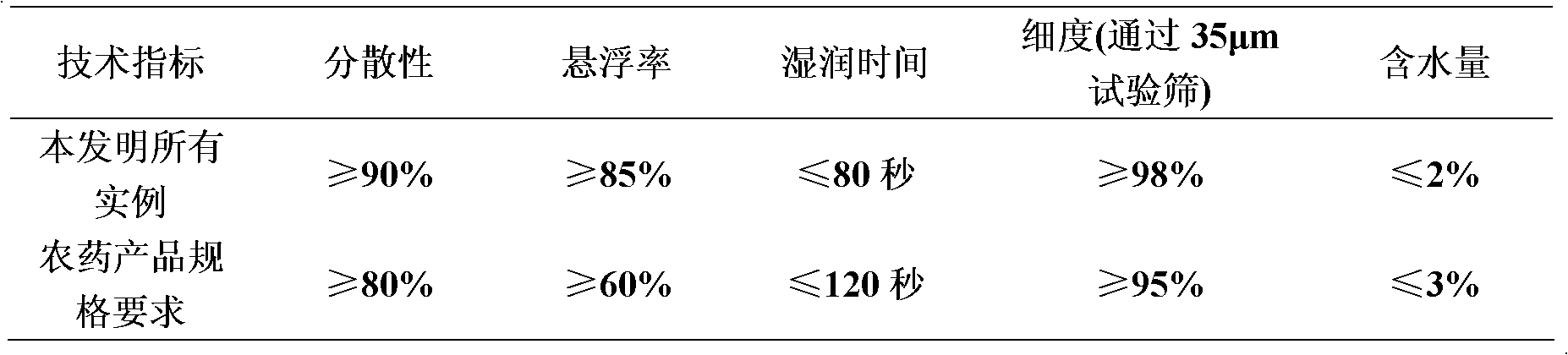
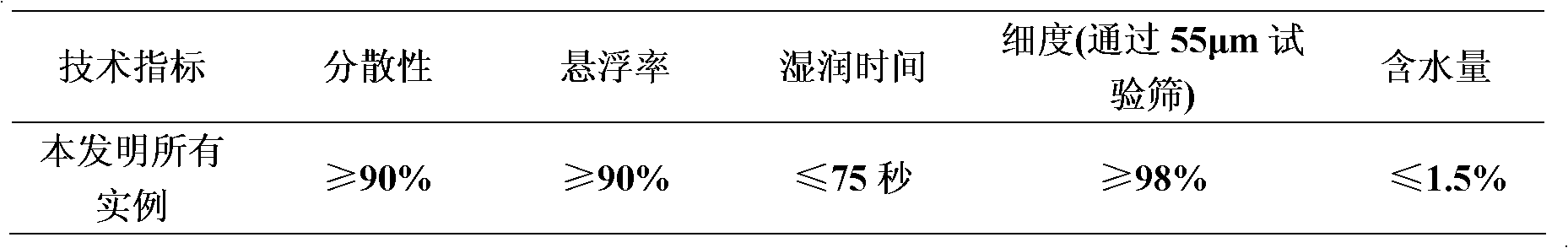
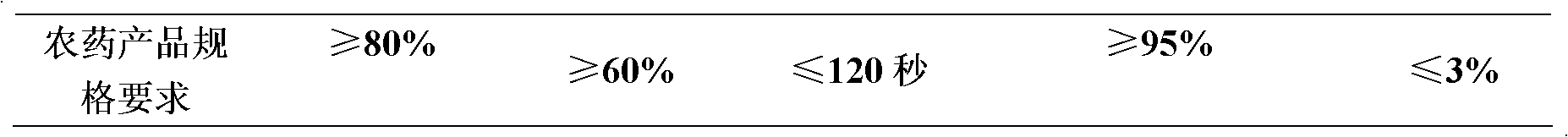Patents
Literature
60 results about "Phytophthora parasitica" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The oomycete Phytophthora parasitica is a very broad host range pathogen that causes destructive diseases of a wide variety of crop plants, nursery and ornamental plants, and forest ecosystems. Some isolates are also effective pathogens of Arabidopsis thaliana and Medicago truncatula.
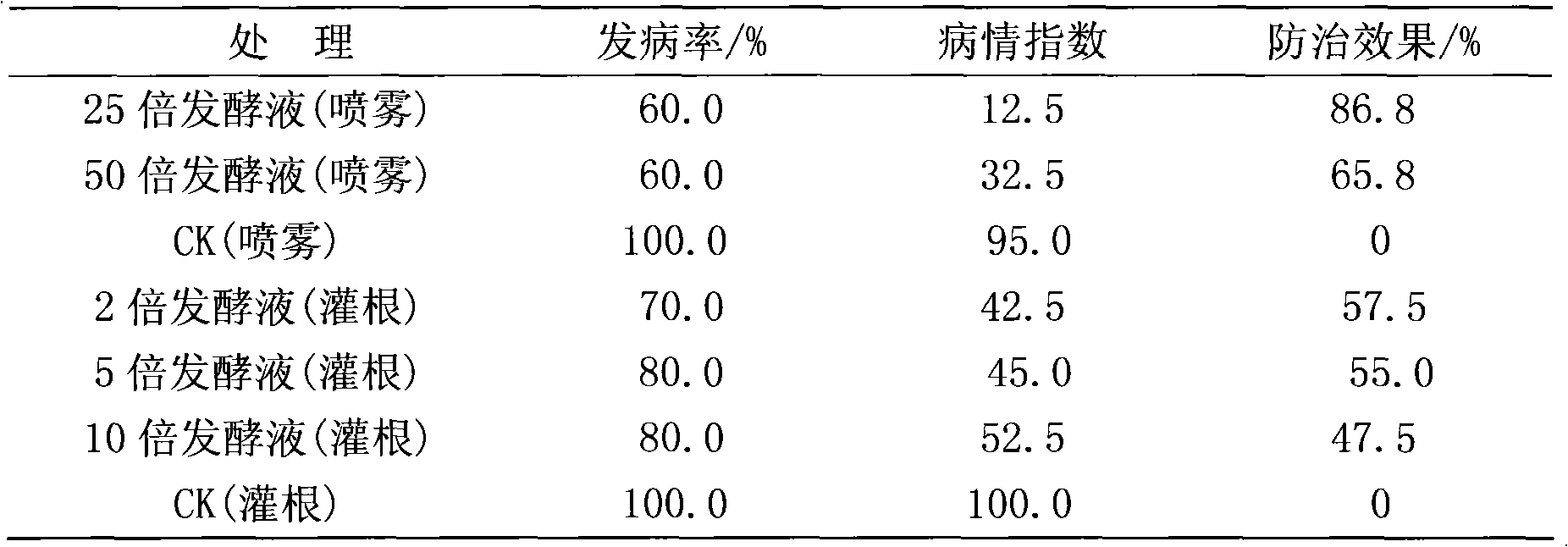
Microbial bactericide and application thereof
ActiveCN102604864AGood antibacterial effectBroad spectrumBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismBacillus amyloliquefaciens
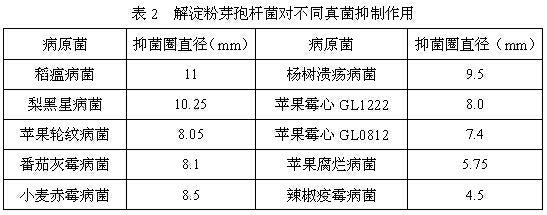
The invention discloses an antibiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with powerful bacteriostasis and wide bactericidal spectrum. The strain has been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and the taxonomy name of the strain is: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with preservation number CGMCCNo.4777. The antibiotic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens has powerful bacteriostasis, wide bactericidal spectrum, high inhibition rate up to above 93.5% on the rice blast fungus, the Botrytis cinerea and the Phytophthora parasitica; the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens also has very strong stress resistance, and very strong resistance to the acid and alkali, and is suitable to be used as microbial bactericide.
Owner:LONGDENG CHEM XIAN
Physiological race identification method of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in disease nursery
InactiveCN101671720AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumPityophthorus nitidulus
A physiological race identification method of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in disease nursery can identify the physiological race of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in disease nursery as soon as possible by means of combining the identification of disease-resistant reaction of host in fields and collection of color change of strains on a TTC solid culture medium flat plate, realize the identification of the physiological race type of tobacco phytophthora parasitica in the existing disease nursery, then directionally carry out the researches such as tobacco disease-resistant germplasm resources screening, breeding of new variety of tobacco and the like, and provide basis for the comprehensive prevention and treatment of tobacco phytophthora parasitica and the establishment of the targetof breeding for disease resistance. The method is economical and practical and has favorable market application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Thaumatin-like protein gene PpTLP from pyrus pyrifolia nakai with antifungal activity and application
InactiveCN101736024AIncrease resistanceReduce usageFungicidesGenetic engineeringGenomicsNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a thaumatin-like protein gene PpTLP from pyrus pyrifolia nakai with antifungal activity and application. The gene PpTLP has the base sequence shown in SEQID and coded thaumatin-like proteins. The invention verifies that the gene PpTLP has the function of improving the antifungal ability of the plants through correlation technique of functional genomics. When the antifungal gene PpTLP is constructed on a plant expression vector and is transformed into tobacco to be overexpressed, the transgenic tobacco has high antifungal activity. The protein from the transgenic tobacco expressing PpTLP has obvious inhibitory effects on various fungi such as sclerotinia sclerotiorum, phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, phomopsis sp. and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis CLP-7, and applications thereof
The invention discloses an acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 which is capable of preventing diseases and promoting growth, and can be used for biocontrol. The acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, on 27th, October, 2016, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13204. The antibacterial spectrum of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is relatively large; the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of inhibiting growth of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, Ralstonia solanacearum, and Alternaria alternata Keissler; the antagonistic activity under acidic conditions is high, the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of producing siderophore, possesses protease and glucanase activity, and potassium releasing capacity. The results of biocontrol pot experiment show that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 is capable of preventing under acidic soil conditions, and promoting growth and chlorophyll synthesis of tobacco seedlings in acidic soil, so that the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 and microorganism bacterium agents of the acid-resistant pseudomonas koreensis strain CLP-7 can be used for preventing tobacco fungi and bacterial root and stem diseases under continuous cropping or acidic soil conditions effectively, and is high in application value.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
Pesticide composition containing picoxystrobin and amides
The invention discloses a pesticide composition containing picoxystrobin and amides. The pesticide composition comprises an active component A and an active component B, wherein the active component A is selected from picoxystrobin; the active component B is selected from any one of the following bactericides: dimethomorph, metalaxyl, Metalaxyl-M, BENALAXYL, Benalaxyl-M, Flutolanil and Pyrimorph; and the weight percentage of A to B is 1%-80%:1%-80%. The composition can prevent and treat a plurality of crop diseases, has a notable synergetic action, enlarges the insecticidal spectrum, and is of high activity on downy mildew, epidemic disease, late blight, Leptosphaeria maculans, Pernophythora litchi, phytophthora, white rust, foot rot, Phytophthora parasitica, Pythium debaryanum, soft rot, damping off, banded sclerotial blight, snow mold, Leaf blight, Septoria nodorum, brown blotch or powdery mildew. The consumption of the pesticide is reduced, the residual quantity of the pesticide on crops is decreased and environmental pollution is abated.
