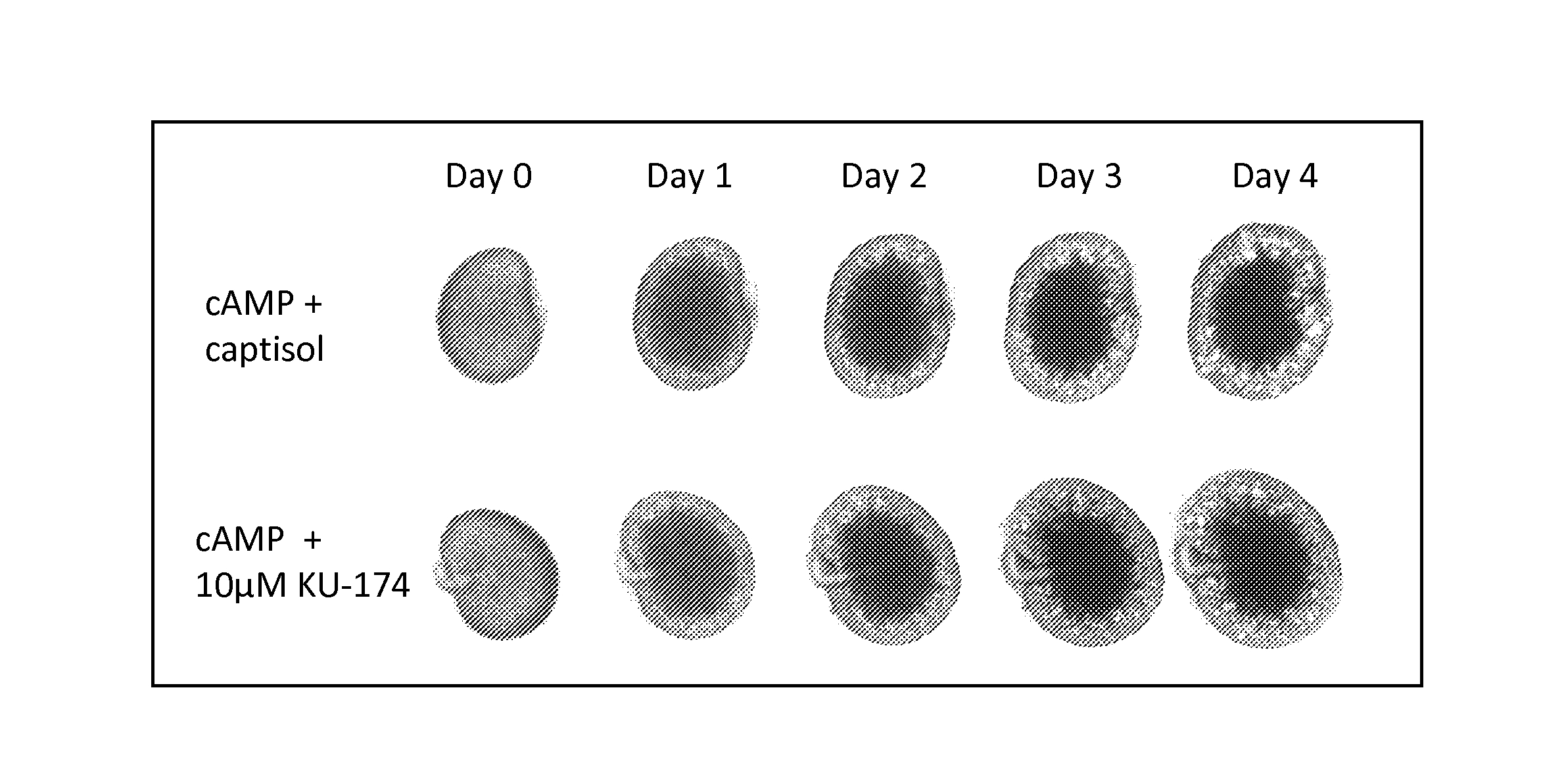
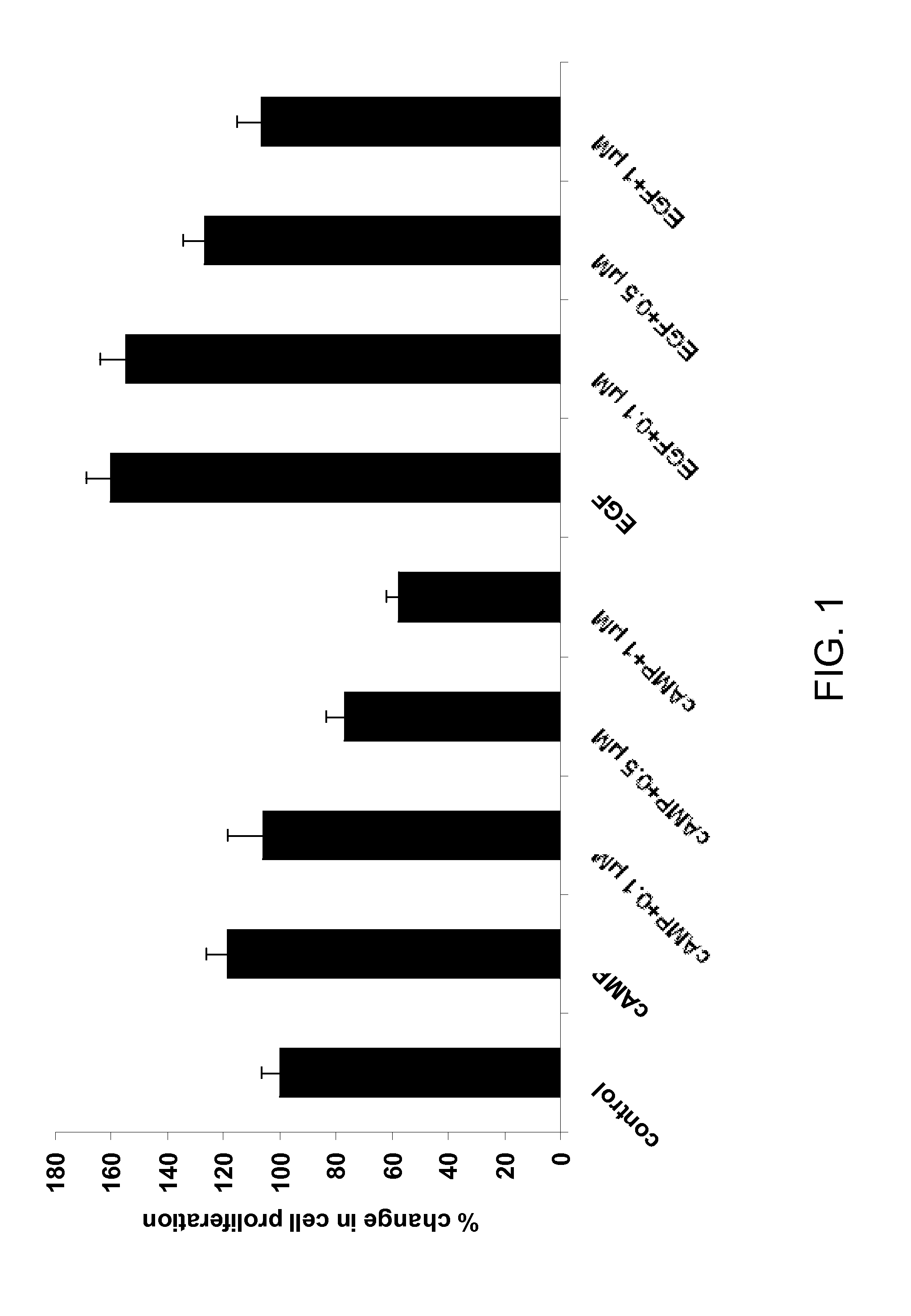
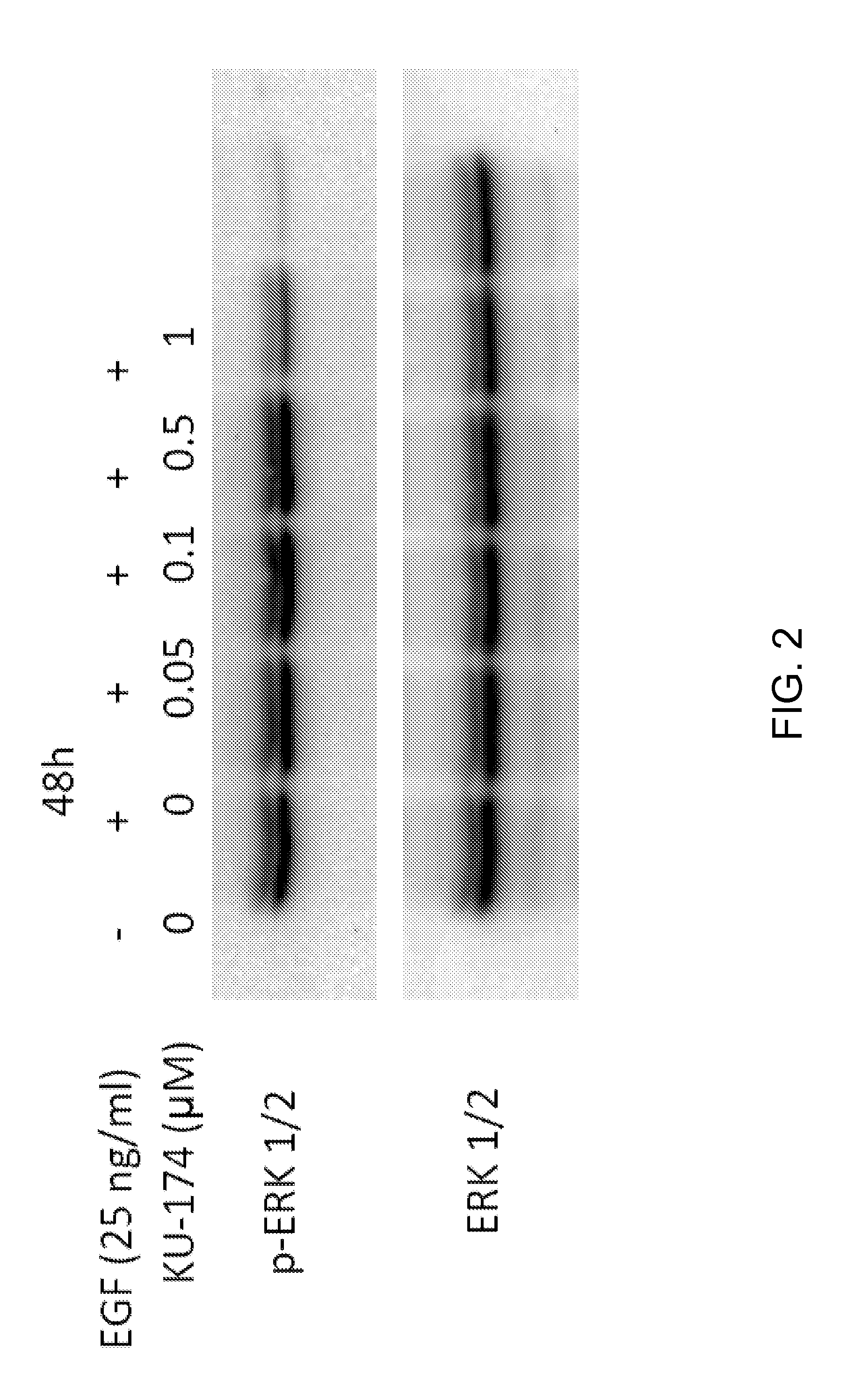
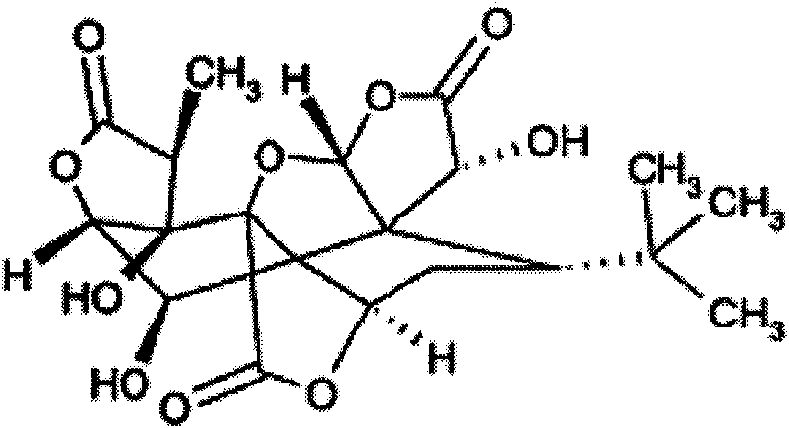
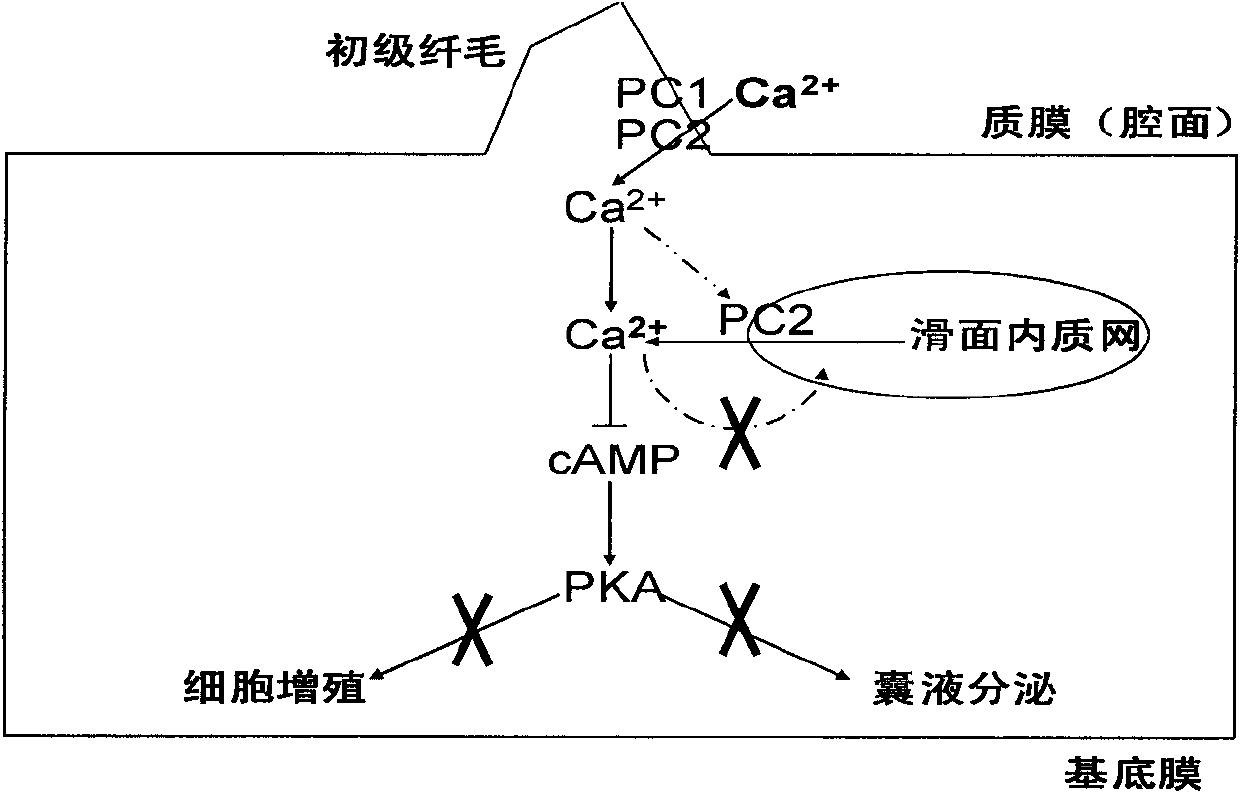
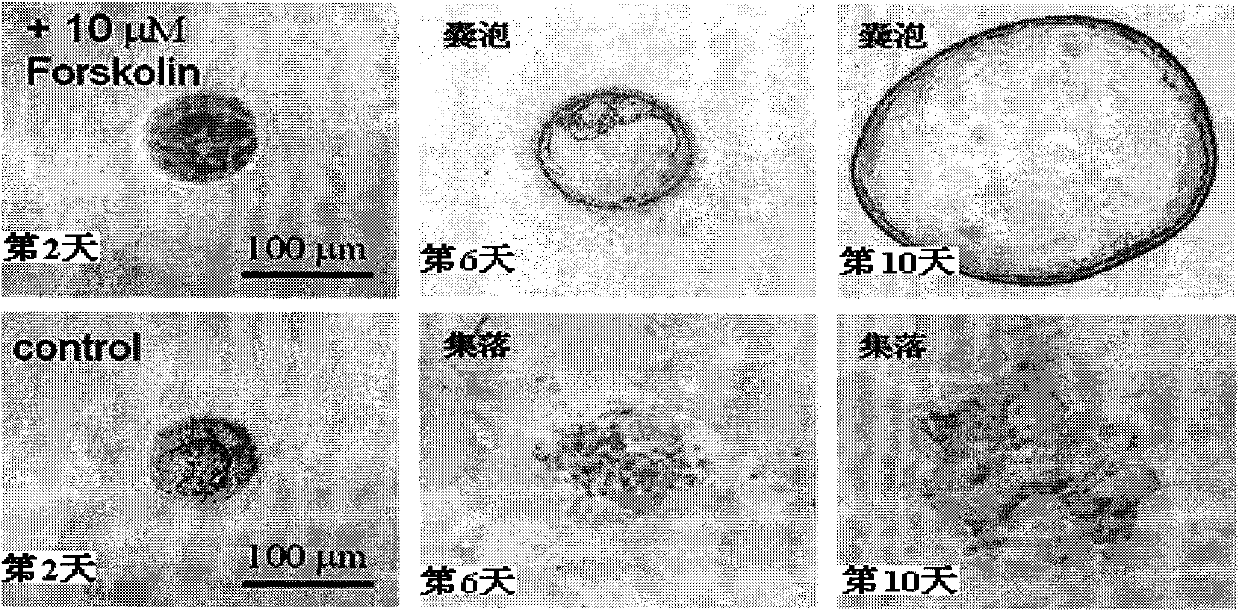
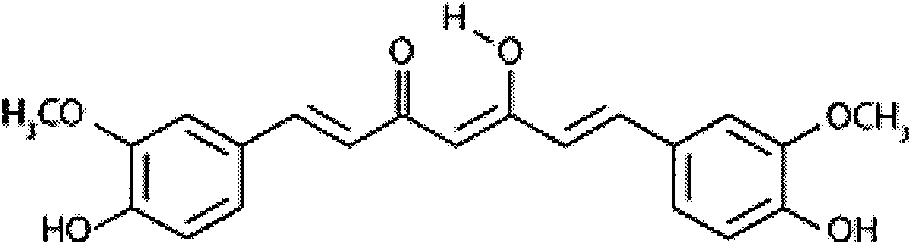
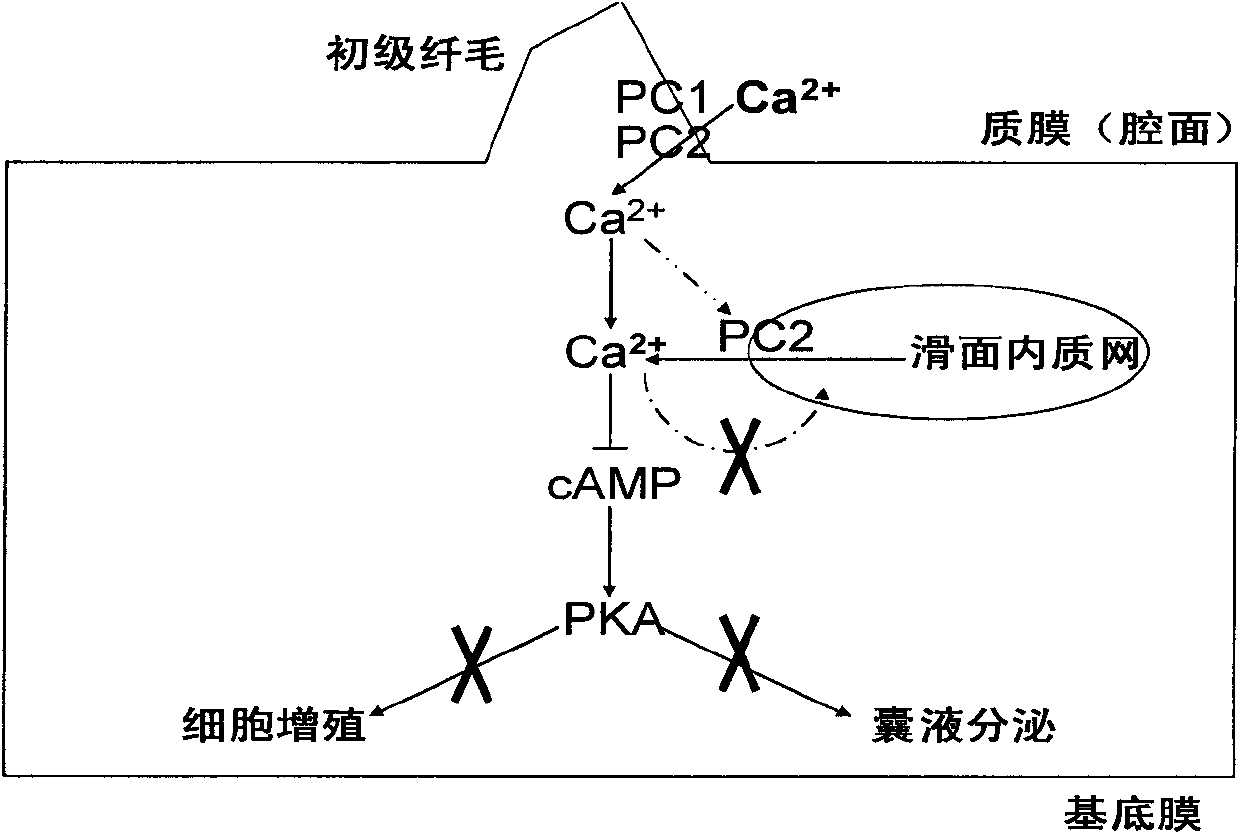
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is an inherited condition that causes small, fluid-filled sacs called cysts to develop in the kidneys.
