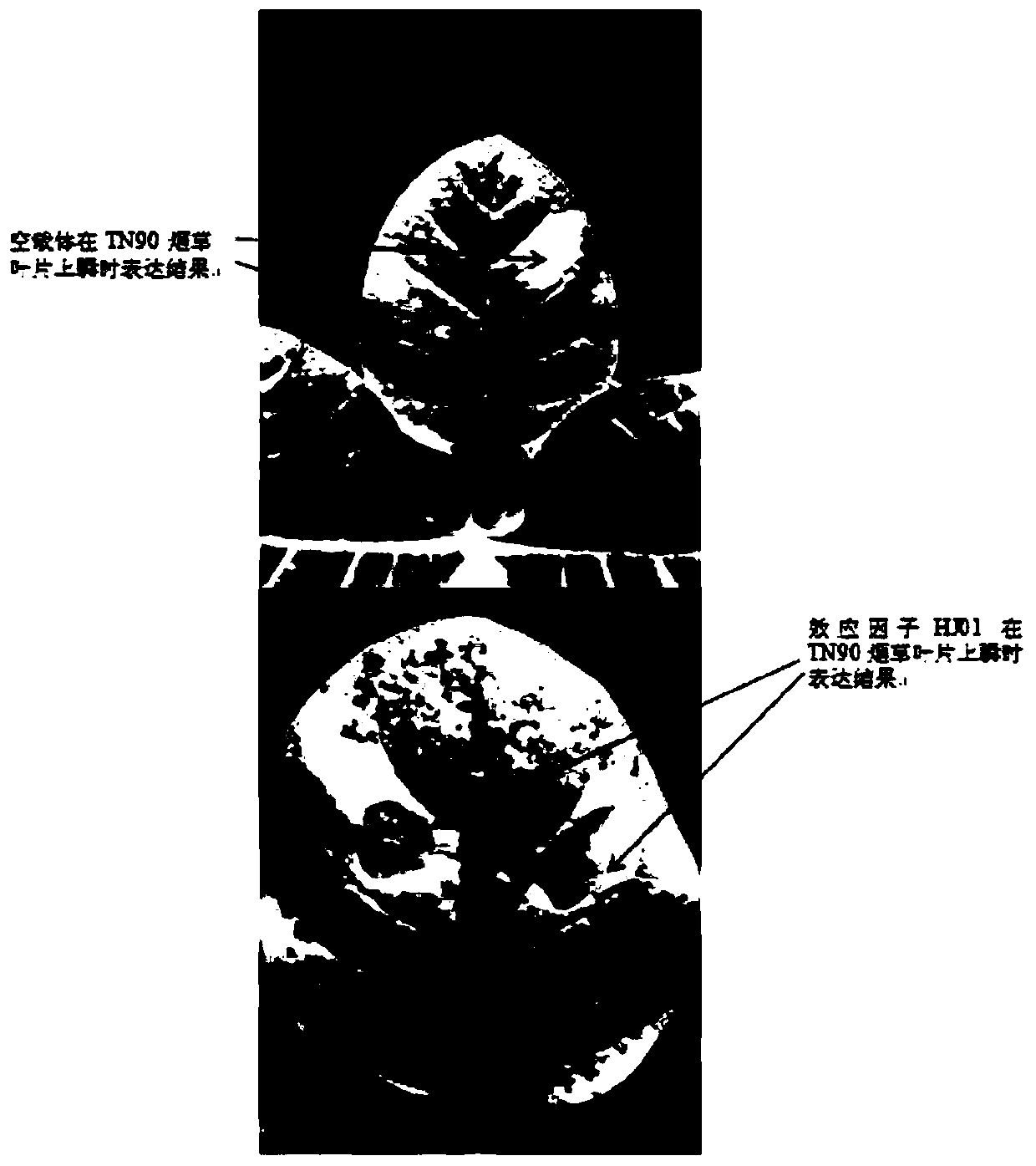
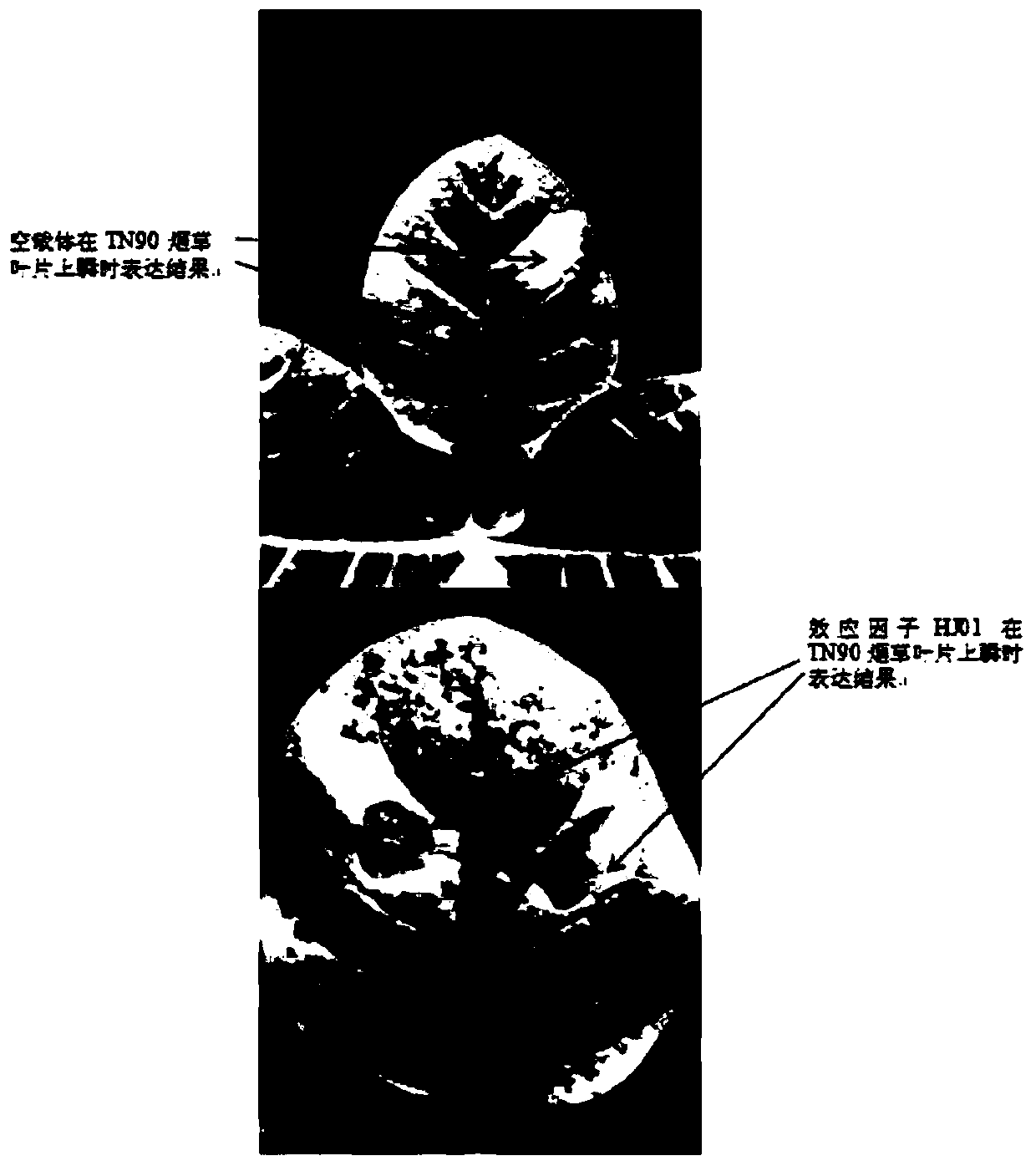
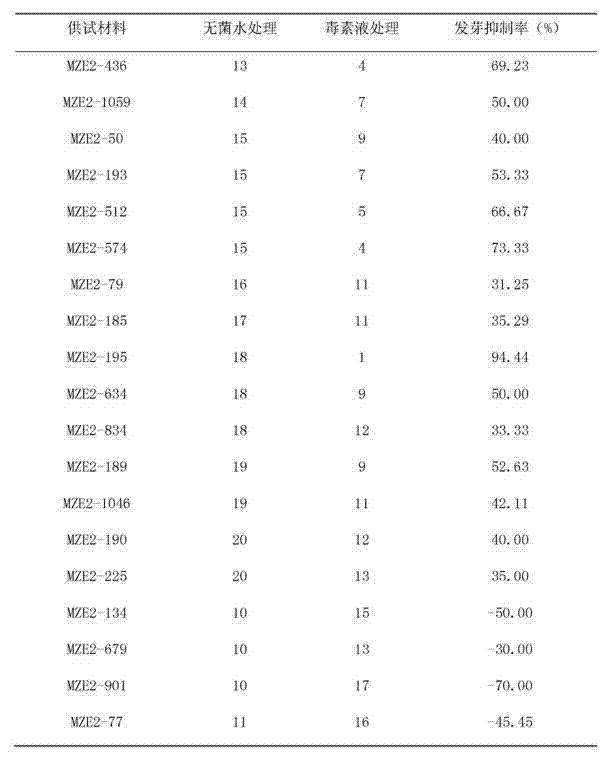
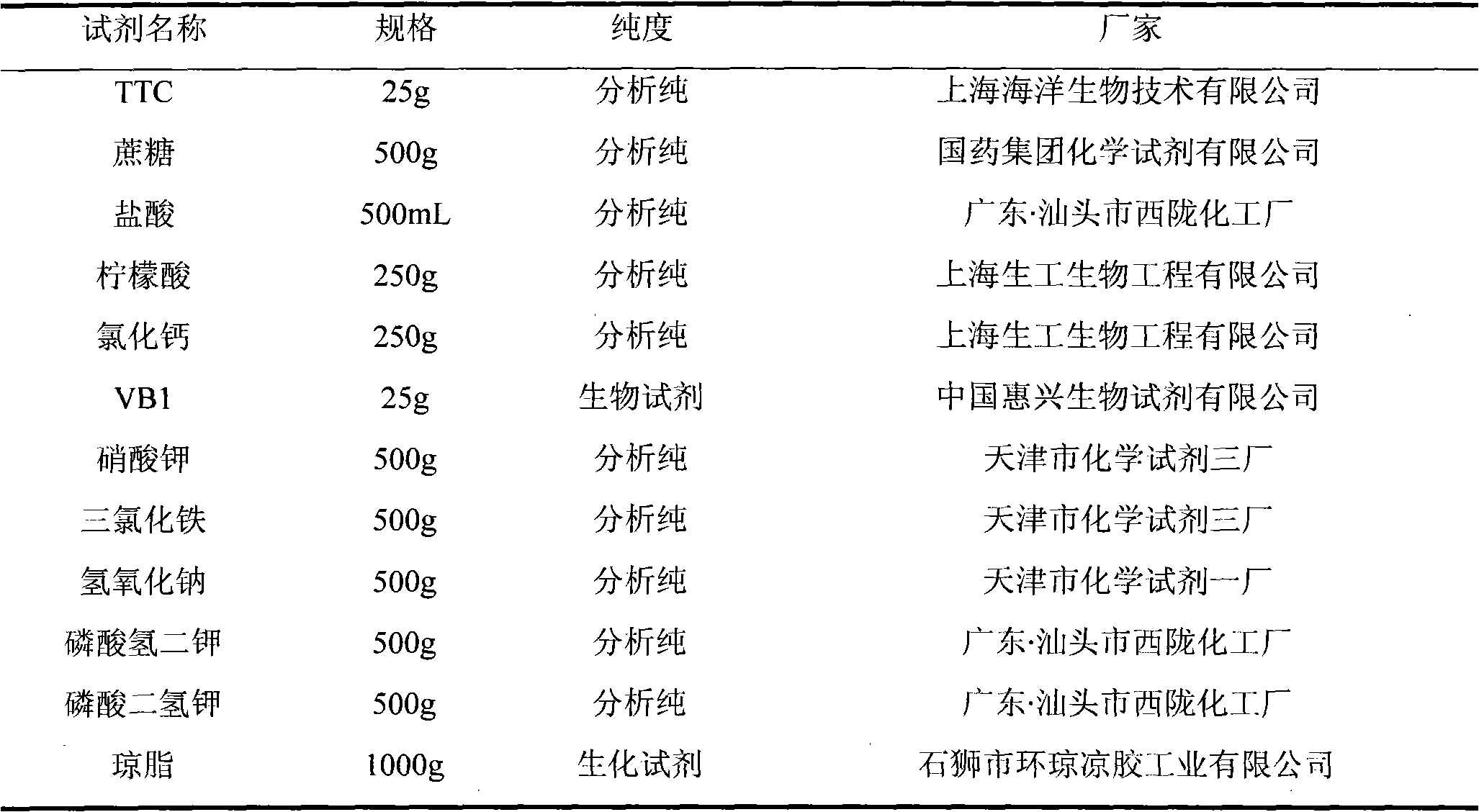
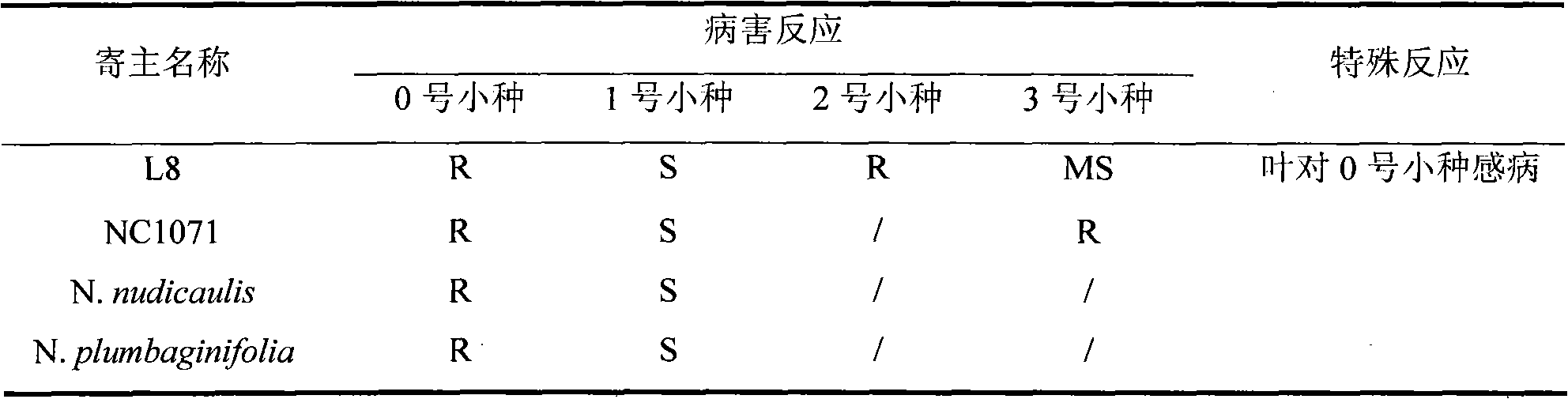
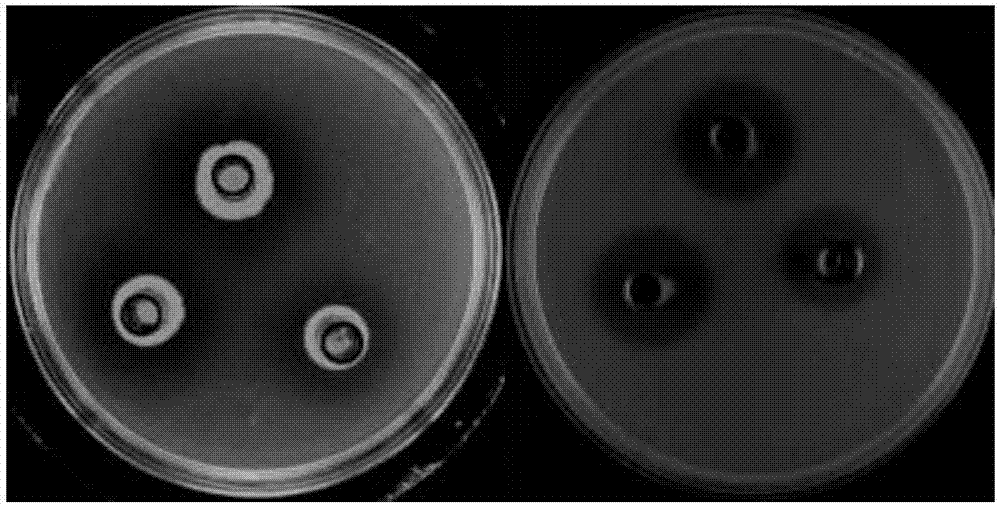
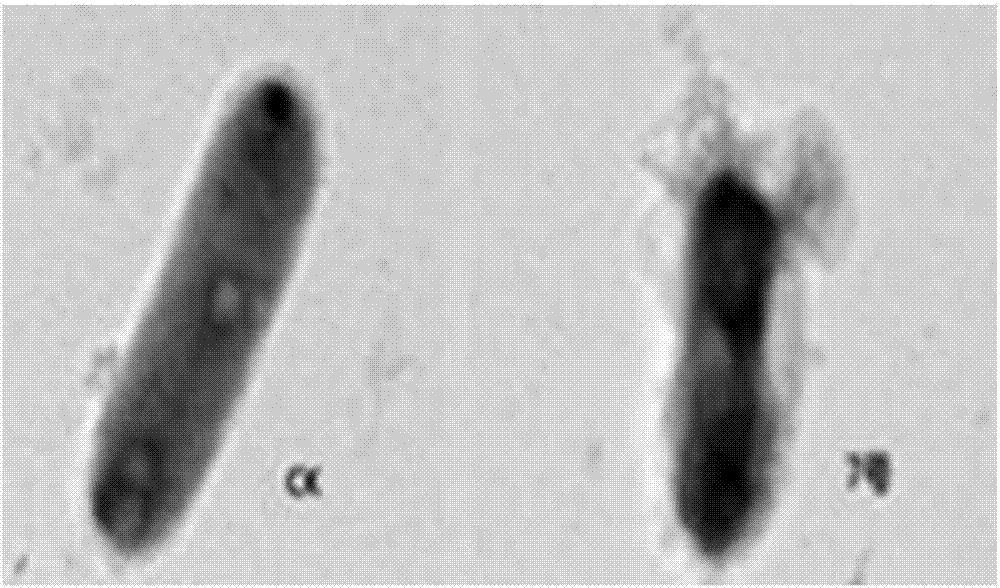
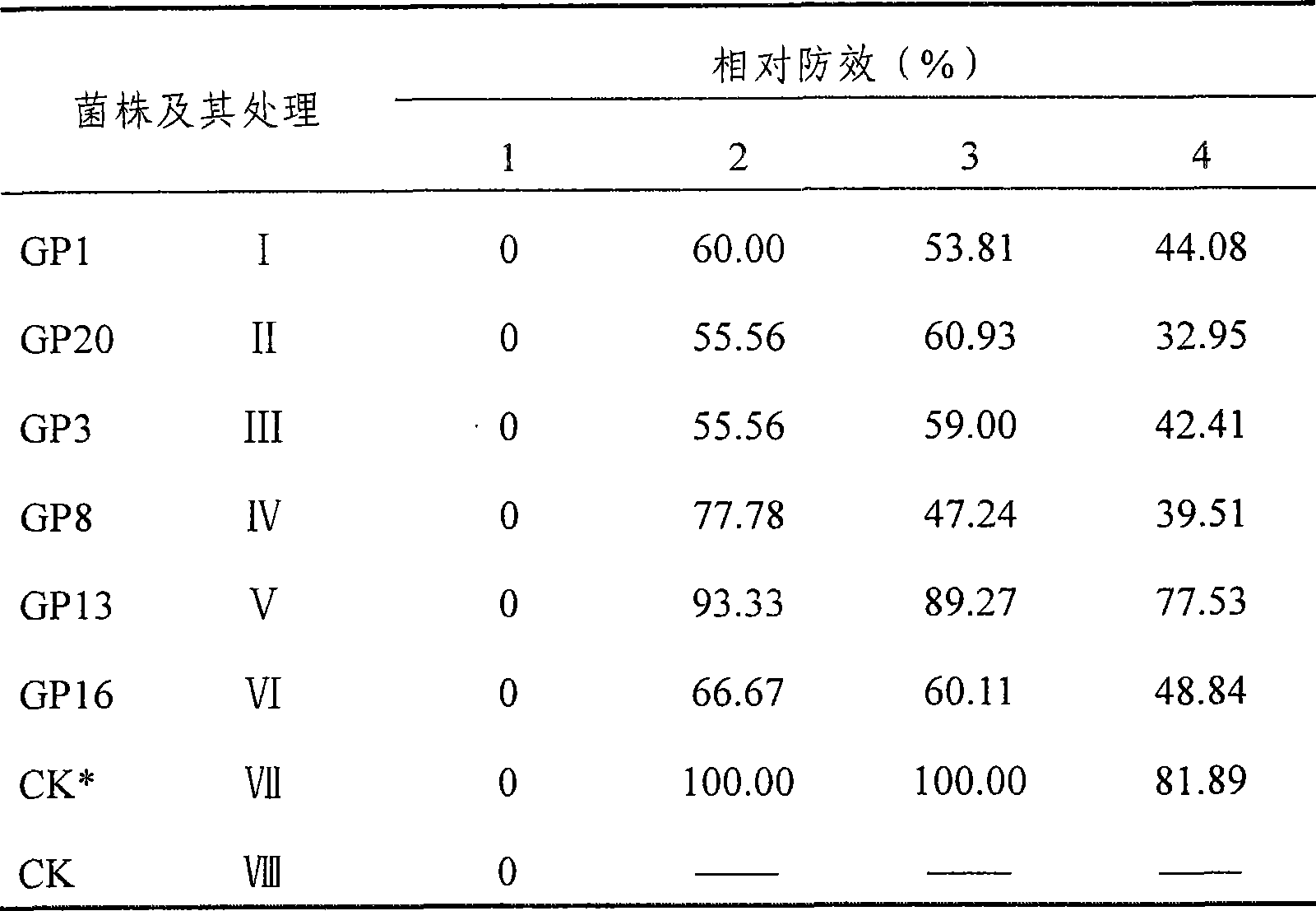
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Pityophthorus nitidulus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B011 for preventing and treating tobacco bacterial wilt and application thereof
ActiveCN104711209AGood control effectAdvantages of prevention and control effectBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumCentrifugation
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens B011 for preventing and treating tobacco bacterial wilt and an application thereof, and relates to the technical field of biological prevention and treatment of plant diseases, wherein the bacillus amyloliquefaciens B011 has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2014576; separation comprises the following steps: firstly, sampling; secondly, grinding, thirdly, centrifugation; fourth, purification, and fifthly, screening. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens B011 has the characteristics of relatively good antagonistic effect on tobacco bacterial wilt, good safety on the environment and easy industrialized production, not only can be used for preventing and treating tobacco bacterial wilt, but also can be used for preventing and treating P.parasitica, A.alternata keissler, also can be used for preventing and treating C.capsici, P.capsici, C.gloeosprioides, P.oryzae, C.cuc-umerinum and other pathogenic fungi.
Owner:湖南省烟草公司永州市公司 +2
Rapid identification method of tobacco black shank resistance
ActiveCN103081678ARapid identificationHigh test costHorticultureAgricultural sciencePityophthorus nitidulus
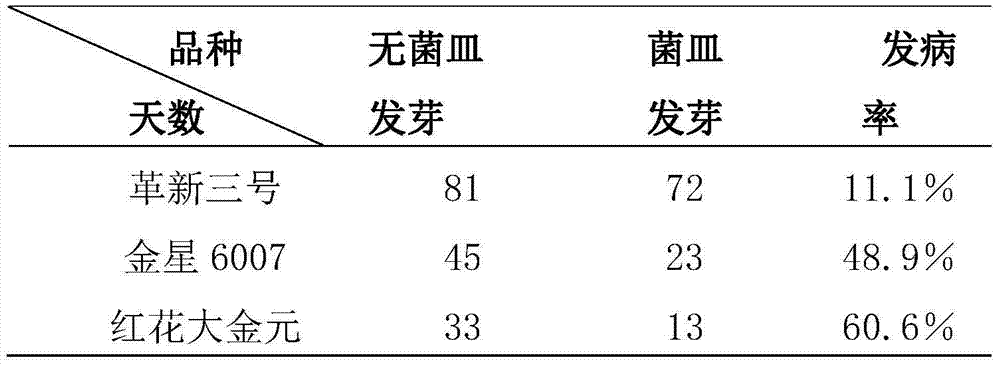
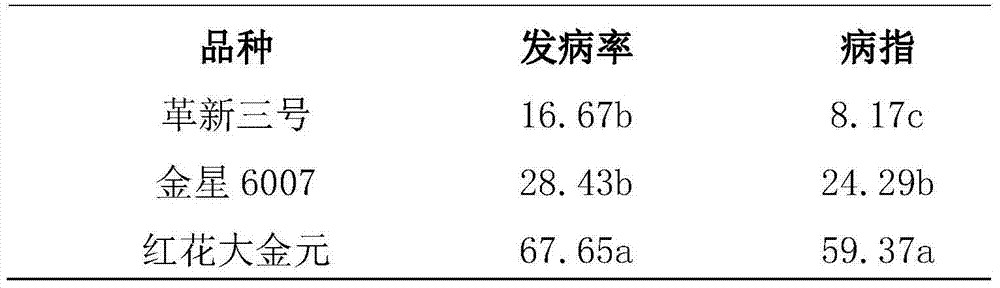
The invention discloses a rapid identification method of tobacco black shank resistance. The rapid identification method of the tobacco black shank resistance includes the following steps of (1) sterilizing the surface of tobacco seeds to be identified; (2) cultivating tobacco blank shank germs and preparing suspension liquid of conidium of the tobacco blank shank germs; (3) extracting toxin liquid of the tobacco blank shank germs; (4) germinating the seeds after soaking seed in the toxin liquid and calculating rate of emergence of the seeds and evaluating the resistance. The rapid identification method of the tobacco black shank resistance is easy to operate, low in cost, rapid, high in accuracy, and appropriate for black shank resistance identification in tobacco breeding research.