Owner:陕西汤普森生物科技有限公司
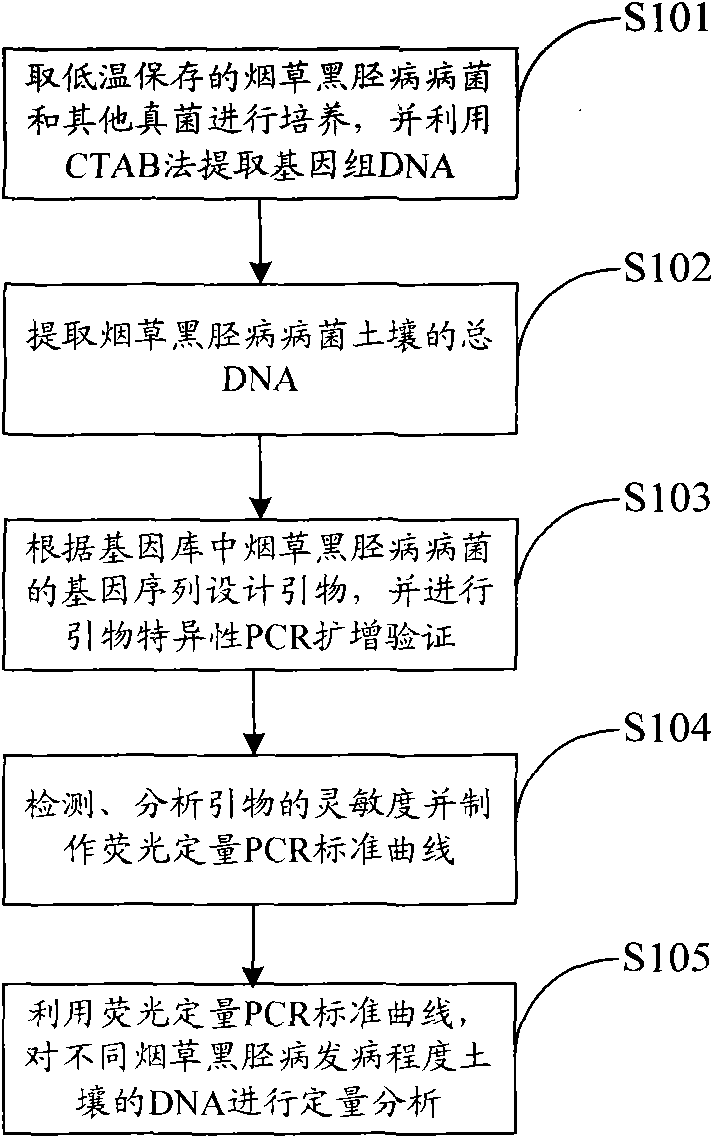
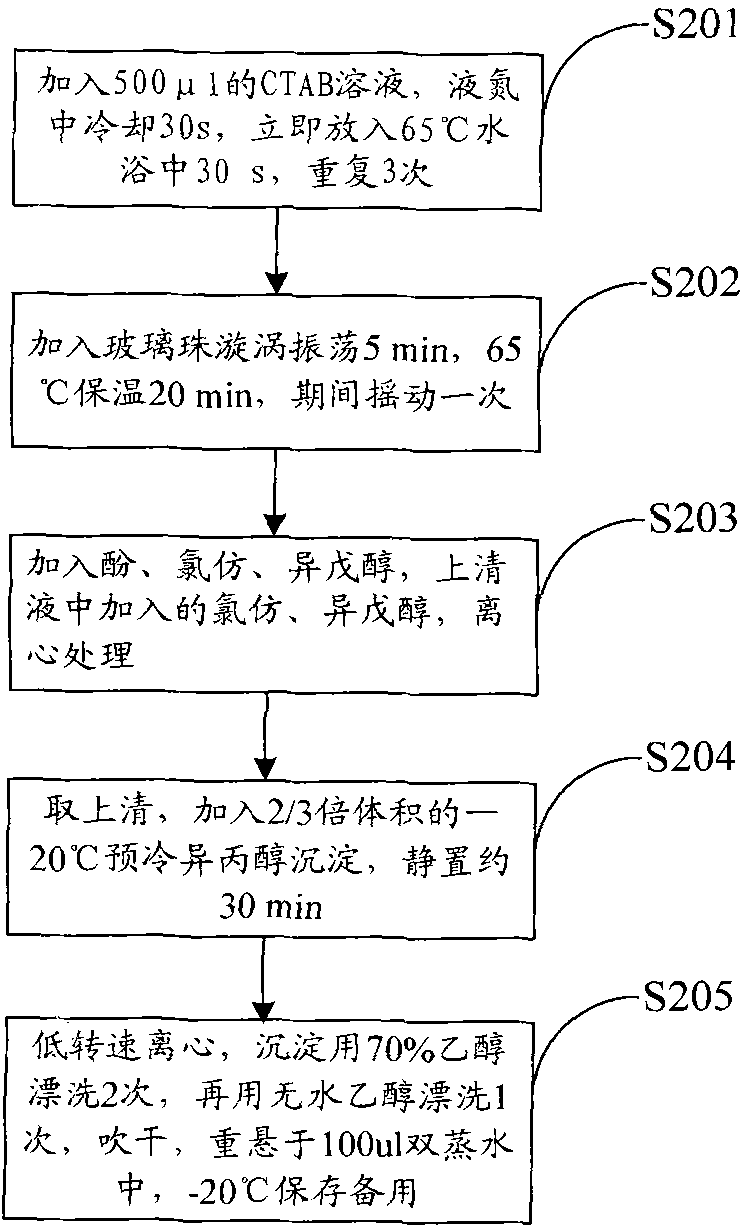
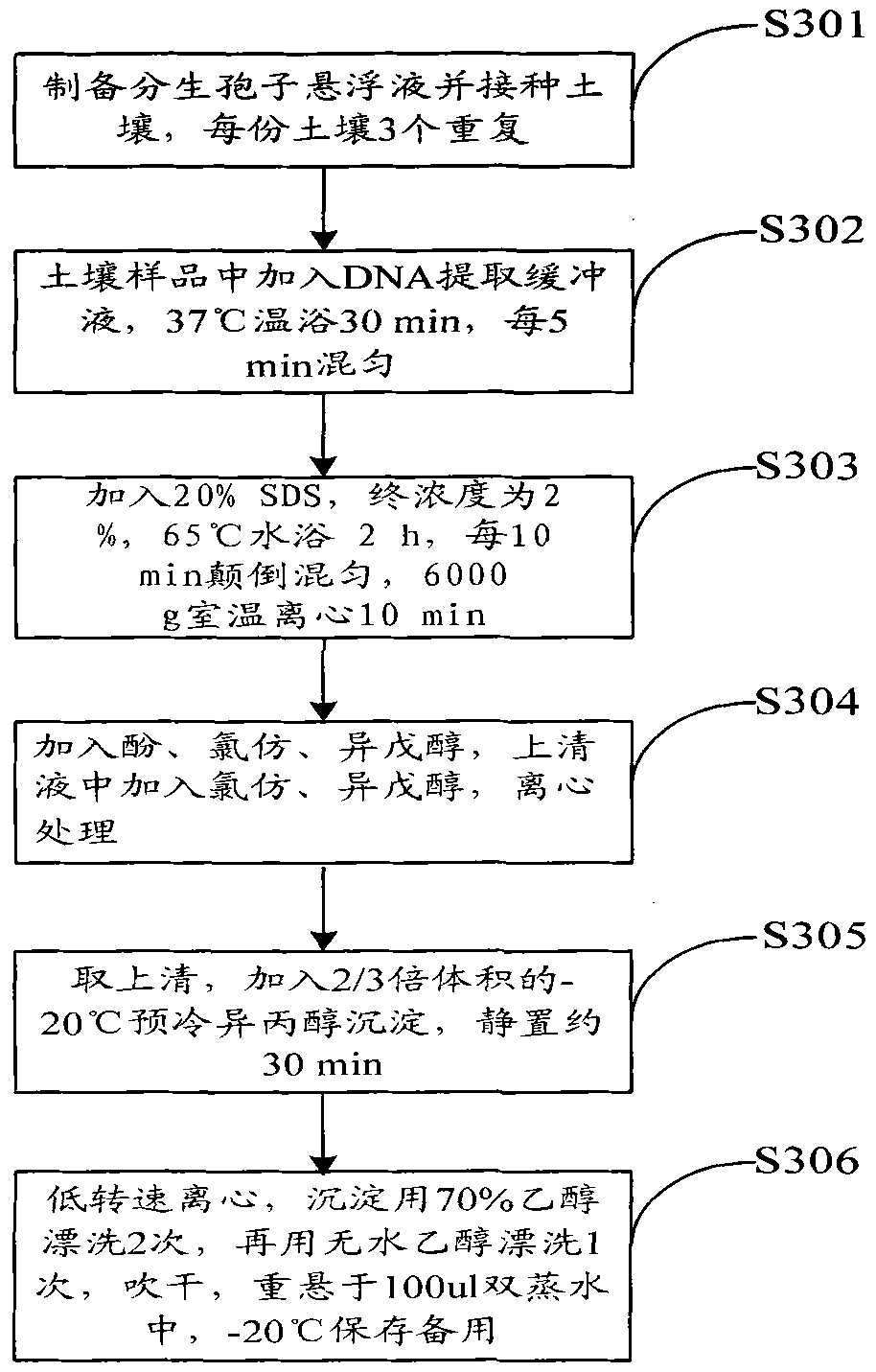
Method for detecting phytophthora parasitica in soil
InactiveCN102399896AReduce the impactShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementNicotiana tabacumQuarantine
The invention belongs to the field of plant disease and pest quarantine, and provides a method for detecting phytophthora parasitica in soil. According to the method for DNA extraction and molecular detection of the phytophthora parasitica in the soil, the conventional isolating culture method is eliminated, and the detection period is greatly shortened; compared with a common polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection method, the method has the advantages that: a subsequent treatment process is not needed, and a result can be monitored in real time; primers are designed on the basis of a changeful area of pathogen ITS, and corresponding bands are not produced when similar species are amplified; the method is high in specificity and suitable for fluorescent quantitative PCR conditions; because 2 percent of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) is added into the total DNA extraction buffer solution of the soil, the pollution of partial impurities in the soil is effectively removed, the influence of the impurities on the PCR effect is reduced, and the detection sensitivity of fluorescent quantitative PCR is improved; meanwhile, the fluorescent quantitative PCR system and the reaction conditions are obtained according to the size study conditions of the designed primers, so the detection sensitivity is high and can reach 2fg / mu l.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Biological pesticide using psoralidin to prevent and control plant fungal diseases
ActiveCN101213980AHigh antibacterial activityImprove efficacyBiocideFungicidesDiseasePyricularia grisea
The invention provides a biological pesticide by using psoralidin to control plant fungous disease. The invention relates to a plant used biological pesticide, in particular to biological pesticide by using psoralidin to control plant fungous disease. Compound is dried Guzhi seed 5Kg. The compound is quenched and extracted four times by using 70 percent of industrial ethanol. After lixivium is decompressed and condensed, ethanol extract is gained. Water is added and mixed with the ethanol extract. Mixture is extracted by using petroleum ether and ethyl acetate in turn. 100g of ethyl acetate extraction part extract is taken, and processed chromatography over again by silica gel column, and processed gradient elution by petroleum ether-ethyl acetate and are separated, and then psoralidin (50mg) is gained (the ratio between the petroleum ether and ethyl acetate is 4 to 1). The invention can restrain common plant pathogen, like apple decay pathogen, apple macrophoma kawatsukai, pyricularia grisea, rice sheath blight fungus, cucumber fusarium wilt, wheat scab pathogen, cucumber anthracnose, phytophthora parasitica and so on.
Owner:沈阳同祥生物农药有限公司
Method for inducing phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae to generate zoosporangium and release spore
ActiveCN102226167AEfficient productionProduce short and focusedMicroorganism based processesSpore processesNicotiana tabacumMycelium
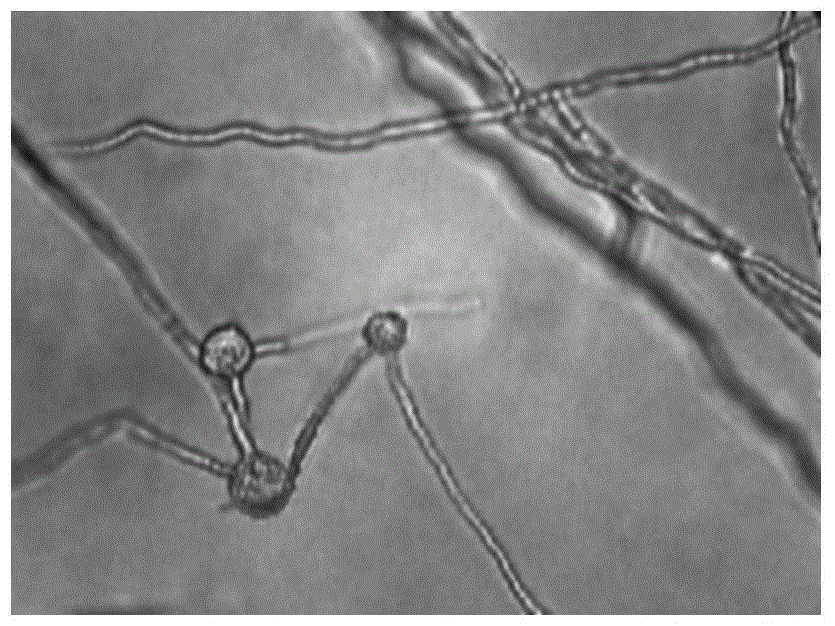
The invention discloses a method for inducing phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae to generate zoosporangia and release spores. The method comprises steps of: culturing phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae mycelia on an oat medium prepared in a narrow mouth conical flask; preparing an induction liquid for generation of zoosporangia by selecting roots of tobacco seedlings, with 6-7 pieces of true leaves completely expanding, of a black shank infected variety; inducing the mycelia with the induction liquid to generate zoosporangia and to release spores. According to the invention, a characteristic that a black shank infected tobacco variety is more easily to generate affinity reaction with phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae is employed, and a filtrate of seedling roots of the black shank infected tobacco variety is used as the induction liquid, so as to induce the cultured mycelia to generate zoosporangia. Proved by tests, the invention has a short induction time, high zoospore release rate, high obtained zoospore content; and scraping mycelia for culture is not needed. Therefore, the invention is of less pollution and easy to operate.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Trichoderma asperellum TD3104 and application thereof in preparation of microbial agent for inhibiting plant pathogenic bacteria
The invention provides Trichoderma asperellum TD3104 and application thereof in preparation of microbial agent for inhibiting plant pathogenic bacteria. The preservation number of the Trichoderma asperellum TD3104 is CGMCC 13161. The invention further provides application of the Trichoderma asperellum in the controlling of the plant pathogenic bacteria of tobacco and apples. The antagonistic Trichoderma asperellum can effectively inhibit the growth of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, ralstonia solannacearum, rhizoctonia solani, tobacco root rot pathogenic fusarium, alternaria alternata and the pathogenic bacteria of apple rot and apple ring rot, can effectively control related diseases, can reduce the use amount of chemical pesticides and accumulation of the chemical pesticides in soil, is beneficial to the increasing of quality and yield of the economic crops of China and is evident in economic and social benefits.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Streptomyces strain for inhibiting harm of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae and application thereof
Aiming at the existing defects in preventing and controlling black shank of tobacco, the invention provides Streptomyces misawanensis D35 for inhibiting Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. The strain was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre (CGMCC) on August 27, 2009 with the collection number of CGMCC No: 3250. The invention also provides application of the strain in effectively inhibiting diffusion of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae in tobacco, reducing disease incidence, improving the tobacco yield and quality, facilitating the development of biological prevention and control products and further promoting the safe control of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae.