Novobiocin analogues and treatment of polycystic kidney disease
InactiveUS20110082098A1Reduction of cyst formationBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsNovobiocinCyst formation
Novobiocin analogues are useful in methods of treating, inhibiting, and / or preventing cyst formation in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) in a subject. The disclosure provides methods of treating ADPKD comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a coumarin-3-carboxamide novobiocin analogue. Accordingly, the method can include administering a novobiocin analogue in a therapeutically effective amount for reducing levels of mTOR pathway phosphoproteins P-mTOR, P-Akt and P-S6K, or combinations thereof. Further, the method can include administering a novobiocin analogue in a therapeutically effective amount for reducing levels of Hsp-90 client proteins CFTR, ErbB2, c-Raf and Cdk4, or combinations thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
New application of ginkgolide B
InactiveCN102018702APromote apoptosisPromote growthOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderCanine kidneyCytotoxicity
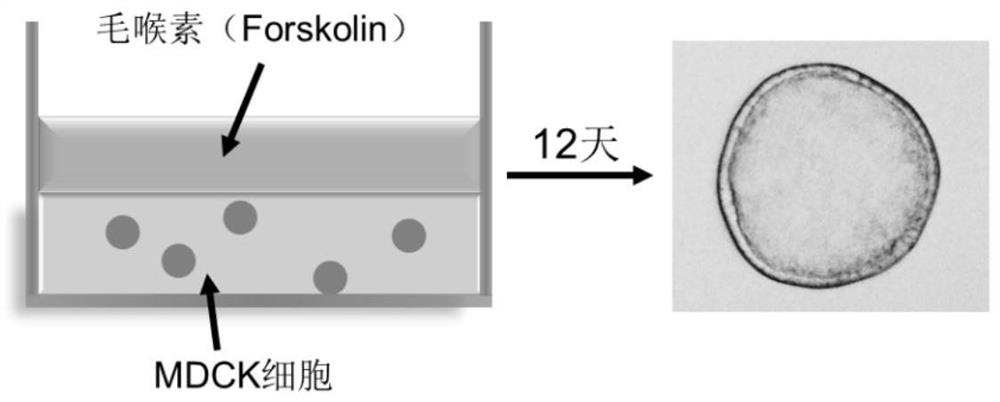
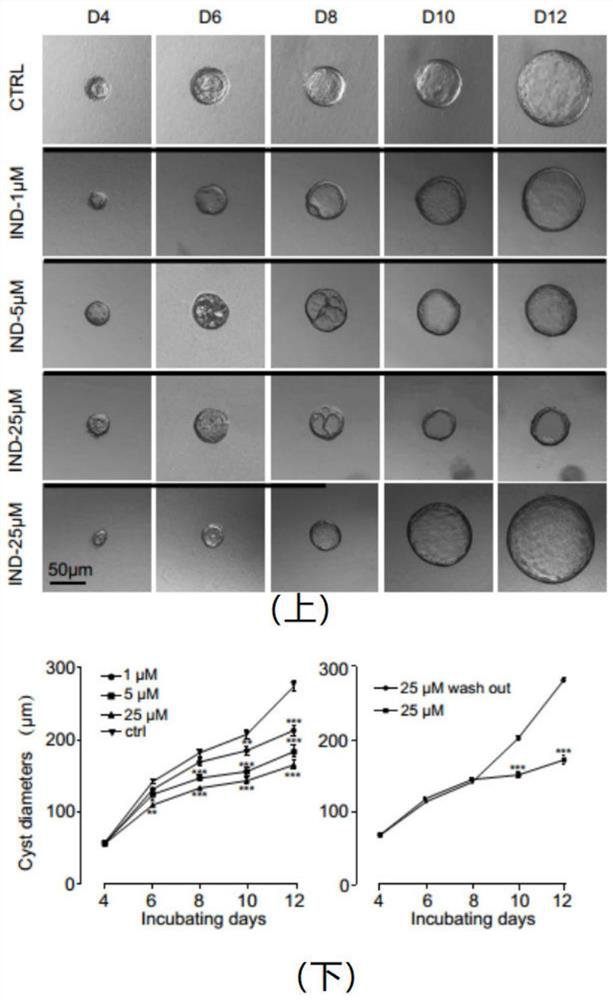
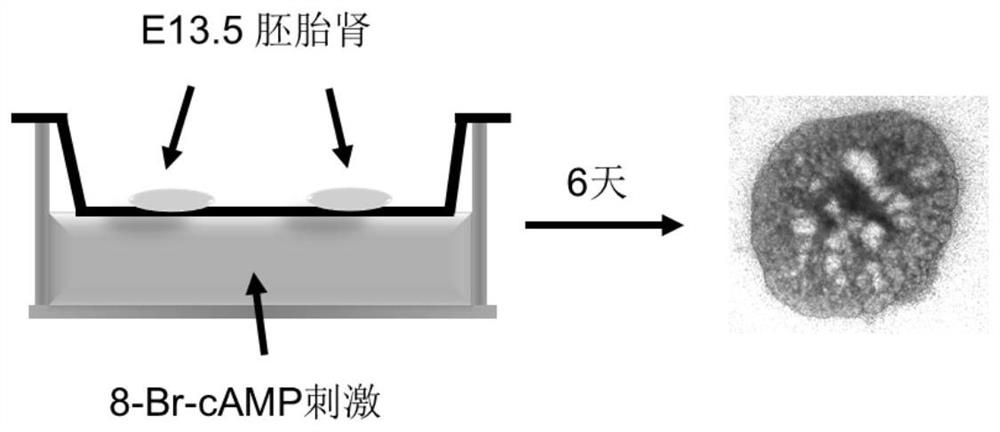
The invention discloses application of ginkgolide B to preparation of medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. A madin-darby canine kidney (MDCK) vesicle model is used for screening to find that the ginkgolide B inhibits formation and growth of vesicles. An experimental result shows that: the ginkgolide B has an obvious inhibiting effect on the formation and growth of MDCK vesicles and the effect of the ginkgolide B is in dose response relationship; the ginkgolide B has no cytotoxicity to MDCK cells, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the ginkgolide B is independent of the cytotoxicity; the ginkgolide B does not obviously induce MDCK cell apoptosis, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the ginkgolide B is independent of cell apoptosis promotion of the ginkgolide B; the ginkgolide B can promote the MDCK cells or vesicles to form tubular structures; and the effect is in dose response relationship; and the ginkgolide B has an inhibiting effect on the growth of the embryonic kidney vesicles. The ginkgolide B provides experimental data for development of a specific medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
New application of curcumin
InactiveCN102018689ADoes not induce apoptosisPromote apoptosisKetone active ingredientsUrinary disorderCanine kidneyCytotoxicity