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Physiological race identification method of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in disease nursery
InactiveCN101671720AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
A physiological race identification method of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in disease nursery can identify the physiological race of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in disease nursery as soon as possible by means of combining the identification of disease-resistant reaction of host in fields and collection of color change of strains on a TTC solid culture medium flat plate, realize the identification of the physiological race type of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in the existing disease nursery, then directionally carry out the researches such as tobacco disease-resistant germplasm resources screening, breeding of new variety of tobacco and the like, and provide basis for the comprehensive prevention and treatment of tobacco phytophthora parasitica and the establishment of the targetof breeding for disease resistance. The method is economical and practical and has favorable market application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis CLP-7, and applications thereof
The invention discloses an acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 which is capable of preventing diseases and promoting growth, and can be used for biocontrol. The acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, on 27th, October, 2016, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13204. The antibacterial spectrum of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is relatively large; the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of inhibiting growth of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, Ralstonia solanacearum, and Alternaria alternata Keissler; the antagonistic activity under acidic conditions is high, the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of producing siderophore, possesses protease and glucanase activity, and potassium releasing capacity. The results of biocontrol pot experiment show that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of preventing under acidic soil conditions, and promoting growth and chlorophyll synthesis of tobacco seedlings in acidic soil, so that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 and microorganism bacterium agents of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 can be used for preventing tobacco fungi and bacterial root and stem diseases under continuous cropping or acidic soil conditions effectively, and is high in application value.