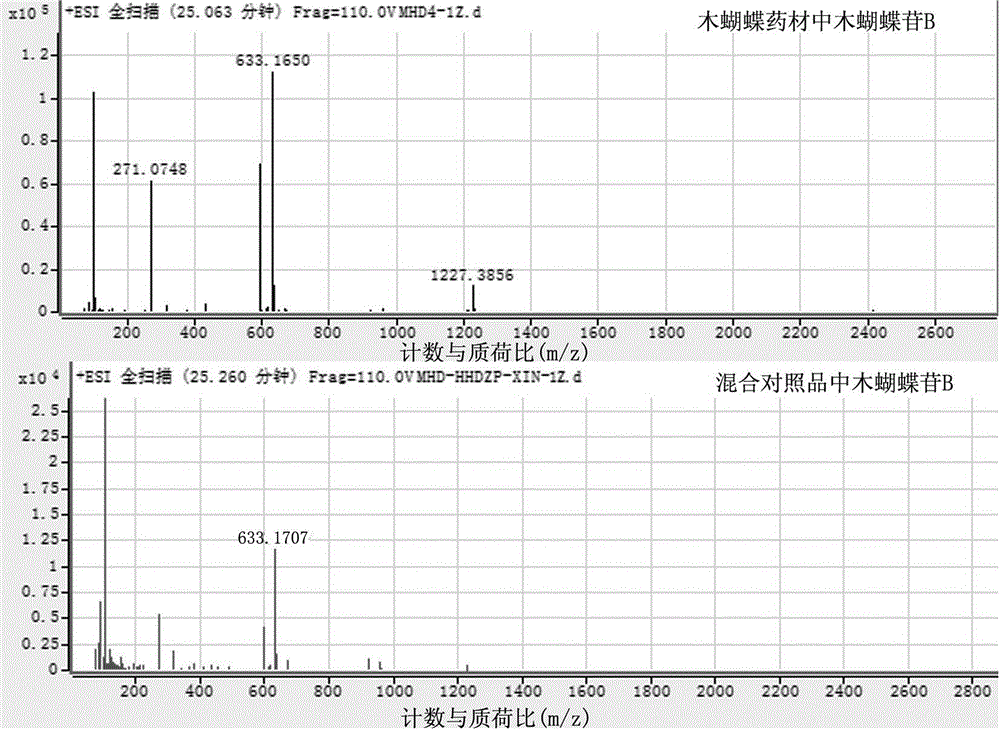
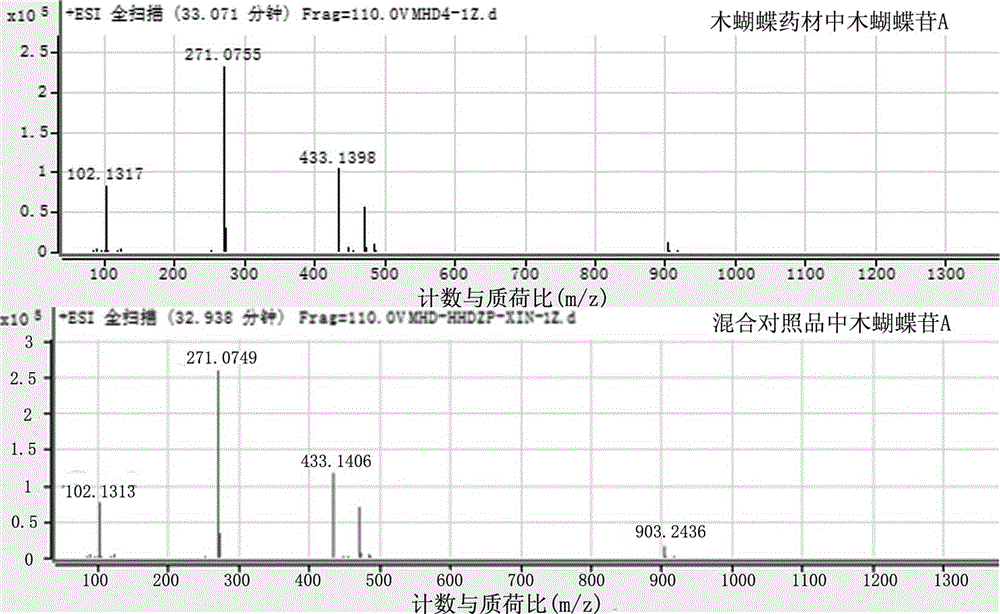
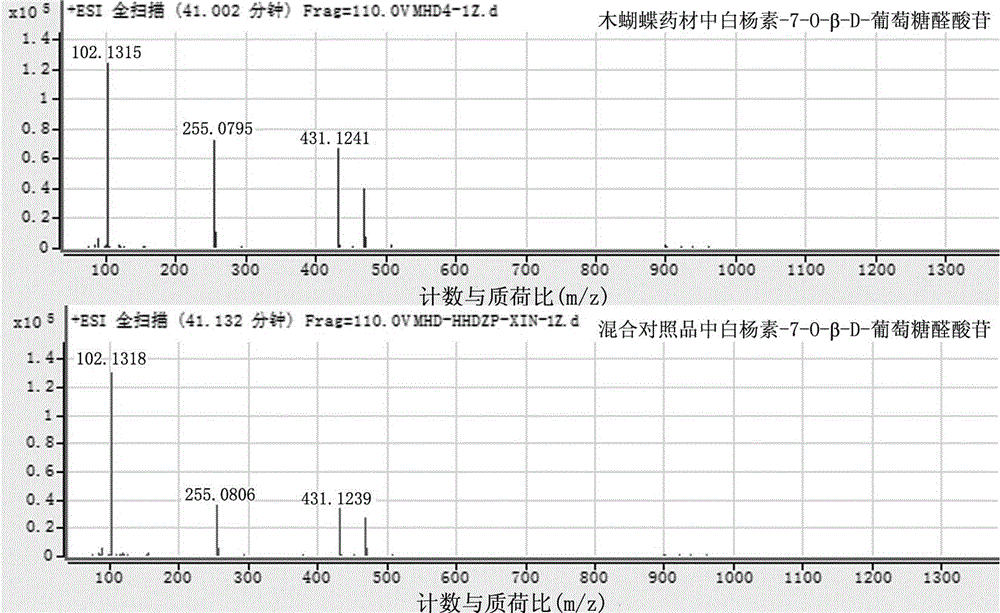
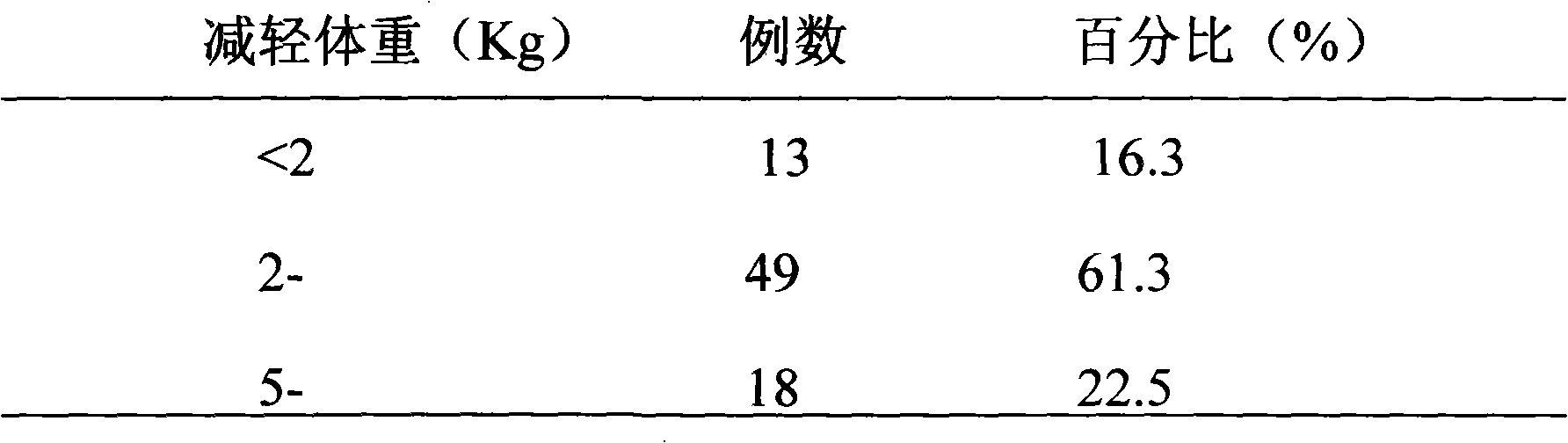
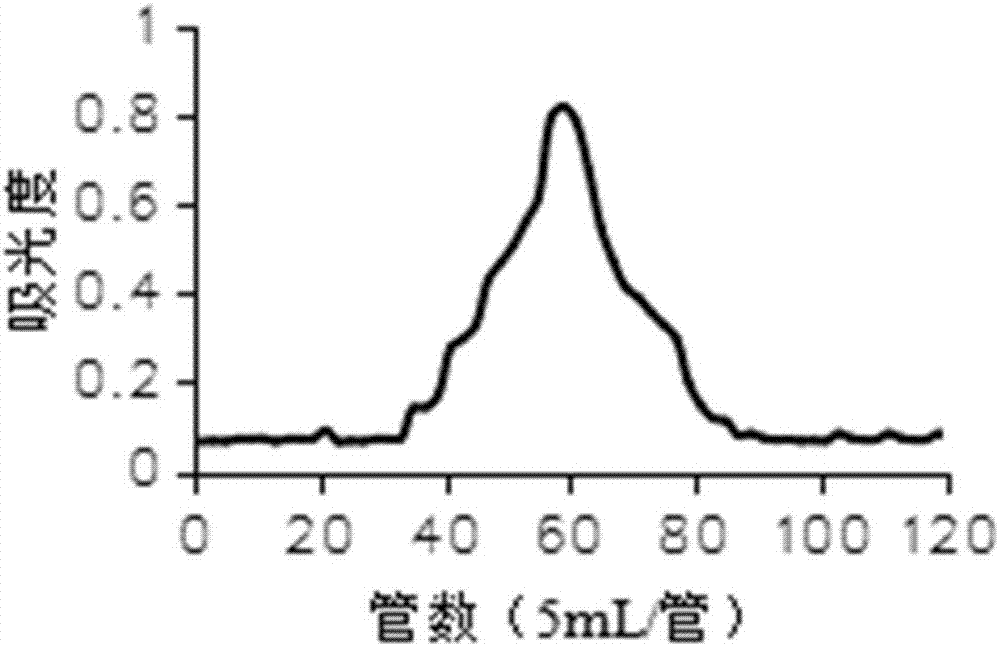
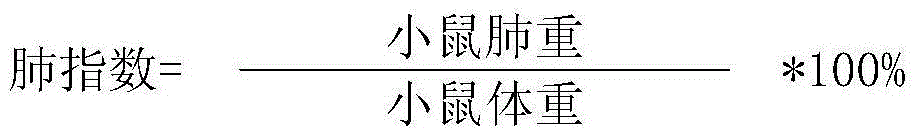
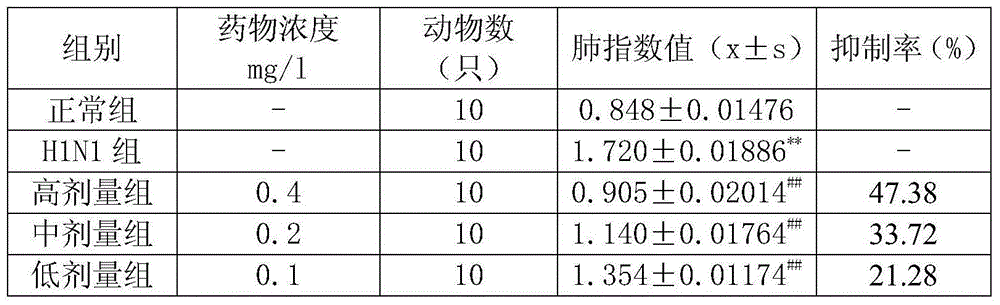
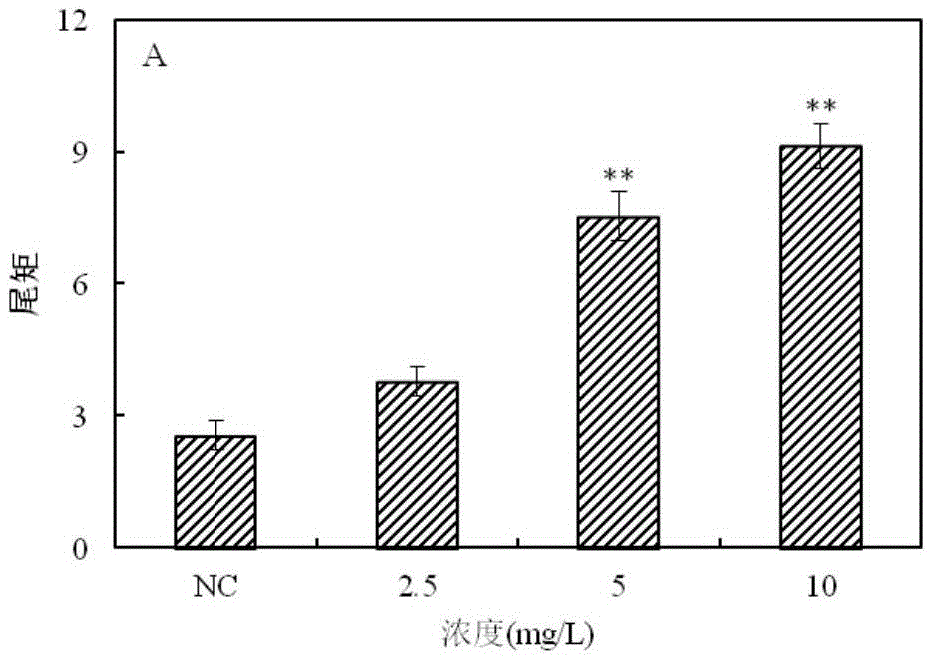
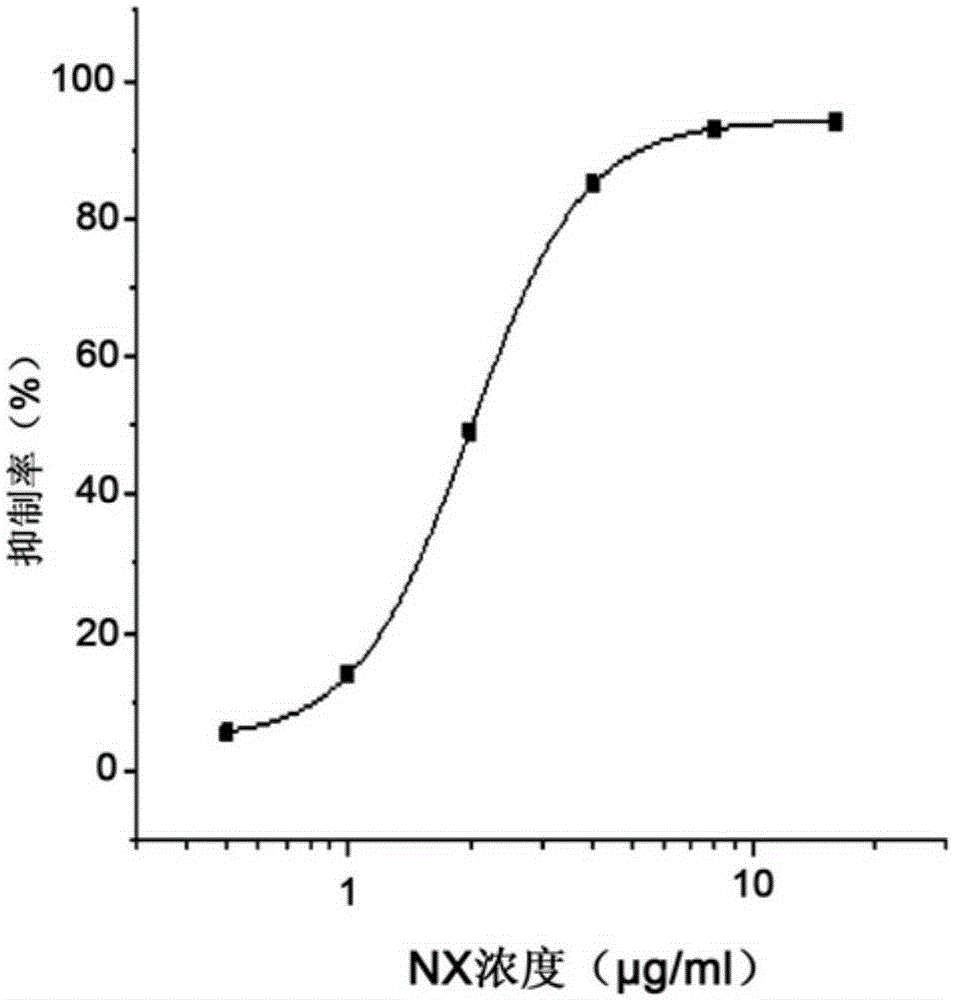
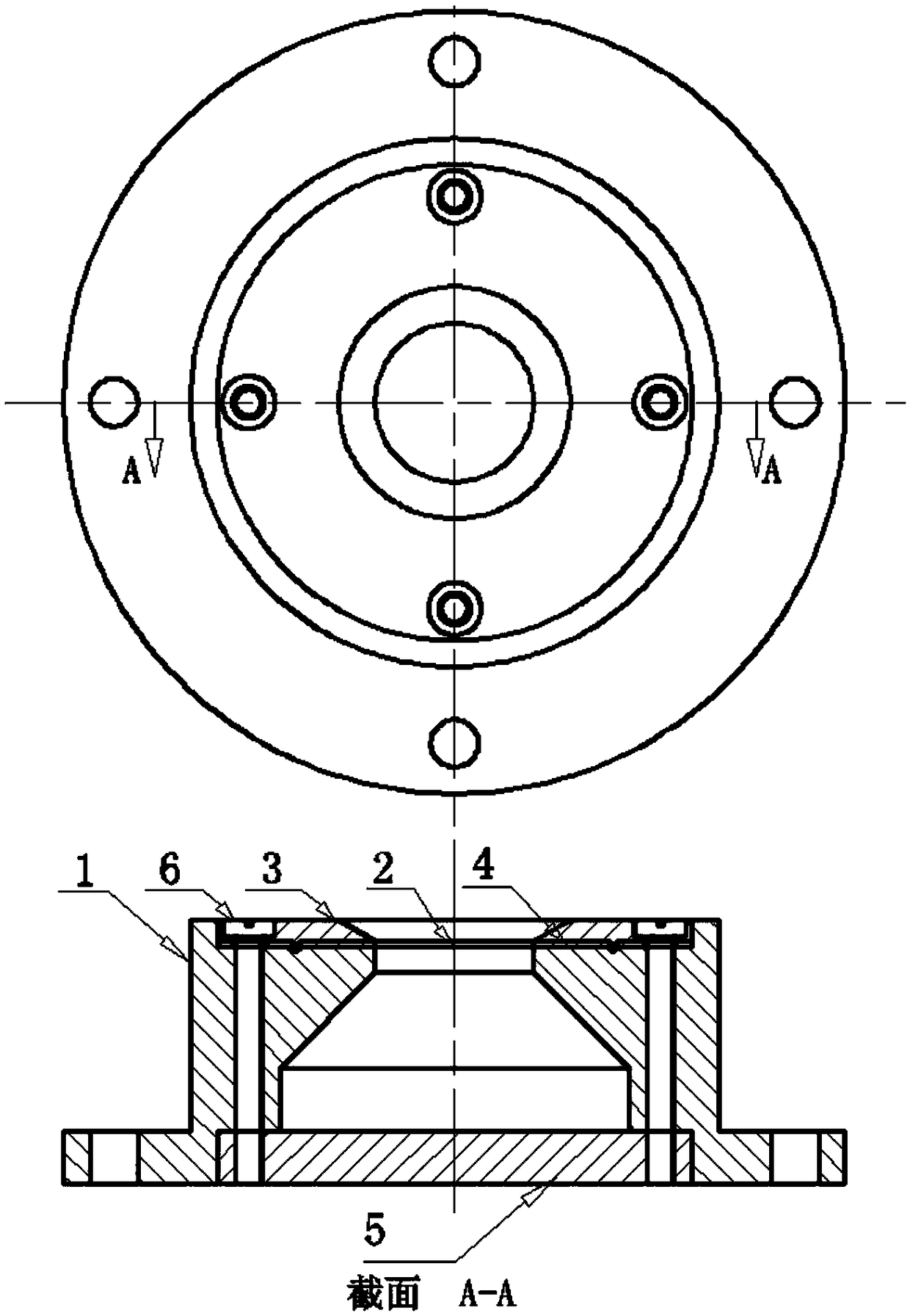
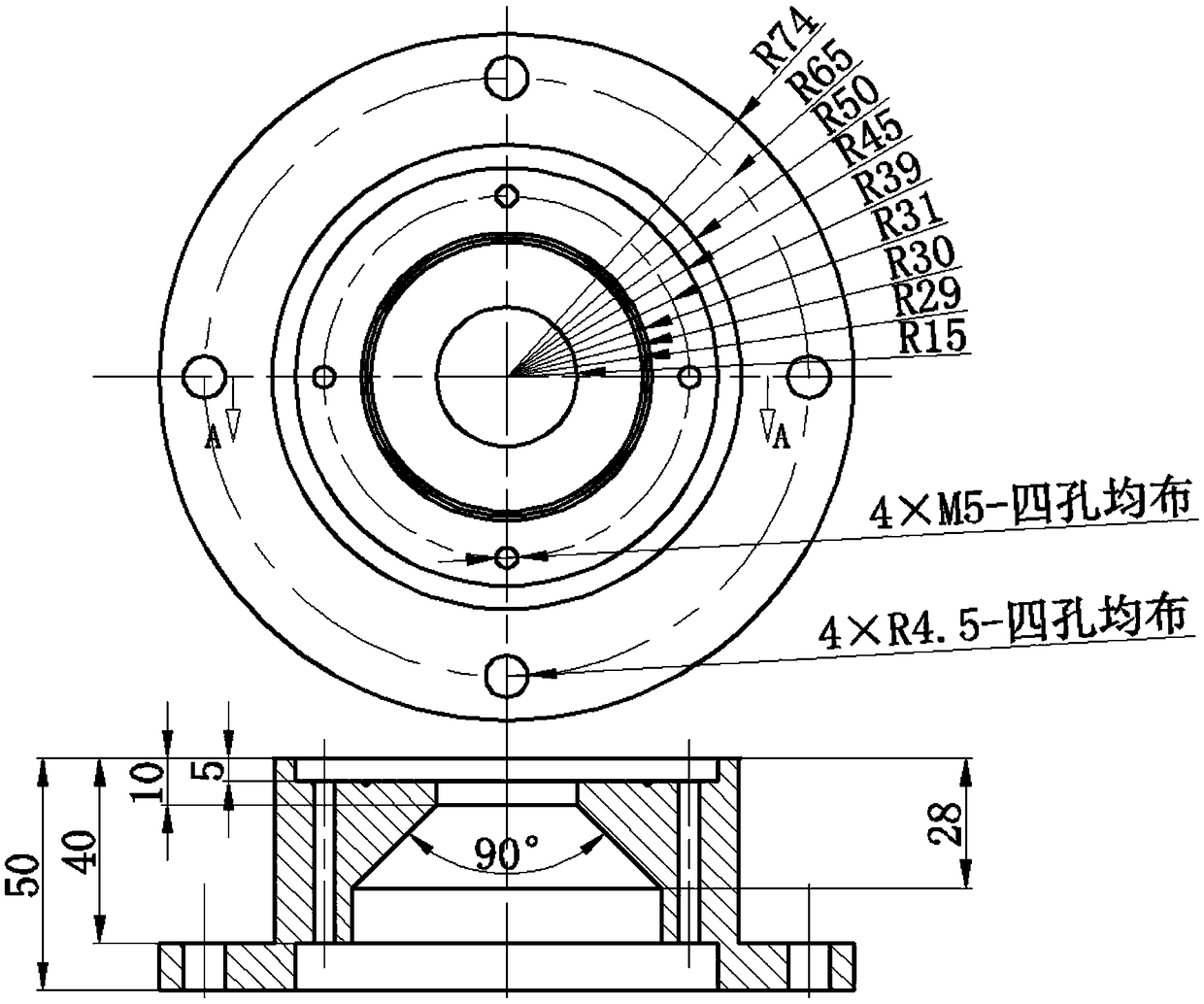
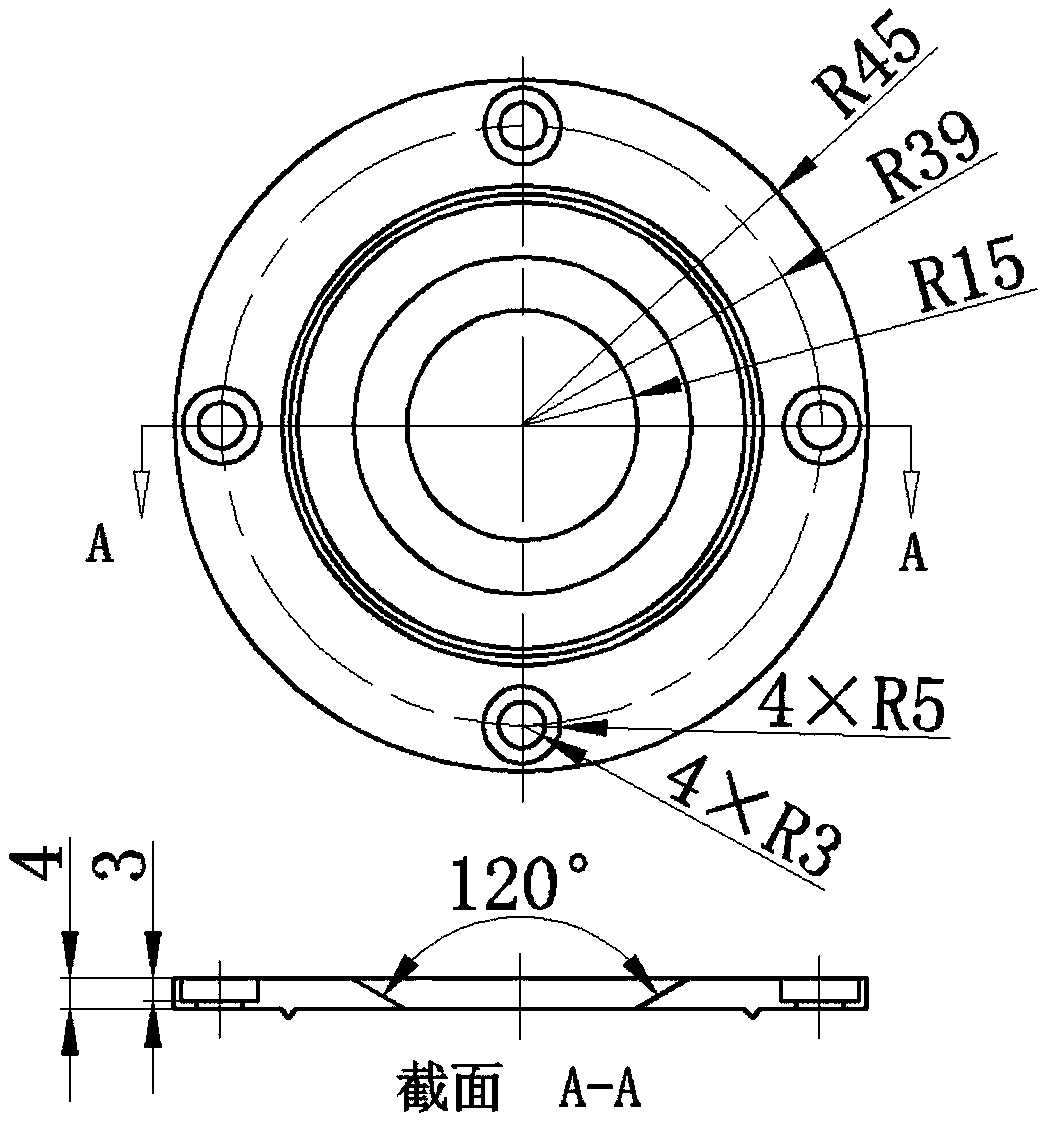
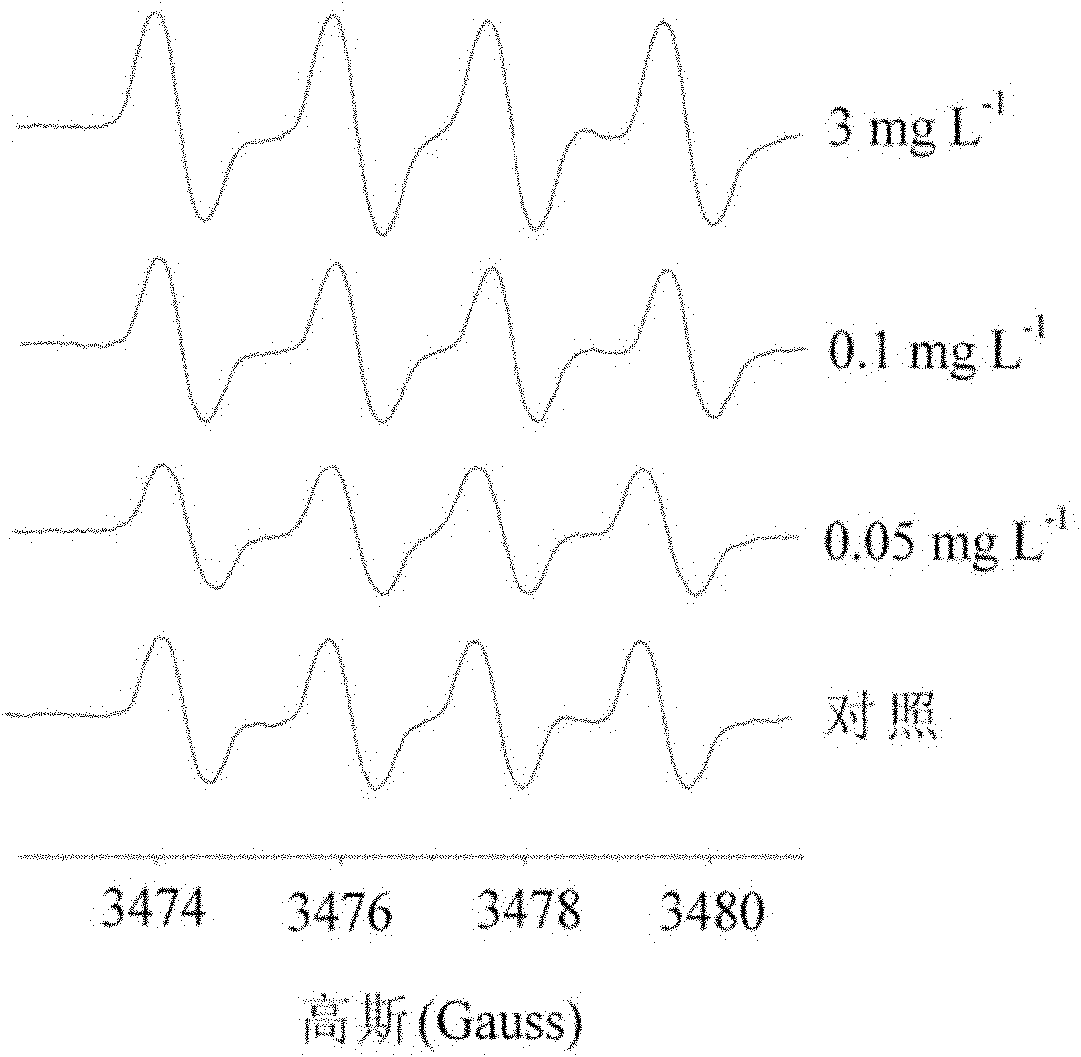Patents
Literature
162 results about "Dose-effect relationship" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Dose-response relationship describes the change in effect on an organism caused by differing levels of exposure (or doses) to a stressor (usually a chemical). This may apply to individuals (eg: a small amount has no observable effect, a large amount is fatal), or to populations (eg: how many people are affected at different levels of exposure).
Shellfish monitoring method for ocean oil spill pollution base on integration biomarker method
InactiveCN103146805AReduced stabilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementShort-necked clamPeroxidase
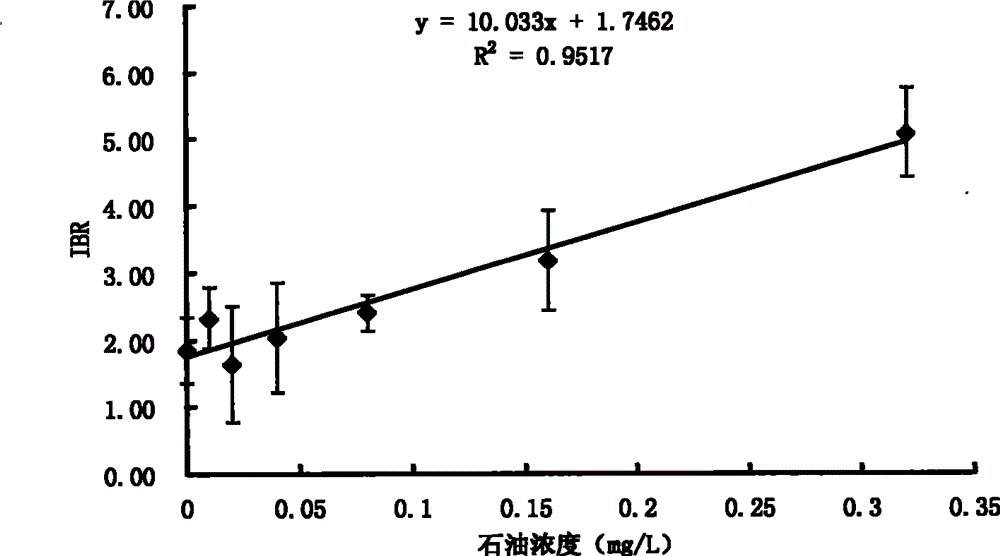
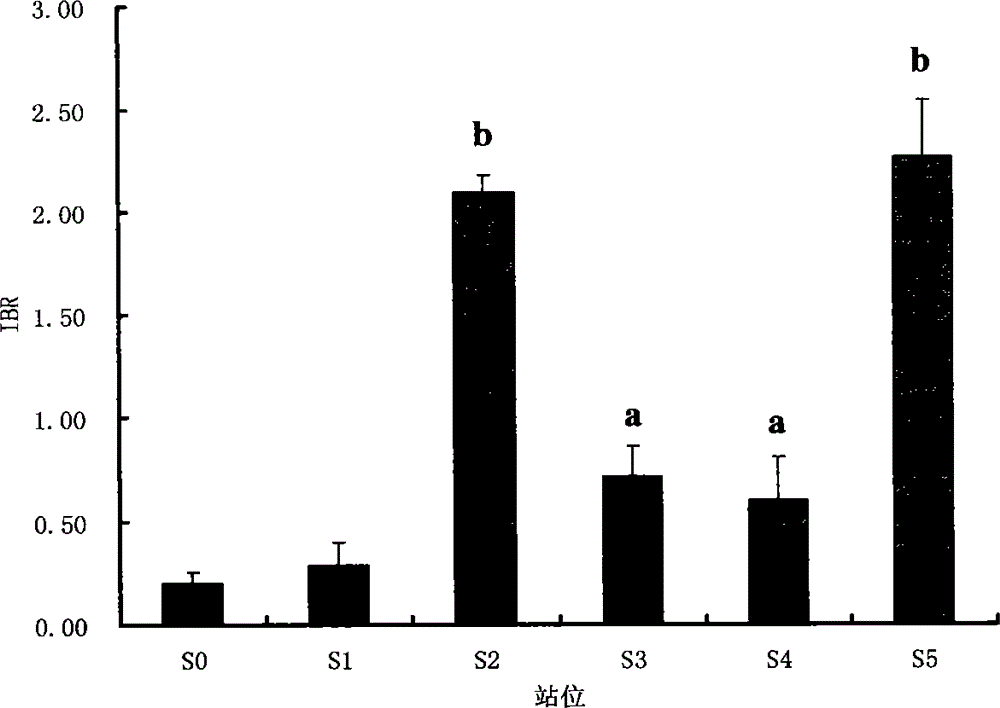
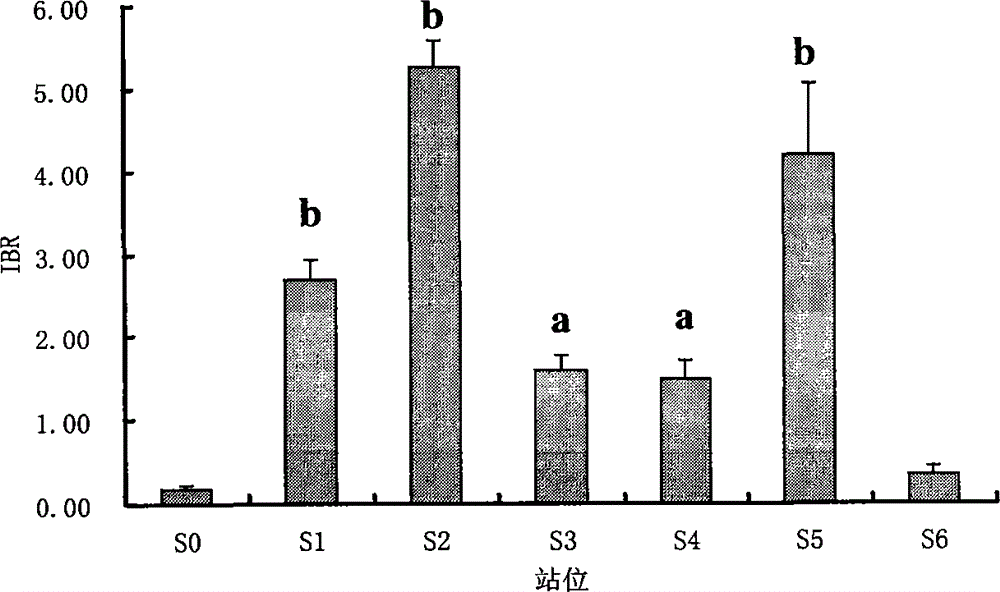
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological monitoring environment, and specifically relates to a shellfish monitoring method for ocean oil spill pollution. The shellfish monitoring method comprises the steps of utilizing typical bivalve mollusk such as short-necked clam and chlamys farreri in China to determine the shellfish visceral mass autioxidant enzyme activities including superoxide dismutase, glutathione glutathione S-transferase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase activity, integrating the enzyme activities so as to form an integration biomarker responding index (IBR), establishing a dose-effect relationship between the IBNNR and petroleum concentration, adopting a one-dimensional variance components method (ANOVA) to carry out notable difference analysis, determining the forcing degree of petroleum pollution on organisms, and finally judging pollution level of the ocean oil spill.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
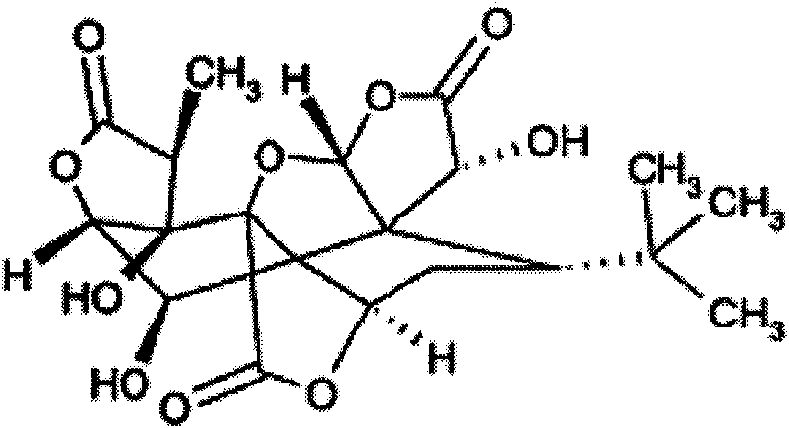
New application of ginkgolide B
InactiveCN102018702APromote apoptosisPromote growthOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderCanine kidneyCytotoxicity
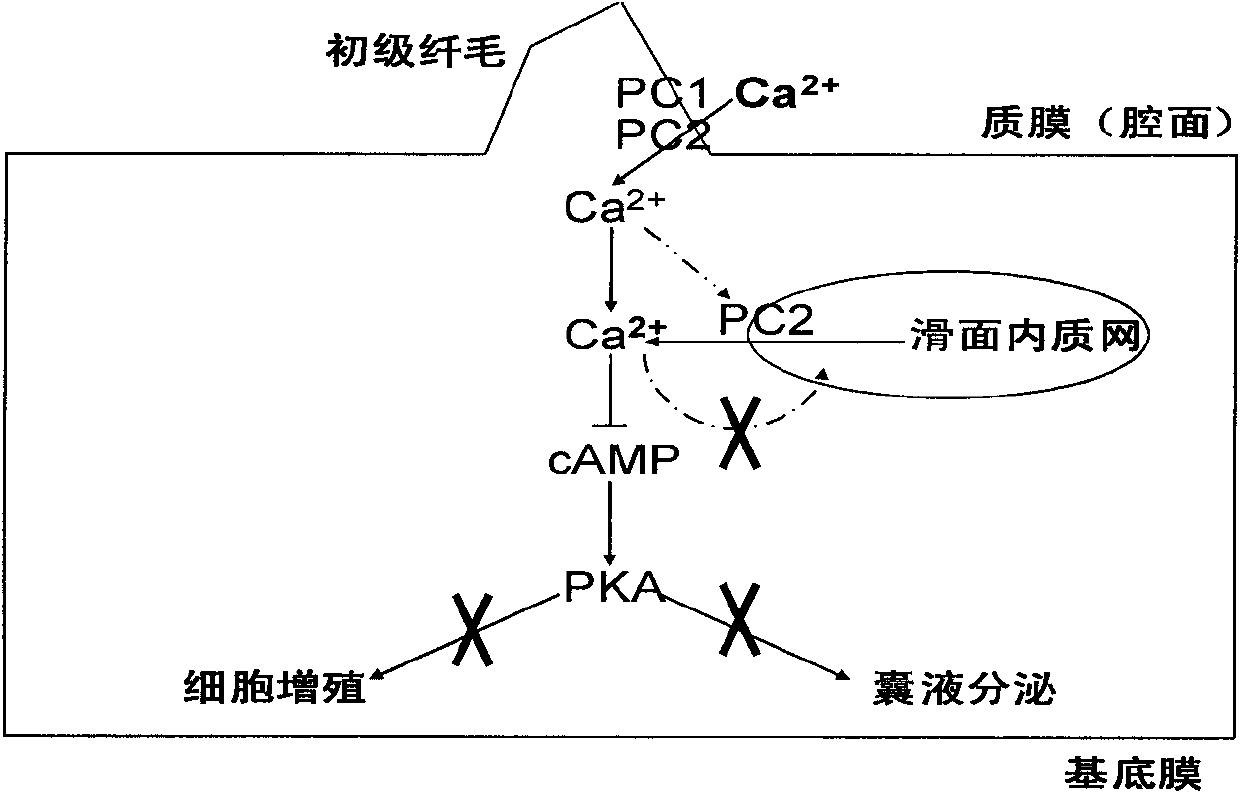
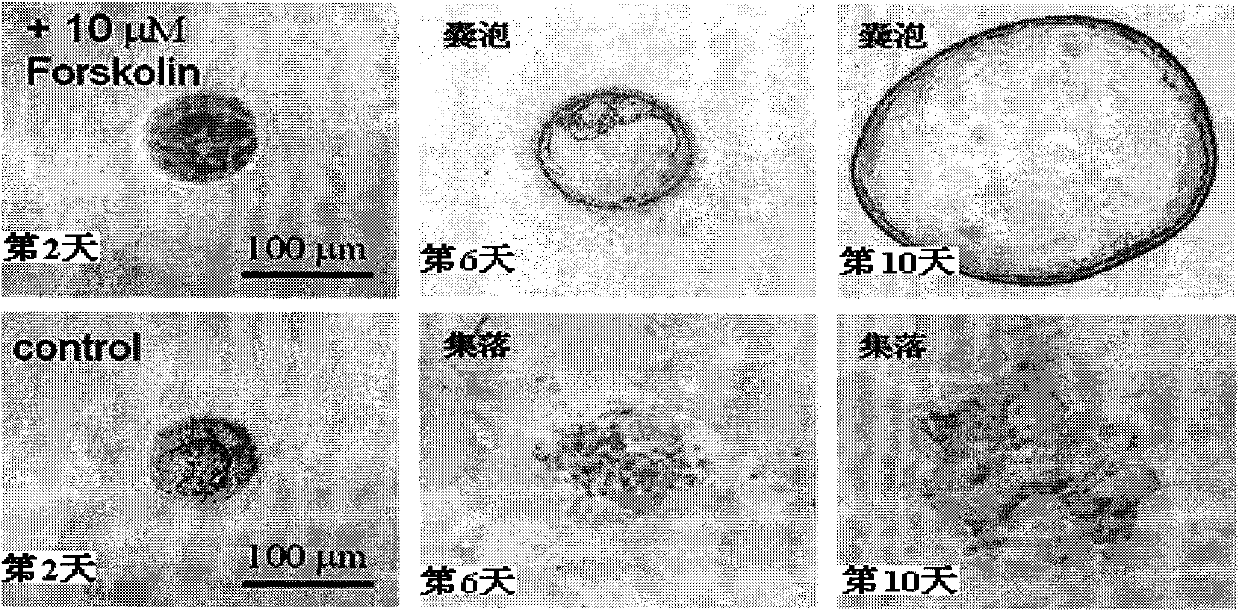
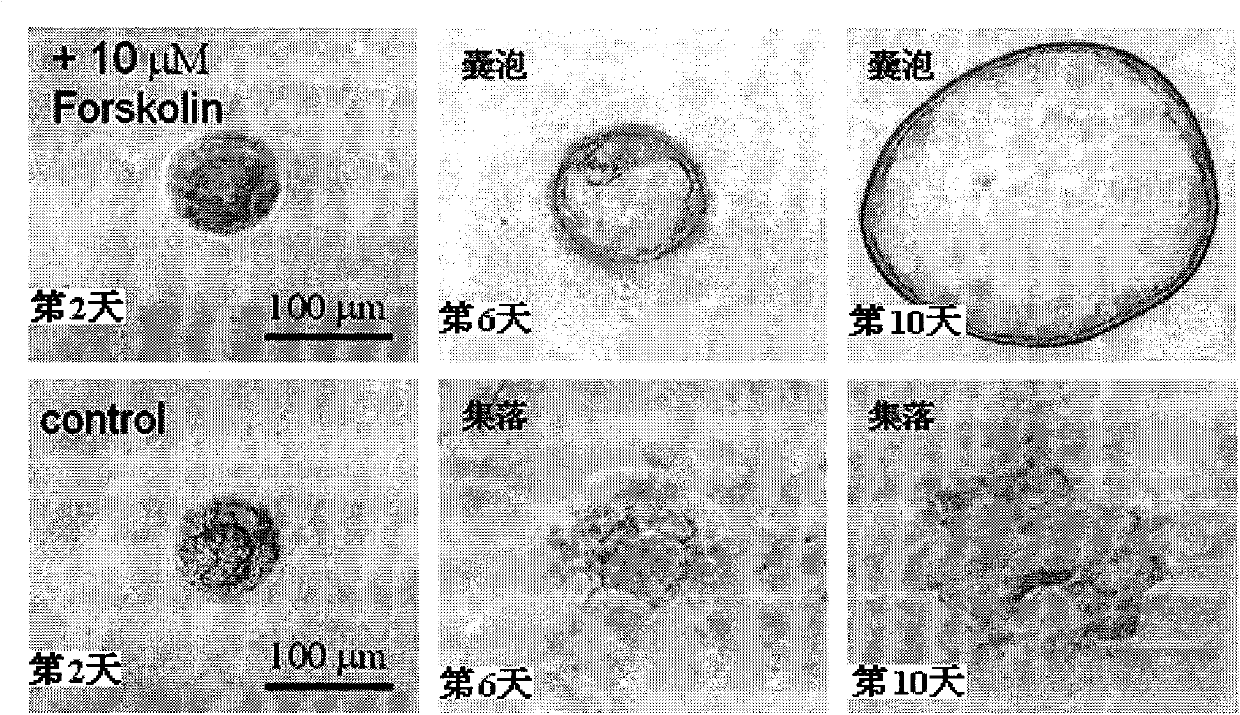
The invention discloses application of ginkgolide B to preparation of medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. A madin-darby canine kidney (MDCK) vesicle model is used for screening to find that the ginkgolide B inhibits formation and growth of vesicles. An experimental result shows that: the ginkgolide B has an obvious inhibiting effect on the formation and growth of MDCK vesicles and the effect of the ginkgolide B is in dose response relationship; the ginkgolide B has no cytotoxicity to MDCK cells, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the ginkgolide B is independent of the cytotoxicity; the ginkgolide B does not obviously induce MDCK cell