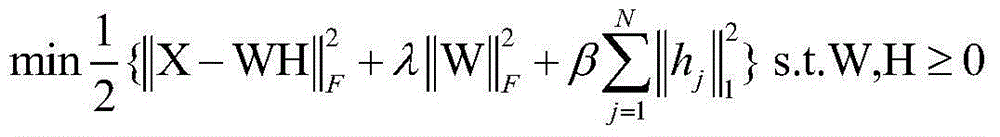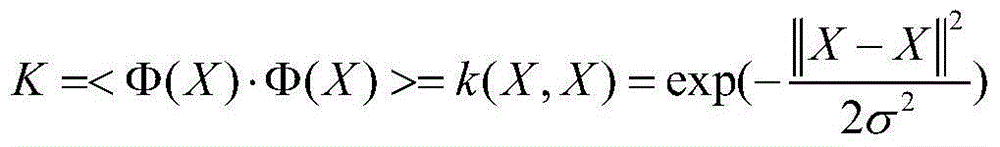Patents
Literature
225 results about "Sparse model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sparse modeling is a rapidly developing area at the intersection of statistical learning and signal processing, motivated by the age-old statistical problem of selecting a small number of predictive variables in high-dimensional datasets.
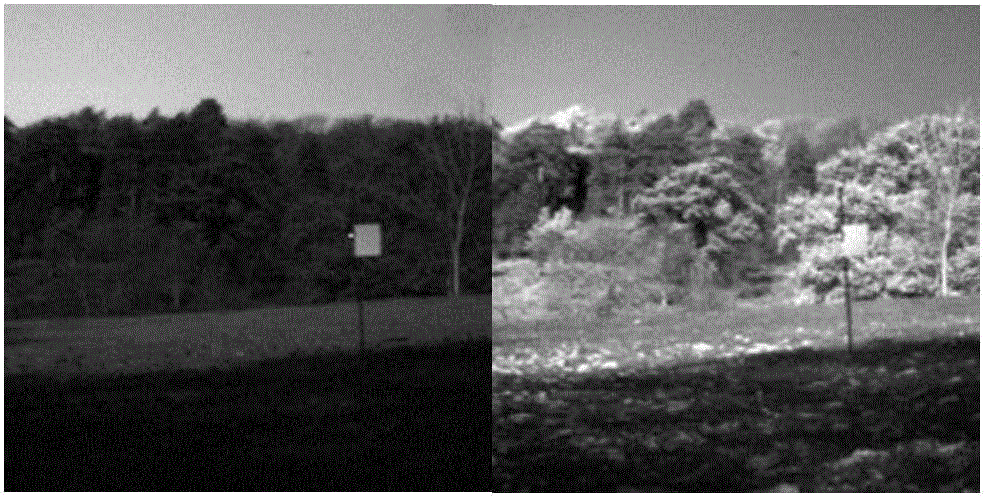
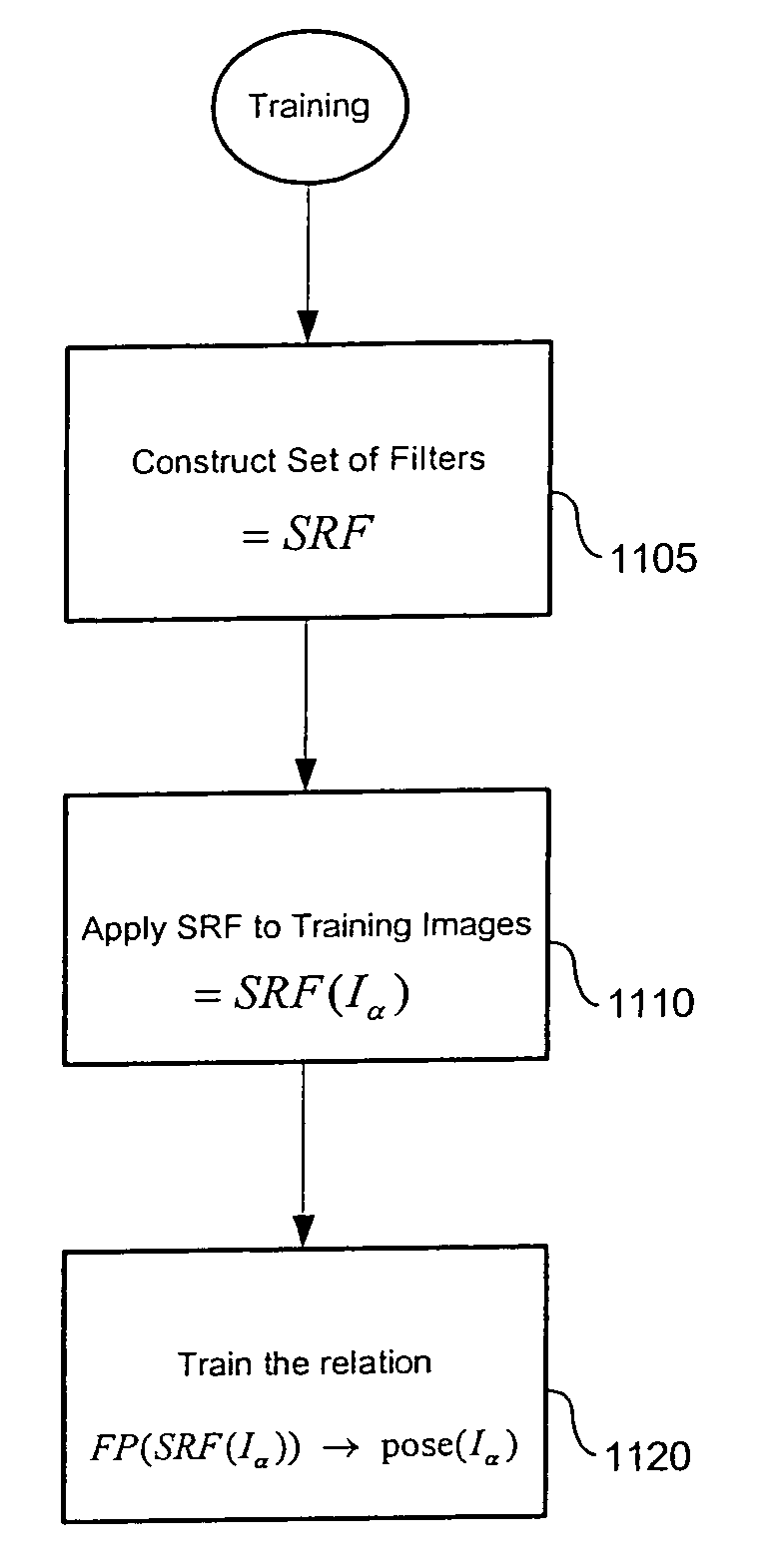
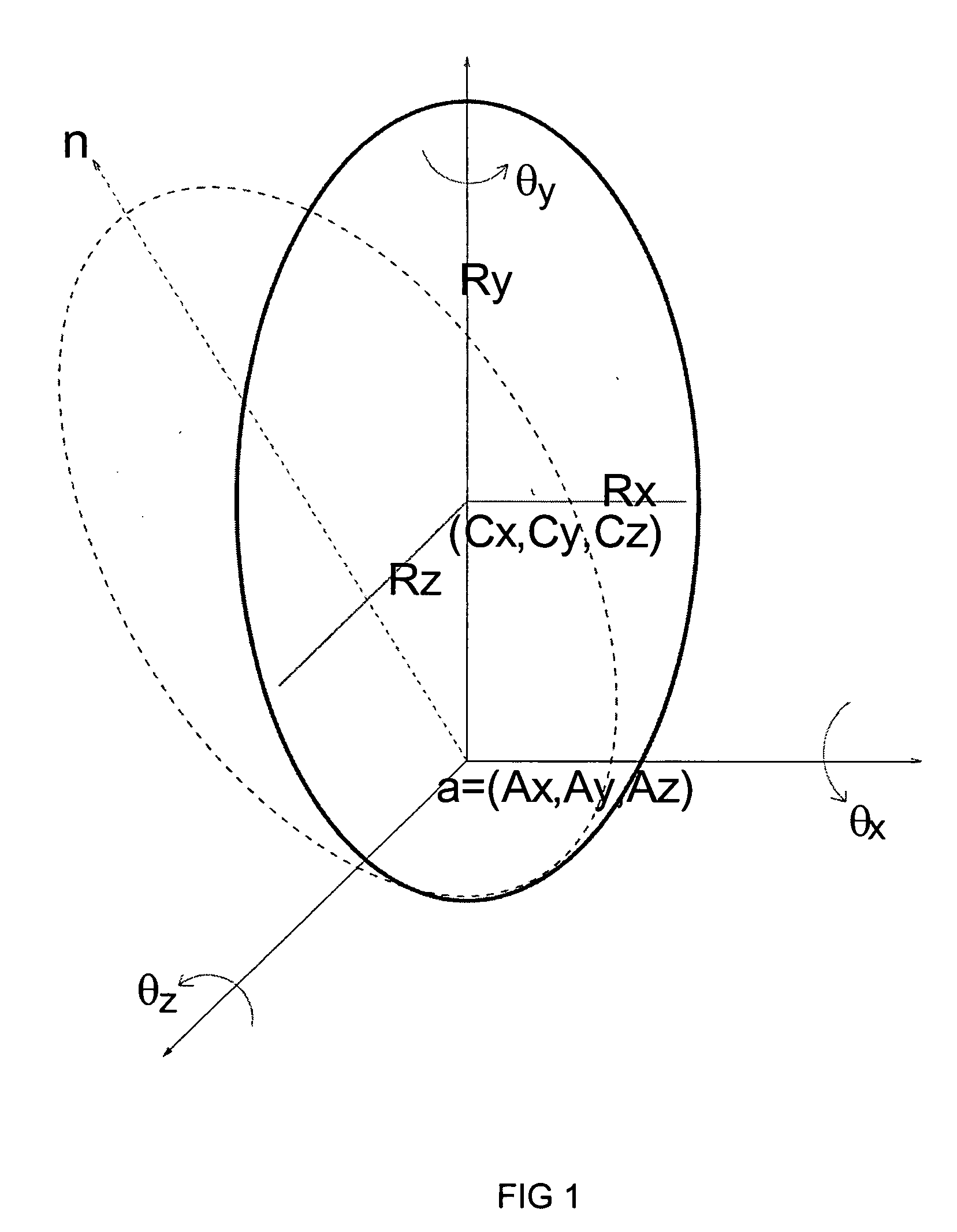
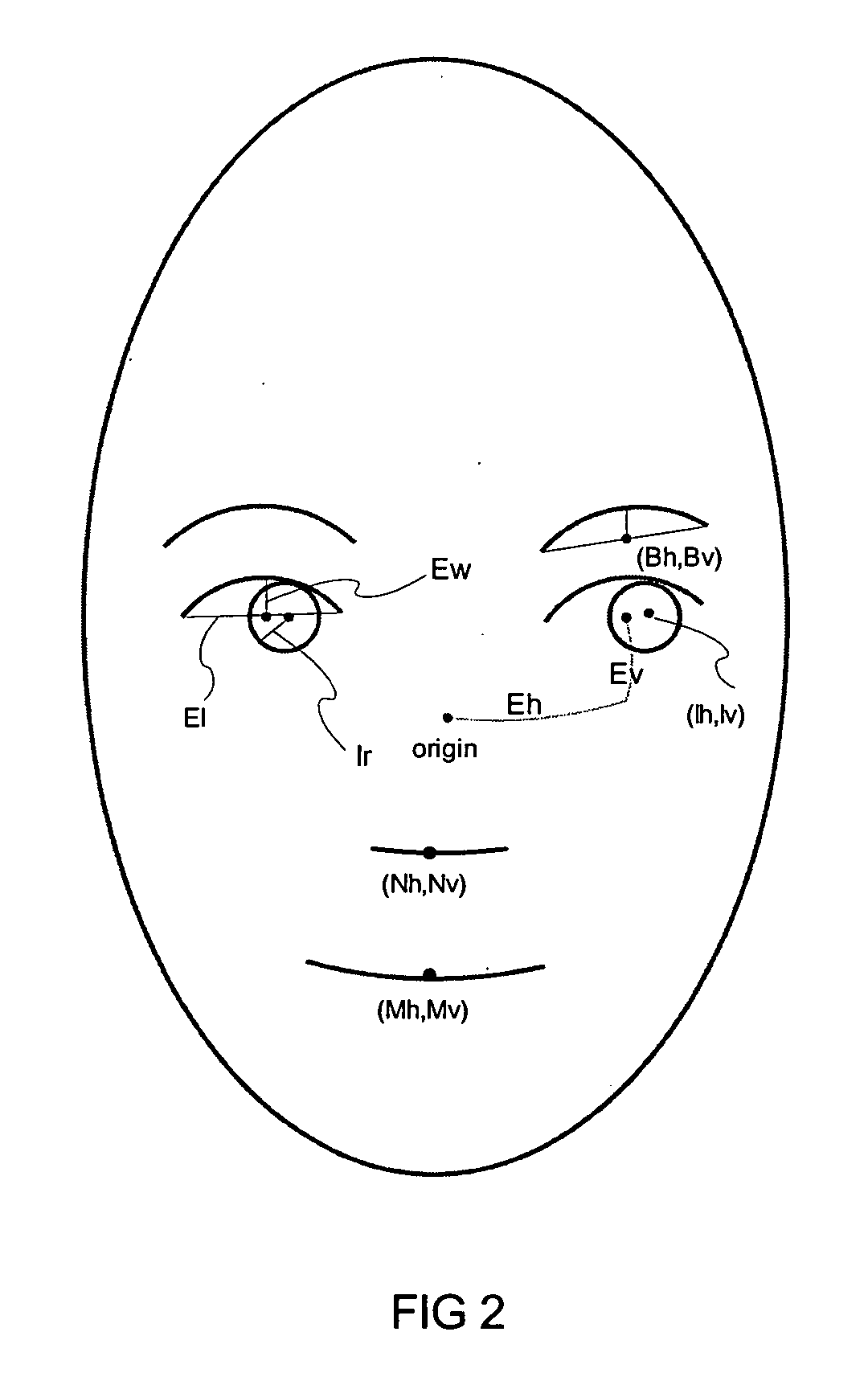
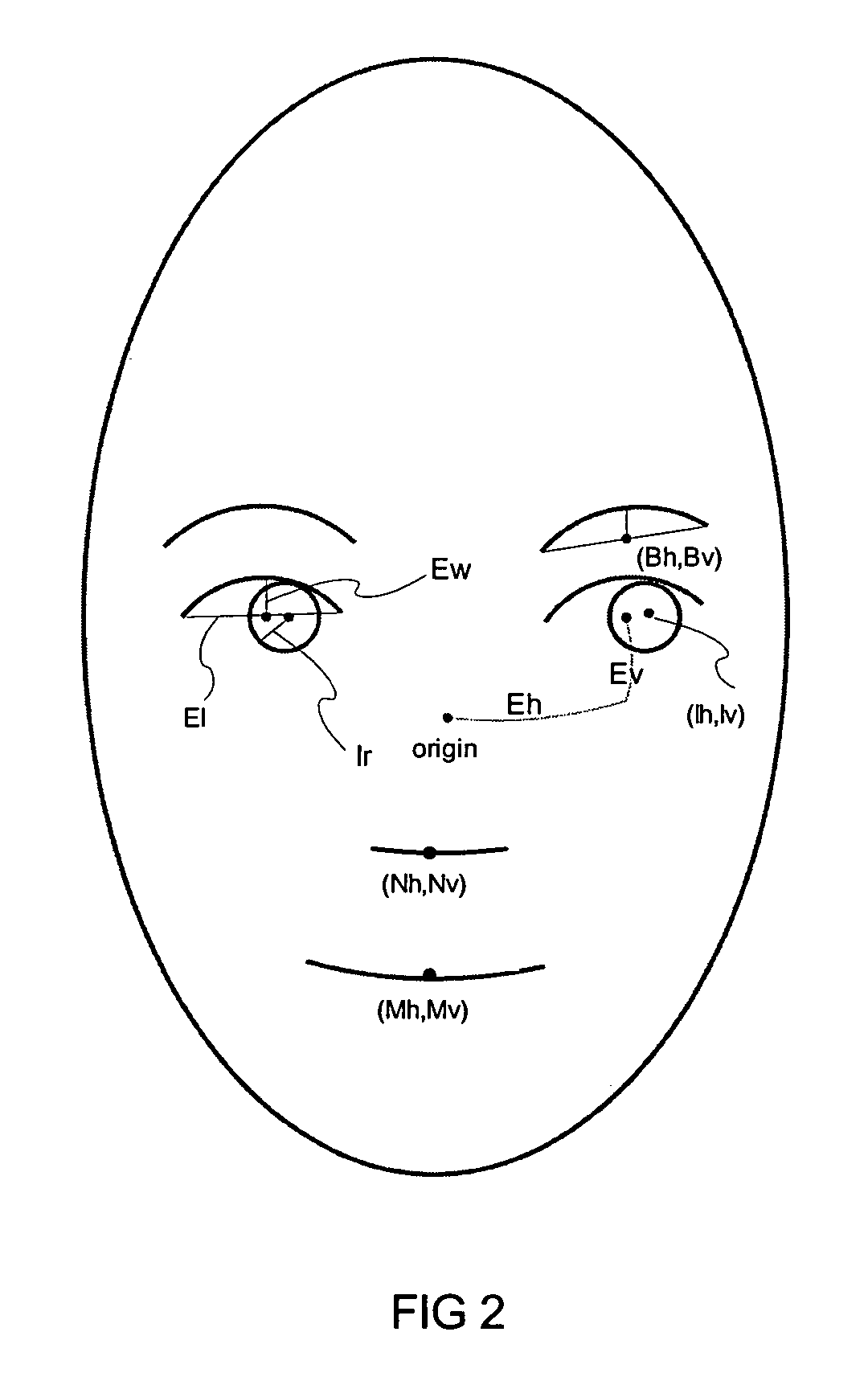
Estimating facial pose from a sparse representation
ActiveUS20050180626A1Accurate estimateGood estimateCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSparse model
A method for accurately estimating a pose of the human head in natural scenes utilizing positions of the prominent facial features relative to the position of the head. A high-dimensional, randomly sparse representation of a human face, using a simplified facial feature model transforms a raw face image into sets of vectors representing the fits of the face to a random, sparse set of model configurations. The transformation collects salient features of the face image which are useful to estimate the pose, while suppressing irrelevant variations of face appearance. The relation between the sparse representation of the pose is learned using Support Vector Regression (SVR). The sparse representation, combined with the SVR learning is then used to estimate a pose of facial images.