The invention discloses application of curcumin to preparation of medicaments for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. A madin-darby canine kidney (MDCK) vesicle model is used for screening to obtain the curcumin which inhibits formation and growth of vesicles. An experimental result shows that: the curcumin has an obvious inhibiting effect on the formation and growth of MDCK vesicles and the effect of the curcumin is in dose response relationship; the curcumin has no cytotoxicity to MDCK cells, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the curcumin is independent of the cytotoxicity; the curcumin does not obviously induce MDCK cell apoptosis, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the curcumin is independent of cell apoptosis promotion of the curcumin; the curcumin can promote the MDCK cells or vesicles to form tubular structures; and the effect is in dose response relationship; and the curcumin has an inhibiting effect on the growth of the embryonic kidney vesicles. The curcumin is expected to be developed into a specific medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Application of EZH2 (enhancer of zeste homolog 2) in preparation of drugs to prevent or treat polycystic kidney disease
InactiveCN109966479AConfirmed inhibitionEZH2 inhibitory inhibition confirmedPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesEZH2Polycystic liver disease
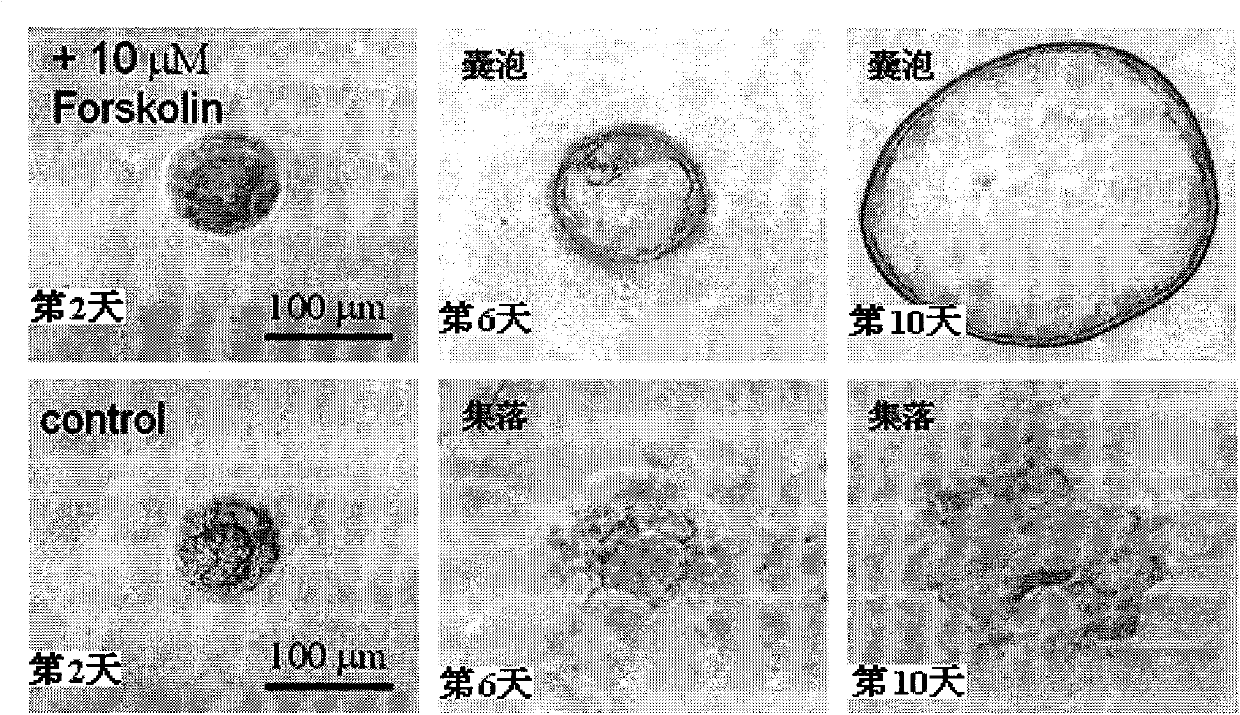
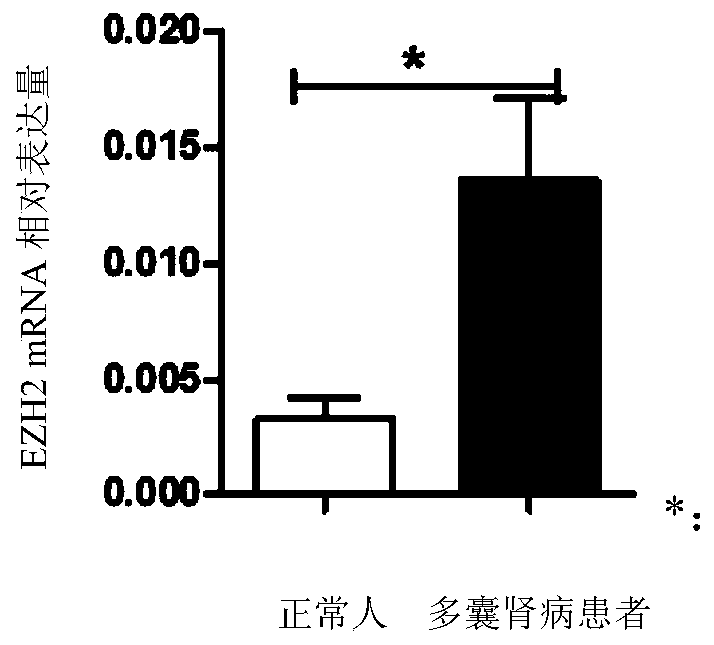
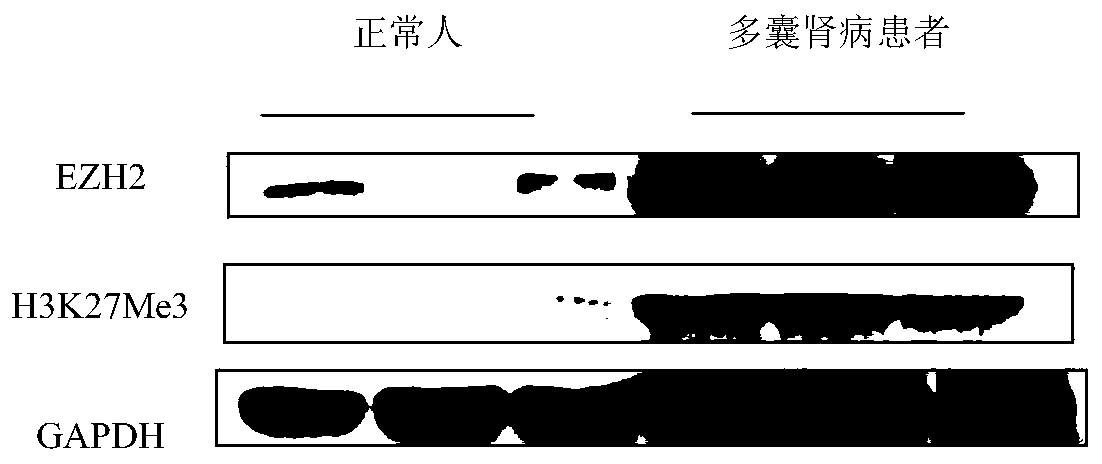
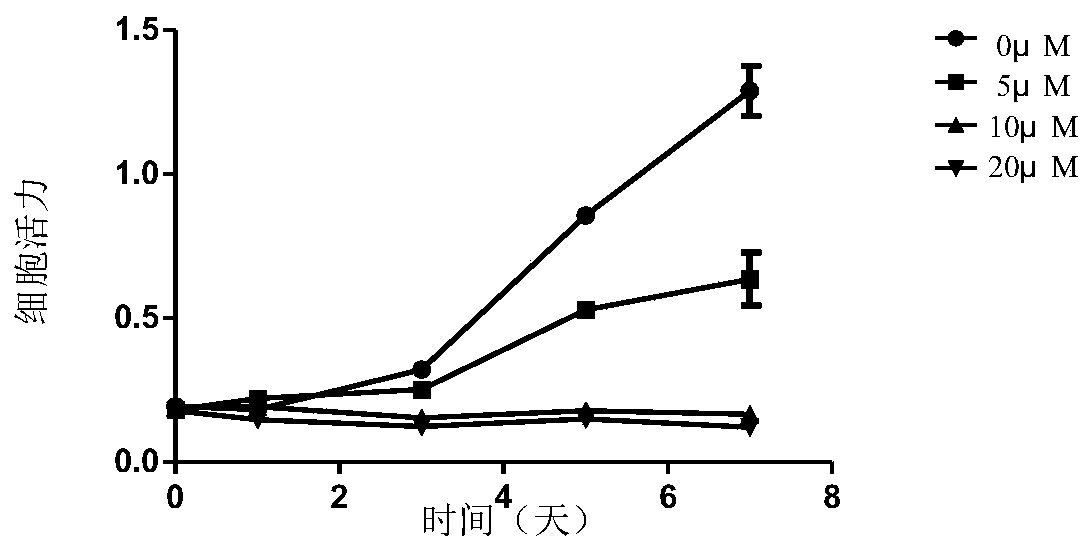
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine, in particular to application of EZH2 (enhancer of zeste homolog 2) in the preparation of drugs to prevent or treat polycystic kidney disease.It is discovered herein that an EZH2 inhibitor can inhibit the proliferation of cyst cells by inducing the apoptosis of polycystic kidney disease cyst lining epithelial cells and regulating cell cycle, and can protect the renal function by inhibiting the growth of renal cysts and enlargement of renal size. It is indicated that EZH2 can act as a novel target for autosomal dominant polycystic kidneydisease and is very significant to the treatment of polycystic kidney disease; the EZH2 inhibitor can be used to develop new pilot compounds to prevent or treat autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and can also be used to prepare drugs to prevent or treat autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
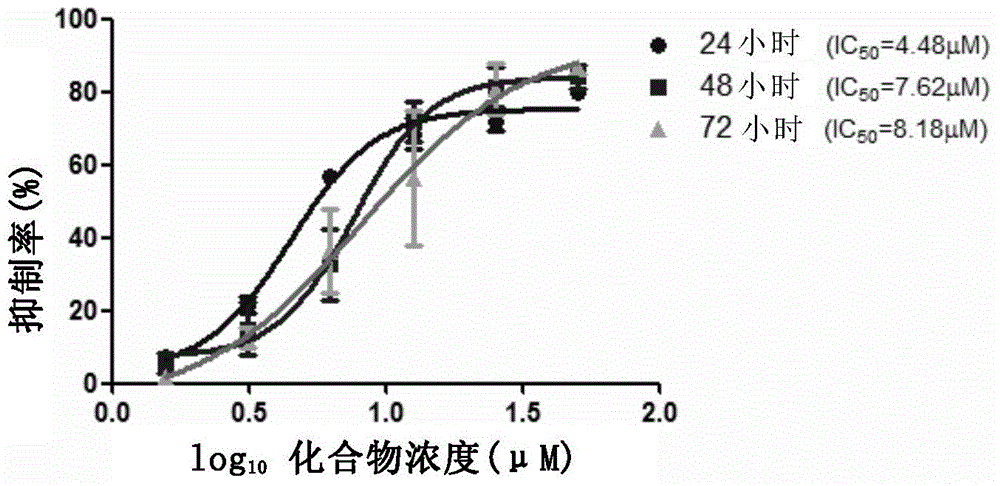
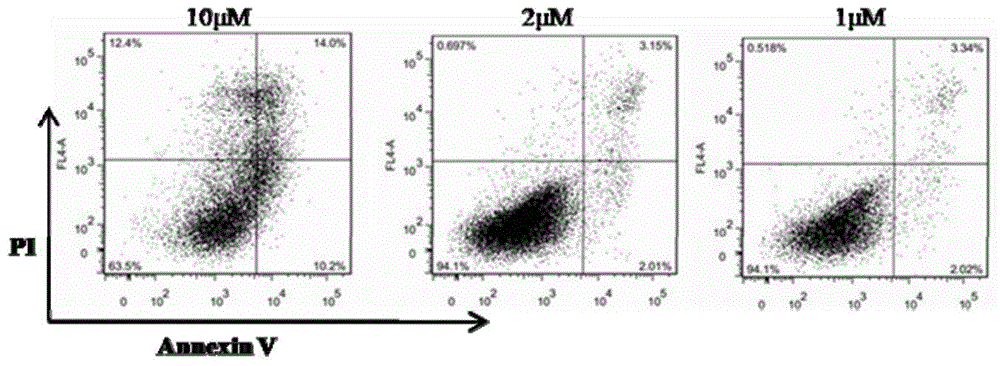
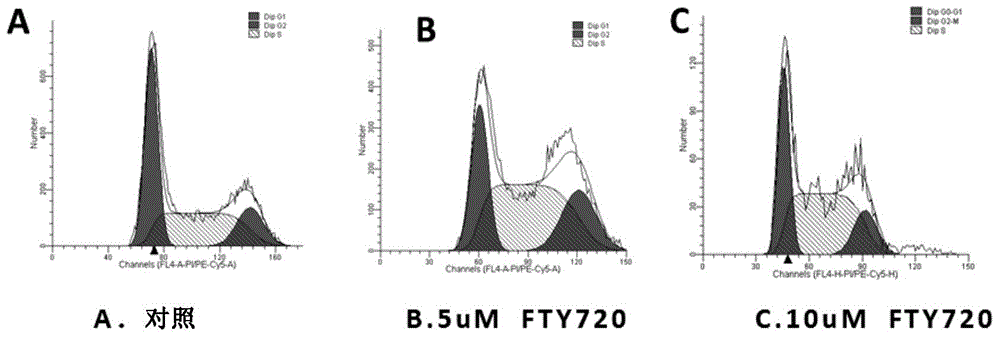
Application of fingolimod or salts thereof in treatment of cystic diseases
InactiveCN105560219AThe effect is accurateCyst size shrinksOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemCystic diseaseCytotoxicity
The invention provides application of fingolimod (2-amino-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl) ethyl]-1,3-propanediol) or salts thereof in preparation of medicinal compositions for treating cystic diseases. Particularly, the inventor finds that fingolimod or salts thereof have the effects of inducing the apoptosis and / or inhibiting the proliferation of a cystic cell by inhibiting HDACs and arresting the cell cycle of the cystic cell at G2 / M so as to reduce the cystic volume and restore the renal function. In addition, cytotoxicity experiments also confirm that during the treatment of the cystic diseases, fingolimod, as a known marketed medicine, has no obvious toxicity under the therapeutic dose. Fingolimod, as a medicine for treating the cystic diseases, especially an autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
