Method for rapidly identifying black shank resistance of tobaccos
A technology for tobacco black shank disease and tobacco black shank bacteria, which is applied in the field of crop disease resistance identification, can solve the problems of relatively harsh conditions for toxin production of pathogenic bacteria, difficult to determine the concentration of toxin, limited amount of toxin extracted, and the like. The effect of accelerating the screening of disease-resistant germplasm resources, saving manpower and material resources, and shortening the identification time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A method for rapidly identifying tobacco black shank resistance, comprising the following steps:
[0023] Step 1, cultivation of tobacco black shank bacteria:
[0024] Tobacco black shank race No. 0; inoculated on oat medium and cultured at 28°C for 7 to 10 days. After the mycelia covered the entire dish, use an inoculation loop to remove the mycelia attached to the surface of the dish and leave the bacteria ready for use;
[0025] Step 2: Disinfect the surface of the tobacco seeds to be tested:
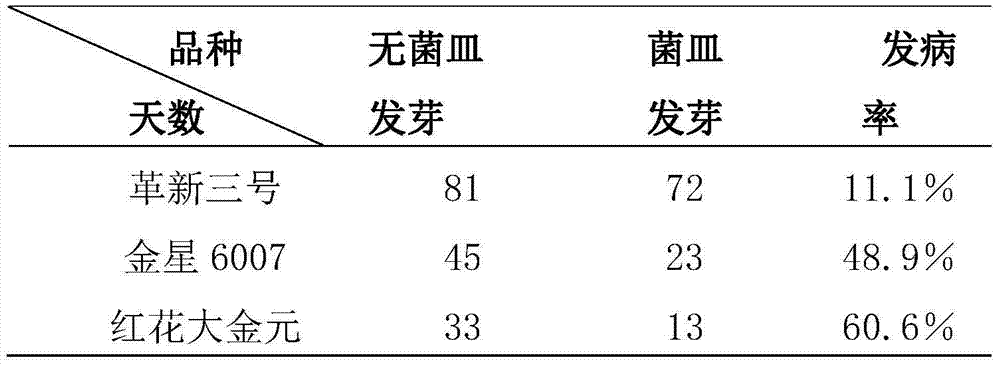
[0026] Take Gexin No. 3 seeds and place them in a sterile petri dish, soak them in 75% alcohol for 3 minutes, then soak them in 10% sodium hypochlorite for 5 minutes, and then wash them repeatedly with sterile water 3 times to reduce the residue of disinfectant;
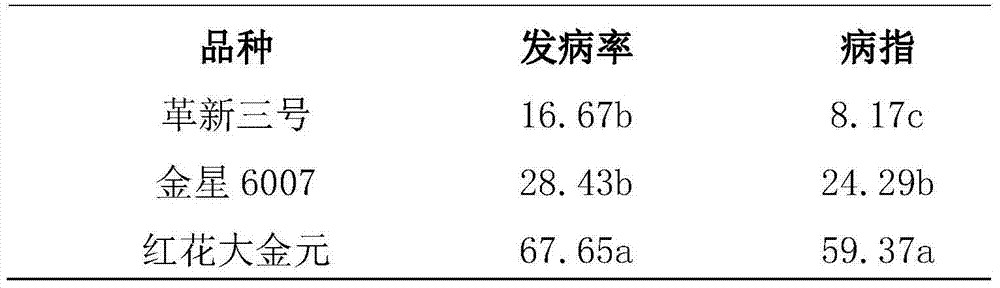
[0027] Step 3, germination rate, morbidity statistics, and disease resistance evaluation:
[0028] Step 2 sterilized tobacco seeds were transferred under aseptic conditions to the tobacco black shank bacteria dish...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for rapidly identifying tobacco black shank resistance, comprising the following steps:
[0031] Step 1, cultivation of tobacco black shank bacteria:
[0032] Tobacco black shank race No. 0; inoculated on oat medium and cultured at 28°C for 7 to 10 days. After the mycelia covered the entire dish, use an inoculation loop to remove the mycelia attached to the surface of the dish and leave the bacteria ready for use;
[0033] Step 2: Disinfect the surface of the tobacco seeds to be tested:
[0034] Take the Jinxing 6007 seeds to be tested and place them in a sterile petri dish, soak them in 75% alcohol for 3 minutes, then soak them in 10% sodium hypochlorite for 5 minutes, and then wash them repeatedly with sterile water 3 times to reduce the residue of disinfectant;
[0035] Step 3, germination rate, morbidity statistics, and disease resistance evaluation:
[0036] Step 2 sterilized tobacco seeds were transferred under aseptic conditions to the tobacco black s...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A method for rapidly identifying tobacco black shank resistance, comprising the following steps:
[0039] Step 1, cultivation of tobacco black shank bacteria:
[0040] Tobacco black shank race No. 0 was inoculated on oat medium and cultured at 28°C for 7 to 10 days. After the mycelia covered the entire dish, the mycelium attached to the surface of the dish was removed with an inoculation loop, and the bacteria remained. ready for use;
[0041] Step 2: Disinfect the surface of the tobacco seeds to be tested:
[0042] Put the safflower dajinyuan seeds to be tested in a sterile petri dish, soak them in 75% alcohol for 3 minutes, then soak them in 10% sodium hypochlorite for 5 minutes, and then wash them repeatedly with sterile water 3 times to reduce the residue of disinfectant ;
[0043] Step 3, germination rate, morbidity statistics, and disease resistance evaluation:
[0044] Step two sterilized tobacco seeds were transferred under aseptic conditions to the tobacco ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com