Owner:NEC CORP
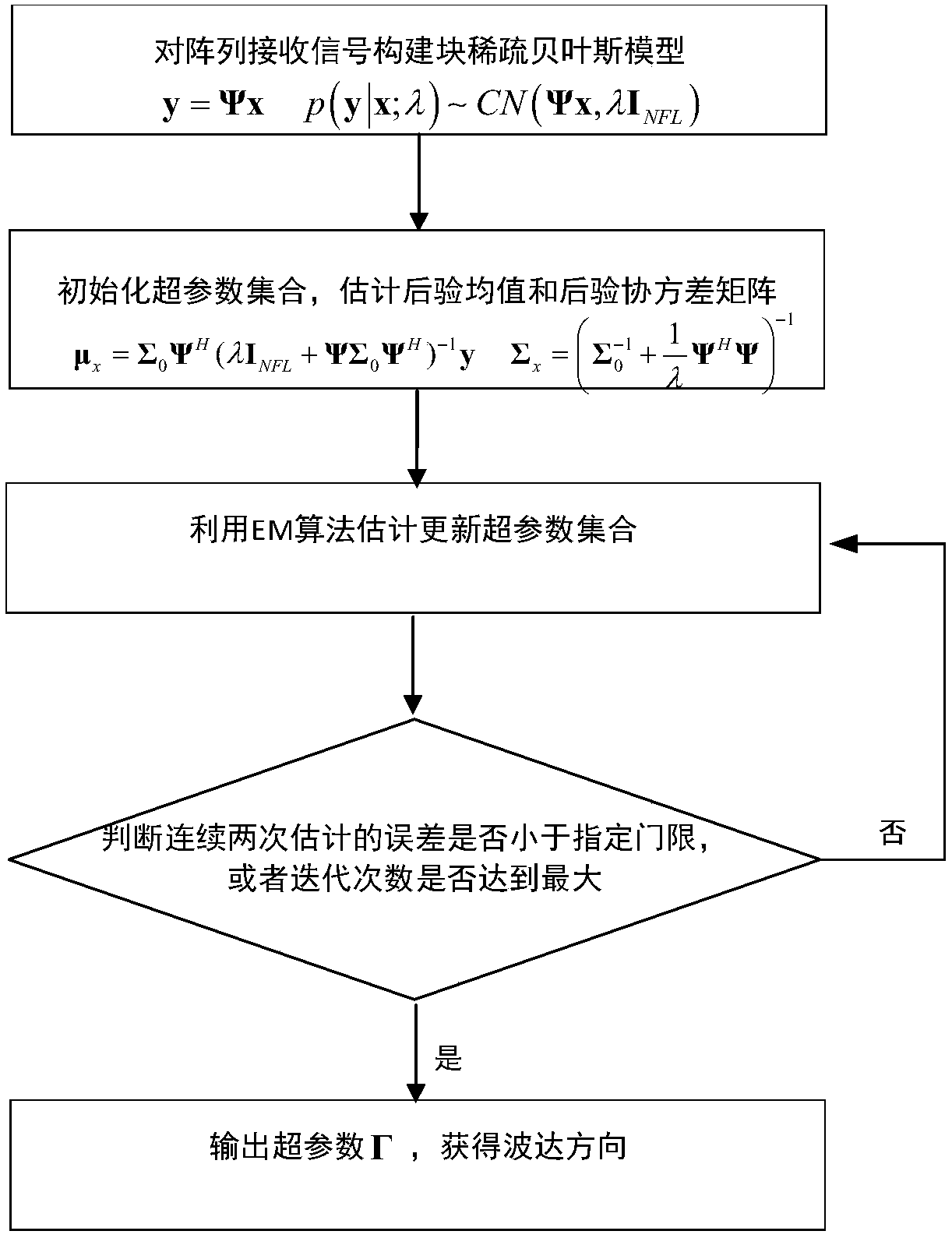
Estimation method of quasi-stationary broadband array signal direction of arrival based on block sparse Bayesian learning
ActiveCN107703477AReduce signal to noise ratioLow number of snapshotsDirection findersExpectation–maximization algorithmFrequency spectrum
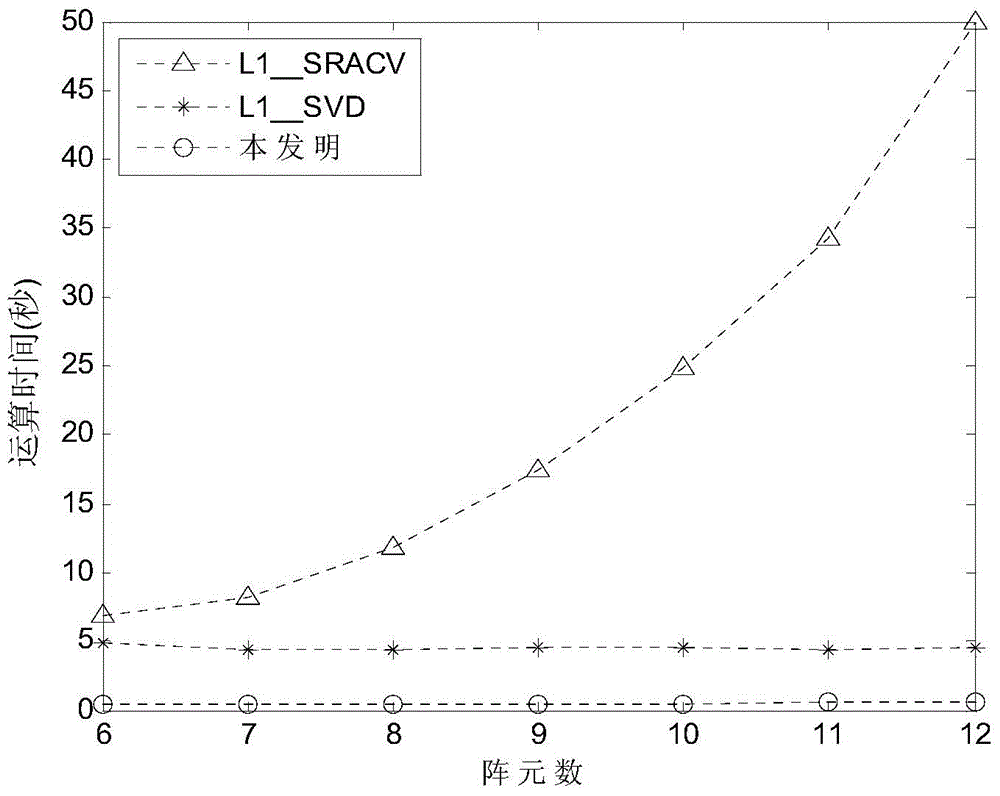
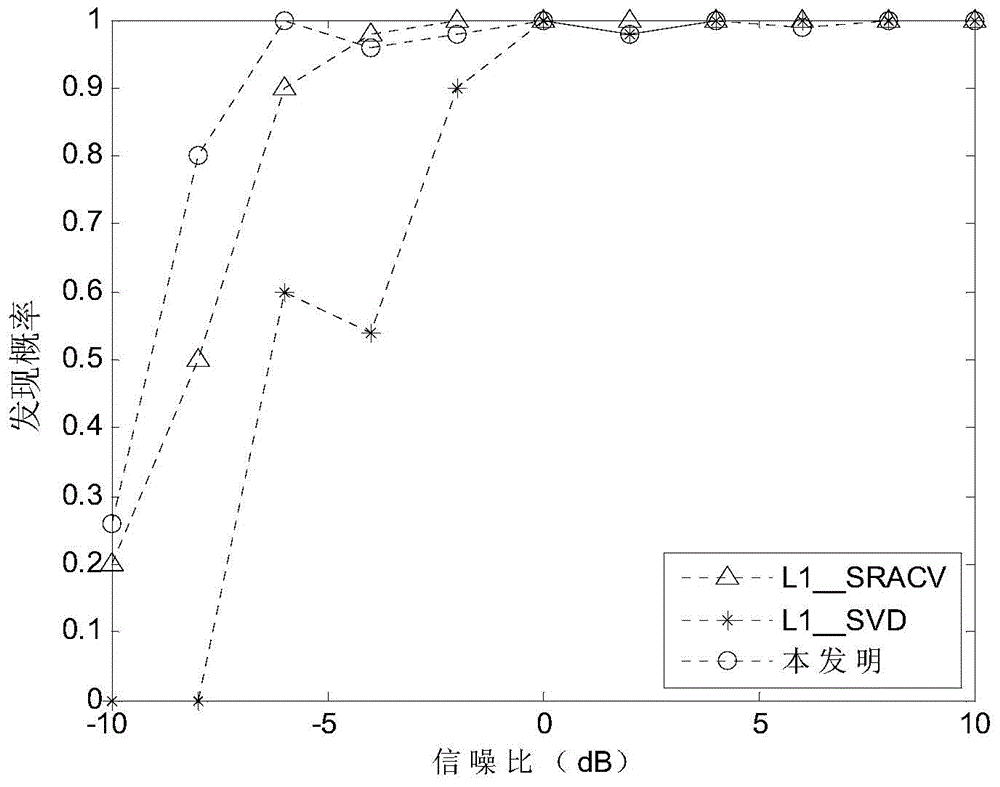
The present invention discloses an estimation method of a quasi-stationary broadband array signal direction of arrival (DOA) based on block sparse Bayesian learning. An intra-frame correlation and aninterframe independence of a quasi-stationary broadband signal frequency spectrum are employed to set a corresponding a block sparse prior distribution model for signals, and a block sparse Bayesian model is employed to perform estimation of sparse signals, so that an estimation result with higher precision is obtained. Array receiving signals are subjected to appropriate framing processing, eachframe of the signal is subjected to Fourier transform, and each block sparse Bayesian model for each signal is established in a frequency domain; under an assumption of each frame of the signal is independent, information of all the frames is combined to establish a total Bayesian model, and hyper-parameter vectors are employed to control a sparsity of all the frames of signals to be reconstructed; and finally, the expectation maximization algorithm (EM) is employed to obtain an iterative update formula of the hyper-parameter vectors. The estimation method of a quasi-stationary broadband arraysignal direction of arrival based on block sparse Bayesian learning fully utilizes a short-time stability feature of quasi-stationary broadband array signals to establish a block sparse model, and therefore a higher DOA estimation precision can be obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
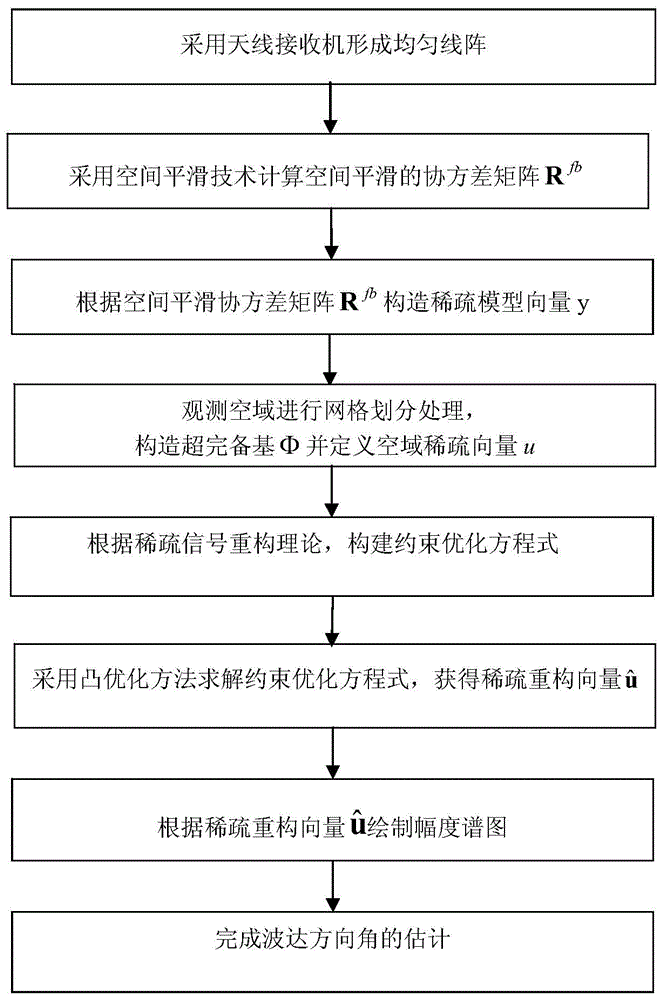
Fast sparse Bayesian learning based direction-of-arrival estimation method
InactiveCN104749553AReduce workloadAvoid anglesRadio wave finder detailsEuclidean vectorCovariance matrix
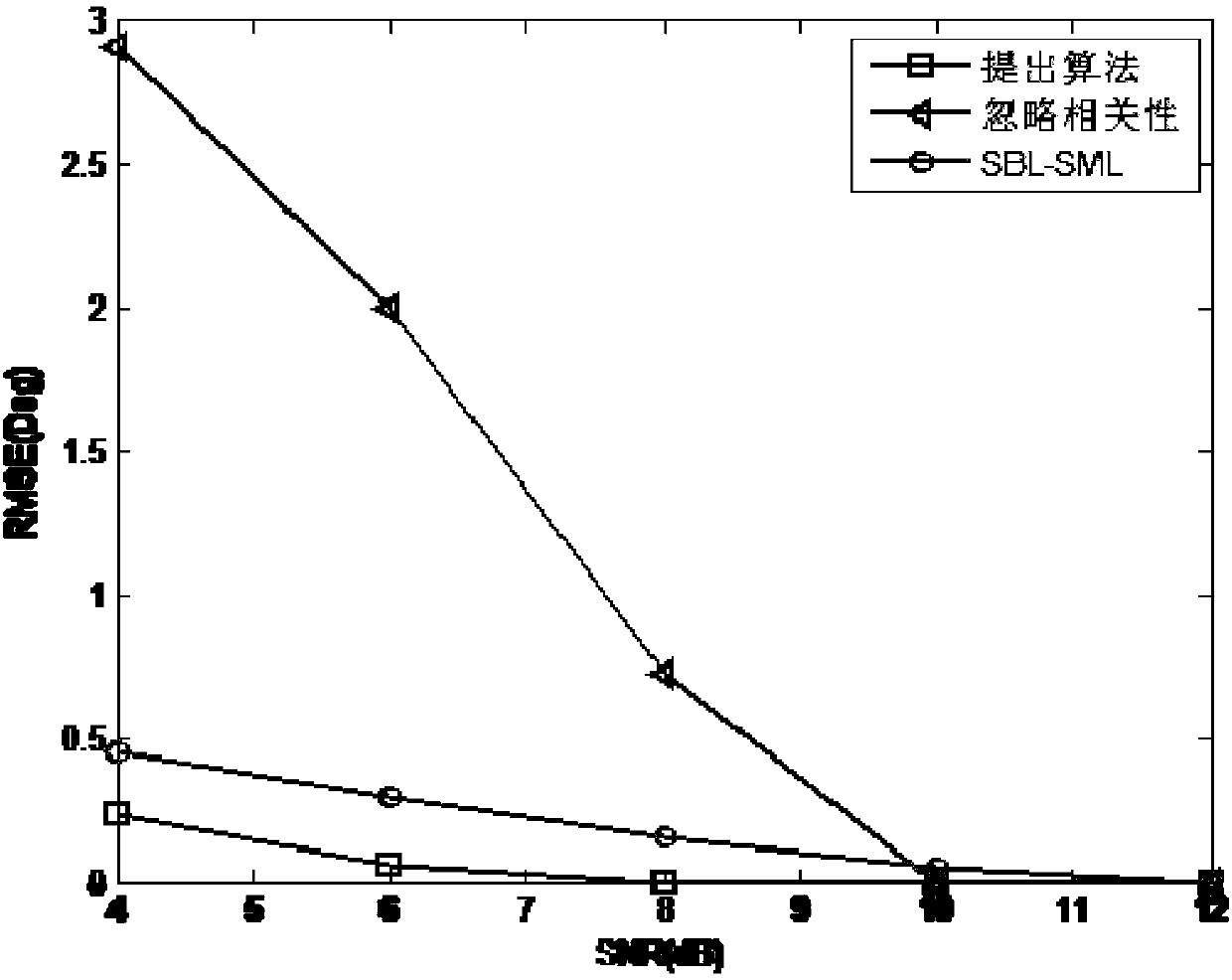
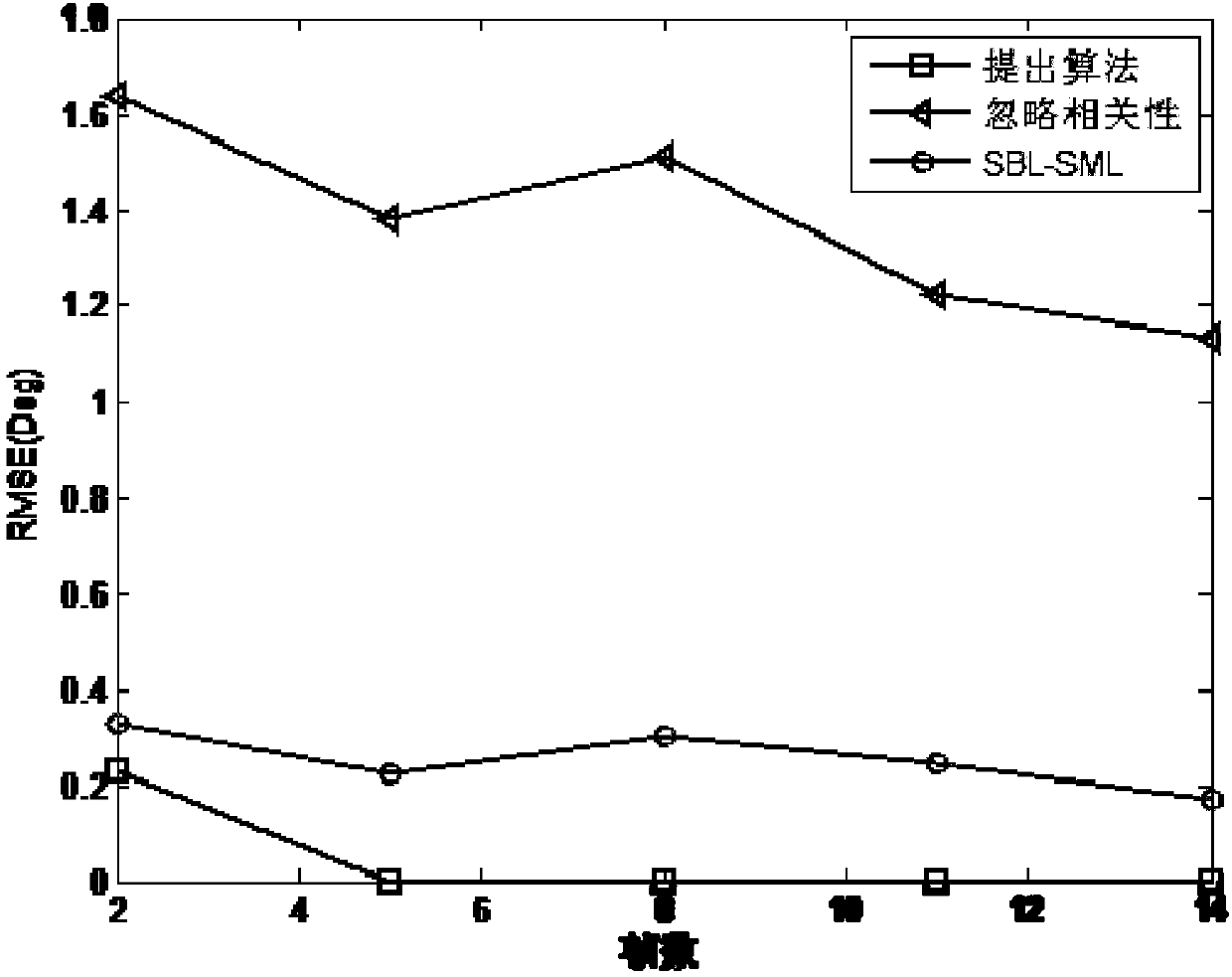
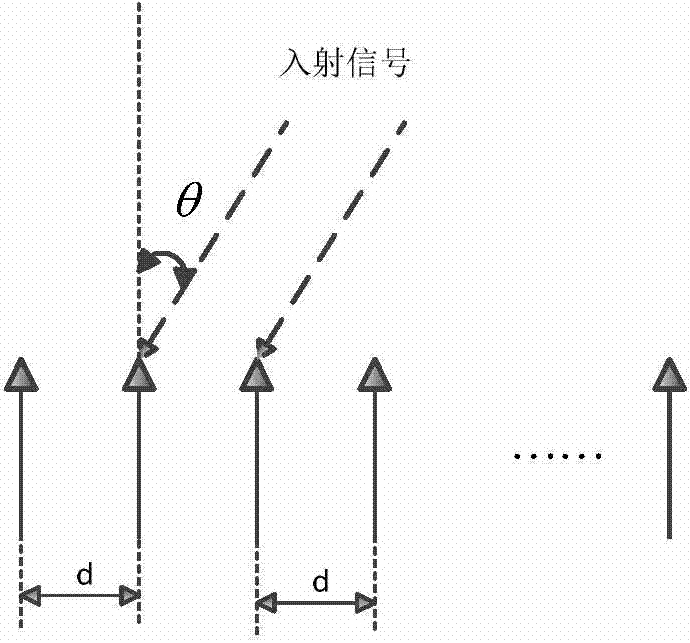
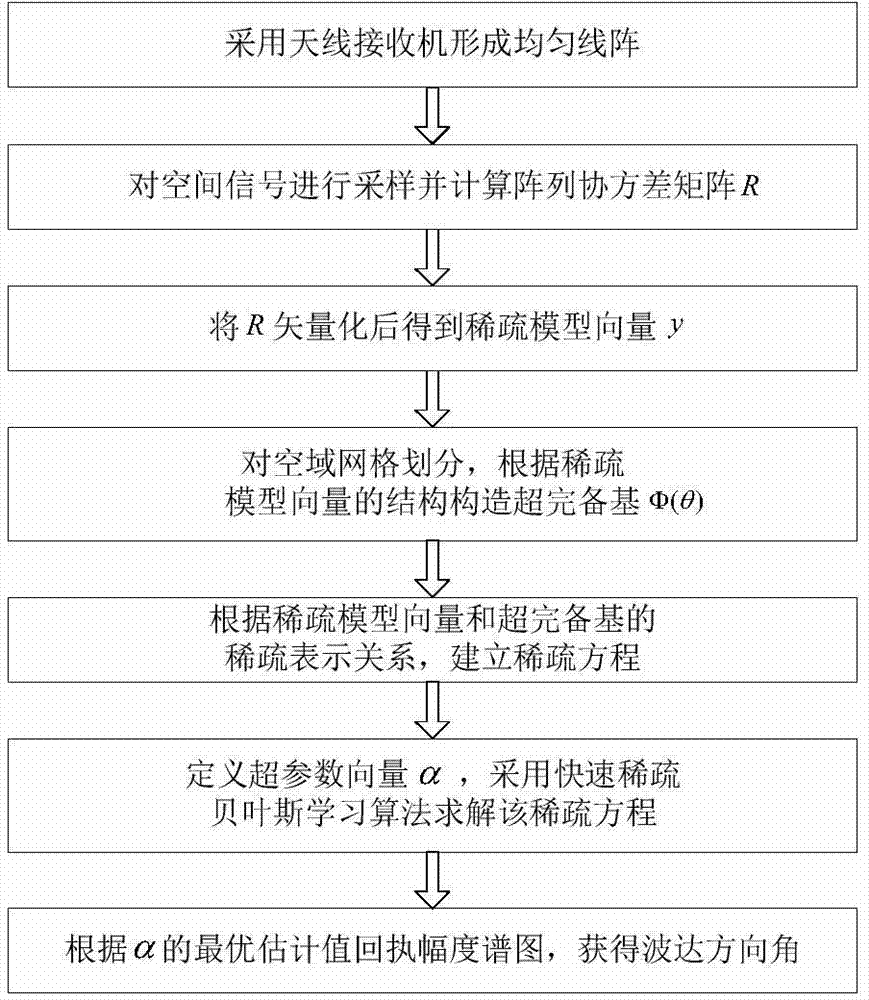
The invention discloses a fast sparse Bayesian learning based direction-of-arrival estimation method and mainly solves the problems of heavy computation and large location estimation error in the prior art. The method includes the implementation steps: (1) adopting antenna receivers to form a uniform linear array; (2) sampling space signals and computing an array covariance matrix R; (3) vectorizing R to obtain a sparse model vector y; (4) dividing space domain grids, and constructing an over-complete base phi(theta) according to the structure of the sparse model vector y; (5) establishing a sparse equation according to the sparse representation relation of the sparse model vector and the over-complete base; (6) defining a hyper-parameter vector alpha, and adopting a fast sparse Bayesian learning algorithm to solve the sparse equation; (7) drawing a magnitude spectrogram according to an optimal estimation value of alpha to obtain a direction-of-arrival value. By the method, estimation accuracy of target reconnaissance and passive location under the conditions of low signal to noise ratio and small snapshot number is improved, computational complexity is lowed, and the method can be applied to target reconnaissance and passive location.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Estimating facial pose from a sparse representation
ActiveUS7526123B2Good estimateAccurate estimateCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSparse model