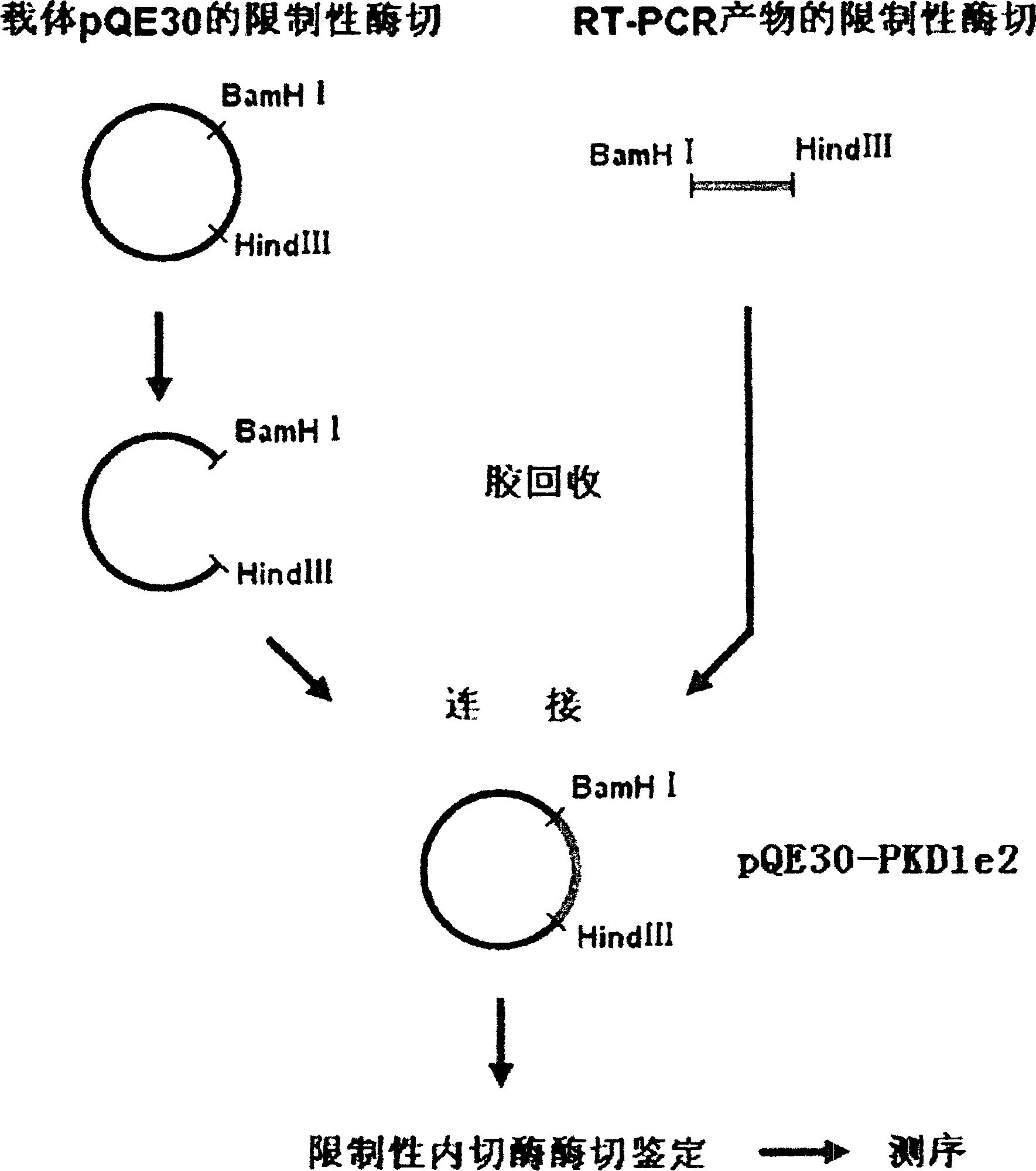
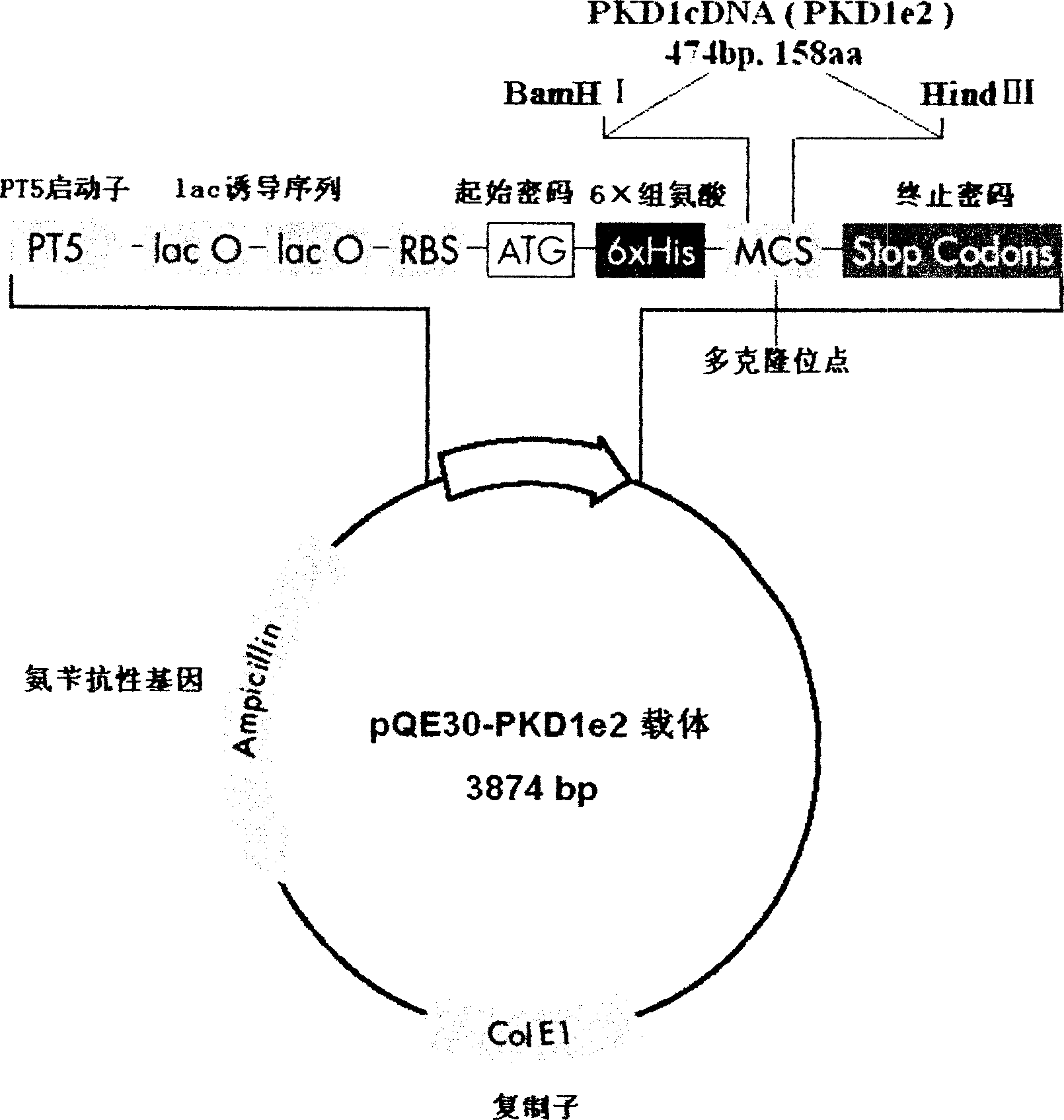
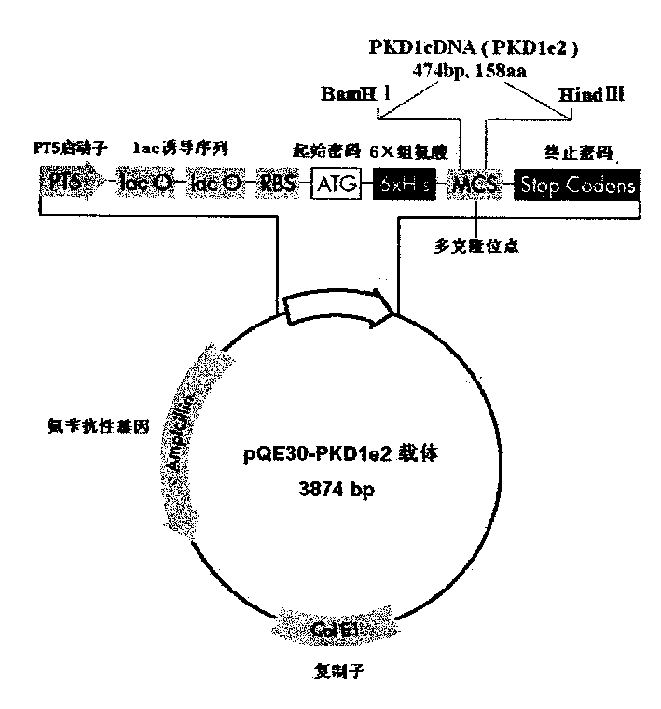
N-end fusion protein PC-1-e2 of human multicapsular protein-1
InactiveCN1526736ALow costNo obvious side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEscherichia coliRenal Tubular Epithelial Cells
The present invention relates to medicine molecular biology engineering technology, and is one kind of 1N-end fusion protein PC-1-e2 of human polycystic protein-1. According to cDNA sequence of human polycystic kidney disease-1 gene and the molecular structure of its encoded product, polycystic protein-1 (PC-1), the gene is cloned to cDNA-PKD1e2 in the N end of the protein and its prokaryotic expression carrier pQE30-PKD1e2 is constituted by means of molecular biology engineering technology. N-end fusion protein PC-1-e2 of PC-1 is induced in colibacillus. Cytobiology experiment shows that the fusion protein has obvious inhibition to the proliferation of the epidermis cell line of in vitro cultured human polycystic kidney cyst lining and the epidermis cell strain of far end renal tubule in dog kidney, so that it may be used in preparing medicine for treating autosomal dominant hereditary polycystic kidney disease, the reagent for the mechanism research of the disease, and anti-PC-1 antibody.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
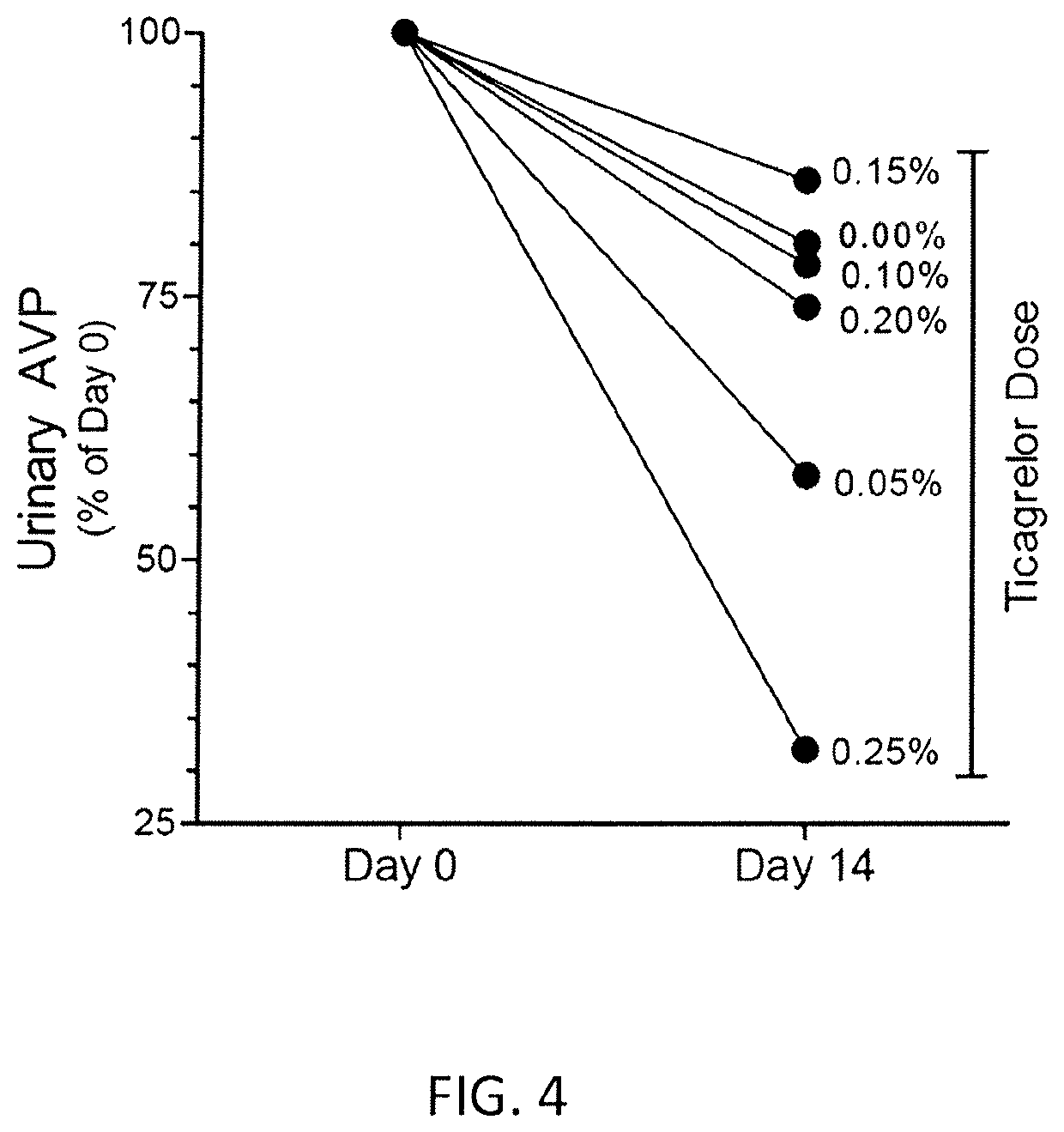
Treatment of kidney diseases associated with elevated AVP
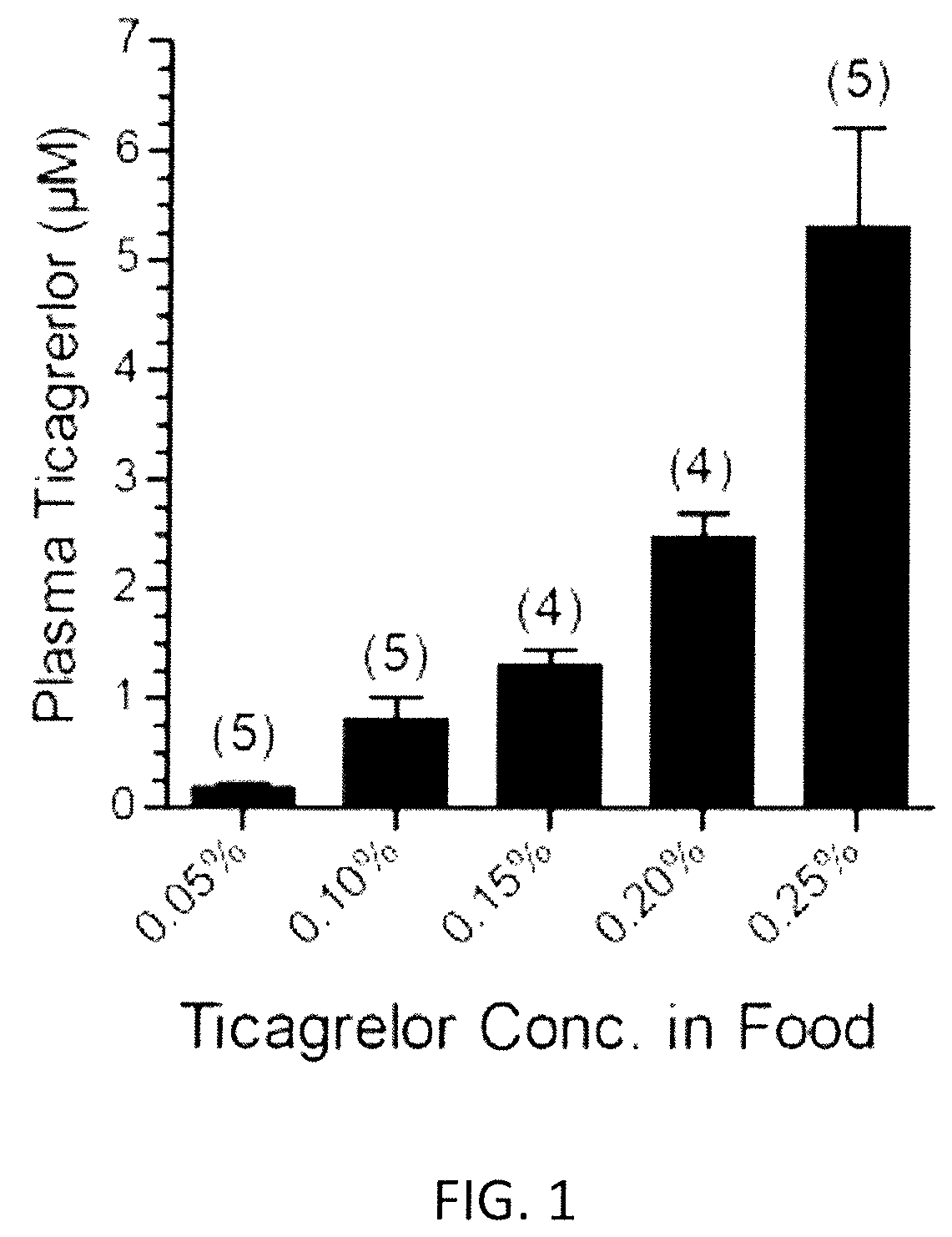
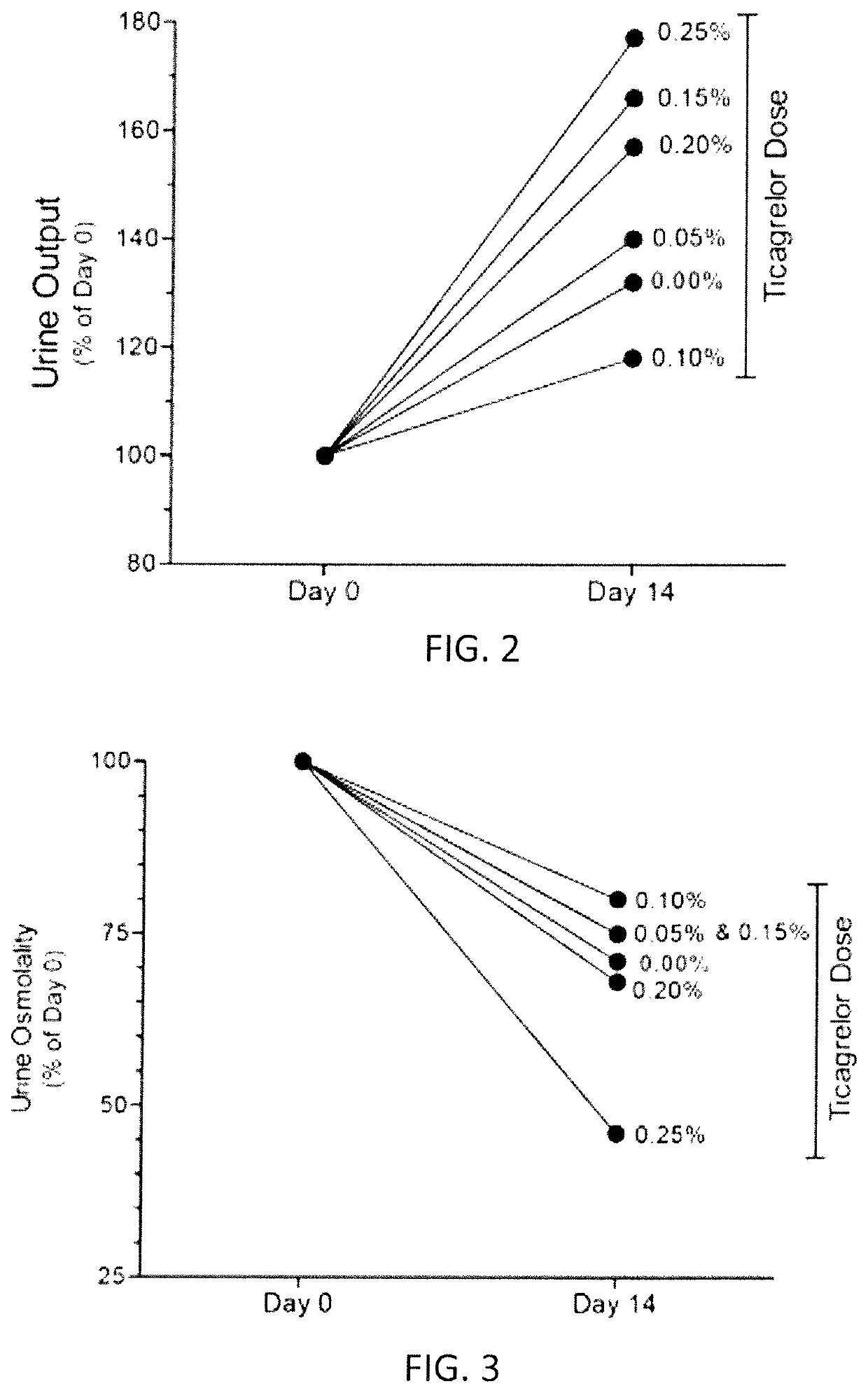
ActiveUS10614684B2Reduce productionInhibit productionPeptide/protein ingredientsUnmanned aerial vehiclesTicagrelorArginine
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Method for testing for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and method for screening agent for treatment of the disease
InactiveUS20170016069A1Reduce usageUseful in treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDisease markersGene
This invention provides a method of comparing disease markers obtained from subject samples to test for, detect, or diagnose autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and a disease marker for such disease. The method for detecting autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and the method for screening for an agent for treatment or prevention of such disease comprise detecting a gene that is expressed specifically in cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, including IGFBP7.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
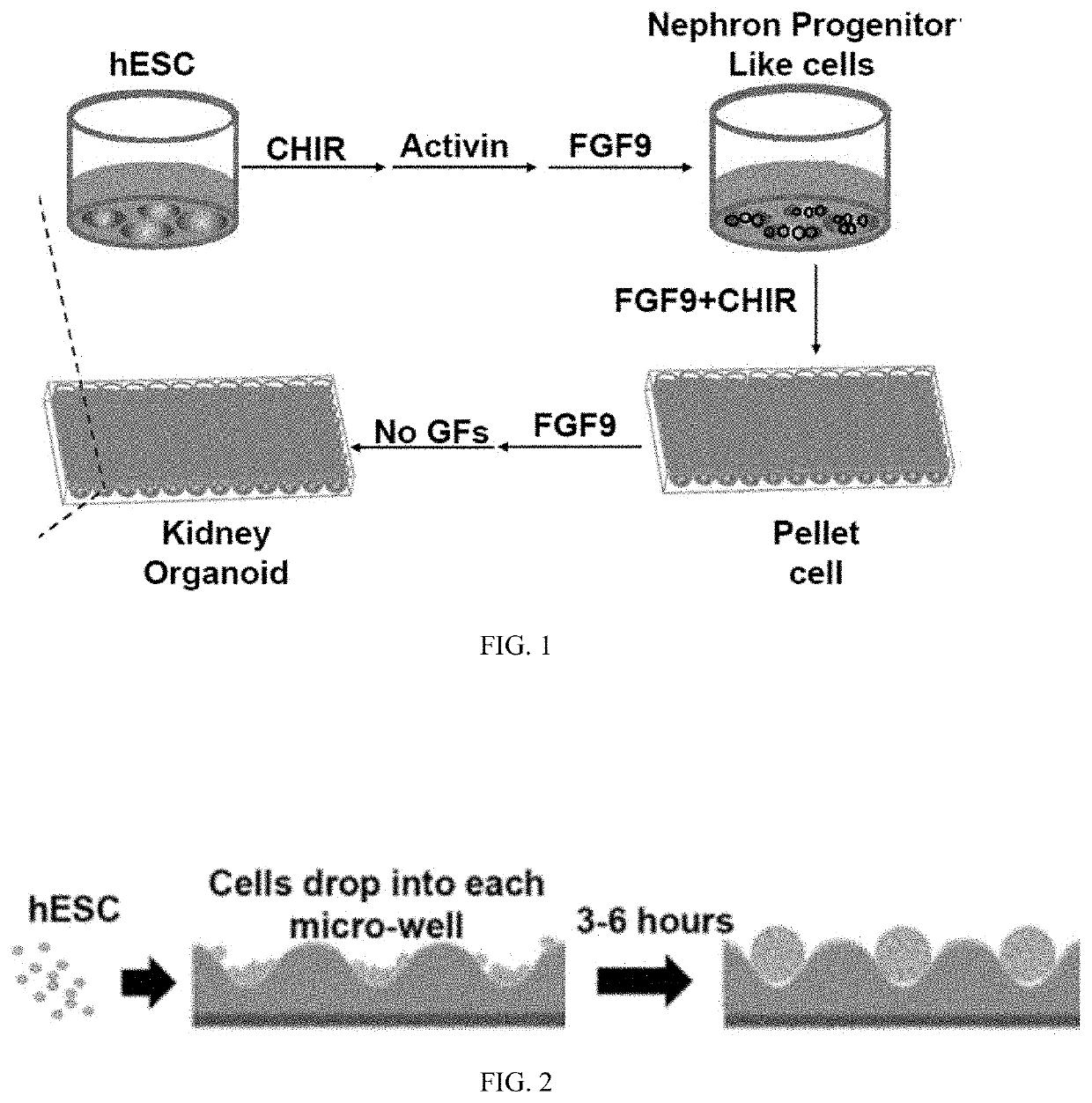
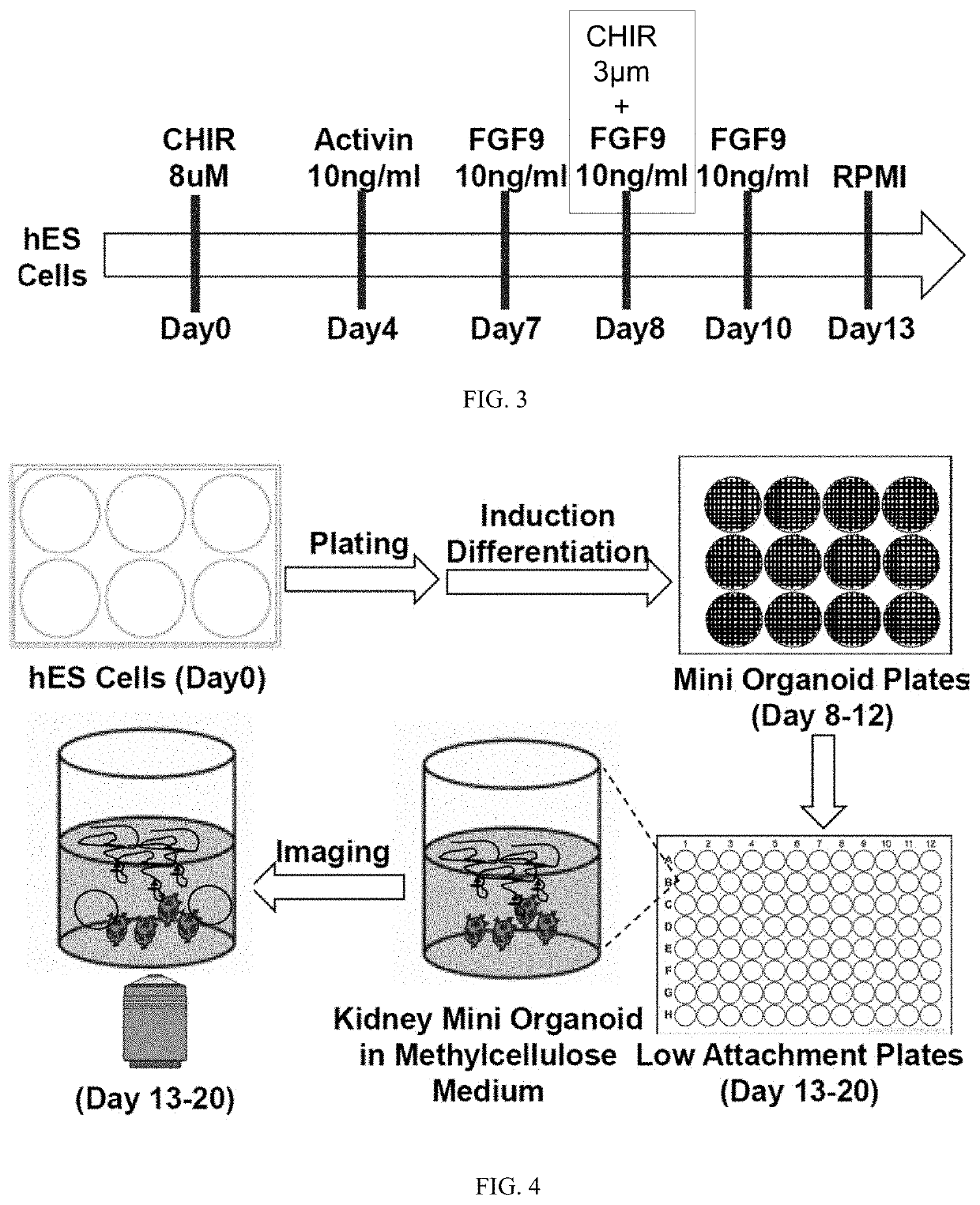
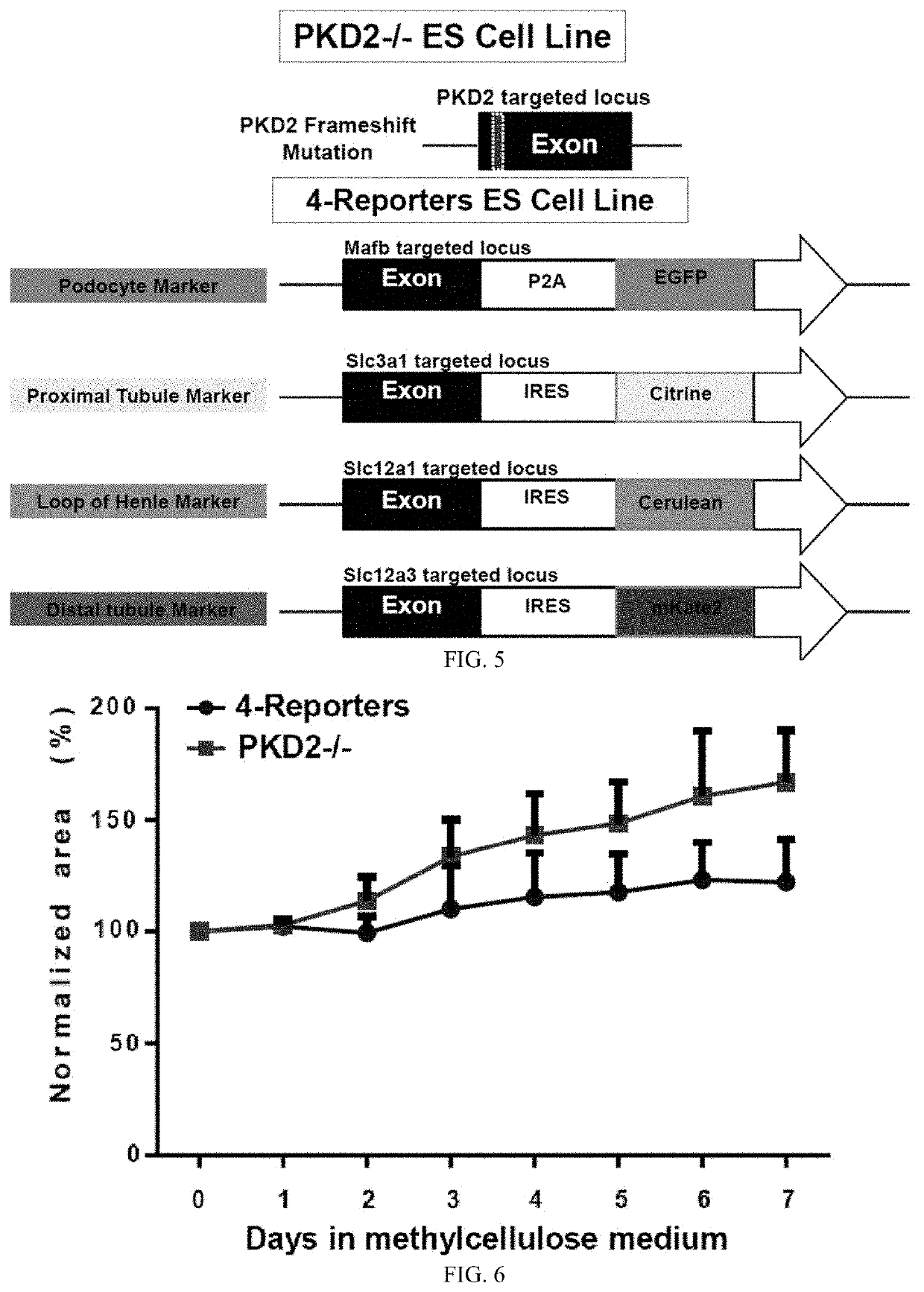