Owner:周倩
Method of control Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae Resistance to Metalaxyl
InactiveCN101032255AReasonable crop rotationScientific ridgingBiocideFungicidesMetalaxylNicotiana tabacum
The present invention relates to method of tackling Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae with resistance on metalaxyl, and belongs to the field of plant protection and agricultural chemical technology. The present invention screens out two kinds of germicides, including Junke and Xiuan, with negative cross resistance to metalaxyl for applying alternately to prevent and control Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae with resistance on metalaxyl. The present invention has simple operation, high effect, reduced agricultural chemical residue, raised tobacco safety and other advantages.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
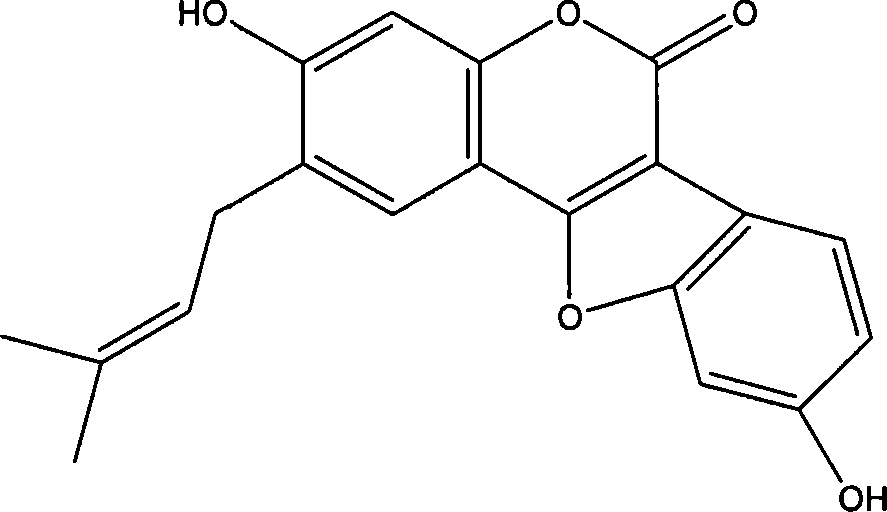
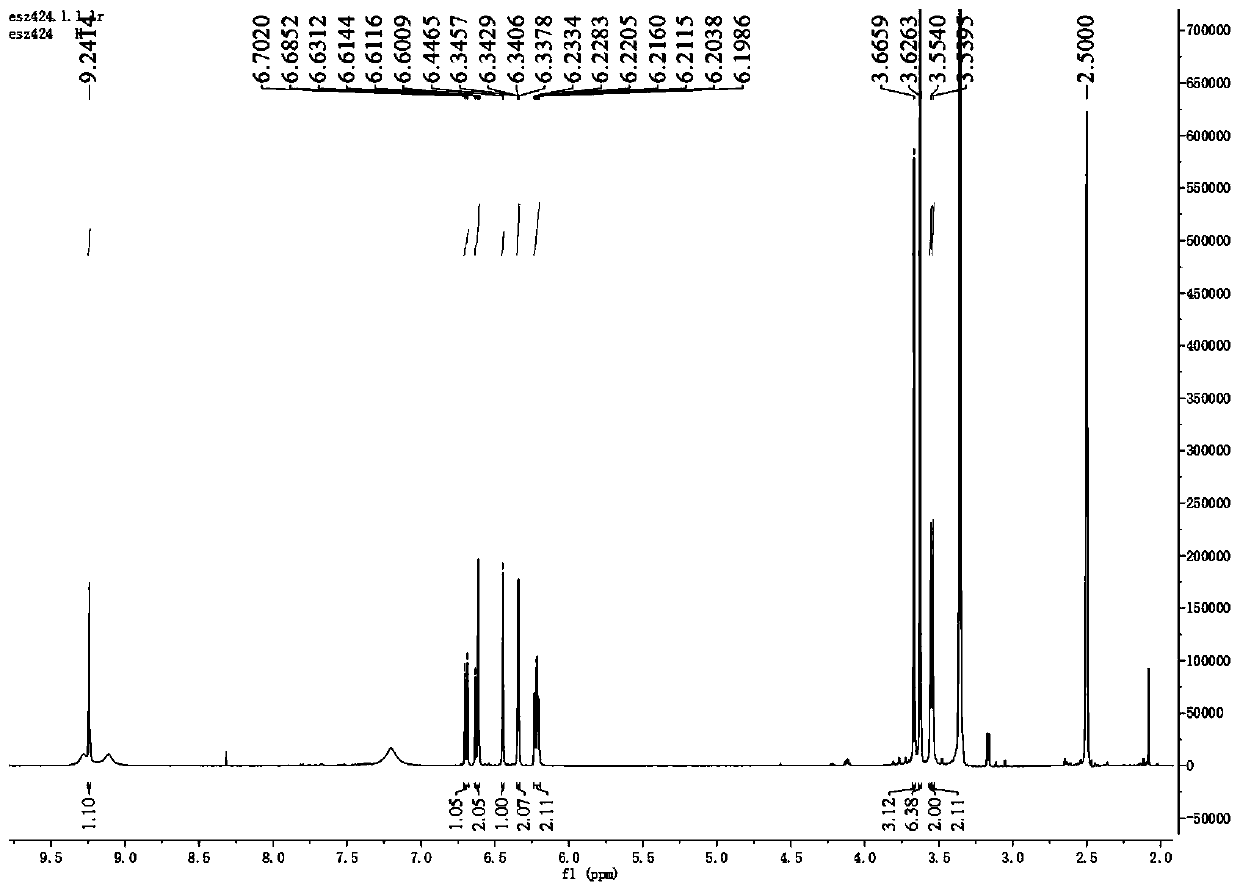
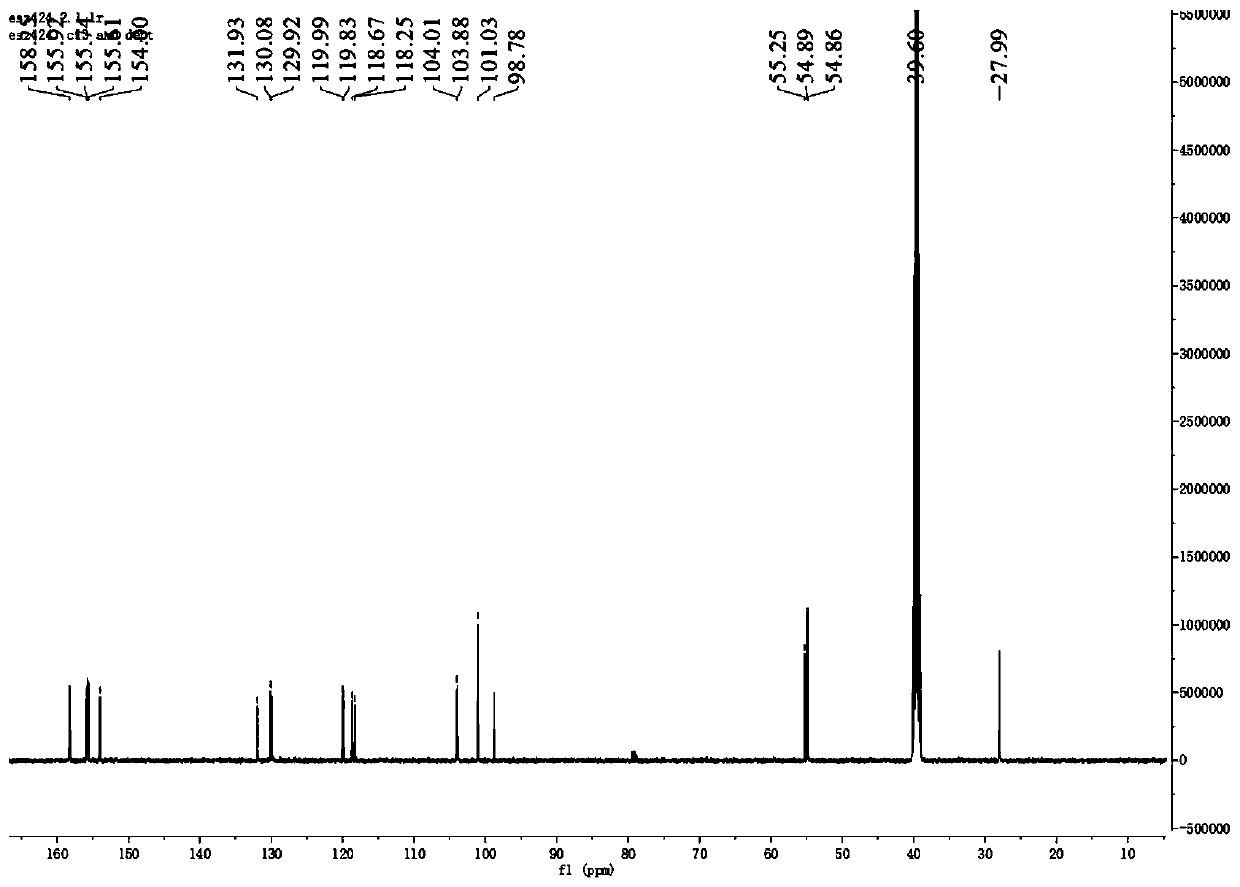
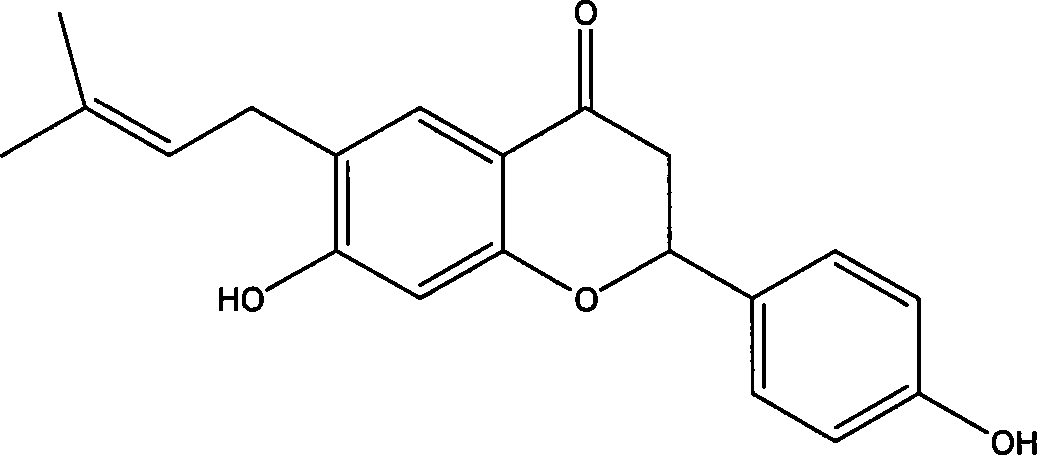
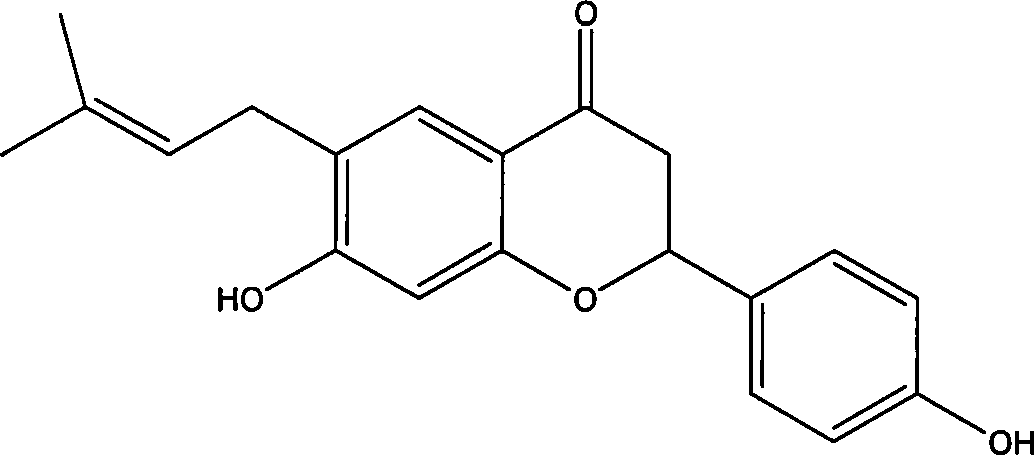
Natural antibacterial polyphenol compound, preparation method thereof and application of natural antibacterial polyphenol compound in electronic cigarettes
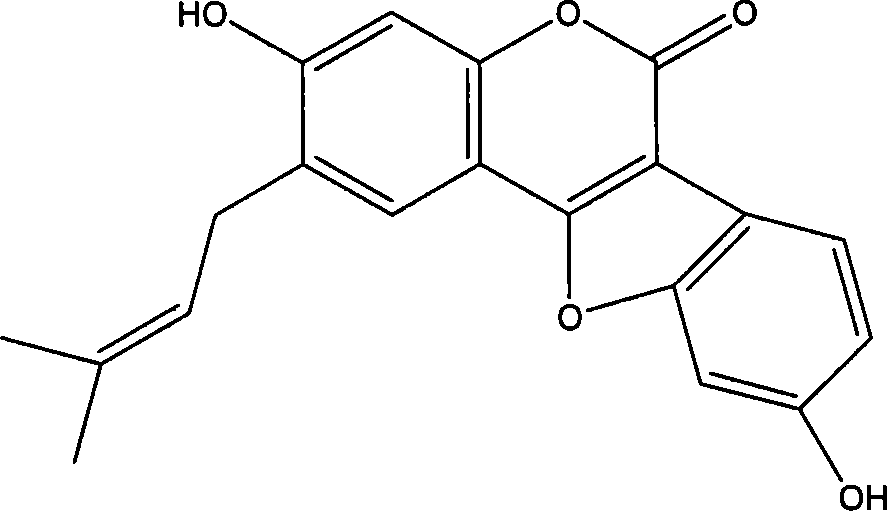
InactiveCN110272334AGood antifungal activityExtended shelf lifeBiocideEther separation/purificationStructural formulaPolyphenol
The invention relates to a natural antibacterial polyphenol compound, a preparation method thereof and application of the natural antibacterial polyphenol compound to electronic cigarettes, and belongs to the technical field of phytochemistry. The structural formula of the compound is shown as a formula (I), wherein the formula (I) is shown in the description. The compound is separated from barks of periploca sepium Bunge for the first time and determined to be the polyphenol compound through a nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry method, and the specific structure of the compound is characterized. The compound shows good inhibitory activity against bacteria such as phytophthora parasitica, fusarium asiaticum and alternaria alternata and good antifungal activity and has good application prospects. Meanwhile, the compound is used in electronic cigarette liquid, can have a good antibacterial effect, prolong the shelf life of the electronic cigarette liquid and reduce the excessive sweetness in the smoking process and is easy to apply and popularize.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
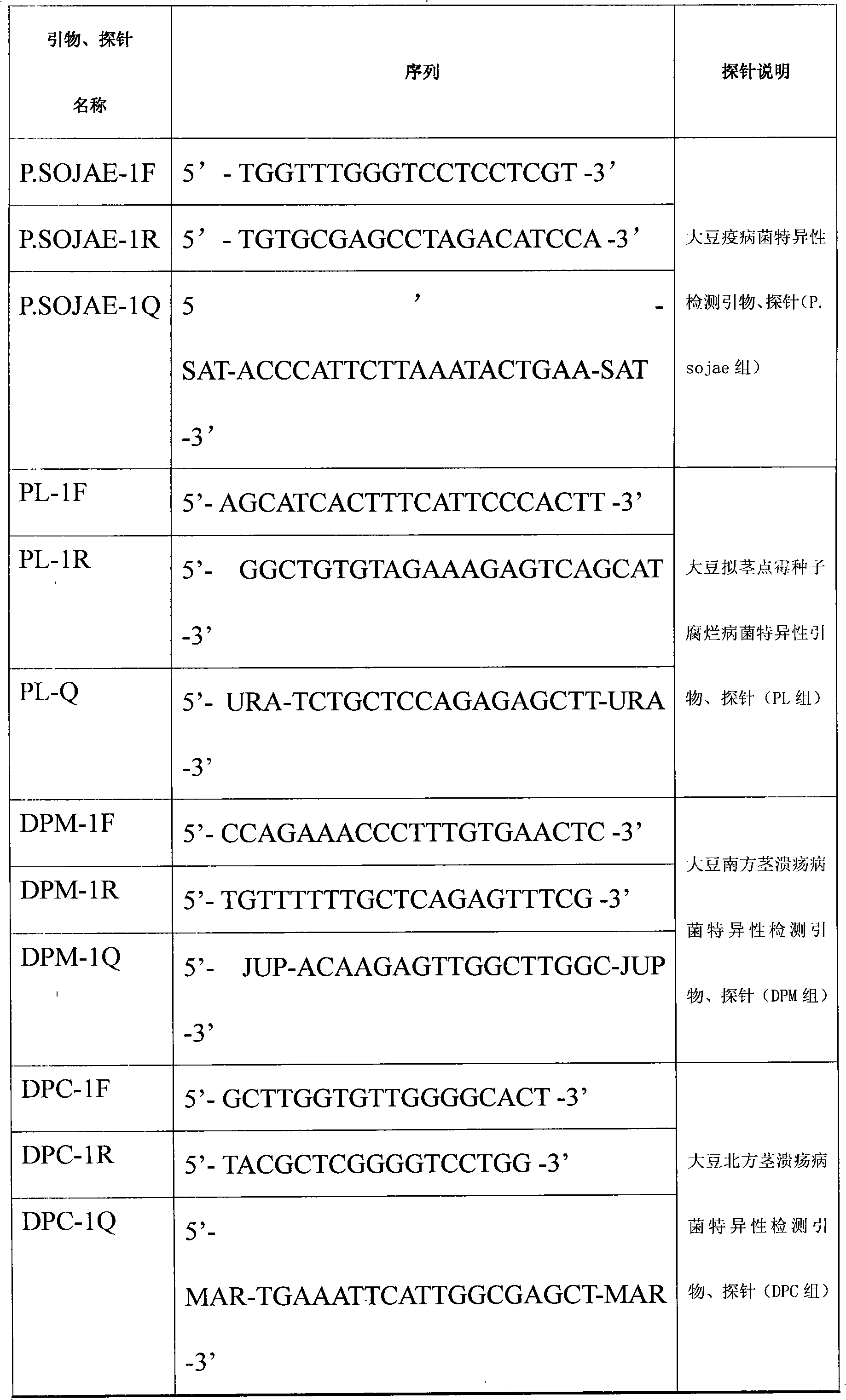
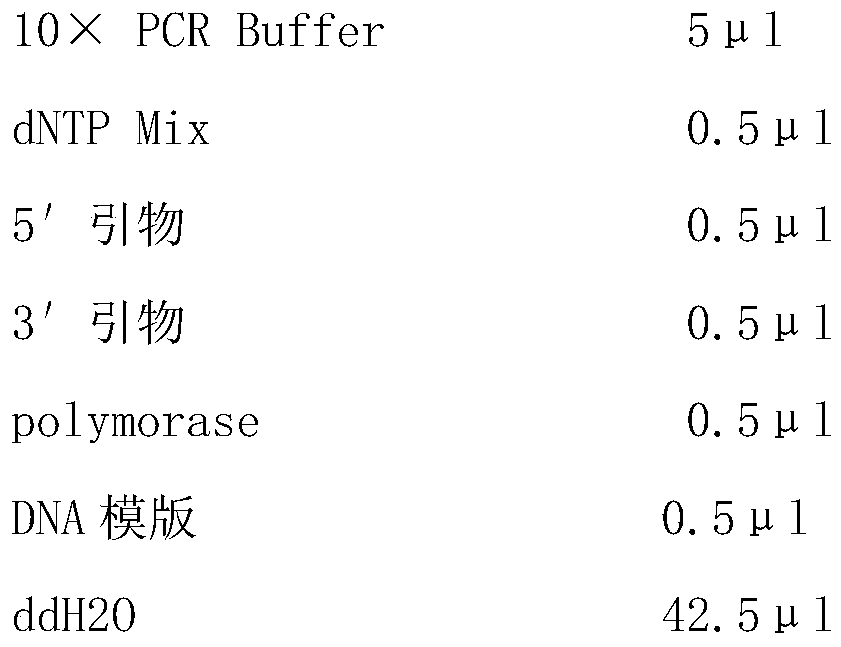
Double-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) molecular detection primer for tobacco phytophthora parasitica and thielaviopsis basicola and detection method
InactiveCN104726557ARealize accurate early warning monitoringImprove the level of prevention and controlMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseased plantThielaviopsis basicola
The invention relates to a double-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) molecular detection primer for tobacco phytophthora parasitica and thielaviopsis basicola and a detection method. The detection primer comprises YYI-F: TCATTACCACACCTAAAAAACT, YYI-R: ACTTTCGTCCCCACAGTATATT, TB1419-F: GTGTTGGAGGACCCGCGTTTAG and TB1419-R: AGTTGAGGGTTTTTCGGCATGTT. The detection method comprises the steps of performing extraction on total DNA, PCR amplification and gel electrophoresis under certain conditions. According to the detection primer and the detection method provided by the invention, a specific and high-sensitivity double-PCR molecular detection system for the tobacco phytophthora parasitica and thielaviopsis basicola is established, and by detecting the total DNA sequences of materials including tobacco diseased plants, soil and the like, the quick, accurate and ultralow-concentration once double-identification of the tobacco phytophthora parasitica and thielaviopsis basicola is finished.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Brevibacillus choshinensis X23 and application thereof
InactiveCN102154175AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntagonisticBiocideBacteriaBrevibacillus choshinensisNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides a set of production technology for preventing ralstonia solanacearum from growing and reproducing in solanaceae crops to increase crop yield by aiming at the defects of the prior art for controlling the damages of the ralstonia solanacearum to the crops. Brevibacillus choshinensis X23 has a wide bacteriostatic spectrum and good environmental safety and has antagonism effects to various pathogenic fungi, such as phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae, pyricularia grisea, alternaria alternate, phytophthora infestans and the like, so that the brevibacillus choshinensis X23 has favorable development prospect and application potential.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Multiple real-time fluorescence PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method and kit of soybean quarantine virus diseases