apoptosis, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the ginkgolide B is independent of cell apoptosis promotion of the ginkgolide B; the ginkgolide B can promote the MDCK cells or vesicles to form tubular structures; and the effect is in dose response relationship; and the ginkgolide B has an inhibiting effect on the growth of the embryonic kidney vesicles. The ginkgolide B provides experimental data for development of a specific medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Effect target device for shock wave pressure measurement of target of moving explosive field
InactiveCN107966227ASolve the measurement problem of large shock wave pressure variation rangeLarge rangeMeasurement of explosion forceShock waveWave pressure
The invention discloses an effect target device for shock wave pressure measurement of a target of a moving explosive field. The effect target device is characterized by comprising a base, an intermediate body, a response diaphragm, a cover plate, a sealing hole, a pressure leading hole, compression bolt holes, compression bolts, an auxiliary hole, and an auxiliary plate. When an external shock wave is applied to the effect target device, the wave is applied to five working areas of the response diaphragm through the pressure leading hole of the cover plate to cause plastic deformation and recession into the sealing hole below; a maximum deflection value is measured; and according to a dose-effect relationship between diaphragm deformation and an impact shock effect, an impact wave pressure peak value is obtained. According to the invention, the effect target device has the following advantages: the effect target device with the light weight is easy to arrange; the sealing performanceis good; the interference of the shock wave diffraction is eliminated; the effective range is wide; the pressure range capable of damaging the target is covered basically; a measurement problem of a large shock wave pressure changing range of the target of the moving explosive field is solved; the precision and reliability of the target pressure measurement in the moving explosive field are improved; and the need of the shock wave pressure measurement of the target of the moving explosive field is met.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
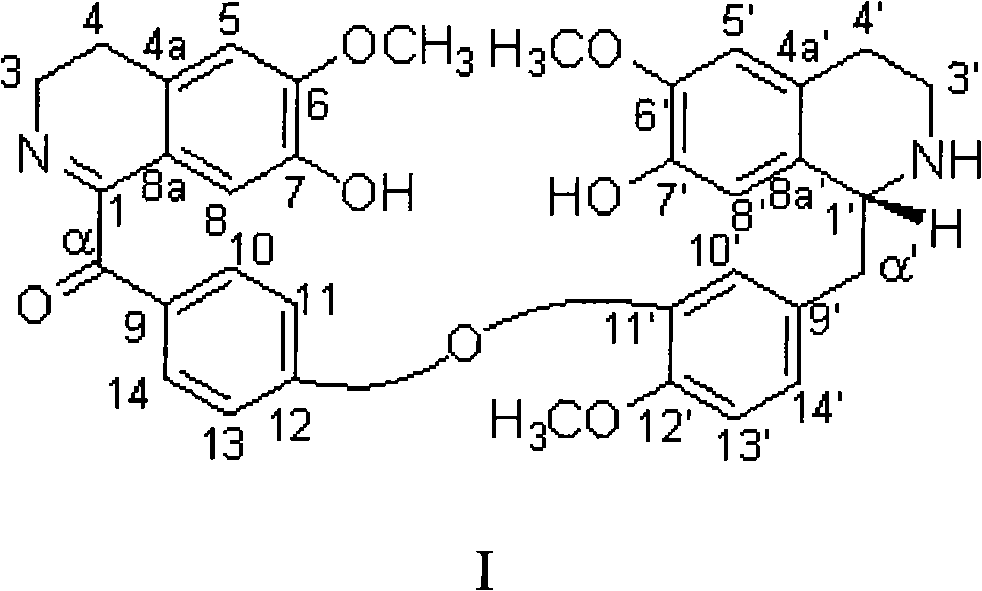
Bisbenzylisoquinoline compounds, preparation method and applications
InactiveCN101284792ANovel structureEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryToxicantGradient elution
The invention provides a bisbenzylisoquinoline compound in lindera aggregate and the preparation method thereof. The lindera aggregate dried root is used as the raw material and is extracted by using an alcoholic solvent, the extractant is produced into extracturm through decompressing concentration, after the extracturm is dissolved and suspended by water and acidified by dilute acid, the neutral component of the extracturm is removed by extraction with an organic solvent, the water phase is adjusted to the pH value of 10 by weak base, extraction is performed by the organic solvent after solvent recovery, the total alkaloid crude product is obtained, fine alkaloid crude is prepared after the crude product is resolved in alcohol and sedimentation process is performed by adding an amount of water, eluting parts are colleted after the chloroform-carbinol system elution and the water-carbinol gradient elution, and the compound can be prepared after removing the solvent by condensation. The compound is used for performing activity inhibition experiments to L1210 and K562 tumor cell strains, results show that both L1210 and K562 tumor cell strains have strong cell-toxicant activity and present dose-effect relationships. The compound can be applied to the preparation of anticancer drugs, and has the above structural formula.