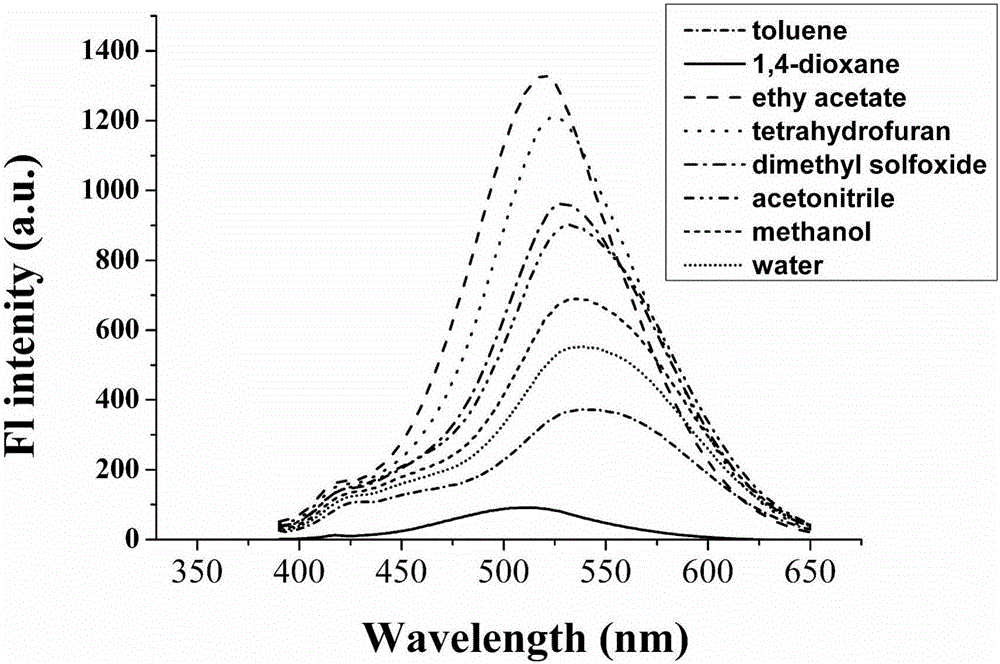
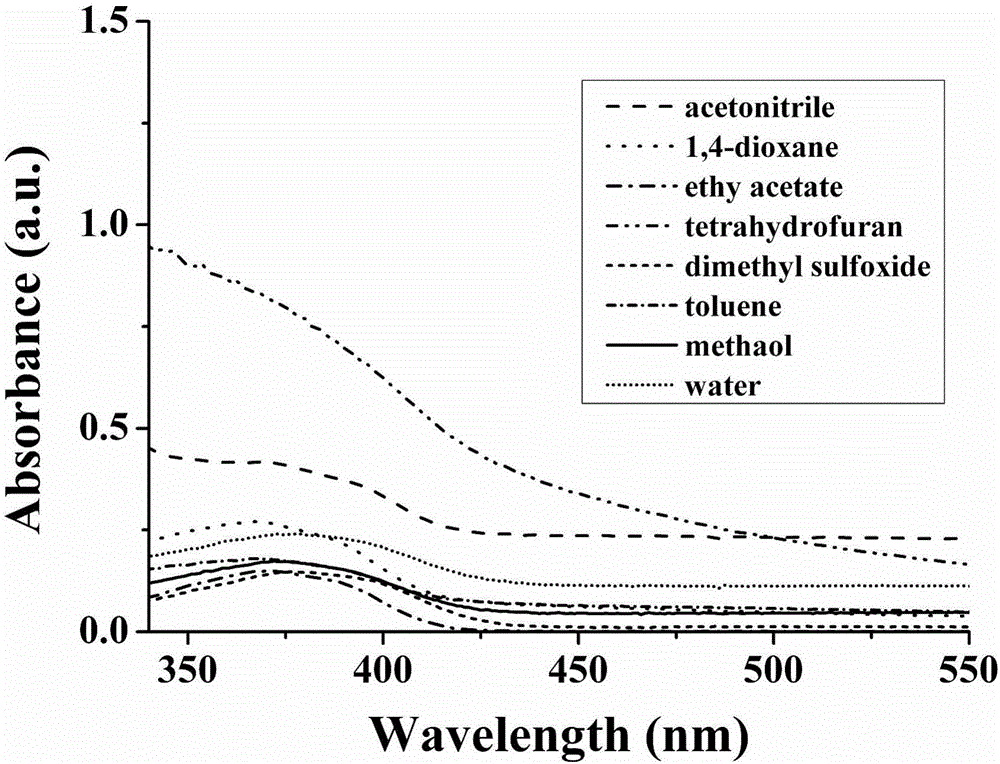
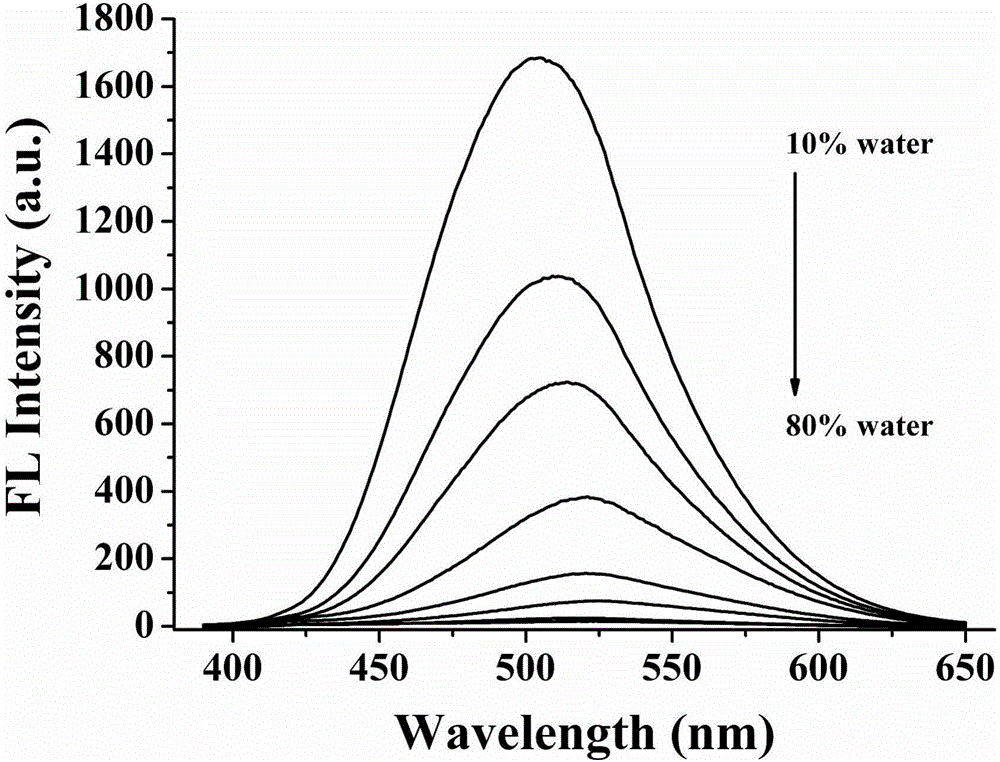
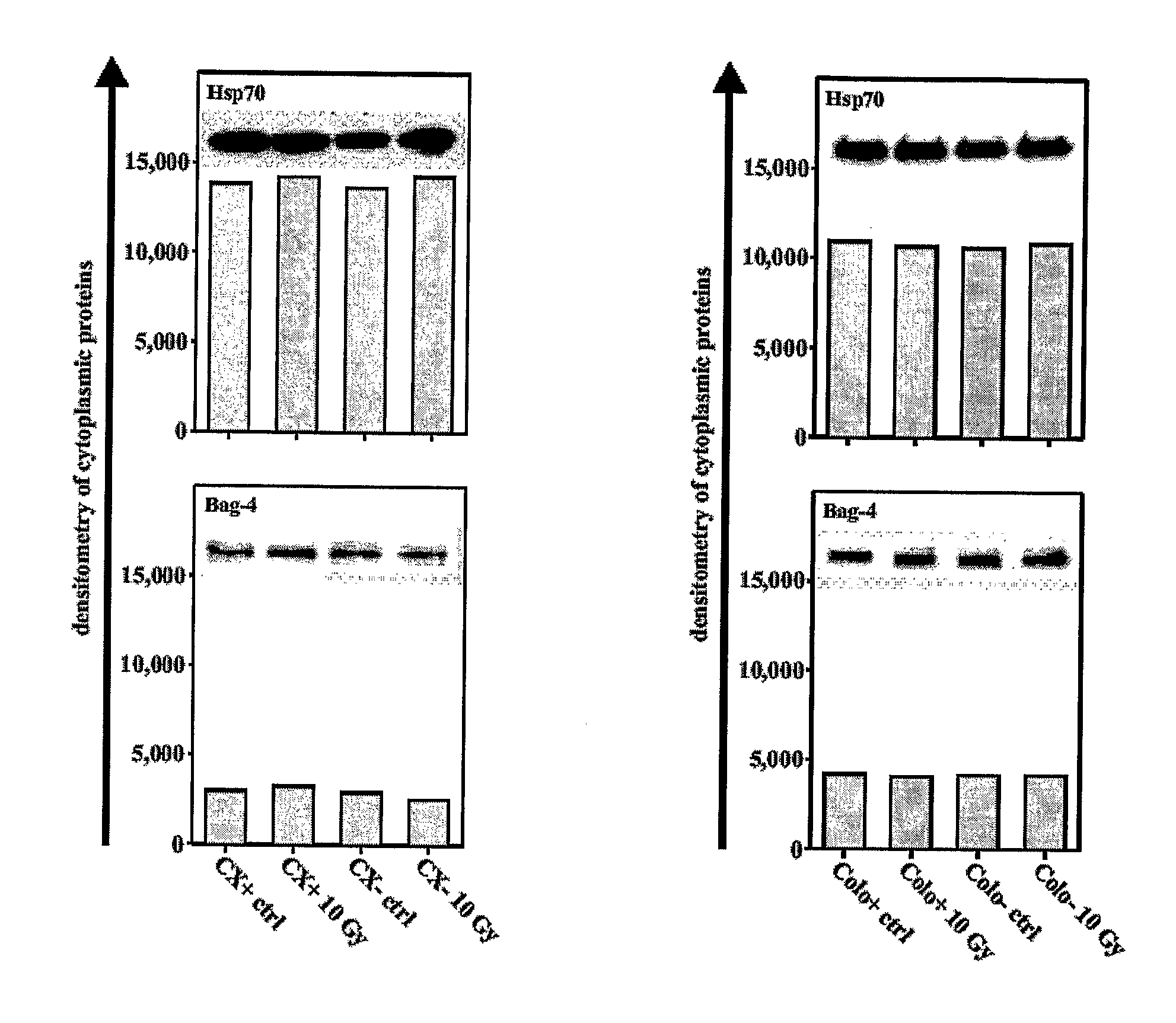
Patents
Literature
74 results about "Co localization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Co-Localization Microscopy Literature References. Co-localization describes the presence of two or more different molecules in very close spatial positions within a specimen, which is often visualized using confocal microscopy with synthetic fluorophores or fluorescent proteins.
Co-localization affinity assays
The invention provides a new assay format for high throughput molecular binding studies at a single molecule level. The invention enables creation of binding event identifiers in a highly parallel way. Individual binding events occur between two agents of a binding pair, e.g., a protein-based binding pair or a binding pair comprising a protein and a chemical moiety. The binding event identifier created through the binding of the two binding agents is unique to that pair, and identification of the binding event identifier is indicative of the binding of these specific may be assessed through a readout that is digital in nature. The invention enables very large sets of thousands or more of different binding agents or potential binding agents to be assayed simultaneously, resolving millions or more of potential interactions, and distinguishing specific interactions from those that are less specific.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
Methods of detecting nucleic acid sequences with high specificity
InactiveUS20130023433A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
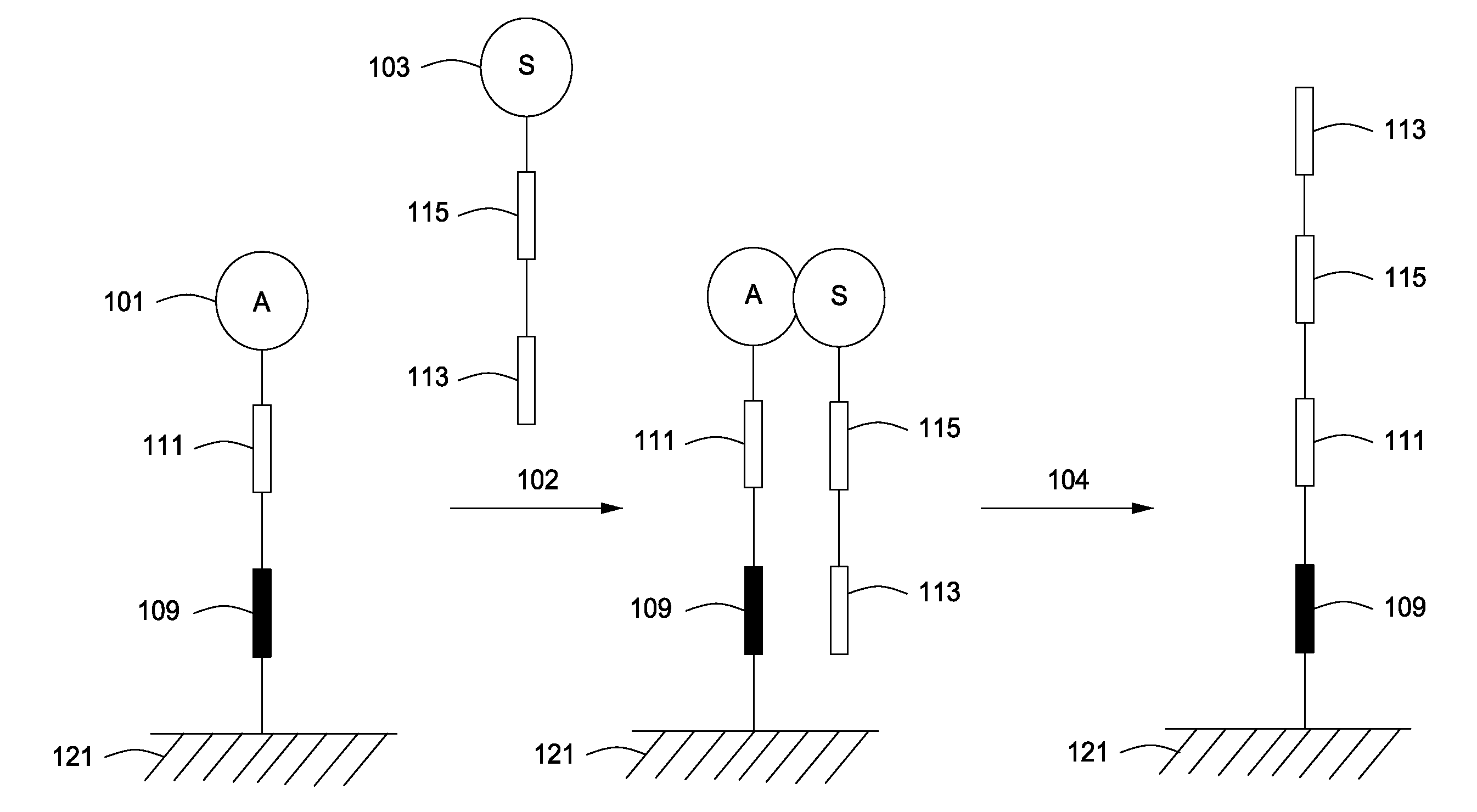
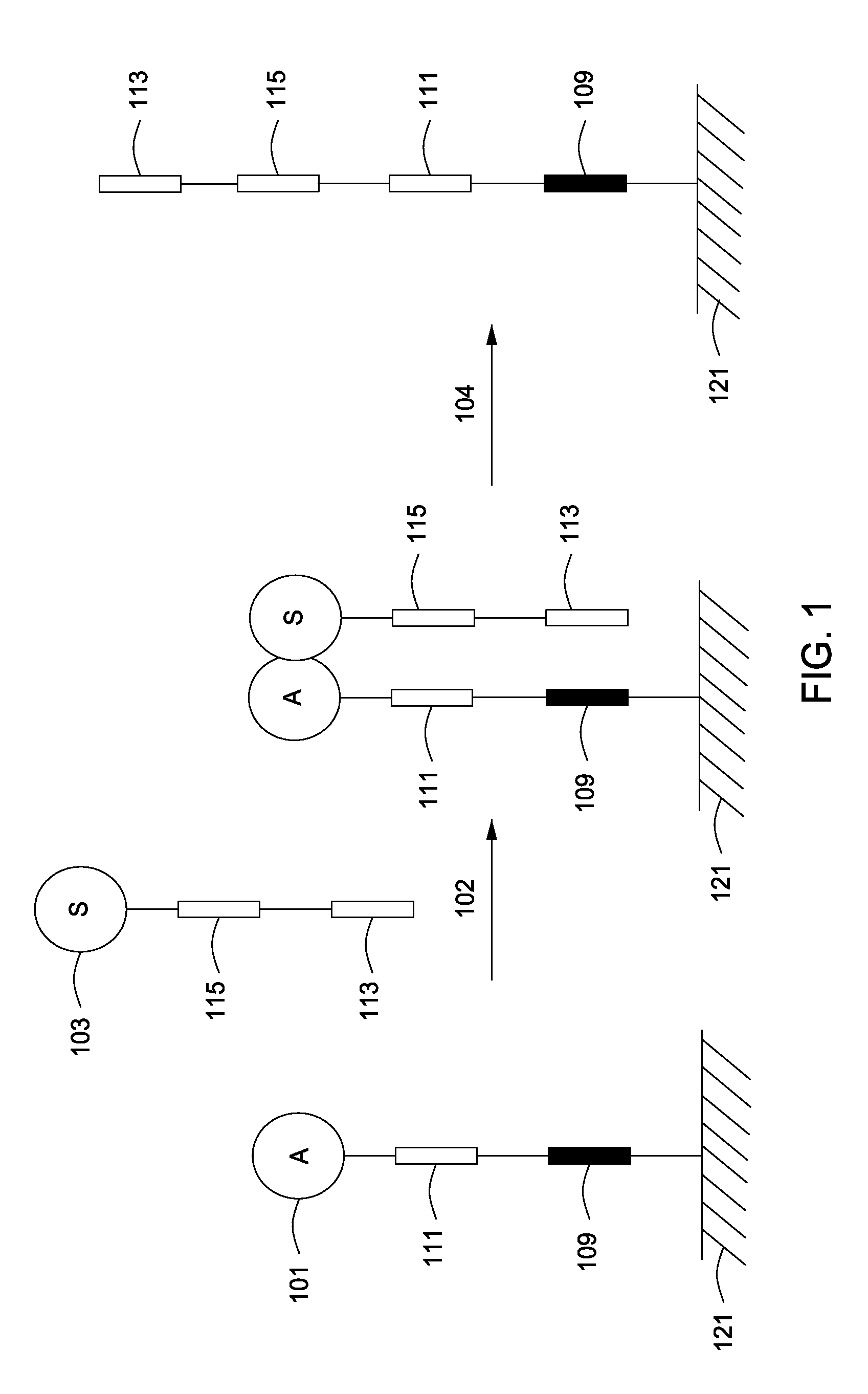
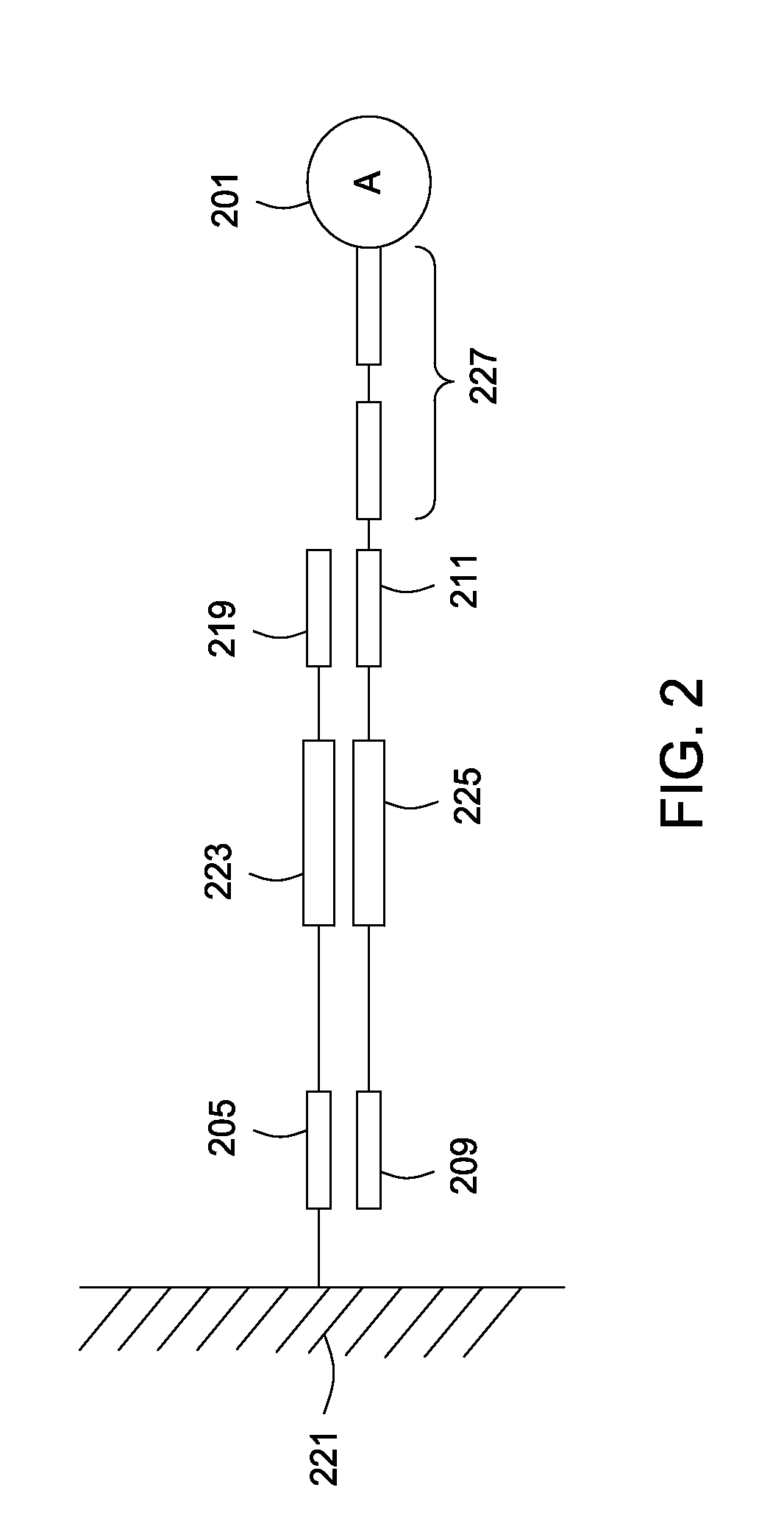
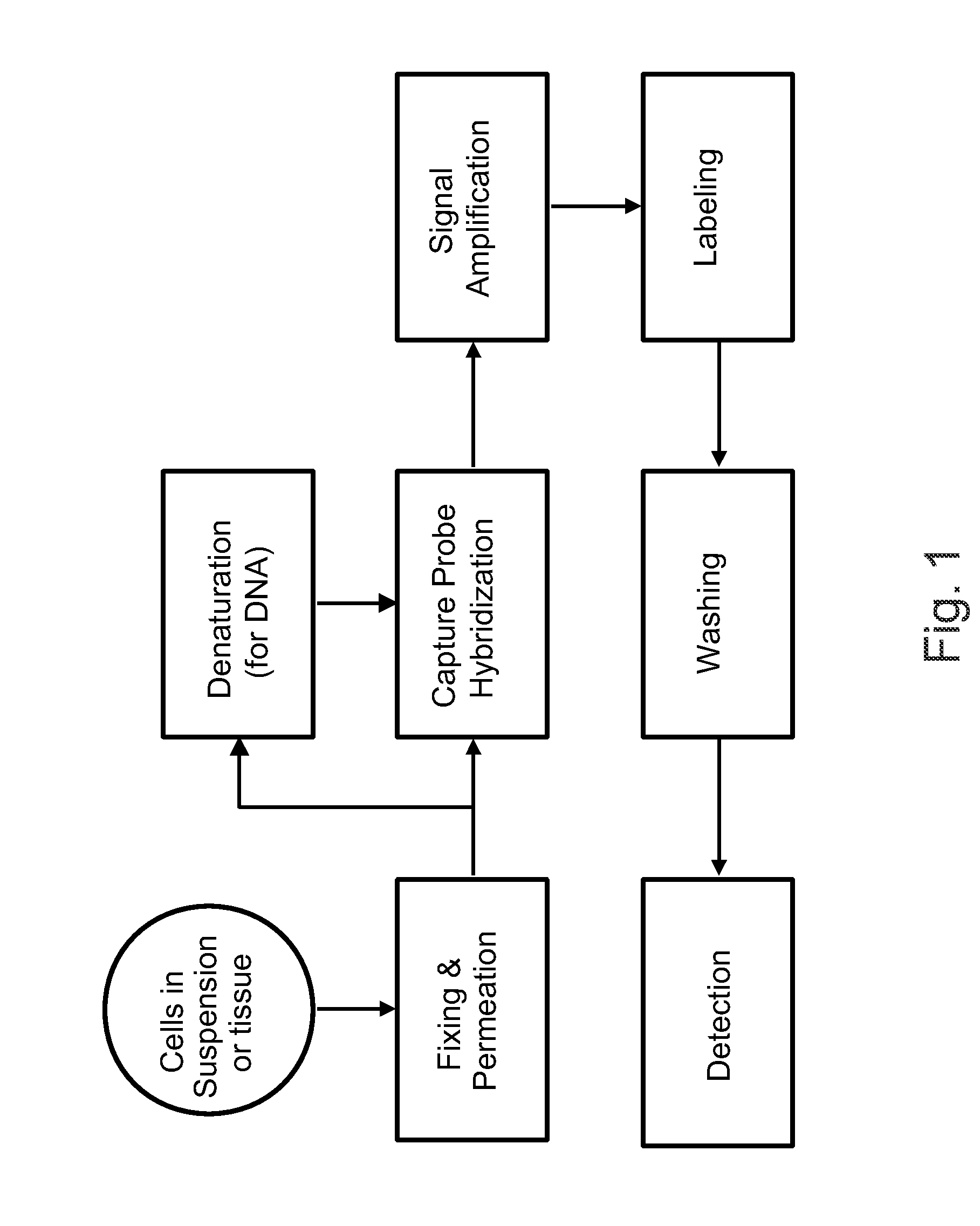
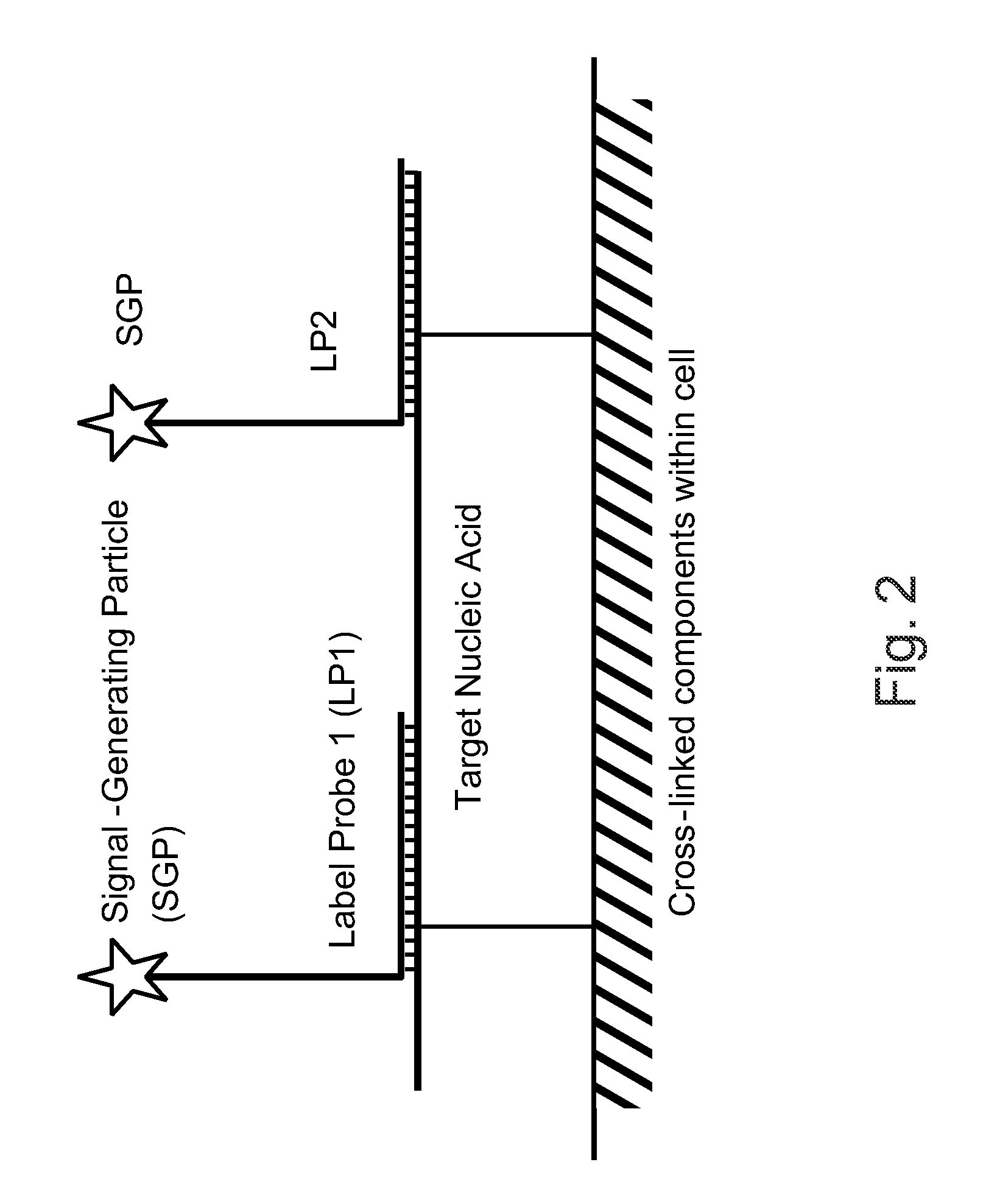
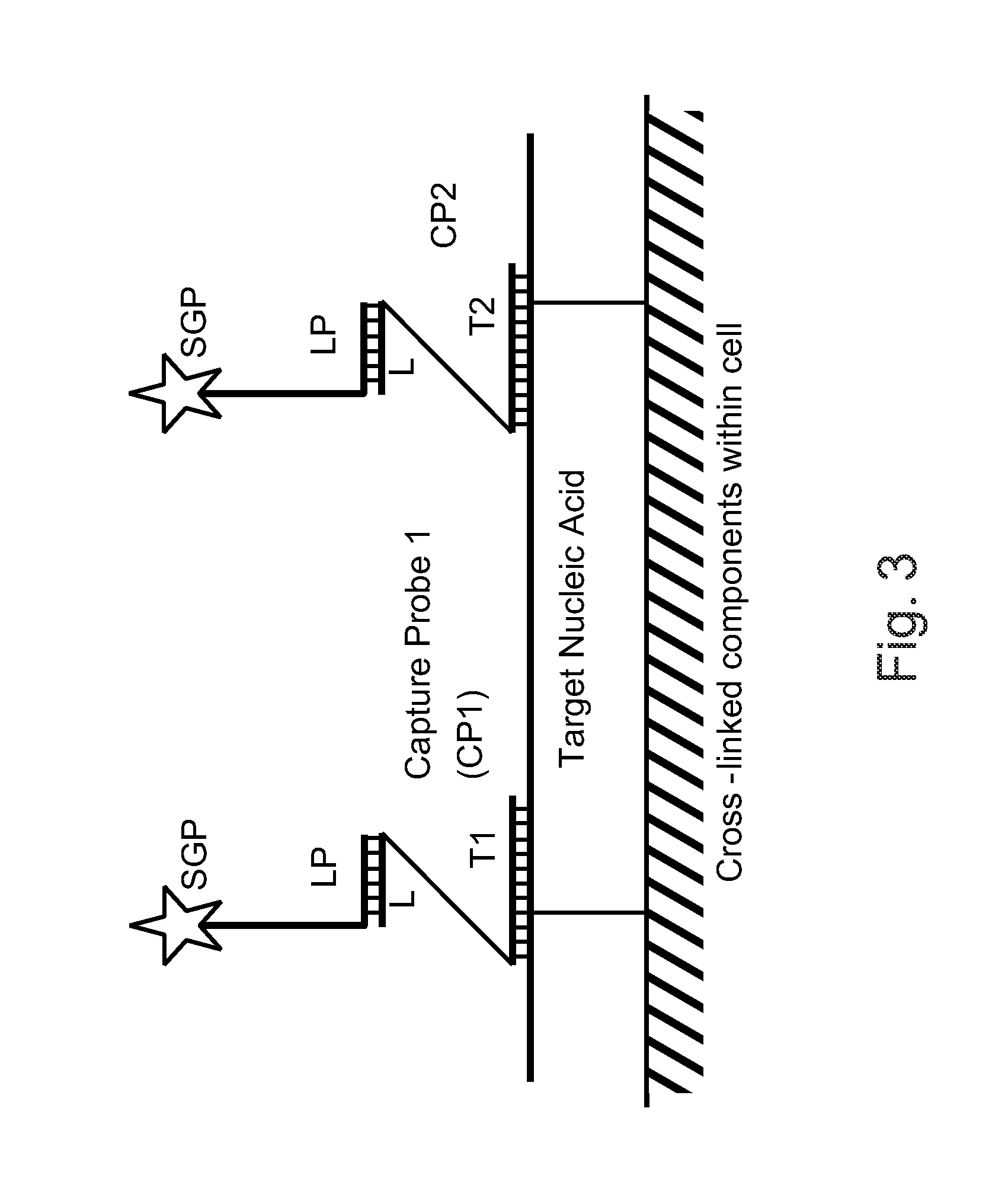
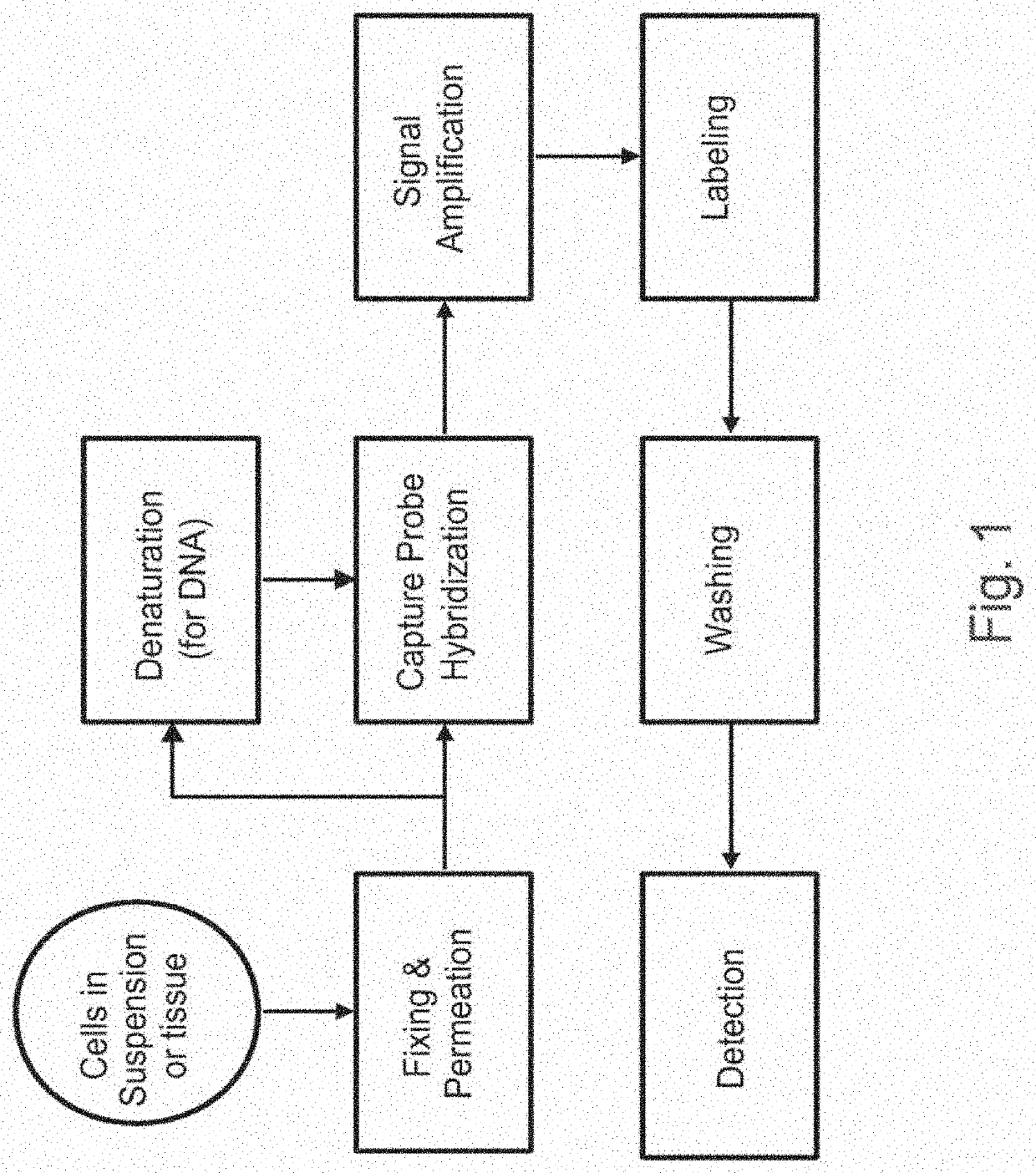
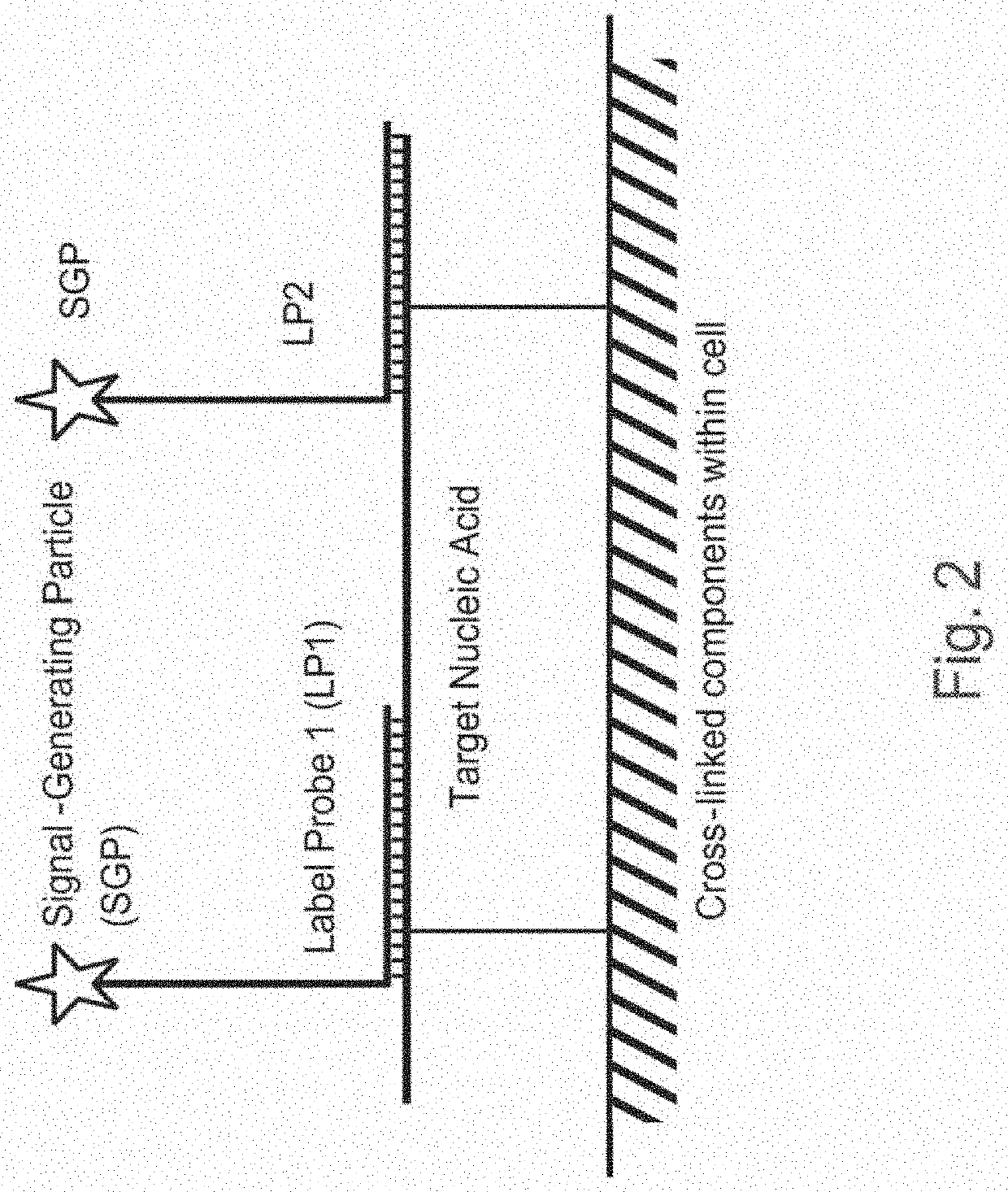
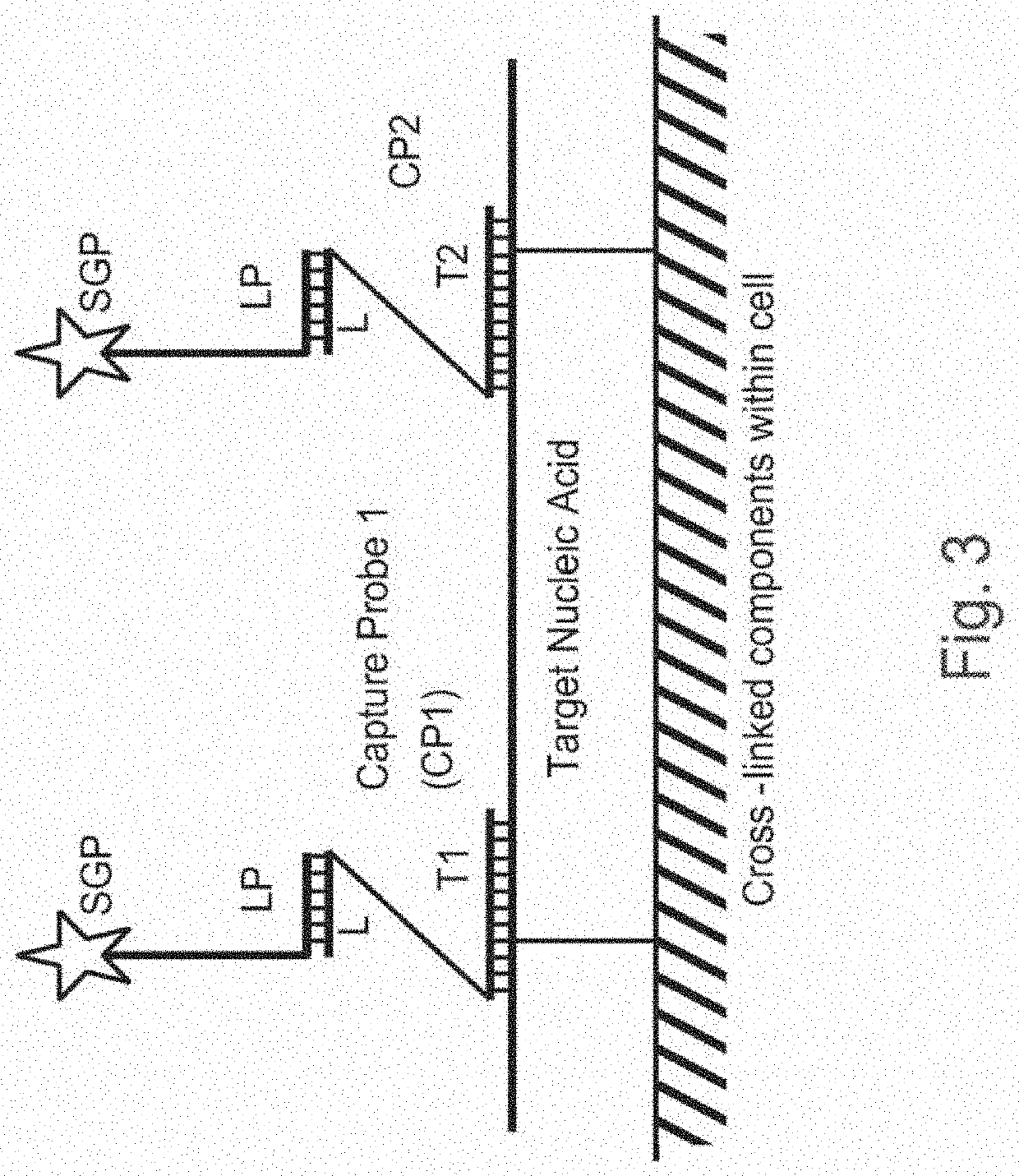
The invention relates to methods of detecting nucleic acids, including methods of detecting one or more target nucleic acid sequences in multiplex branched-chain DNA assays, are provided. Nucleic acids captured on a solid support or suspending cells are detected, for example, through cooperative hybridization events that result in specific association of a label with the nucleic acids. The invention further relates to methods to improve probe hybridization specificity and their application in genotyping. The invention also relates to in situ detection of mis-joined nucleic acid sequences. The invention relates to reducing false positive signals and improve signal-to-background ratio in hybridization-based nucleic acid detection assay. The invention further relates to method to improve specificity in hybridization based nucleic acid using co-location probes. Compositions, tissue slides, sample of suspended cells, kits, and systems related to the methods are also described.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Fluorescent dye based on naphthalimide, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a fluorescent dye based on naphthalimide, and a preparation method and an application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a naphthalimide fluorophore which has a structure as shown in a general formula I which is described in the speicification, wherein groups in the formula I are described in the specification. The compound provided by the invention has good water solubility and high fluorescent quantum yield in an aqueous solution, and can be used for two-photon imaging and co-localization imaging to living cells.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Spatial and cellular mapping of biomolecules in situ by high-throughput sequencing
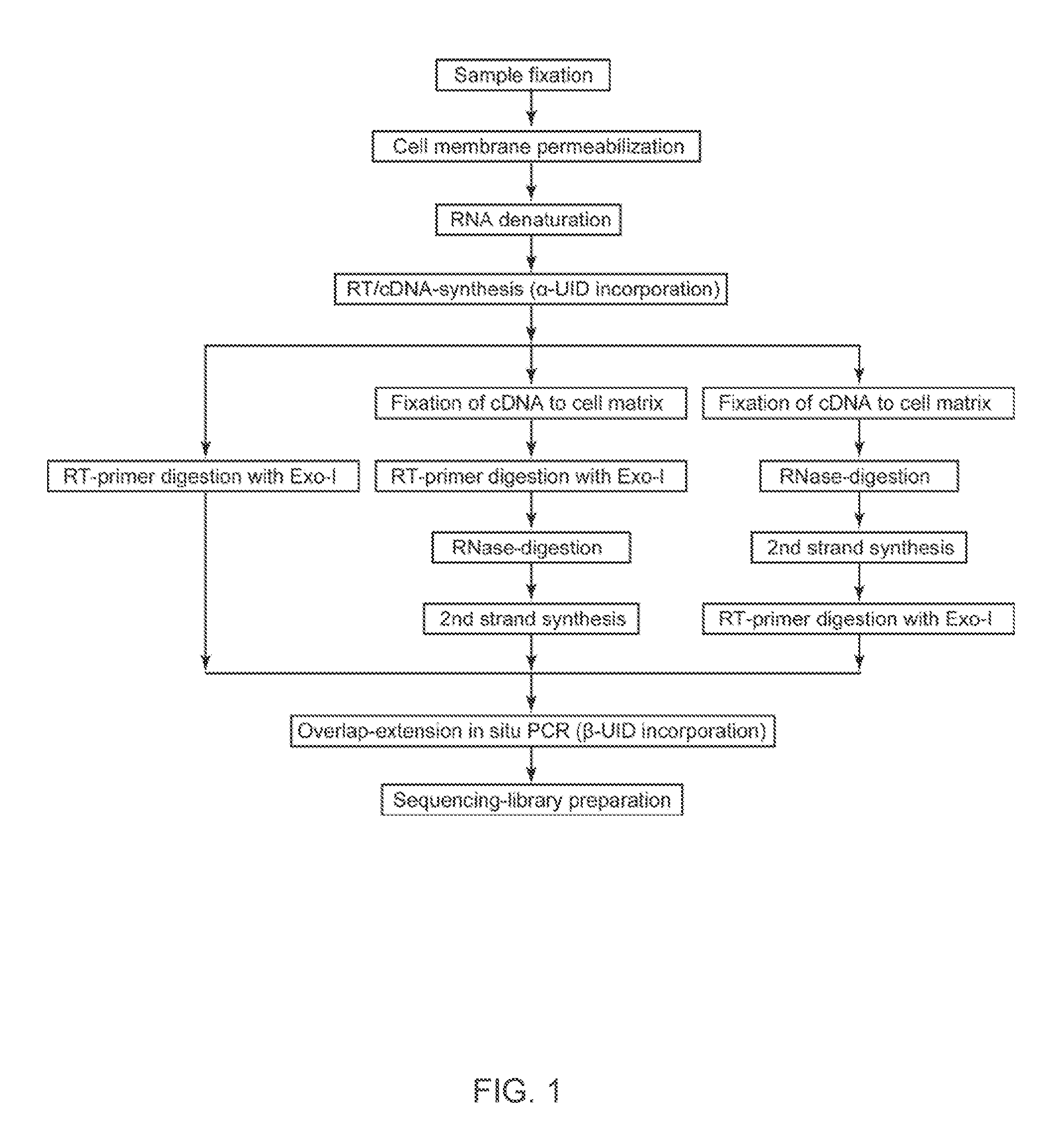
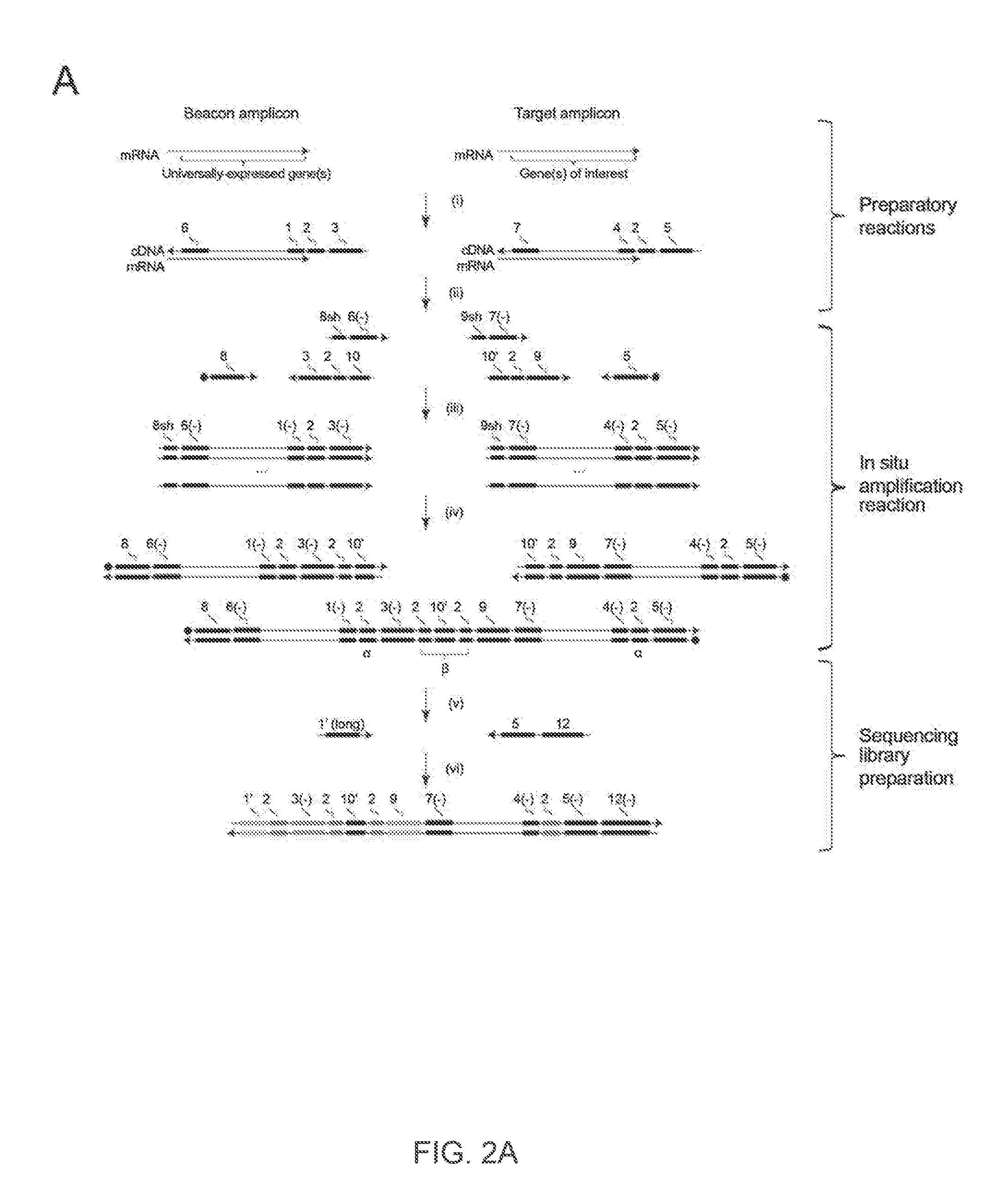
The present invention relates to molecular microscopy or volumetric imaging by proximal unique molecular identifiers (“UID”) reaction (“VIPUR”) microscopy methods to record the cellular co-localization and / or spatial distributions of arbitrary nucleic acid sequences, or other biomolecules tagged with nucleic sequences. The method involves one or both of two DNA sequence-components such as an α-UID, which may identify the targeted sequences-of-interest themselves and / or spatial beacons relative to which their distances are measured, and a −β-UID, which labels α-UID association events.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