InactiveCN101857905AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFungal diseaseFluorescence
The invention relates to a simple, quick, specific and sensitive real-time fluorescence PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method and a kit thereof for simultaneously detecting one or more soybean fungal diseases of soybean phytophthora parasitica, soybean phomopsis seed rot germs, soybean south stem ulcer germs and soybean north stem ulcer germs. The real-time fluorescence PCR detection method and the kit are suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine, agricultural production, plant protection, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
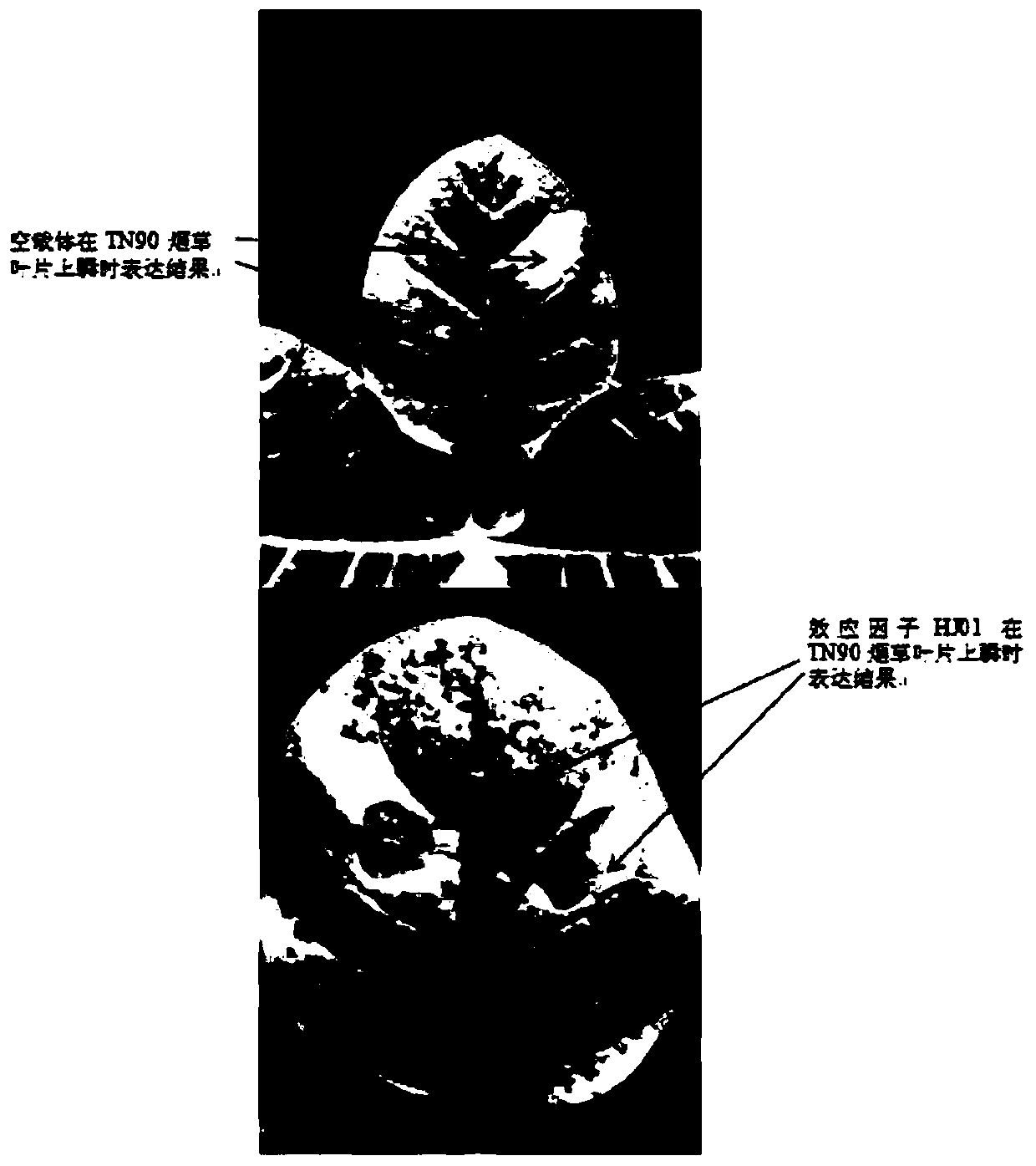
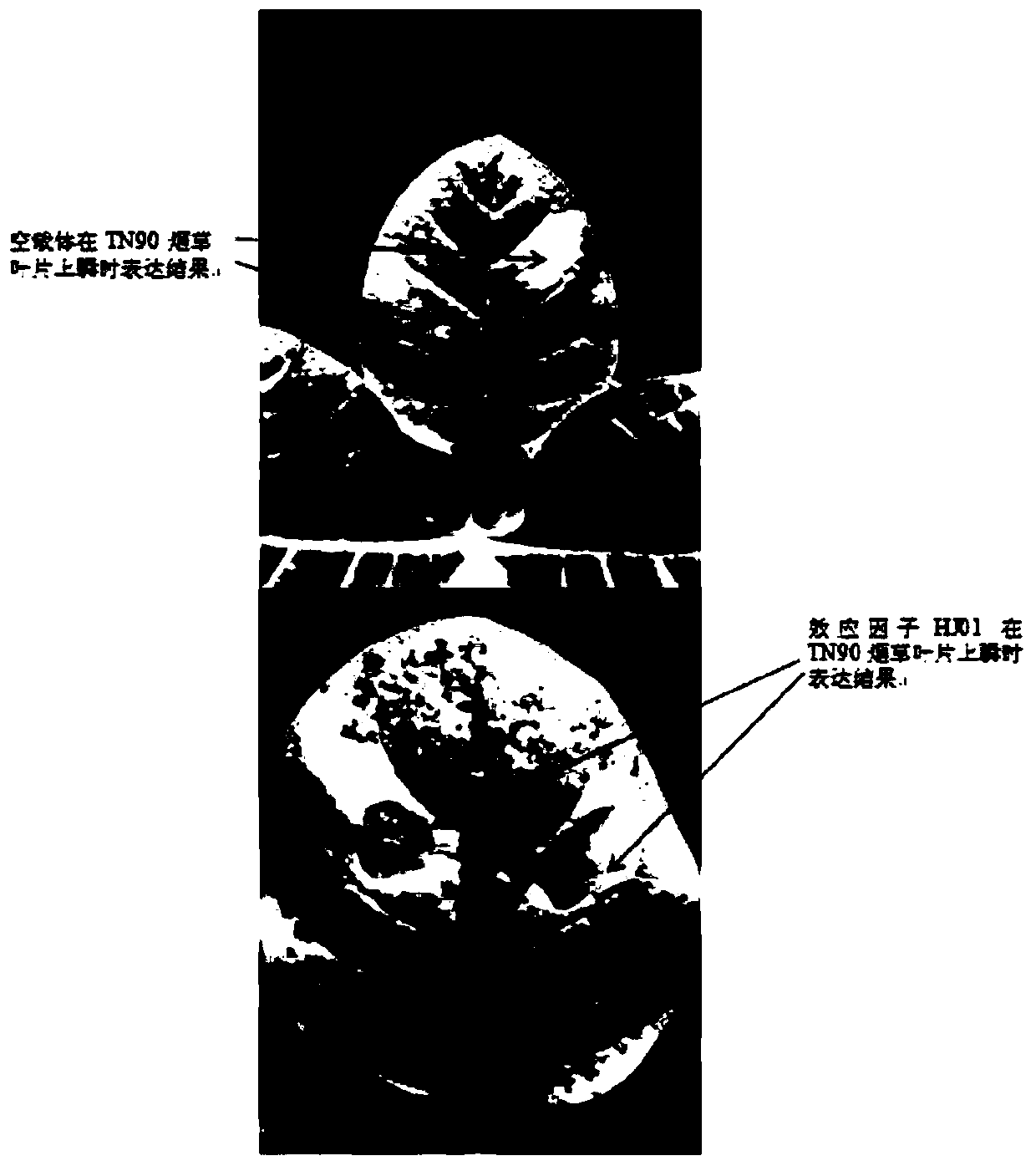
Method of cloning Phytophthora parasitica effector
The invention discloses a method of cloning Phytophthora parasitica effector. The method comprises: designing primers; extracting Phytophthora parasitica genome DNA; performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on tobacco Phytophthora parasitica effector gene; recycling and purifying the PCR product; preparing Escherichia coli DH5lapha competence; linking the amplification product withpMDTM 19-T Vector, and converting Escherichia coli DH5alpha; converting Escherichia coli; screening a positive clone, and performing PCR identification on a bacterial liquid; subjecting the screenedpositive clone to sequencing identification to obtain the Phytophthora parasitica effector. The method has the advantages that the Phytophthora parasitica effector is cloned and its functionality is analyzed.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Bavachin with plant epiphyte resisting activity
ActiveCN101215278AHigh antibacterial activityImprove efficacyBiocideOrganic chemistrySilica gelEthyl acetate
An anti-phytopathogenic fungi activity psoralen flavanone relates to a compound, in particular to anti-phytopathogenic fungi activity psoralen flavanone. The preparation process of the compound comprises drying psoralen seeds, coldly soaking and extracting industrial alcohol four times, decompressing and condensing leachate to obtain alcohol extract, mixing solution with appropriate amount of water, extracting with petroleum ether and acetic acid ethyl ester in turn, taking acetic acid ethyl ester to extract position extract, conducting silica gel column chromatography, eluting in gradient with petroleum ether-acetic acid ethyl ester, separating to obtain psoralen flavanone (petroleum ether: acetic acid ethyl ester =85:15). The compound can be used as bactericide to prevent various plant diseases such as valsa mali, physalospora piricola nose, pyricularia oryzae, rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA, cucumber fusarium oxysporum, gibberella zeae, cucumber anthracnose and phytophthora parasitica and the like.
Owner:沈阳同祥生物农药有限公司
Method for identifying phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains
PendingCN105177104ARapid identificationRace rapidMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a method for identifying phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains, and belongs to the technical field of plant pathogen identification. According to the method, a tissue culture vessel method is used for identifying the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains; the environment conditions of culture and impregnation are more stable; the growth of tobacco pathogens is favorably accelerated; the seedling culture period and the dip dyeing period are greatly shortened; meanwhile, the interference of infectious microbes and other physiological strains on the identification result can also be avoided; the flux is high; labor and materials can be saved to the greatest degree; the high-flux, fast and accurate identification on the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae physiological strains is realized. Compared with a land method and a greenhouse method, the method has the advantages that the identification is fast; the result is more accurate, stable and reliable; higher application values are realized; meanwhile, a thought can also be provided for the identification of physiological strains of other disease pathogenic bacteria of tobaccos.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