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Water comprehensive toxicity rapid detection method based on algae chlorophyll fluorescene
ActiveCN103728284AShort durationRapid and sensitive toxicity responseFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceOrganism
The invention discloses a water comprehensive toxicity rapid detection method based on algae chlorophyll fluorescene. According to the method, toxic and sensitive unicellular scenedesmus obliquus is selected as a testing organism, an experimental group and a blank control group of a to-be-tested water sample are subjected to adaptive cultivation for 24 hours, fast-phase chlorophyll fluorescene of two groups of algae samples is measured, fluorescence parameters in the energy transfer process of main photosynthesis are analyzed and obtained, an inhibition ratio of to-be-tested water of the experimental group on the photosynthesis of algae is calculated, and the comprehensive toxicity intensity of the to-be-tested water is calculated according to the dose-effect relationship between the substance toxicity intensity and the inhibition ratio of photosynthesis. The method has the characteristics of sensitive toxicity response, simple and fast test and the like and is a new method for rapid evaluation of ecological risk and emergency monitoring of sudden pollution accidents.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
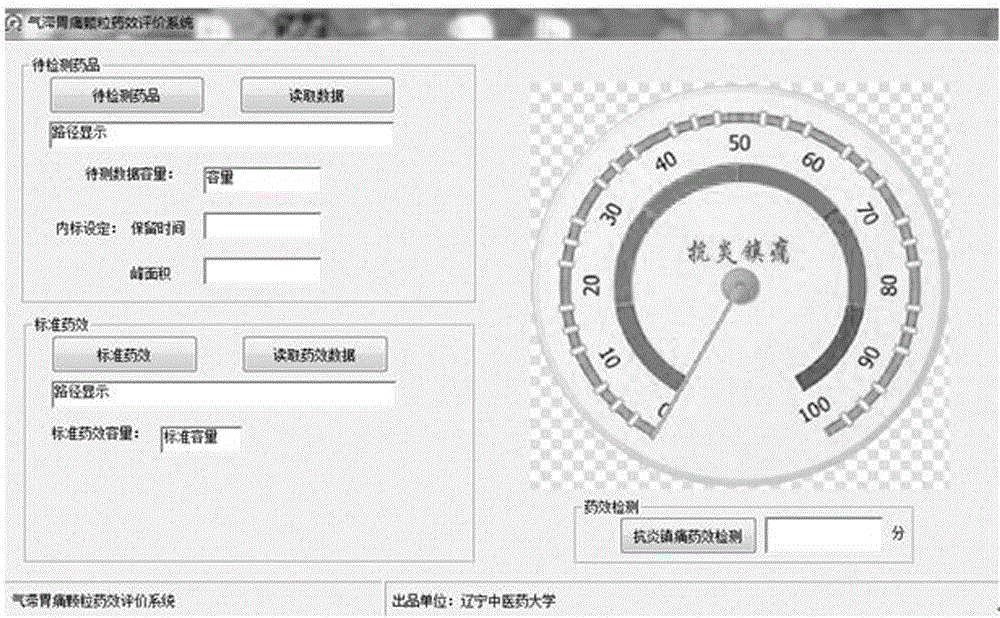
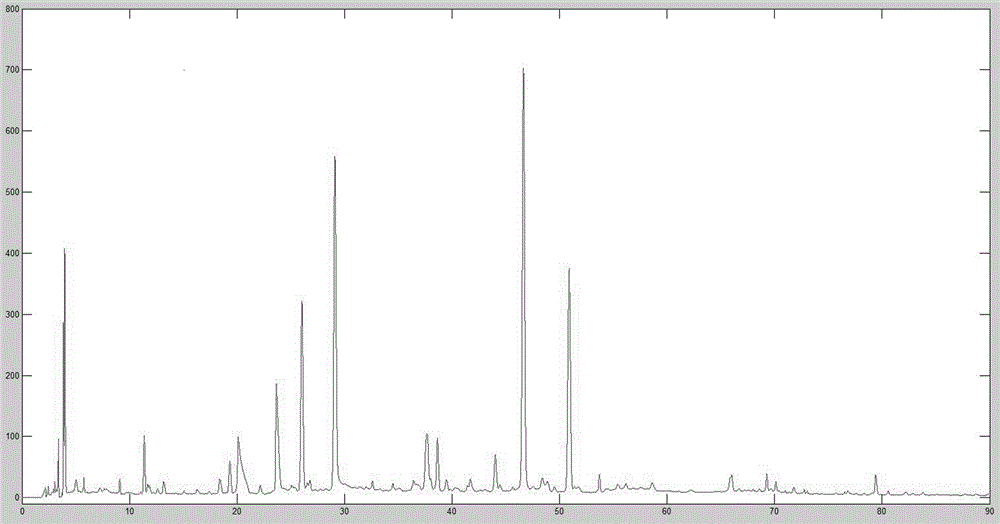
Quality control method based on dose-effect color card for anti-inflammatory and analgesia action of qi-stagnation and stomachache granules
ActiveCN105758950AQuality improvementRealize "visual" predictionComponent separationMedicinePeak area
The invention discloses a quality control method based on a dose-effect color card for anti-inflammatory and analgesia action of qi-stagnation and stomachache granules. According to the quality control method, correlation between the quality and the medicine effect of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules is evaluated through construction of a fingerprint of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules and evaluation of the anti-inflammatory and analgesia action of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules; a dose-effect relationship equation is constructed; the dose-effect color card for the anti-inflammatory and analgesia action of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules is successfully constructed; and the anti-inflammatory and analgesia action can be intuitively reflected in a form of the 'color card' by detecting the relative peak area of specific components in the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules. The quality control method can be used for evaluating the anti-ulcer action degree and the quality of the qi-stagnation and stomachache granules.