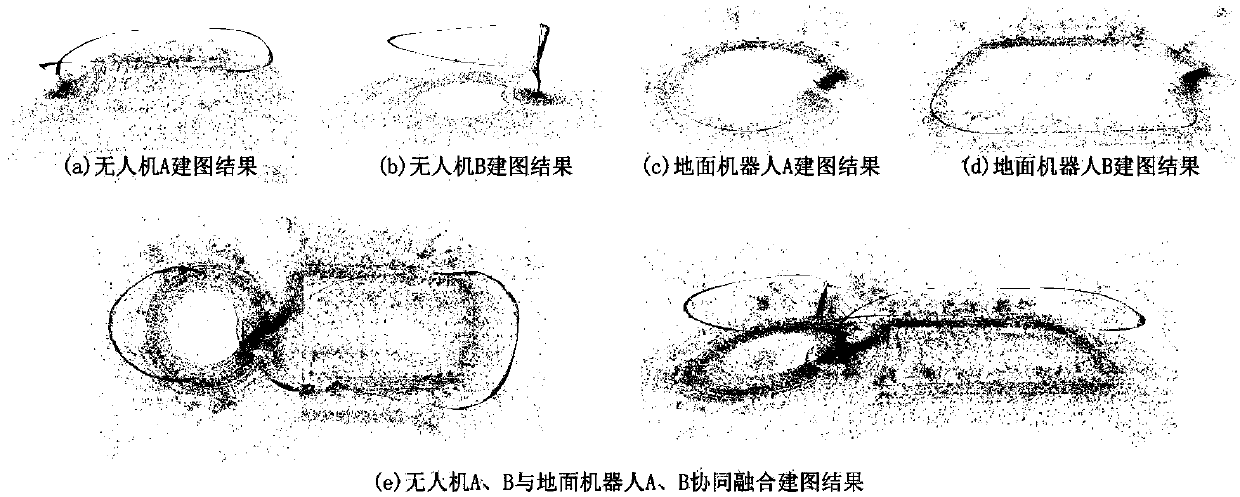
Multi-robot co-localization and fusion mapping method under multi-view in open space
ActiveCN109579843AReduce mistakesReliable environmental informationNavigational calculation instrumentsSensing by electromagnetic radiationPoint cloudVision based
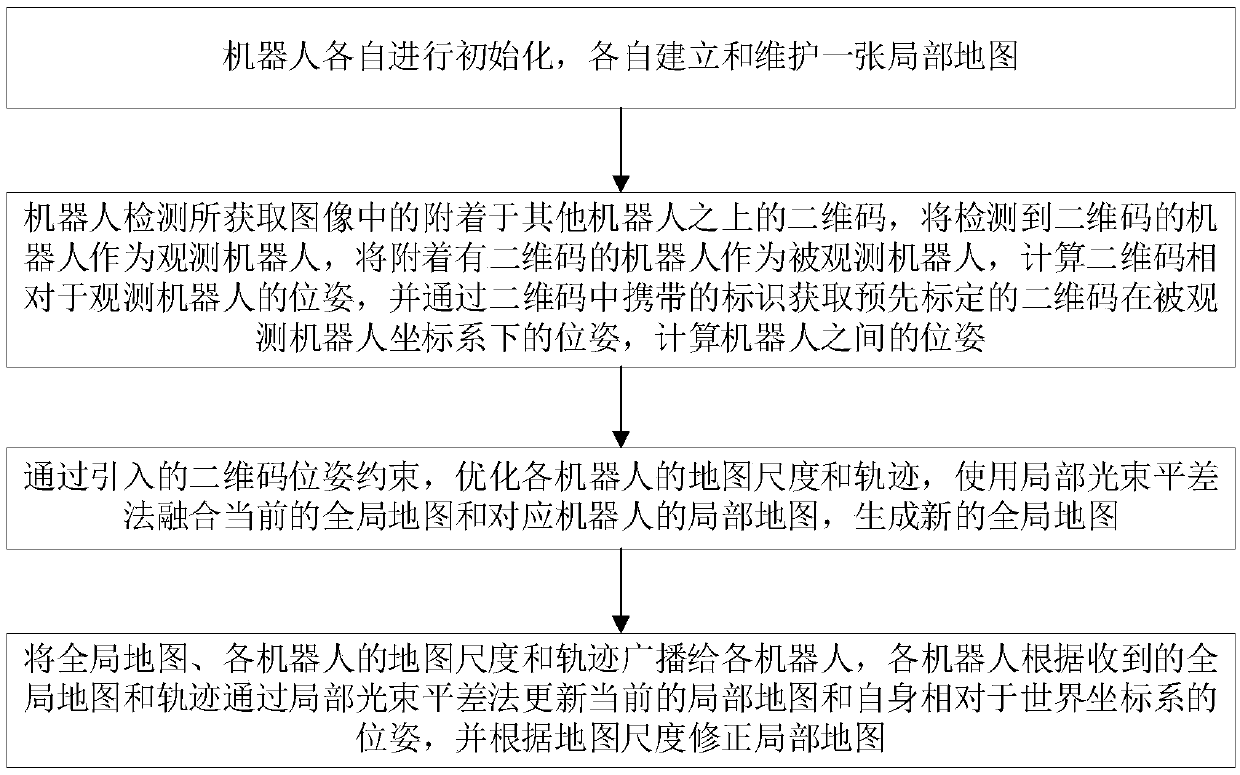
The invention discloses a multi-robot co-localization and fusion mapping method under multi-view in an open space. The method comprises the following steps of: completely covering a detection scene byusing multiple observations in the air and the ground, integrating scene image data collected by aerial robots and ground robots, and positioning the robots by visual constraints and restoring three-dimensional scene information; optimizing three-dimensional point cloud map of the mapping and positioning system and six-degree-of-freedom pose of the robots by specific visual features adhered to the robot. The pose optimization and map fusion algorithm based on visual features significantly improve reconstruction and positioning accuracy, revise map scales, so that local maps of each robot canbe shared among multiple heterogeneous robots, the coverage of three-dimensional reconstruction is improved, the reliable environmental information is quickly provided for mission planning, disaster environment search and rescue, and military anti-terrorism.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
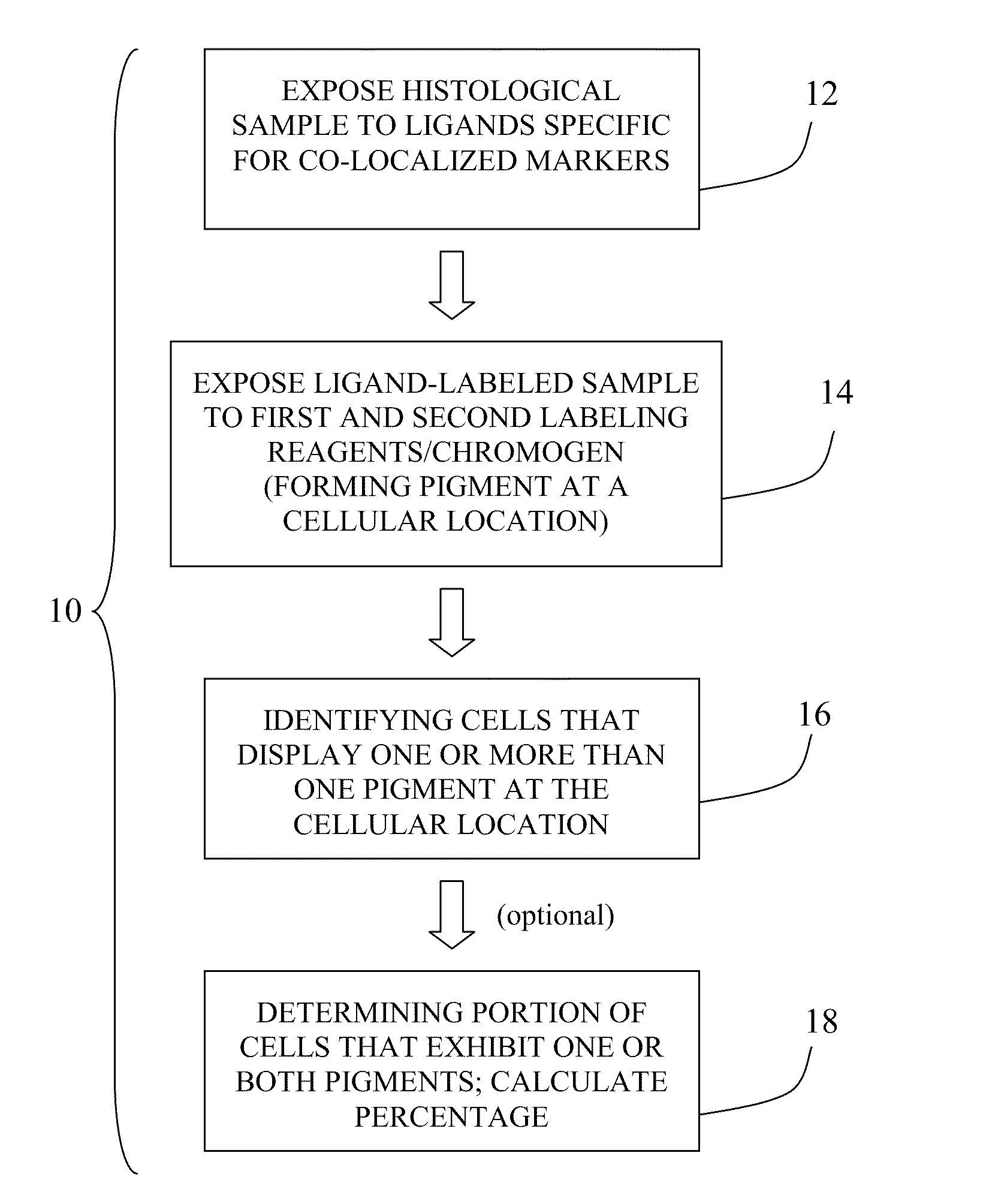
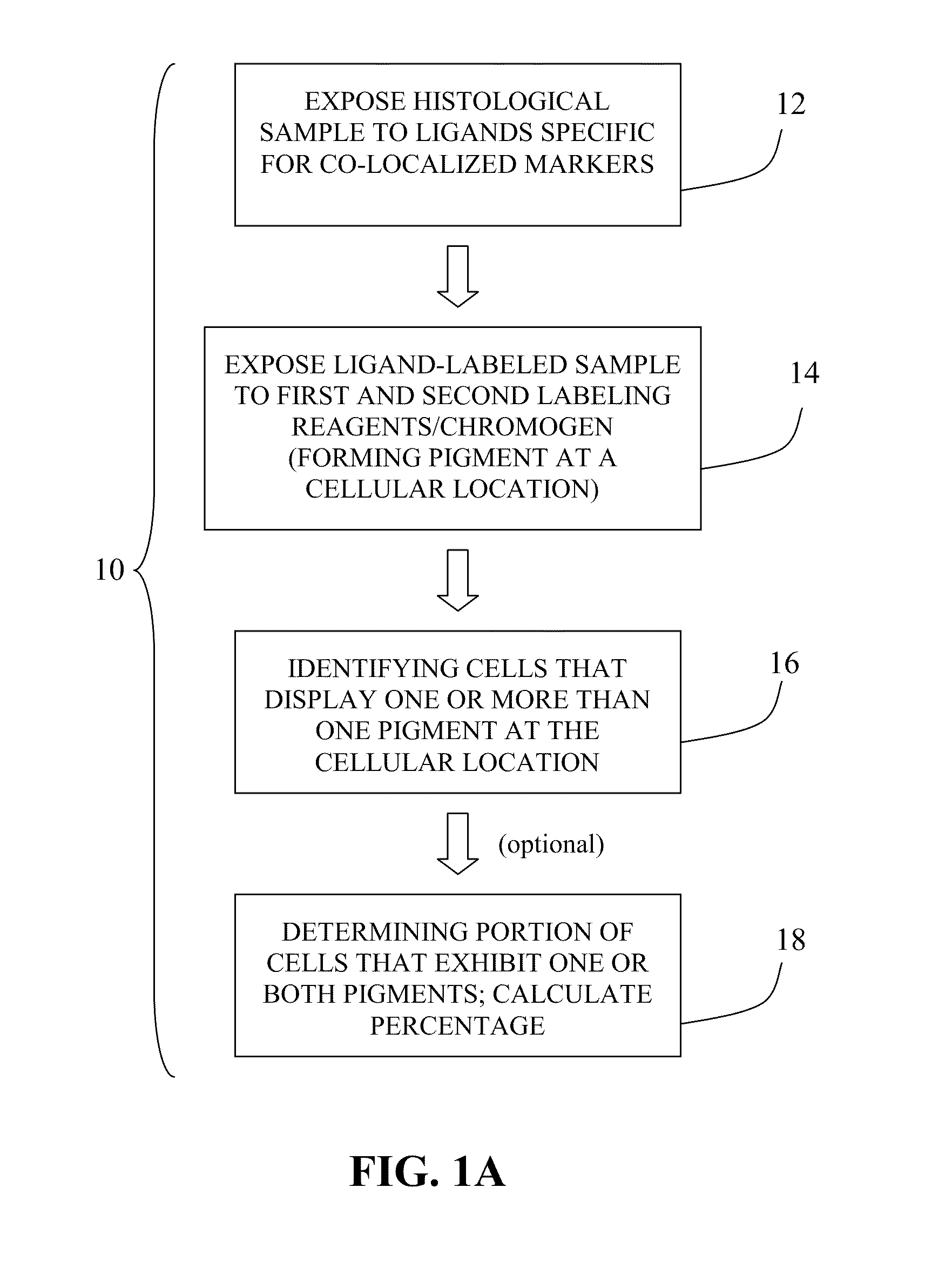
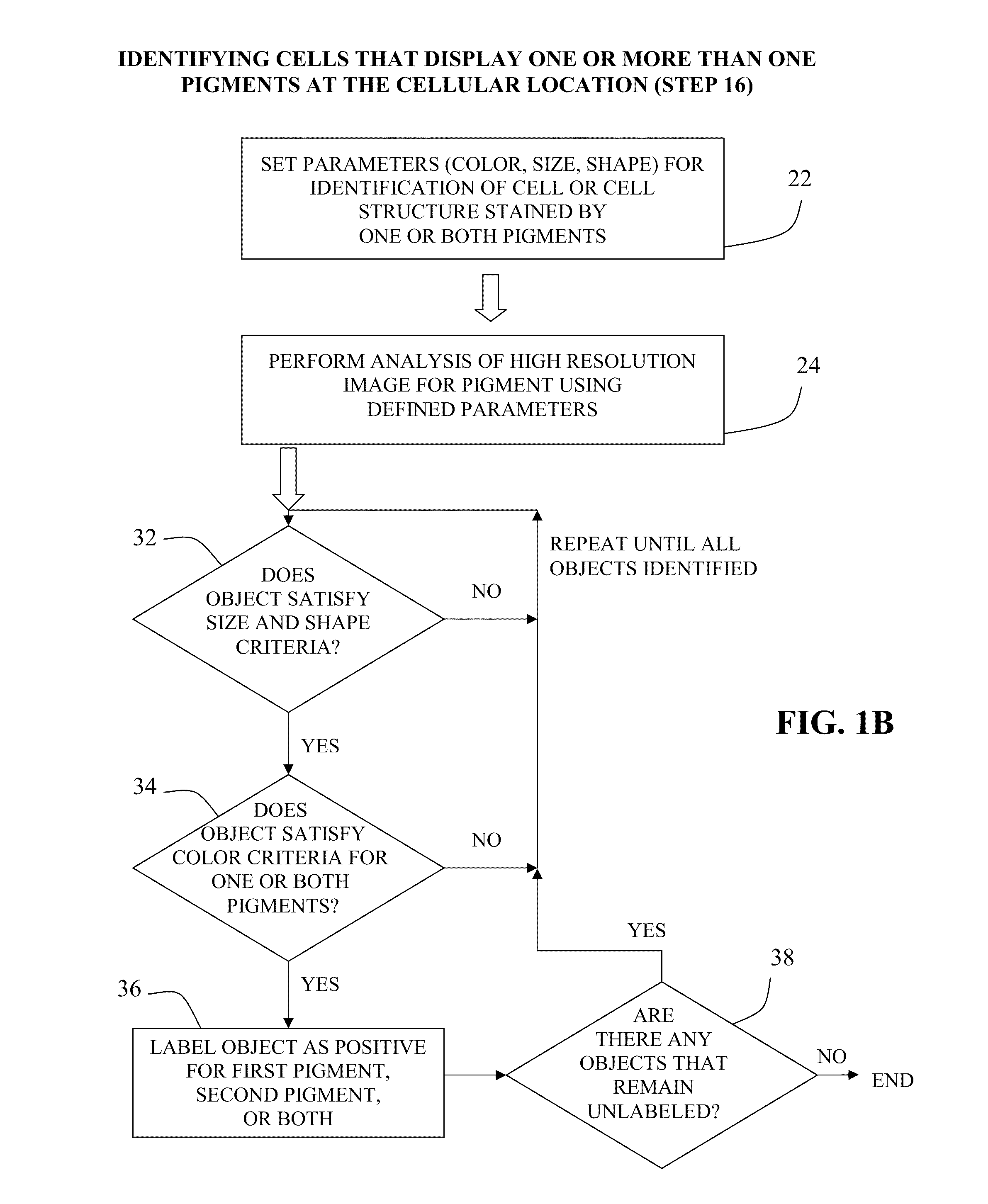
Method for double staining in immunohistochemistry
ActiveUS20100151447A1Measurably differentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTissue sampleCo localization
The present invention relates to kits and methods for performing dual-staining immunohistochemistry (IHC) for the detection of specific cell populations in tissue samples containing heterogeneous populations of cells, which can be observed by a light microscope for co-localization of distinct pigments. The method includes providing a tissue sample comprising fixed cells; exposing the sample to first and second ligands that recognize different marker proteins found at the same cellular location, thereby forming a ligand-labeled sample; exposing the ligand-labeled sample to first and second labeling reagents, the first labeling reagent binding to the first ligand and the second labeling reagent binding to the second ligand, the first and second labeling reagents each forming distinct pigments; and identifying the number of cells that display only one particular pigment, or more than one pigment, by the different coloration of the cellular location labeled by the distinct pigment.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Methods of detecting nucleic acid sequences with high specificity
PendingUS20200399689A1Strong specificityEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexNucleic acid detection
The invention relates to methods of detecting nucleic acids, including methods of detecting one or more target nucleic acid sequences in multiplex branched-chain DNA assays, are provided. Nucleic acids captured on a solid support or suspending cells are detected, for example, through cooperative hybridization events that result in specific association of a label with the nucleic acids. The invention further relates to methods to improve probe hybridization specificity and their application in genotyping. The invention also relates to in situ detection of mis-joined nucleic acid sequences. The invention relates to reducing false positive signals and improve signal-to-background ratio in hybridization-based nucleic acid detection assay. The invention further relates to method to improve specificity in hybridization based nucleic acid using co-location probes. Compositions, tissue slides, sample of suspended cells, kits, and systems related to the methods are also described.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Direct fluorescene immunoassay for viral antigens
The present invention describes a liquid direct fluorescence antibody assay that is rapid and sensitive to detect respiratory virus in infected cells. The assay includes centrifugation of the specimen, incubation of sample and reagents in solution, and detection of the absence or presence of respiratory virus. Sapogenin is used as a detergent to permeabilize the cells for entry of the monoclonal antibodies to react with intracellular antigens. The cells are stained with fluorescently labeled monoclonal antibodies against the viral antigens along with a background stain and a fluorescent nuclear stain. This counter staining decreases background and allows co-localization of antigen and nuclear structures for enhanced detection.
