Patents
Literature
43 results about "Focal adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cell biology, focal adhesions (also cell–matrix adhesions or FAs) are large macromolecular assemblies through which mechanical force and regulatory signals are transmitted between the extracellular matrix (ECM) and an interacting cell. More precisely, focal adhesions are the sub-cellular structures that mediate the regulatory effects (i.e., signaling events) of a cell in response to ECM adhesion.
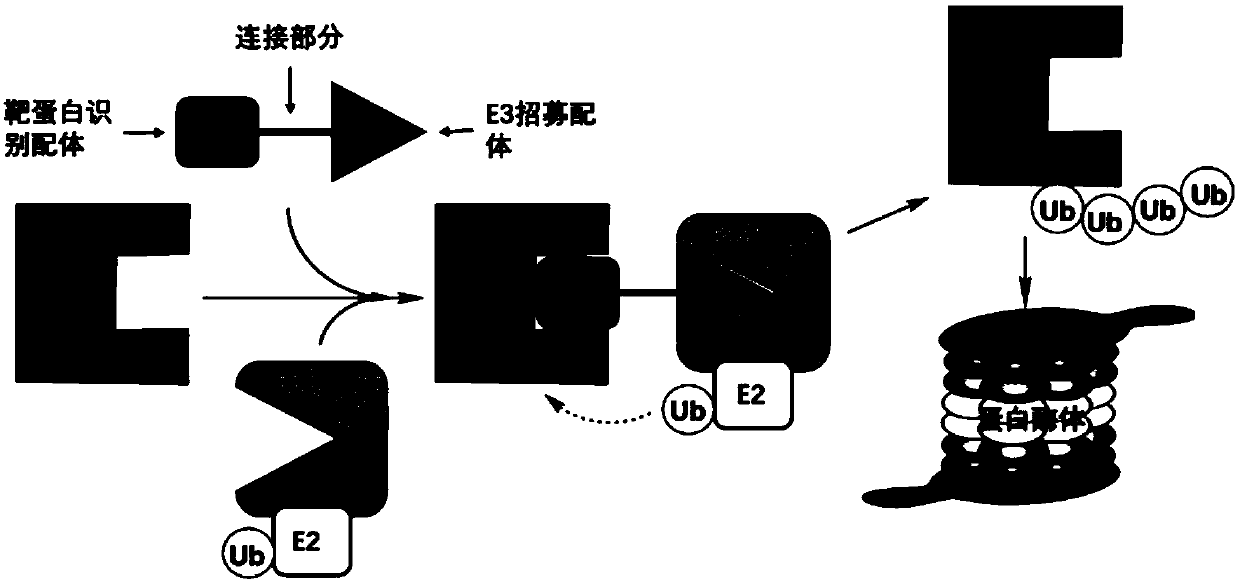
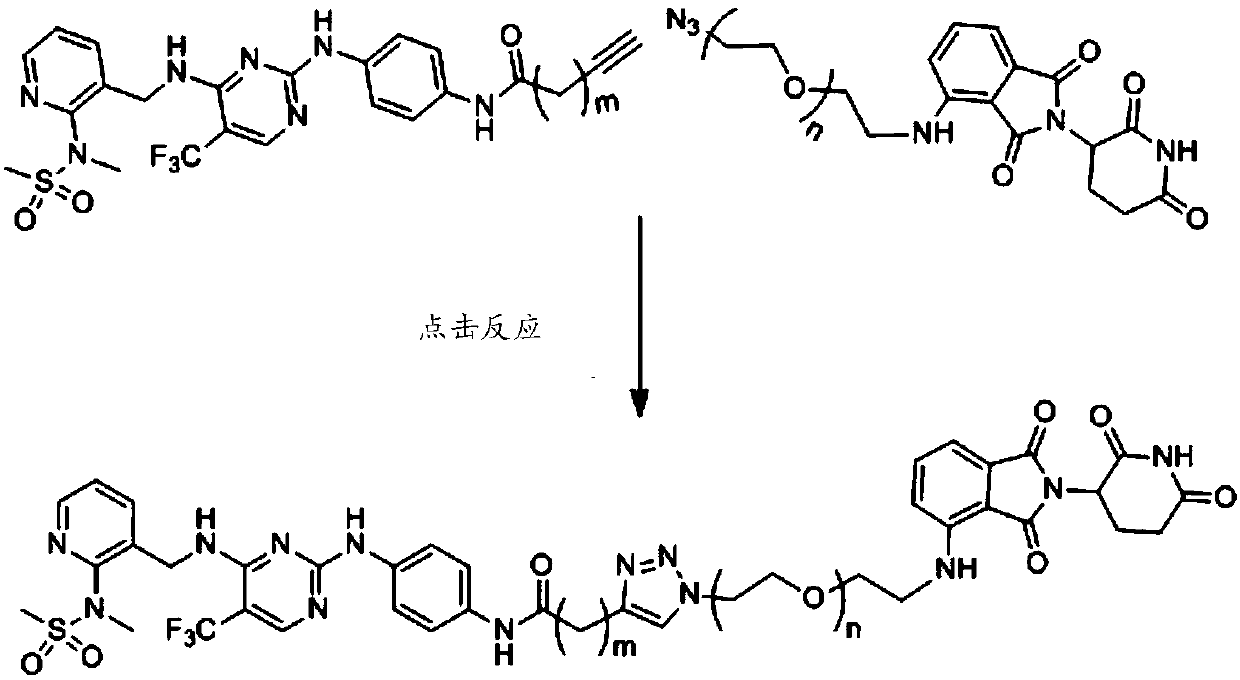
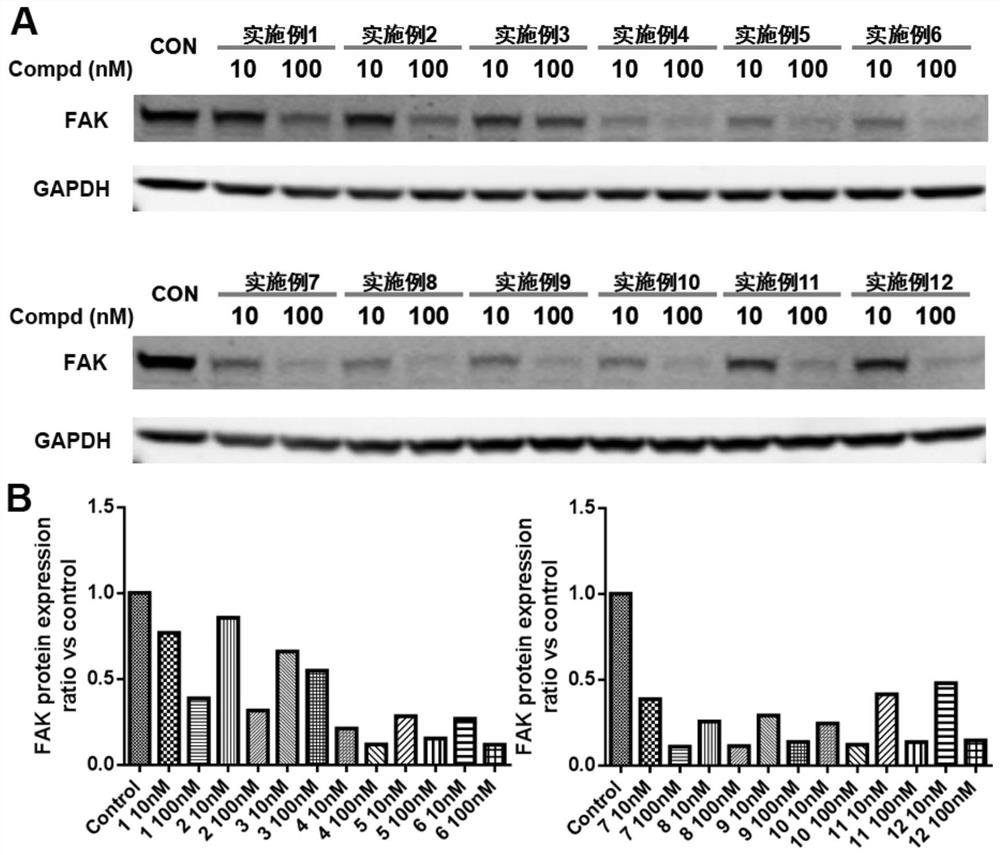
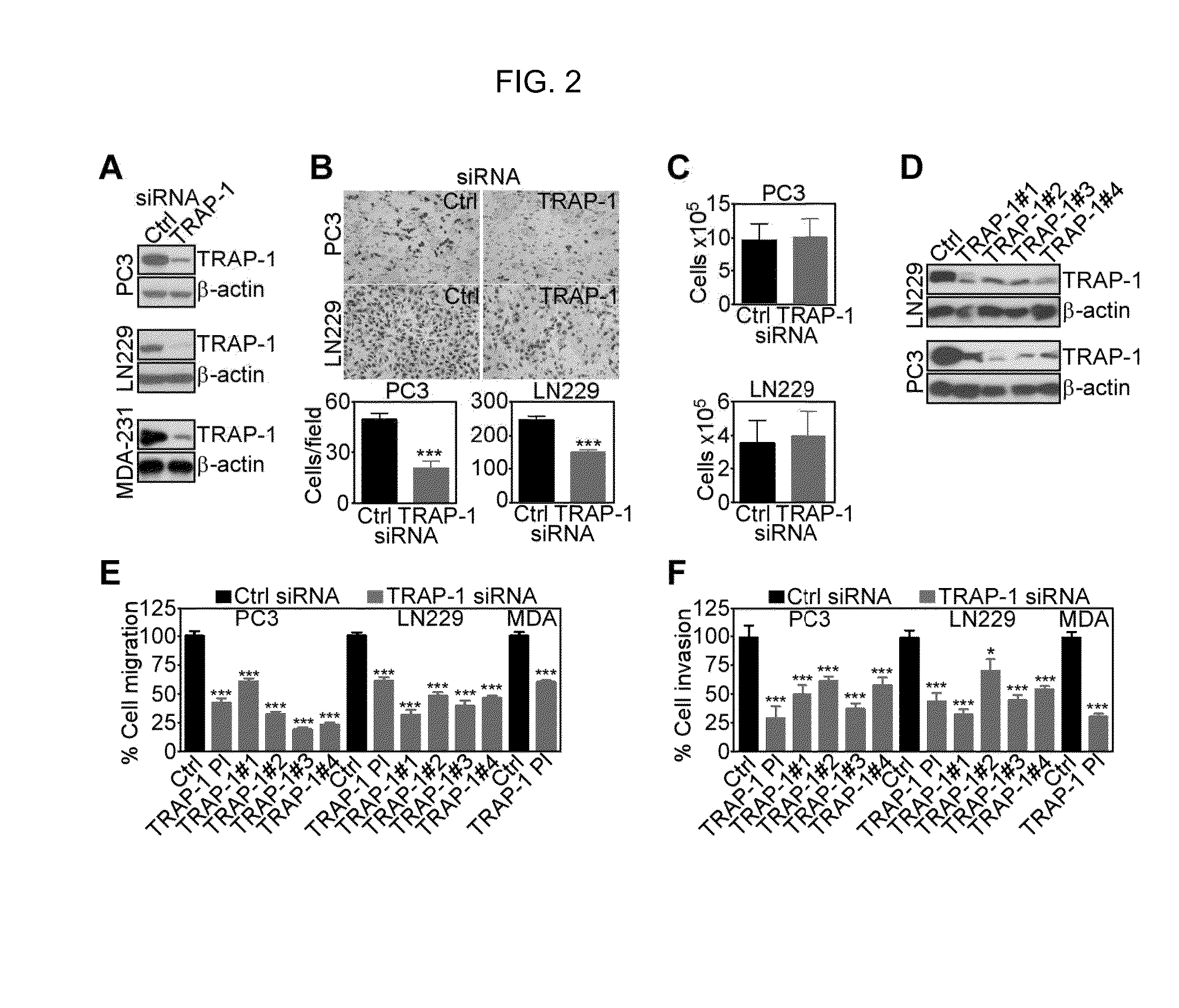
Compounds for targeted degradation of focal adhesion kinase and application of the compounds in medicine
InactiveCN111285851APromote degradationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseFocal adhesion
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine and drug synthesis, in particular to compounds for targeted degradation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) protein, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates or prodrugs of the compounds, preparation methods of the compounds and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates or prodrugs, and application of the compounds as therapeutic agents, especially as FAK degradation agents. The structures of the compounds, and the geometric isomers or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates or prodrugs thereof are shown inthe specification. The compounds provided by the invention have a good degradation effect on FAK kinase, and can be used for preventing, treating or adjunctively treating various diseases related tothe expression or activity of FAK kinase.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for treating cellular response to injury and other proliferating cell disorders regulated by hyaladherin and hyalurons
InactiveUS20050058646A1Inhibit cell proliferationPrevent proliferationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCancer cell
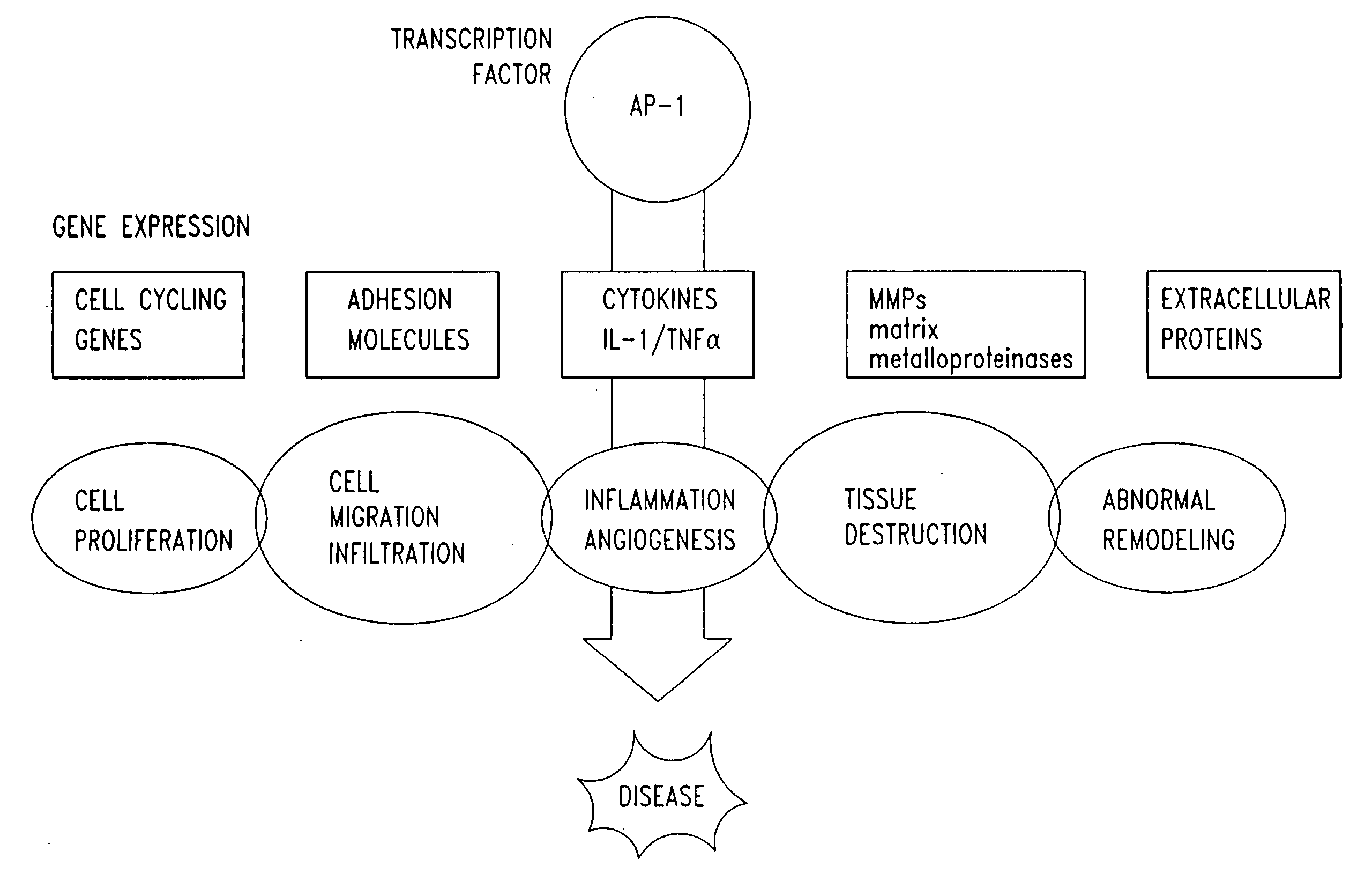
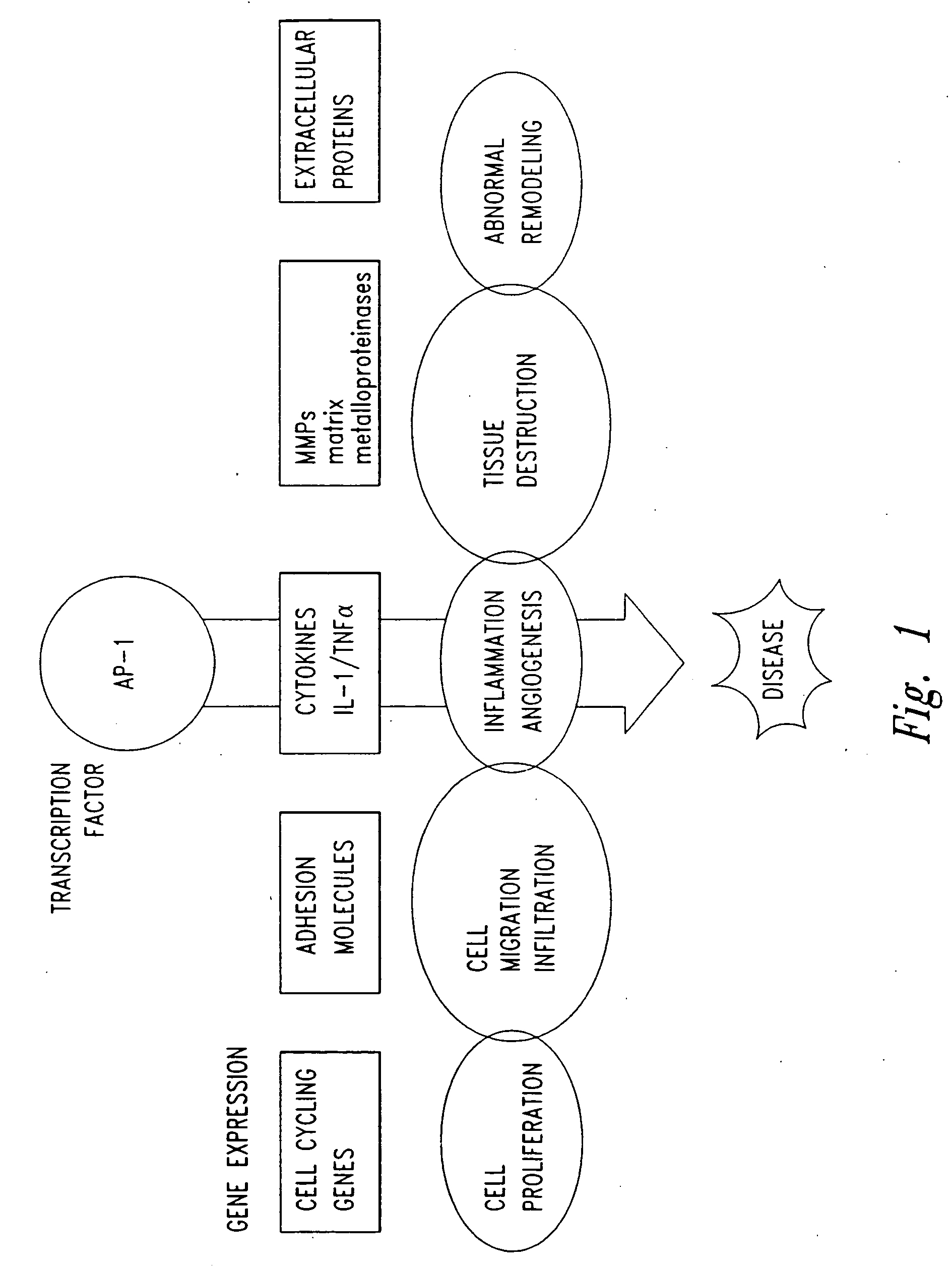
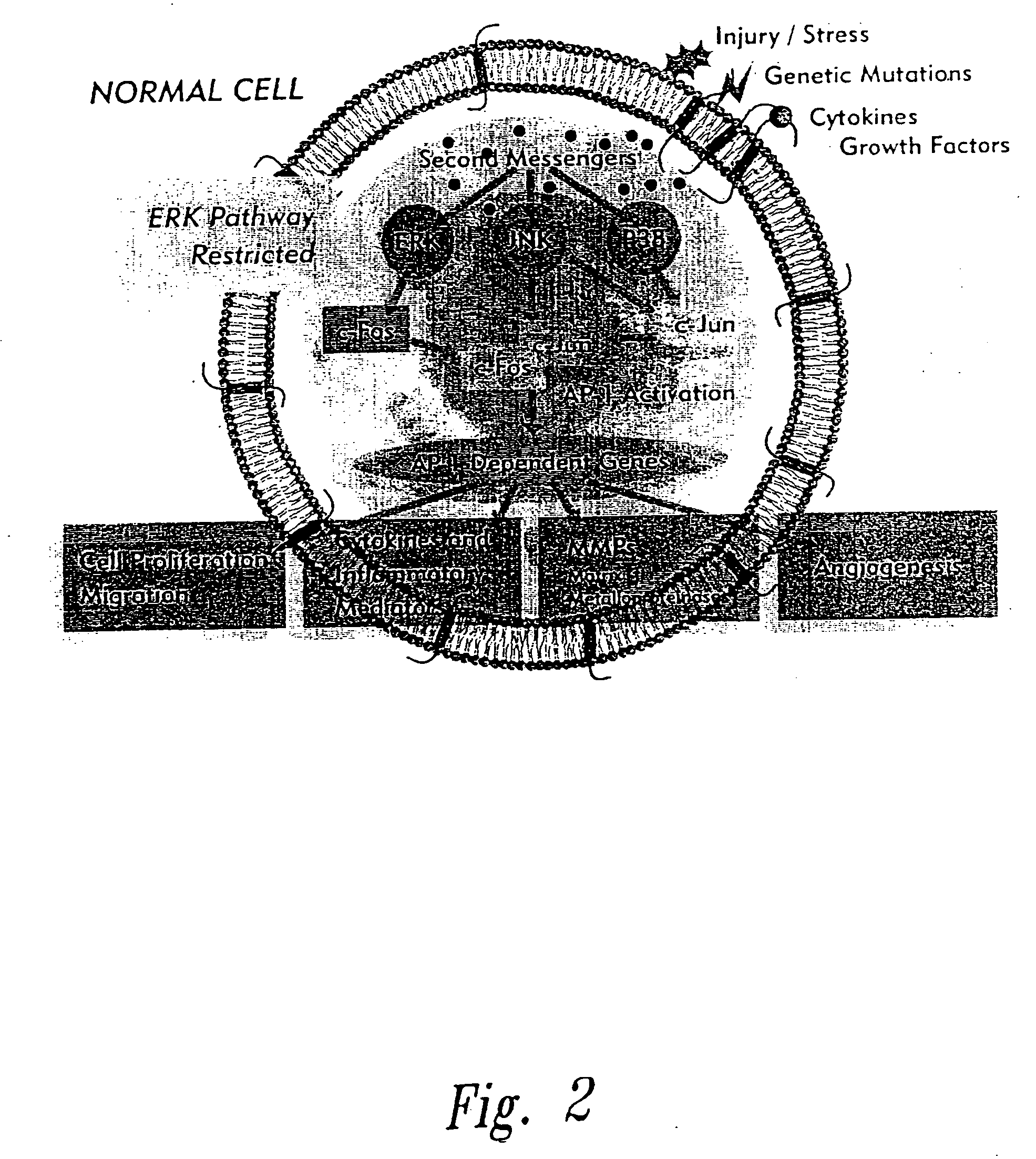
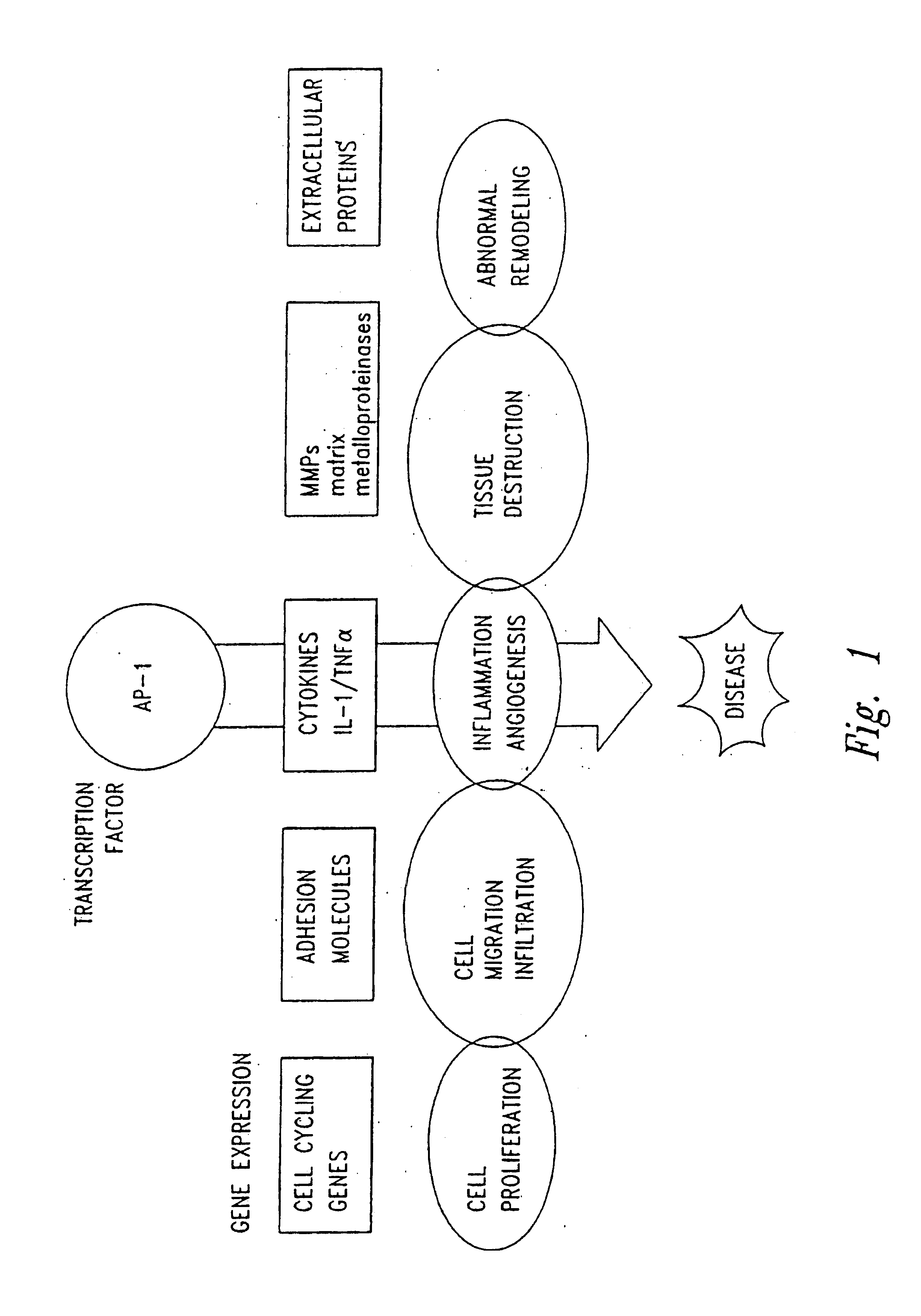
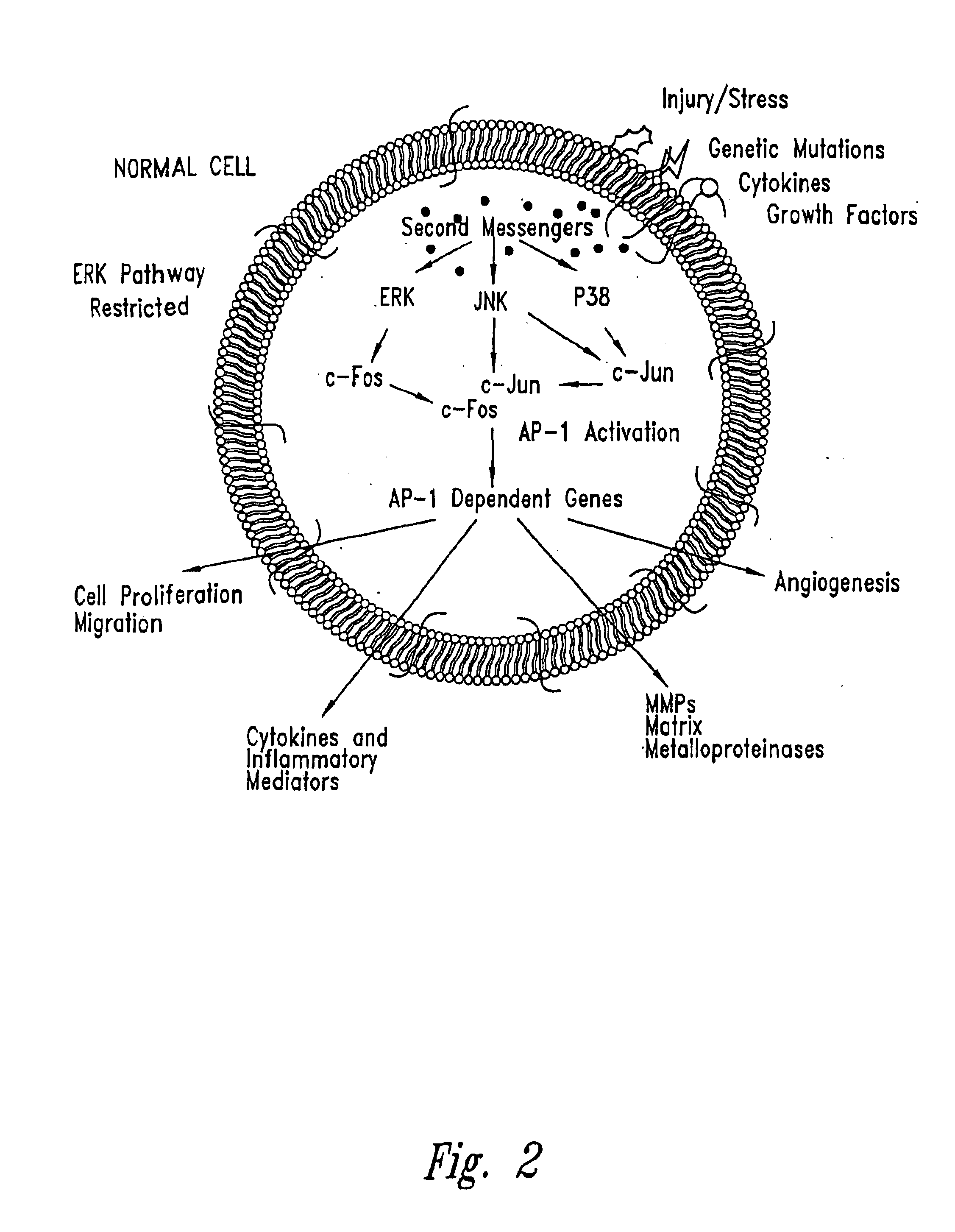
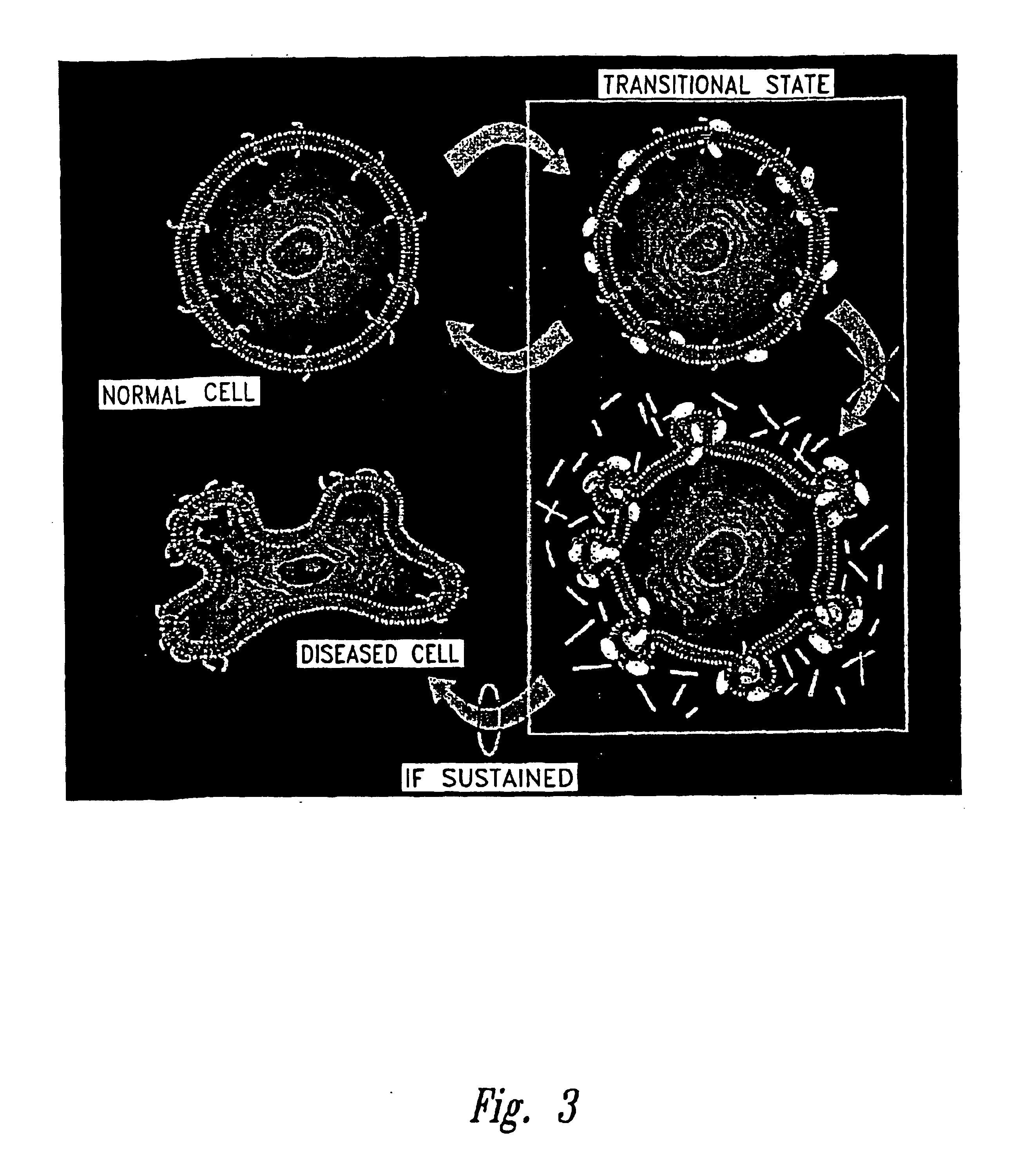
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating a tissue disorder associated with a response-to-injury process or proliferating cells in a mammal. These tissue disorders are associated with a novel cellular phenotype designated as “transition cells” which are described herein. This cellular phenotype is characterized in having an activated erk kinase signaling activity, a stimulated AP-1 binding activity, and at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of: (a) increased podosome formation, (b) increased flux of intracellular or extracellular hyaluronans or hyaladherins, (c) increased expression of a hyaladherin, (d) an inability to form focal adhesions, (e) increased metalloproteinase activity, and (f) increased expression of a hyaladherin. Example tissue disorders include fibrosis, inflammation, degeneration and invasive disorders such as occur in cancerous cells. The methods provided herein include administering to the mammal, an effective amount of a composition that alters the activity of transition molecules within a cell Transition molecules are shown to be comprised of hyaladherins, hyaluronans and associated molecules that regulate the transitional phenotype. A novel cell culture comprising transition cells is also provided, as well as compositions comprising particular peptides, polypeptides, and antibodies that affect the transitional phenotype.
Owner:TURLEY EVA +1
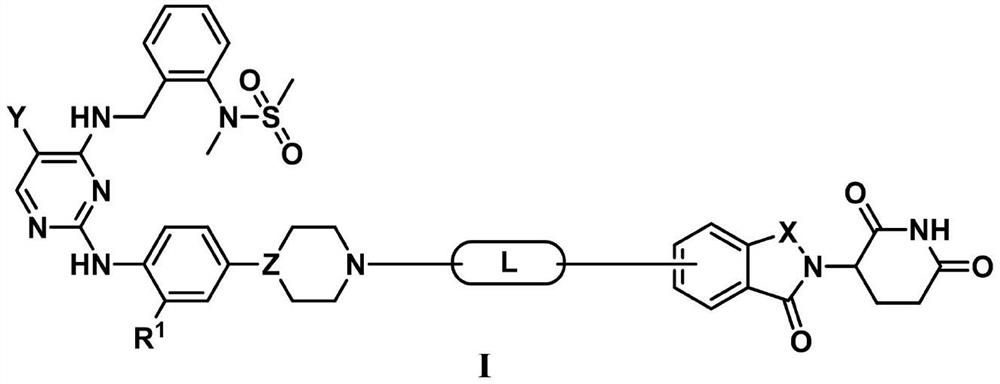
Compound for degrading FAK (Focal Adhesion Kinase) protein in targeting manner and application thereof
The invention provides a compound. The compound is a compound shown as a formula I or a stereoisomer, a geometric isomer, a tautomer, nitrogen oxide, hydrate, a solvate, a metabolic product, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or a prodrug thereof: X-Y-Z (formula I), wherein X represents a ligand of FAK protein, Z represents ligand of E3 ligase and Y represents a chain for connecting the X and the Z.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
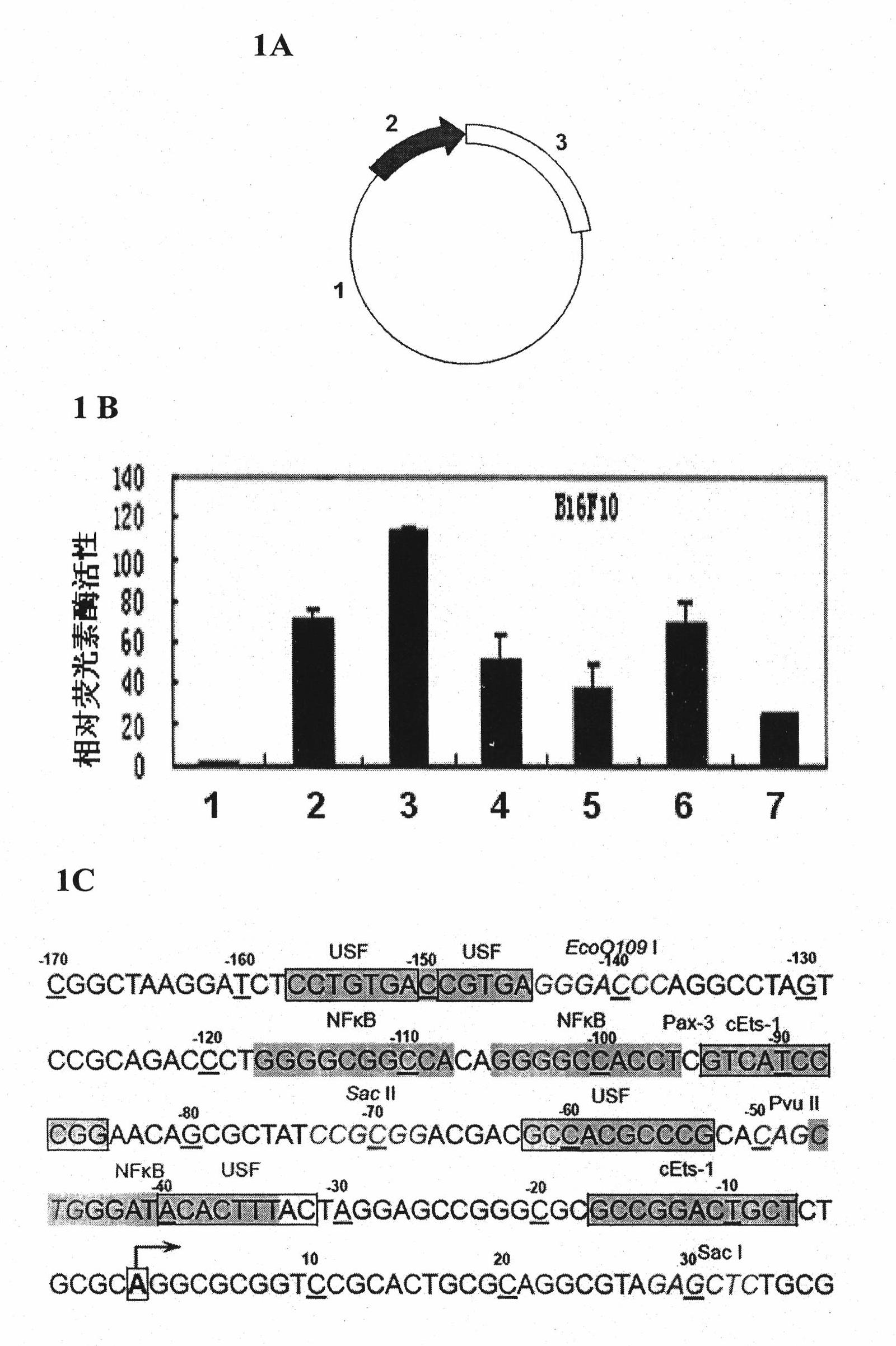
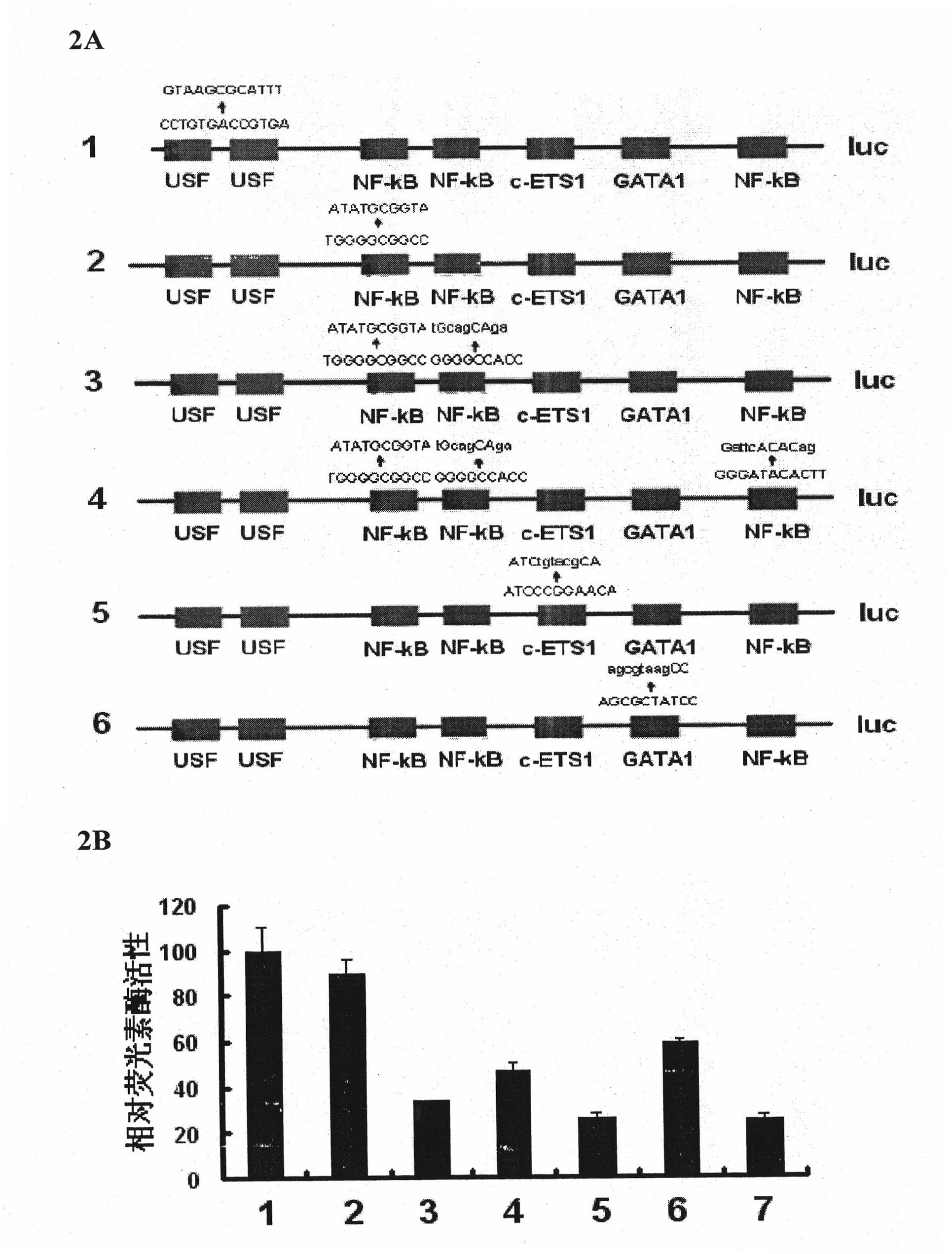
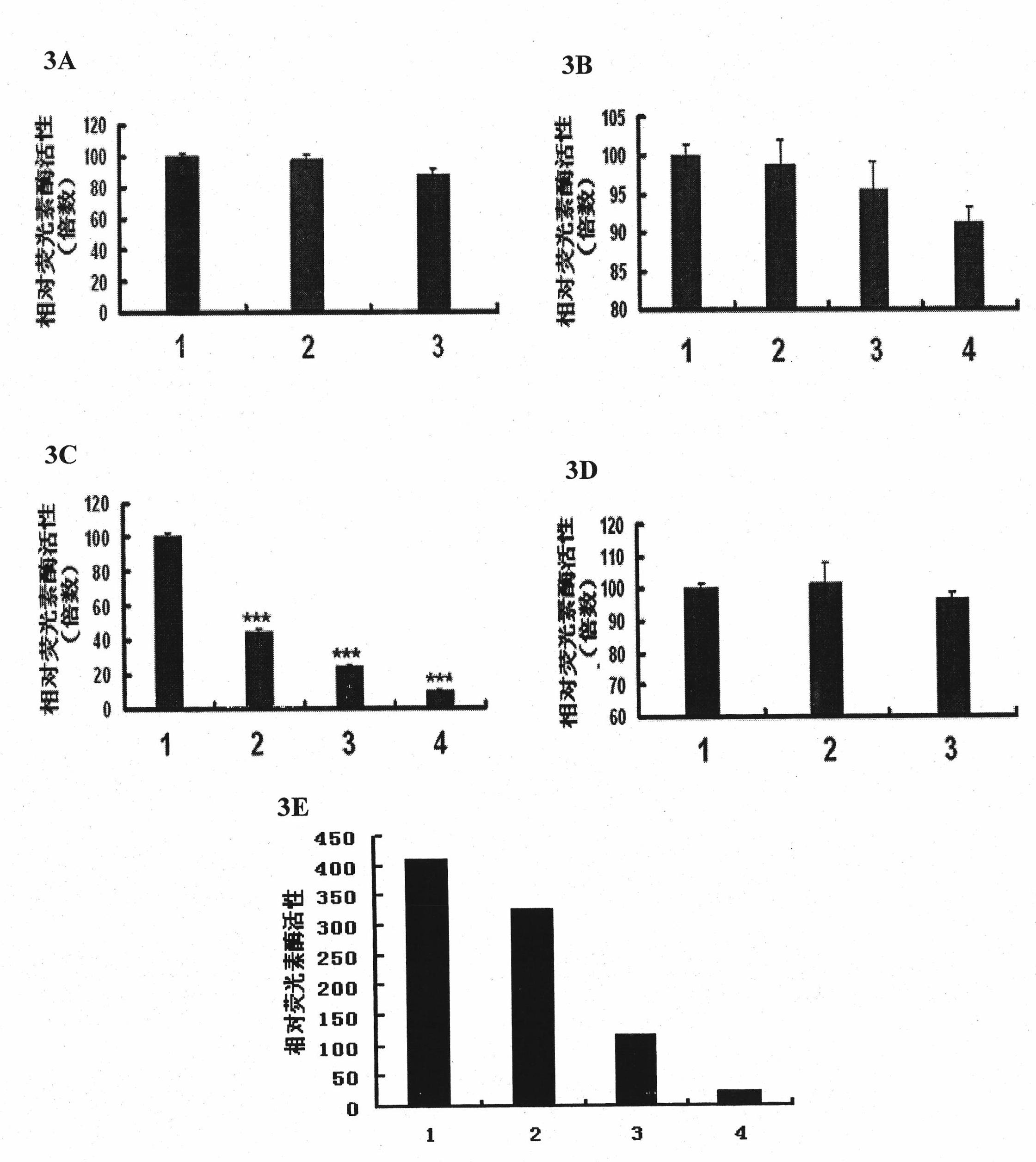
