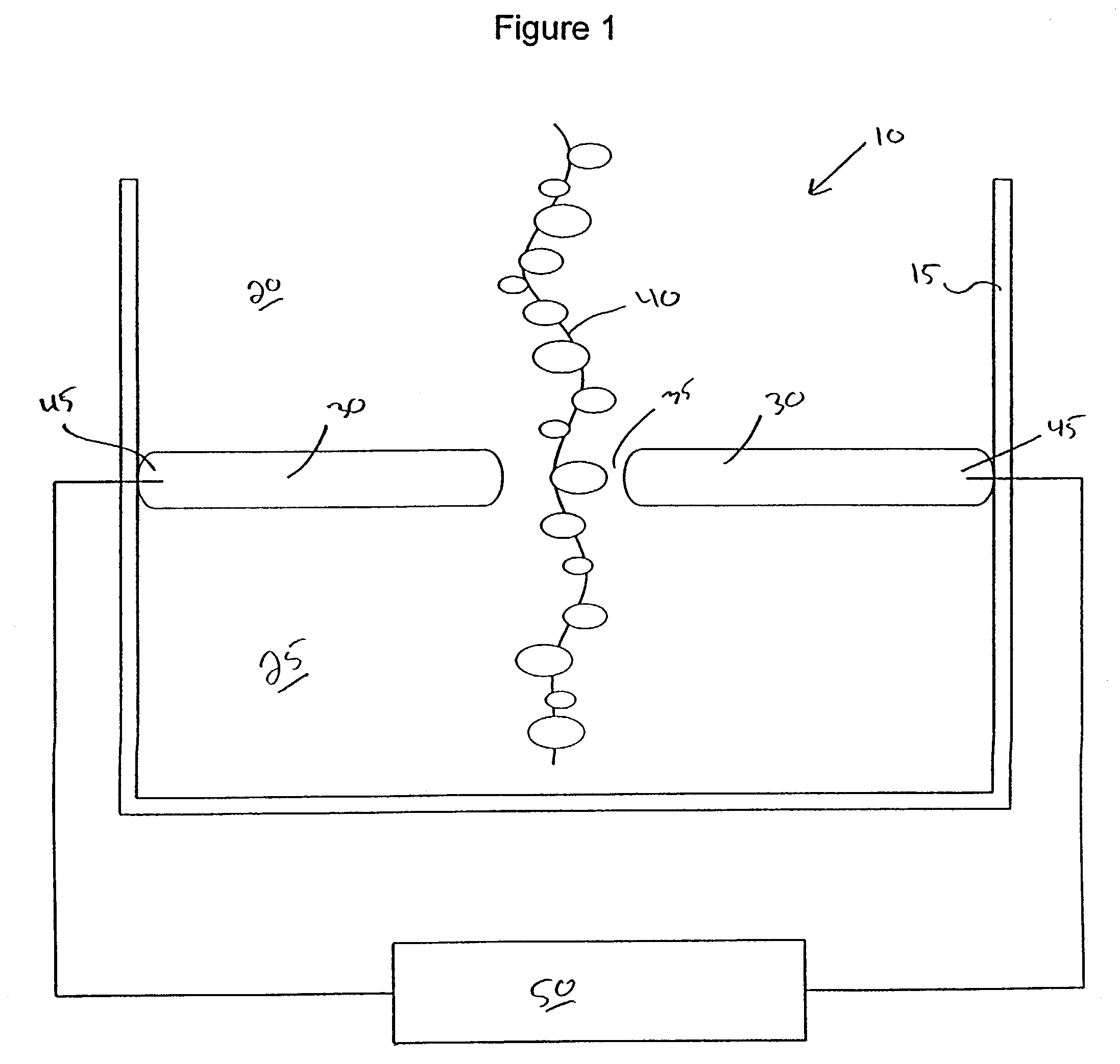
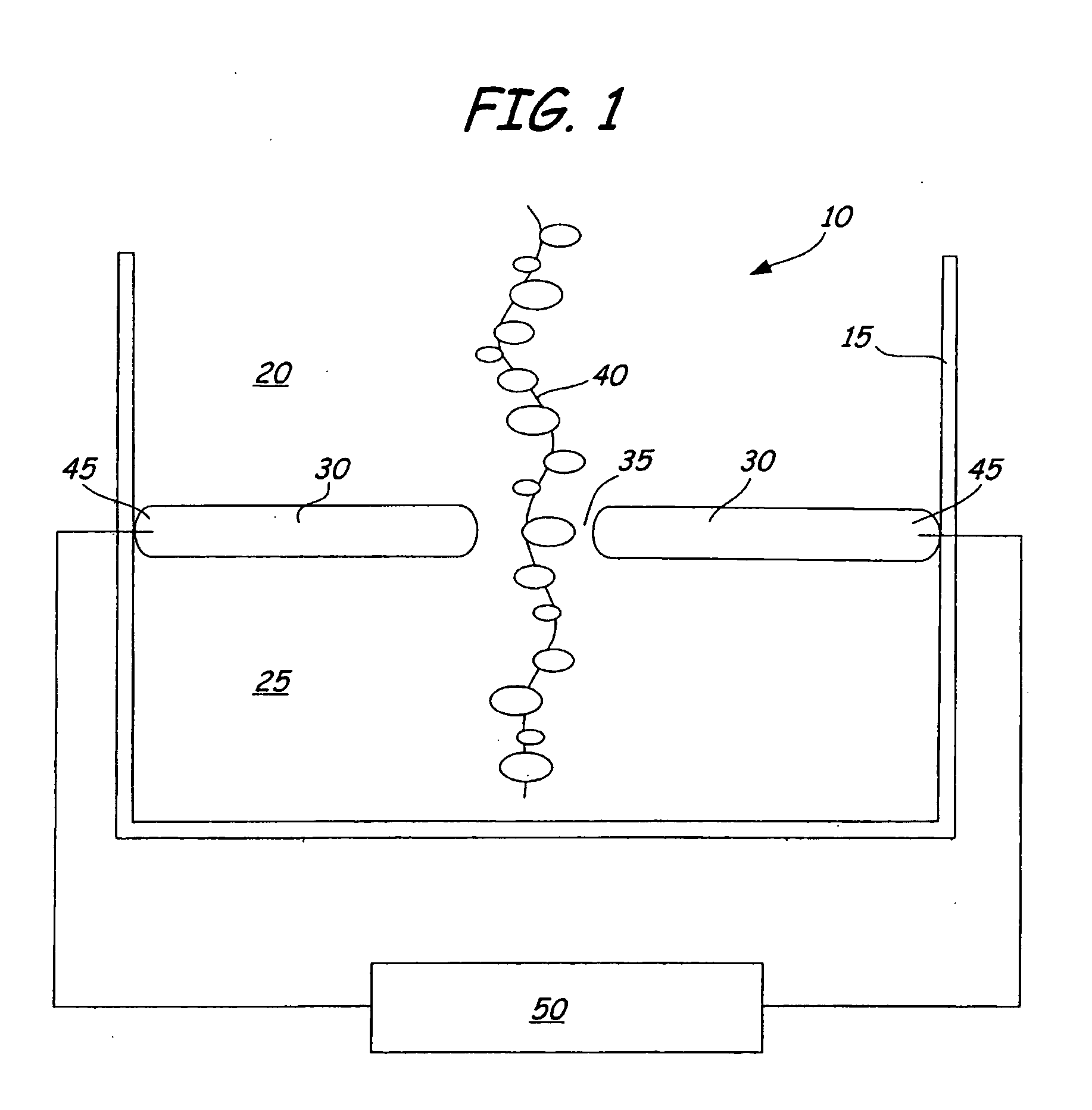
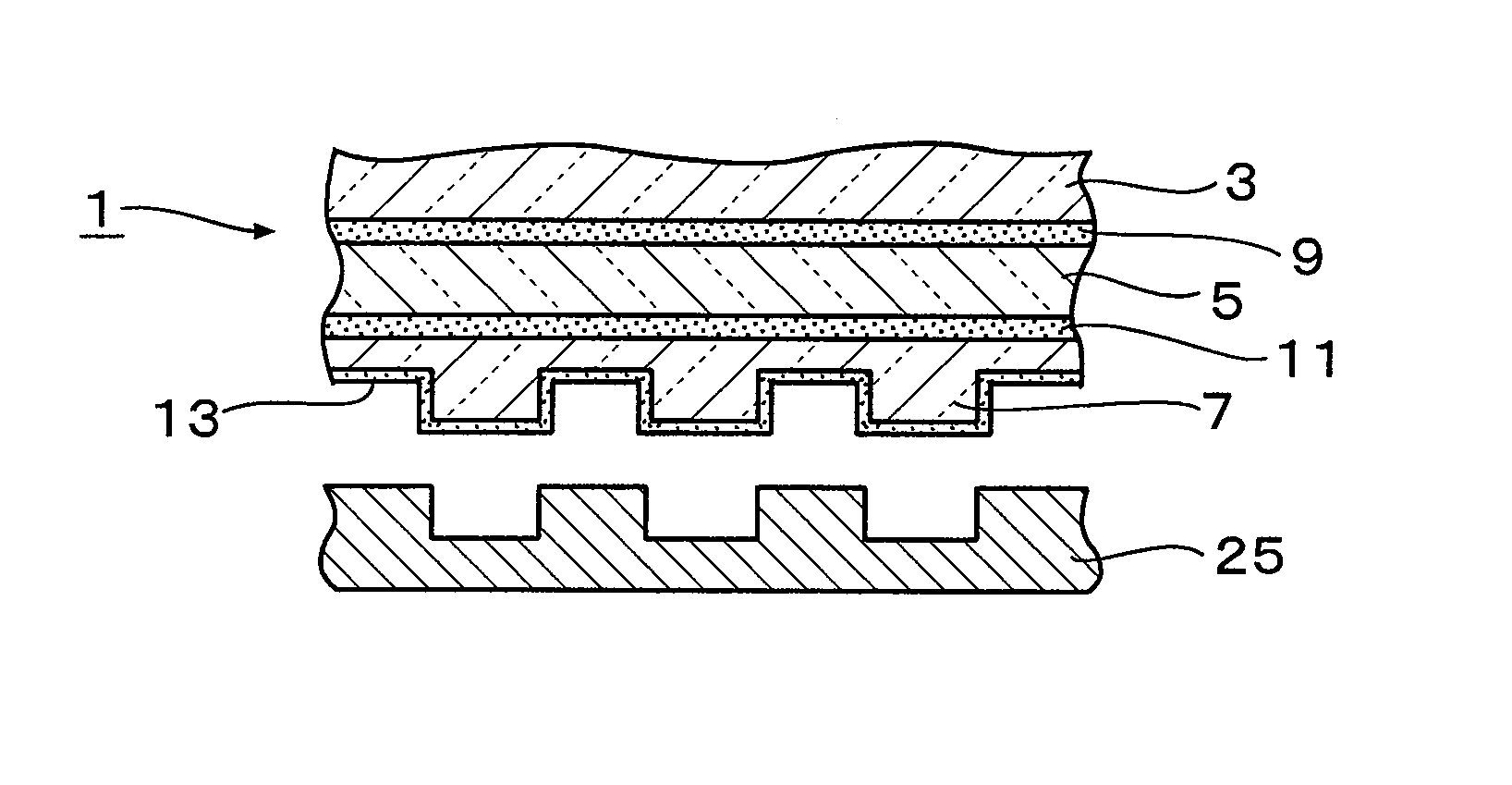
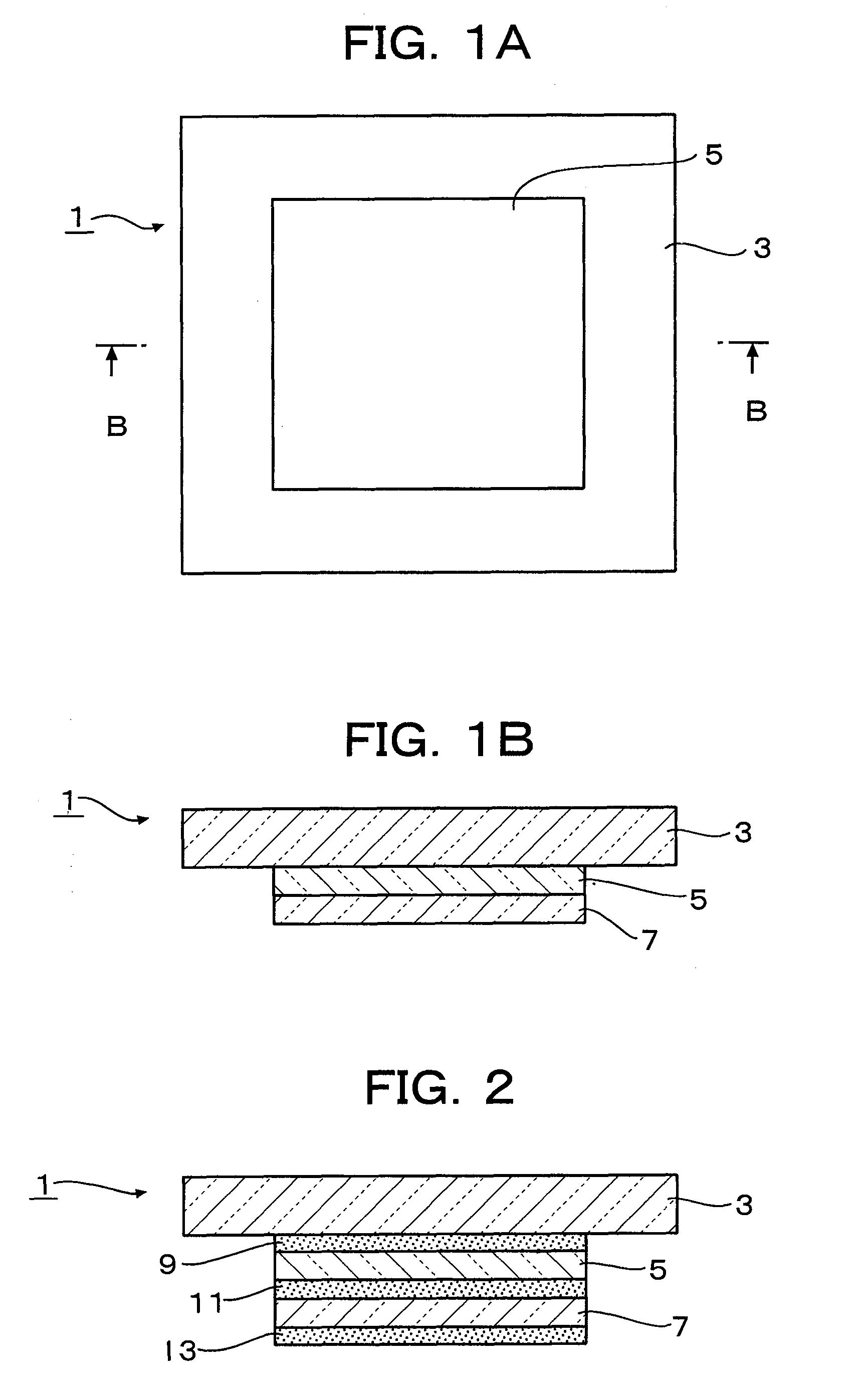
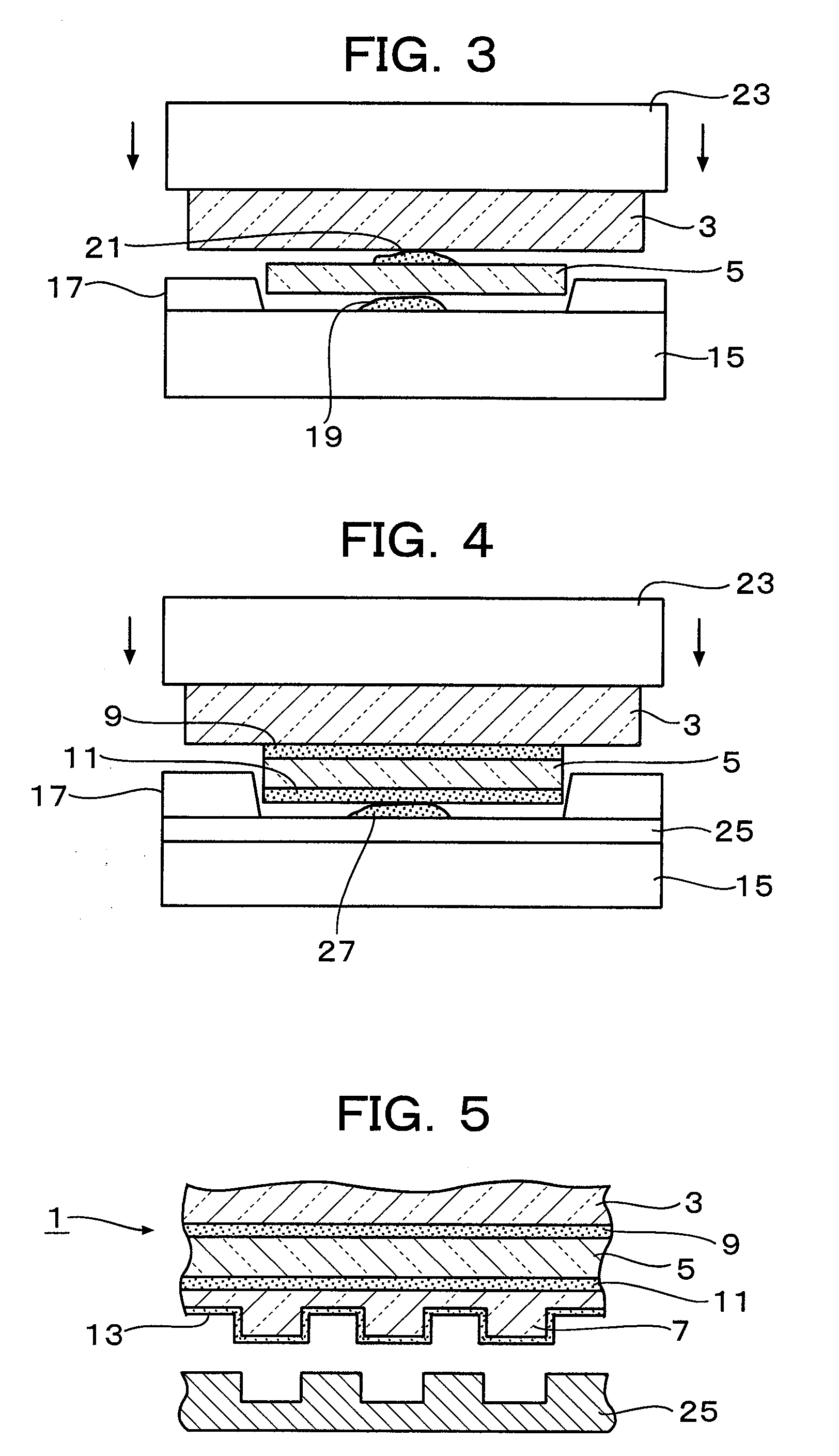
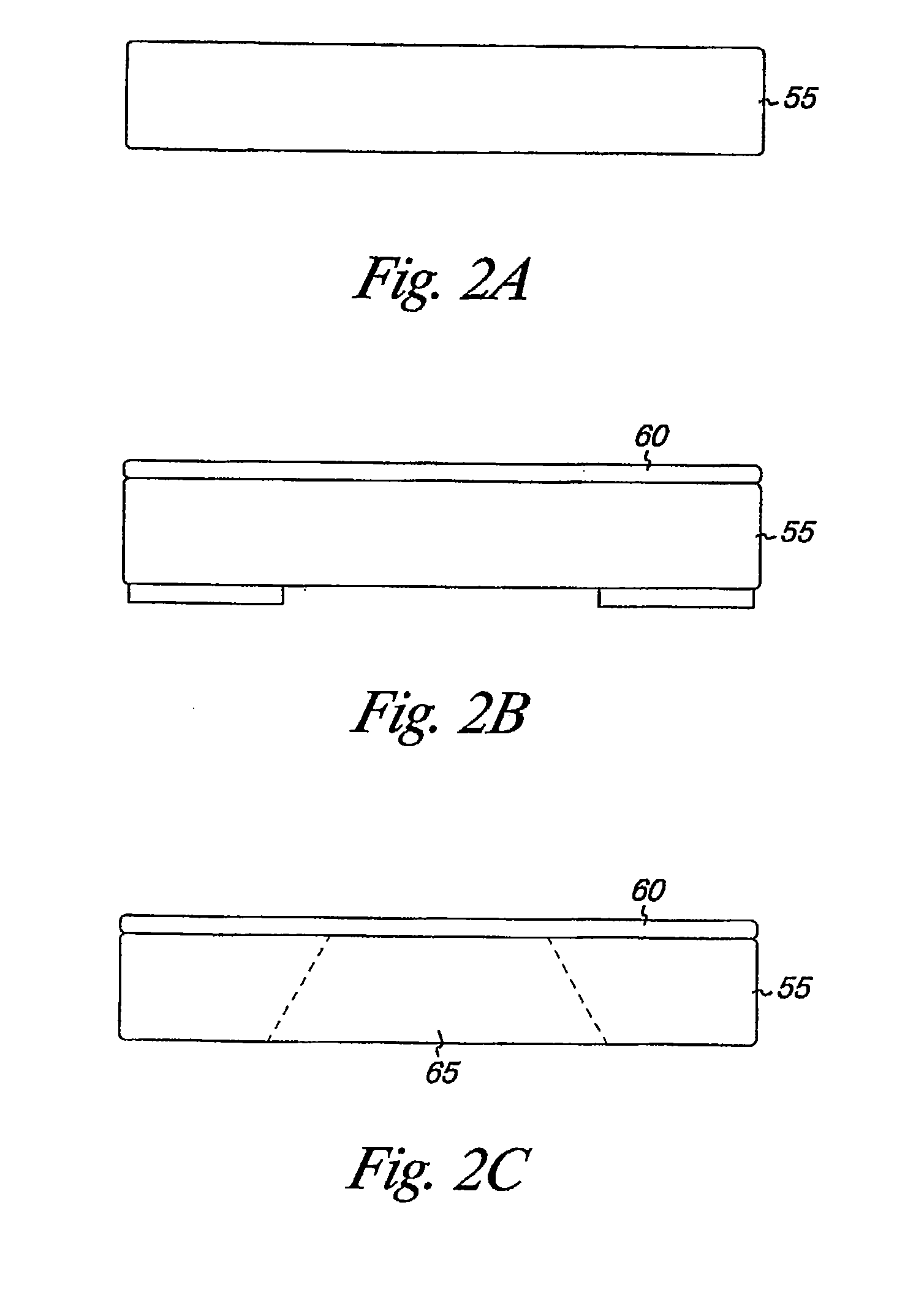
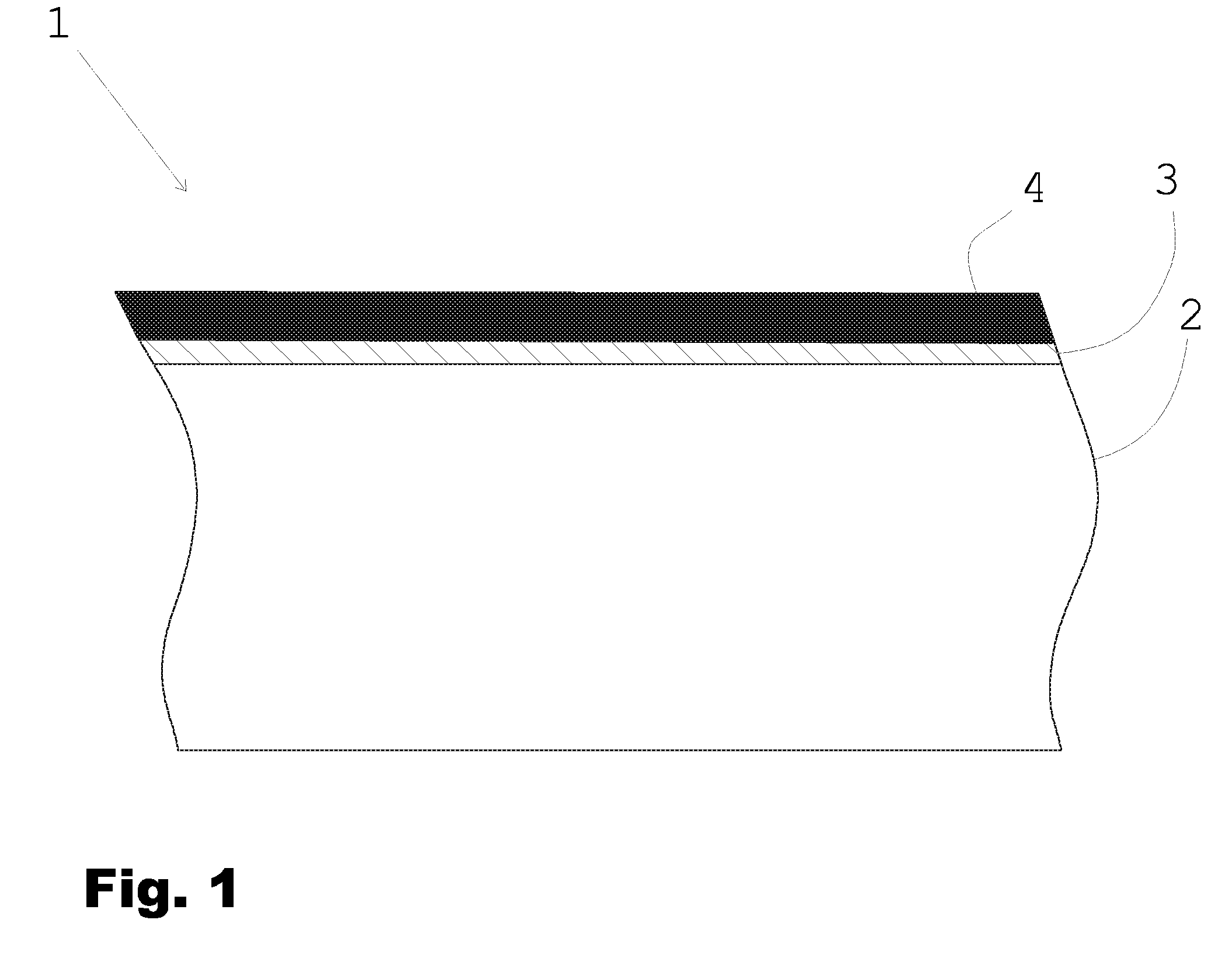
Material delivery tension and tracking system for use in solid imaging
ActiveUS20070259066A1Low costAccurate layeringAdditive manufacturing apparatusConfectioneryOptical radiationHigh resolution imaging
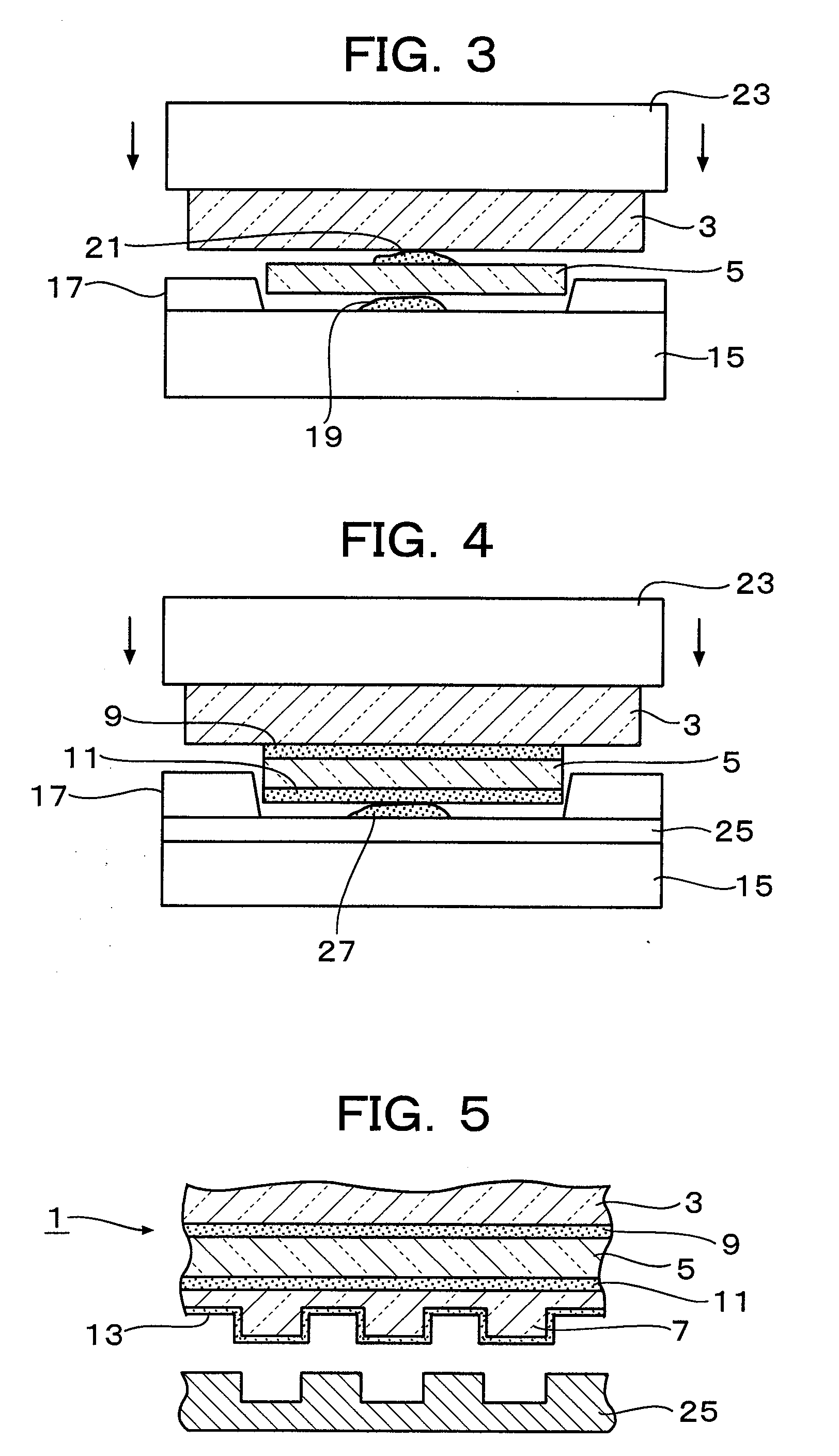
A solid imaging apparatus and method employing a radiation transparent build material carrier and a build material dispensing system that accurately controls the thickness of the transferred layer of solidifiable liquid build material to the radiation transparent build material carrier to achieve high resolution imaging in three-dimensional objects built using an electro-optical radiation source.
