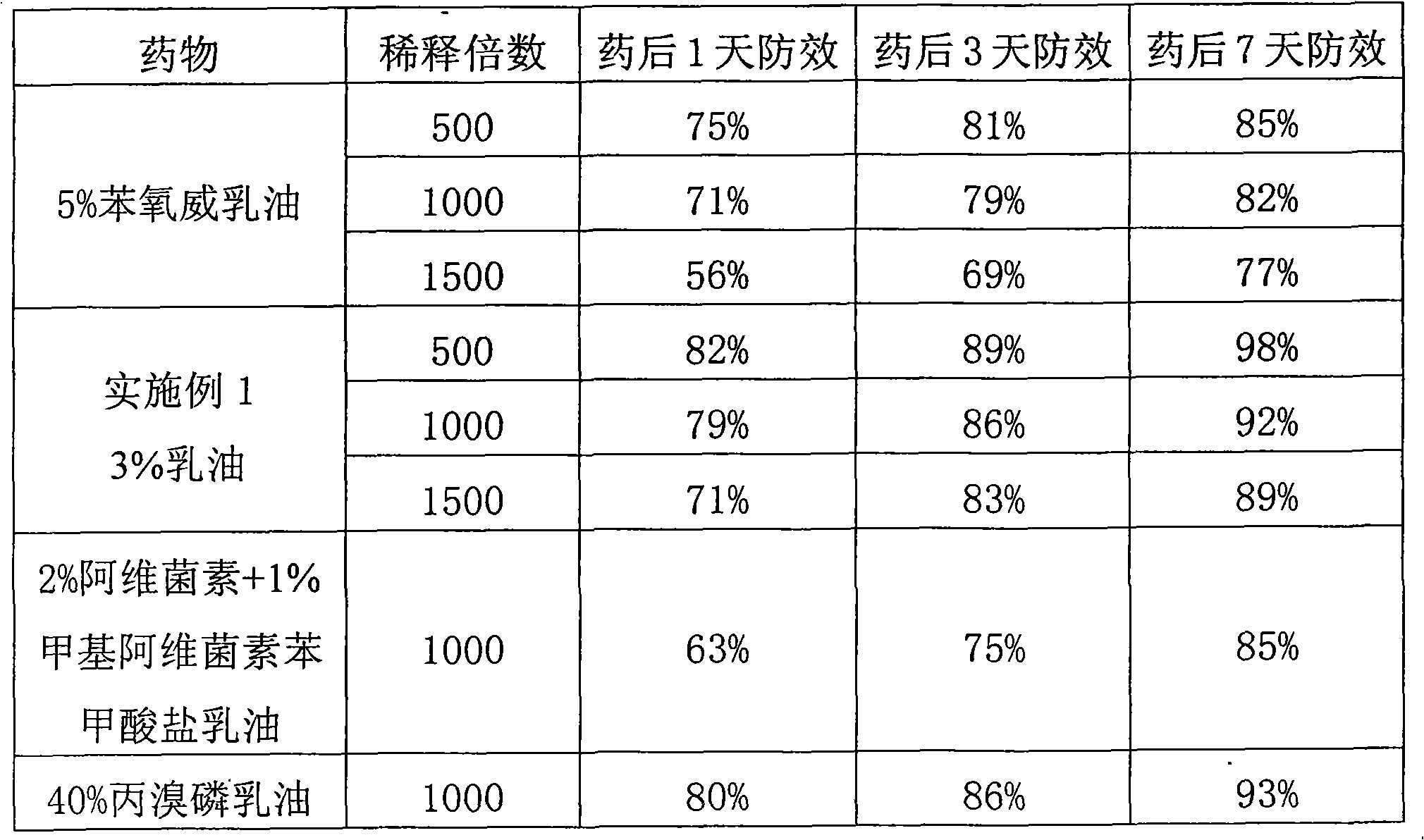
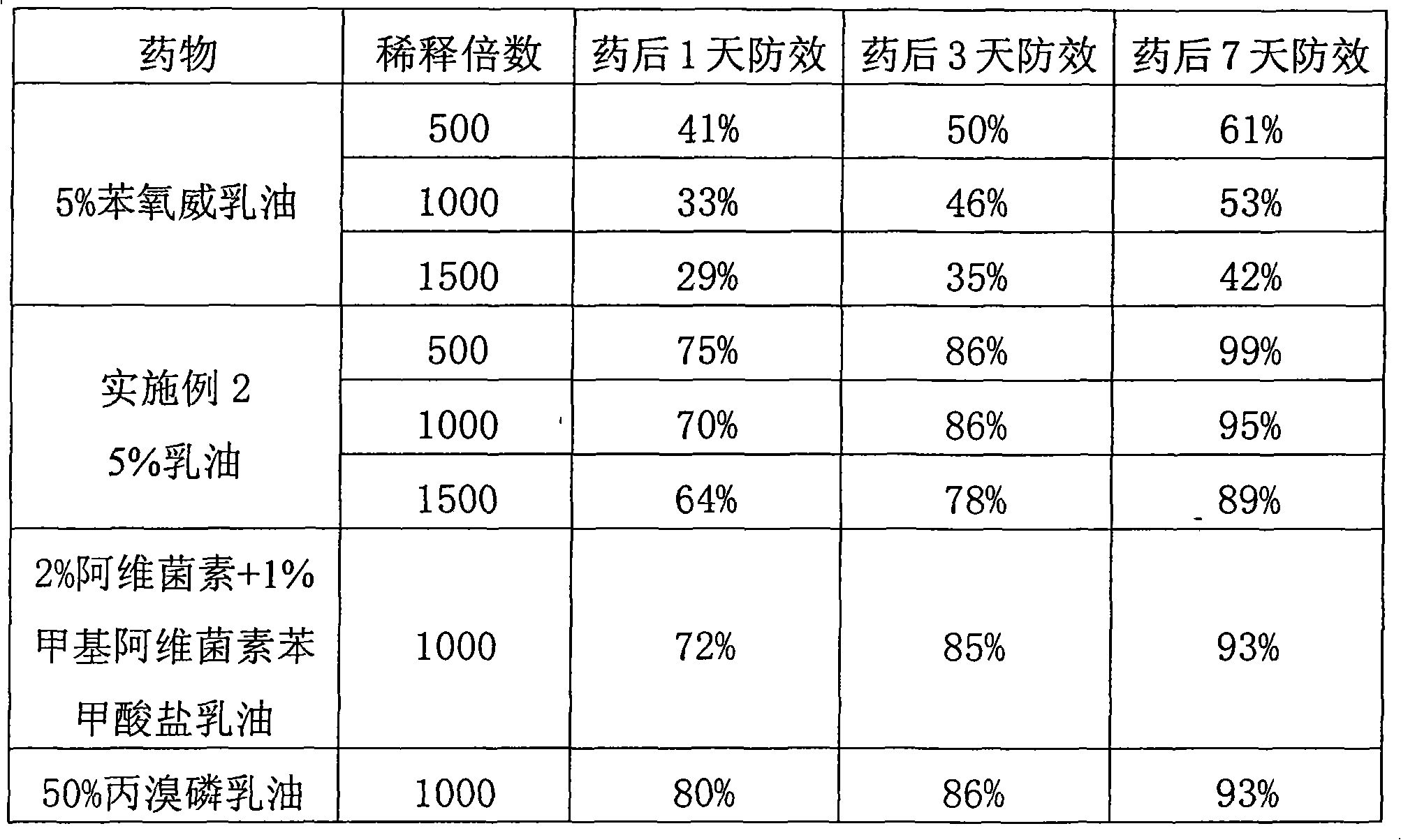
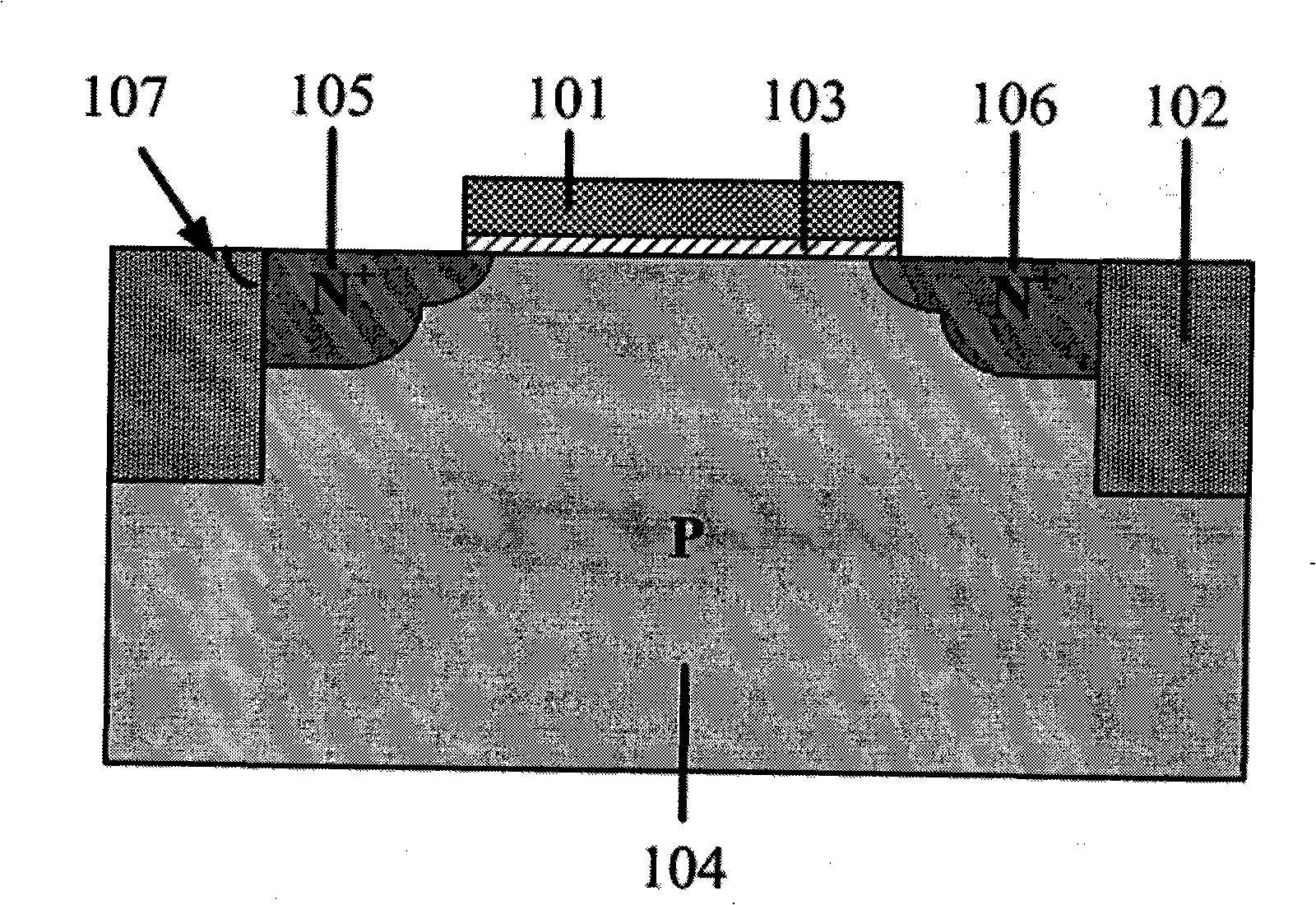
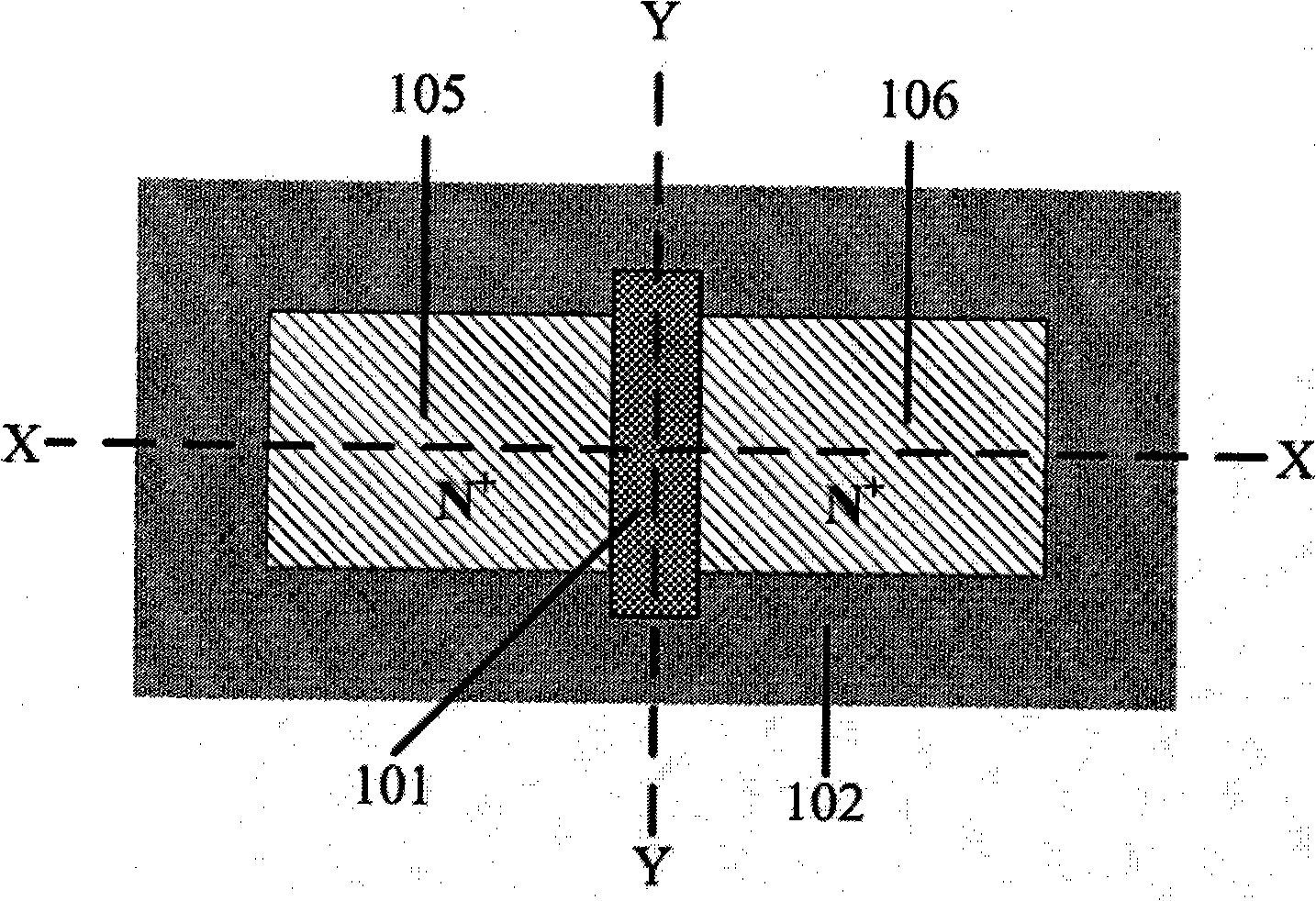
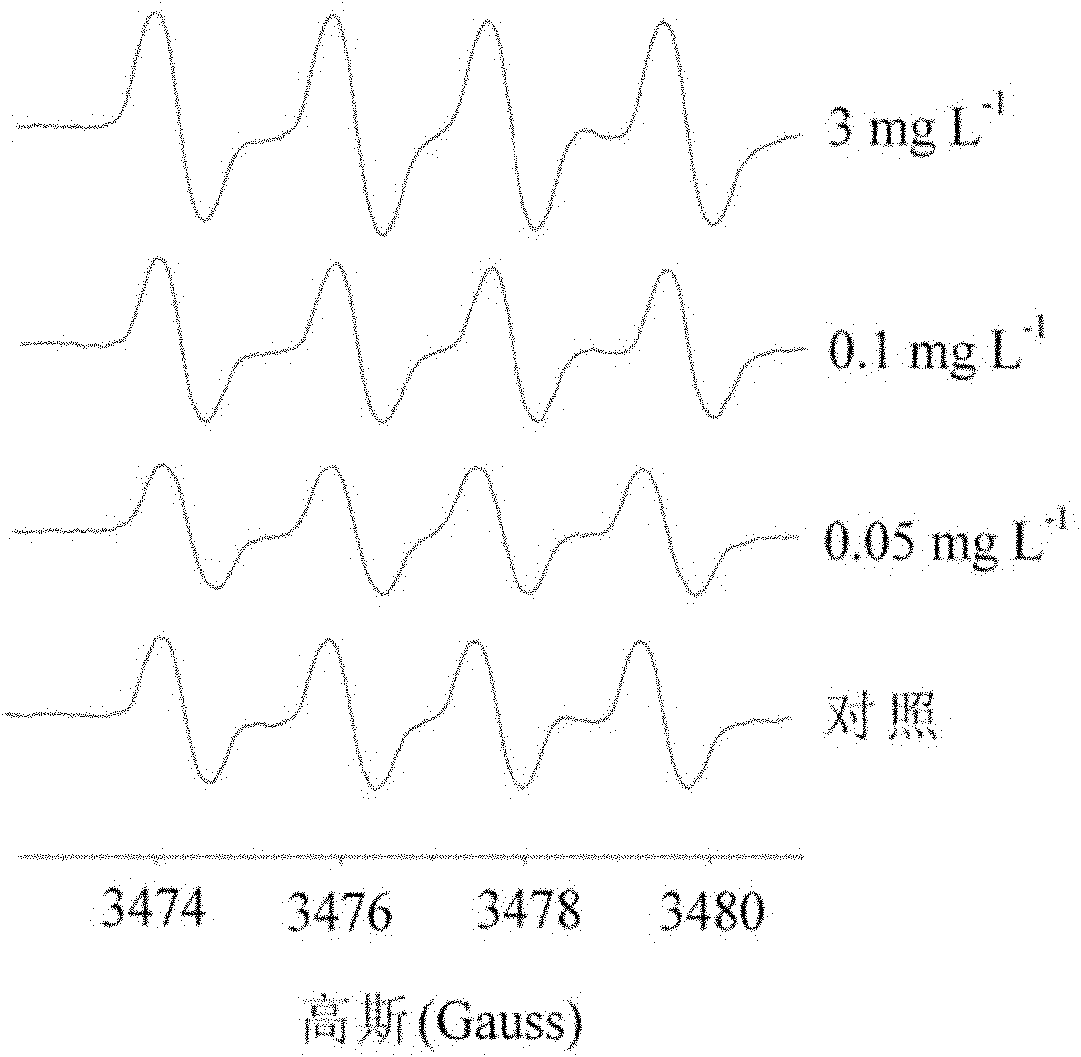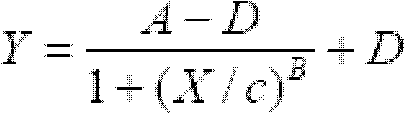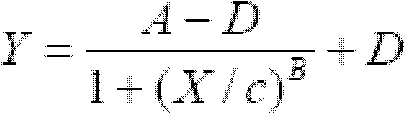Patents
Literature
74 results about "Dosage effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
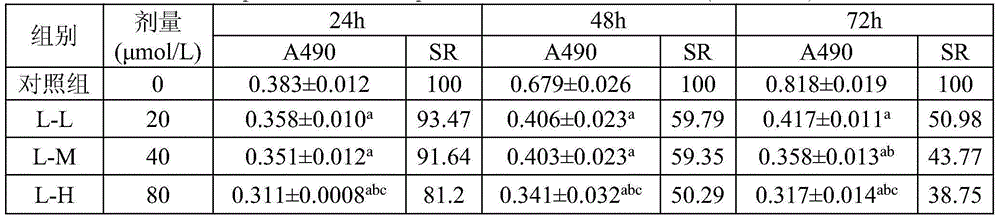
Method for measuring superoxide anion radicals in tape grass leaves
InactiveCN101936930AEasy to operateEasy to masterAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceSuper oxide dismutasePlant roots
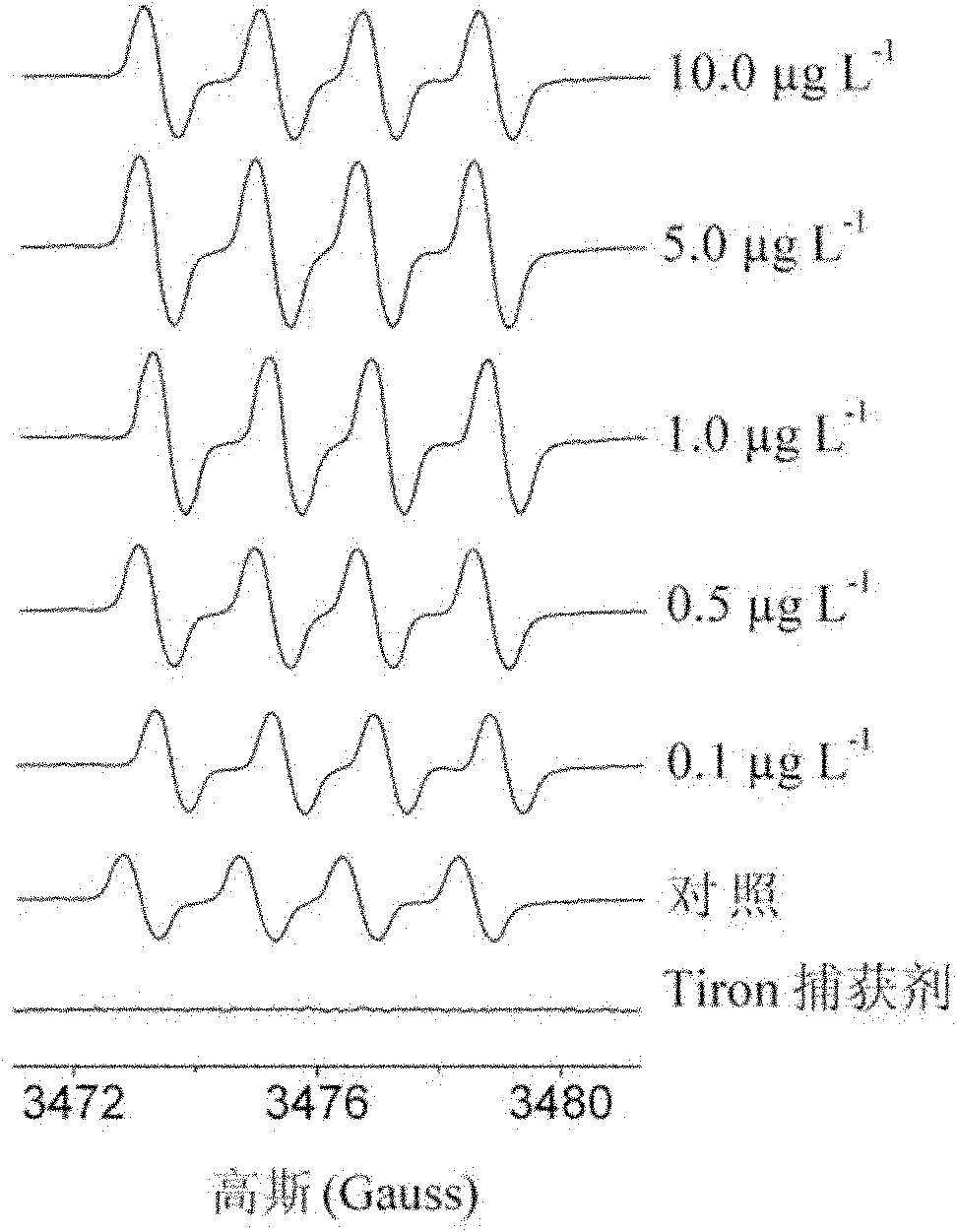
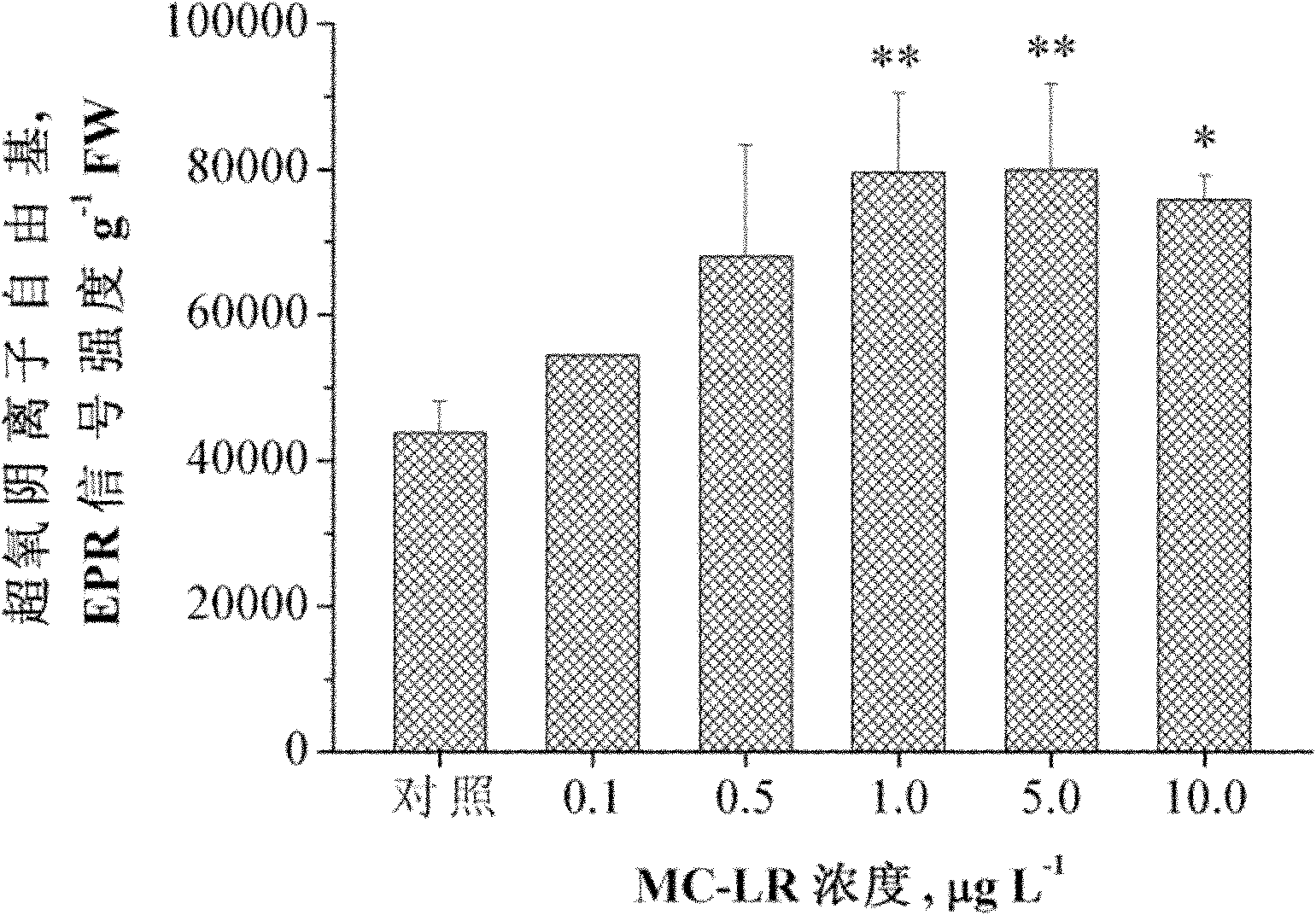
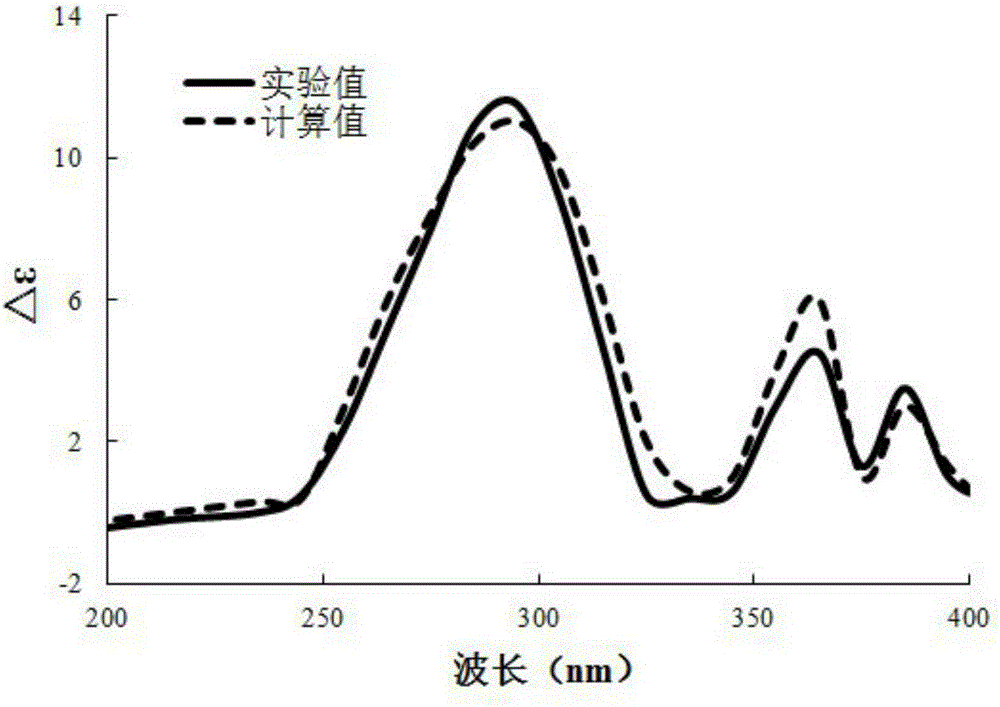
The invention discloses a method for measuring superoxide anion radicals in tape grass leaves, belonging to the measuring field of the measuring of superoxide anion radicals. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, collecting and cleaning the tip parts of fully exposed small and tender tape grass leaves; carrying out Tiron captureing on the Tiron of radicals in a closed operation box in a closed nitrogen environment; and finally measuring by using an EPR (Electron Paramagnetic Resonance) technology. The invention has the advantages of simpler operation and easy grasping, and can measure the superoxide anion radicals of the tape grass leaves in a very short time;, find that and the measured radicals are found to be the superoxide anion radicals according to the superfine structure constant and, the spectrogram shape analysis of an EPR spectrogram and the combination of the remarkable decreases of the radical strength of the leaves pretreated by SOD (Super Oxide Dismutase), and therefore the invention is the most direct, accurate and effective method for measuring the superoxide anion radicals. Superoxide anions are sensitive to pollutants and have a favorable dosage effect relation. The invention is also suitable for other aquatic plant and terrestrial plant species and can be suitable for measuring the radicals of the plant root tissue.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for improving total dosage effect of anti-ionizing radiation of device
InactiveCN103996673AImprove shielding effectImprove total dose effect against ionizing radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionDosage effect
The invention relates to a method for improving the total dosage effect of anti-ionizing radiation of a device. The method comprises the first step of manufacturing a single-layer structure composite material, the second step of manufacturing a multi-layer structure composite material, the third step of measuring transmission coefficients of an electron beam in the composite materials, the fourth step of simulating and calculating theoretical transmission coefficients of the materials based on the Monte Carlo particle transporting method, the fifth step of correcting the electronic transmission coefficients, and the sixth step of carrying out secondary packing on corresponding chips of the device through the composite materials with the best shielding effect. By means of the method, the shielding effect is best, the packing weight is minimal, and the total dosage effect of anti-ionizing radiation of the spacecraft device can be improved.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
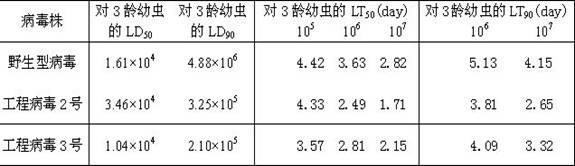
Prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and building method thereof
InactiveCN102329783AFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeUridine diphosphate
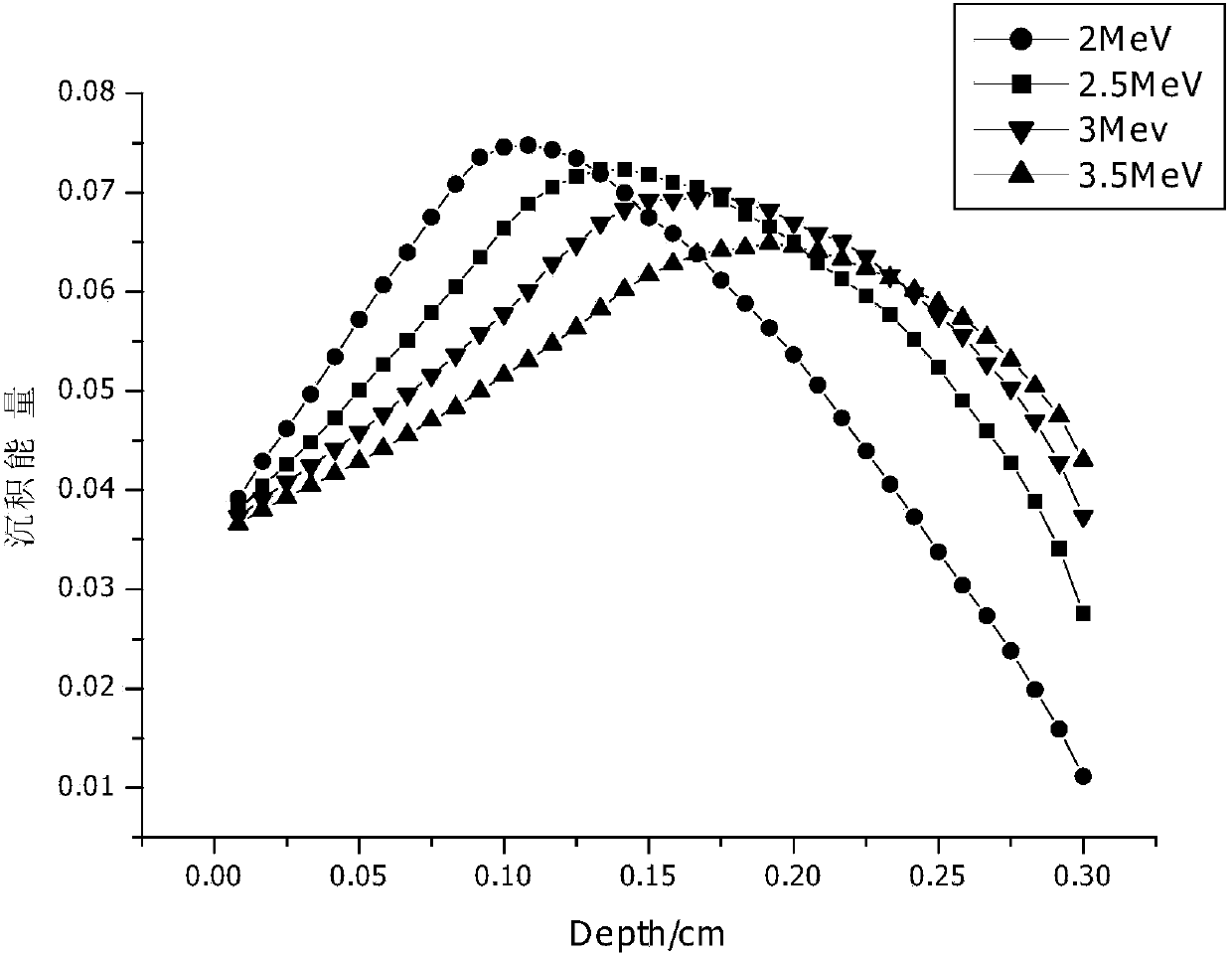
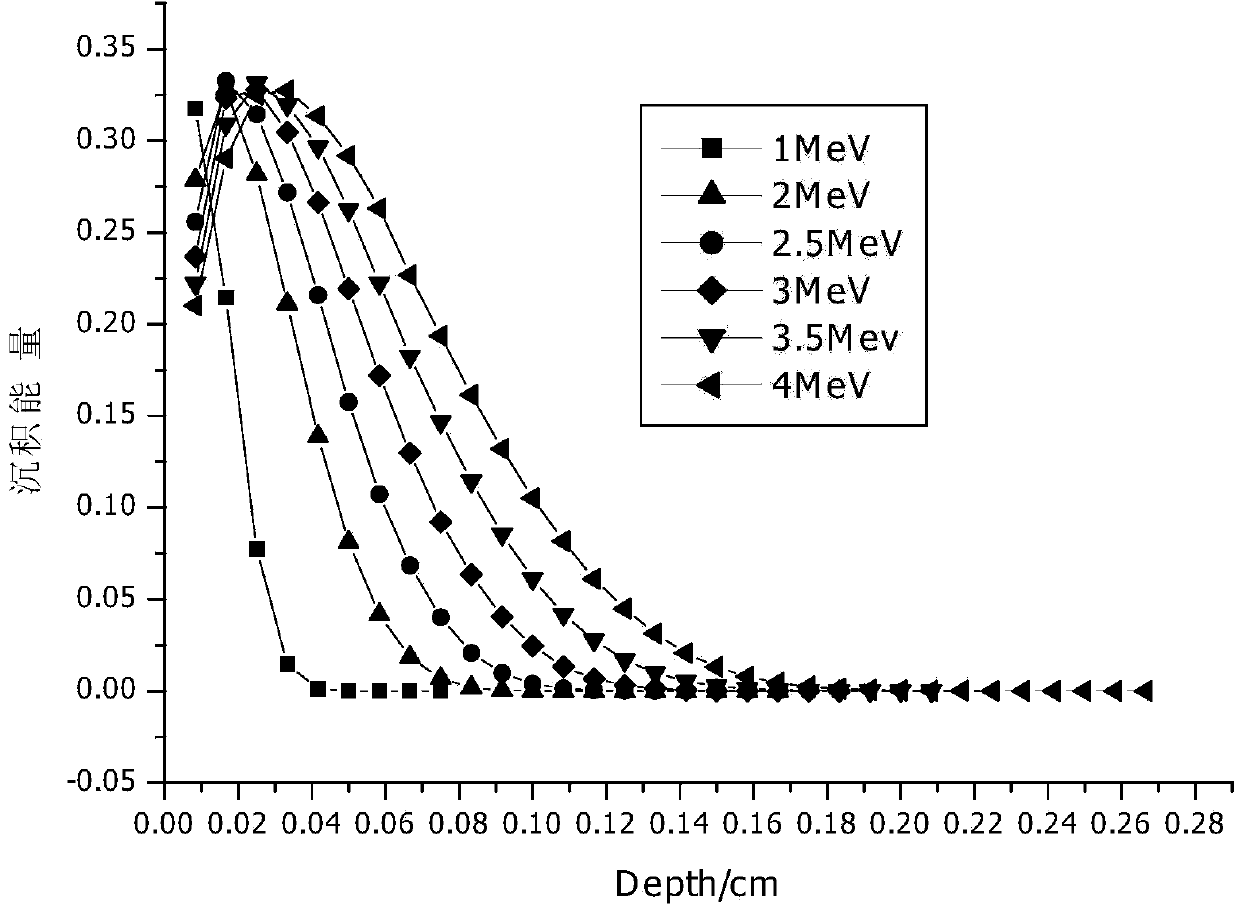
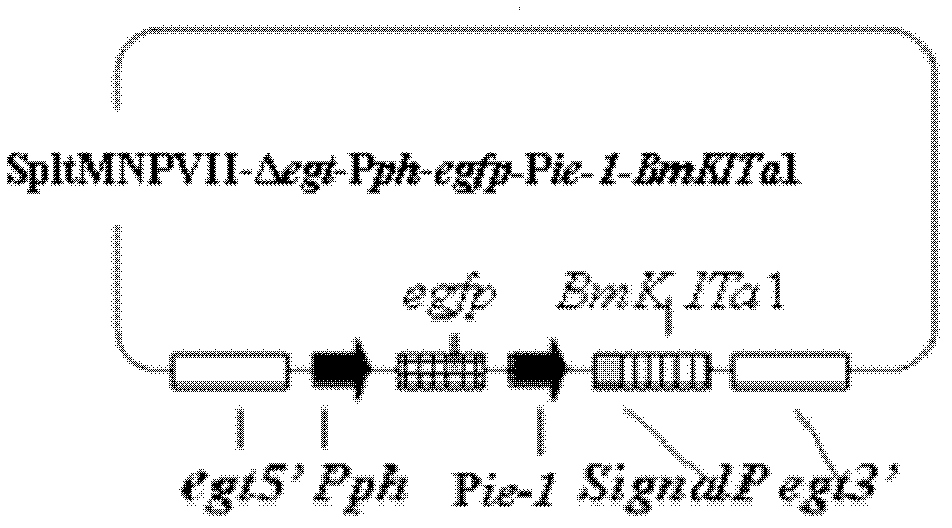
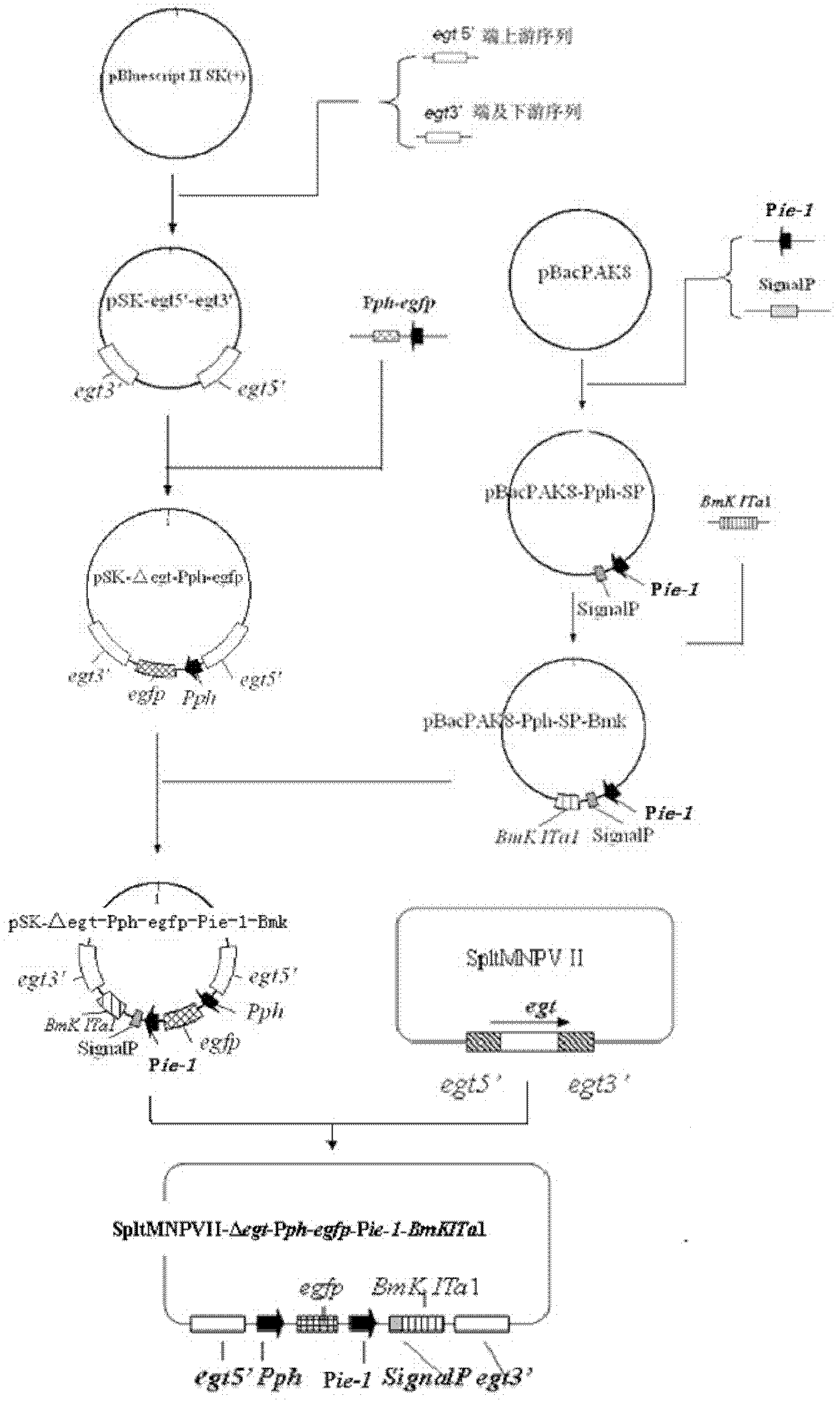
The invention discloses a prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and a building method thereof, in particular relates to a prodenia litura gene engineering virus used for carrying out deficiency and recombination on a wild type virus (SpltMNPV II) by utilizing a gene engineering method. The genome of the virus is deficient in an egt gene, namely an ecdysteroid UDP (uridine diphosphate) glucosyltransferase gene; and at the site of the deficient egt gene, a BmKITa1 gene controlled by a wild type virus, namely an early gene-1(ie-1) starter, and a marker gene, namely an enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene, which is controlled by the wild type virus, namely a polyhedron gene (ph) starterare inserted. The prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of faster insecticidal speed, less dosage effect and better field application effect compared with the wild type virus. Compared with the prior art, the prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 provided by the invention has less dosage effect and lower LT50 at low dose (105 polyhydral bodies / larva).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
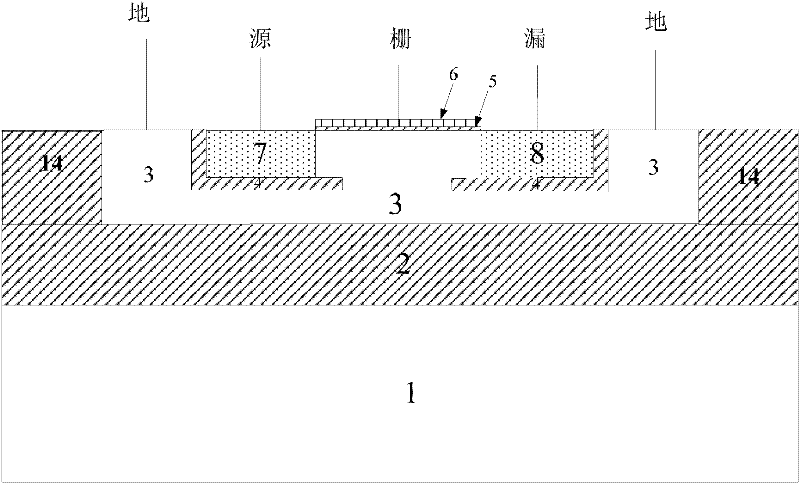
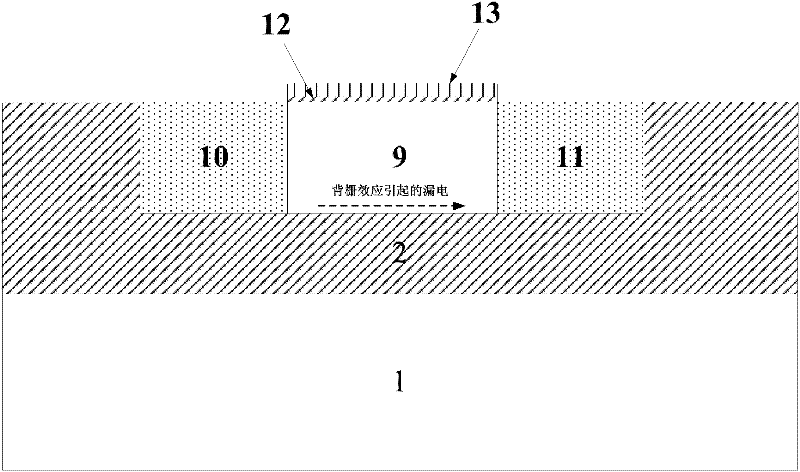
Structure of radiation-resistant MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device based on partially-consumed type SOI (Silicon-On-Insulator) process
