Patents
Literature
121 results about "Biological network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
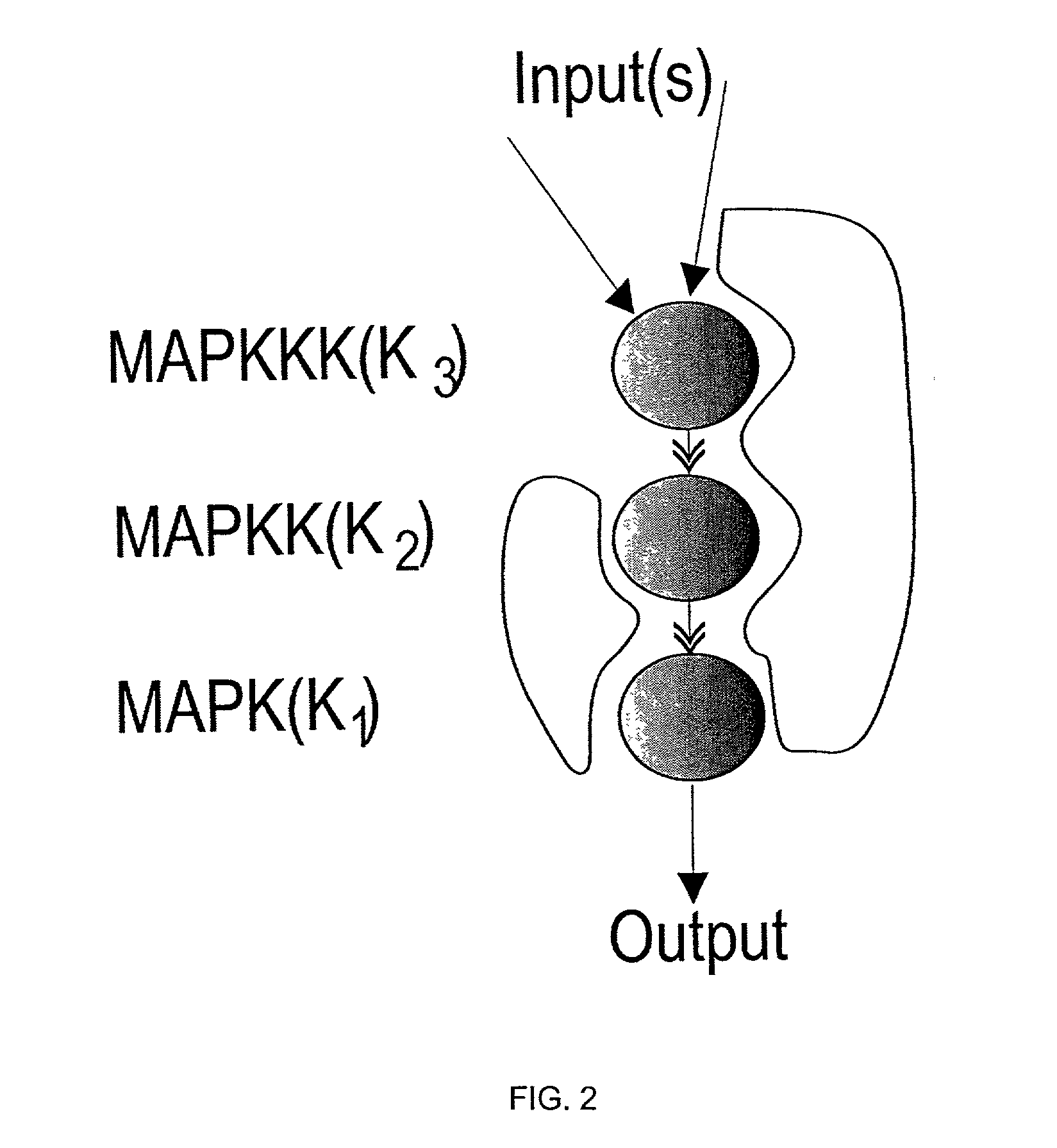
A biological network is any network that applies to biological systems. A network is any system with sub-units that are linked into a whole, such as species units linked into a whole food web. Biological networks provide a mathematical representation of connections found in ecological, evolutionary, and physiological studies, such as neural networks. The analysis of biological networks with respect to human diseases has led to the field of network medicine.
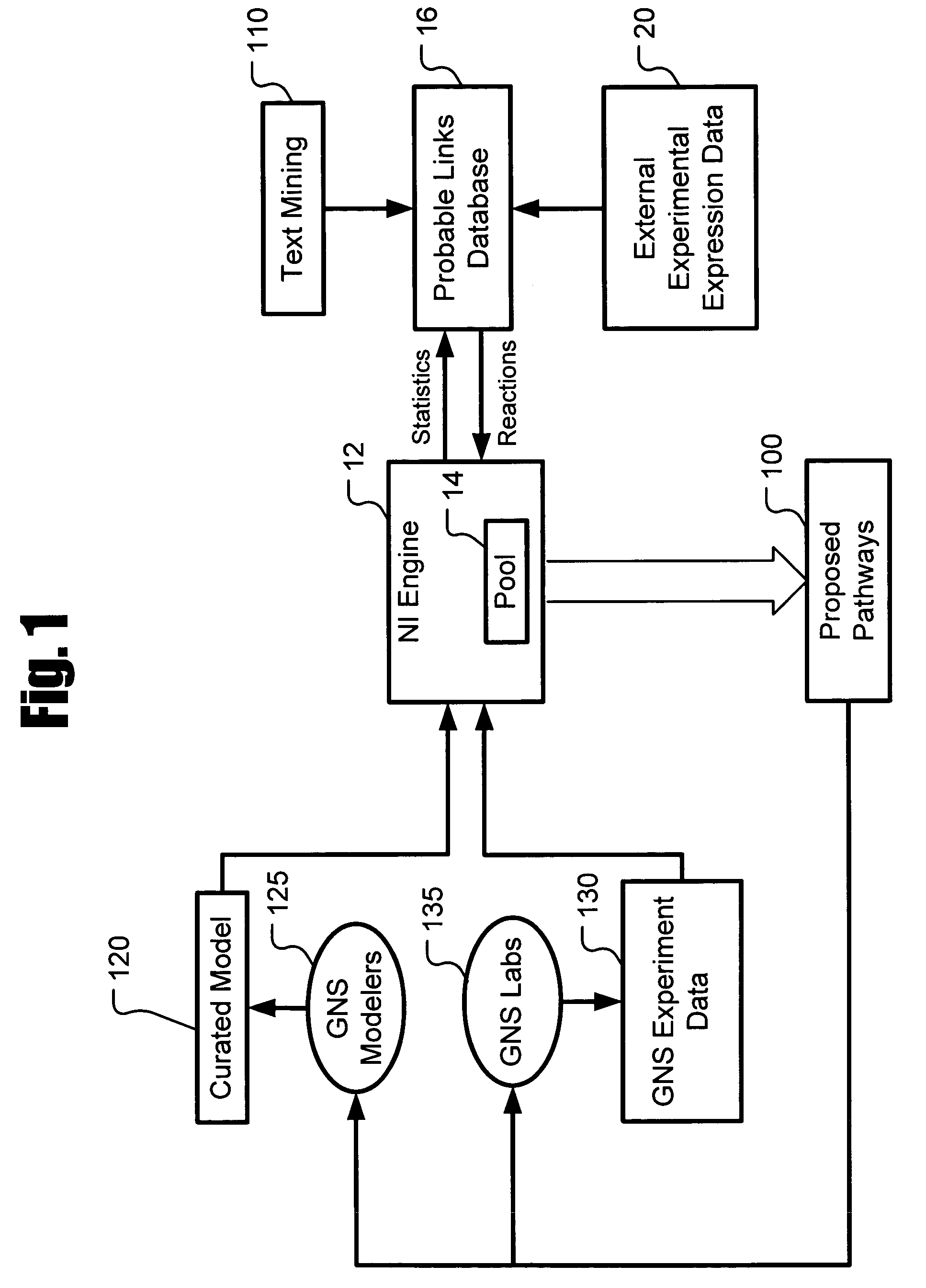
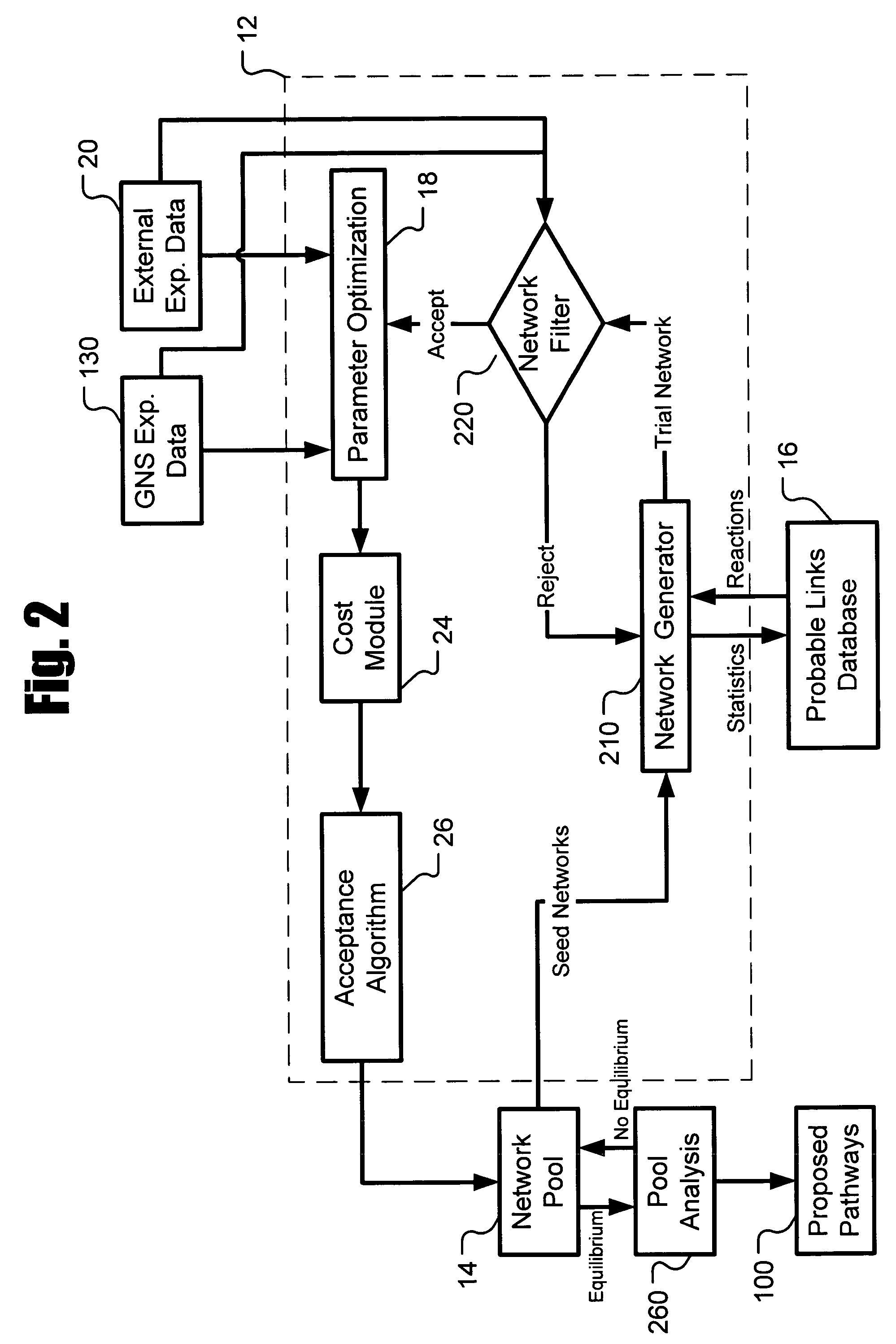
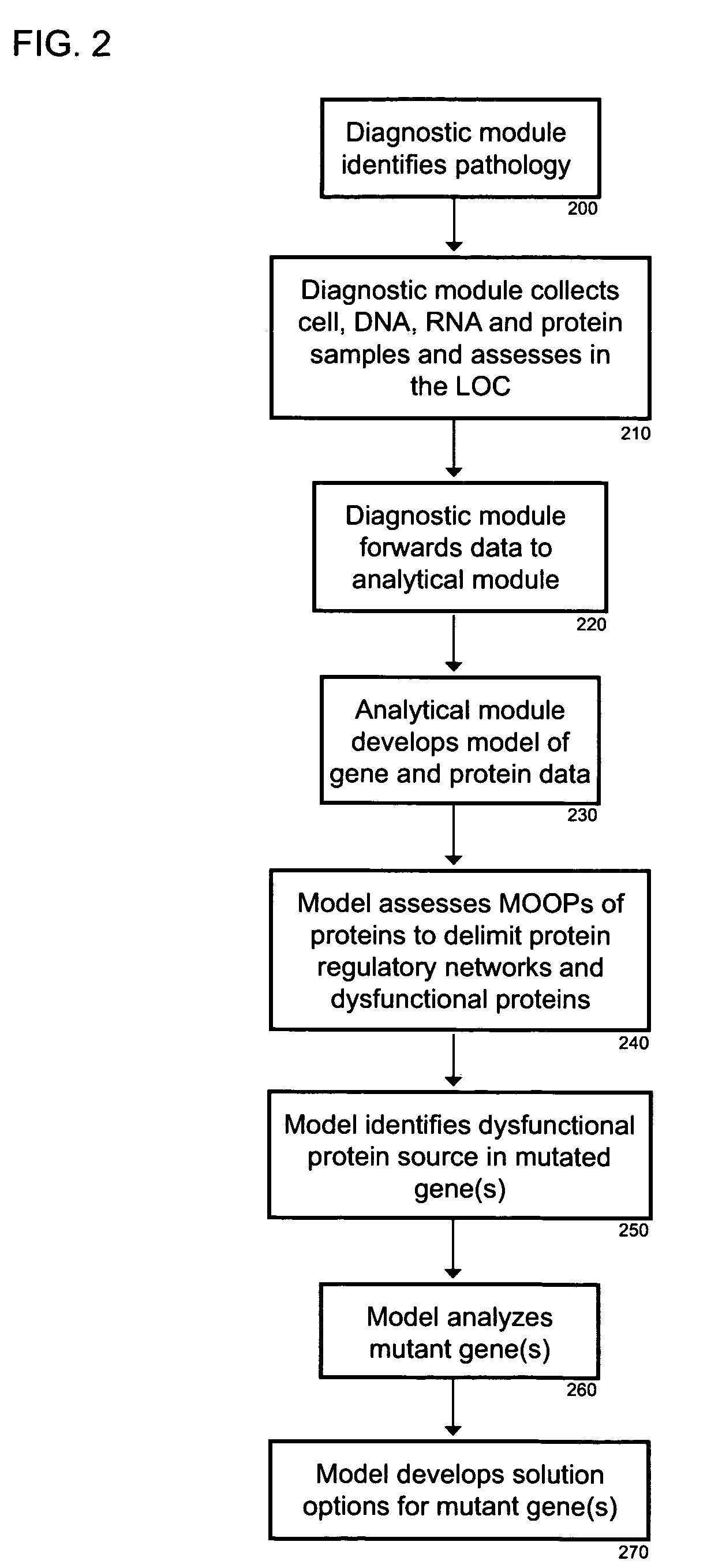
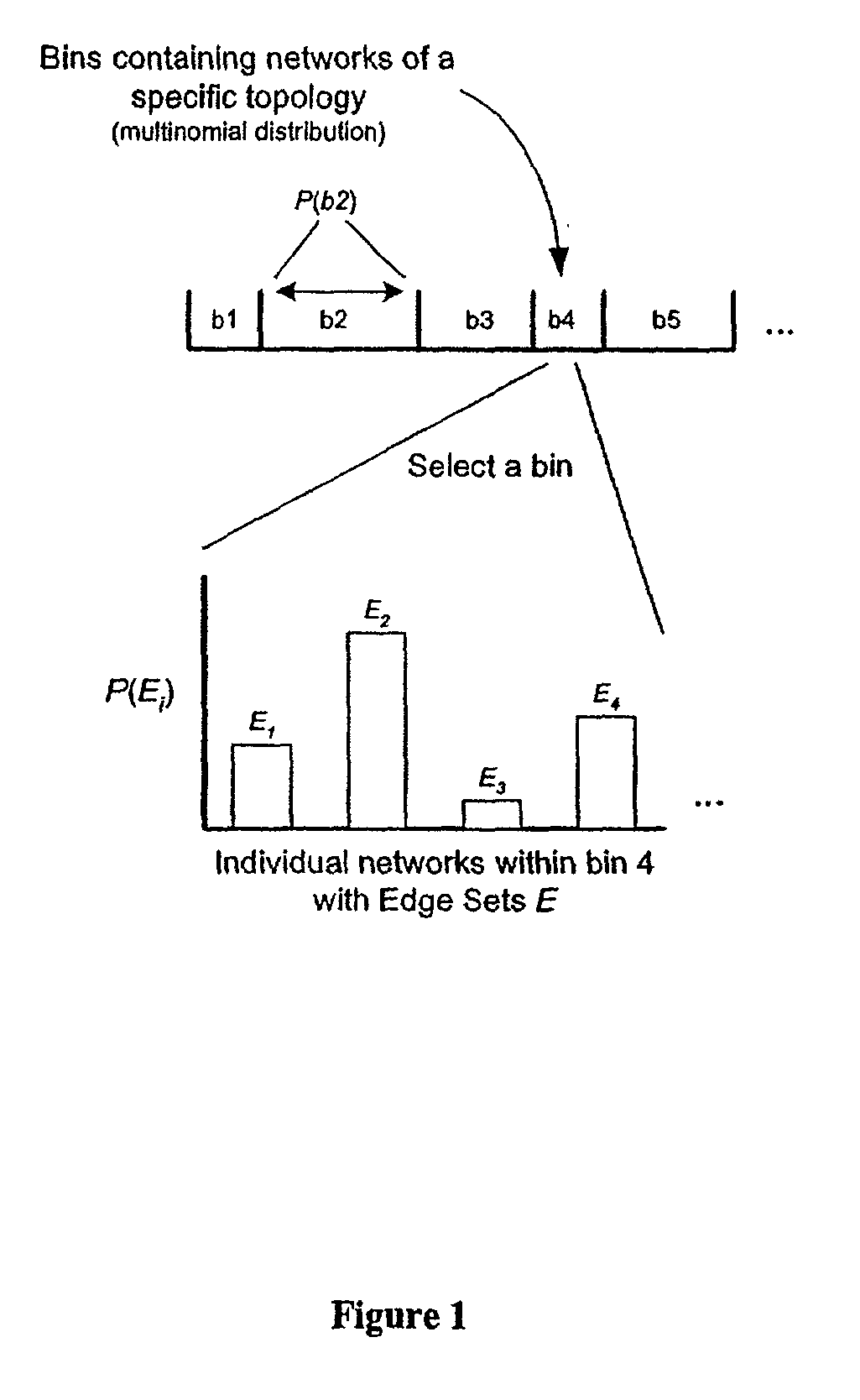
Systems and methods for modeling and analyzing networks
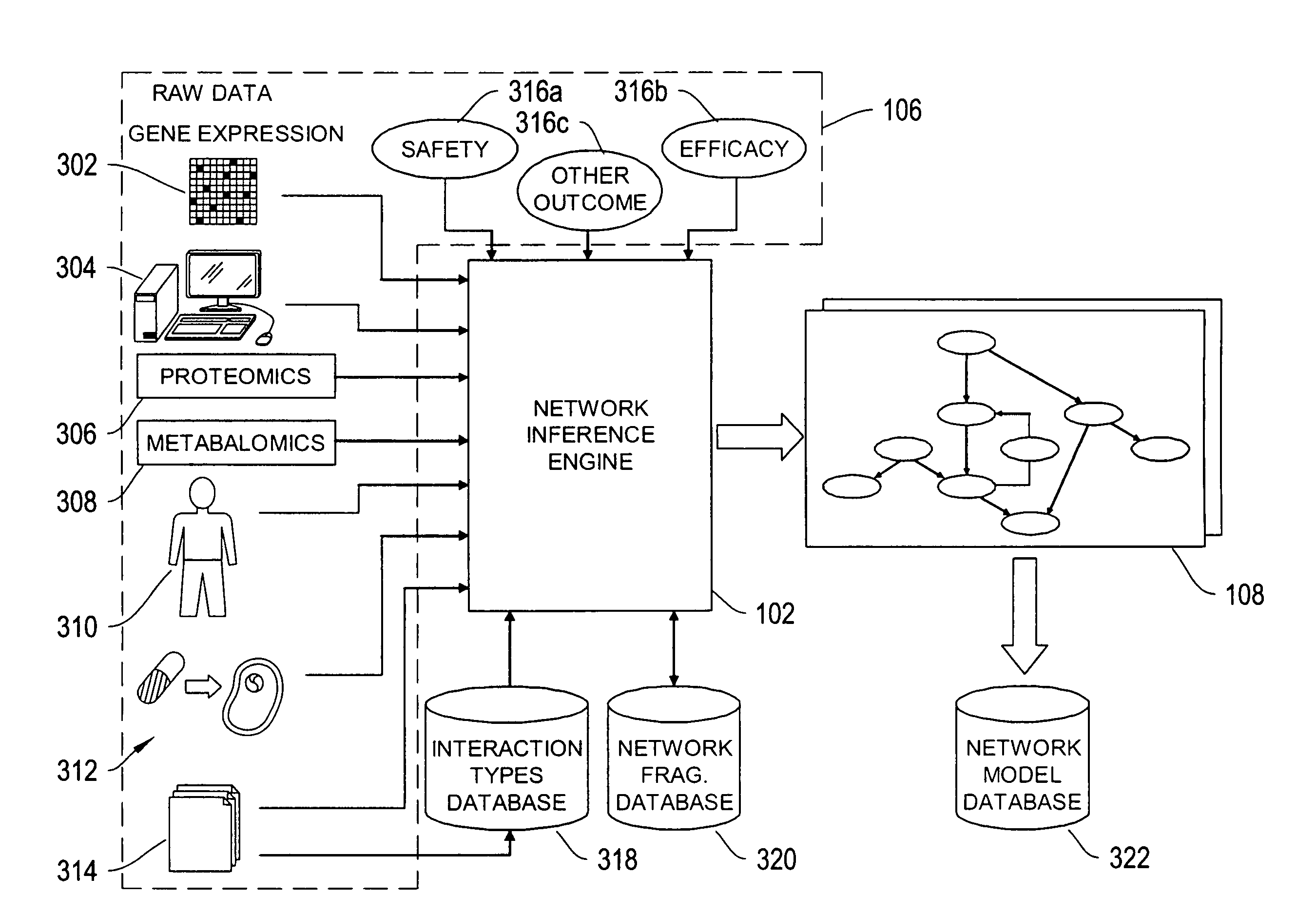
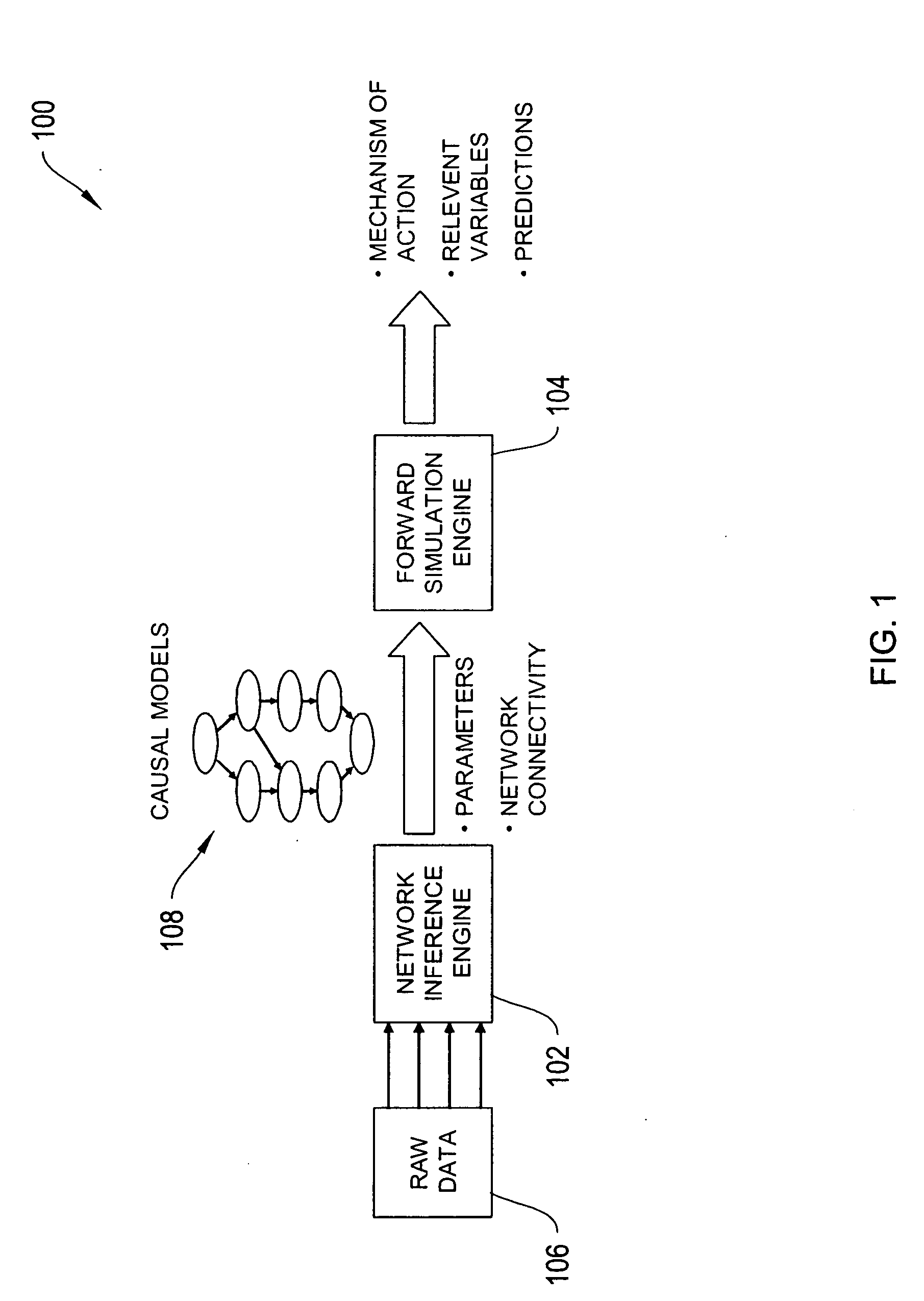
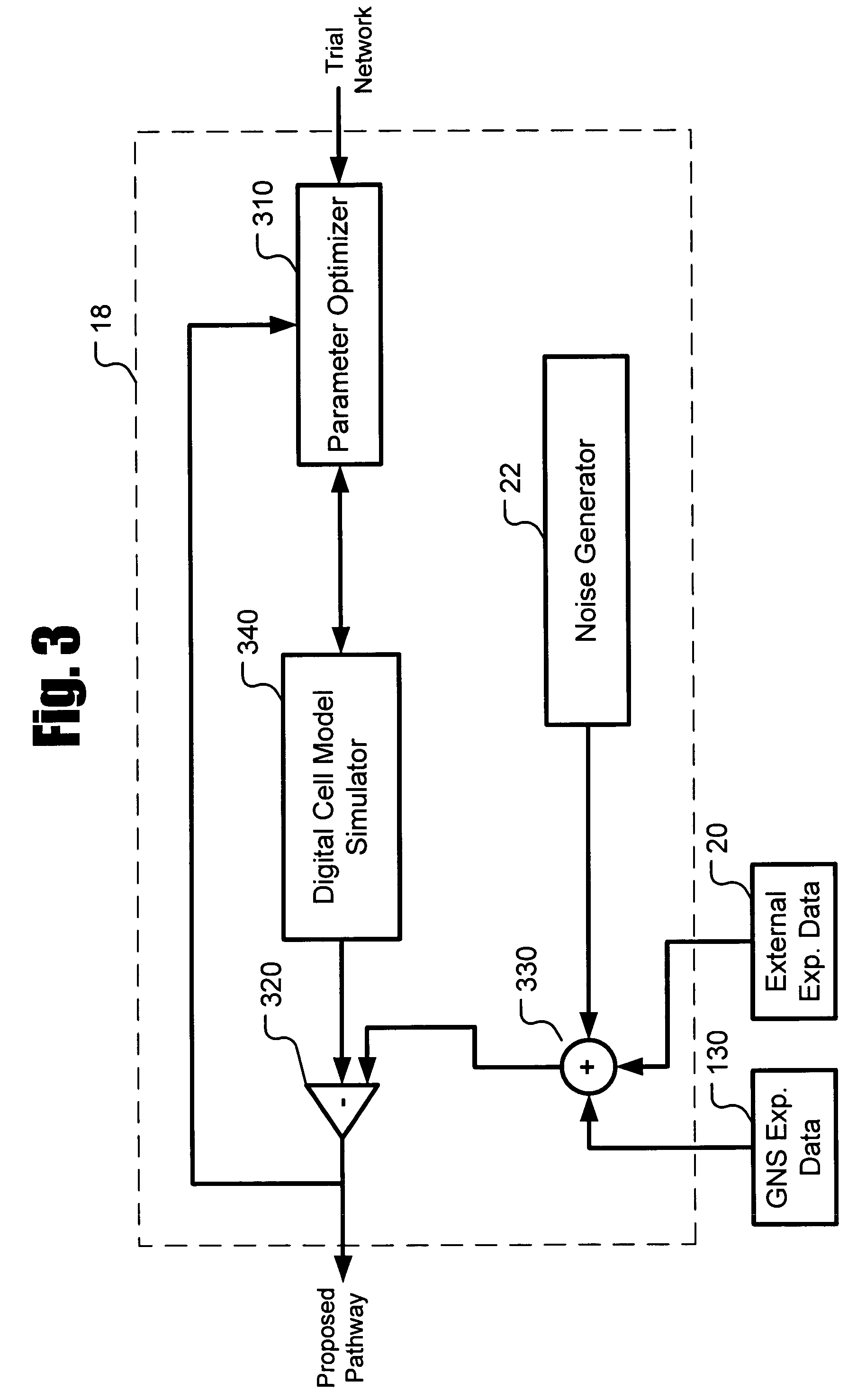
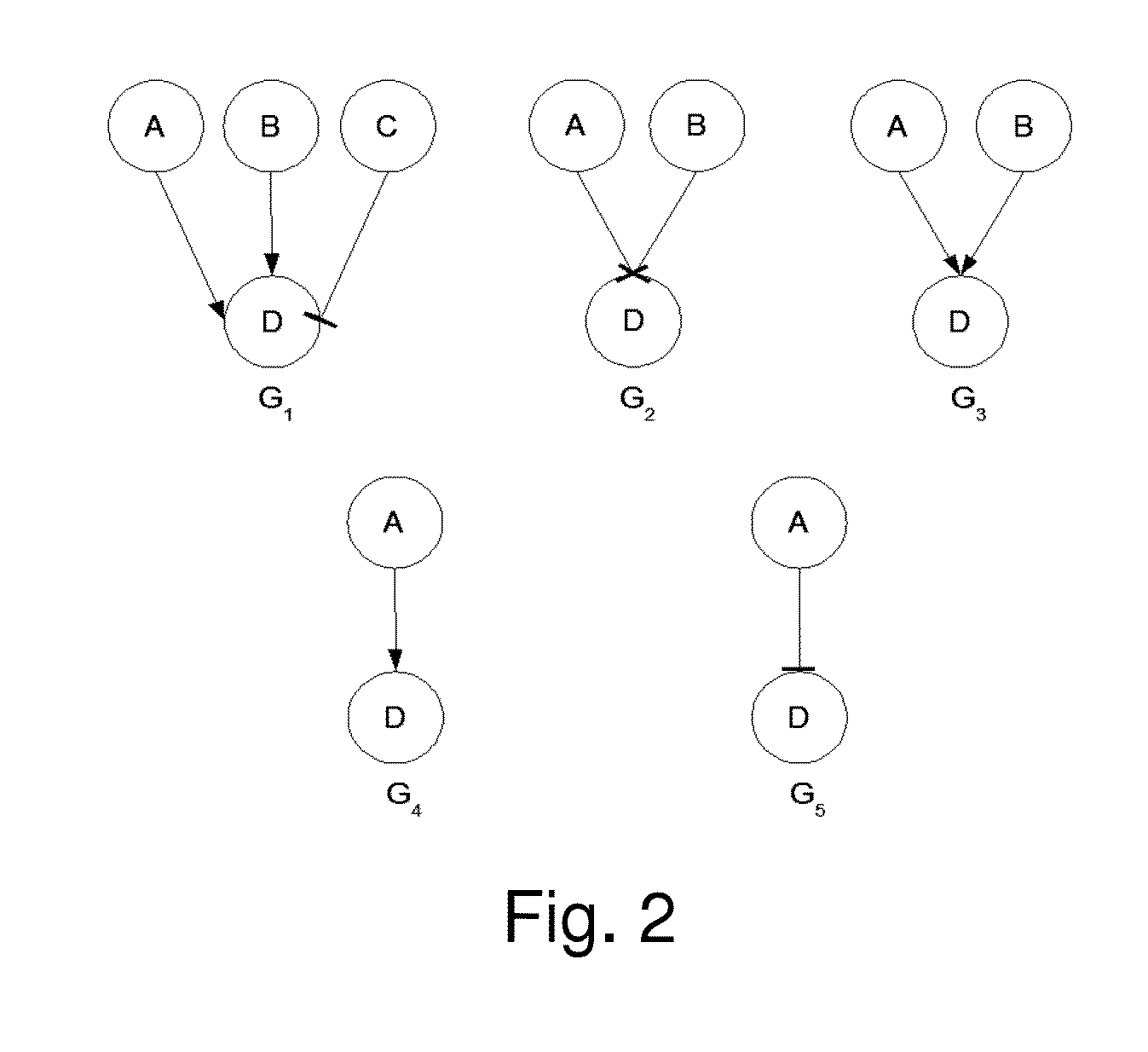
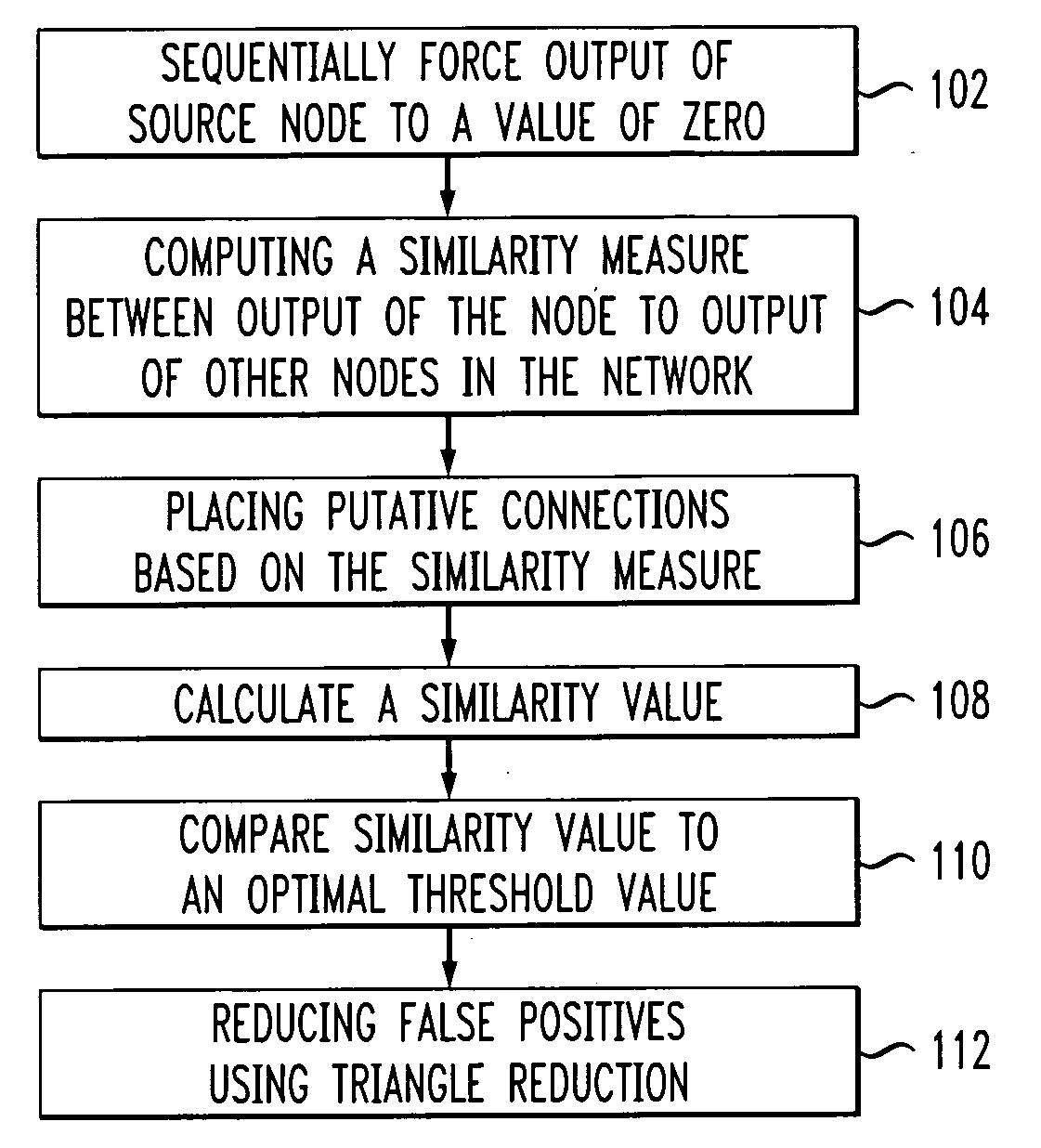
The systems and methods described herein utilize a probabilistic modeling framework for reverse engineering an ensemble of causal models, from data and then forward simulating the ensemble of models to analyze and predict the behavior of the network. In certain embodiments, the systems and methods described herein include data-driven techniques for developing causal models for biological networks. Causal network models include computational representations of the causal relationships between independent variables such as a compound of interest and dependent variables such as measured DNA alterations, changes in mRNA, protein, and metabolites to phenotypic readouts of efficacy and toxicity.
Owner:GENE NETWORK SCI
System, method and apparatus for causal implication analysis in biological networks
InactiveUS20050165594A1Efficient modelingRapidly and efficiently analyzingAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsSystems approachesOrganism
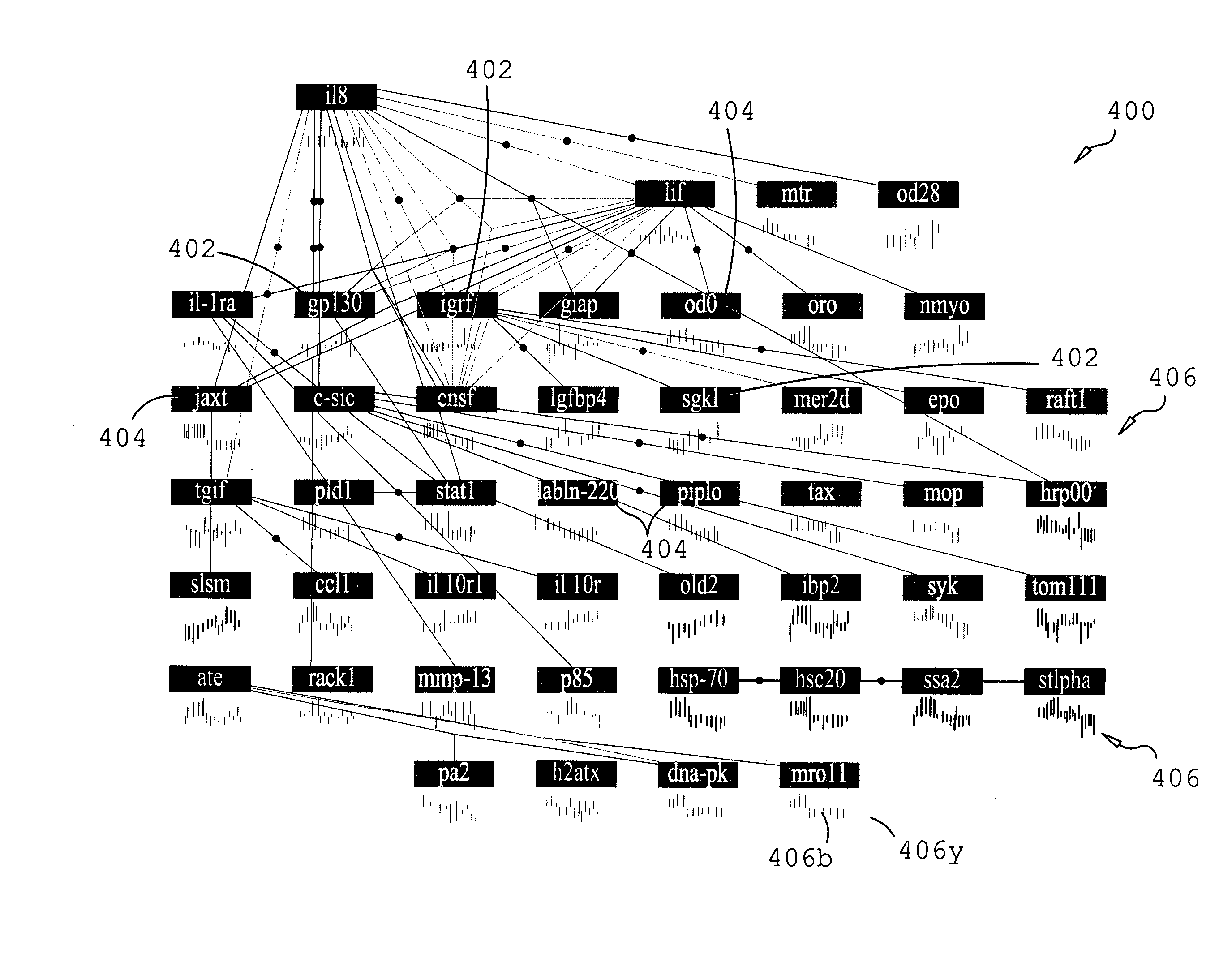