Method for screening medicament taking focal adhesion kinase (FAK) transcriptional regulation as target spot and application
InactiveCN101845481AEasy to useRich in natureMicrobiological testing/measurementFocal adhesionScreening method
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for screening a medicament taking focal adhesion kinase (FAK) transcriptional regulation as a target spot. The method mainly comprises the steps of: expressing a reporter gene in a tumour cell by an expression vector which contains an FAK promoter and the reporter gene driven by a core segment; and detecting an expression level of the reporter gene by using a cell model, and evaluating the regulation of the medicament for the FAK promoter and the influence on a cell function which is medicated by the FAK. By using the method, the medicament taking the FAK transcriptional regulation as the target spot can be screened, and a compound obtained by screening has the application prospect for preparing an anti-metastasis medicament.
Owner:JIANGSU TARGET BIOMEDICINE RES INST
Compositions and methods for treating cellular response to injury and other proliferating cell disorders regulated by hyaladherin and hyaluronans
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating a tissue disorder associated with a response-to-injury process or proliferating cells in a mammal. These tissue disorders are associated with a novel cellular phenotype designated as “transition cells” which are described herein. This cellular phenotype is characterized in having an activated erk kinase signaling activity, a stimulated AP-1 binding activity, and at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of: (a) increased podosome formation, (b) increased flux of intracellular or extracellular hyaluronans or hyaladherins, (c) increased expression of a hyaladherin, (d) an inability to form focal adhesions, (e) increased metalloproteinase activity, and (f) increased expression of a hyaladherin. Example tissue disorders include fibrosis, inflammation, degeneration and invasive disorders such as occur in cancerous cells. The methods provided herein include administering to the mammal, an effective amount of a composition that alters the activity of transition molecules within a cell Transition molecules are shown to be comprised of hyaladherins, hyaluronans and associated molecules that regulate the transitional phenotype. A novel cell culture comprising transition cells is also provided, as well as compositions comprising particular peptides, polypeptides, and antibodies that affect the transitional phenotype.
Owner:TRANSITION THERAPEUTICS INC
Compound for targeted degradation of focal adhesion kinase and application of compound
ActiveCN111892578APromote degradationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryGeometric isomerChemical compound
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and provides a compound represented by a general formula (I) and a geometrical isomer or pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, solvate and prodrug thereof, and preparation methods thereof. The compound has good degradation activity on focal adhesion kinase (FAK). The compound and the geometrical isomer thereof or the pharmaceuticallyacceptable salt, hydrate, solvate or prodrug thereof are represented by the general formula I, wherein Y, L, X, Z and R1 are shown in the claims and the specification.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
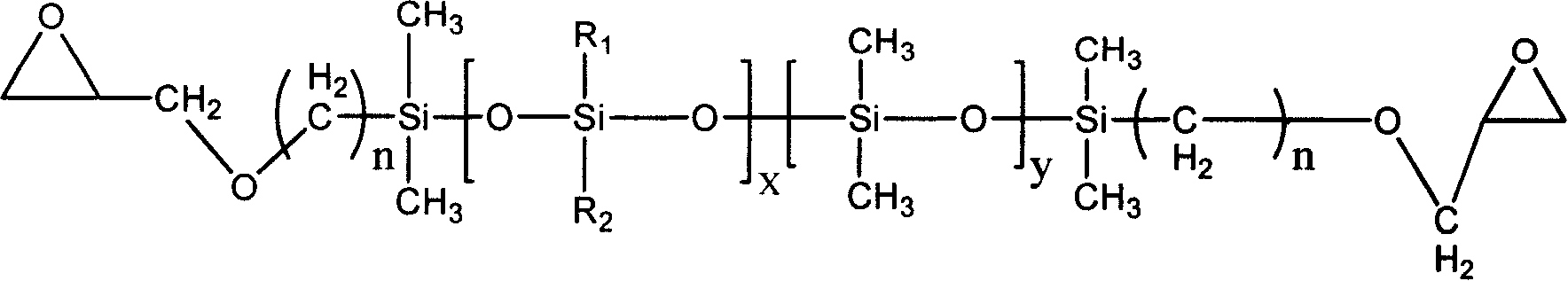
Non-conducting adhesion material composition
ActiveCN1990807ACircuit Conduction Structural BondingTight jointEpoxy resin adhesivesEpoxyOrganic solvent
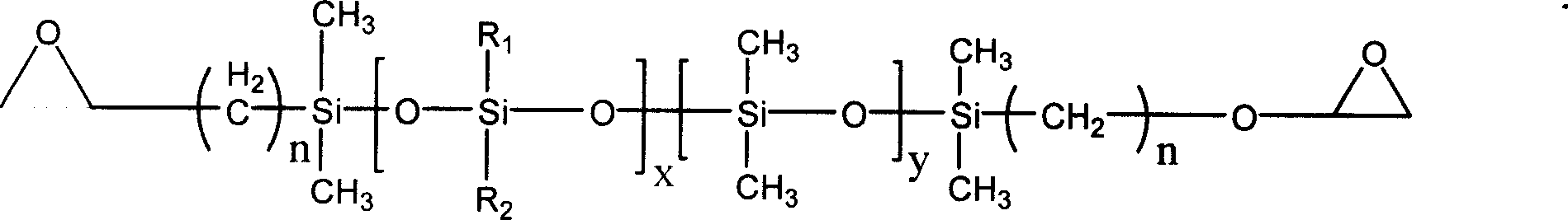
The invention relates to a non-conducting focal adhesion material, comprising following components: (a) at least one epoxy resin of non siloxane epoxy resin, and the epoxy equivalent weight is larger than 150 g / e and smaller than 3000 g / e; (b) siloxane epoxy resin, with the content being 10- 30 wt% of that of (a), and the epoxy equivalent weight is between 250- 1500 g / e; (c) imidazole or sclerosing agent of its derivative, with its content being 5- 15 wt% of the total weight of (a) and (b); (d) phenol compound catalyst, with the content being 1- 8 wt% of that of (a) and (b); (e) toughening agent, with the content being 5- 16 wt% of that of (a) and (b); and (f) organic solvent, with the content being 25- 55 wt5 of the total weight of (a) (b) (c) (d) and (e).