ActiveCN102347367AImprove radiation resistanceReduce junction depthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRadiation resistantIsolation layer
The invention relates to a structure of a radiation-resistant MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device based on a partially-consumed type SOI (Silicon-On-Insulator) process. The structure comprises an SOI substrate and the SOI substrate comprises a silicon film; the upper part of the silicon film is etched with a groove and first isolation layers grow on the side wall and the bottom of the groove; the first isolation layers are etched to form a growing window corresponding to a central region which is located at the bottom part of the groove, mono-crystalline silicon grows in the groove through the growing window and the mono-crystalline silicon grows to cover the corresponding first isolation layers; a grid region is arranged on the central region of the mono-crystalline silicon; and a source region and a drain region are respectively formed in the mono-crystalline silicon corresponding to two sides of the grid region. With the adoption of the first isolation layers provided by the invention, the influence of a threshold voltage shift of a back grid and an opening effect of the back grid on a front grid, which is caused by that a buried oxidation layer is influenced by a total dosage effect, is eliminated; meanwhile, the junction depths of the source region and the drain region of the MOS device are also reduced so that the influence of single event effects on the MOS device is reduced and the radiation-resistant capability of the device is further improved. The structure provided by the invention has the advantages of compact structure, improved radiation-resistant capability, and safety and reliability.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
Method for detecting dioxins in environment
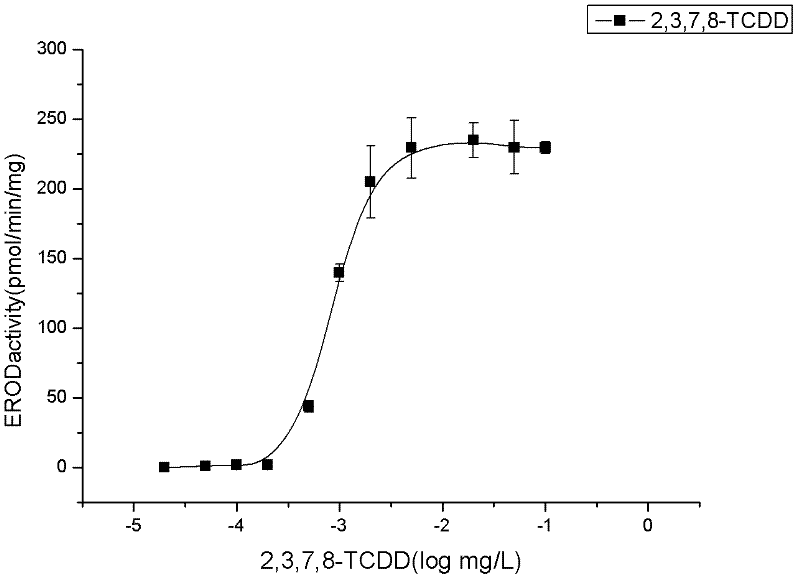
ActiveCN102520154ASimple test methodLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsOrganic solventDioxin Compound
The invention relates to a method for detecting dioxins in environment. Rat hepatocyte hepatoma H4IIE cells are used as detection means; the cells are treated with adherent culture for 24h; environment sample organic solvent extract or chemicals dissolved by organic solvent is added into the cells; the cells are further cultured for 72 h; a dosage-effect relation standard curve of EROD enzyme vitality induction of 2,3,7,8-TCDD on H4IIE cells is drafted by determining an EROD enzyme activity and using 2,3,7,8-TCDD as a standard compound, so as to further evaluate toxicity effect of dioxin compound in a sample. The invention has advantages of simple operation, low cost, short detection time and high flux, and can be used as rapid screening means for environment sample and suspected dioxin compound.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
Method for performing low-dosage radiant biology early warning by utilizing luminous bacteria
The invention relates to a method for performing low-dosage radiant biology early warning by utilizing luminous bacteria. According to the method, a dosage-effect relationship between a radiant dosage acceptable by the bacteria and a luminous intensity can be established by utilizing a sensitivity of the luminous bacteria to the low-dosage radiation, and the luminous intensity of the bacteria has positive correlation with the activity of luminous elements such as fluorescein, luciferase and ATP in the bacterial cells. Therefore, through calculation of a luminous intensity suppression ratio of the luminous bacteria, the comprehensive toxicity of the low-dosage radiation for the luminous bacteria can be estimated, and a biology early warning method is established. The method for performing low-dosage radiant biology early warning by utilizing the luminous bacteria has multiple advantages of being convenient, simple and fast to operate, low in cost, high in sensitivity, good in accuracy, low in environment risk and the like.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Rare minnow beta type estrogen receptor and use thereof
InactiveCN101469020ARegulation of reproductive capacitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementReceptors for hormonesMinnowCarp
The invention provides a rare golden carp beta type estrogen receptor and an encoded gene thereof. The invention also provides a method for detecting the chemical toxicity of an aquatic environment and a kit for diagnosing the diseases of aquatics. The method and the kit both relate to the detection of the expression level of the receptor. The invention is applied to detecting the chemical toxicity of the aquatic environment and diagnosing the diseases of aquatics, in particular the piscine genital system diseases, thereby realizing the aim of regulating the piscine reproductive ability. Experimental results show that: the expression of the GrER beta gene has a dosage-effect relationship with the estrogen effect; therefore the method has the advantage of simple, quick and correct operation.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting pesticide residue pollution of corn