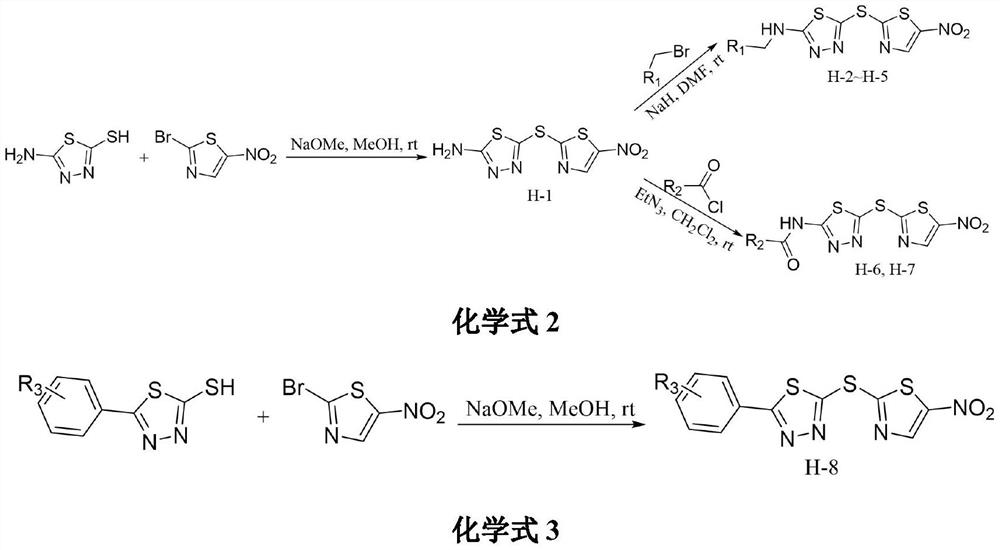
Application of thio-thiadiazole containing nitrothiazole compound in prevention and treatment of agricultural plant diseases
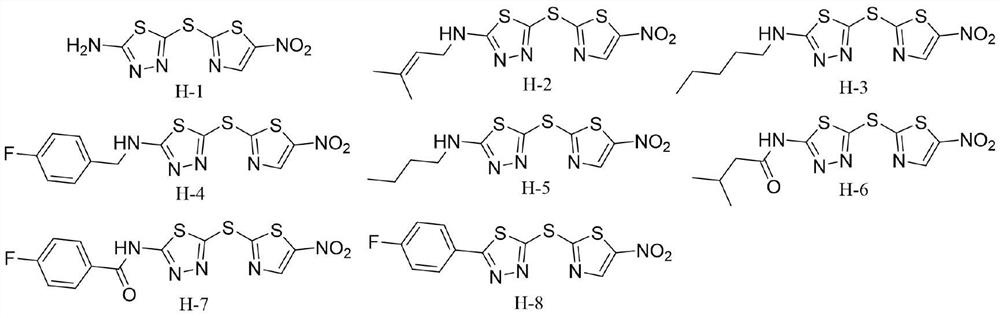
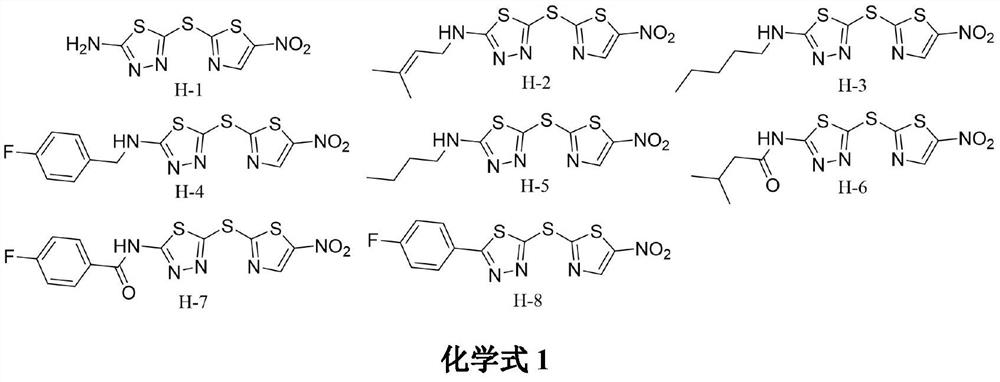
The invention relates to the field of medicinal chemistry, and discloses an application of 5-((5-nitrothiazole-2-yl)sulfo)-1,3,4-thiadiazole compounds H-1 to H-8 in resisting phytopathogens. Bioactivity tests find that the compound has potential inhibitory activity on eight agricultural diseases such as rhizoctonia solani, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, fusarium graminearum, botrytis cinerea, cotton fusarium oxysporum, magnaporthe grisea, citrus canker and phytophthora parasitica, and part of the compounds have high inhibitory activity. The compound is simple to prepare, raw materials are cheap andeasy to obtain, and the compound is expected to be developed into a novel bacteriostatic agent.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
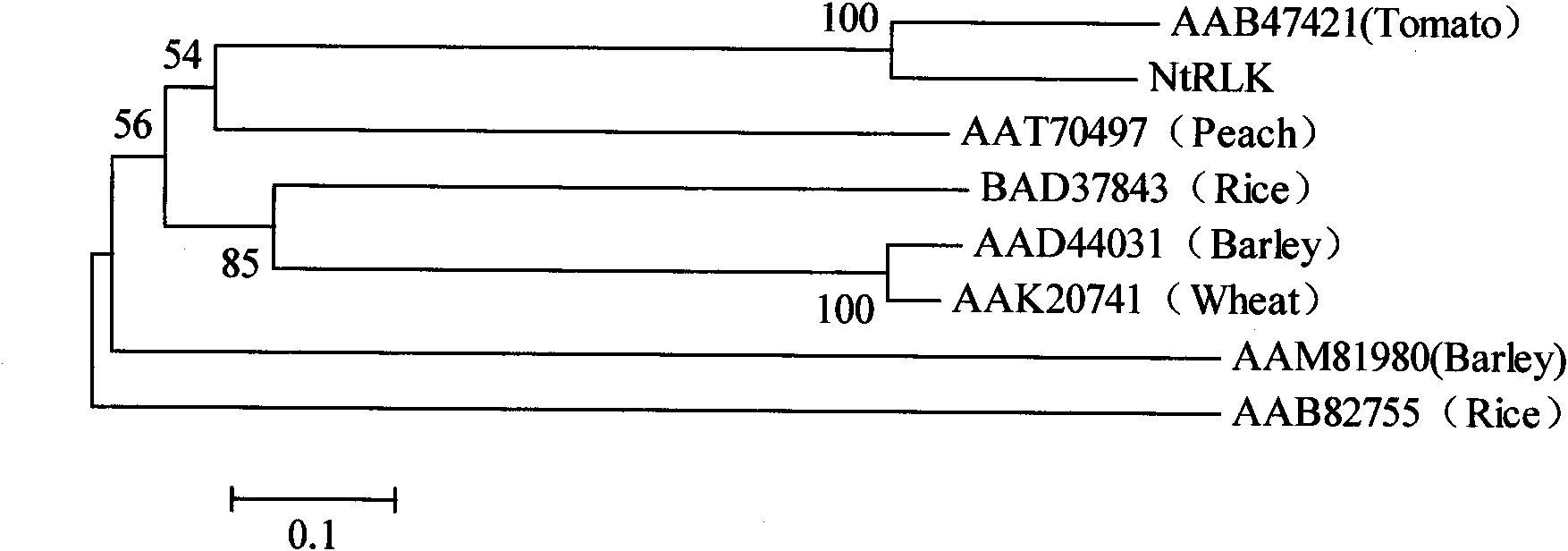
Tobacco receptor albuminoid kinase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101550420AIncreased blackleg resistanceIncrease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHigh resistanceBiotechnology
The invention relates to the cloning of a tobacco receptor albuminoid kinase gene, belonging to the field of plant genetic engineering. The invention clones a full-length sequence of a tobacco receptor albuminoid kinase (NrRLK) gene cDNA, therefore, a semi-quantitative PCR (RT-PCR) method for a pair NrRLK gene specific primer is designed for detecting the expression of reactive wild tobacco N. rependa in different periods after the inoculation with phytophthora parasitica, and the result shows that the gene is expressed only after being infected for 9 days by the phytophthora parasitica. The analysis on the theoretic amino acid sequence encoding the gene shows that the protein can be involved in plant defense response, so the gene can have a direct relationship with the resistance of the phytophthora parasitica. Taking the gene as a target gene, by the method of genetic engineering, the resistance of existing tobacco to the phytophthora parasitica is improved, and the tobacco variety with high resistance to black shank pathogen is cultivated to be used in tobacco production.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Simple and convenient separation method for phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae
InactiveCN101914454AHigh purityMaintain wild-type propertiesFungiMicroorganism based processesDiseased plantMicroorganism
The invention provides a simple and convenient separation method for phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae. By the method, a clean working environment is built by using simple equipment and spatial conditions so as to fast separate the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting and collecting diseased or infected plants; (2) purifying working environment; (3) separating germs; and (4) culturing the germs at room temperature; and the like. Namely, the method comprises the following steps of: building the clean working environment under simple conditions; sterilizing the working environment by the flame of an alcohol burner to form a sterile microenvironment; dissecting diseased or infected stems; picking up disk-shaped diseased or infected medullary slices in the diseased or infected stems with tweezers; placing the medullary slices on oat or lima bean medium plates, wherein the medium plates are sealed by sealing films, and 3 to 5 plates are arranged in a sealed culture box; and culturing the medullary slices for 3 to 5 days at room temperature to obtain target germs by colonial morphology. The method is suitable for field sampling and timely separating, uses simple equipment in the whole operation, and can separate the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae without microbiology laboratories. The separated germs have high purity and the characteristics of germ wild types.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
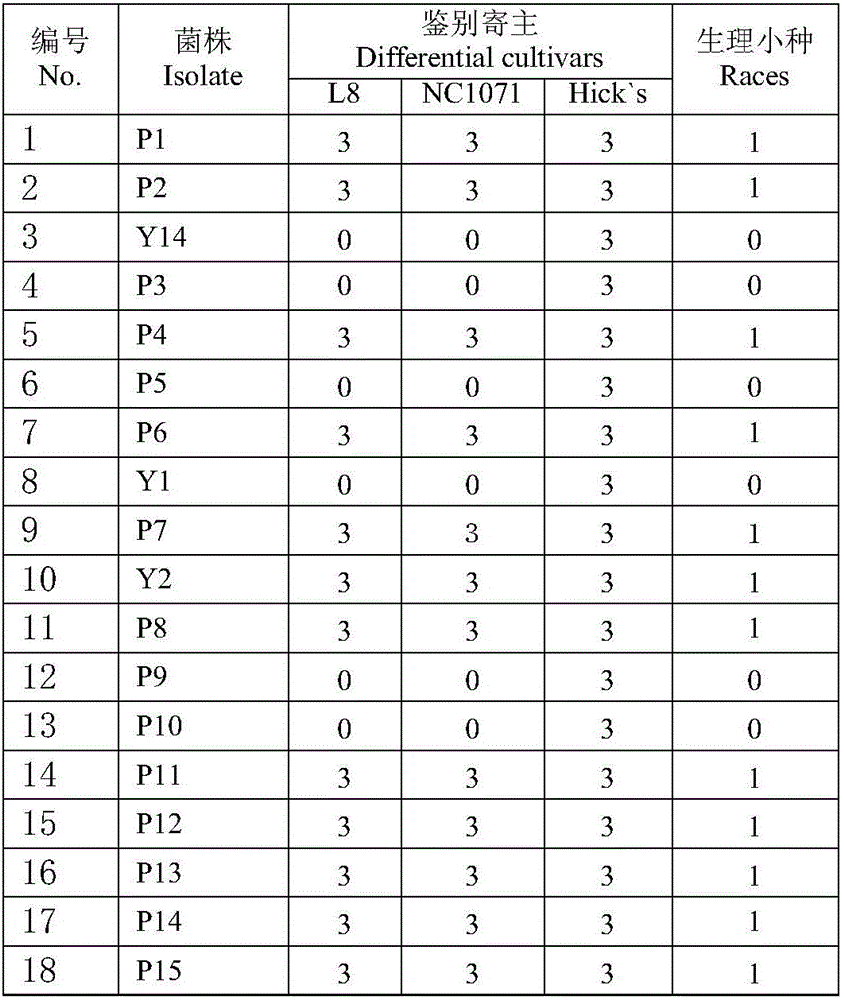
Physiologic race identification method for Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae
InactiveCN105886594ASmall footprintLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumOperability
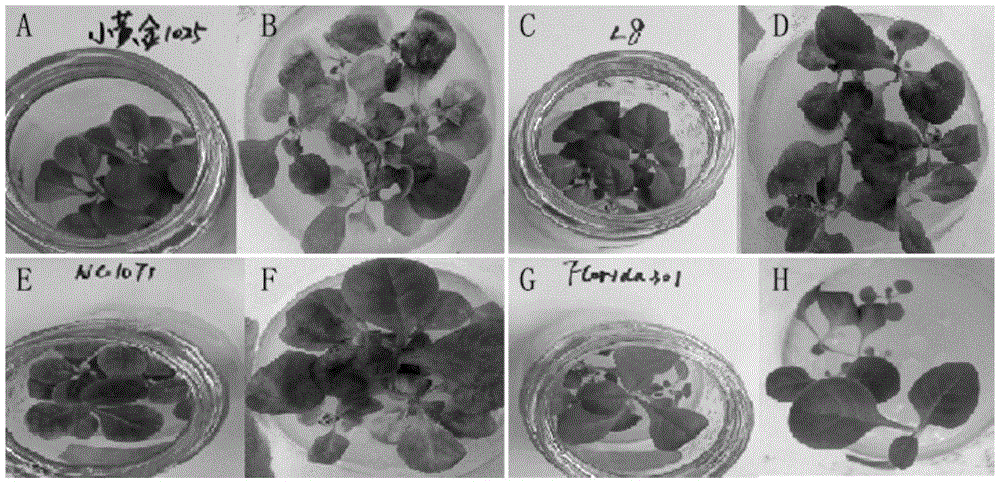