Owner:3D SYST INC
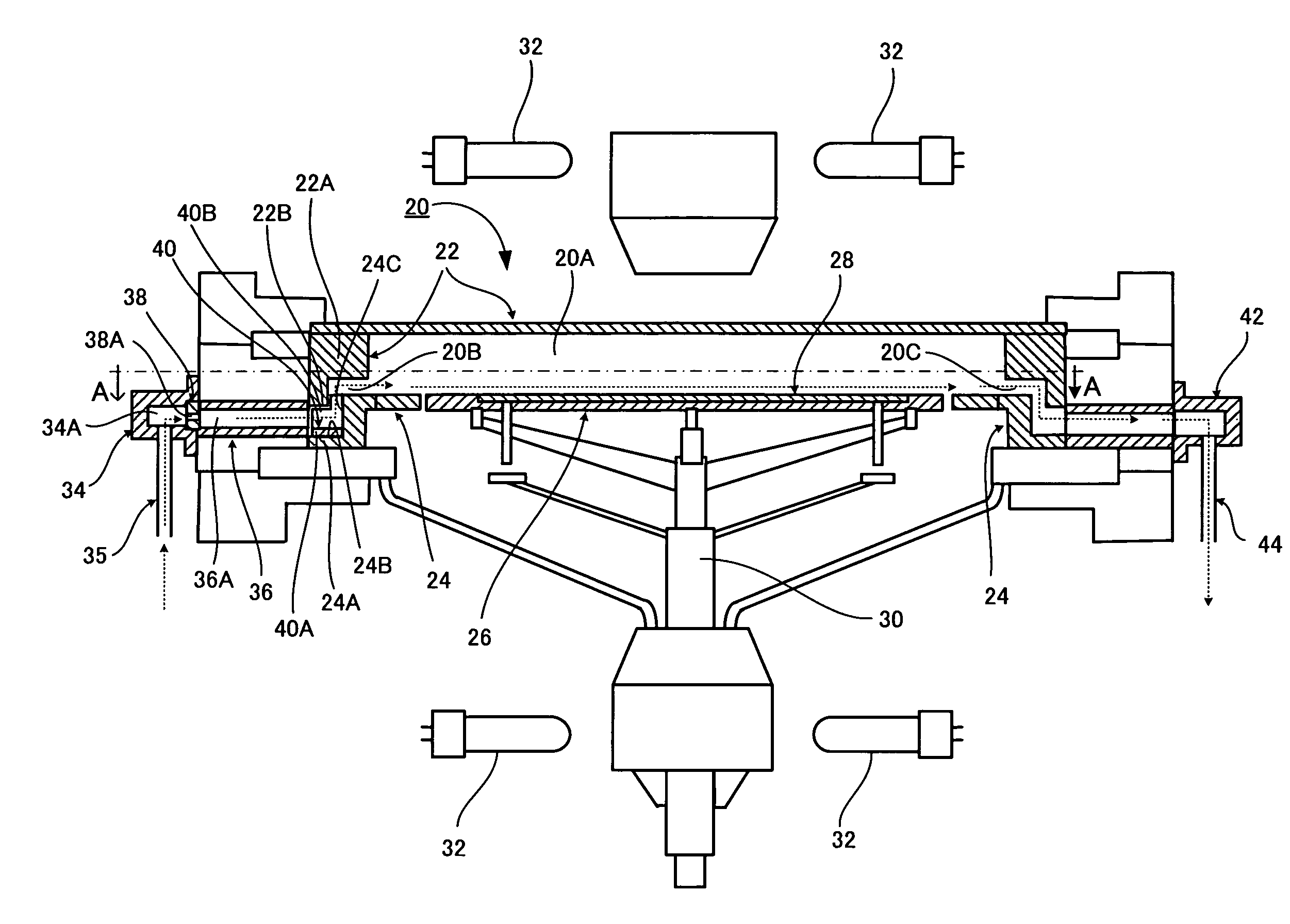
Apparatus and method for depositing layer on substrate
InactiveUS20070281084A1Reduce biasEasy to controlLiquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringReaction chamber
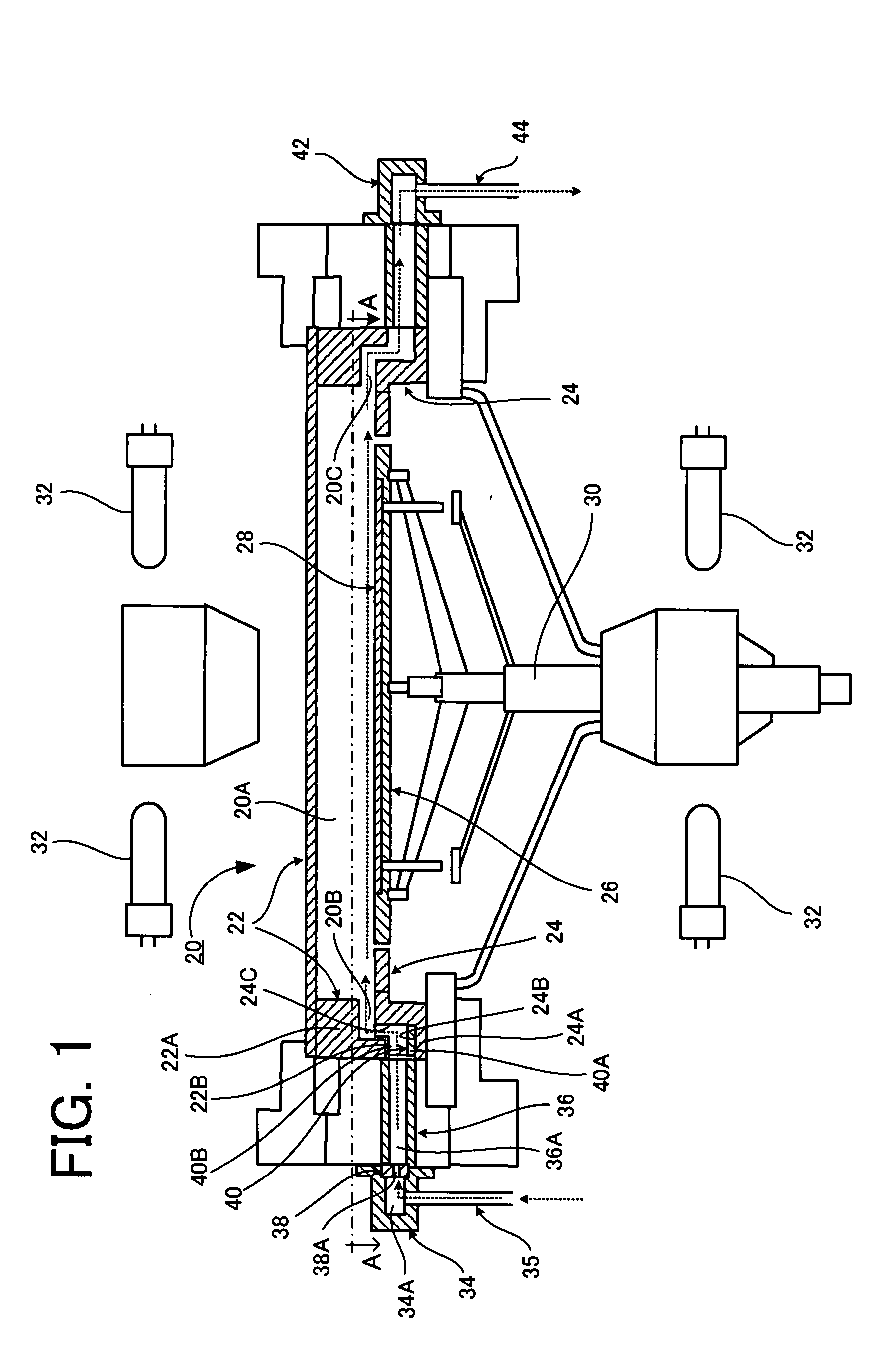
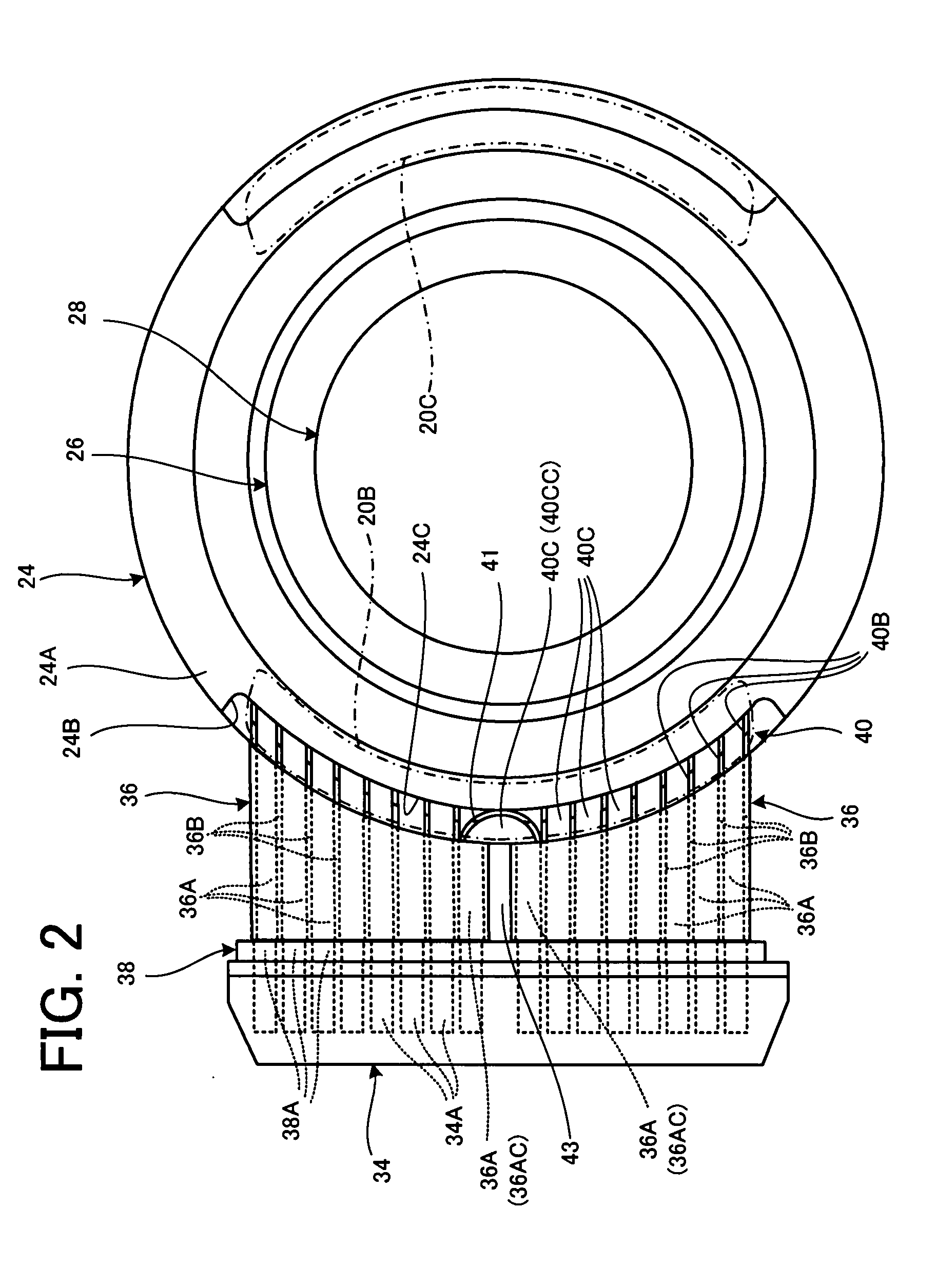
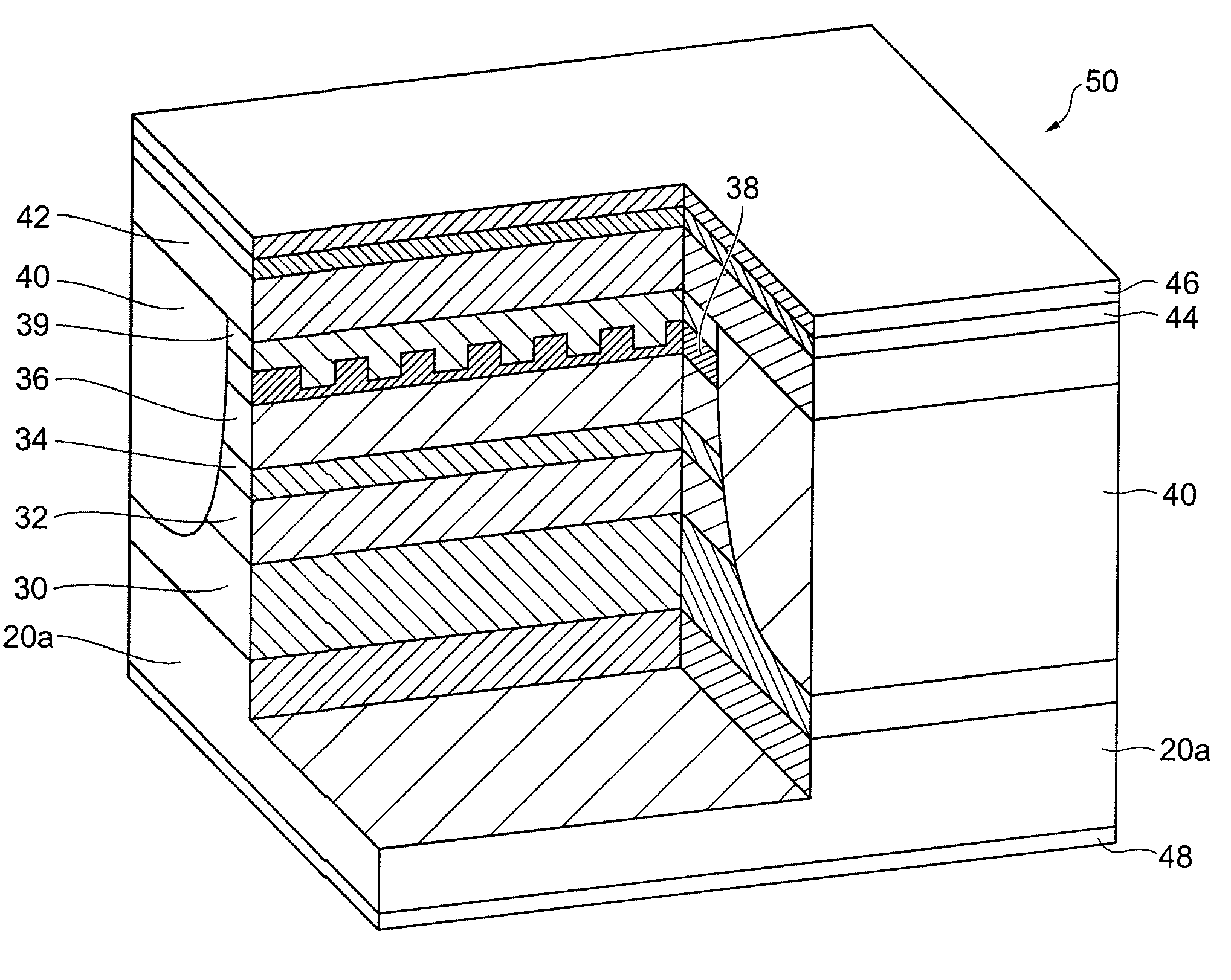
A reactant gas is supplied to a gas inlet port 40B of a reaction chamber 20A from a plurality of gas flow paths 36A. The number of gas flow paths 36A is five or more within a range of one side of the gas inlet port 40B divided in two at the center thereof. The pitch between adjacent gas flow paths 36A is 10 mm or more. A baffle 38 having a plurality of slit holes 38A is disposed upstream of the gas flow paths 36A. The gas flow rates of the respective gas flow paths 36A are adjusted by recurrent calculation using layer growth sensitivity data that defines the relation between the gas flow rates of the respective gas flow paths 36A.
Owner:SUMCO TECHXIV
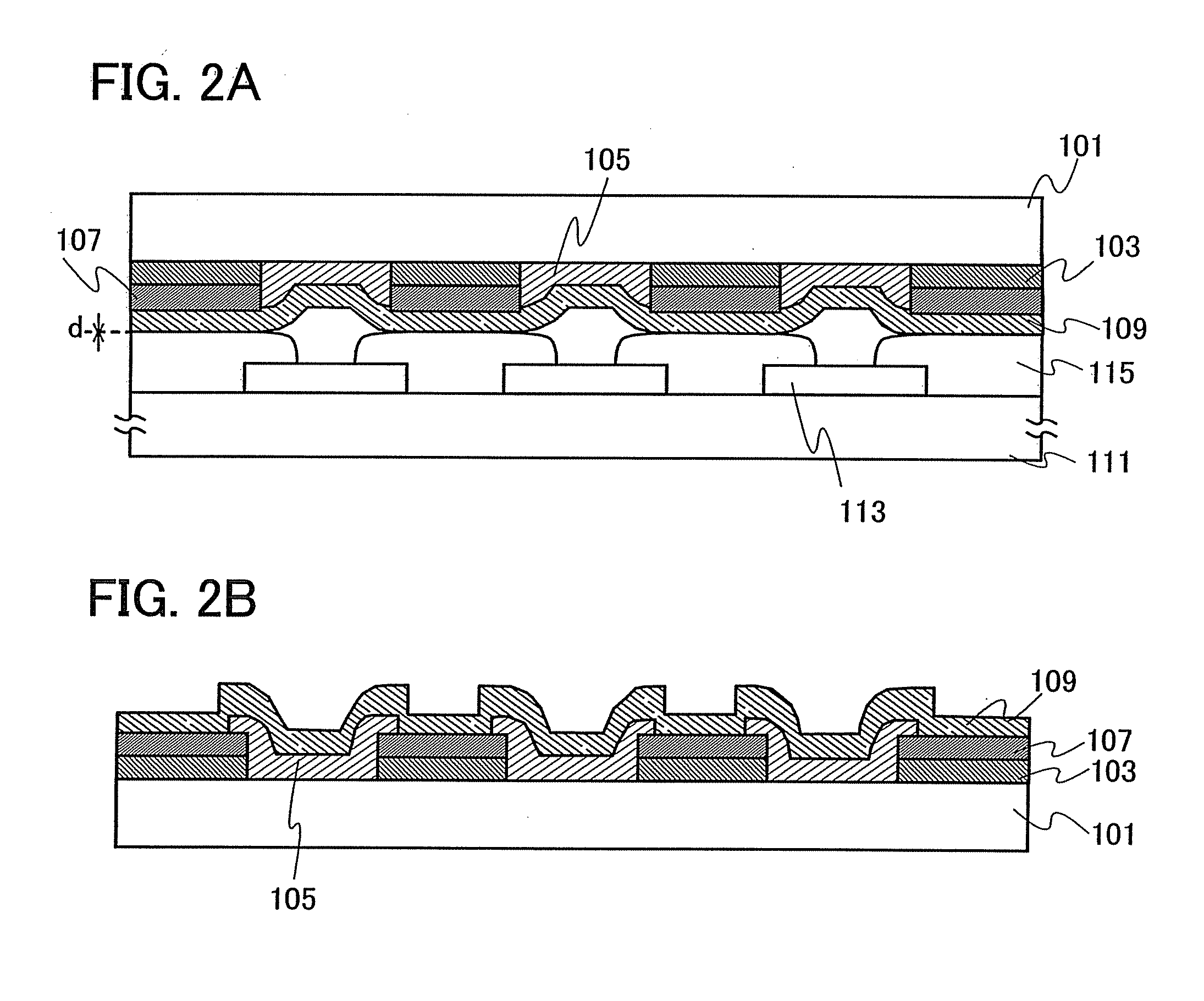
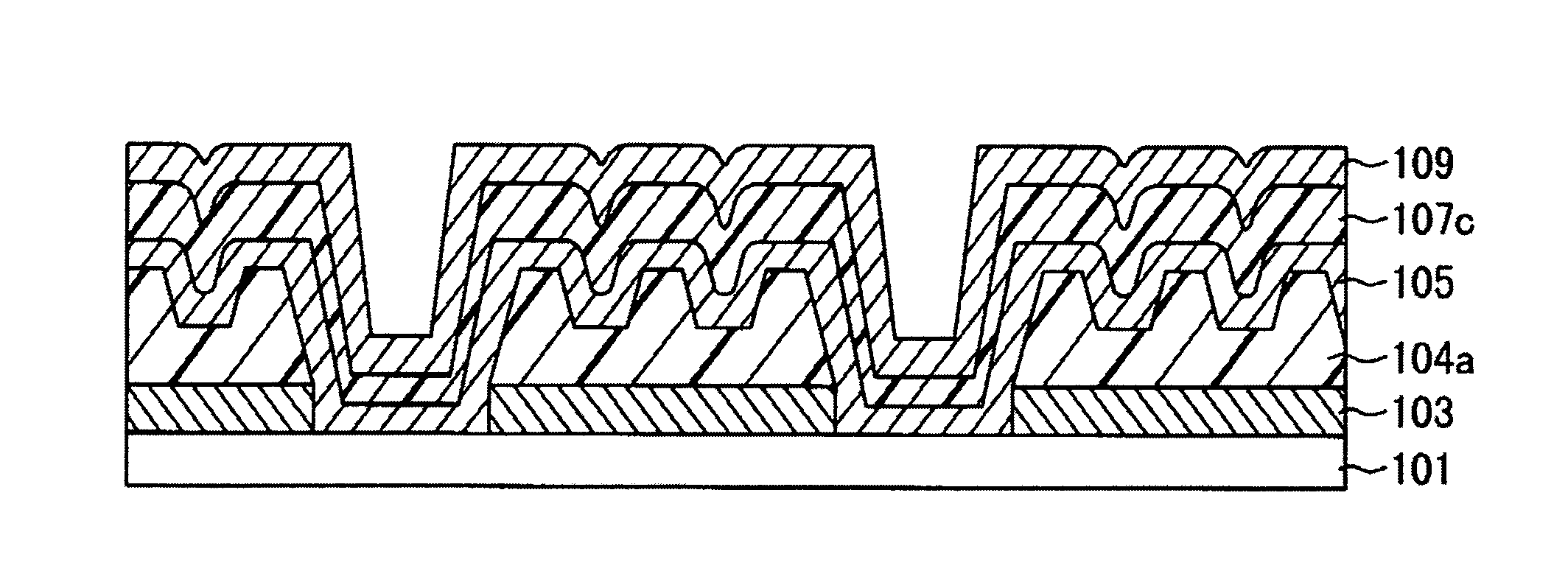
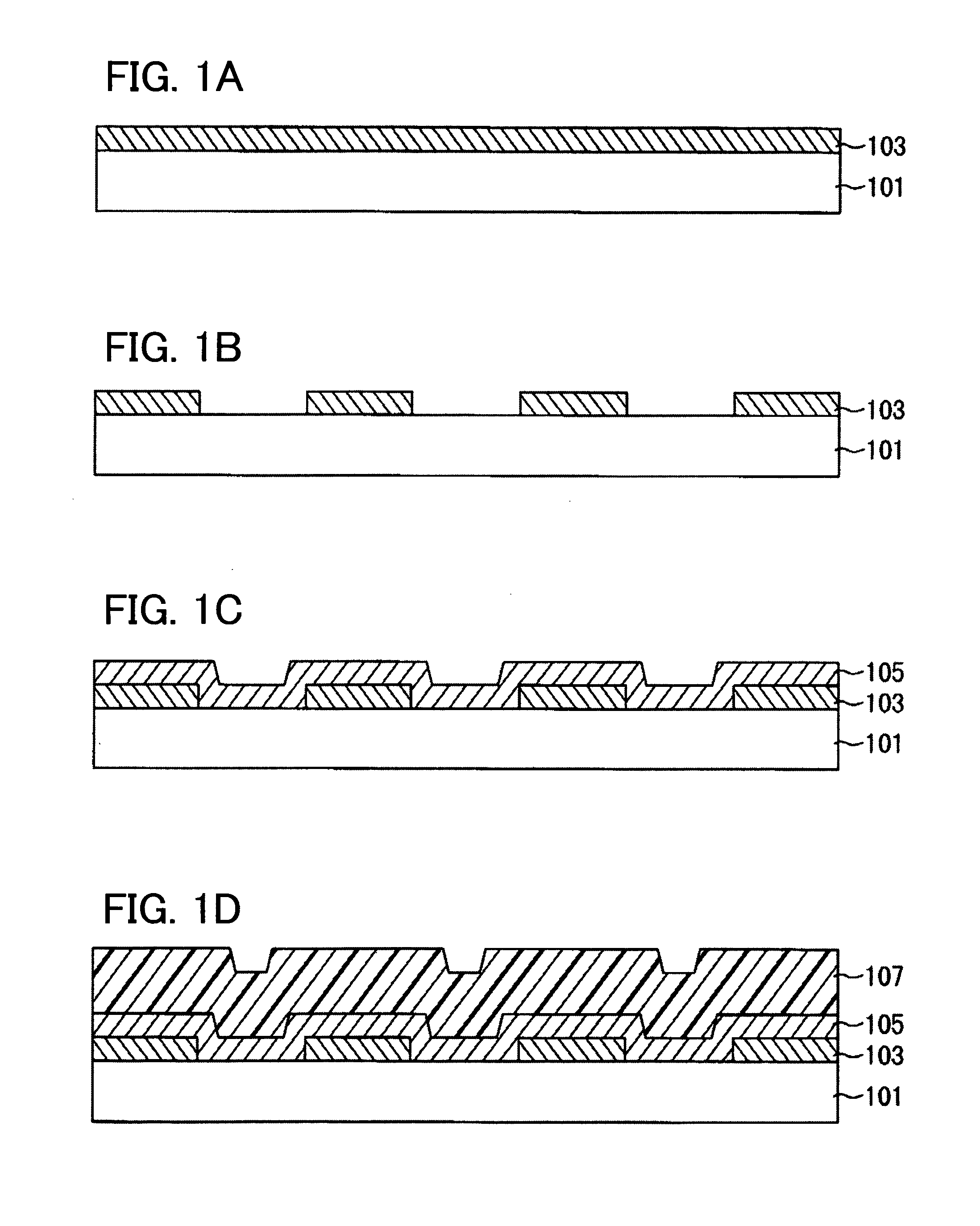
Method of Manufacturing Light-Emitting Device, and Evaporation Donor Substrate
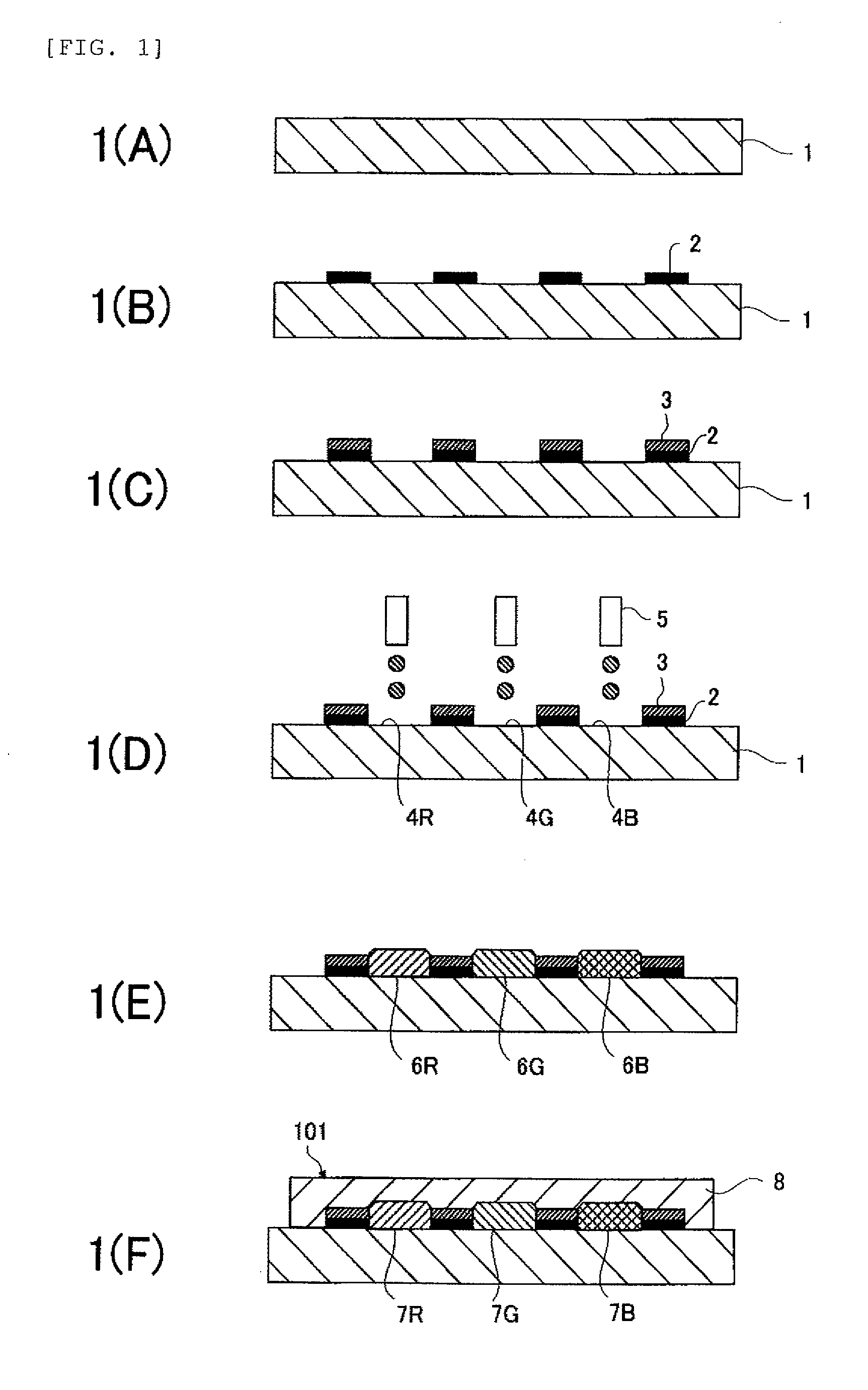
ActiveUS20090104835A1Well formedEnhancement in definitionLayered productsDuplicating/marking methodsTarget surfaceDisplay device
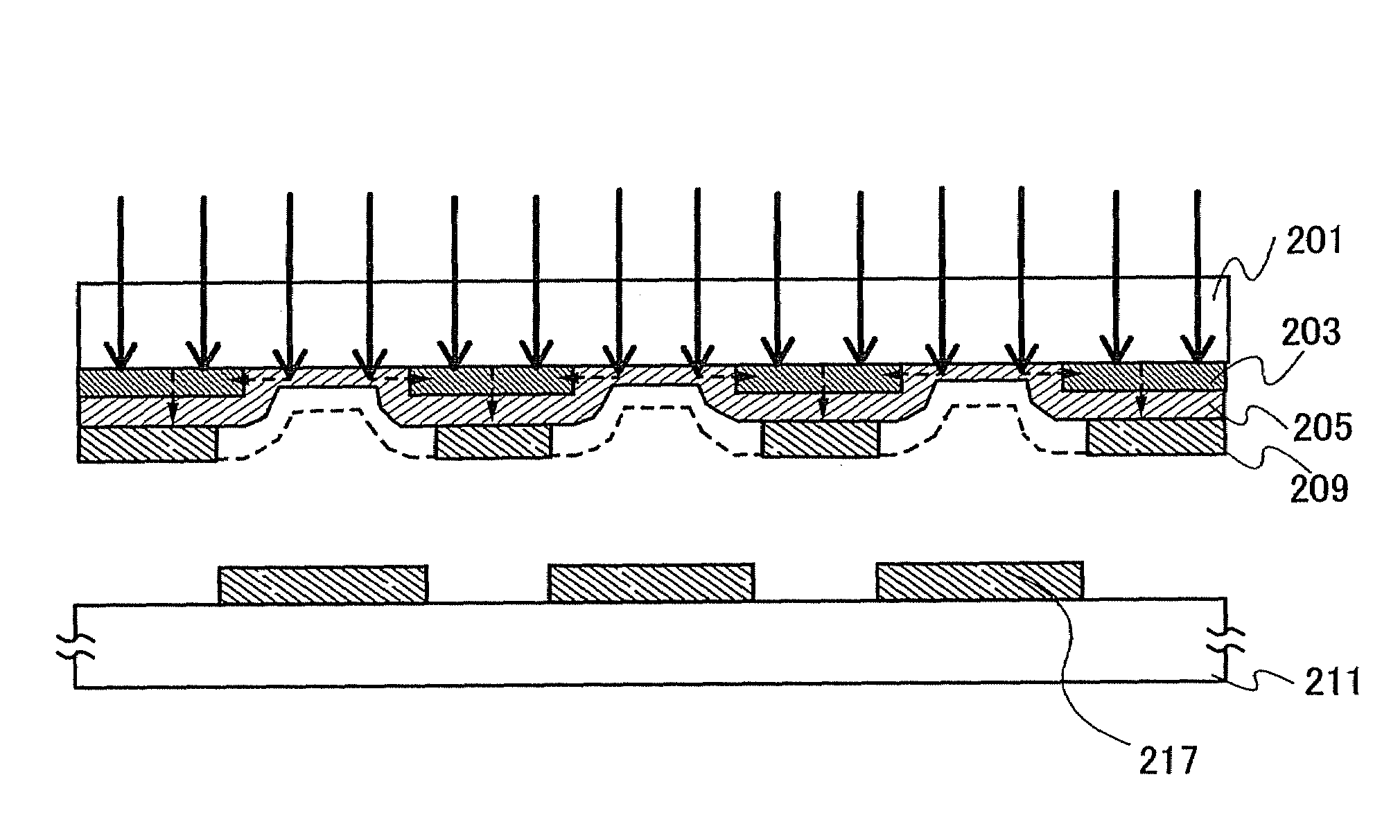
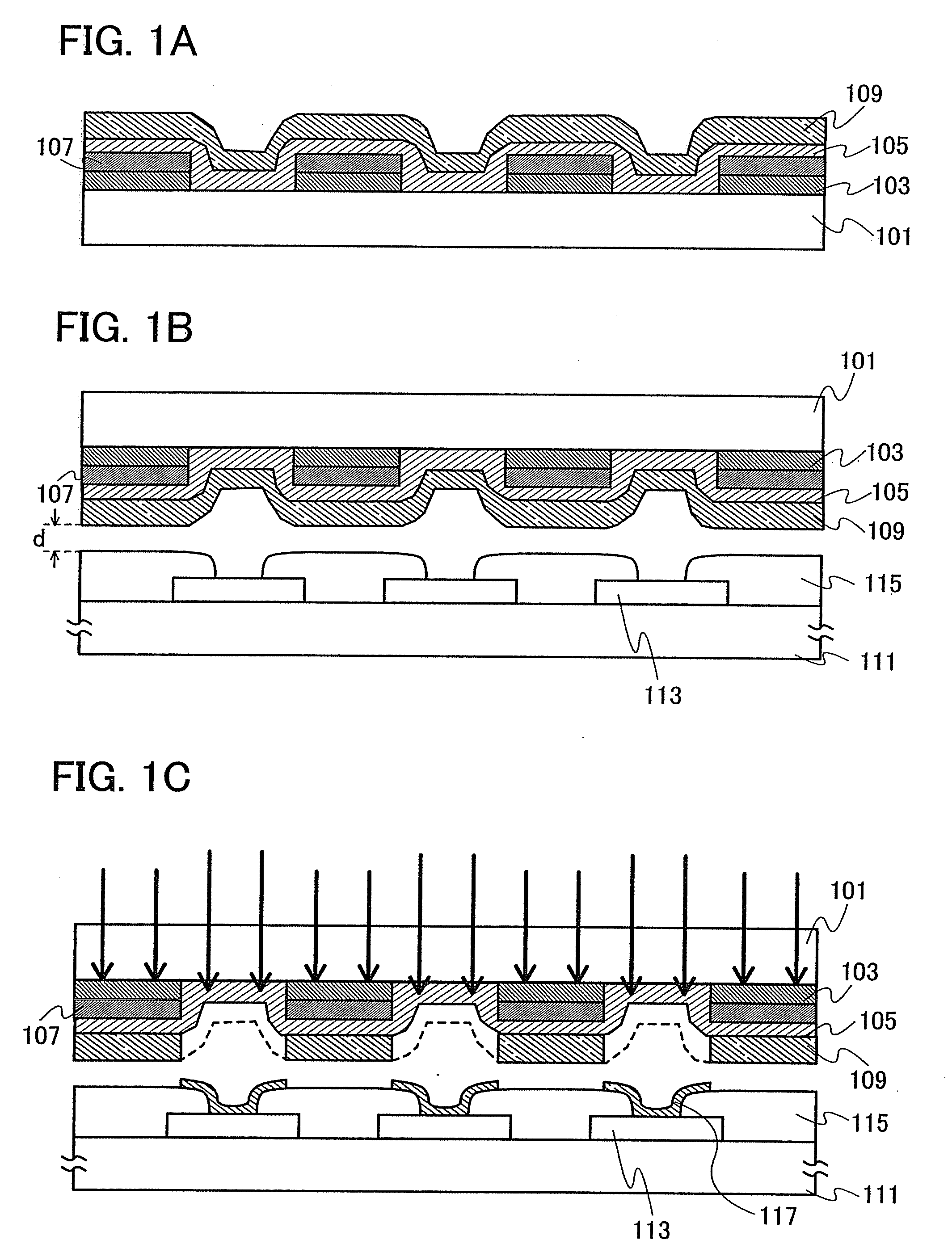
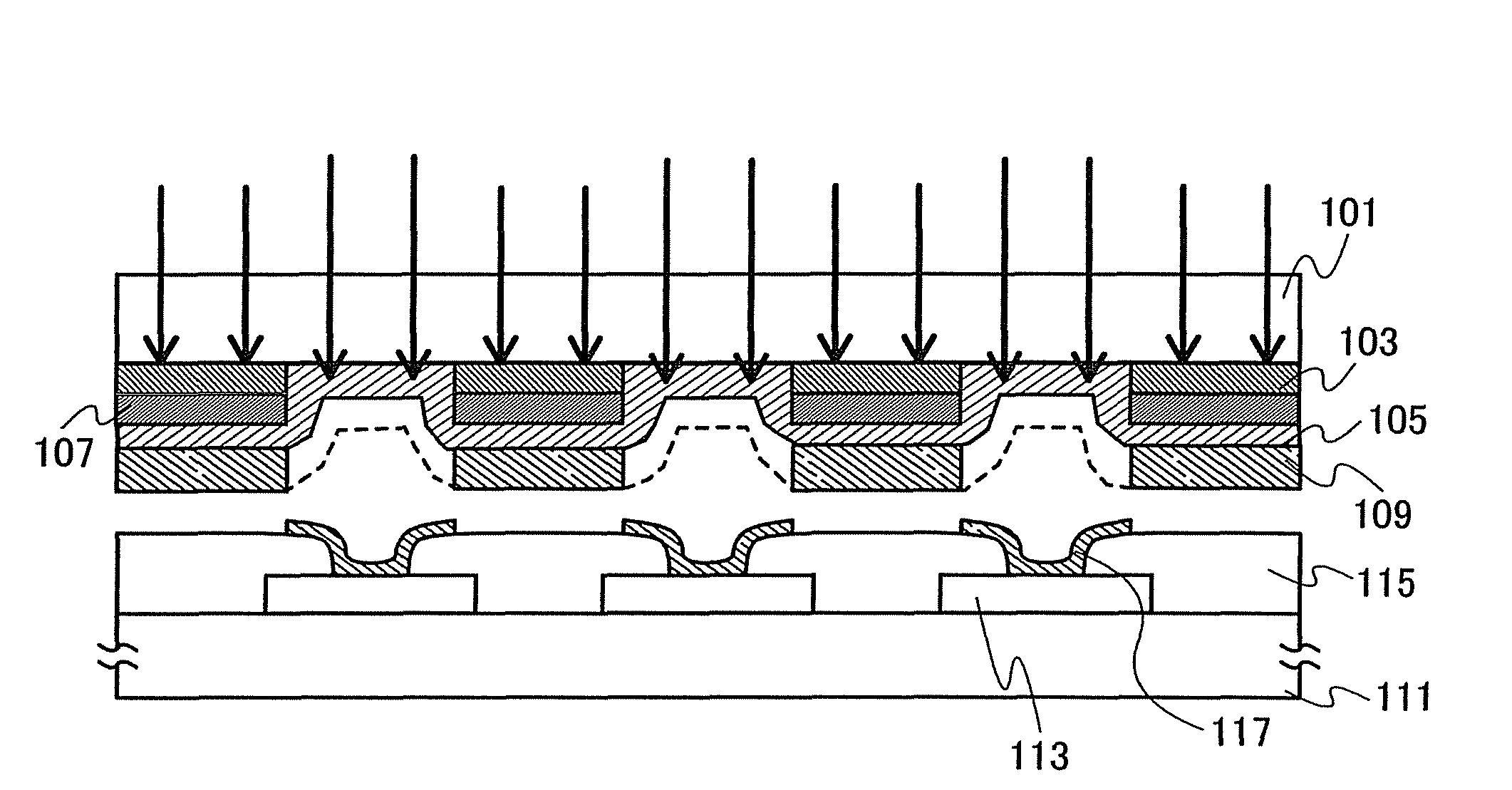
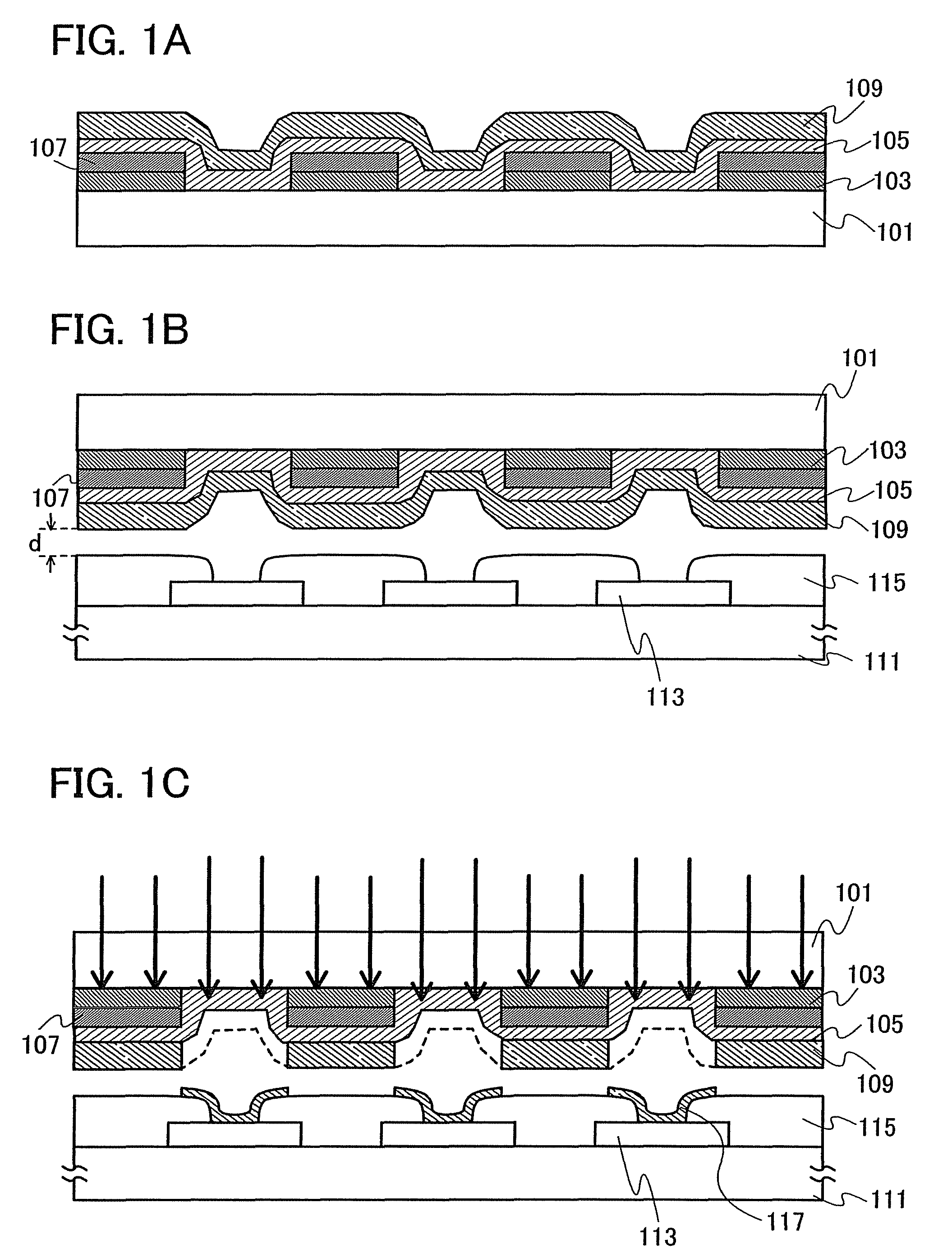
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a light-emitting device and an evaporation donor substrate, by which the precision of patterning of an EL layer of each color can be improved in manufacture of a full color flat panel display using emission colors of red, green, and blue. A first substrate which includes a reflective layer including an opening portion, a heat insulating layer including an opening portion in a position overlapped with the opening portion of the reflective layer over the reflective layer, a light absorption layer covering the opening portion of the reflective layer and the opening portion of the heat insulating layer over the