InactiveCN106501413ARapid Prediction of PhytotoxicityEasy to operateComponent separationPhytotoxicityPesticide residue
The invention discloses a method for detecting pesticide residue pollution of corn. The method comprises the following steps: spraying a group of nicosulfuron solutions with gradient concentration into a group of test soil, and sowing corn seeds into the test soil after spraying; one day after spraying, collecting in-situ porous water of the soil, and testing the concentration of nicosulfuron in the in-situ porous water; performing culture for multiple days, and testing the height of corn plants; finally performing fitting so as to obtain a dosage effect curve equation of the height of the corn plants and the concentration of the nicosulfuron in the in-situ porous water, and the concentration IC50 of the nicosulfuron in the in-situ porous water when the corn plant height inhibition rate is 50%; testing the concentration of the nicosulfuron in the in-situ porous water of the soil, and predicting the plant height inhibition rate of the corn planted in the soil according to the dosage effect curve equation. The method is simple and rapid to operate, and the plant toxicity of the nicosulfuron in the soil to be tested can be rapidly predicted according to the dosage effect curve equation of the nicosulfuron in the soil and the concentration of the nicosulfuron in the in-situ porous water of the soil to be tested.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method of reducing content of amylase in hybrid rice
The invention discloses a method of reducing the content of amylase in hybrid rice and belongs to the technical field of rice genetic breeding. In the method, an original hybrid rice combination: one of a parent of a non-glutinous sterile line / a non-glutinous restorer is modified into a glutinous parent. The hybrid rice is prepared through a hybridization method of a glutinous sterile line / non-glutinous restorer or a non-glutinous sterile line / a glutinous restorer to obtain a hybrid rice variety in which the content of the amylase is lower than that of the original hybrid rice. In the invention, by means of a genetic effect and a genetic dosage effect of a glutinous gene wx, a near-isogenic line combination is reduced in the content of the amylase. In addition, a growth period, a plant and leaf form, panicle traits, floral organ traits, yield traits, disease resistant performance, adaptability and the like of the near-isogenic line combination are free of significant different when the near-isogenic line combination is compared with the original hybrid rice combination. Through quality analysis and taste evaluation, a new hybrid rice variety being appropriate in the content of the amylase and having the taste and the quality which are suitable for people in different region, thereby achieving an object of genetically improving a poor taste and a poor quality due to a high amylase content in the hybrid rice in the prior art.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Application of triptolide and triptolide derivative to preparation of medicine for treating and/or preventing lung injury diseases
InactiveCN106994129APrevent proliferationInhibition of replicationOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseMethylprednisolone
The invention provides a novel purpose of triptolide and a triptolide derivative. The triptolide can obviously inhibit the GFP fluorescent protein and P24 antigen rise effect in a phorbol ester activated lymphocyte model. When the concentration of the lymphocyte concentration is higher, the GFP positive cell percentage and the P24 antigen concentration are lower; the negative dosage-effect relationship exists. Even when the concentration of the methylprednisolone is as high as 400 uM, the inhibition effect cannot reach the inhibition effect of the triptolide with the concentration being 0.02 uM; the cell apoptosis proportion obviously exceeds the triptolide with the concentration being 0.02 uM. According to the principle, the triptolide inhibits the G0 / G1 period cell proportion rise and S period cell proportion descending due to PMA; the cell period is promoted to be stopped in the unactivated state; the triptolide achieves the effect of inhibiting the lymphocyte cell proliferation and activation through regulating the cell period; meanwhile, the effect of inhibiting the virus replication is also achieved. The triptolide and the triptolide derivative can replace glucocorticoid analogues or can be combined with the glucocorticoid analogues to be used, and are used for treating and / or preventing lung injury diseases.
Owner:王晓辉
Method for detecting toxicity influence of stomach toxicity pesticides or transgene insecticidal protein to Propylaea japonica
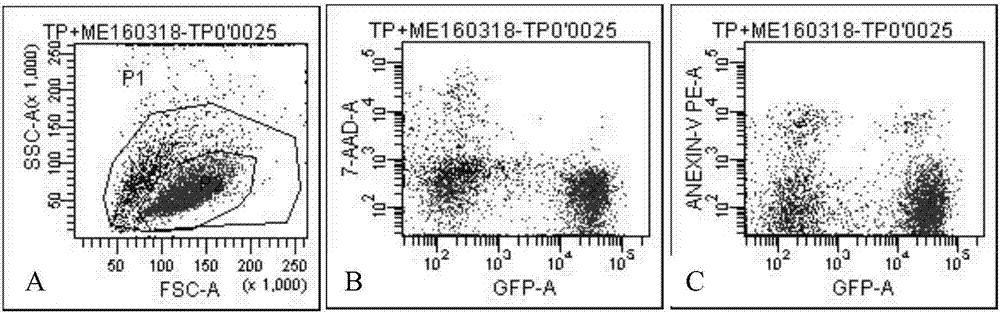
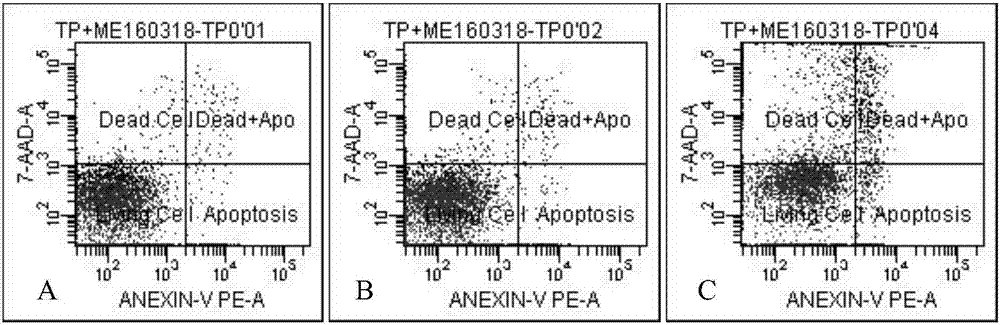
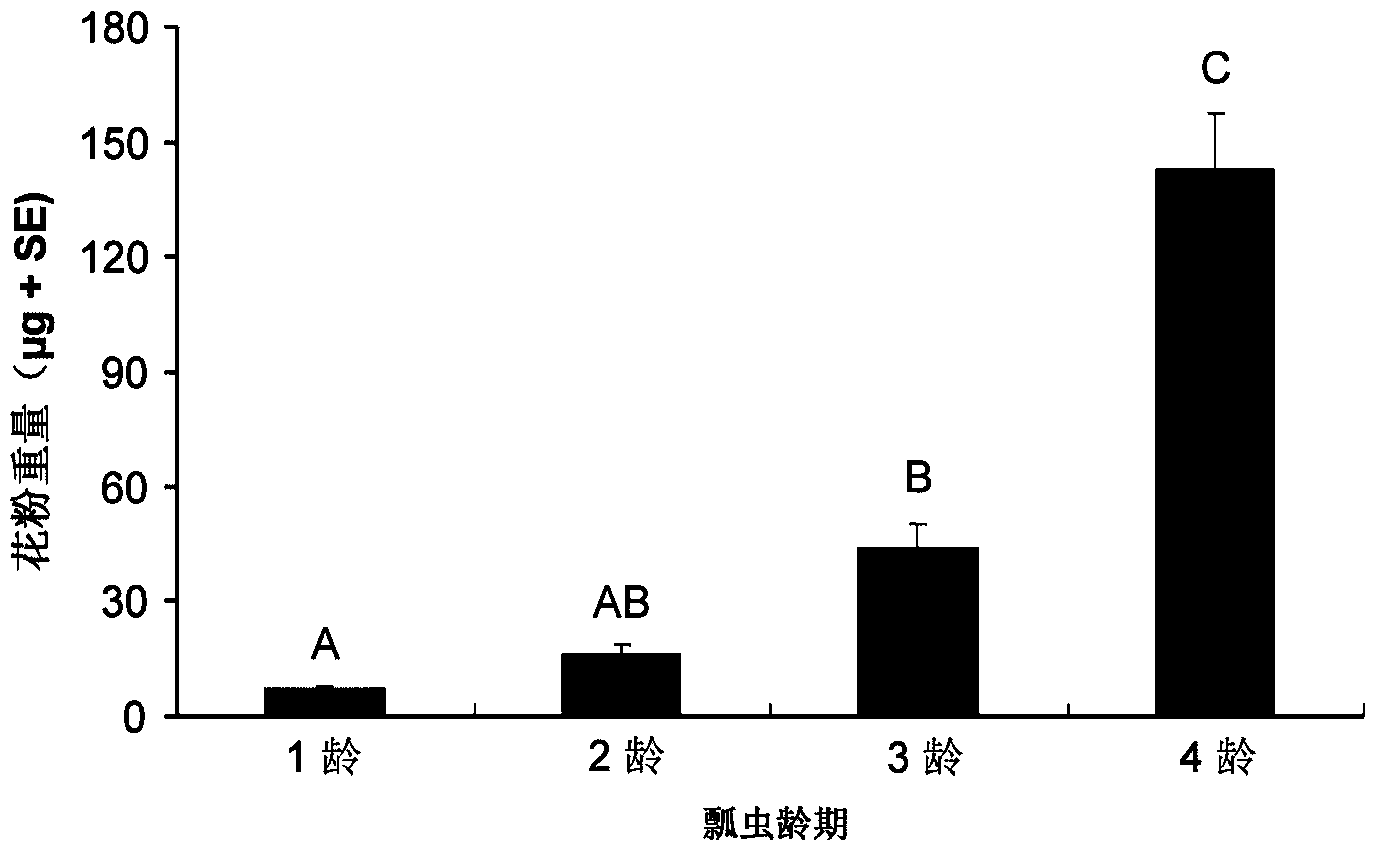
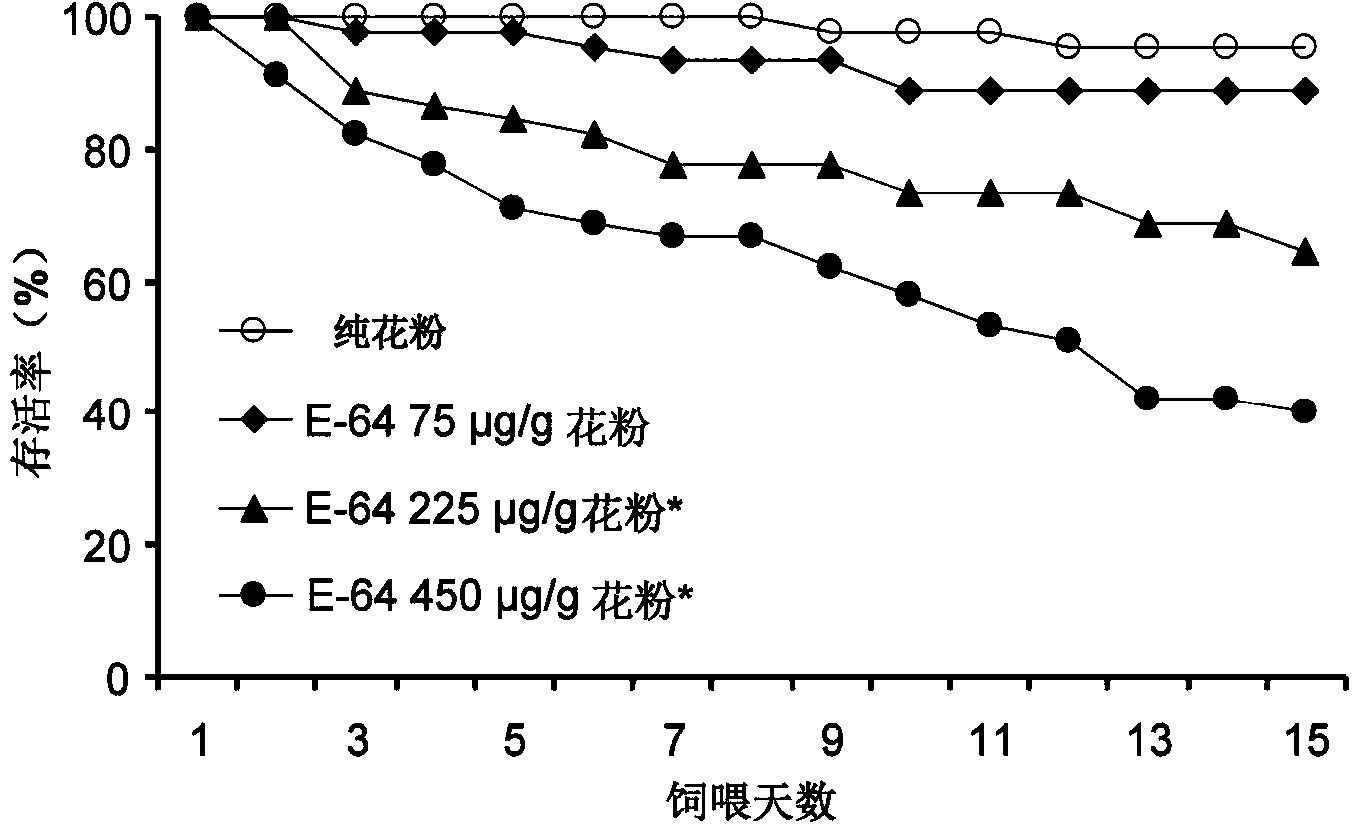
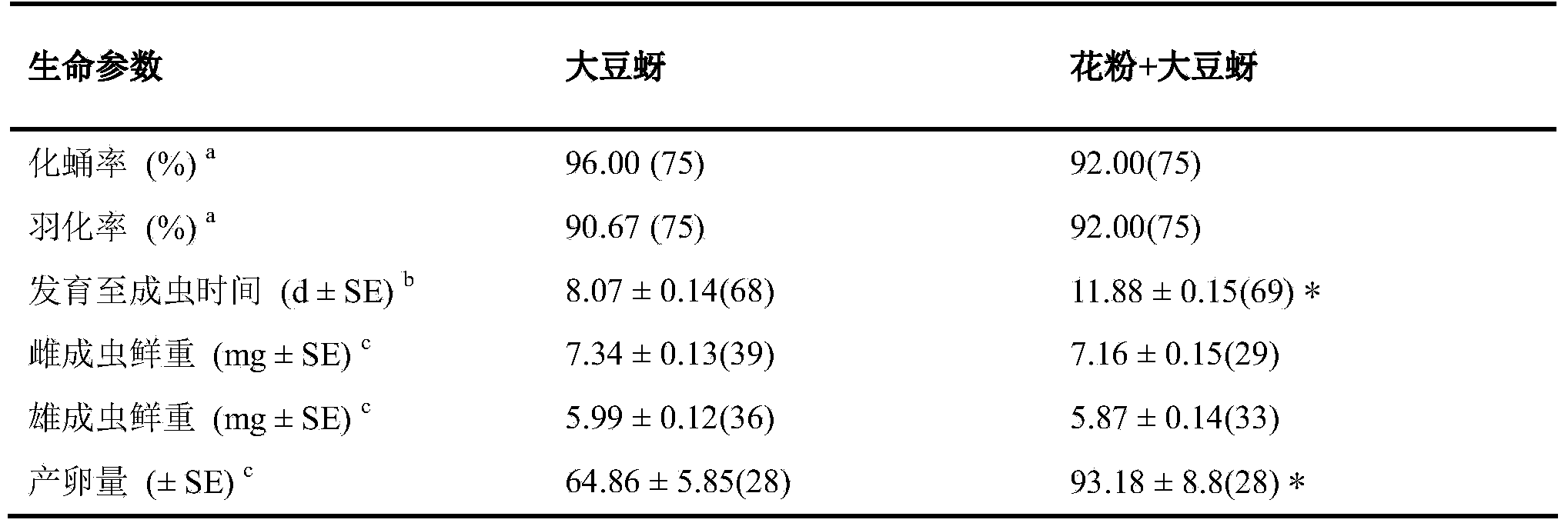
ActiveCN103609877AEfficient determinationEffective direct toxic effectsAnimal feeding stuffMaterial analysisPositive controlPollen