The invention relates to a physiologic race identification method for Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. Aiming at tobacco black shank which is a soil-borne disease, field pathogen infection ways are simulated. The method includes: propagating the Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae; making bacterial discs, inoculating to wheat grains subjected to moist heat sterilization, well shaking, and culturing at 26DEG C until each wheat grain is uniformly covered with hyphae; inoculating to soil with seedlings of differential hosts NC 1071, L8 and Hick's or Mini Gold 1025 in 3-5-leaf stage, wherein each seedling is inoculated with two grains; checking death count of the differential hosts 12 days after inoculation, determining that the seedlings are susceptible if more than two of three differential hosts are dead, and otherwise, determining that the seedlings are resistant; determining corresponding physiologic races according to resistance and susceptibility reaction. The method has advantages of high operability, high accuracy, high speed, simple equipment and small floor area and can be used for physiologic race identification of large-scale Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae in a greenhouse in a short time.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
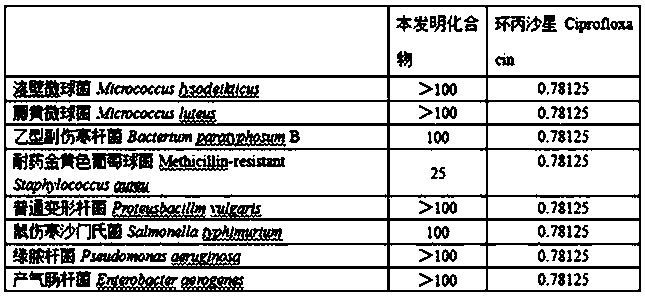
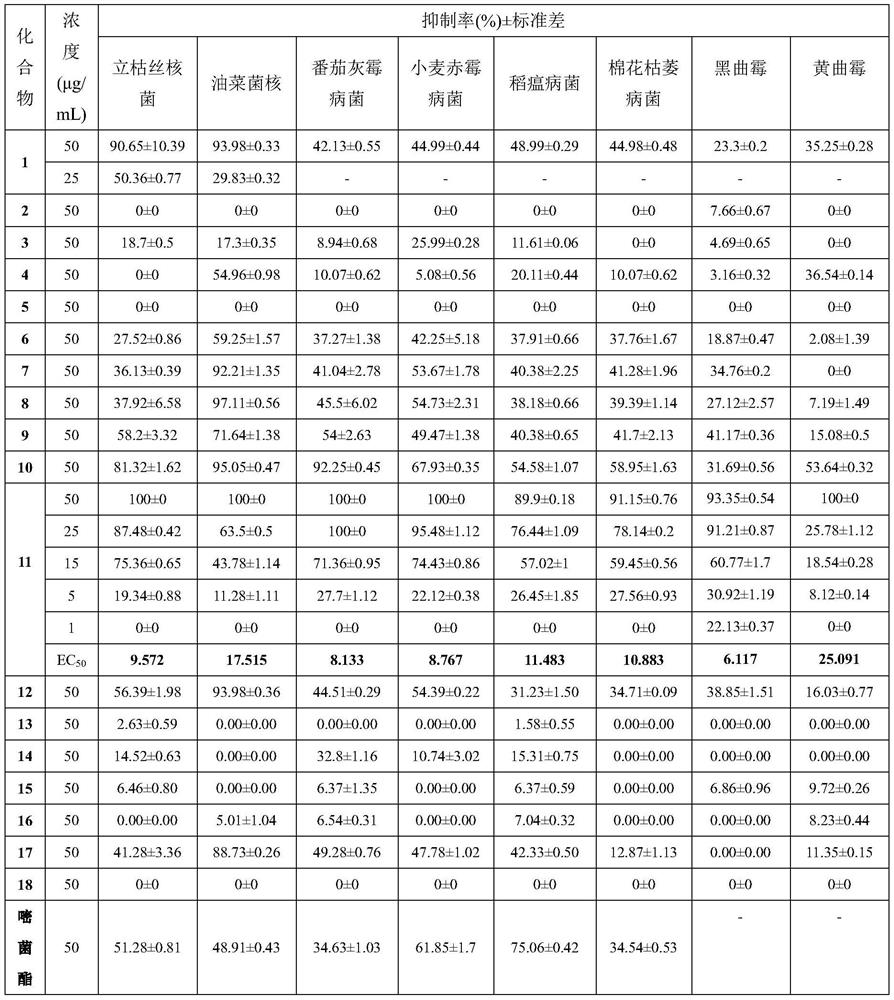
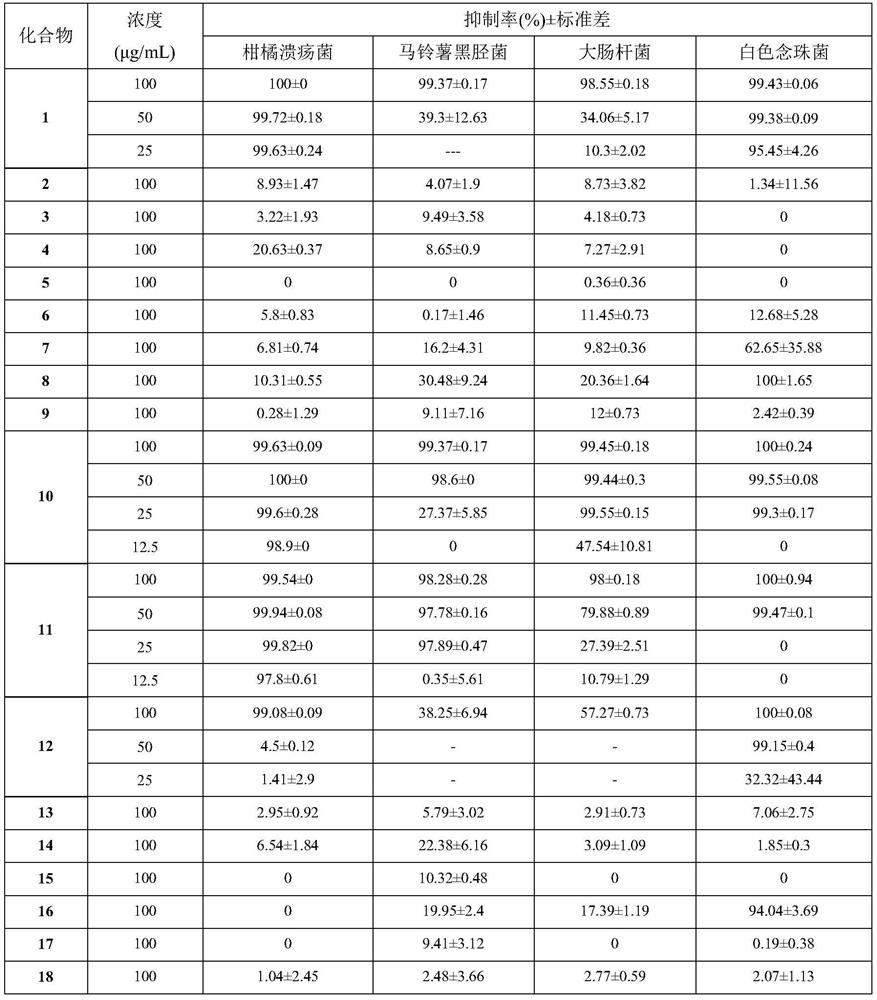
Application of disulfide bond compounds in prevention and treatment of microbial diseases
PendingCN112385659AHigh bactericidal activityBroad spectrumBiocideFungicidesDisulfide bondingCitrus volkameriana
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry, and discloses application of disulfide bond compounds in prevention and treatment of diseases caused by sclerotinia sclerotiorum, rhizoctoniasolani, botrytis cinerea, fusarium graminearum, cotton fusarium oxysporum, magnaporthe grisea, aspergillus flavus, aspergillus niger, citrus canker, potato phytophthora parasitica, escherichia coli and candida albicans. A part of the compounds show a high inhibition effect and can be used for developing bactericidal lead compounds.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting sensitivity of phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae to bactericide
InactiveCN103555811AIncreased sensitivityEffective controlMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySporeling
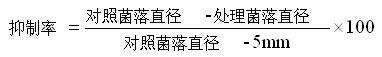
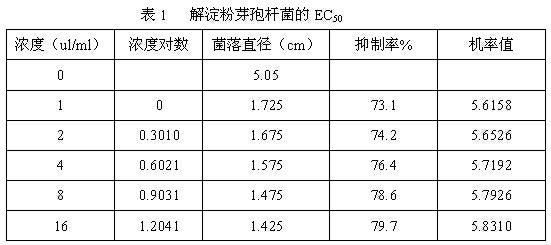
The invention discloses a method for detecting the sensitivity of phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae to a bactericide. The method comprises the following steps of diluting dimethomorph by using a lima bean liquid culture medium or an oat liquid culture medium to prepare agents with various mass concentrations; culturing the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae on a lima bean solid culture medium plate, inducing by using a V8 liquid culture medium to obtain a zoospore suspension liquid, regulating the concentration of the zoospore suspension liquid to be 1+10<4> / mL; placing a 96-hole micropore plate in a monitoring culture box, culturing in the dark at a temperature of 28 DEG C for 72h, reading data of a phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae growth curve of 0-72h by adopting growth curve monitoring software; and when culturing for 0 and 72h, determining an OD value of the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae in each pore of 590nm by adopting turbidity determination software, calculating an inhibition rate of phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae spore germination and mycelial growth of the bactericide according to a formula (1), and calculating an EC50 value of the bactericide to a strain. According to the method, the sensitivity of the phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae to the bactericide can be detected conveniently, simply, rapidly, efficiently and accurately.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST +1
Method for preventing and treating eggplant diseases and insect pests
The invention discloses a method for preventing and treating eggplant diseases and insect pests, and relates to the technical field of crop plant disease and insect pest prevention and treatment. The method is characterized by including the steps of eggplant phomopsis rot prevention and treatment, phytophthora parasitica prevention and treatment, greensickness prevention and treatment, and polyphagotarsonemus latus and red spider prevention and treatment. The method is reasonable, convenient and rapid to operate and good in effect.