heat insulating layer, and a material layer over the light absorption layer is used. While one surface of the first substrate is disposed close to a deposition target surface of a second substrate, the first substrate is irradiated with light from the other surface of the first substrate. The irradiation light is absorbed in the light absorption layer in the position overlapped with the opening portion of the reflective layer to heat an evaporation material. The heated evaporation material is evaporated onto the second substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
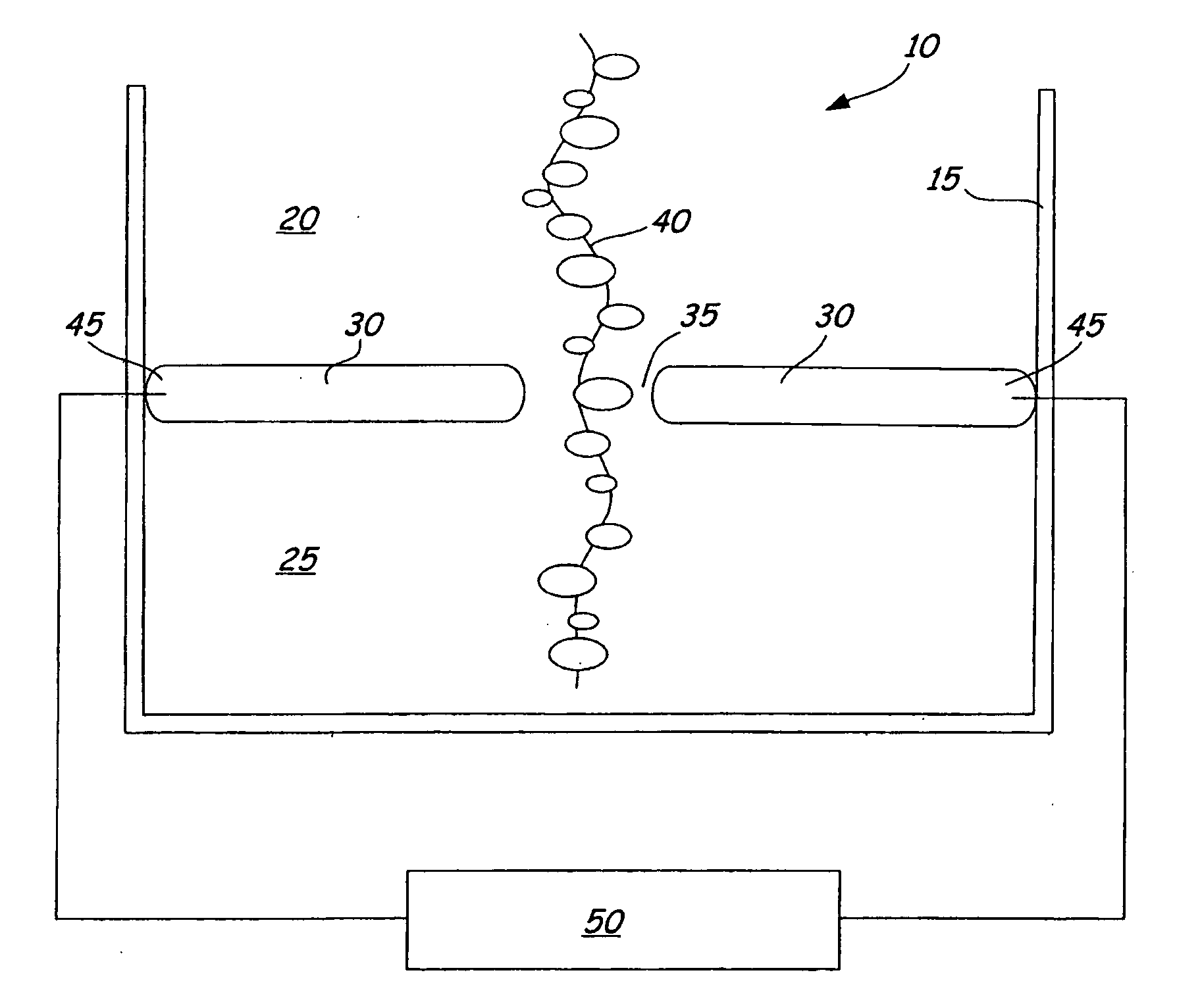
Material delivery tension and tracking system for use in solid imaging
ActiveUS7467939B2Low costAccurate layeringAdditive manufacturing apparatusConfectioneryOptical radiationHigh resolution imaging
A solid imaging apparatus and method employing a radiation transparent build material carrier and a build material dispensing system that accurately controls the thickness of the transferred layer of solidifiable liquid build material to the radiation transparent build material carrier to achieve high resolution imaging in three-dimensional objects built using an electro-optical radiation source.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method and a device for depositing a film of material or otherwise processing or inspecting, a substrate as it passes through a vacuum environment guided by a plurality of opposing and balanced air bearing lands and sealed by differentially pumped groves and sealing lands in a non-contact manner
ActiveUS20070031600A1Quantity minimizationIncrease the areaLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingAir bearingPorous medium
A method and apparatus for coating and baking and deposition of surfaces on glass substrate or flexible substrate, such as films and thin glass sheets or other similar work pieces as it transitions thru and between small gaps of aero-static or hydro-static porous media bearings and differentially pumped vacuum grooves, in a non-contact manner, in order to process within a vacuum environment. The process is also intended to incorporate simultaneous and immediately sequential ordering of various processes.