The invention provides a method for detecting toxicity influence of stomach toxicity pesticides or transgene insecticidal protein to Propylaea japonica. The method is characterized in that the pesticides or transgene insecticidal protein can be uniformly mixed in a feed which takes pollen as a base to directly feed in Propylaea japonica, taking a feed (225mumg E-64 / g of pollen) mixed with a protease inhibitor E-64 as a positive control, taking the feed without mix of any insecticidal compound as a negative control, and evaluating the latent toxicity of the insecticidal compound by comparing the important life index of Propylaea japonica such as survival rate, growth stage, body weight and oviposition amount of a processing group and a control group. According to the invention, the method is employed to detect the biology reaction of Propylaea japonica to E-64 with different concentration, different life parameters of Propylaea japonica display obvious a dosage-effect relation with the changer of E-64 concentration, so that validity and sensitivity of the method can be proved.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting genetic toxicity of organic pollutants in water
InactiveCN103276042AGenotoxic Hazard Status GoodEasy to standardize researchMicrobiological testing/measurementGobiocypris rarusWater quality
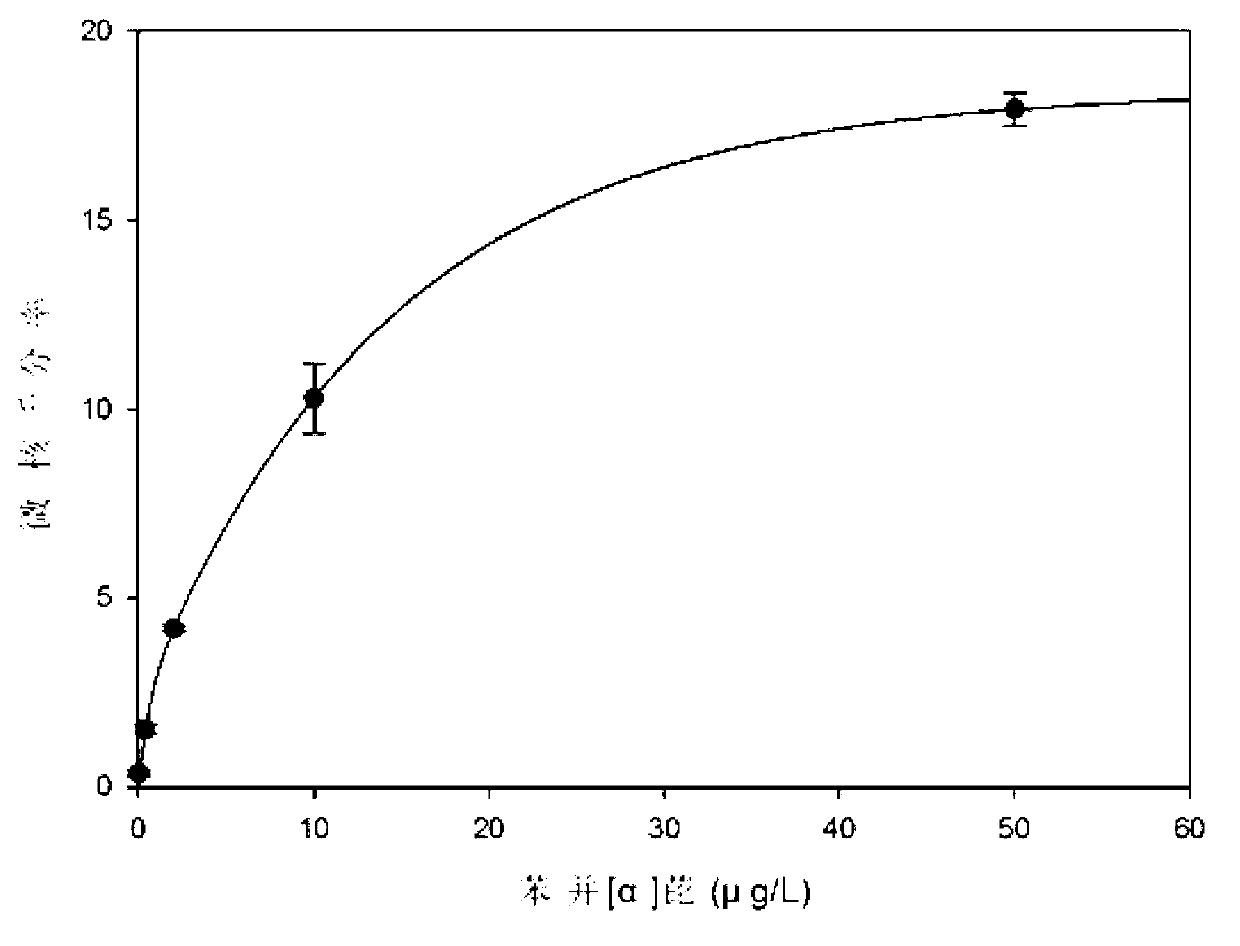
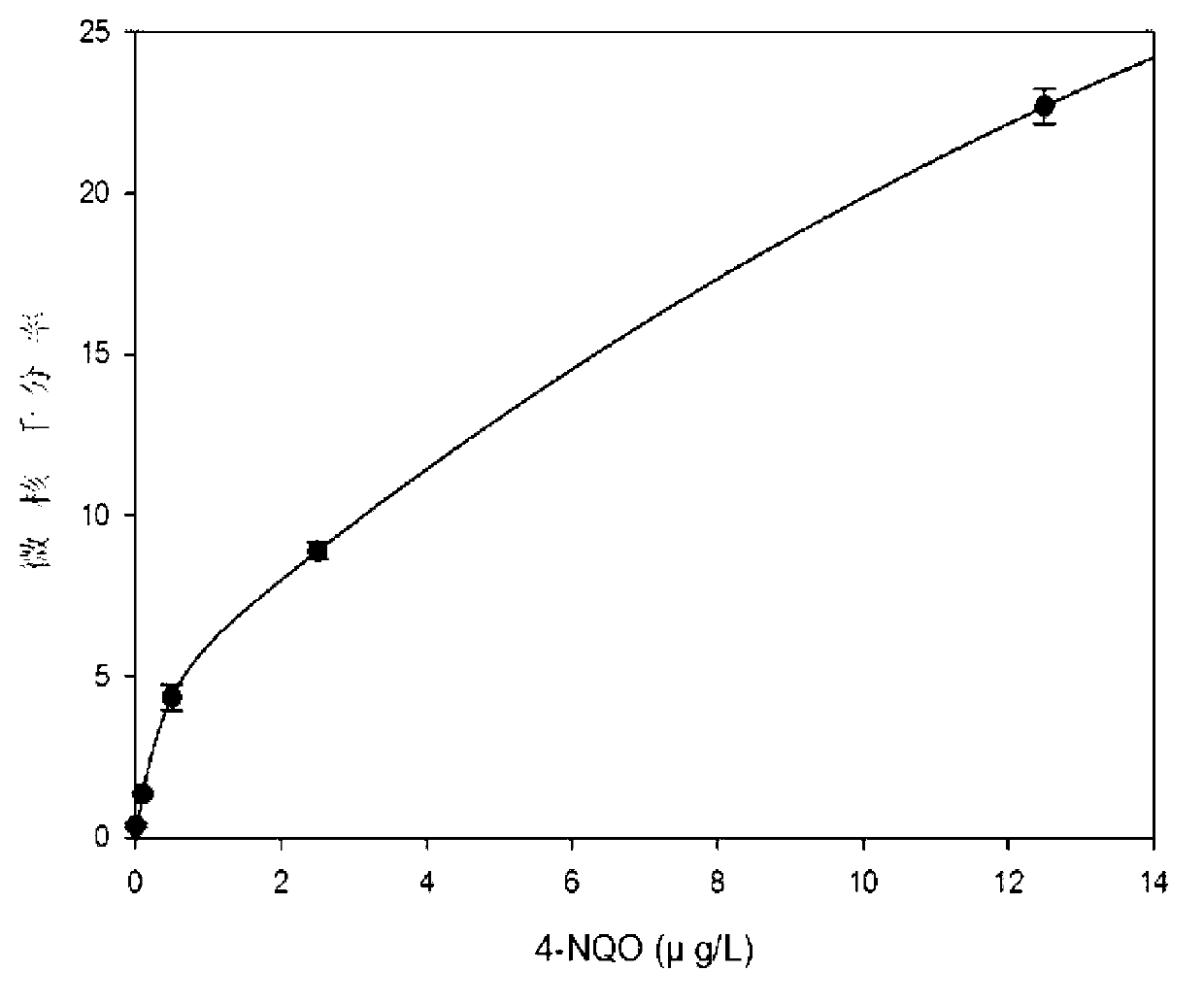
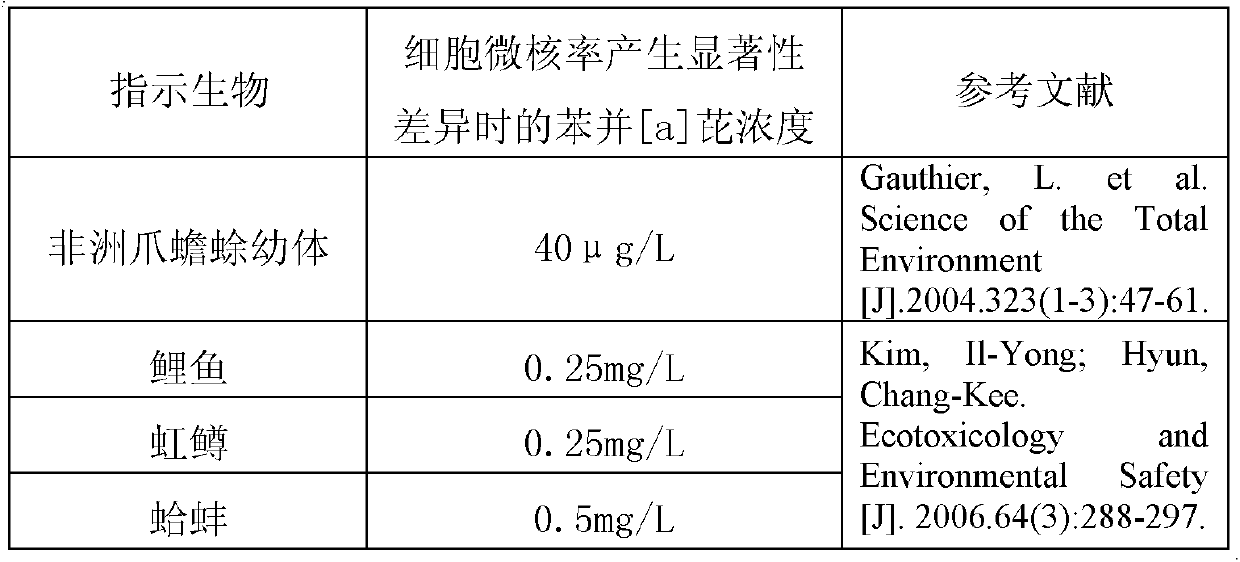
The invention provides a method for detecting the genetic toxicity of organic pollutants. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) treating gobiocypris rarus by a water solution of an organic-pollutant-containing sample to be detected in an exposed way; and (2) detecting the peripheral blood erythrocyte of the gobiocypris rarus which is treated in the exposed way, carrying out statistics on cell micronucleus rate and drawing a dosage-effect curve. The detection method is sensitive, simple, convenient, rapid, more visual and accurate, has good result repeatability, and has important significance for the research of genetic toxicity of water quality.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of anti-hantavirus medicament arbidol
InactiveCN101461805AInhibition of replicationInduces antiviral state effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsSide effectMortality rate
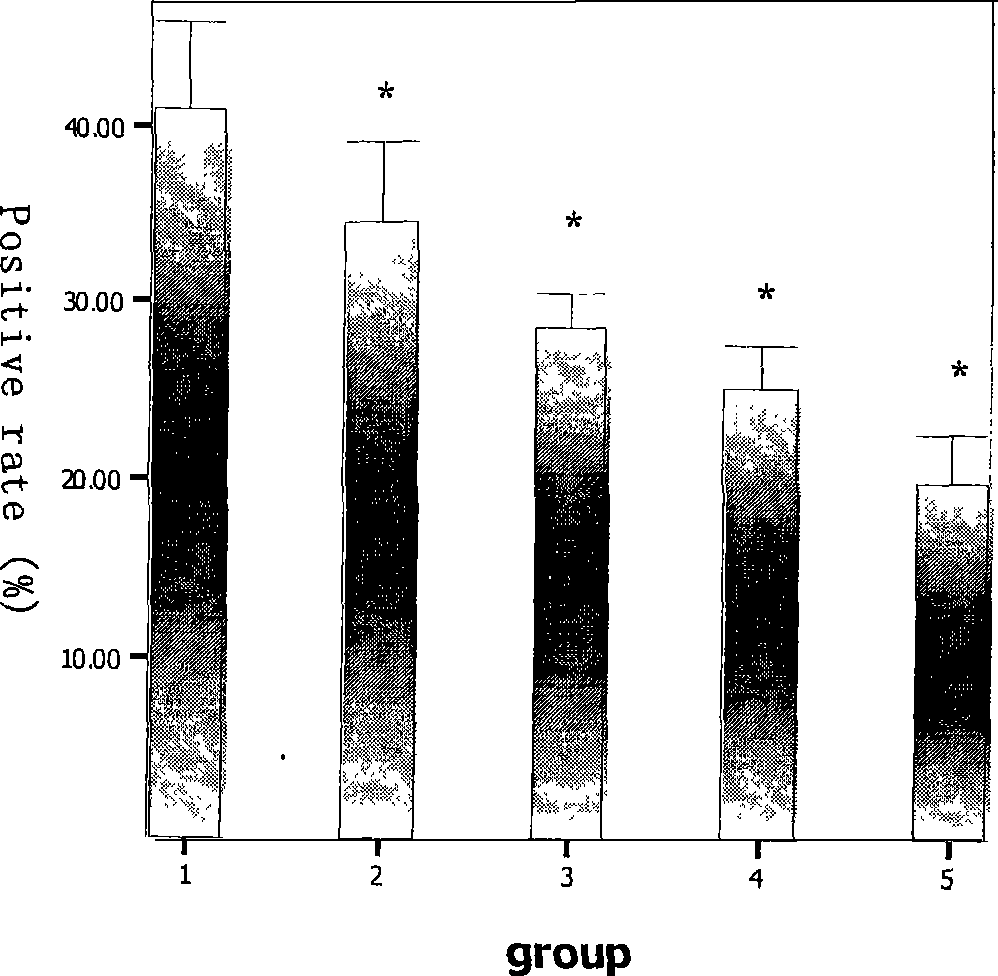
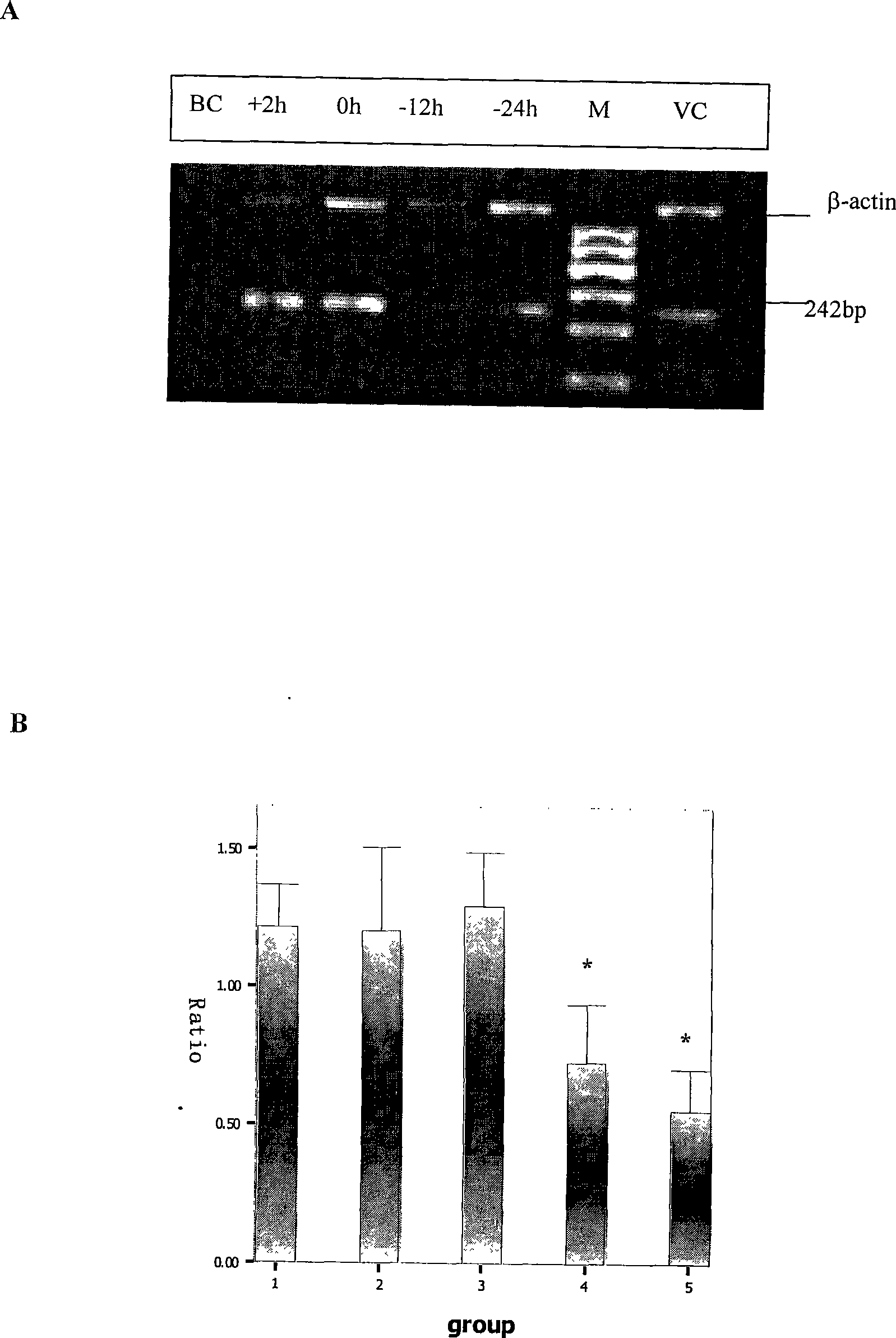
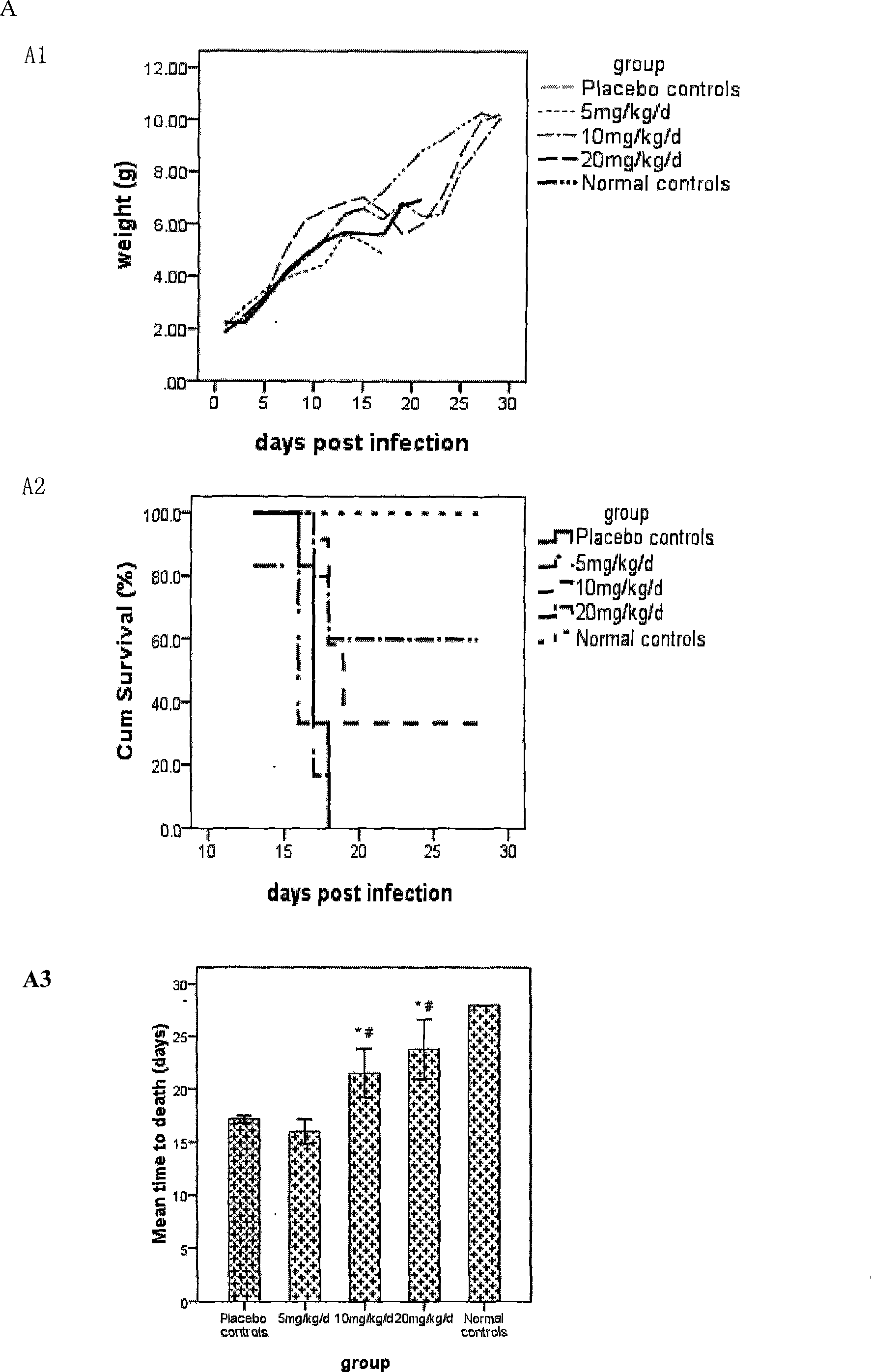
The invention discloses application of a medicine in resisting Hantaan viruses, namely arbidol. The arbidol has obvious effect of inhibiting the Hantaan viruses in vitro, and the antivirus effect of drug administration before the viruses enter a cell is stronger than that of the drug administration after the viruses enter the cell. The concrete embodiment comprises the following: the drug administration is performed before and after the infection, the positive rate of virus-infected cells and the fluorescence intensity are reduced along with the concentration increase, and the medicine has dosage effect; and the medicine can obviously reduce the positive rate of virus infection, and the mRNA expression of the viruses is reduced. The arbidol has protection and treatment effect on the infection of the Hantaan viruses on a suckling mouse, and the protection effect is stronger than the treatment effect. The drug administration is performed within 24h before the infection; and with the increase of the dosage of the medicine, the death rate of the mouse is reduced, and the average survival days are extended. The drug administration within 24h after the infection can not improve the survival rate of an animal, but can extend the average survival days of the animal. The arbidol has the effect of inhibiting the Hantaan viruses in a body of the animal. The drug administration within 24h before the infection can lighten the pathologic change of tissues (lung, kidney, and brain), and has treatment effect on HFRS. The medicine has prevention effect and also has treatment effect on patients with the hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by the Hantaan viruses, and no toxic side effect is found.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
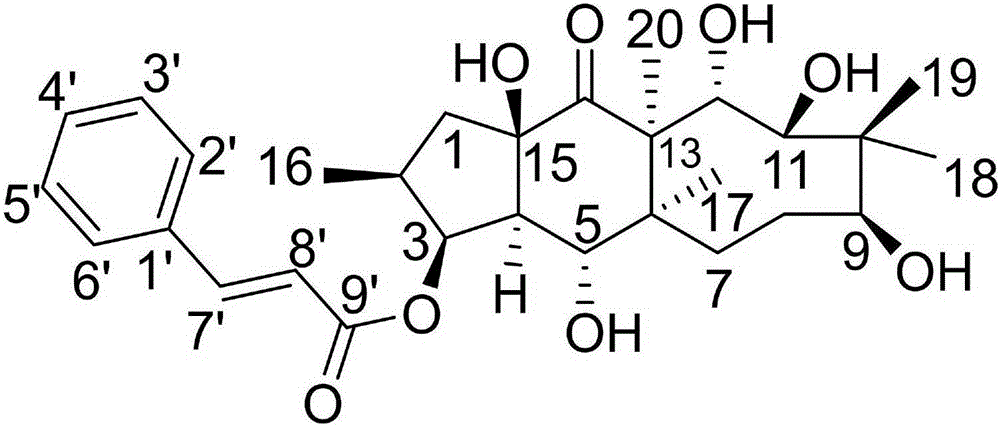
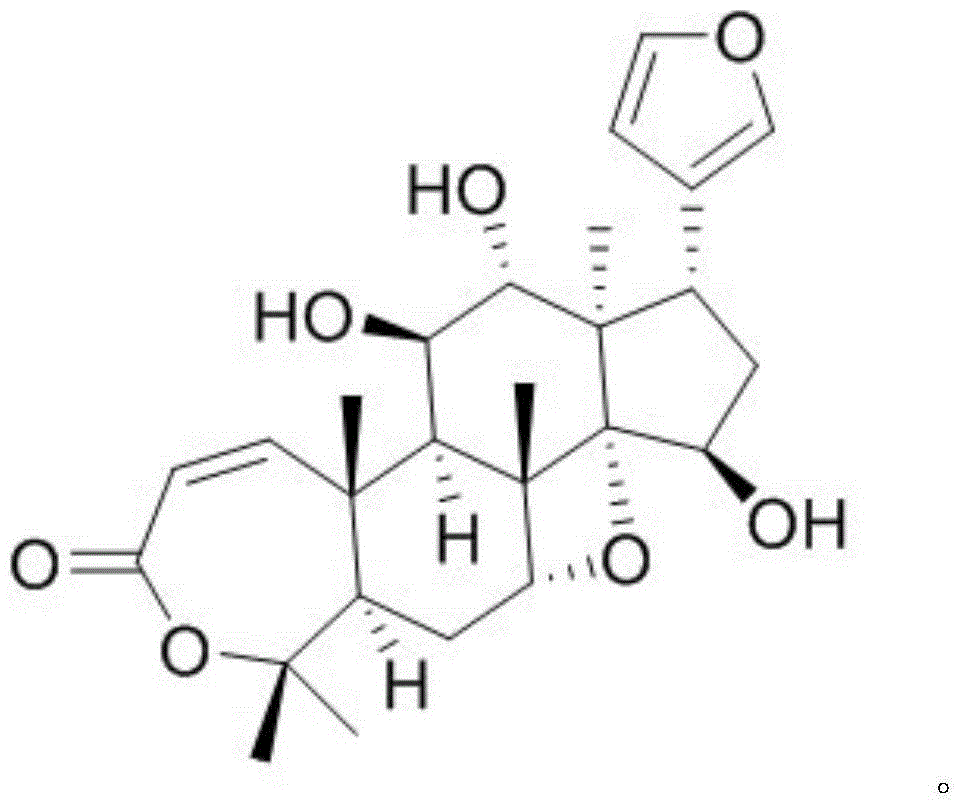
Novel diterpenoid compound for treating liver cancer
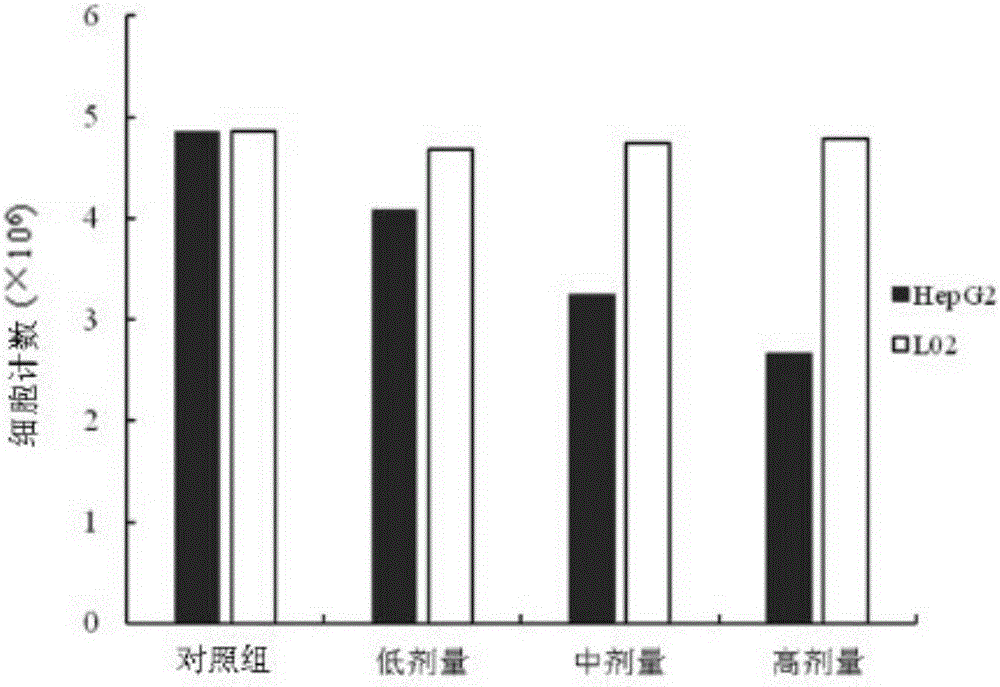
The invention discloses a novel diterpenoid compound for treating a liver cancer, belongs to the field of medicines, and particularly relates to the novel diterpenoid compound obtained by separation from a dry whole herb of plectranthus excises, and a preparation method and medical application thereof. Based on a first report, the compound can be obtained by extraction, separation and purification from the dry whole herb of the plectranthus excises, and is high in purity. An in-vitro test proves that the compound can effectively inhibit the growth and proliferation of HepG2 cells, the decrease degree and the concentration of the compound (I) present a certain dosage effect trend, and a medicine for treating the liver cancers can be further researched and developed.