Described are methods, systems and apparatus for hypothesizing a biological relationship in a biological system. A database of biological assertions is provided consisting of biological elements, relationships among the biological elements, and relationship descriptors characterizing the properties of the elements and relationships. A biological element may be selected from the database and a logical simulation may be performed within the biological database, from the selected biological element, through relationship descriptors, along a path defined by potentially causative biological elements to discern a biological element hypothetically responsible for the change in the selected biological element. The logical simulation may be either a backward logical simulation, performed upstream through the relationship descriptors to discern a hypothetical responsible biological element, or a forward logical simulation, performed downstream through the relationship descriptors to discern the extent to which the perturbation generates the observed change in the selected biological element.
Owner:GENSTRUCT
Method, system and apparatus for accessing, modulating, evoking, and entraining global bio-network influences for optimized self-organizing adaptive capacities
InactiveUS20070016096A1Improve abilitiesEnhance priori knowledgeElectroencephalographyAnalogue computers for chemical processesAdaptive learningState variation
The invention interacts with a subject to query, challenge and identify multiple aspects and multidimensional influences that provide access to, allow modulation of, and entrainment of, state-specific global bio-regulatory self-organizing controllers and evocable triggers. Modulation of state-specific regulatory triggers may evoke optimized newly emergent self-organizing principles within the subject and ultimately support up-regulation of “states of presence” that include newly emergent controllers of additional optimal regulation of bio-chemical expressions. The “state” measures of a person may include the status of a combination of any number of identified biological qualities. The invention includes systems and methods that support access to a subject's state controller functions, for various aliments, to empower shifting ones' biology from a symptomatic to an asymptomatic state and to optimal adaptive learning and readiness. The system of the invention investigates and accesses the capacities that control such state shifts so that they can be broadly challenged, expanded, and entrained for optimized global regulatory function in reversing a myriad of pathological symptoms, learning limitation, and adaptive dysregulations.