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Method for detecting phytophthora parasitica in soil
InactiveCN102399896AReduce the impactShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementNicotiana tabacumQuarantine
The invention belongs to the field of plant disease and pest quarantine, and provides a method for detecting phytophthora parasitica in soil. According to the method for DNA extraction and molecular detection of the phytophthora parasitica in the soil, the conventional isolating culture method is eliminated, and the detection period is greatly shortened; compared with a common polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection method, the method has the advantages that: a subsequent treatment process is not needed, and a result can be monitored in real time; primers are designed on the basis of a changeful area of pathogen ITS, and corresponding bands are not produced when similar species are amplified; the method is high in specificity and suitable for fluorescent quantitative PCR conditions; because 2 percent of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) is added into the total DNA extraction buffer solution of the soil, the pollution of partial impurities in the soil is effectively removed, the influence of the impurities on the PCR effect is reduced, and the detection sensitivity of fluorescent quantitative PCR is improved; meanwhile, the fluorescent quantitative PCR system and the reaction conditions are obtained according to the size study conditions of the designed primers, so the detection sensitivity is high and can reach 2fg / mu l.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Method for rapidly identifying black shank resistance of tobaccos
InactiveCN104745672ARapid identificationEasy to breedFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseAnimal science
The invention belongs to the field of crop disease resistance identification and especially a method for rapidly identifying the black shank resistance of tobaccos. The method for rapidly identifying the black shank resistance of the tobaccos is capable of effectively overcoming the defects of exiting identification, and comprises the following steps: step 1, culturing tobacco black shank bacteria; step 2, taking tobacco seeds to be tested and sterilizing the surface; and step 3, performing germination rate and morbidity statistics and performing disease resistance evaluation. The method is capable of saving manpower and material resources and also greatly reducing the identification time; the resistance level to the black shank is not limited by the growth seasons; besides, the method is simple in identification operation steps and relatively low in test room requirement conditions; according to the method, the purpose of rapidly identifying the black shank resistance of the tobaccos at low cost and high flux is achieved; the method is suitable for identifying the black shank resistance of a large batch of germplasm materials in tobacco breeding study; and as a result, the anti-disease germplasm resource screening, the resistance hereditary character study and the anti-disease variety breeding and popularization / application can be accelerated.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
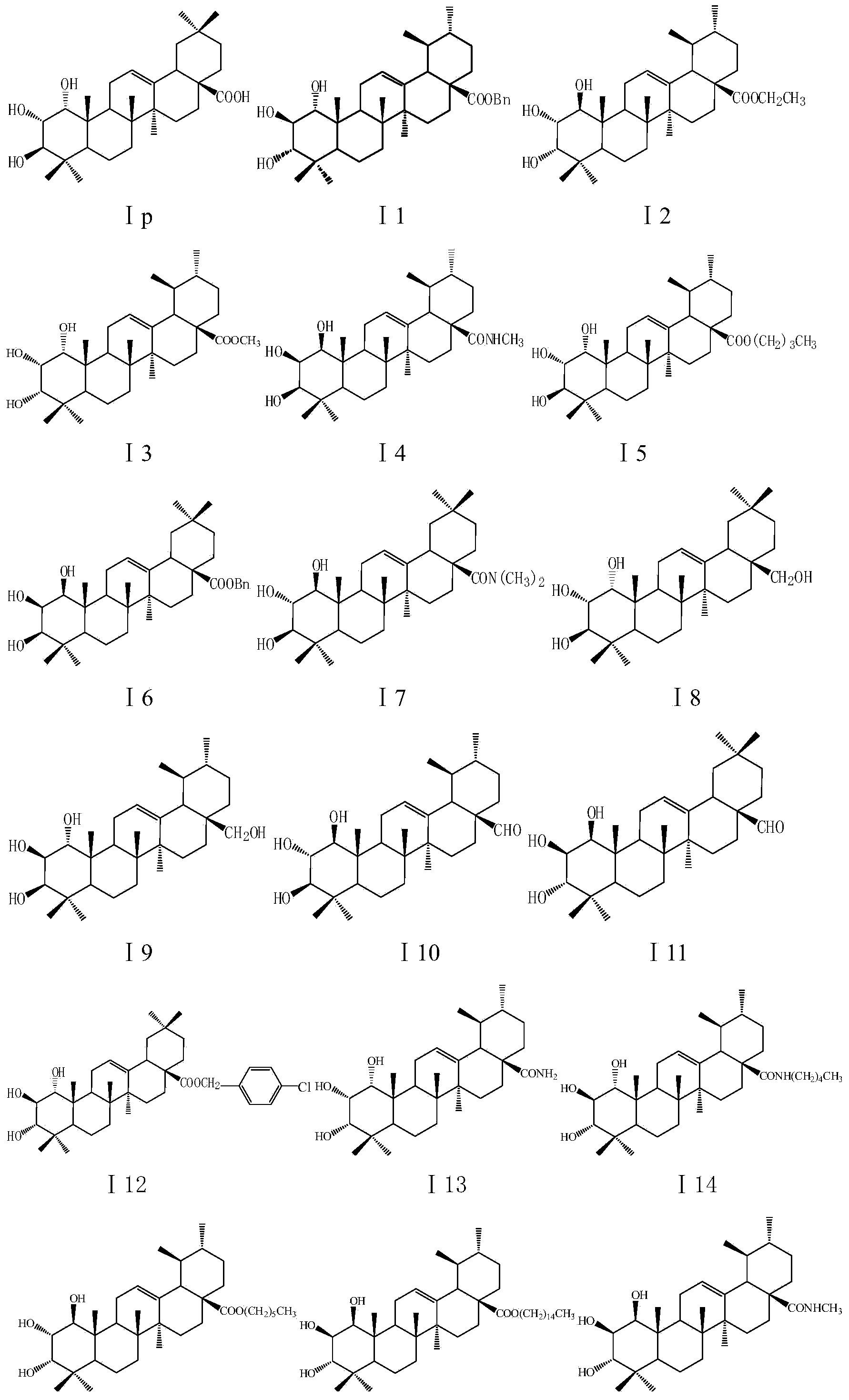
Application of A-ring trihydroxyl substituted pentacyclic triterpene compound to pharmacy
ActiveCN103919784AStrong inhibitory activityGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsBiocidePhytophthora sp.Tobacco mosaic virus
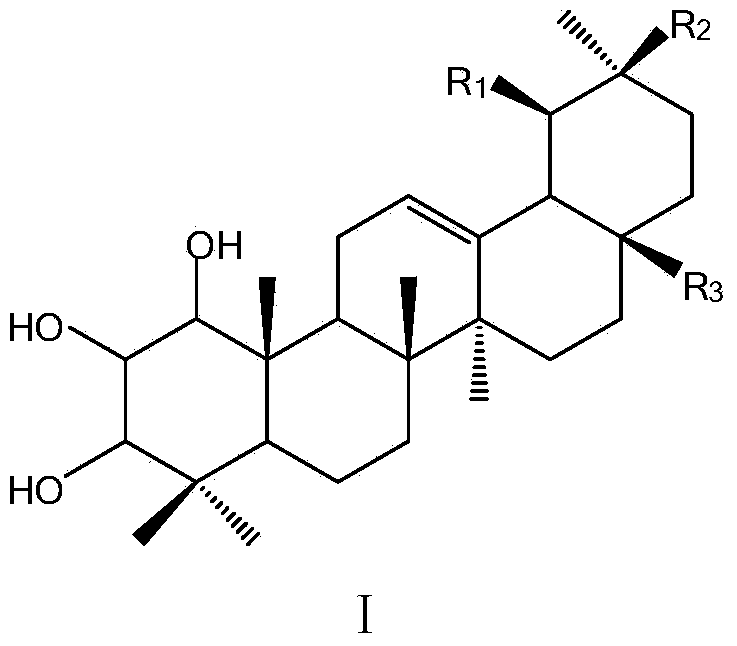
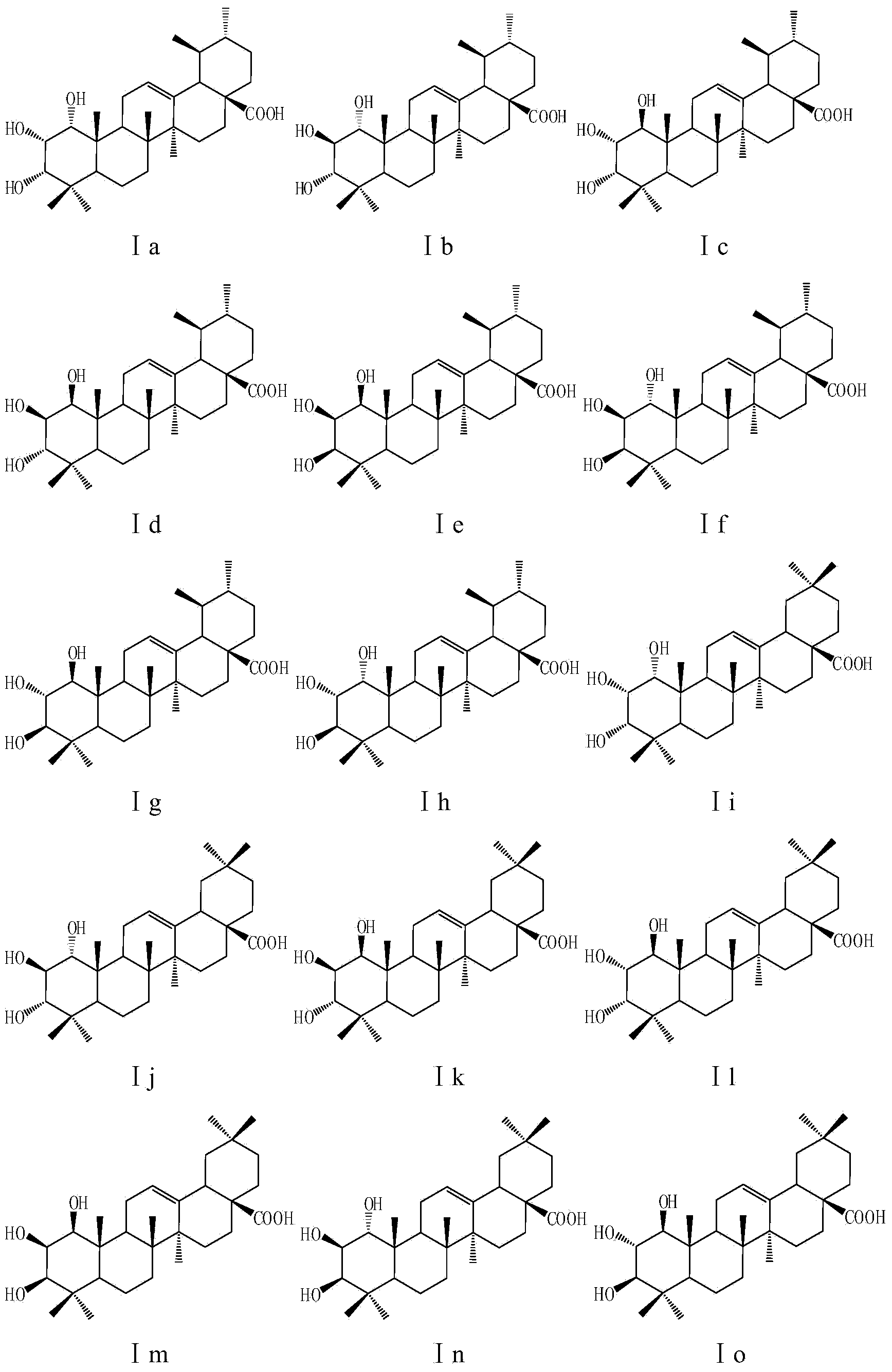
The invention discloses an application of an A-ring trihydroxyl substituted pentacyclic triterpene compound to preparation of an antibacterial or anti-tobacco mosaic virus drug. The general formula of the compound is as shown in the specification, wherein hydroxyls of C1, C2 and C3 are respectively in alpha configuration or beta configuration; R1 and R2 are selected from hydrogen or methyl and are different from each other; R3 is selected from -COOH, -CH2OH, -CHO, -COOR1, -CONH2, -CONHR1 and -CONR1R2; R1 and R2 are selected from alkyl containing 1-15 carbon atoms, substituted or unsubstituted phenyl and substituted or unsubstituted phenyl alkyl; and the substituent group is selected from halogen, hydroxyl, cyan, amino, nitryl, sulfydryl or phenyl, acyl, aryl, alkoxy and alkyl containing 1-15 carbon atoms. The compounds have antibacterial or anti-tobacco mosaic virus activity, have extremely high bacteriostatic activity especially to gram positive bacteria, phytophthora nicotiana and tobacco mosaic virus, and have a good application prospect in fields of medicines and pesticides.