Owner:ZIBO KUAKE MEDICINE TECH
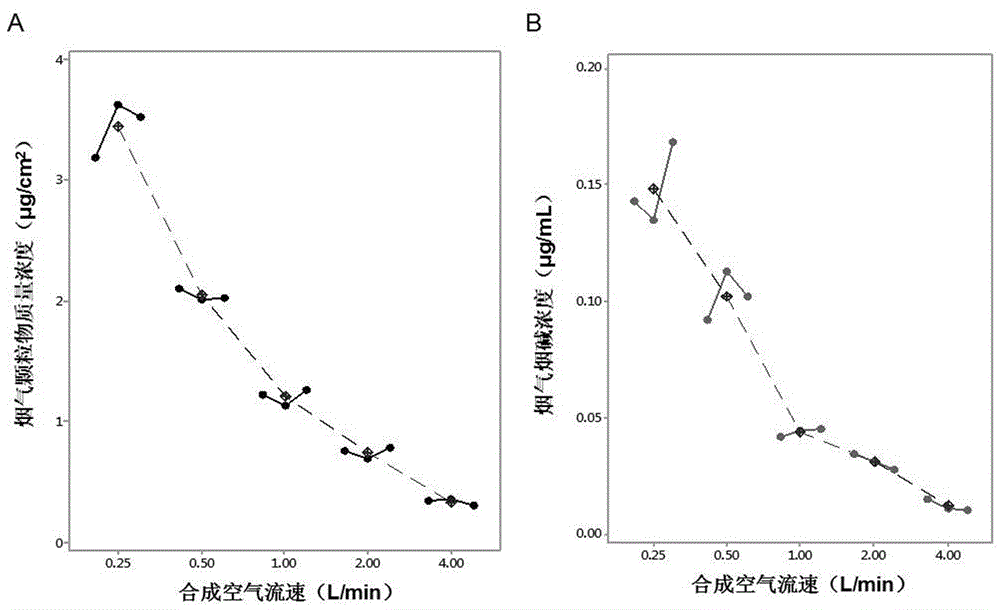
Dosimetric smoke determination method used in full-smoke exposure experiment
ActiveCN106840945AExplain the mechanism of toxicityGood repeatabilityComponent separationParticle suspension analysisIn vitro toxicologyEngineering
A dosimetric smoke determination method used in a full-smoke exposure experiment is used for real-time and quantitative determination of smoke dosage in a full-smoke exposure bin through combination of a quartz micro balance wafer and an inserted cell culture dish. The method has the maximum characteristic that an actual microenvironment for smoke exposure is simulated, the actual concentration (including the mass concentration of smoke particulate matter and nicotine concentration) of cigarette smoke in the full-smoke exposure bin is detected in a real-time, sensitive and quantitative mode, the dosage-effect relation of a smoke toxicity effect is accurately represented, and a real smoke dosage basis is provided for evaluation of cigarette smoke in-vitro toxicology. By applying method, the toxicity mechanism of the cigarette smoke can be better interpreted, and a method basis and technical support are provided for health risk assessment and research of tobacco products. In addition, the method is wide in applicability and can be applied to in-vitro toxicity testing and research of cigarettes, electronic cigarettes, cigarettes non-combustible in heating and aerosols different in source, and testing results are good in repeatability, high in stability and strong in sensitivity.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
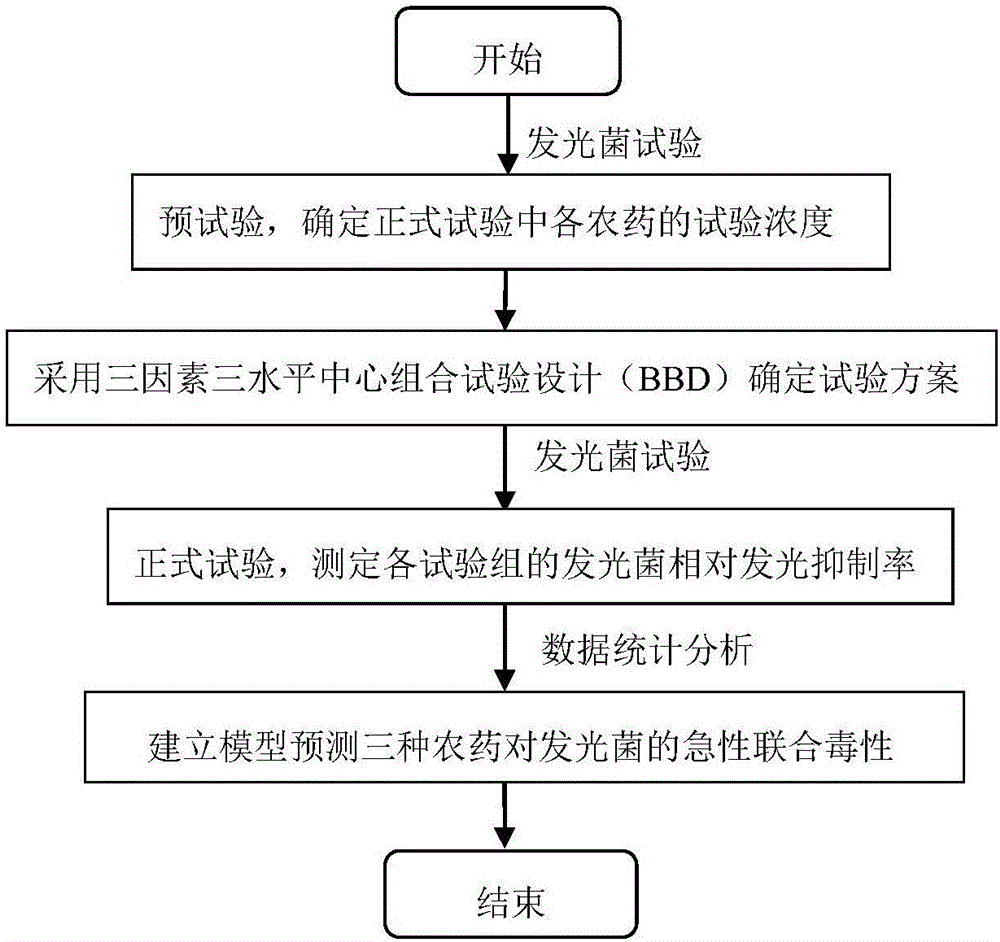
Method for predicting acute joint toxicity of three pesticides to photogenic bacteria
InactiveCN106525822ARealize Quantitative PredictionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceThree levelPathogenic bacteria
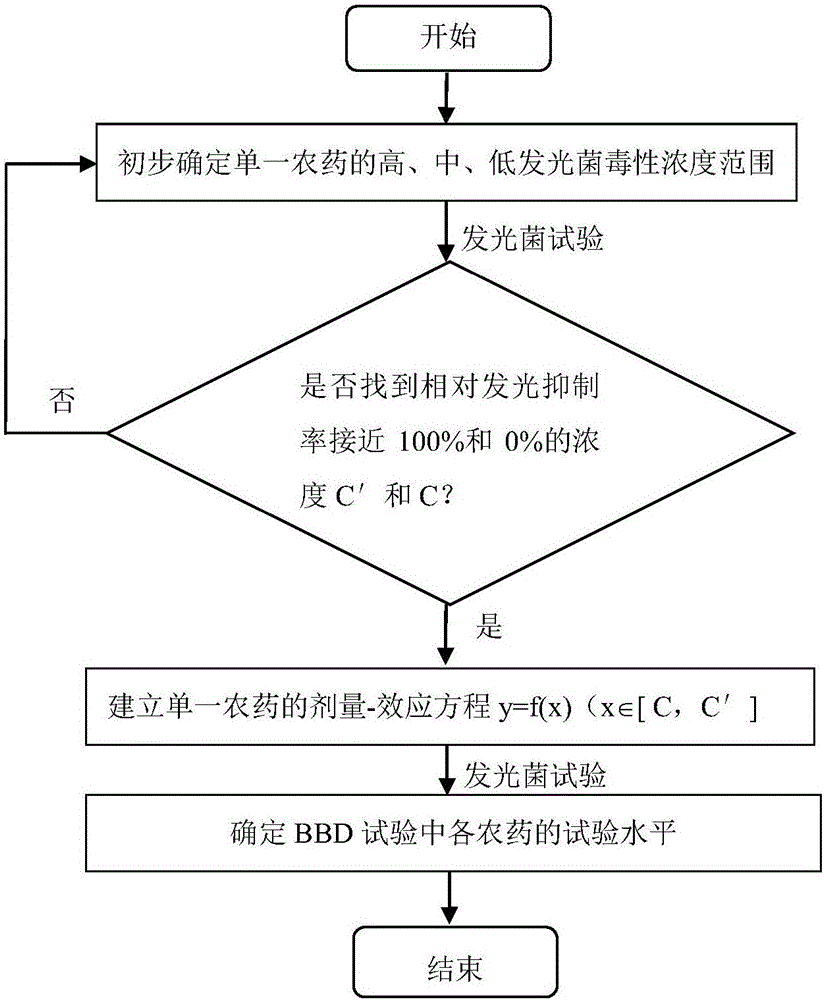
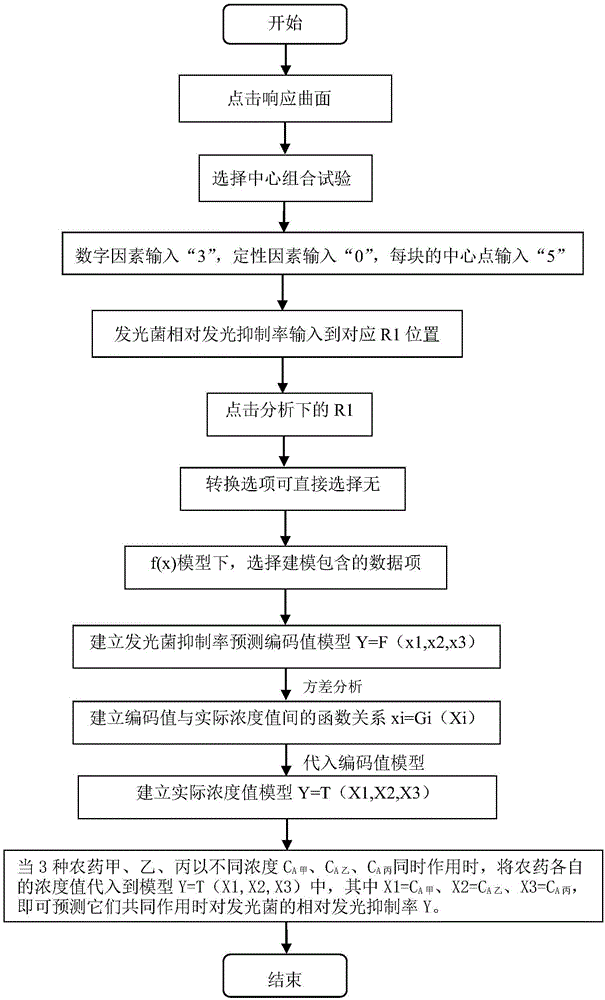
The invention discloses a method for predicting acute joint toxicity of three pesticides to photogenic bacteria, which aims to overcome problems that a conventional toxicology acute joint toxicity evaluation technique is large in testing workload and quantitative evaluation and acute joint toxicity action prediction methods are not available. The method for predicting the acute joint toxicity of three pesticides to photogenic bacteria comprises the following steps: (1) performing pretesting, namely confirming the testing concentration of different pesticides in official tests, wherein the step of performing pretesting, namely confirming testing concentrations of different pesticides in official tests comprises the following steps: (1) primarily confirming high, medium and low photogenic bacteria toxicity concentration ranges of a single pesticide; (2) establishing a dosage-effect equation that y is equal to f(x)(x belongs to [C,C']) of the single pesticide; (3) confirming the testing concentrations of different pesticides in the BBD tests; (2) confirming testing schemes through three-factor three-level center combined testing design (BBD); (3) performing official testing, namely, testing the relative light emission inhibition rates of different test groups of photogenic bacteria; and (4) establishing a model to predict the acute joint toxicity of the three pesticides to the photogenic bacteria.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
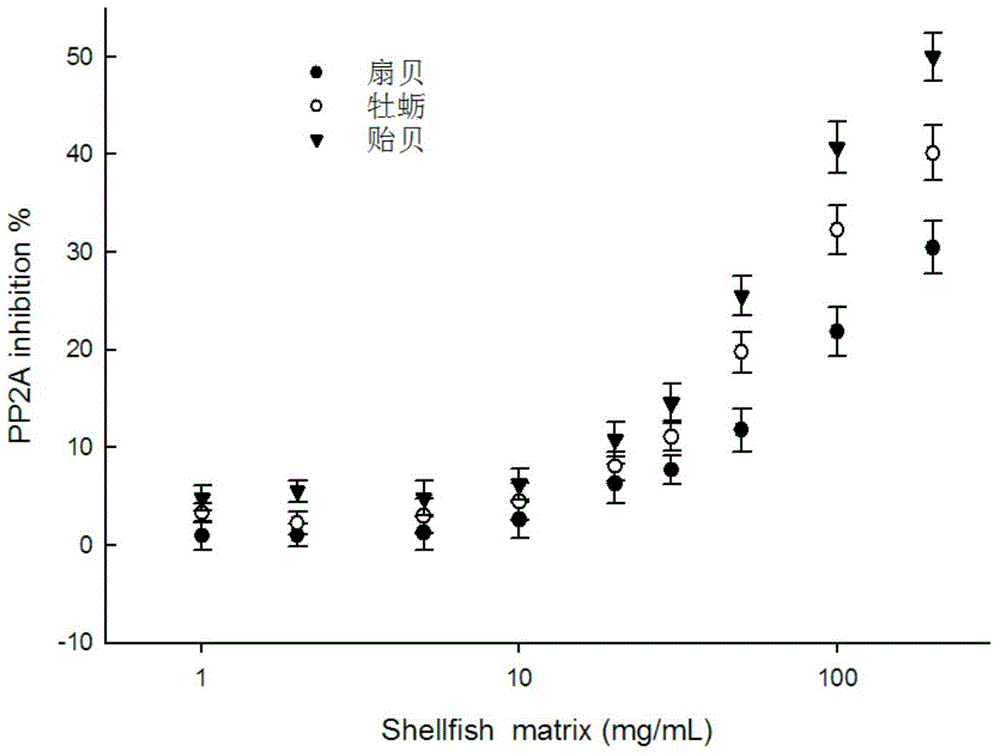
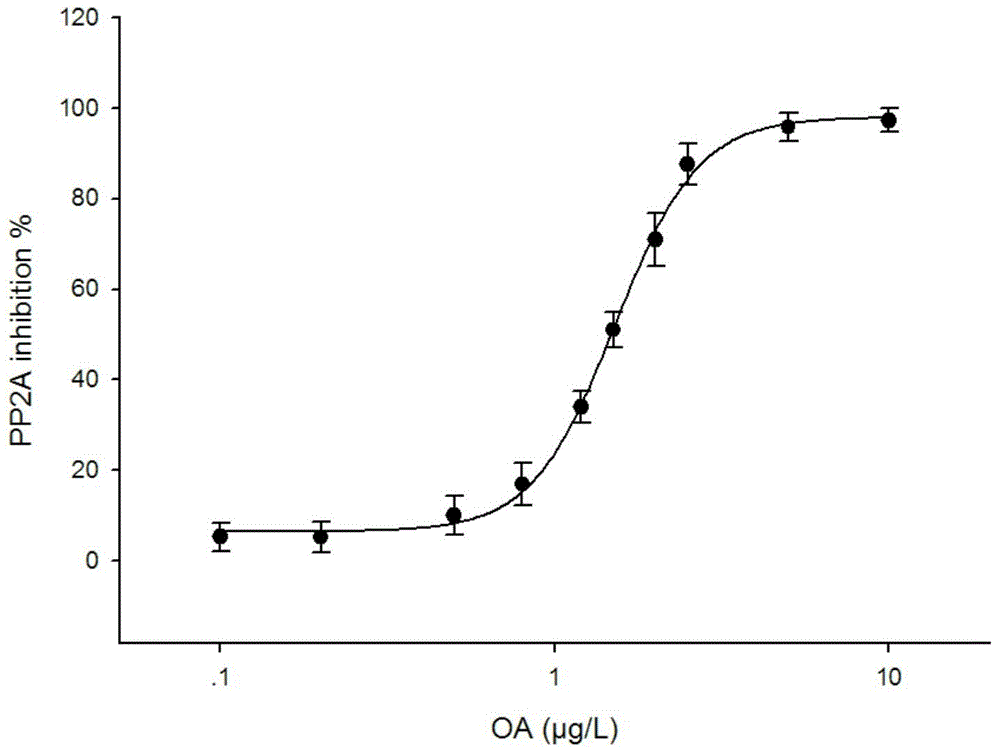
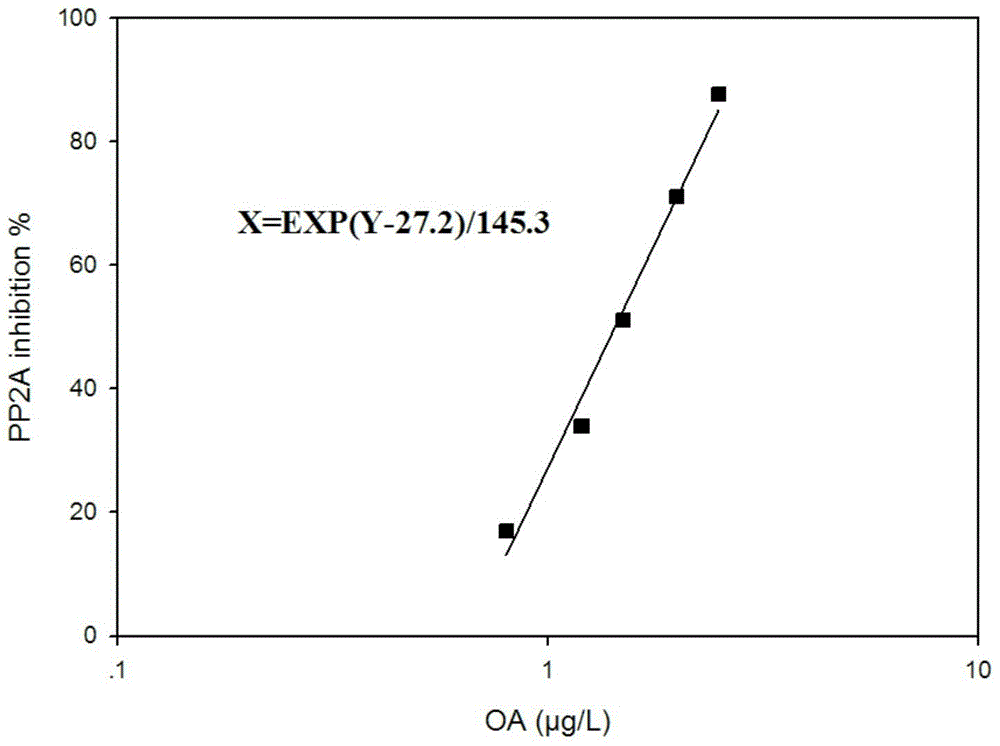
Quick detection kit for okadaic acid toxins in shellfish
InactiveCN104089954ALow costSimple and fast operationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh concentrationFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a quick detection kit for okadaic acid toxins in shellfish, belonging to the technical field of food detection. The quick detection kit comprises (1) protein phosphatase 2A freeze-dried powder, (2) an okadaic acid concentration gradient series standard solution, (3) a buffer solution, (4) a protein phosphatase 2A dilute solution, (5) a substrate developing solution, and (6) a high-concentration marking solution. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the quick detection kit inherits the advantage that a mouse bioassay can establish a dosage-effect relation, so that the relative toxicity of the toxins can be directly reflected; compared with the mouse bioassay, the quick detection kit has the advantage that a large batch of samples (84 samples can be detected within 4 hours) can be detected within short time. The detection limit of the method disclosed by the invention is 50 microgram OA eq. / kg shellfish tissue; compared with the detection limit, 200 microgram OA eq. / kg shellfish tissue, of the conventional mouse bioassay, the detection limit of the method disclosed by the invention is greatly reduced; meanwhile, the ethic problem of an animal experiment is solved. The kit disclosed by the invention is low in cost and easy to operate.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Protease K multi-copy strain construction method