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Senolytic compounds
PendingCN110678187AHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsCyclic peptide ingredientsDiseaseNitrofurazone
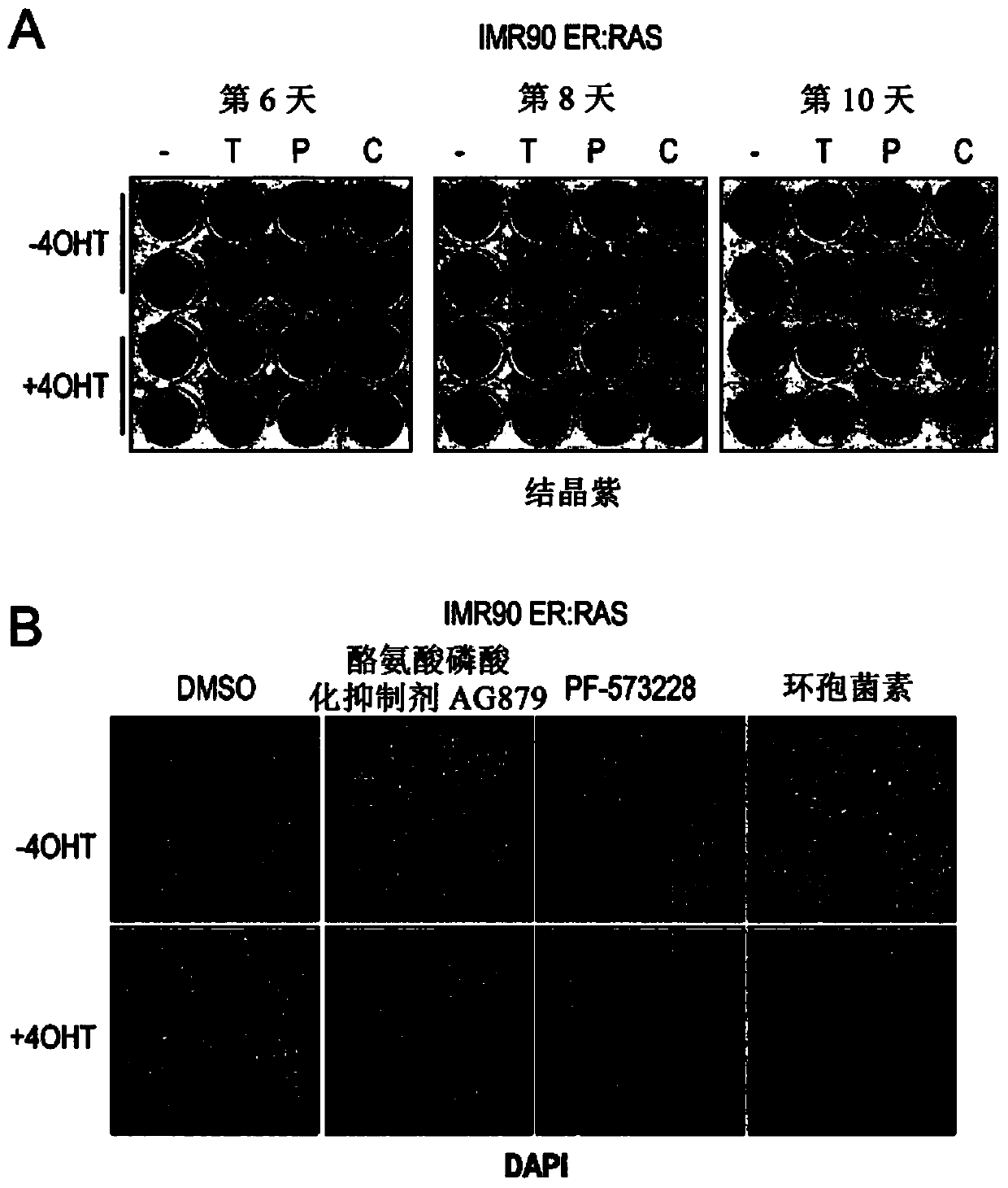
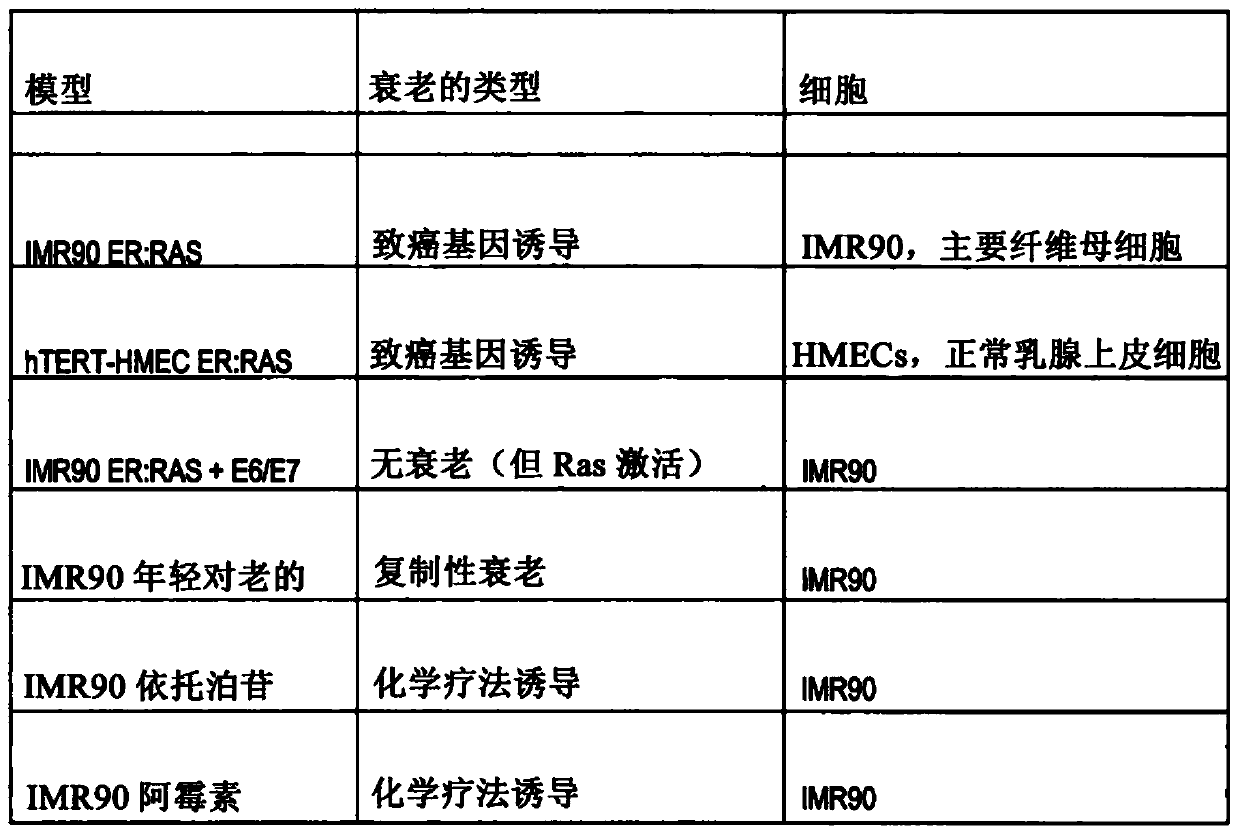
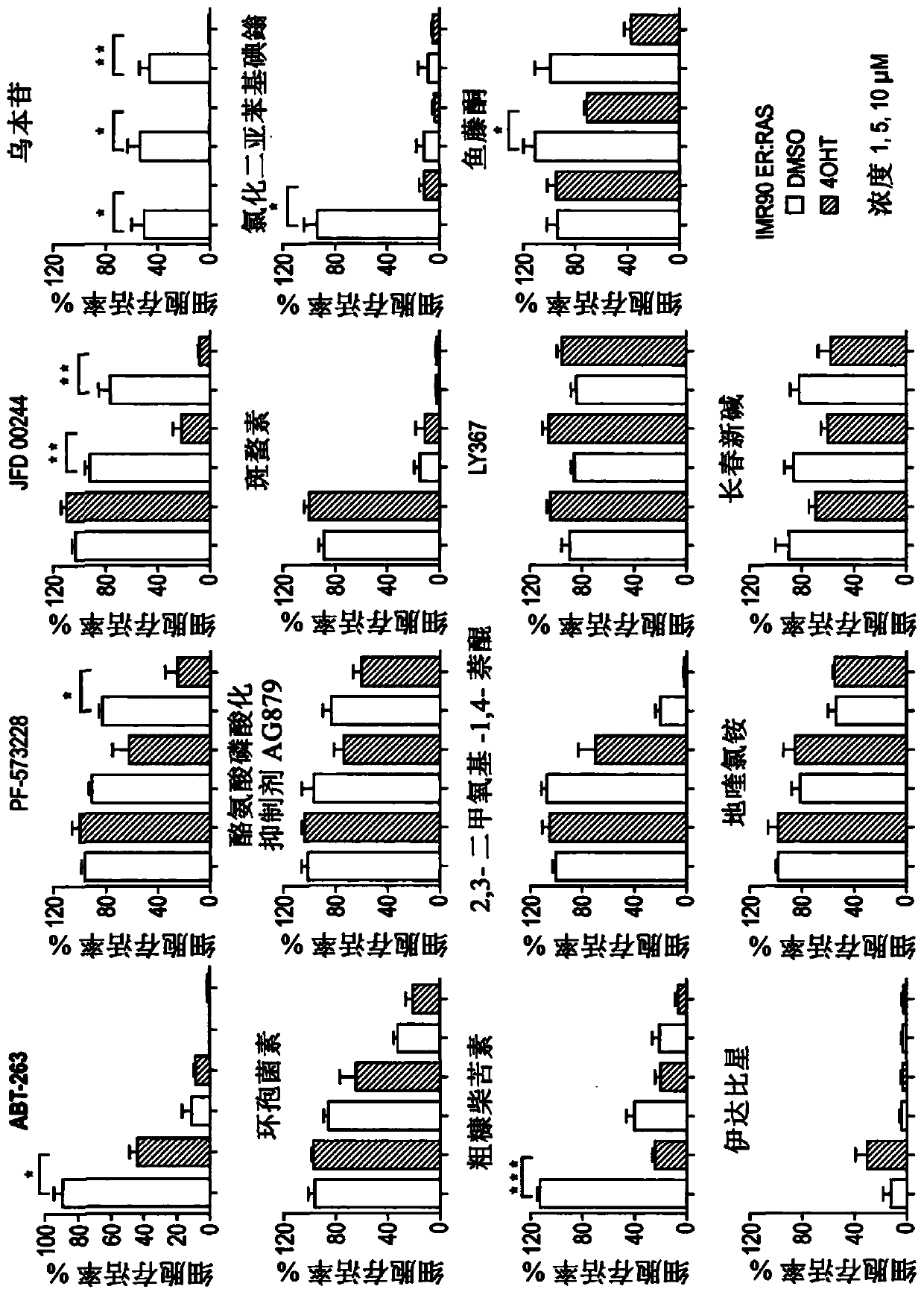
The present invention relates to an agent for use in selectively killing one or more senescent cells, wherein the agent is selected from the following: a cardiac glycoside or alglycone, a focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitor, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, JFD00244, Cyclosporine, Tyrphostin AG879, Cantharidin, Diphenyleneiodonium chloride, Rottlerin, 2,3-Dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, LY-367,265,Rotenone, Idarubicin, Dequalintum chloride, Vincristine, Nitazoxanide, Nitrofurazone, Temsirolimus, Eltrombopag, Adapalene, Azacyclonol, Enoxacin and Raltegravir, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Another aspect relates to compounds for use in treating or preventing a senescence- associated disease or disorder, and methods relating thereto.
Owner:英国研究与创新公司
Yeast extract, oligopeptide-1 and acetyl hexapeptide-1 V-shaped face stock solution capable of enabling faces to be compact in skin
InactiveCN109718194AGood treatment effectNo dependencyCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBetaineFocal adhesion
The invention discloses a yeast extract, oligopeptide-1 and acetyl hexapeptide-1 V-shaped face stock solution capable of enabling faces to be compact in skin. The yeast extract, oligopeptide-1 and acetyl hexapeptide-1 V-shaped face stock solution contains water, butanediol, glycerine, betaine, beta-glucan, a