Pluripotent stem cell-directed model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease for disease mechanism and drug discovery
PendingUS20200390825A1Reduce artifactsReduce vibrationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionPluripotential stem cellAssay
A new type of kidney miniature organoids based on human embryonic stem cells are prepared and tested as forming cysts in vitro or ex vivo. Assays are developed for screening useful candidate molecules towards inhibiting or treating polycystic kidney disease. This provides a new system for modeling polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Methods for treatment of polycystic kidney disease
InactiveUS20190345494A1Increase slowlySlows rate of decline of glomerular filtration ratePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPhysiologyPolycystic liver disease
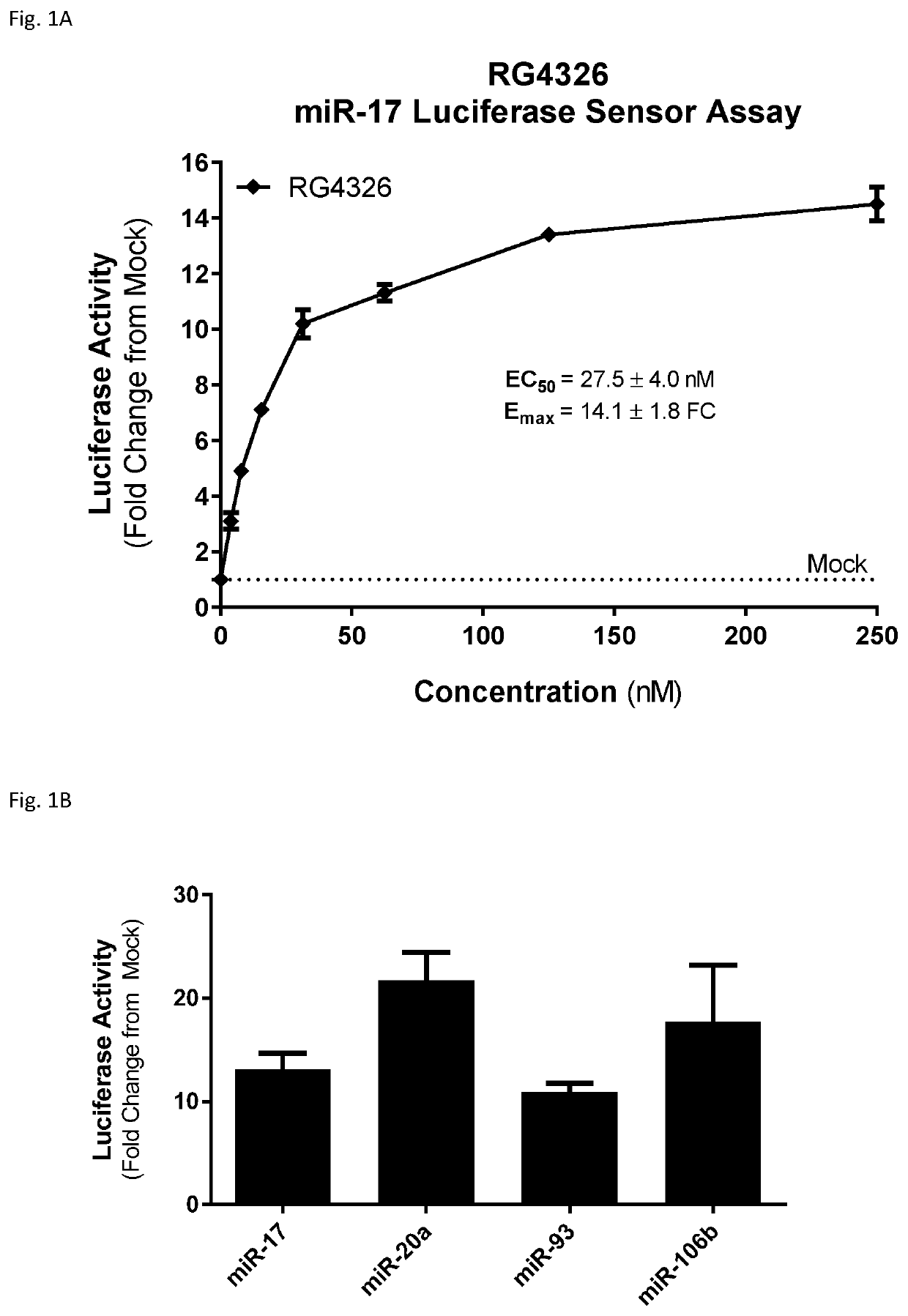
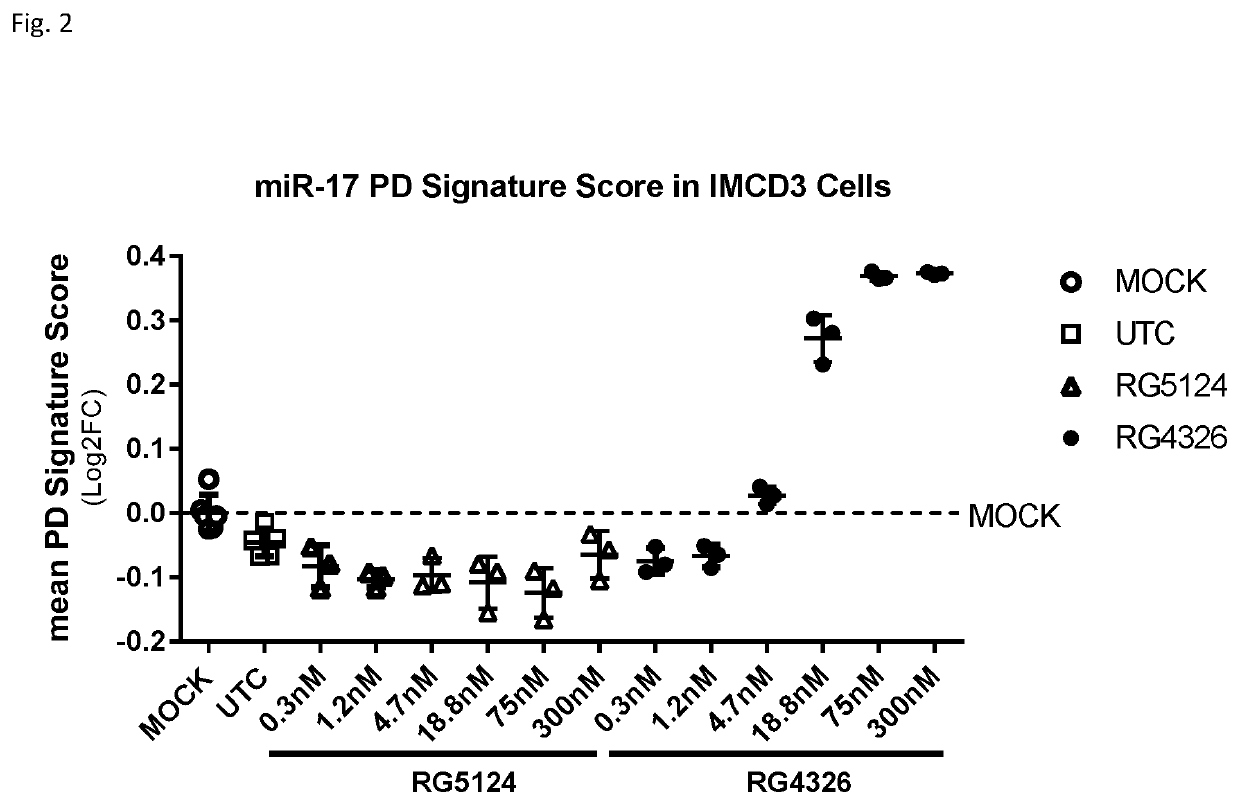
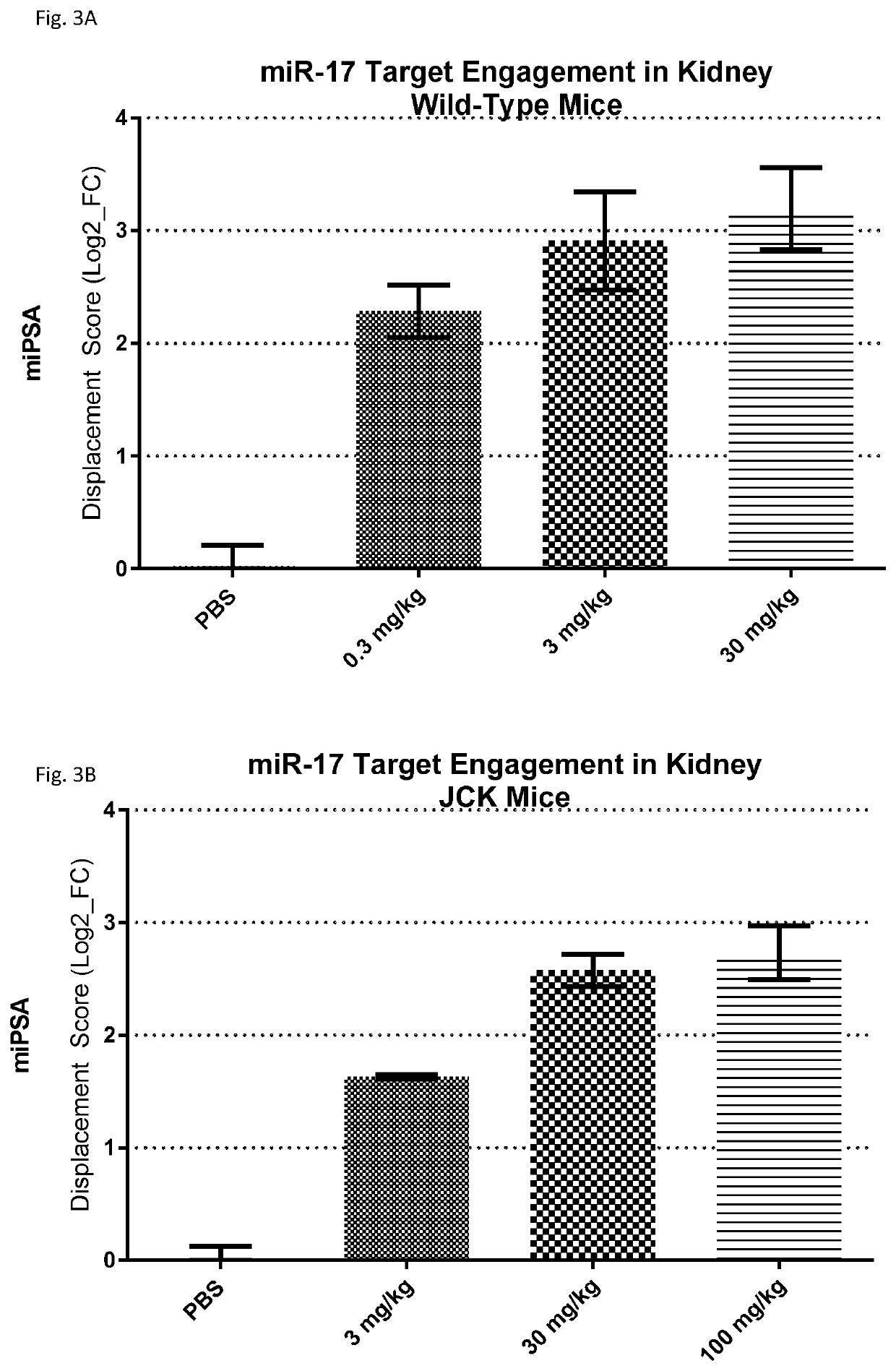
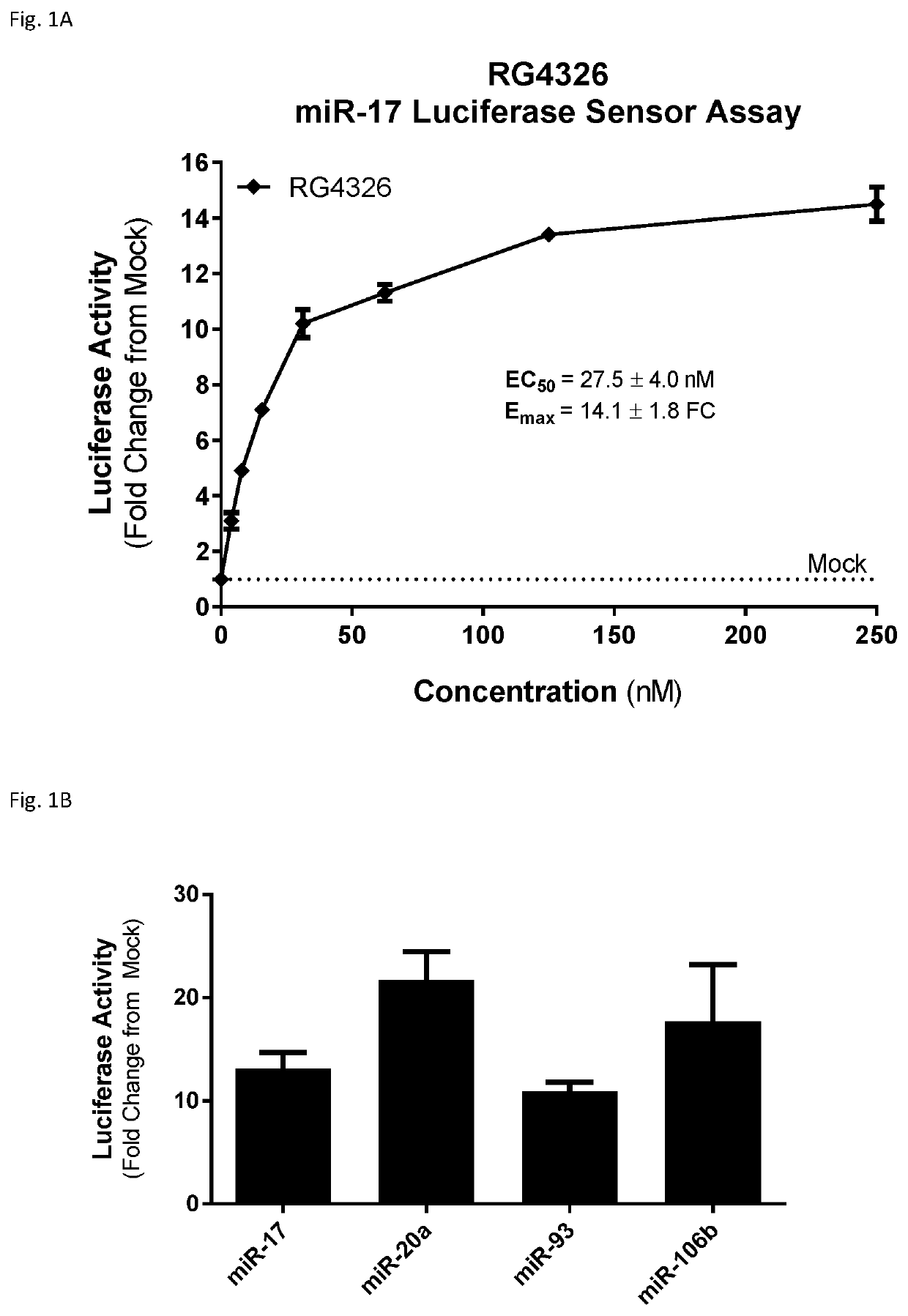
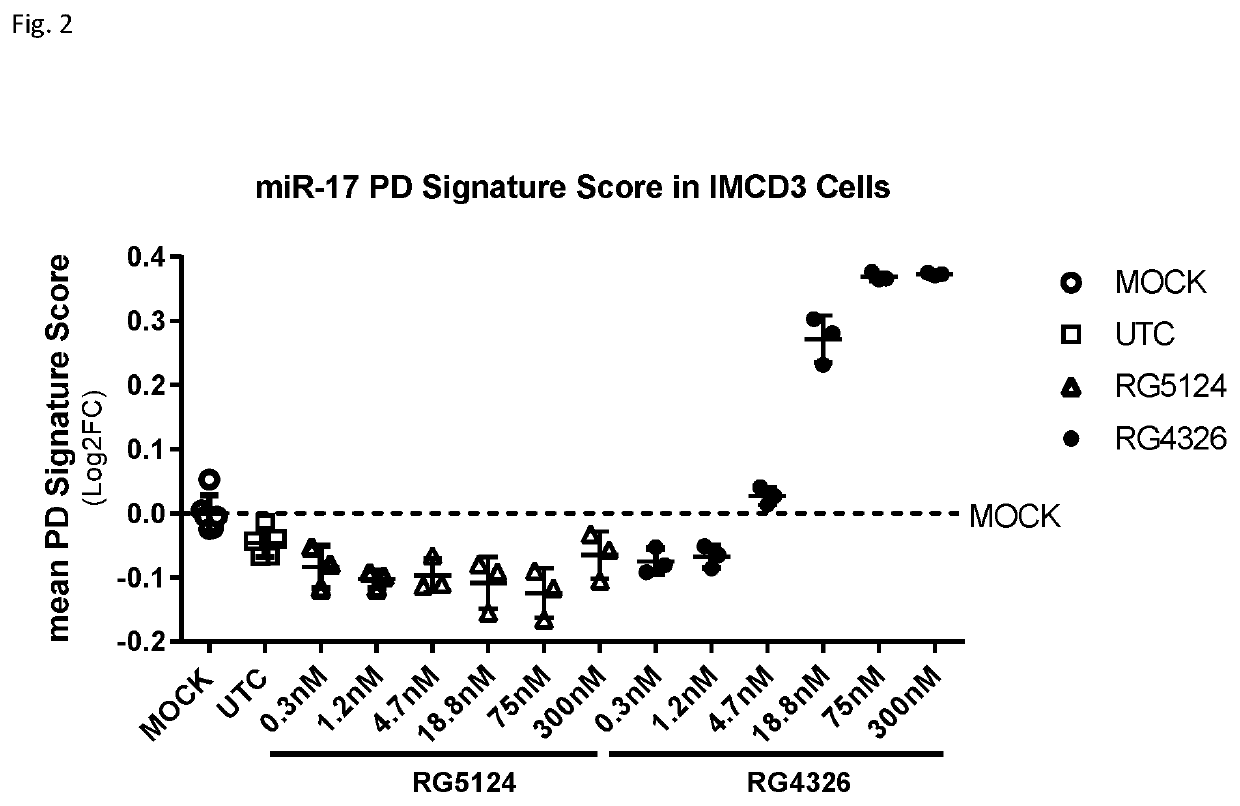
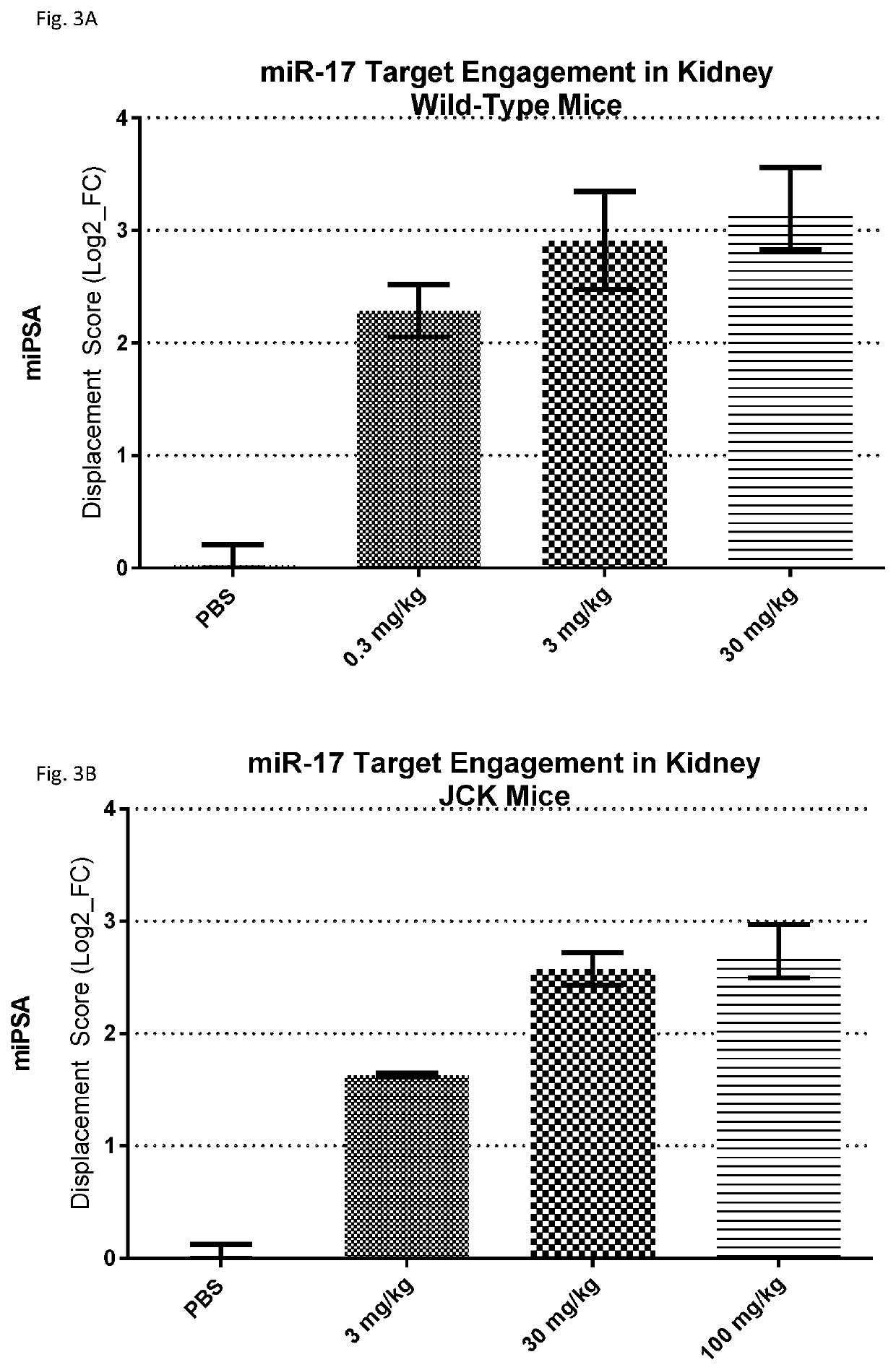
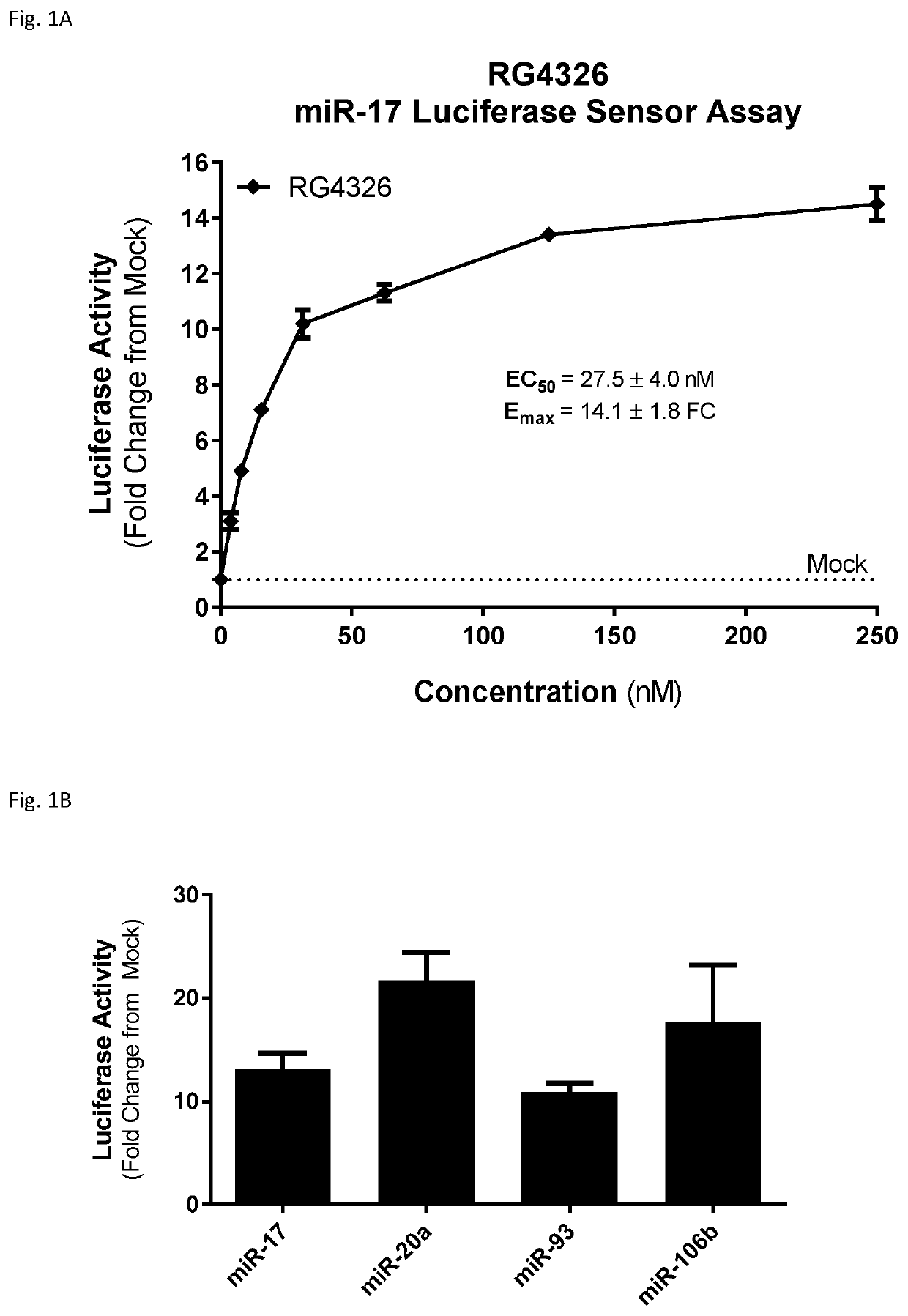
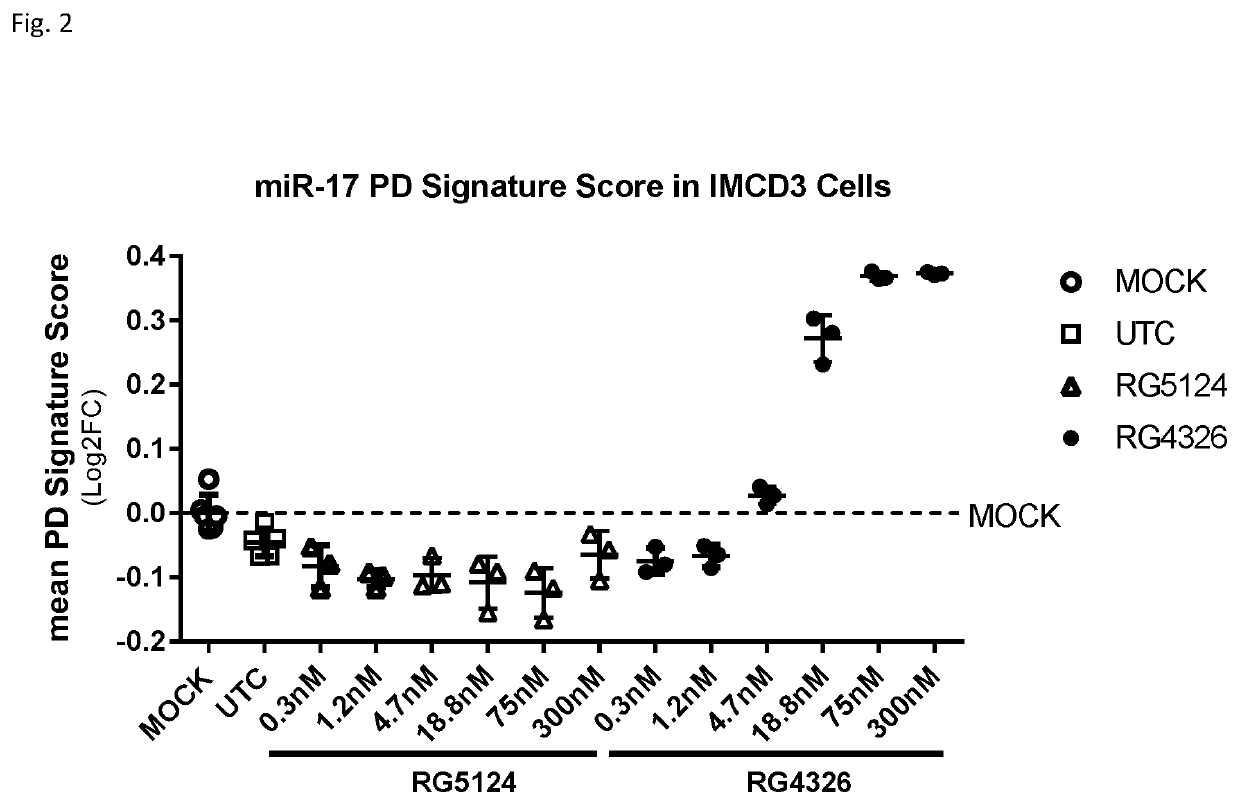
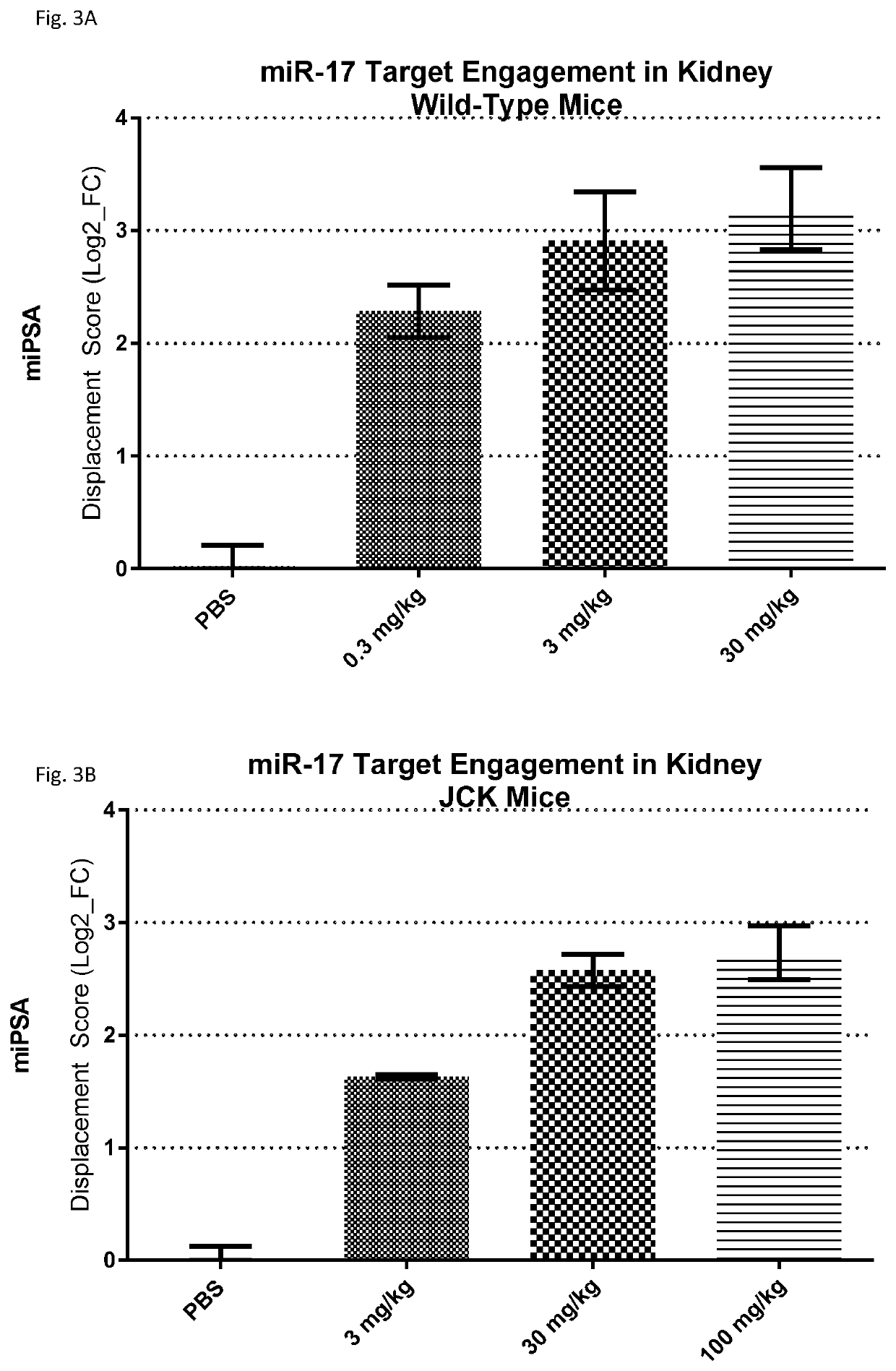
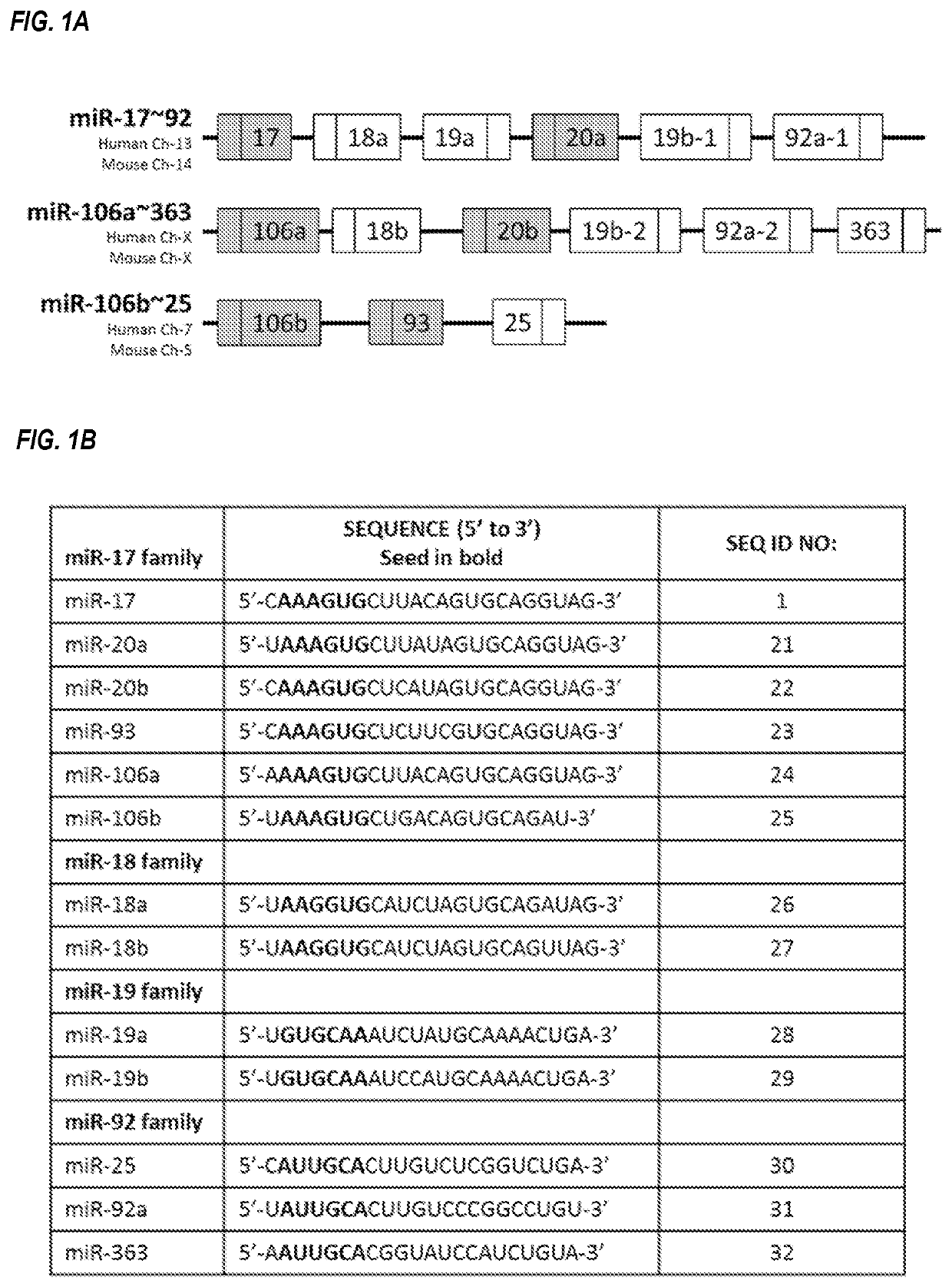
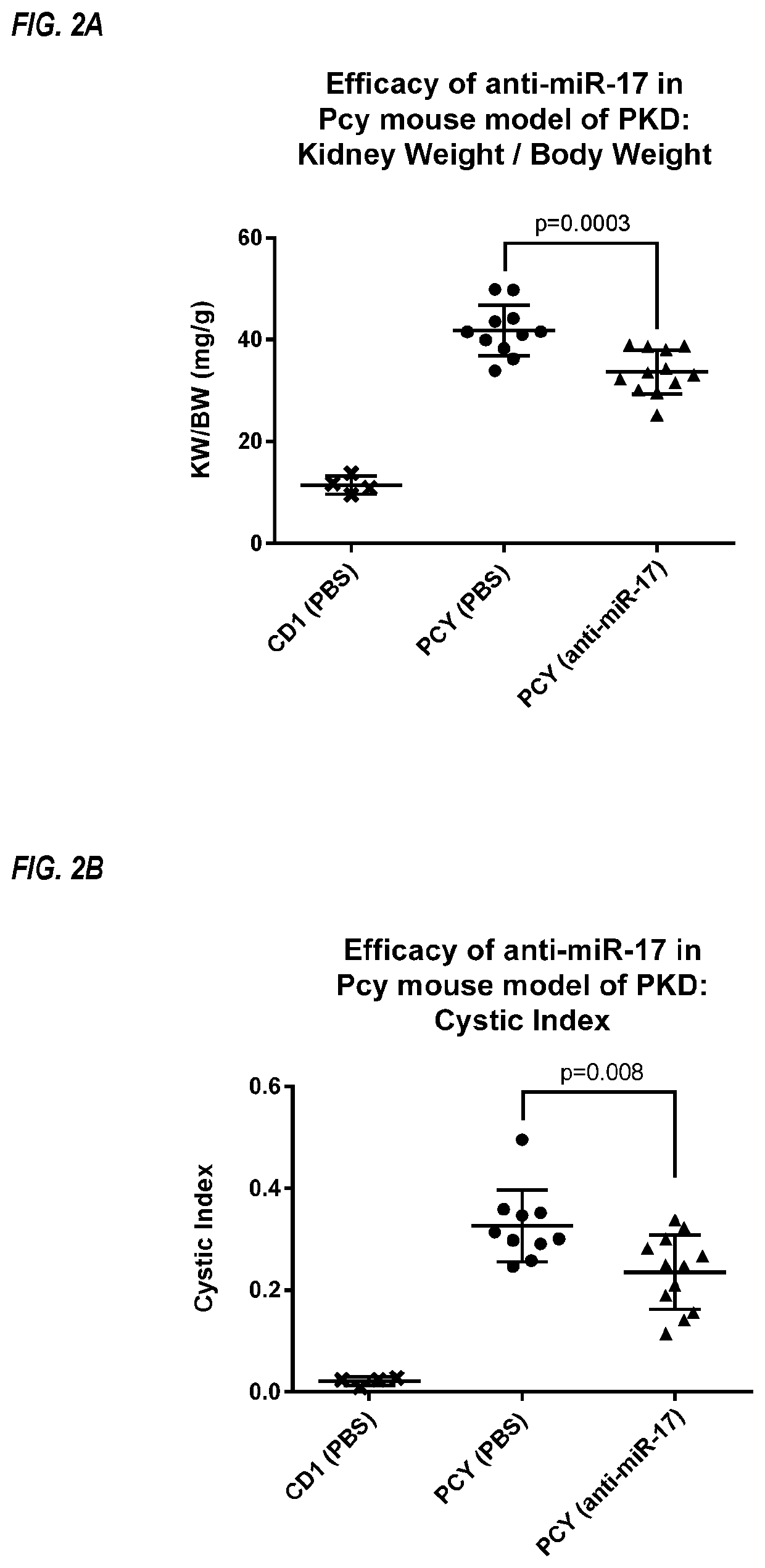
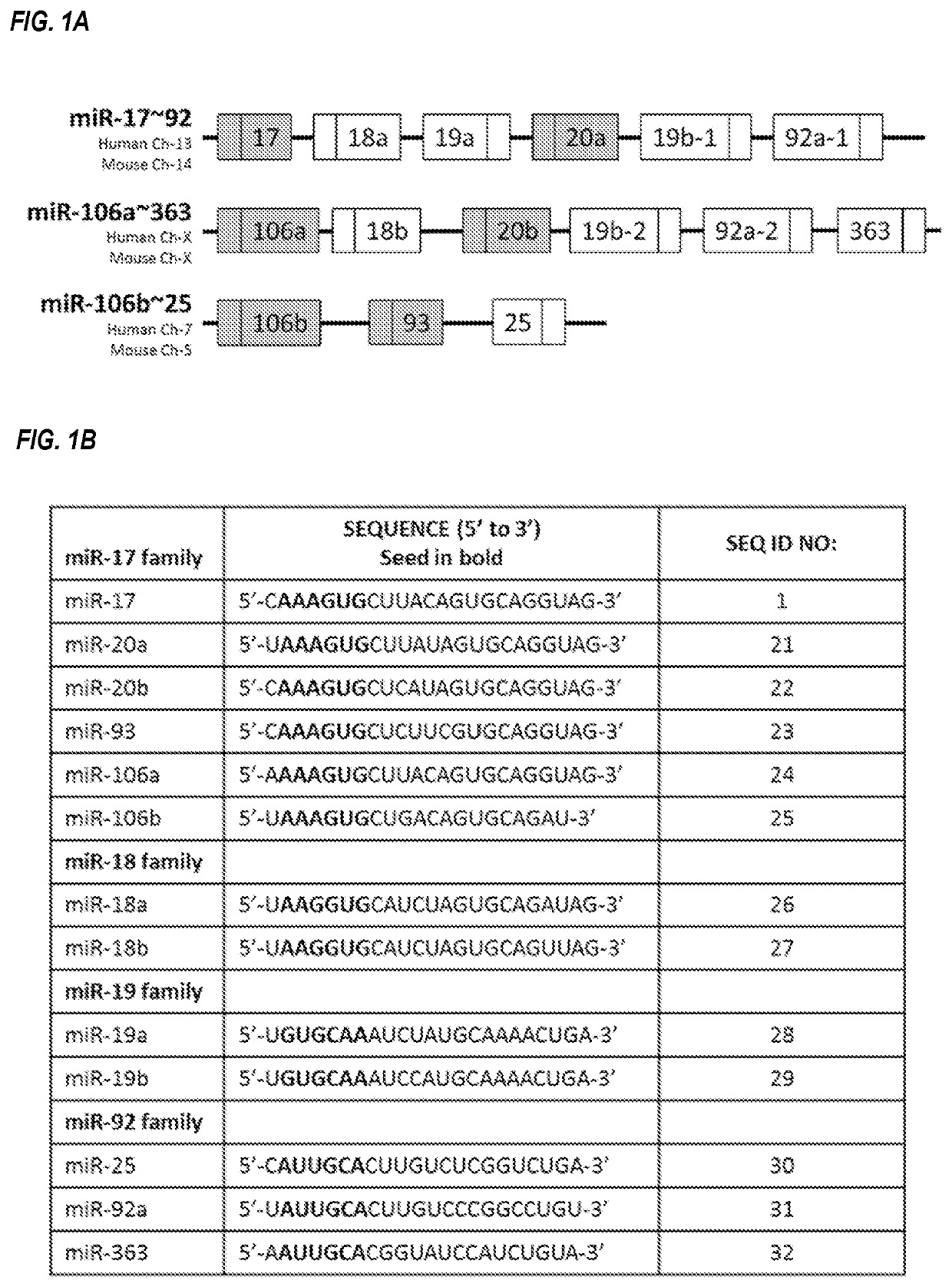
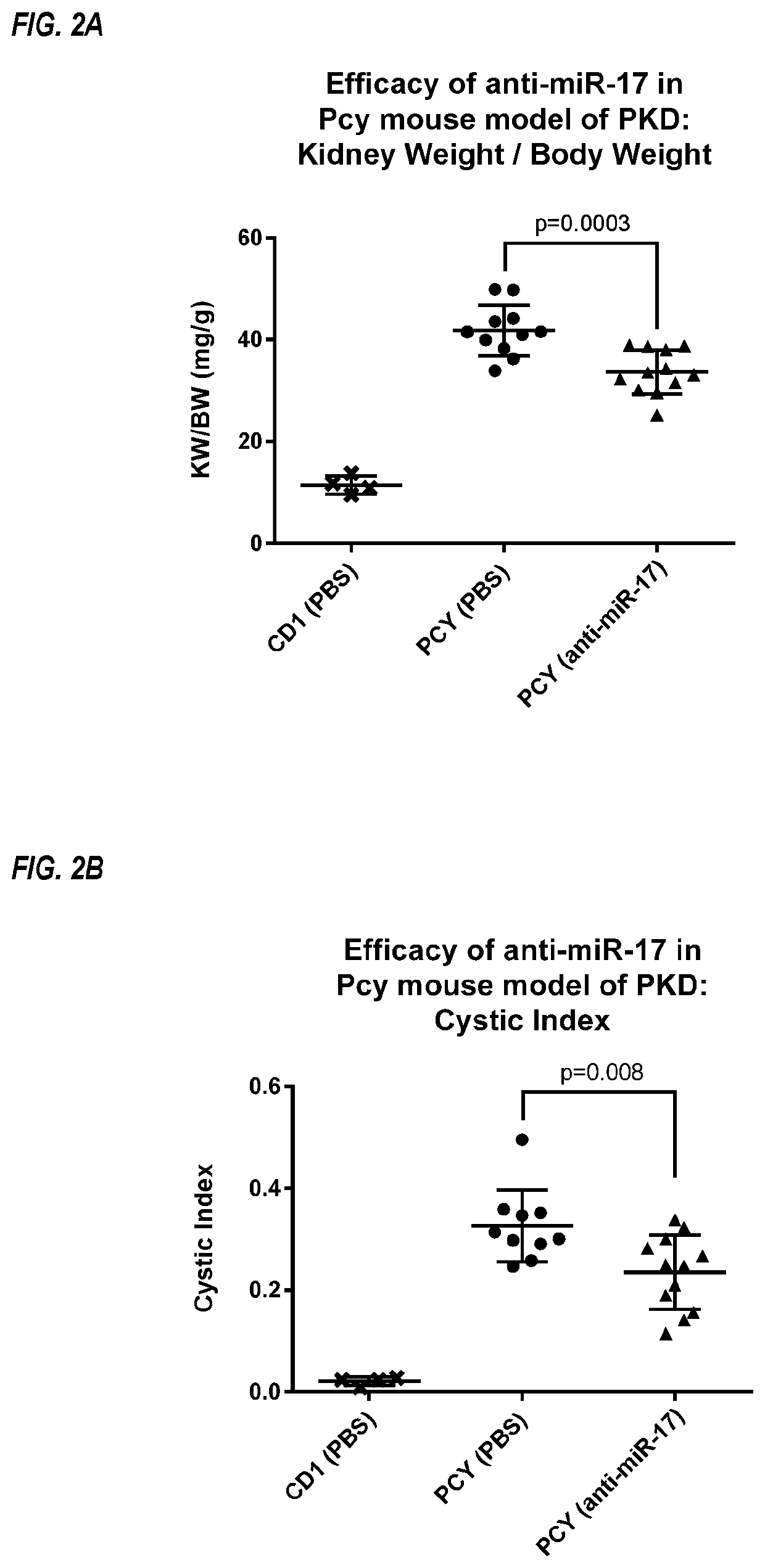
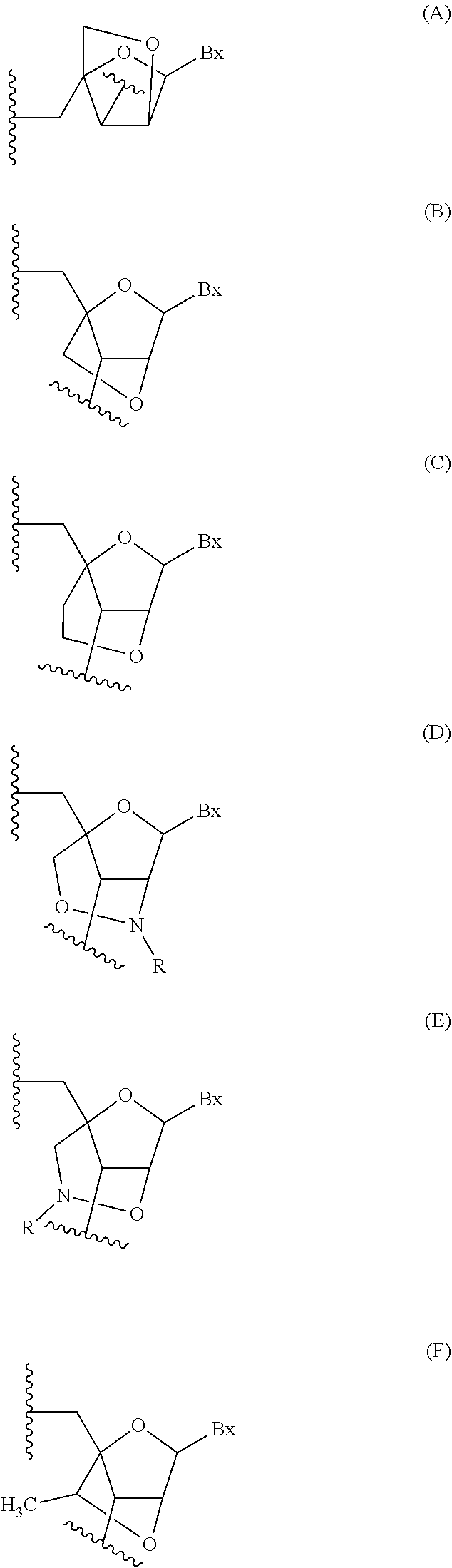
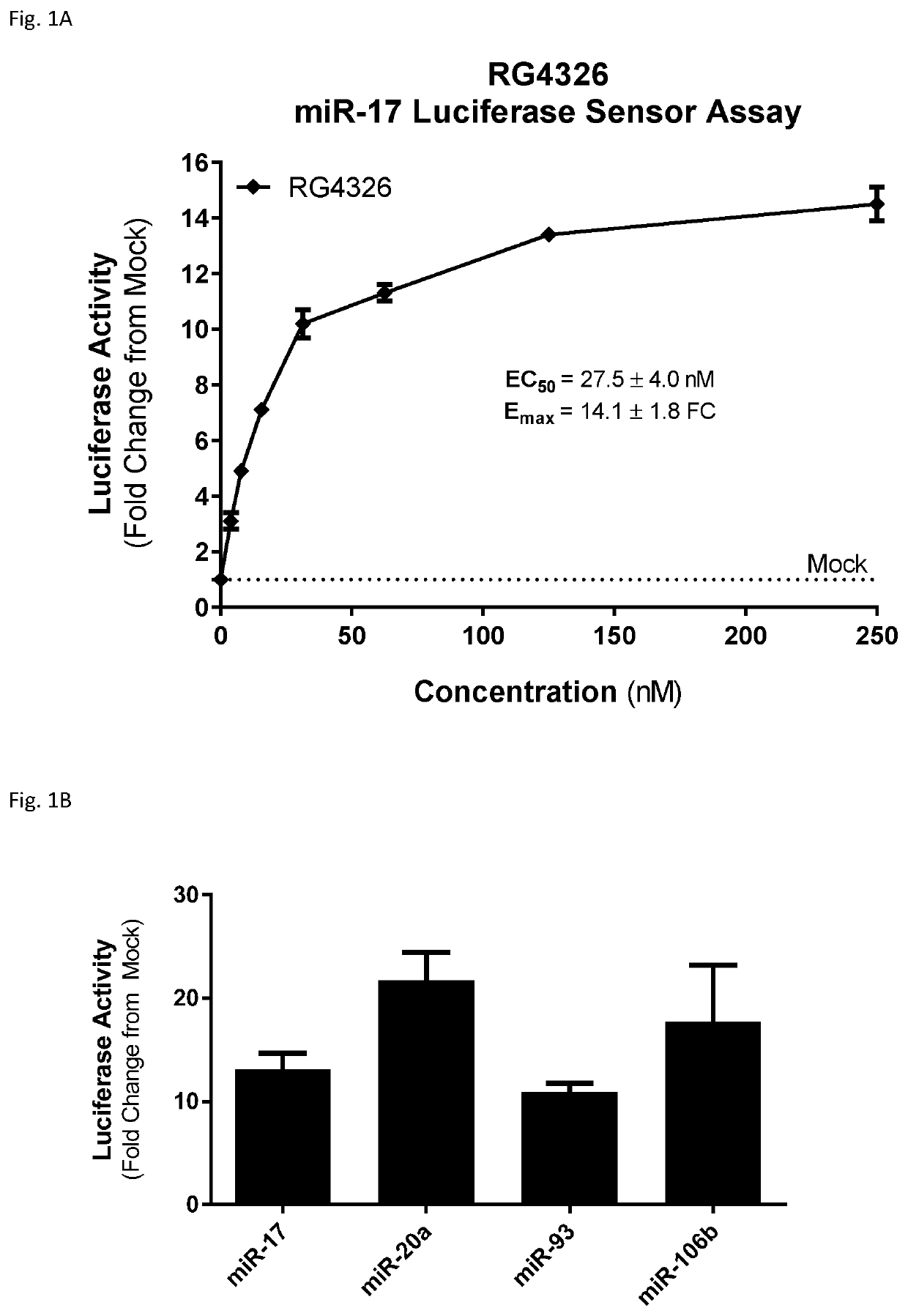
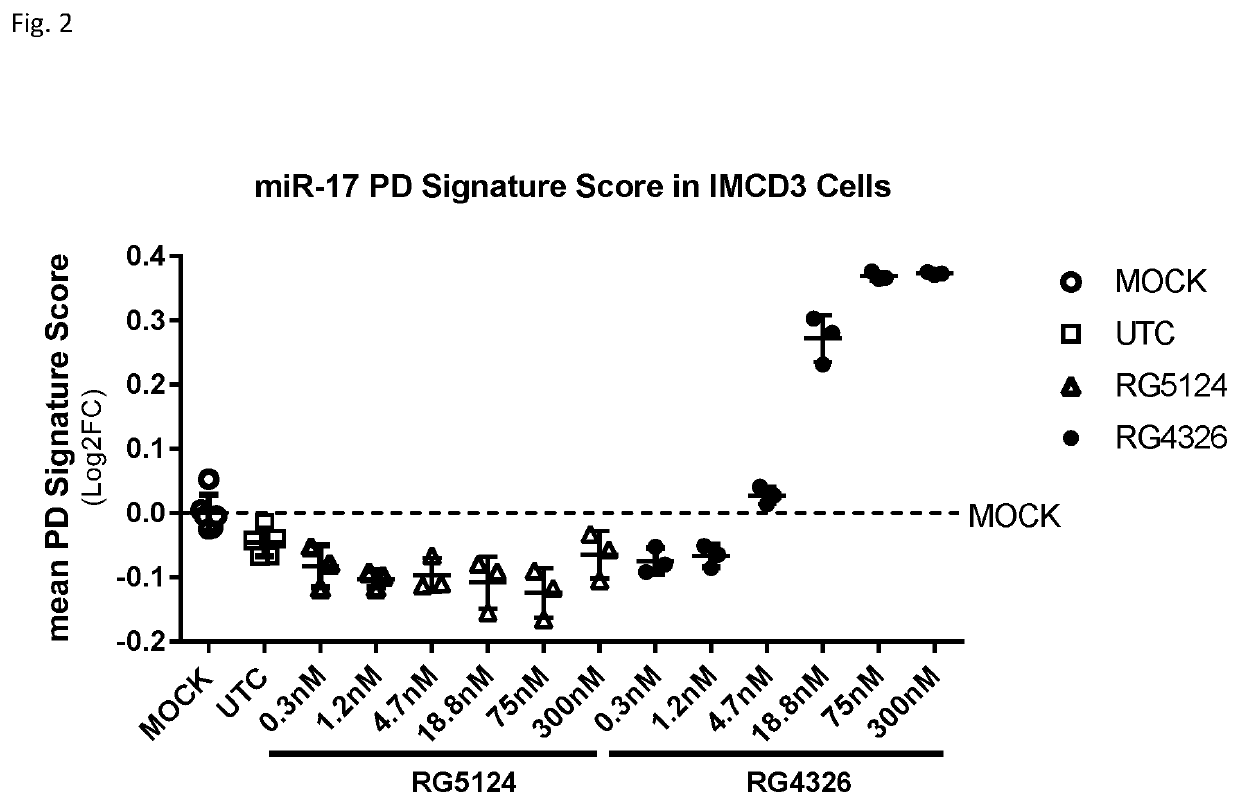
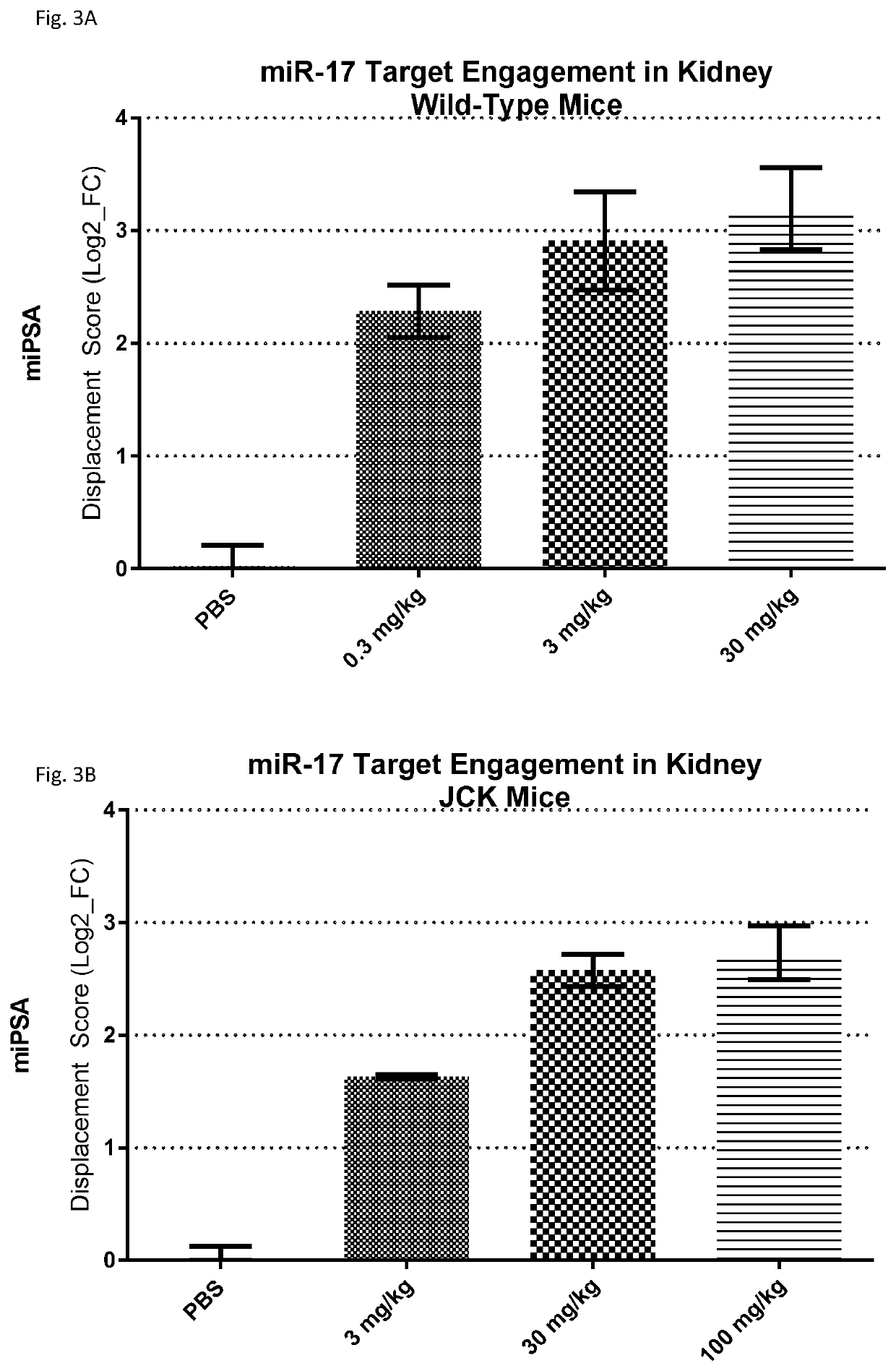
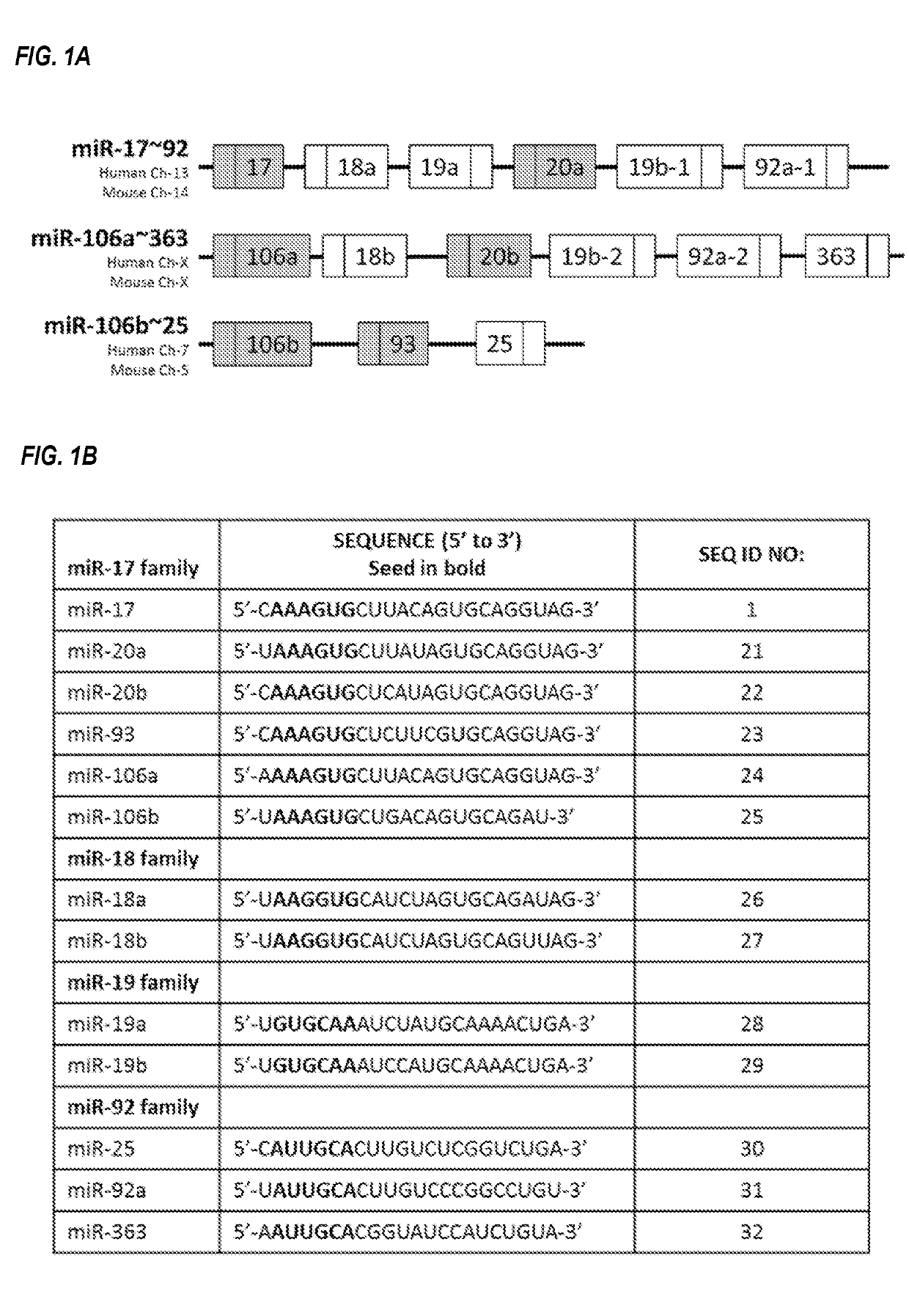
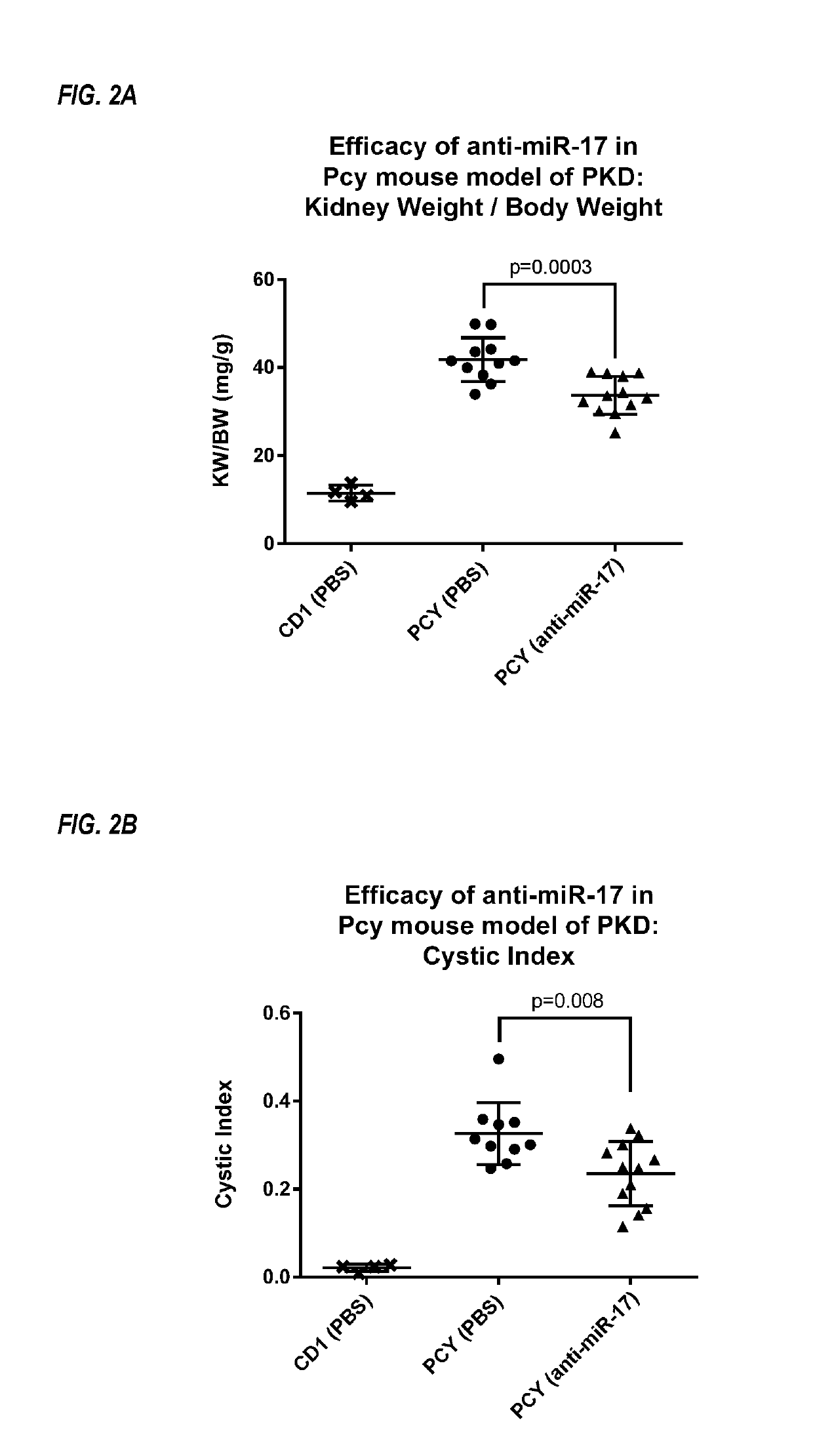
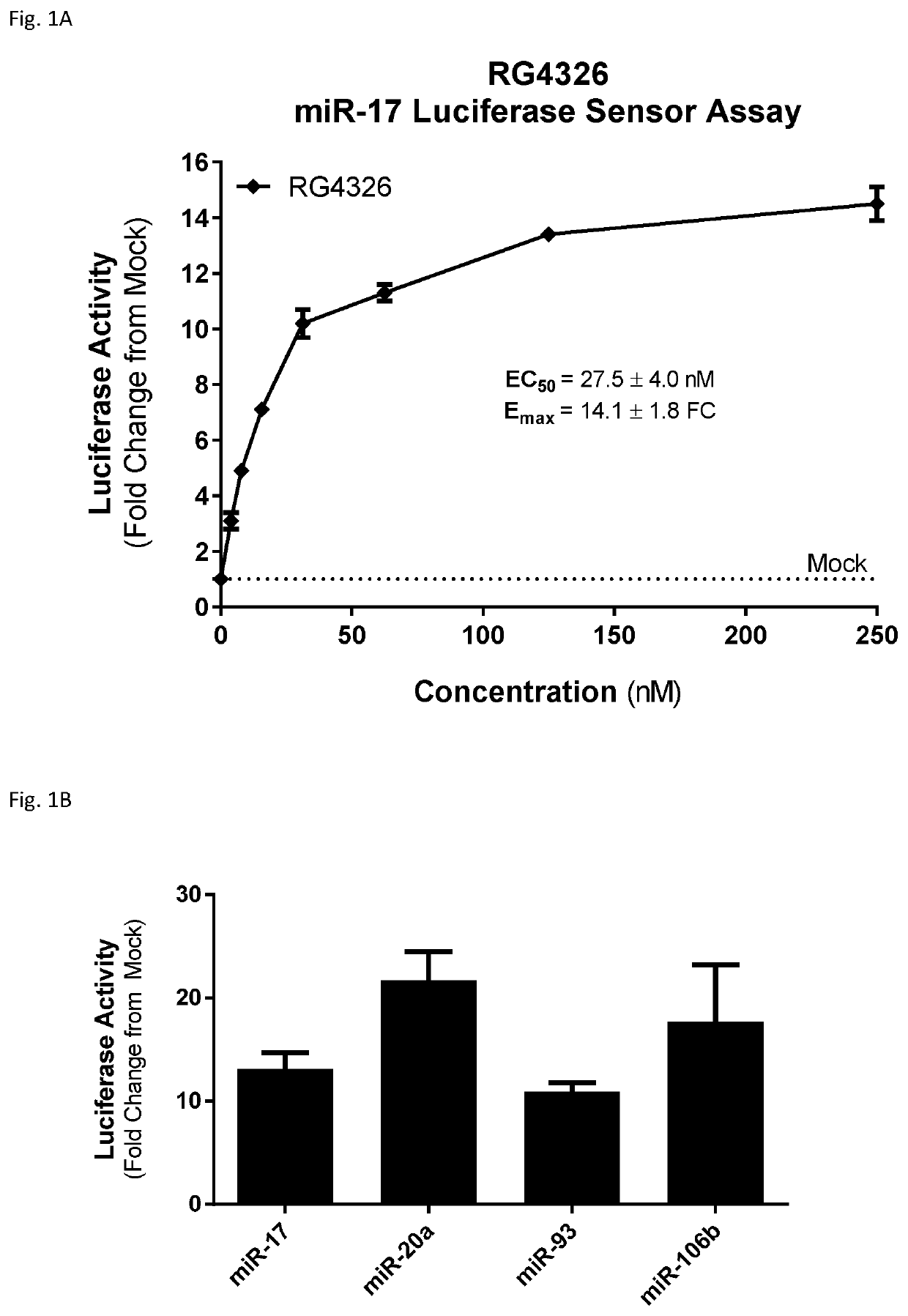
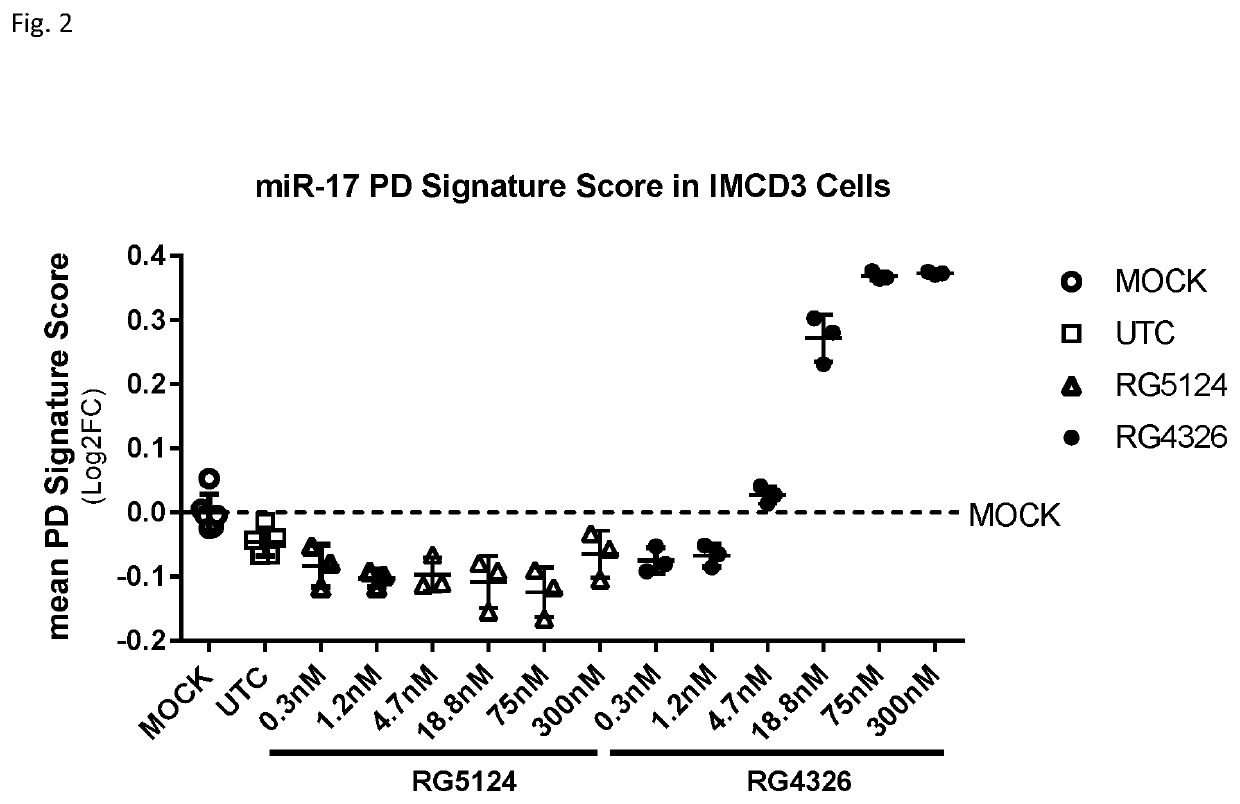
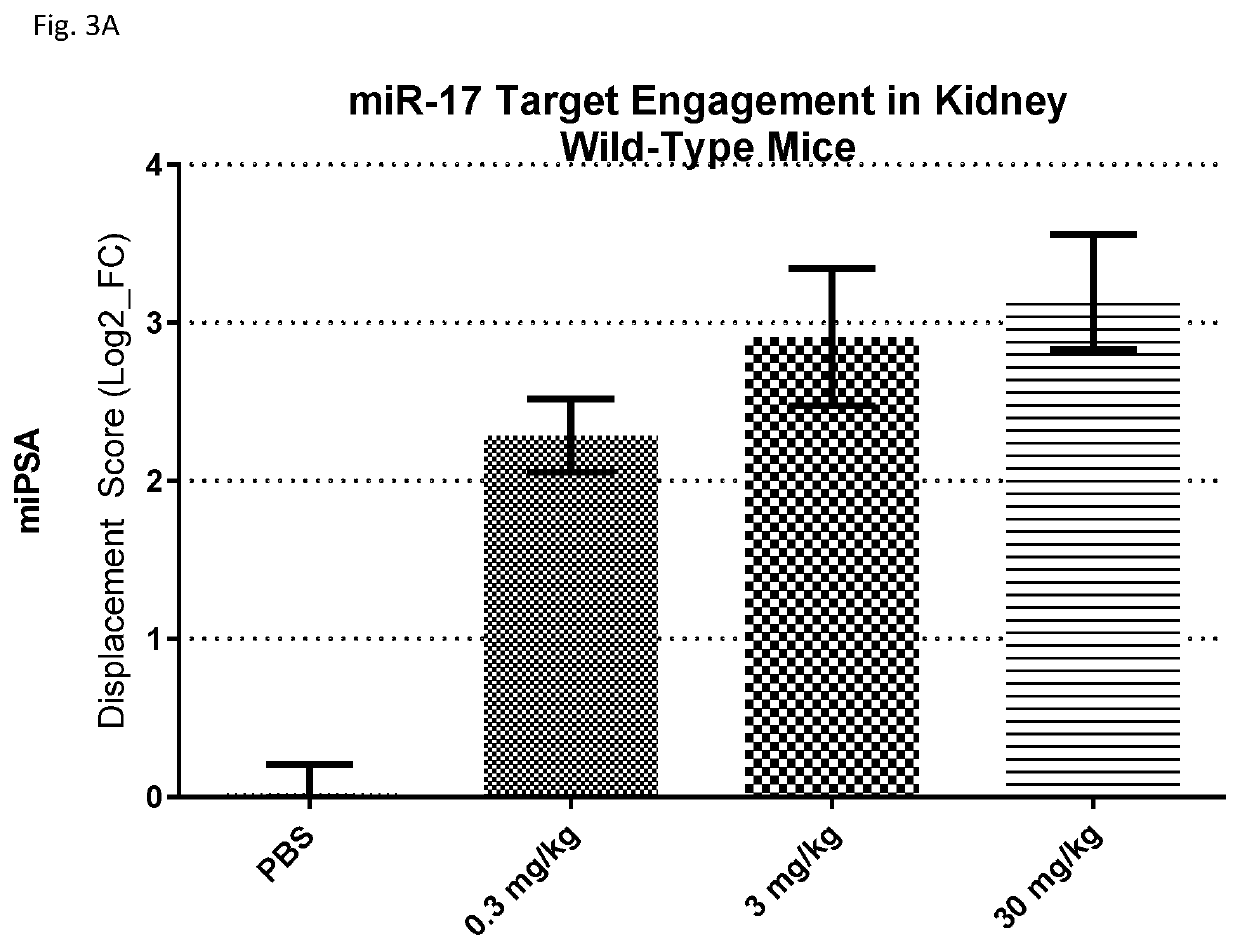
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Methods for treatment of polycystic kidney disease
InactiveUS20200392501A1Increase slowlySlows rate of decline of glomerular filtration ratePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOligonucleotideInternal medicine
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:REGULUS THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Modified Oligonucleotides for Treatment of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:REGULUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for treatment of polycystic kidney disease
ActiveUS10633657B2Improve life expectancyDelay worsening of functionOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderOligonucleotideInternal medicine
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of poly-cystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:REGULUS THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Methods for treatment of polycystic kidney disease
ActiveUS20200231971A1Improve life expectancyDelay worsening of functionOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderOligonucleotideInternal medicine