The invention discloses a protease K multi-copy strain construction method, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the protease K multi-copy strain construction method, protease Kmulti-copy strains is artificially constructed in vitro by utilizing a Biobrick method, and the protease K multi-copy strain construction method mainly comprises the following specific steps: S1, constructing a multi-copy vector; S2, screening multi-copy strains; and S3, carrying out multi-copy strain large-scale fermentation. A protease K multi-copy tandem expression cassette is artificially constructed in vitro by using a Biobrick method; the construction method has the advantages that the copy number of recombinant plasmids is controllable, dependence on screening of high-concentration resistant drugs is not needed, large-scale screening is also not needed, the gene dose effect is considered as the most important factor for expression of foreign protein by pichia pastoris, and the expression quantity of the multi-copy strains is many times higher than that of single-copy strains; therefore, the yield of the protease K is increased, the price is lower, and the protease K can be applied to various fields.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
Naphthenic acid, 1,10-phenanthroline rare earth complex, preparation method and antimycotic application thereof
InactiveCN101235048AThe synthesis method is simpleEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRare-earth elementYeast
The invention discloses a naphthoic acid and 1, 10-o-phenanthroline rare-earth complex and relative function for inhibiting yeast, which is represented as REL3phen nH2O, wherein RE is rare-earth element as Eu3+, Tb3+, Gd3+, La3+ or Y3+, L is one of alpha-Naphthoic acid, beta-Naphthoic acid, alpha-Naphthlcetic acid and beta-Naphthlcetic acid, n=0 or 1. The preparation method comprises using L as first ligand and o-phenanthroline as second ligand while RE3+: L: phen is 1:3:1, adding alcohol and dissolving, mixing the two ligands to be added into a rare-earth chloride solution, mixing and reacting to synthesize rare-earth complex. The bacteriostatic test of filter paper method on fungus proves that the rare-earth complex has significant inhibition on yeast stronger than pure ion and complex, with concentration dosage effect. The invention provides useful reference for microbe bacteria inhibitor development.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Method for performing biological pre-warning on low-dosage gamma radiation by adopting teratogenesis rate of zebrafish embryos
The invention relates to a method for performing biological pre-warning on low-dosage gamma radiation by adopting a teratogenesis rate of zebrafish embryos. The comprehensive toxic effect of the low-dosage gamma radiation on the zebrafish embryos is estimated by calculating the teratogenesis rates of the zebrafish embryos under different conditions of low-dosage gamma radiations according to a dosage-effect relation between the radiation dosages on the zebrafish embryos and the teratogenesis rates via adopting the sensitive characteristic of the zebrafish embryos to the low-dosage gamma radiation, so that a biological pre-warning method is implemented. The method has multiple advantages of simple and fast operation, low cost, high sensitivity, high accuracy, low environmental risk and the like.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Breeding method for fragrant purple hard rice three-line hybrid rice for processing purple fragrant rice noodles
InactiveCN105325284ALightly scentedStrong fragrancePlant genotype modificationDosage effectFood flavor
The invention discloses a breeding method for fragrant purple hard rice three-line hybrid rice for processing purple fragrant rice noodles. The breeding method includes the following steps that 1, a fragrant purple hard rice maintaining variety containing purple rice genes P with the dosage effect, allelic fragrance genes a and allelic hard rice genes H and a fragrant purple hard rice restoring variety containing purple rice genes P with the dosage effect, allelic fragrance genes a and allelic hard rice genes H; 2, the fragrant purple hard rice maintaining variety is bred to obtain a fragrant purple hard rice maintenance line with the gene type of aaPPHH and a fragrant purple hard rice male sterility line with the gene type of aaPPHH; 3, the fragrant purple hard rice restoring variety is bred to obtain a fragrant purple hard rice restoring line with the gene type of aaPPHH; 4, the fragrant purple hard rice male sterility line serves as a female parent, the fragrant purple hard rice restoring line serves as a male parent, and the fragrant purple hard rice hybrid rice with the high yield, the wide application range and the gene type of aaPPHH is obtained through matching. The bred fragrant purple hard rice hybrid rice is fragrant in flavor and high in yield, seed coats are purple, and the processed rice noodles are low in breaking rate and good in cooking performance and mouthfeel.