yeast extract, a bacillus fermentation product, oligopeptide-1,acetyl hexapeptide-1, a honey extract, a paeonia suffruticosa root extract, an arnica extract, an althea root extract, a tilia europaea flower extract, propylene glycol, hydroximic acid, glycerol caprylate, hydroxyacetophenone,DL-1,2-Hexanediol, Arabic gum, xanthan gum, glycerine, a wild soybean seed extract, sodium hyaluronate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt. The yeast extract, oligopeptide-1 and acetylhexapeptide-1 V-shaped face stock solution contains various natural plant extract essence, is prepared from a pure traditional Chinese medicine formula, is free from any hormones, can provide nutrients for skin and muscle, can promote cell energy, can enable the skin to be compact, can strengthen skin cohesion, and can strengthen focal adhesion. The yeast extract, oligopeptide-1 and acetyl hexapeptide-1 V-shaped face stock solution is natural, mild, good in safety and notable in V-shaped face effect of enabling the skin to be compact.
Owner:广州珈源日化用品有限公司
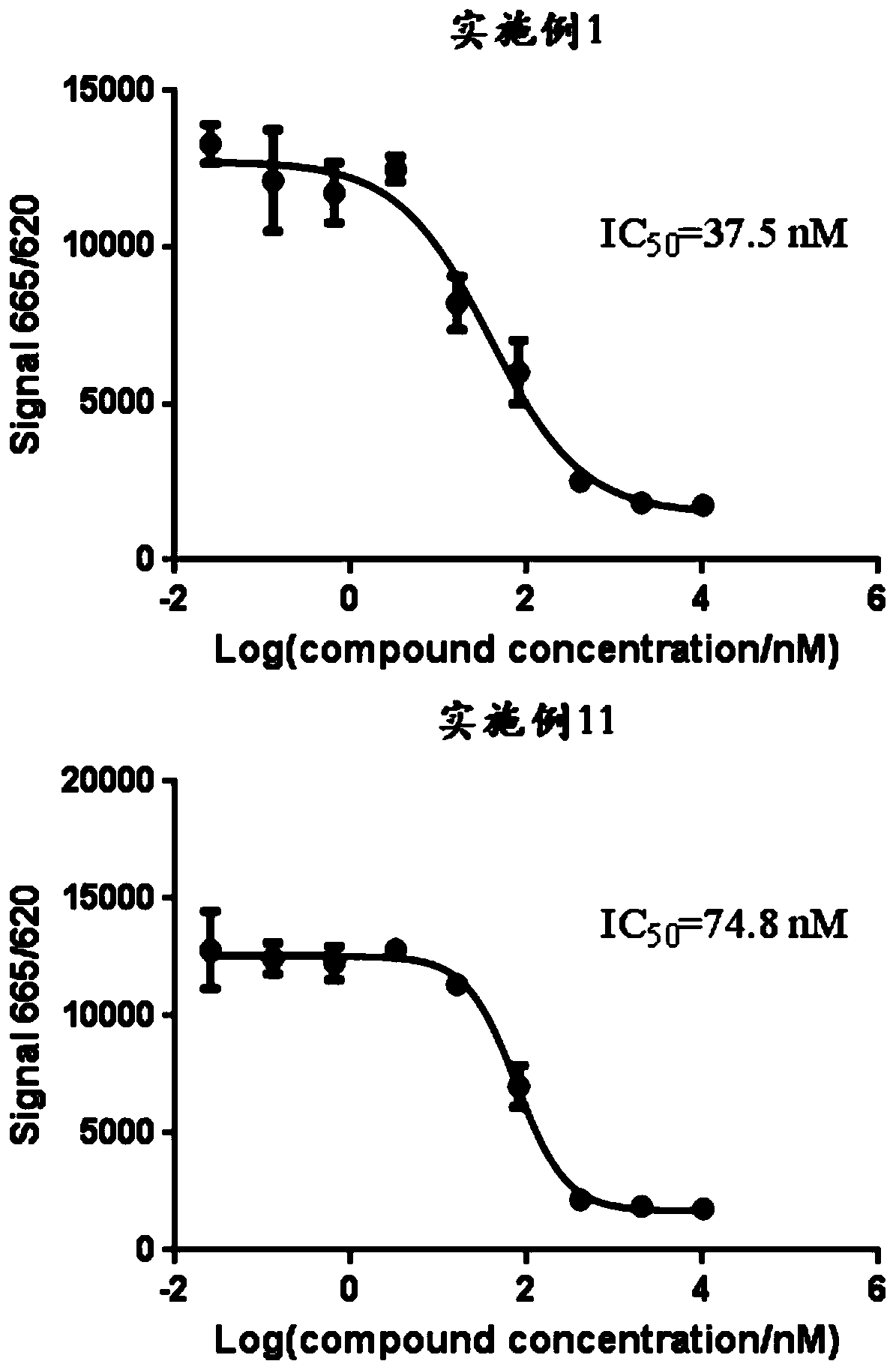
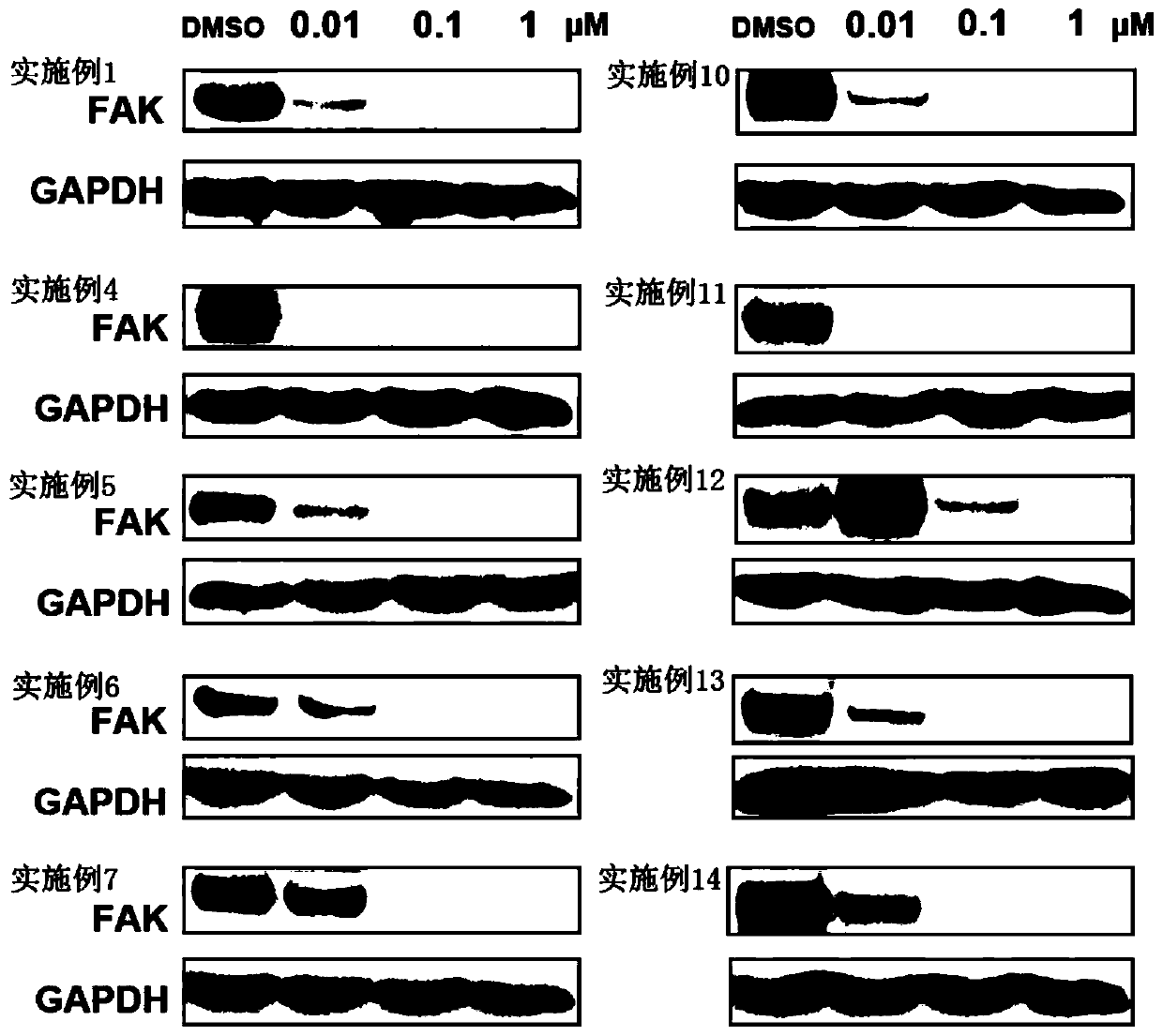
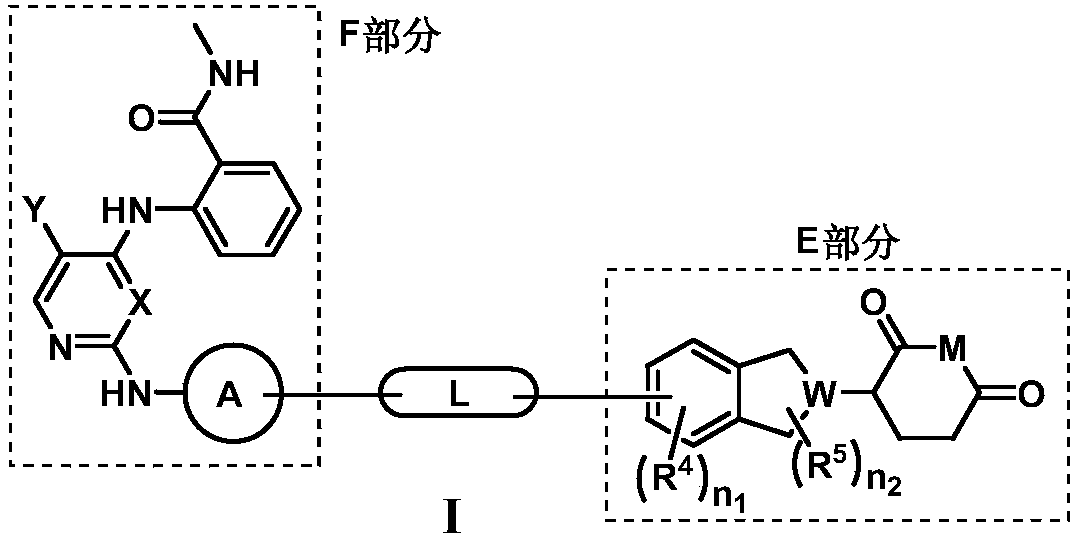
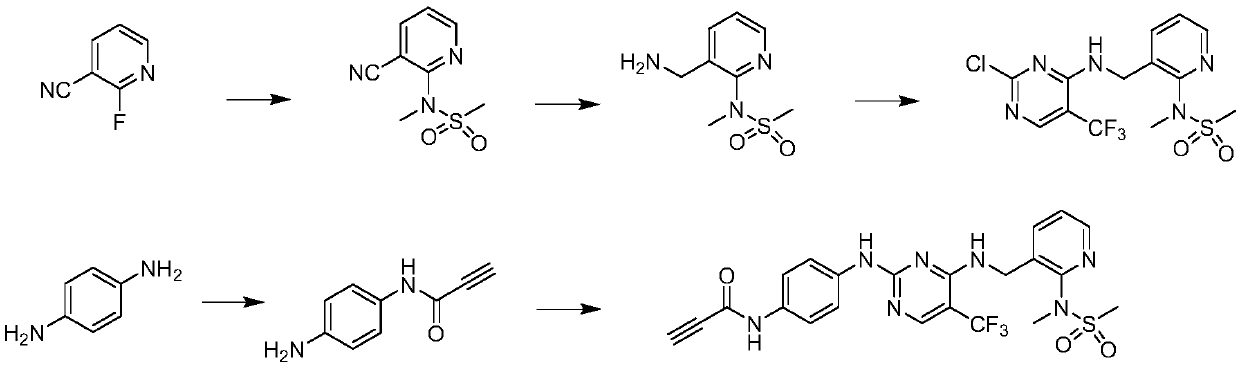
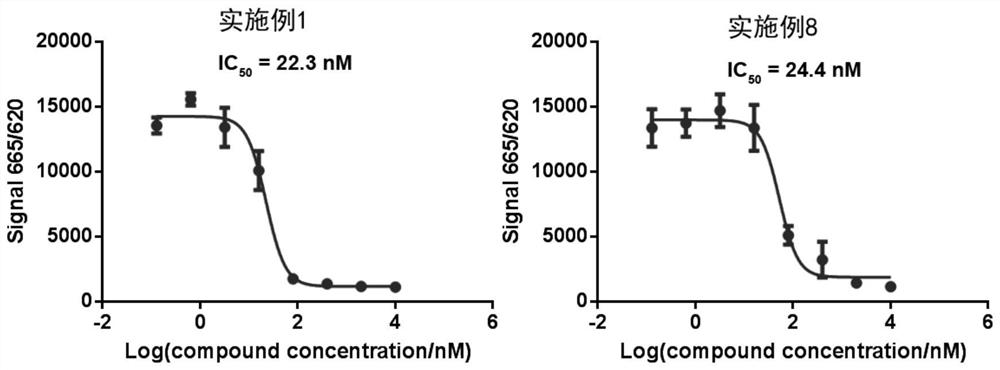
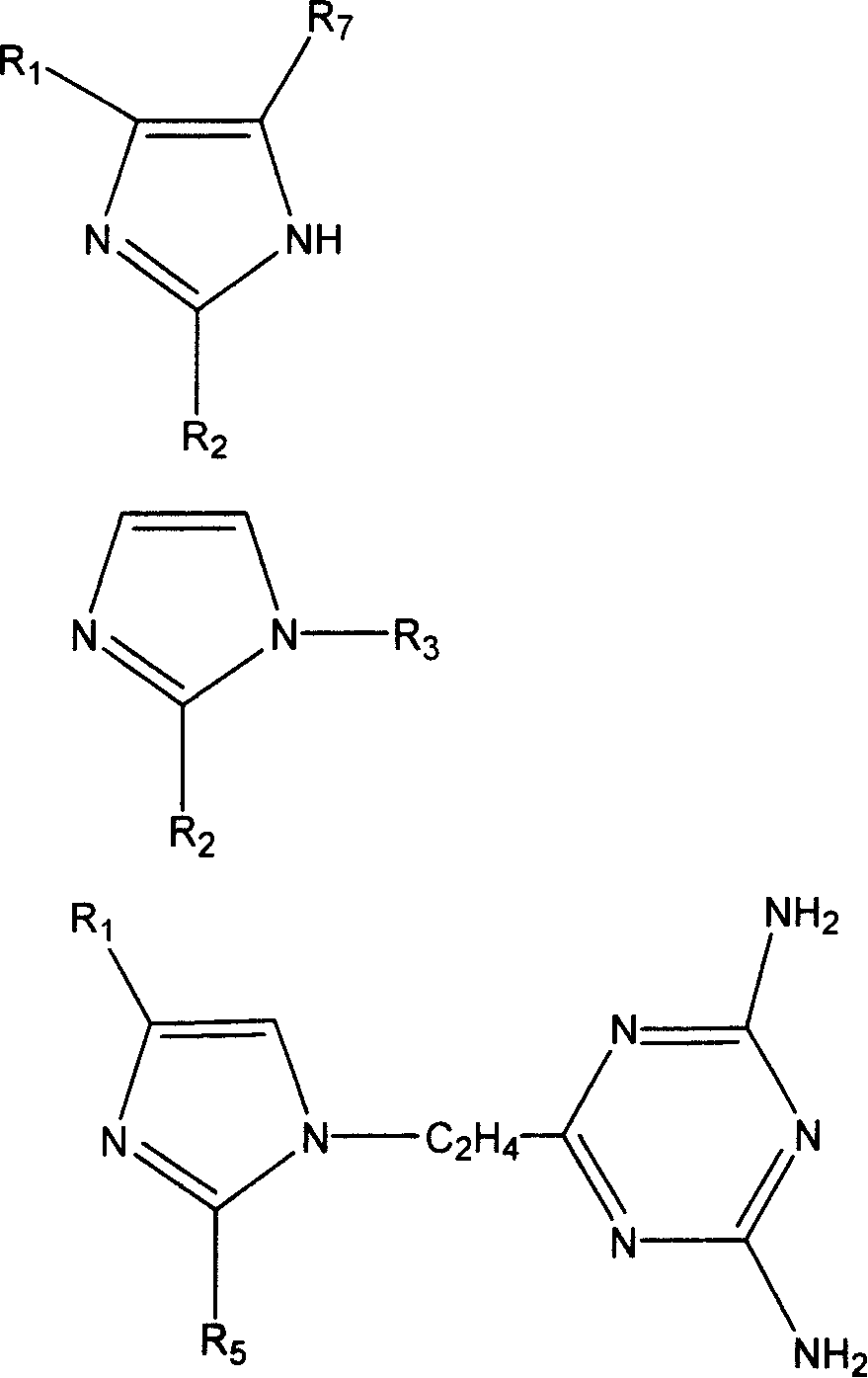
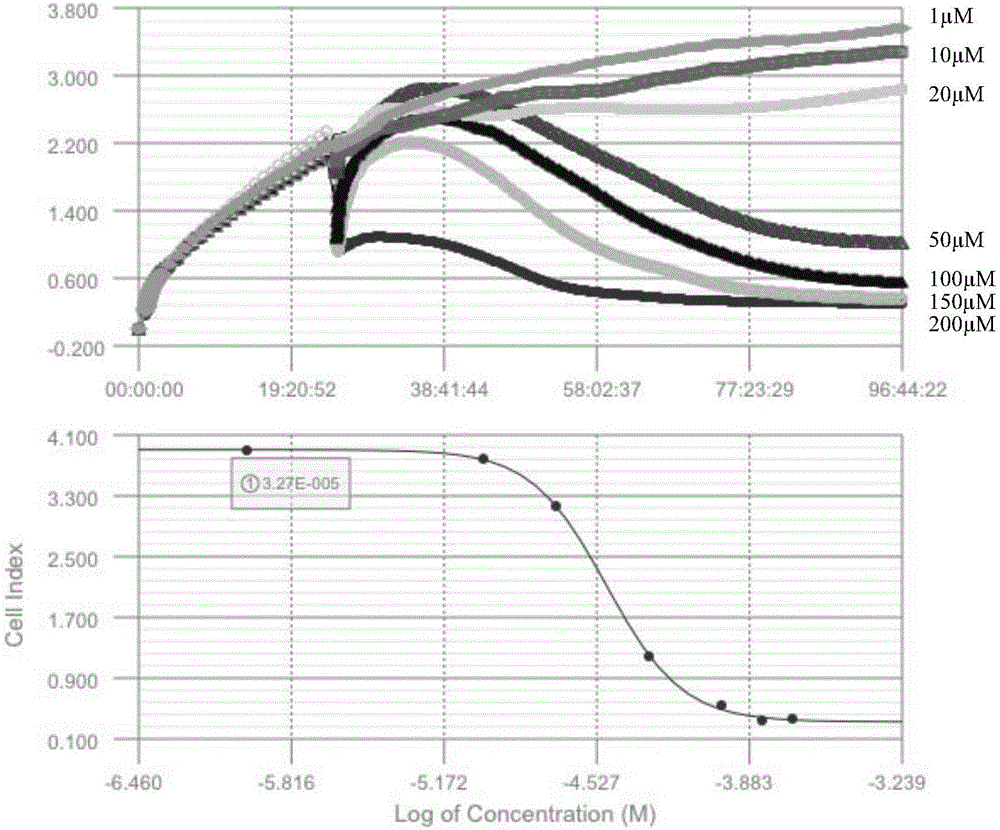
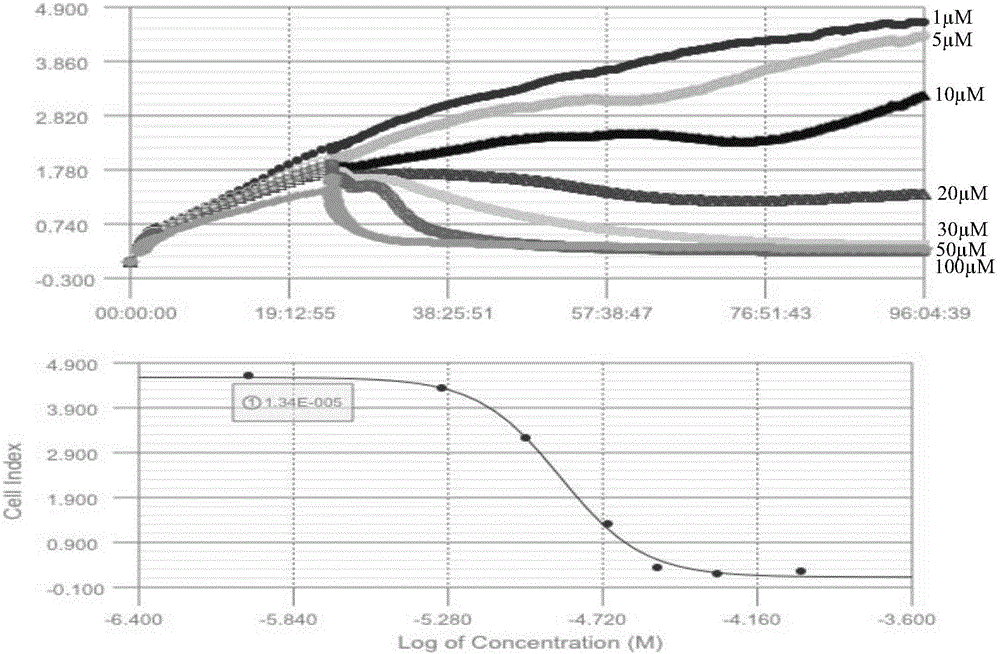
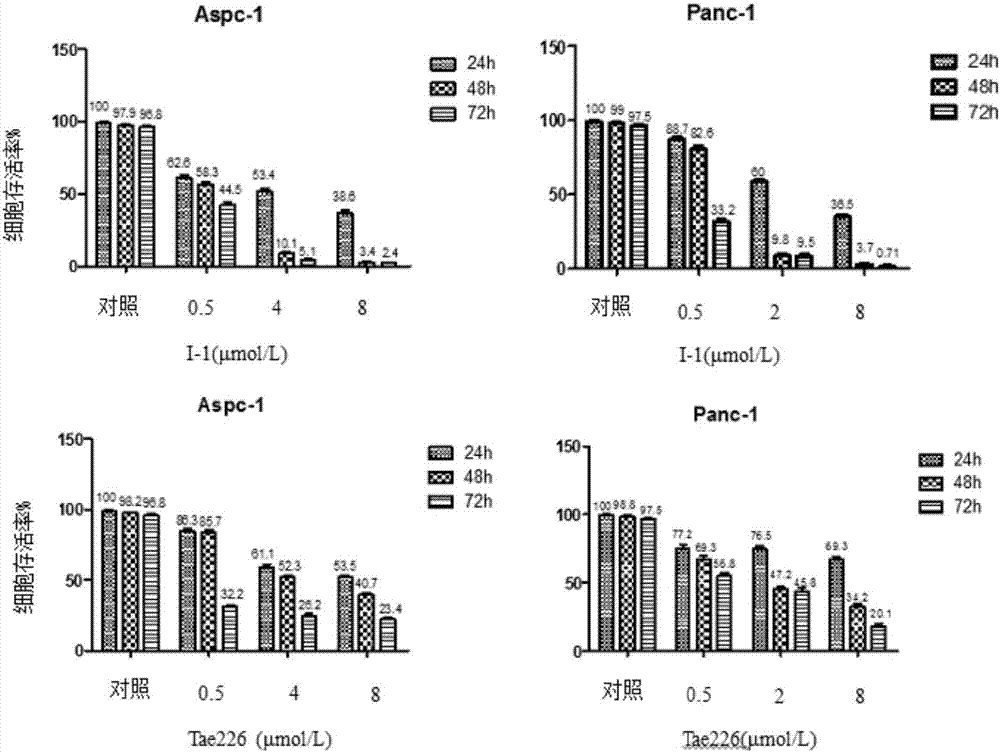
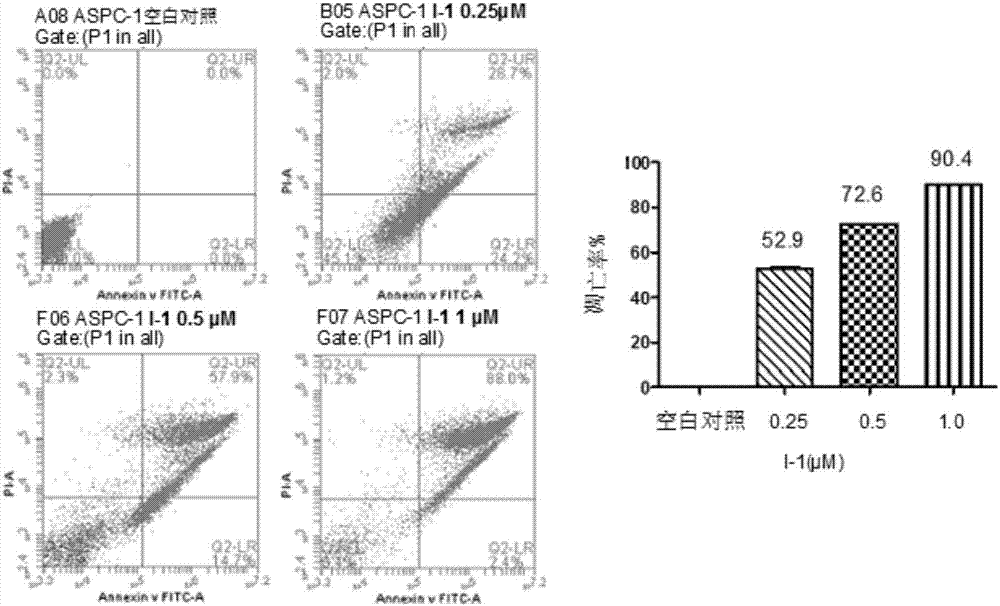
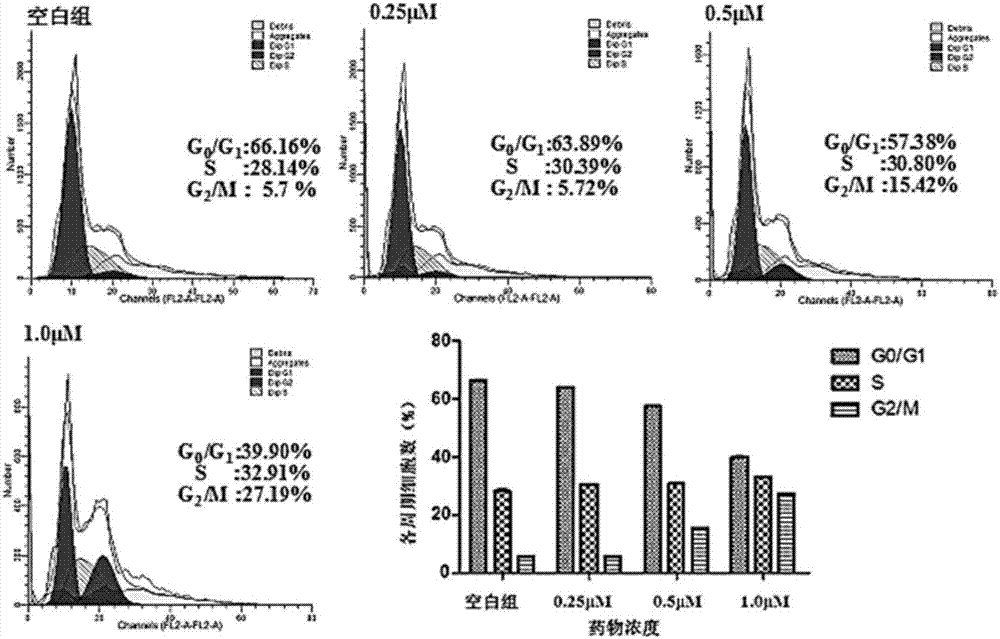
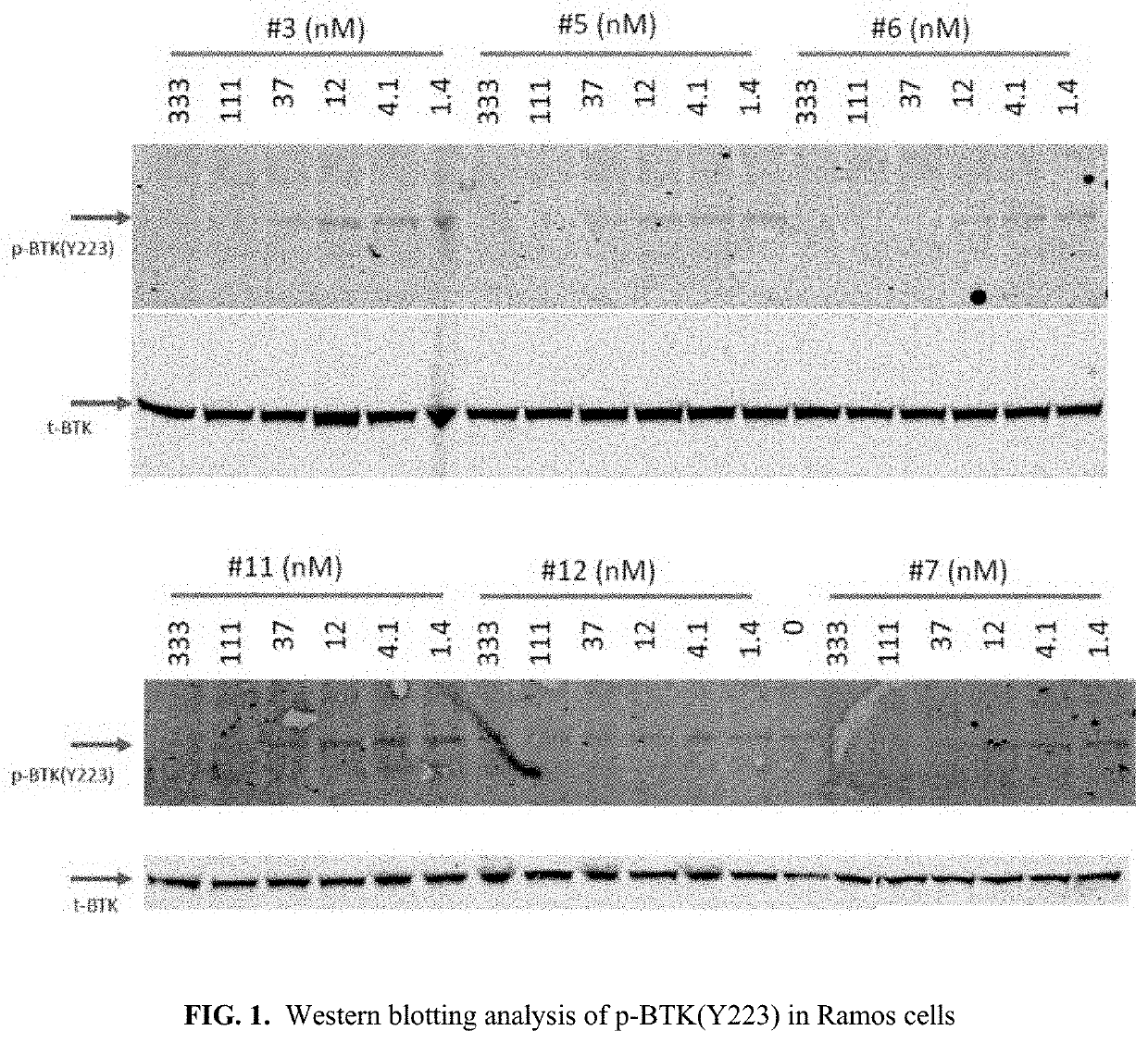
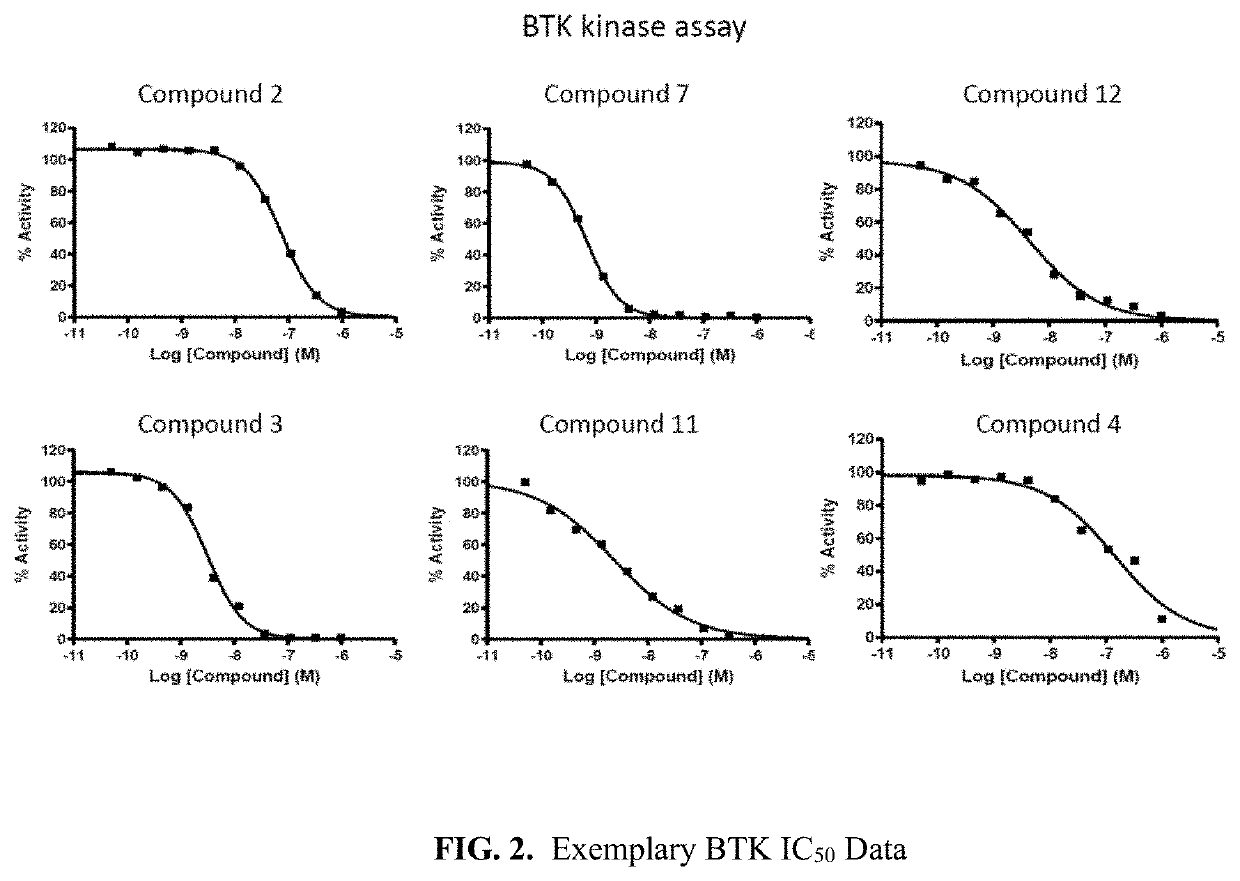
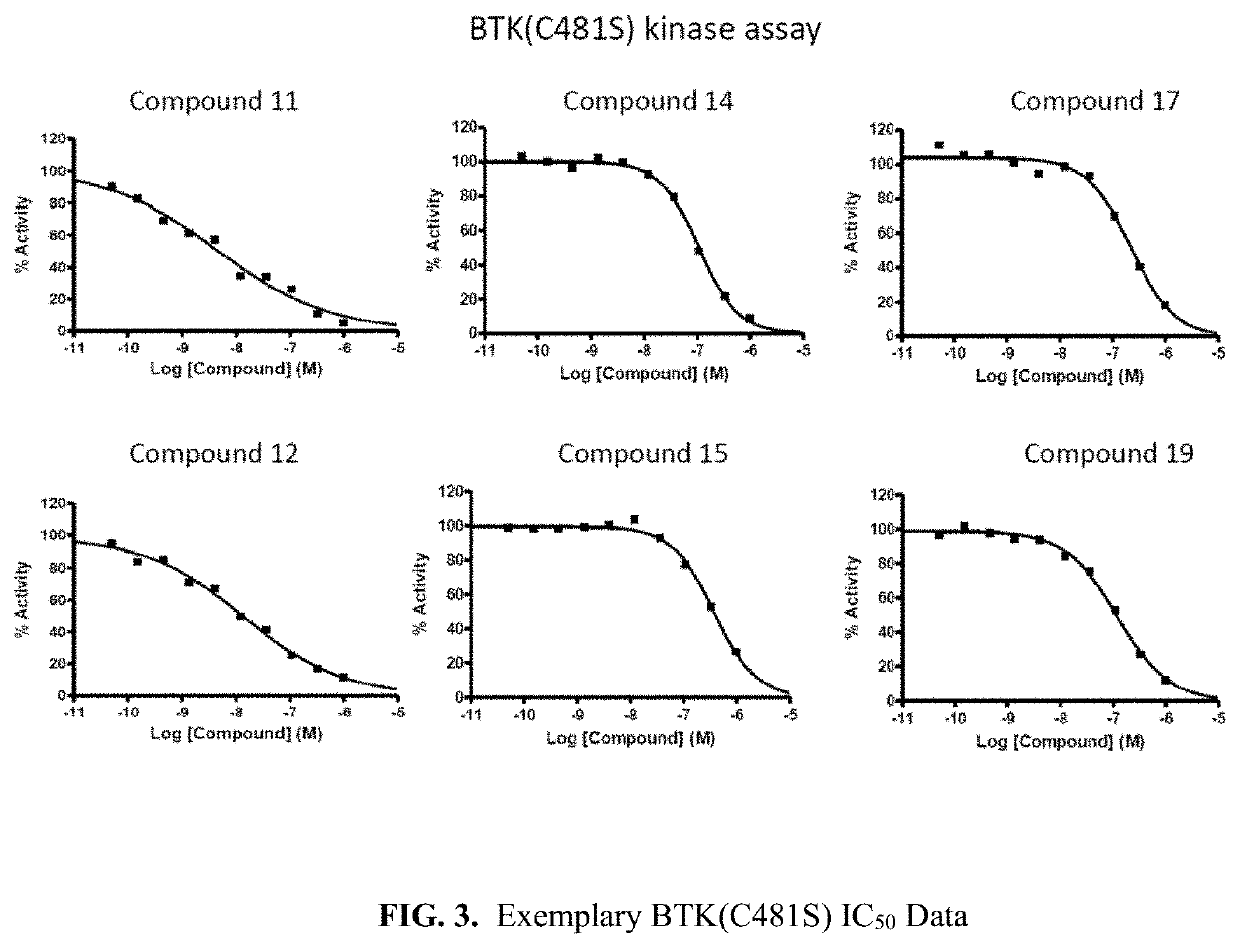
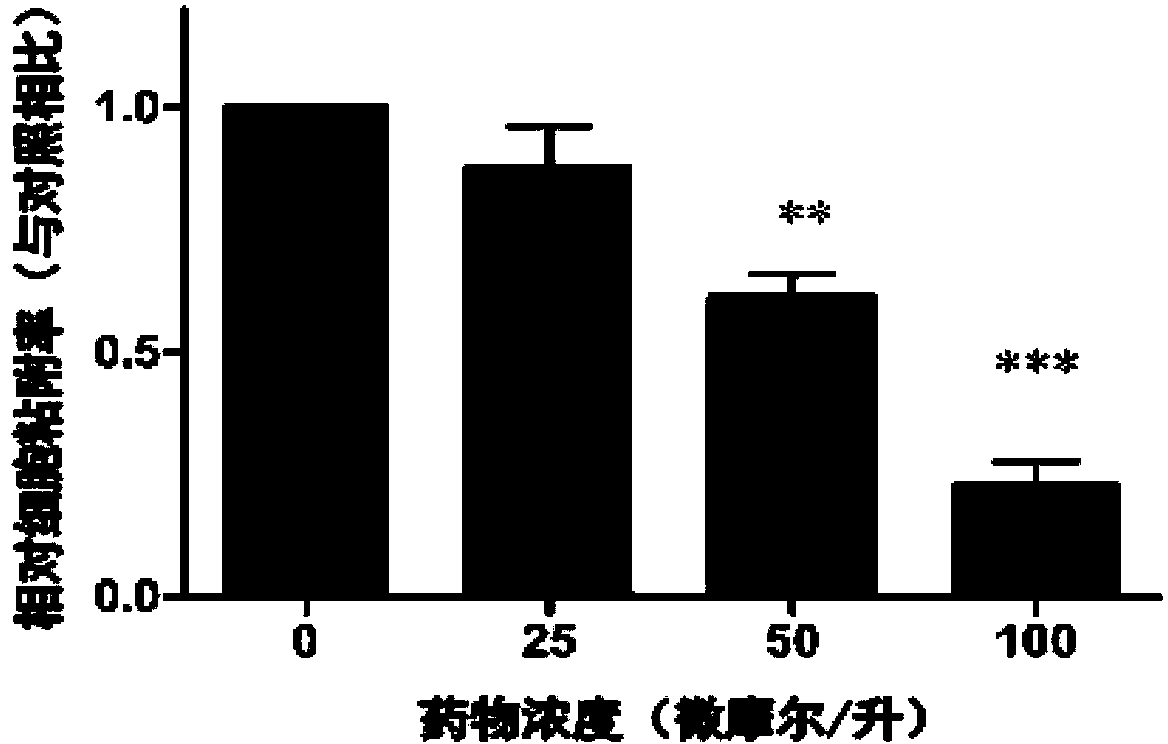
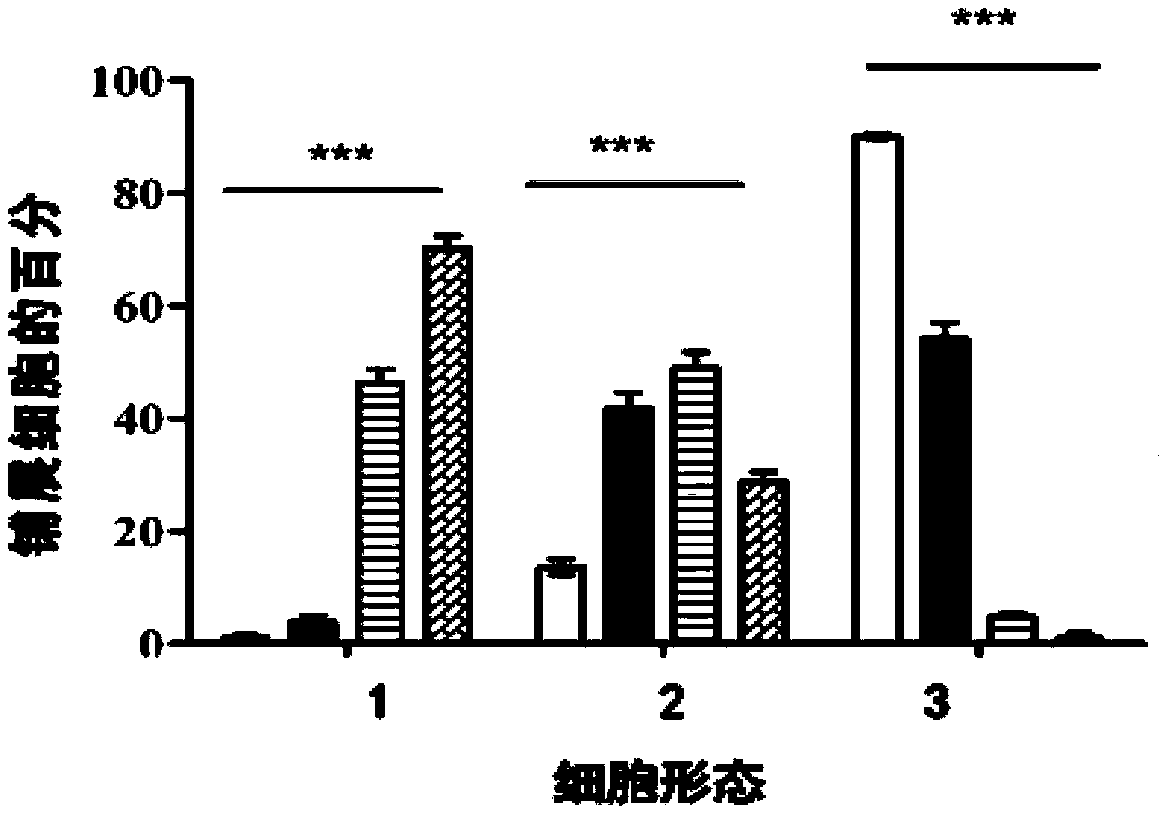