Owner:MCNABB GARY
Methods and systems for extension, exploration, refinement, and analysis of biological networks
InactiveUS20050197783A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsKnowledge extractionQualitative simulation
Systems, methods and recordable media for facilitating user-guidance of computational analysis and knowledge extraction tools for use with biological data for disambiguation and determination of causation in representations of the data. Systems, methods, tools and computer readable media for user-guided expansion of biological networks and manipulations of the same. Tools for qualitative simulation of network models, for identifying interactions between multiple networks and form maintaining knowledge about multiple alternative biological networks. Combinations of portions of networks may be constructed to provide optimal networks. Networks may be evaluated against experimental data and networks of interest may be identified based on experimental data.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Systems and methods for reverse engineering models of biological networks
InactiveUS20070016390A1Analogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsNetwork modelSensitivity analyses
The present invention provides methods and accompanying computer-based systems and computer-executable code stored on a computer-readable medium for constructing a model of a biological network. The invention further provides methods for performing sensitivity analysis on a biological network and for identifying major regulators of species in the network and of the network as a whole. In addition, the invention provides methods for identifying targets of a perturbation such as that resulting from exposure to a compound or an environmental change. The invention further provides methods for identifying phenotypic mediators that contribute to differences in phenotypes of biological systems.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
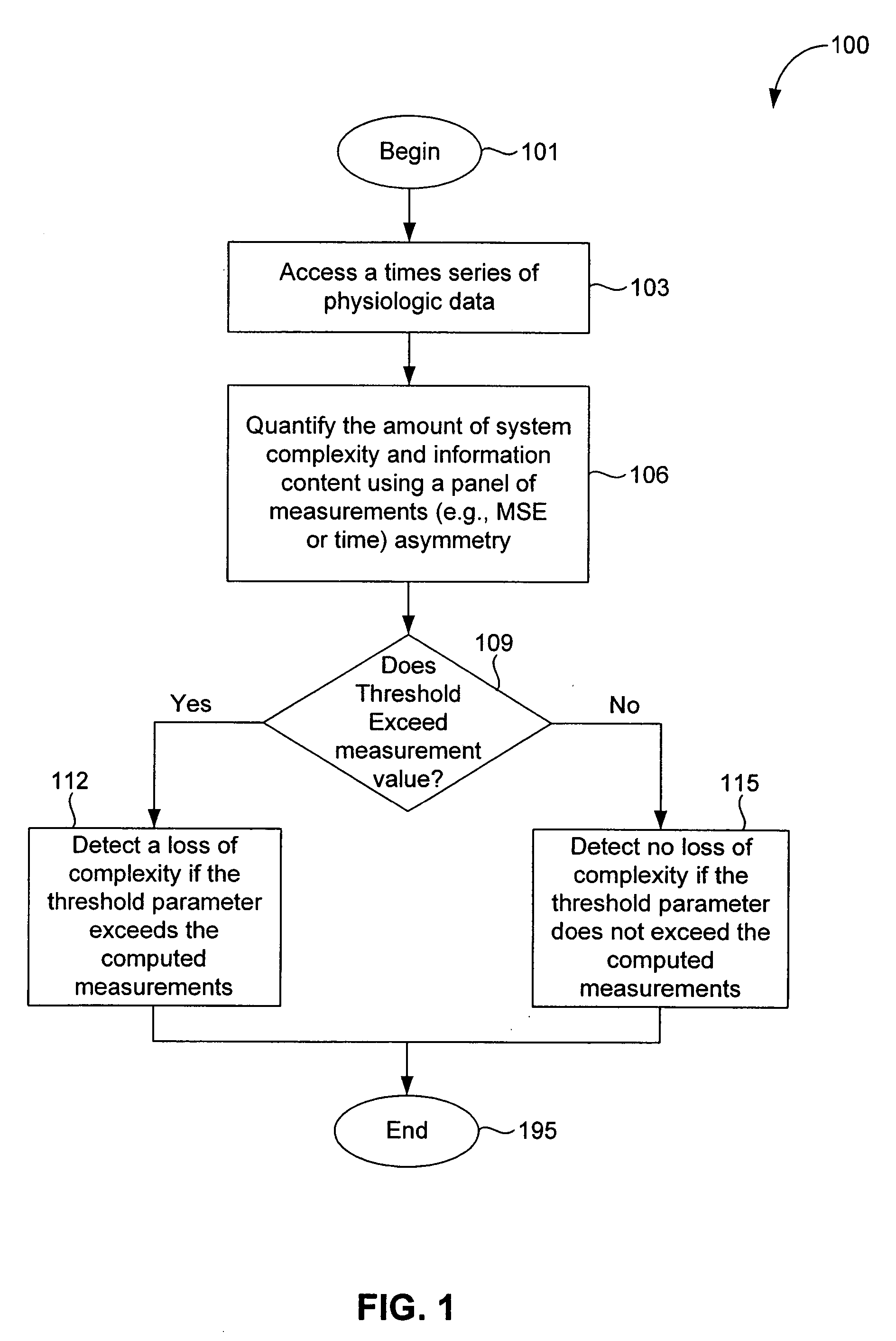
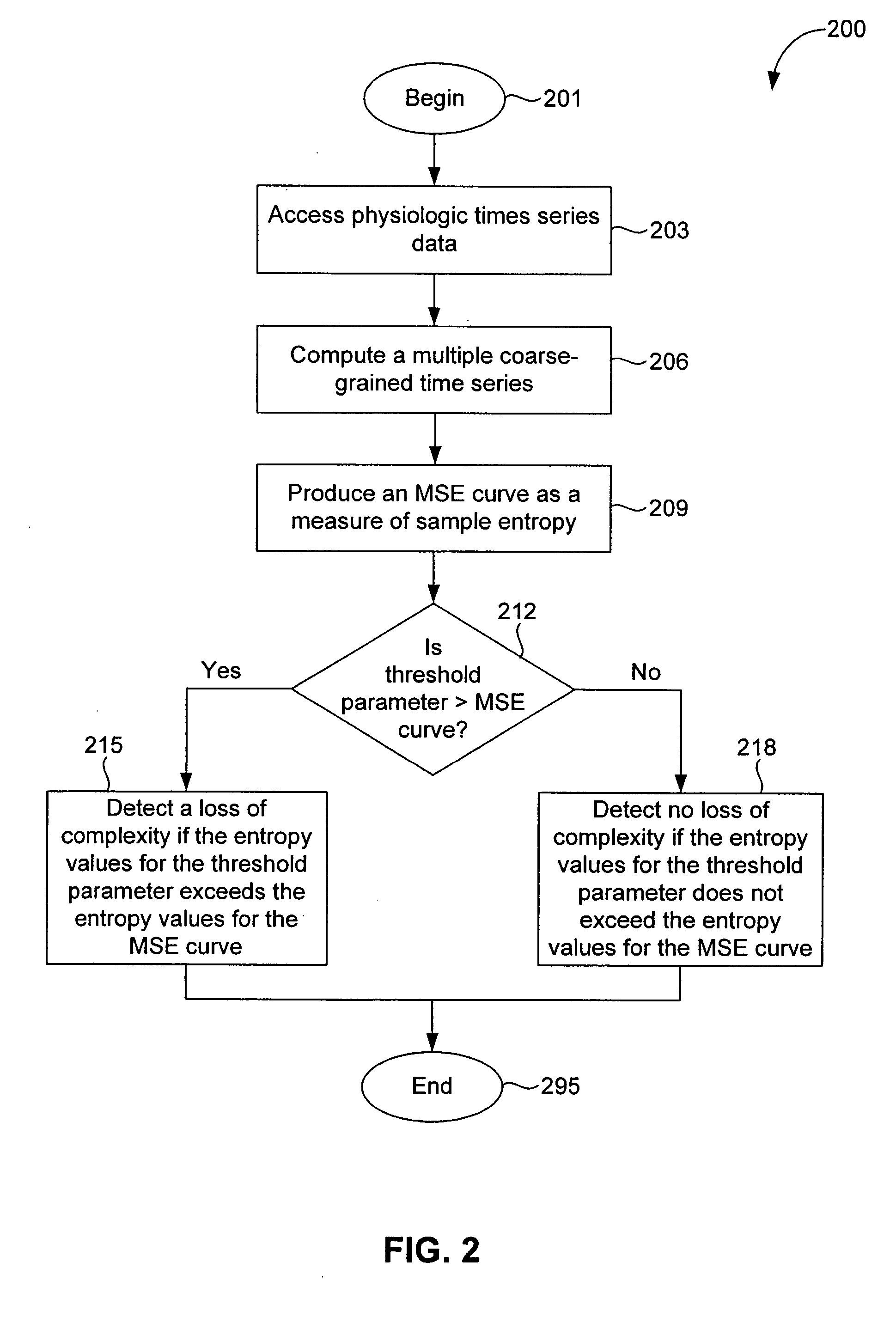
Complexity-based dynamical analysis of a network
InactiveUS20070066906A1ElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyClinical psychologyBiological network
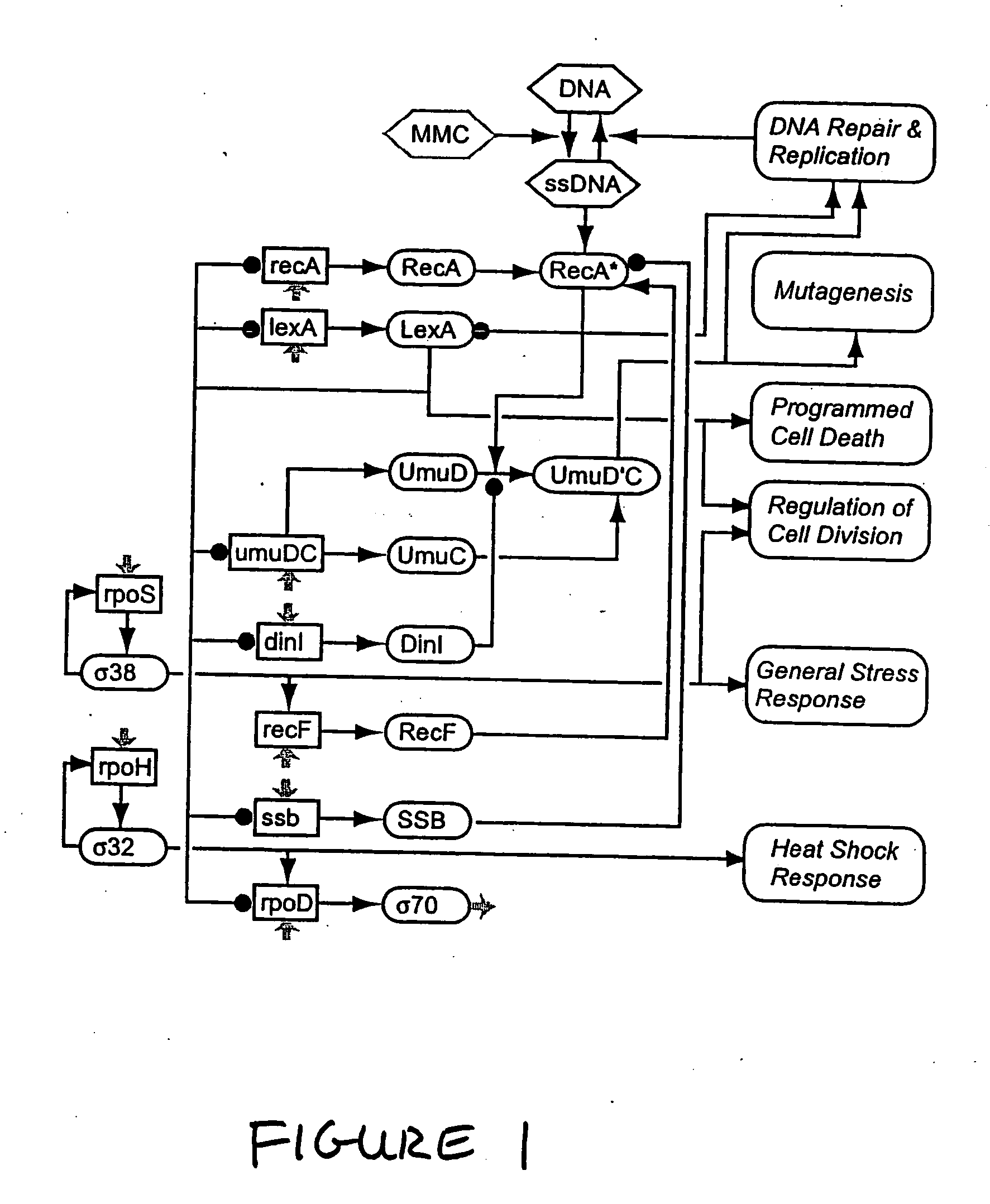
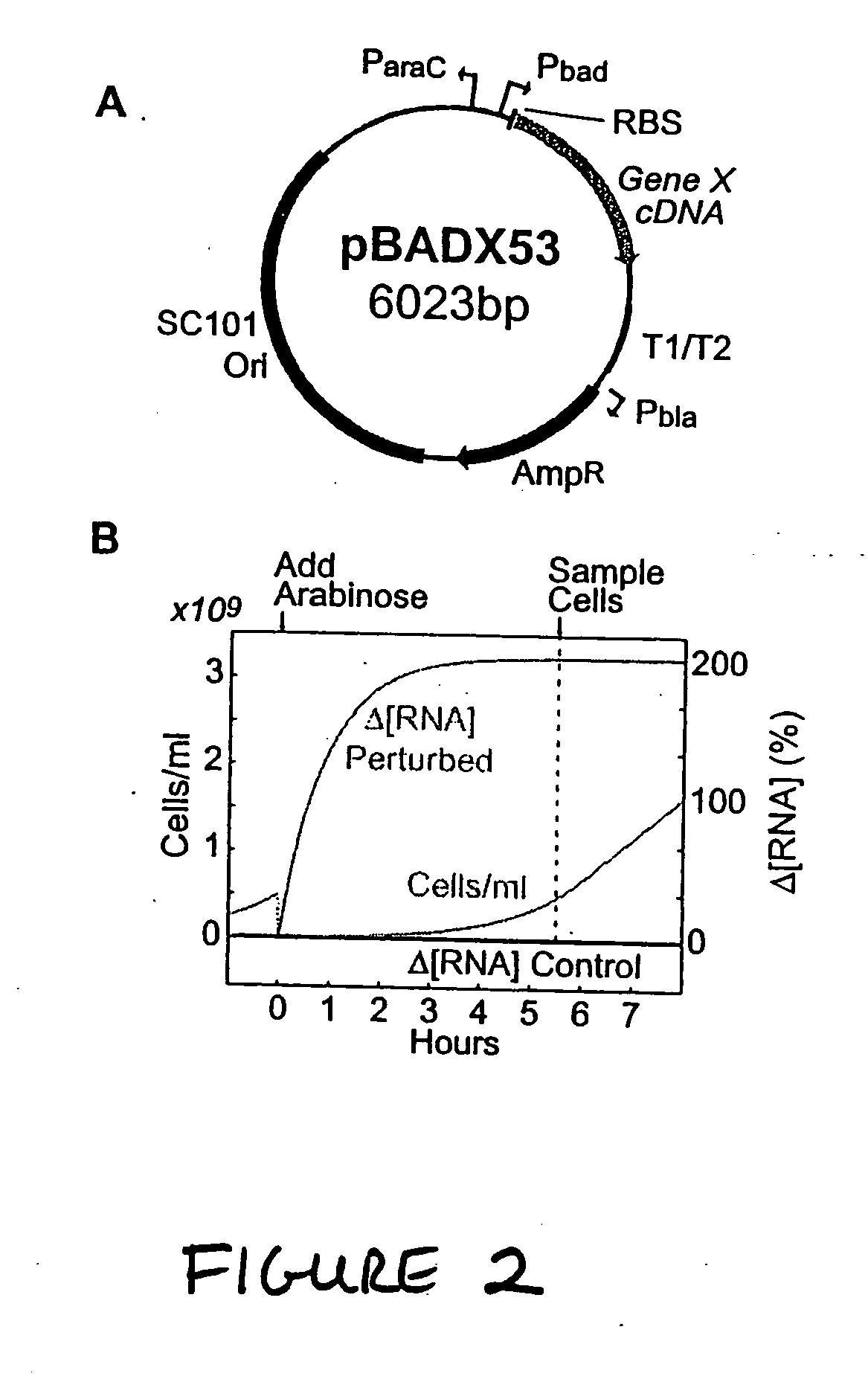
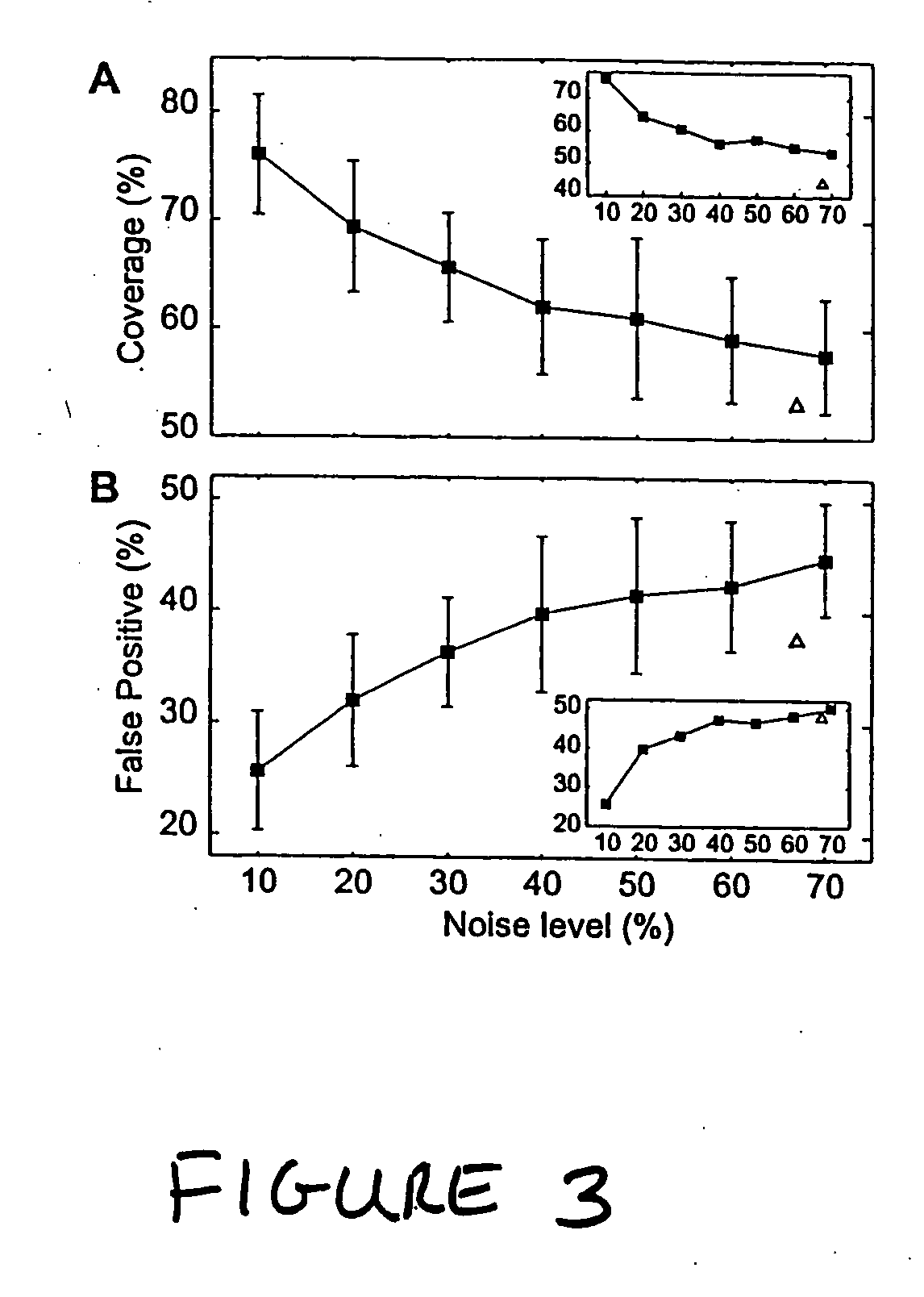
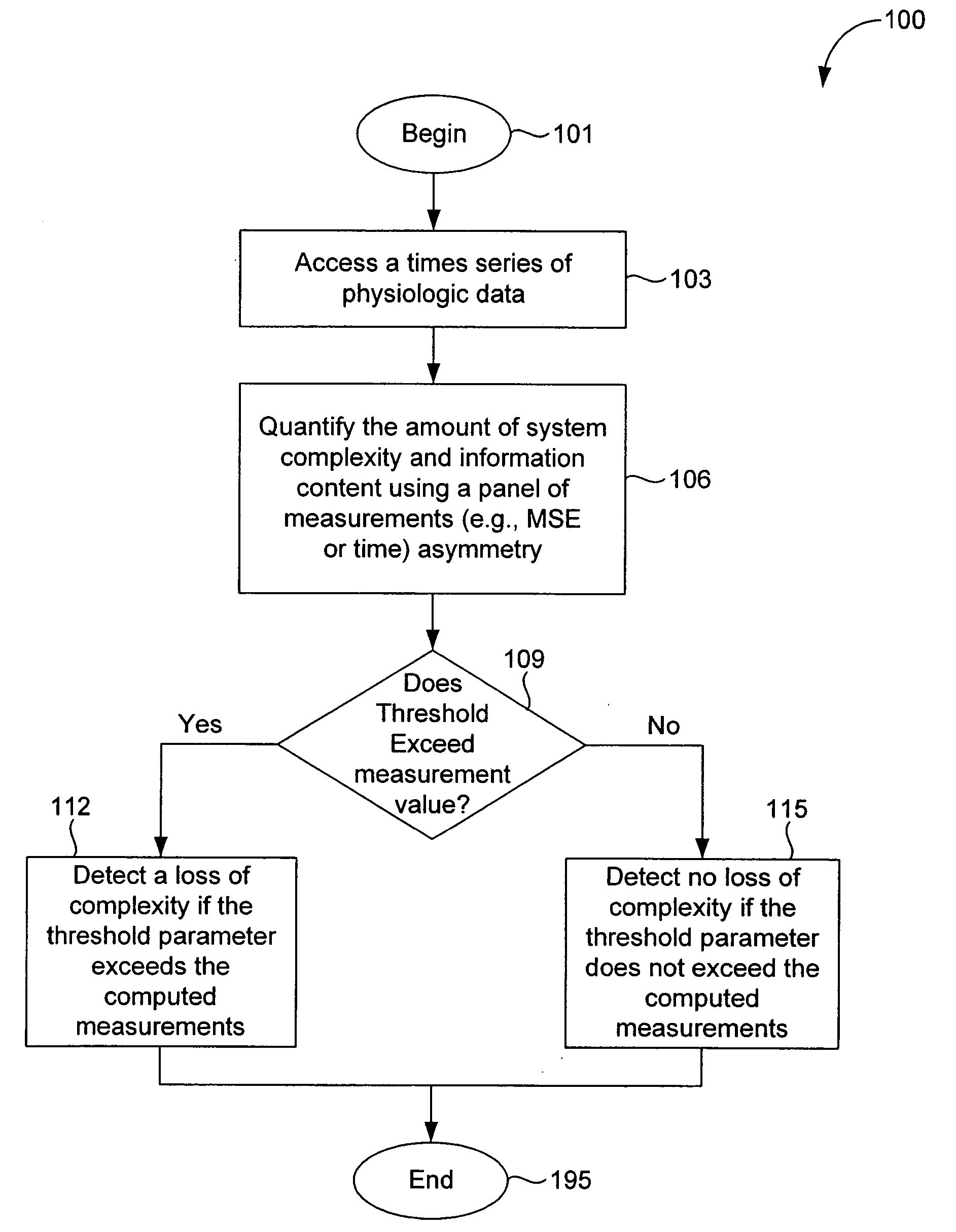
In a subject undergoing therapeutic intervention, efficacy of the therapeutic intervention is assessed based on a series of physiologic data associated with the subject. The series of physiologic data is analyzed to produce a measure of complexity. The complexity measure is then compared to a control. The efficacy of the therapeutic intervention is assessed based on the comparison of the complexity measure to the control. The control may be, for example, a complexity measure taken prior to initiation of the therapeutic intervention, a complexity measure taken from a different subject, or a predetermined threshold value. The measure of complexity is generated using, for example, a multiscale entropy measurement (MSE), a time asymmetry measurement, and / or an information-based similarity measurement. An increase in complexity indicates a positive effect of the therapeutic intervention, while a decrease in complexity indicates a negative effect of the therapeutic intervention. Stability of a non-biologic network, such as a computer network, communications network or transportation network can also be assessed.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
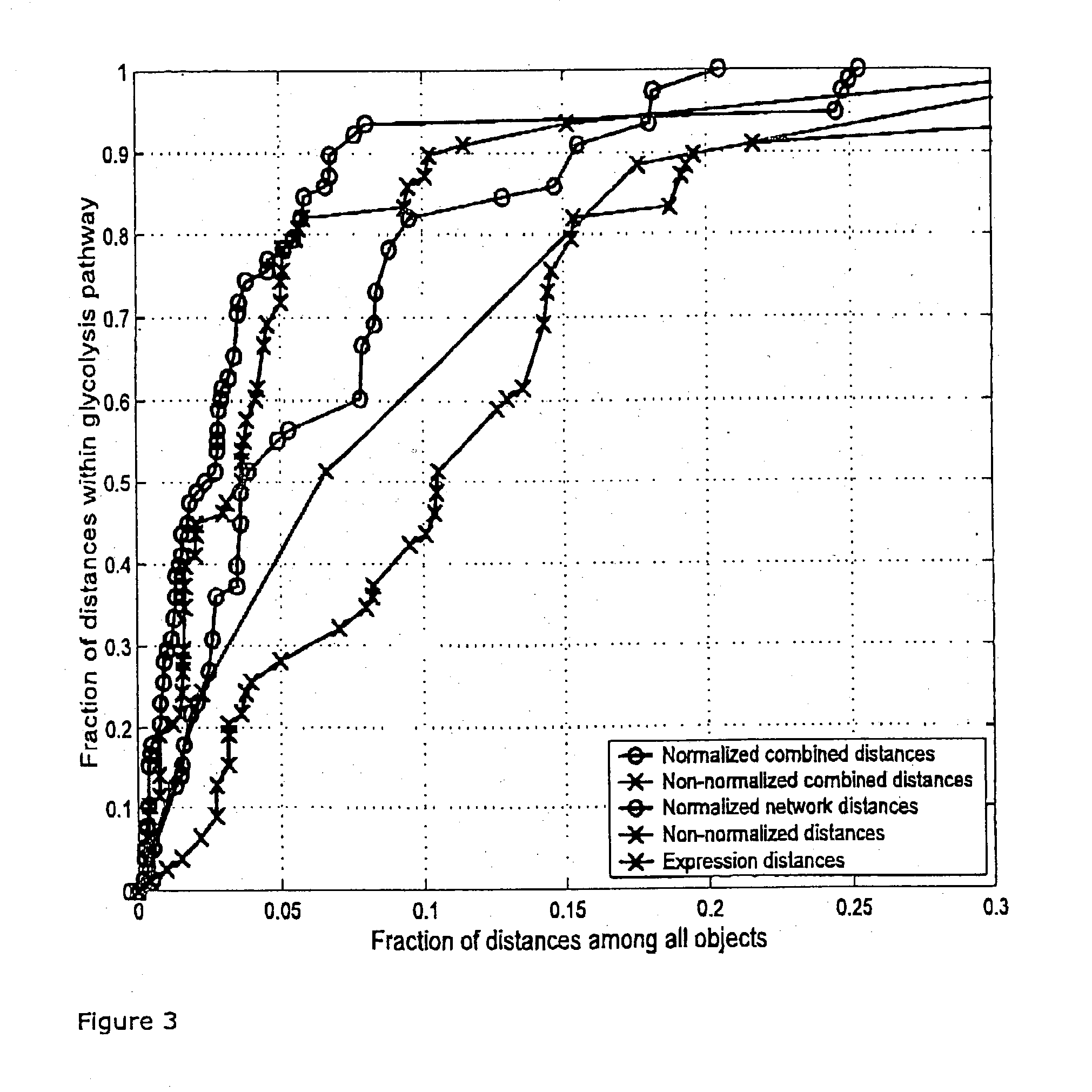
Efficient method for the joint analysis of molecular expression data and biological networks
A method for the joint analysis of molecular expression data and biological networks by clustering comprising the steps of defining a matrix of distances between molecules or sets of molecules that incorporate both the relation of corresponding expression profiles and information on their relation within a biological network; and clustering the molecules based on said distances.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
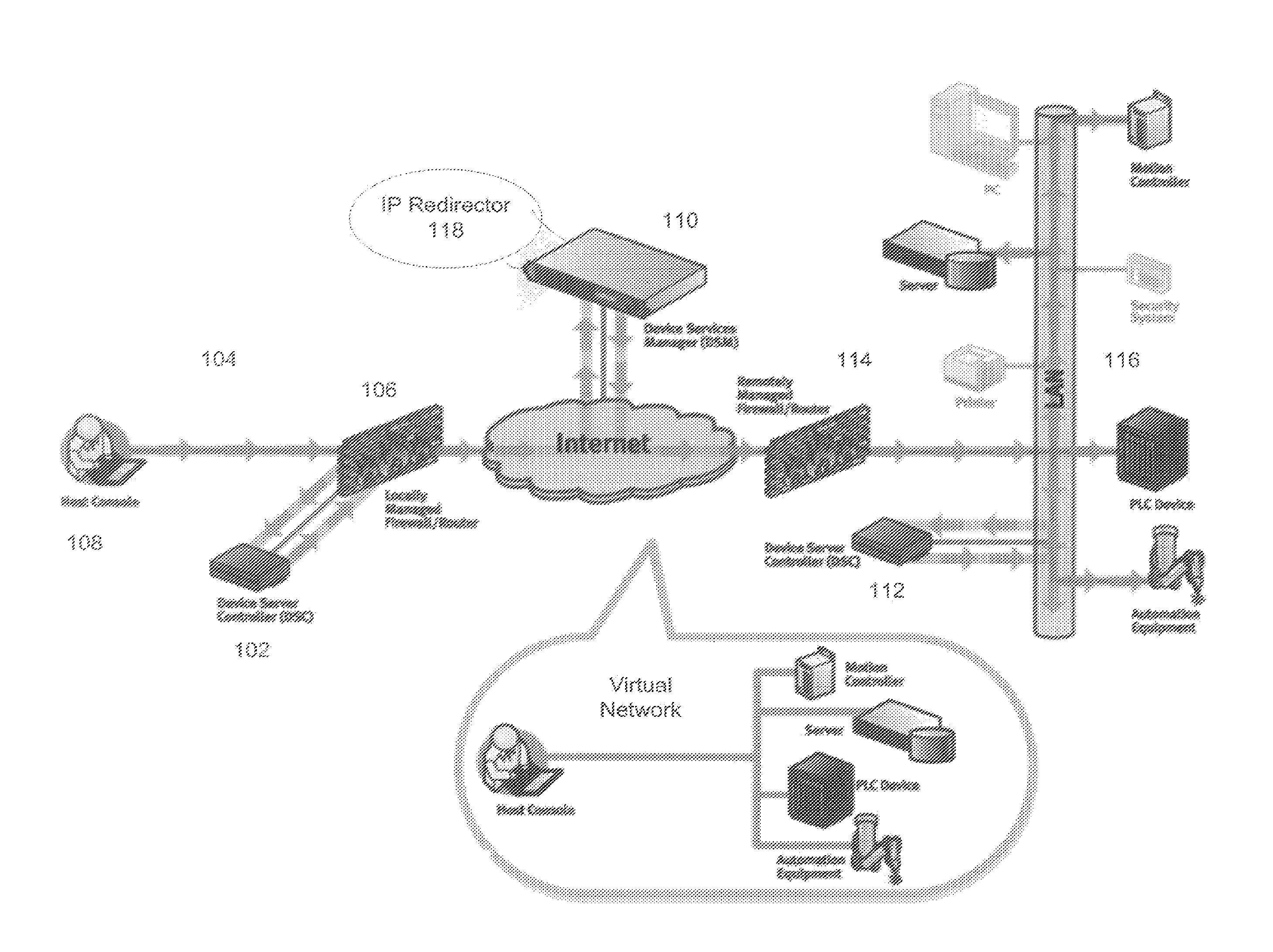
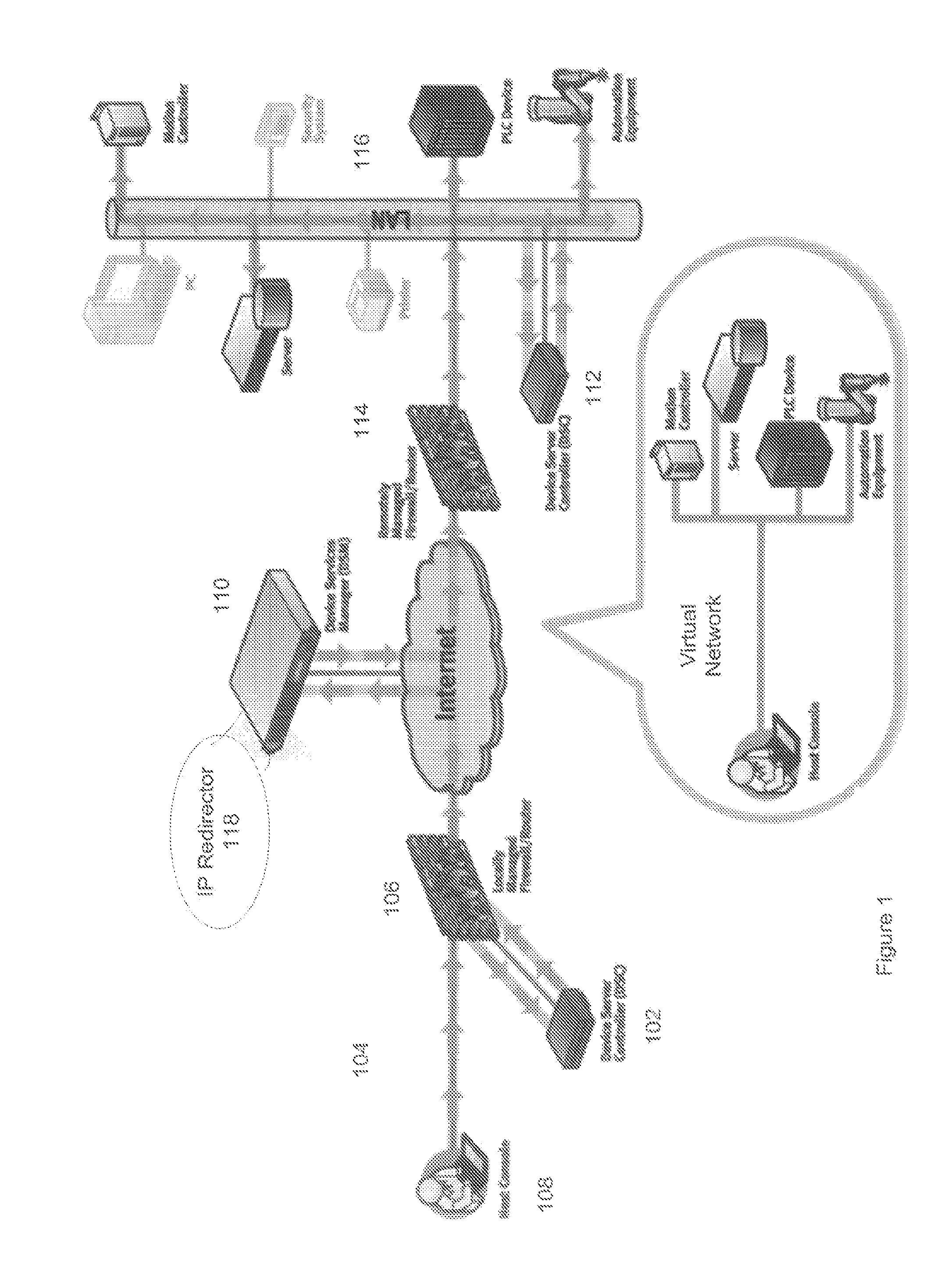
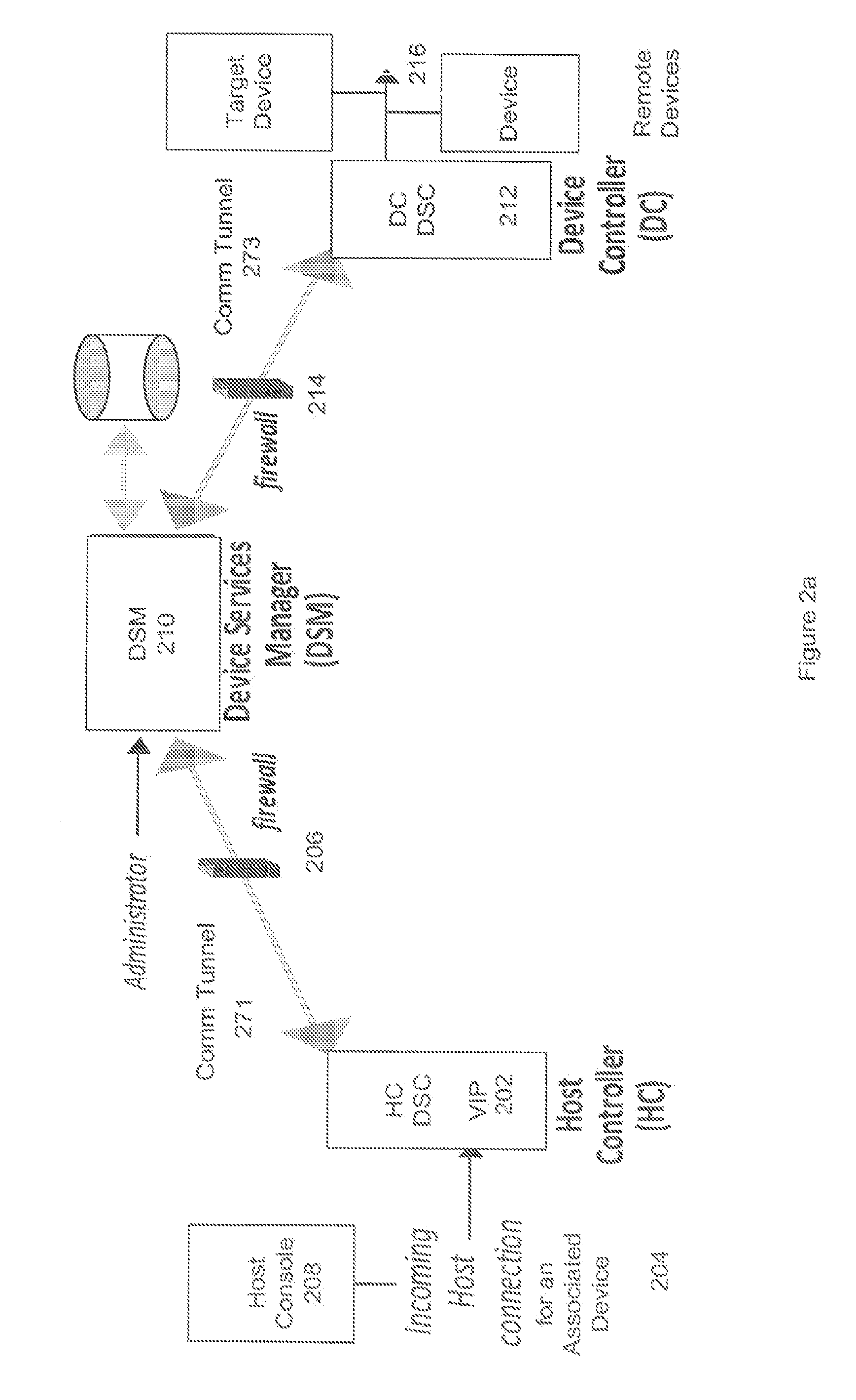
Simple Remote Access Through Firewalls For Networked Devices and Applications
InactiveUS20140181248A1Improve data integrityImprove integrityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTraffic capacityArea network
A method, apparatus, and system are described for accessing networked devices without accessible network addresses via Virtual IP (VIP) addresses. The system consists of a soft Device Services Controller (DSC), downloaded on a first local network from the device service manager (DSM) on a wide area network, and a VIP Access enabled device on a second local network separate from the first area network. The soft DSC and associated VIP Access enabled device create a virtual network interface and corresponding virtual IP address (VIP) to permit outgoing TCP / IP conduit connection to the DSM. When networking traffic arrives at the virtual networking interface with the associated VIP, the soft DSC automatically processes and forwards that traffic to the DSM. Using this mechanism, it is possible for two networked devices on separate networks to communicate in spite of firewalls and without knowledge of each other's network.
Owner:LANTRONIX
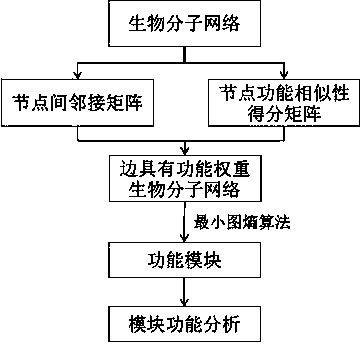
Biomolecular network analysis method based on function module
ActiveCN103778349AHigh functional relevanceEfficient integrationSpecial data processing applicationsRegulation of gene expressionComputer science