Owner:文山壮族苗族自治州农业科学院
High speed simulation method of ion implantation including dose effect
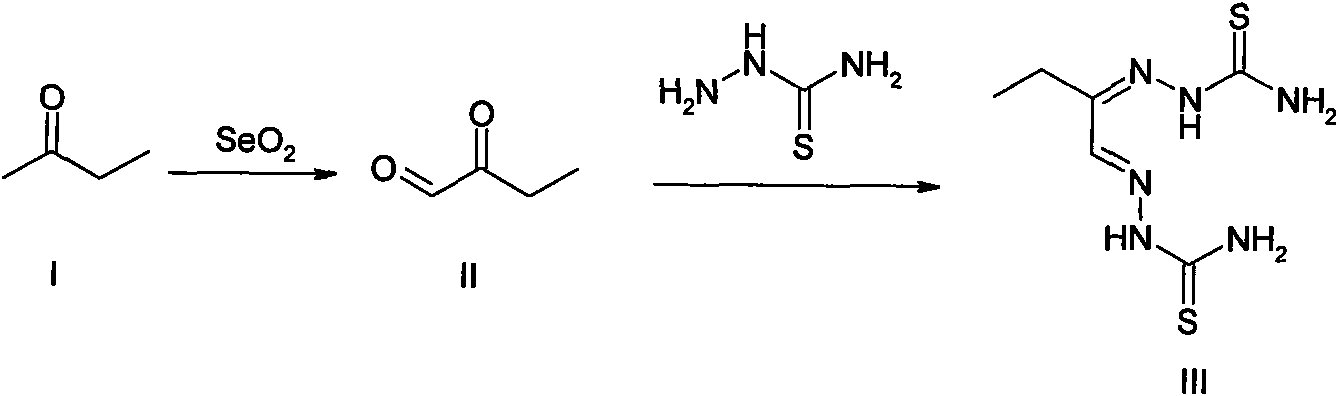
InactiveCN1448991AIn line with the experimental resultsHigh precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesMedicineDosage effect
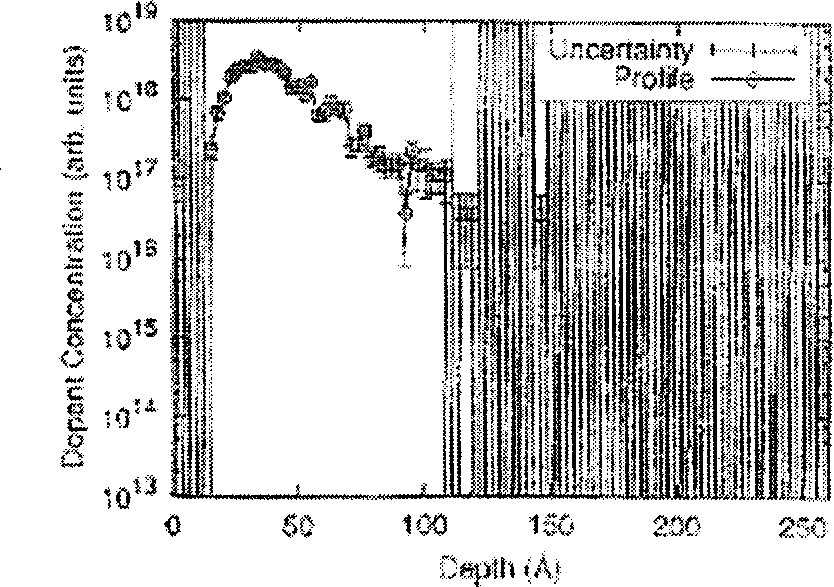
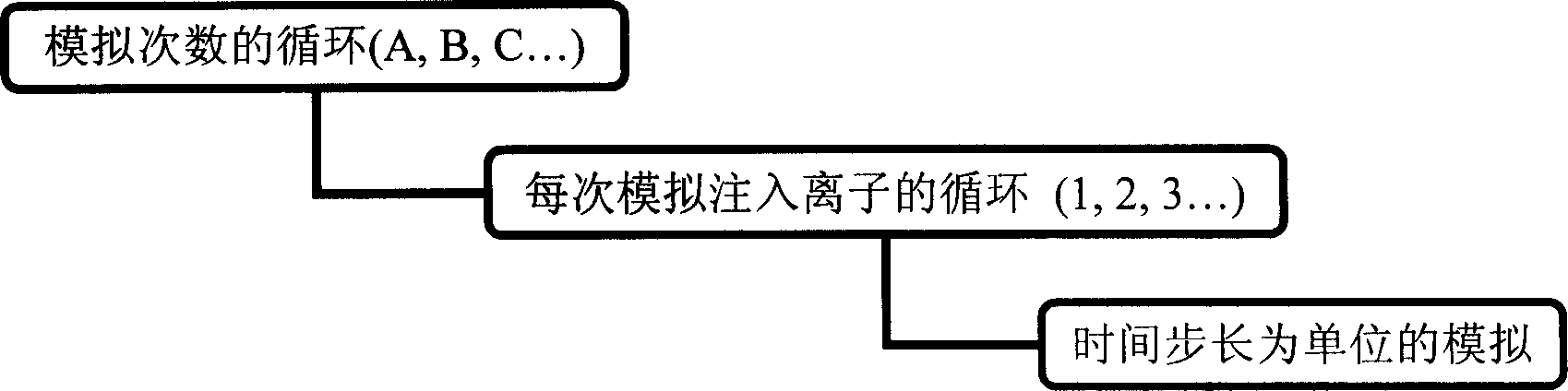
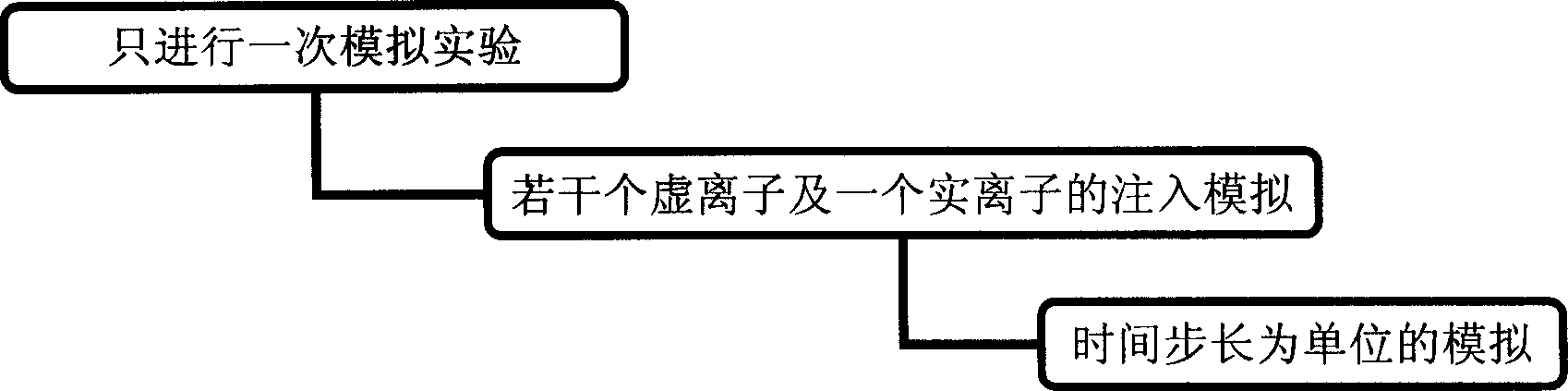
The high-speed ion implantation simulating method including dosage effect combines the splitting method and dosage effect and is specifically to simulate alternate implantation of virtual ion and true ion until finishing the implantation of all true ions. In the only once simulation, implanted ions are divided into true ions and virtual ions artificially, the true ions are used to simulate cascade collision to produce defect distribution during the implantation; and the virtual ions are used to simulate range distribution. The said simulation method can simulate well the range distribution with experiment result coinciding with SIMS, and has high precision, high speed and high effect of simulation. The introduced defect production produces defect distribution capable of being used in subsequent annealing simulation for ultimate realization of technological simulation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
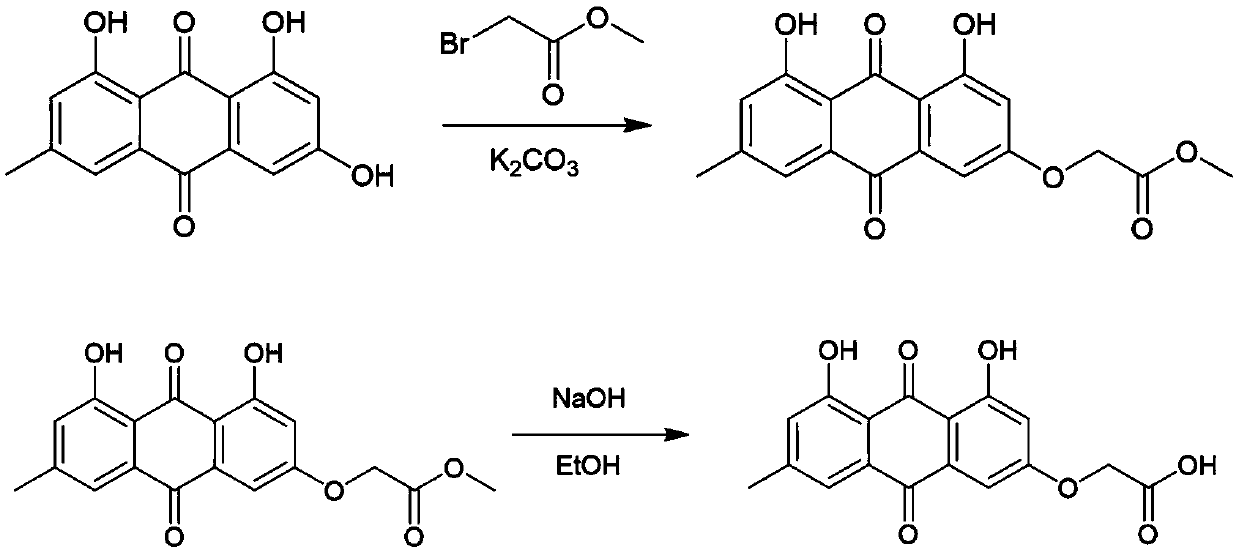
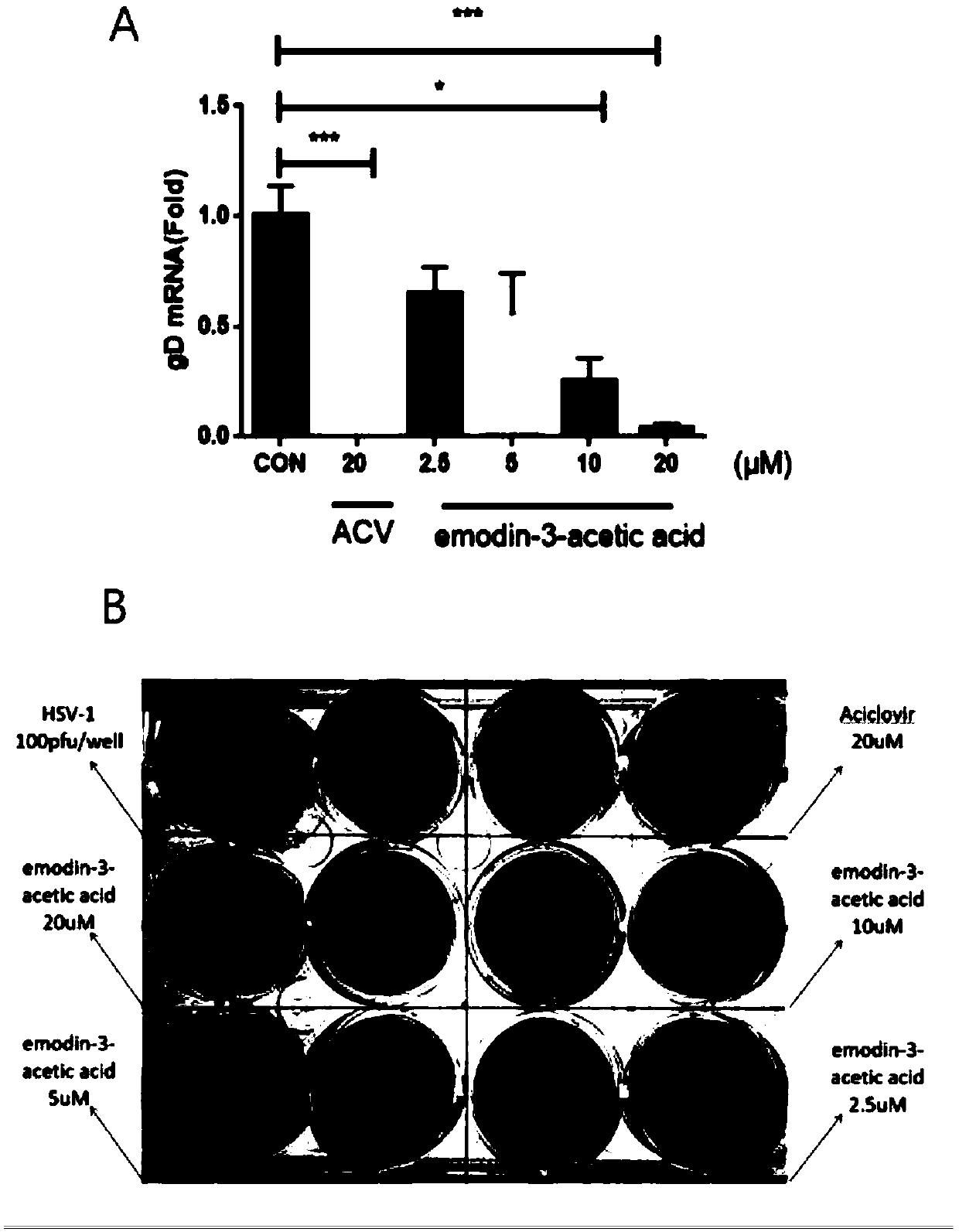
Application of emodin-3-acetic-acid to preparation of drugs for resisting herpes simplex virus type I
ActiveCN109528703AInhibition of replicationAvoid infectionOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsSolubilityHerpes simplex disease
The invention provides an application of emodin-3-acetic-acid to preparation of drugs for resisting herpes simplex virus type I, and belongs to the technical field of antiviral drugs. According to theprovided emodin-3-acetic-acid, hydroxyl on C3 of emodin is replaced with acetate, so that the solubility is greatly improved, and the emodin-3-acetic-acid has good druggability. Experiment proves that the emodin-3-acetic-acid has low toxins to Hep-2 cells infected with HSV-1 toxin strains, the gene expression of HSV-1 gD in the Hep-2 cells can be notably reduced by the emodin-3-acetic-acid, and besides, the duplication and infection of the HSV-1 in the Hep-2 cells are restrained. The emodin-3-acetic-acid has concentration dosage effects. The prepared emodin-3-acetic-acid has notable characteristic of resisting HSV-1 viruses, and becomes a drug candidate for clinical treatment of symptoms infected with the HSV-1 viruses.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Application of Flt-3 Ligand in serving as biological indicator for quickly estimating ionization radiation dosage
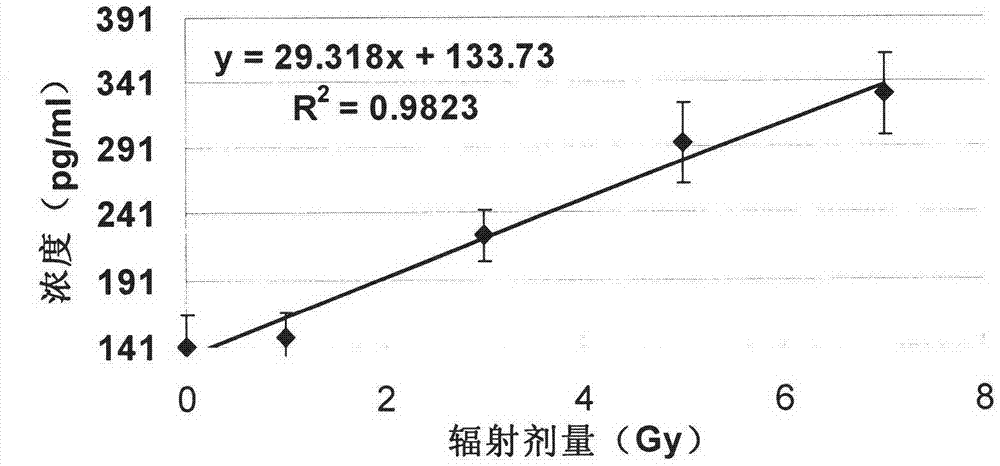
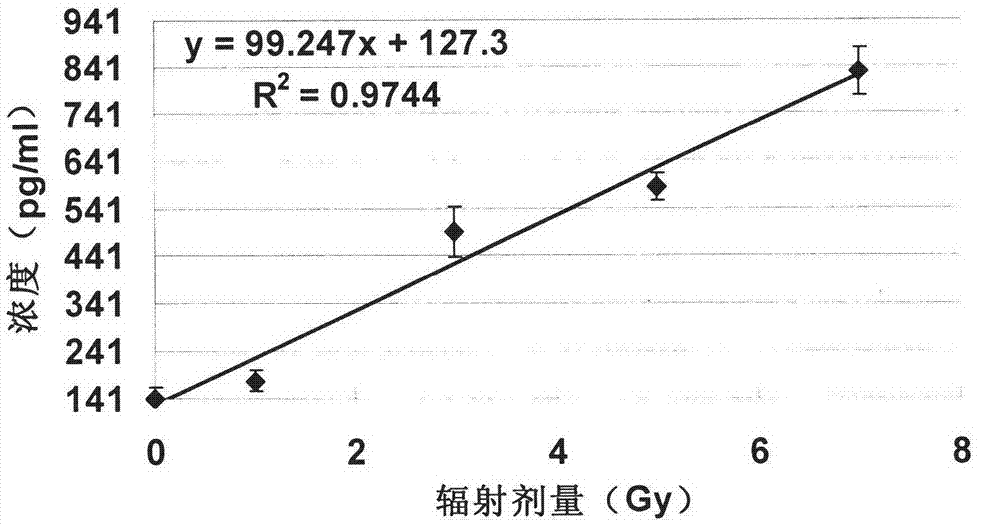
InactiveCN103675290AEasy to collectLess sample requiredDosimetersDisease diagnosisRadiation DosagesStatistical analysis
The invention belongs to a biological indicator for quickly estimating the ionization radiation dosage and in particular relates to application of Flt-3 Ligand in serving as the biological indicator for quickly estimating the ionization radiation dosage. After irradiation is executed, the expression quantity of Flt-3L in serum or plasma, the after-irradiation time and the radiation dosage have a time-dosage-effect relation; response curve surfaces and reduction formulas of all the parameters (the expression quantity of the Flt-3L, the after-irradiation time and the radiation dosage) are fit through statistic analysis; therefore, the radiation dosage is estimated according to the response curve surfaces and the reduction formulas under the condition that the expression quantity of the Flt-3L and the after-irradiation time are known; moreover, the expression quantity of the Flt-3L can be quickly detected by a simple feasible method such as ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) and a protein chip; the number of samples for detection is small, sampling and storage are convenient, the time is short, and the result is objective, so that the Flt-3 Ligand can serve as the biological indicator for quickly estimating the ionization radiation dosage.
Owner:NAVY MEDICINE RES INST OF PLA
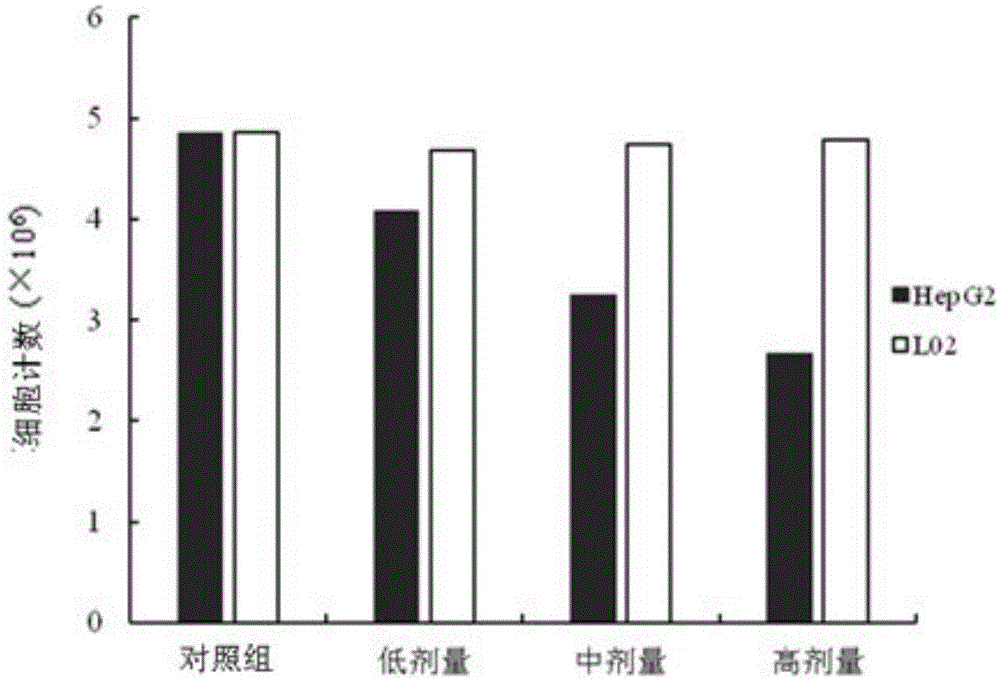
Application of aphanalide J to preparation of drugs for treating liver cancer
The invention discloses application of aphanalide J to preparation of drugs for treating liver cancer and belongs to the field of drugs. The aphanalide J can effectively restrain growth and proliferation of HepG2 cells, a survival rate of cells of an interfered group is obviously reduced in comparison with that of a control group, the decreased degree presents a certain dosage effect trend with the concentration of the aphanalide J, and meanwhile, under the same concentration of the aphanalide J, the survival rate of cells is continuously reduced with the increase of interfering time. At the same time, intervention of aphanalide J with same dosage does not have an inhibiting effect on L02 common hepatic cells and cytotoxicity does not exist. The aphanalide J can further be researched and developed to be used for preparing drugs for treating liver cancer.