Owner:GUZHEN WANJIA ECOLOGICAL LIVESTOCK FARM
Bacterium for inhibiting pathogenic bacteria of tobacco diseases and application
ActiveCN113969247AStrong stress resistanceEnhance colonization abilityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
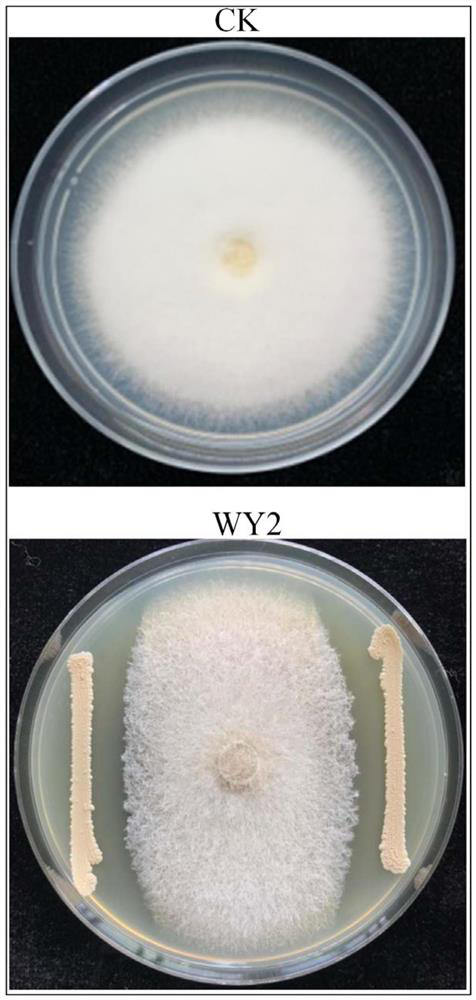
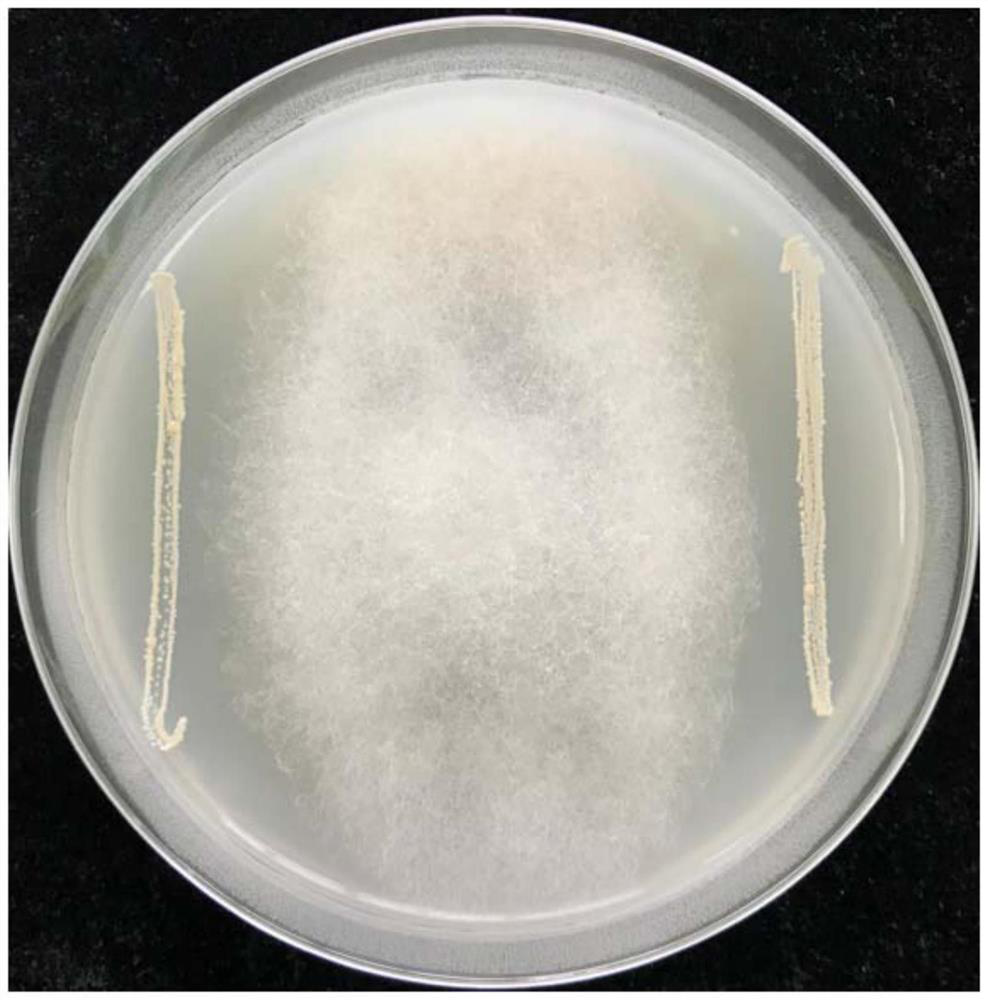
The invention relates to a bacterium. The bacterium is Bacillus velezensis WY2. The preservation place is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dadn Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.6662. According to the bacillus velezensis WY2 disclosed by the invention, the effective control on the tobacco root rot can be realized, and the relative control effect is over 60 percent; and the bacterium also has a very good bacteriostatic effect on phytophthora parasitica, botrytis cinerea, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, target leaf pathogen, mildew pathogen, alternaria alternata and the like. The bacterium is good in prevention and treatment effect and has high application and popularization value.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
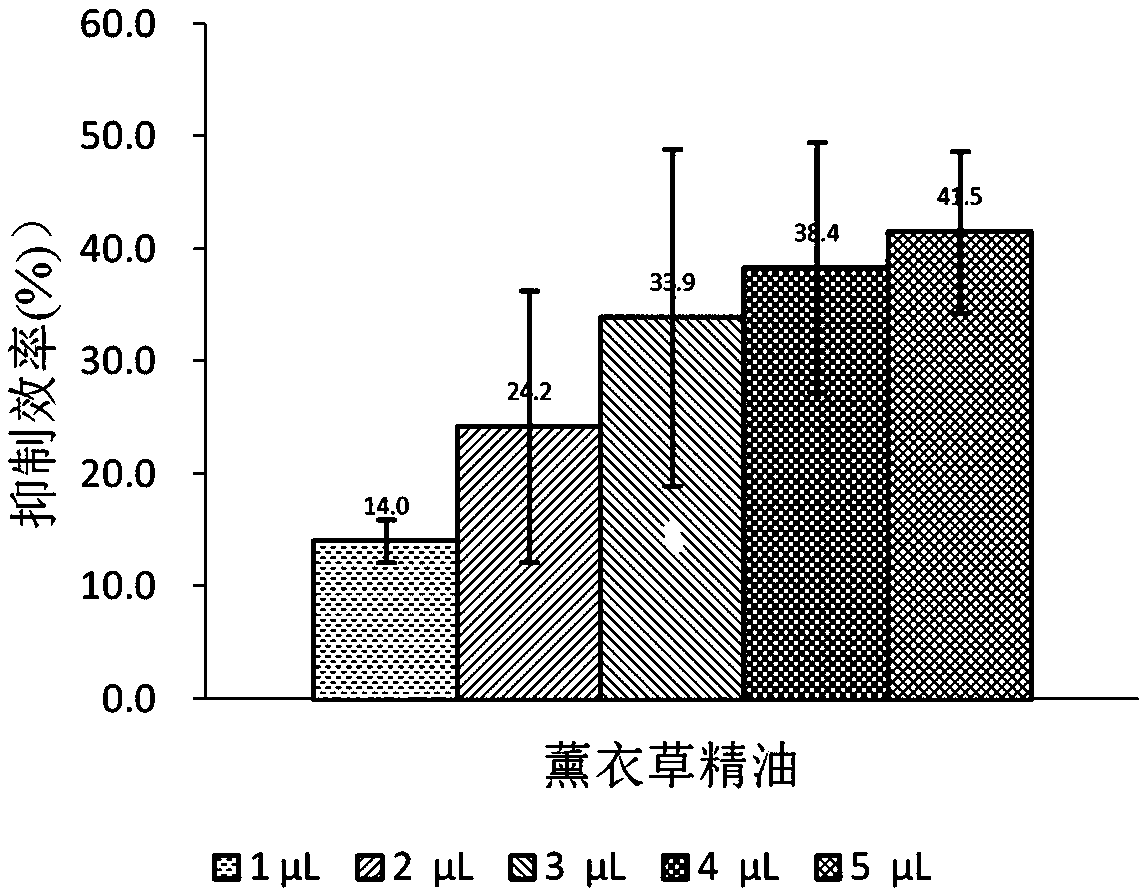
Application of lavender essential oil
InactiveCN109566660AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideFungicidesNicotiana tabacumCytotoxicity
The invention discloses an application of lavender essential oil. In order to achieve green control of crop diseases, efficient sterilization activity components are selected from aromatic plant sources, and antibacterial activity of the lavender essential oil for phytophthora parasitica is detected by a mycelial growth method. The results show that when the concentration of the lavender essentialoil reaches 250 micro-liters / liters, the lavender essential oil has remarkable inhibiting effect on the phytophthora parasitica. Dosage effect experiment results show that by a fumigation mode, an EC50 value of the lavender essential oil for inhibiting the phytophthora parasitica is 255.20 micro-grams / milliliters. Piece inserting method experiment results show that the lavender essential oil hasa certain effect on phytophthora parasitica mycelial growth. The lavender essential oil has the advantages that the oil is environmentally friendly, low in cytotoxicity and wide in spectrum, strain drug resistance is avoided and the like. The lavender essential oil is expected to be an environment-friendly novel pesticide for preventing and treating the phytophthora parasitica.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
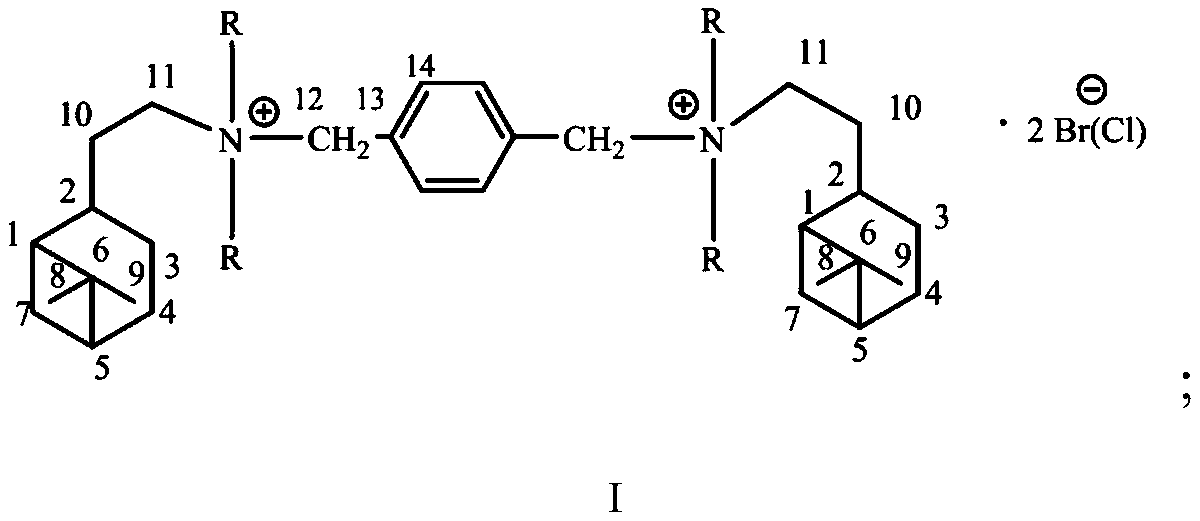
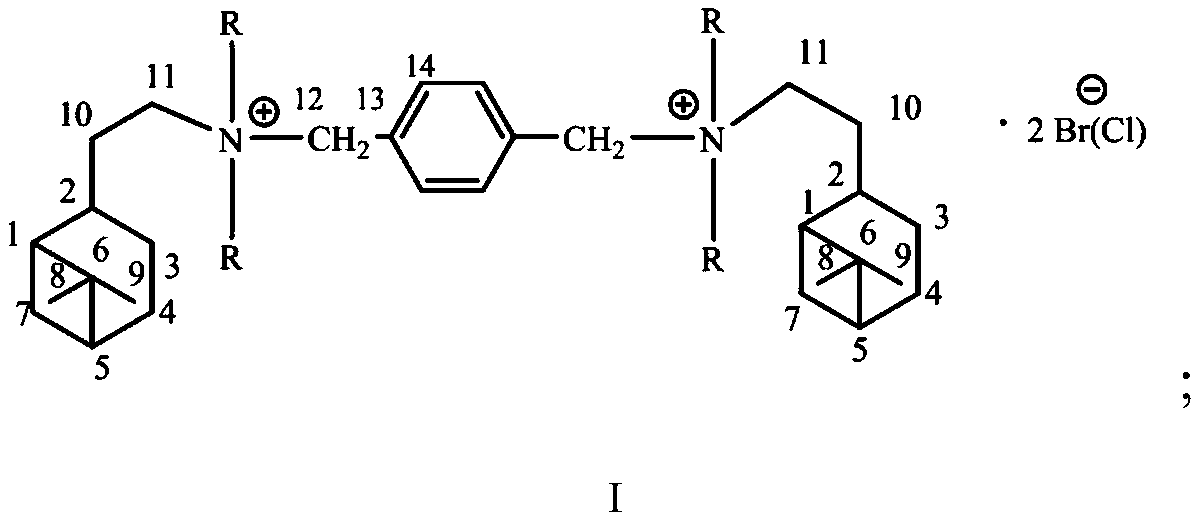
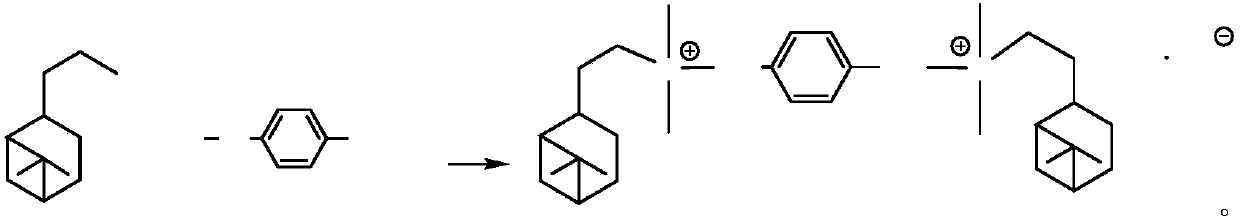
Hydrogenated nopyl gemini quaternary ammonium salt containing rigid hydrocarbon chain linking group, synthesis method and application thereof, and antibacterial agent
InactiveCN111393307AHigh yieldHigh purityBiocideOrganic compound preparationChemical synthesisCamellia oleifera
The method is suitable for the technical field of chemical synthesis and antibiosis, and provides a hydrogenated nopyl gemini quaternary ammonium salt containing a rigid hydrocarbon chain linking group, a synthesis method and application thereof, and an antibacterial agent. The synthesis method of the hydrogenated nopyl gemini quaternary ammonium salt comprises the following steps: carrying out reflux reaction on a tertiary amine compound containing hydrogenated nopyl and a halide in a weak polar solvent to obtain a reaction product; wherein