A method for accurately estimating a pose of the human head in natural scenes utilizing positions of the prominent facial features relative to the position of the head. A high-dimensional, randomly sparse representation of a human face, using a simplified facial feature model transforms a raw face image into sets of vectors representing the fits of the face to a random, sparse set of model configurations. The transformation collects salient features of the face image which are useful to estimate the pose, while suppressing irrelevant variations of face appearance. The relation between the sparse representation of the pose is learned using Support Vector Regression (SVR). The sparse representation, combined with the SVR learning is then used to estimate a pose of facial images.
Owner:NEC CORP
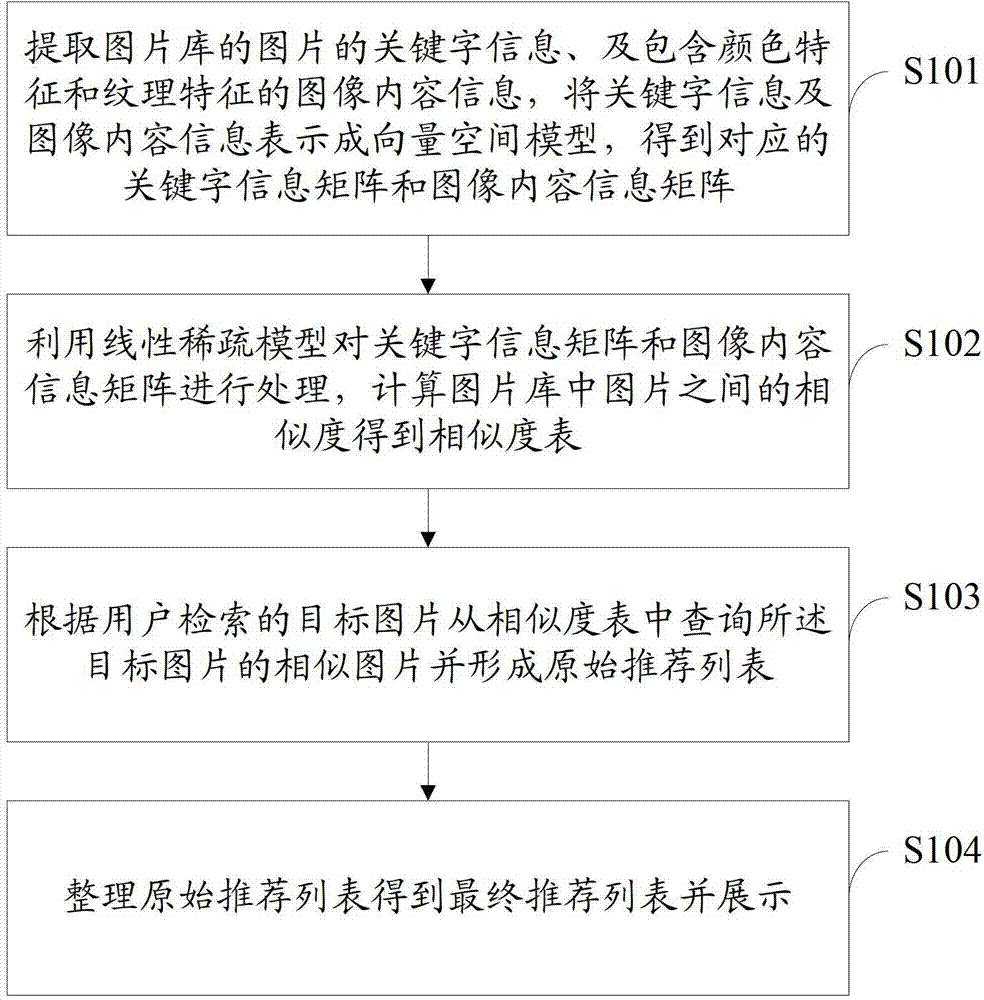
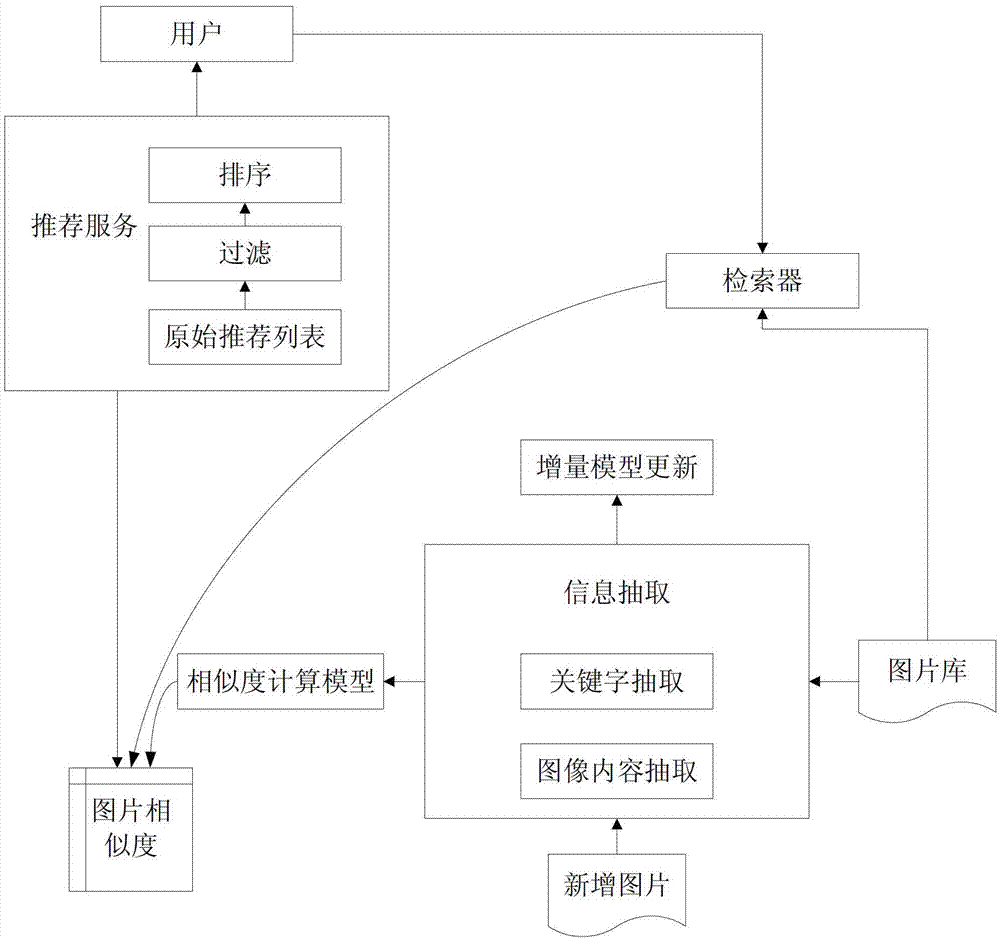
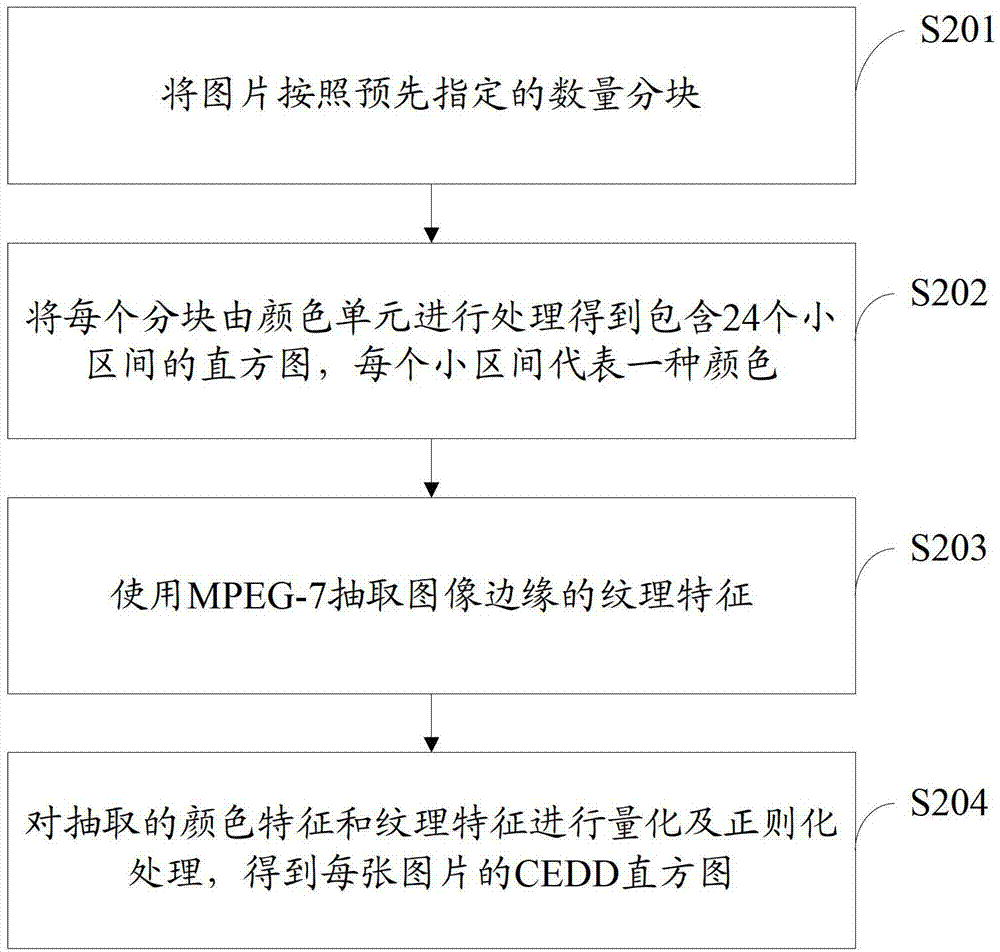
Information recommendation method and system combining image content and keywords
ActiveCN103544216AFulfill referral requestAdaptableCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSparse modelInformation representation
The invention discloses an information recommendation method and system combining image content and keywords. The information recommendation method combining image content and keywords comprises the steps that keyword information of images in an image library and image content information containing color features and textural features are extracted, the keyword information and the image content information are expressed as a vector space model, and a corresponding keyword information matrix and an image content information matrix are obtained; the keyword information matrix and the image content information matrix are processed by utilizing a linear sparse model, and a similarity chart is obtained by calculating the similarity among the images; an image similar to a target image is inquired from the similarity chart according to the target image searched by a user, and an original recommendation list is formed; the original recommendation list is arranged to obtain a final recommendation list, and the final recommendation list is displayed.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sparse representation of spatial smoothing covariance matrix
InactiveCN104020439AAvoid anglesBreaking through the Rayleigh limit of resolutionRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEuclidean vectorCovariance matrix
The invention discloses a direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sparse representation of a spatial smoothing covariance matrix. The method mainly solves the problems that the calculation amount is large, the performance of processing coherent signal sources is poor and consequently errors in passive location estimation are large in the prior art. The method comprises the implementation steps: (1) forming a uniform linear array by antenna receivers, (2) the spatial smoothing covariance matrix output by the array is calculated according to the spatial smoothing technology, (3) vectorizing the spatial smoothing covariance matrix to obtain sparse model vectors, (4) carrying out mesh generation on a spatial domain to construct a perfect base, (5) establishing a constrained optimization equation based on the sparse representation relation between the sparse model vectors and the perfect base, (6) solving the constrained optimization equation according to the convex optimization method to obtain an optimal estimation value, and (7) drawing a magnitude spectrum according to the optimal estimation value to obtain the value of direction of arrival. By means of the method, the calculation speed of passive direction finding is increased, and the performance of estimating the coherent signal sources at a low signal-to-noise ratio is improved. The method can be applied to target reconnaissance and passive localization.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image denoising method based on non-local sparse model
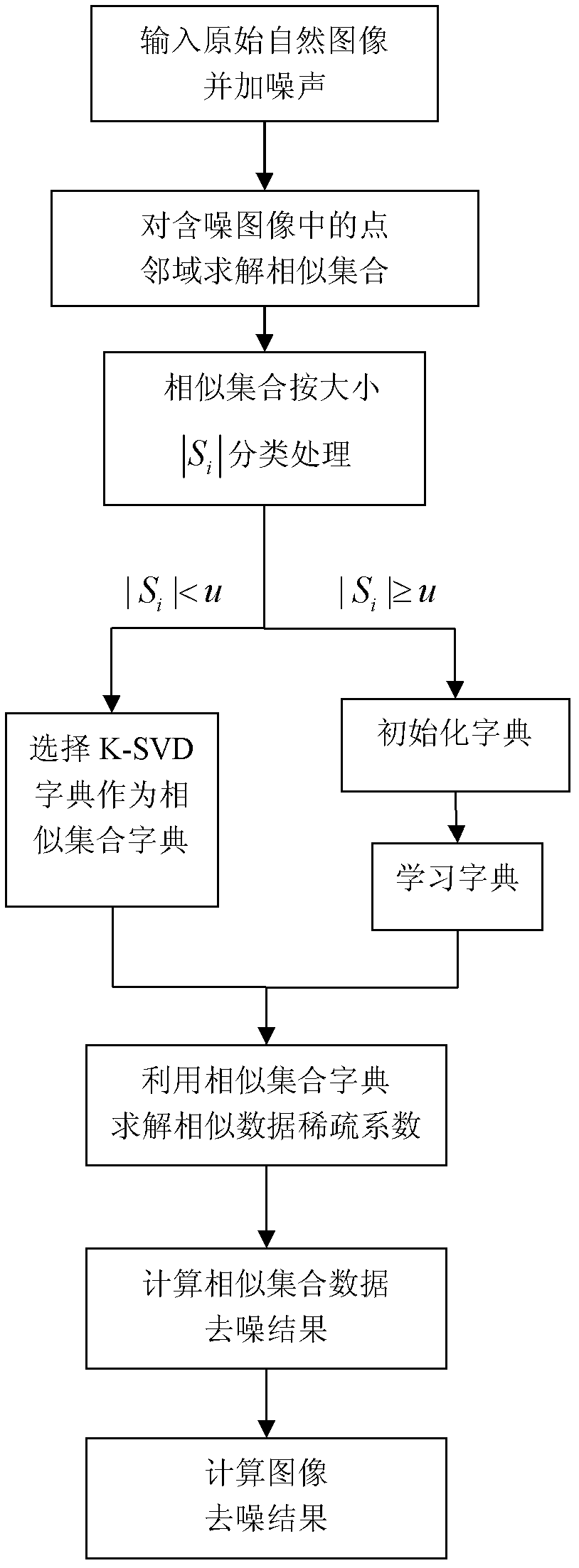
InactiveCN102542542ANoise removal is simpleReduce redundancyImage enhancementImage denoisingPattern recognition
