A Visual and Quantitative Method for Labeling Aggregated Functional Proteins in Cells
A medium-aggregation-type, cell-model technology, applied in the field of biological probes and protein detection, can solve the problems of aggregation quenching effect, fluorescence quenching of fluorescent molecules, etc., achieve simple operation, good biocompatibility, and avoid aggregation quenching effect of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Construction and characterization of aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD
[0031] The aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD contains aggregation luminescent molecules and peptides targeting integrin, 1,2-bis(4-carboxyphenyl)-1,2-styrene and cRGD are mixed according to the same molar ratio, and then Add the catalyst EDC-NHS for catalysis, and react overnight to obtain the aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD;
[0032]Dimethyl sulfoxide DMSO and water were formulated into a test system at a ratio of 1:100, and the ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence spectra of the aggregation-induced luminescence probe AIE-cRGD with different concentrations were measured in the test system, and the ultraviolet absorption spectra showed that different concentrations of AIE-cRGD The aggregation-induced luminescence probe AIE-cRGD has an absorption peak at 230nm, and the fluorescence spectrum shows that the aggregation-induced luminescence probe A...
Embodiment 2
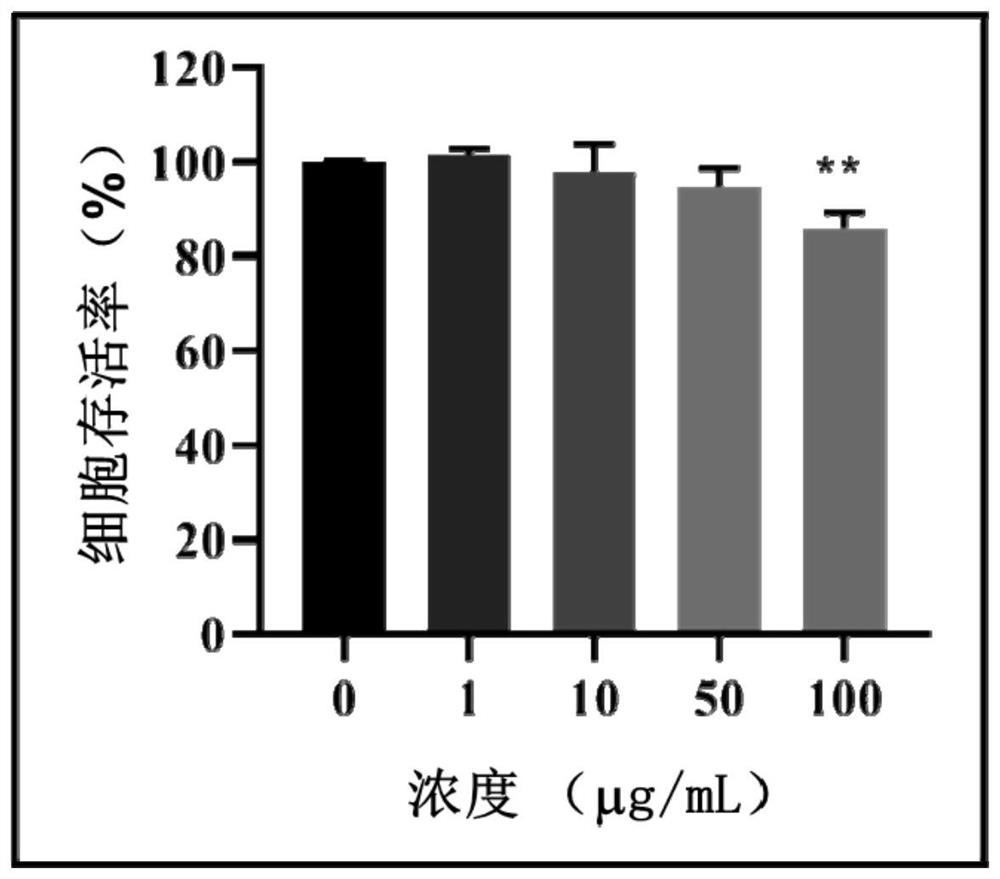
[0033] Example 2: Concentration of aggregation-induced luminescence probe AIE-cRGD
[0034] Taking breast tumor cell MCF-7 as an example, determine the concentration of AIE-cRGD; set the concentration of AIE-cRGD to 1 μg / mL, 10 μg / mL, 50 μg / mL and 100 μg / mL respectively. mL, and then MCF-7 cells were placed in various concentrations of aggregation-induced luminescence probe AIE-cRGD solutions, and the cell counting reagent CCK-8 was used to detect the concentration of MCF-7 cells in different concentrations of aggregation-induced luminescence probe AIE-cRGD solutions. By analyzing the effect of the concentration of aggregation-induced luminescence probe AIE-cRGD on cell viability, it was found that when the concentration of aggregation-induced luminescence probe AIE-cRGD was 1 μg / mL, 10 μg / mL and 50 μg / mL, the cell viability did not occur significantly changes, and when the aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD concentration was 100 μg / mL, the cell viability decreased...