Owner:DIAGNOSTIC HYBRIDS
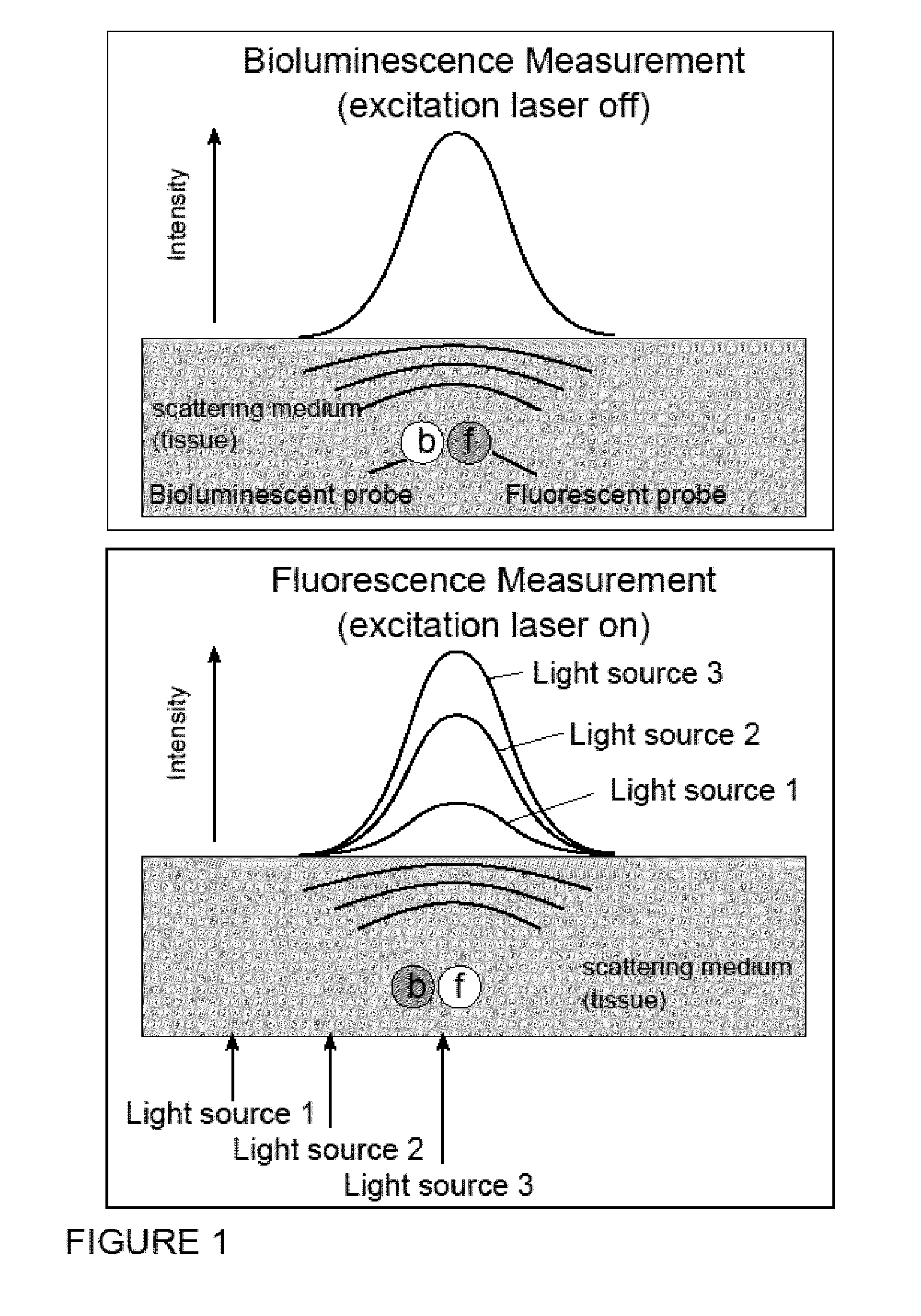
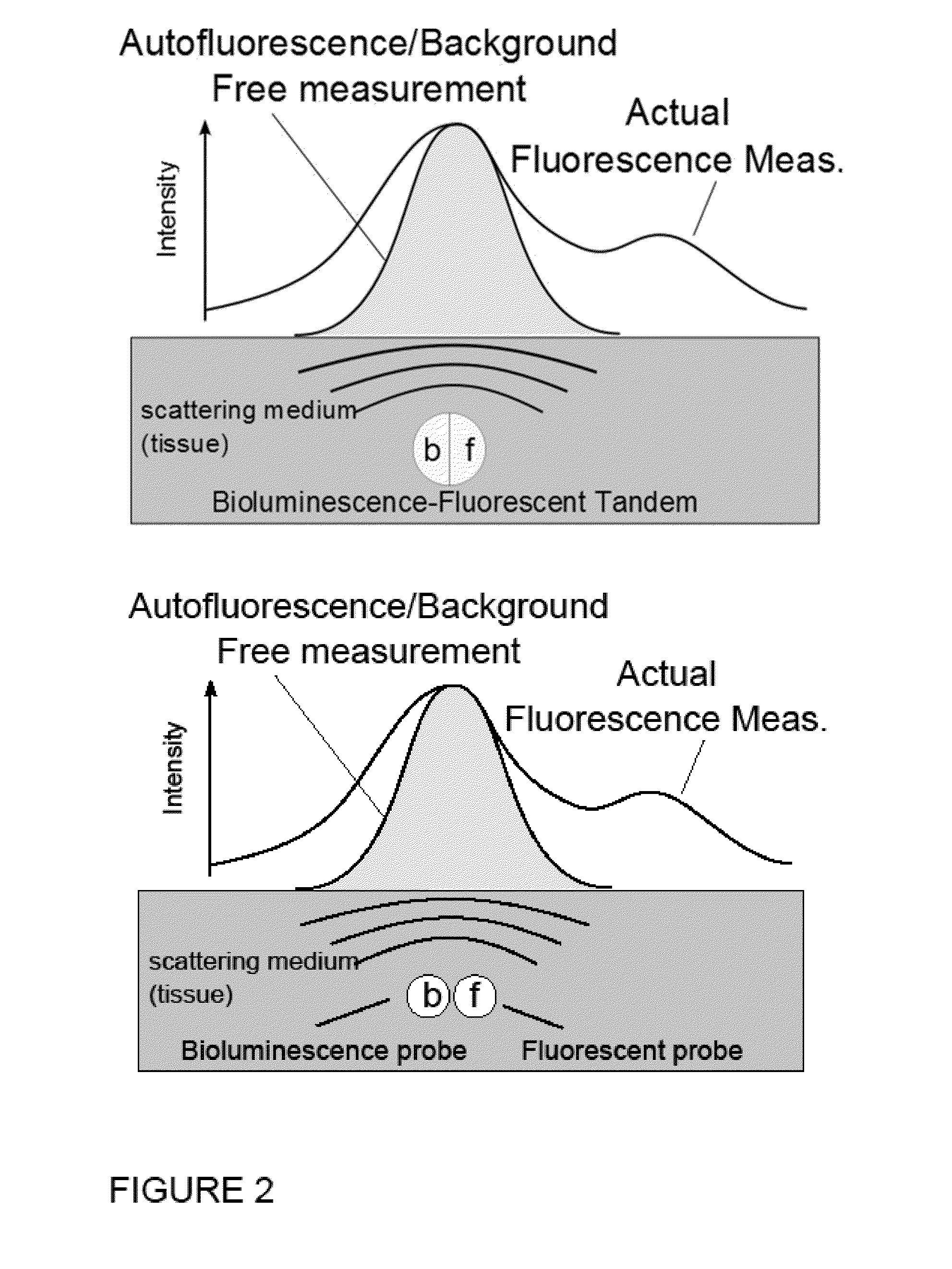
Systems, Methods, and Apparatus for Imaging of Diffuse Media Featuring Cross-Modality Weighting of Fluorescent and Bioluminescent Sources
ActiveUS20140105825A1Promote reconstructionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryCross modalityMean free path
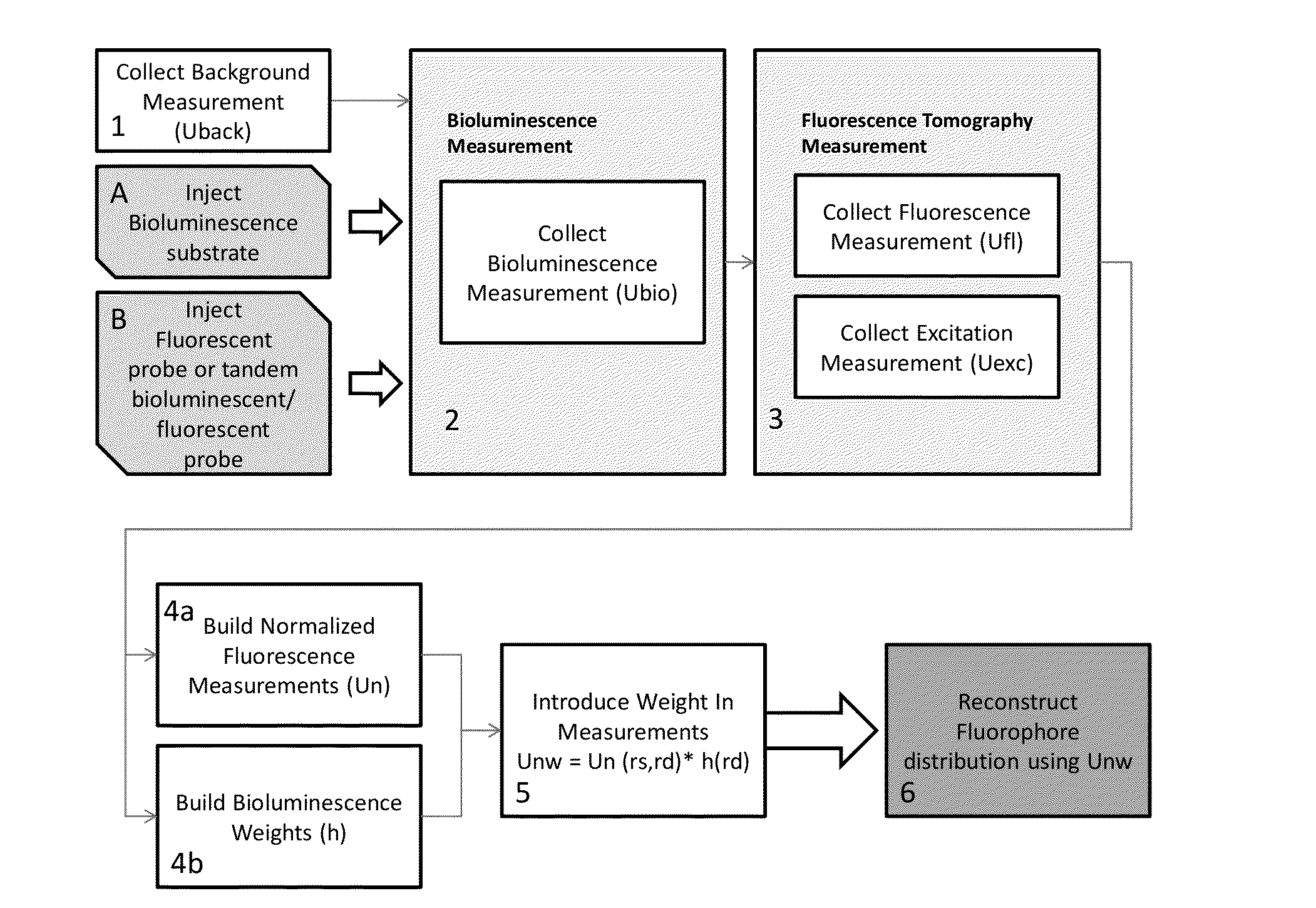
In certain embodiments, the invention relates to systems and methods for in vivo tomographic imaging of fluorescent probes and / or bioluminescent reporters, wherein a fluorescent probe and a bioluminescent reporter are spatially co-localized (e.g., located at distances equivalent to or smaller than the scattering mean free path of light) in a diffusive medium (e.g., biological tissue). Measurements obtained from bioluminescent and fluorescent modalities are combined per methods described herein.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Group sparsity model for image unmixing
Systems and methods described herein relate, among other things, to unmixing more than three stains, while preserving the biological constraints of the biomarkers. Unlimited numbers of markers may be unmixed from a limited-channel image, such as an RGB image, without adding any mathematical complicity to the model. Known co-localization information of different biomarkers within the same tissue section enables defining fixed upper bounds for the number of stains at one pixel. A group sparsity model may be leveraged to explicitly model the fractions of stain contributions from the co-localized biomarkers into one group to yield a least squares solution within the group. A sparse solution may be obtained among the groups to ensure that only a small number of groups with a total number of stains being less than the upper bound are activated.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Application of fluorescent probe to hydrogen peroxide molecule detection
InactiveCN104949946AGood choiceStrong interference abilityColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceLysosomeFluorescence
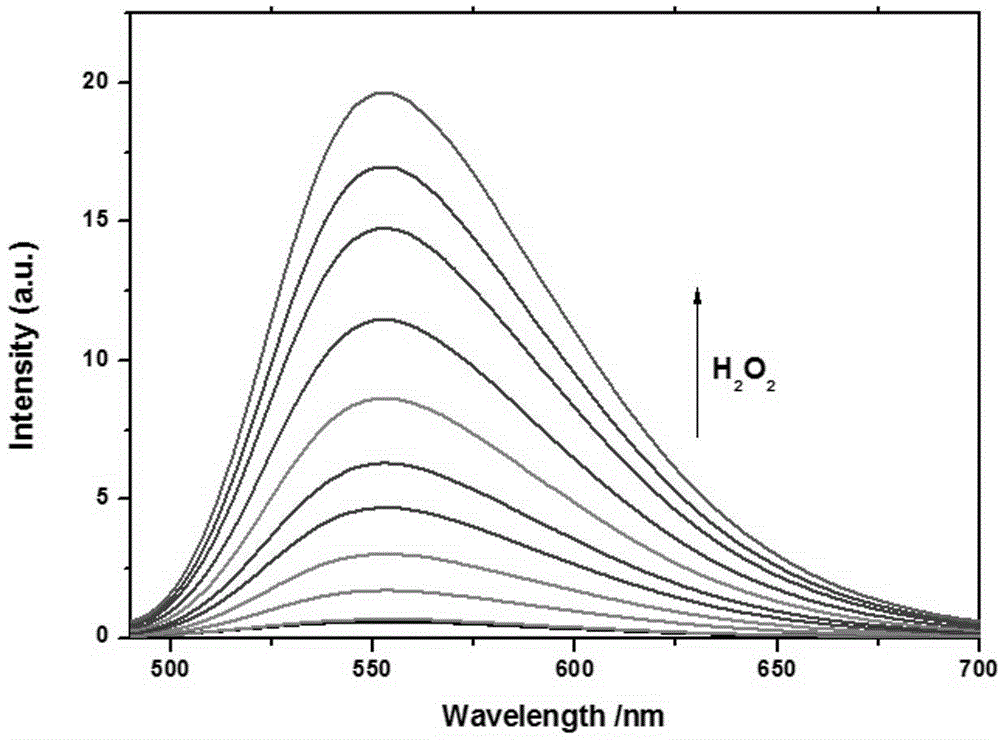
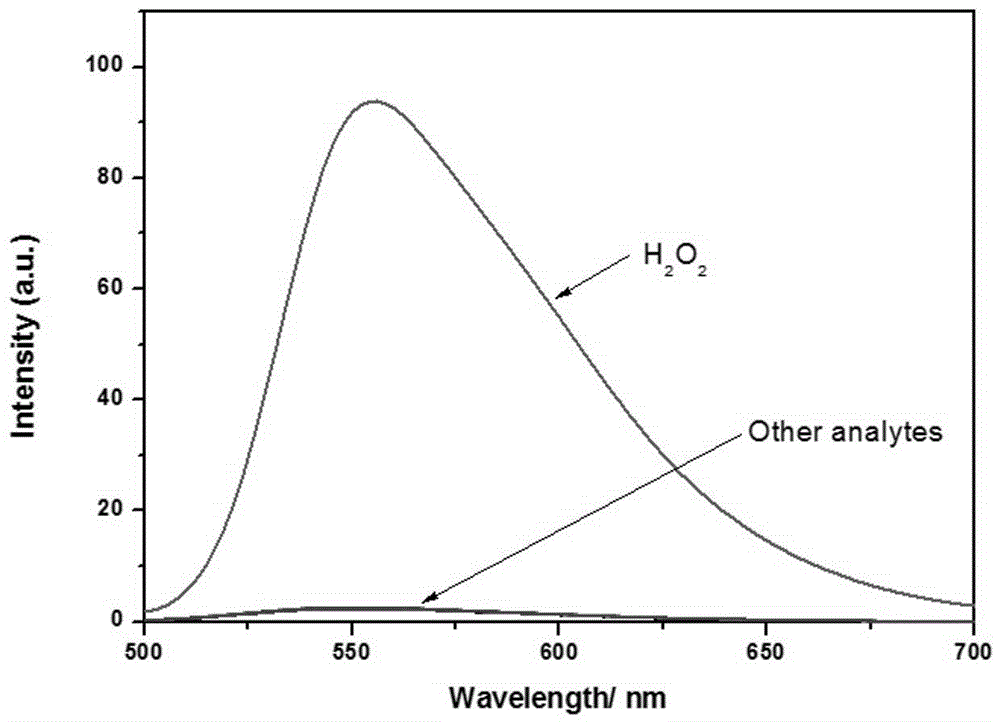
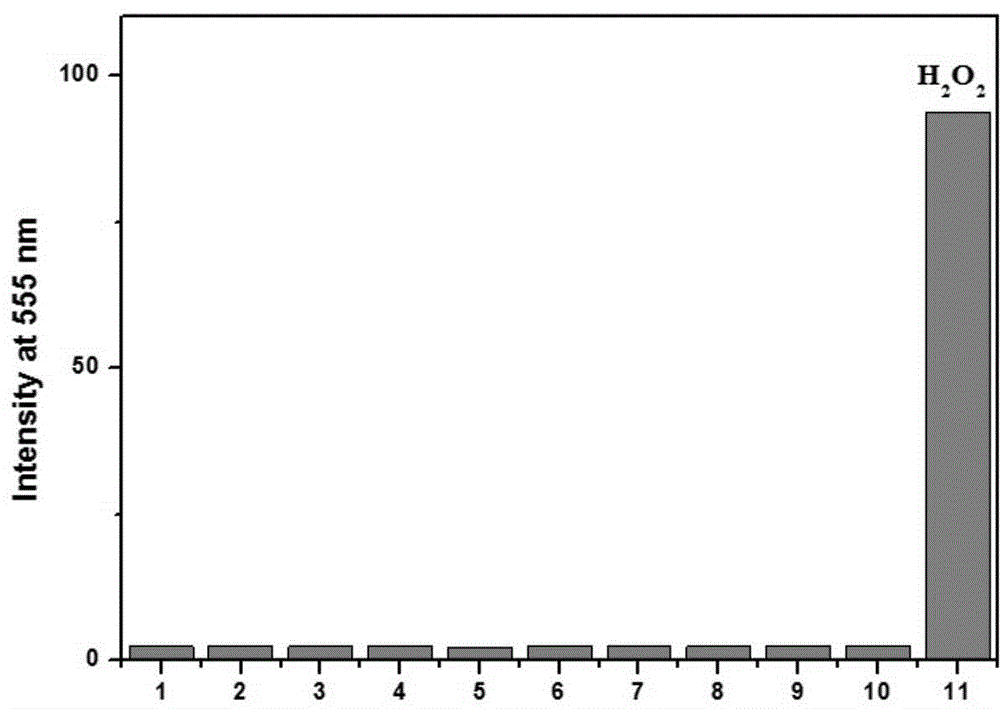
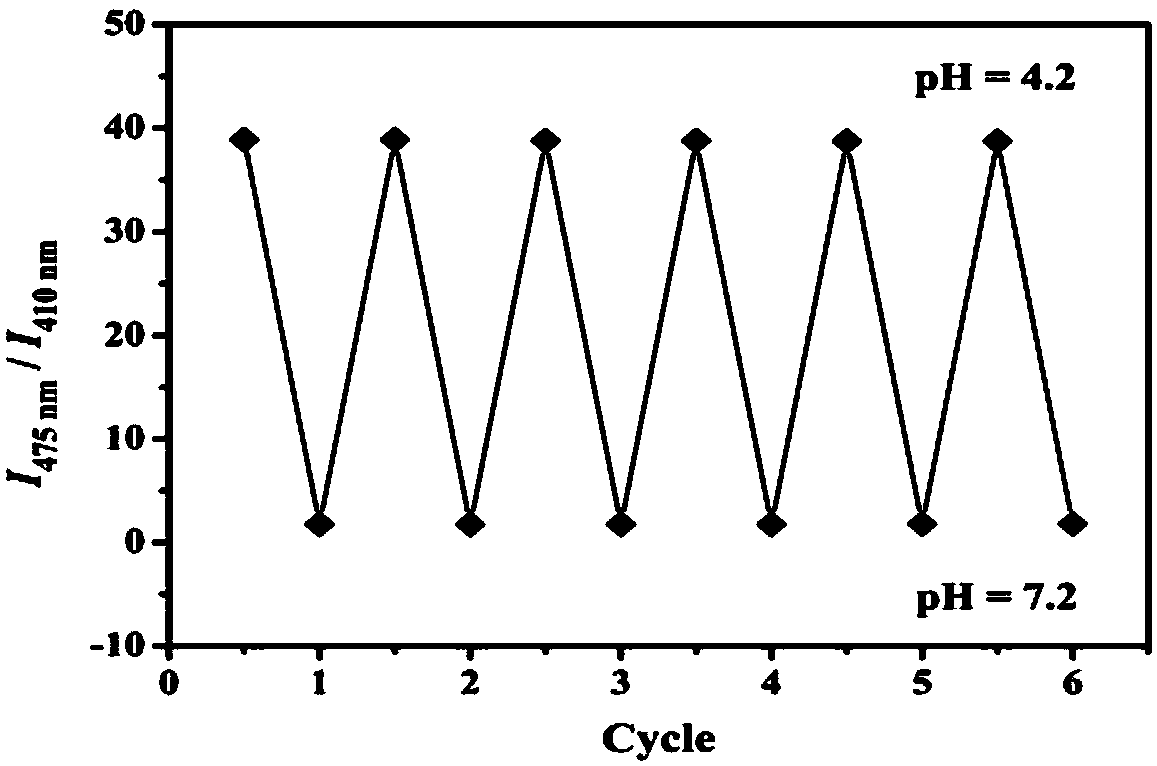
The invention discloses application of a fluorescent probe to hydrogen peroxide molecule detection. The fluorescent probe is used for sensing and detecting the content of hydrogen peroxide in a water environment and a cytolysosome by the processes of fluorescent detection, visual quantitative detection and cell imaging detection. The H2O2 molecular probe can realize selective quick detection and is good in selectivity and strong in ability to resist interference of other molecules. Besides, color changes of a solution can be observed with the naked eyes, and the fluorescent color changes can also be observed under a UV lamp, so that the fluorescent probe has a chromophoric sensing function. The probe can be used for detecting hydrogen peroxide in the cytolysosome, and compared with a commercial lysosome dye, the imaging superposition rate of hydrogen peroxide in the lysosome is high, and the co-localization coefficient of two dyes is 0.94.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
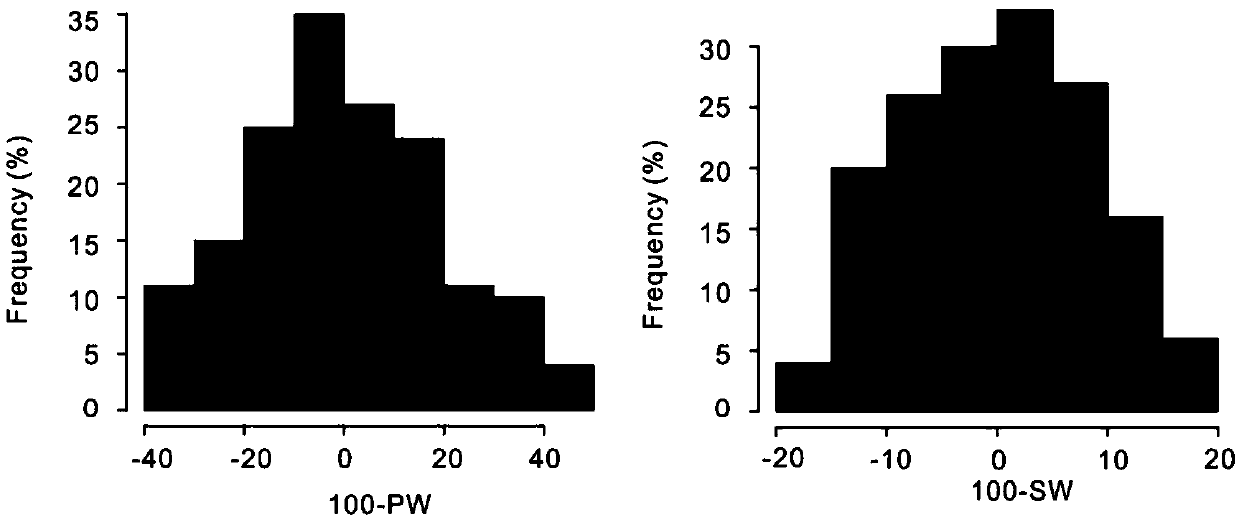
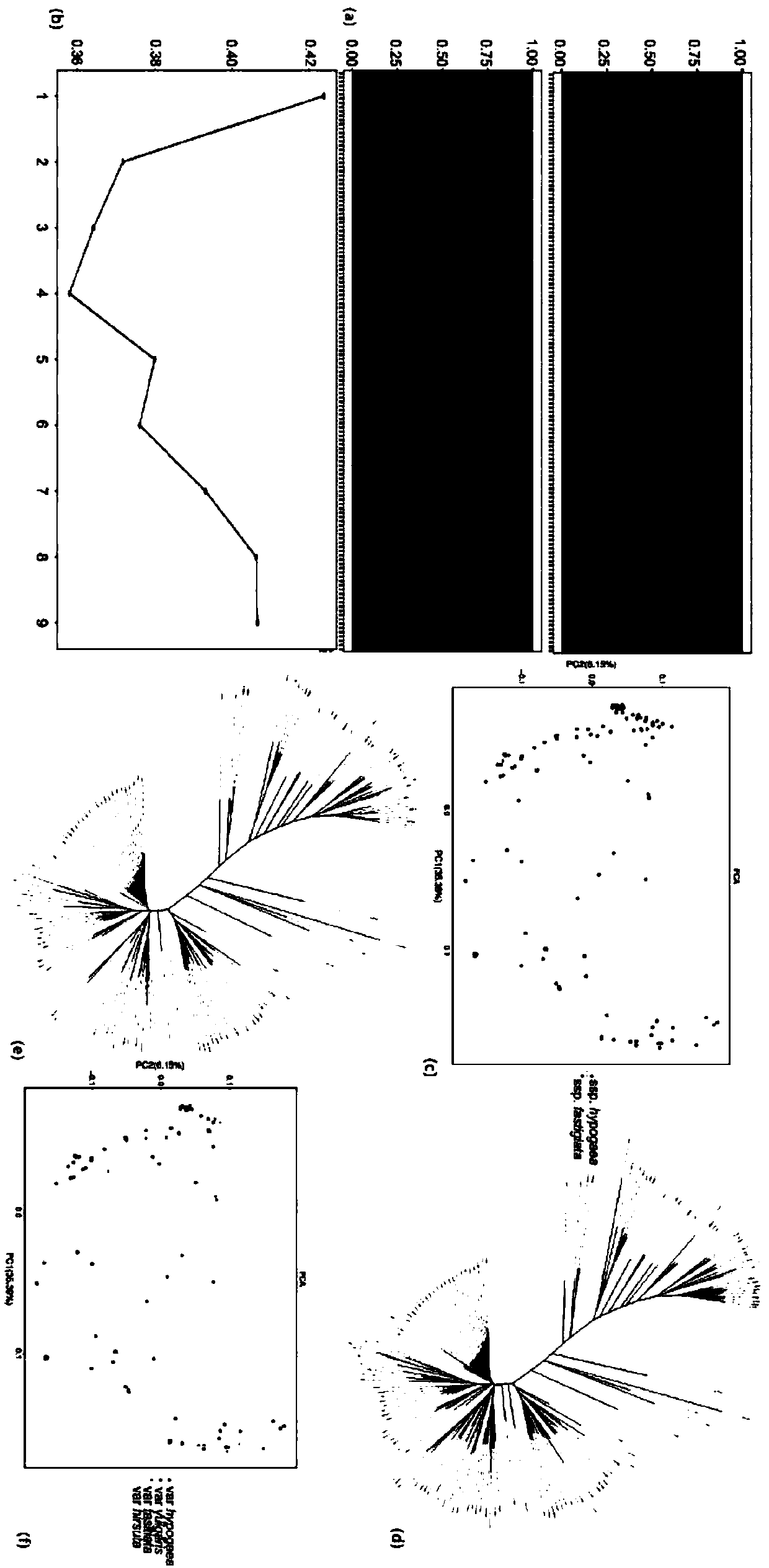
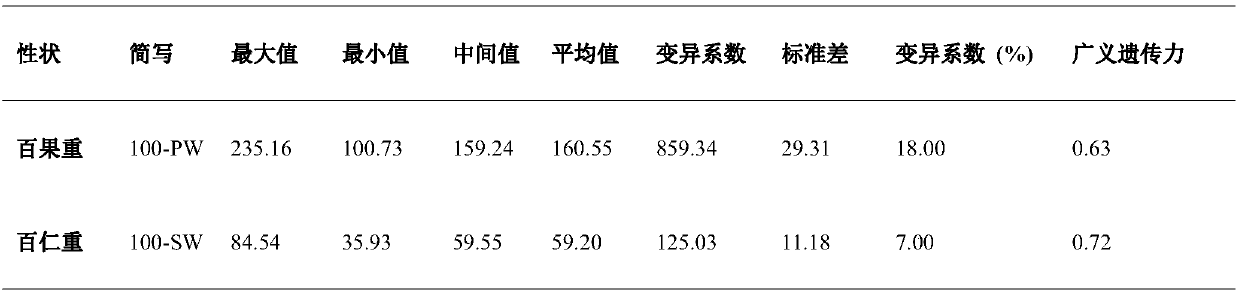
Method for effectively anchoring candidate gene region of peanut quantitative traits
InactiveCN109694924AAchieve positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenetic linkage disequilibrium
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and in particular to a method for effectively anchoring a candidate gene region of a quantitative trait. The method is co-localized with a genome-wide association study and a quantitative trait localization method to achieve efficient anchoring of the quantitative trait candidate gene regions. The method achieves effective anchoring of the candidate gene region of the peanut quantitative trait by co-localization with the genome-wide association study and the quantitative trait localization. The method is exemplified by quantitative granule weight, firstly, through a simplified genome sequencing technology, the genome-wide SNP marker development of 165 cultivar peanut core collections in China is carried out; based on a principle of linkage disequilibrium, combined with peanut 100-fruit weight and 100-kernel weight breeding value, the related gene regions related to peanut weight traits are associated; in the previous reports, the QTLmapping results of the grain weight traits are converted to the corresponding genomic physical locations, the co-localization region of the two methods can be obtained, and the method can effectivelyand accurately realize the localization of the genome-wide particle weight-related trait genes.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