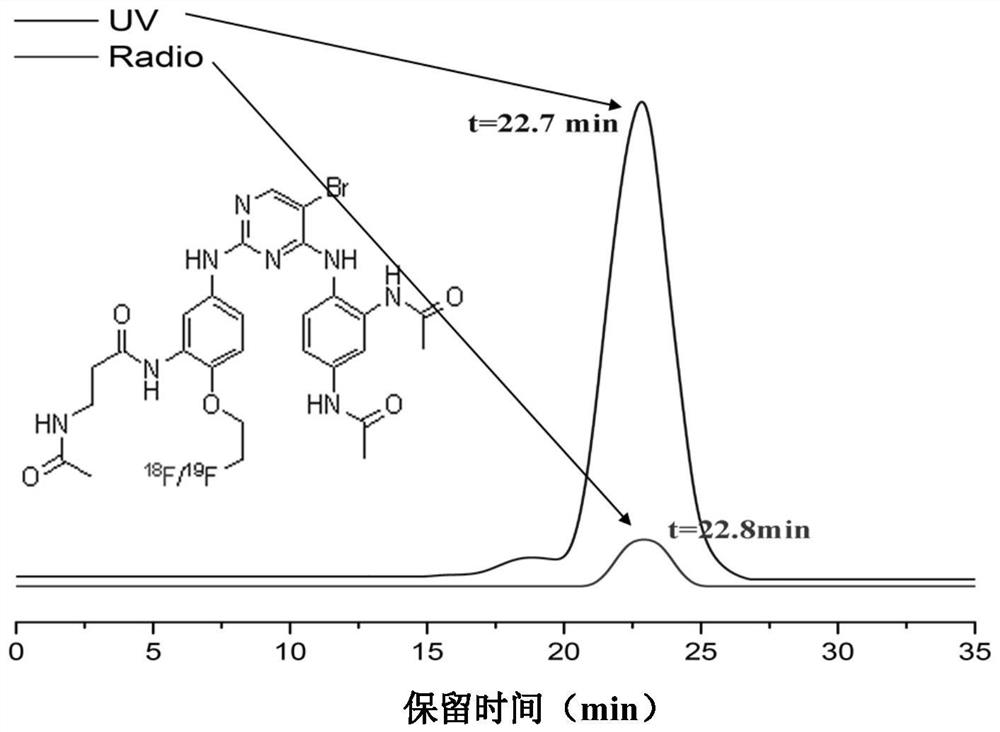
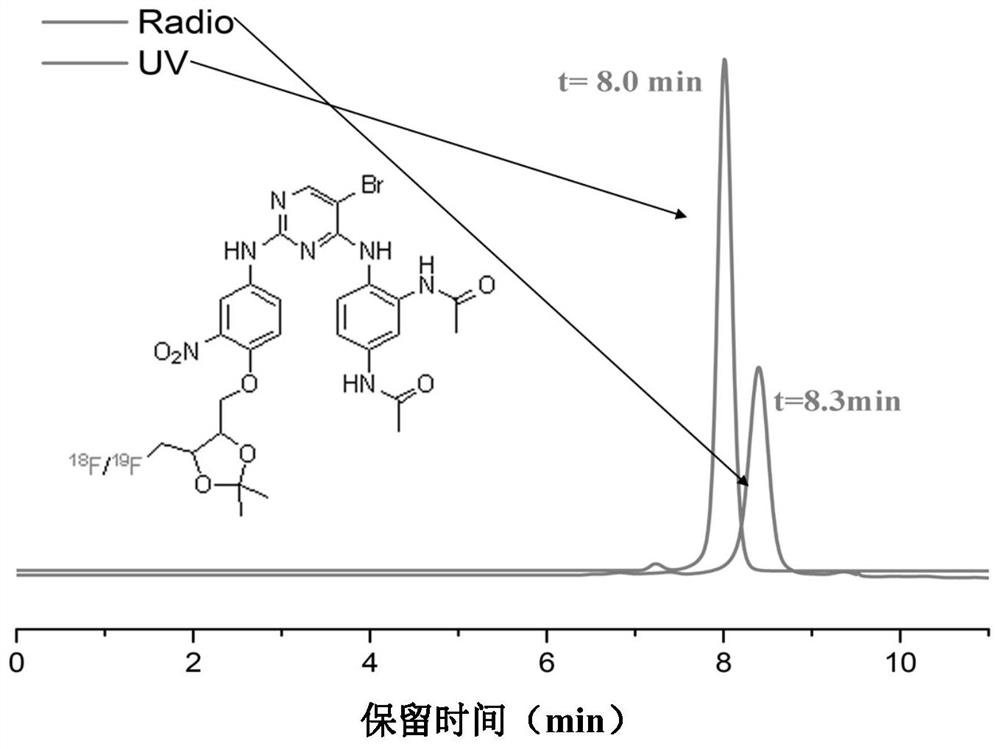
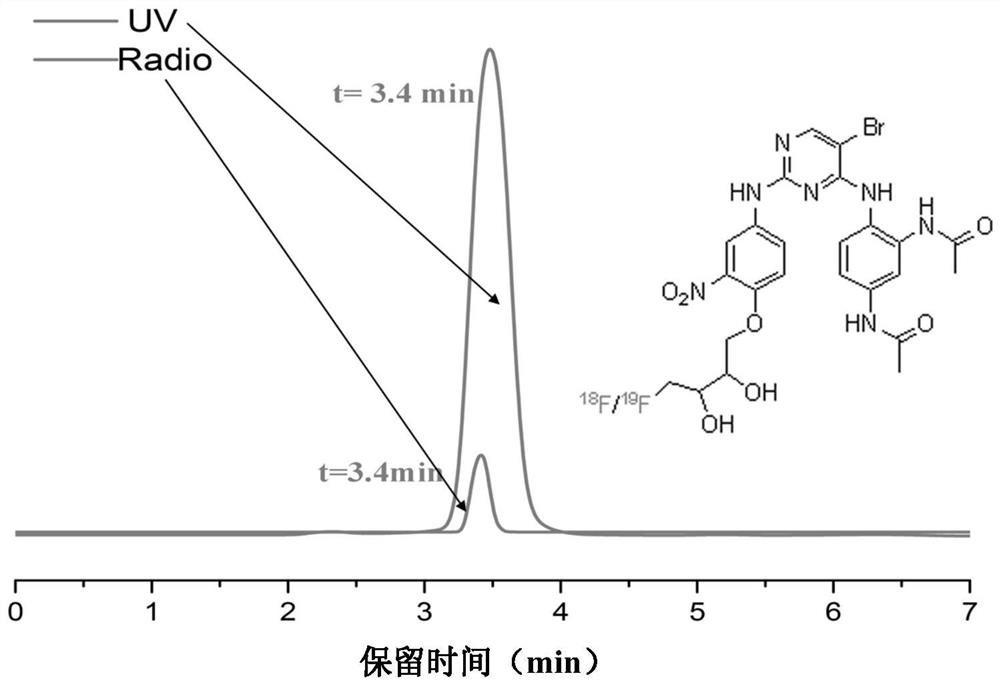
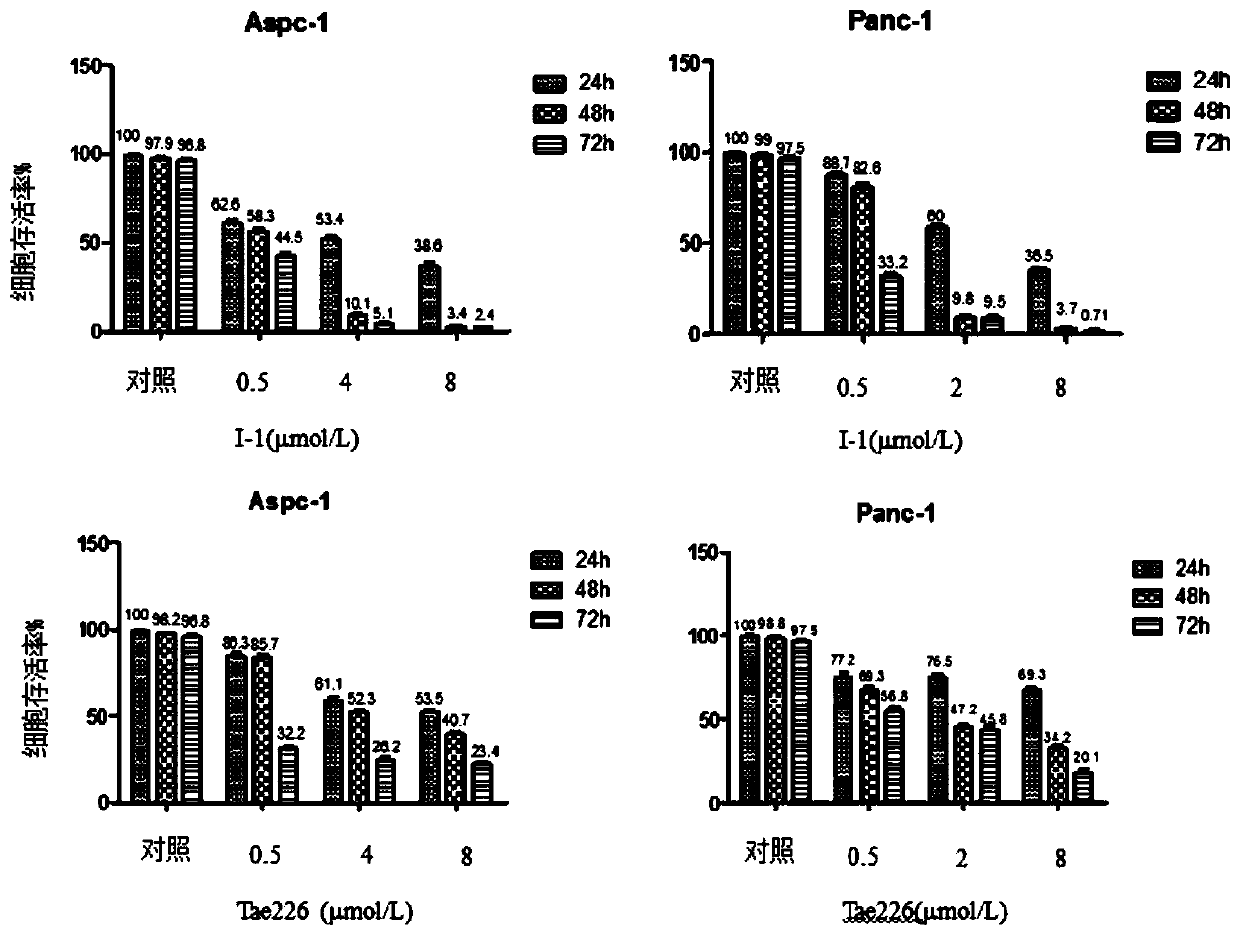
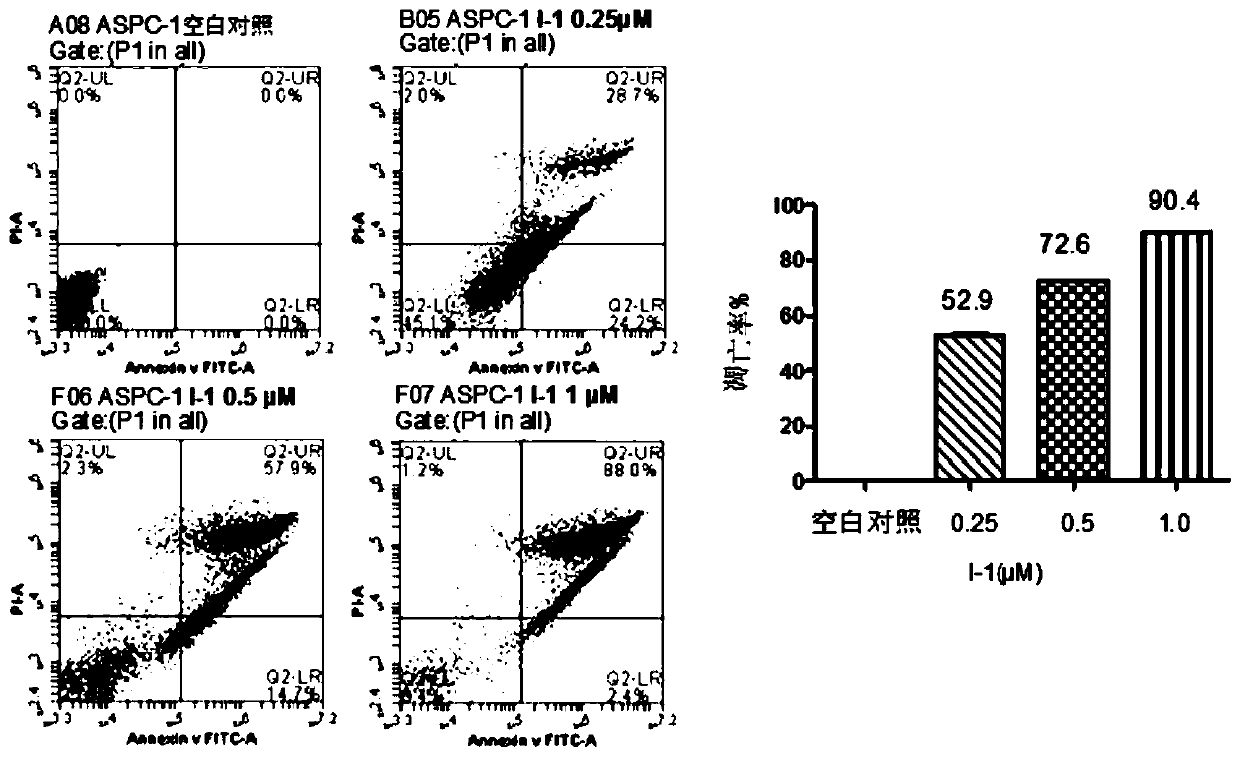
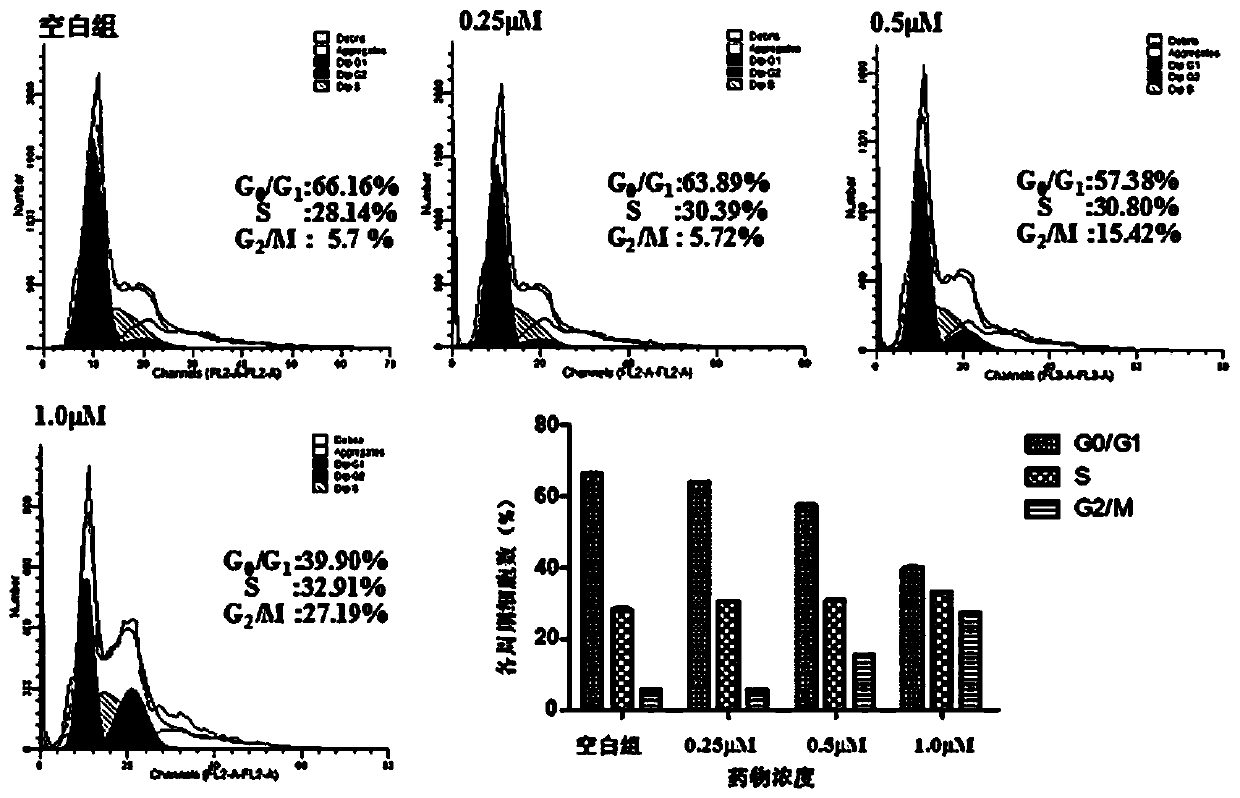
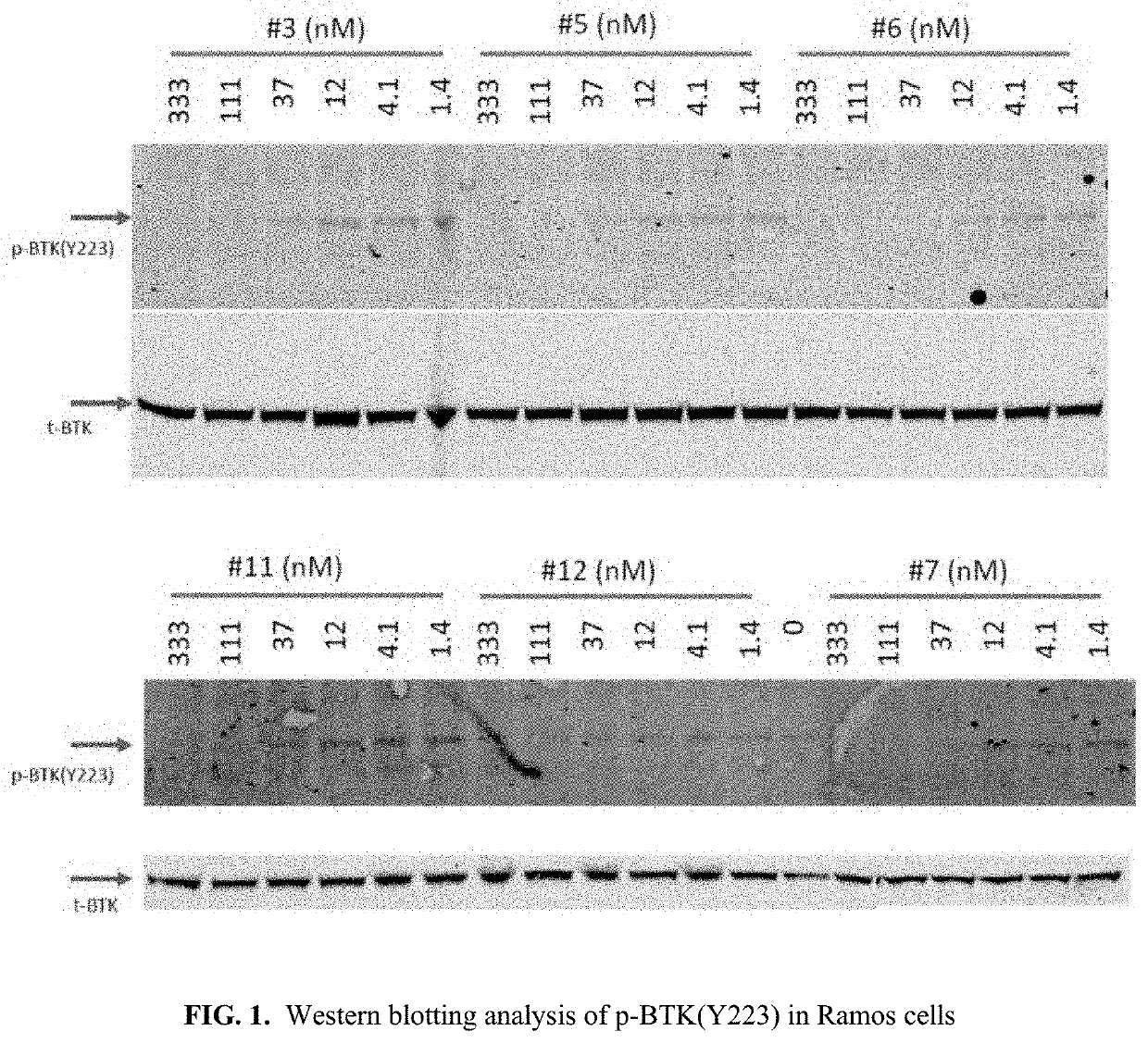
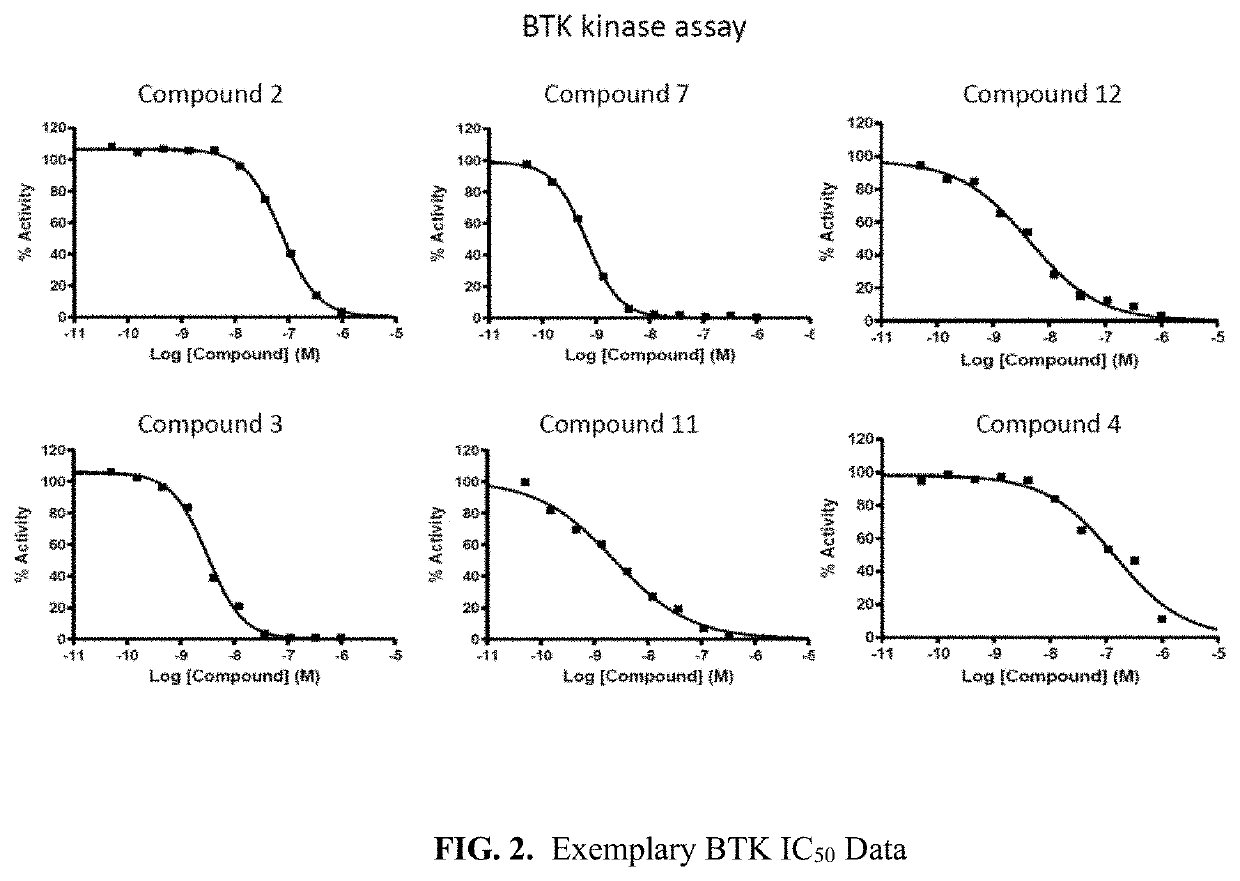
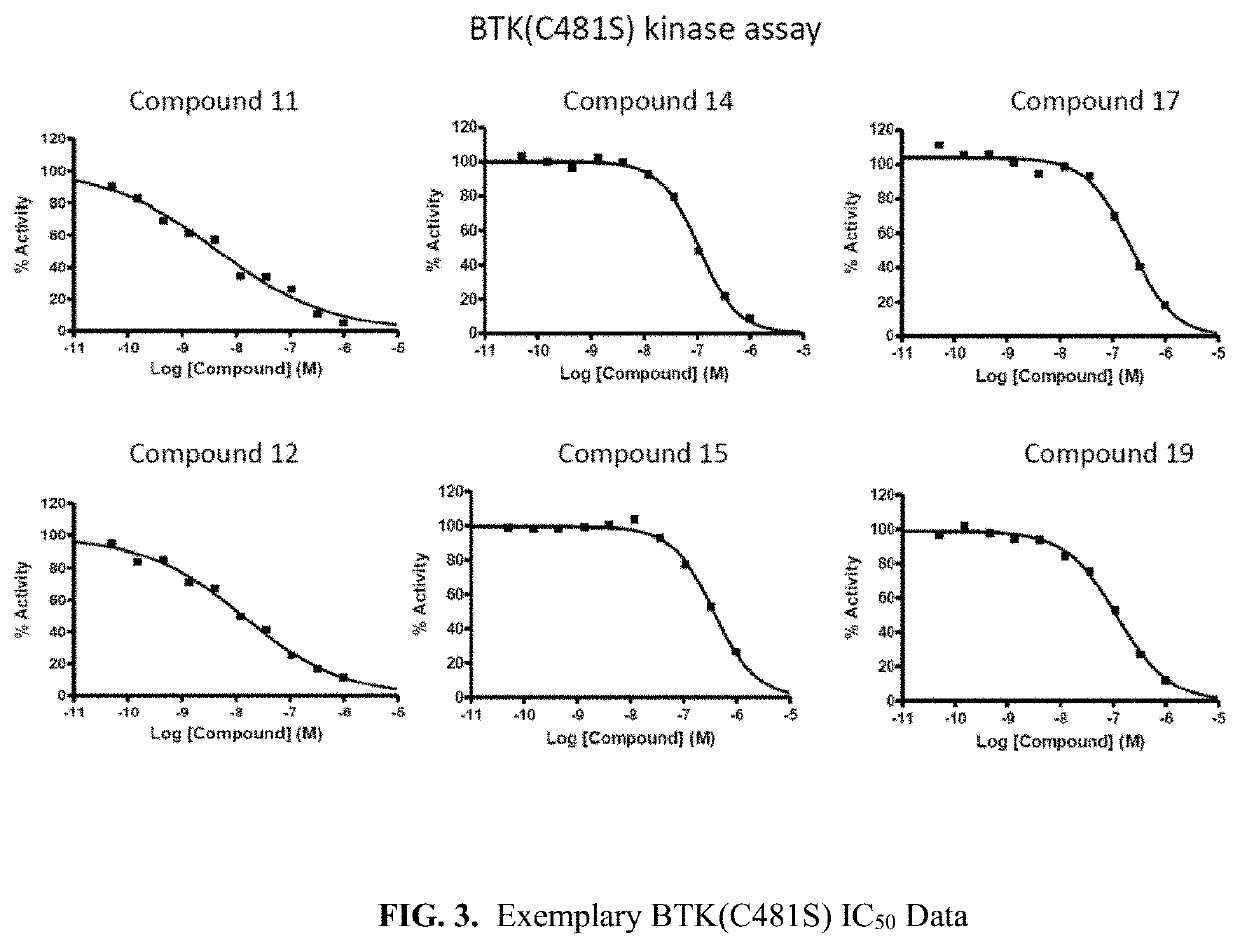
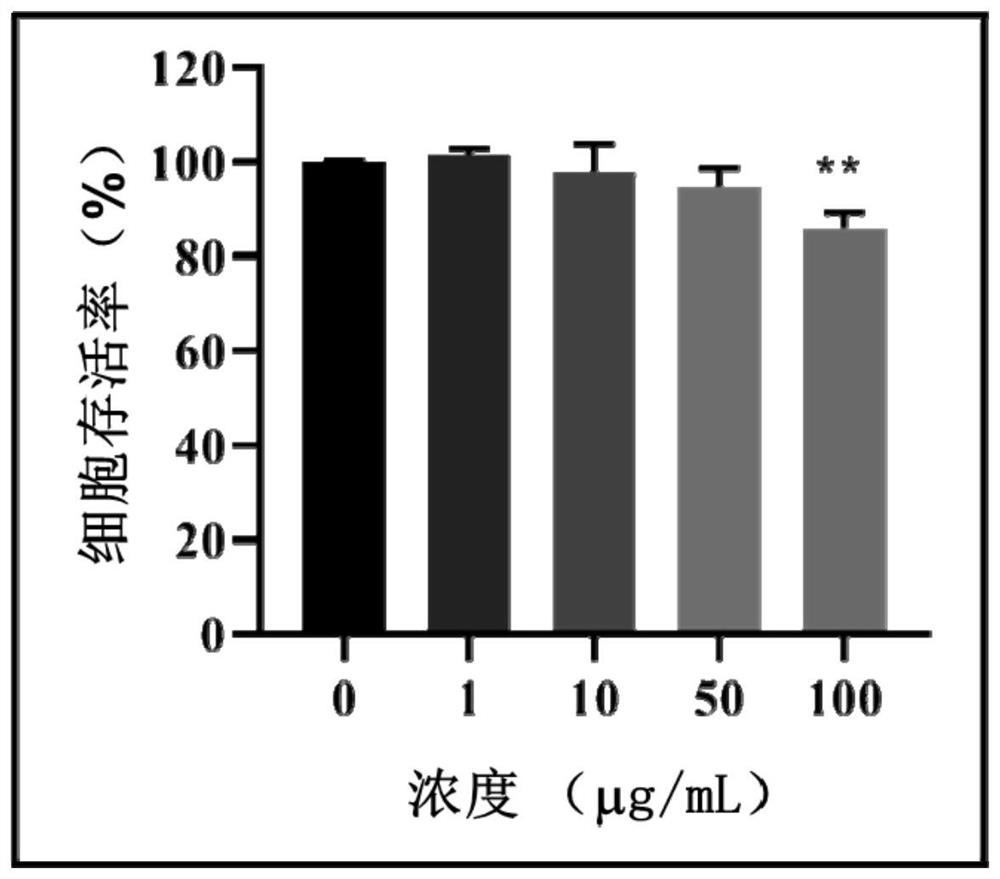
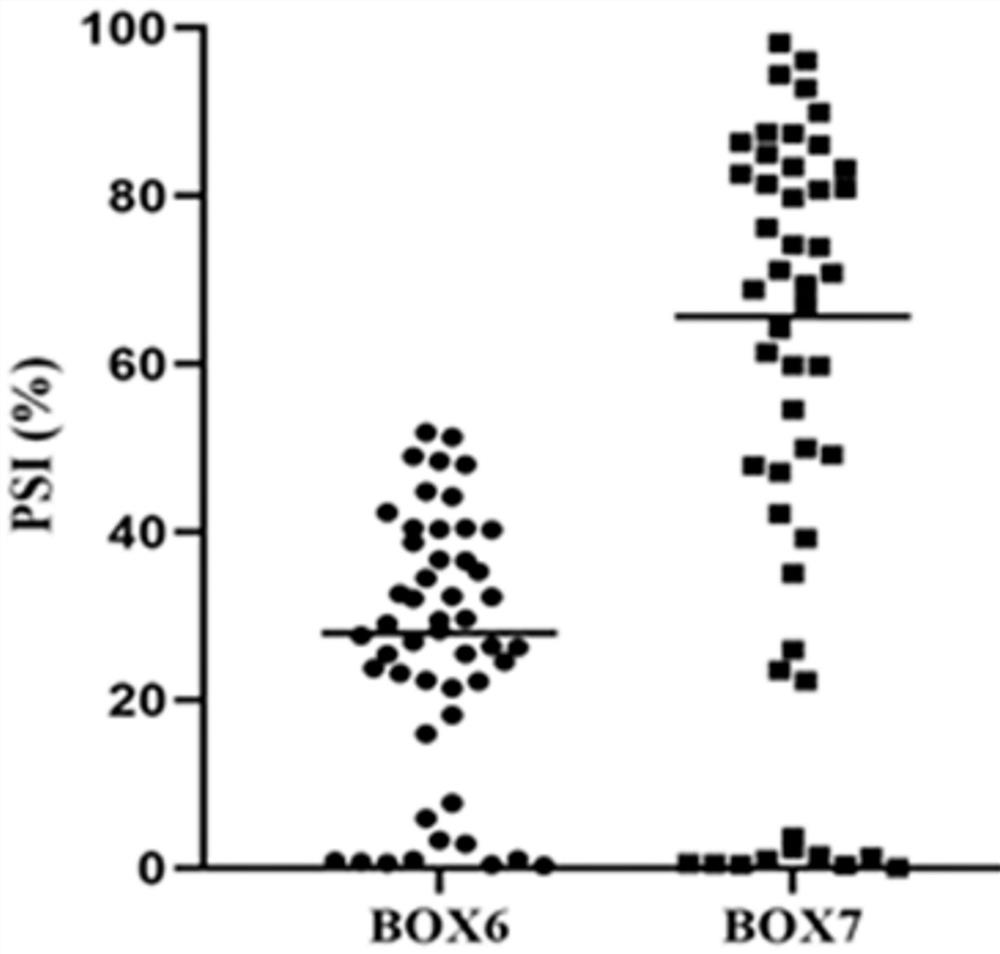
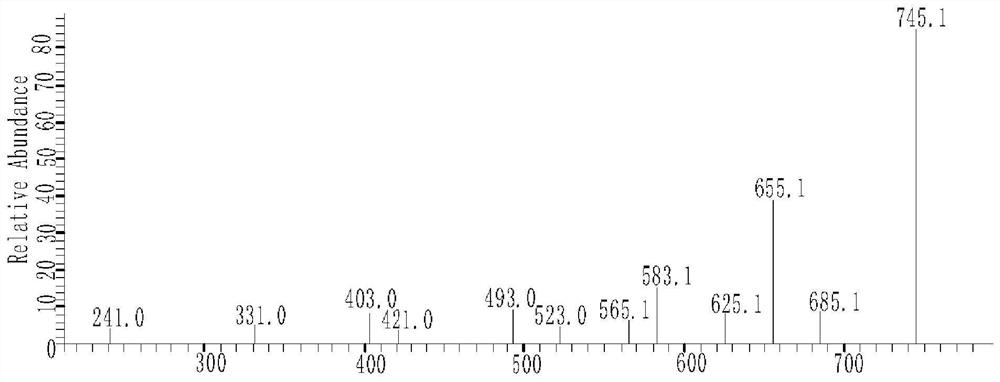
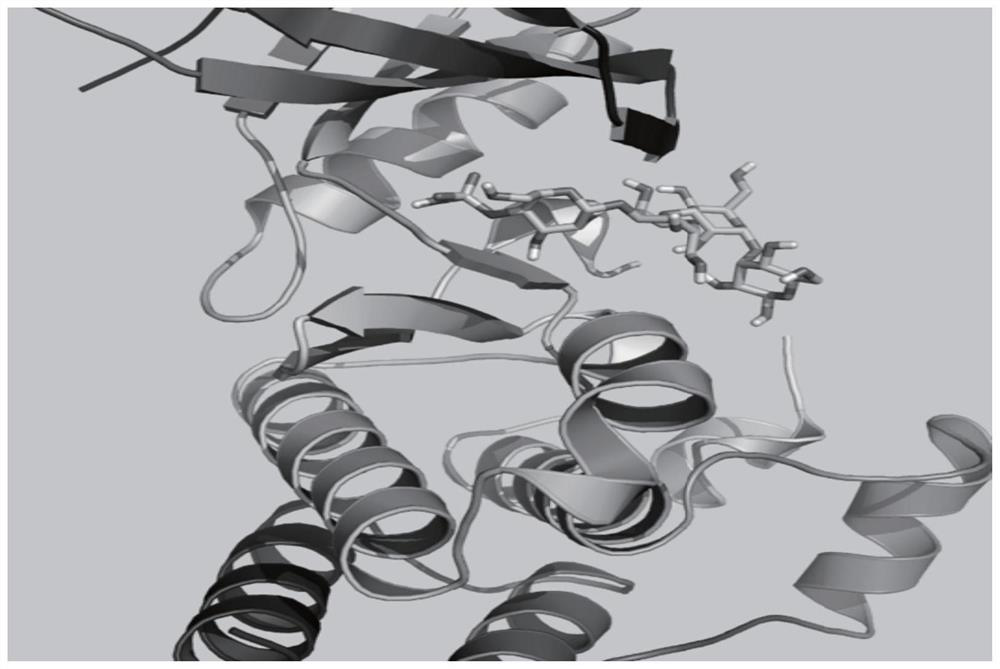
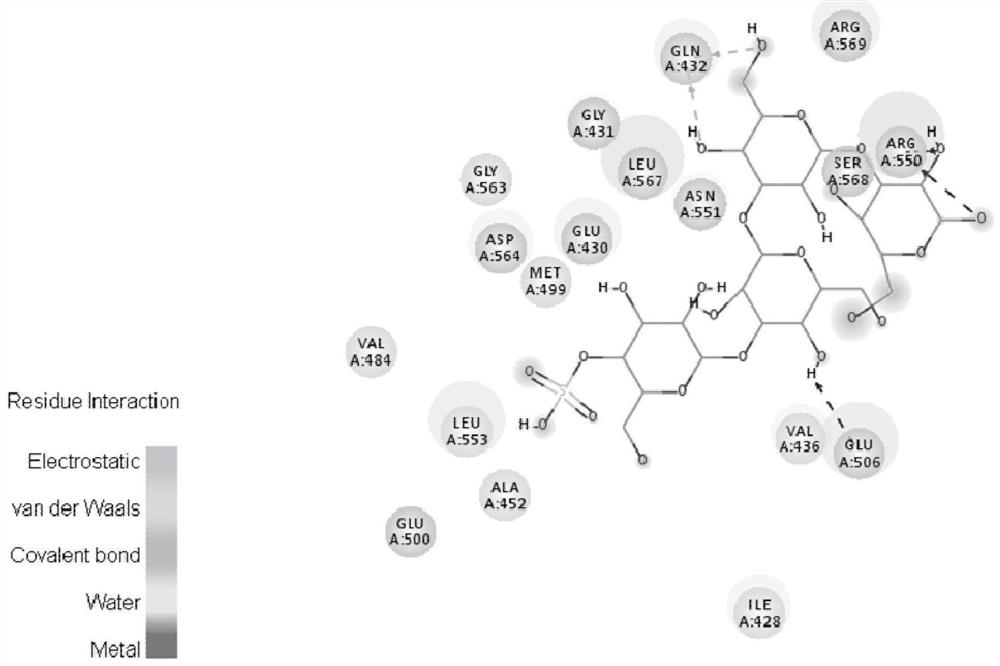
Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medical use
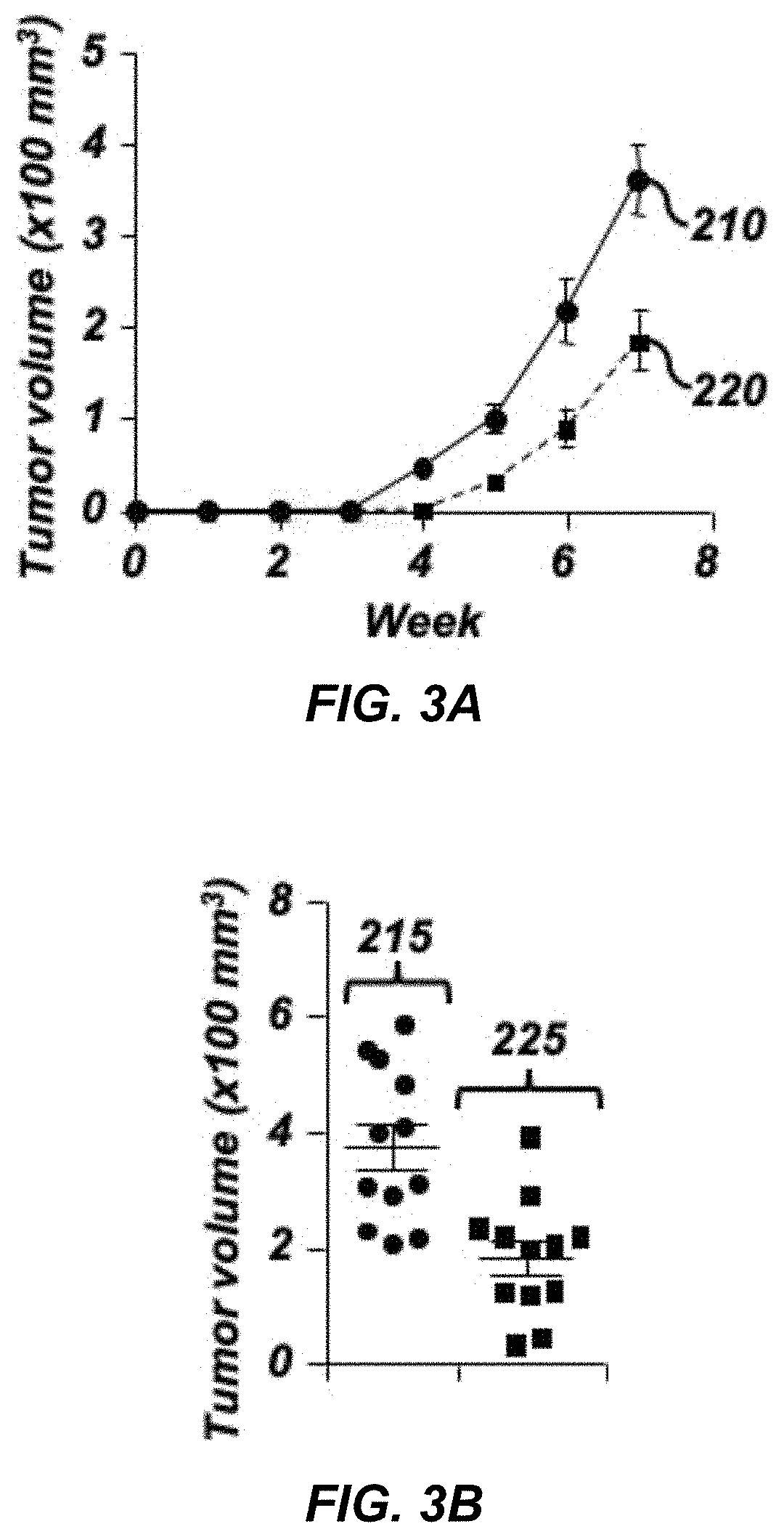
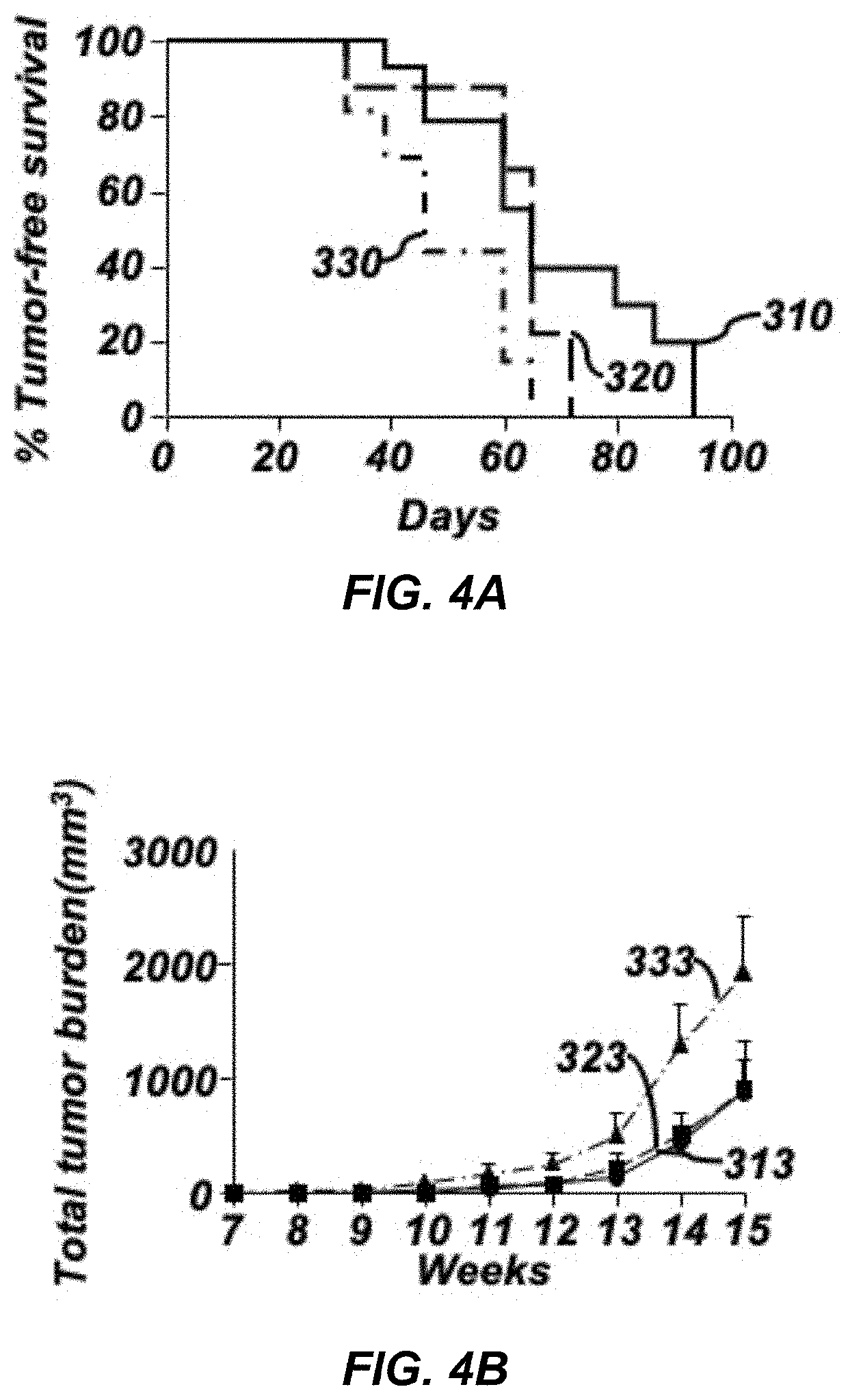
The invention belongs to the field of organic chemistry and drug synthesis, and relates to pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof. The compounds and salts thereof have a remarkable inhibiting effect on focal adhesion kinase, and can be used for preparing medicines for treating related diseases of the focal adhesion kinase, especially can be used for preparing medicines for treating related tumors with high expression of the focal adhesion kinase.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Research on antitumor mechanism of Combretastatin A-4 derivative
InactiveCN106727629AInhibit migrationInhibit phosphorylationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsVascular endotheliumFocal adhesion
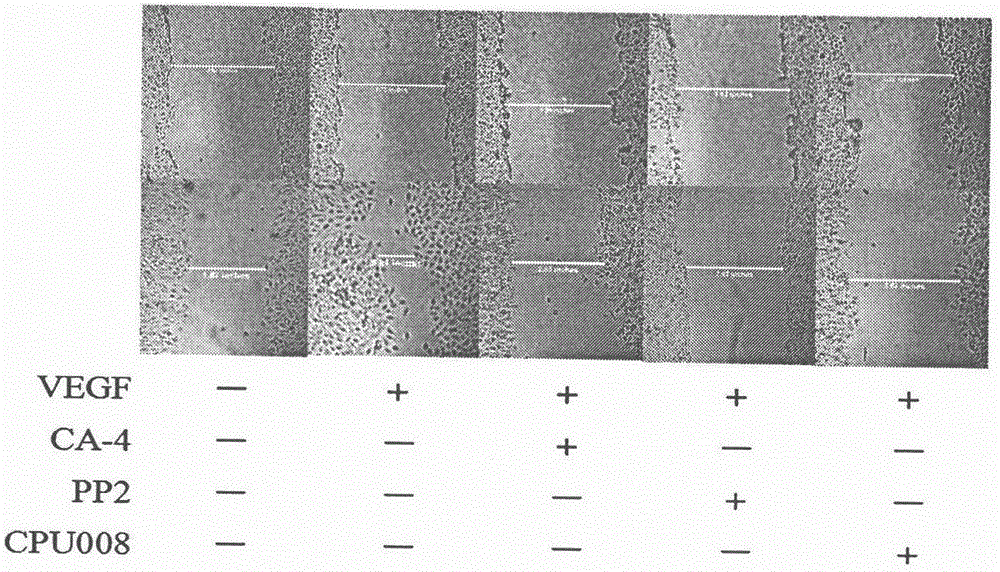
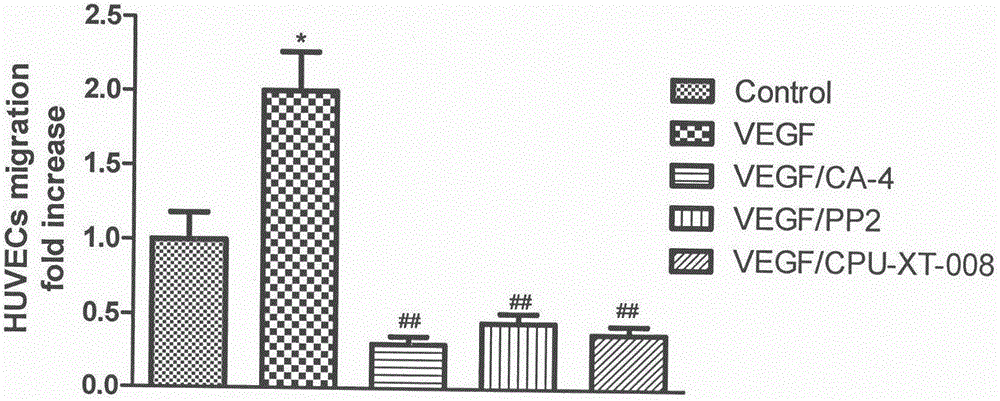
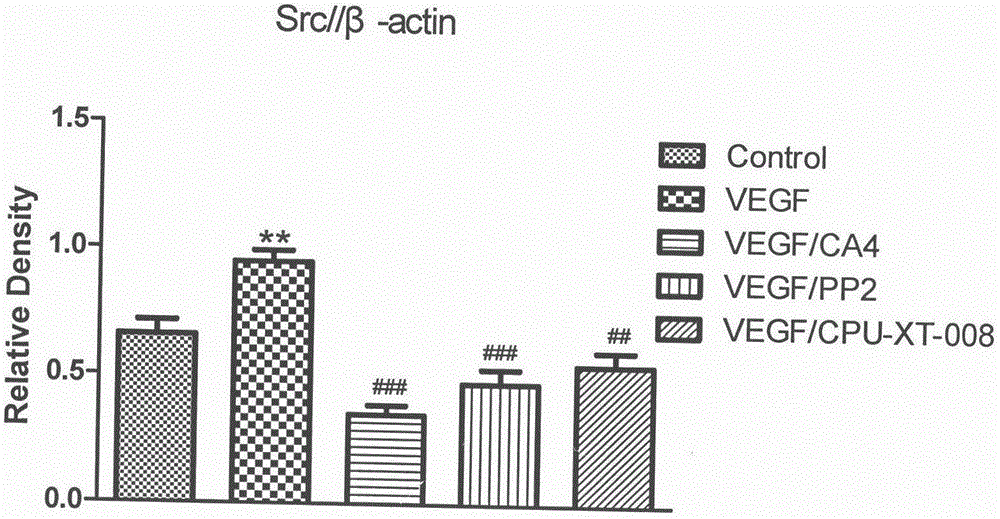