Owner:辽宁华润本溪三药有限公司
New application of curcumin
InactiveCN102018689ADoes not induce apoptosisPromote apoptosisKetone active ingredientsUrinary disorderCanine kidneyCytotoxicity
The invention discloses application of curcumin to preparation of medicaments for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. A madin-darby canine kidney (MDCK) vesicle model is used for screening to obtain the curcumin which inhibits formation and growth of vesicles. An experimental result shows that: the curcumin has an obvious inhibiting effect on the formation and growth of MDCK vesicles and the effect of the curcumin is in dose response relationship; the curcumin has no cytotoxicity to MDCK cells, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the curcumin is independent of the cytotoxicity; the curcumin does not obviously induce MDCK cell apoptosis, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the curcumin is independent of cell apoptosis promotion of the curcumin; the curcumin can promote the MDCK cells or vesicles to form tubular structures; and the effect is in dose response relationship; and the curcumin has an inhibiting effect on the growth of the embryonic kidney vesicles. The curcumin is expected to be developed into a specific medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for measuring superoxide anion radicals in tape grass leaves
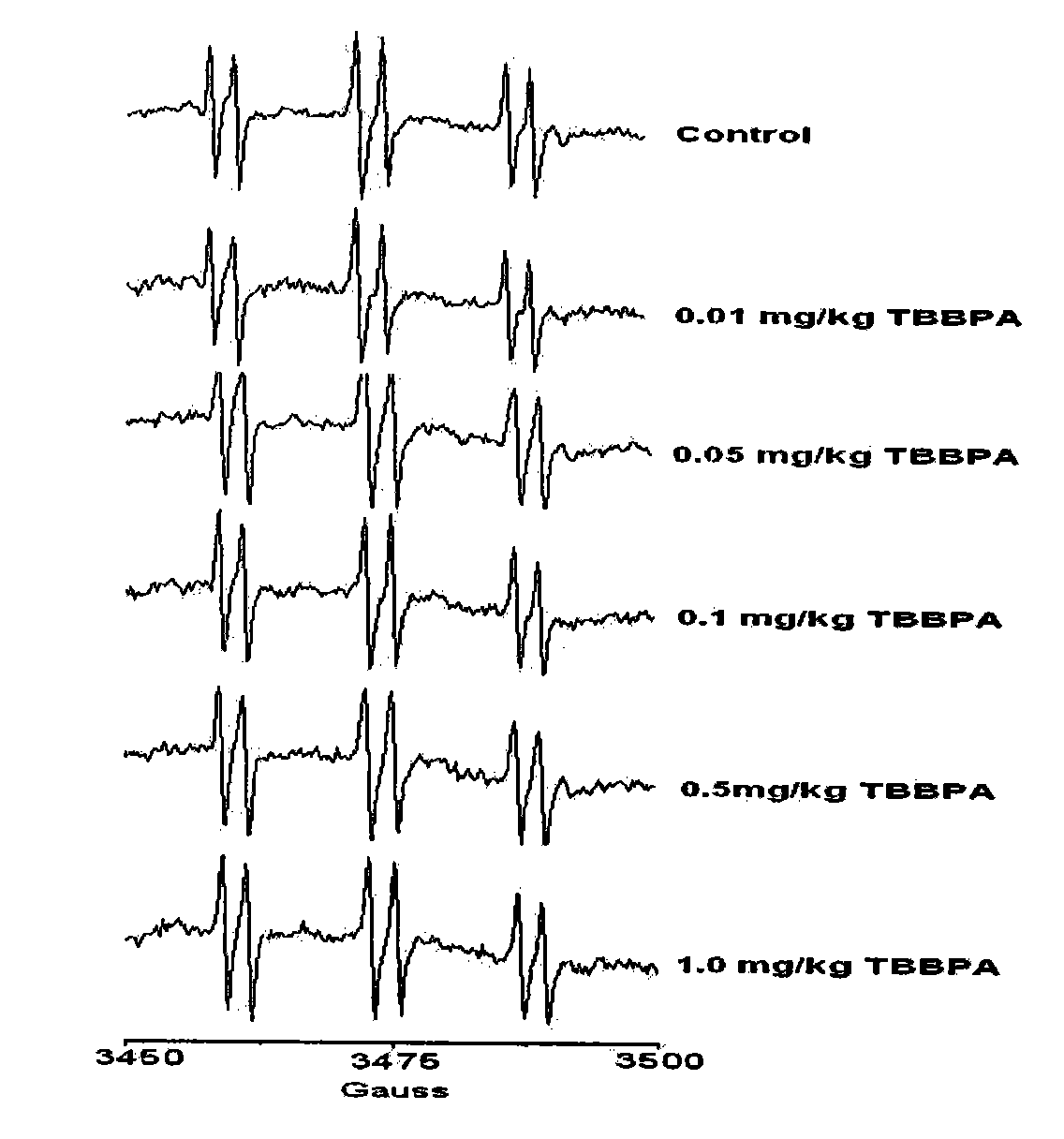
InactiveCN101936930AEasy to operateEasy to masterAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceSuper oxide dismutasePlant roots
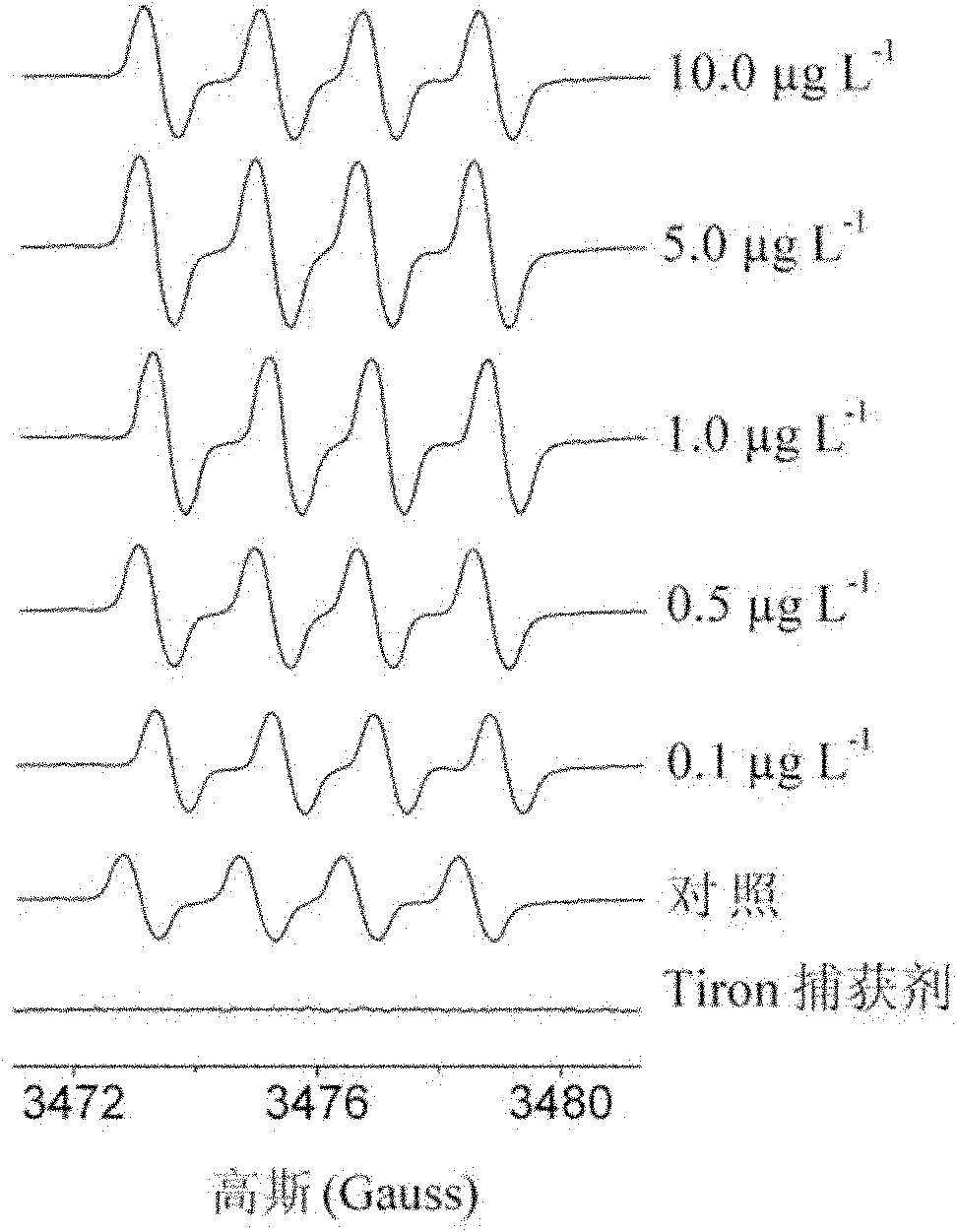
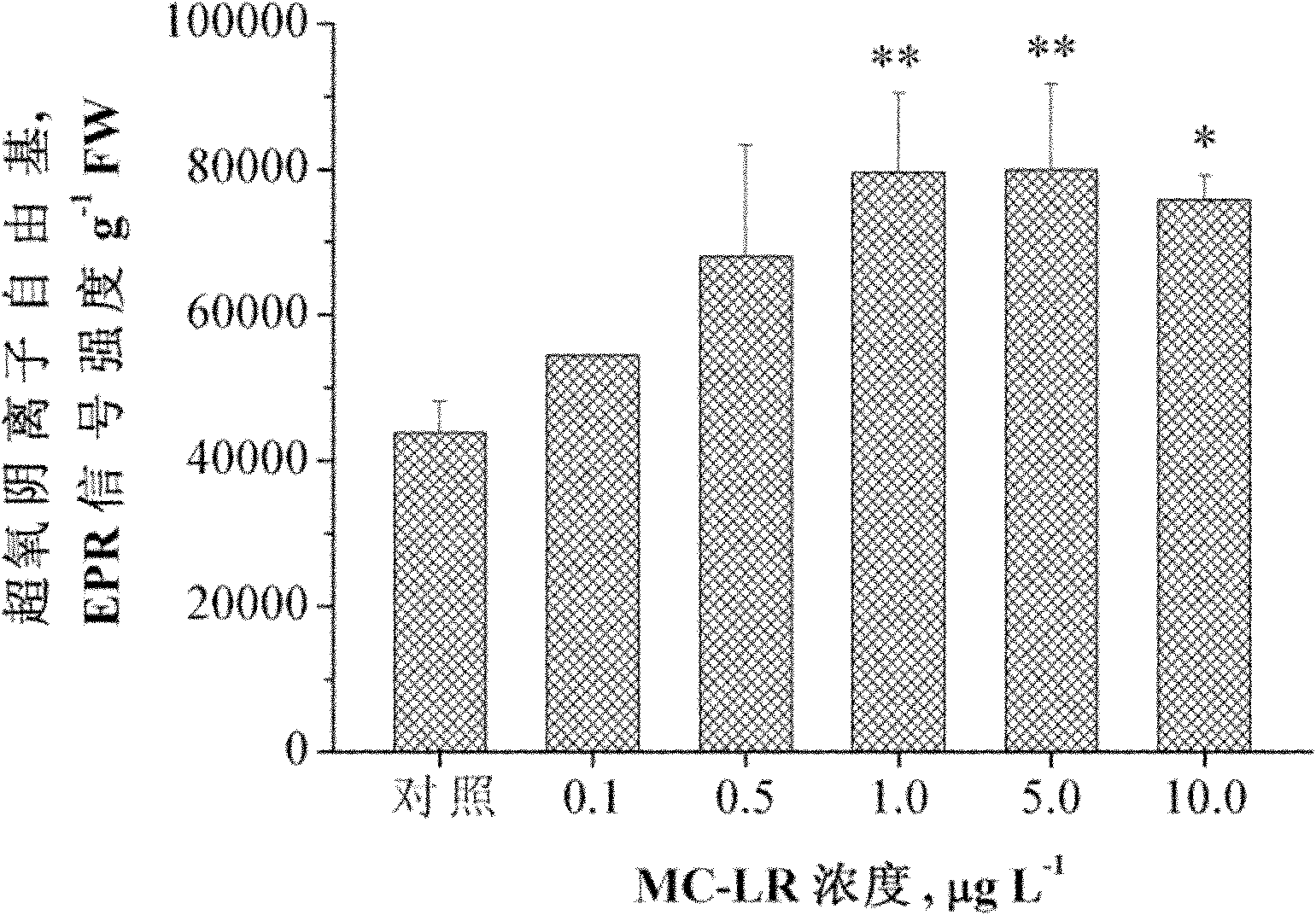
The invention discloses a method for measuring superoxide anion radicals in tape grass leaves, belonging to the measuring field of the measuring of superoxide anion radicals. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, collecting and cleaning the tip parts of fully exposed small and tender tape grass leaves; carrying out Tiron captureing on the Tiron of radicals in a closed operation box in a closed nitrogen environment; and finally measuring by using an EPR (Electron Paramagnetic Resonance) technology. The invention has the advantages of simpler operation and easy grasping, and can measure the superoxide anion radicals of the tape grass leaves in a very short time;, find that and the measured radicals are found to be the superoxide anion radicals according to the superfine structure constant and, the spectrogram shape analysis of an EPR spectrogram and the combination of the remarkable decreases of the radical strength of the leaves pretreated by SOD (Super Oxide Dismutase), and therefore the invention is the most direct, accurate and effective method for measuring the superoxide anion radicals. Superoxide anions are sensitive to pollutants and have a favorable dosage effect relation. The invention is also suitable for other aquatic plant and terrestrial plant species and can be suitable for measuring the radicals of the plant root tissue.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Application of cyclin G1 as low-dose ionizing radiation biodosimeter
InactiveCN103642904AHigh sensitivityQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementIonizationPeripheral blood lymphocyte
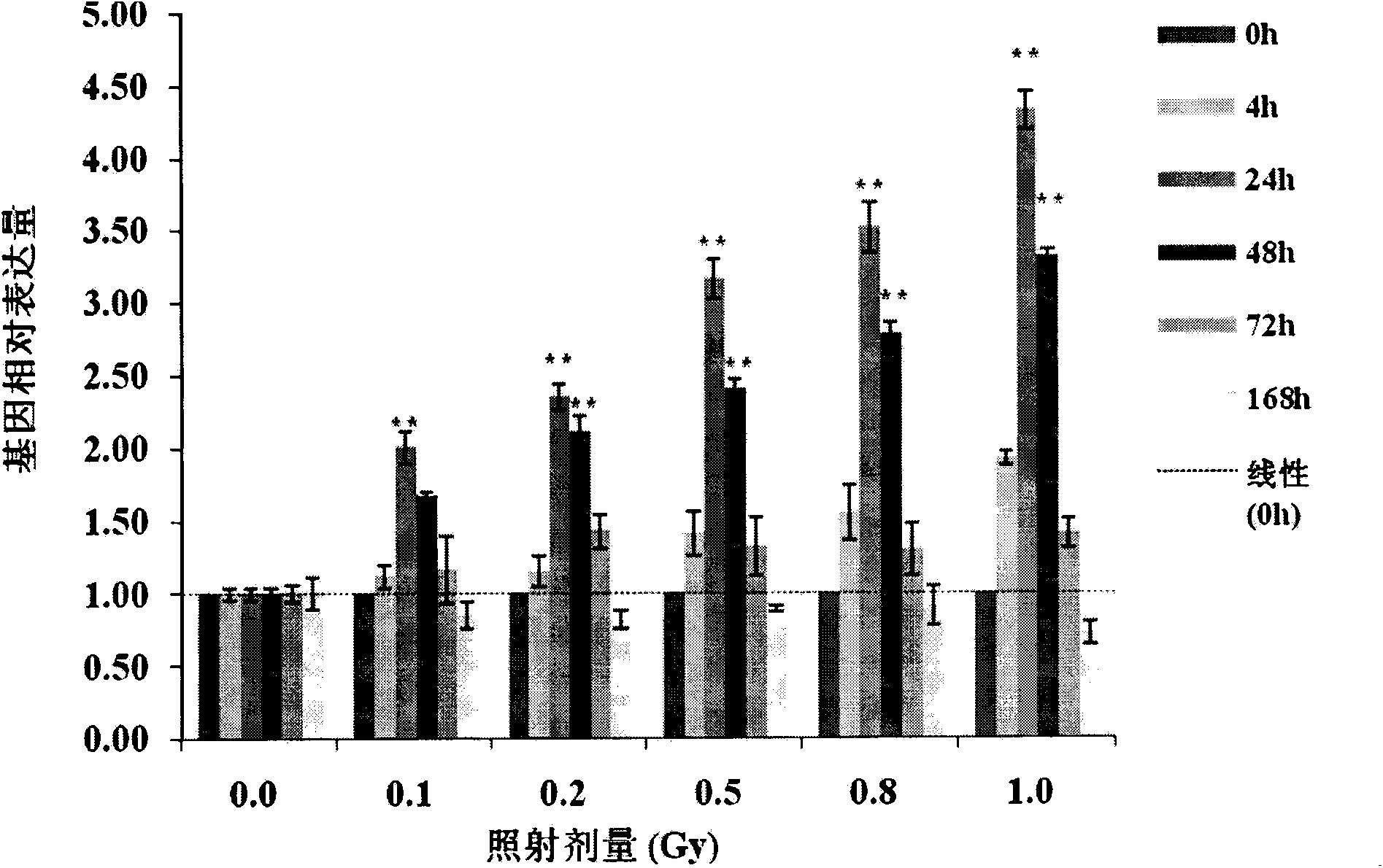
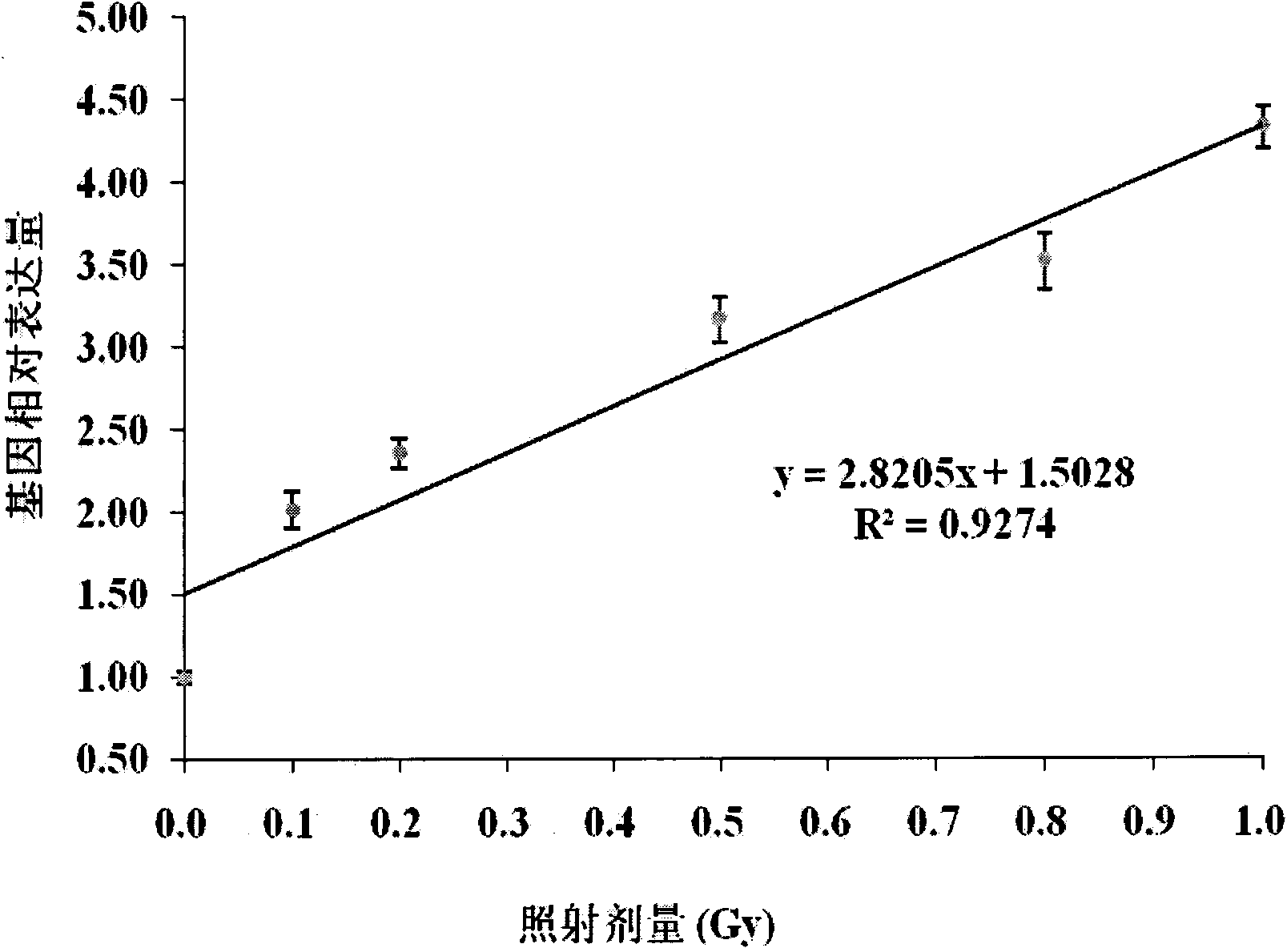
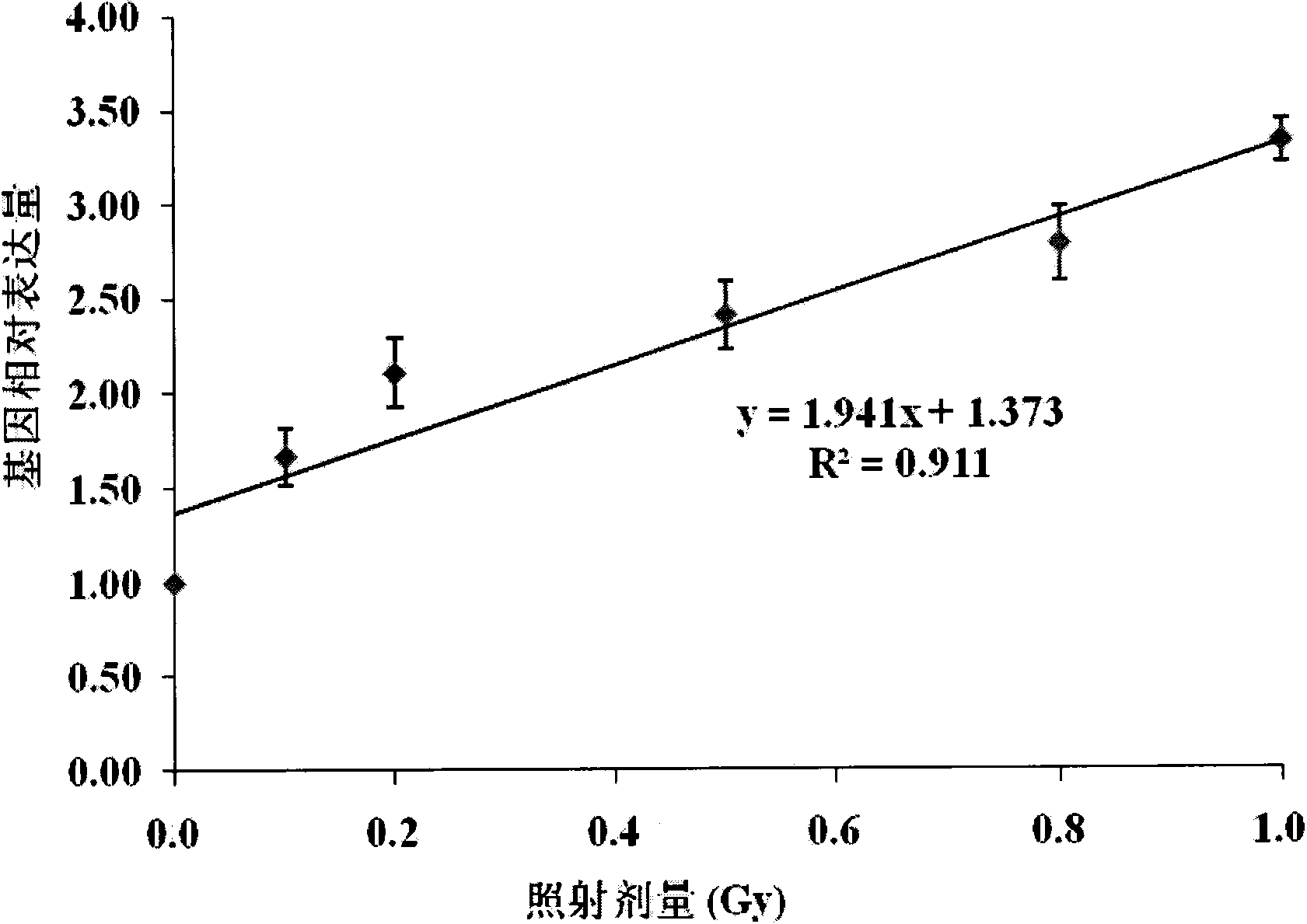
The invention belongs to an ionizing radiation biodosimeter, and concretely relates to an application of a cyclin G1 (CCNG1) gene as the ionizing radiation biodosimeter. After low-dose ionizing radiation of a human lymphoblast and the radiation of mammals, the increase of the expression level of the mRNA of the CCNG1 gene in a peripheral blood lymphocyte is directly proportional to the applied ionizing radiation dose, there is a certain dose-effect relation, and a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method is adopted 24h and 48h after the radiation to realize the fast and simple quantitative detection, so the CCNG1 can be used as a biodosimeter of a low-dose ionizing radiation range, and the dose of the low-dose ionizing radiation to the human bodies and the mammals can be evaluated through a CCNG1 gene expression quantitative-analysis method.