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:REGULUS THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Modified Oligonucleotides for Treatment of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:REGULUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for treatment of polycystic kidney disease
ActiveUS20190153442A1Increased total kidney volumeImprove kidney functionOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderPhysiologyPolycystic liver disease
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of poly-cystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:REGULUS THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Azaheterocyclyl derivatives of androstanes and androstenes as medicaments for cardiovascular disorders
Owner:CVIE THERAPEUTICS LTD
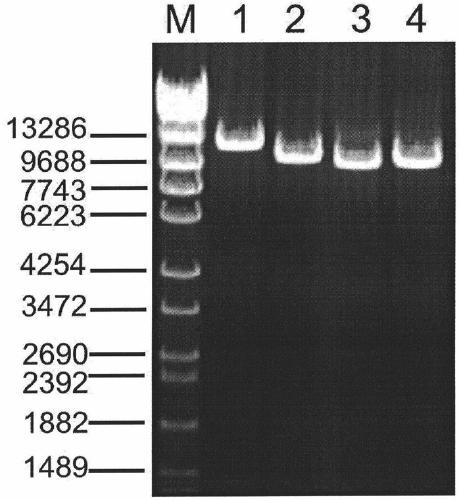
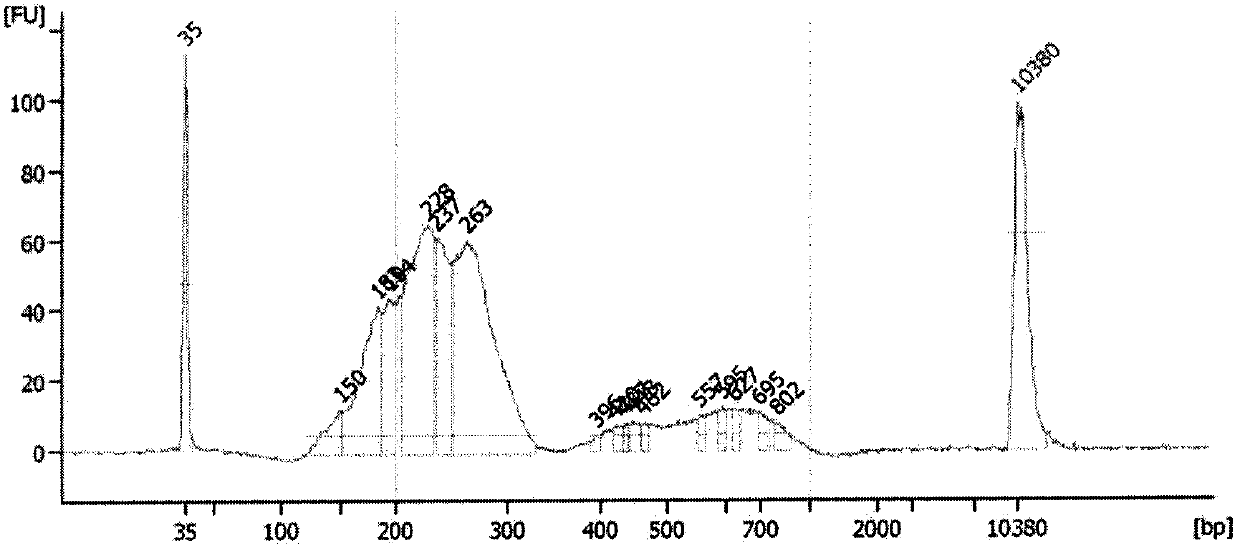
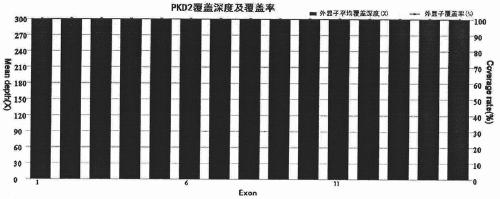
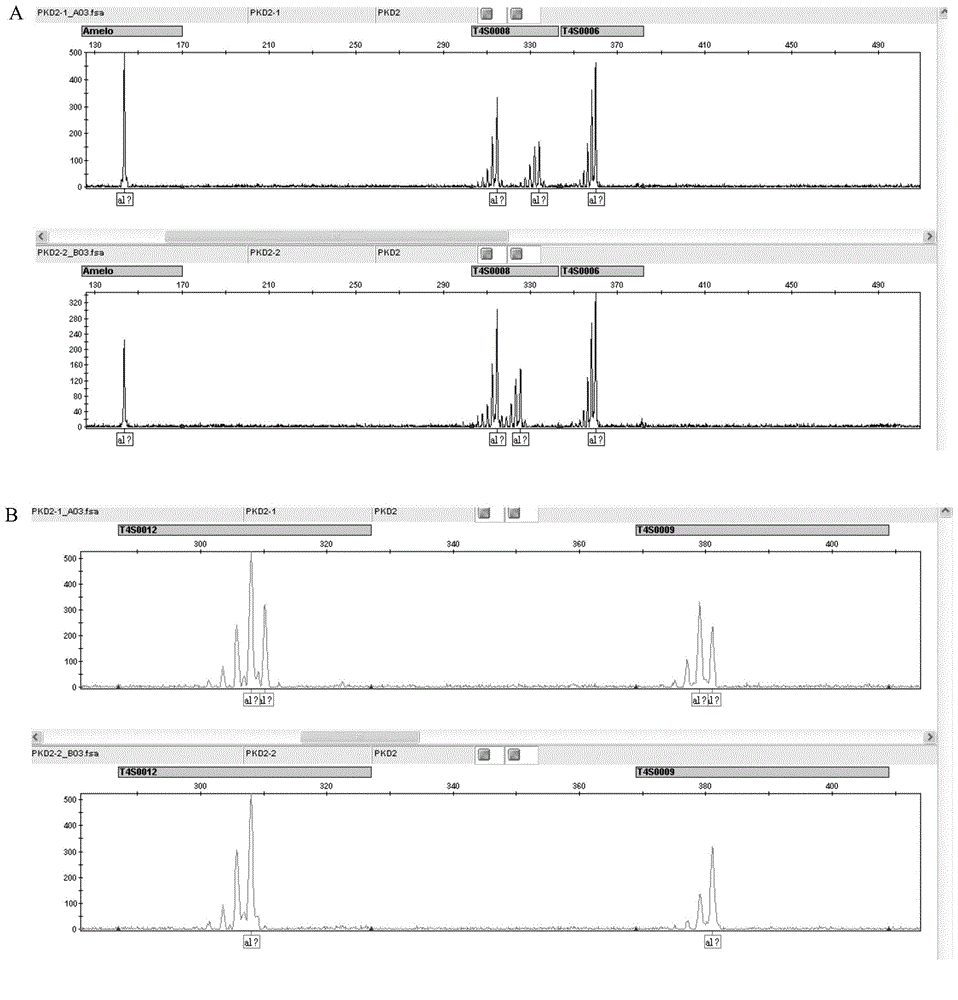
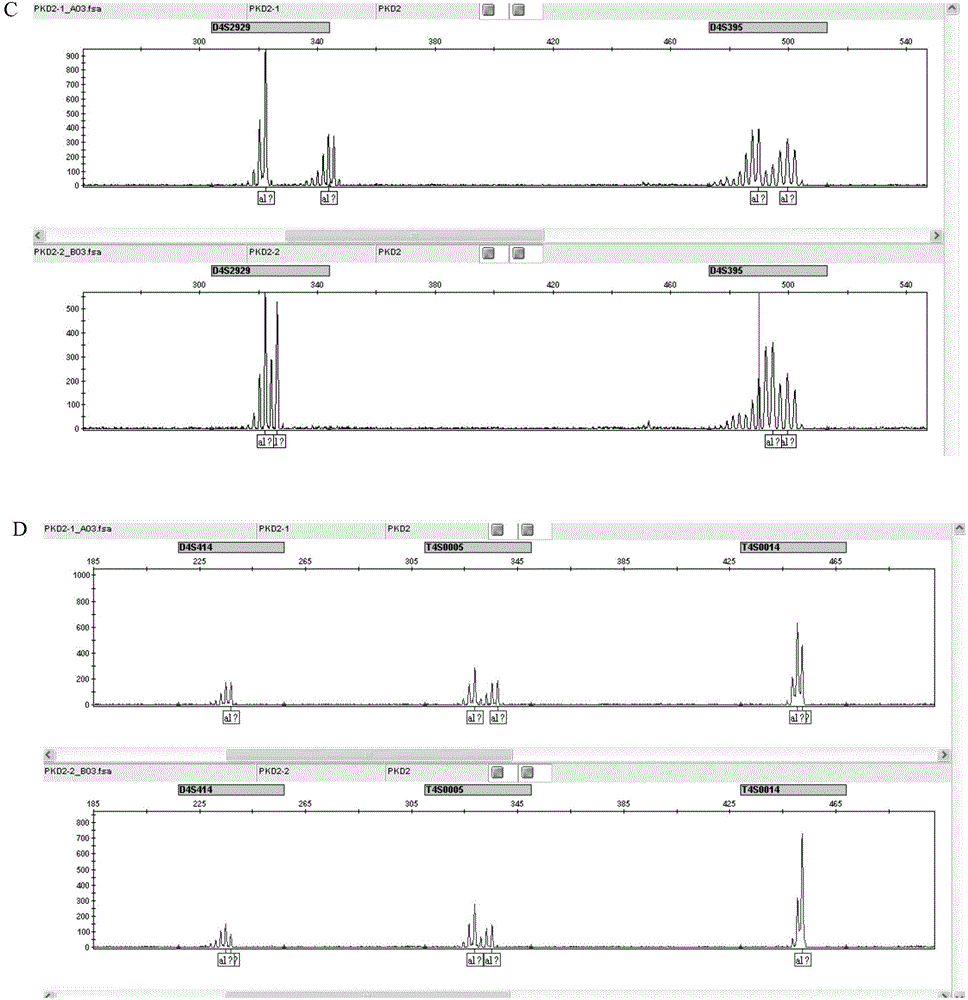
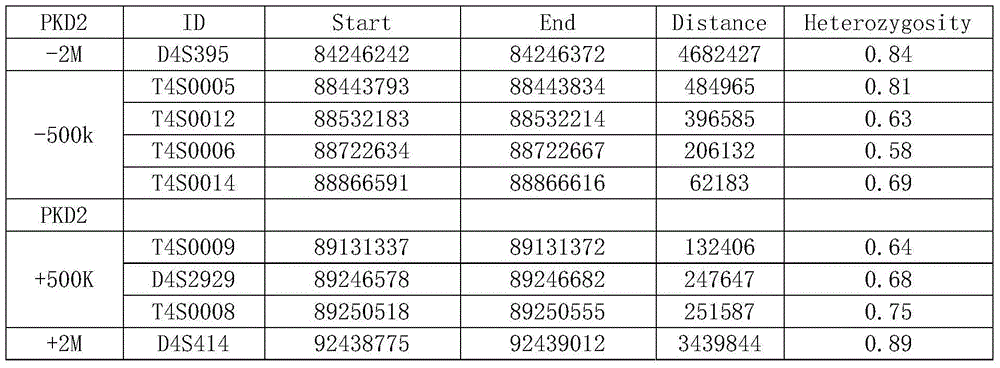
Amplification primer and detection method for pkd2 gene mutation detection
ActiveCN105886605BIncreased sequencing depthGood amplification effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInteinExon
The invention belongs to a technology of medical in vitro diagnosis, and in particular relates to an amplification primer for detecting mutation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease-causing gene PKD2 as well as a detection method. The amplification primer, in accordance with the sequence information of the PKD2 gene, designs four pairs of PCR primers; the PKD2 is subjected to targeted amplification by virtue of long-chain PCR; and an amplification region includes all exon sequences and most intron sequences, as well as partial 5' untranslated region sequences and 3' untranslated region sequences. According to the method, by combining long-chain PCR targeted amplification to the newest developed next generation of sequencing technology, a targeted sequencing process is simplified, the scope and flux of detecting the PKD2 gene mutation are improved, a detection cycle is shortened and cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING MATERNITY & CHILD HEALTH CARE HOSPITAL
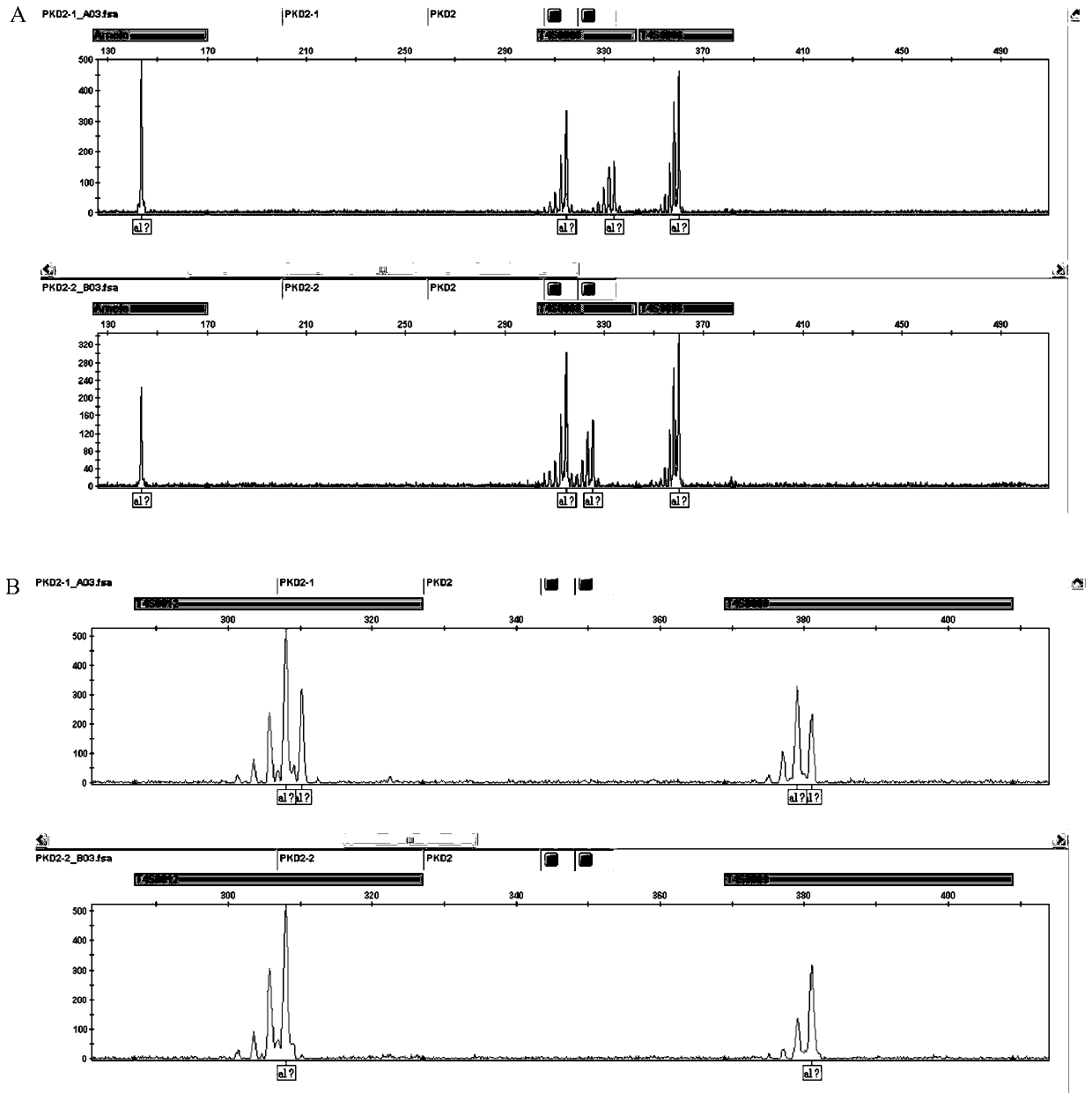
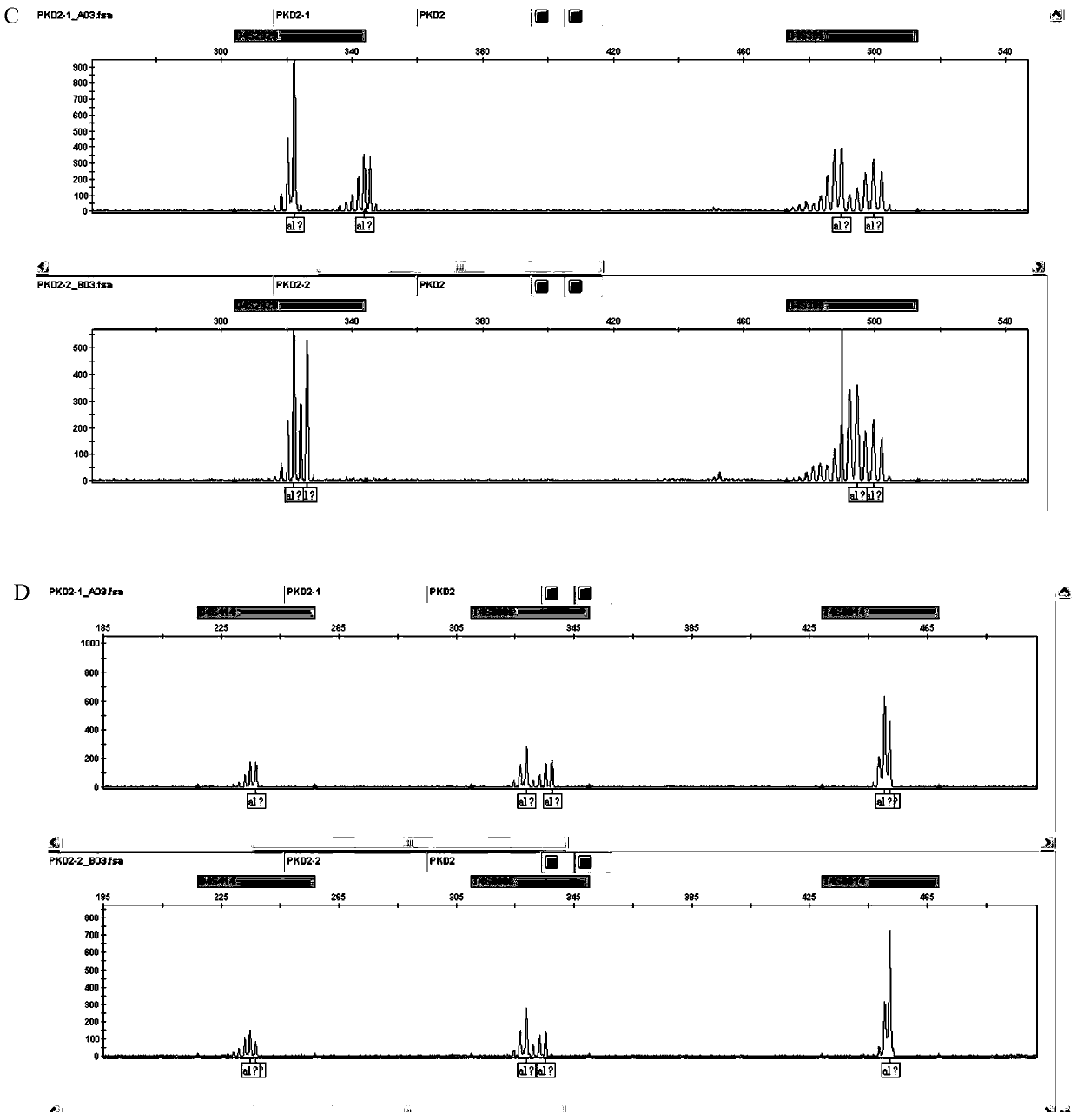
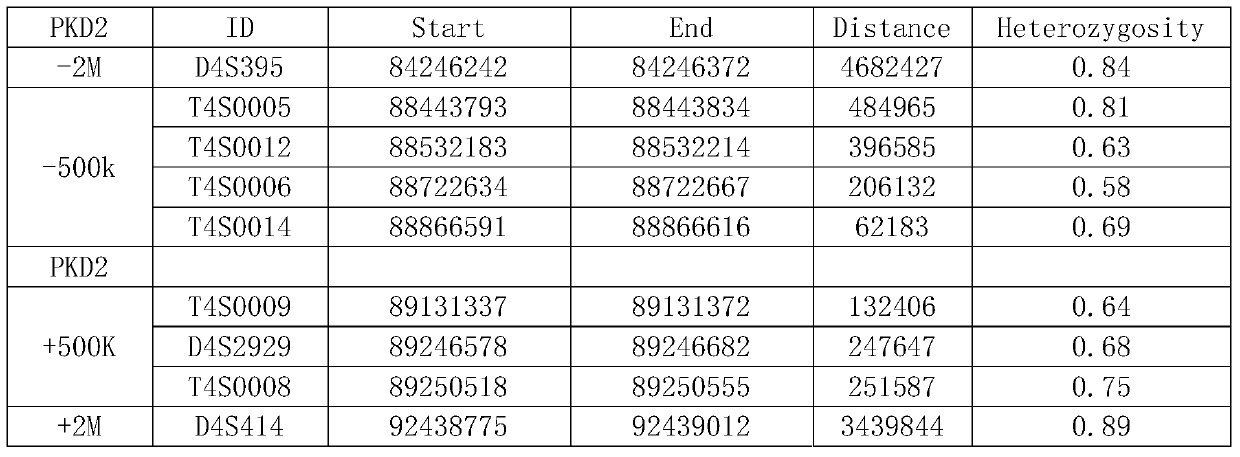
The str site of pkd2 gene and its application
ActiveCN106282171BWide range of choicesHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPrenatal diagnosisPhysiology
The invention discloses STR sites of a PKD2 gene. The STR sites are selected from nucleotide sequences as show in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.6. The invention also discloses an application of the STR sites of the PKD2 gene, wherein the STR sites are applicable to preimplantation genetic diagnosis or prenatal disgnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. The STR sites of the PKD2 gene are higher in resolution ratio; and the STR sites, when applied to linkage genetic analysis of the PKD2 gene, can significantly improve typing recognition efficiency and accuracy; therefore, a basis is provided for the clinical preimplantation genetic diagnosis of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:苏州天昊医学检验实验室有限公司