The invention discloses and relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to inhibition of Src-FAK (Src focal adhesion kinase) signal pathways by Combretastatin A-4 derivative CPU-TX-008 to inhibit VEGF-induced (vascular endothelial growth factor induced) migration of vascular endothelial cells. As a CA-4 (Combretastatin A-4) derivative, CPU-TX-008 is acquired by replacing hydroxy of CA-4 structure with more water-soluble glucosamine groups. In-vitro cell experiments show that the derivative plays a role in inhibiting the migration of HUVECs (human umbilical vein endothelial cells); it is discovered through the research on the influence of related migrated proteins Src and FAK that CPU-TX-008 inhibits cell migration by inhibiting the phosphorylation of Src and FAK proteins in HUVECs, finally inhibiting the growth of tumor vessels; by adding chemical groups to CA-4 to prepare tumor vessel inhibitory drugs, new clinical antitumor paths are provided.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Quinazoline compound, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN106518849AStrong inhibitory activityInhibit biological activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryFocal adhesionTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a quinazoline compound represented by formula I, or a pharmaceutical salt thereof, and also discloses a preparation method of the quinazoline compound, and applications of the quinazoline compound in preparing drugs used for treating cancer. The quinazoline compound is capable of inhibiting the activity of FAK (focal adhesion kinase), and inhibiting cancer cell proliferation effectively, possesses excellent treatment effect on a plurality of cancers, especially possesses obvious treatment effect on liver cancer, and is promising in application prospect.