Owner:NAVY MEDICINE RES INST OF PLA
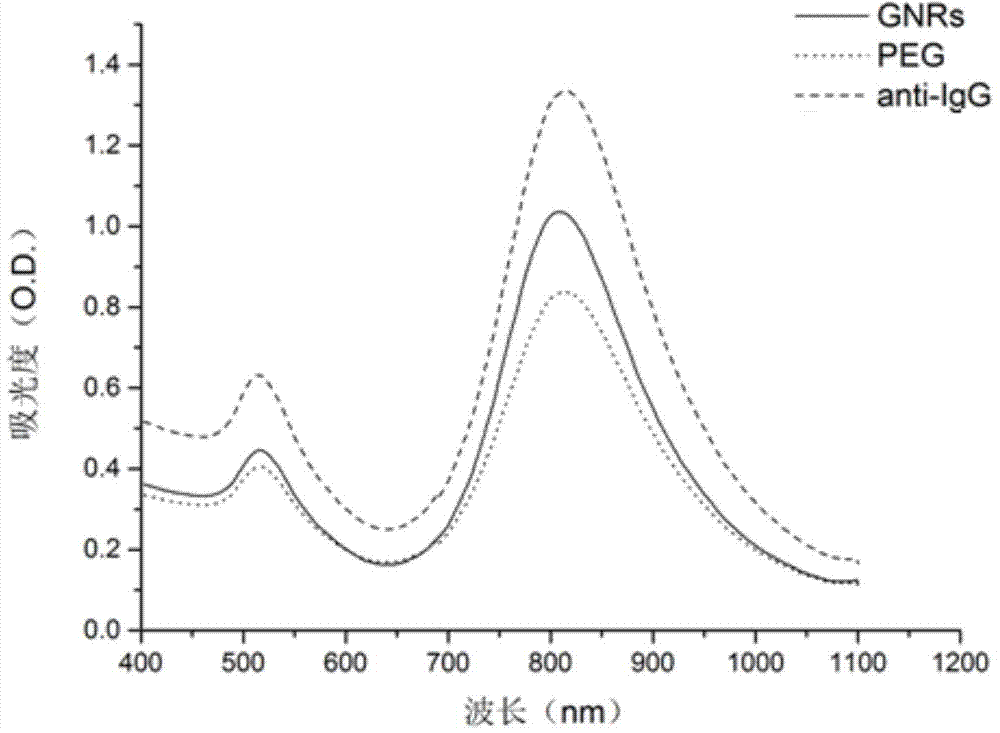
Novel functionalized gold nanorod immune probe as well as preparation method and application of gold nanorod biological chip
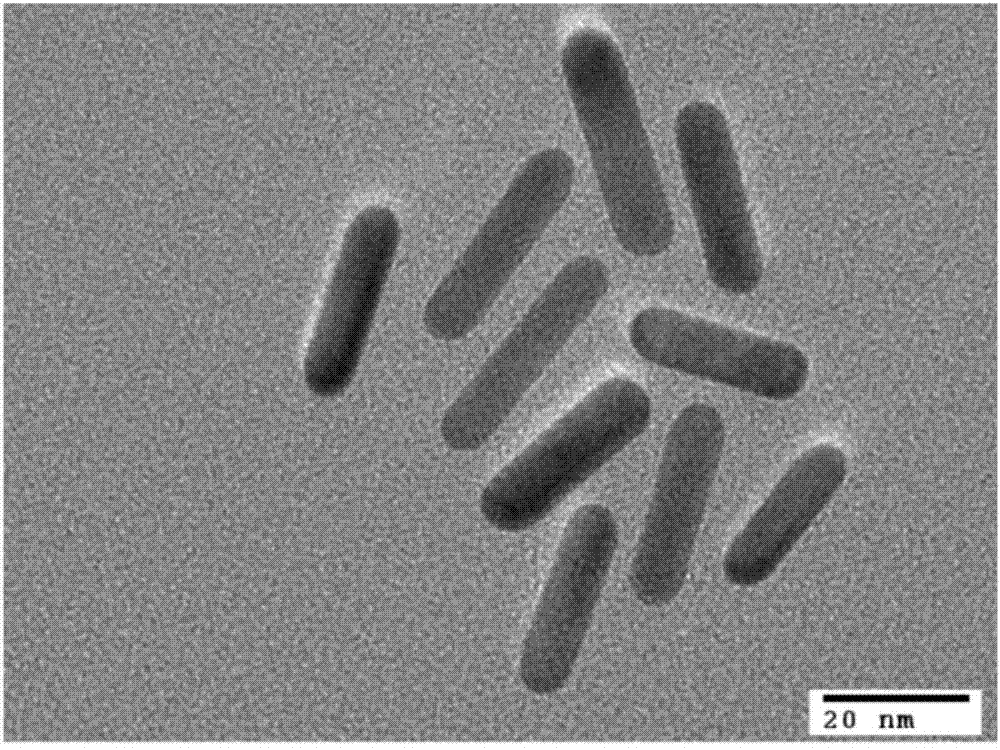
InactiveCN103575875ANot easy to accumulateThe result is stableMaterial analysisGold nanorodGamma globulin
The invention discloses a novel functionalized gold nanorod immune probe as well as a preparation method and an application of a gold nanorod biological chip. The preparation method comprises the following steps of modifying a human IgG (Intravenous Gamma Globulin) antibody by a Traut reagent; coupling the modified IgG antibody with a sulfydryl having high affinity with gold; and covalently binding the modified IgG antibody with a gold nanorod directly through -SH. The operation method is simple, the conditions are mild, the functionalization of the gold nanorod can be quickly realized, the functionalized gold nanorod fixed on a slide can be used as an unmarked biological chip for specifically detecting a human IgG antigen which can be obtained according to an offset dose-effect relationship curve of a nanorod vertical plasma absorption peak, and each nano vertical plasma absorption peak offset is capable of detecting the human IgG antigen at 137 pM. Therefore, the gold nanorod immune probe prepared by the method and used for antigen-antibody detection has the advantages of simple operation, high detection sensitivity, good specificity and a small number of needed instruments and equipment and is clinically popularized possibly.
Owner:ZHENJIANG NO 1 PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
Use of deuteroporphyrin derivates
ActiveCN101467996ANo inhibitory effectNo lethal effectAntineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSide effectPositive control
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicament and specifically relates to use of a deuteroporphyrin derivative. The invention provides use of deuteroporphyrin derivative in preparing medicament for treating squamous carcinoma or adenocarcinoma. The treatment with the deuteroporphyrin derivative or composition and medicament thereof to squamous carcinoma or adenocarcinoma has obvious growth-inhibiting effect and good dose effect relationship. A group with high dosage has strong and stable effect and stronger inhibiting effect than the positive control medicament, hemoporphyrin. The deuteroporphyrin derivative has no growth-inhibiting effect on tumour cells under a condition of non-laser radiation, no damaging effect on normal histiocytes with light or without light and little side effect.
Owner:上海复旦张江生物医药股份有限公司
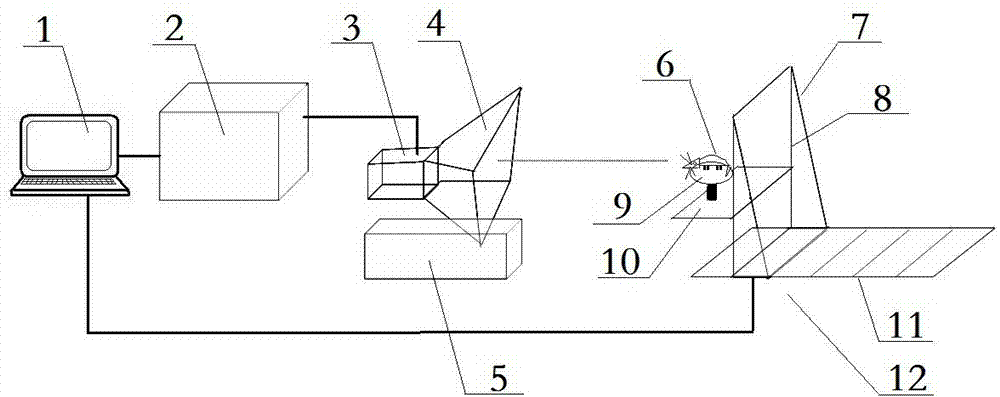
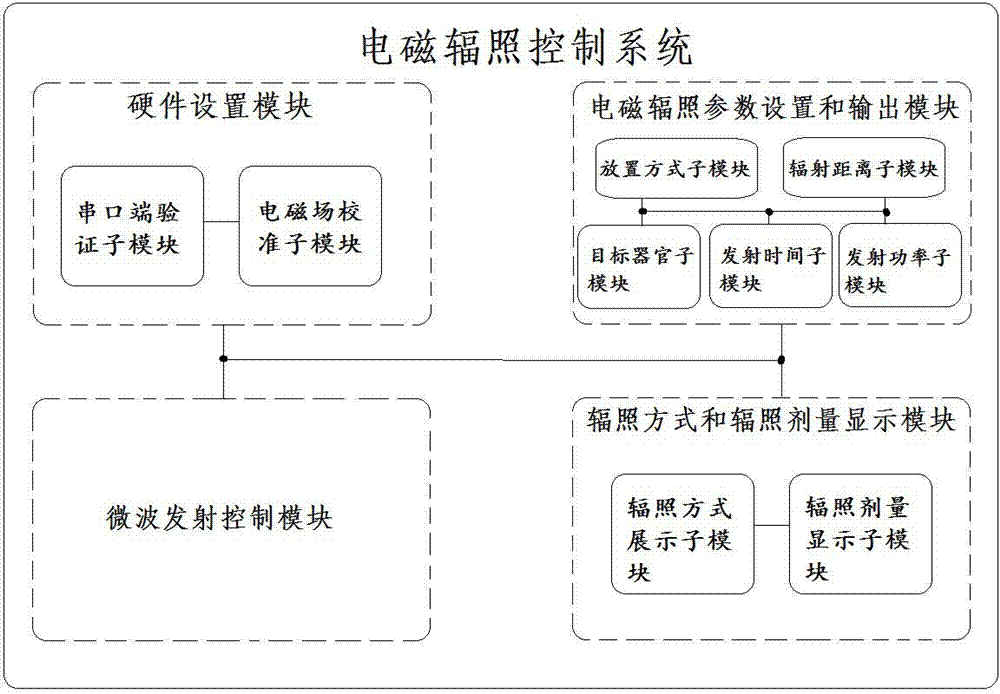
Living animal electromagnetic irradiation system and application method thereof
InactiveCN103499928AControl safetyProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersControl systemEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of researches on an electromagnetic biological effect and particularly relates to a living animal electromagnetic irradiation system and an application method thereof. The living animal electromagnetic irradiation system consists of an electromagnetic irradiation control system, a microwave device, a three-dimensional object carrying platform and a microwave anechoic chamber, wherein the electromagnetic irradiation control system at least comprises a hardware setting module, an electromagnetic irradiation parameter setting and output module, a microwave emission control module and an irradiation method and irradiation dose display module. All modules are mutually connected. The living animal electromagnetic irradiation system and the application method thereof have the advantages that multiple irradiation parameters which influence irradiation dose in animal bodies can be set through the electromagnetic irradiation control system, the placing posture of the living animals relative to the emitting direction of microwaves can be intuitively given out and can be adjusted through the three-dimensional object carrying platform, the irradiation dose of up to eleven important organs can be given out after the irradiation parameters are set, data is provided for establishing an accurate dose-effect relationship between the irradiation dose and the animal effect and the goal of remotely controlling the microwave device to emit microwaves is realized.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
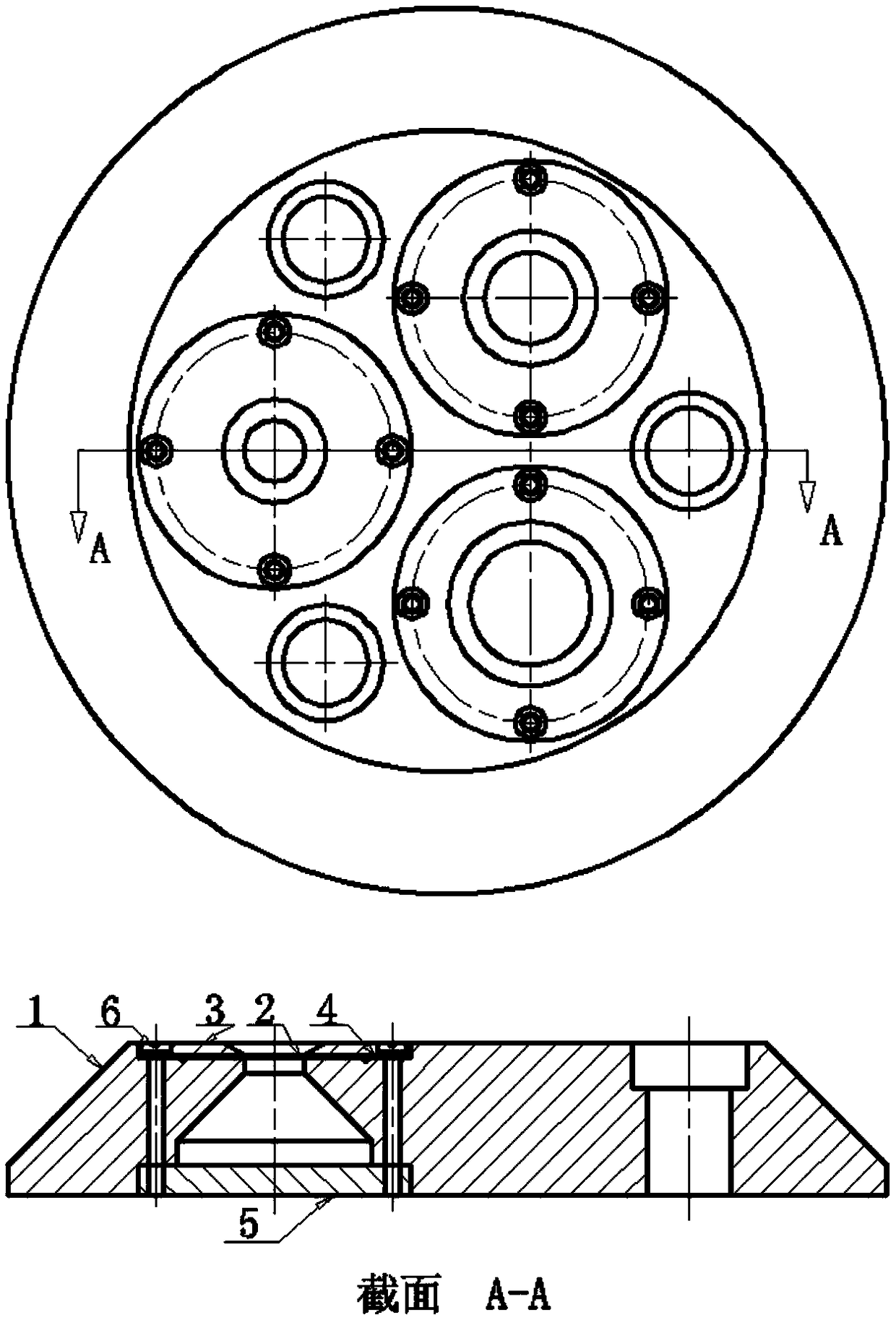
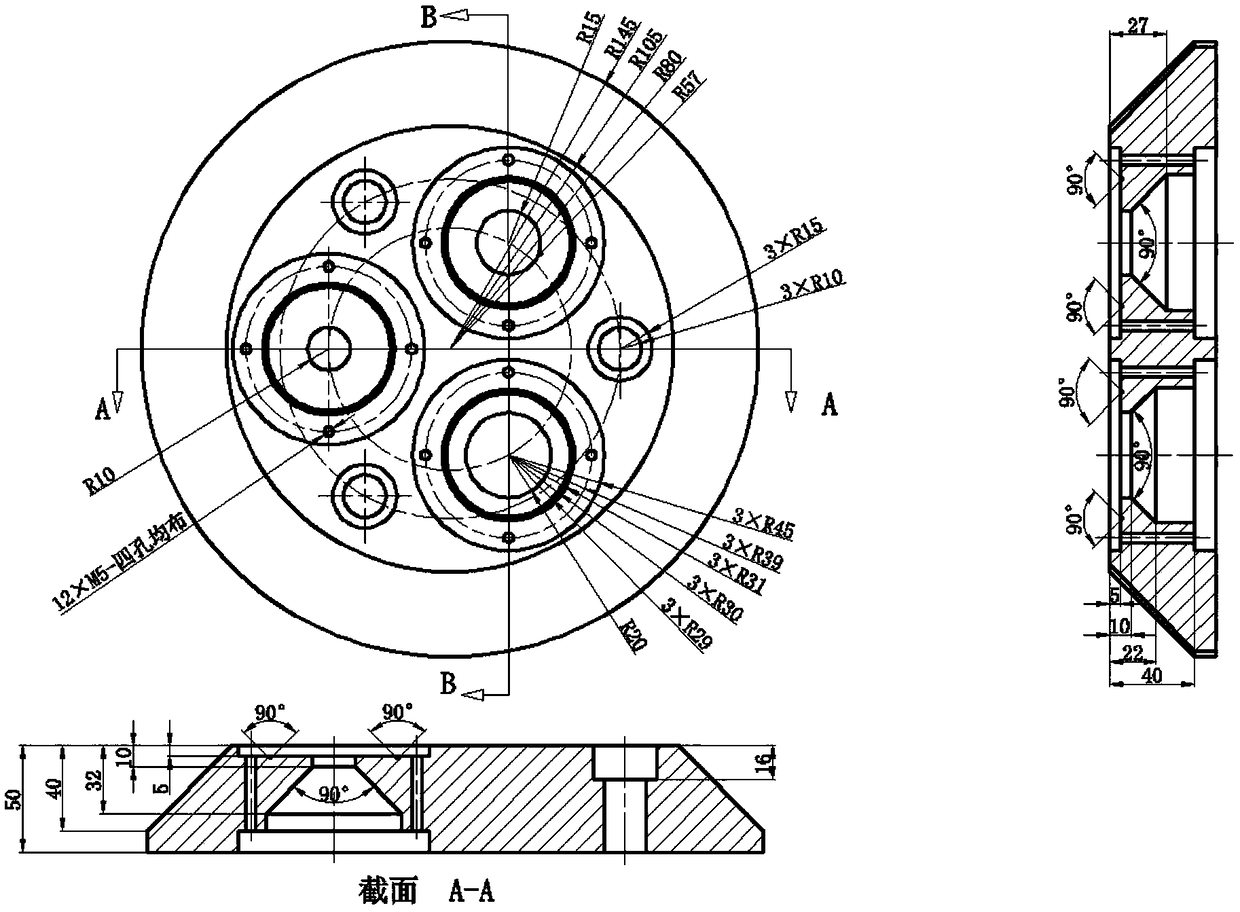
Connector effect target device suitable for measurement of target shock wave pressure of movable explosion field
The invention discloses a connection effect target device suitable for measurement of target shock wave pressure of a movable explosion field. The effect target device is mainly characterized by beingcomposed of a base, a response membrane, a pressing ring, a buffering pad, a bottom cover and pressing bolts; external shock waves act on the effect target device and three working areas, with different pressure measurement ranges, on the response membrane after passing through pressure guiding holes, the maximal deflection value of the response membrane is measured after testing, and the pressure peak of the shock waves is obtained according to a dose-effect relationship of deformation of the membrane and the shock waves. The device has the significant advantages that the mass and size of aneffect target are greatly reduced, and movement, assembly and disassembly of the effect target in the movable explosion field are facilitated; circular structures are adopted for all parts of the effect target device, and the processing period can be shortened; on the condition that the size and mass of the effect target are reduced, the wide effective measuring range is guaranteed, a shock wavepressure range within which the target can be damaged is basically covered, and the requirement of the target of the movable explosion field for the measurement of shock wave pressure is met.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
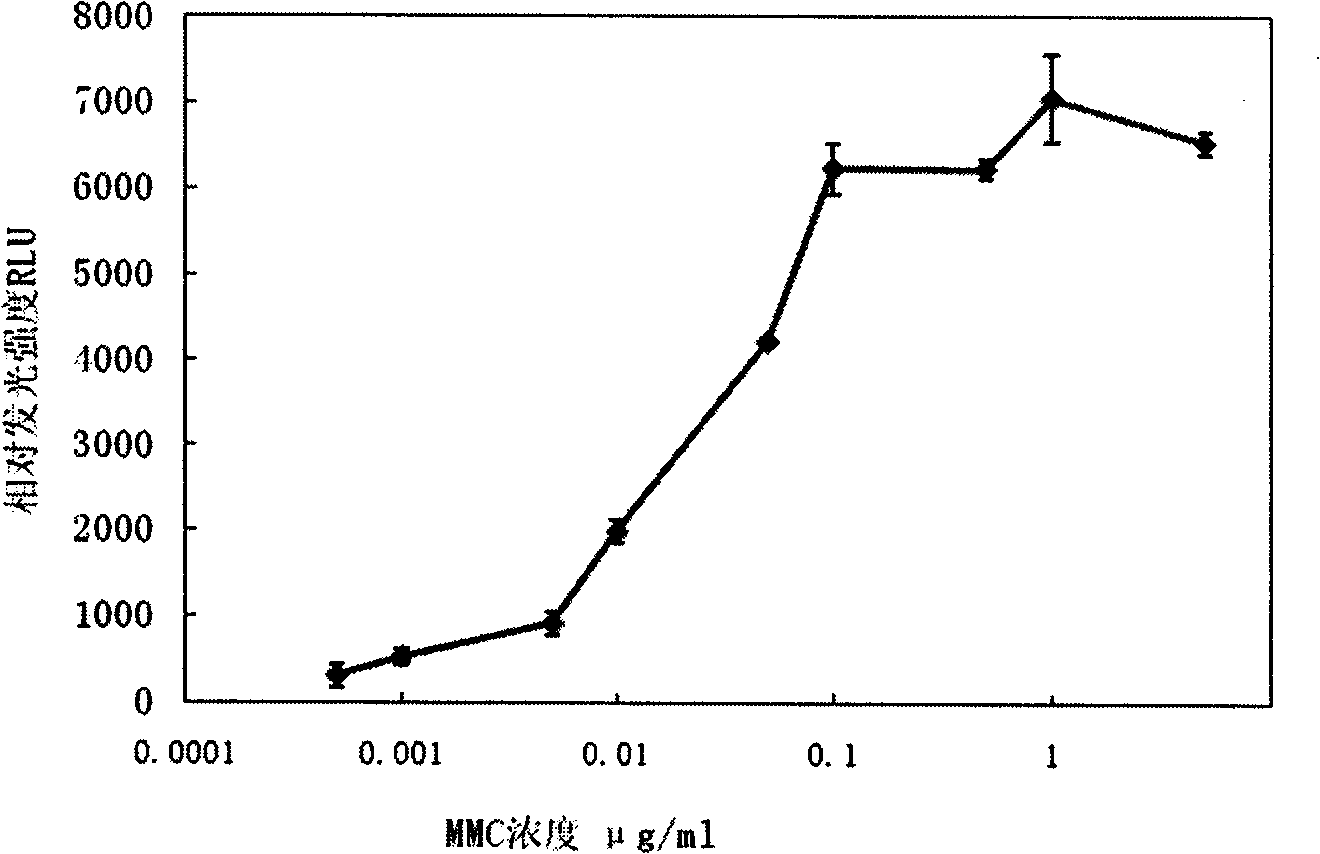
Recombinant strain representing genetic toxicity, construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant strain representing genetic toxicity, a construction method and application thereof. The recA gene of the chromosome in the recombinant strain includes the Acinetobacter (Acinetobacter sp.) ADP1 of a reporter gene. The reporter gene has the same promoter with the recA gene. The recA gene therein further contains a selective marker gene that is located at the terminal 3' of the reporter gene. The selective marker gene carries a promoter. The recombinant strain is exposed in substances with genetic toxicity or radiation with DNA damage capacity, the reporter gene expresses and generates reporter products, the amount of the reporter products has a dose-effect relationship with the genetic toxicity. The recombinant strain can be used for evaluating the genetic toxicity of a sample and the DNA damage intensity of radiation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
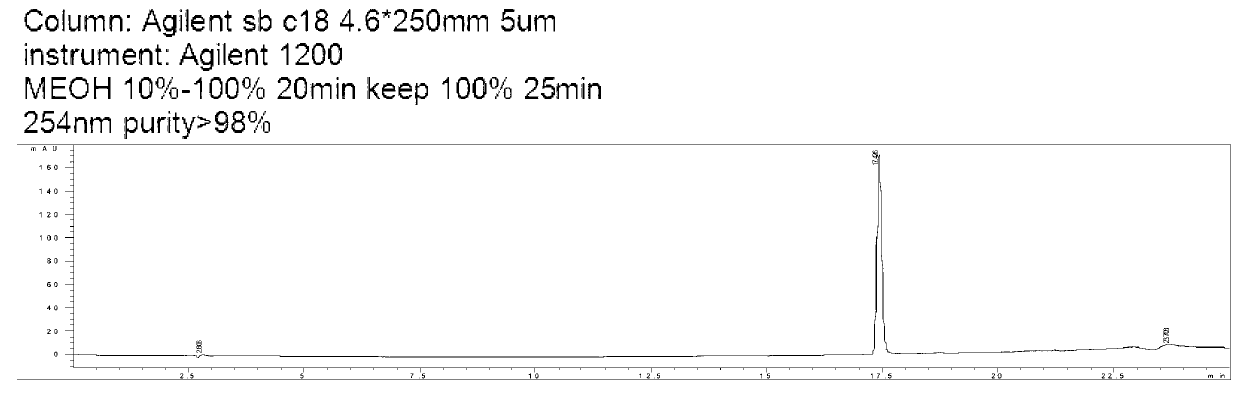
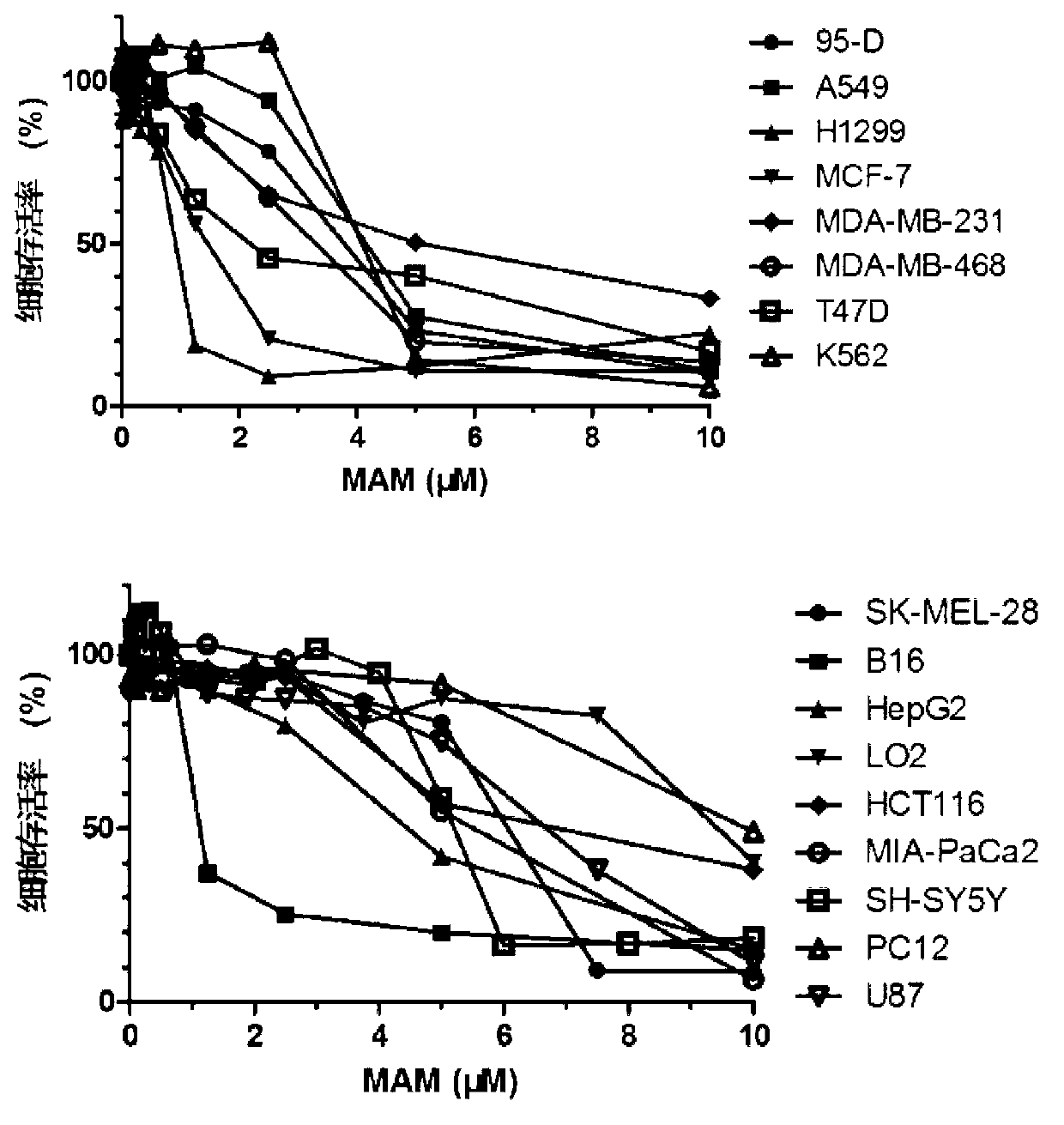
Application of 2-methoxy-6-acetyl-7-methyljuglone (MAM) for preparing medicine for treating neoplastic diseases