The invention belongs to the field of a biotechnology, and provides a comparison method based on a function module and used for biomolecular networks such as a genetic expression regulatory network or protein-protein interaction and the like. The method mainly comprises steps as follows: an adjacency matrix Madj of a biological network is built, a function similarity matrix Msim between network nodes is calculated, a function weight matrix ME of a network side is calculated according to the formula as follows: ME=Madj.*Msim, a network module is mined with a minimum graph entropy algorithm, and finally, function enrichment analysis is performed on the network module, wherein the symbols are defined in the instruction.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
Systems and methods for inferring biological networks
ActiveUS7512497B2Reduce computing loadData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsChemical reactionData mining
Described herein is a system for inferring one or a population of biochemical interaction networks, including topology and chemical reaction rates and parameters, from dynamical or statical experimental data, with or without spatial localization information, and a database of possible interactions. Accordingly, the systems and methods described herein may be employed to infer the biochemical interaction networks that exist in a cell. To this end, the systems and methods described herein generate a plurality of possible candidate networks and then apply to these networks a forward simulation process to infer a network. Inferred networks may be analyzed via data fitting and other fitting criteria, to determine the likelihood that the network is correct. In this way, new and more complete models of cellular dynamics may be created.
Owner:GENE NETWORK SCI
Automated methods for simulating a biological network
InactiveUS7319945B1Efficient mappingImprove design flexibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological bodyGraphics
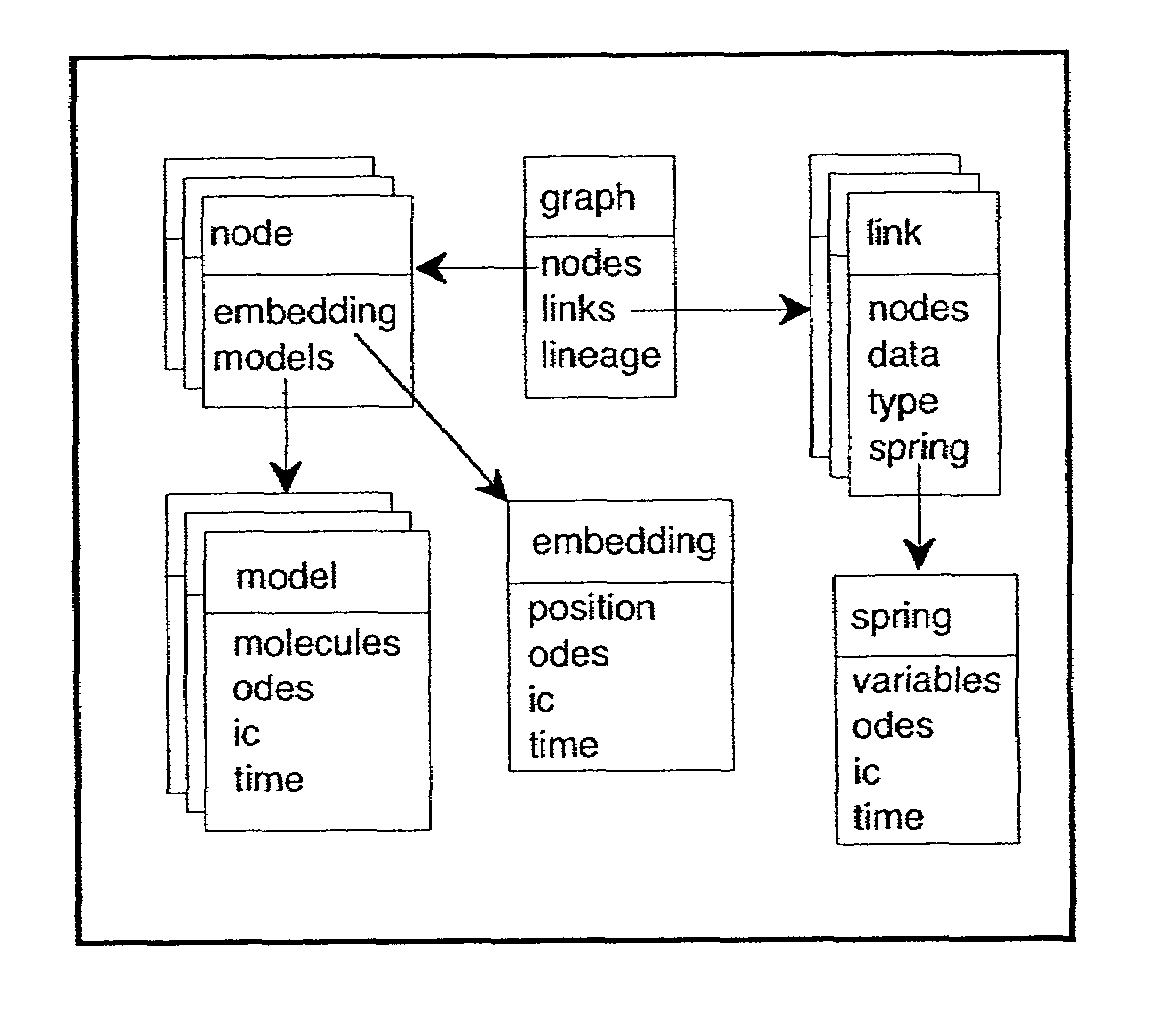
The present invention relates to methods, computer systems, and computer programs for simulating a biological network. The methods of the present invention facilitate biological network simulations via automated equation generation based on the concept of a hierarchy of canonical forms that describe biological processes at various levels of detail. At each level of hierarchy two classes of canonical forms can be identified: the input canonical form, that is used to supply information to the program, and the output canonical form that is produced by a simulator. The methods in certain preferred embodiments include explicit output description and flexible user intervention at several steps through the model generation. Furthermore, preferred embodiments of the present invention provide the modeling of developmental networks using an organism-as-a-graph approach using domains and fields.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Network-based approaches to identifying significant molecules based on high-throughput data analysis
Methods, systems and computer readable media for network-based identification of significant molecules, for which at least one biological network is provided to include significant molecules to be identified. A node in the network is identified. A member-specific sub-network containing nodes connected to the identified node is identified for L levels of nearest neighbors, wherein L is a positive integer, and a connectivity score is calculated for the molecule represented by the identified node based on significance scores of each node contained in the member-specific sub-network. These steps are repeated for other nodes in the network. Methods, systems and computer readable media for network-based identification of significant molecules, for which at least one biological network is provided to include significant molecules to be identified, a data set including data values characterizing molecules experimented on is provided, and an interesting list of molecules is provided as a subset of the molecules from the dataset, the interesting list including significance scores for the molecules in the list. Such identification includes identifying a node in the network; identifying a member-specific sub-network containing nodes connected to the identified node for L levels of nearest neighbors, wherein L is a positive integer; extracting the member-specific sub-network from the network; and repeating these steps for each of the other nodes in the network that corresponds to a molecule in the interesting list.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Dynamics bionems sensors and arrays of bionems sensor immersed in fluids
InactiveUS7375321B2Small sizeMore responsiveMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSurface/boundary effectActivation energyCarrier signal
A bioNEMS device comprises a piezoresistive cantilever having flexing legs of which attach the cantilever to a support and a biofunctionalized portion at the tip. A bias current applied to the legs is limited by a maximal acceptable temperature increase at the biofunctionalized tip. The length of the cantilever has a magnitude chosen to minimize background Johnson noise. A catalyzed receptor on the device binds to a ligand whose binding rate coefficient is enhanced. The catalyst lowers the receptor-ligand binding activation energy and is designed by forced evolution to preferentially bind with the ligand. A carrier signal is injected by a magnetic film disposed on the cantilever which is electromagnetically coupled to a source of the carrier signal. A plurality of NEMS fluidicly coupled transducers generate a plurality of output signals from which a collective output signal is derived, either by averaging or thresholding. The NEMS devices are disposed in microfluidic flow channels and fabricated in a membrane. A linking molecule is attached to the tip of the transducer and a fluffball attached to the linking molecule to increase damping.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