the halide is 1, 4-benzyl dibromide or 1, 4-benzyl dichloride; carrying out cooling crystallization on the reaction product, and then carrying out suction filtration, washing and vacuum drying treatment to obtain the hydrogenated nopyl gemini quaternary ammonium salt. The hydrogenated nopyl gemini quaternary ammonium salt has a good inhibition effect on phytopathogens like rhizoctonia solani, camellia oleifera colletotrichum, gloeosporium eriobotryae speg, sphaeropsis sapinea, fusicoccum aesculi, coriolus versicolor, phytophthora parasitica and fusarium oxyspirum F sp niveum.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
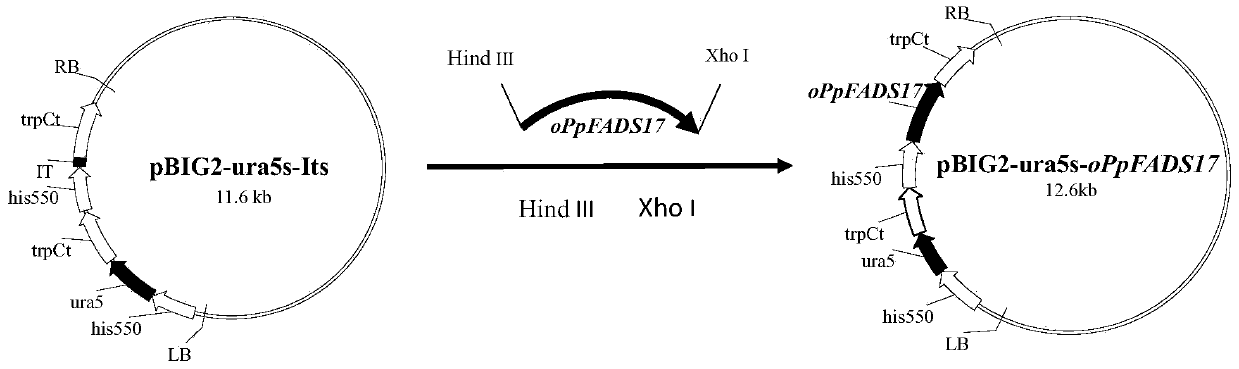
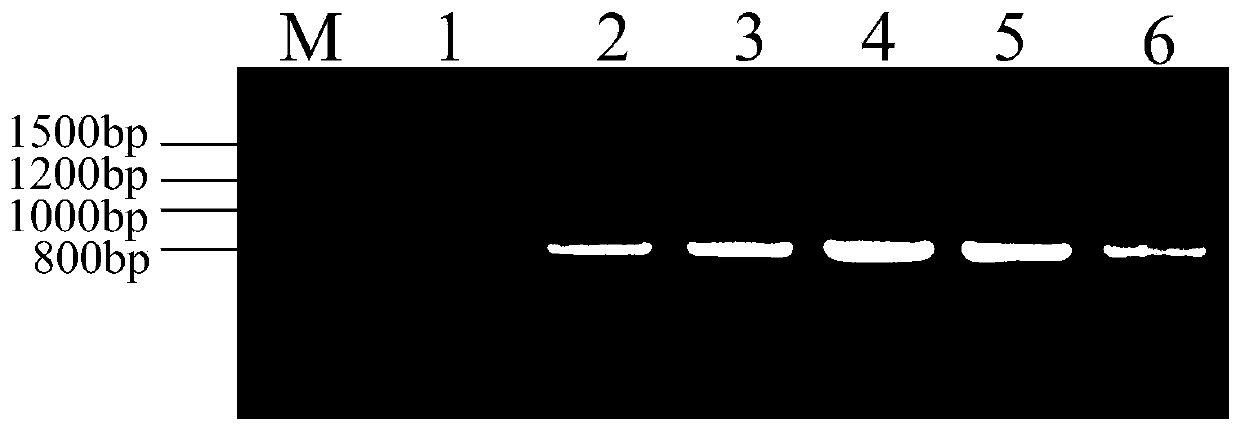
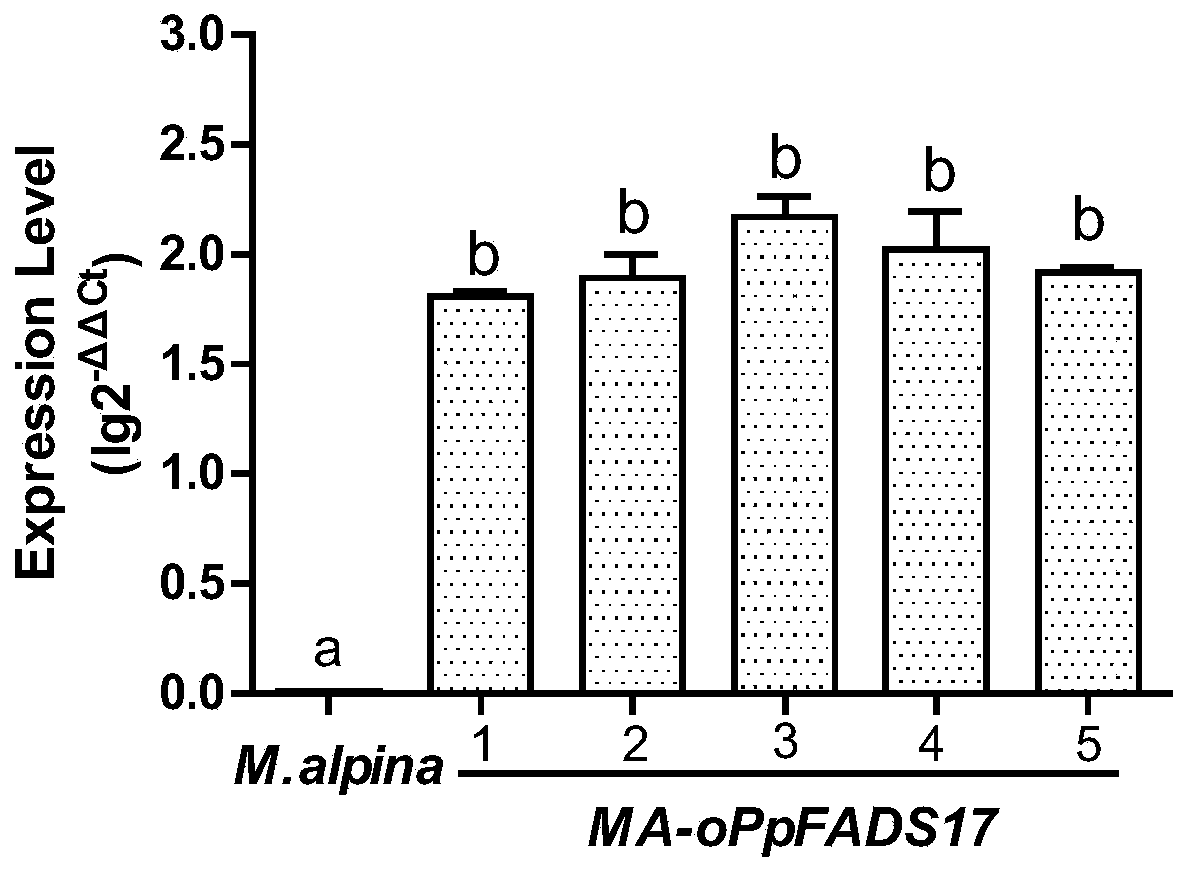
A recombinant Mortierella alpina overexpressing ω-3 desaturase derived from Phytophthora parasitica, its construction method and application
The invention provides restructured mortierella alpina strain MA-oPpFADS17-4 with heterologous experession from omega-3 desaturase genes of phytophthora parasitica, and provides a method for establishing the restructured mortierella alpina. The mortierella alpina uracil heterotrophia type strain is used as materials and produces a constant-temperature high-yield EPA restructured strain through the genetic operation technology of agrobaterium tumefaciens mediate. Production of EPA reaches 1197.3 mg / L and accounts for 31.5% of TFA content, and conversion rate for AA is 77.6%. The restructured mortierella alpina strain is of great significance for basic theory research and product development of the oil-producing fungus, mortierella alpina.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
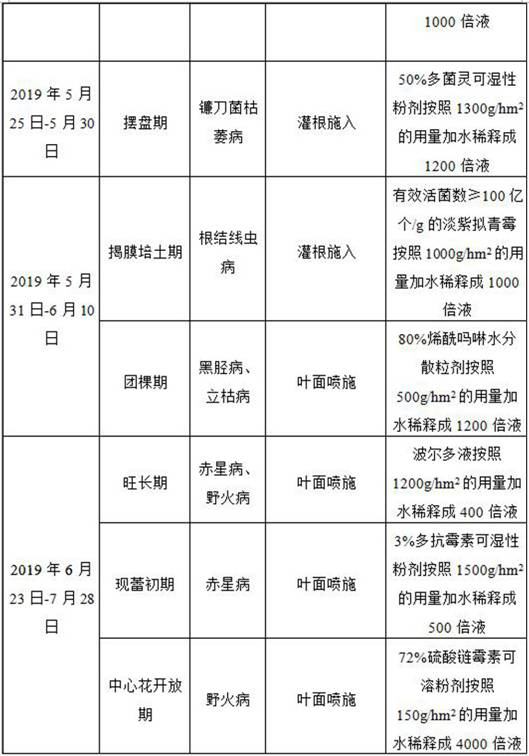
Pesticide applying control method for susceptible diseases of Mammoth gold under acid soil condition
The invention discloses a pesticide applying control method for susceptible diseases of Mammoth gold under acid soil condition, and belongs to the technical field of tobacco planting. The pesticide applying control method comprises the steps of improving soil with quick lime at the stage of preparing soil for ploughing and sowing, during simultaneous control, and simultaneously applying medicamentfor controlling phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae and rhizoctonia solani Kuhn and medicament for controlling meloidogyne spp. to lands for growing field crops in different growing stages. Special control on fusarium axysporum is performed from the stage of placing plates to rosette stage. During alternative control, medicament for controlling alterna ria alterna ta and medicament for controlling Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tacaci are alternatively applied to the lands for growing field crops from the vigorous growing stage, wherein the time intervals for applying the medicament each time is 7-10 days. According to control risk degrees, the number of applying numbers of the control medicament is adjusted during simultaneous control, special control and alternative control, and accordingto the disease generation kinds, the kinds and the applying manners of the control medicaments can be adjusted in the total growth stage of the tobacco plants. The medicament applying control methodcan perform pinpoint control on various susceptible diseases in the planting process of the Mammoth gold, and the effect is notable.
Owner:YUNNAN TOBACCO CO LTD KUNMING BRANCH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com