InactiveCN102988334AStrong inhibitory activityDecreased mitochondrial membrane potentialOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseApoptosis
The invention discloses application of 2-methoxy-6-acetyl-7-methyljuglone (MAM) for preparing a medicine for treating neoplastic diseases. According to the invention, found from research on the anti-neoplastic activity of MAM, MAM has obvious inhibitory activity on proliferation of a plurality of measured neoplastic cells in vitro; the better cytotoxic effect is shown; the IC50 (50% inhibiting concentration) of MAM is less than or equal to 10 mu M; furthermore, MAM has good dose-effect relationship; simultaneously, when MAM is acted on a normal hepatic cell strain LO2, the cytotoxicity of MAM is lower than the toxic reaction of MAM on a hepatic neoplastic cell HepG2; and furthermore, the research also finds that MAM is capable of obviously reducing mitochondrial membrane potential of neoplastic cells and inducing apoptosis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
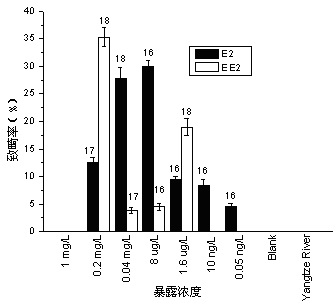
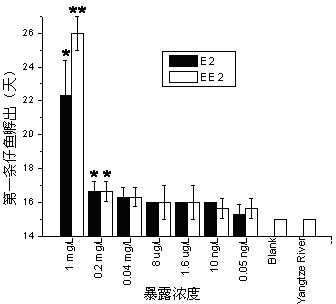
Method for testing toxicity of environmental estrogen on whitebait embryonic development
The invention discloses a method for testing toxicity of environmental estrogen on whitebait embryonic development. The method of the invention utilizes the sensitivity of embryo to the simulation of environmental pollutant or chemical matter to perform a test under semi-static state on whitebait embryo which is exposed in standard diluted aqueous solution of subject having a series of concentrations. The test lasts about 30 days, begins as exposing a live embryo at the blastula stage in the aqueous solution of subject, and ends with hatching all embryos in a control group and an exposed group. The toxicity endpoint contains death, monstrosity and delayed hatching. The method comprises the steps of confirming the toxicity of the subject on the whitebait embryonic development by observing the toxicity endpoint of the exposed group and comparing with the control group; researching on the influence of two natural estrogens E2 and EE2 on the whitebait embryo-yolk sac stage so as to confirm the toxic dose-effect relationship of the natural estrogens to the whitebait embryonic development, and evaluating the potential risk of this type of fish exposed under the estrogen with environmental concentration.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES +1
A test method for detecting the potential toxic influence of stomach poisoning insecticide compounds on folsomia candida
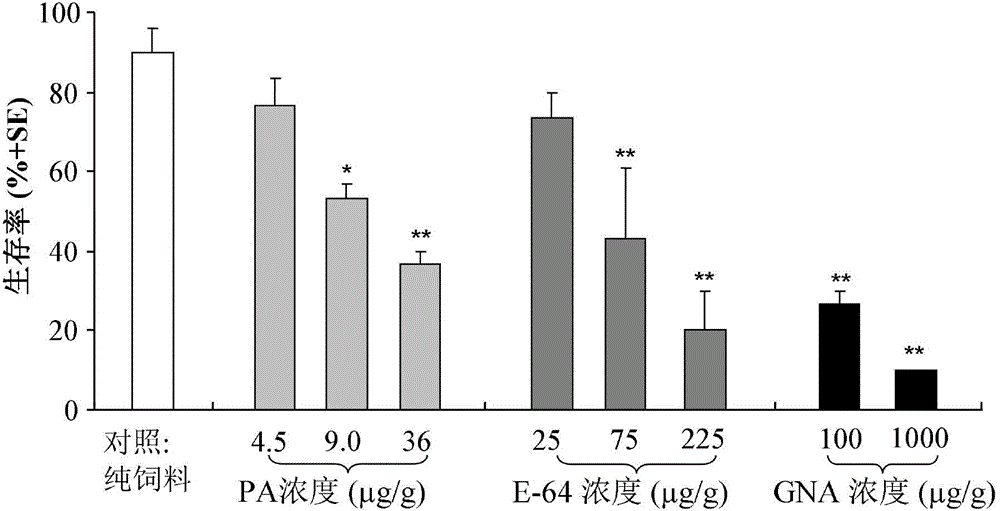
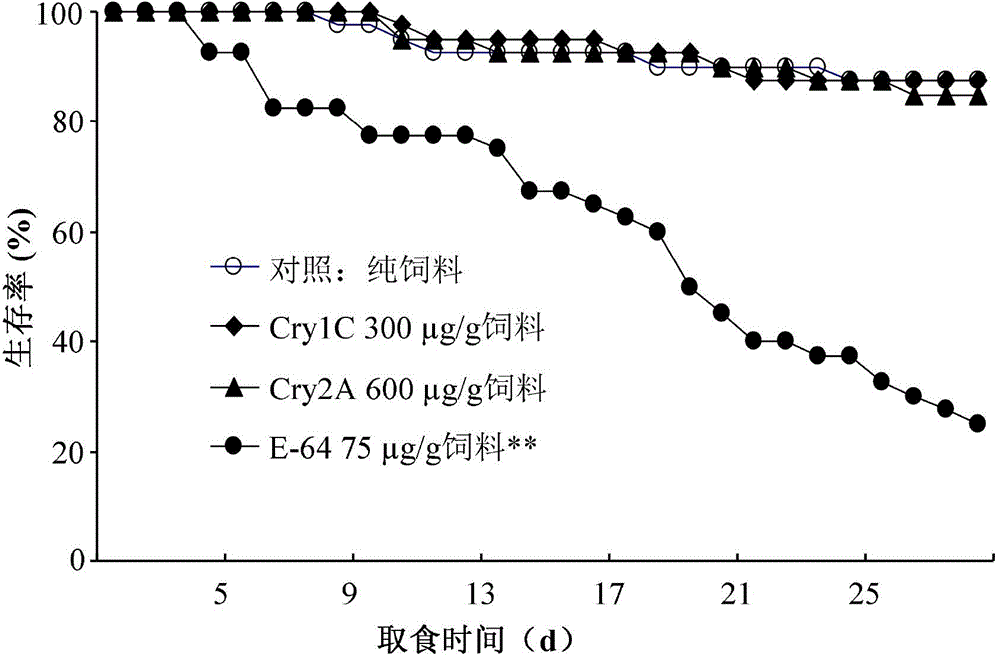
InactiveCN105075991ARapid detection of potential toxic effectsSimple methodAnimal husbandryPotential toxicityPositive control
The invention provides a test method for detecting the potential toxic influence of stomach poisoning insecticide compounds on folsomia candida. The method is characterized in that an insecticide or transgenic insecticidal protein is added into yeast powder (feed) uniformly and the mixture is directly delivered to folsomia candida; yeast mixed with a protease inhibitor with a concentration of 75 micrograms E-64 / g is used for positive control treatment and feed without any insecticide compounds is used for negative control treatment; potential toxicity of the tested insecticide compounds on spring tails is assessed by comparing the important life parameters such as the survival rate, the head breadth, the body length and the egg laying amount of folsomia candida of the treatment group and the control groups. By using the method, the biological reaction of folsomia candida to potassium arsenate [PA], E-64 and galanthus nivalis agglutinin (GNA) with different concentrations can be tested. It is shown that the different life parameters of folsomia candida show an obvious dose-effect relationship along with the change of the concentrations of PA, E-64 and GNA, so that the effectiveness and the sensitivity of the method are testified.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Biochemical method for detecting ionizing radiation dose
InactiveCN102508283AHigh precisionQuantitatively accurateDosimetersMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh dosesGamma ray
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, in particular to a biochemical method for detecting the ionizing radiation dose. According to the principle that a cell cycle can be interfered by ionizing radiation and cytochalasin B can retard cell division but cannot retard cell nucleus division, after different doses of gamma rays are used for irradiating lymphocyte, a certain quantity of cytochalasin B is added for processing so as to detect the four-core rate and the double-core rate of the lymphocyte irradiated with different doses of gamma rays. An experiment result shows that the four-core rate of the irradiated lymphocyte and the irradiated dose are in a linear dose-effect relationship within a low-dose range of 0-6.4cGY, a relevant coefficient is 0.957, and the radiation excitability effect is presented; and within a high-dose range of 0.4-20Gy, the double-core rate of the irradiated lymphocyte and the irradiated dose are in an exponential equation dose-effect relationship, the relevant coefficient is 0.978, and the radiation damage effect can be favorably reflected. The biochemical method for detecting the ionizing radiation dose is visual in detection indexes, is simple to operate, is quick and economic and is accurate in detection result.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Oroxylum indicum general flavone extraction and purification method and application thereof
InactiveCN104958330AMaterial basis is clearImprove efficacyAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsPurification methodsSemen
The invention relates to an oroxylum indicum general flavone extraction and purification method. Ethyl alcohol backflow and macroporous resin adsorption are used for separating, extracting and purifying oroxylum indicum general flavone, non-flavonoid impurities are removed as many as possible, and finally enrichment is carried out to obtain the high-purity general flavone. The oroxylum indicum general flavone comprises five chemical components including semen oroxyli glycoside B, semen oroxyli glycoside A, chrysin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide, baicalein and chrysin. The invention further provides application of the oroxylum indicum general flavone to prepating medicine for treating liver cancers. In-vitro pharmacological tests show that the general flavone has the obvious restraining effect on proliferation of liver cancer cells and trends to have the obvious dose-effect relationship, and meanwhile the pharmacological effect is obviously improved along with increase of the purity of the general flavone; in addition, oroxylum indicum general flavone matter analysis studying is carried out, the material basis of oroxylum indicum for playing a role in anti-cancer pharmacological effect is defined, and the material basis and the experiment basis are laid for developing clinical application of oroxylum indicum general flavone enrichment matter, anti-cancer new medicine researching and development and industrial production.