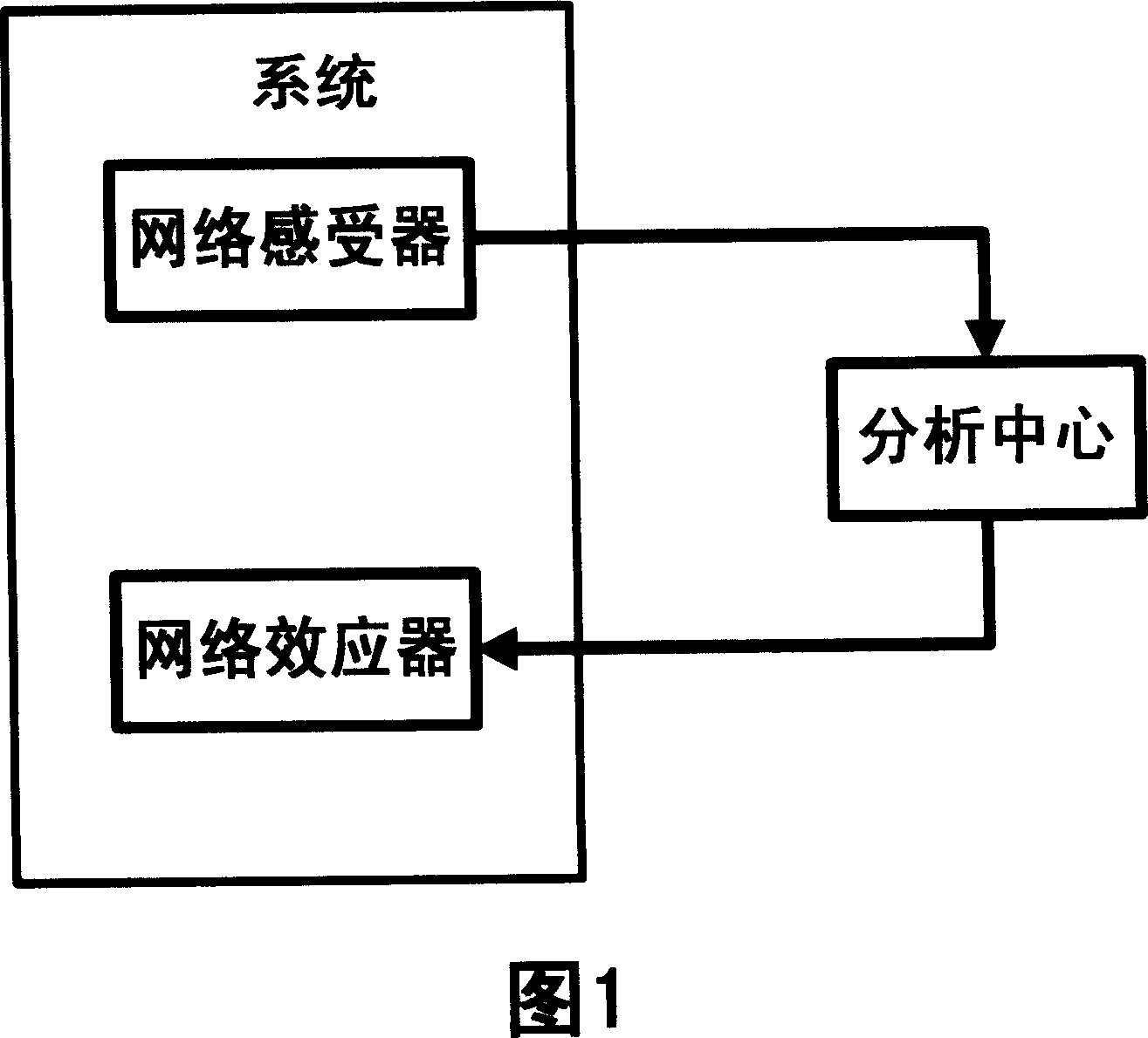
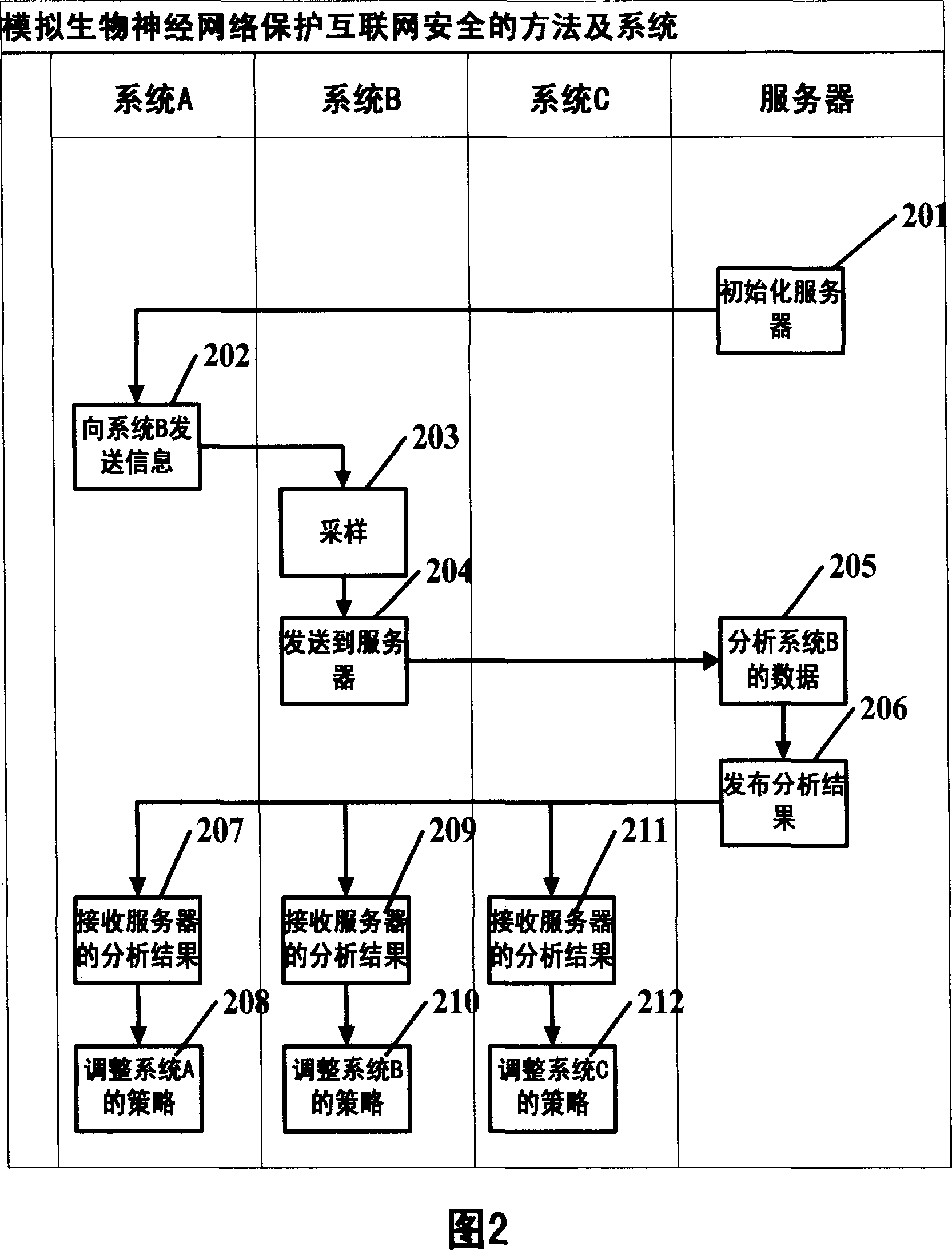
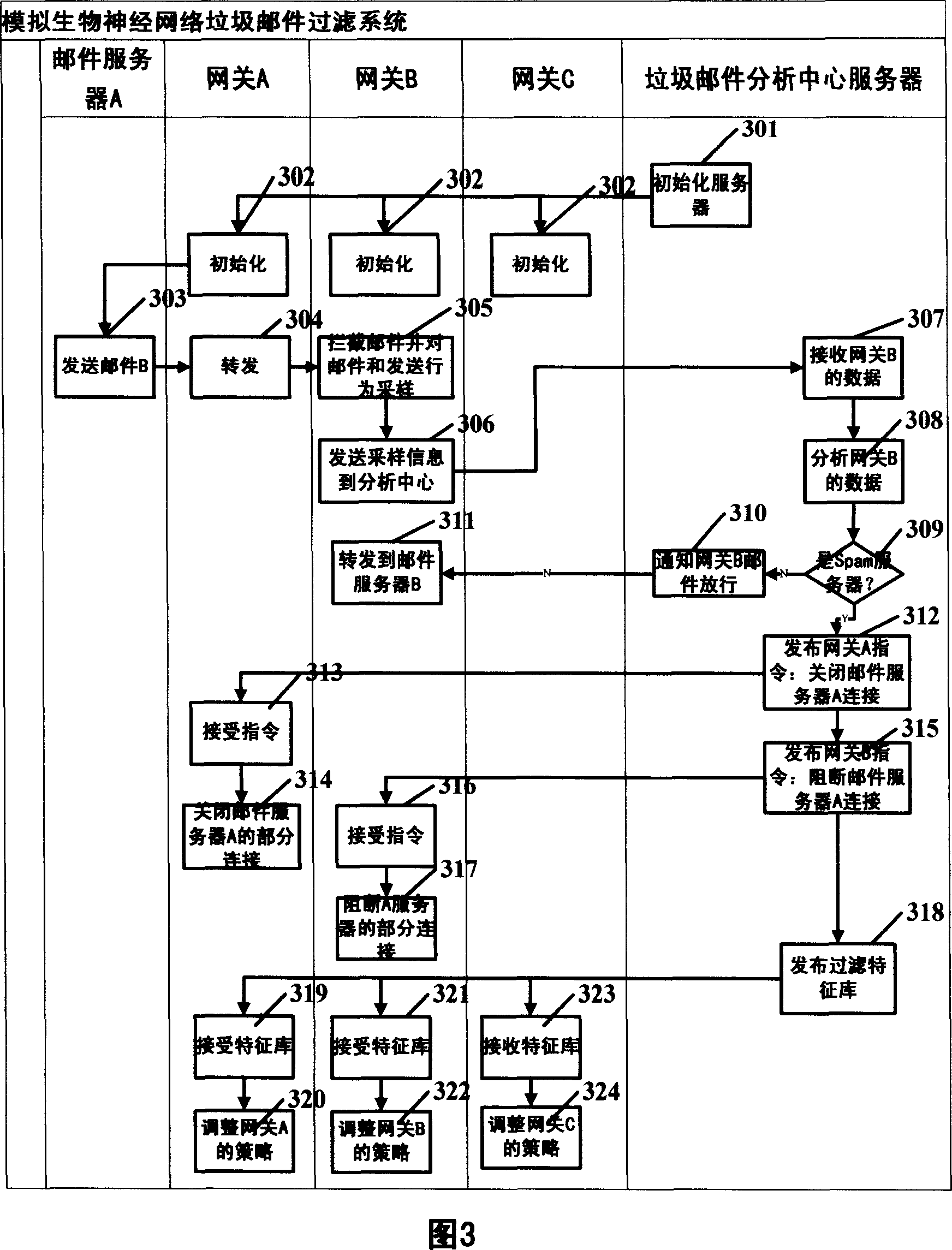
Method and system for protecting security of Internet by simulating biological neural network
InactiveCN1960369AProtection securityReduce waste of resourcesData switching networksNerve networkNetwork behavior
The invention is used for ensuring the safety of content, anti junk mail, antivirus, and anti attack. The method thereof comprises: monitoring the suspicious network behaviors through internet nodes; all collected suspicious behaviors and sampled data are sent to the information security analyzing center to analyze; the information security center uses the release processing strategy and feature base to block the attack behavior and the traffic concerning illegal content.
Owner:董孝峰
Method for analyzing biological networks
ActiveUS8068994B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesDiseaseBiological pathway
Significance of biological pathway in disease state is predicted by (a) providing expression level data for a plurality of biomolecules differentially expressed in a disease state, compared with same biomolecules expressed in a non-diseased state: (b) determining presence probability of the biomolecules in disease state; (c) determining effect of each biomolecule from the plurality of biomolecules on the expression of different downstream biomolecules within pathway to provide perturbation factor for each biomolecule in the pathway; (d) combining statistical significance of differentially expressed biomolecules present in the disease state, with a sum of perturbation factors for all of the biomolecules, generating an impact factor; (e) calculating statistical significance of impact factor based upon determined probability of having statistical significant presence of differentially expressed biomolecules in step (b) and the sum of perturbation factors in step (c); and (f) outputting statistical significance of impact factor for the pathway relevant to the disease.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Method for estimation of information flow in biological networks
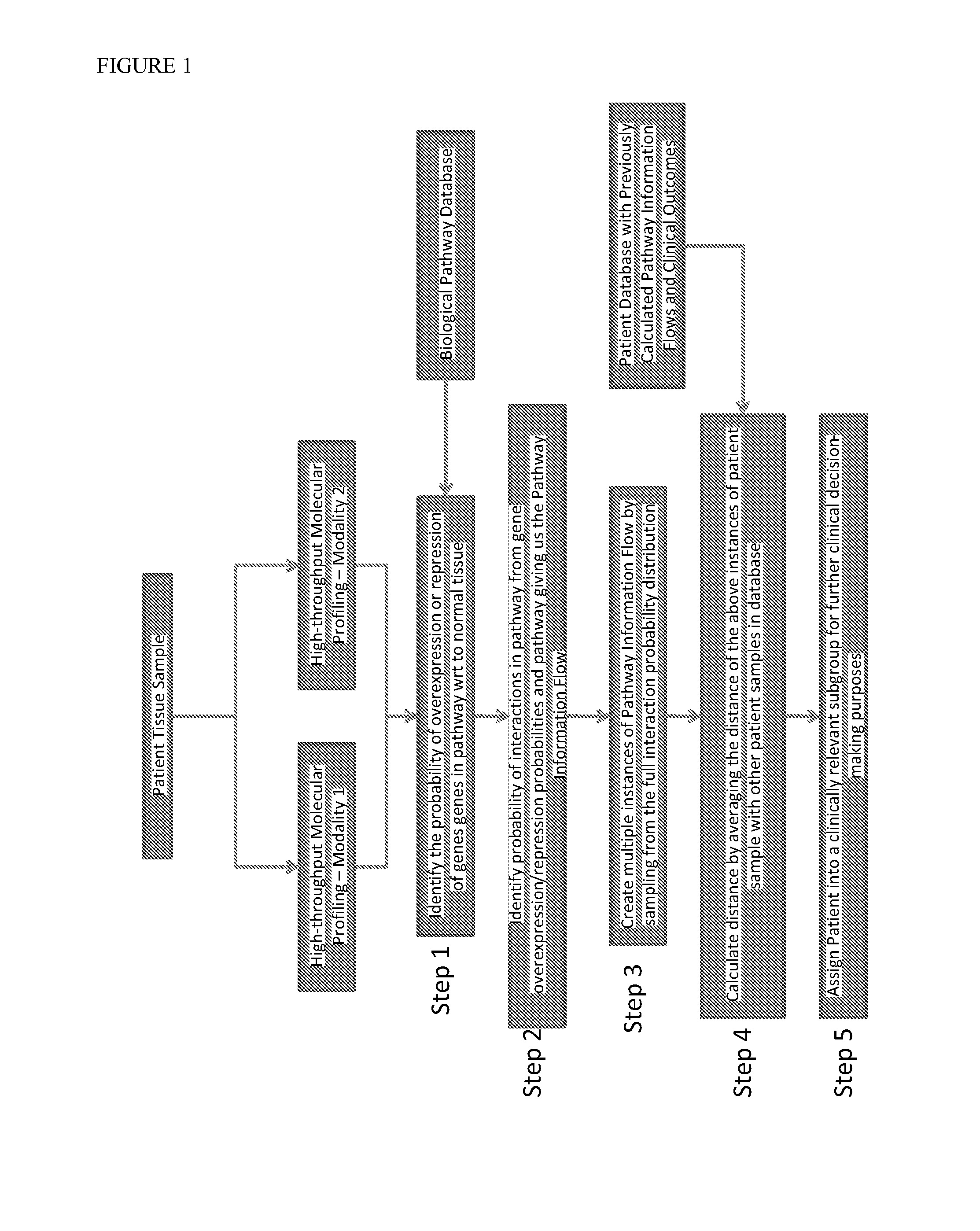
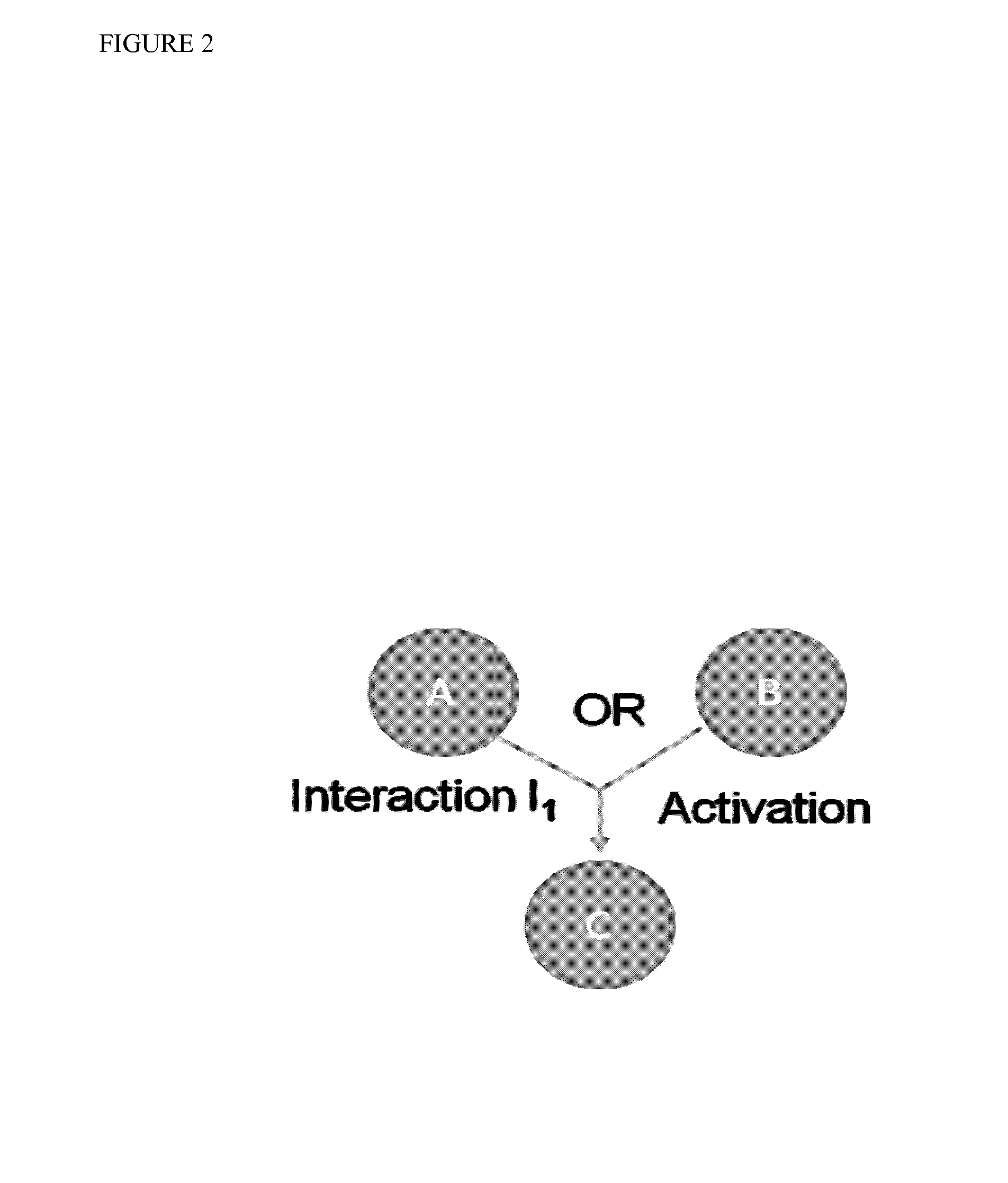
InactiveUS20140040264A1Stratify patients into clinically relevant groups very accuratelyAccurate layeringDigital data processing detailsBiostatisticsPatient databaseNetwork information flow
The present invention relates to a method for stratifying a patient into a clinically relevant group comprising the identification of the probability of an alteration within one or more sets of molecular data from a patient sample in comparison to a database of molecular data of known phenotypes, the inference of the activity of a biological network on the basis of the probabilities, the identification of a network information flow probability for the patient via the probability of interactions in the network, the creation of multiple instances of network information flow for the patient sample and the calculation of the distance of the patient from other subjects in a patient database using multiple instances of the network information flow. The invention further relates to a biomedical marker or group of biomedical markers associated with a high likelihood of responsiveness of a subject to a cancer therapy wherein the biomedical marker or group of biomedical markers comprises altered biological pathway markers, as well as to an assay for detecting, diagnosing, graduating, monitoring or prognosticating a medical condition, or for detecting, diagnosing, monitoring or prognosticating the responsiveness of a subject to a therapy against said medical condition, in particular ovarian cancer. Furthermore, a corresponding clinical decision support system is provided.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
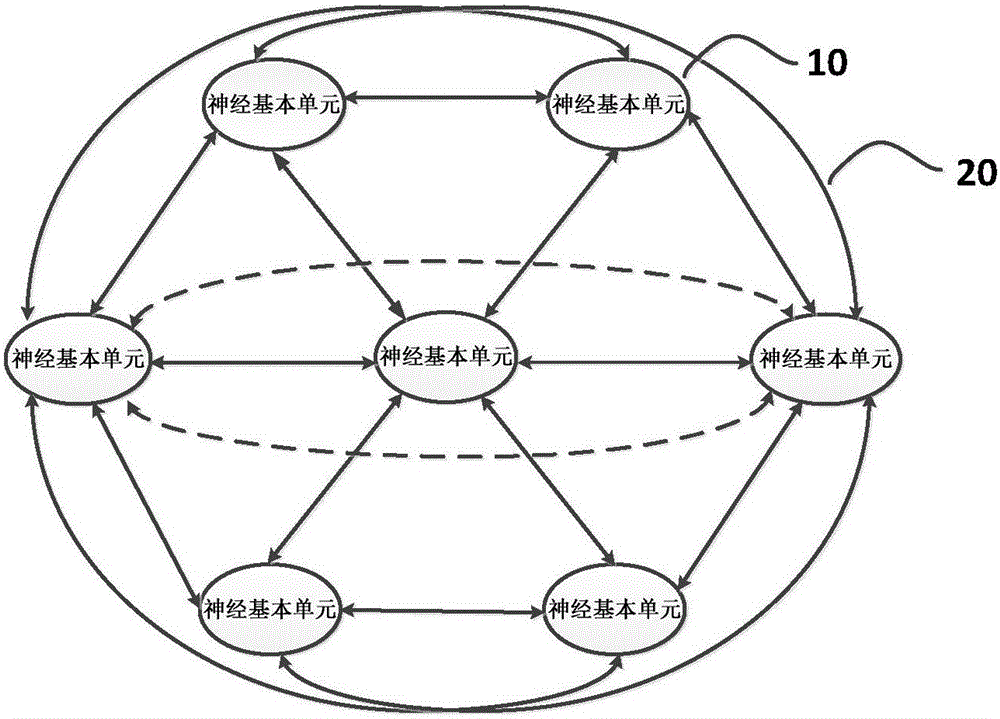
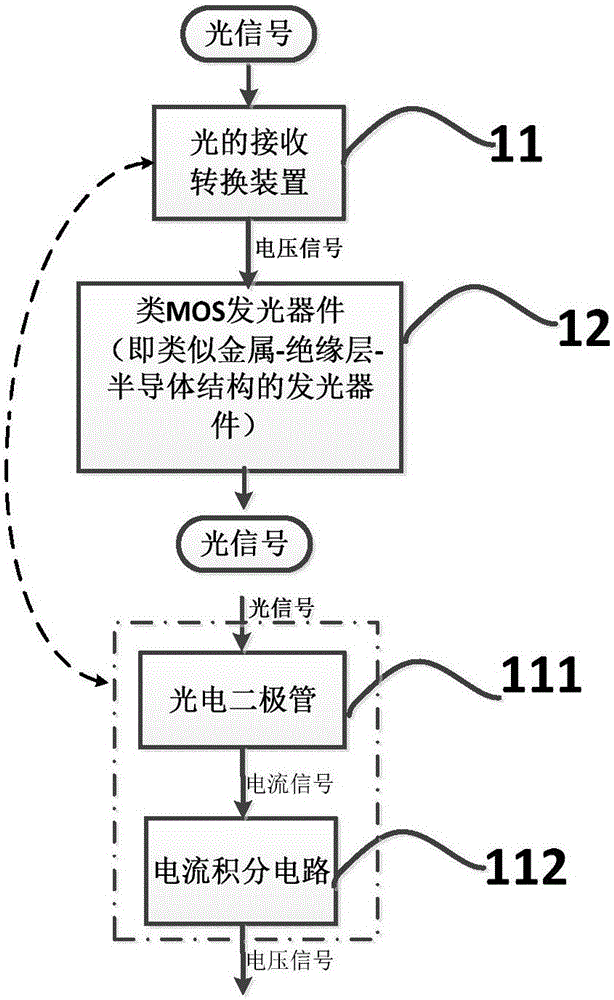
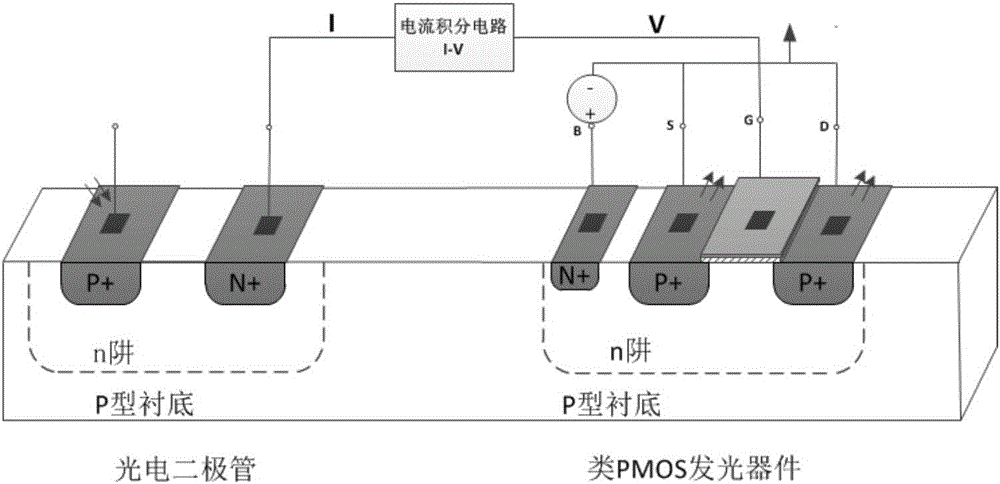
Circuit simulating biological neural network based on similar MOS luminescent devices
A circuit simulating a biological neural network based on similar MOS luminescent devices belongs to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuits and biological neural networks. The circuit comprises more than two basic neural units and light transmission paths, wherein each basic neural unit comprises neural synapses, of the biological neural network, which are simulated by optical reception and conversion devices which receive optical signals and convert the optical signals into electric signals, and neurons, of the biological neural network, which are simulated by similar MOS luminescent devices which convert electric signals into optical signals, and the light transmission paths simulate axons of the biological neural network. The more than two basic neural units are connected serially or / and in star-shape through the light transmission paths, so as to simulate the biological neural network. The circuit is compatible with the CMOS process, small in area, high in efficiency and convenient for integration, and is of a great importance to research and development of artificial intelligence.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
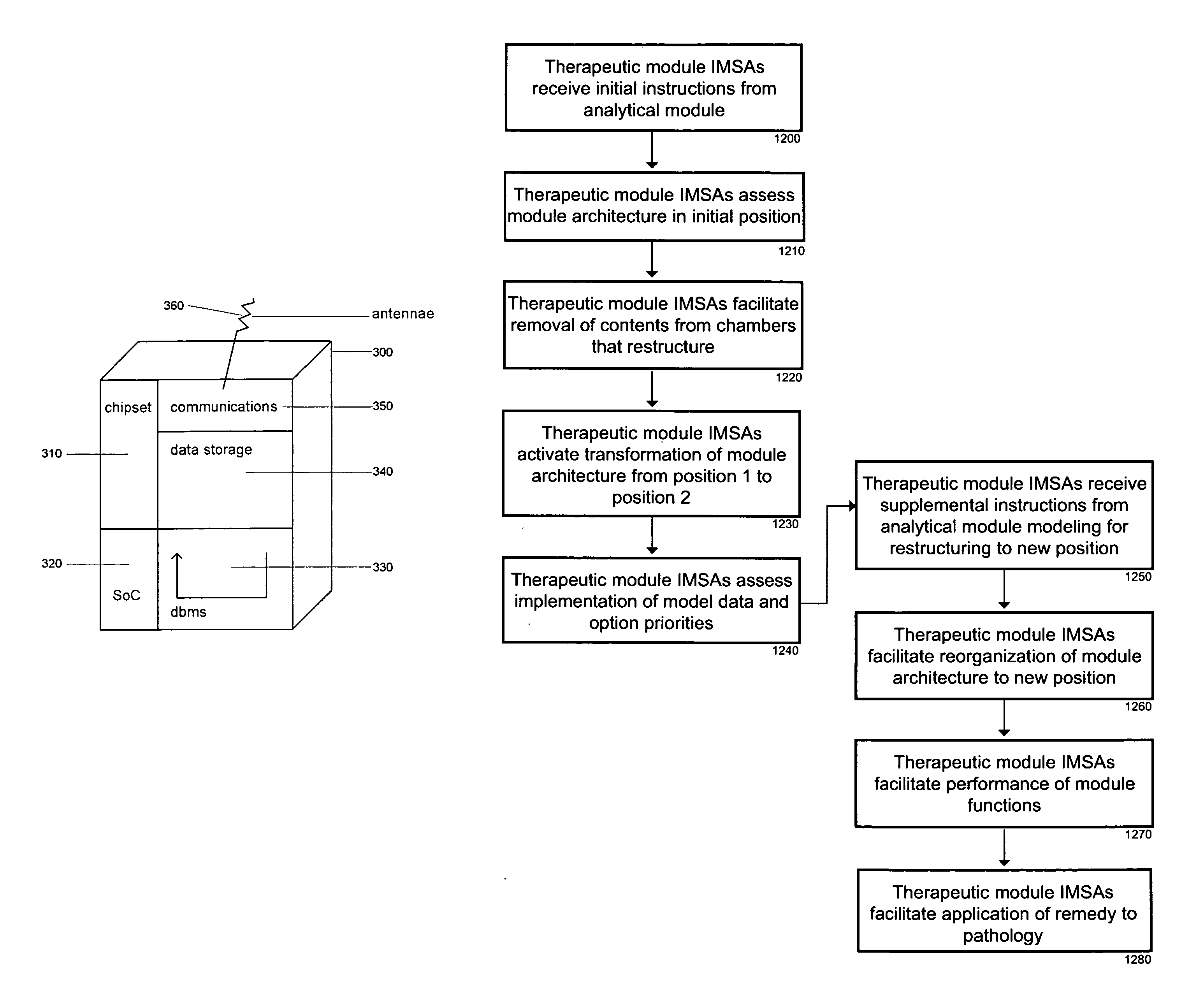
Intelligent medical device system dynamics for biological network regulation
The intelligent medical device (iMD) system coordinates the dynamics of hardware and software components in a self-organizing autonomous system. The iMD system uses advanced modeling and metaheuristics to solve complex optimization problems involving the customization of medical therapies. The system uses evolvable hardware and reprogrammable features to coordinate the diagnostic and therapeutic functions of the iMDs.