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Optical lens with scratch-resistant anti-reflective layer
ActiveUS8982466B2Improved beadingSliding frictionSpectales/gogglesOptical partsRefractive indexVisible spectral range
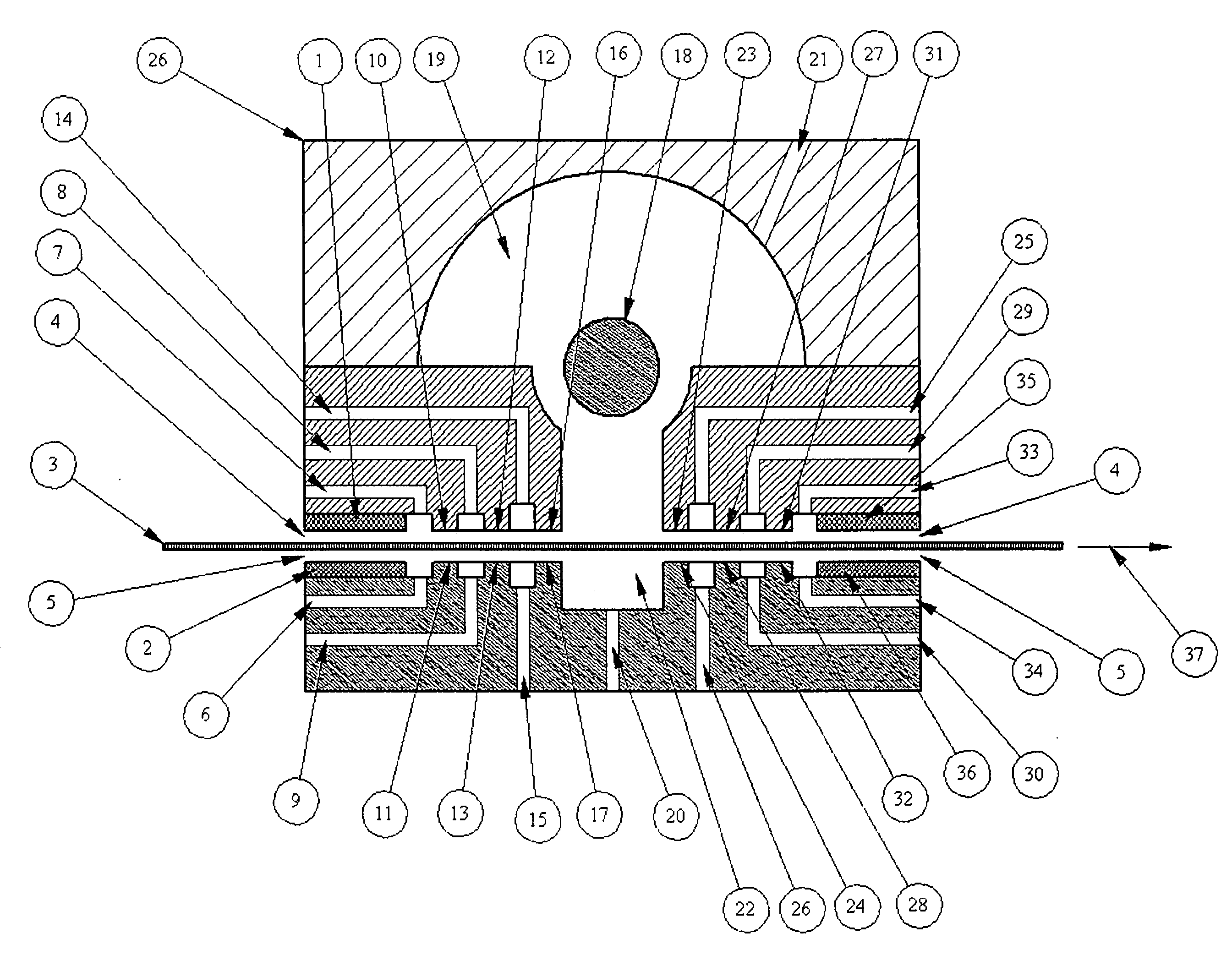
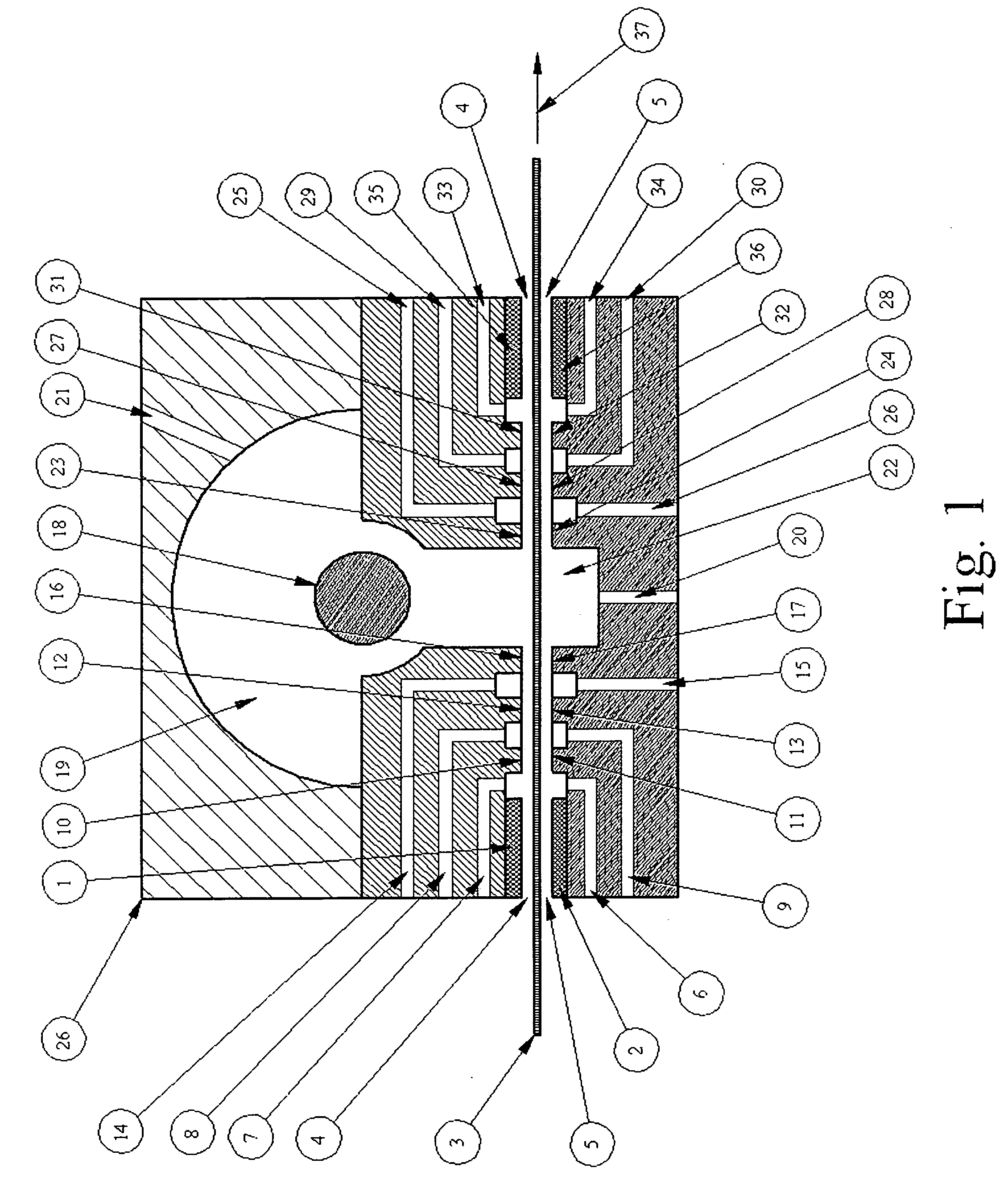
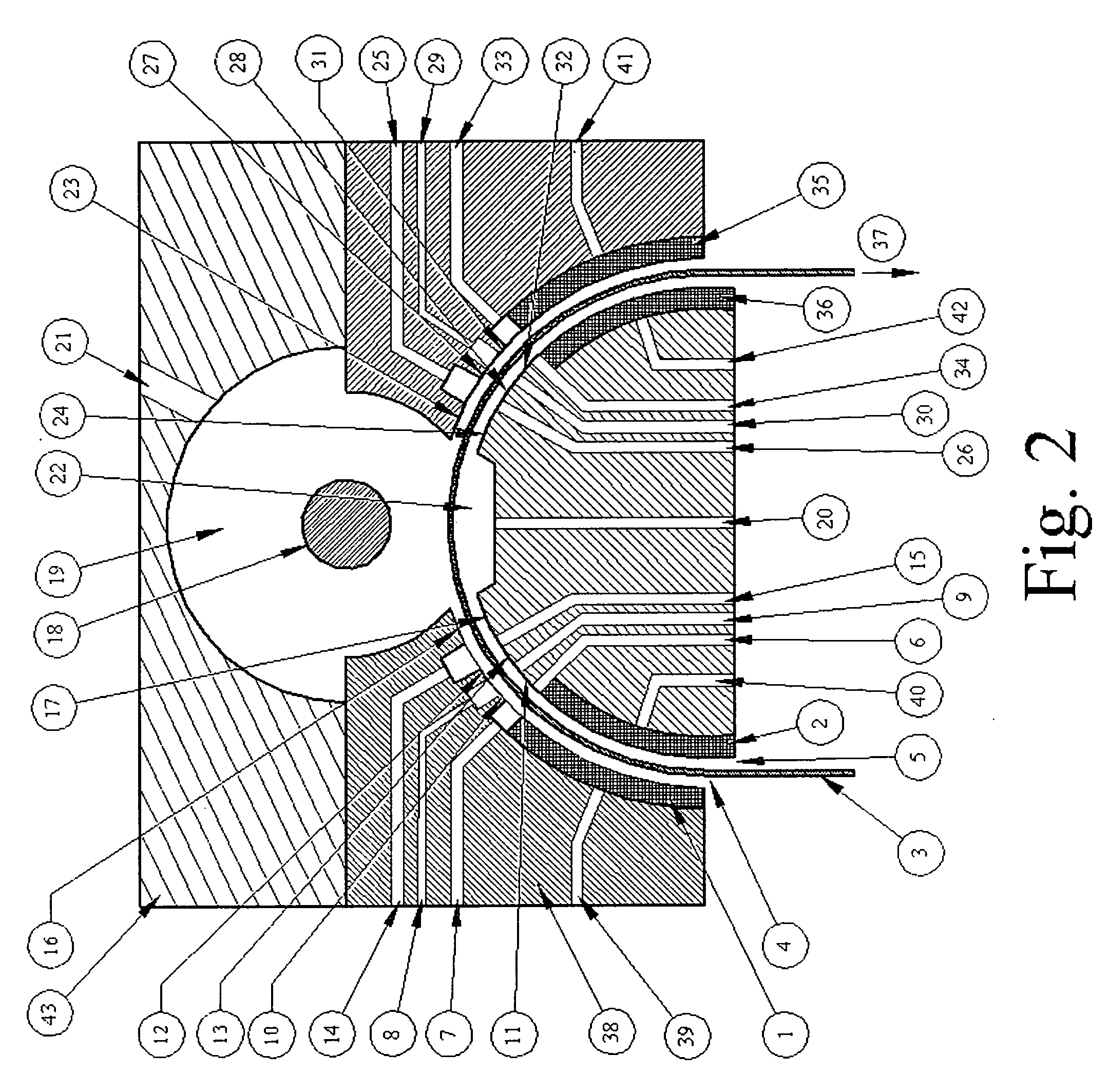
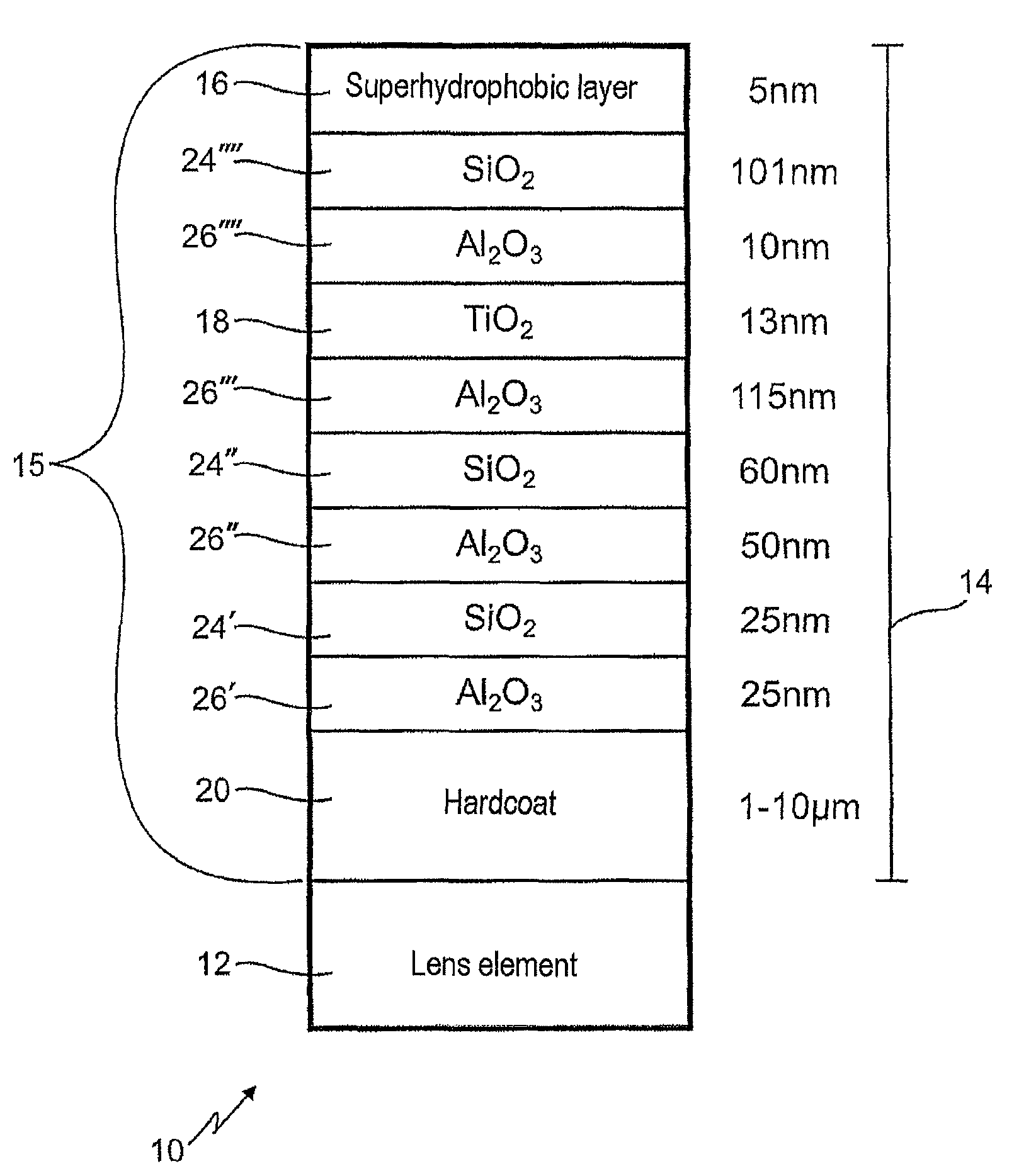
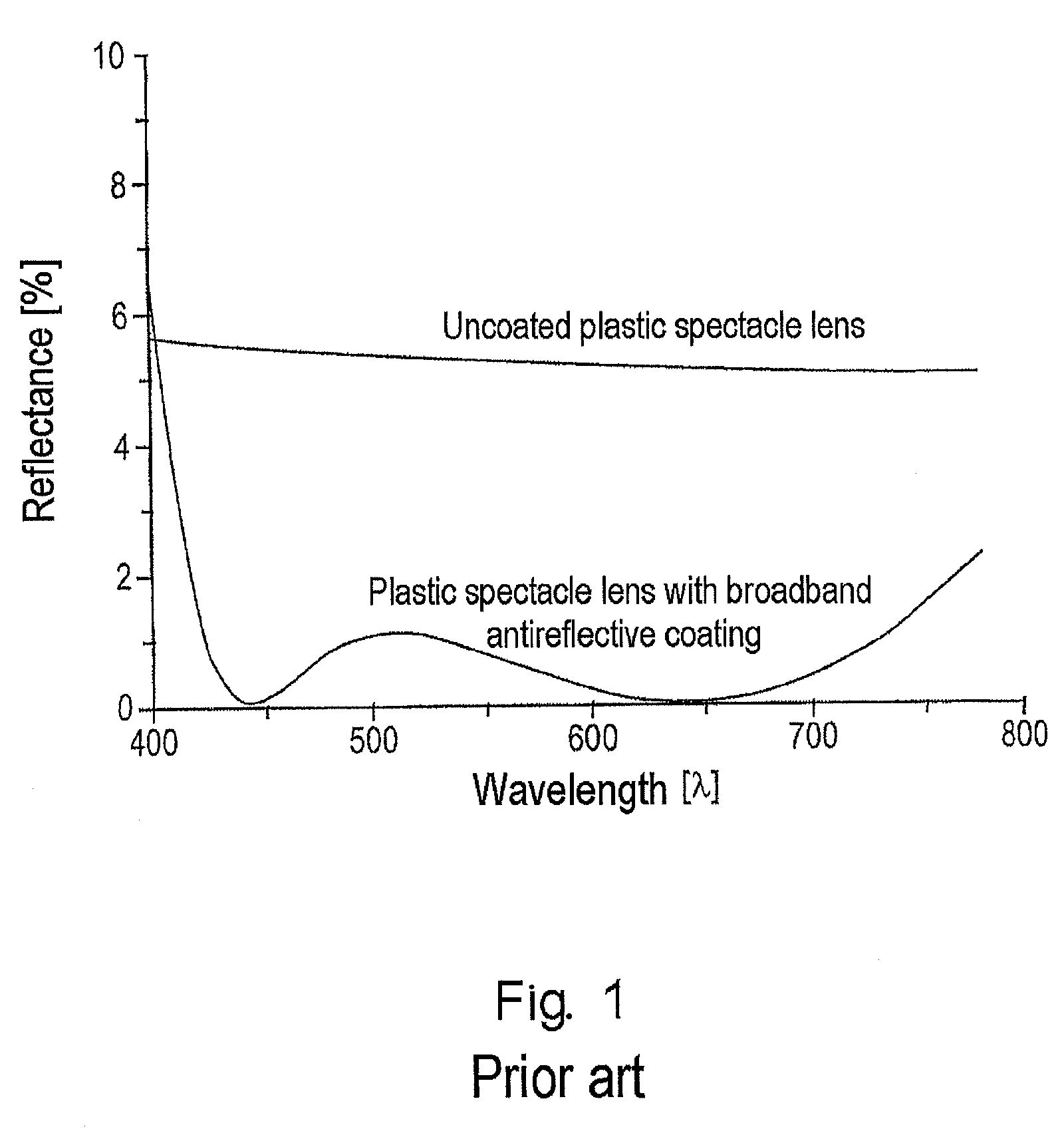
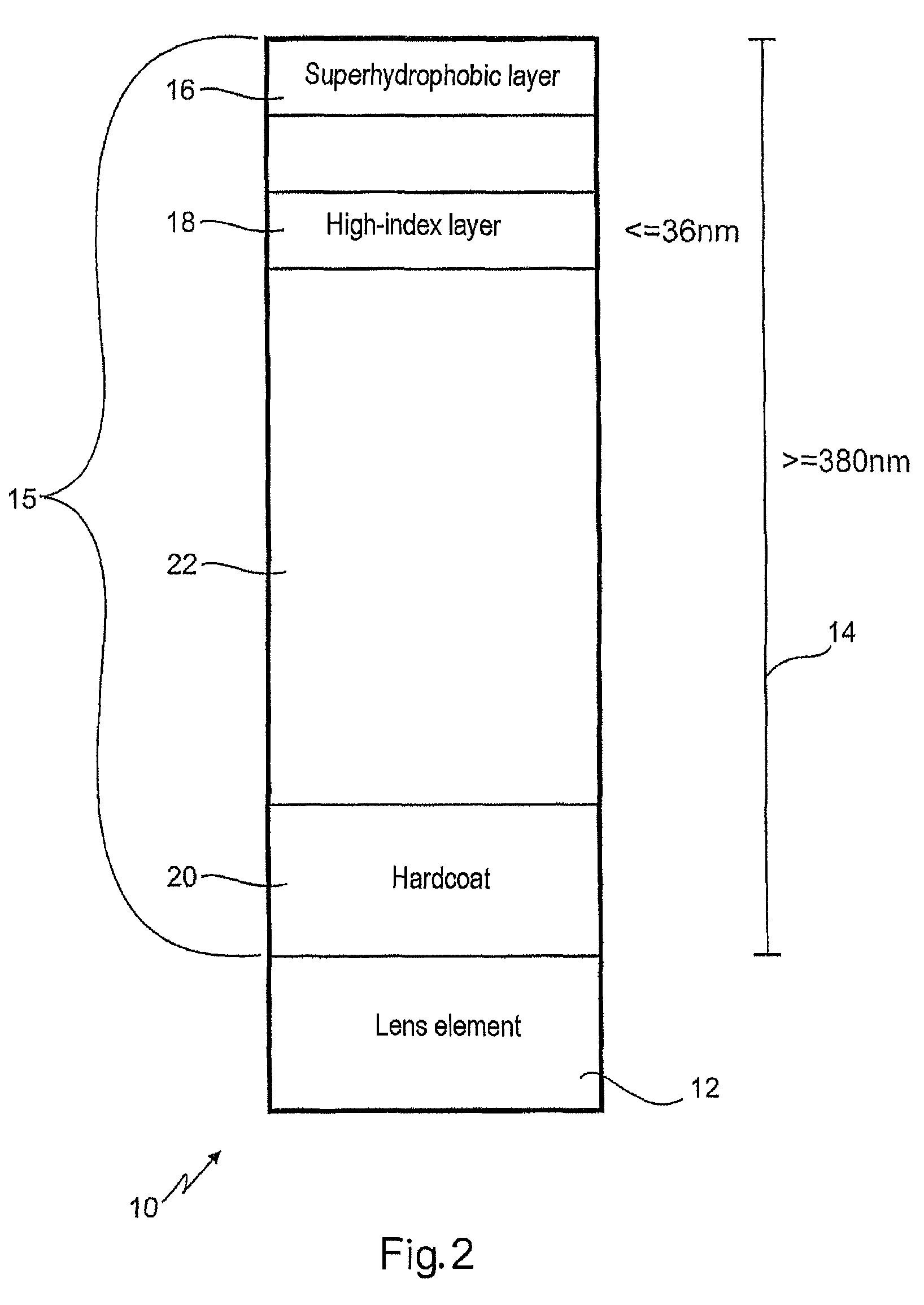
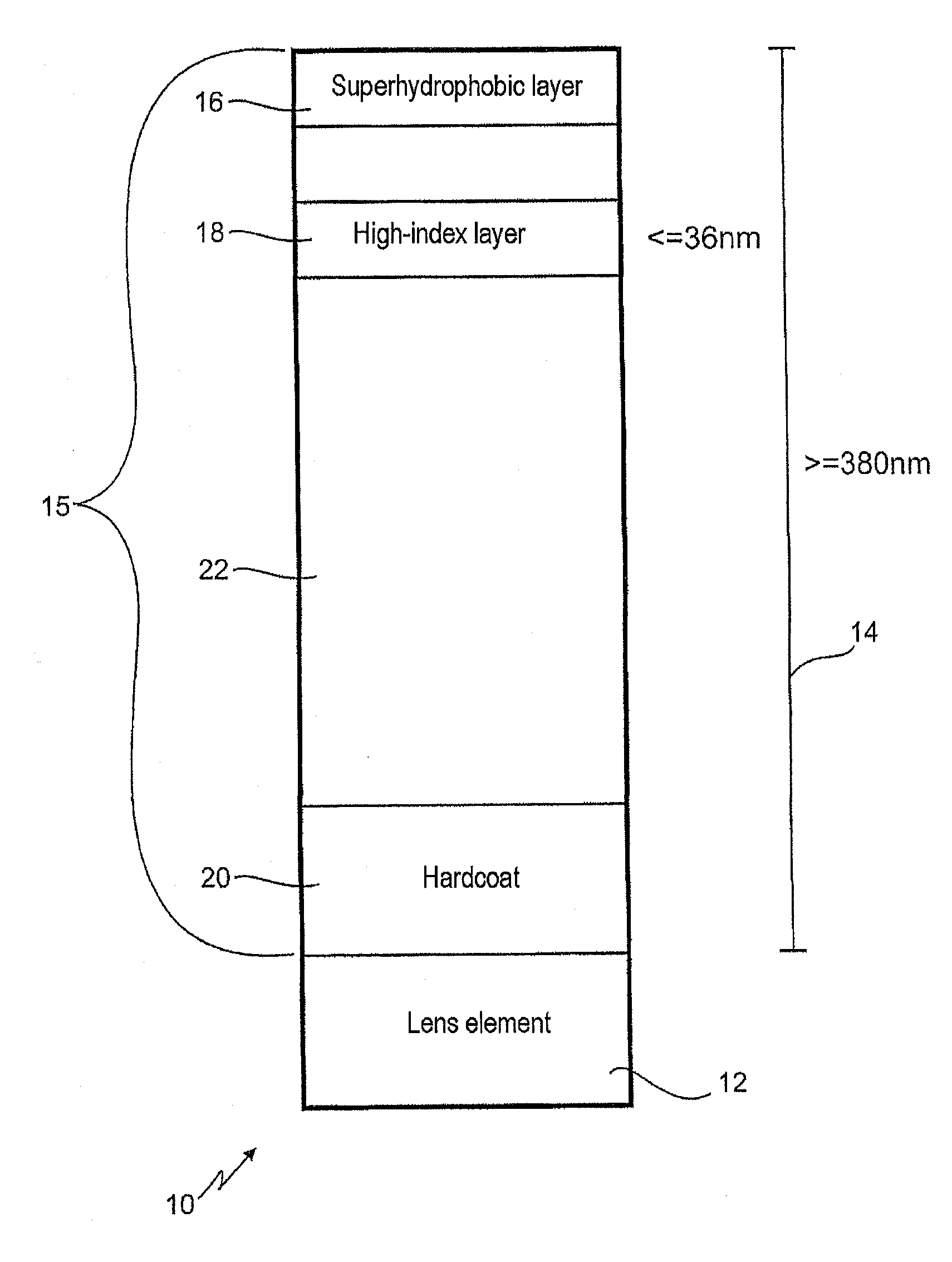
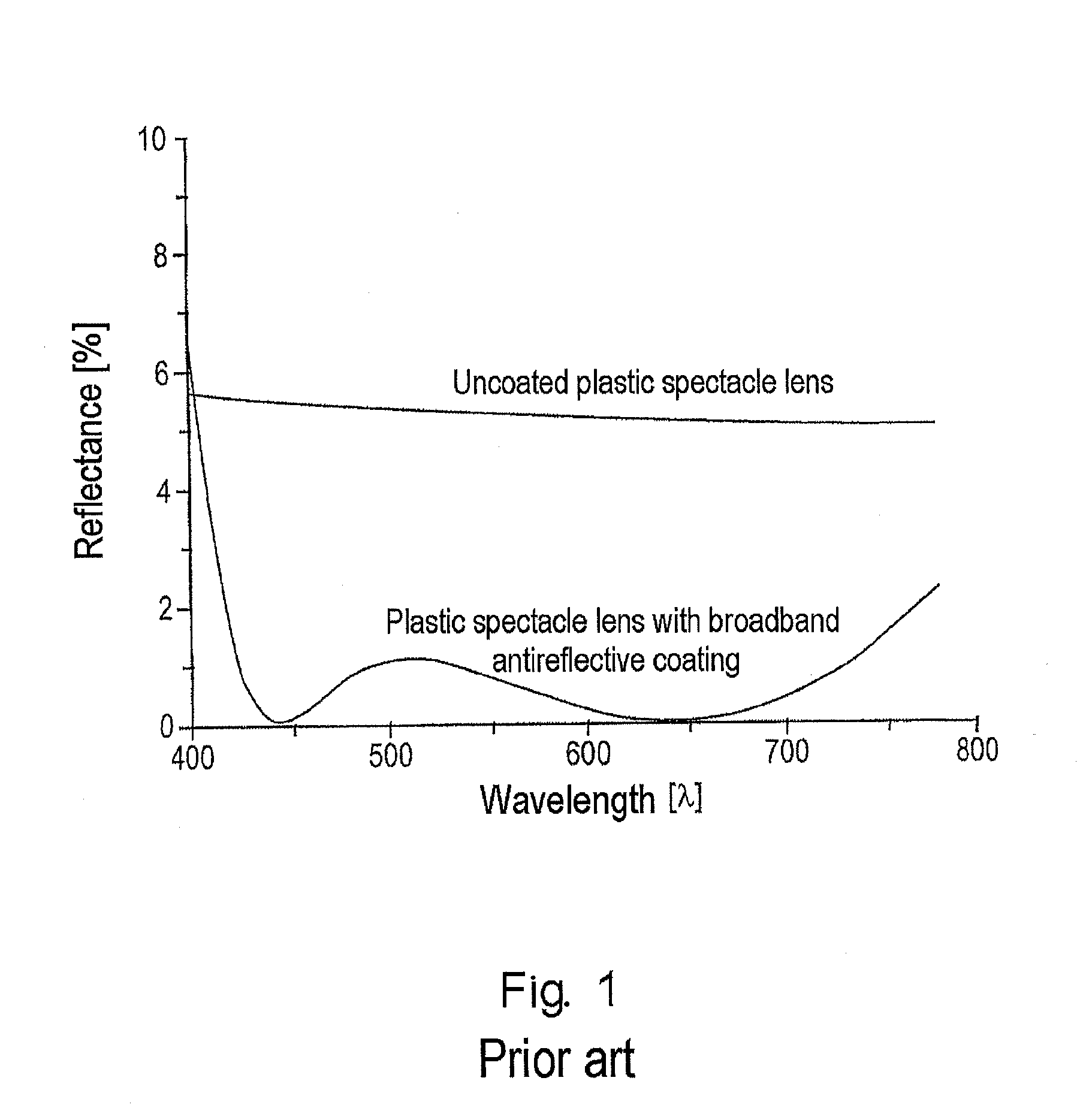
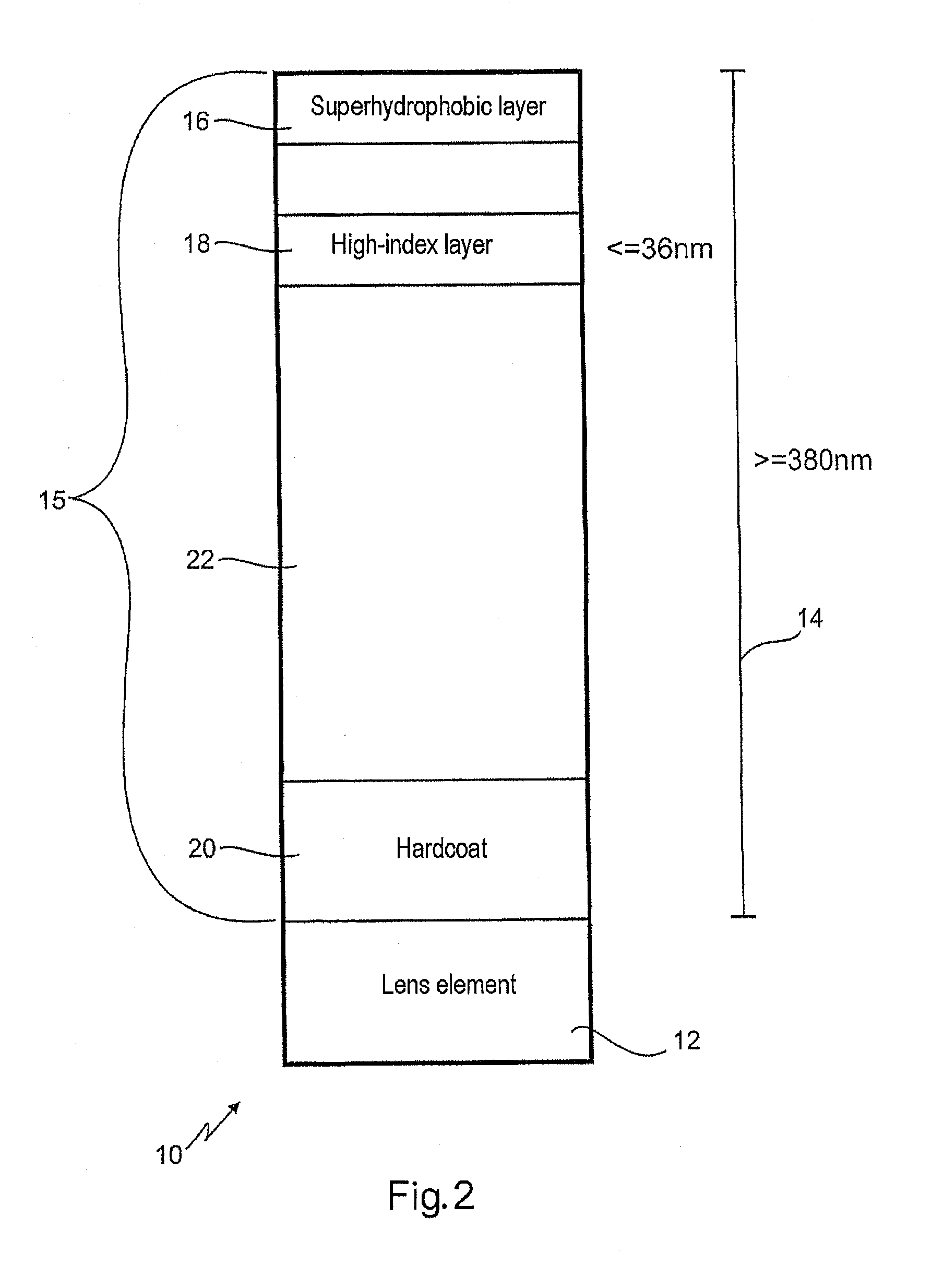
The present invention relates to an optical lens having a lens element produced of plastic, more particularly of plastic which is transparent in a visible spectral range, and having a coating comprising a plurality of layers, the plurality of layers comprising at least one high-refractive-index layer. Furthermore, a hardcoat layer is formed adjacent to the lens element, and a superhydrophobic layer concludes the coating in opposition to the lens element. The at least one high-refractive-index layer has a thickness of less than 40 nm, and the coating overall has a thickness of more than about 380 nm.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION INT GMBH
Method of manufacturing light-emitting device, and evaporation donor substrate
ActiveUS8153201B2Accurate layeringHigh precisionDiffusion transfer processesLiquid surface applicatorsTarget surfaceDisplay device
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a light-emitting device and an evaporation donor substrate, by which the precision of patterning of an EL layer of each color can be improved in manufacture of a full color flat panel display using emission colors of red, green, and blue. A first substrate which includes a reflective layer including an opening portion, a heat insulating layer including an opening portion in a position overlapped with the opening portion of the reflective layer over the reflective layer, a light absorption layer covering the opening portion of the reflective layer and the opening portion of the heat insulating layer over the heat insulating layer, and a material layer over the light absorption layer is used. While one surface of the first substrate is disposed close to a deposition target surface of a second substrate, the first substrate is irradiated with light from the other surface of the first substrate. The irradiation light is absorbed in the light absorption layer in the position overlapped with the opening portion of the reflective layer to heat an evaporation material. The heated evaporation material is evaporated onto the second substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for forming opening
InactiveUS20070054486A1Contamination problemEnhance the imageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal silicideOptoelectronics
A method for forming an opening. The method comprises steps of providing a substrate having at least one element structure formed thereon and then forming a dielectric layer over the substrate to cover the element structure. A patterned metal silicide layer is formed on the dielectric layer and then the dielectric layer is etched to form at least one opening by using the patterned metal silicide layer as an etching mask, wherein the opening exposes the corresponding element structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Optical lens with scratch-resistant Anti-reflective layer
ActiveUS20120081792A1Improved beadingSliding frictionSpectales/gogglesCoatingsRefractive indexVisible spectral range
The present invention relates to an optical lens having a lens element produced of plastic, more particularly of plastic which is transparent in a visible spectral range, and having a coating comprising a plurality of layers, the plurality of layers comprising at least one high-refractive-index layer. Furthermore, a hardcoat layer is formed adjacent to the lens element, and a superhydrophobic layer concludes the coating in opposition to the lens element. The at least one high-refractive-index layer has a thickness of less than 40 nm, and the coating overall has a thickness of more than about 380 nm.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION INT GMBH
Small perturbance stratified substrate sludge in-situ sampler and sampling method thereof
InactiveCN101620037ADoes not disturb the distributionAccurate layeringWater resource protectionWithdrawing sample devicesEngineeringSludge
The invention relates to a small perturbance stratified substrate sludge in-situ sampler used for collecting deposits in water and a sampling method thereof. The sampler consists of a C-shaped inner tube, a C-shaped outer tube, an outer tube conical head, an inner tube handle, an outer tube handle and an inflatable plug, wherein the outer tube and the inner tube are sleeved together and are respectively formed by fixedly connecting a plurality of sections; the inner tube can be rotated by the inner tube handle at the top so as to superpose or close C-shaped openings of the inner tube and the outer tube. The inner tube is firstly rotated so as to close the C-shaped opening when substrate sludge is fetched; the inner tube is rotated so as to open the C-shaped opening after being inserted by a predetermined depth, and then the inner tube and the outer tube are rotated after being inclined by a small angle together so as to rotate the substrate sludge into the inner tube. Then the inflatable plug is put on the sludge surface and is inflated; the inner tube is rotated to close the C-shaped opening; finally, the inner tube and the outer tube are lifted from the water and laid on the ground for stratified sampling. The invention has small perturbance to the substrate sludge, does not change stratified and physical properties of the substrate sludge, has light weight, portability, convenient operation and wide generalization and application values and , is suitable for sampling work of substrate sludge of hydraulic reclamation yards of river and lake.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Nanoimprint resin stamper
InactiveUS20090123590A1Low costImprove throughputConfectioneryNanoinformaticsEngineeringNanostructure