Owner:CHINESE NAT HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI +1
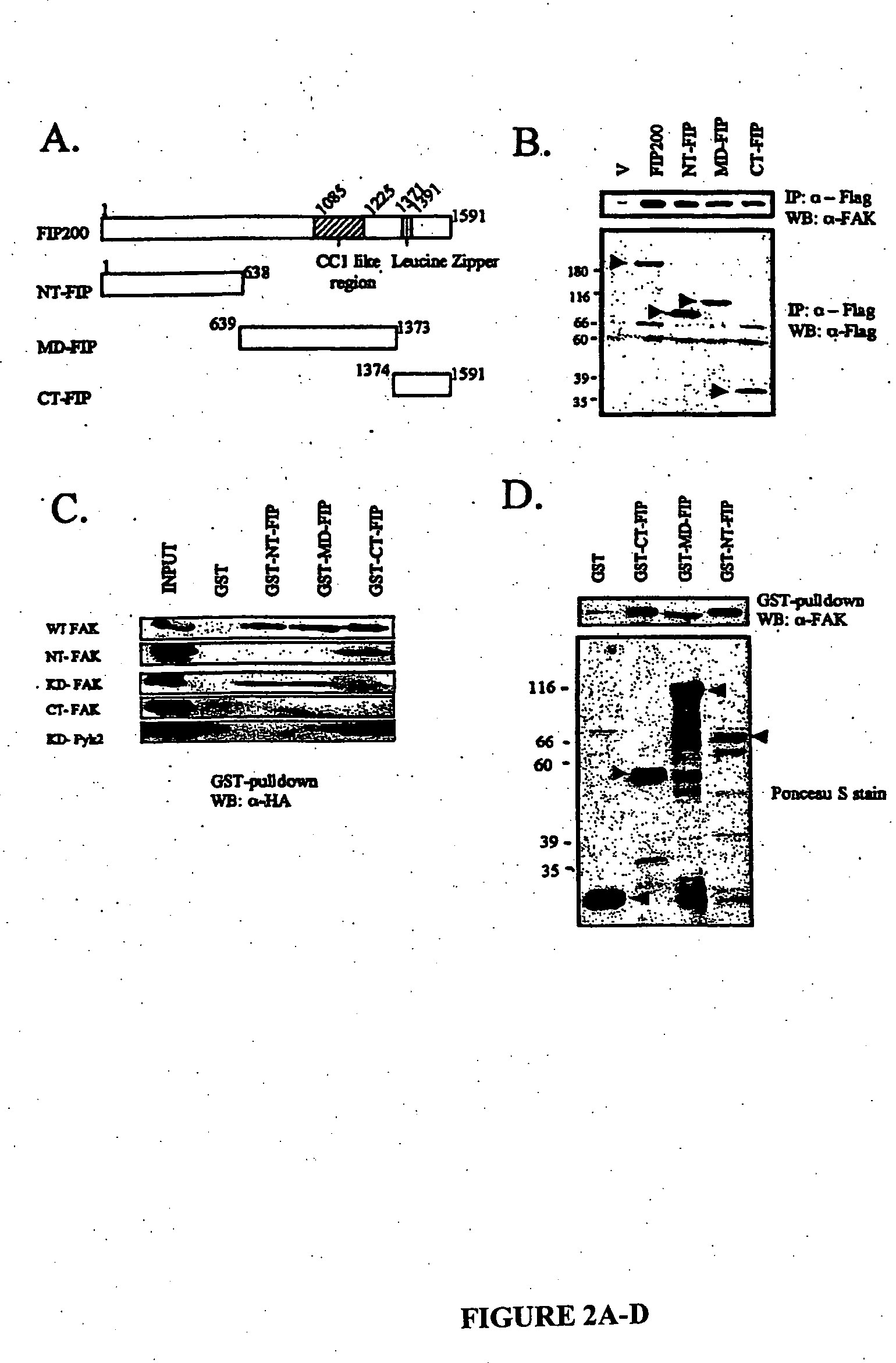
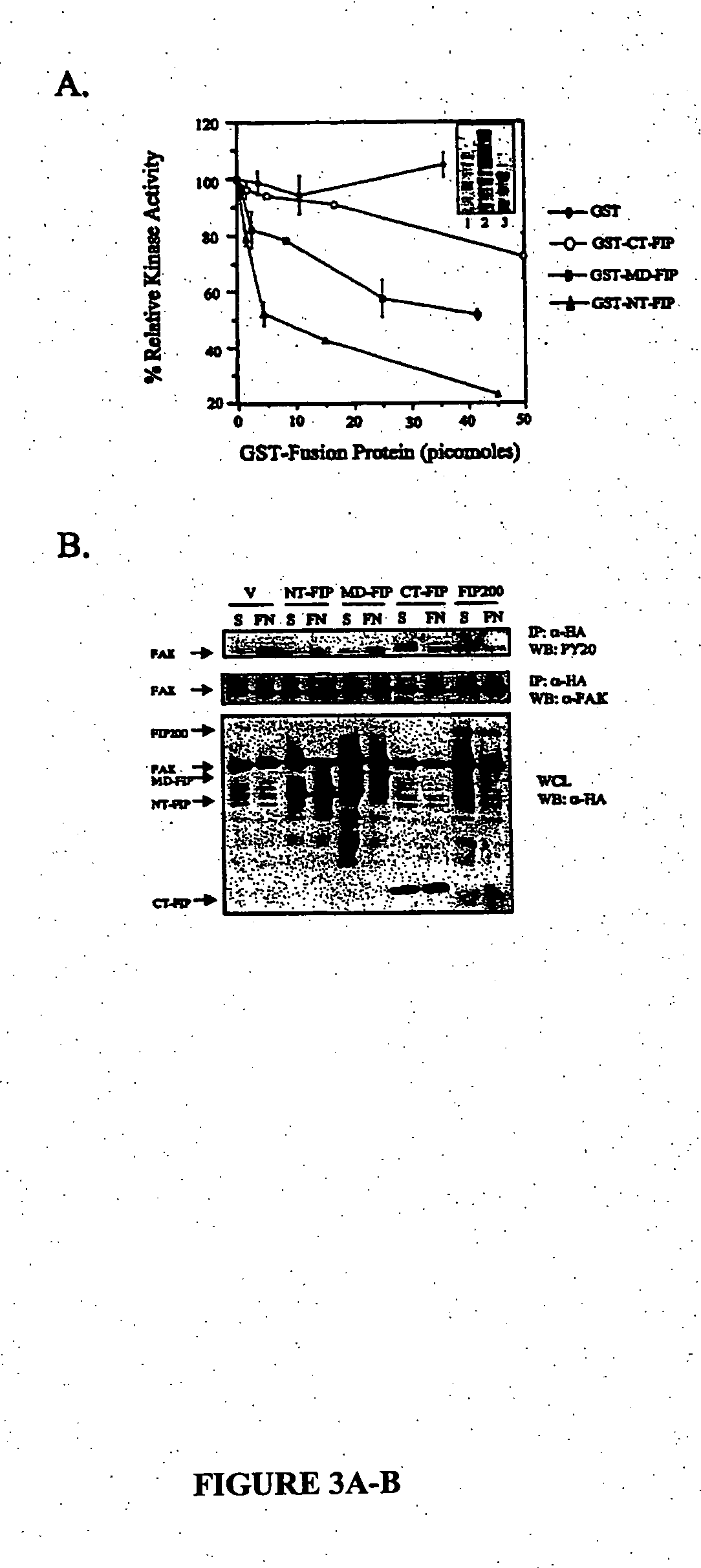
Methods of regulating focal adhesion kinase and its associated cellular functions by fak family-interacting protein
InactiveUS20050037963A1Inhibit cell proliferation disorderSenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseFocal adhesion
The present invention is directed to treating a subject suffering from a disorder mediated by cell proliferation, such as cancer, by administering a fragment of focal adhesion kinase family kinase-interacting proteins. This method can involve regulating tumor formation or tumor growth in the subject. In addition, the present invention relates to the use of these proteins for regulating G1 to S phase progression of a cell, regulating the expression of p21 in a cell, regulating the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein in a cell, regulating retinoblastoma protein / E2F transcription factor 1 complex formation in a cell, regulating detachment-induced apoptosis of a cell, and regulating anchorage-independent growth of a cell.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Novel pyrimidine anti-tumor compound and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel pyrimidine anti-tumor compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The novel pyrimidine anti-tumor compound is a compound shown in a formula (I), wherein each substituted group in the formula (I) is defined in the description. The invention also relates to the compound shown in the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or application of a medicine composition containing the compound in inhibiting focal adhesion kinase, further treating tumor diseases, and especially treating pancreatic cancers, lung cancers and breast cancers. The formula (I) is shown in the description.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Preparation method of porous scaffold material for tissue engineering
ActiveCN105418961AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous scaffold material for tissue engineering, which belongs to the field of medical material preparation. The method is implemented by taking sodium alginate with good biocompatibility and lotus fibers as raw materials through the steps of oxidizing sodium alginate, nanocrystallizing lotus fibers, crosslinking the obtained object by using carboxymethyl chitosan, and carrying out vacuum freeze-drying on the obtained product, so that the porous scaffold material is obtained; and according to the invention, the defect that polymeric biomaterials are poor in biocompatibility is overcome, and the shortcomings that pure sodium alginate as a tissue material is poor in mechanical property and slowly degraded are made up. The porous scaffold material prepared according to the invention has good biodegradability, the porous scaffold material is degraded in the process of cell growth and reproduction, and degradation products are non-toxic and harmless; and the porous scaffold material has high porosity and specific surface area, so that the porous scaffold material is applicable to the focal adhesion and growth of cells, the intercellular signal transduction and nutrient transfer, and the discharge of degradation products and metabolic products.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Methods and Compositions for Neoadjuvant Therapy
InactiveUS20140271667A1Reduce metastatic migrationBiocideSugar derivativesCancer cellLymphatic Spread
A method for inhibiting tumor cell migration or metastasis of a cancer in a mammalian subject comprises one or more of the steps of administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of a composition comprising a molecule that: suppresses focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity or phosphorylation; suppresses ULK1 kinase activity; suppresses activation or signaling of the mTORC1 (Ser757) pathway; activates AMPK; activates FIP200; or activates LKB1, in a cancer cell. Still another method of inhibiting tumor cell migration involves inhibiting phosphorylation of ULK1 on Ser757 in subjects with lung cancer. Suppressing activation or signaling of the mTORC1 (Ser757) pathway in subjects is in one aspect useful in treating lung cancer.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY
Substituted pyrimidines, pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods thereof
The invention provide novel pyrimidine derivatives and analogs having inhibitory activities towards certain tyrosine kinases, e.g., Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) and / or Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treatment, reduction or prevention of certain diseases or conditions mediated by such by tyrosine kinases, e.g., cancers, tumors, fibrosis, inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, diabetes, or immunologically mediated diseases.
Owner:CHEN ZHIHONG
Application of galangin in preparation of anti-tumour metastasis medicine
InactiveCN103565789AAvoid stickingPrevent infiltrationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCell adhesionTranscriptional expression
The invention belongs to the field of natural medicines and in particular discloses application of galangin in inhibition of transcription and expression of an FAK (focal adhesion kinase) gene, inhibition of functions of FAK through phosphorylation, inhibition of cell adhesion, infiltration and migration and inhibition of tumour metastasis. The invention also relates to a galangin medicine prepared by adopting the conventional medicine preparation method, galangin can be combined with the conventional tumour treatment medicine and treatment method when being used, and treatment application is carried out by adopting the conventional oral, intravenous and intraperitoneal administration routes, so that a foundation is laid for further application of the galangin.
Owner:JIANGSU TARGET BIOMEDICINE RES INST +1
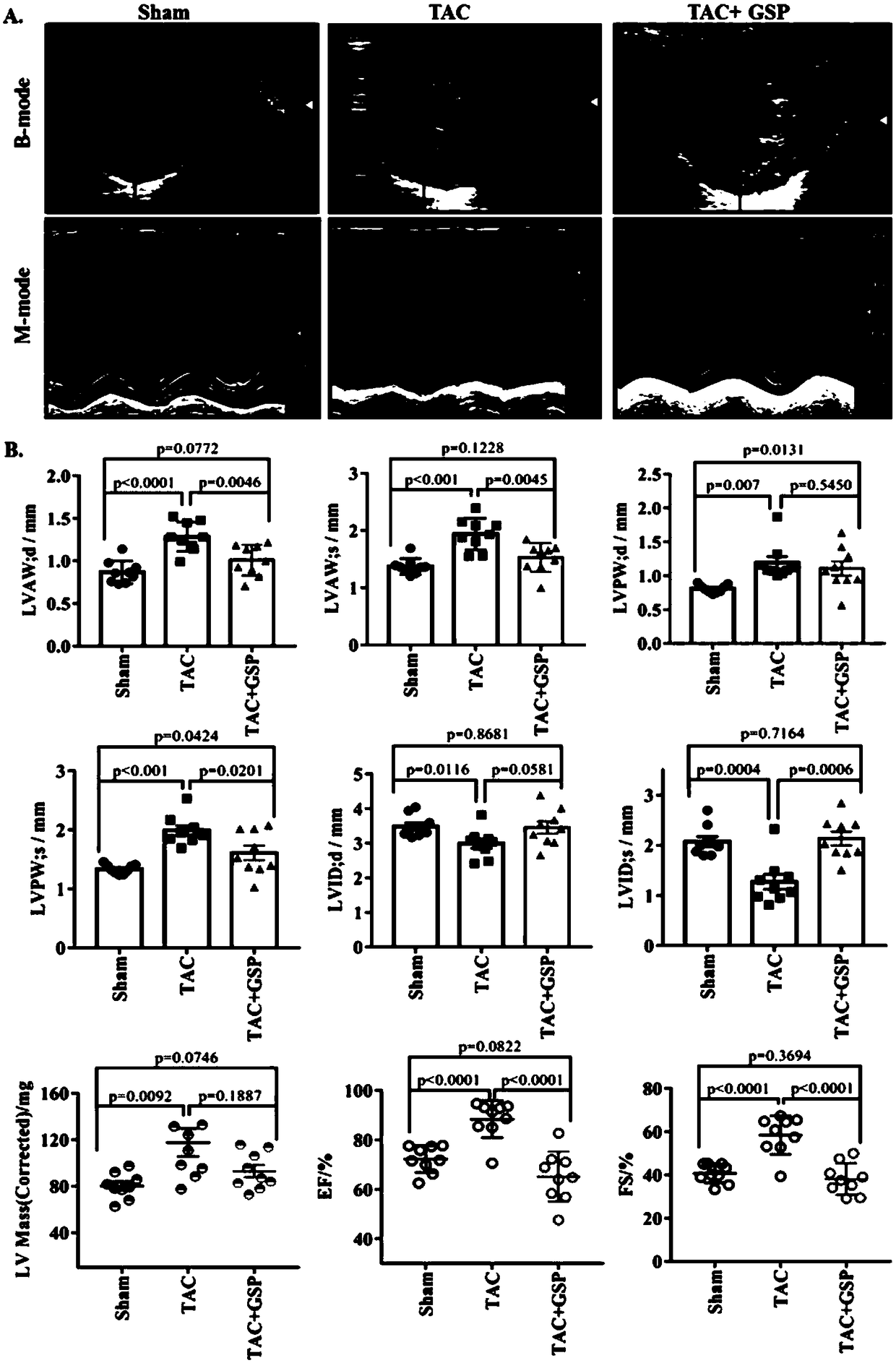
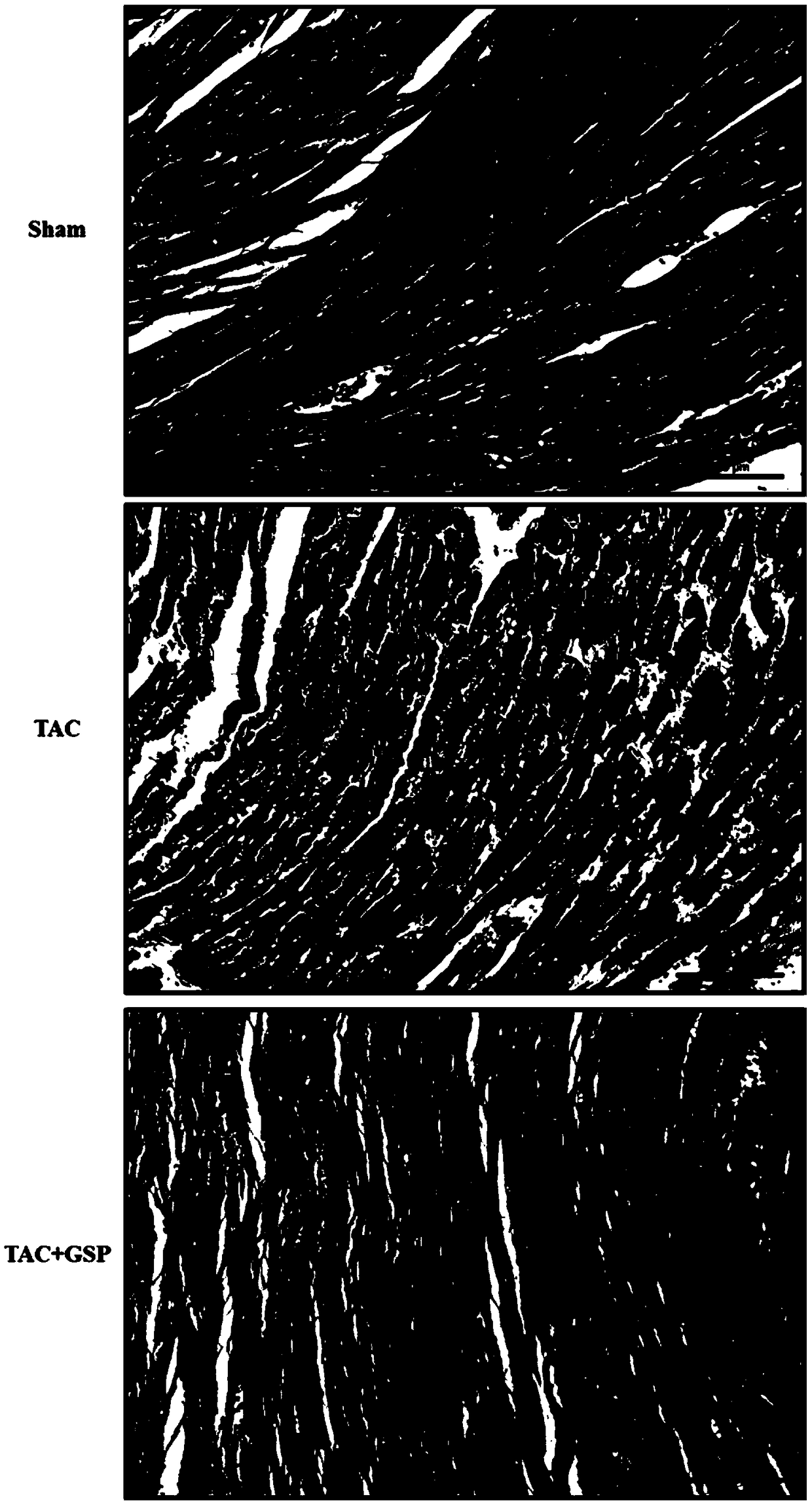
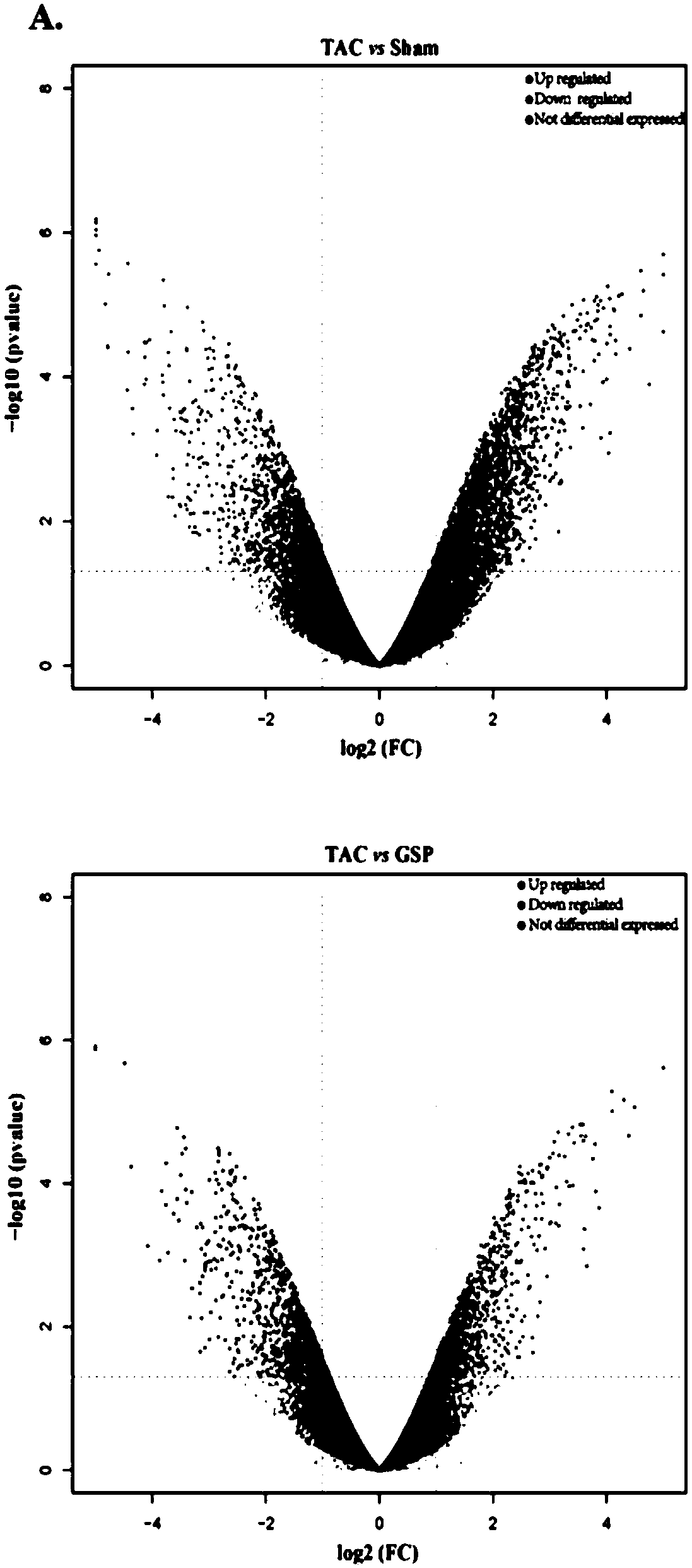
Application of ganoderma lucidum spore powder in preparing medicine for preventing and treating compensatory cardiac hypertrophic heart disease
InactiveCN108721342AInhibit hypertrophyPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderFreeze thawingDisease
The invention discloses application of ganoderma lucidum spore powder in preparing medicine for preventing and treating compensatory cardiac hypertrophic heart disease. The ganoderma lucidum spore powder is preferably the ganoderma lucidum spore powder obtained by an ultra-low temperature freeze-thawing breaking method. In the invention, a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy is induced by pressureoverload, the morphological structure and function of the heart of the mouse are evaluated by the left ventricular wall thickness, the inner diameter, the ejection fraction, and the histopathology andother indexes, and results indicate that the ganoderma lucidum spore powder (150 mg / (kg.BW)) can correct the morphological structure and function of the heart of the mouse with myocardial hypertrophyinduced by pressure overload. At the same time, the gene sequencing technology and bioinformatics analysis are applied, and it is found that ganoderma lucidum spore powder can protect the heart fromheart injury caused by pressure overload by regulating the changes of mRNA expression profile and by the multi-target and multi-channel integration regulation, wherein endocytosis, insulin signaling pathway and focal adhesion signaling pathway may be important regulatory mechanisms thereof.