Owner:SOLOMON NEAL
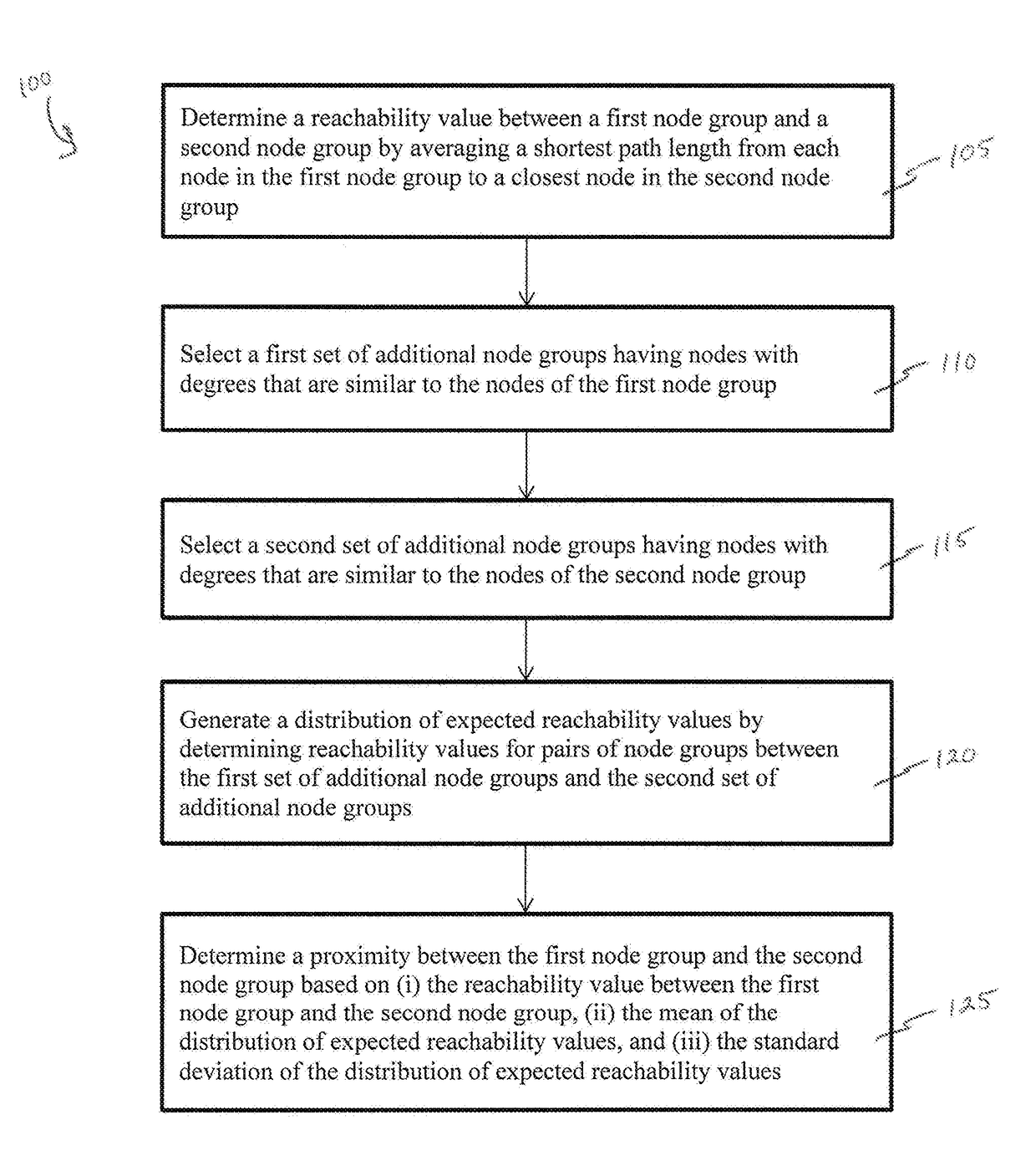
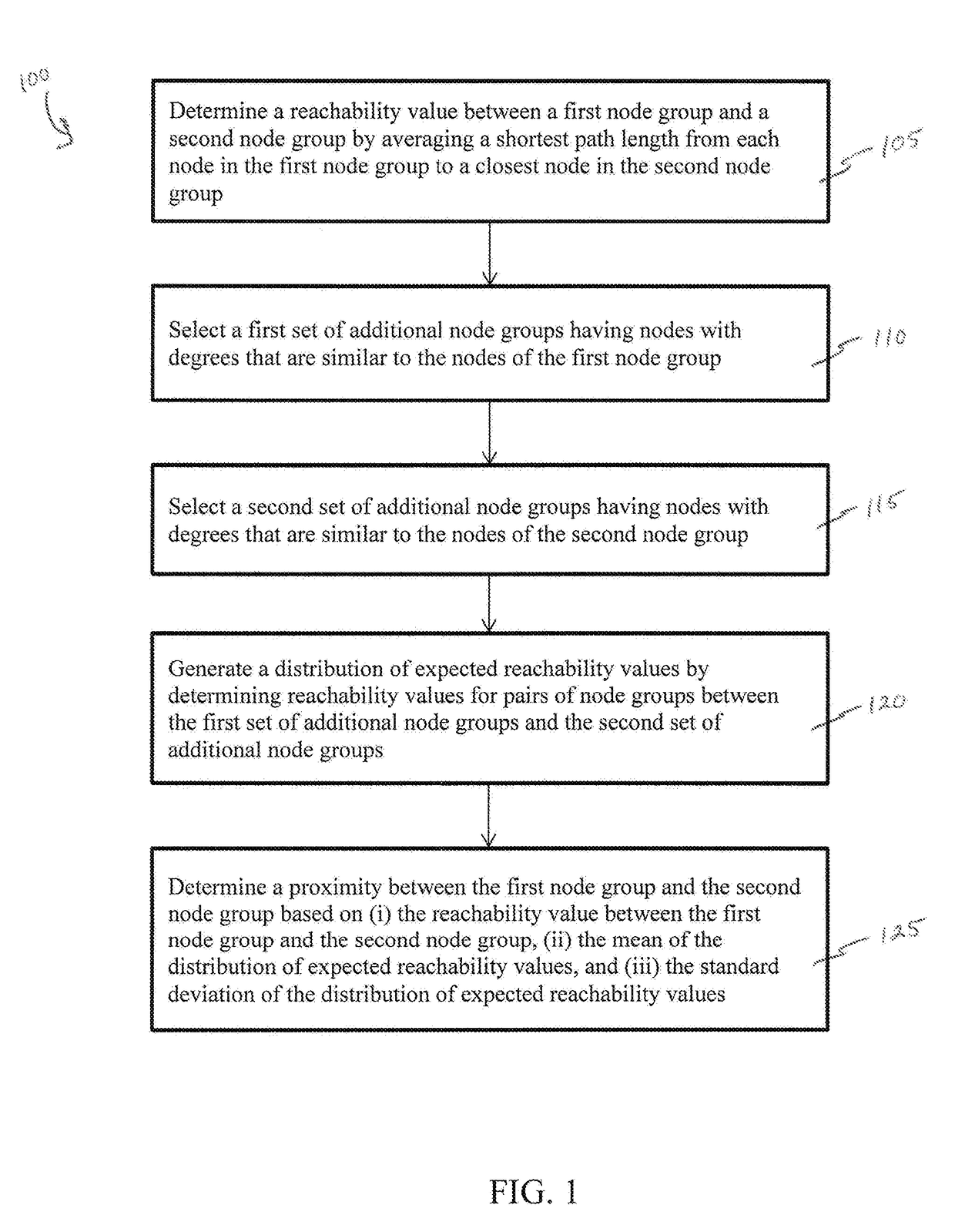
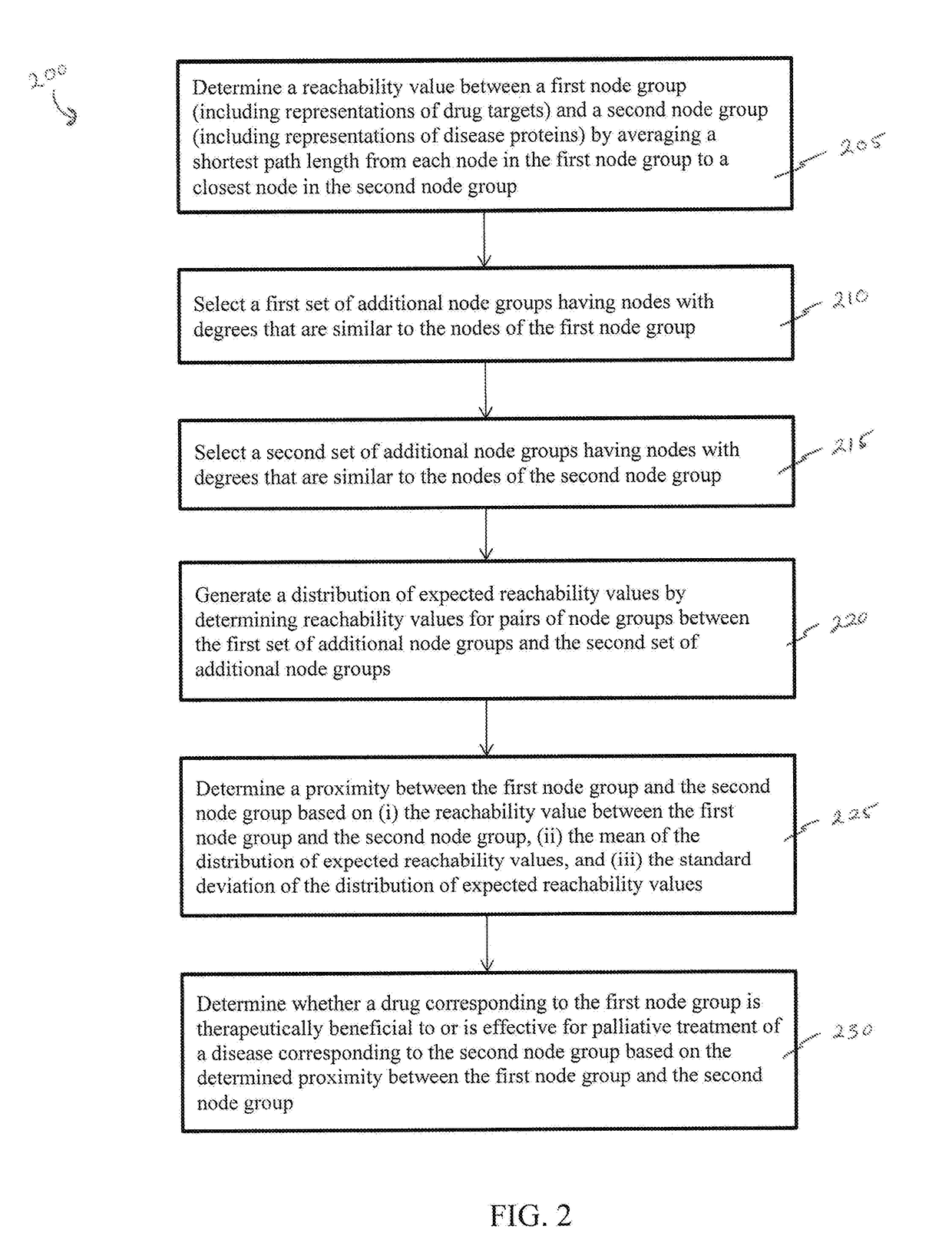
Methods and systems for quantifying closeness of two sets of nodes in a network
Network-based relative proximity measures according to the present invention quantify the closeness between any two sets of nodes (e.g., drug targets and disease genes in a biological network, or groups of people in a social network). The proximity takes into account the scale-free nature of real-world networks and corrects for degree-bias (i.e., due to incompleteness or study biases) by incorporating various distance definitions between the two sets of nodes and comparison of these distances to those of randomly selected nodes in the network (i.e., the distance relative to random expectation), therefore improving processing of the network data. In brief, the proximity offers a formal framework to characterize the distance between two sets of nodes in the network with key applications in various domains from network pharmacology (e.g., discovering novel uses for existing drugs) to social sciences (e.g., defining similarity between groups of individuals).
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Systems and methods for reverse engineering models of biological networks
InactiveUS20060293873A1Function increaseEnhance physical fitnessAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsNetwork modelSensitivity analyses
The present invention provides methods and accompanying computer-based systems and computer-executable code stored on a computer-readable medium for constructing a model of a biological network. The invention further provides methods for performing sensitivity analysis on a biological network and for identifying major regulators of species in the network and of the network as a whole. In addition, the invention provides methods for identifying targets of a perturbation such as that resulting from exposure to a compound or an environmental change. The invention further provides methods for identifying phenotypic mediators that contribute to differences in phenotypes of biological systems.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
System and method for obtaining information about biological networks using a logic based approach
InactiveUS20100299289A1Efficient solutionEffectively scaledDigital computer detailsSystems biologyConcept developmentStructure function
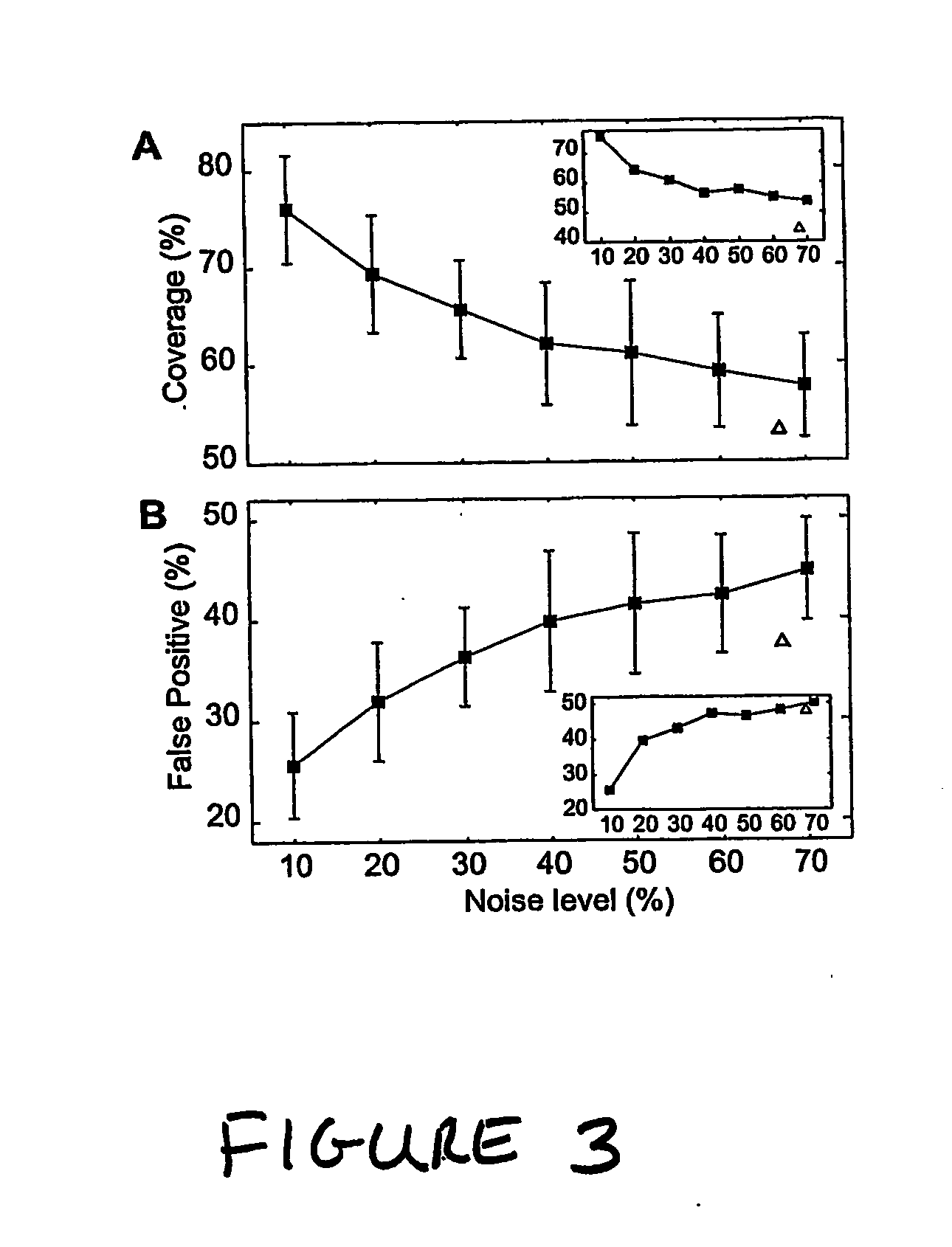
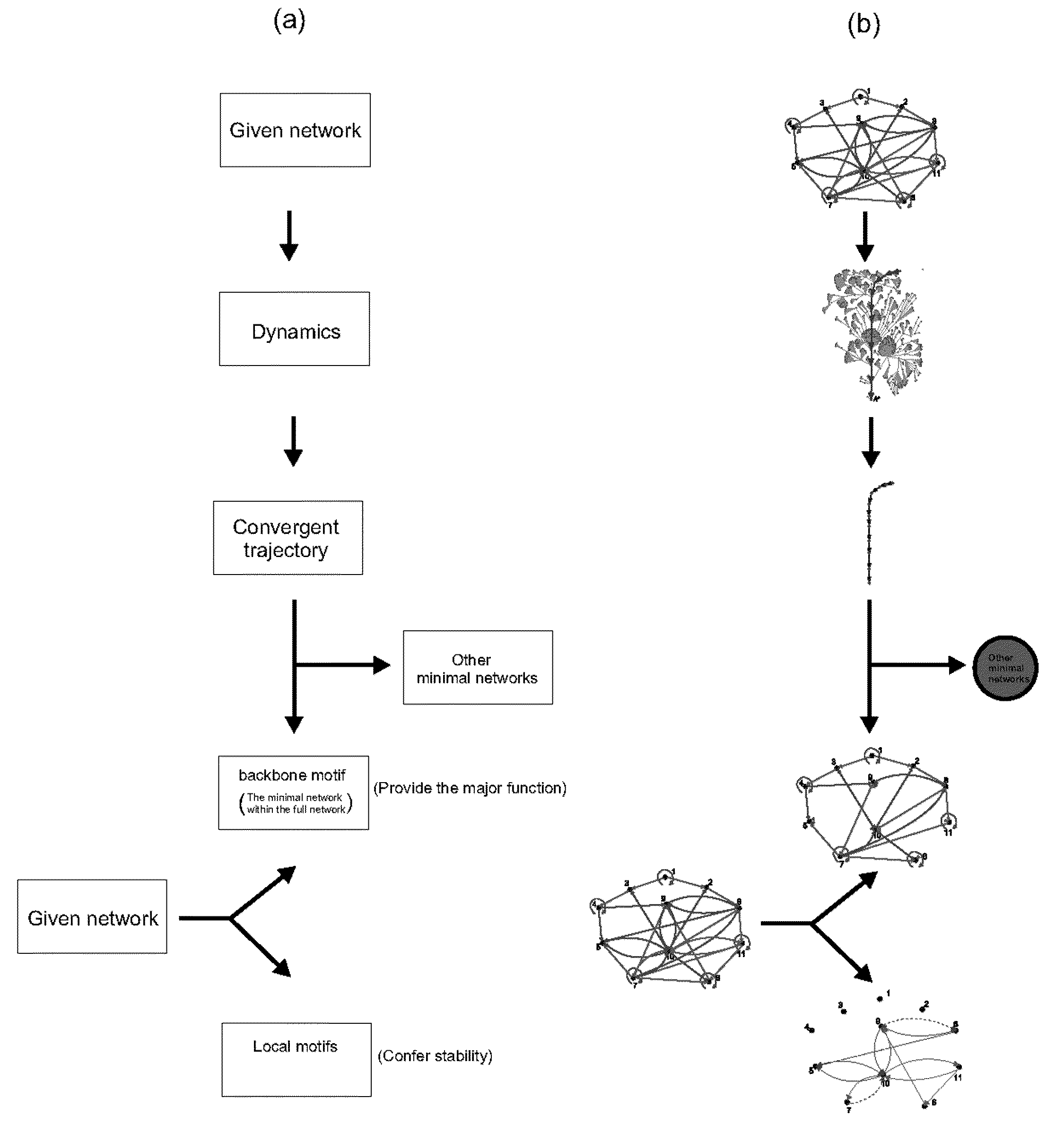
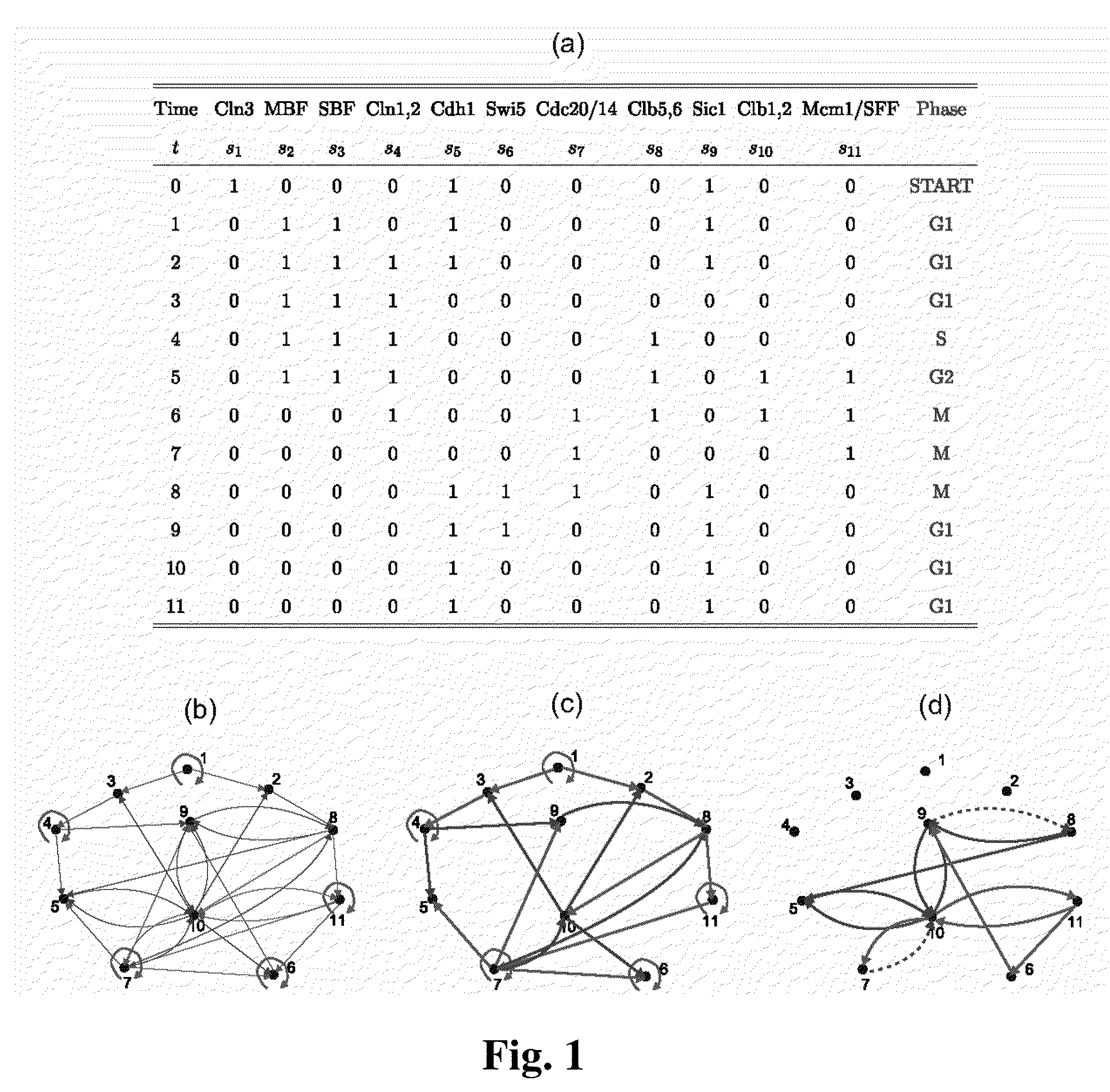
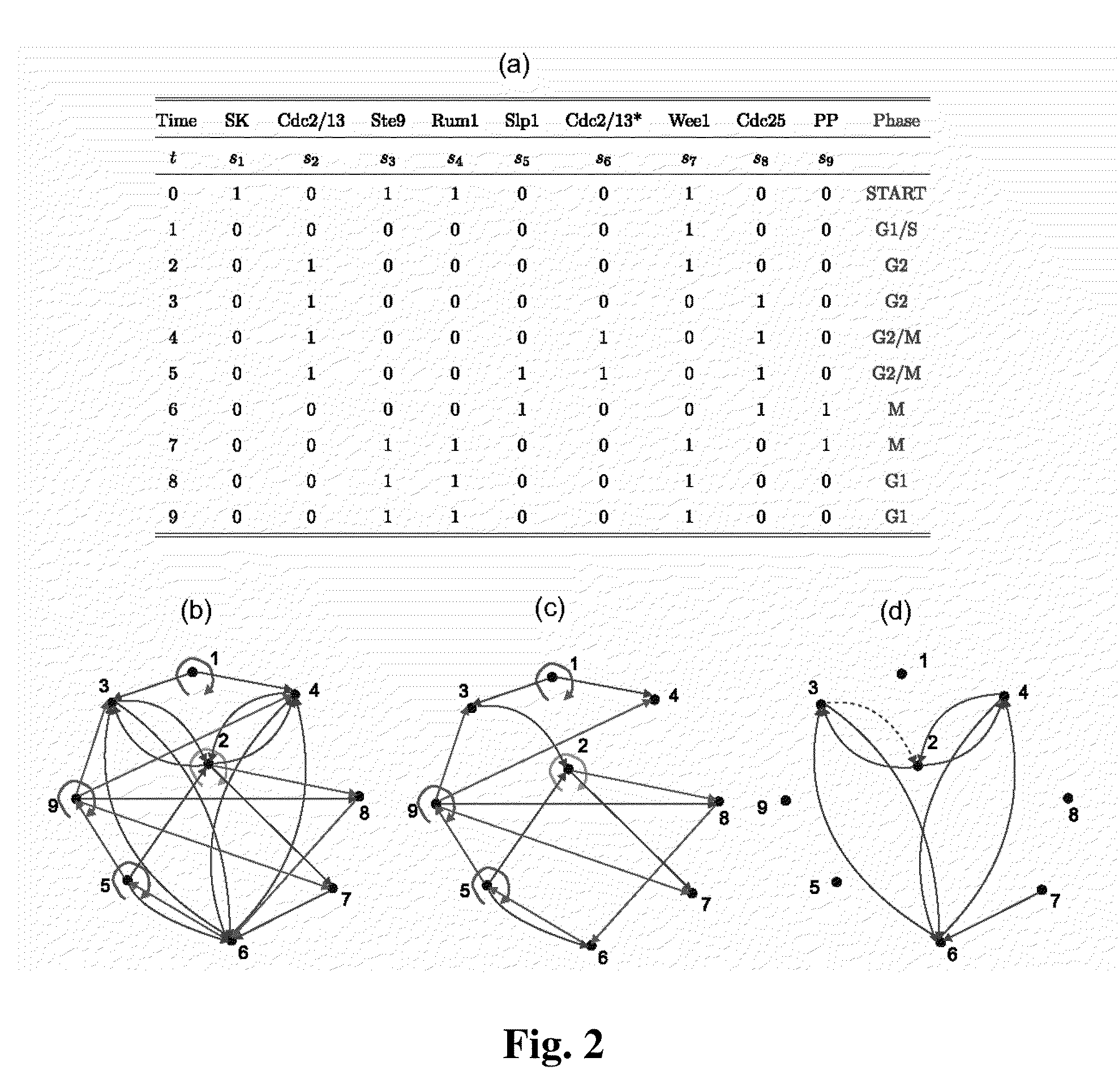
A system and method of obtaining information concerning the structure-function relationship of biological networks can be studied holistically through the ensemble characterization of all the networks that realize a given biological function. A logic-based approach enables significant advances in computability and concept development (minimality and reducibility). The approach is applied to a biologically relevant trajectory and reveals some interesting properties. By using the approach, a cell cycle network is decomposed into three components with the functioning of each component explained.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
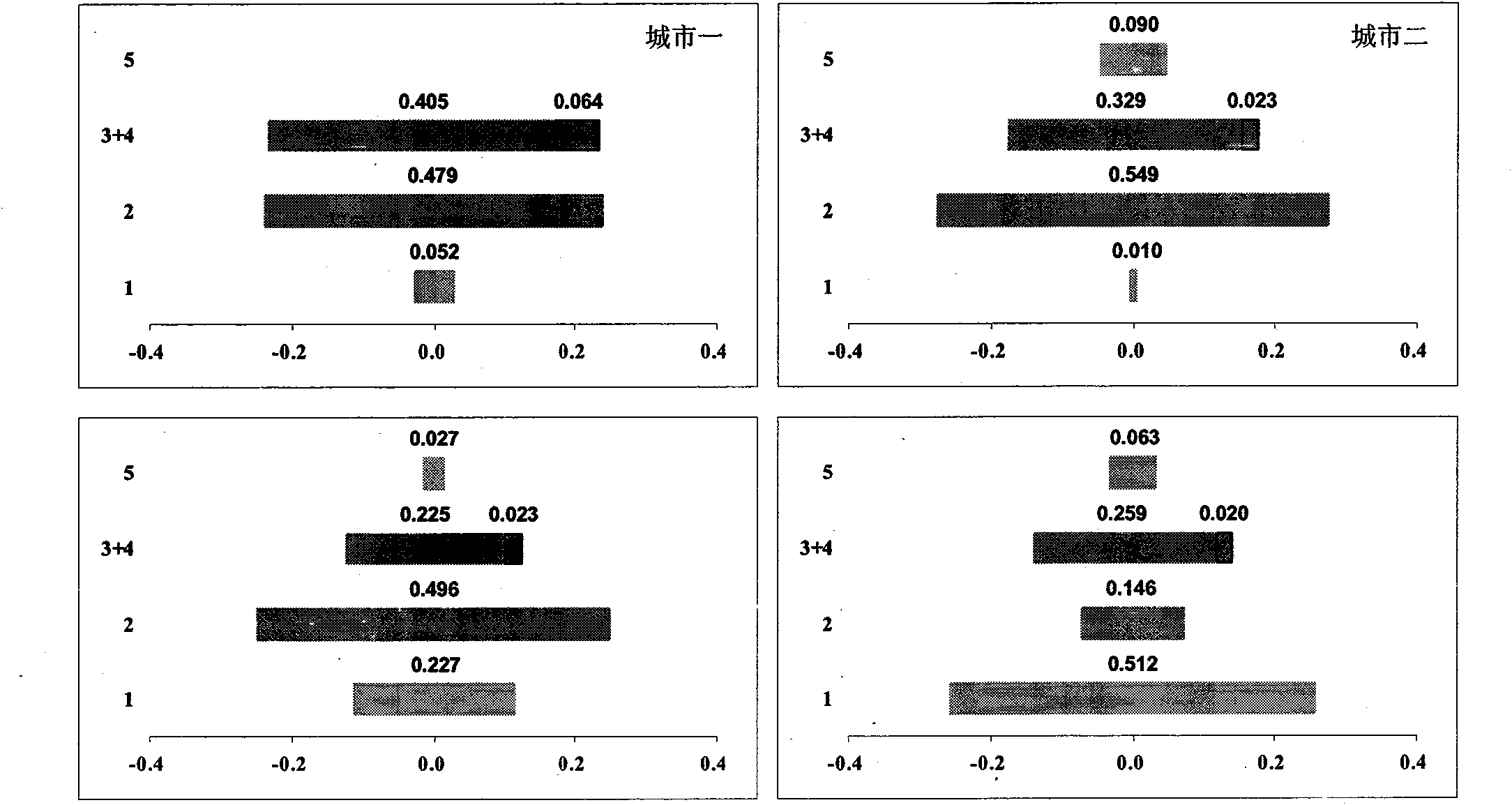
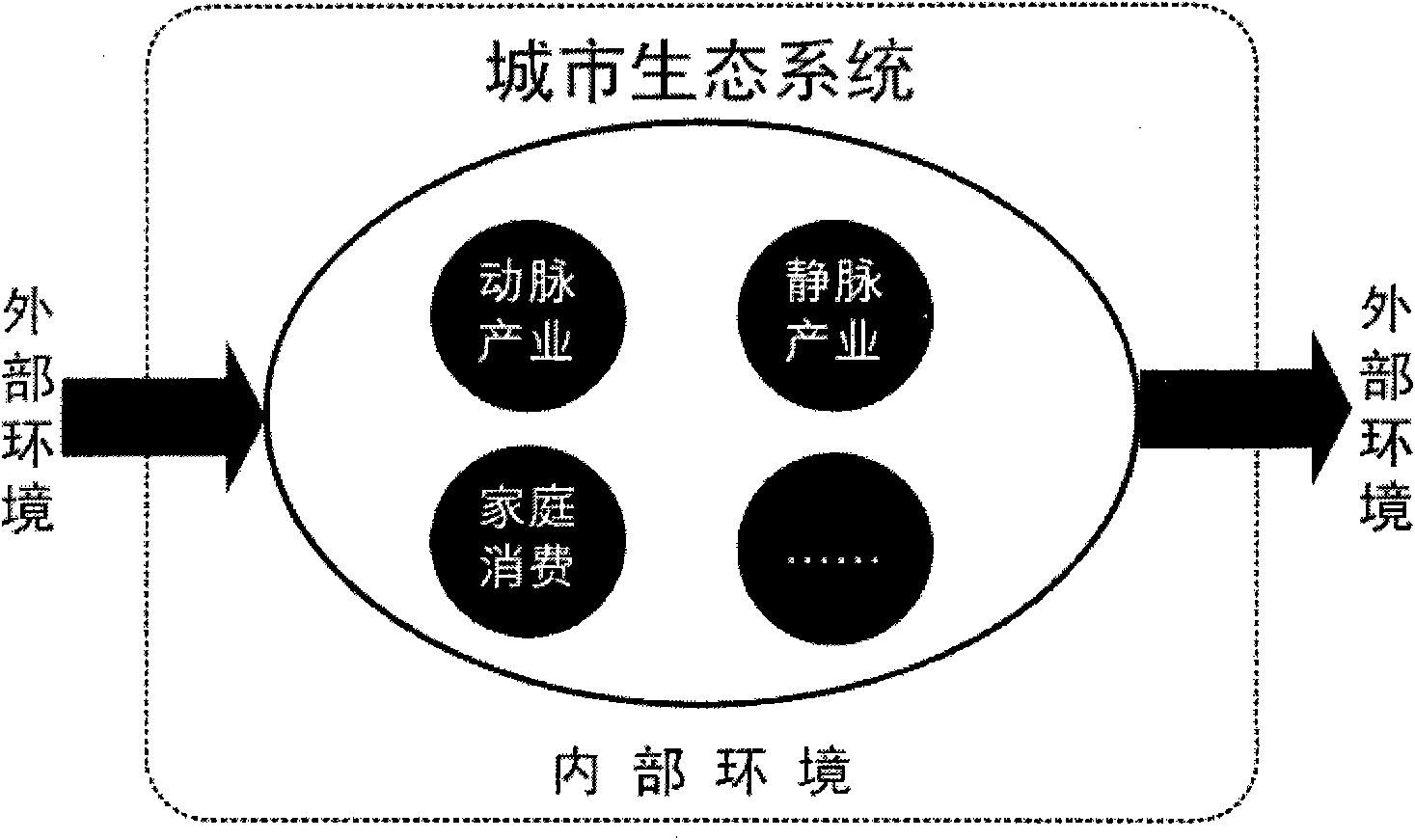
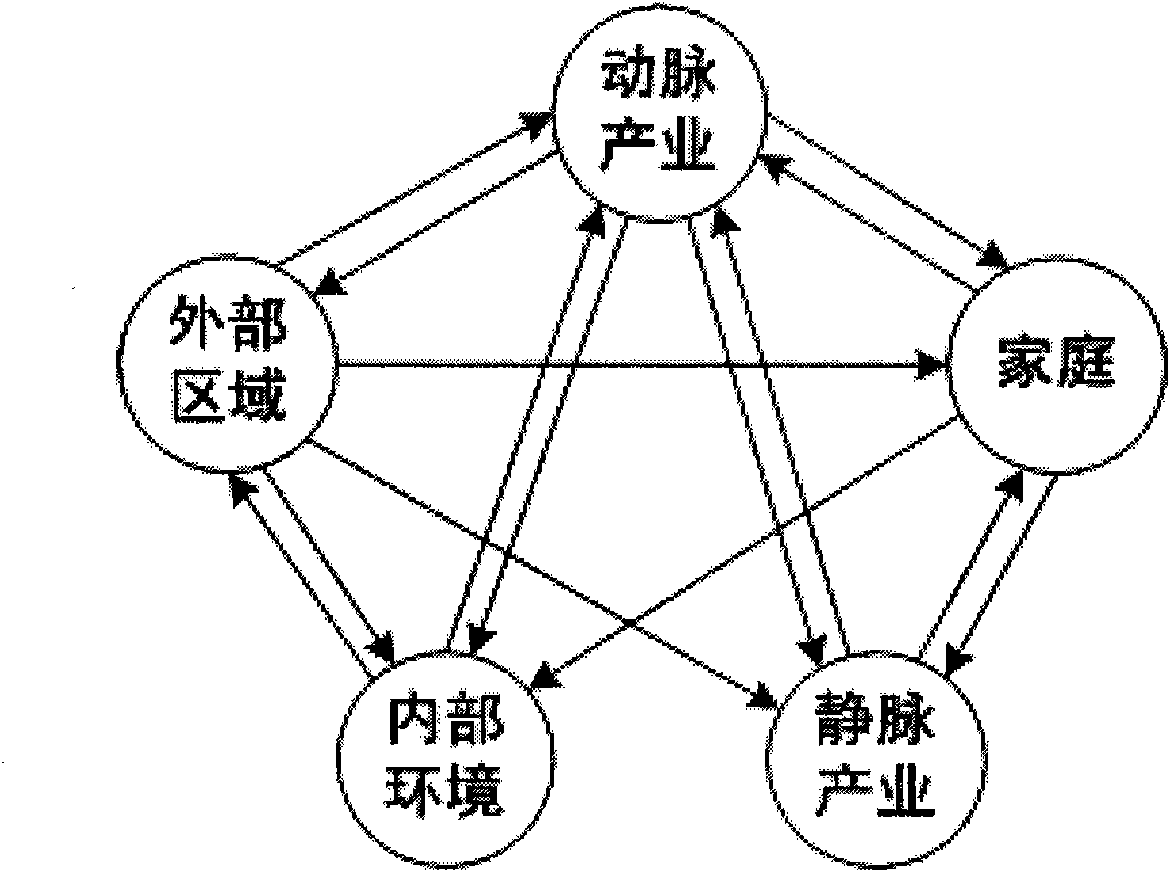
Analysis method of urban ecosystem