The invention discloses an image denoising method based on a non-local sparse model, and is mainly used for solving the problems that the details, textures and marginal region information are difficult to retain when a noise-containing image is subjected to sparse representation denoising in the prior art. The method comprises the implementation processes of: (1) solving similar set of each point neighborhood in the noise-containing image; (2) designing a sparse representation dictionary for the similar sets according to the sizes of the similar sets; (3) carrying out sparse decomposition and sparse reconstruction on the similar set data by using an SOMP algorithm utilizing the obtained dictionary, thus denoising the similar set data; and (4) summarizing the all denoising results of every point in the noise-containing image, and taking the average value as the final denoising result of the point, so as to further obtain the denoising result of the whole image. According to the invention, the image denoising effect and sparse representation efficiency of the image signals are improved, and the method can be used for target tracking and identifying.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Linear frequency modulation radar signal processing method based on compressed sensing
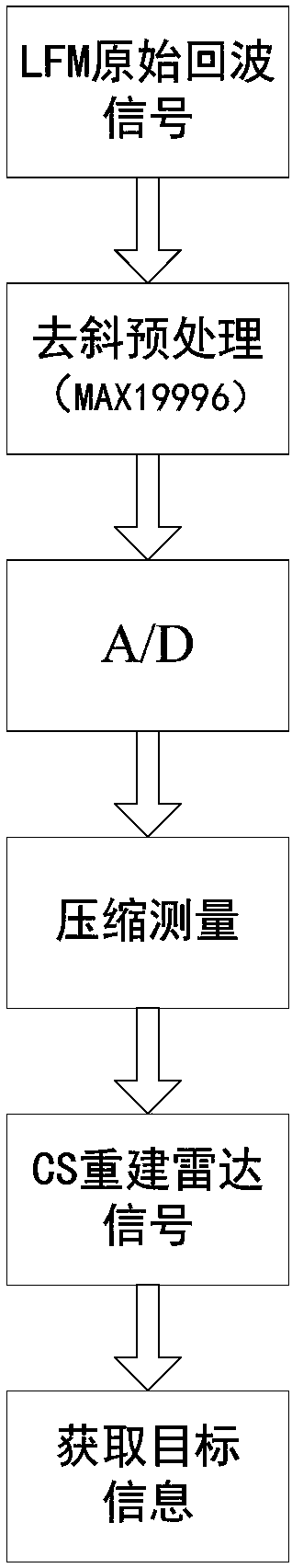
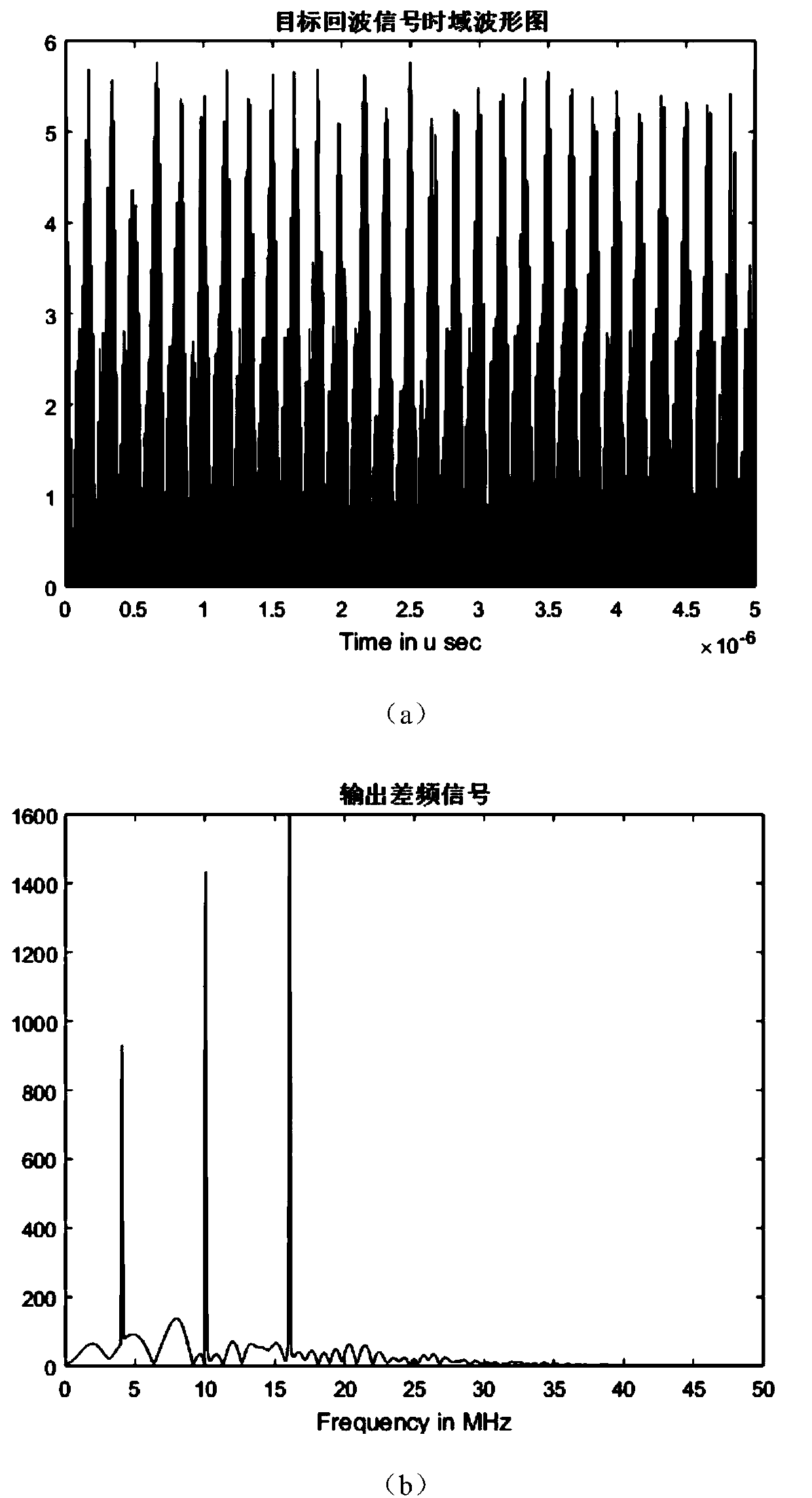
ActiveCN107064883AEfficient acquisitionAchieve compressionWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar observations
The invention discloses a linear frequency modulation radar signal processing method based on compressed sensing. The method comprises the steps of (1) emitting a linear frequency modulation signal to a radar and preprocessing an echo signal, which means that the deramping processing of the echo signal is carried out, a difference frequency signal is outputted, and a signal model of deramping processing is established in a time domain, (2) according to the sparsity of the difference frequency signal in a frequency domain, constructing a sparse conversion matrix, and establishing a sparse representation model of the radar echo signal, (3) constructing a measurement matrix, and realizing the projection transformation of a difference frequency sparse signal to a low dimensional space, and (4) using an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm, reconstructing a radar difference frequency signal, and efficiently obtaining target information. Accoding to the method, the compression of radar echo signal data can be fundamentally realized, the change of a sparse model according to a radar observation distance is not needed, finally the target information is obtained, and the method is suitable for the echo signal processing of an actual radar.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
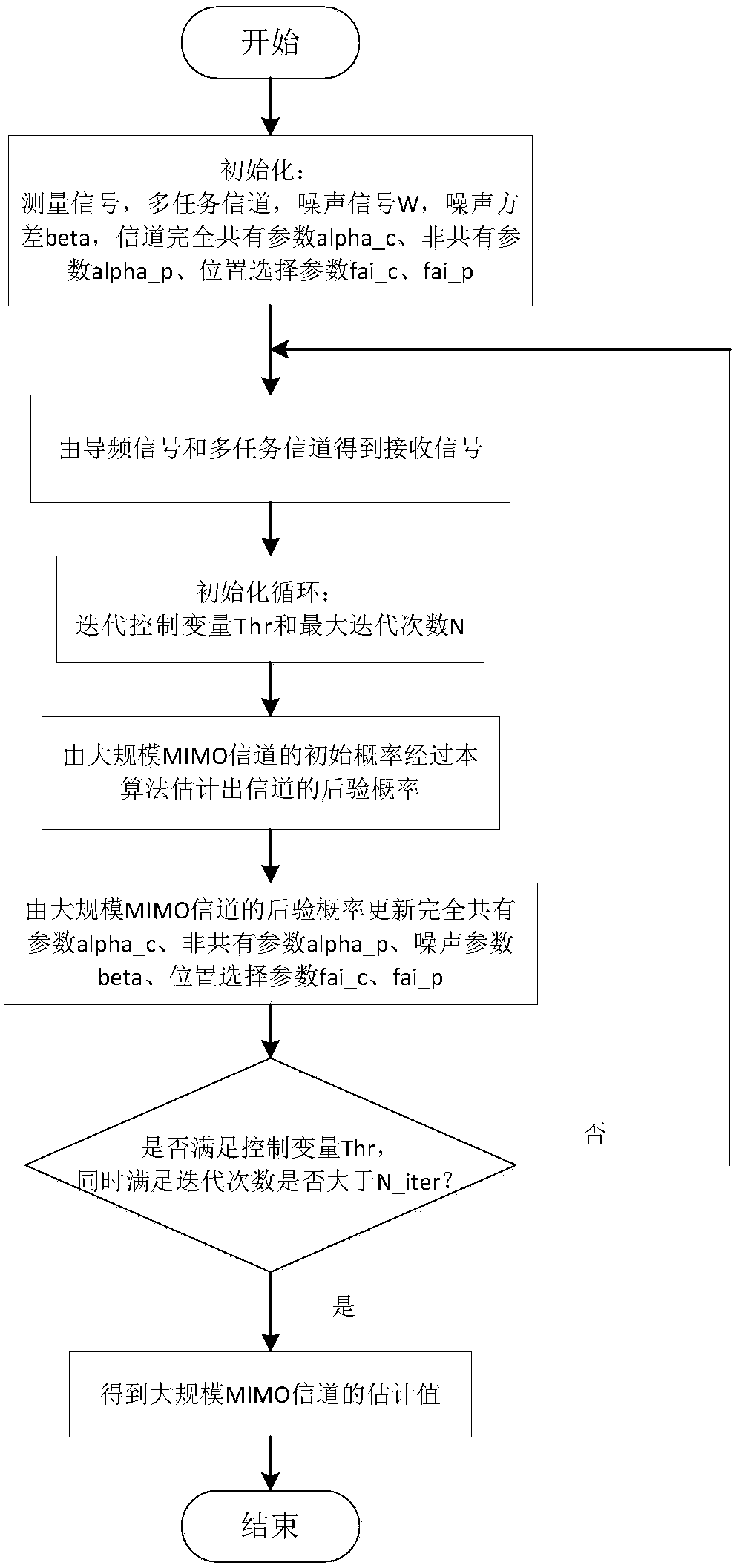
Channel estimation method based on variational Bayesian inference
ActiveCN108111441AImprove accuracyRadio transmissionChannel estimationSparse modelEstimation methods
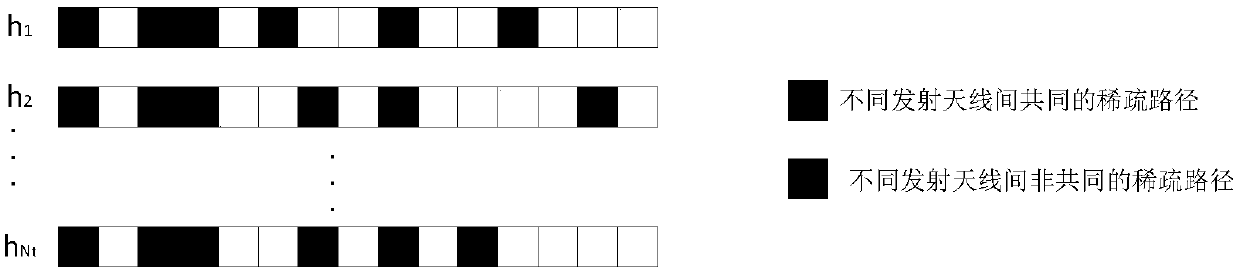
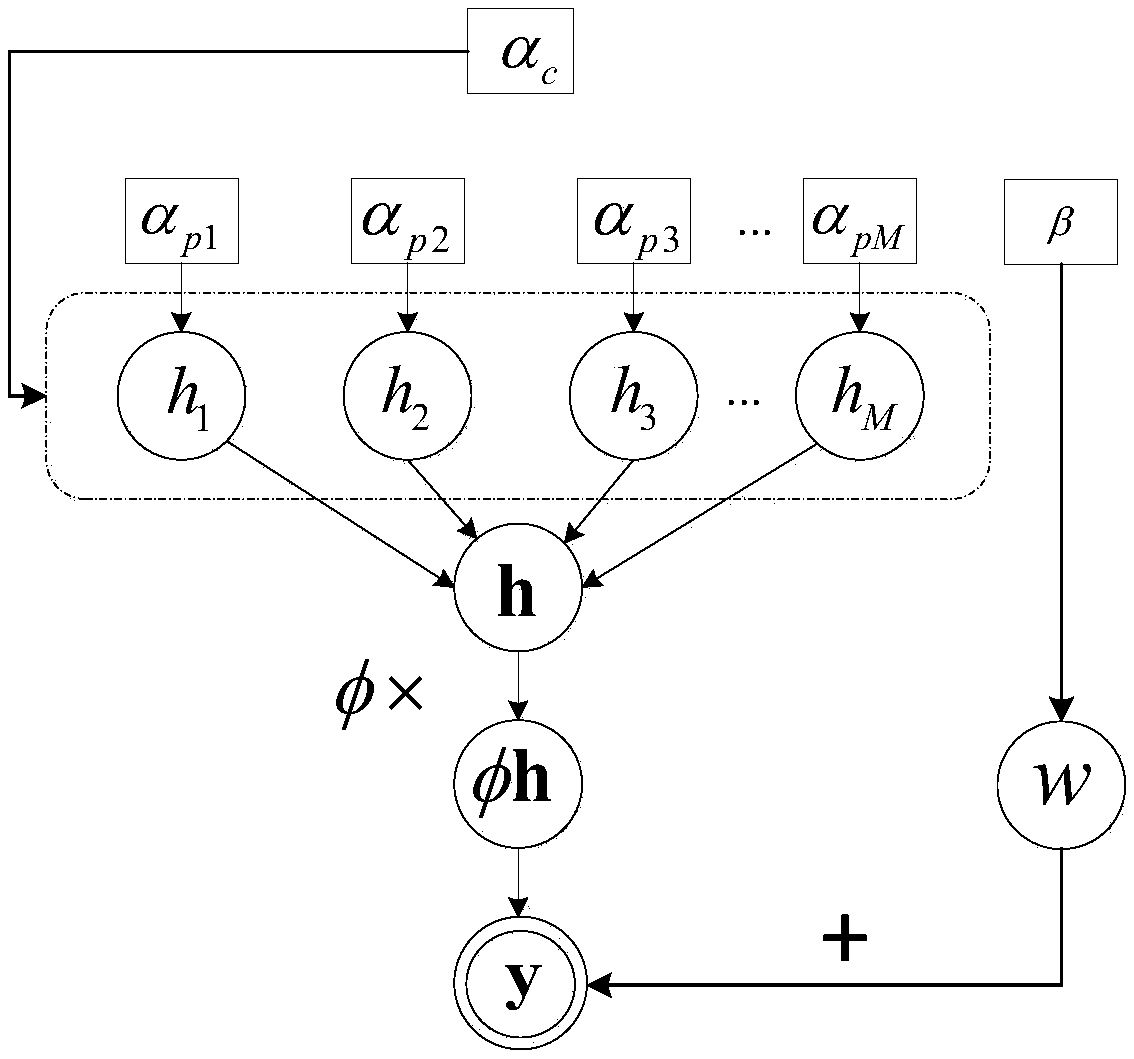
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communications, and in particular relates to a channel estimation method based on variational Bayesian inference. According to the method provided by the invention, the similarity between a sparse structure of a large-scale MIMO channel and a structure thereof is utilized, a sparse model (hierarchical prior model) of the large-scale MIMO channel is innovatively constructed, a probability event is imported to control the location of the channel to be completely common or not, a channel estimation algorithm based on variational Bayesian inference (abbreviated as Mixture_VBI) is proposed, and compared with OMP, ASSP, Geniu-LS, and other channel estimation methods, the channel estimation method provided by the invention has the advantages of improving the accuracy of channel estimation, and the channel estimation error can reach 10-3 under certain conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
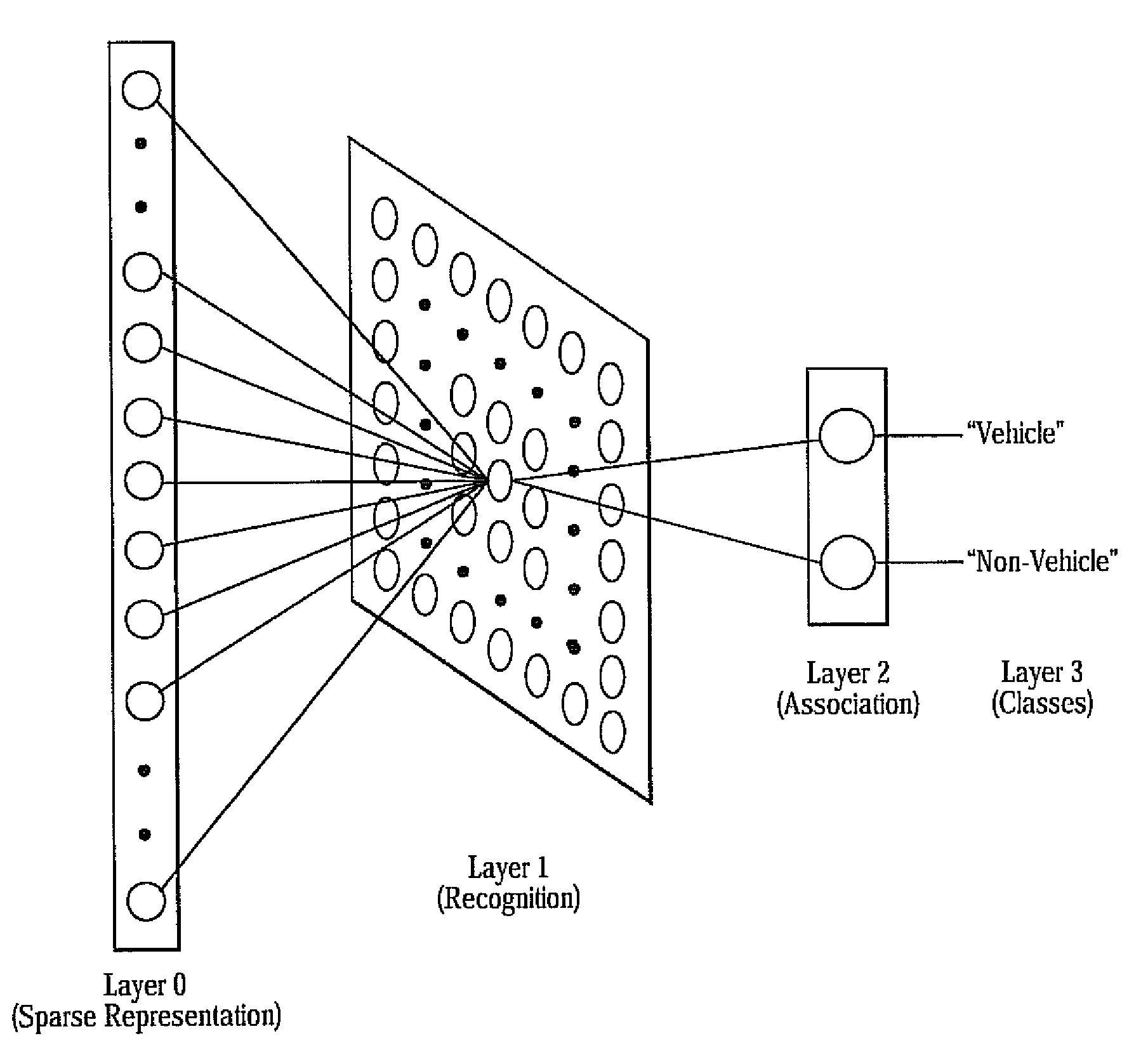
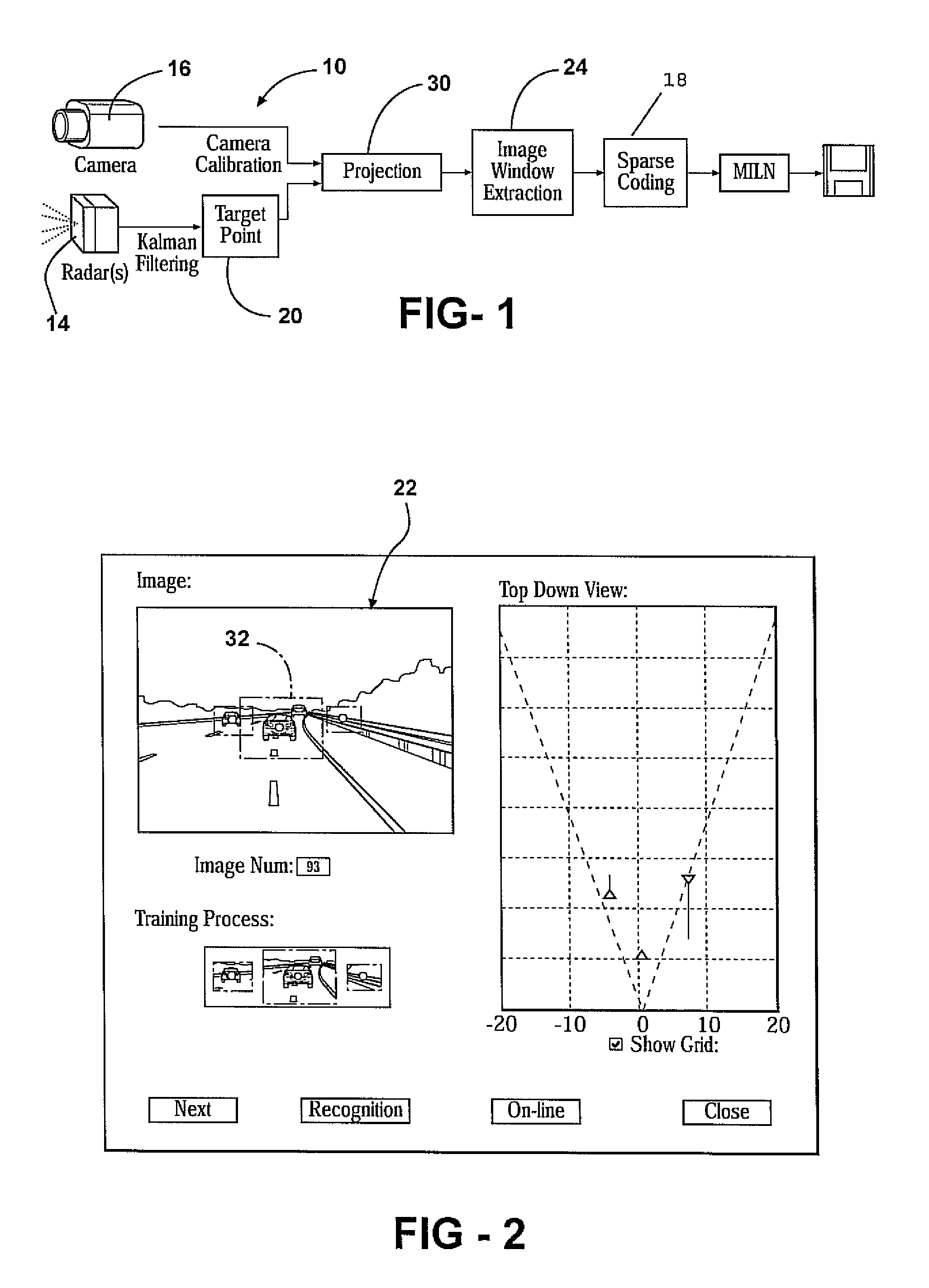
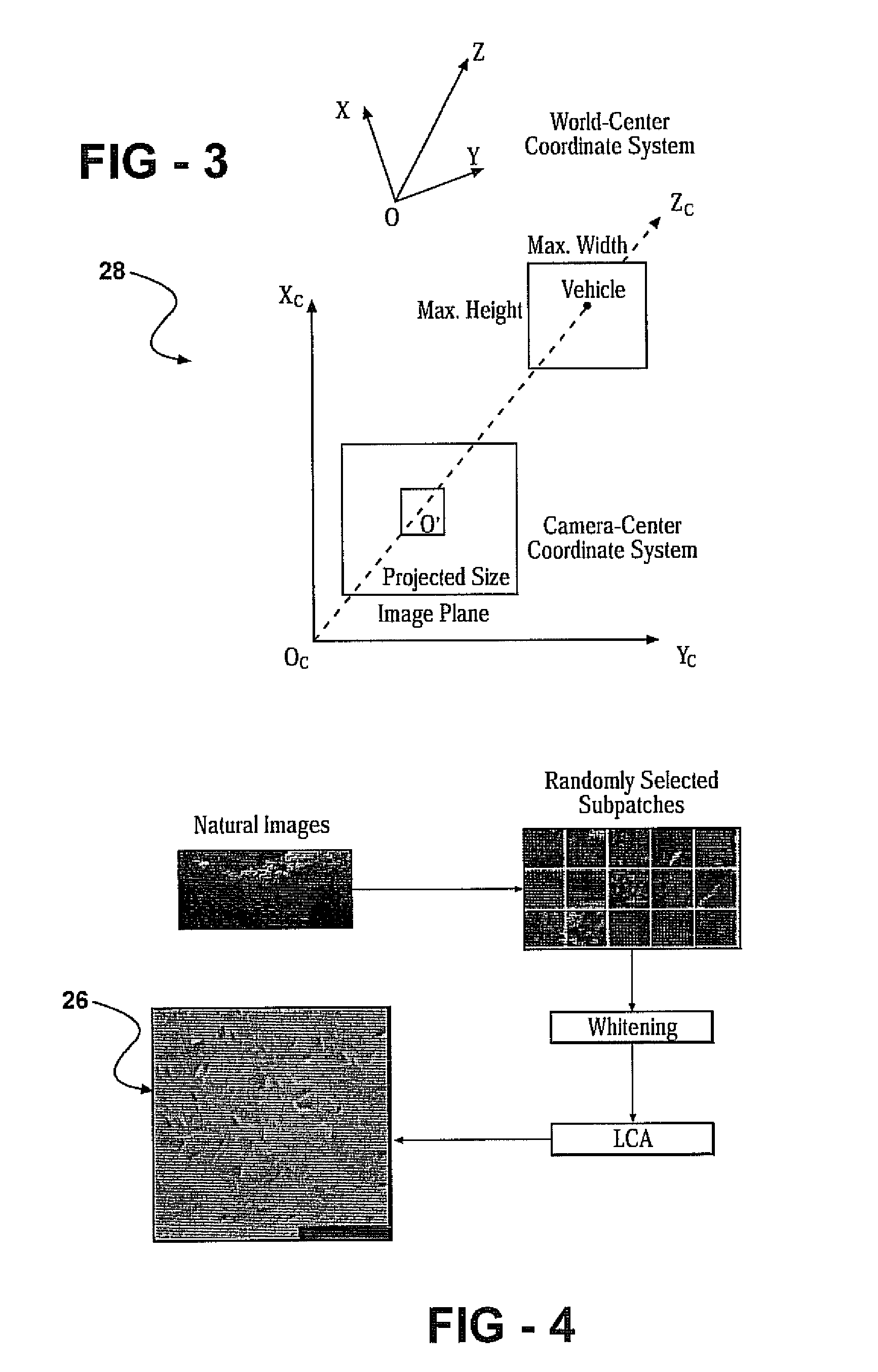
Method and system of sparse code based object classification with sensor fusion