A resin stamper is provided that is intended for use in an optical transfer-based nanostructure transfer apparatus and which is capable of automatic transport and alignment. The resin stamper comprises a support member made of a light transmitting material and having mechanical strength, an intermediate layer also made of a light transmitting material, and a patterned resin layer which is also made of a light transmitting material, the support member being larger in size than the intermediate layer and the patterned resin layer, the intermediate layer being more flexible than the patterned resin layer, and the patterned resin layer having a pattern of high and low areas formed in a surface thereof that is the obverse of the pattern of high and low areas in a mold.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Stamper and transfer apparatus
InactiveUS7374417B2Accurate transferHigh elastic modulusRecord carriersLayered productsFine structureEngineering
A stamper and a transfer apparatus that utilizes the stamper, which is capable of accurately transferring its own pattern onto an article, such as a substrate, without being affected by any distribution of convex portions on the stamper surface or any contour of the substrate. The stamper has a fine concave-convex pattern on a surface thereof for forming a fine structure on a substrate using a pressing machine. The stamper is flexible and includes a buffer formed on an opposite side to the side on which the concave-convex pattern is formed. The buffer has a longitudinal distribution of moduli of elasticity.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Abrasive material jet injection device
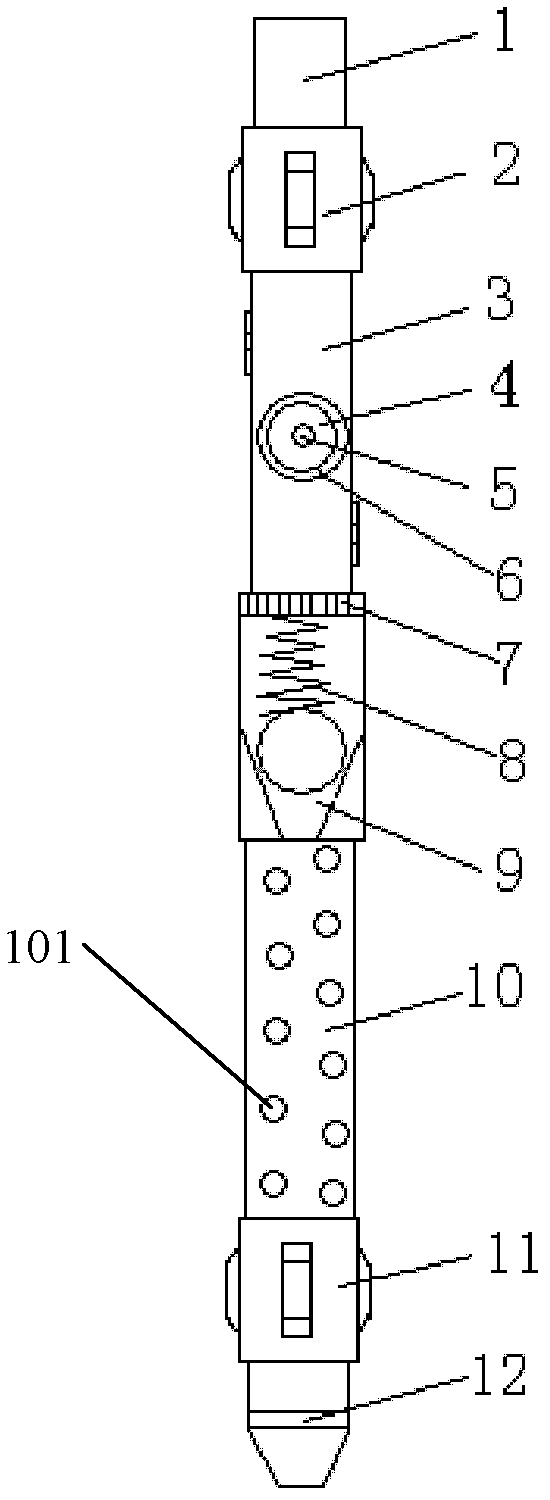
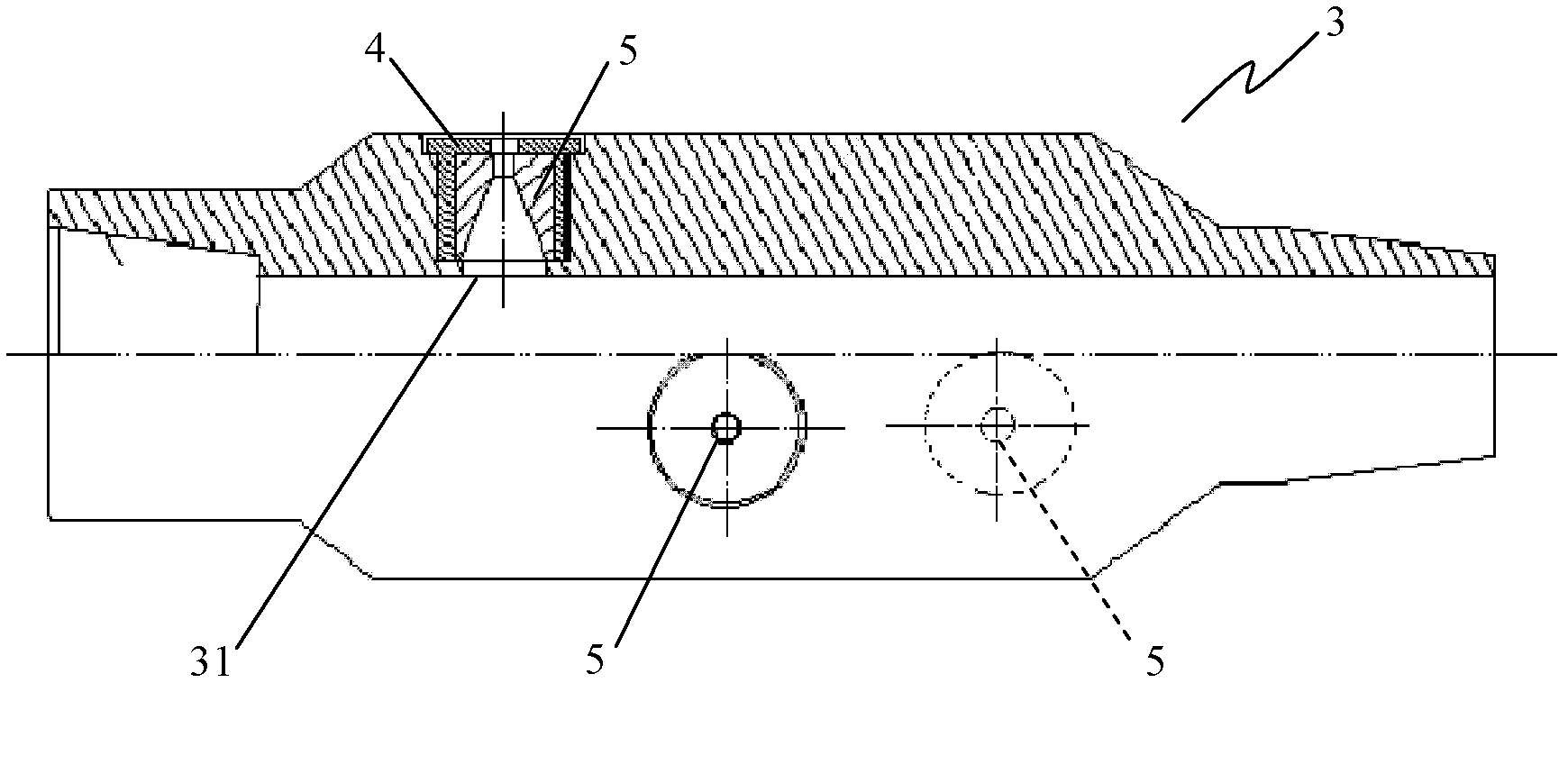
InactiveCN102493791APrecisely targeted layered fracturingAvoid blindnessFluid removalJet injectionSpray nozzle
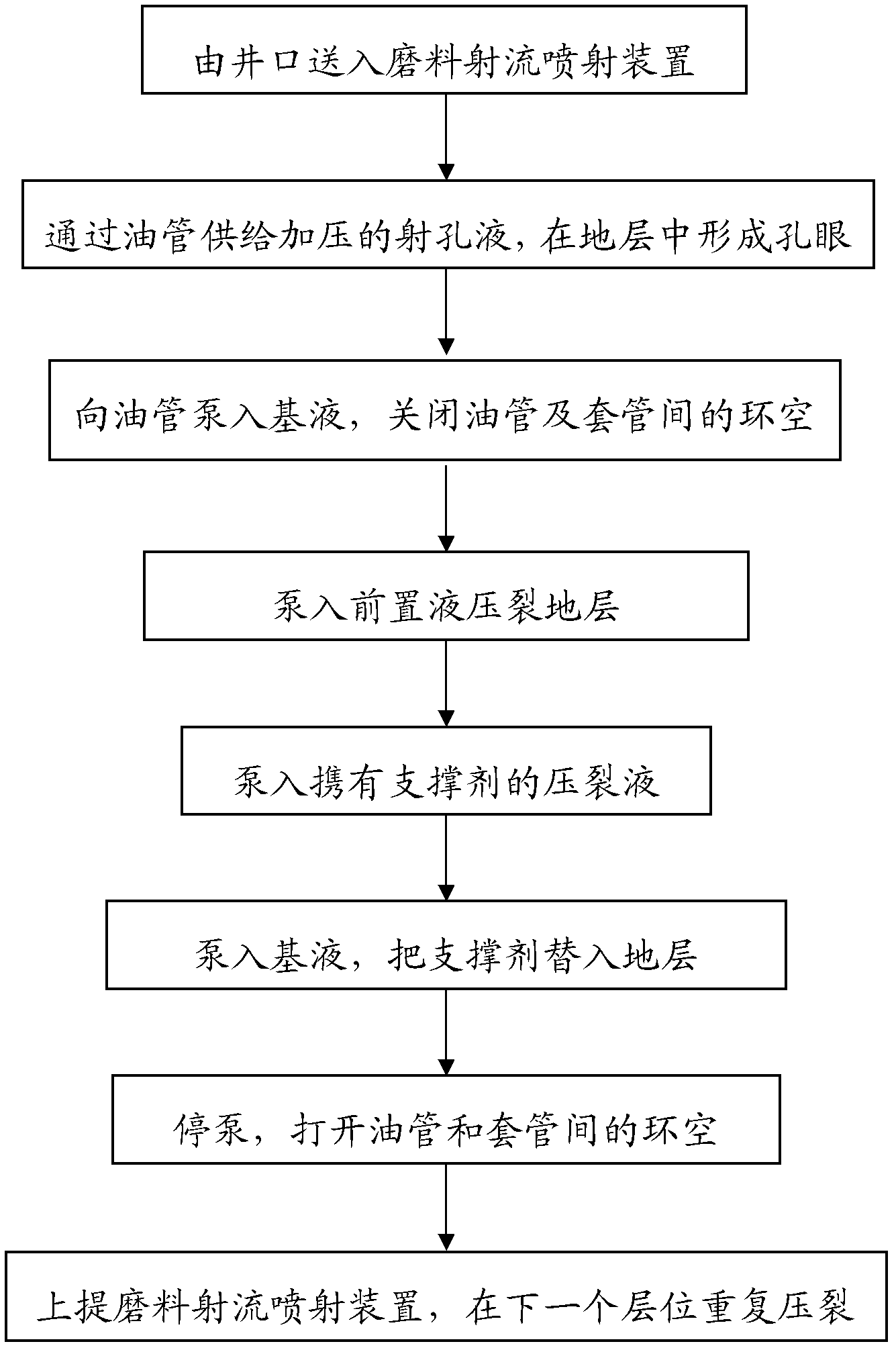
The invention relates to an abrasive material jet injection device which is provided with a spray gun for injecting abrasive material jet, wherein the spray gun is provided with at least two nozzles, and the spray gun is connected with an oil tube. The abrasive material jet injection device has simple structure and is easy to assemble and maintain. The key part (nozzle) in the device has longer service life so as to satisfy the requirements of two operations of perforating and fracturing. Because a check valve and a sieve tube are arranged, the phenomenon that the nozzle of the injection device is subjected to sand jamming can be greatly lowered; meanwhile, when the device is subjected to sand jamming faults, base fluid is pumped into the annulus of an annular tube, the base fluid enters the injection device via the check valve by the sieve tube, which is convenient to flush the device, and therefore the well can be subjected to backflushing to ensure that the operation is successfully carried out. Because a packer is omitted, construction equipment is simplified. According to the abrasive material jet injection device, the defect of the known technology is overcome, abrasive material jet pore forming and fracturing are combined, and therefore layering can be precisely carried out in a vertical well or sectional fracturing can be precisely carried out in a horizontal well section.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Solid state membrane channel device for the measurement and characterization of atomic and molecular sized samples
InactiveUS7235184B2Effectively protect and insulateSimple manufacturing processNanostructure manufacturePaper/cardboard articlesMaterial removalMembrane channel
A solid state device is formed through thin film deposition techniques which results in a self-supporting thin film layer that can have a precisely defined channel bored therethrough. The device is useful in the chacterization of polymer molecules by measuring changes in various electrical characteristics as molecules pass through the channel. To form the device, a thin film layer having various patterns of electrically conductive leads are formed on a silicon substrate. Using standard lithography techniques, a relatively large or micro-scale aperture is bored through the silicon substrate which in turn exposes a portion of the thin film layer. This process does not affect the thin film. Subsequently, a high precision material removal process is used (such as a focused ion beam) to bore a precise nano-scale aperture through the thin film layer that coincides with the removed section of the silicon substrate.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
Solid state membrane channel device for the measurement and characterization of atomic and molecular sized samples
InactiveUS20060292041A1Effectively protect and insulateSimple manufacturing processMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansMembrane channelOptoelectronics
The present invention relates to an apparatus for characterization of molecules through measurement of various electrical characteristics. The apparatus has a substrate on which is formed a thin film layer. Further, the apparatus has an insulation layer formed on the thin film layer. The thin film layer has a defined channel bored therethrough, the substrate has an aperture bored therethrough, and the insulation layer has a hole formed therethrough.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
Method for Detecting Metastasis of GI Cancer
InactiveUS20110306055A1Reduce restrictionsAccurate layeringMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCyclaseLymphatic Spread
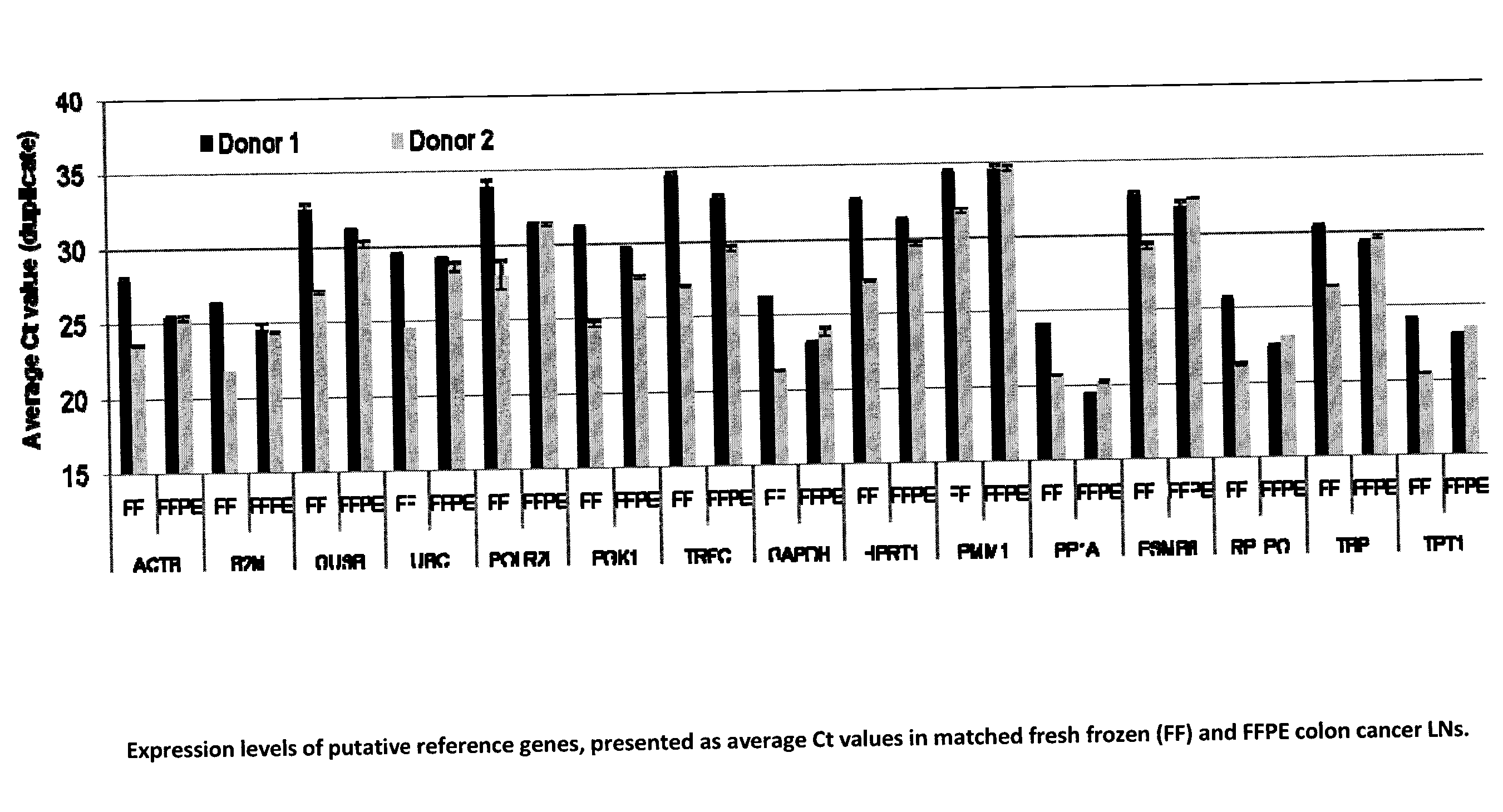
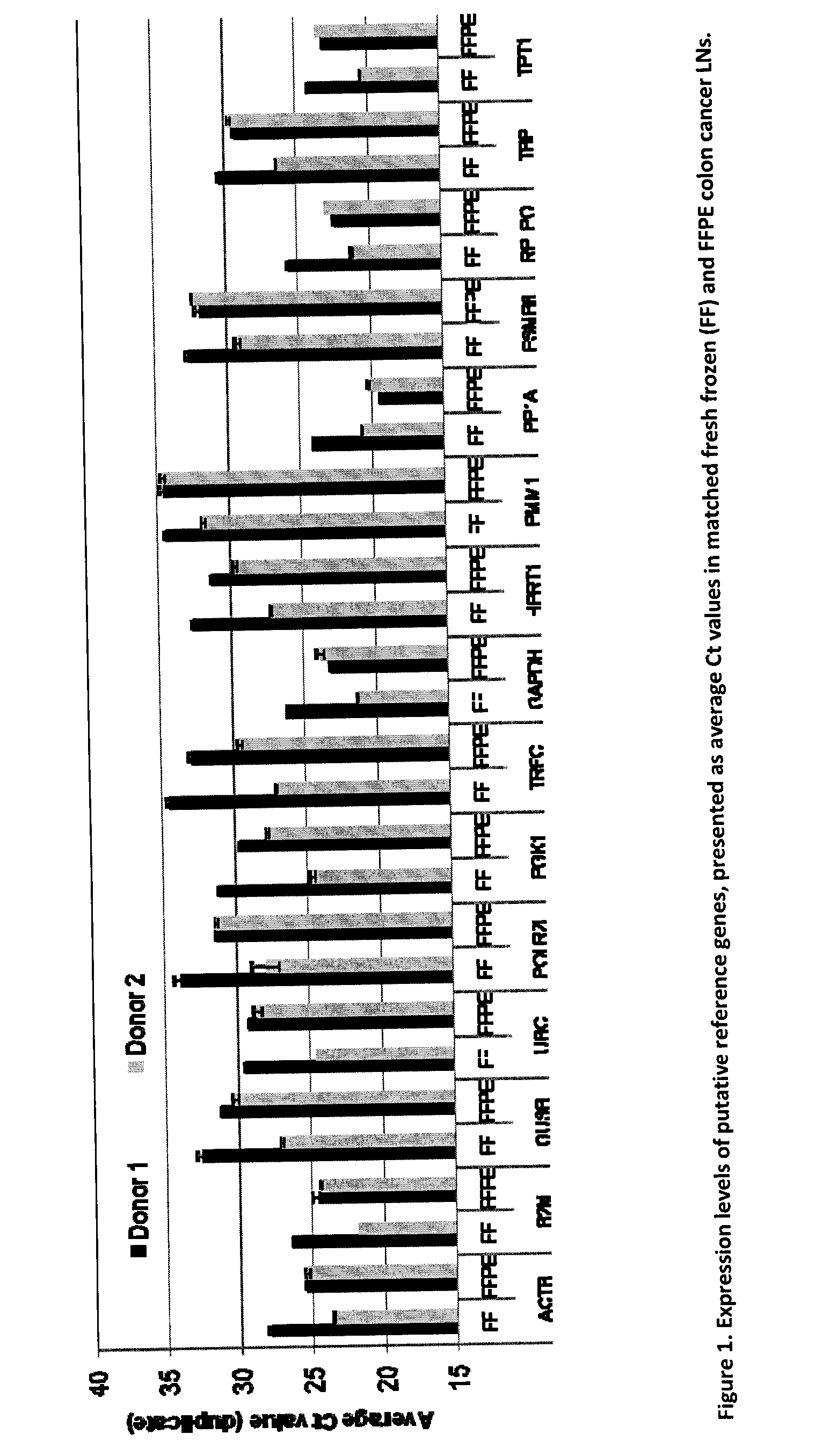
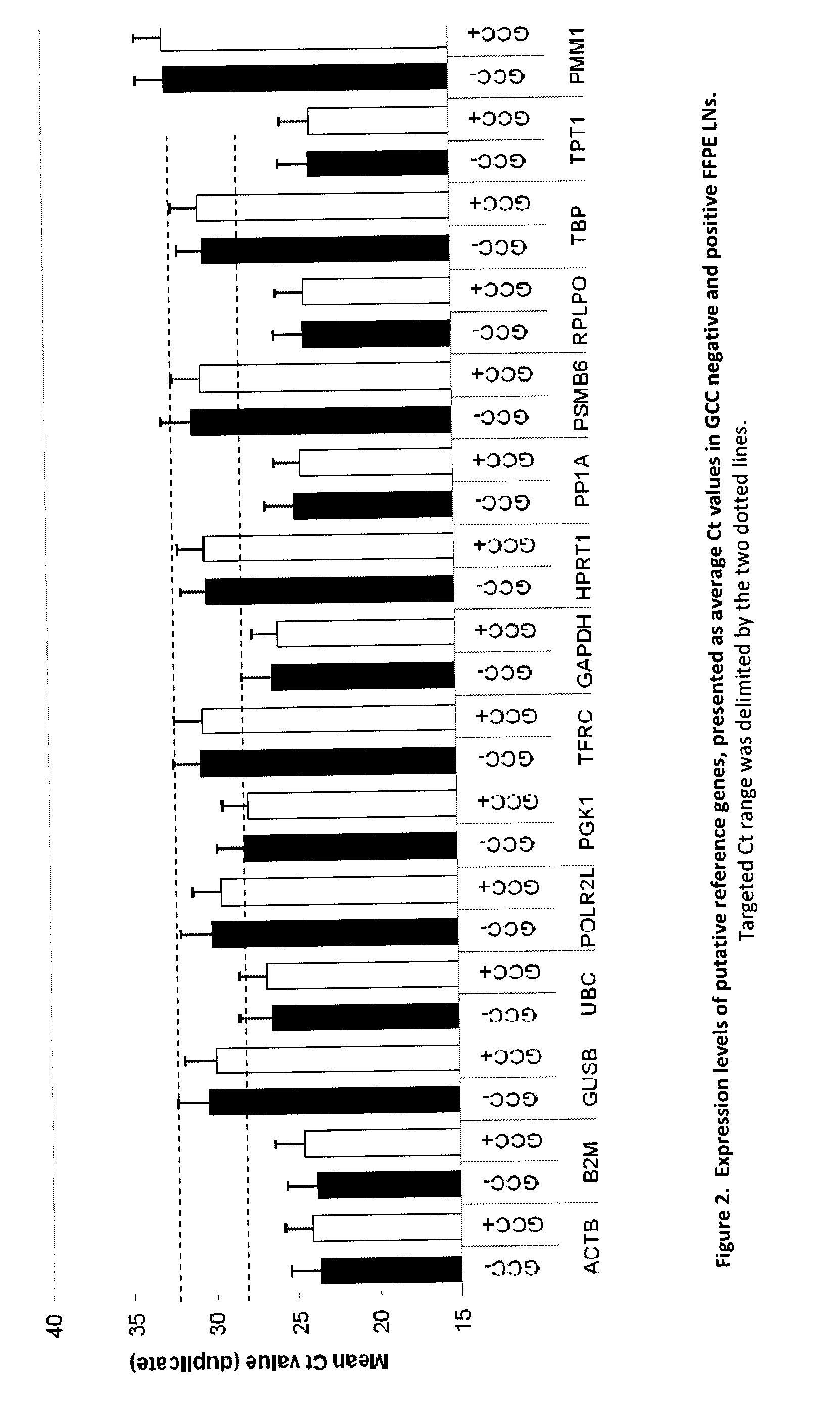
The present invention provides a novel method for diagnosing, monitoring, prognosing and staging Lymph Node (LN) status in colorectal cancer (CRC) that is more sensitive and accurate than conventional detection technologies such as histopathology. The Guanylyl Cyclase C (GCC) gene is specifically expressed in apical epithelial cells of the GI tract from the duodenum to the rectum and the detection of GCC mRNA in LNs is indicative of the presence of metastases. Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) detection of GCC mRNA to identify the presence of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells in LNs has the potential to aid in CRC staging. When used in combination with glucuronidase B (GUSB), accurate quantification of GCC can be achieved with less than a 2-fold variation between intact and highly degraded RNA specimens. The invention also relates to a newly designed GCC / GUSB assay that uses relative quantification having improved prognostic value for time to recurrence and relapse-free survival in Stage I or II colon cancer patients. The GCC / GUSB assay also improves the statistical power of prognosis stratification for relative risk of recurrence and relapse-free survival.