Owner:THE KEY LAB OF CHEM FOR NATURAL PROD OF GUIZHOU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Pseudomonas aeruginosa XCS007 and application thereof to prevention and control of tobacco black shank
ActiveCN107099467AHigh antagonistic activityProduce efficientlyBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumChitinase
The invention provides pseudomonas aeruginosa XCS007. A category name is Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the pseudomonas aeruginosa XCS007 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), wherein the preservation date is on April 5, 2016, the address is #3, No. 1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 12330. The pseudomonas aeruginosa XCS007 can be used for efficiently producing chitinase and the maximum activity reaches 12.25U / mL; the pseudomonas aeruginosa XCS007 has a good antagonistic effect on the tobacco black shank: the inhibition rate of bacterium liquid and bacterium liquid crude extract on hyphae of the tobacco black shank reaches 91 percent or more. The pseudomonas aeruginosa XCS007 has a good biological control effect: the prevention and control effect of the bacterium liquid and the bacterium liquid crude extract on tobacco plants inoculated with tobacco black shank pathogenic bacteria can reach 80 percent or more. The pseudomonas aeruginosa XCS007 is used for biological control, is environmentally friendly, does not easily generate drug resistance and is safe to human and livestock, so that conditions for green prevention and control development of tobaccos are created.
Owner:中国烟草总公司海南省公司 +2
Trichoderma asperellum TD3104 and application thereof in preparation of microbial agent for inhibiting plant pathogenic bacteria
The invention provides Trichoderma asperellum TD3104 and application thereof in preparation of microbial agent for inhibiting plant pathogenic bacteria. The preservation number of the Trichoderma asperellum TD3104 is CGMCC 13161. The invention further provides application of the Trichoderma asperellum in the controlling of the plant pathogenic bacteria of tobacco and apples. The antagonistic Trichoderma asperellum can effectively inhibit the growth of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, ralstonia solannacearum, rhizoctonia solani, tobacco root rot pathogenic fusarium, alternaria alternata and the pathogenic bacteria of apple rot and apple ring rot, can effectively control related diseases, can reduce the use amount of chemical pesticides and accumulation of the chemical pesticides in soil, is beneficial to the increasing of quality and yield of the economic crops of China and is evident in economic and social benefits.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
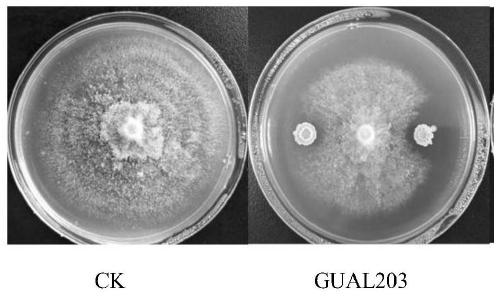
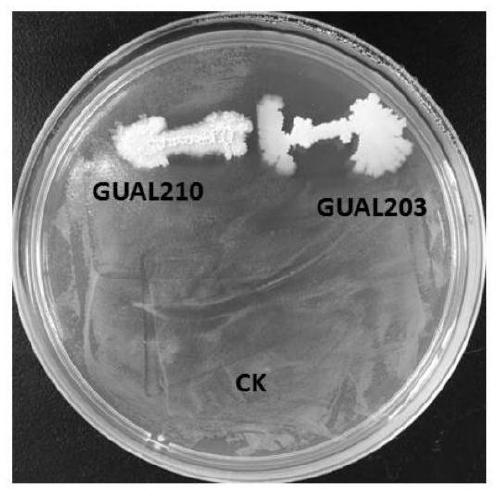
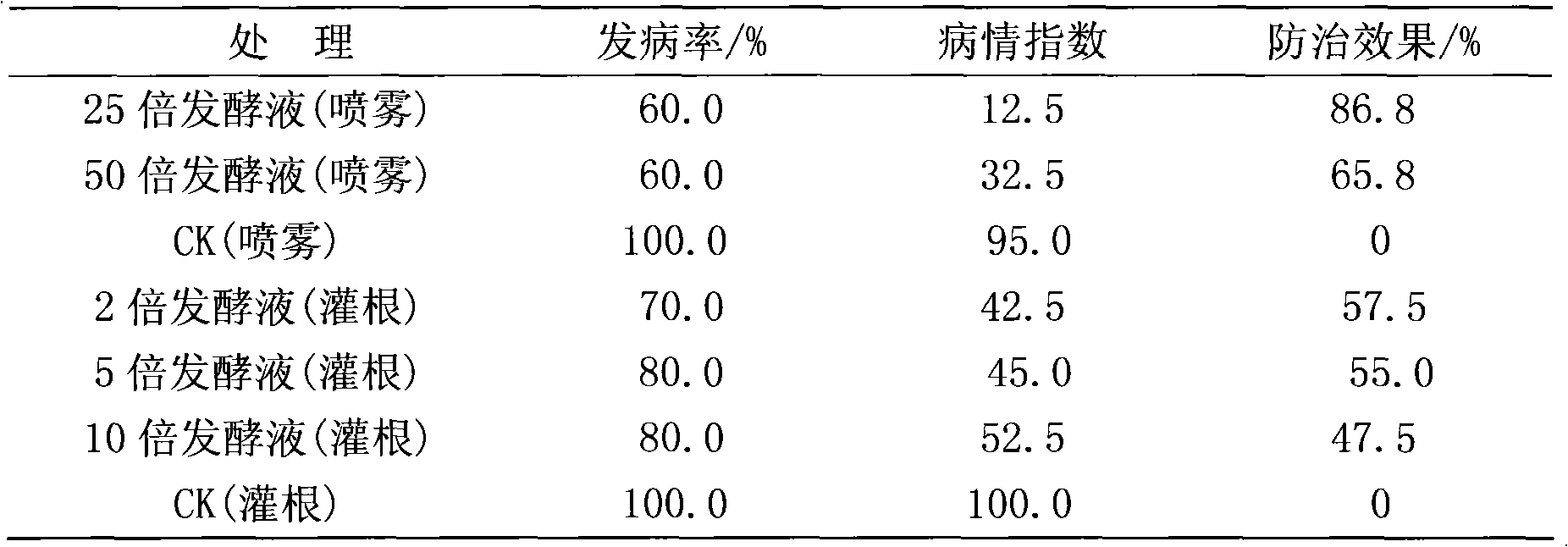
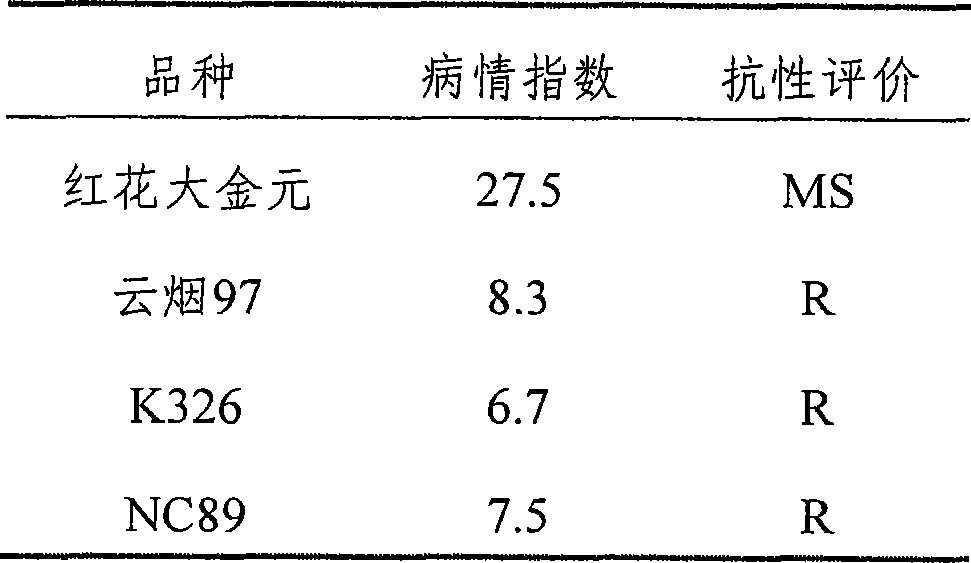
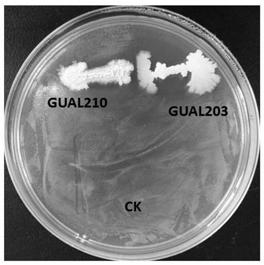
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL203 and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL203 preserved at the China Center for Type Culture Collection under the accession number CCTCC NO: M 2018870. The invention also discloses an application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL203 in simultaneously controlling tobacco black shank and tobacco bacterial wilt. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL203 has the obvious capability ofsimultaneously antagonizing tobacco black shank germs and tobacco bacterial wilt germs and the capability of antagonizing pepper anthracnose.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Streptomyces strain for inhibiting harm of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae and application thereof
Aiming at the existing defects in preventing and controlling black shank of tobacco, the invention provides Streptomyces misawanensis D35 for inhibiting Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. The strain was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre (CGMCC) on August 27, 2009 with the collection number of CGMCC No: 3250. The invention also provides application of the strain in effectively inhibiting diffusion of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae in tobacco, reducing disease incidence, improving the tobacco yield and quality, facilitating the development of biological prevention and control products and further promoting the safe control of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae.