ActiveUS8081209B2Provide capabilityColor television detailsScene recognitionSparse modelRadar systems
A system and method for object classification based upon the fusion of a radar system and a natural imaging device using sparse code representation. The radar system provides a means of detecting the presence of an object within a predetermined path of a vehicle. Detected objects are then fused with the image gathered by the camera and then isolated in an attention window. The attention window is then transformed into a sparse code representation of the object. The sparse code representation is then compared with known sparse code representation of various objects. Each known sparse code representation is given a predetermined variance and subsequent sparse code represented objects falling within said variance will be classified as such. The system and method also includes an associative learning algorithm wherein classified sparse code representations are stored and used to help classifying subsequent sparse code representation.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
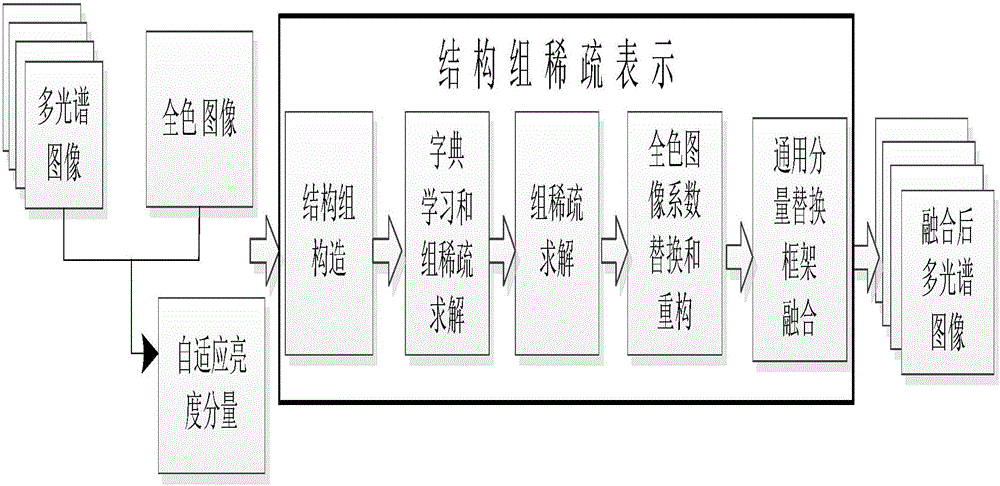
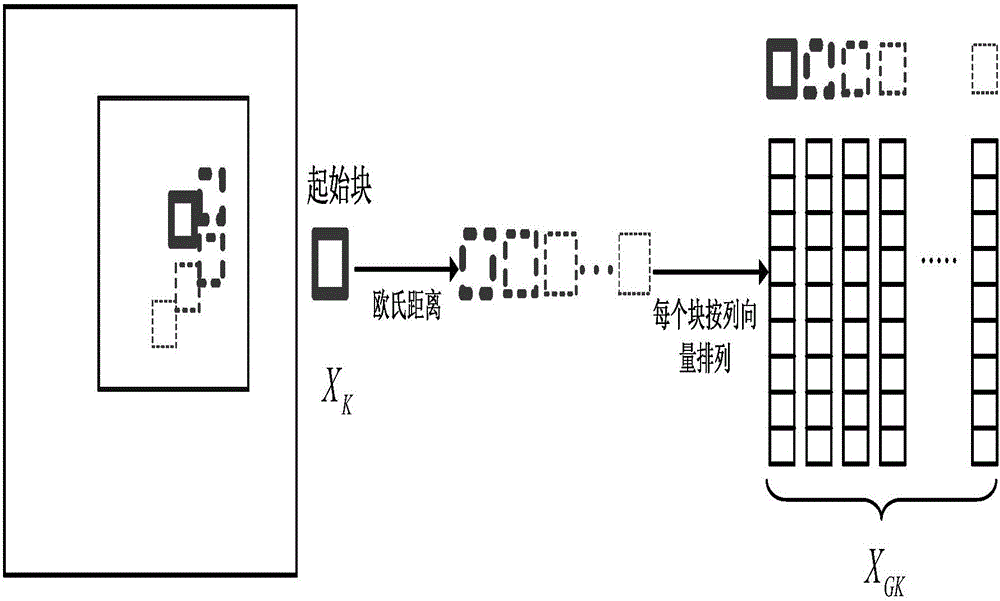
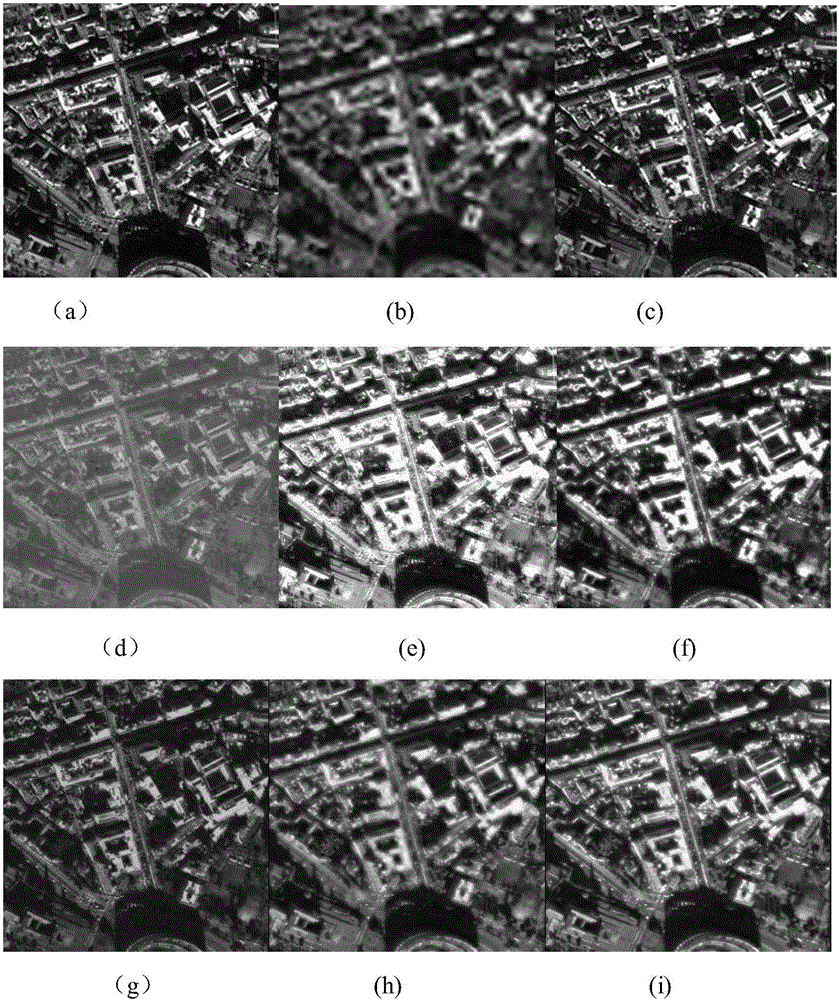
Structure sparse representation-based remote sensing image fusion method
InactiveCN105761234AImprove spatial resolutionHigh spectral informationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionRemote sensing image fusion
The invention discloses a structure sparse representation-based remote sensing image fusion method. An adaptive weight coefficient calculation model is used for solving a luminance component of a multi-spectral image, similar image blocks are combined into a structure group, a structure group sparse model is used for solving structure group dictionaries and group sparse coefficients for the luminance component and a panchromatic image, an absolute value maximum rule is applied to partial replacement of the sparse coefficients of the panchromatic image, new sparse coefficients are generated, the group dictionary and the new sparse coefficients of the panchromatic image are used for reconstructing a high-spatial resolution luminance image, and finally, a universal component replacement model is used for fusion to acquire a high-resolution multi-spectral image. The method of the invention introduces the structure group sparse representation in the remote sensing image fusion method, overcomes the limitation that the typical sparse representation fusion method only considers a single image block, and compared with the typical sparse representation method, the method of the invention has excellent spectral preservation and spatial resolution improvement performance, and greatly shortens the dictionary training time during the remote sensing image fusion process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
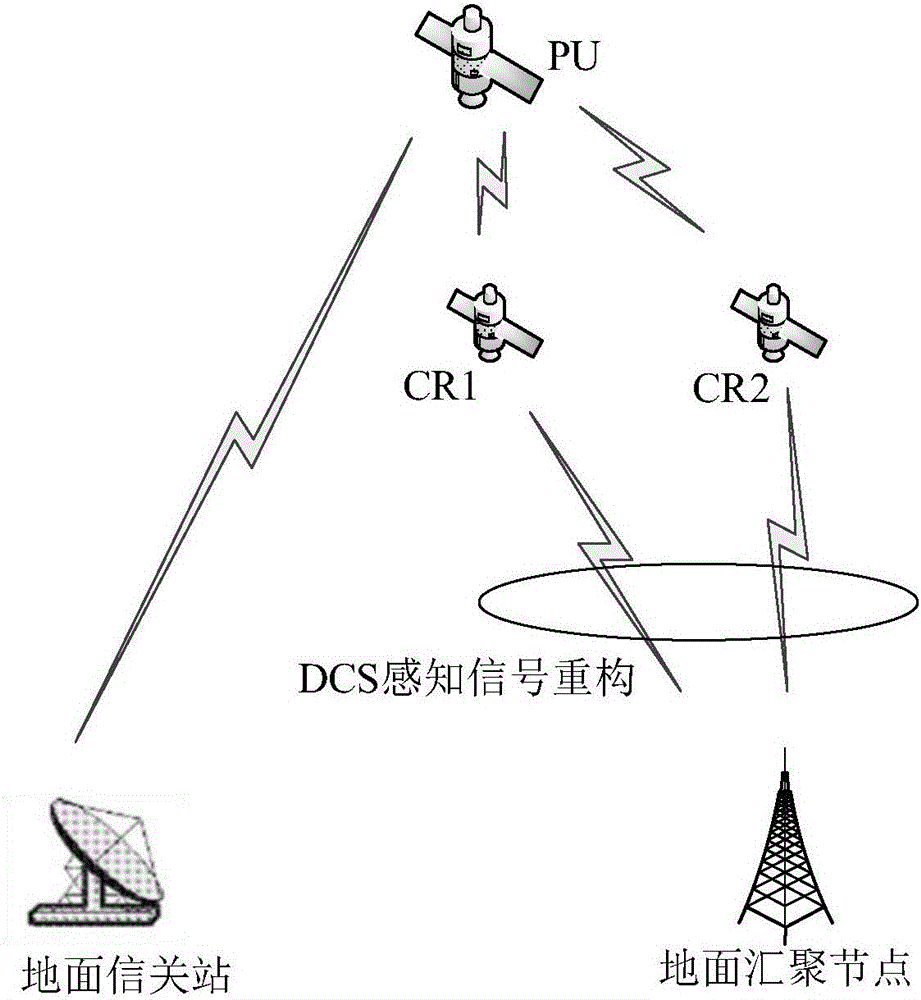
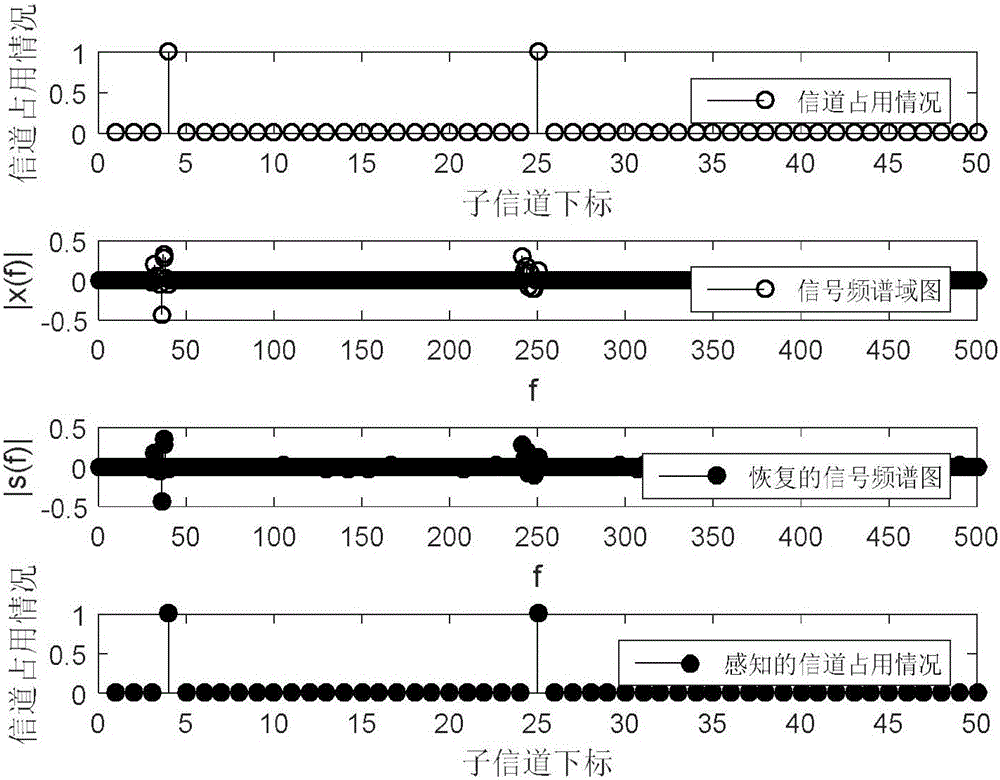
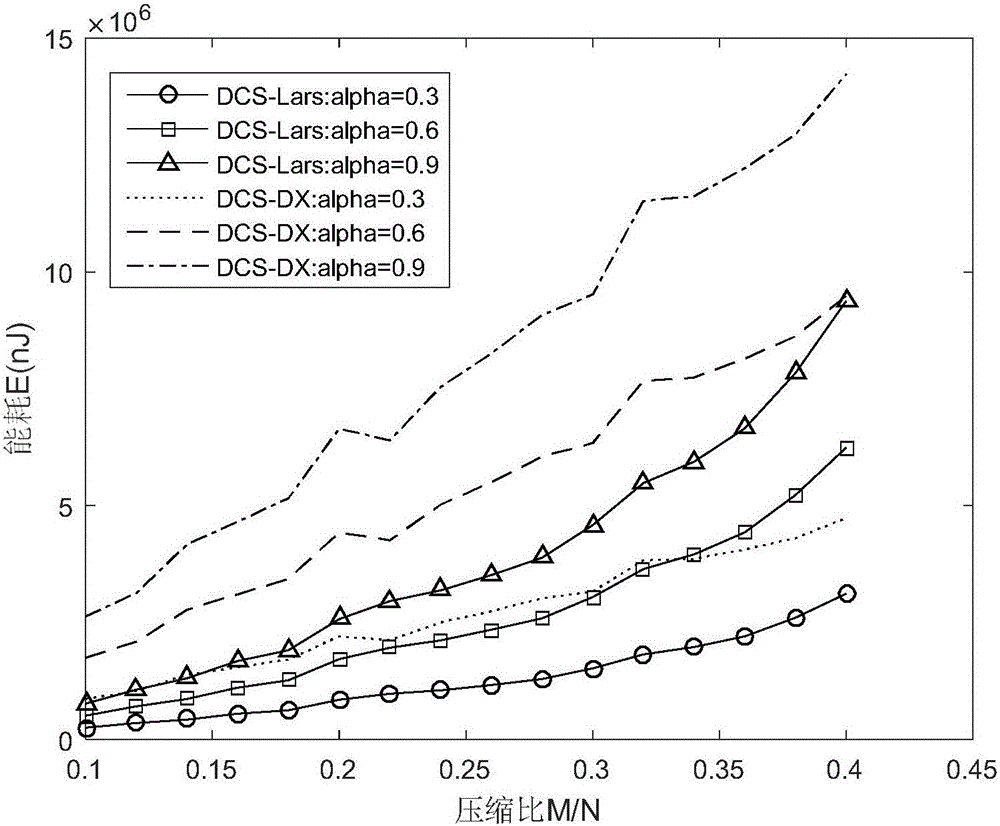
LEO system DCS signal reconstruction method achieving energy efficiency priority delay tolerance
ActiveCN106162659AValid judgmentGood refactorabilityNetwork planningHigh level techniquesFrequency spectrumSparse model
The invention discloses an LEO system DCS signal reconstruction method achieving energy efficiency priority delay tolerance. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a time-varying LEO satellite perception channel model is built; 2, a distributed compressive sensing joint sparsity model is built; 3, signal reconstruction and spectrum detection based on DCS comprises a signal reconstruction stage and a spectrum detection stage; 4, DCS signal reconstruction and detection energy consumption under the condition of a lower signal-to-noise ratio is calculated; 5, a DCS perception signal reconstruction energy consumption optimization scheme under the delay tolerance condition is determined. According to the LEO system DCS signal reconstruction method achieving energy efficiency priority delay tolerance, a good reconstruction property is achieved under the conditions of the low signal-to-noise ratio and low compression ratio, and the reconstruction complexity is obviously reduced when effective judgment is conducted on an LEO spectrum. Meanwhile, for energy efficiency of an L-CR system, the energy consumption of the two methods in signal reconstruction and spectrum detection stage is taken into account, and weighted energy consumption functions of the two stages are constructed.