Owner:DIAGNOCURE
Nanoimprint resin stamper
A resin stamper is provided that is intended for use in an optical transfer-based nanostructure transfer apparatus and which is capable of automatic transport and alignment. The resin stamper includes a support member made of a light transmitting material and having mechanical strength, an intermediate layer also made of a light transmitting material, and a patterned resin layer which is also made of a light transmitting material. The support member is larger in size than the intermediate layer and the patterned resin layer. The intermediate layer is more flexible than the patterned resin layer. Also, the patterned resin layer has a pattern of high and low areas formed in a surface thereof that is the obverse of the pattern of high and low areas in a mold.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
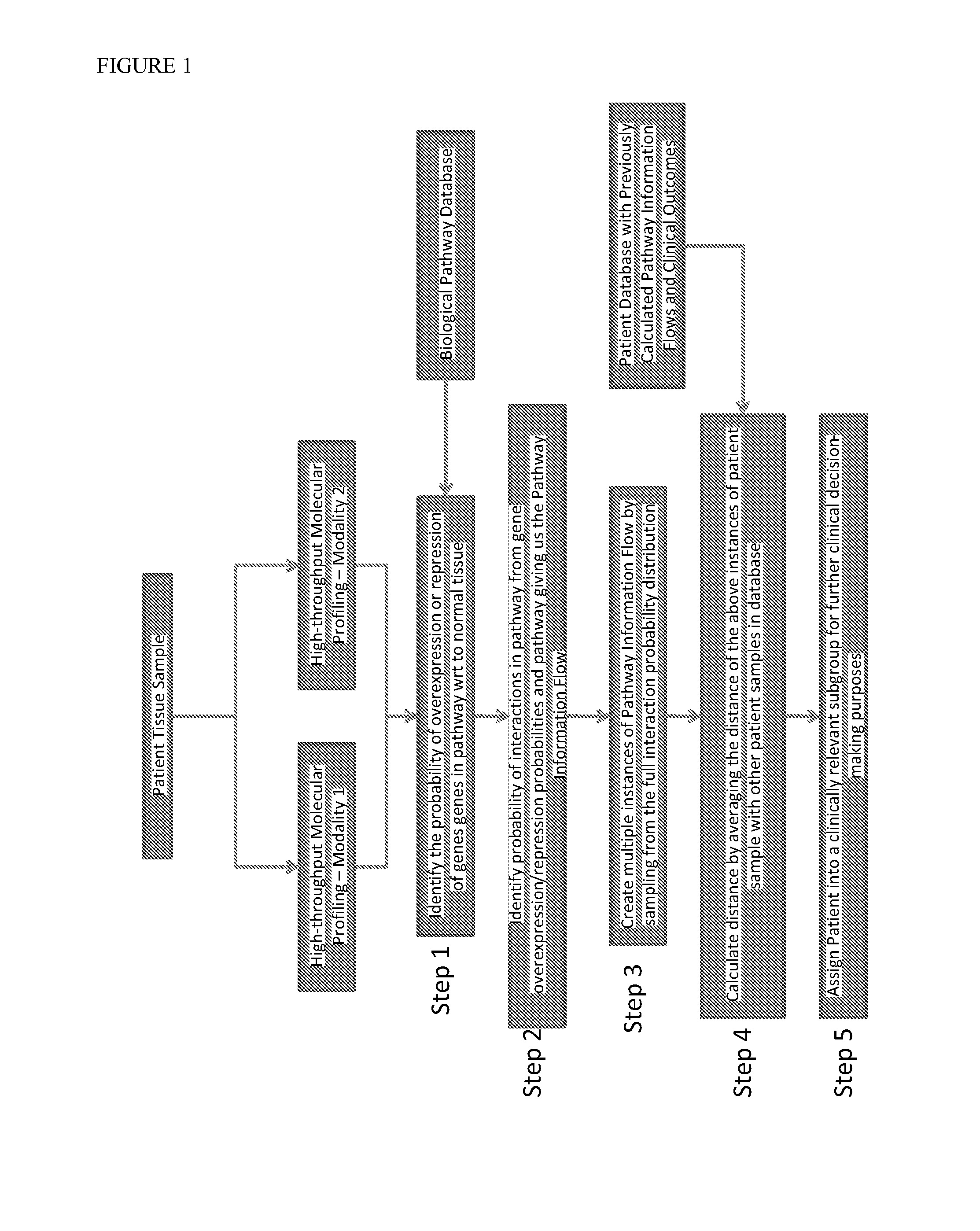
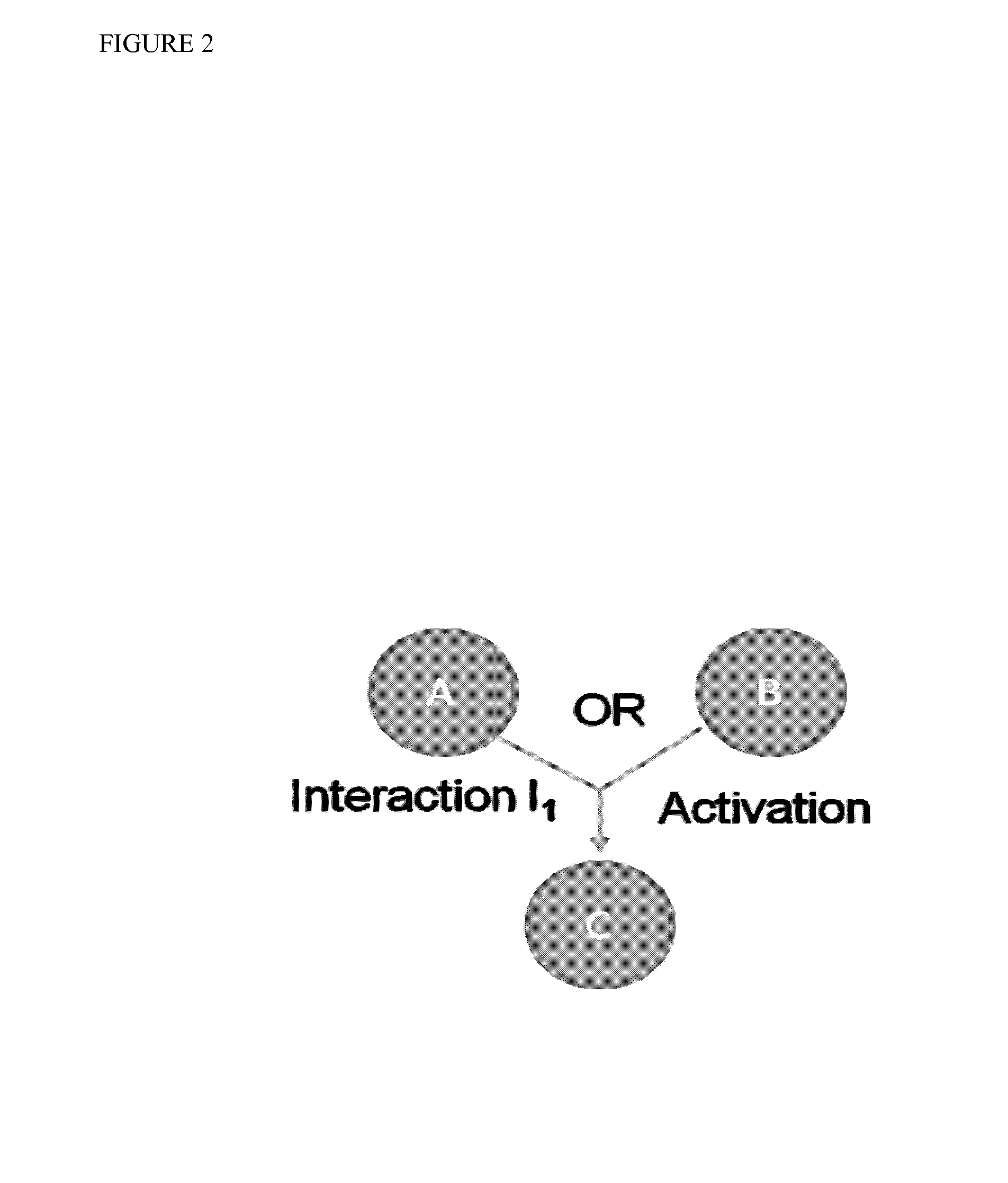
Method for estimation of information flow in biological networks
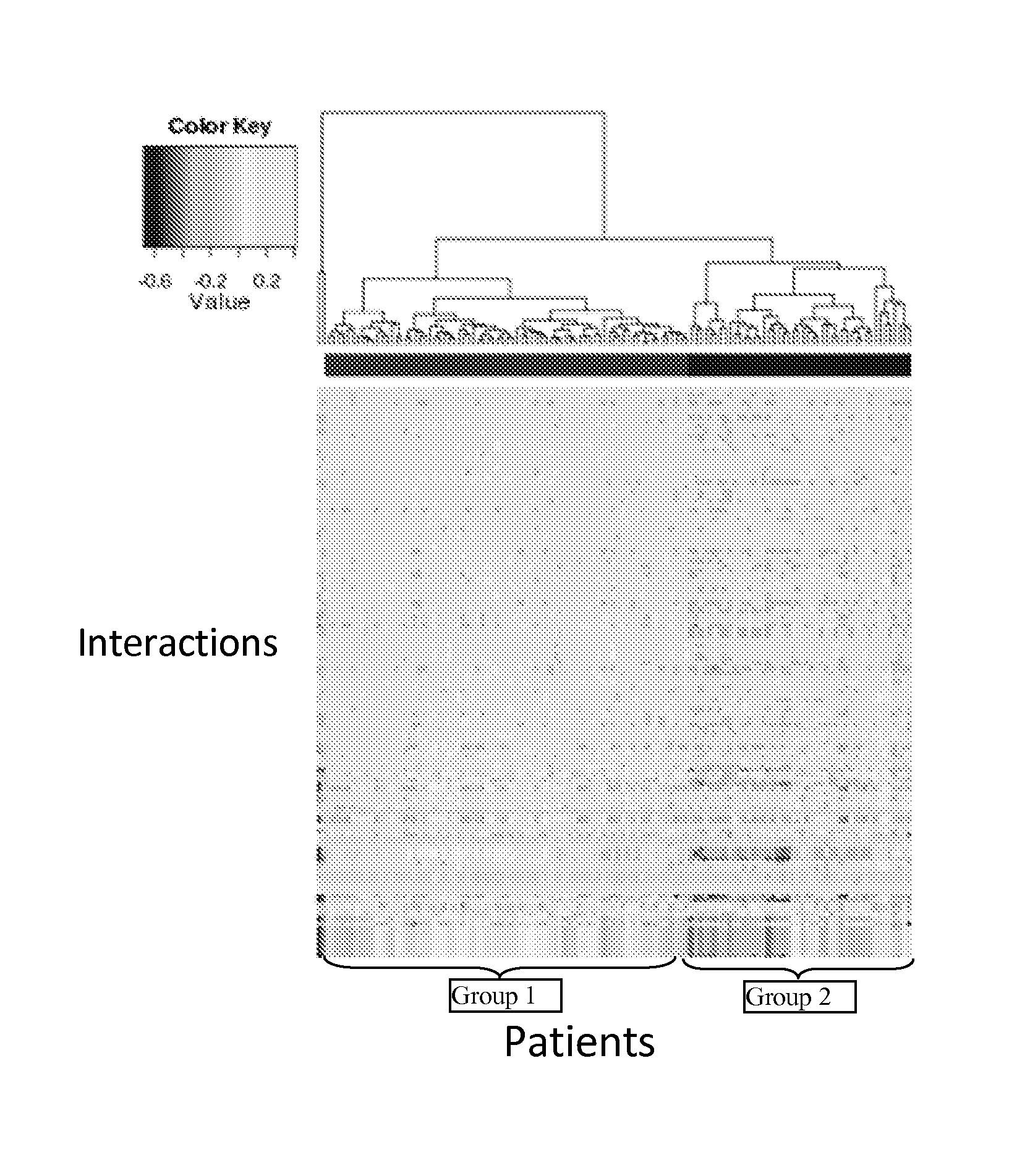
InactiveUS20140040264A1Stratify patients into clinically relevant groups very accuratelyAccurate layeringDigital data processing detailsBiostatisticsPatient databaseNetwork information flow
The present invention relates to a method for stratifying a patient into a clinically relevant group comprising the identification of the probability of an alteration within one or more sets of molecular data from a patient sample in comparison to a database of molecular data of known phenotypes, the inference of the activity of a biological network on the basis of the probabilities, the identification of a network information flow probability for the patient via the probability of interactions in the network, the creation of multiple instances of network information flow for the patient sample and the calculation of the distance of the patient from other subjects in a patient database using multiple instances of the network information flow. The invention further relates to a biomedical marker or group of biomedical markers associated with a high likelihood of responsiveness of a subject to a cancer therapy wherein the biomedical marker or group of biomedical markers comprises altered biological pathway markers, as well as to an assay for detecting, diagnosing, graduating, monitoring or prognosticating a medical condition, or for detecting, diagnosing, monitoring or prognosticating the responsiveness of a subject to a therapy against said medical condition, in particular ovarian cancer. Furthermore, a corresponding clinical decision support system is provided.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Solid state membrane channel device for the measurement and characterization of atomic and molecular sized samples
InactiveUS20090277869A1Effectively protect and insulateSimple manufacturing processVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFixed microstructural devicesMembrane channelMaterial removal
A solid state device is formed through thin film deposition techniques which results in a self-supporting thin film layer that can have a precisely defined channel bored therethrough. The device is useful in the chacterization of polymer molecules by measuring changes in various electrical characteristics as molecules pass through the channel. To form the device, a thin film layer having various patterns of electrically conductive leads are formed on a silicon substrate. Using standard lithography techniques, a relatively large or micro-scale aperture is bored through the silicon substrate which in turn exposes a portion of the thin film layer. This process does not affect the thin film. Subsequently, a high precision material removal process is used (such as a TEM) to bore a precise nano-scale aperture through the thin film layer that coincides with the removed section of the silicon substrate.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
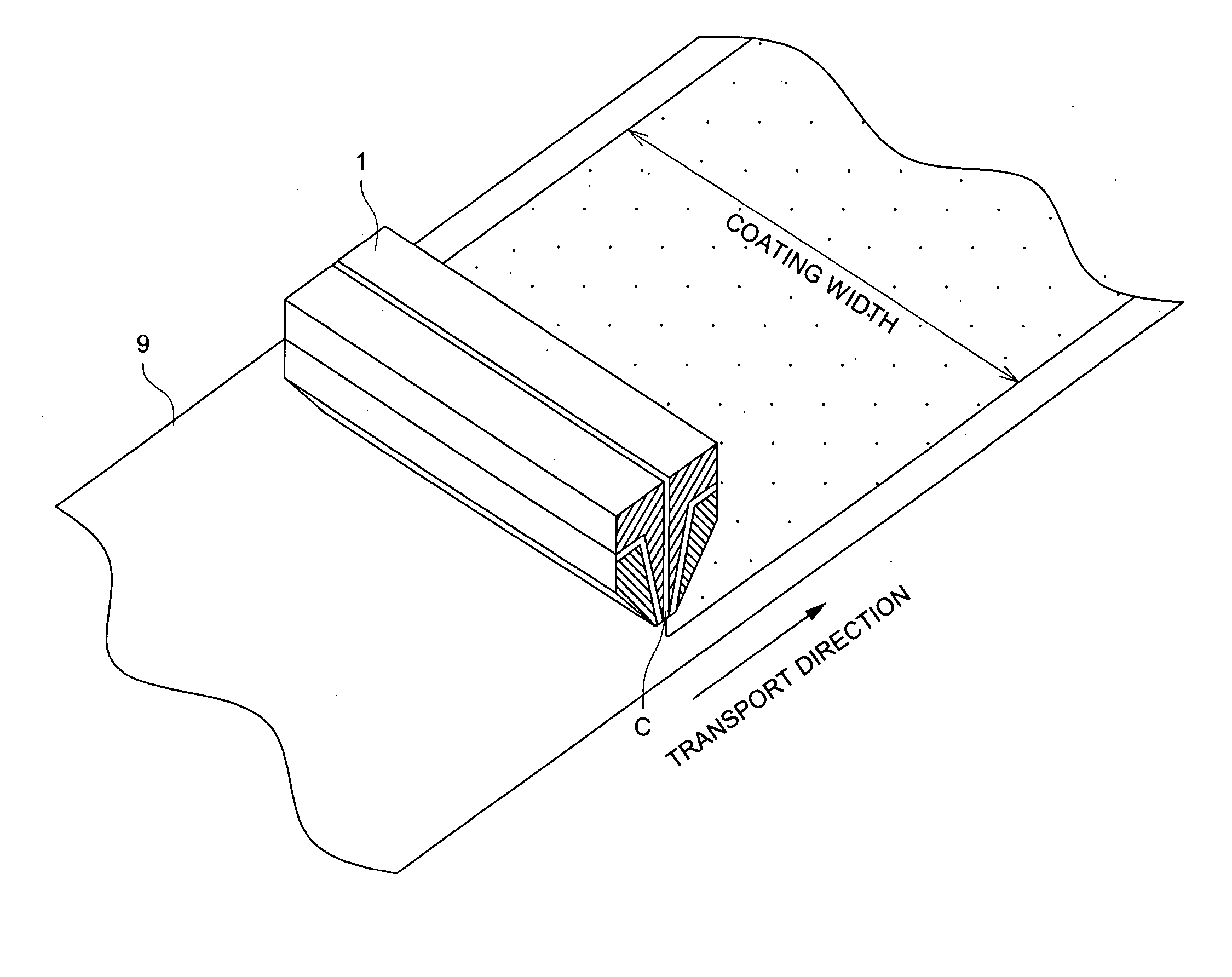
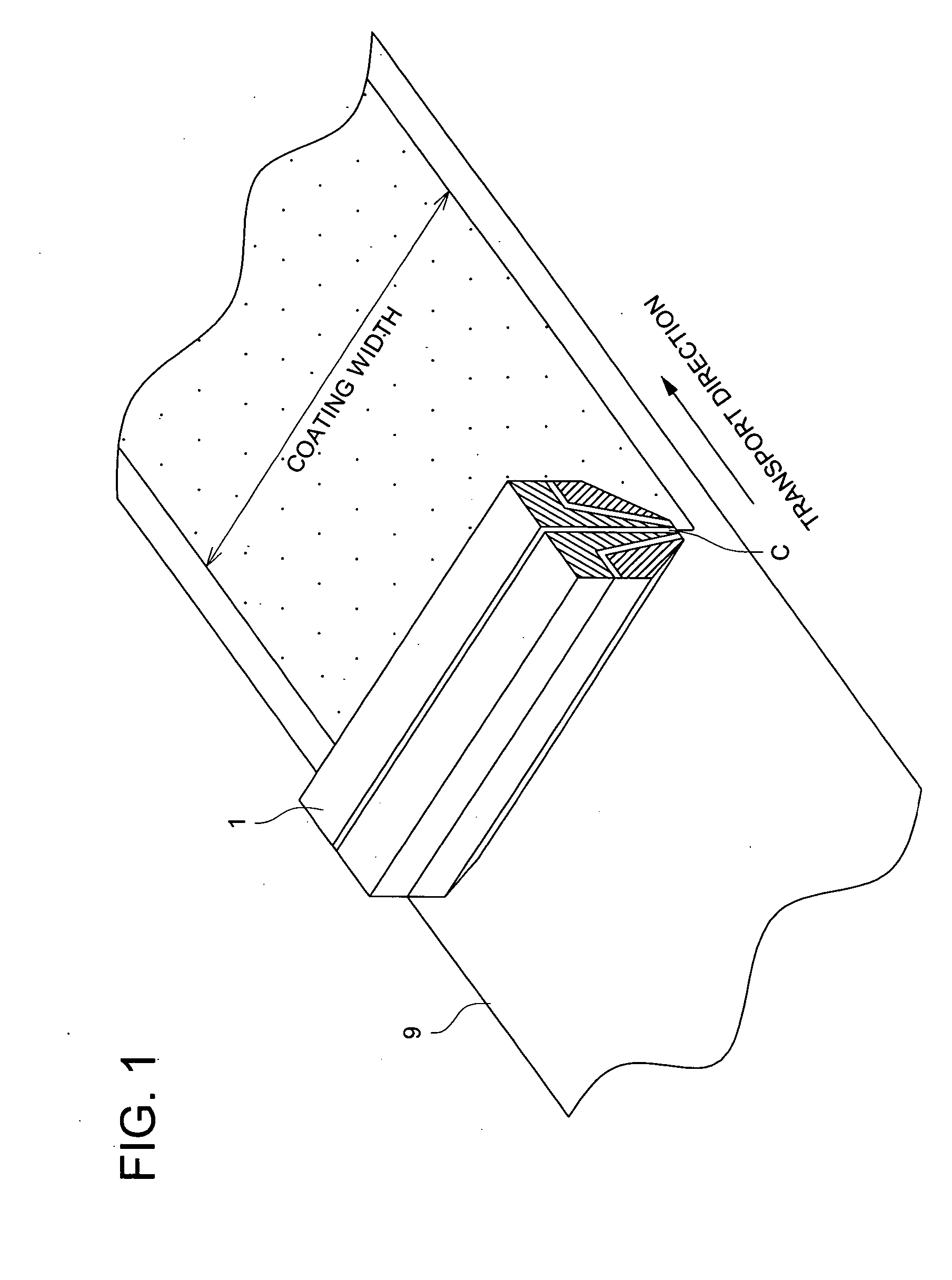
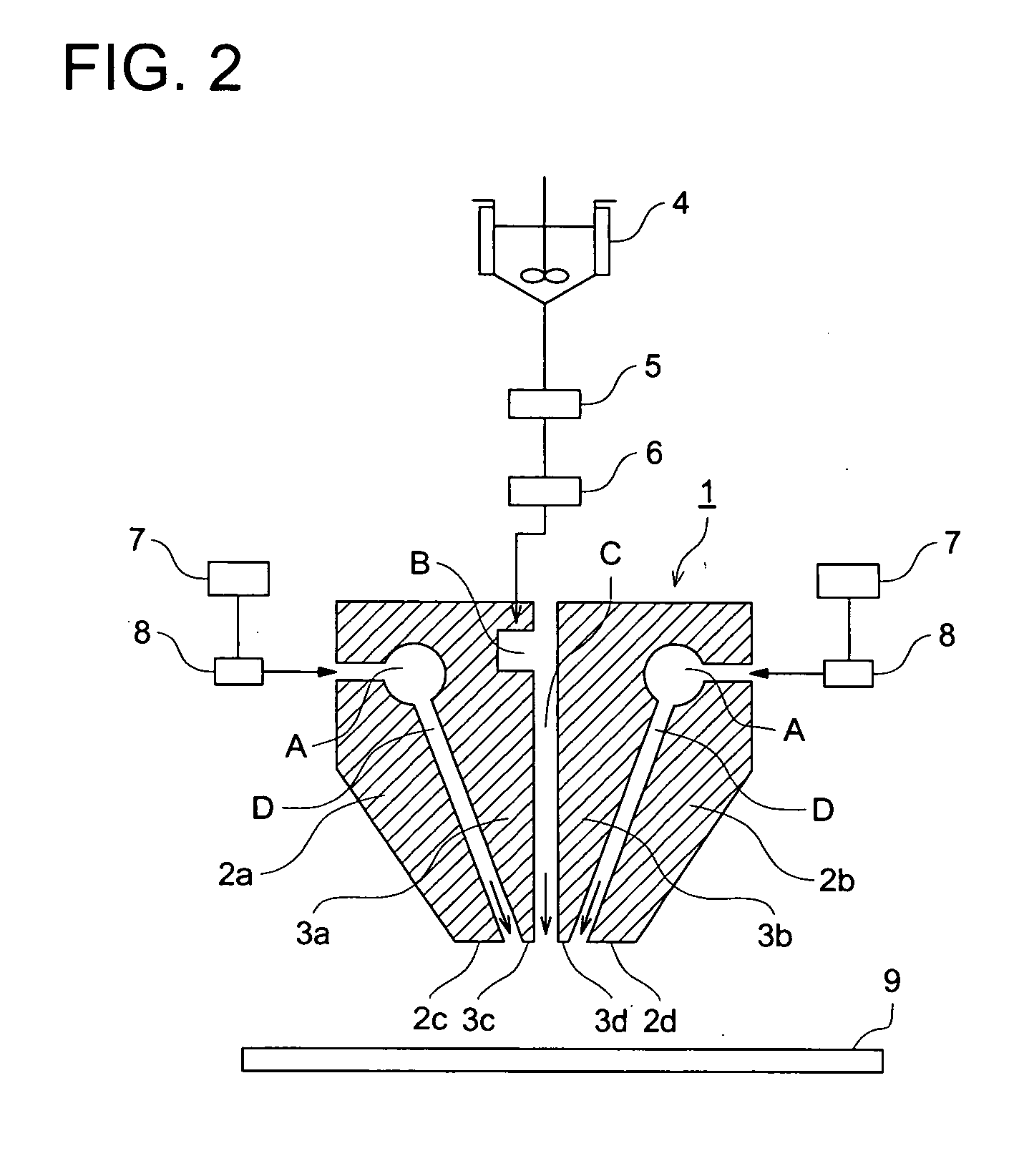
Coating apparatus and coating method
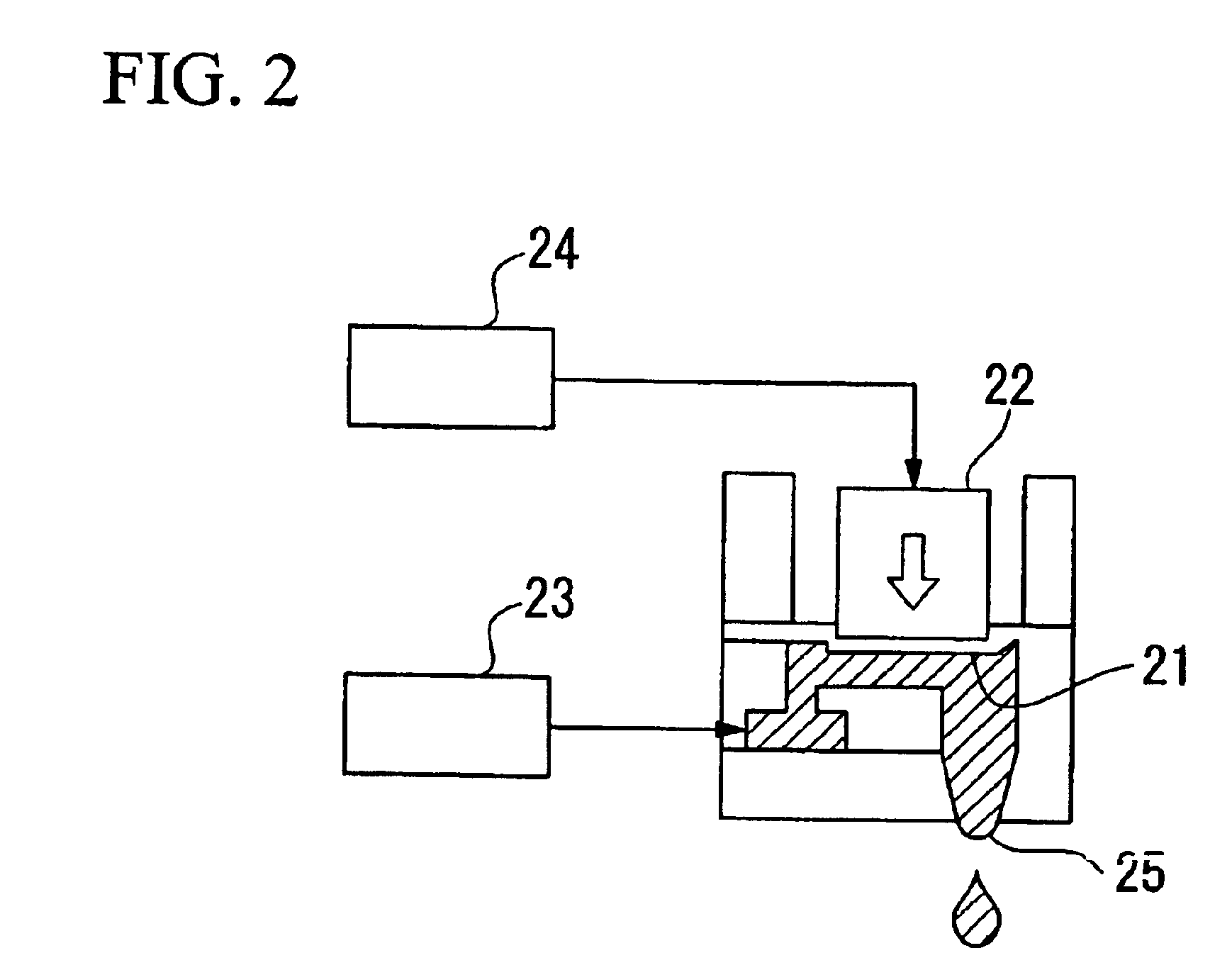
InactiveUS20050120947A1Accurate layeringSmall loadLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid spraying apparatusSolution flowCoating
A coating apparatus comprising: a slot nozzle spraying apparatus provided with a pair of inner die blocks and outer die blocks at the outside of said pair of inner die blocks, having a coating solution nozzle formed between said pair of inner die blocks, and gas nozzles constituted between one inner die block and outer die block adjacent thereto, and between another inner die block and outer die block adjacent thereto, wherein, angle β between the solution flow passage of said coating solution nozzle and the gas flow passage of one of said gas nozzle is 15-60 degree.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA PHOTO IMAGING
Modifying the optical properties of a nitride optoelectronic device
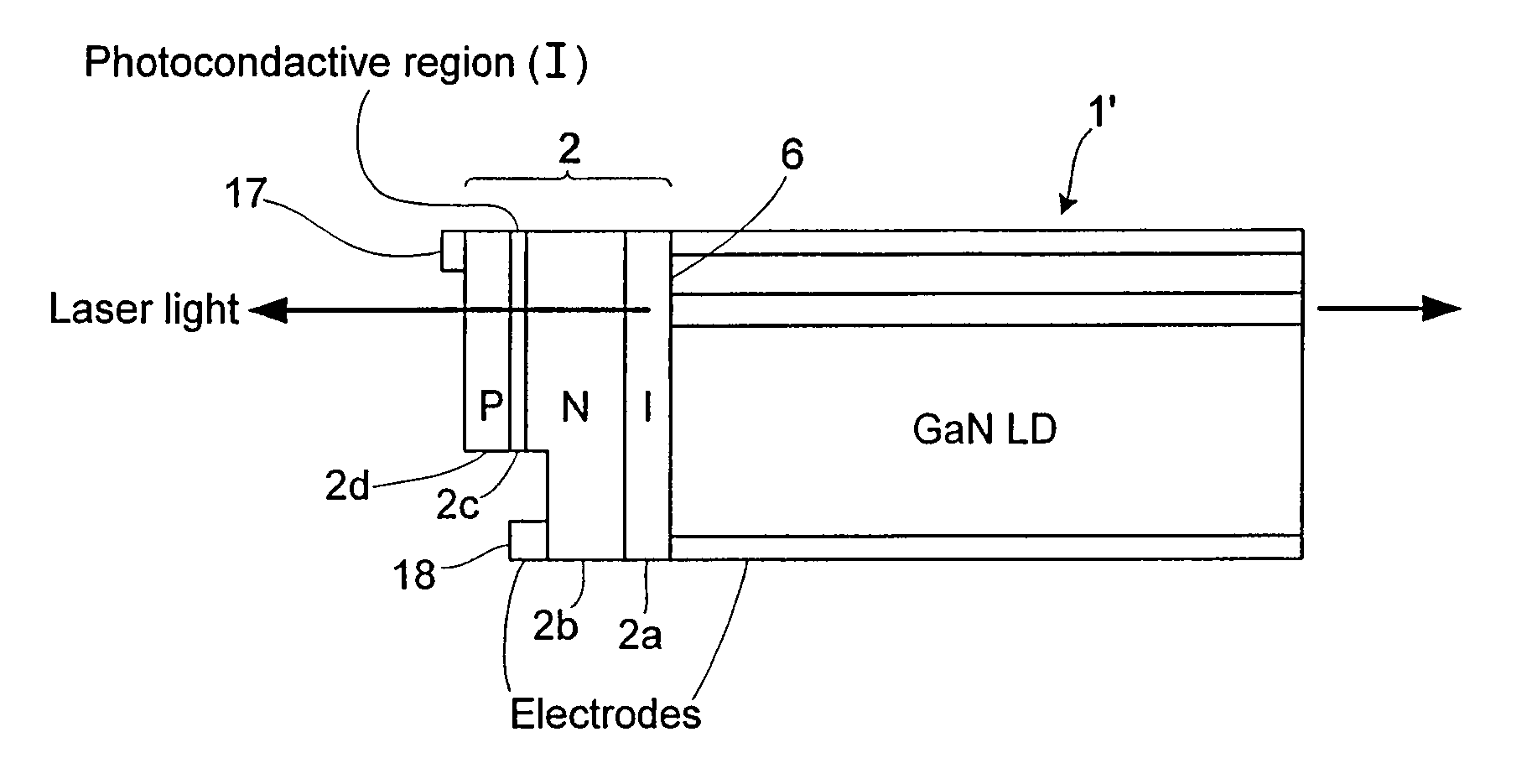
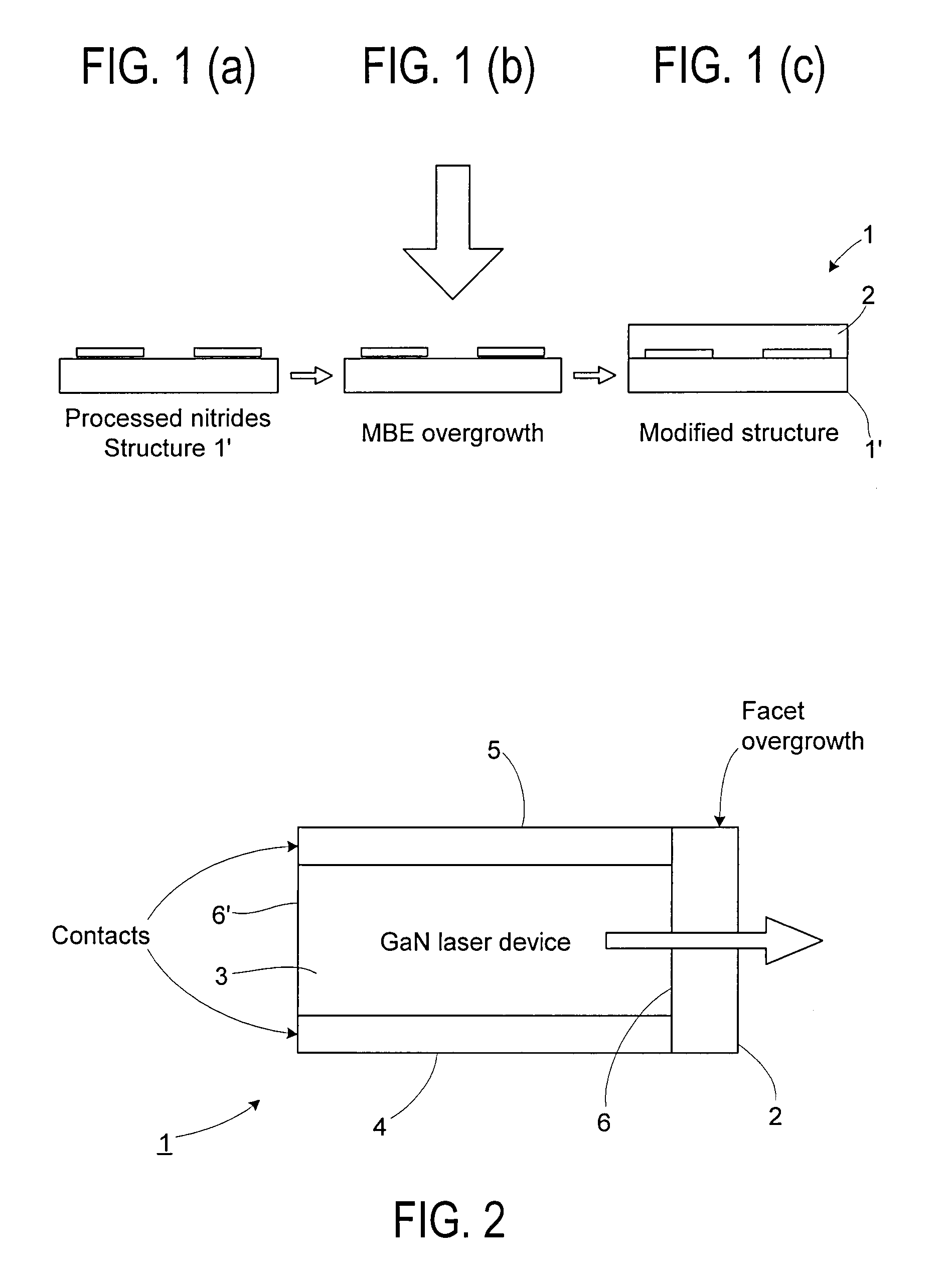
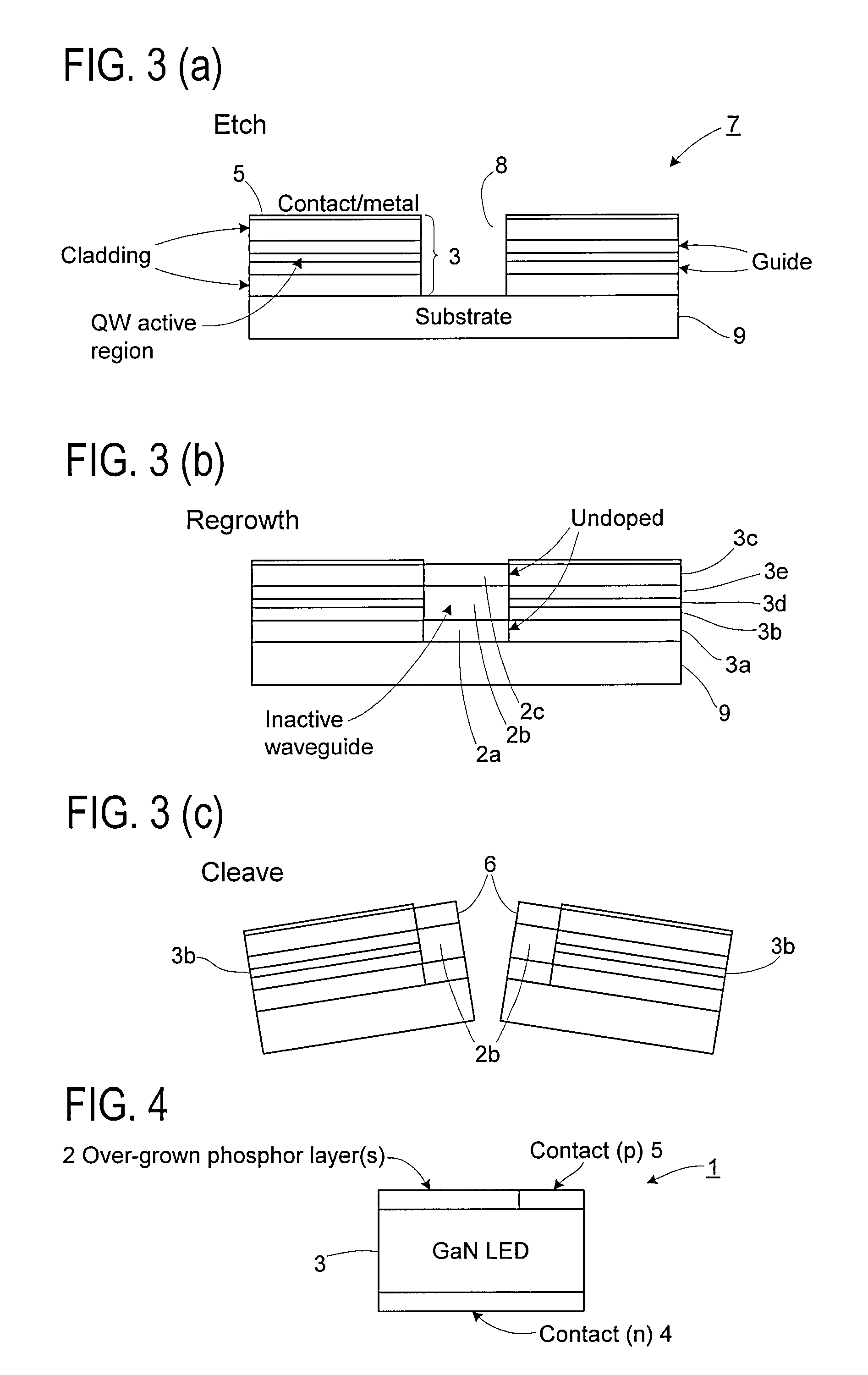