Owner:周倩
Preparation method of tobacco black shank inoculum
InactiveCN101381685AReduce incubation timeSmall particlesFungiMicroorganism based processesPityophthorus nitidulusMoisture
The invention discloses a method for preparing tobacco black shank bacterium inoculum. The method comprises the following steps: culturing tobacco black shank bacteria sclertium at constant temperature of 28 DEG C for 5 to 6 days; placing the culture in a fluid nutrient medium for 7 to 8 days at constant temperature of 28 DEG C at 150 revolutions / minute; placing the fluid bacterium solution in a solid medium for 10 to 12 days at constant temperature of 28 DEG C, according to the volume ratio of between 3 and 5 percent; crushing the qualified solid culture into the sclertium; evenly mixing the scertium with rough rice bran and rough wheat bran; spreading the mixture for ventilating and drying, thereby obtaining the required tobacco black shank bacterium inoculum after the moisture is reduced to 35 to 40 percent. By the technology, the culture period can be shortened by 10 to 15 days, and the inoculum obtained by culturing can be easily dispersed with large number of effective infections, so the method has the potential of expanding culture, and has few polluting sundry bacteria. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation and low cost, and has good application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Actinomycetes having Phytophthora melonis inhibition effect, and screening method thereof
InactiveCN104862243ANon-pathogenicSignificant development potentialBiocideBacteriaSnow moldScreening method
The present invention discloses actinomycetes having a Phytophthora melonis inhibition effect, and a screening method thereof, wherein the actinomycetes are a Streptomyces virginiae X54 strain with a preservation number of CGMCC No.10042, and are preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. According to the present invention, the actinomycetes do not produce pathogenicity to humans and animals, are antagonistic actinomycetes capable of preventing and controlling Phytophthora melonis in a safe, non-toxic and effective manner, provide a certain inhibition effect for hot pepper anthracnose bacteria, tobacco black shank bacteria, rice sheath blight disease bacteria, wheat scab bacteria, citrus anthracnose bacteria, and cucumber fusarium wilt bacteria, and especially provide great development potential in prevention and control of cucumber blight.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Aspergillus niger strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a strain of Aspergillus niger Ty-3 and application thereof. The strain has been deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on July 8, 2011 with the accession number of CCTCC NO.: M 2011241. The mycelia of the strain can adhere to and wind around the mycelia of tobacco black shank and parasitize on the mycelia of tobacco black shank and grow; through long time parasitic growth, the mycelia of the strain can kill and decompose pathogens, thereby exerting a strong inhibitory effect on the growth of pathogens. The Aspergillus niger strain is applicable to preparation of bactericides used for controlling tobacco diseases.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Method of control Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae Resistance to Metalaxyl
InactiveCN101032255AReasonable crop rotationScientific ridgingBiocideFungicidesMetalaxylNicotiana tabacum
The present invention relates to method of tackling Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae with resistance on metalaxyl, and belongs to the field of plant protection and agricultural chemical technology. The present invention screens out two kinds of germicides, including Junke and Xiuan, with negative cross resistance to metalaxyl for applying alternately to prevent and control Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae with resistance on metalaxyl. The present invention has simple operation, high effect, reduced agricultural chemical residue, raised tobacco safety and other advantages.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Brevibacillus choshinensis X23 and application thereof
InactiveCN102154175AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntagonisticBiocideBacteriaBrevibacillus choshinensisNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides a set of production technology for preventing ralstonia solanacearum from growing and reproducing in solanaceae crops to increase crop yield by aiming at the defects of the prior art for controlling the damages of the ralstonia solanacearum to the crops. Brevibacillus choshinensis X23 has a wide bacteriostatic spectrum and good environmental safety and has antagonism effects to various pathogenic fungi, such as phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae, pyricularia grisea, alternaria alternate, phytophthora infestans and the like, so that the brevibacillus choshinensis X23 has favorable development prospect and application potential.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method of cloning Phytophthora parasitica effector
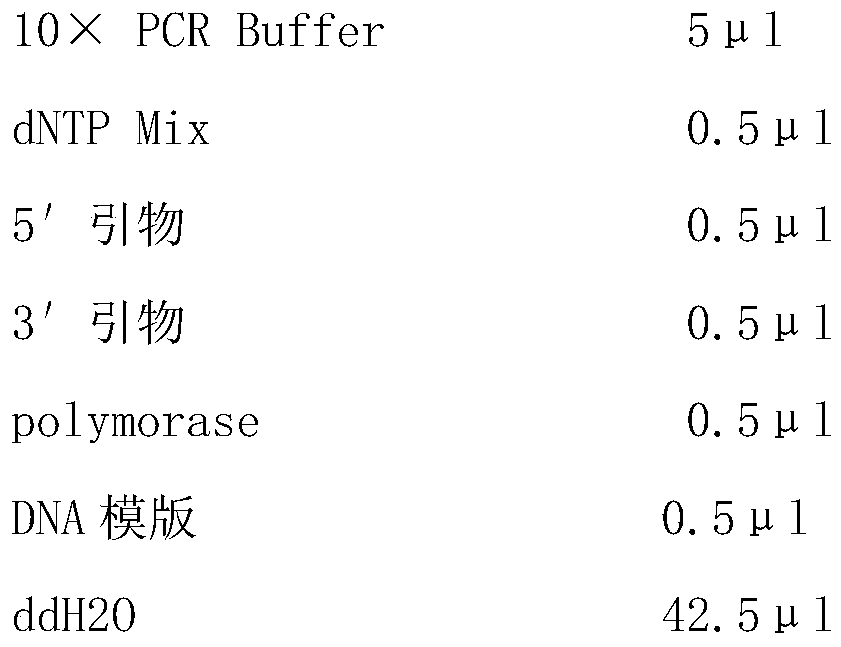
The invention discloses a method of cloning Phytophthora parasitica effector. The method comprises: designing primers; extracting Phytophthora parasitica genome DNA; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on tobacco Phytophthora parasitica effector gene; recycling and purifying the PCR product; preparing Escherichia coli DH5lapha competence; linking the amplification product withpMDTM 19-T Vector, and converting Escherichia coli DH5alpha; converting Escherichia coli; screening a positive clone, and performing PCR identification on a bacterial liquid; subjecting the screenedpositive clone to sequencing identification to obtain the Phytophthora parasitica effector. The method has the advantages that the Phytophthora parasitica effector is cloned and its functionality is analyzed.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Eugenol aqueous emulsion, preparation method thereof and application thereof in controlling mycosis of tobacco
ActiveCN106538530ASimple processing technologyEasy to useBiocideDead animal preservationEmulsionPityophthorus nitidulus
The invention provides a eugenol aqueous emulsion, comprising the following components in mass contents: 20-30% of eugenol, 1-5% of an emulsifying agent, 0.1-0.3% of a thickening agent, 3-5% of an antifreezing agent, 0.1-0.5% of a defoamer and the balance of water. The invention also provides application of the eugenol aqueous emulsion in controlling mycosis of tobacco. The inhibition rate of the eugenol aqueous emulsion provided by the invention on black shank of tobacco is 52.56%-97.44%, and the inhibition rate of the eugenol aqueous emulsion on brown spot of tobacco is 35.82%-65.67%, showing that the eugenol aqueous emulsion can effectively control black shank of tobacco and brown spot of tobacco. The eugenol is biological source pesticide, easily degrades in the environment and has the characteristic of environmental friendliness, and simultaneously the prepared preparation aqueous emulsion is an environment-friendly form, thereby greatly reducing chemical injury to crops and further improving the safety of agricultural products.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Screening method of biocontrol bacteria and dosage for tobacco black shank