Owner:东开数科(山东)产业园有限公司
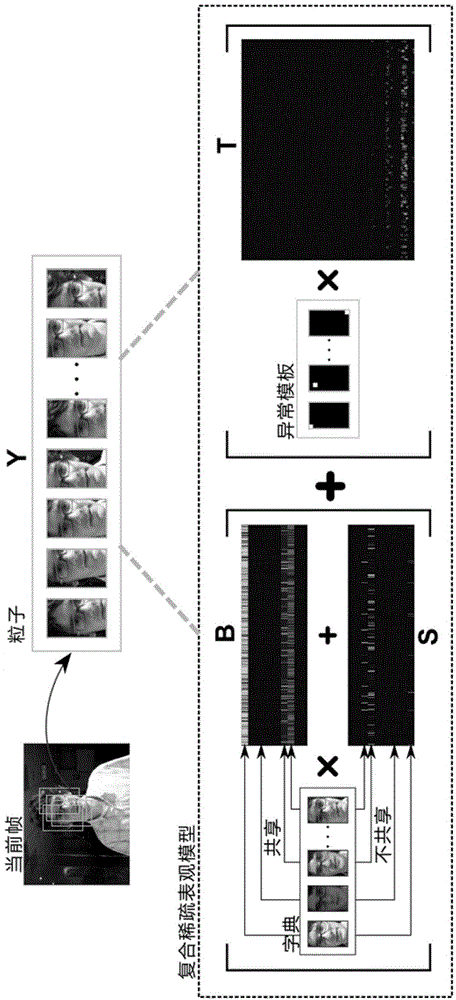
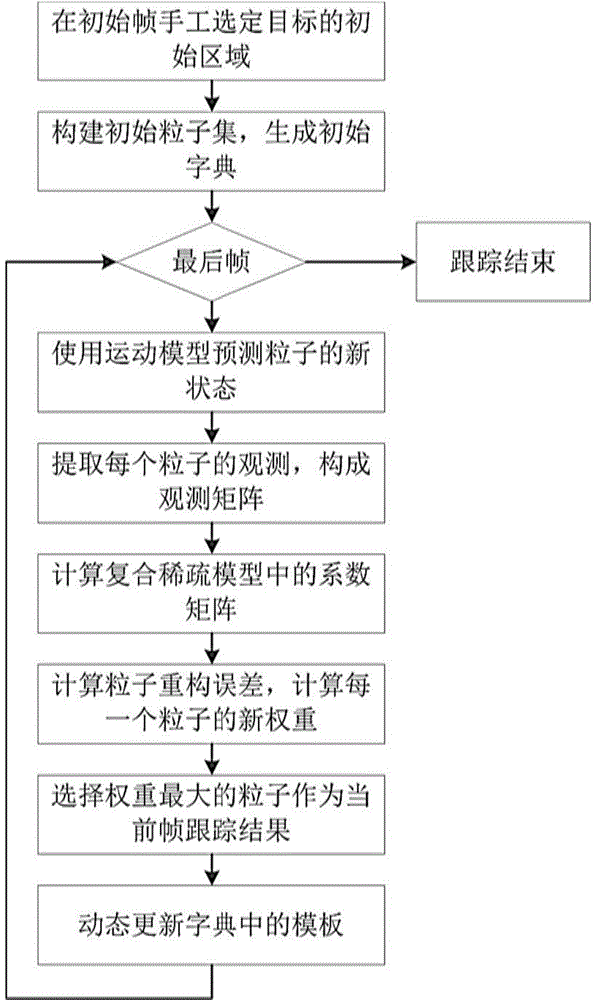
Video target tracking method based on compound sparse model
The invention discloses a video target tracking method based on a compound sparse model and belongs to the field of computer vision. According to the method, a combined sparse coefficient matrix capable of observing all particles is divided into set sparsity, element sparsity and abnormal sparsity under the condition that a compound sparse appearance model is under a particle filtering framework; sharing and unsharing characteristics of the particle in a dictionary and additive sparse noise are represented; norms from L1 to infinite number and norms L1 and 1 are regularized to implement the compound sparsity; the optimization problem is solved by using a direction-variable mutiplier method, so that the higher calculation efficiency is realized. The invention also provides a dynamic dictionary updating method, so that the change of target appearance can be adapted. Experiment shows that the tracking performance and robustness of the algorithm are superior to several compared conventional video target tracking algorithm. The video target tracking method can be applied to the fields of man-machine interaction, intelligent monitoring, intelligent traffic, vision navigation, video retrieval, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Construction method and device as well as sorting method and device for support vector machine sorter
InactiveCN103559294AAccurate feature selectionGood predictive accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexitySmall sample
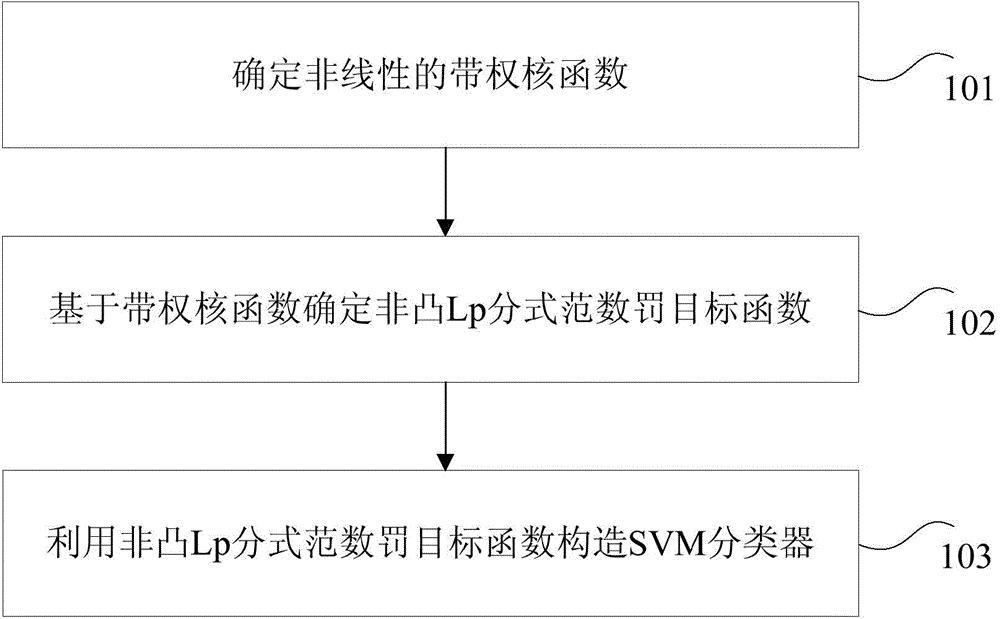
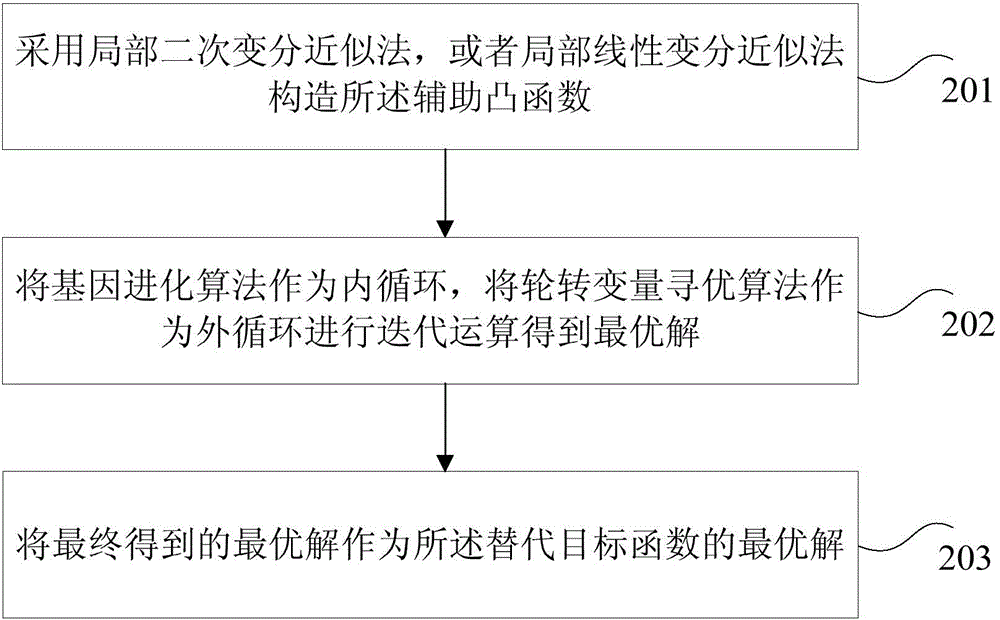
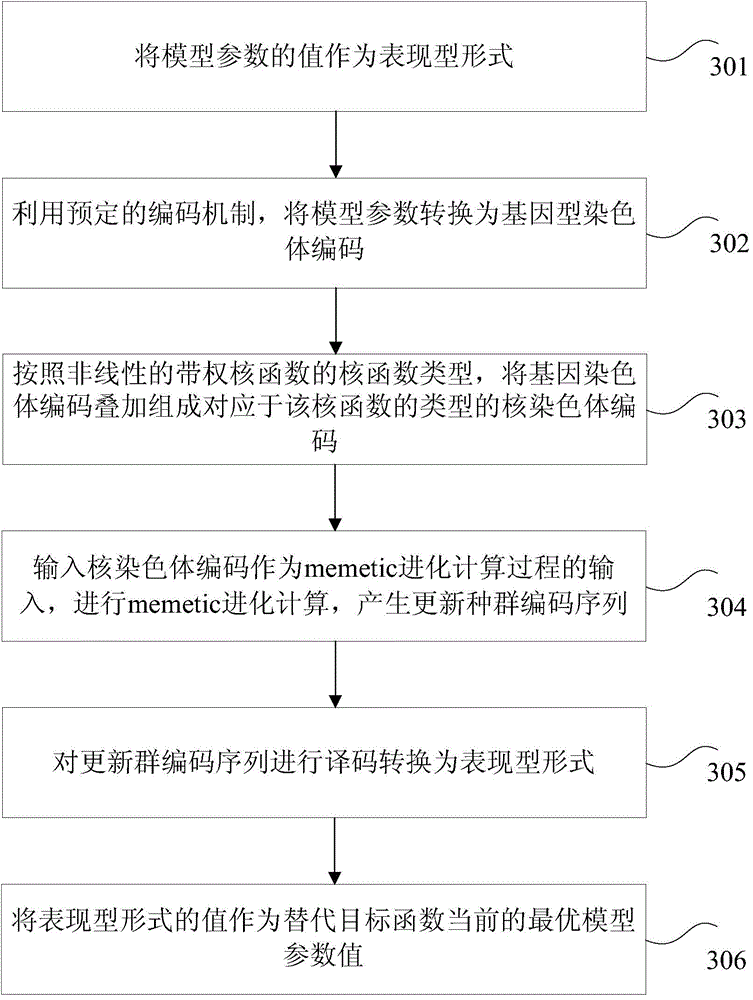
The invention provides a construction method and a construction device as well as a sorting method and a sorting device for a support vector machine sorter, wherein the method comprises the steps of determining a non-linear weighted kernel function; determining a non-convex Lp fraction norm punishment target function based on the weighted kernel function; constructing the support vector machine sorter by utilizing the non-convex Lp fraction norm punishment target function. Compared with the technical scheme in the prior art, in which when high-dimensional small sample data are sorted, all characteristic-dimensional combinations need to be traversed to find the needed characteristics, the method has the advantage that the constructed support vector machine sorter can realize the characteristic selecting function of a sample original space after the non-linear kernel mapping; the method can be used for sorting the high-dimensional data to generate a more sparse model, realize more accurate characteristic selecting and obtain a better predication accuracy, so the calculation complexity is greatly reduced, and a data disaster is avoided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Pattern recognition classification method expressed based on grouping sparsity
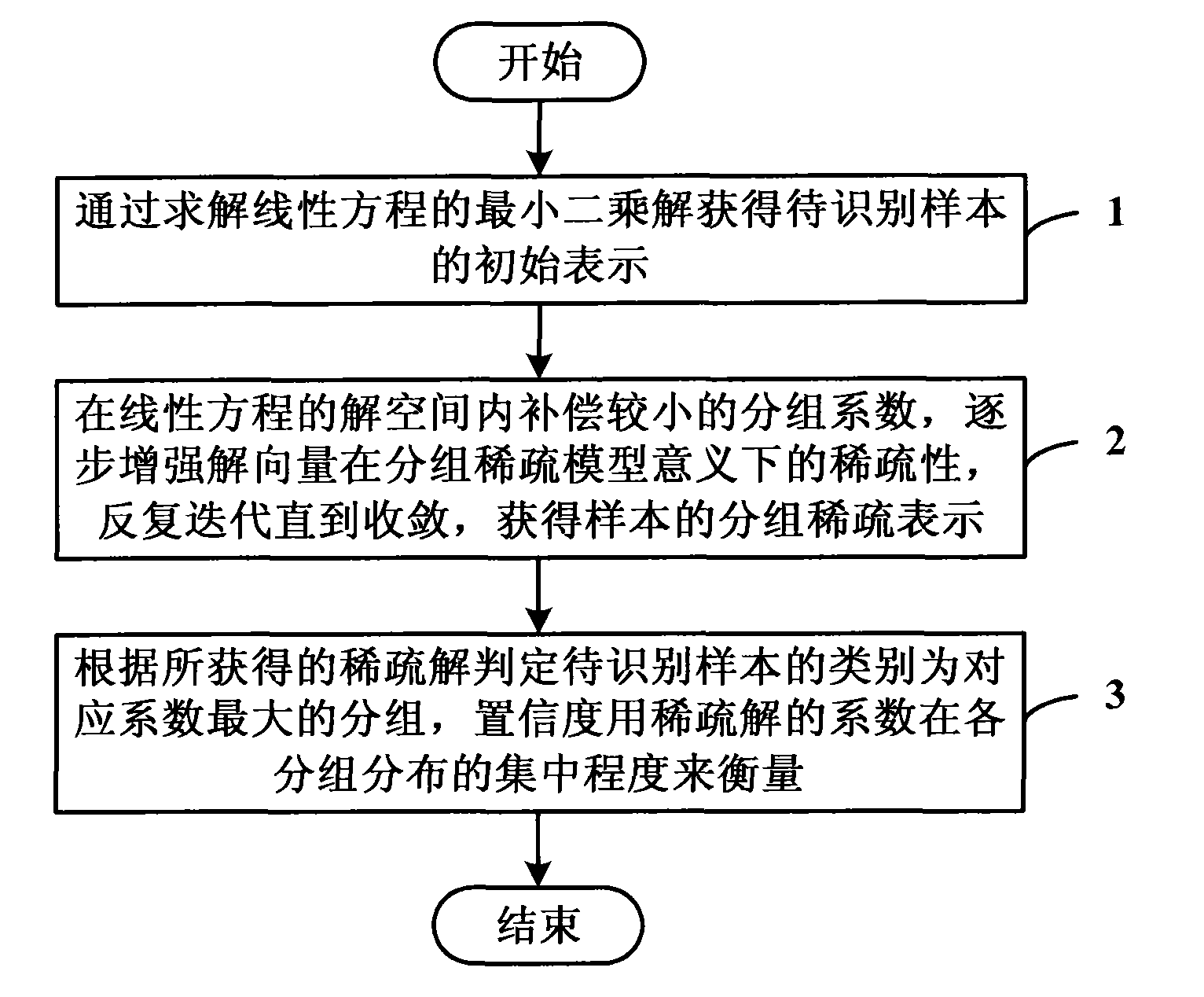
InactiveCN101833667AEasy to identifyImprove sparsityCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse modelClassification methods