InactiveCN101908197AReflect rich contentClearly show the basic structureData processing applicationsEnvironmental resource managementFunctional profiling
The invention belongs to the field of environmental science research, in particular to a synthetic systems analysis method for evaluating an urban ecosystem. Aiming at the problems that the internal construction and the functions of the urban ecosystem can not be effectively analyzed and evaluated and subjectivity and discreteness can not be avoided by using a traditional method, the invention integrates the prior arts, such as an urban compound biological system theory, material flow accounting, biological network analysis, mathematical statistics simulation analysis, and the like into a whole. The method for simulating, estimating and analyzing the urban ecosystem comprises the following contents, such as system definition, biological network model construction, structure and function analysis, and the like. The method is suitable for analyzing the structure and the functions of the urban ecosystem, and comprehensively estimating the operation conditions of the urban ecosystem, and can be popularized in other complicated systems, such as an industry system, a consumption system and single factor systems of energy resources, water and the like.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for the prediction of molecular interaction networks
The present invention relates to a method for identifying unknown molecular interactions within biological networks based on representations of molecules as sets of conserved features. Such molecules include but are not limited to proteins and nucleic acid molecules which can be represented as collections of conserved features, such as domains and motifs in proteins. The method of the invention comprises computing the attraction probabilities between molecules followed by calculation of the probability of a biological network. The method of the invention can be applied across species, where interaction data from one, or several species, can be used to infer molecular interactions between molecules acting within or between organisms. The method of the present invention may be used to identify molecular interactions which can serve as drug screening targets.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Unsupervised Deep Learning Biological Neural Networks
InactiveUS20190065961A1Minimized LMS errorImprove uniformityAutonomous decision making processNeural architecturesMassively parallelNerve network
An experience-based expert system includes an open-set neural net computing sub-system having massive parallel distributed hardware processing associated massive parallel distributed software configured as a natural intelligence biological neural network that maps an open set of inputs to an open set of outputs. The sub-system can be configured to process data according to the Boltzmann Wide-Sense Ergodicity Principle; to process data received at the inputs to determine an open set of possibility representations; to generate fuzzy membership functions based on the representations; and to generate data based on the functions and to provide the data at the outputs. An external intelligent system can be coupled for communication with the subsystem to receive the data and to make a decision based on the data. The external system can include an autonomous vehicle. The decision can determine a speed of the vehicle or whether to stop the vehicle.