InactiveUS20080014667A1Short timeNovel and improved optical characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical propertyNitrogen
A method of modifying the optical properties of a processed nitride semiconductor light-emitting device initially comprises disposing the processed nitride semiconductor light-emitting device in a vacuum chamber. One or more nitride semiconductor layers are then grown by molecular beam epitaxy thereby to modify the optical properties of the processed light-emitting device. Activated nitrogen, for example from a plasma source, is supplied to the vacuum chamber during growth of the nitride semiconductor layer(s). The use of activated nitrogen reduces the growth temperature required for the growth of the nitride semiconductor layer(s), as the need for thermal activation of a nitrogen species is eliminated. Moreover, use of a growth method such as, for example, plasma-assisted MBE to grow the nitride semiconductor layer(s) allows much more precise control of their thickness and composition.
Owner:SHARP KK
Inkjet ink composition for color filter, production method for color filter, and color filter
InactiveUS20090061167A1Improve heat resistanceMaintain good propertiesDecorative surface effectsLayered productsVinyl etherEpoxy
An ink-jet composition for a color filter excellent in storage stability, straightness and sustainability at the time of ejection from a head, wherein a cured layer thereof is excellent in heat resistance, adhesive property, and solvent resistance. The ink-jet ink composition for a color filter is a specific epoxy group-containing polymer (A), a specific epoxy group-containing compound (B) having two or more specific epoxy groups and a polycarboxlic acid derivative (C) in which specific carboxylic acid (cl) having alicyclic hydrocarbon is rendered latent by vinyl ether (c2), wherein the equivalence ratio of carboxyl groups rendered latent by the polycarbonoxylic acid derivative (C) to the total epoxy groups contained in the epoxy-group containing polymer (A) and the epoxy-group containing compound (B) is in the range from 0.7 to 1.1.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD +1
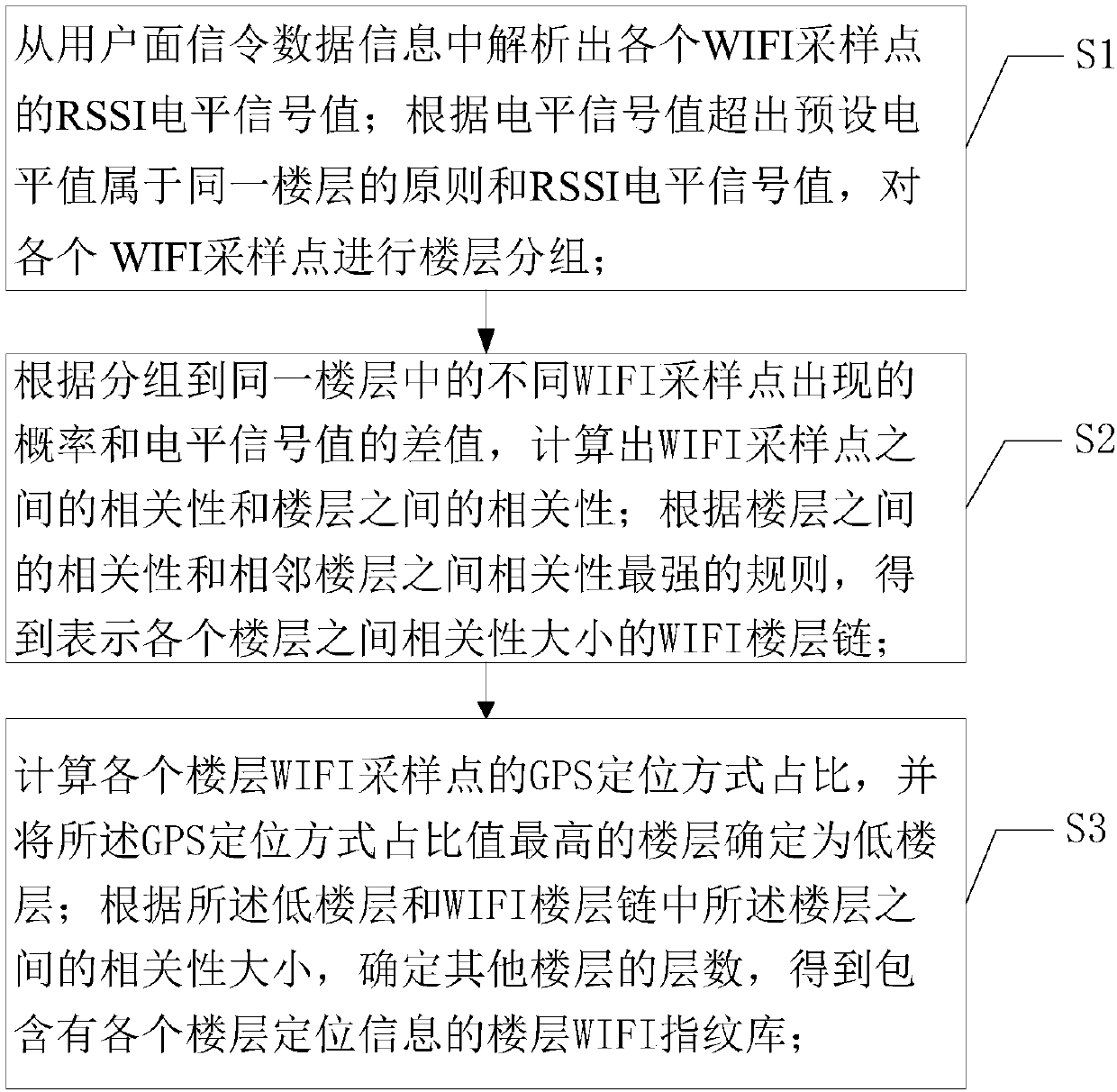
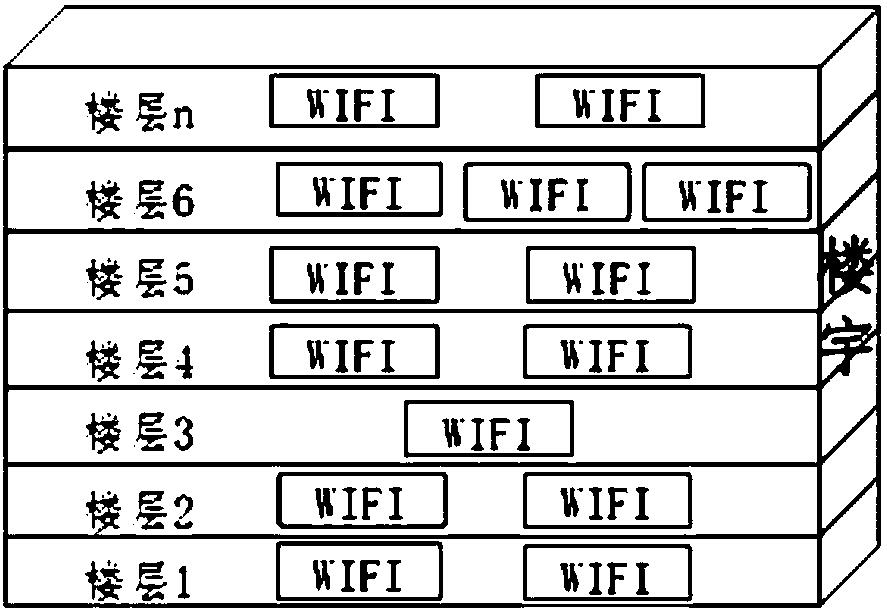
Three-dimensional indoor positioning method, device and equipment based on big data and medium
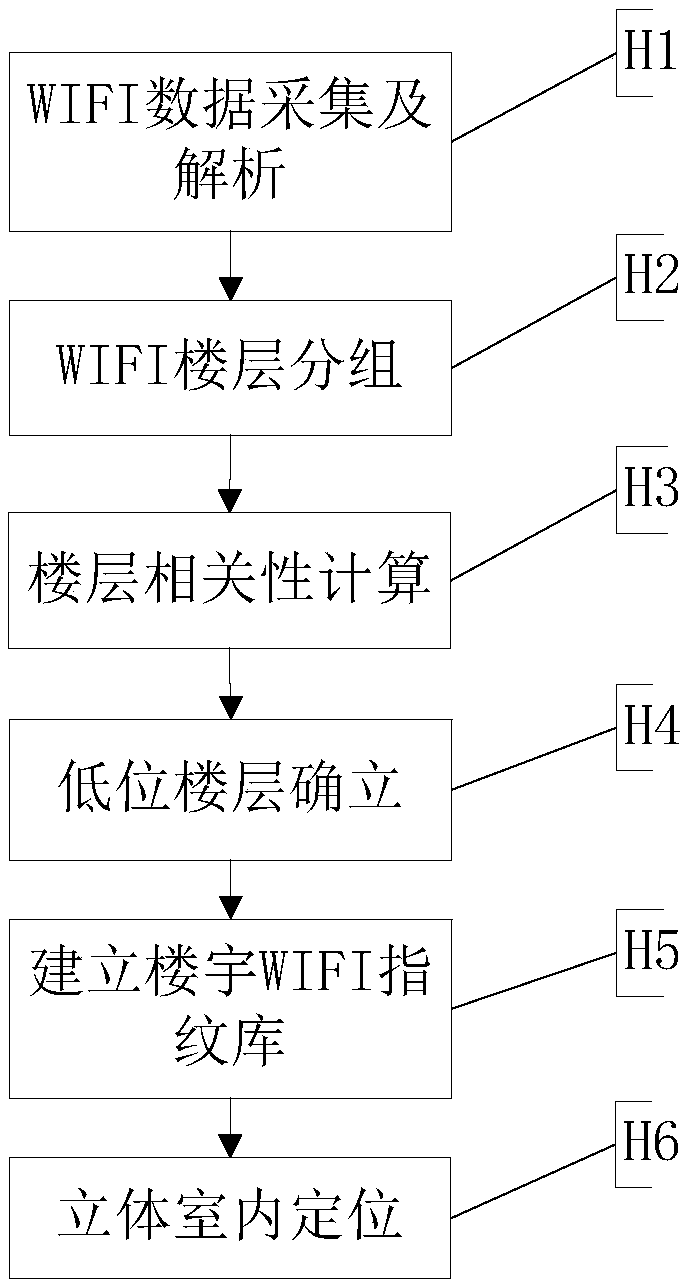
ActiveCN109996181AAvoid Positioning ErrorsAccurate layeringParticular environment based servicesPosition fixationData informationComputer science
The invention provides a three-dimensional indoor positioning method and device based on big data, equipment and a medium. According to the big data-based three-dimensional indoor positioning method,RSSI level signal values of all WIFI sampling points are analyzed from user plane signaling data information, the WIFI sampling points are subjected to floor grouping, and the correlation between thedifferent WIFI sampling points and the correlation between floors are calculated; a WIFI floor chain is obtained according to the correlation between the floors; a low floor is determined according tothe GPS positioning mode proportion of each floor WIFI sampling point; according to the calculated position relation between the low floor and the floors in the WIFI floor chain, the number of the other floors is determined, a floor WIFI fingerprint database is obtained; the WIF sampling point information is compared with the WIFI fingerprint database, and the specific position of each user sampling point is positioned according to a matching result. According to the invention, accurate assessment of building hierarchical network coverage can be realized.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SICHUAN +1
Method of forming diffraction grating and method of fabricating distributed feedback laser diode
ActiveUS20100081224A1Low viscosityEasily to move into recessLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtmospheric pressureClosed pattern
A method of forming a diffraction grating according to the present invention includes a step of preparing a mold having projections and recesses for forming a diffraction grating, a step of bringing the projections and recesses of the mold into contact with a resin layer in a chamber at a first pressure less than atmospheric pressure, a step of setting a pressure in the chamber to a second pressure more than the first pressure while maintaining the contact, and a step of hardening the resin layer while maintaining the contact between the resin layer and the projections and recesses so as to form a pattern for the diffraction grating on the hardened resin layer. The recesses in the projections and recesses of the mold form a closed pattern in the plane of the mold including the projections and recesses.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical device and method of manufacture of the same, display device, electronic device, and detection device
InactiveUS6919991B2Improve product qualityImprove the display effectOptical filtersOptical articlesLens materialsEngineering
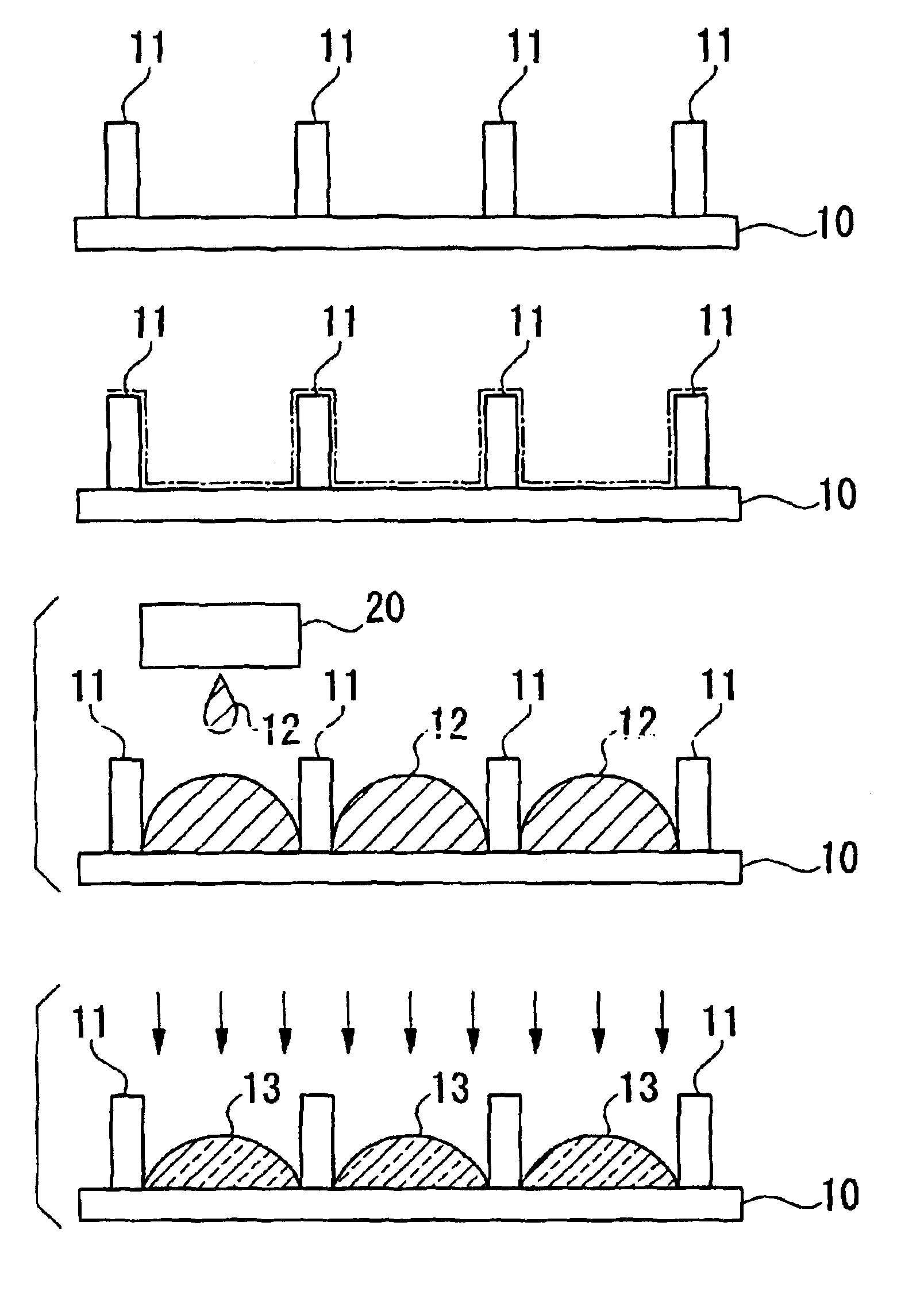
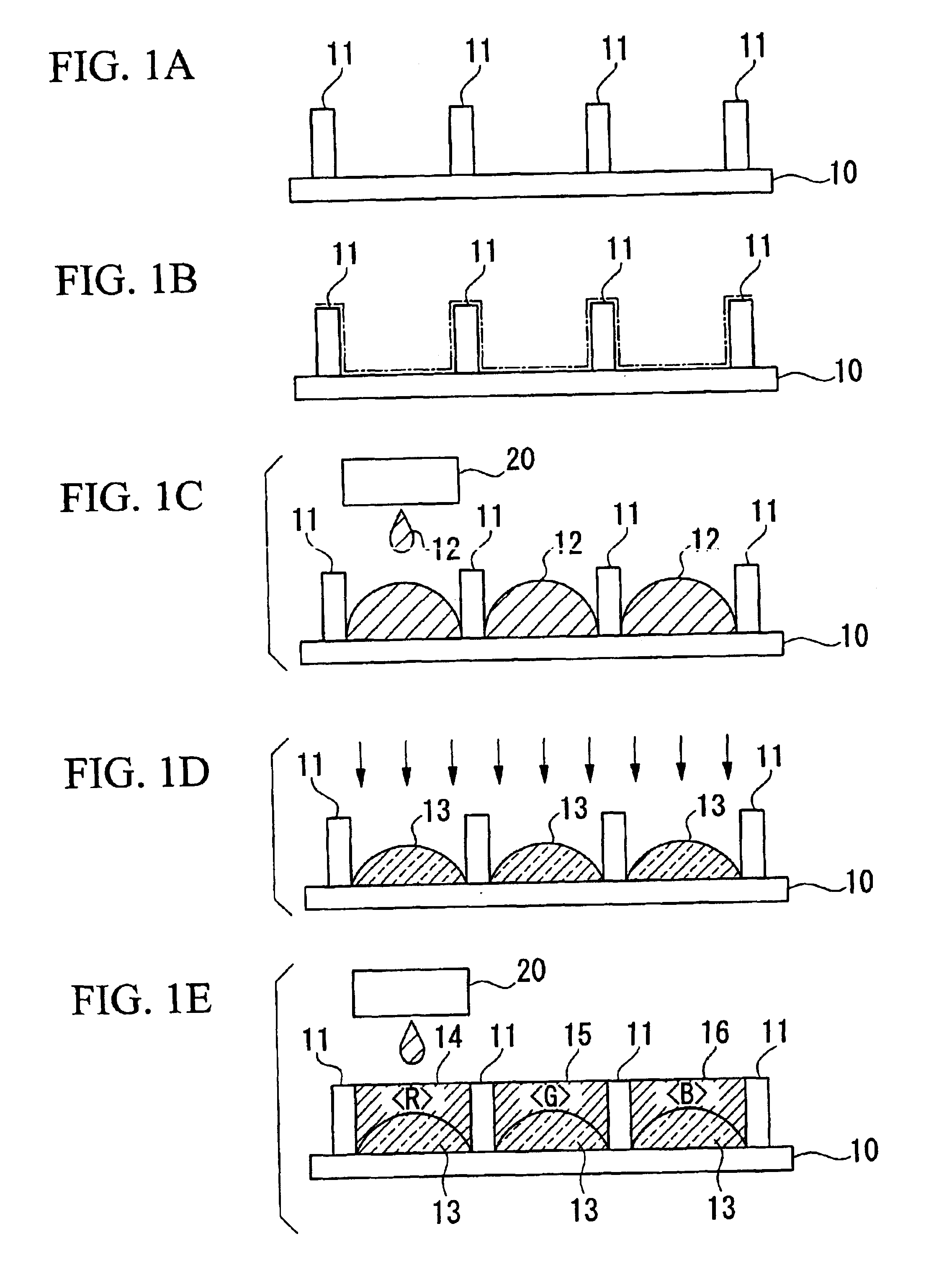