The invention discloses a pattern recognition classification method expressed based on grouping sparsity, comprising the steps of: obtaining an initial expression of a sample to be recognized by solving a least square solution of a linear equation; compensating a smaller grouping coefficient in the solution space of the linear equation, gradually enhancing the sparsity of solution vectors in the meaning of a grouping sparse model, and carrying out repeated iteration until constringency to obtain the grouping sparse expression of the sample; and judging the classification of the sample to be recognized as the largest grouping of the corresponding coefficient according to the obtained sparsity, and balancing the confidence coefficient by the concentration degree of the distribution in each group of the coefficient with the sparsity. The grouping model adopted by the invention is more suitable for the requirement on the classification, and improves the recognition capability. The sparsity of the solution is improved by combining the method of compensating the coefficient in the solution space, and the calculation amount is reduced. The method is not only suitable for the classification of pattern recognition, but also can be used in the fields of compressed sensing, and the like, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Priori shape modeling method based on combined sparse model
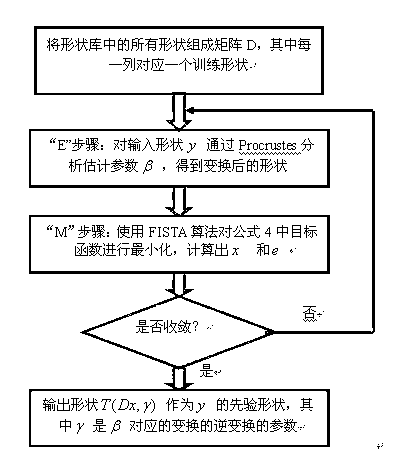
ActiveCN102760236ASolve key problemsEasy to useImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse modelImage segmentation
The invention discloses a priori shape modeling method based on a combined sparse model, and belongs to the technical field of medical image segmentation. Through priori shape modeling, a shape library obtained by collecting clinical data is established in allusion to a specific tissue organ, wherein the shape library consists of segmented shapes of image data from different patients, so as to establish a golden standard for corresponding organs of the patients. The priori shape modeling method based on a combined sparse model comprises the following steps: 1, gridding the surfaces of the shapes in advance by sampling points on the golden standard surfaces, wherein gridded shapes in the shape library are taken as training data of a model; 2, representing the gridded shapes by a sparse shape combining model, wherein coordinates of each shape in the shape library corresponding to all vertexes of a grid are arrayed as a column vector and an array D is obtained from the whole shape library; 3, performing optimization algorithm on the sparse shape combining model to obtain a corresponding parameter; and 4, performing inverse transformation on the corresponding parameter obtained in the optimization algorithm to obtain a required priori shape.
Owner:SUZHOU DIKAIER MEDICAL TECH
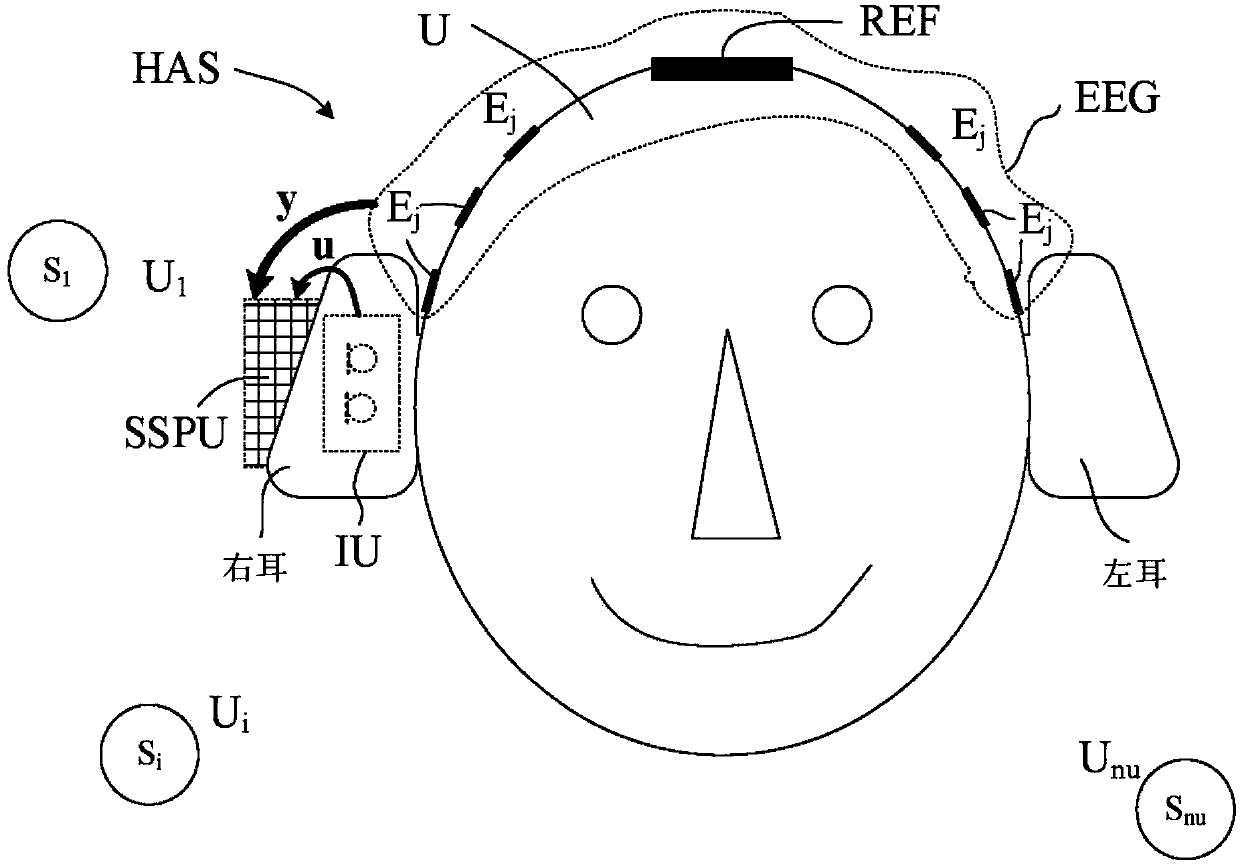
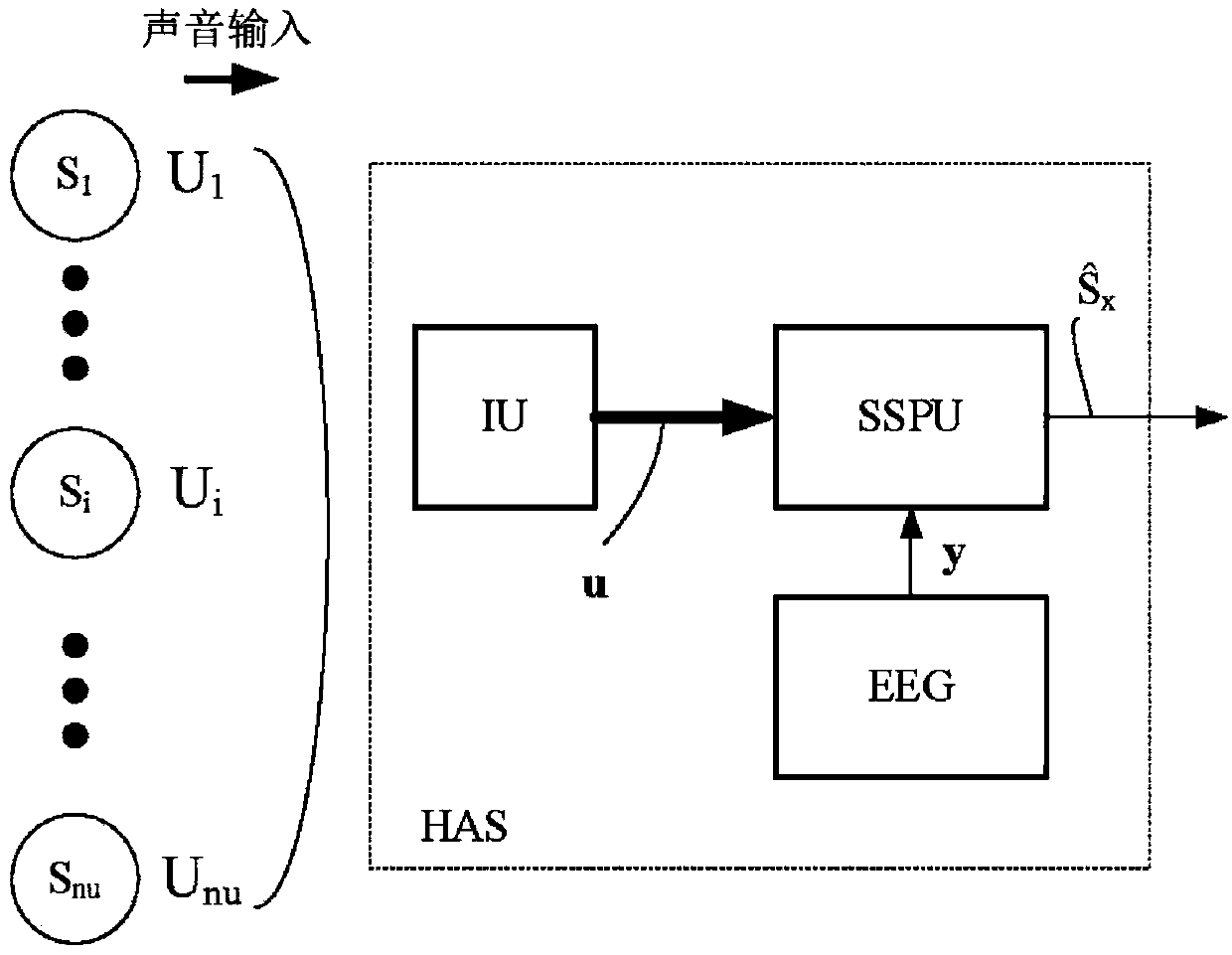
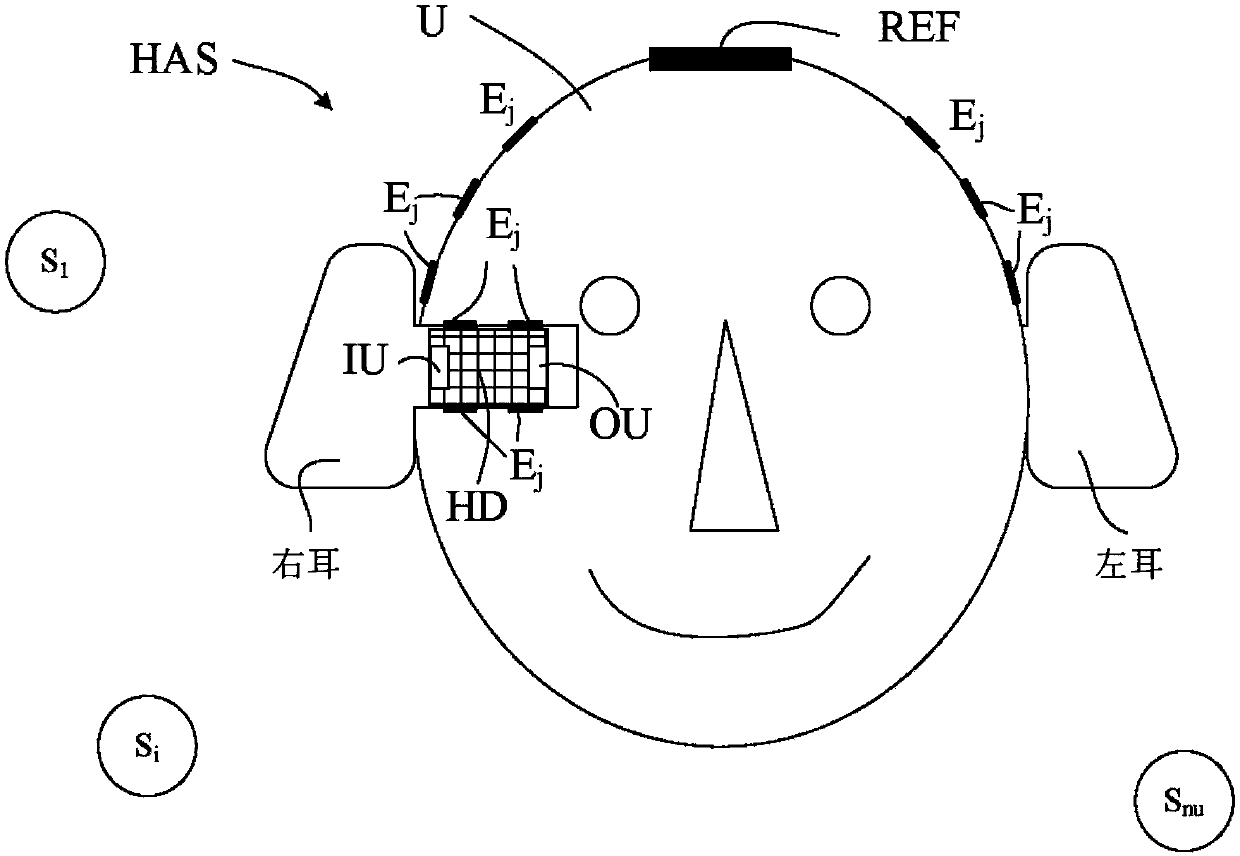
A hearing assistance system comprising an eeg-recording and analysis system
ActiveCN107864440ALess computing resourcesLess energyElectrotherapyEar treatmentElectricitySound sources
A hearing assistance system comprises an input unit for providing electric input sound signals u i , each representing sound signals U; from a multitude n u of sound sources S i , an electroencephalography (EEG) system for recording activity of the auditory system of the user's brain and providing a multitude ny of EEG signals yj , and a source selection processing unit receiving said electric input sound signals ui and said EEG signals yj , and in dependence thereof configured to provide a source selection signal Sx indicative of the sound source Sx that the user currently pays attention to using a selective algorithm that determines a sparse model to select the most relevant EEG electrodes and time intervals based on minimizing a cost function measuring the correlation between the individual sound sources and the EEG signals, and to determine the source selection signal Sx based on the cost functions obtained for said multitude of sound sources.
Owner:OTICON
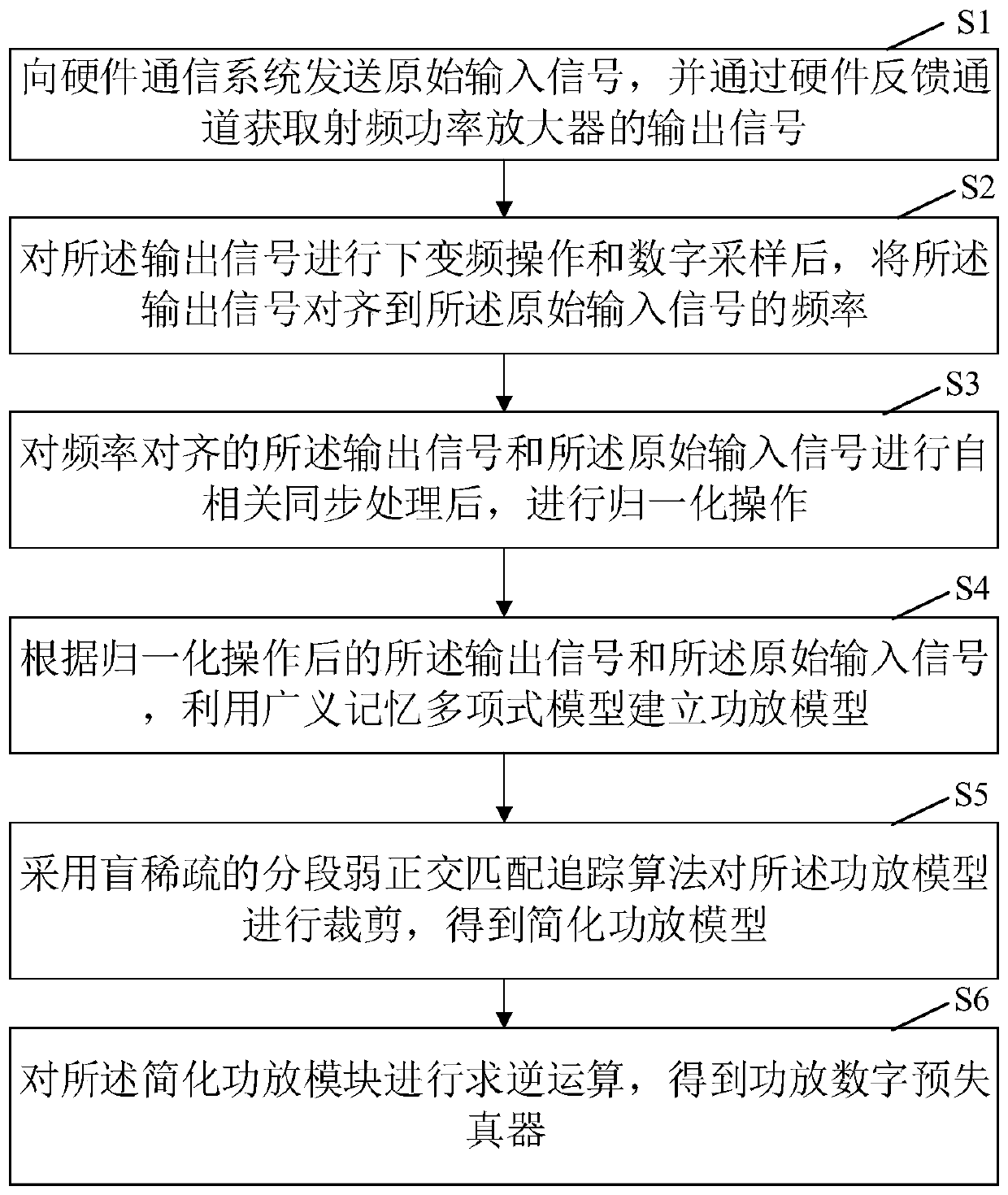
Digital predistorter design method and device based on power amplifier model cutting
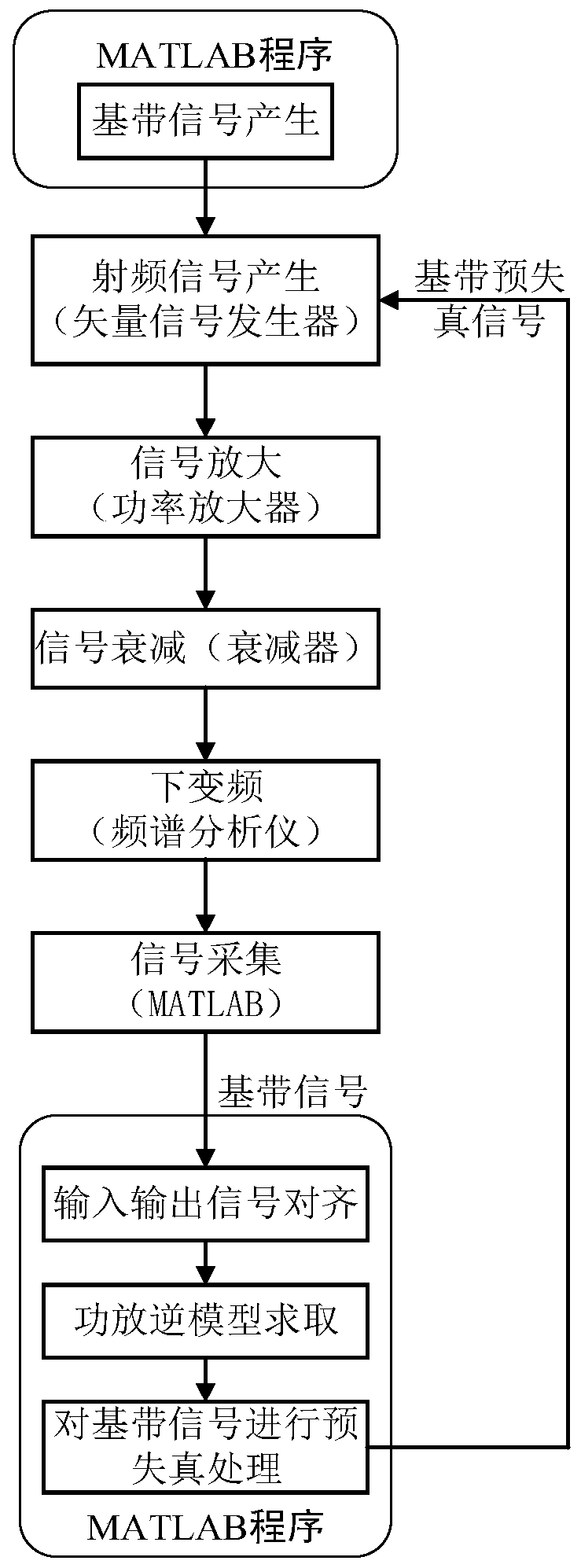
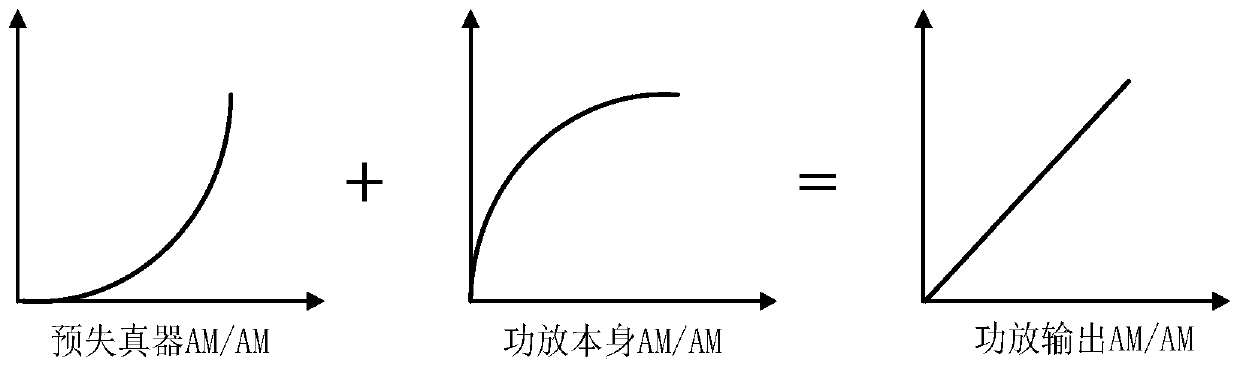
ActiveCN110601665AReduce complexitySparse ability is strong and accuratePower amplifiersSpecial data processing applicationsSparse modelCommunications system