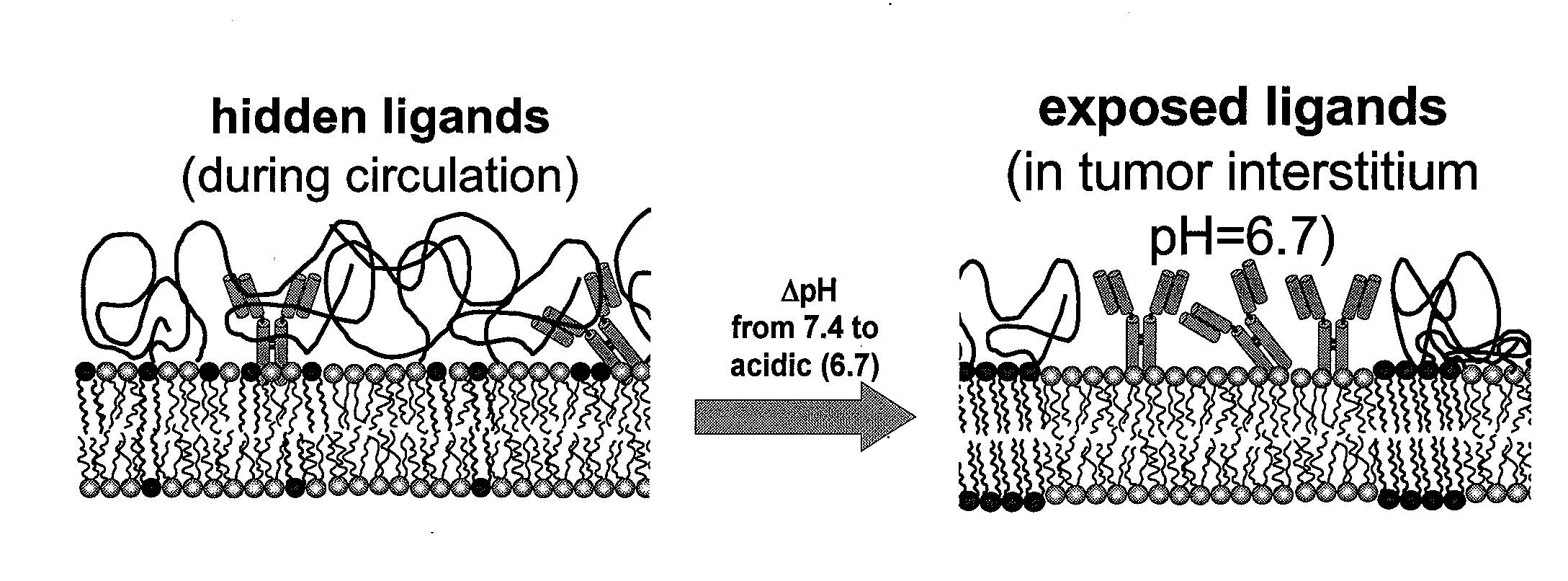
Ph sensitive liposome compositions for controlling surface topography and binding reactivity in functionalized liposomes
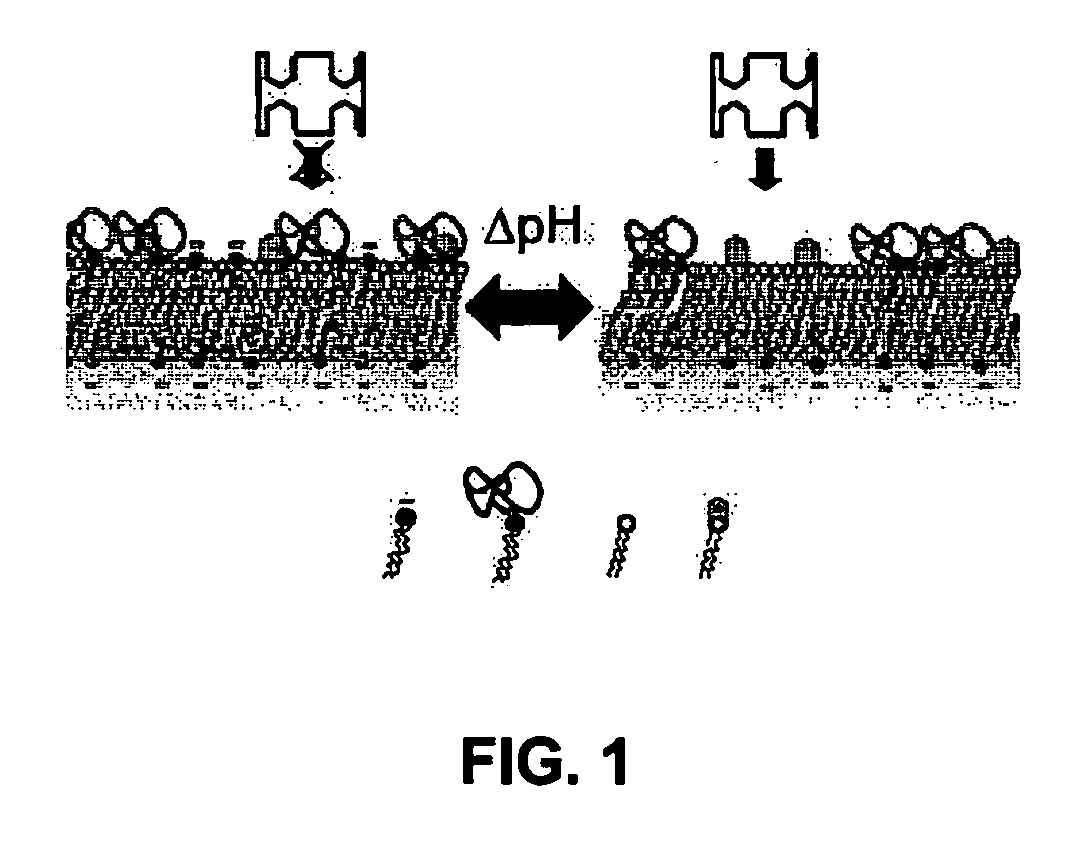
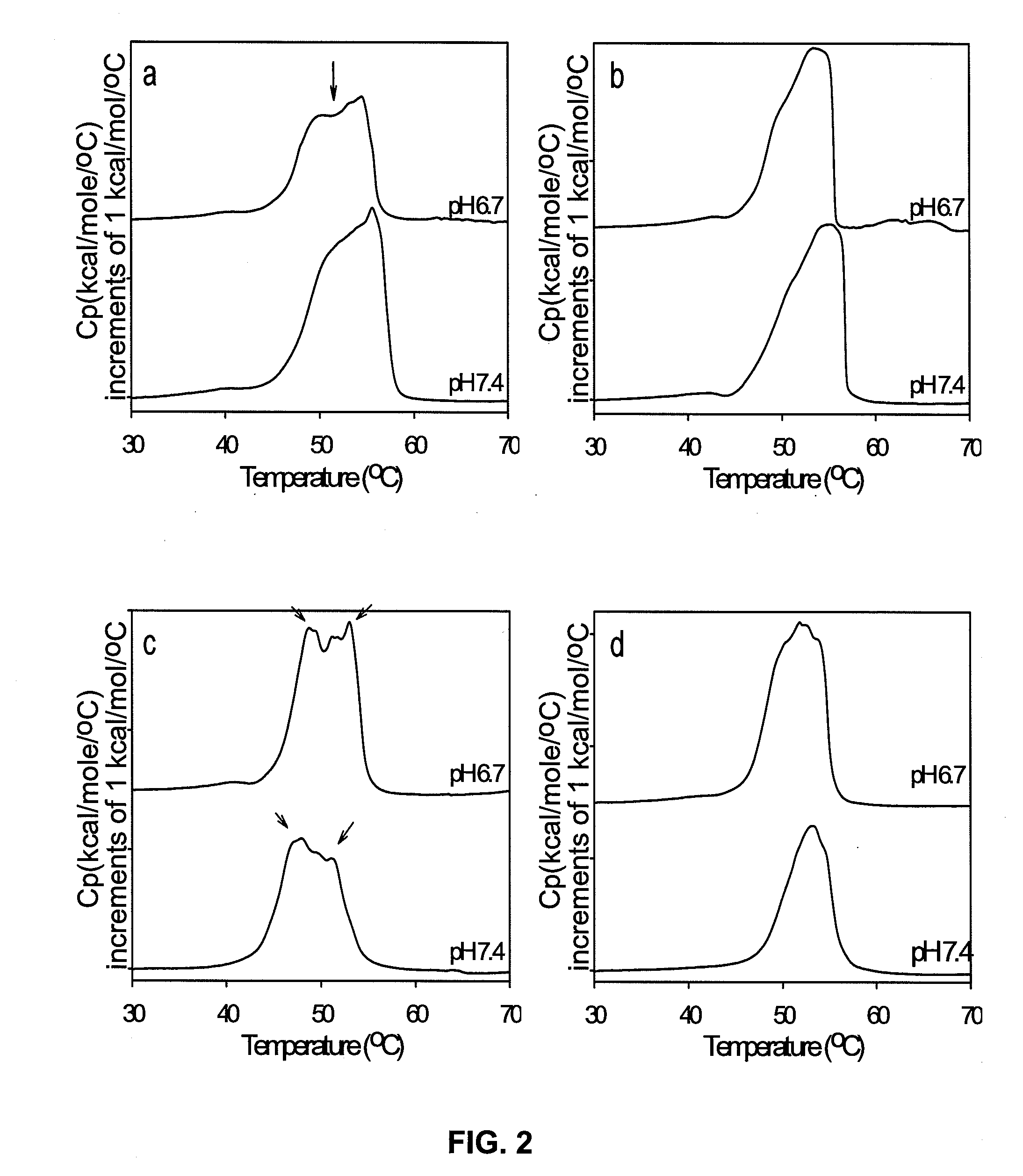
Methods for controlling surface topography and binding reactivity in functionalized lipid layers, including in the form of liposomes, using pH-dependent processes. During direct cell-to-cell communication, lipids on the extracellular side of plasma membranes reorganize, and membrane associated communication-related molecules co-localize. At co-localization sites, sometimes identified as rafts, the local cell surface topography and reactivity are altered. Integration of these processes on nanometer-sized lipid vesicles used as drug delivery carriers would precisely control their interactions with diseased cells minimizing toxicities. Included are pH-dependent processes on functionalized lipid bilayers demonstrating reversible sharp changes in binding reactivity within a narrow pH window. Cholesterol enables tuning of the membrane reorganization to occur at pH values not necessarily close to the reported pKa's of the constituent titratable lipids. One illustrative function of the invention is to use liposomes to deliver bioactive agents to cancer or tumor cells and compositions of specific lipids that form liposomes to deliver a biologically active agent.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
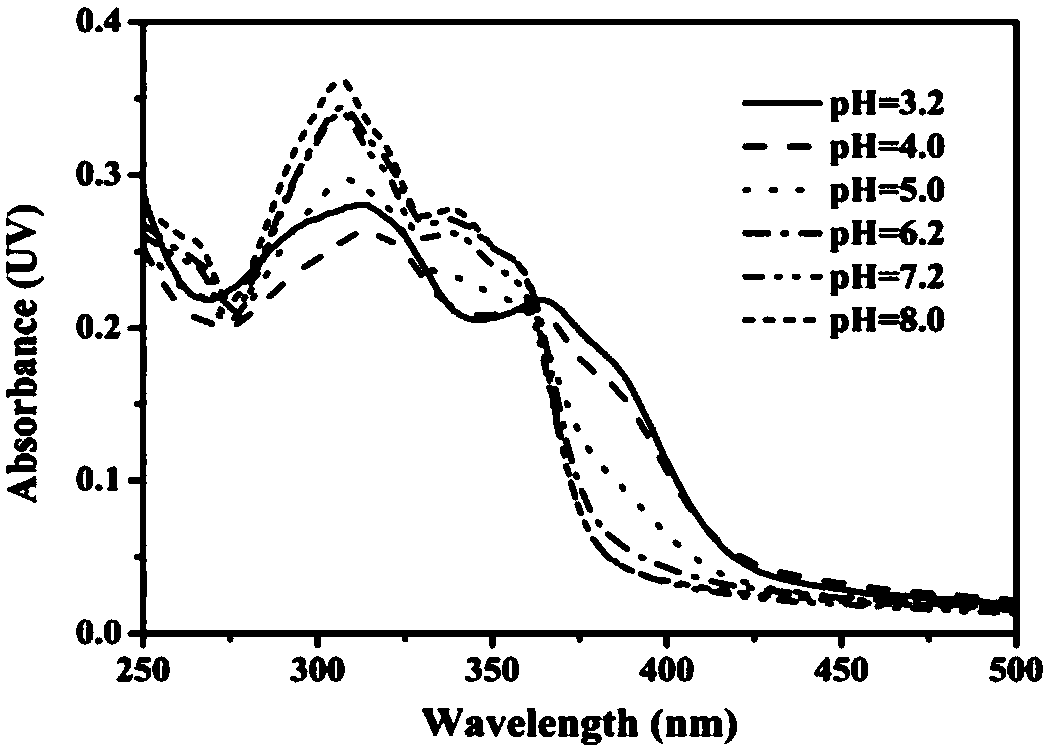
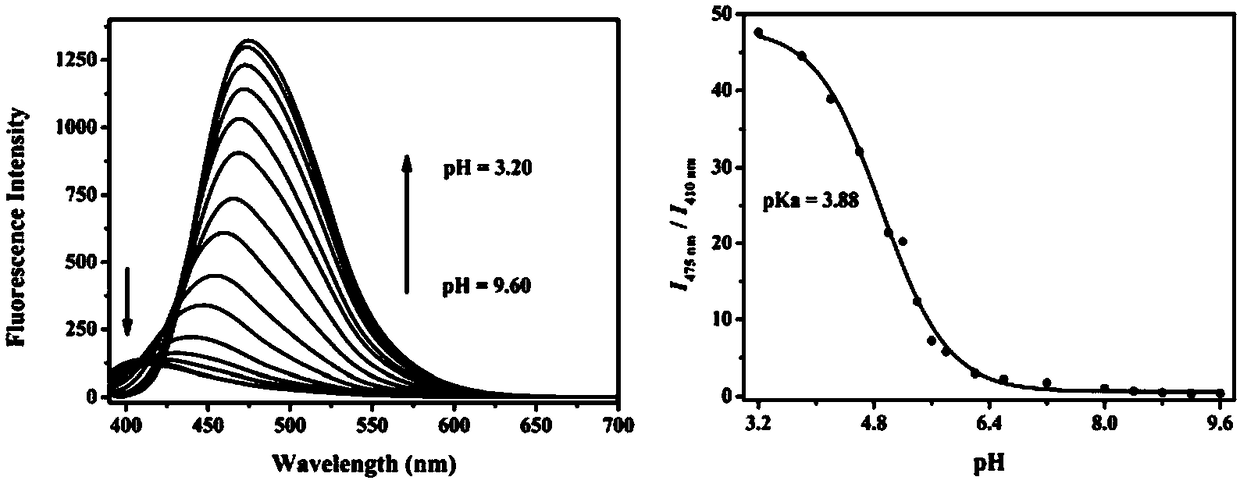
Two-photon pH (potential of hydrogen) ratio measurement fluorescence probe for monitoring cell autophagy, preparation method of fluorescence probe and application
ActiveCN108329301ASimple structureEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingSide effect
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Multifunctional beads and methods of use for capturing rare cells
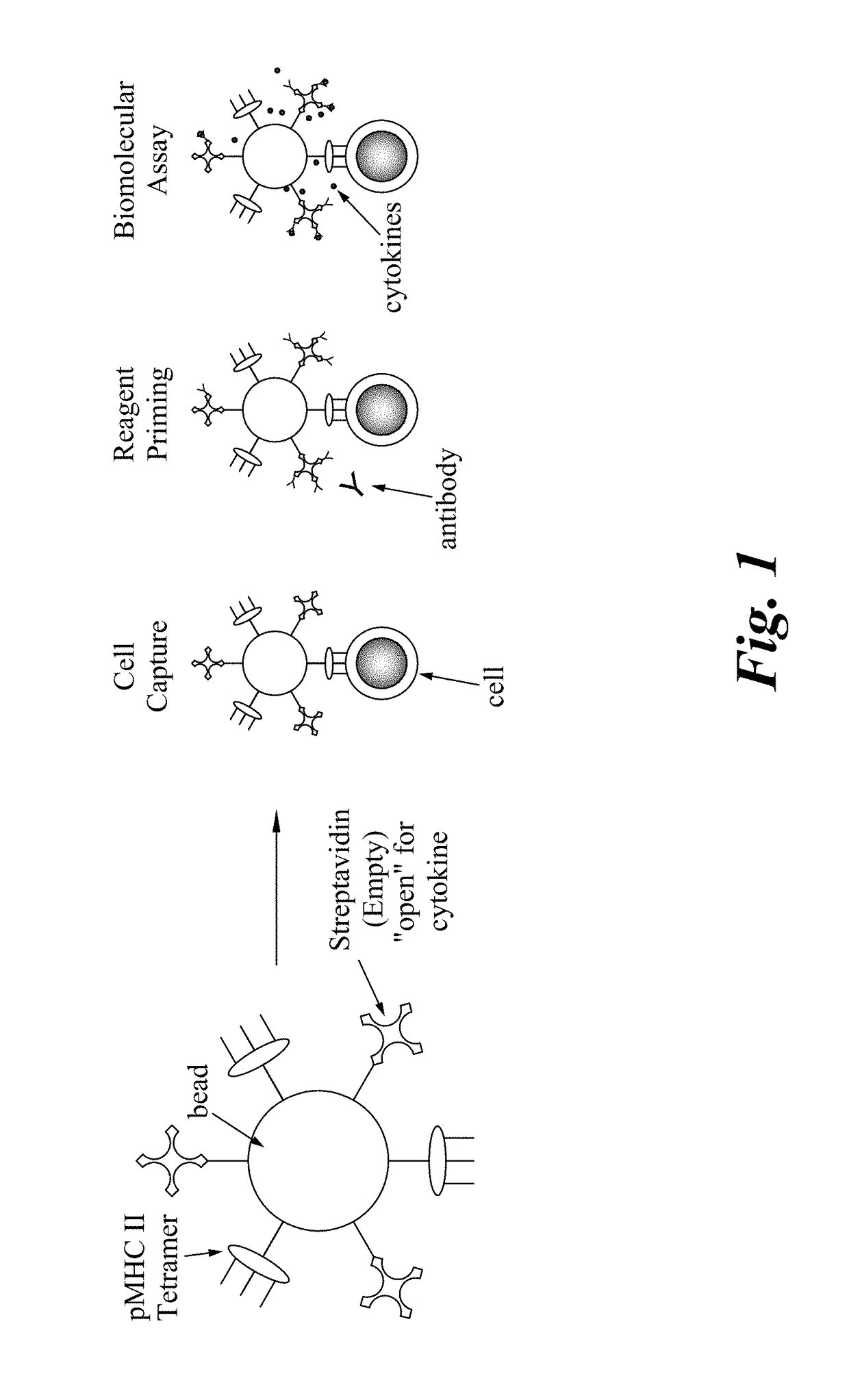
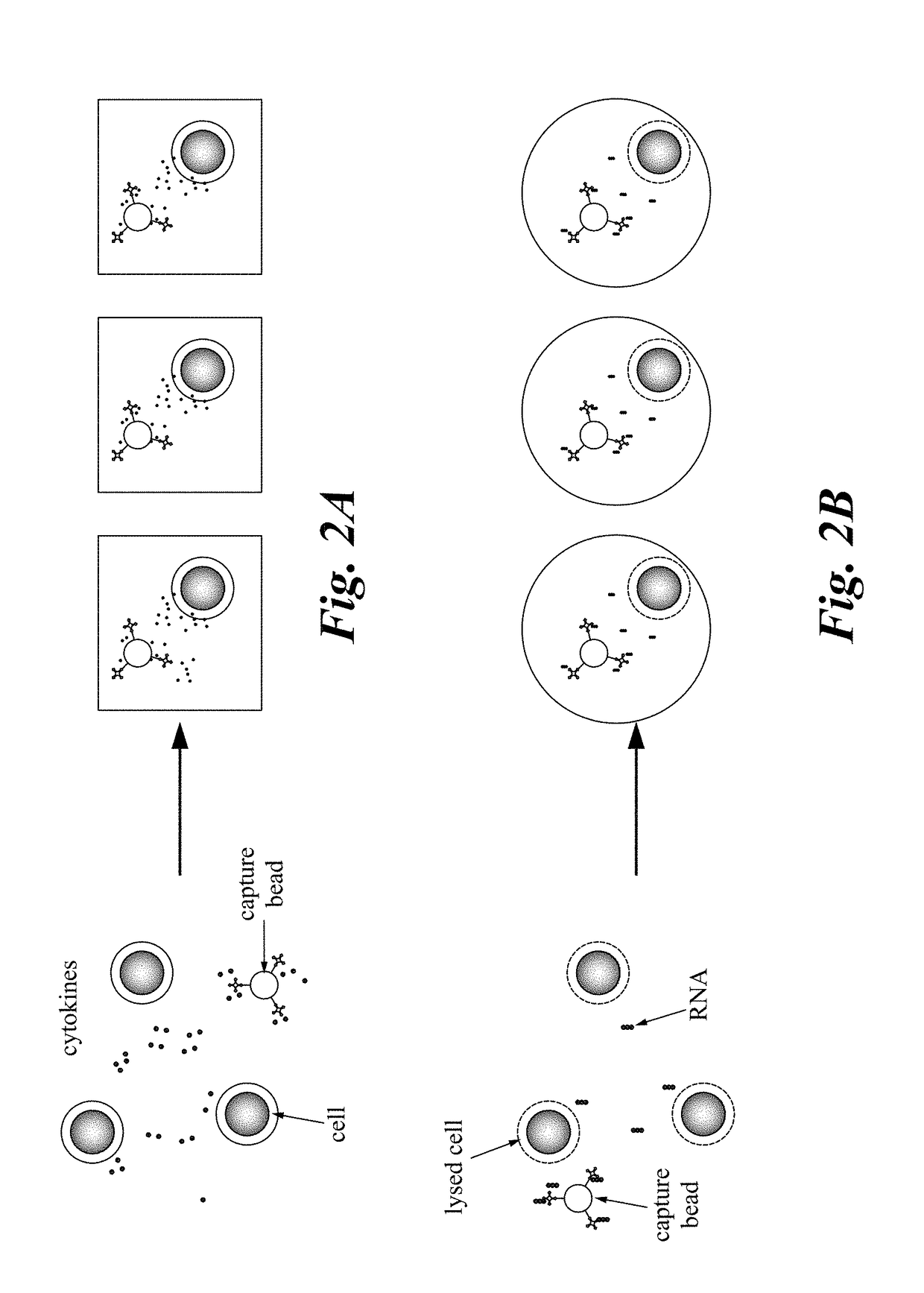
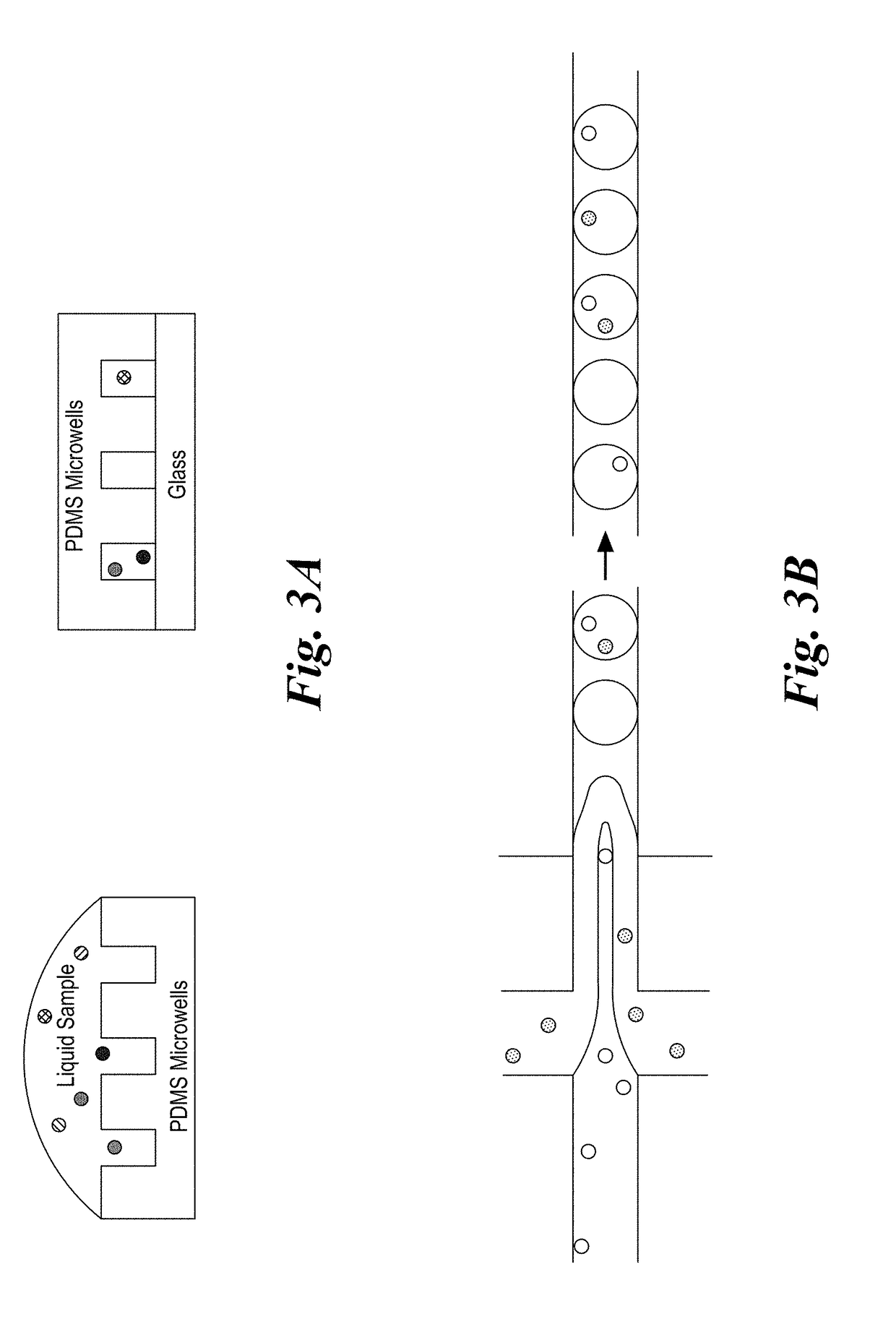
Described are multi-functional beads and methods to capture rare cells directly from low-volume biological samples and perform both functional and genomic assays from those cells. This is accomplished using a multifunctional capture bead that allows co-localization of both the single cell capture element and the molecular assay components. When combined with a digital microfluidic platform this enables encoding and / or barcoding of specific single cells.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Recombinant salmonella capable of expressing red fluorescence protein and building method of recombinant salmonella
ActiveCN105695384AReduce false positivesSolve real-time monitoring problemsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesImmunofluorescent stainCo localization
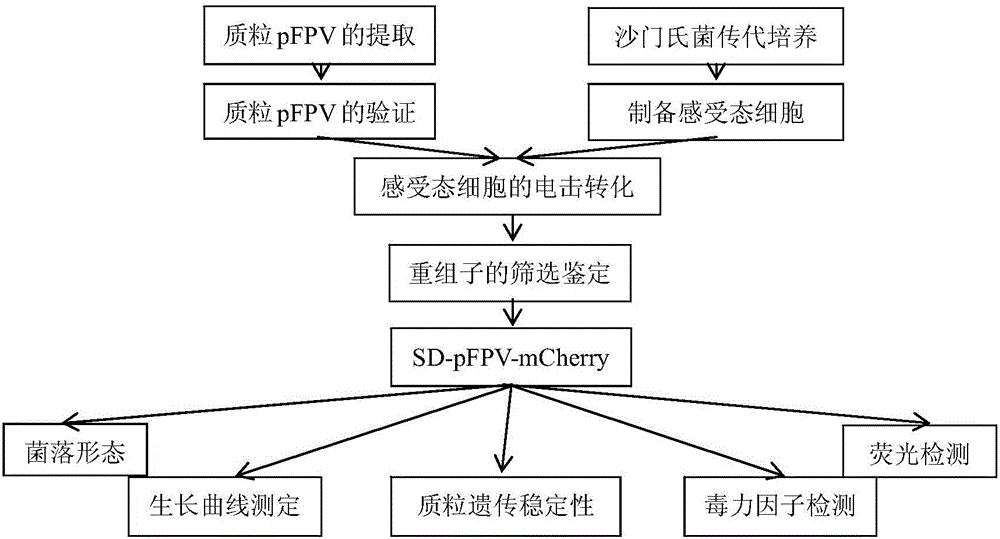
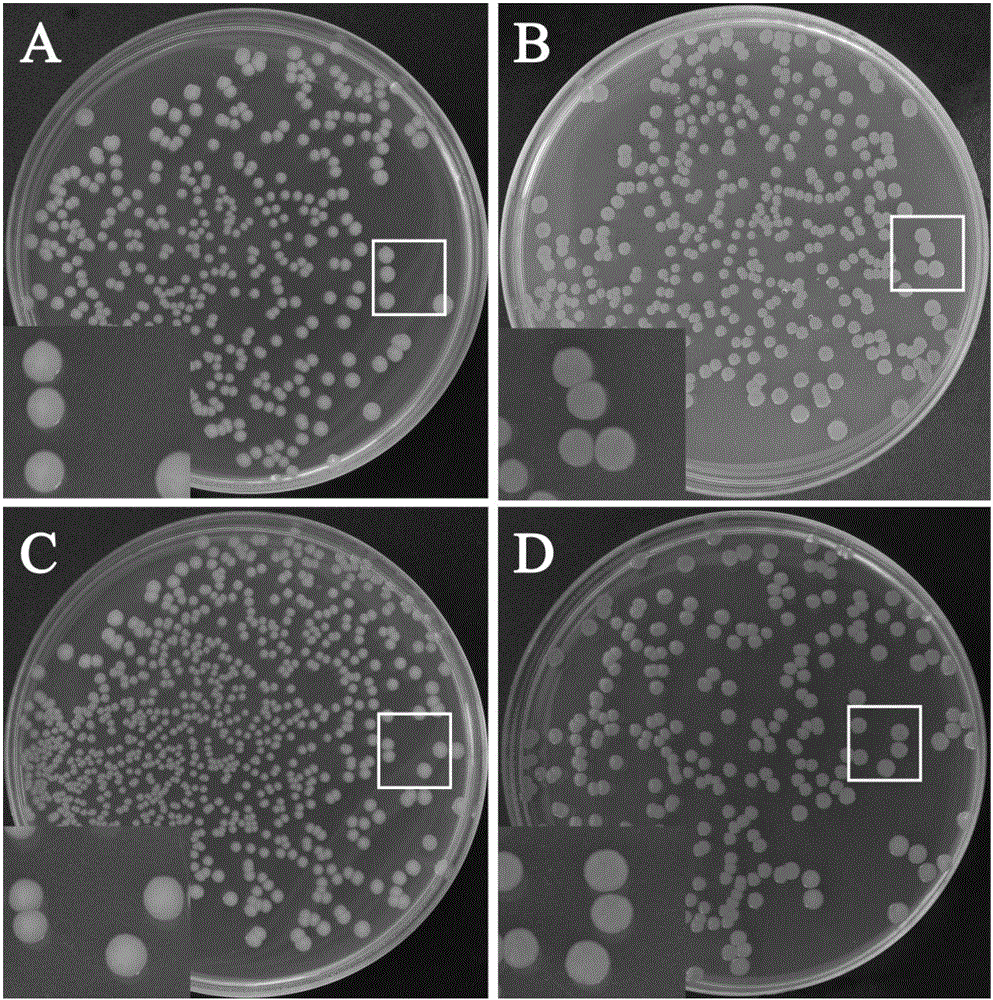
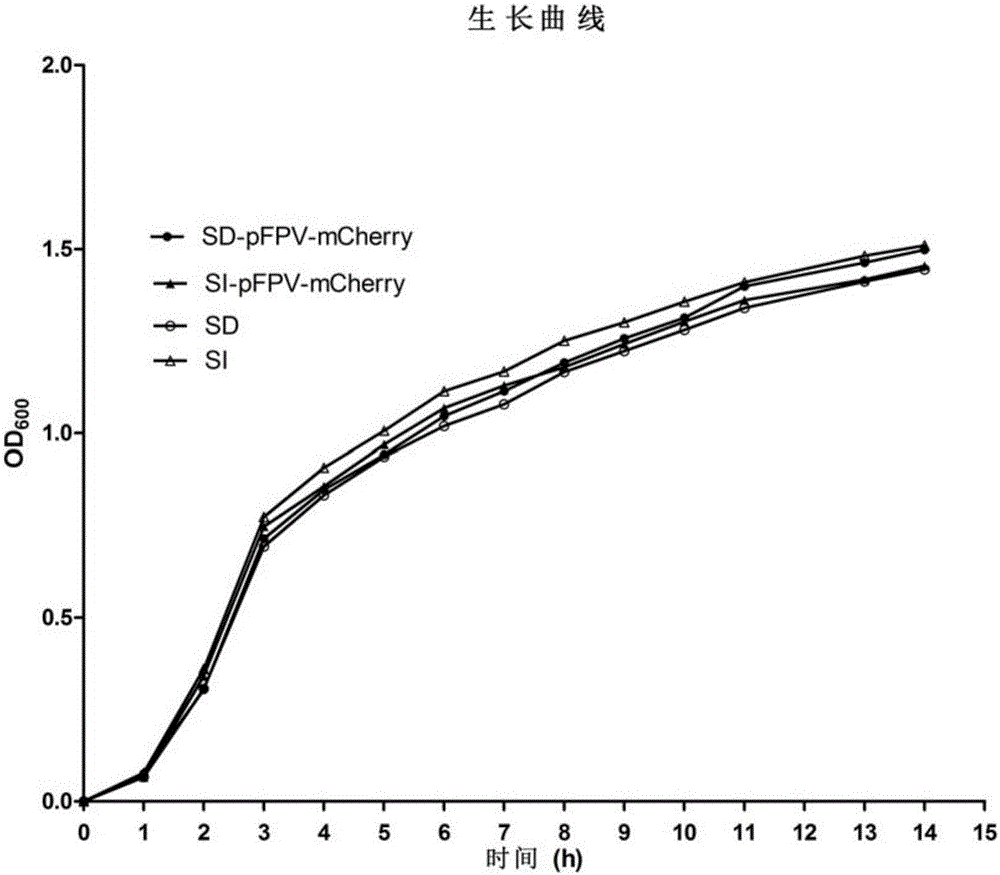
The invention relates to recombinant salmonella capable of expressing red fluorescence protein and a building method of the recombinant salmonella. The clinically isolated salmonella is utilized as a transformation receptor, plasmids pFPV-mCherry with red fluorescence protein gene segments inserted enter a bacterium through electroporation, and the salmonella capable of expressing the red fluorescence protein is built accordingly. The built recombinant salmonella can be used for marking and tracing in-vitro and in-vivo test processes of the salmonella, and the problem that the real-time monitoring cannot be performed in the salmonella test is solved; the recombinant salmonella can express the fluorescence protein and can replace an expensive salmonella specific antibody, not only is the research grant saved, but also the false positive caused by utilization of the antibody is greatly reduced; co-localization can be performed through combination with immunofluorescent staining with related protein, and an effective means is provided for in-depth study of the clinically isolated salmonella.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