Owner:LIAONING UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Flower silk leaf bagged tea and its preparation method
InactiveCN101283717APromote secretionGreat tasteMetabolism disorderTea substituesIcing sugarTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a bagged tea containing plant flowers, stigma and leaves and a preparation method thereof. The bagged tea is produced by pretreating corn stigma, Cassia occidentalis, chrysanthemum flower, hawthorn and pagodatree flowers and leaves, boiling in water; filtering, collecting supernatant, concentrating, extracting with ethanol, removing ethanol, uniformly spraying the resulting ethanol extract to lotus leaf coarse powder, adding sugar powder 6 times the weight of the drug powder and dextrin double the weight of the drug powder, and stirring thoroughly. The bagged tea has good palatability, convenient use, high therapeutic effect, and hypolipidemic and anti-obesity effects. It is proven that the blood fat level is significantly reduced after taking the bagged tea continuously for 30-40 days, with a dose-effect relationship; and the body weight is remarkably reduced after taking the bagged tea continuously for more than 60 days.
Owner:杨灵华
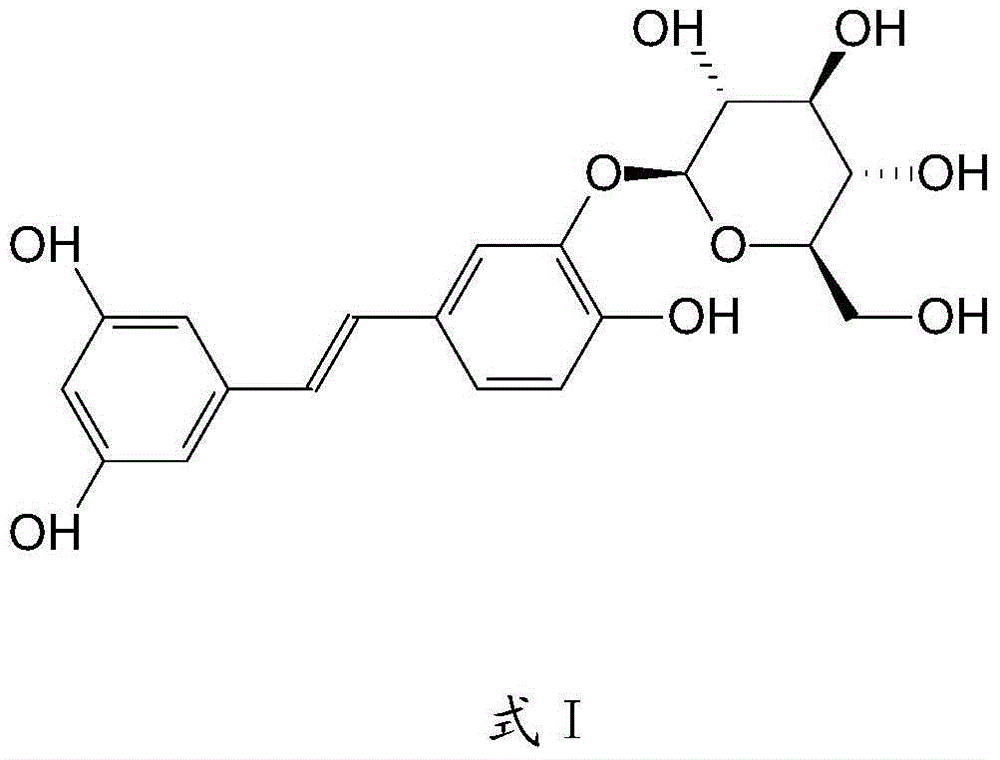
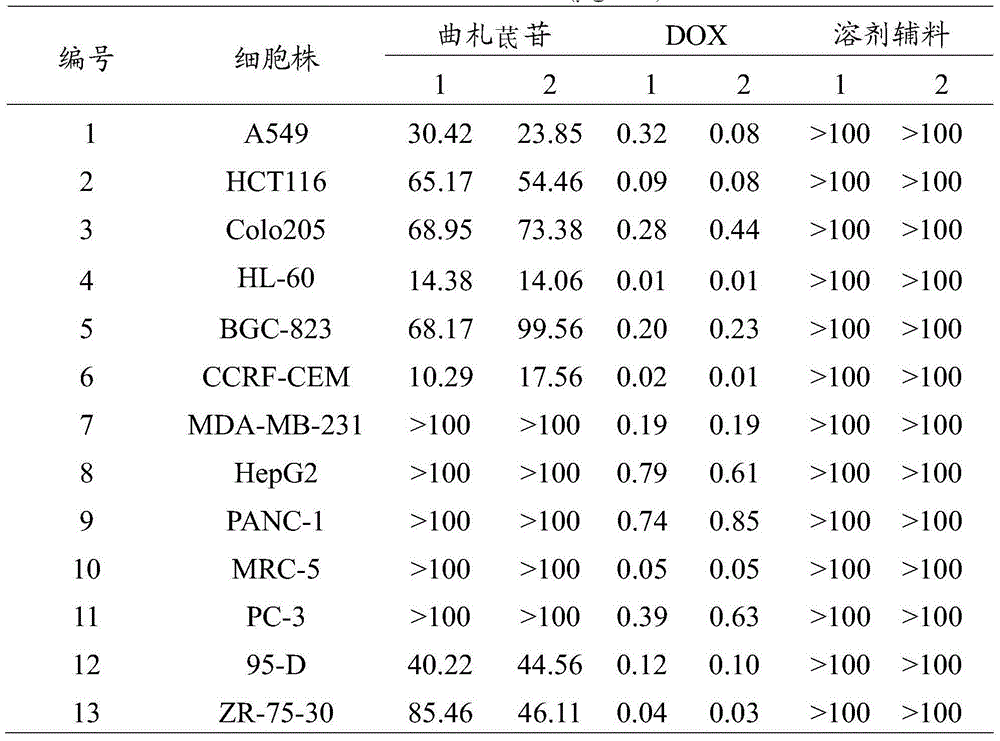
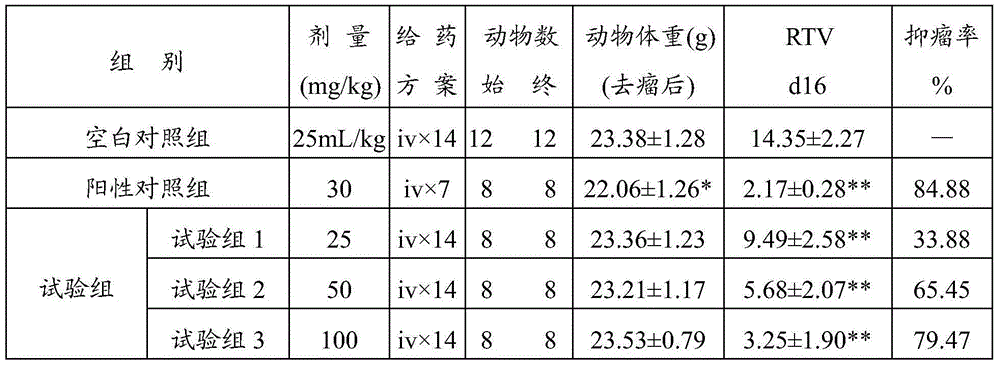
Application of 3,5,3',4'-trihydroxy-stilbene-3'-b-D-glucoside in preparation of medicines for treating cancers
ActiveCN104666320APrevent proliferationEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHuman tumorHuman breast
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine preparation, and in particular relates to application of 3,5,3',4'-trihydroxy-stilbene-3'-b-D-glucoside in preparation of medicines for treating cancers. The cytotoxic effect of the 3,5,3',4'-trihydroxy-stilbene-3'-b-D-glucoside on 12 human tumor cells cultured in vitro and a human normal cell is tested through an MTT method; and the 3,5,3',4'-trihydroxy-stilbene-3'-b-D-glucoside has a relatively good inhibiting effect on proliferation of a human lung cancer cell line, a human colon cancer cell line, a human erythroleukemia cell line, a human gastric cancer cell line and a human breast cancer cell line, and has no inhibiting action on proliferation of human normal cells. The curative effect of the 3,5,3',4'-trihydroxy-stilbene-3'-b-D-glucoside on a nude mouse transplantation tumor of a human lung cancer cell line A549 is also tested. The result shows that the 3,5,3',4'-trihydroxy-stilbene-3'-b-D-glucoside has obvious inhibiting action on proliferation of the nude mouse transplantation tumor of the human lung cancer cell line A549 after continuous intravenous injection for 14 days; and the dose-effect relationship is obvious.
Owner:KPC PHARM INC
Compound, muscarine M receptor antagonist, composition and application
The invention discloses a discovery and application of an acting target of hydroxyl cinnamamide compound separated from solanaceae plants, and particularly relates to a discovery of an acting target of hydroxyl cinnamamide compound N1, N8-bis (dihydrocaffeoyl) spermidine (BDCS for short) and application thereof in spasmolysis drug. Unmarked cell target pharmacology technology finds that the compound has high muscarine M receptor antagonistic activity, dose-effect relationship researches show that dose is dependently antagonistic to DMR response signals caused by acetylcholine and BDCS is a muscarine M receptor antagonist. BDCS and one or more than two of pharmaceutically-acceptable salts of BDCS are used as active ingredients of the muscarine M receptor antagonist. Current researches show that muscarine M receptor is related to diseases like spasm, analgesia, sedation and schizophrenia, so that an efficient novel ligand with the acting target being clear can be provided for related diseases.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Enzyme process extracted Radix angelicae anomalae polysaccharide, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an enzyme process extracted Radix angelicae anomalae polysaccharide, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The Radix angelicae anomalae polysaccharide has alpha-configuration and beta-configuration polysaccharide linking modes, the apparent molecular weight of the Radix angelicae anomalae polysaccharide is 3.93 kDa. The Radix angelicae anomalae polysaccharide is obtained through enzyme process extraction of a Radix angelicae anomalae medicinal material, alcohol precipitation and impurity removal, protein and salt removal, and DEAE-agarose gel FF column and agarose gel 6FF gel column chromatography separation. The Radix angelicae anomalae polysaccharide obtained in the invention has good whitening activity and has an inhibitory effect on the tyrosinase activity, and the tyrosinase inhibition rate gradually increases with the increase of concentration, and the dose-effect relationship is obvious. The method for extracting the Radix angelicae anomalae polysaccharide has the advantages of small dosage of an enzyme preparation, simple process and low production cost.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Application of Anerning granules in preparing medicament for treating viral pneumonia
InactiveCN103550596ALower lung indexProtect deathAntiviralsUnknown materialsCurative effectDeath cause
The invention discloses application of Anerning granules in preparing a medicament for treating viral pneumonia. The granules have a remarkable curative effect on viral pneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial virus and influenza virus, can be used for remarkably reducing the lung index, and is in dose-effect relationship. The Anerning granules can be used for protecting experimental animal death caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and has a remarkable inhibition effect on spleen index and thymus index reduction caused by RSV, can be used for reducing animal death cased by viral pneumonia, and can be used for remarkably protecting the immunity of experimental animals.
Owner:SHANDONG JINHE DRUG RES DEV
Antitumor medicine and its production process
InactiveCN1608663AGood anti-tumor effectLow toxicityUnknown materialsAntineoplastic agentsCurative effectLung cancer
The present invention is one kind of antitumor medicine and its production process, and belongs to the field of Chinese medicine technology. The antitumor medicine of the present invention has the material including wild buckwheat rhizome and Sarcandrae. The medicine of present invention can inhibit S180 caruncle obviously with tumor inhibiting rate raising with increased dosage and coinciding with the dose-effect relationship, has obtain Lewis lung cancer inhibiting effect, and has obvious immunity strengthening effect. Therefore, the present invention has high antitumor effect and low toxicity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for detecting genotoxic agent in water by utilization of Pseudorasbora parva
InactiveCN105510543AFully assess health risksComprehensive assessment of health risksMaterial analysis by optical meansTesting waterPositive controlToxicant
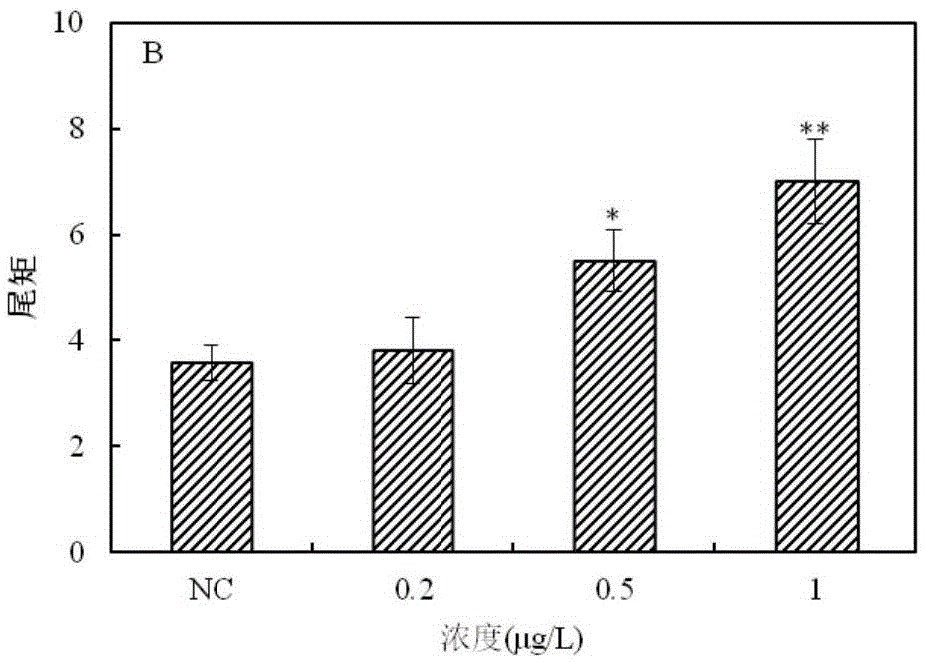
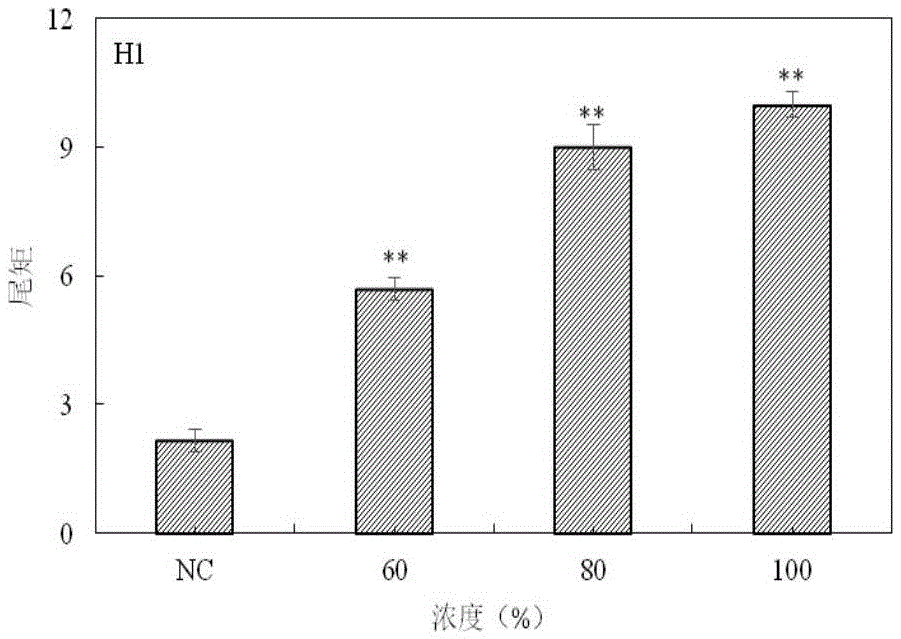