InactiveCN102277408AAvoid missingAvoid screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for screening biocontrol bacteria and dosage thereof against tobacco black shank. The method comprises the following steps: a. cultivating sterile tobacco seedlings on filter paper in a petri dish; b. on the basis of step a , add bacterial culture solution with biocontrol potential in the petri dish; c, after the tobacco seedlings and the bacterial suspension with biocontrol potential are cultivated together for 24 hours, add the zoospore suspension of tobacco black shank bacteria to the petri dish d, on the basis of step c, give the tobacco seedlings normal growth conditions, detect the control effect of the bacteria with biocontrol potential added by observing the morbidity of the tobacco seedlings after 7 days, and screen out the biocontrol that can prevent and treat tobacco black shank bacteria. Compared with the traditional method, the present invention has many advantages. It is simple, fast, less workload, high efficiency, accurate and reliable screening result, and can screen bacteria with bio-control function from a large number of unknown bacteria in a short period of time.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI INST
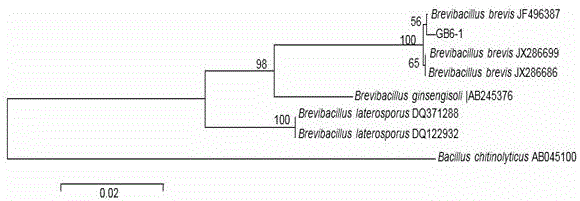
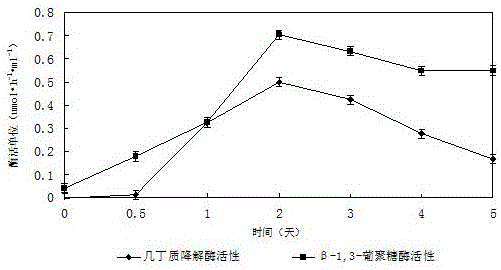
Brevibacillus brevis for preventing and controlling tobacco black shank and application thereof
InactiveCN105132334AEnhanced inhibitory effectGreat application potentialBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumChitinase
The invention provides brevibacillus brevis for preventing and controlling tobacco black shank and application thereof and belongs to the fields of microorganisms and microorganism application. According to the classification and naming, 16S rRNA sequence (1031bp) of B. brevis GB6-1 of the brevibacillus brevis is already uploaded to a GenBank database (serial number: KP 715564) of the NCBI and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the preservation number of the brevibacillus brevis is CGMCC No.11135. A lot of biological experiments prove that the brevibacillus brevis has the characteristics of efficiently secreting chitinase and Beta-1,3-glucosanase and has the obvious inhabiting effect on the tobacco black shank.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +2
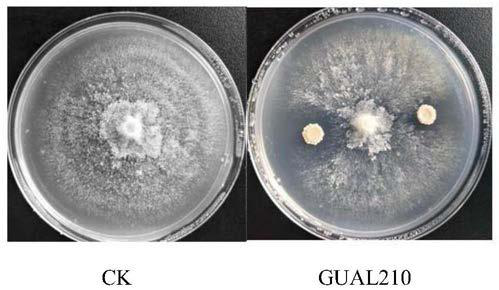
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210 and application thereof
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210, which is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2018871. The invention furtherdiscloses application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210 to simultaneous control of tobacco black shank and tobacco bacterial wilt. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens GUAL210 has an obvious ability of antagonizing both phytophthora nicotianae and ralatonia solanacearum simultaneously and the ability of antagonizing pepper anthracnose.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method for identifying phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains
PendingCN105177104ARapid identificationRace rapidMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for identifying phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains, and belongs to the technical field of plant pathogen identification. According to the method, a tissue culture vessel method is used for identifying the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains; the environment conditions of culture and impregnation are more stable; the growth of tobacco pathogens is favorably accelerated; the seedling culture period and the dip dyeing period are greatly shortened; meanwhile, the interference of infectious microbes and other physiological strains on the identification result can also be avoided; the flux is high; labor and materials can be saved to the greatest degree; the high-flux, fast and accurate identification on the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains is realized. Compared with a land method and a greenhouse method, the method has the advantages that the identification is fast; the result is more accurate, stable and reliable; higher application values are realized; meanwhile, a thought can also be provided for the identification of physiological strains of other disease pathogenic bacteria of tobaccos.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 327 and application thereof
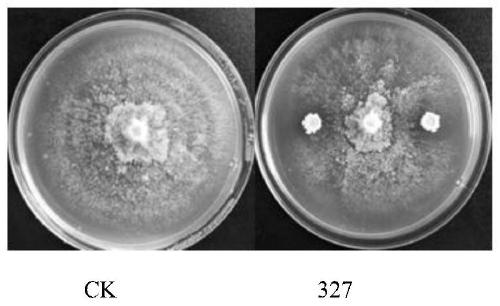
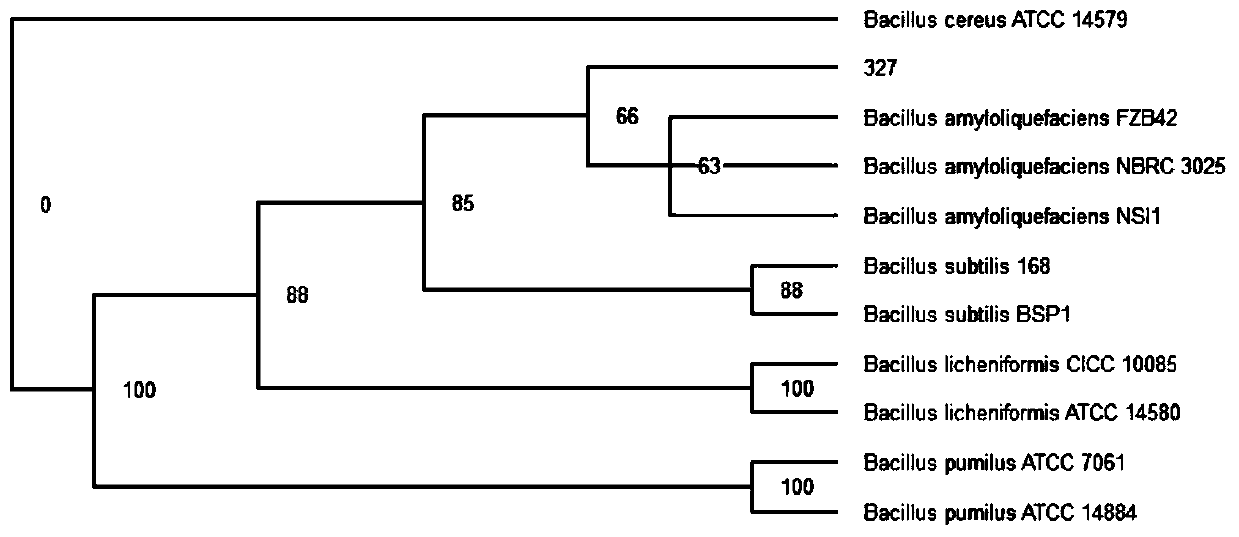
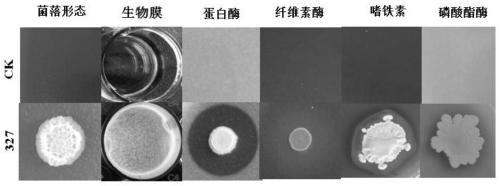
PendingCN109852564ASignificantly antagonize tobacco black shank pathogen (Phytophthoranicotianae)Ability to manifest Raltonia solanacearumBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens 327. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens 327 is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2019045. The invention also discloses an application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens 327 to prevention and treatment of tobacco black shank. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens 327 disclosed by the inventionhas obvious capacity for antagonizing the tobacco black shank bacteria, and the capacity for antagonizing pepper anthracnose.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO CORP QIANXINAN CORP +1
(Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1 and application of (Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1
InactiveCN102533566AGrowth inhibitionEffective controlBiocideFungiPityophthorus nitidulusAspergillus
The invention relates to (Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1 screened out from in-situ soil and application of the (Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1. The depositary institution of the (Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1 is China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the depositary date of the (Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1 is October 16, 2011, and the depositary number of the (Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1 is CCTCC M 2011353. According to the invention, the hyphae of (Aspergillus fumigates)Ty-1 can be attached and wound on the hyphae of tobacco black shanks, and the hyphae of pathogenic bacteria are finally decomposed because the protoplasm of the hyphae of the pathogenic bacteria is concentrated and vacuolated and collapses. The cell wall of the attached and wound host hyphae body is adhered by a sucker of the host hyphae body and grows through sucking nutritive substances in the host hyphae body by using the sucker, so that the strong inhibition on the growth of the pathogenic bacteria is generated.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
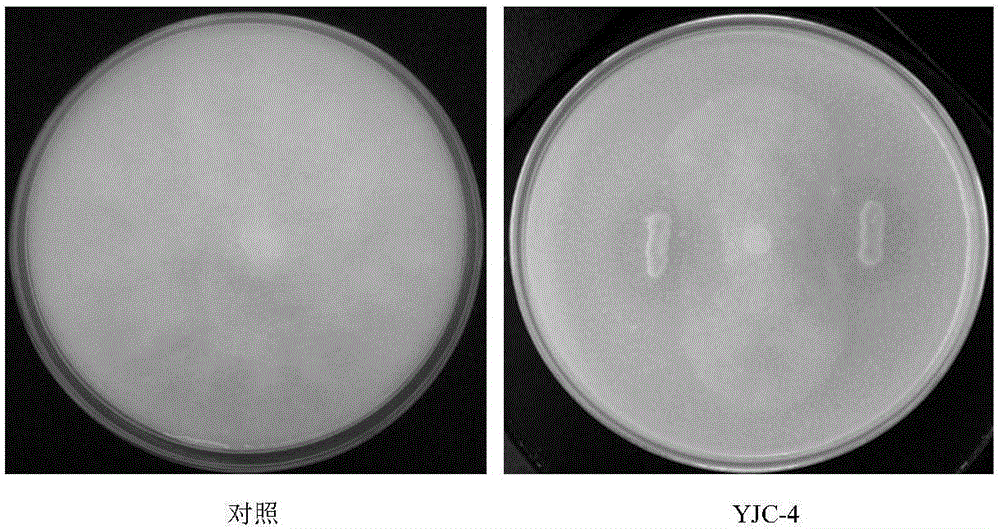
Bacillus safensis YJC-4 and application thereof to prevention and control of tobacco black shank and growth promotion
ActiveCN106635926AHigh antagonistic activityGood biological control effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsNicotiana tabacumGrowth promoting
The invention provides bacillus safensis YJC-4. The class name is bacillus safensis and the bacillus safensis YJC-4 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC); the preservation date is April 15, 2016, the preservation address is #3, No.1 Yard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.12356. The strain has the following advantages that (1) the bio-control effect is good; in a pot culture experiment, YJC-4 bacterium liquid is used for treating tobacco plants inoculated with tobacco black shank bacteria and the prevention and control effect reaches 81.59 percent and is remarkably better than that of 58 percent metalaxyl.mancozeb and a biological preparation, namely bacillus subtilis; the bacillus safensis YJC-4 has a potential application value in the aspect of biological prevention and control of the tobacco black shank and has good development and application prospects; the biological prevention and control is environment-friendly, does not easily have drug resistance and is safe to people and livestock, and conditions are created for green and prevention and control development of tobaccos; (2) the growth promoting effect is good; the biological amount and agronomic characters of YJC-4 bacterium liquid tobacco plants are remarkably promoted and the promoting effect is remarkably different from a control group.