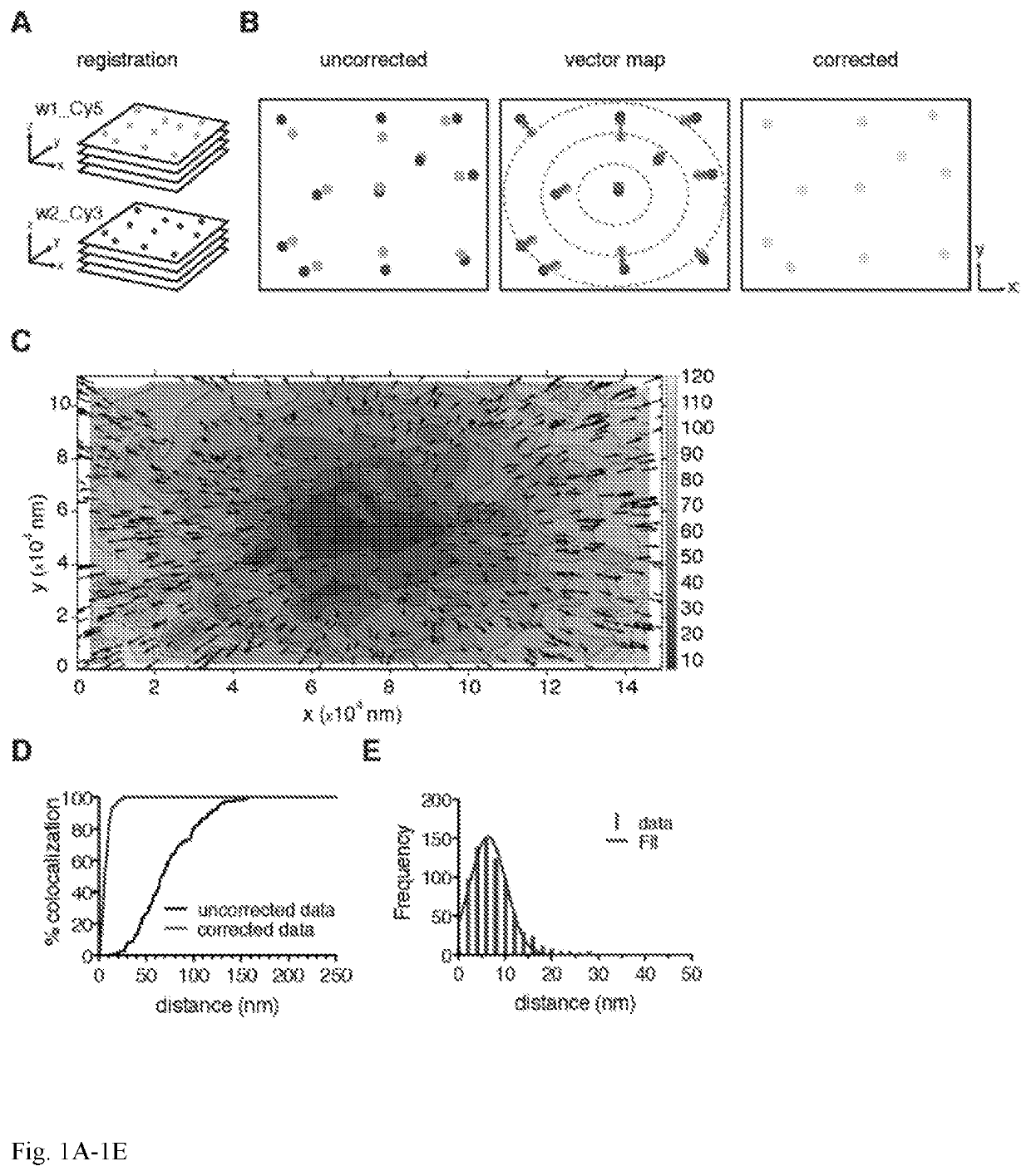
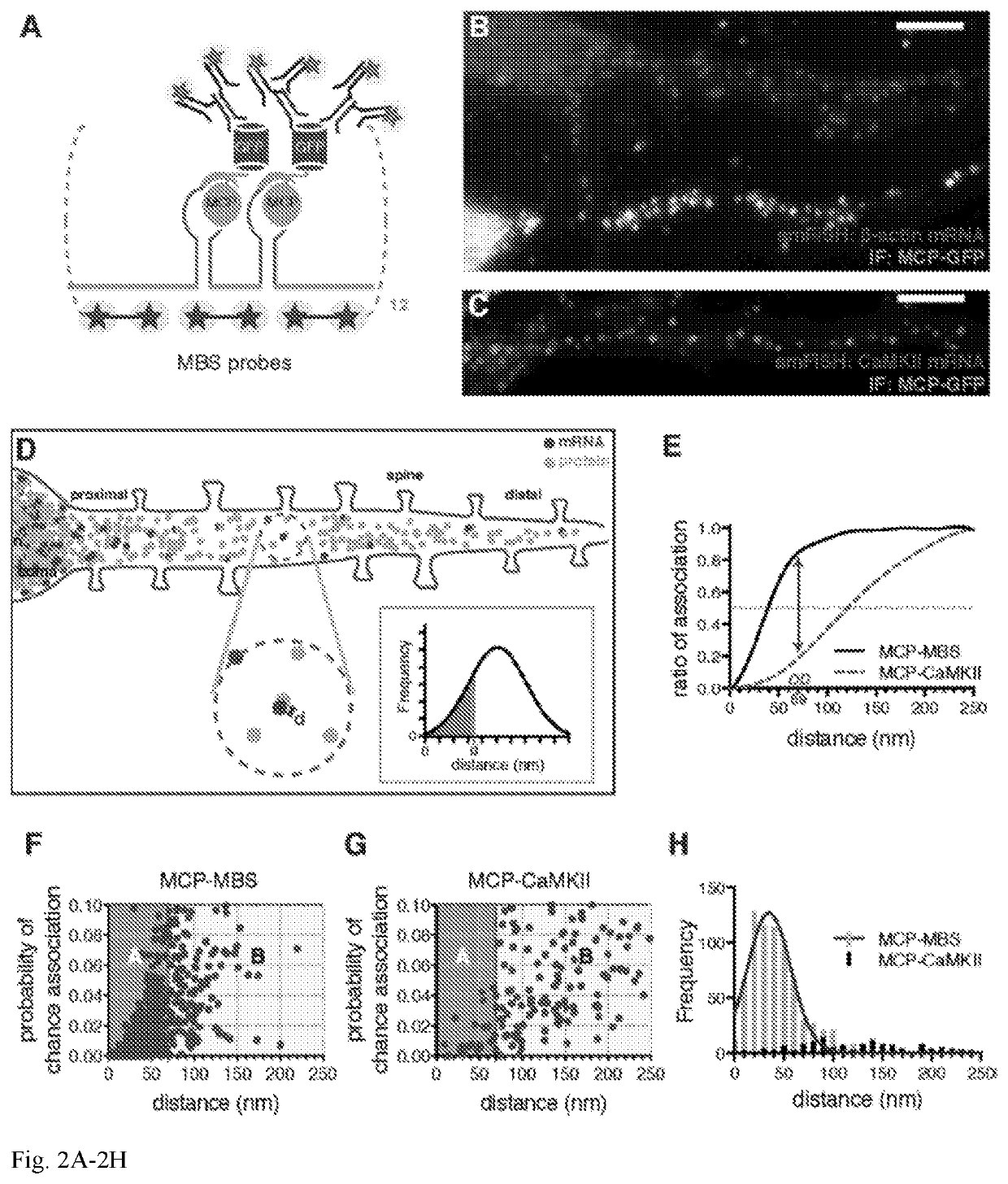
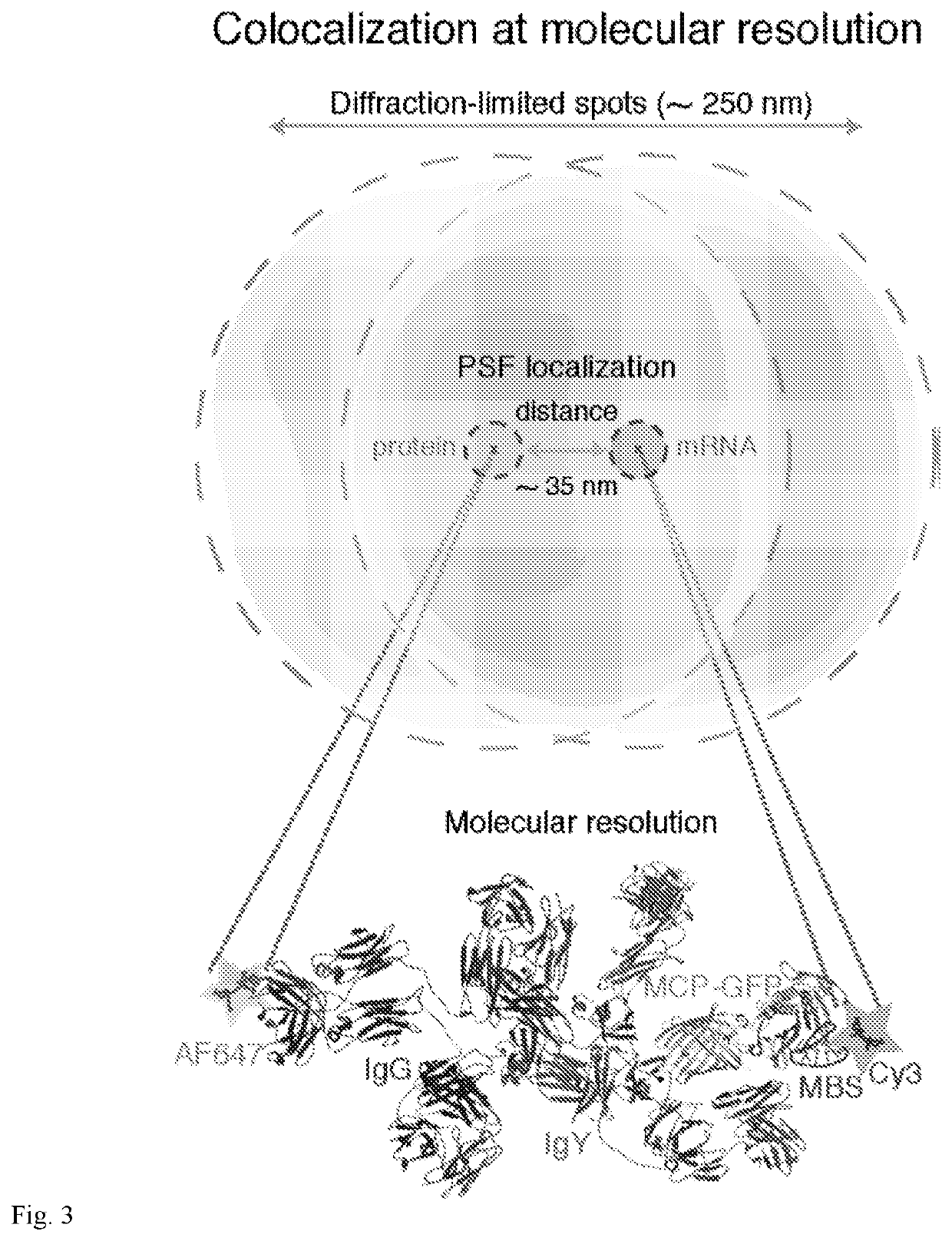
Co-localization at molecular resolution of multiple fluorescence channels acquired using optical microscopy
InactiveUS20190339204A1Aberration correctionExcellent fluorescence performanceMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceImage resolutionFluorescence
A method for improving the performance of a fluorescence microscopy imaging system and for correcting chromatic aberration of an optical objective in a fluorescence microscopy system.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
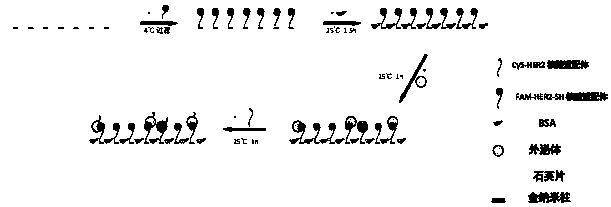
Manufacturing method and application of immunofluorescence co-localization imaging platform
PendingCN111077298AHas the characteristic of flickeringEnabling immunoassay researchBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerImaging chain
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and an application of an immunofluorescence co-localization imaging platform. A detection platform generates a gold nano array pattern through an electron beam lithography technology, and a surface is coupled with an HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor-2) nucleic acid aptamer with a fluorophore FAM through a gold sulfur bond. The platform canspecifically capture exosomes secreted by HER2 high-expression tumor cells; an imaging chain is an HER2 nucleic acid aptamer probe with another fluorophore Cy5; and two probes have fluorescence scintillation characteristics and can be used for super-resolution monomolecular positioning imaging (SMLM). Through an SMLM imaging technology, the captured exosomes can be subjected to super-resolution optical imaging; in combination with a double-color fluorescence co-localization technology, a false positive event can be judged at a single molecular level, and accuracy of a sandwich immunoassay technology is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Cell autophagy monitoring probe, preparation method therefor and use of cell autophagy monitoring probe
ActiveCN106588845AMonitoring the autophagy processSimple structureOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementLysosomeElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a cell autophagy monitoring probe, a preparation method therefor and use of the cell autophagy monitoring probe. The structure of the cell autophagy monitoring probe is represented by a formula shown in the description. Cellular co-localization experiments confirm that the cell autophagy monitoring probe can be specifically located to a lysosome; and shown by two-photon fluorescence microscopic imaging experiments, the cell autophagy monitoring probe disclosed by the invention has relatively good infiltration to MCF-7, Hela cells and the like, can be used for detecting changes of polarity of the lysosome and is suitable for being located to the lysosome in cells and detecting the change condition of the polarity of the lysosome. The cell autophagy monitoring probe disclosed by the invention can be used for monitoring an autophagy process of the cells through instantly detecting the change of internal polarity of the lysosome.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Compositions and Methods for the Treatment and Diagnosis of Neoplastic and Infectious Diseases
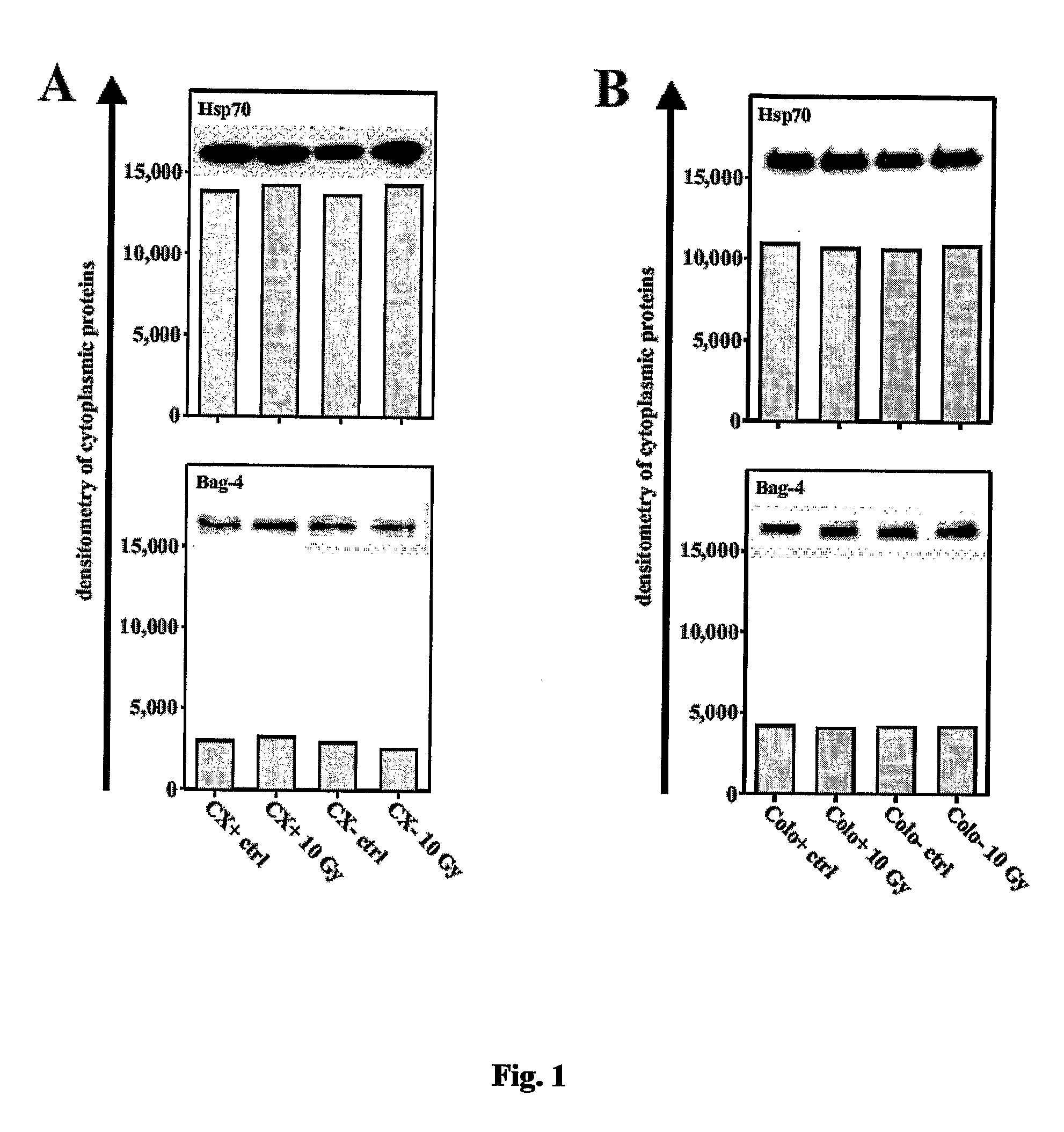
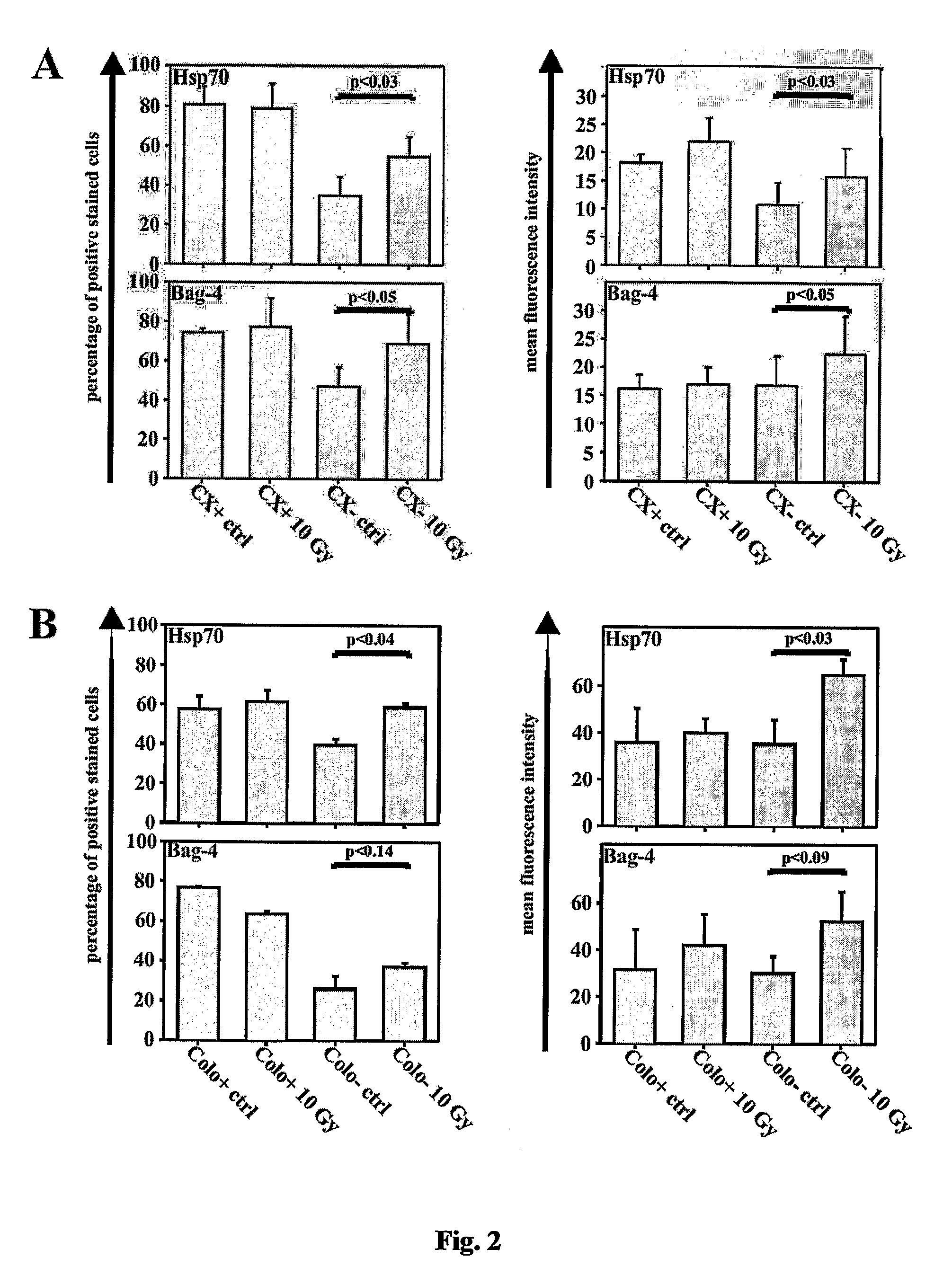
Methods and compositions for the detection, prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases, including, but not limited to human sarcomas and carcinomas are provided. In particular, the detection, prevention and treatment of infectious diseases and cancer mediated and / or indicated by the presence and co-localization of a member of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2-associated athanogene (Bag) family, especially Bag4 and membrane-bound heat shock protein (Hsp) on the cell surface of diseased tissue or cells are described.
Owner:MULTIMMUNE
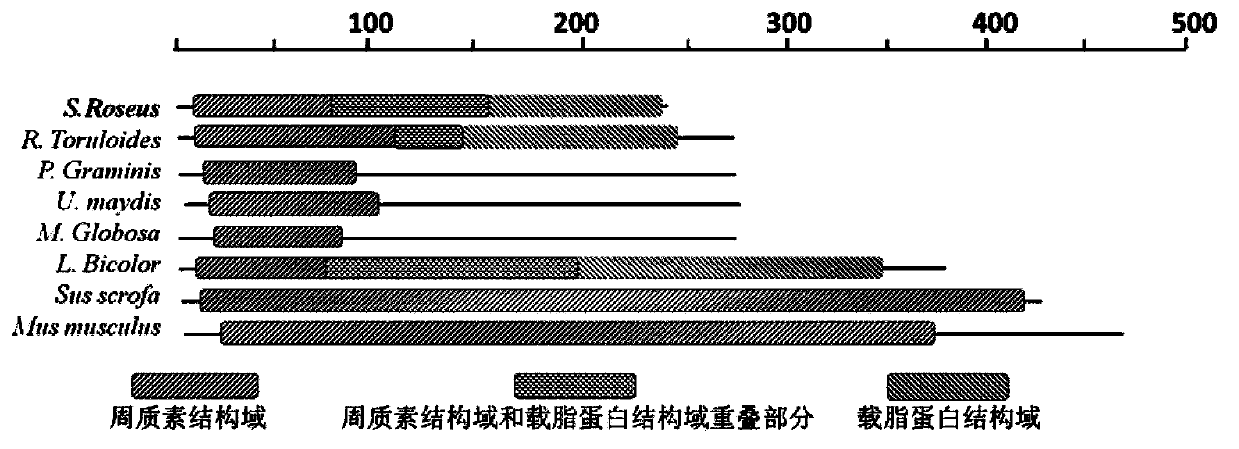
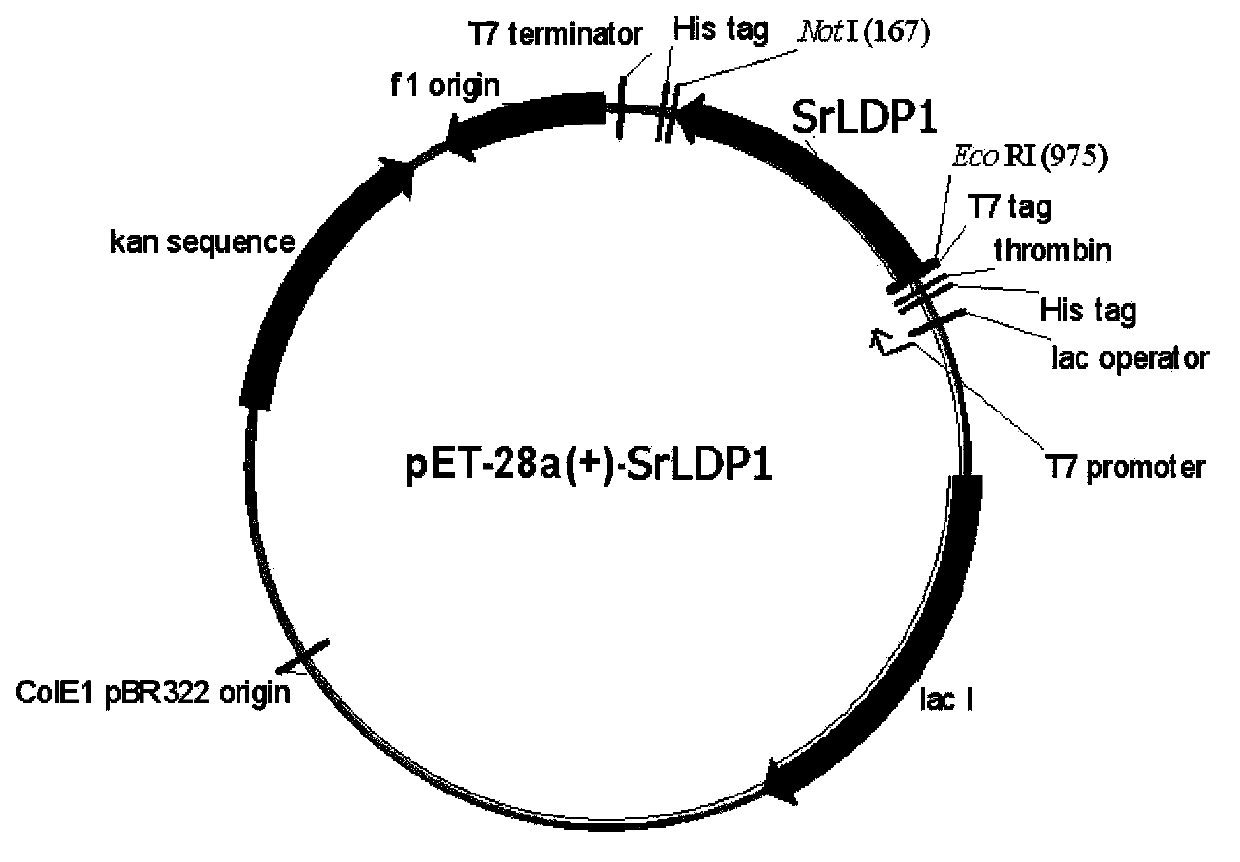
Oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein, coding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to an oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein, coding gene and application thereof. The oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein is the protein shown as the following (a) or (b): (a) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1; and (b) a SEQ ID NO:1 derived protein that is obtained by subjecting the amino acid of SEQ ID NO:1 to substitution and / or deletion and / or adding by one or several amino acids and has related activity of the lipid droplet protein. Green fluorescent protein co-localization and grease fermentation analysis show that the oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein and its coding gene provided by the invention can significantly improve the cellular grease accumulation and storage capacity. According to the invention, a recombinant engineering strain able to significantly improve grease accumulation can be obtained by heterologous expression of gene. The oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein and its coding gene provided by the invention can be applied to construction of strains producing microbial oil and fatty acid derivatives, and can be used as the target for screening of drugs treating obese patients.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
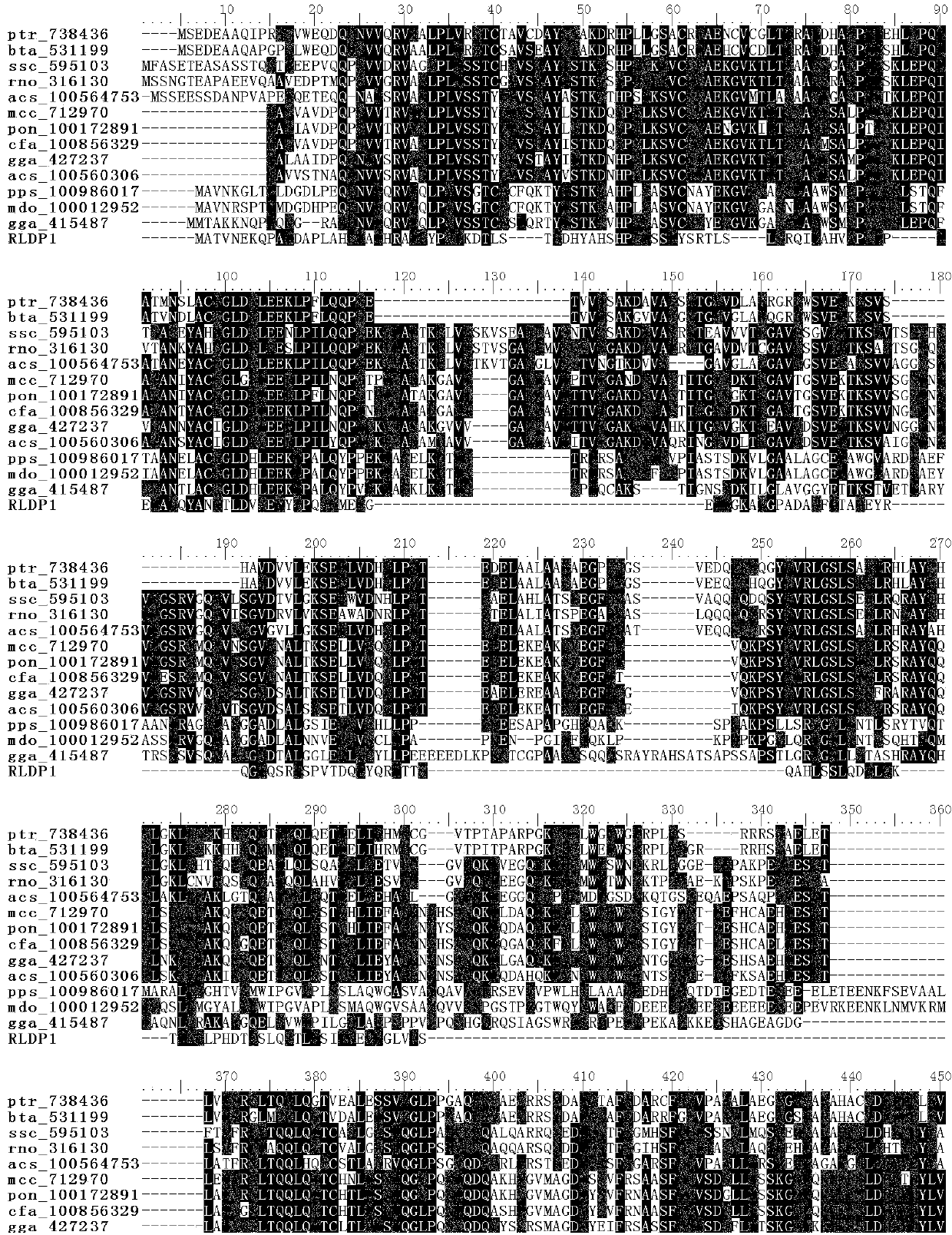
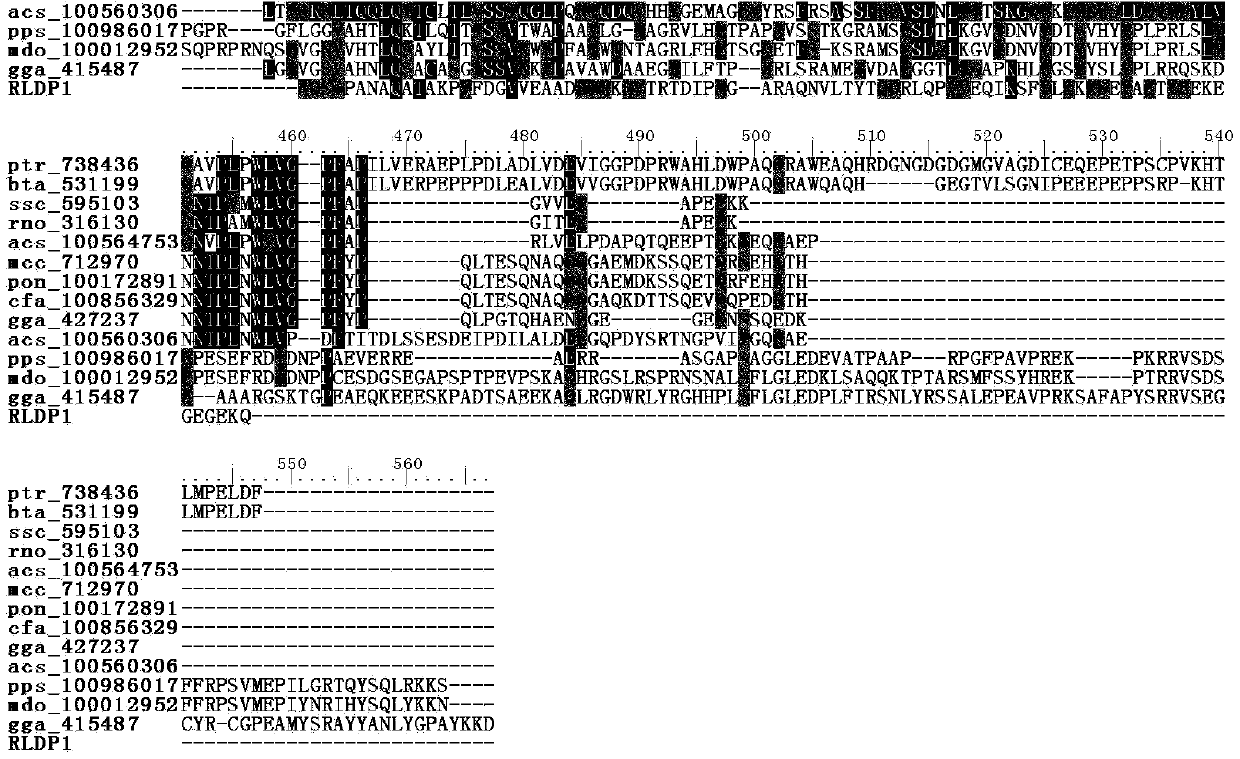
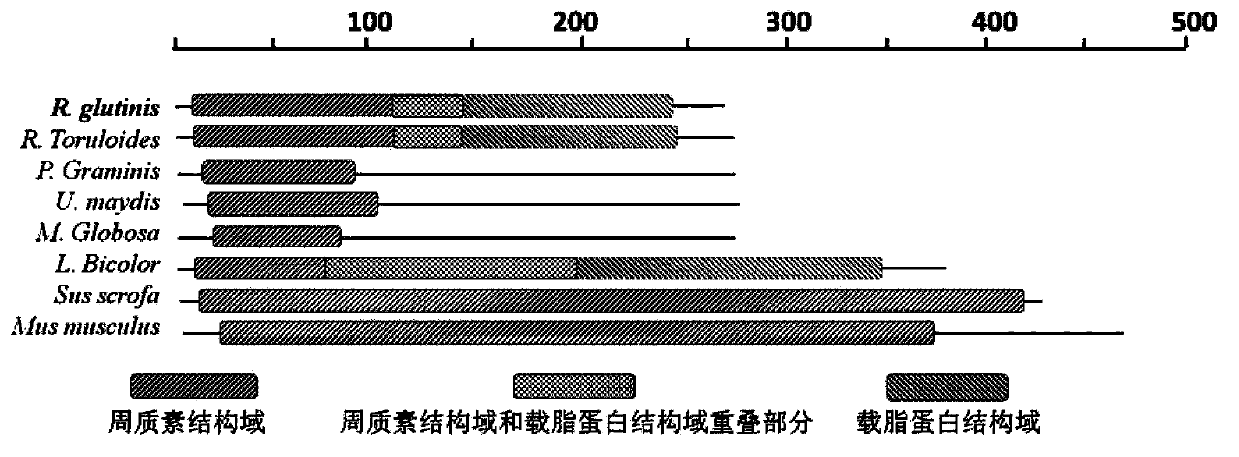
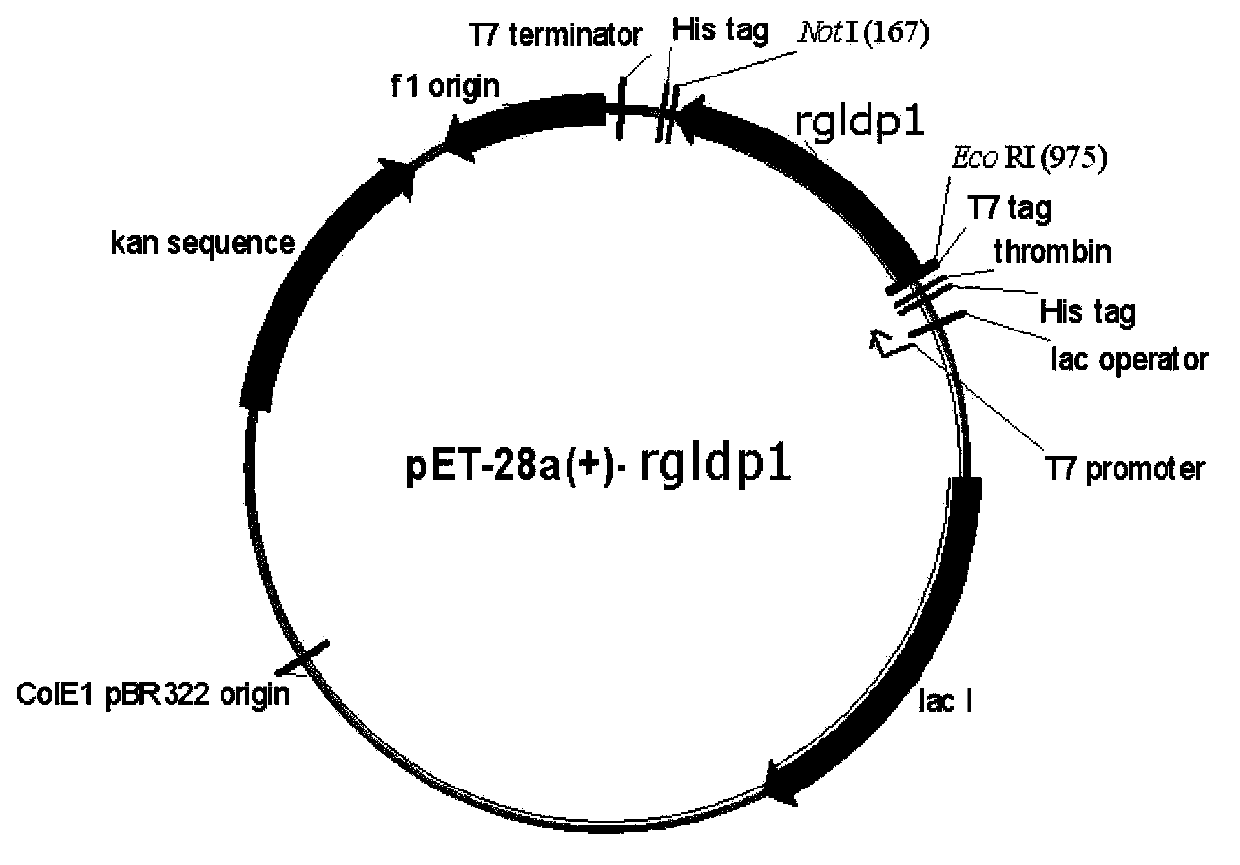
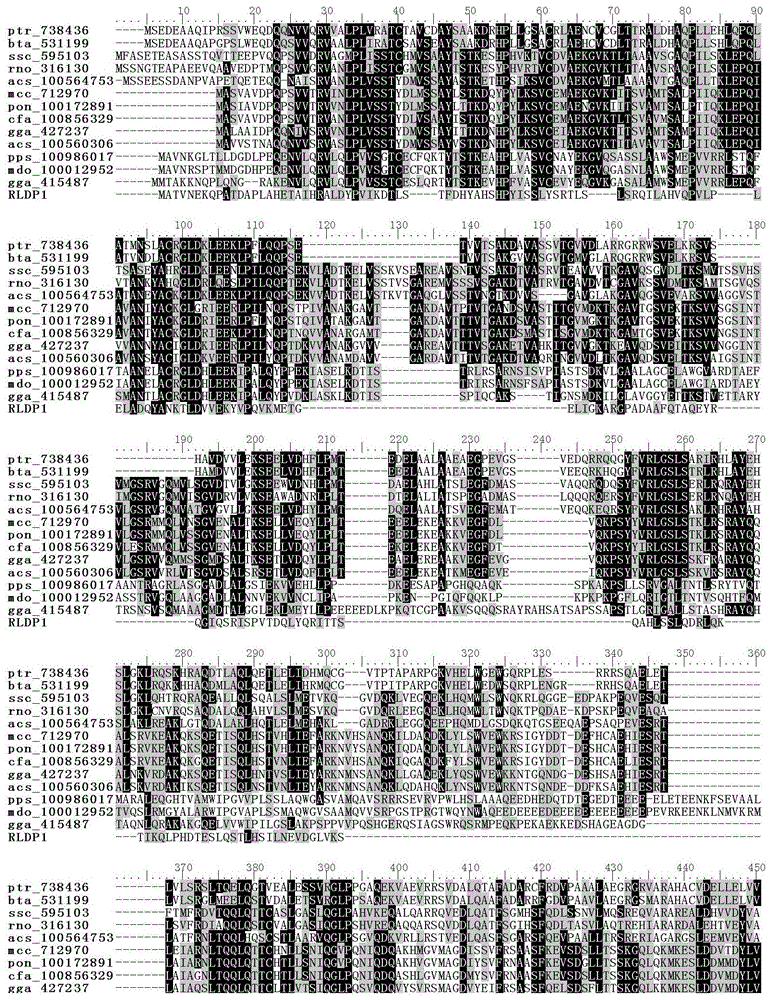
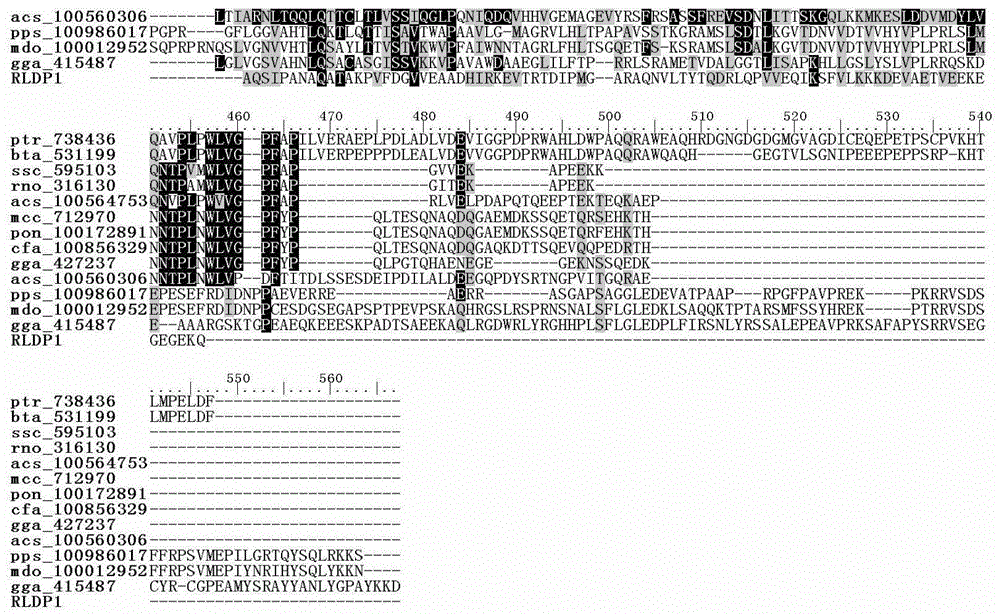
R.glutinis lipid droplet protein 1, coding gene and application thereof
The present invention relates to R.glutinis lipid droplet protein 1, a coding gene and an application thereof. The R.glutinis lipid droplet protein 1 is the following protein (a) or (b), wherein the protein (a) is a protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, and the protein (b) is a protein obtained by carrying out substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acids on the amino acid represented by SEQ ID NO:1, has the droplet protein related activity, and is derived from the SEQ ID NO:1. Results of green fluorescent protein co-localization and grease fermentation analysis demonstrate that the cell grease accumulation and storage amount can be significantly increased with the R.glutinis lipid droplet protein 1 and the coding gene thereof. According to the present invention, a recombinant engineering strain capable of significantly increasing the grease accumulation amount is obtained through heterologous expression of the gene. The R.glutinis lipid droplet protein 1 and the coding gene can be applied for construction of microorganism grease and fatty acid derivative production strains, and can further be used as a target for screening obesity patient treatment drugs.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
S.roseus lipid droplet protein 1, coding gene and application thereof
The present invention relates to S.roseus lipid droplet protein 1, a coding gene and an application thereof. The S.roseus lipid droplet protein 1 is the following protein (a) or (b), wherein the protein (a) is a protein comprising the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1, and the protein (b) is a protein obtained by carrying out substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acids on the amino acid represented by SEQ ID NO:1, has the droplet protein related activity, and is derived from the SEQ ID NO:1. Results of green fluorescent protein co-localization and grease fermentation analysis demonstrate that the cell grease accumulation and storage amount can be significantly increased with the S.roseus lipid droplet protein 1 and the coding gene thereof. According to the present invention, a recombinant engineering strain capable of significantly increasing the grease accumulation amount is obtained through heterologous expression of the gene. The S.roseus lipid droplet protein 1 and the coding gene can be applied for construction of microorganism grease and fatty acid derivative production strains, and can further be used as a target for screening obesity patient treatment drugs.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
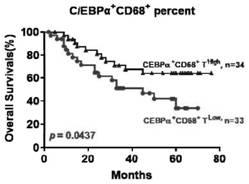
Application of C/EBP alpha and CD68 as prognostic markers in preparation of liver cancer prognostic prediction kit
InactiveCN112698035APredict prognosisThe test method is matureDisease diagnosisBiological testingIndividualized treatmentPrognostic prediction