The invention provides a method for detecting a genotoxic agent by the utilization of Pseudorasbora parva and belongs to the field of chemicals safety evaluation and environmental monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: (1) processing Pseudorasbora parva by exposure treatment by the use of a water sample to be tested; and (2) carrying out single cell gel electrophoresis assay by using hepatic cells of Pseudorasbora parva processed after exposure treatment, detecting and counting cell tail length, DNA content and tail moment, and drawing a dose-effect curve. Through comparison between the result and a blank control and a positive control and through the dose-effect relationship, genetic toxicity of the test sample is determined. The detection method of the invention can sensitively and rapidly determine genetic toxicity of chemicals. The invention provides a China native species-based detection method for chemicals genetic toxicity evaluation and environmental genetic toxicity monitoring.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Processing method and processing device for efficacy of combined medicine
ActiveCN105224799ARealize detectionSolve problems that cannot be accurately detectedChemical property predictionMathematical modelsMedicineToxicology studies
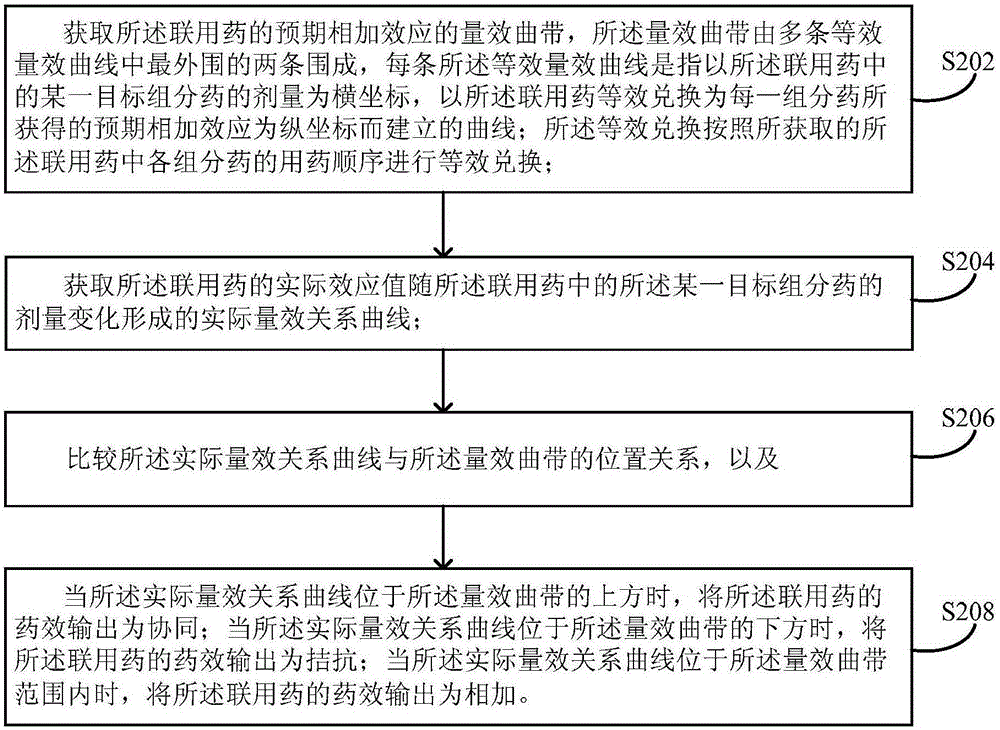
The invention provides a processing method and a processing device for efficacy of combined medicine. The processing method comprises: obtaining a dose-effect curved band of expected additive effect of combined medicine; obtaining an actual dose-effect relationship curve formed by variation of actual effect value of the combined medicine with variation of dosage of a certain target component medicine in the combined medicine; comparing position relationships of the actual dose-effect relationship curve and the dose-effect curved band, and when the actual dose-effect relationship curve is above the dose-effect curved band, efficacy output of the combined medicine being synergy; when the actual dose-effect relationship curve is below the dose-effect curved band, efficacy output of the combined medicine being antagonism; and when the actual dose-effect relationship curve is in the dose-effect curved band range, the efficacy output of the combined medicine being addition. The processing method solves a problem in the prior art that efficacy cannot be accurately detected when multiple medicines are used in a combined manner. The method can be widely applied in research and development of compound medicines, toxicologic study, efficacy and safety evaluation of the combined medicine, and environmental evaluation.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Single body effect target device suitable for measurement of target shock wave pressure of movable explosion field
ActiveCN109459179AReduce quality problemsReduce volumeMeasurement of explosion forceShock waveEngineering
The invention discloses a single body effect target device suitable for measurement of target shock wave pressure of a movable explosion field. The effect target device is mainly characterized by being composed of a base, a response membrane, a pressing ring, a buffering pad, a bottom cover and pressing bolts; external shock waves act on the effect target device and a working area of the responsemembrane, so that the response membrane is plastically deformed and sunken towards a lower sealing hole, the maximal deflection value is measured, and the pressure peak of the shock waves is obtainedaccording to a dose-effect relationship of deformation of the membrane and the effect of the shock waves. The device has the significant advantages that the mass and size of the effect target device are greatly reduced, movement and disassembly are facilitated, the processing cost can be reduced at the same time, and the processing period can be shortened; the effect of fixing the response membrane is reinforced, the area where the response membrane is plastically deformed is controlled, and the measurement precision of the shock wave pressure is guaranteed on the condition that the mass of the device is reduced; a deflection testing unit interface is reserved for the response membrane, the upgradability of a shock wave pressure effect target of the movable explosion field is improved, andthe requirement of the target of the movable explosion field for the measurement of the shock wave pressure is met.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Application of Lambda interferon in resisting human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveCN101574515AInhibition of replicationAvoid infectionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsSerum igeAbnormal macrophage
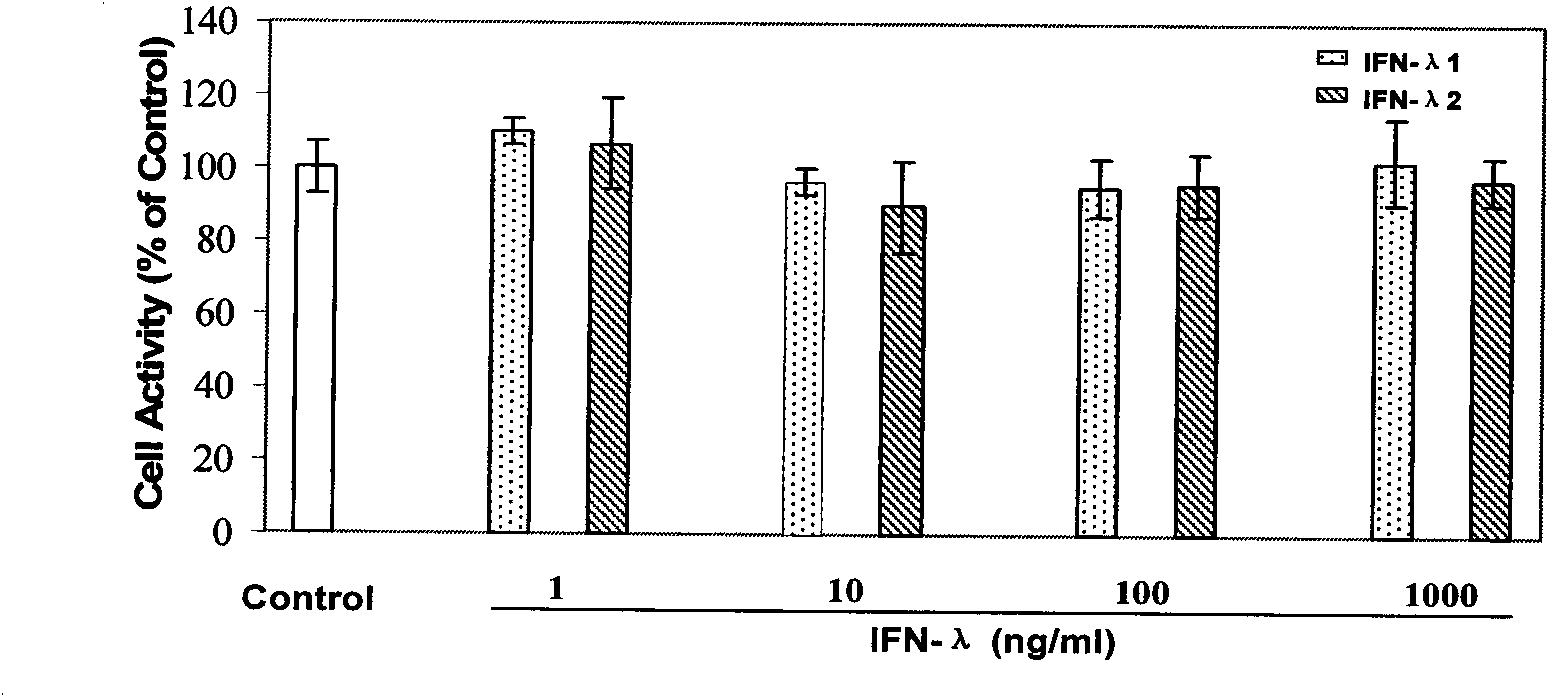
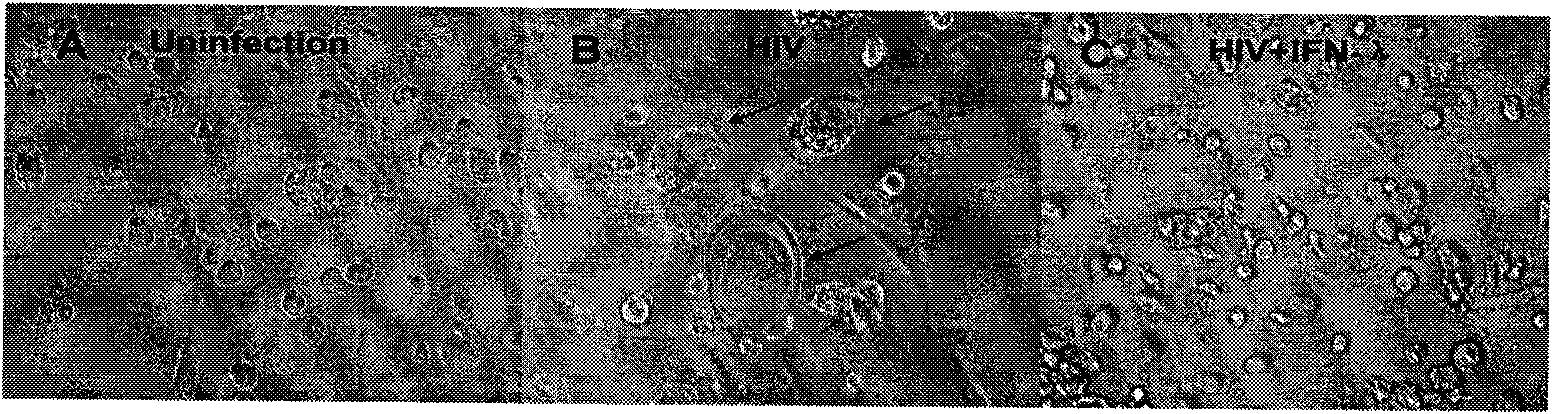
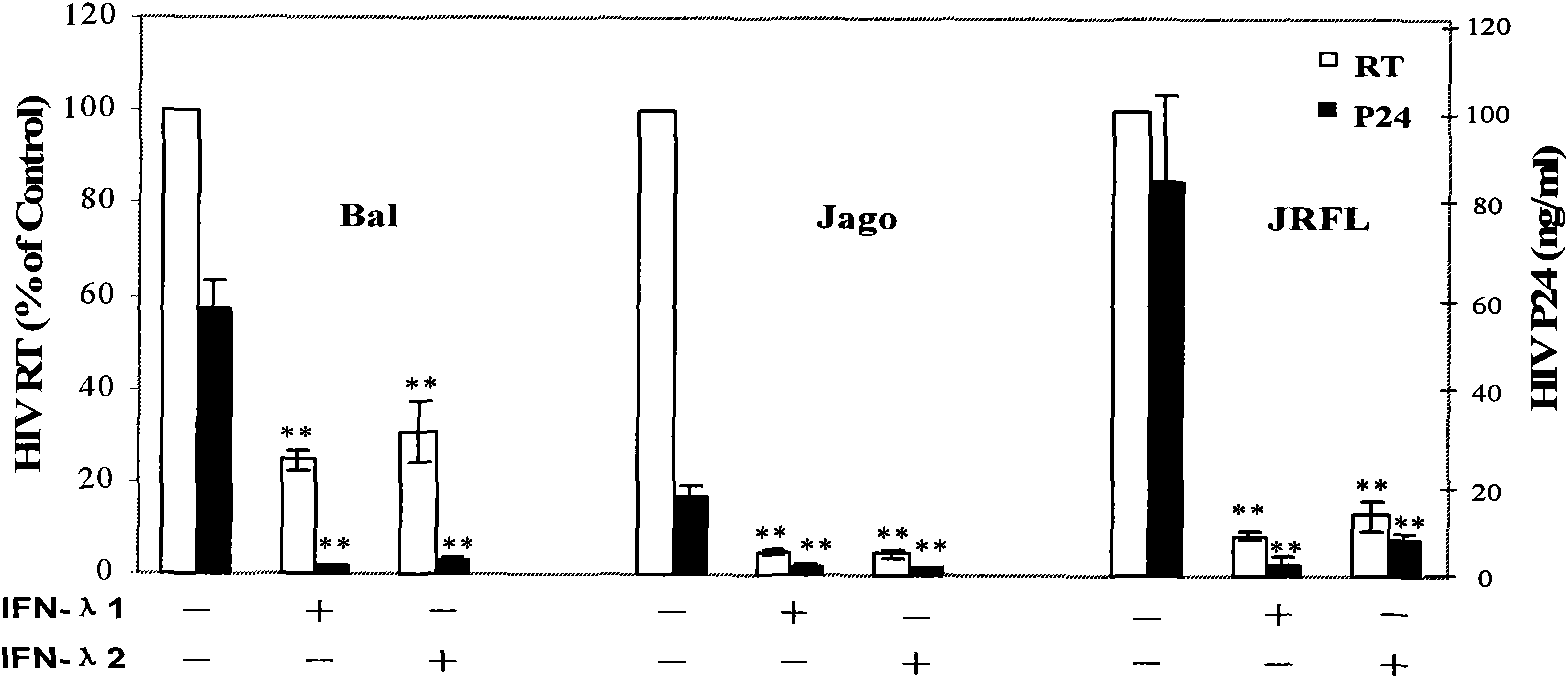
The invention discloses an application of Lambda interferon in resisting human immunodeficiency virus. IFN-Lambda resisting HIV infection can inhibit the infection and replication of HIV-1 in human macrophage, which is presented by the following processes: (1) IFN-Lambda1 / Lambda2 differentiates mature human macrophage through pretreatment, then HIV-1R5 type strain respectively infects the cells, a DMEM culture medium is used for washing and then a DMEM culture medium containing 10 percent of fetal calf serum is added for culture; and (2) after infection, the formed multinucleate giant cells of IFN-Lambda treatment group are rather less than those of a virus contrast group, and the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and envelope protein P24 in culture supernatant fluid of the IFN-Lambda treatment group are detected to be rather less than that of the virus contrast group. After infection, the HIV-1RT in the culture supernatant fluid is respectively detected. The effect of inhibiting the HIV-1 is obvious after infection. The IFN-Lambda treatment group has obvious time and dose-effect relationship in inhibiting the activity of HIV-1RT after infection. The function of IFN-Lambda in resisting the HIV-1 is similar to that of other interferons and has the antivirus effect. The IFN-Lambda shows obvious effect of inhibiting the replication of virus as regards to the human macrophage before, in and after the infection of the HIV-1 virus.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for detecting hydroxyl radicals in earthworm body
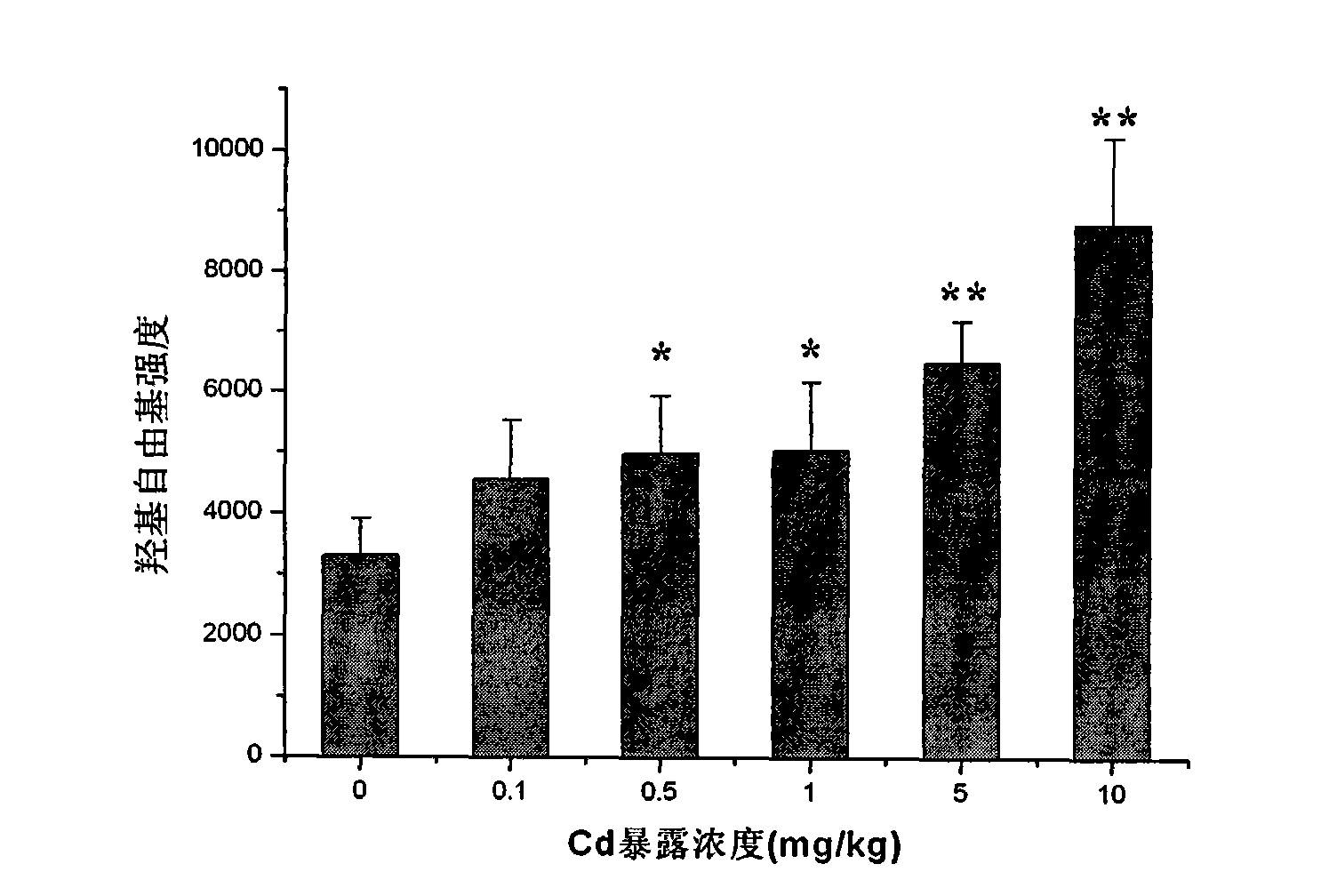
InactiveCN101639454AEasy to operateEasy to masterAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceDose–response relationshipUltimate tensile strength
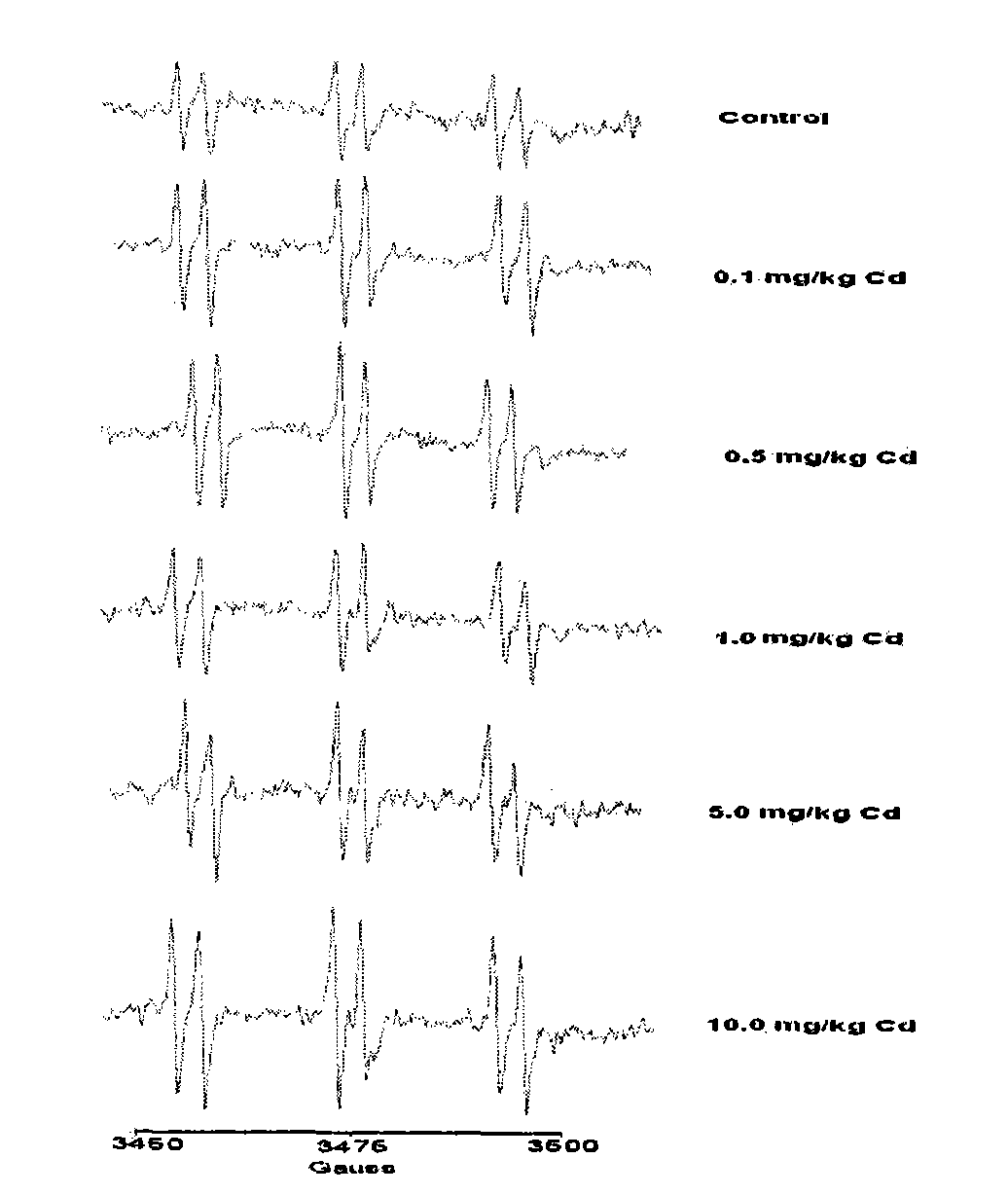
The invention discloses a method for detecting hydroxyl radicals in an earthworm body. Firstly, a fully exposed earthworm undergoes bowel clearing and is then cleaned. Radical PBN capture is carried out in a deoxygenated hermetical operation box. Finally, EPR technology is used for detection. The method has the advantages that the operation is relatively simple and easy to master and the hydroxylradicals of the earthworm can be detected within a short time; according to a hyperfine structure constant of an EPR spectrogram and the shape analysis of the spectrogram, the method discovers the detected radicals to be the hydroxyl radicals and is the most direct, accurate and effective method at present for detecting the hydroxyl radicals; and the method has a good dose-response relationship. Research results show that the strength of the hydroxyl radical and the exposed concentration are in good dose-response relationship.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com