Owner:刘高志
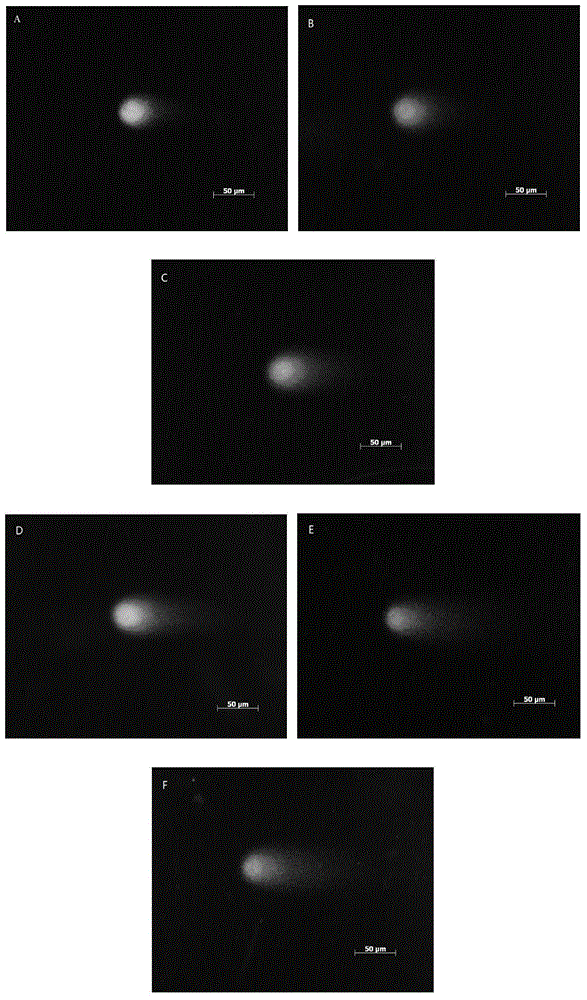
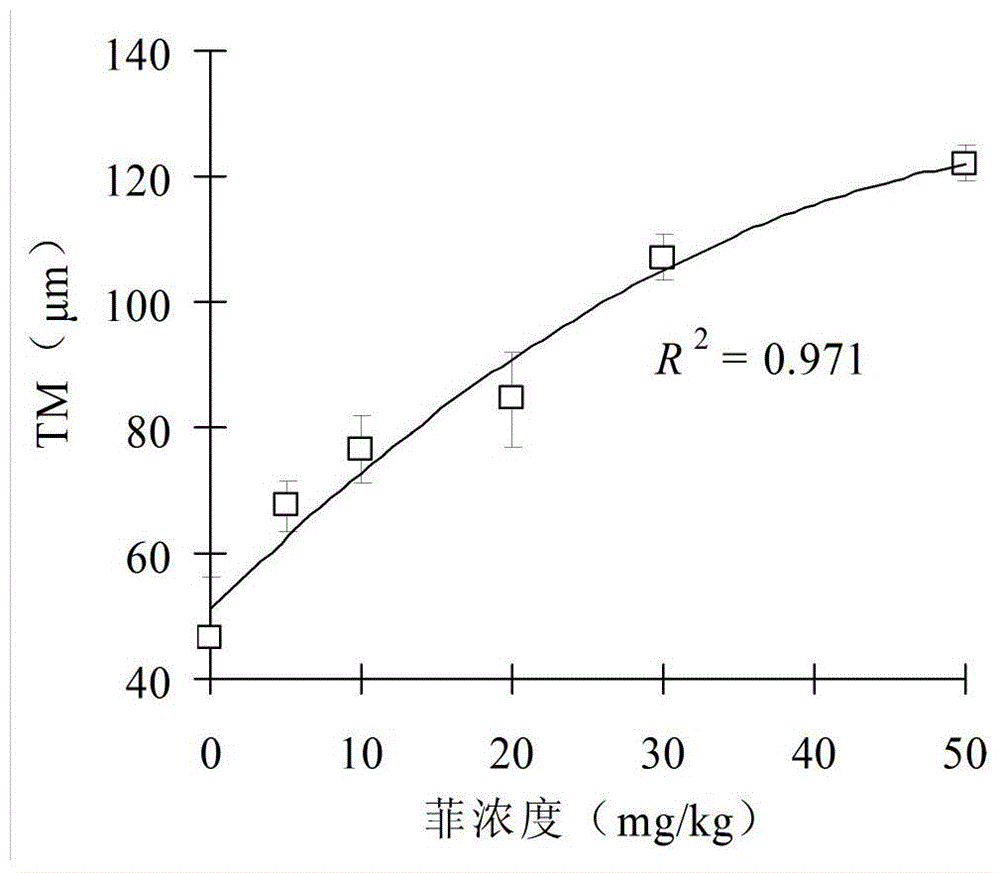
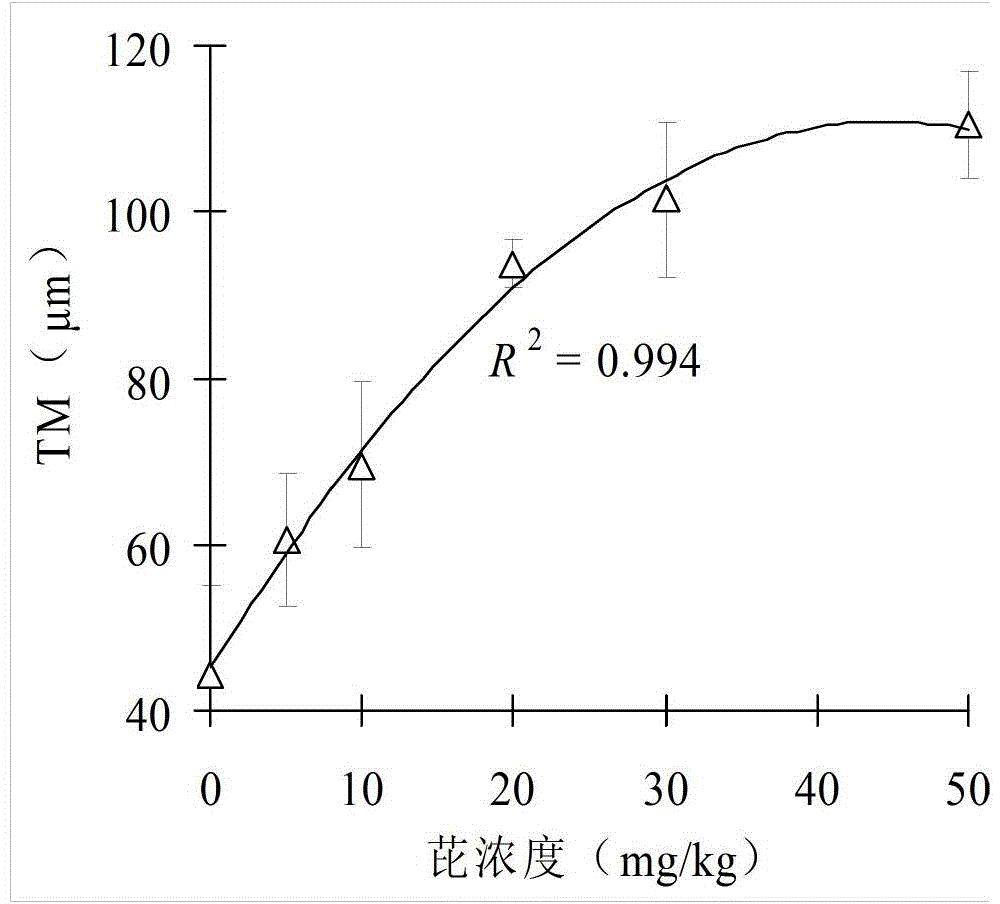
Method for evaluating toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) gene by utilizing plant comet assay
InactiveCN104458873AApplicable quantitative evaluationMethod scienceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOrganismContamination
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the toxicity of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) gene by utilizing a plant comet assay, belonging to the technical field of pollutant toxicity evaluation. The method is characterized in that root tips of contaminated vicia faba are utilized for the plant comet assay; a comet image is analyzed by utilizing Komet Version 6.0 software, wherein the TM value of the comet image and the PAHs contamination concentration have an obvious dosage-effect relationship; the TM value can act as an evaluation parameter for balancing the DNA damage by PAHs, and is directly used for evaluating the toxicity of the PAHs gene. The established method for evaluating the toxicity of the PAHs gene by utilizing the plant comet assay has the characteristics of science, high efficiency, rapidity and accuracy, and is suitable for quantitatively evaluating the toxicity of genes of toxic organisms such as PAHs.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Insecticidal composition containing fenoxycarb and application thereof
InactiveCN101574088AImprove insecticidal effectSynergistic effect is obviousBiocideAnimal repellantsBenzoic acidAbamectin
The invention discloses an insecticidal composition containing fenoxycarb. The composition comprises the following active components in portion by mass: 1 to 50 portions of the fenoxycarb, 0.05 to 5 portions of abamectin, 0.01 to 1 portion of emamectin benzoate, and 0.1 to 10 portions of profenofos. The invention also discloses application of the insecticidal composition in the aspects of preventing and controlling rice leaf rollers, diamond back moths or beet armyworms. Proved by field pesticide efficacy test, the insecticidal effect of the composition is remarkably higher than corresponding single-dosage effect; and the composition has remarkable synergic function, not only enlarges the insecticidal spectrum, improves the control effect, reduces the control cost and reduces the using amount of a pesticide, but also avoids injury to beneficial insects.
Owner:JIANGSU FUTIAN AGROCHEM CO LTD
Method for improving MOSFET anti-single particle radiation and MOSFET component
InactiveCN101266972AReduces off-state leakage currentImproving the ability to resist single event radiation effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionMOSFET
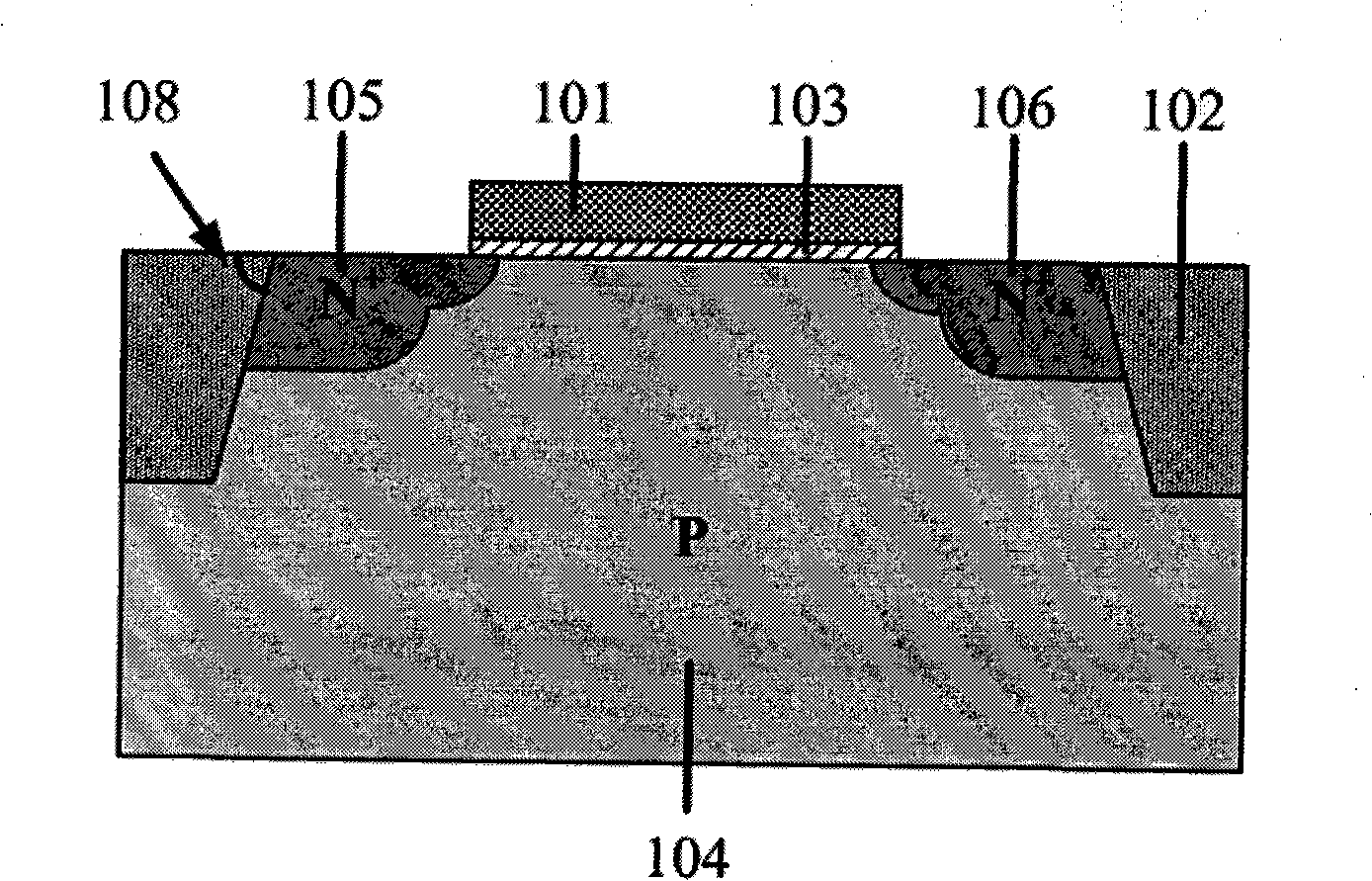
The invention discloses a method for enhancing anti-single particle radiation ability of MOSFET and a MOSFET element, belonging to field effect transistor technology field. In the MOSFET element according to the invention, an acute angle between the side wall of channel in STI region and the active region of the element is defined as the angle of micro-dosage effect caused by the anti-single particle radiation of the element, with value ranged between 78 degrees to 86 degrees. By using the MOSFET element structure according to the invention, the off-state leakage current of the element caused by the single-particle radiation is lower than that the traditional structure by one magnitude. The structure according to the invention has simple process, completely compatible with traditional CMOS process, capable of enhancing the anti-single particle radiation ability of the element and effectively reducing the manufacturing costs simultaneously.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
New use of glyoxal bis (thiosemicarbazone) compound
InactiveCN101569619AGood killing effectGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsRelapse preventionExperimental research
The invention discloses new use of glyoxal bis (thiosemicarbazone) compound. The new use relates to an application of glyoxal bis (thiosemicarbazone) compound or salt or a solvate of the compound in antineoplastic drug preparation. The glyoxal bis (thiosemicarbazone) compound of the invention can effectively kill a large number of tumour cells and dosage-effect relation and time-effect relation are obvious. Thus, the invention provides a new way for practice and research of tumour treatment and / or relapse prevention and also can be taken as reagent used for experimental researches relevant to cell cycle, cell proliferation, and apoptosis as well as a certain of signal passage regulation and control. The invention has wide application in tumour treatment and relapse prevention.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Fusion protein of tumor vascular targeted peptide and novel tumor necrosis factor
InactiveCN101481418AReduce clinical dosageSmall toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsEscherichia coliAbnormal tissue growth
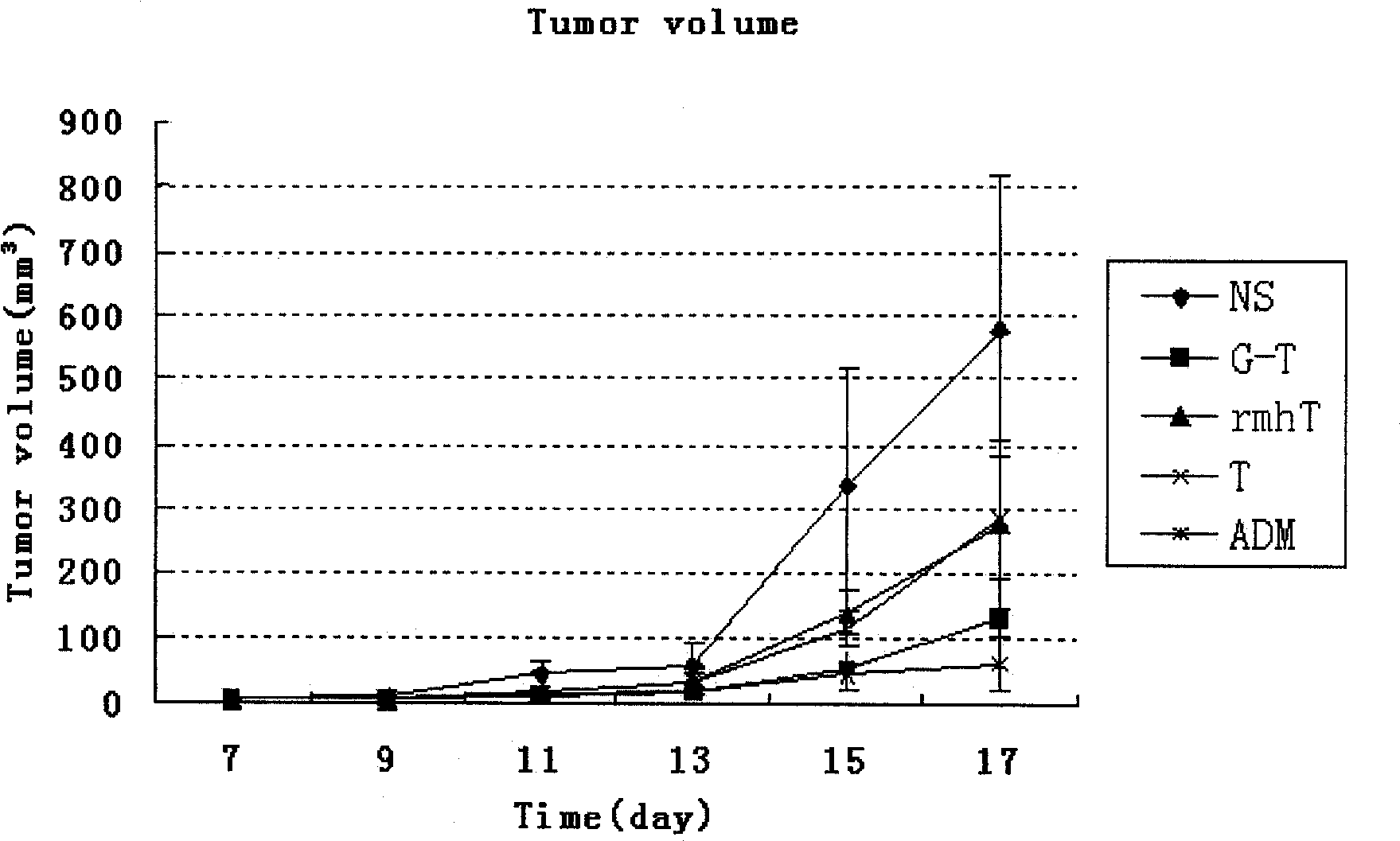
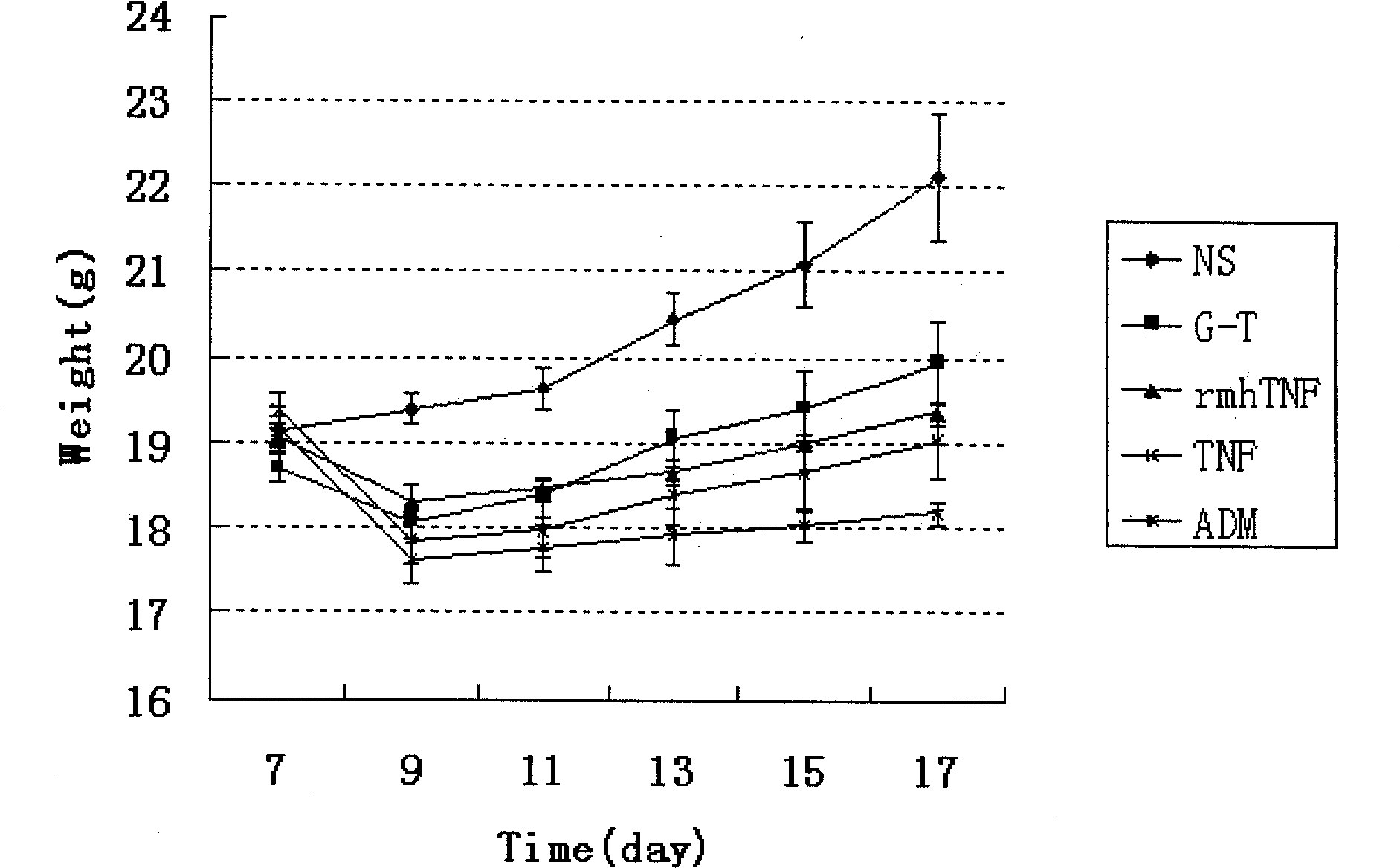
The invention belongs to the pharmaceutical biotechnology field, in particular relates to gene cloning, expression of an exogenous gene in a procaryotic cell, purification of target protein, and novel tumor necrosis factor fusion protein of tumor blood vessel targeted peptide. The invention is characterized in that a small bacteriophage peptide capable of being specifically combined with a blood vessel with gastric cancer is obtained by applying a bacteriophage peptide library in vivo screening technology, and is fused into Escherichia coli together with a novel human tumor necrosis factor alpha (rmhTNF) to obtain high-level expression, the target protein is purified by ammonium sulfate salting-out or an anion-cation exchange method, and the obtained target protein is subject to an activity test. The target protein has the advantages of high efficiency and low toxicity of a novel recombinant human tumor necrosis factor, and can gather in a new blood vessel of a gastric cancer tissue, thus further lowering the clinical dosage for the human tumor necrosis factor, improving the dosage-effect ratio and lowering the toxic and side effect during gastric cancer treatment.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com