A method of manufacture of an optical device comprises a process of forming a bank 11 which demarcates a region in which a functional material is distributed, and a process of distributing a lens material 12 in the liquid state in the region which is demarcated by the bank 11, and of thereby forming a lens 13 which is layered against the functional material 14, 15, 16.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Glass product and a method for manufacturing a glass product
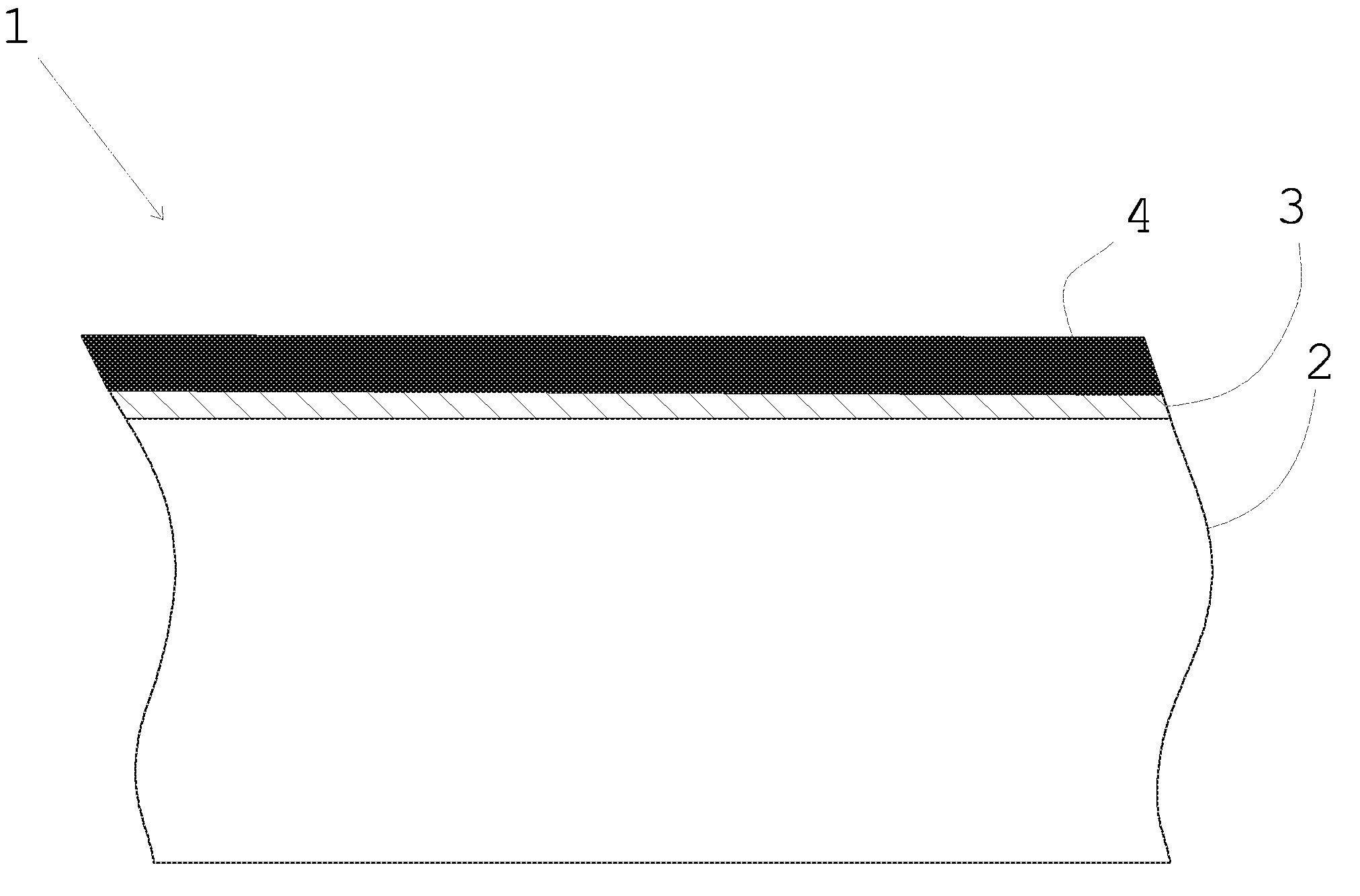
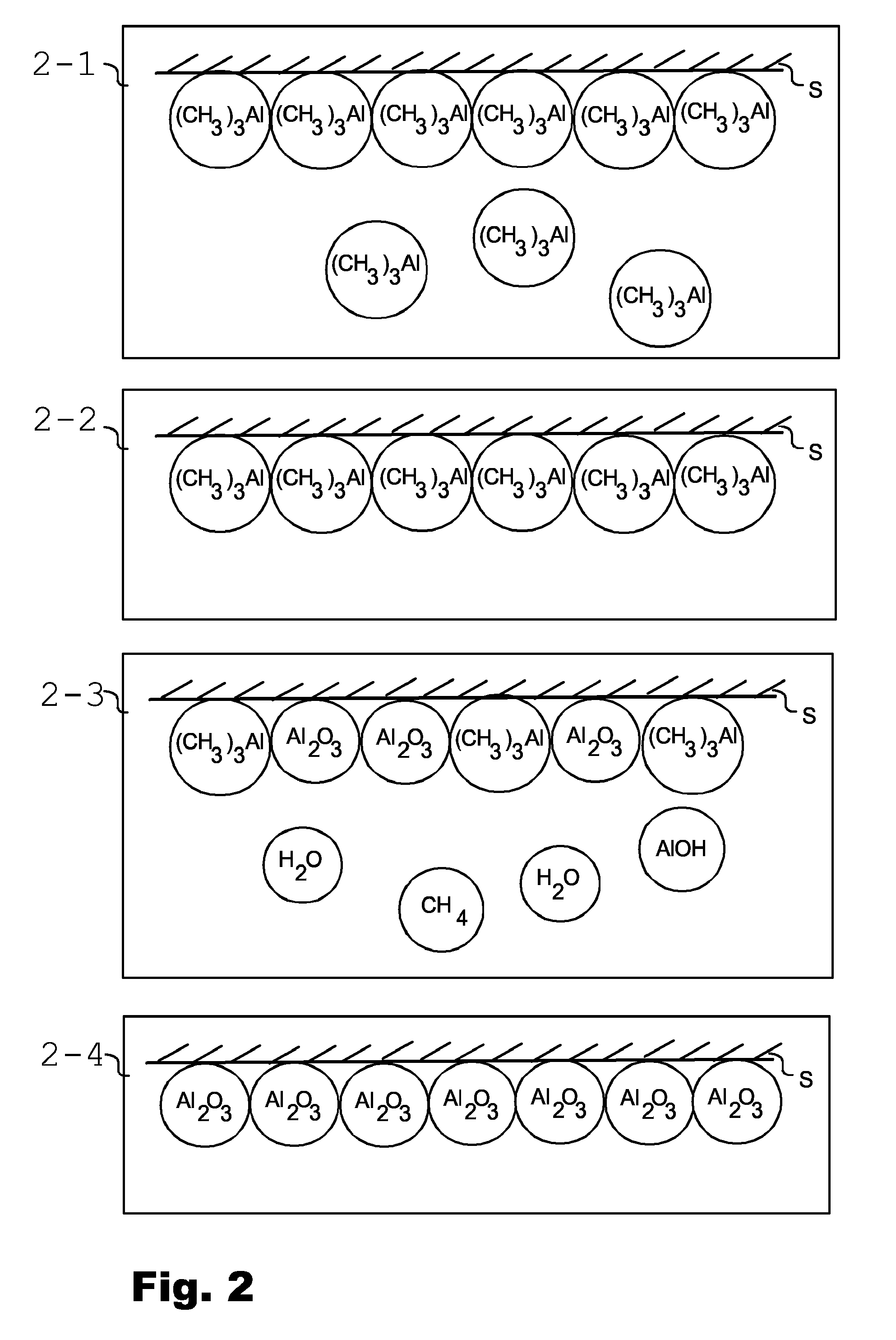
InactiveUS20110003125A1Accurate and well controlled productionAccurate layeringLiquid surface applicatorsMirrorsAtomic layer depositionMetal
A glass product of the present invention (1) comprises a glass substrate (2), a reflective metal layer (3) deposited on the glass substrate, and a passivation layer (4) deposited on the reflective metal layer. According to the present invention, the passivation layer (4) is deposited using an Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) process.
Owner:BENEQ OY
Method and apparatus for levitation additive welding of superalloy components
InactiveUS20170252876A1Accurate layeringAdd dimensionTurbinesEvacuating shieldingLevitationRelative motion
Superalloy components for turbine engines are additively welded by propelling a stream of powdered filler, which includes superalloy powder filler, through a nozzle at a powder stream mass flow rate, with pressurized gas. The powdered filler stream is melted and agglomerated into a continuous melt stream with a laser or arc heating source located downstream of the nozzle. The melt stream is levitated within a magnetic field generated by at least one electromagnet coil that is oriented downstream of the heating source, and directed onto the superalloy component, by relative motion between the melt stream and the superalloy component.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Apparatus for manufacturing an inorganic thin-film solar cell, and method for controlling same
ActiveUS20140030825A1Improve efficiencyReduce manufacturing costLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufacturePowder AerosolMaterials science
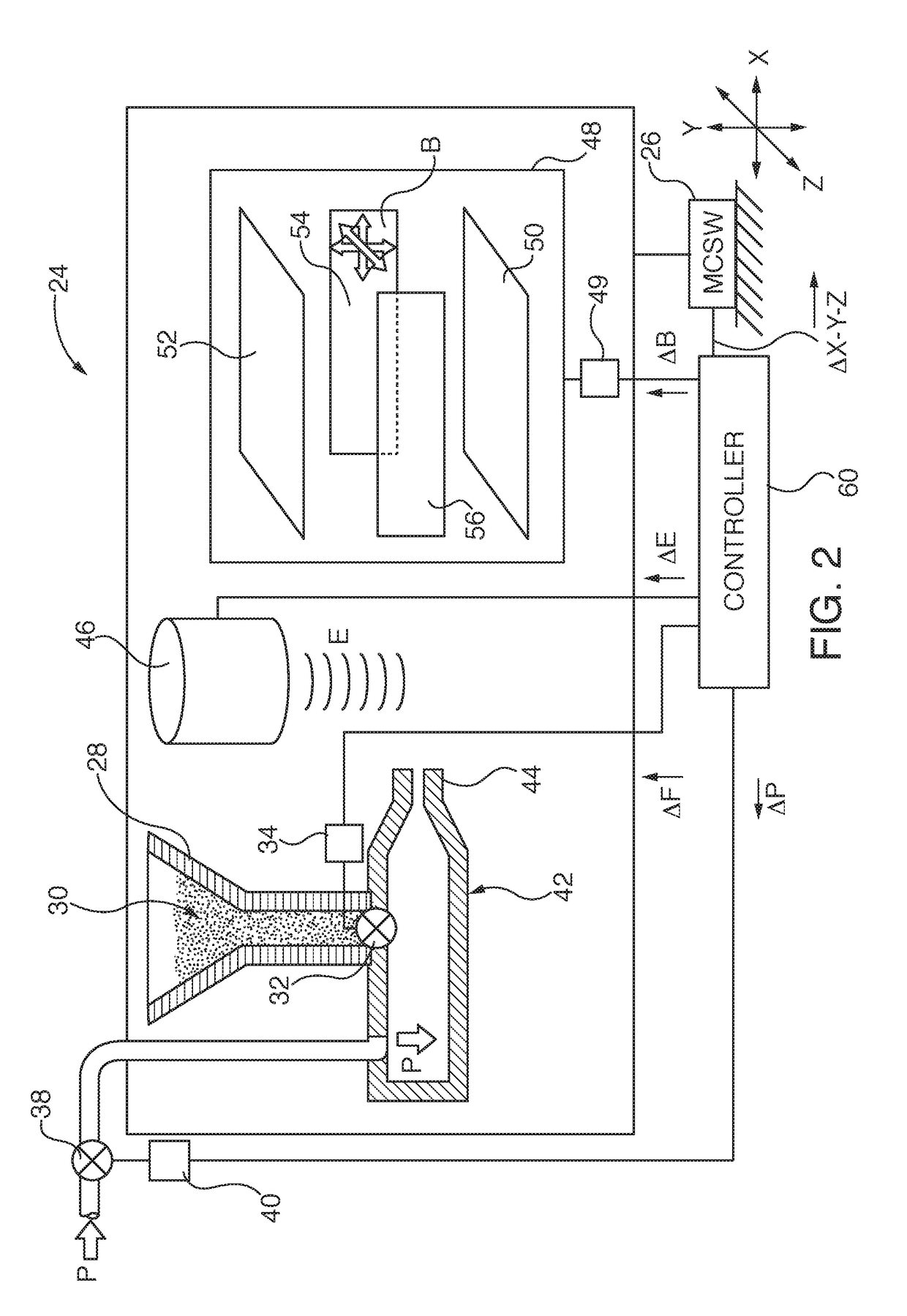
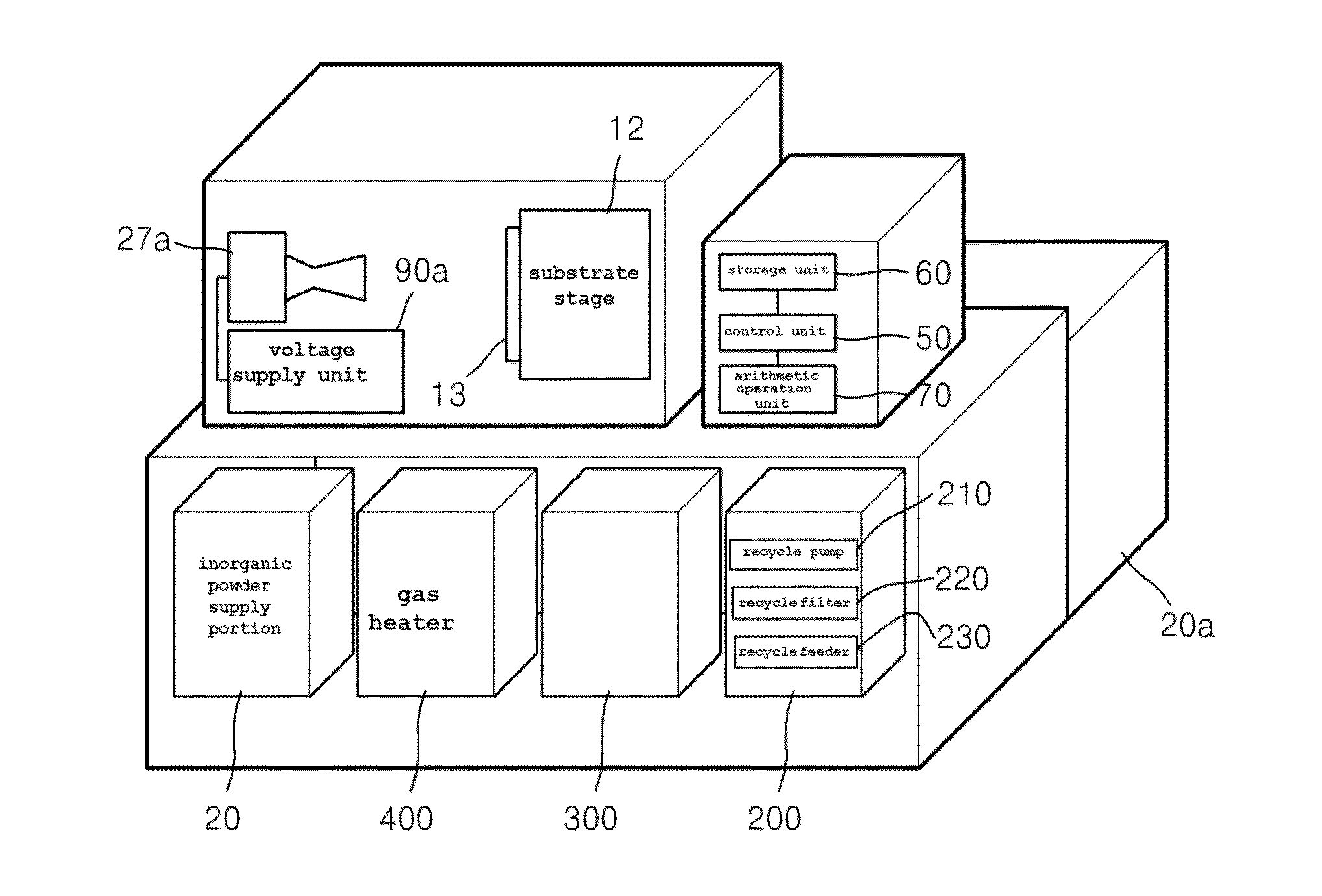
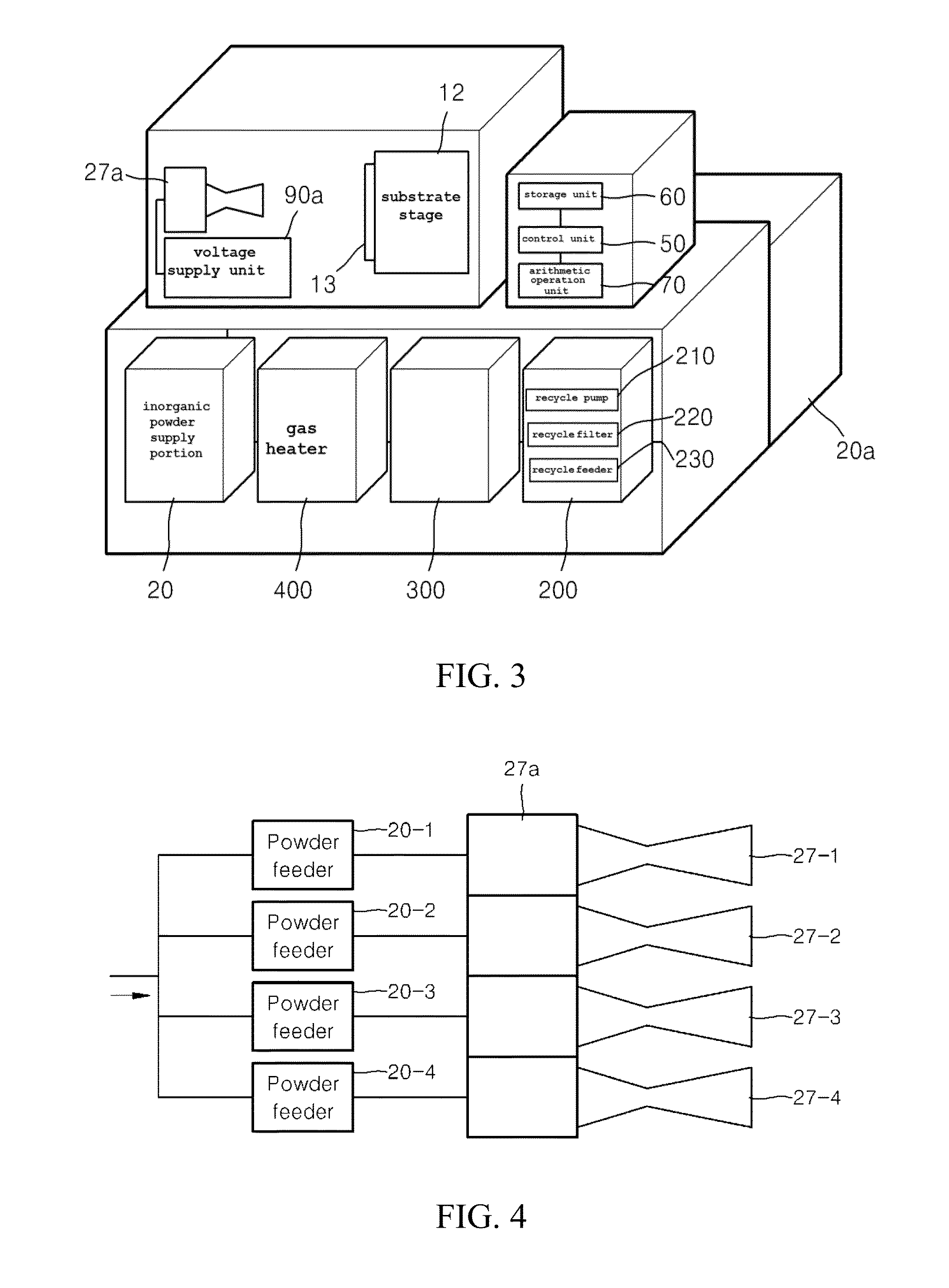
The present invention relates to an apparatus for manufacturing an inorganic thin-film solar cell, the apparatus including: a substrate stage which is mounted in a chamber and in which a solar cell substrate is disposed; and an inorganic powder supply unit including a nozzle configured to discharge an inorganic powder aerosol containing an inorganic powder onto the substrate stage in a supersonic flow so as to form a solar cell layer on the solar cell substrate, and an inorganic powder supply portion configured to supply the inorganic powder aerosol to the nozzle.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Stratified sampling system
InactiveCN105973646AEasy to operateSimple structureWithdrawing sample devicesPeristaltic pumpWater quality
The invention discloses a stratified sampling system, and aims to provide a stratified sampling system which is simple in structure, precise in control and capable of achieving stratified sampling. The stratified sampling system comprises a base and support racks, wherein the support racks are mounted at two side ends of the base; helix roller is mounted between the support racks; a sampling tube matched with the helix roller is arranged on the helix roller; servo steering engines connected with the helix roller are arranged on outer end surfaces of the support racks; a vacuum rotating connector communicated with the sampling tube is arranged inside the helix roller; a peristaltic pump communicated with the vacuum rotating connector is further arranged on the base; a water outlet is formed in the peristaltic pump; a water outlet tube is arranged at the water outlet. The stratified sampling system is applied to the technical field of water quality sampling.
Owner:珠海科微智能科技有限公司
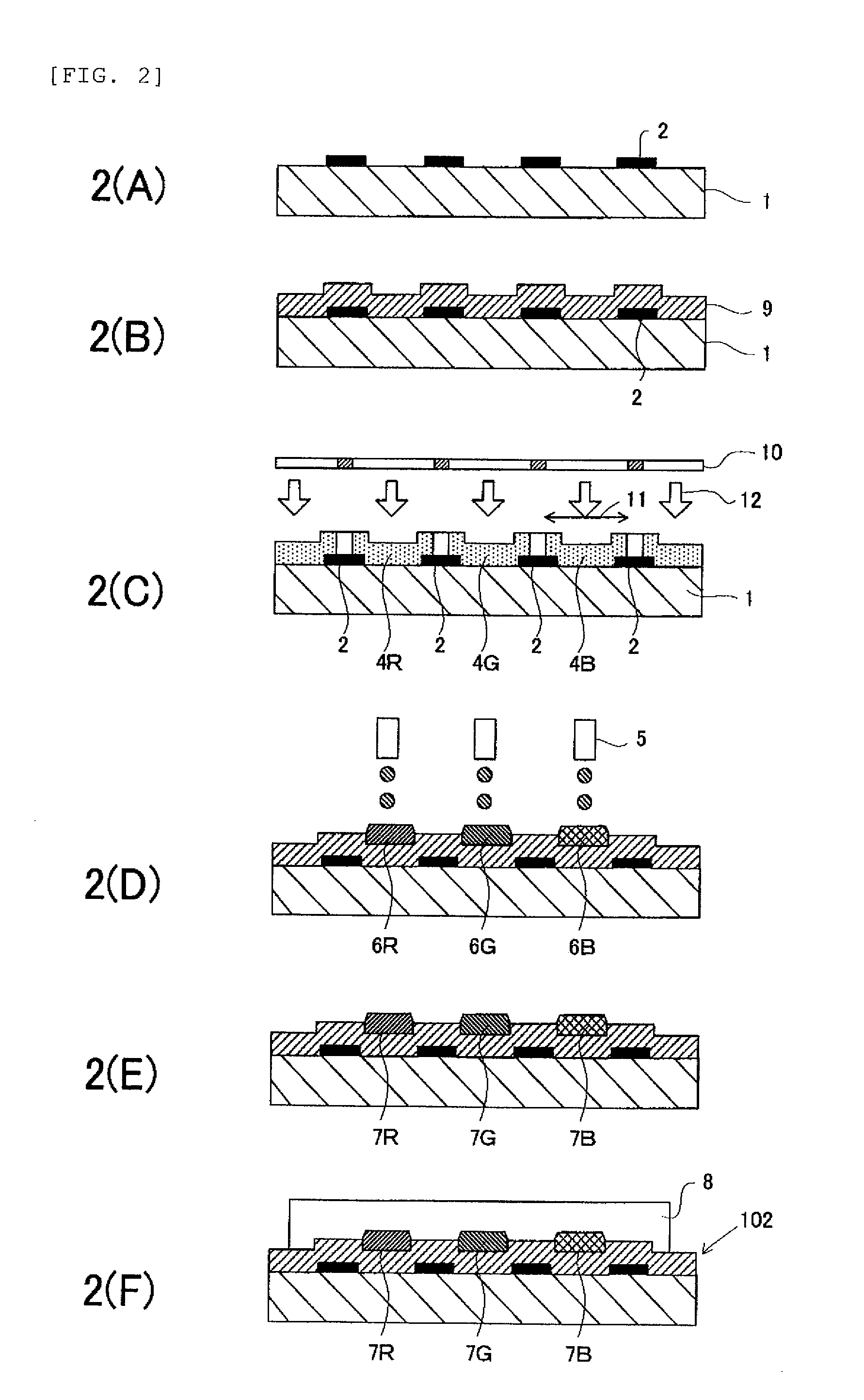
Method for manufacturing light-emitting device and film formation substrate
InactiveUS8618568B2High precisionAccurate layeringLayered productsSolid-state devicesLight irradiationReflective layer
In a method for manufacturing a light-emitting device according to an embodiment of the present invention, one surface of a first substrate including a reflective layer including an opening, a light absorption layer formed over the reflective layer to cover the opening in the reflective layer, a protective layer formed over the light absorption layer and including a groove at a position overlapped with the opening in the reflective layer, and a material layer formed over the protective layer and a deposition surface of a second substrate are disposed to face each other and light irradiation is performed from the other surface side of the first substrate, so that an EL layer is formed in a region on the deposition surface of the second substrate, which is overlapped with the opening in the reflective layer.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com