Owner:中国烟草总公司海南省公司 +3
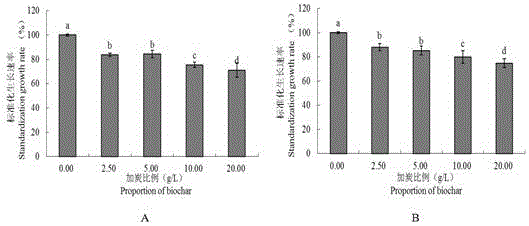
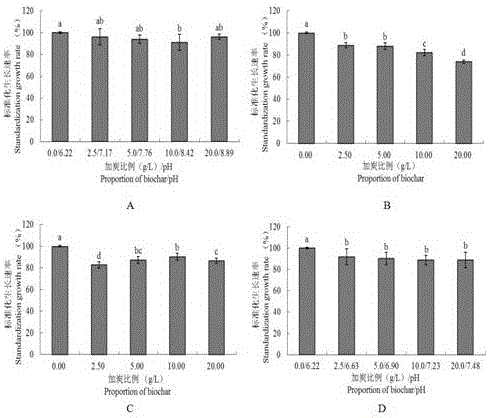
Method of utilizing biomass charcoal to inhibit phytophthora nicotianae
InactiveCN106577049AEnhanced inhibitory effectSimple methodBiocideFungicidesNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
The invention discloses a method of utilizing biomass charcoal to inhibit phytophthora nicotianae. The method includes the following steps: firstly, configuring and adding a biomass charcoal medium; secondly, adjusting pH with the added biomass charcoal medium to be original pH of the medium; and thirdly, configuring bacteria soil. The method is simple, is convenient to use, and has a great effect to inhibit phytophthora nicotianae. Two types of biomass charcoal different in proportion are added separately or added together to an oat medium, the influence of biomass charcoal on phytophthora nicotianae is determined through determination of relevant indexes, and relevant experiments are designed to conduct mechanism verification on the basis of the property of biomass charcoal. Brown soil is selected and rice husk charcoal with different proportions is added in a potted condition to verify an effect of biomass charcoal on phytophthora nicotianae prevention. Therefore, theoretical bases are provided for reasonable applications of biomass charcoal and related research and comprehensive control and treatment of phytophthora nicotianae.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Simple and convenient separation method for phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae
InactiveCN101914454AHigh purityMaintain wild-type propertiesFungiMicroorganism based processesDiseased plantMicroorganism
The invention provides a simple and convenient separation method for phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae. By the method, a clean working environment is built by using simple equipment and spatial conditions so as to fast separate the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting and collecting diseased or infected plants; (2) purifying working environment; (3) separating germs; and (4) culturing the germs at room temperature; and the like. Namely, the method comprises the following steps of: building the clean working environment under simple conditions; sterilizing the working environment by the flame of an alcohol burner to form a sterile microenvironment; dissecting diseased or infected stems; picking up disk-shaped diseased or infected medullary slices in the diseased or infected stems with tweezers; placing the medullary slices on oat or lima bean medium plates, wherein the medium plates are sealed by sealing films, and 3 to 5 plates are arranged in a sealed culture box; and culturing the medullary slices for 3 to 5 days at room temperature to obtain target germs by colonial morphology. The method is suitable for field sampling and timely separating, uses simple equipment in the whole operation, and can separate the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae without microbiology laboratories. The separated germs have high purity and the characteristics of germ wild types.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
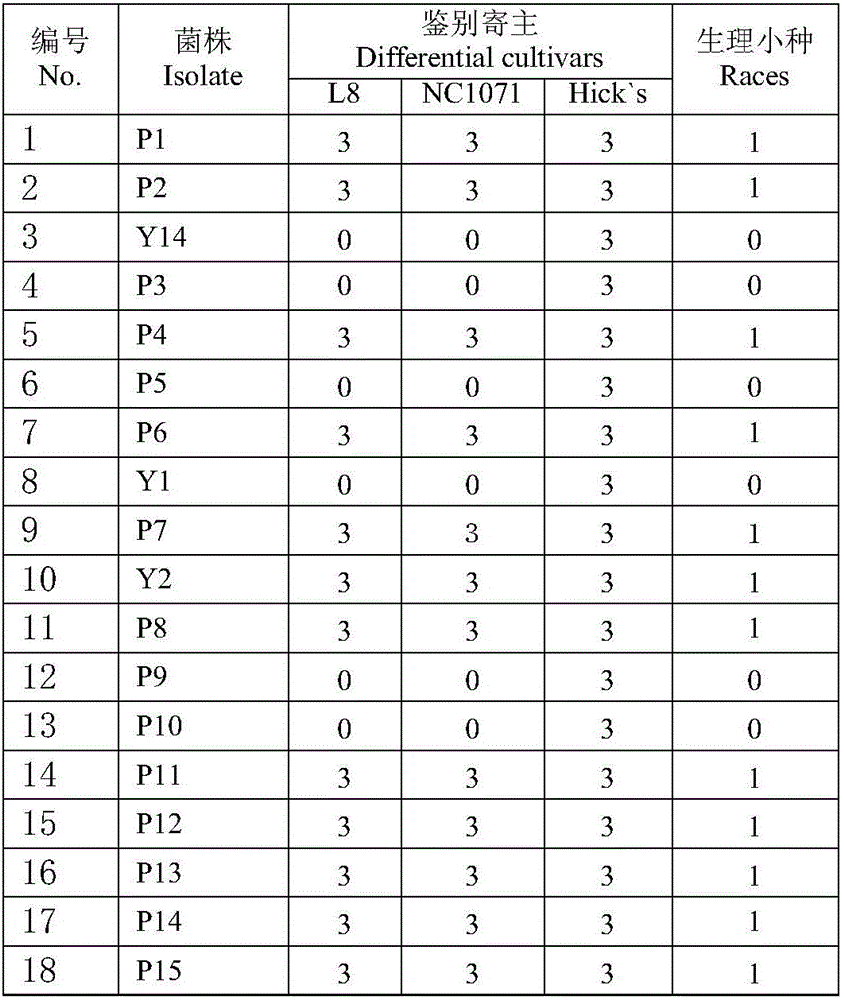
Physiologic race identification method for Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae
InactiveCN105886594ASmall footprintLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumOperability
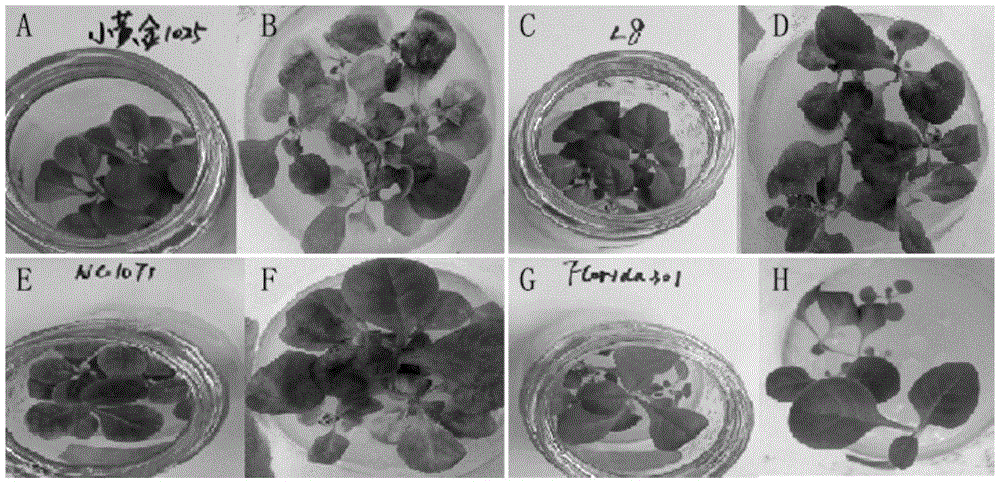
The invention relates to a physiologic race identification method for Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. Aiming at tobacco black shank which is a soil-borne disease, field pathogen infection ways are simulated. The method includes: propagating the Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae; making bacterial discs, inoculating to wheat grains subjected to moist heat sterilization, well shaking, and culturing at 26DEG C until each wheat grain is uniformly covered with hyphae; inoculating to soil with seedlings of differential hosts NC 1071, L8 and Hick's or Mini Gold 1025 in 3-5-leaf stage, wherein each seedling is inoculated with two grains; checking death count of the differential hosts 12 days after inoculation, determining that the seedlings are susceptible if more than two of three differential hosts are dead, and otherwise, determining that the seedlings are resistant; determining corresponding physiologic races according to resistance and susceptibility reaction. The method has advantages of high operability, high accuracy, high speed, simple equipment and small floor area and can be used for physiologic race identification of large-scale Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae in a greenhouse in a short time.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
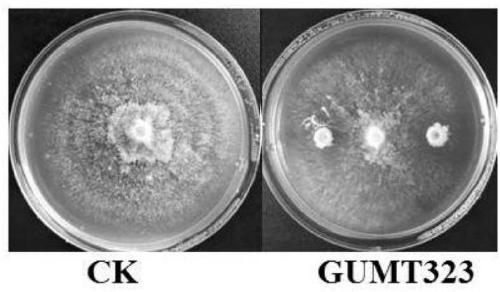
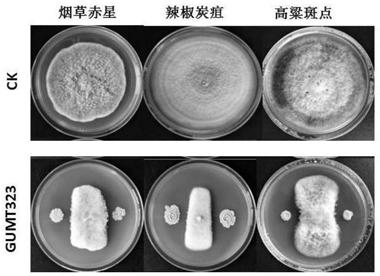
Bacillus subtilis GUMT323 and application thereof
ActiveCN109504640AAbility to significantly antagonize tobacco blackleg pathogen (Phytophthoranicotianae)BiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis GUMT323, which is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2018873. The invention further discloses application of the bacillus subtilis GUMT323 to control of tobacco black shank. The bacillus subtilis GUMT323 has an obvious ability of antagonizing both phytophthora nicotianae and the ability of antagonizing pepper anthracnose.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method of quickly identifying tobacco black shank resistance via artificial disease nursery
The invention discloses a method of quickly identifying tobacco black shank resistance via an artificial disease nursery. The method comprises steps of manufacturing a black shank inoculants bacteria valley, forming an artificial disease nursery via a layer-cake type inoculating coverage method, maintaining moisture and inducing via an intermittent way and elevating resistance. A feature of susceptibility to diseases of tobacco at a plant field crop land resettling stage and a vigorous-growing period, and biological features of tobacco black shank bacterium surviving, growing and propagating the 5cm depth surface soil are utilized, and the periphery of tobacco plant root parts are inoculated, and a layered-cake type inoculating and covering method of covering a thin layer of organic substance and a thin layer of particular soil to form the artificial disease nursery; and artificial simulation of morning-night intermittent moisture-remaining facilitates shower weather when the black shank disease often happen, and meets high-moisture and ventilating environment requirement for disease occurrence, so the disease can be effectively induced and accuracy and repeatability of tobacco black shank resistance identification can be improved. The method of quickly identifying tobacco black shank resistance via the artificial disease nursery is advantaged by simple operation, water and labor work use reduction and accurate tobacco black shank resistance phenotype identification, thereby being worthy of promotion.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com