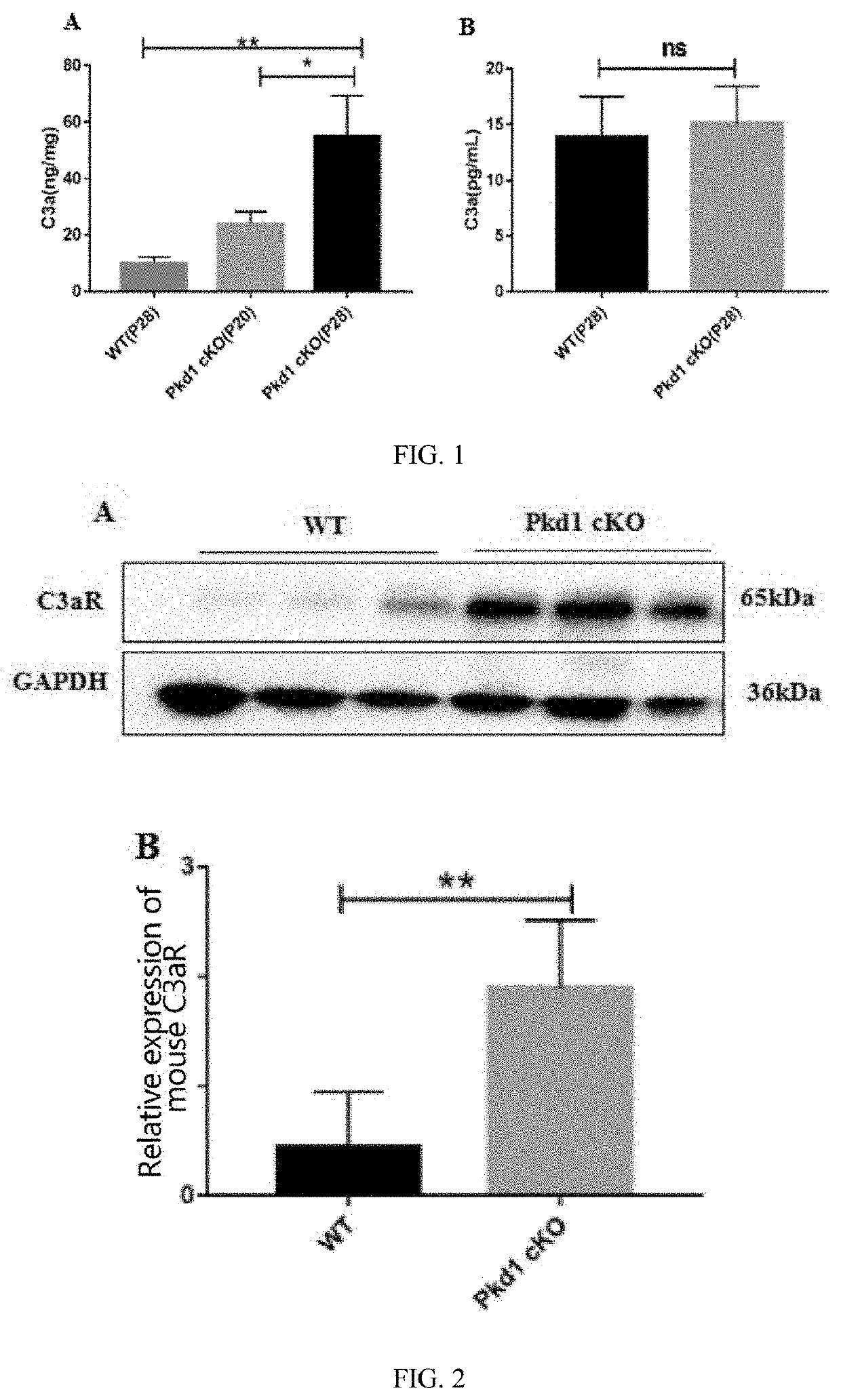
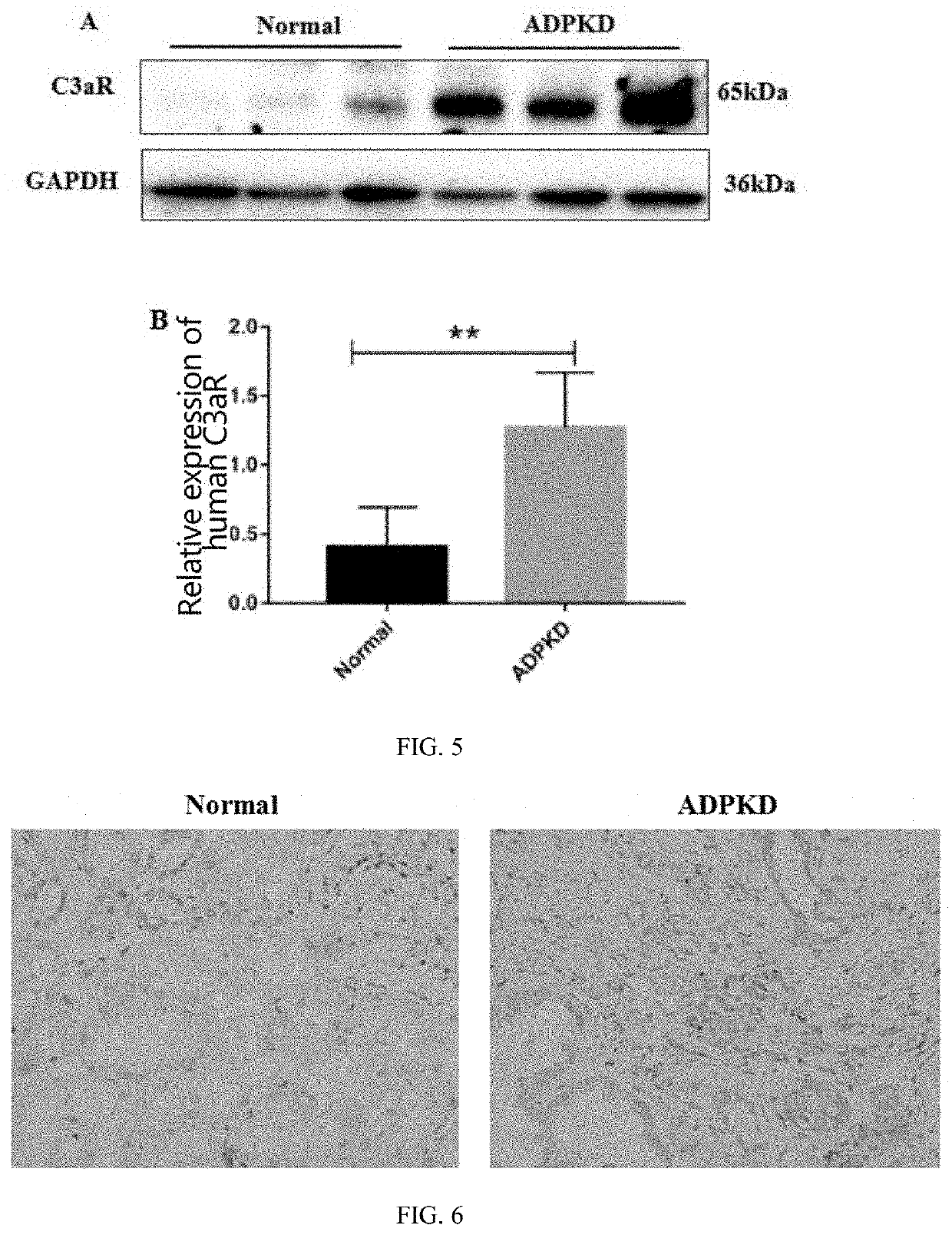
USE OF C3aR IN PREPARING DRUG FOR PREVENTING OR TREATING POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE
PendingUS20220287998A1Prevent proliferationBlocking chemotaxis of C3a-C3aROrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderPharmaceutical drugChemotaxis
The disclosure provides a use of C3aR in preparing drugs for preventing or treating polycystic kidney disease, belonging to the technical field of medicines. The disclosure discovers that C3aR inhibitor can down-regulate or reduce the C3aR level by inhibiting proliferation of cyst epithelial cells, blocking chemotaxis of C3a-C3aR on macrophages, inhibiting the interaction between C3a and C3aR, and expressing the p-ERK, p-P65 proteins, and then prevent cyst growth, improve the inflammatory state, thus treating polycystic kidney disease. The C3aR inhibitor can be used for the development of novel lead compounds for preventing or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, and also can be used for preparing drugs for preventing or treating polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
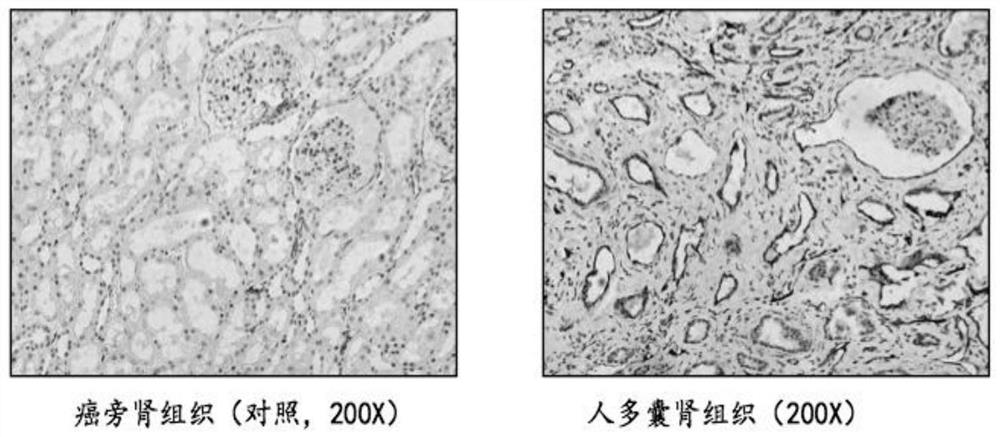
InactiveUS20150346150A1Prevent hypertrophic phenomenonShorten the progressSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementBacteriuriaPolycystic kidney disease
The process for the diagnosis, early detection and prognosis of the clinical development of autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) comprises the step of determining the presence or absence or amplitude of at least three polypeptide markers in a urine sample, the polypeptide markers being selected from the markers characterized in Table 1 by values for the molecular masses and migration times.
Owner:MOSAIQUES DIAGNOSTICS THERAPEUTICS AG (DE)
Application of cyclodextrin in preparation of medicine for treating and/or preventing polycystic kidney disease
InactiveCN112138019AInhibit expressionReduce sizeOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderGenes mutationCyclodextrin
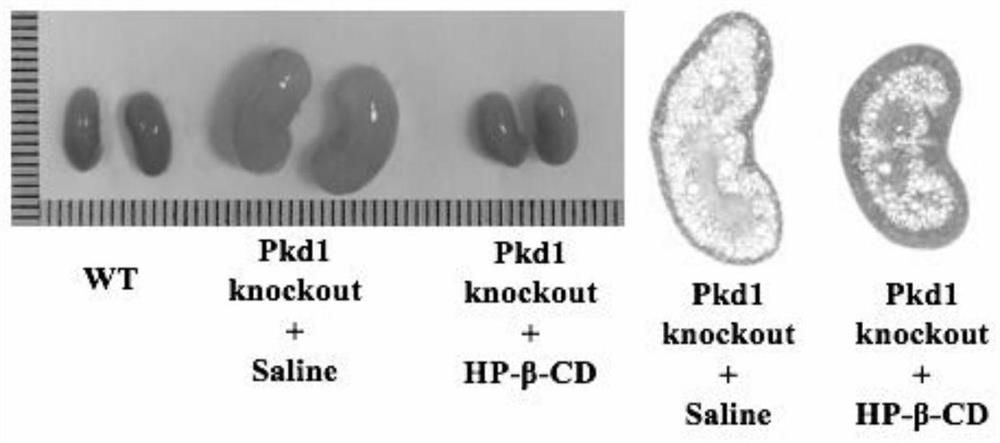
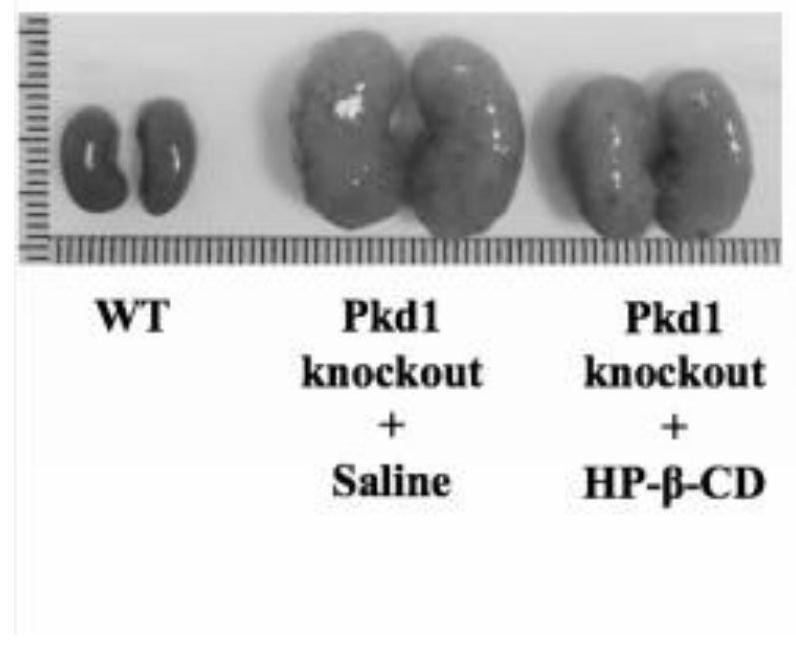
The invention provides an application of cyclodextrin in preparation of a medicine for treating and / or preventing polycystic kidney disease, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According tothe invention, an ADPKD model is applied to prove that after hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin removes a fossa structure on the surface of a polycystic kidney cyst tissue cell membrane, the expressionof caveolin-1 (CAV1) is reduced, so that the purpose of treating and / or preventing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease caused by gene mutation is achieved.