The invention discloses an application of C / EBP alpha and CD68 as prognostic markers in preparation of a liver cancer prognostic prediction kit. Researches show that the in-situ differentiation and maturation state of mononuclear / macrophages in liver cancer tissues can be judged according to the in-situ co-localization condition of C / EBP alpha and CD68 in the tissues, so that the in-situ immune response condition of the tissues of liver cancer patients is determined, clinicians are helped to better judge the prognosis survival condition of the patients, and an immunological theoretical basis is provided for selecting proper individualized treatment. The invention also provides an application of the double-antibody combined fluorescence detection kit for detecting the differentiation maturity of mononuclear / macrophages in liver cancer tissues, the double-antibody combined fluorescence detection kit comprises a first antibody and a second antibody, the first antibody is a combination of C / EBP alpha and CD68 antibodies, and the second antibody is a fluorescently labeled second antibody.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
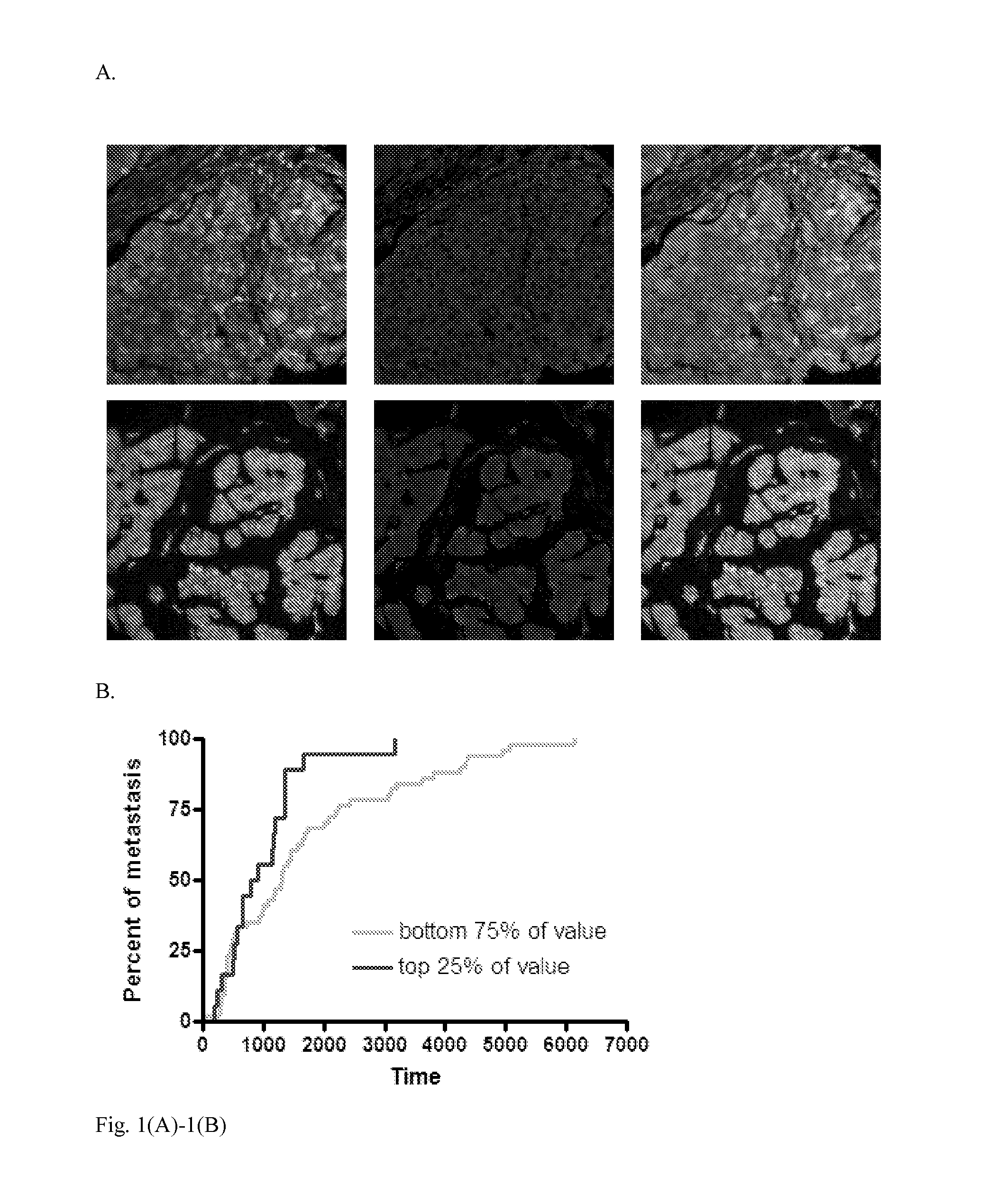
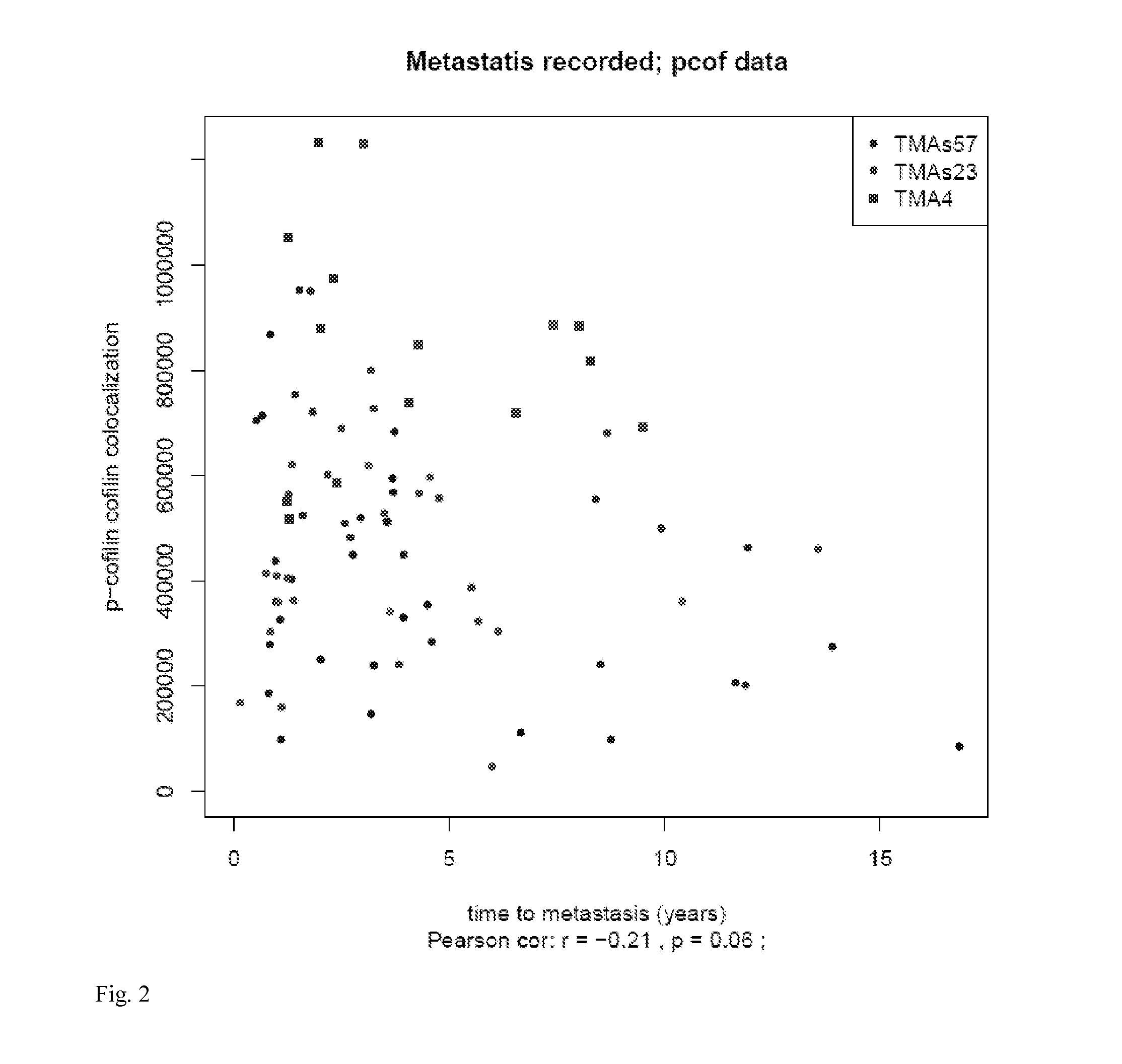
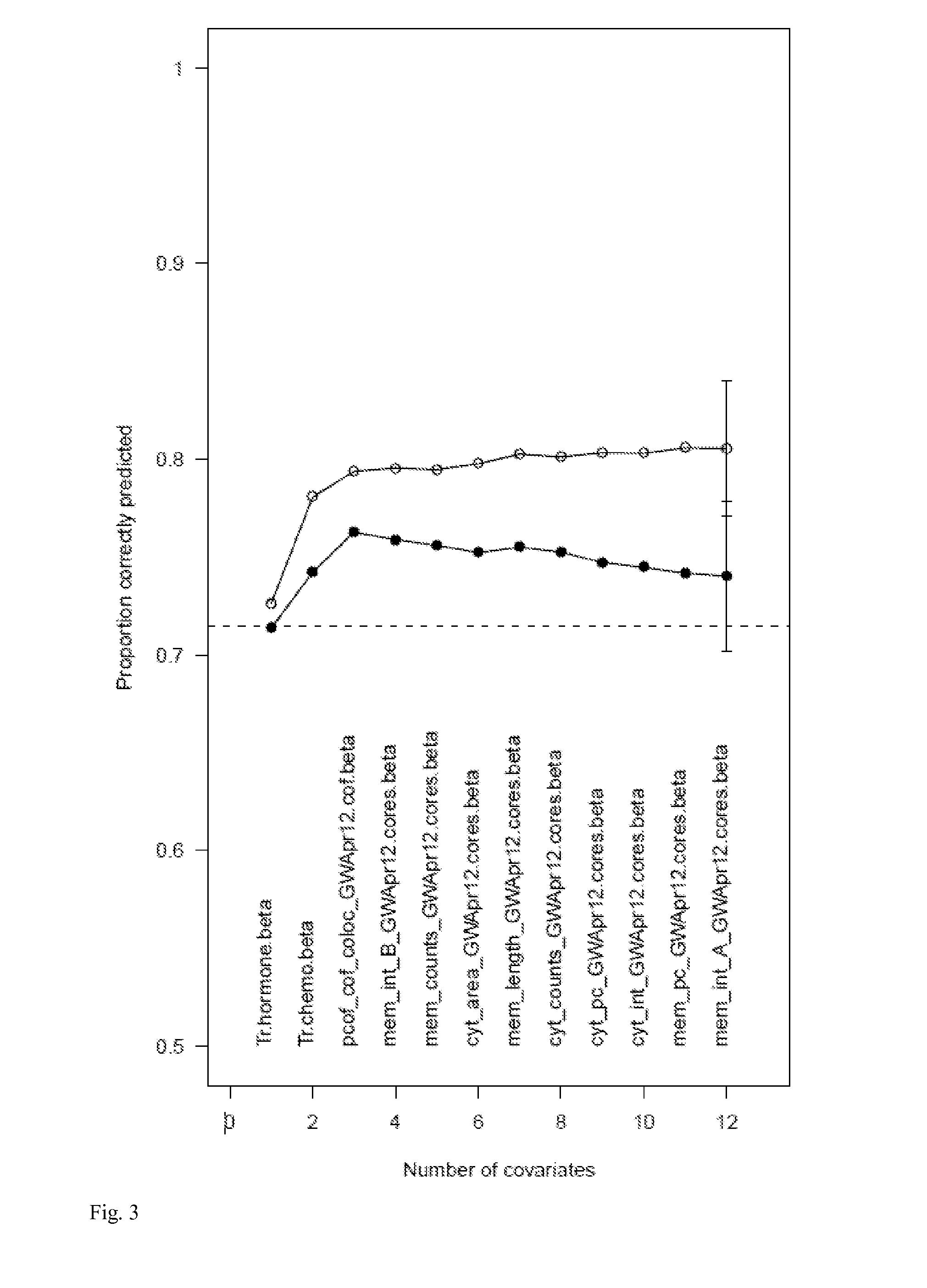
Phosphocofilin: cofilin co-localization intensity as a predictor of metastatic recurrence
Methods and products are provided for determining if a subject having a tumor is at risk of metastasis of the tumor. Specifically, the methods comprise detecting phosphorylated cofilin, and both phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated cofilin; quantifying the phosphorylated cofilin, and the total of phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated cofilin; and determining if a subject having the tumor is likely to experience metastasis of the tumor, based on the ratio of the amount of detected phosphorylated cofilin: total amount of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated cofilin detected. Further disclosed are the types of tumor metastases that can be determined using the methods provided.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE INC
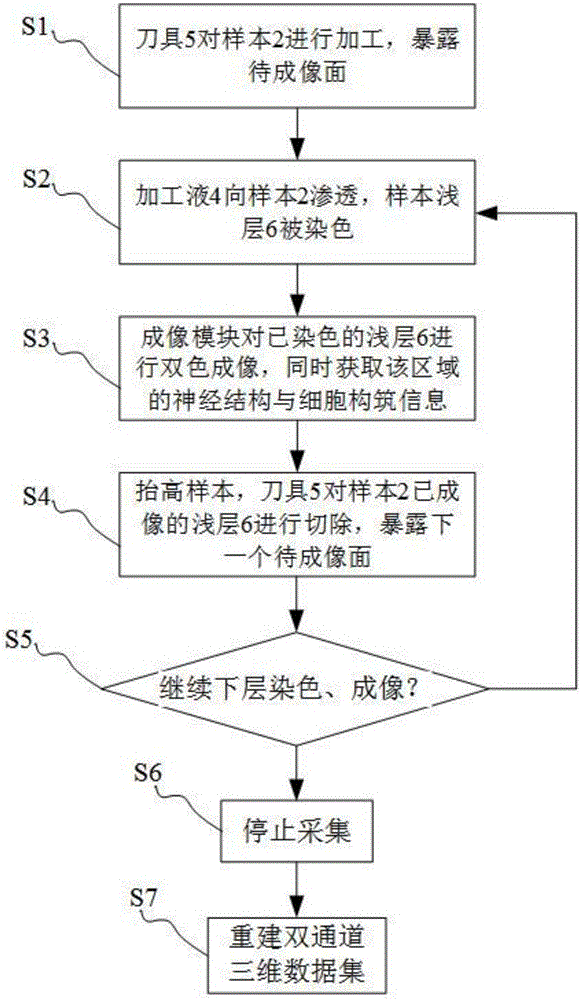
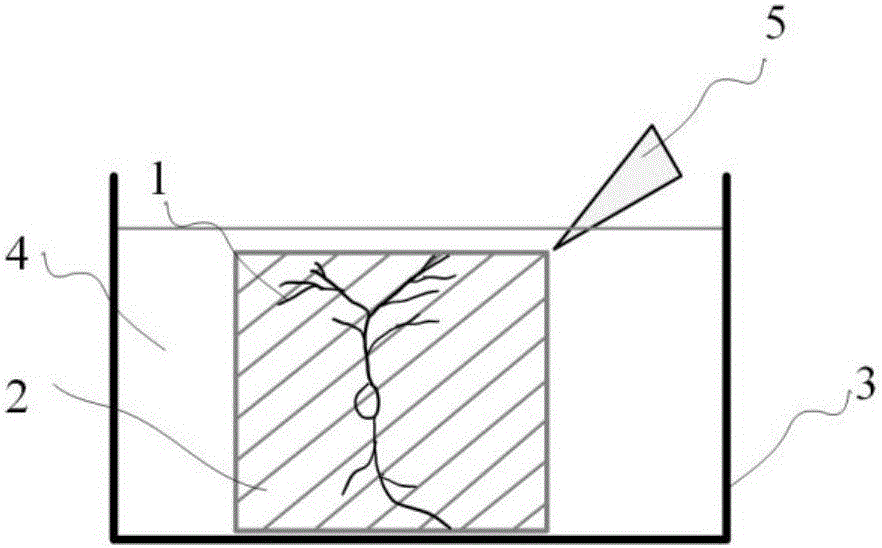
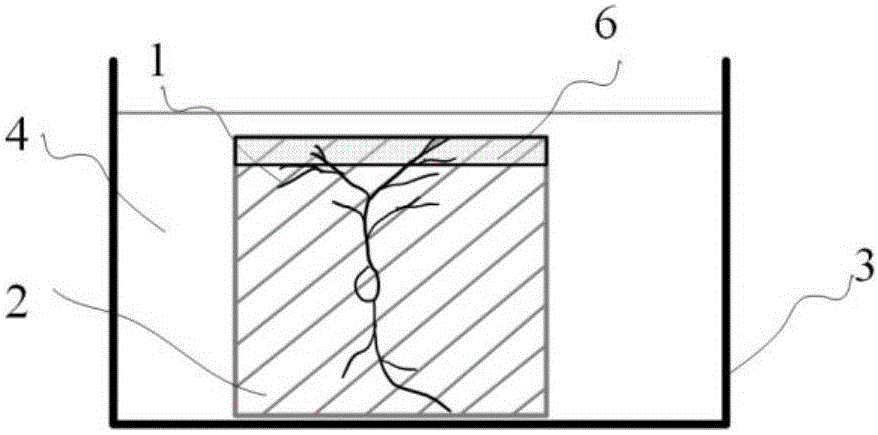
Method for simultaneously obtaining whole brain neural information and co-localization cell construction
ActiveCN105928941AAccurate anatomical positioningAvoid complexityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansChannel dataData set
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously obtaining whole brain neural information and co-localization cell construction. The method comprises the following steps: processing a sample by a cutting module to generate a flat fracture surface; painting the fracture surface by a processing liquid so as to make dye molecules in processing liquid penetrate into the deep part of the sample to dye the superficial layer of the sample; subjecting the superficial part to be imaged of the sample to a dual-color imaging treatment by an imaging module; lifting the sample to a certain height, cutting the imaged part to expose a new surface to be imaged; repeating the steps mentioned above until the information of whole sample is obtained; processing the obtained information by a computer, and then establishing a dual-channel three-dimensional dataset layer by layer, wherein one channel represents the neural information, the other channel represents the cell construction information of the sample, and two channel data are precisely matched. According to the method, during the sample processing process, the superficial layer part of a sample labeled with neural information is subjected to real-time cell construction dyeing and dual-color imaging so as to simultaneously obtain whole brain neural information and co-localization cell construction.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein and its coding gene and application
The invention relates to an oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein, coding gene and application thereof. The oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein is the protein shown as the following (a) or (b): (a) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1; and (b) a SEQ ID NO:1 derived protein that is obtained by subjecting the amino acid of SEQ ID NO:1 to substitution and / or deletion and / or adding by one or several amino acids and has related activity of the lipid droplet protein. Green fluorescent protein co-localization and grease fermentation analysis show that the oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein and its coding gene provided by the invention can significantly improve the cellular grease accumulation and storage capacity. According to the invention, a recombinant engineering strain able to significantly improve grease accumulation can be obtained by heterologous expression of gene. The oleaginous yeast lipid droplet protein and its coding gene provided by the invention can be applied to construction of strains producing microbial oil and fatty acid derivatives, and can be used as the target for screening of drugs treating obese patients.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