Owner:SZU HAROLD
Drug-target interaction prediction method based on hypergraph neural network
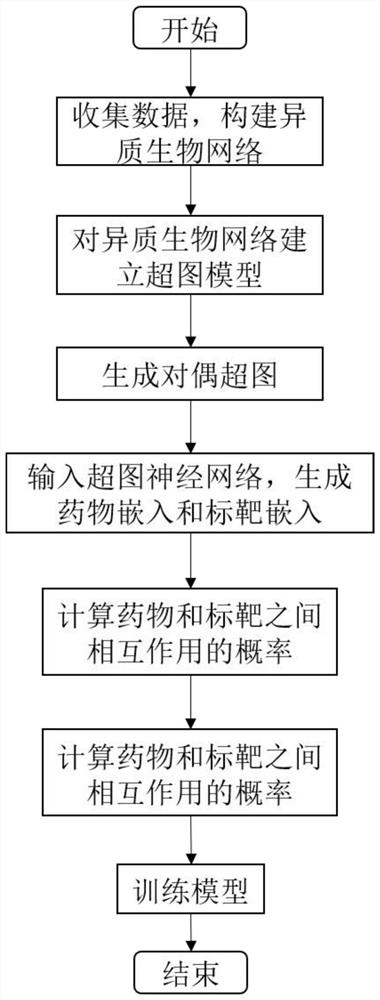
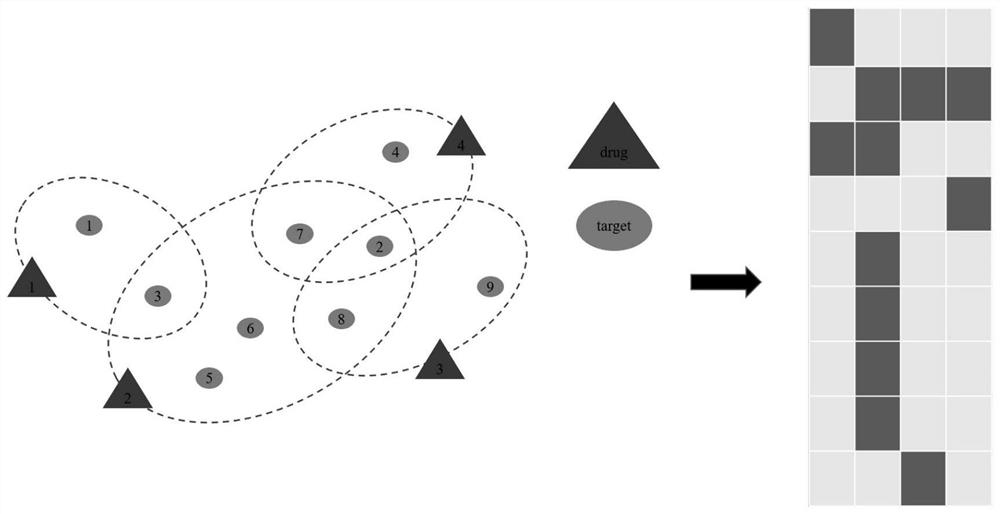
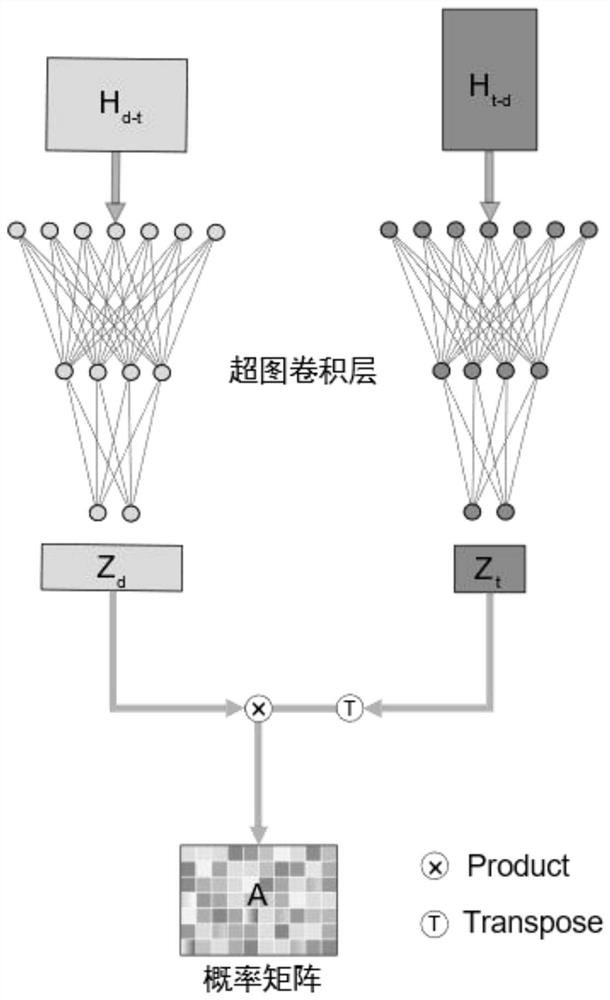
PendingCN112070277AFully learn high-order complex relationsGood forecastForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionData setPredicting performance
The invention provides a drug-target interaction prediction method based on a hypergraph neural network, and the method comprises the steps: firstly searching drug target interaction information froma public database as a data set, dividing the obtained data set into a training set and a test set, building a heterogeneous biological network for modeling through employing the data in the trainingset, modeling the heterogeneous biological network to obtain a heterogeneous biological hypergraph, generating a dual hypergraph of the heterogeneous biological hypergraph according to the obtained heterogeneous biological hypergraph, performing drug and target feature extraction by utilizing a hypergraph neural network, generating drug embedding and target embedding, and finally calculating the probability of interaction between a drug and a target. According to the technical scheme, the heterogeneous biological network is modeled into the hypergraph, the high-order complex relation between the medicine and the target can be fully learned, and a better prediction effect is brought.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
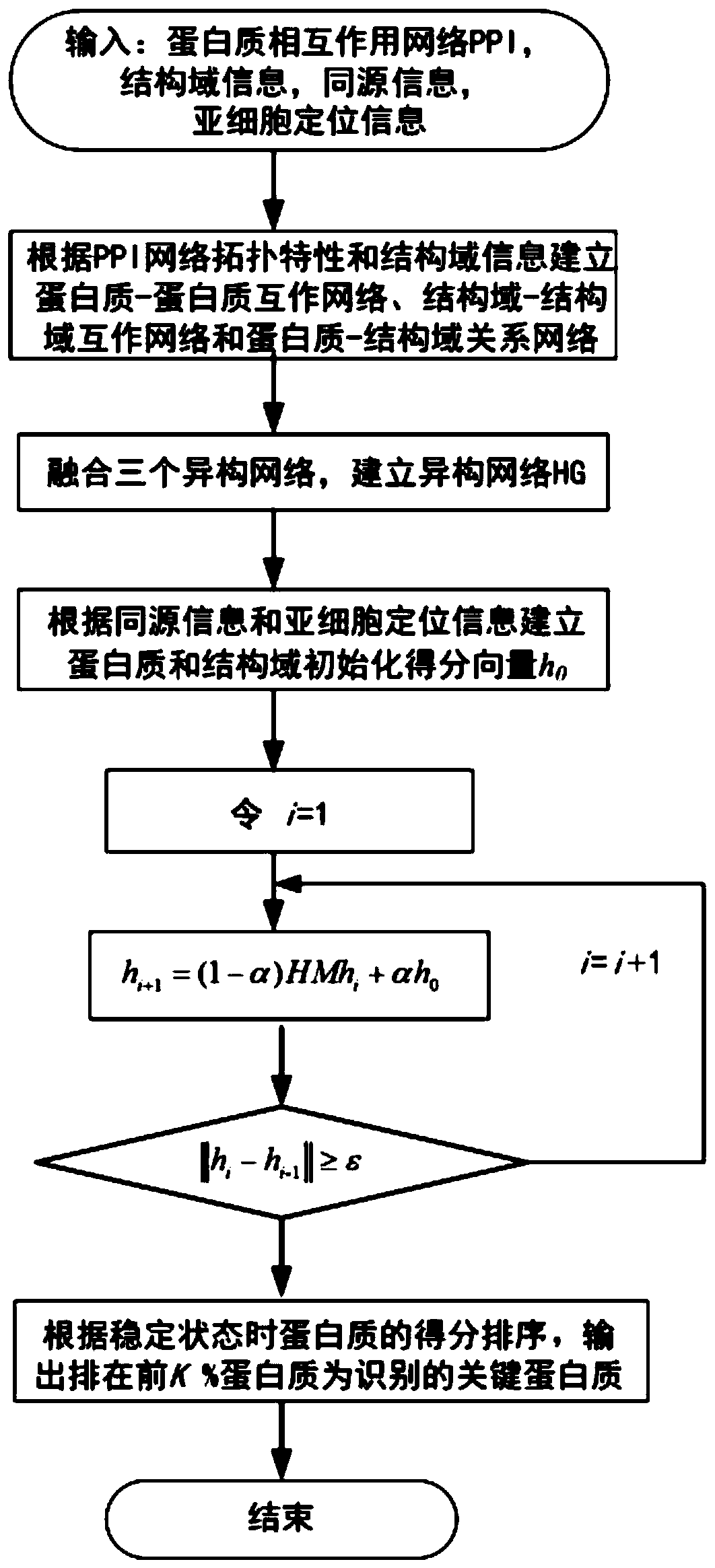
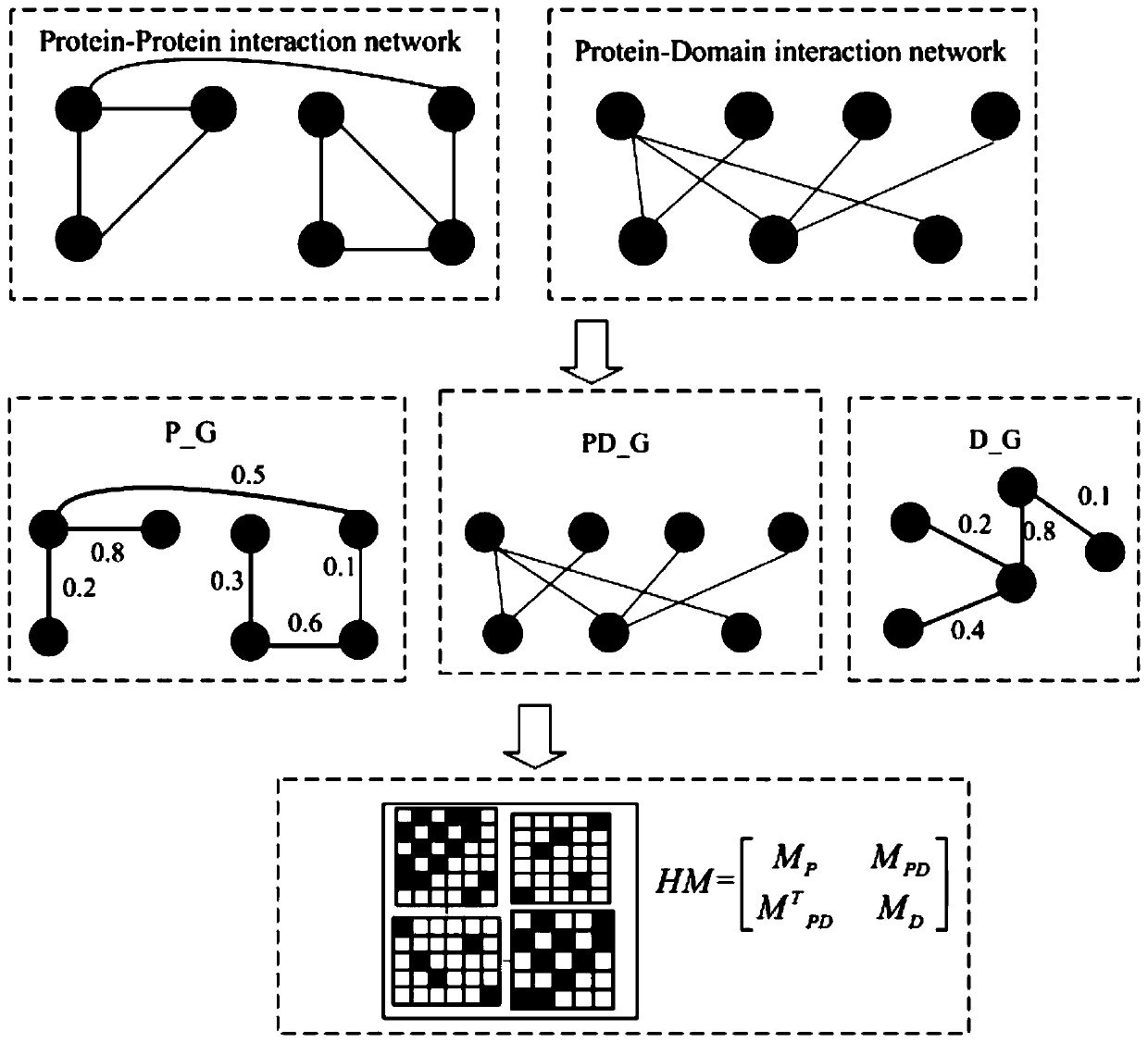
Key protein recognition method based on heterogeneous biological network fusion
ActiveCN109801674AImprove recognition accuracyBiostatisticsInstrumentsYeast ProteinsHeterogeneous network
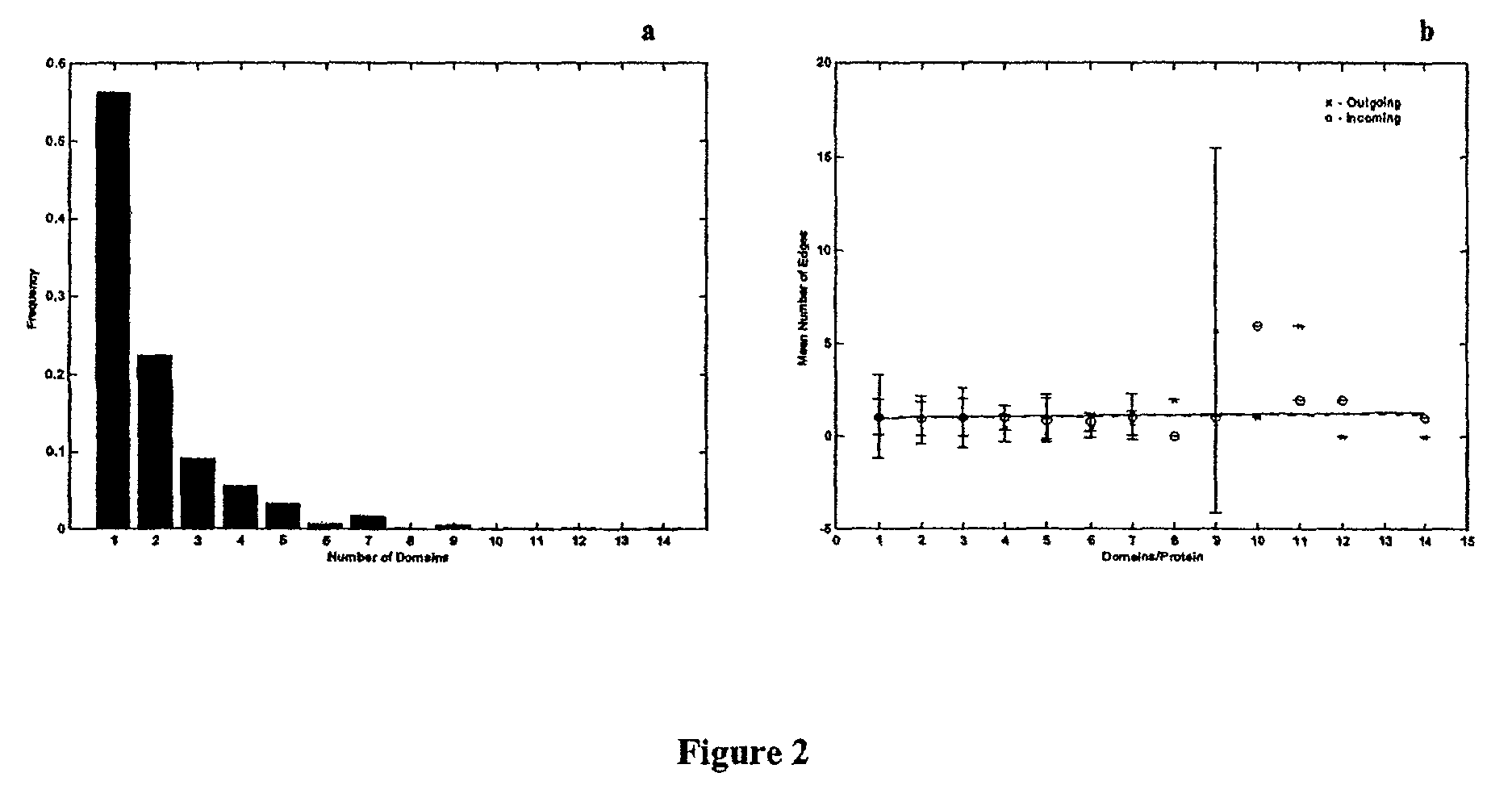
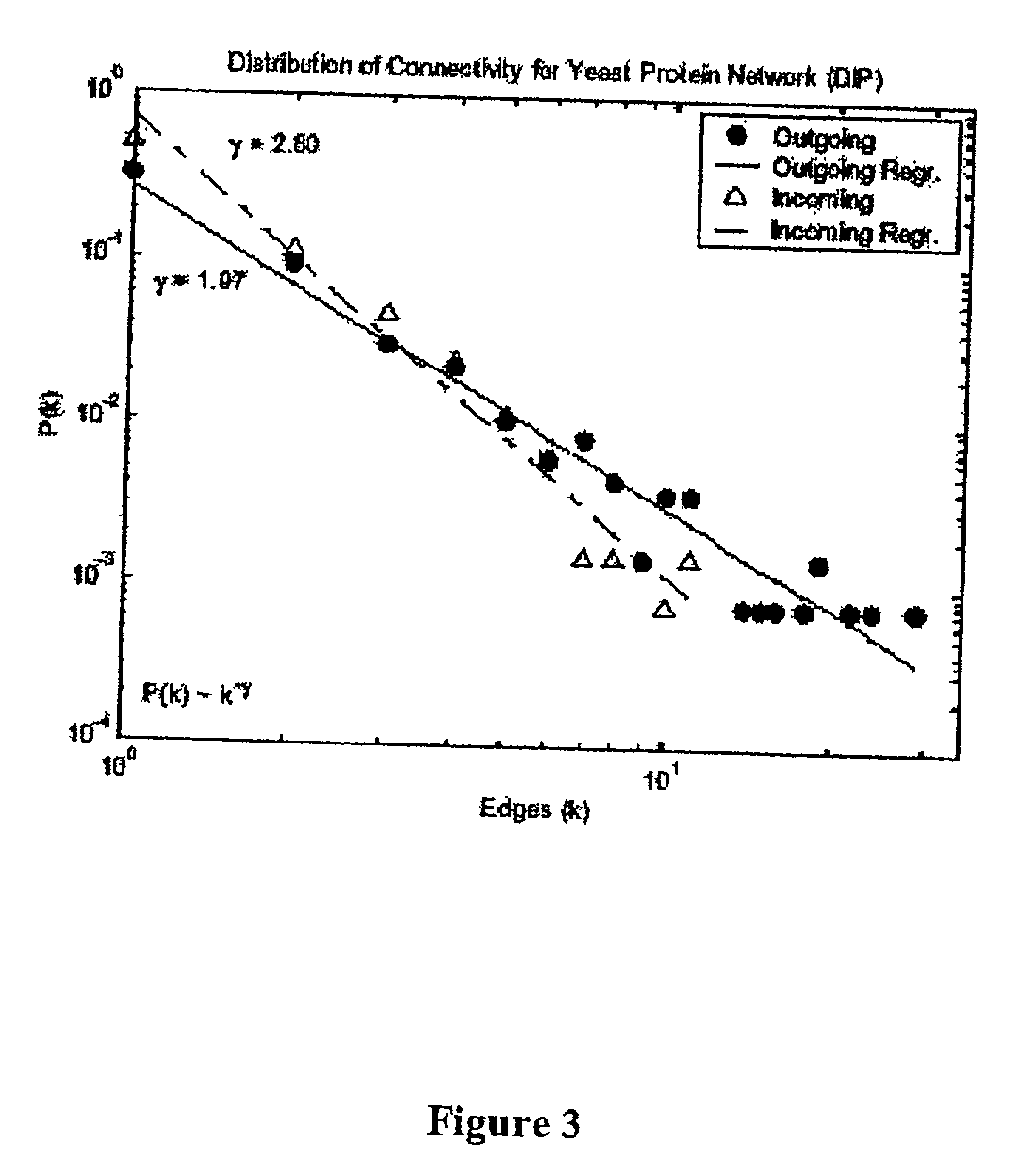
The invention discloses a key protein recognition method based on heterogeneous biological network fusion. The key protein recognition method includes the steps: obtaining a yeast protein interactionnetwork topology, protein domain information, protein homology information, and protein subcellular localization information; respectively establishing a protein-protein interaction network P_G, a structural domain-structural domain interaction network D_G and a protein-structural domain network PD_G; fusing the three networks PD_G three networks, and establishing a heterogeneous network HG; establishing an initialized score vector h0 of the protein and structural domain; iteratively calculating the score vector h(i)t( / i) of the protein and structural domain based on a random walk model untila steady state is achieved; and sorting according to the score of the protein in the steady state, and identifying the key protein. The key protein recognition method based on heterogeneous biologicalnetwork fusion improves the fusion mode of multi-source biological data in the research of key protein recognition methods, and greatly improves the recognition accuracy of key proteins.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY
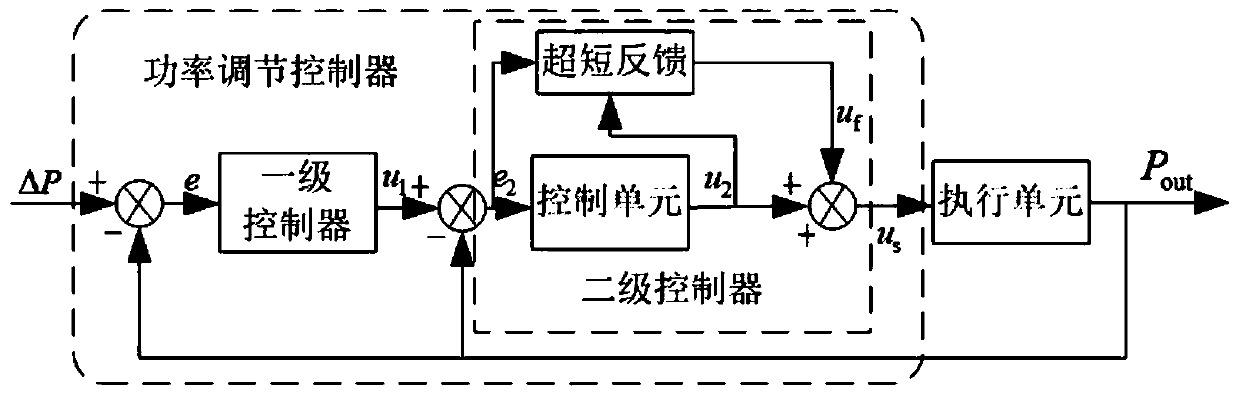
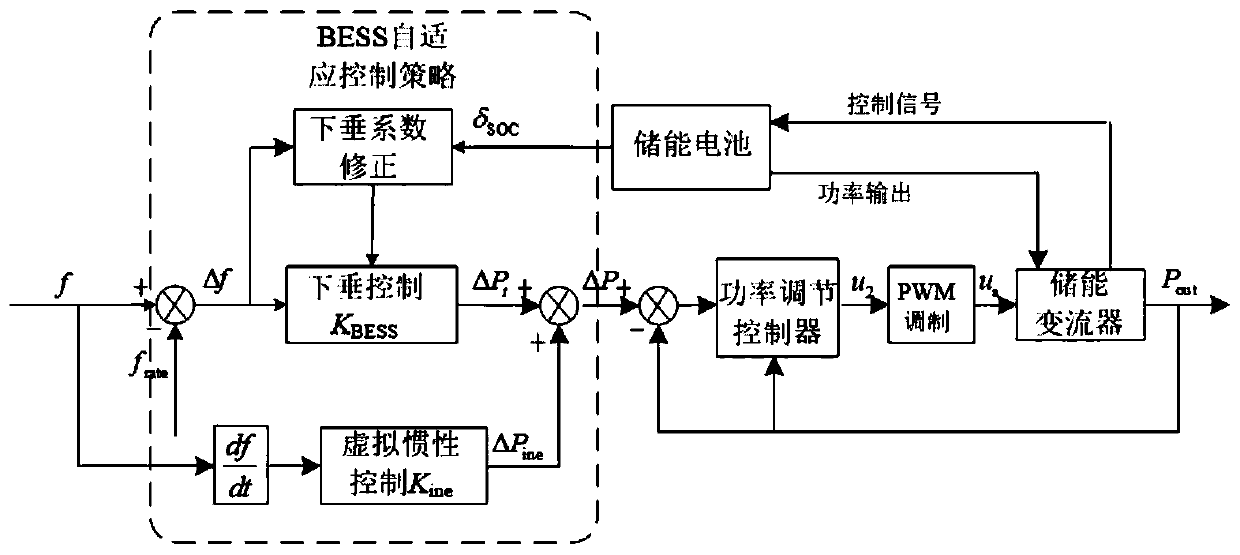
Intelligent comprehensive control method for participation of BESS in primary frequency modulation of power grid
ActiveCN110048460AImprove speedImprove stabilityFlexible AC transmissionClimate change adaptationPrediction algorithmsDiscretization
The invention discloses an intelligent comprehensive control method for participation of BESS in primary frequency modulation of a power grid. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis ofanalyzing a power grid frequency modulation demand and a BESS charged state SOC, proposing a BESS adaptive control strategy, and converting a power grid frequency deviation [delta]f into a referenceabsorption or output power [delta]P of the BESS through the control strategy; in order to improve the frequency response speed and precision of the BESS and enable the BESS to provide rapid and stablepower support for a power grid, providing a double-layer structure power regulation controller based on biological network regulation to control output [delta]P; and in order to improve the dynamic response capability of the double-layer structure power regulation controller, introducing a multi-parameter self-tuning controller based on a discretization prediction algorithm, and providing a dynamic tuning method of control parameters of the double-layer structure power regulation controller. According to the method, active power support can be effectively provided for the power grid, the problem of overcharge and overdischarge of the energy storage battery is solved, the circulation efficiency of the BESS is improved, and the maintenance cost of the energy storage system is reduced.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Systems and Methods for Identifying Drug Targets Using Biological Networks
ActiveUS20130151452A1Impossible to determineImprove learning accuracyChemical property predictionMathematical modelsDiseaseAlgorithm
Certain embodiments of the invention may include systems and methods for identifying drug targets using biological networks. According to an example embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for predicting the effects of drug targets on treating a disease. The method can include constructing a structure of a Bayesian network based at least in part on knowledge of drug inhibiting effects on a disease; associating a set of parameters with the constructed Bayesian network; determining values of a joint probability distribution of the Bayesian network via an automatic procedure; deriving a mean Bayesian network with one or more averaged parameters based at least in part on the joint probability values; and calculating a quantitative prediction based at least in part on the mean Bayesian network.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Techniques for reconstructing synthetic networks using pair-wise correlation analysis
InactiveUS20050096887A1Computation using non-denominational number representationSystems biologyCorrelation analysisChain network
Techniques for reconstructing networks are provided. In one aspect, a method for reconstructing a synthetic network, such as a synthetic biological network, is provided. In another aspect, a method for reconstructing a supply chain network is provided. Exemplary supply chain networks include supply chains for petroleum distribution.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
A method and a device for detecting time-varying stable communities in a time-varying network
ActiveCN109921921AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityData switching networksComplex network analysisCommunity structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of complex network analysis, and particularly relates to a method and a device for detecting aging stability communities in a time-varying network. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring the change condition of connection between nodes along with time, and constructing a time-varying network; Using the volatility to quantitatively describe the dynamic change degree of the connection edge in the network; Initializing a community structure, and calculating the dynamic modularity of the time-varying network in combination with the fluctuation rate; And optimizing the dynamic modularity, wherein the community structure corresponding to the maximum value is the time-varying stable community of the time-varying network. According to the invention, the network dynamic change is quantitatively described by using the volatility; the network dynamic change characteristics are combined with a community detection method; The method for identifying the stable community in the time-varying network is provided, the accuracy and reliability of community detection are improved, the method has wide application prospects in different fields of social networks, biological networks, traffic networks and the like, and meanwhile a new visual angle is provided for understanding the functions and the dynamic process ofthe community structure in a complex system in actual life.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com