Owner:广东仁源健康管理有限公司 +1
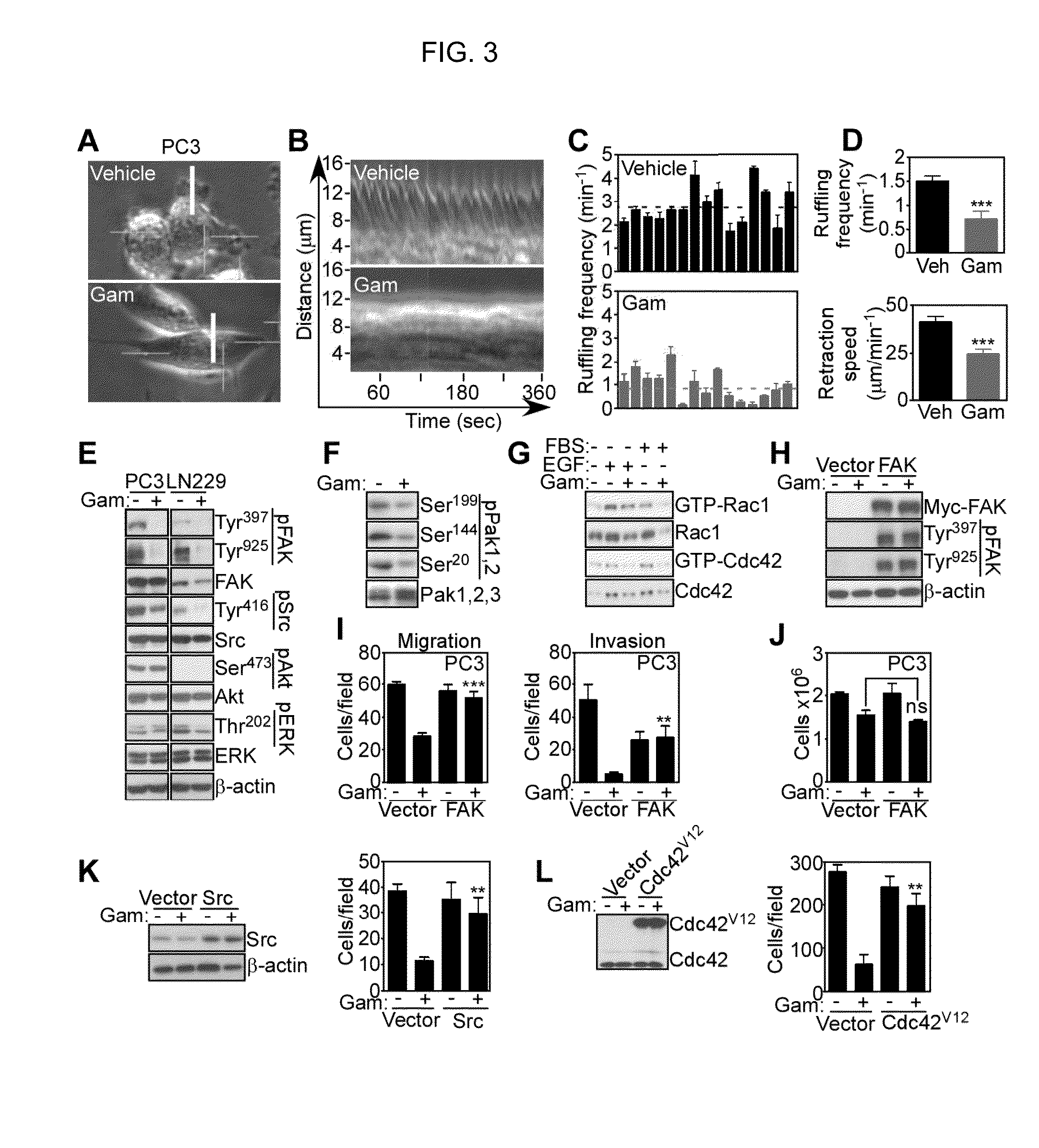
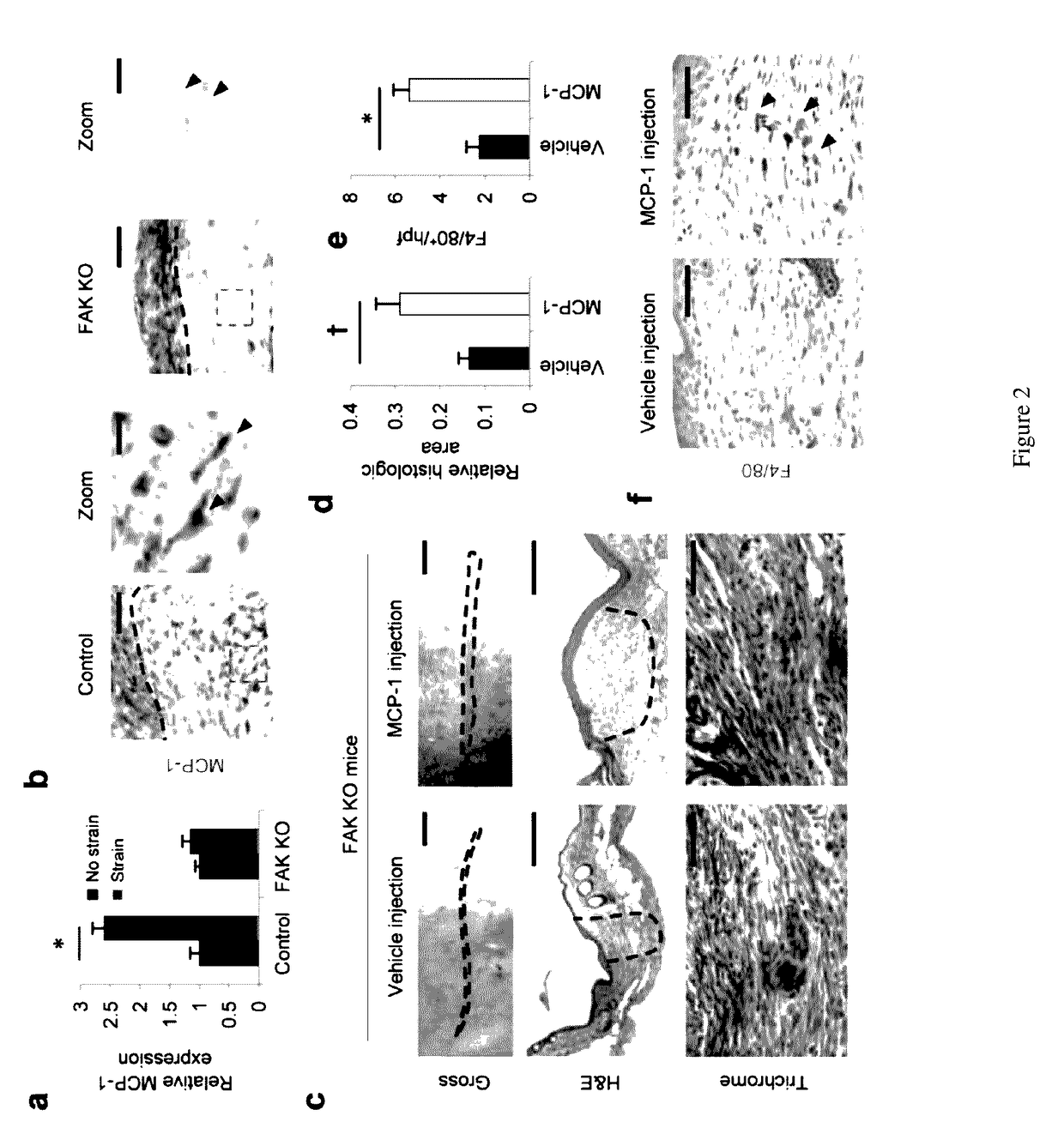
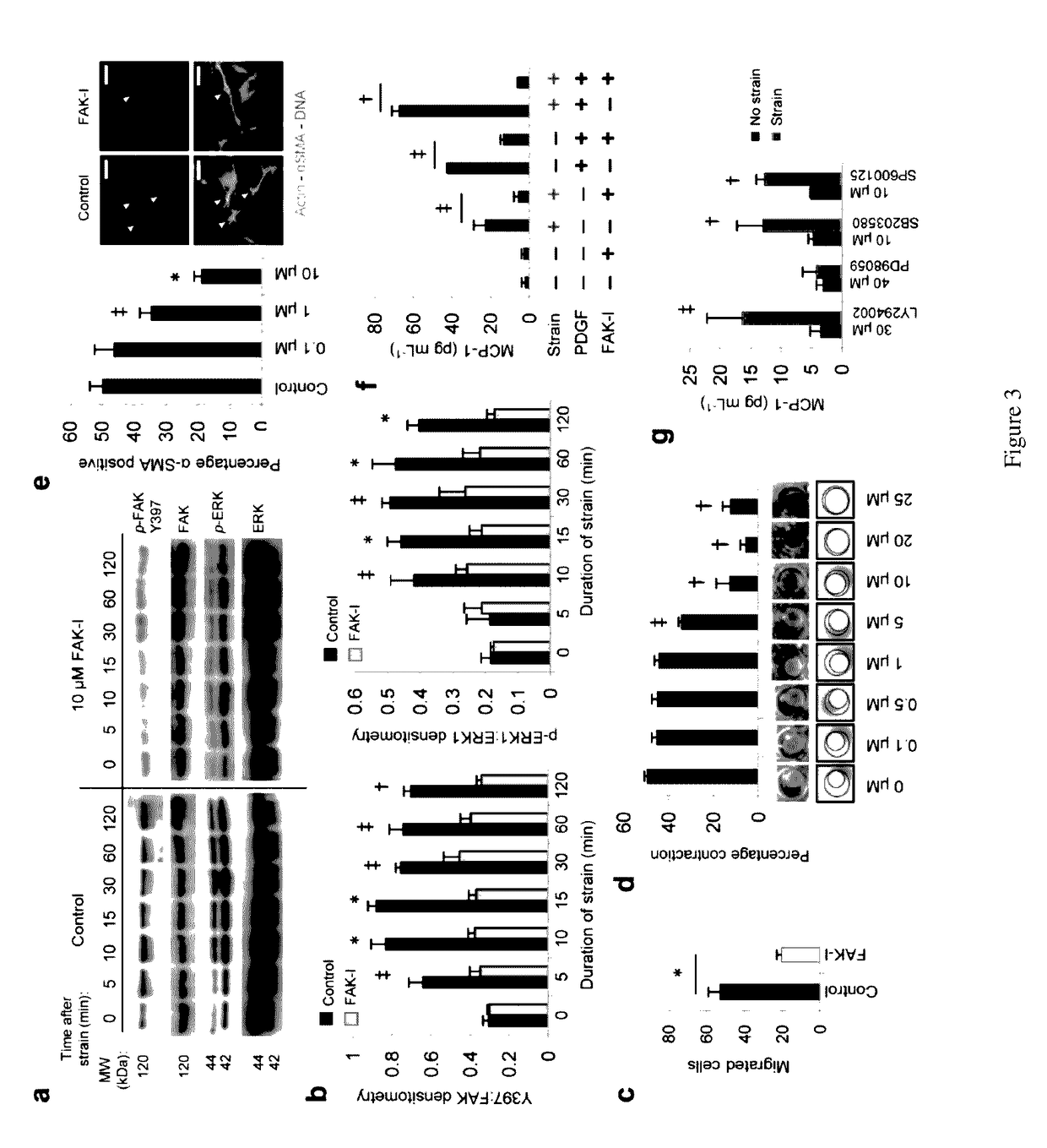
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase for control of scar tissue formation
The formation of scars at a wound site is reduced by contacting the wound site with an effective dose of an inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity or expression. Blockade of FAK is sufficient to prevent mechanical and inflammatory stimuli from activating MCP-1 pathways. In addition to these chemokine-mediated mechanisms, inhibition of FAK may control fibrosis by blocking fibroblast collagen production. Pharmacologic blockade of FAK significantly reduces scar formation in vivo.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-targeting compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112390760AHigh affinityStrong specificityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsNeoplasm diagnosisChemical compound
An embodiment of the invention provides an FAK-targeting compound as well as a preparation method and application of the compound. The compound has a structure as shown in a general formula (I) whichis described in the specification. The compound provided by the invention has high affinity with FAK, and can be used as a compound for targeting FAK. Furthermore, since the FAK-targeting compound provided by the invention has an inhibition effect on FAK, the FAK-targeting compound can be used for preparing tumor treatment medicines; Besides, after the FAK-targeting compound provided by the invention is subjected to radiochemical labeling, the FAK-targeting compound can be used as a tumor diagnosis imaging agent for preparing tumor diagnosis drugs. The FAK-targeting compound provided by the invention has the characteristics of good affinity, strong specificity and high selectivity, and has clinical application value.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Novel pyrimidine antitumor compound and its preparation method and use
The invention relates to a novel pyrimidine anti-tumor compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The novel pyrimidine anti-tumor compound is a compound shown in a formula (I), wherein each substituted group in the formula (I) is defined in the description. The invention also relates to the compound shown in the formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or application of a medicine composition containing the compound in inhibiting focal adhesion kinase, further treating tumor diseases, and especially treating pancreatic cancers, lung cancers and breast cancers. The formula (I) is shown in the description.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Substituted pyrimidines, pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods thereof
The invention provide novel pyrimidine derivatives and analogs having inhibitory activities towards certain tyrosine kinases, e.g., Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) and / or Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treatment, reduction or prevention of certain diseases or conditions mediated by such by tyrosine kinases, e.g., cancers, tumors, fibrosis, inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, diabetes, or immunologically mediated diseases.
Owner:CHEN ZHIHONG
A polypeptide for inhibiting focal adhesion kinase and its application
InactiveCN103739680BInhibition of activityImprove survival ratePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesNew medicationsKinase activity
The invention relates to the field of medicines, in particular to a polypeptide capable of inhibiting the activity of adhesion plaque kinase and treating acute lymphocytic leukemia. Its sequence is ADLIDGYRLVNGTSQRALERLV is a brand-new sequence, they can inhibit the activity of focal adhesion kinase in vitro, and improve the survival rate of tumor-bearing mice in vivo, and have potential new drug development value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YUANTAI BIOTECH CO LTD
A Visual and Quantitative Method for Labeling Aggregated Functional Proteins in Cells
ActiveCN112964682BAccurate evaluation of molecular contentAchieve imagingFluorescence/phosphorescenceStainingProtein detection
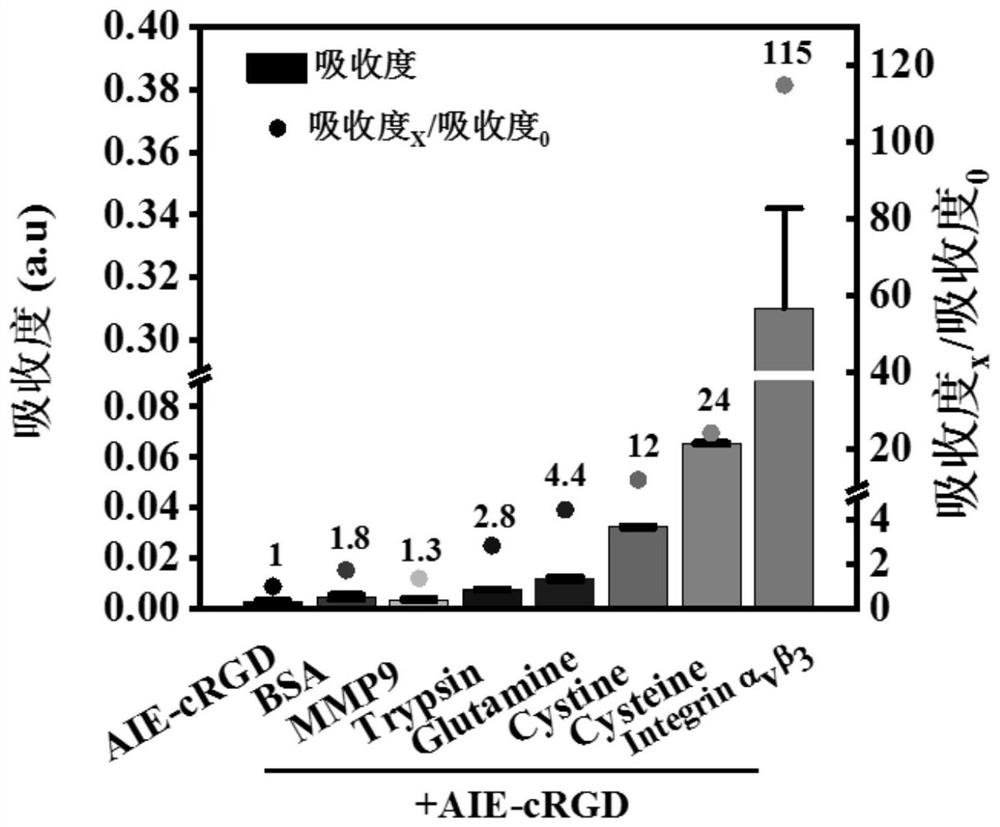
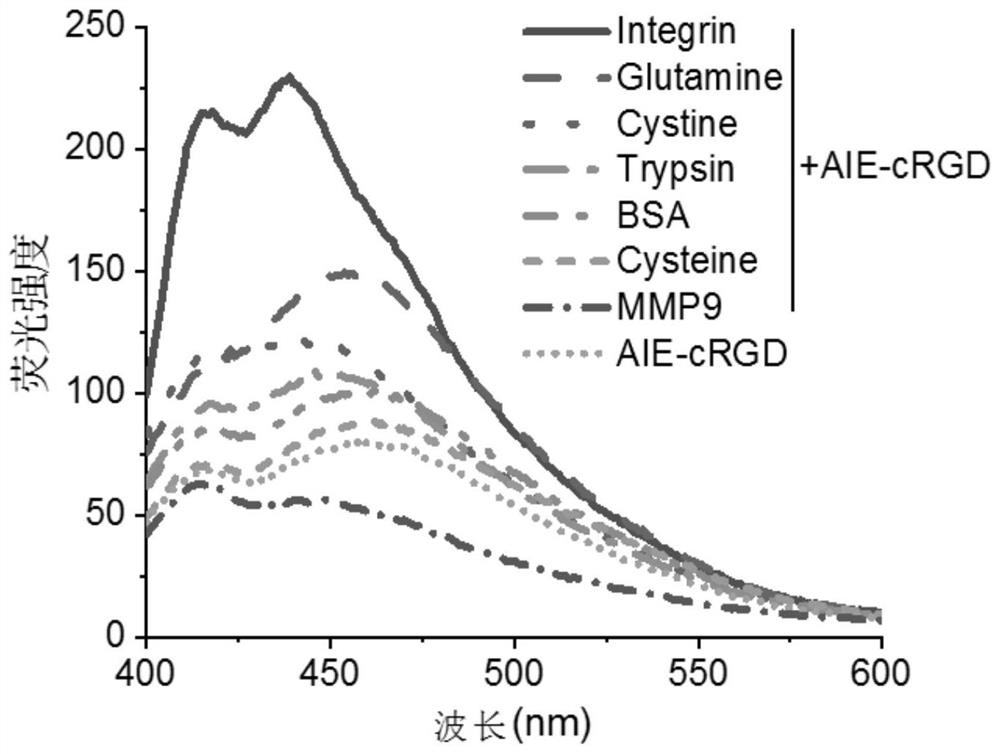
The invention relates to the technical field of biological probes and protein detection, and provides a method for visually and quantitatively labeling aggregated functional proteins in cells, by constructing and characterizing the aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD, and measuring the absorption peak of the probe AIE-cRGD and the fluorescence emission peak and the applicable concentration, the detection confirmed that the target protein of the probe was integrin αvβ3, the suspension survival cell model was established based on the poly-HEMA plating method, and the cells in the suspension survival cell model were induced to grow in an environment of detachment, Simulate the anti-apoptotic state of cells, use probes to label integrins in cells and perform imaging. When integrins are internalized into endosomes, determine the distribution of integrins in detached cells and detect phosphorylation Colocalization of focal adhesion kinase p‑FAK with activated integrins on endosomes determines cell resistance to apoptosis The invention can be directly used for the staining of living cells, lays a foundation for the visualization of physiological functions, and is beneficial to high-quality imaging and high-sensitivity online sensing monitoring.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
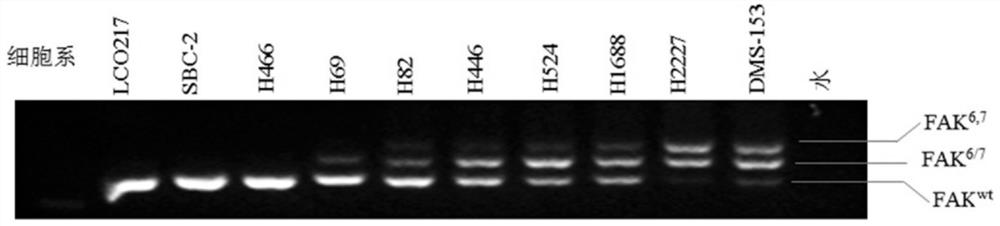
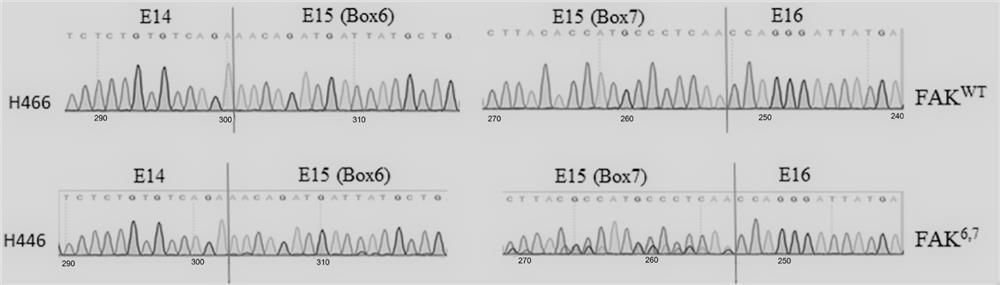
Focal adhesion kinase splice isoforms and their applications
ActiveCN113186296BMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDiagnostic agentFocal adhesion
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of galactotetraose sulfate and derivatives thereof in preparation of drugs for resisting epithelial cell adhesion
PendingCN111904968AHigh affinityInhibition of adhesionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical drugFocal adhesion
The invention provides application of galactotetraose sulfate and derivatives thereof in preparation of drugs for resisting epithelial cell adhesion. The galactotetraose sulfate or the derivatives thereof are applied to the drugs for resisting the epithelial cell adhesion, or the galactotetraose sulfate or the derivatives thereof are applied to a functional food for resisting the epithelial cell adhesion. The galactotetraose sulfate can achieve target binding with focal adhesion kinas (FAK). In this way, the adhesion capability of epithelial cells is effectively inhibited.
Owner:QINGDAO CENT HOSPITAL
Methods for treating adult respiratory distress syndrome
ActiveUS8420080B2Organic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTFocal adhesion
We have discovered that the activated phosphorylated form of focal adhesion kinase (hereafter “FAKp”) strengthens the microvascular endothelial cell (EC) junctions that form a barrier in pulmonary endothelia, and the increased barrier helps to prevent acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Thus certain embodiments of the invention are directed to prevention and treatment of ALI and ARDS by administering a therapeutically effective amount of FAKp to subjects at risk of developing or diagnosed as having either ALI or ARDS.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method and system for treating cancer utilizing tinagl1
PendingUS20210379147A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsFocal adhesionIntegrin
Disclosed is a method of treating cancer, involving the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway and the integrin / focal adhesion kinase (FAK) pathway to a patient in need of such treatment, where the inhibitor comprises at least the first 94 amino acids of a Tinagl1 protein, any fragments with conservative substitution showing 90% or greater homology to amino acids 22-94 of a Tinagl1 protein, or a signaling peptide fused or attached to a fragment with conservative substitution showing 90% or greater homology to amino acids 22-94 of a Tinagl1 protein.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medicinal use thereof
The invention belongs to the field of organic chemistry and drug synthesis, and relates to pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof. The compounds and salts thereof have a remarkable inhibiting effect on focal adhesion kinase, and can be used for preparing medicines for treating related diseases of the focal adhesion kinase, especially can be used for preparing medicines for treating related tumors with high expression of the focal adhesion kinase.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medical use Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medical use](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/58983c4a-6f34-4b4e-886d-d38db6c1a81b/BDA0001109210770000011.png)
![Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medical use Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medical use](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/58983c4a-6f34-4b4e-886d-d38db6c1a81b/BDA0001109210770000021.png)
![Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medical use Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medical use](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/58983c4a-6f34-4b4e-886d-d38db6c1a81b/BDA0001109210770000031.png)

![Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medicinal use thereof Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medicinal use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/82088d3e-8b8f-4018-a4b0-52479f13a449/BDA0001109210770000011.png)
![Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medicinal use thereof Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medicinal use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/82088d3e-8b8f-4018-a4b0-52479f13a449/BDA0001109210770000021.png)
![Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medicinal use thereof Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine compounds and salts thereof, preparation method and medicinal use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/82088d3e-8b8f-4018-a4b0-52479f13a449/BDA0001109210770000031.png)