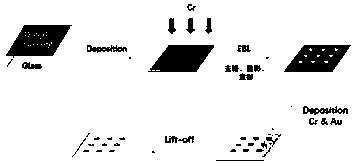
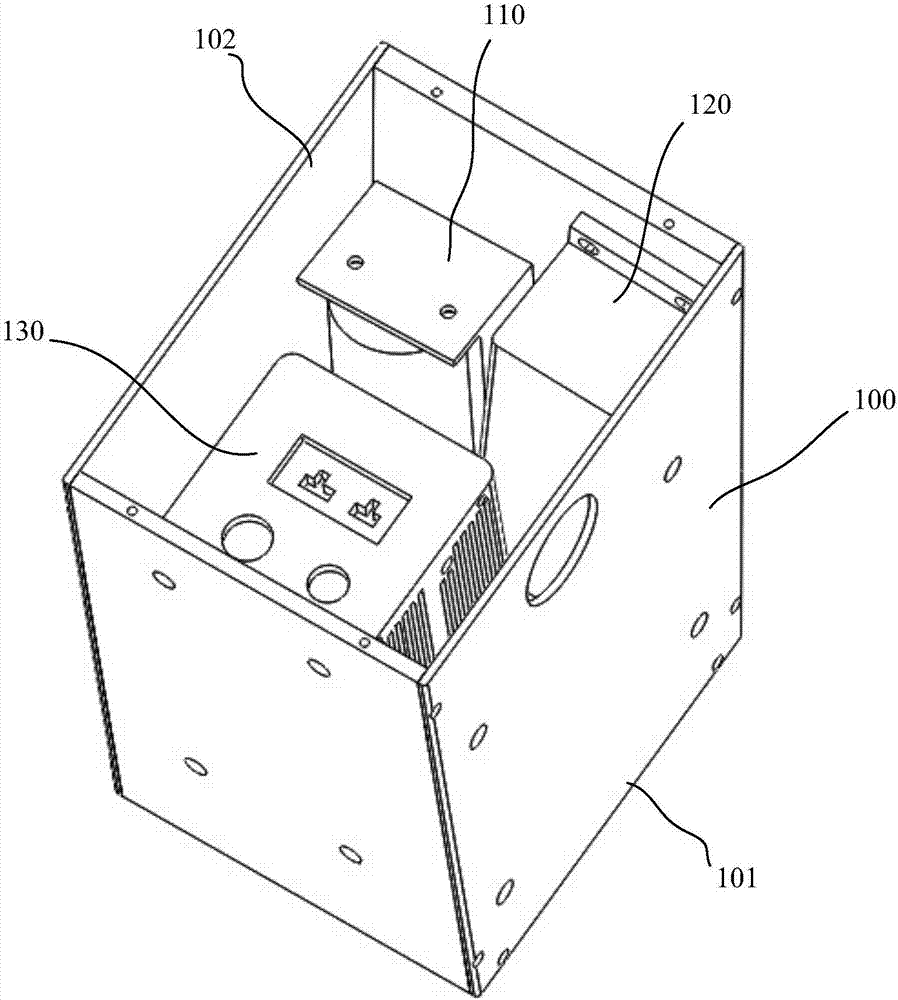
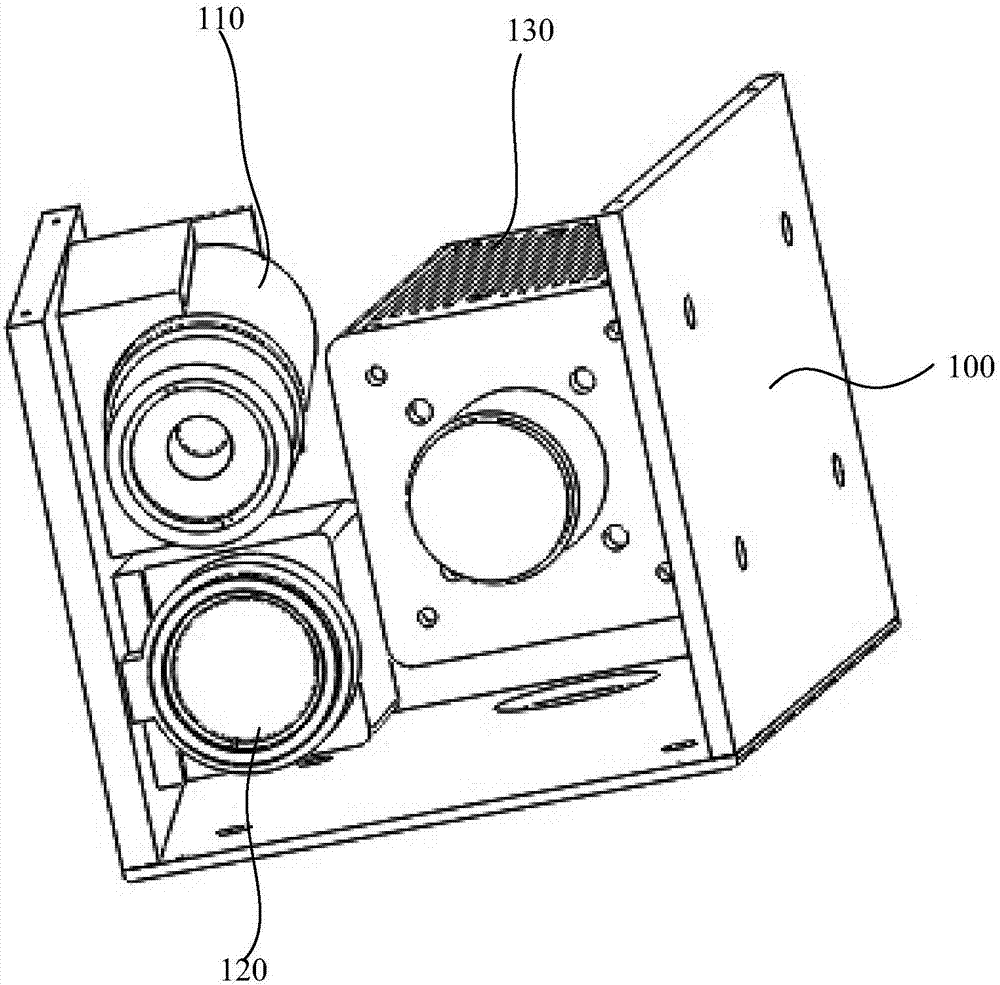
Co-localization surgical navigation system and camera lens
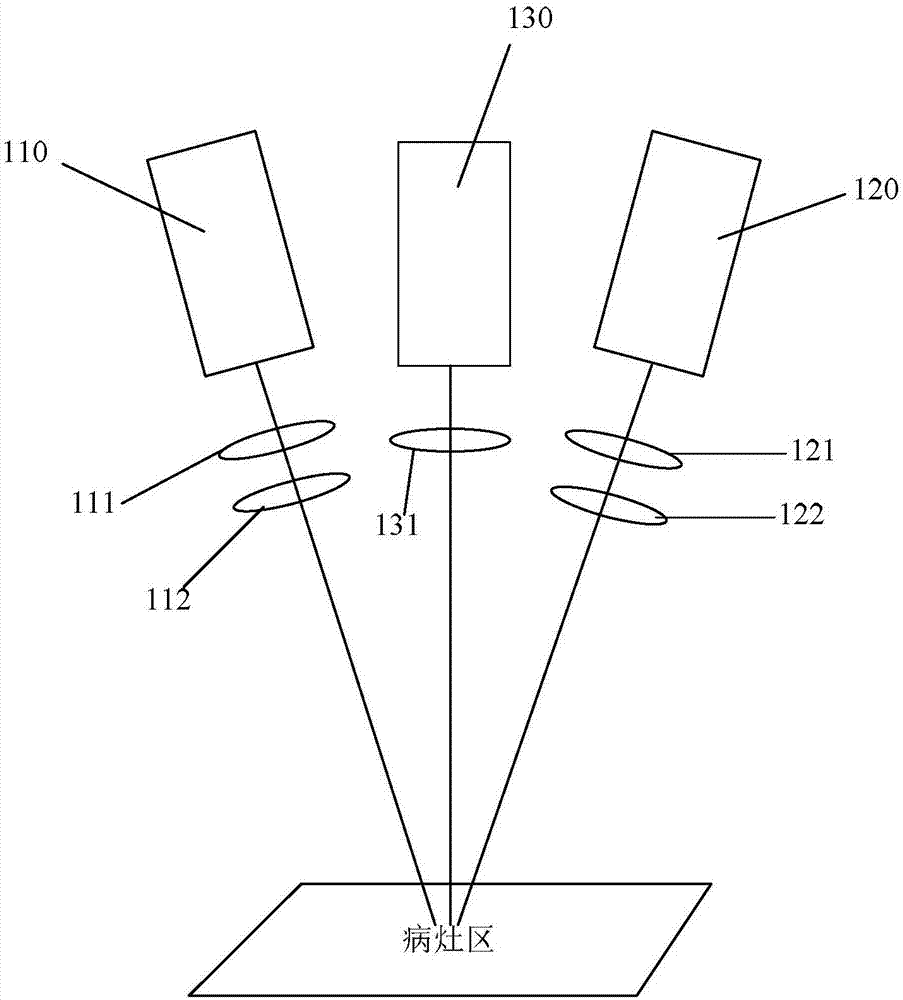
PendingCN106943193AReduce volumeHigh precisionSurgical navigation systemsCamera lensNavigation system
The invention provides a co-localization surgical navigation system and a camera lens. The navigation system comprises a first light source, a second light source and an image acquisition unit, wherein the first light source is used for providing visible light; the second light source is used for providing infrared light; centers of the visible light provided by the first light source and the infrared light provided by the second light source are overlapped; the image acquisition unit comprises a first image sensor and a second image sensor; the first image sensor is used for imaging based on the visible light provided by the first light source; the second image sensor is used for imaging based on fluorescent light excited by the infrared light provided by the second light source, wherein the first image sensor and the second image sensor share an optical path. The co-localization surgical navigation system and the camera lens, provided by the embodiment of the invention, have the advantages of small size, high precision and small interference, and can provide accurate positions of tumors.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for detectingprotein interaction by co-immunoprecipitation on basis of two-color fluorescent tag proteins GFP and mCherry
ActiveCN110456075ALow similarityVerify the authenticity of the interactionBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein targetNicotiana tabacum
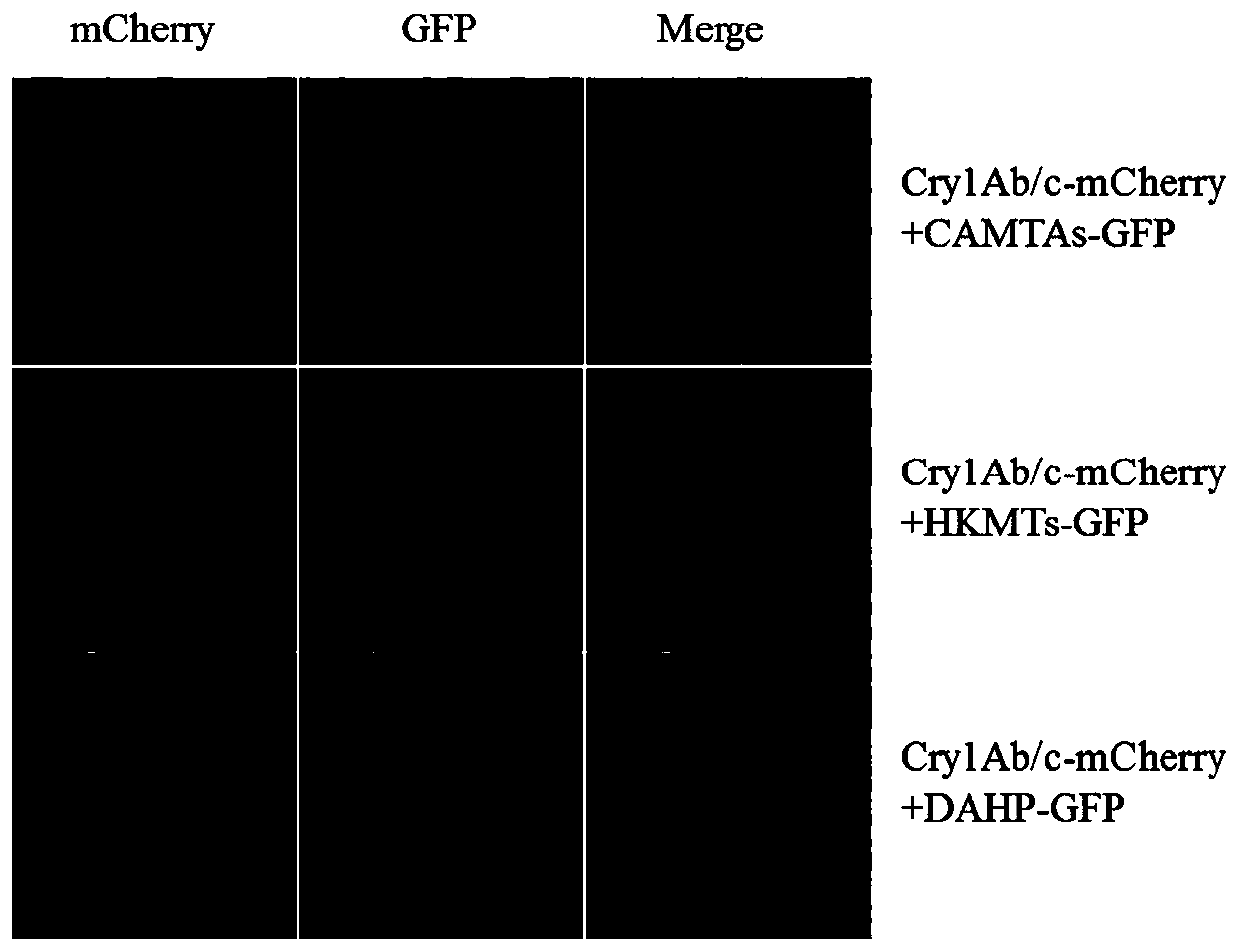
The invention discloses a method for detectingprotein interaction by co-immunoprecipitation on the basis of two-color fluorescent tag proteins GFP and mCherry. The method comprises steps as follows: target genes are constructed to N ends of expression vectors respectively, agrobacteria are transformed after plasmid is extracted, agrobacterium infection liquid co-injection model plant is prepared,a co-injection tobacco leaf protein is extracted, target proteins with GFP tags are enriched with GFP-Trap A beads, meanwhile, other target proteins with mCherry tagsare immunized, and finally, expression and interaction conditions of the target proteins before immunization and after immunization are detected by the GFP and mCherry tag antibodies respectively. According to the method, while real-time fluorescent visual monitoring for expression and co-localization of the target proteins in living cells is realized,the protein interaction can be directly and effectively verified through the co-immunoprecipitationby selecting the stage of the highest expression quantity in real time, the success rate of protein interaction verification is greatly increased, and time and economic cost is substantially reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method and system for the analysis of co-localizations
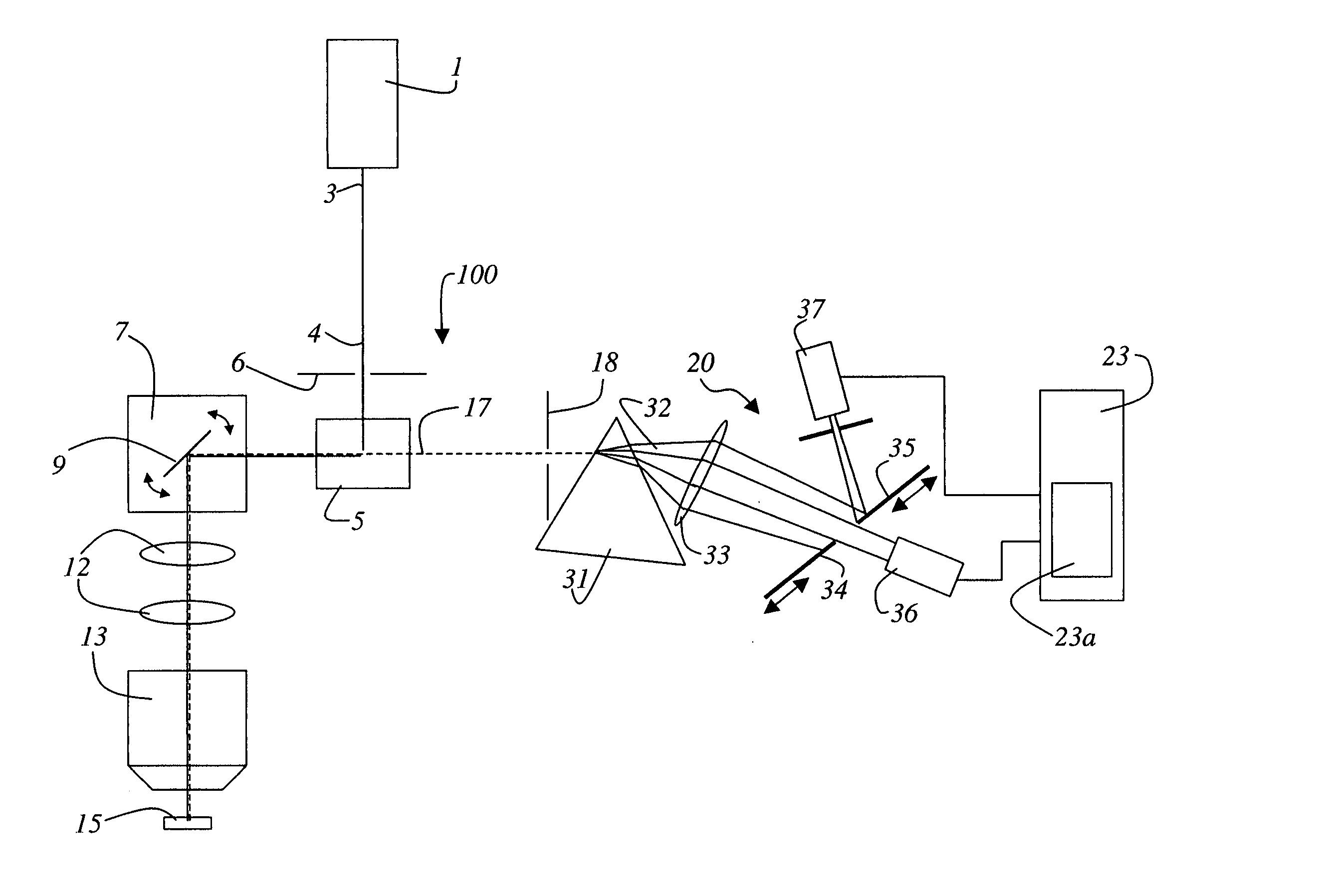
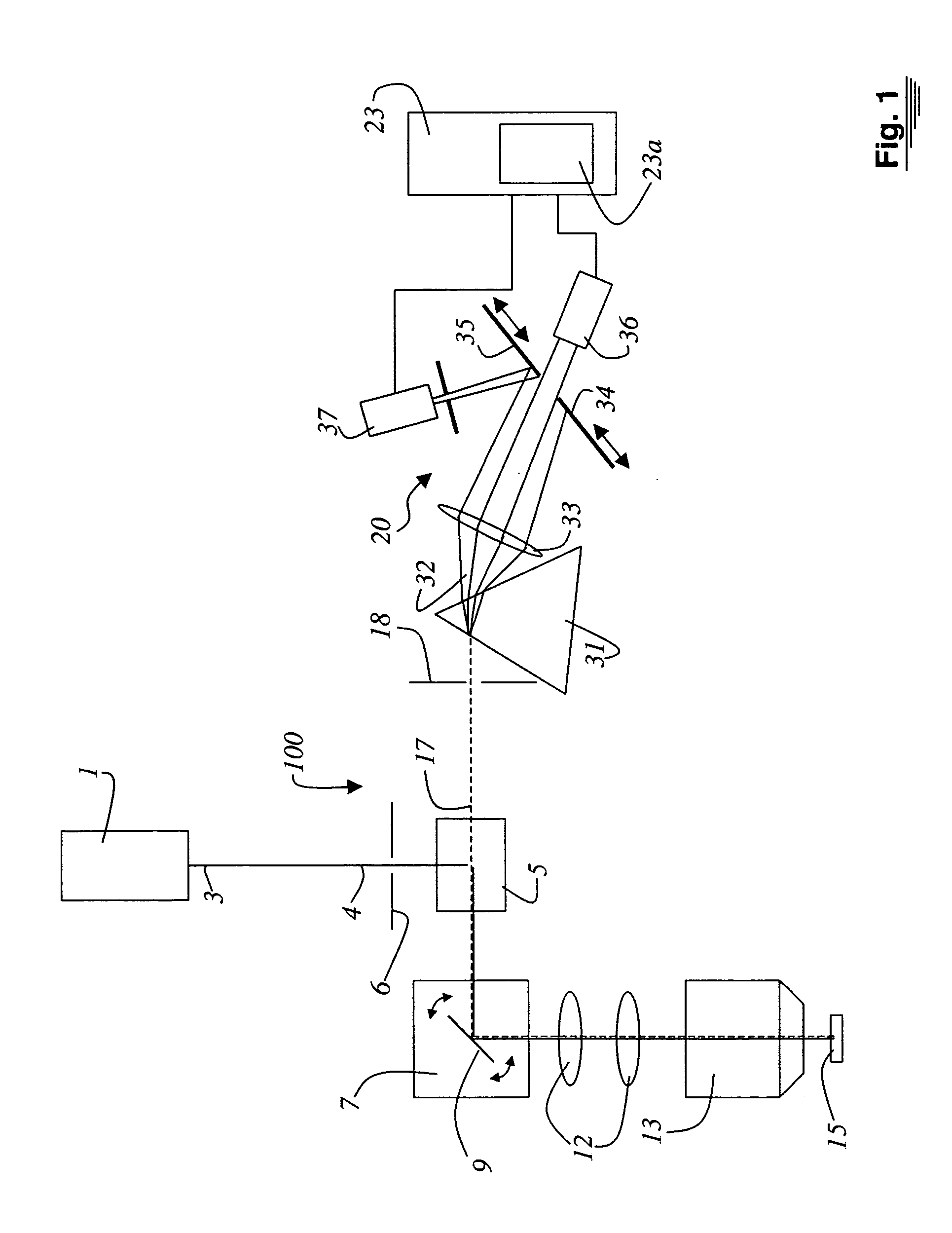
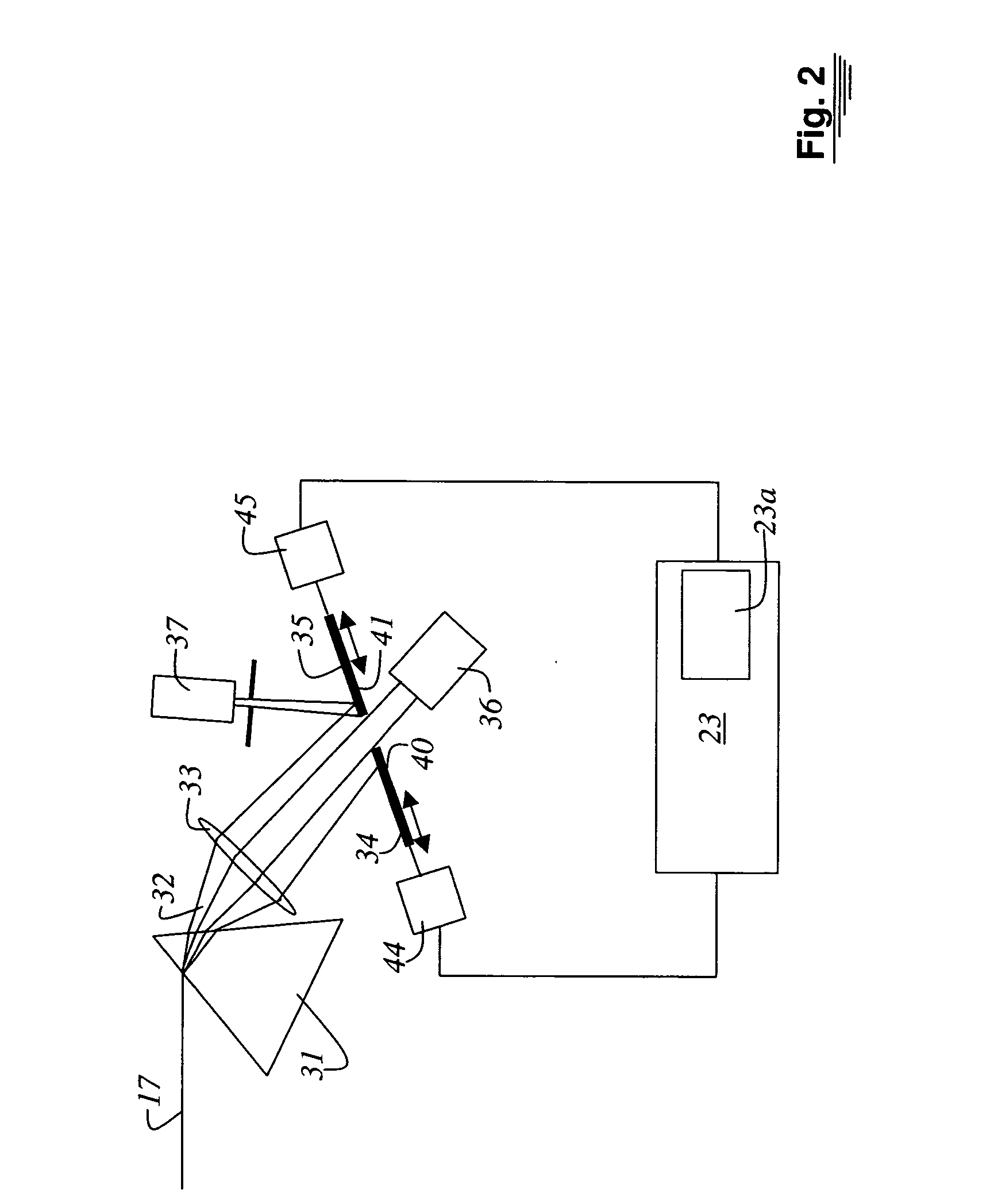
ActiveUS20050109949A1Weight optimizationEasy to analyzePhotometryLuminescent dosimetersFluorescence spectrometryDisplay device
A method and a system for the analysis of co-localizations of dyes present in a specimen (15) are disclosed. For that purpose, the various fluorescence spectra of all dyes present in the specimen (15) are determined. A tolerance region around each of the fluorescence spectra is selected. The spectra of the specimen (15), in which at least two dyes are present, are then acquired pixel by pixel. Those spectra that lie within the tolerance region around the fluorescence spectra are then calculated. A lambda vector is calculated for each pixel and assigned to a spectrum. Images can be outputted on the display in accordance with the assignment to the spectra.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com