Owner:梅长林
Methods for treating polycystic kidney disease
ActiveUS9457016B2Block cyst formation and proliferationPromote growthOrganic chemistryAerosol deliveryPhysiologyPolycystic liver disease
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
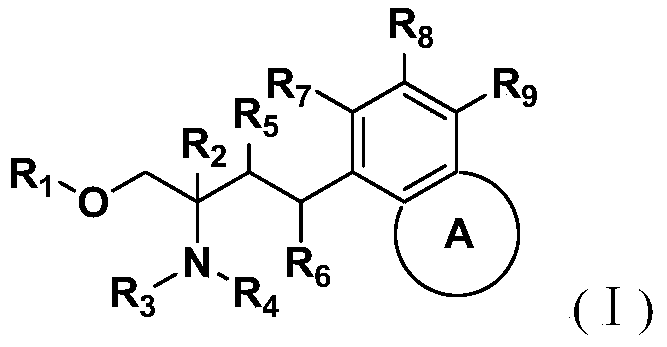
Amino alcohol compounds, their preparation methods, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and their uses
InactiveCN105017034BNovel structureEnhanced inhibitory effectCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAlcoholChemical compound
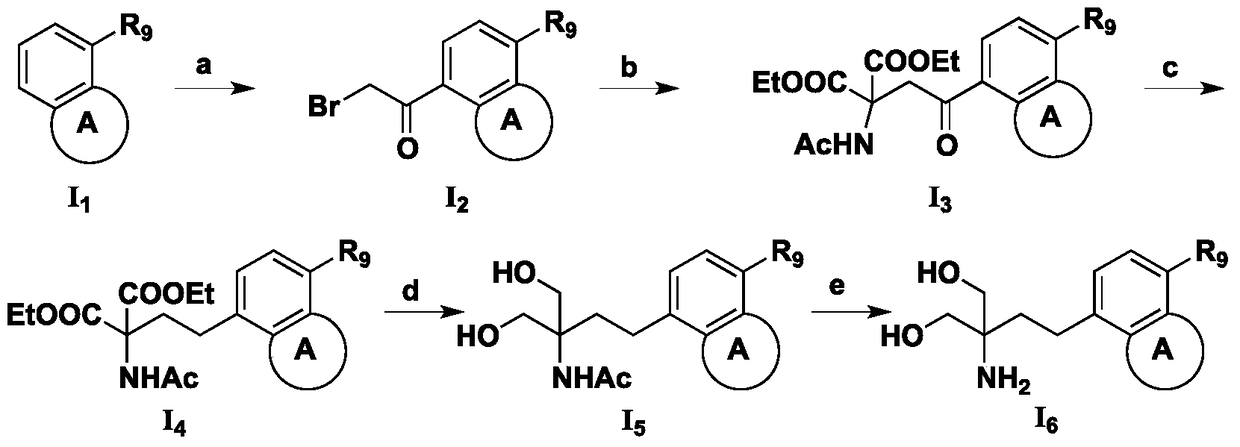
The invention discloses an aminoalcohol compound, its preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound and an application of the compound. The structure of the compound is as shown in the general formula (I), wherein A, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8 and R9 are as defined in the specification and the claims. The compound provided by the invention can be used in the preparation of drugs for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Method for diagnosing and treating predisposition for accelerated autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
InactiveUS20050064429A1Rapid and reliable and easy screeningShorten the progressSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologyGene
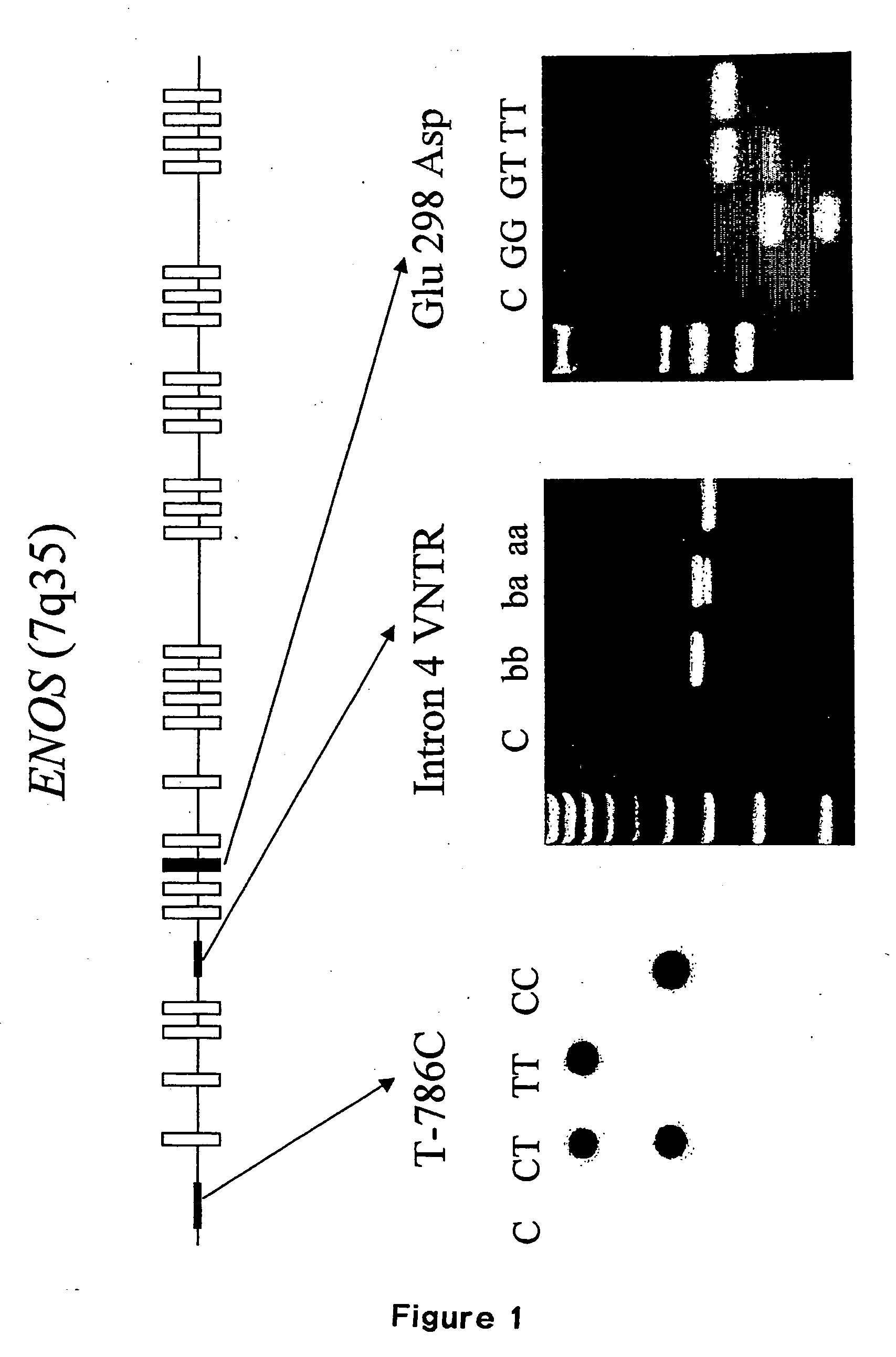
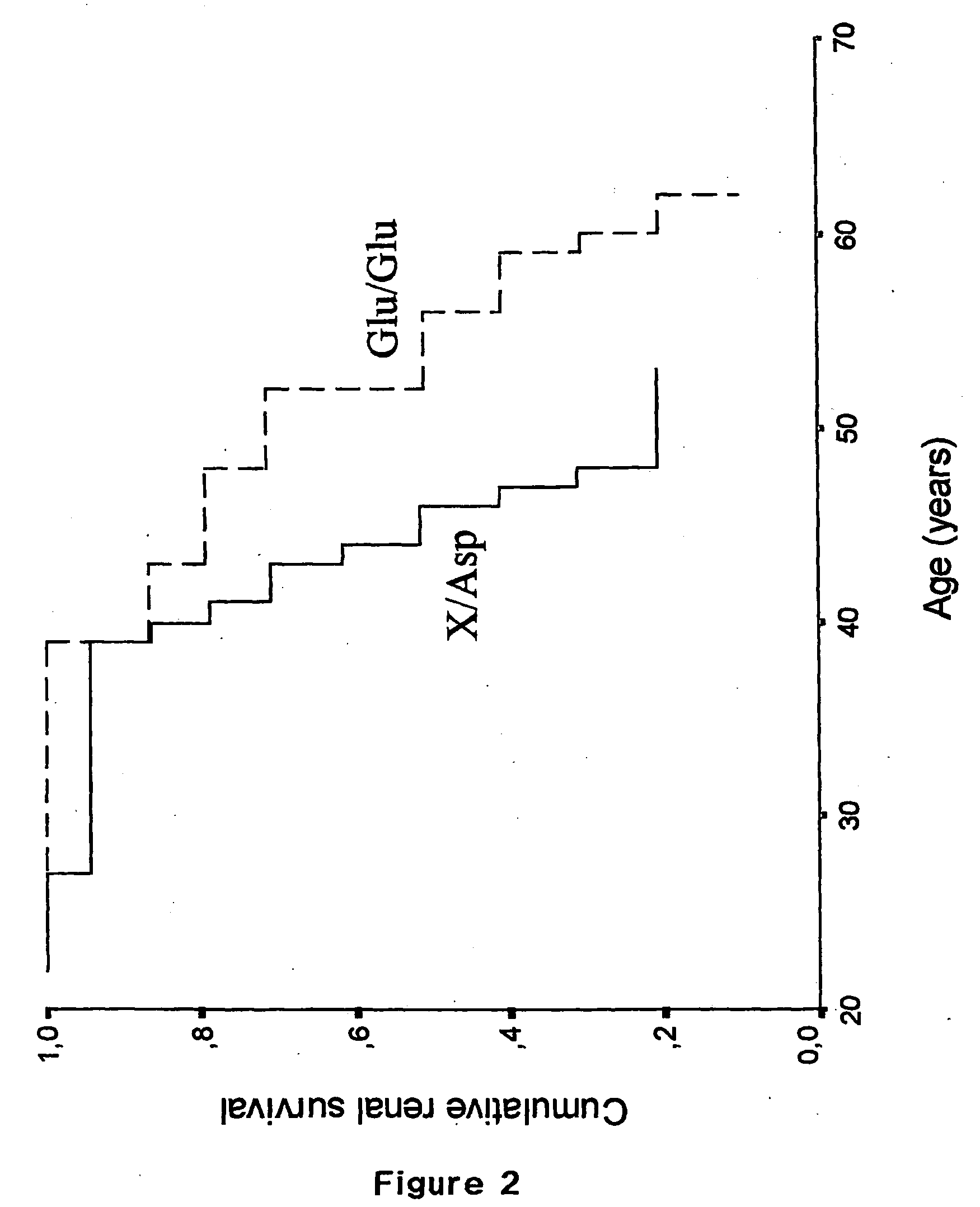
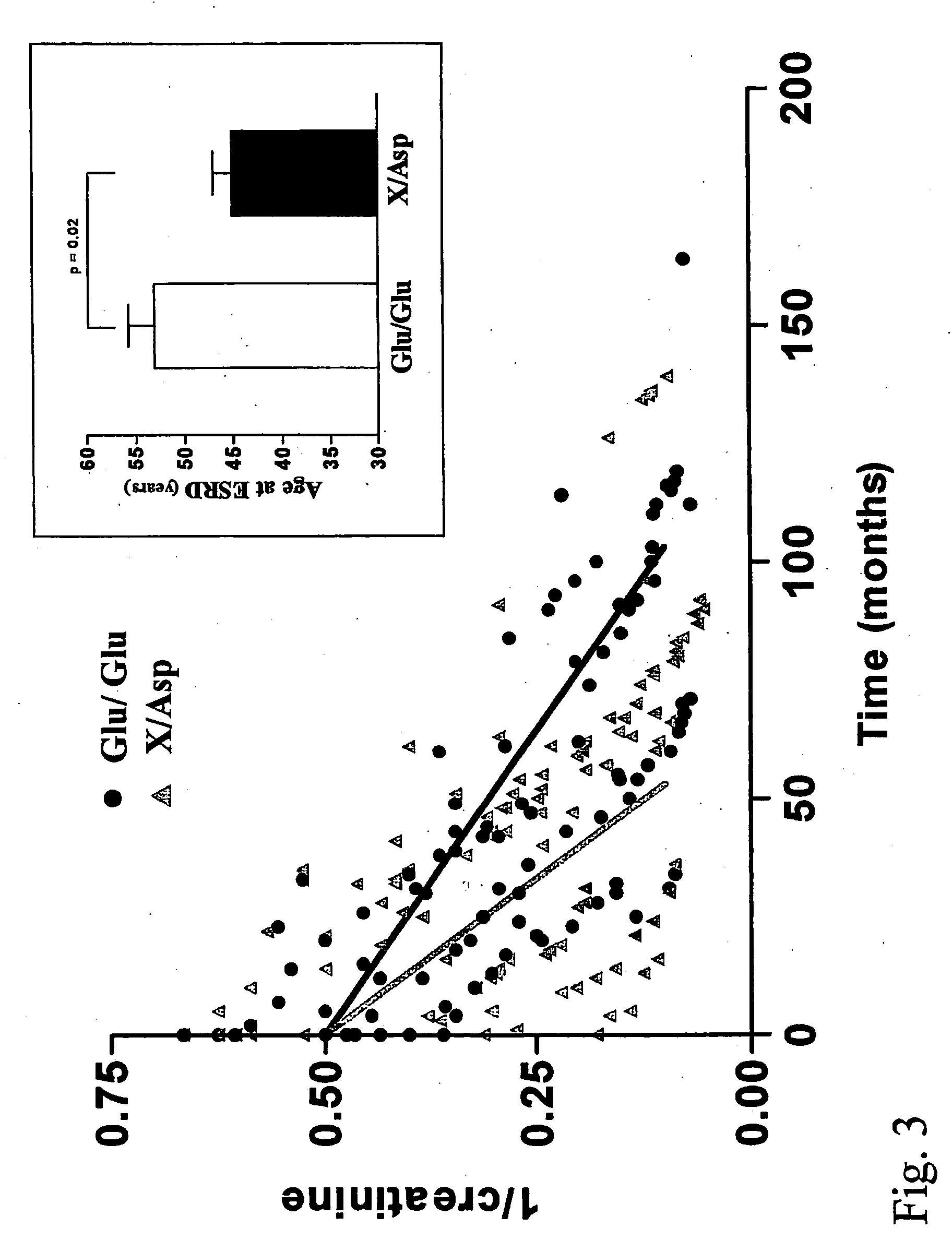
A method for diagnosing a predisposition for accelerated autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) in a human male subject by detecting the Glu 298 Asp polymorphism of the ENOS gene is described. A diagnostic kit for detecting predisposition for accelerated ADPKD in a human subject is also disclosed. In addition, a method for treating a human subject predisposed to develop accelerated APDKD using NO-enhancing compounds is provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Methods and compositions for treatment of polycystic kidney disease
InactiveUS20200392503A1Increase slowlySlows rate of decline of glomerular filtration rateSugar derivativesUrinary disorderOligonucleotideInternal medicine
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, using modified oligonucleotides targeted to miR-17.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
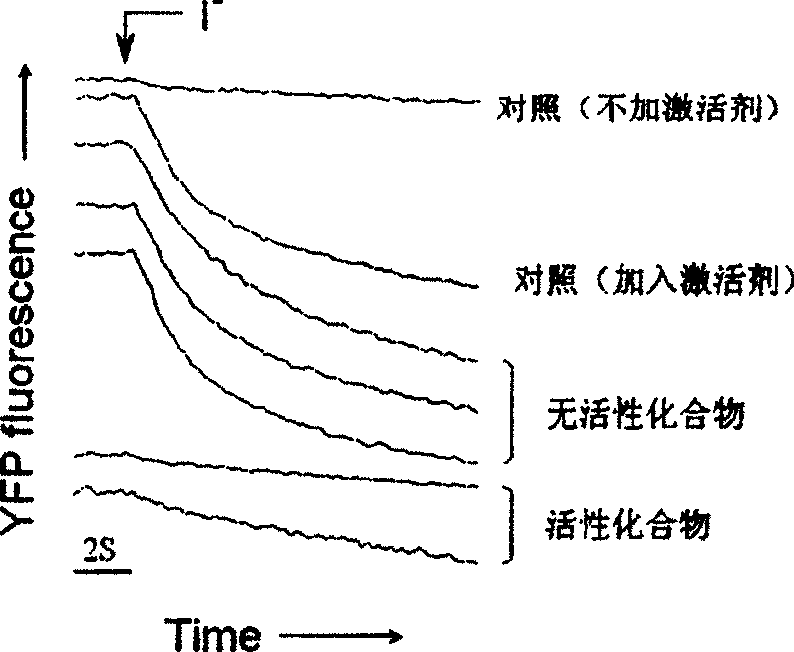
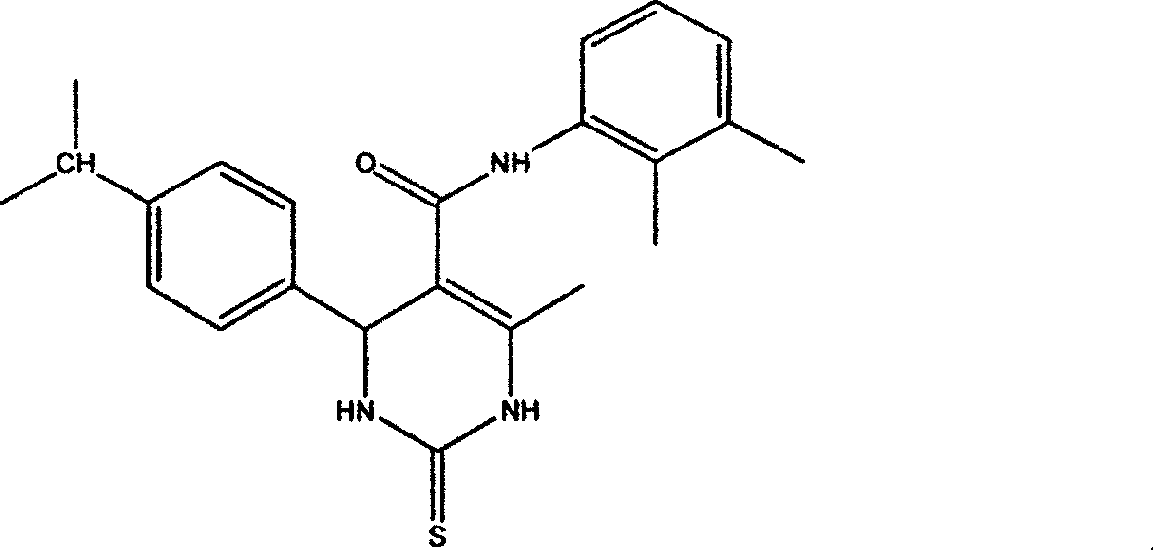
Application of pyrimidone compounds in preparing medicine
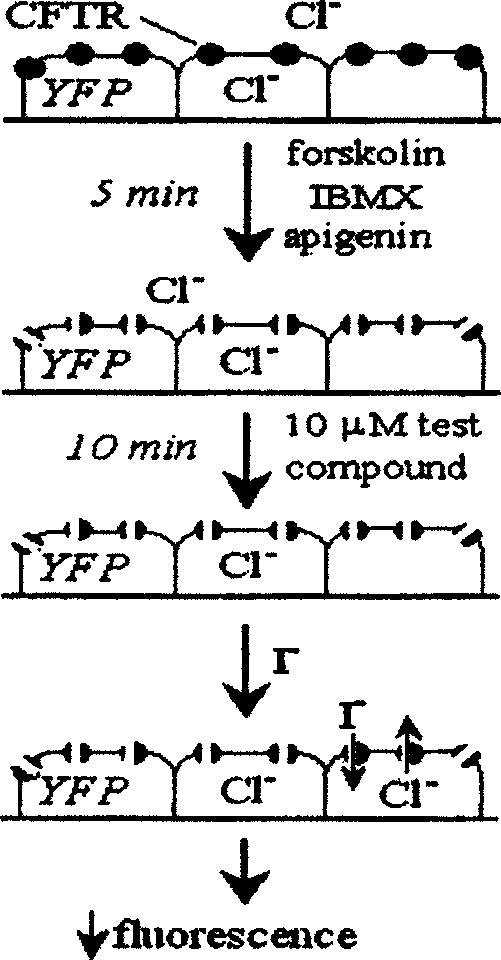
The invention relates to the application of pyrimidine (thio) ketone compounds in the preparation of medicines for treating secretory diarrhea and autosomal dominant hereditary polycystic kidney disease. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is a Cl-channel protein activated by cyclic adenosine monophosphate. During the design of the model, multiple activation pathways of CFTR were considered, and multiple activation pathways were combined to screen During the process, it binds at the Cl-transport channel. The application of pyrimidine (thio) ketone compounds in the preparation of drugs for treating secretory diarrhea and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is screened on the basis of screening a large number of compounds by using the model for screening inhibitors directly combined with CFTR. It can effectively prevent and treat the occurrence of swine diarrhea. Effectively inhibits fluid secretion from epithelial cells lining autosomal dominant polycystic kidney cysts. The inhibitory effect is rapid, and there is no obvious toxic effect.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
STR sites of PKD2 gene and application of STR sites of PKD2 gene
ActiveCN106282171AWide range of choicesHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPrenatal diagnosisNucleotide
The invention discloses STR sites of a PKD2 gene. The STR sites are selected from nucleotide sequences as show in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.6. The invention also discloses an application of the STR sites of the PKD2 gene, wherein the STR sites are applicable to preimplantation genetic diagnosis or prenatal disgnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. The STR sites of the PKD2 gene are higher in resolution ratio; and the STR sites, when applied to linkage genetic analysis of the PKD2 gene, can significantly improve typing recognition efficiency and accuracy; therefore, a basis is provided for the clinical preimplantation genetic diagnosis of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:苏州天昊医学检验实验室有限公司
Application of 1-indanone in preparation of medicine for treating or preventing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
ActiveCN111467331BInhibition formationGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderPharmacometricsPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides the application of 1-indanone in the preparation of medicine for treating or preventing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. The present invention uses the MDCK vesicle model to prove that 1-indanone can inhibit the formation and growth of vesicles, and determines the renal pharmacological activity of 1-indanone through the in vitro embryonic kidney vesicle model, which has a significant effect on the development of vesicles in the kidney. Finally, it was further proved in the polycystic kidney mouse model that 1-indanone also had the effect of inhibiting the occurrence and development of vesicles in vivo. The above-mentioned vesicle inhibitory effects in vitro and in vivo showed a dose-effect relationship.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
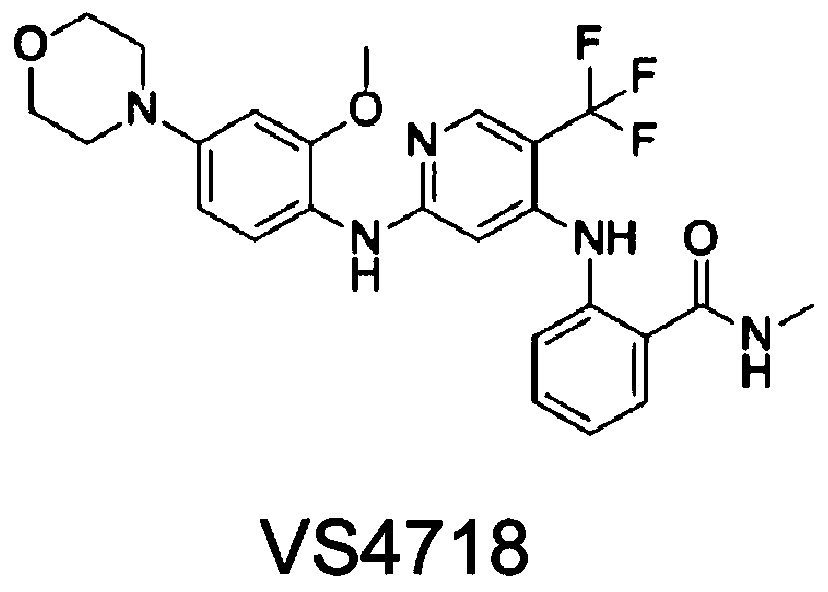
Application of FAK (focal adhesion kinase) inhibitor in treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
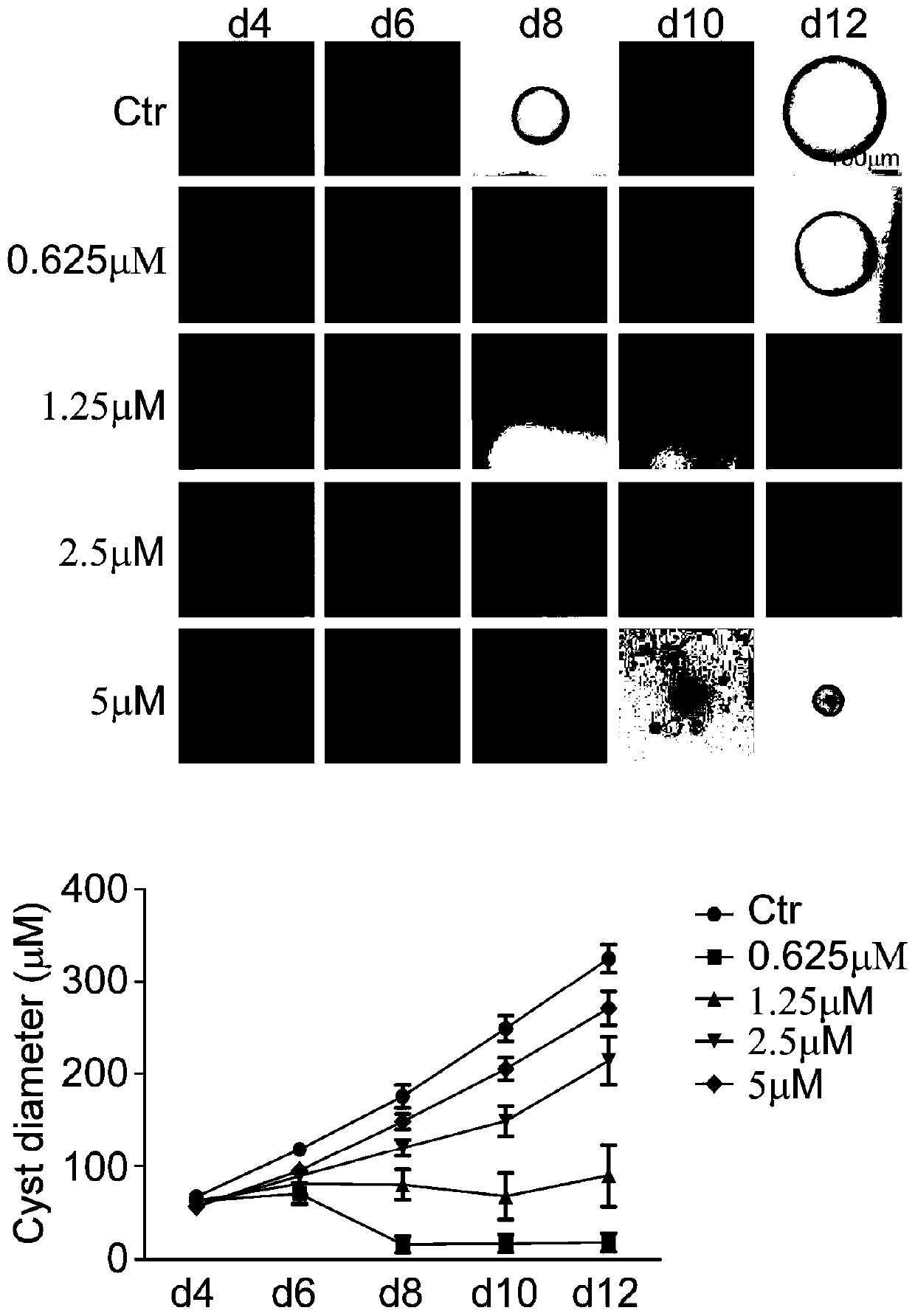
PendingCN110201171AInhibition formationGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderMadin Darby canine kidney cellFocal adhesion
The invention proves, through the application of an MDCK (Madin-Darby canine kidney cells) vesicular model, that an FAK (focal adhesion kinase) inhibitor can inhibit the generation and growth of vesicles, can determine intrarenal pharmacological activity of the FAK inhibitor through an in-vitro embryonal vesicular model, and can inhibit the progress of intrarenal vesicles significantly. The invention further proves finally, in a polycystic renal mouse model, that the FAK inhibitor can also inhibit the progress of vesicles in vivo, while the in-vitro and in-vivo vesicular inhibitory actions arein dose-effect relationship. The FAK inhibitor never affects the activity of renal cells; it is indicated that the ability of the FAK inhibitor to polycystic kidney is irrelevant to its cytotoxicity,and that the FAK inhibitor can regulate intracellular signal pathways, which may be one of its important mechanisms to inhibit the progress of renal vesicles. The FAK inhibitor is VS4718 which is suitable for treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com