Embodiment 3
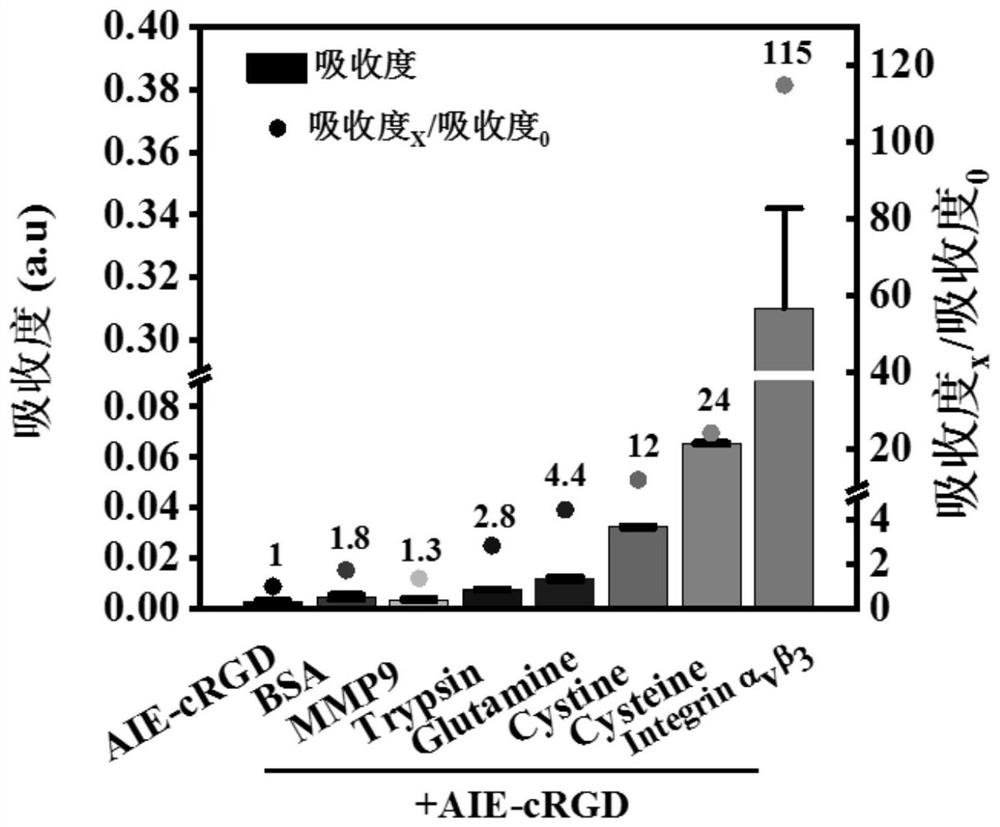
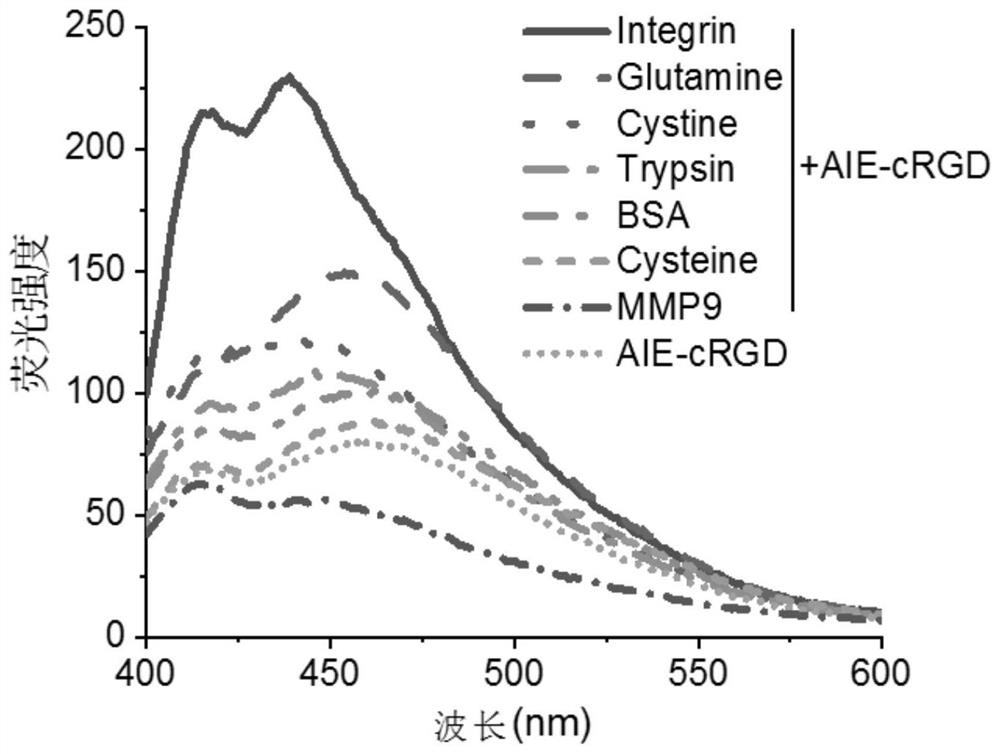
[0035] Example 3: Detection of the targeting protein of the aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD
[0036] Dilute bovine serum albumin BSA, trypsin, glutamine Glutamine, cysteine Cysteine, cystine Cystine, matrix metalloproteinase MMP9 and integrin αvβ3 to 100 μg / mL respectively, and aggregate-induced luminescent probe AIE - Dilute the concentration of cRGD to 100 μg / mL, then add each protein solution and aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD solution into 300 μL phosphate buffered saline solution according to the volume ratio of 1:1 and mix, and measure 230nm for each protein solution Changes in the ultraviolet absorption intensity of the aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD at the place, and analyze the response of the aggregation-induced luminescent probe AIE-cRGD to each protein, such as figure 2 and image 3 As shown, the absorbance of the AIE-cRGD solution at 230nm is 0.0027, and the absorbance of the AIE-cRGD solution at 230nm is 0.31 aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com