The invention discloses a digital predistorter design method and device based on power amplifier model cutting, and the method comprises the steps: transmitting an original input signal to a hardwarecommunication system, and obtaining an output signal of a radio frequency power amplifier through a hardware feedback channel; carrying out down-conversion operation and digital sampling on the outputsignal, and then carrying out frequency alignment on the output signal and the input signal; carrying out autocorrelation synchronization processing and normalization operation on the output signal and the input signal; establishing a power amplifier model between the input signal and the output signal by using the generalized memory polynomial model; cutting the power amplifier model by adoptinga blind sparse segmented weak orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm to obtain a simplified power amplifier model; and performing inversion operation on the simplified power amplifier module to obtainthe power amplifier digital predistorter. According to the method, the GMP model is cut through the blind sparse SWOMP algorithm, and the power amplifier sparse model with high sparse capability andaccuracy is constructed, so that the digital predistorter with low complexity and high accuracy is obtained.
Owner:海南电网有限责任公司
Compressive sensing radar imaging algorithm based on subspace tracking
ActiveCN102495393AGood effectDownsamplingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsPhysical optics
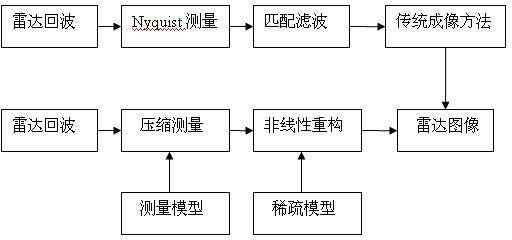
The invention discloses a compressive sensing radar imaging algorithm based on subspace tracking. By using a physical optical method, corresponding echo data are calculated, radar echo data are analyzed, a sparse model of a signal is established, and echo reconstruction is realized by using an effective and steady subspace tracking algorithm, so that synthetic aperture radar imaging is realized. The signal is subjected to non-adaptive sampling by using a compressive sensing theory at the speed rate which is much lower than Nyquist sampling rate. Therefore, the compressive sensing theory is applicable to synthetic aperture radar imaging, an imaging effect can be achieved, and the aim of reducing the sampling rate of the echo data is fulfilled, so that simulation time is shortened, and the cost of a radar system can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
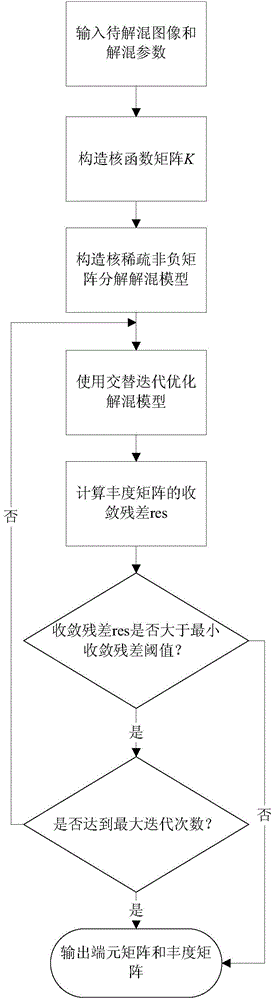
Nonlinear un-mixing method of hyperspectral images based on kernel sparse nonnegative matrix decomposition
InactiveCN104392243ASolve nonlinear unmixingOvercoming the Insufficiency of Linear UnmixingCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix decompositionAlgorithm
The invention relates to a nonlinear un-mixing method of hyperspectral images based on kernel sparse nonnegative matrix decomposition. The nonlinear un-mixing method comprises the following steps: estimating the number of end members for hyperspectral images by utilizing a dimension virtual method; then, popularizing the conventional un-mixing algorithm based on a linear mixing model to a nonlinear characteristic space by utilizing a kernel method, and solving a nonlinear spectrum un-mixing problem by using an alternative iterative optimization method. The nonlinear un-mixing method of hyperspectral images based on kernel sparse nonnegative matrix decomposition has the beneficial effects that from a mixing model of hyperspectral observation pixels, the sparsity of the hyperspectral abundance is added into a sparse model, and the linear mixing model is mapped into a nonlinear mixing model by virtue of the kernel method, so that the defects of linear un-mixing are effectively overcome, and good noise resistances are simultaneously achieved, and therefore, the nonlinear un-mixing method can be used as an effective means for solving the un-mixing of hyperspectral remote sensing images.
Owner:扬州匠新精密数控设备有限公司
Flexible deep learning network model compression method based on channel gradient pruning
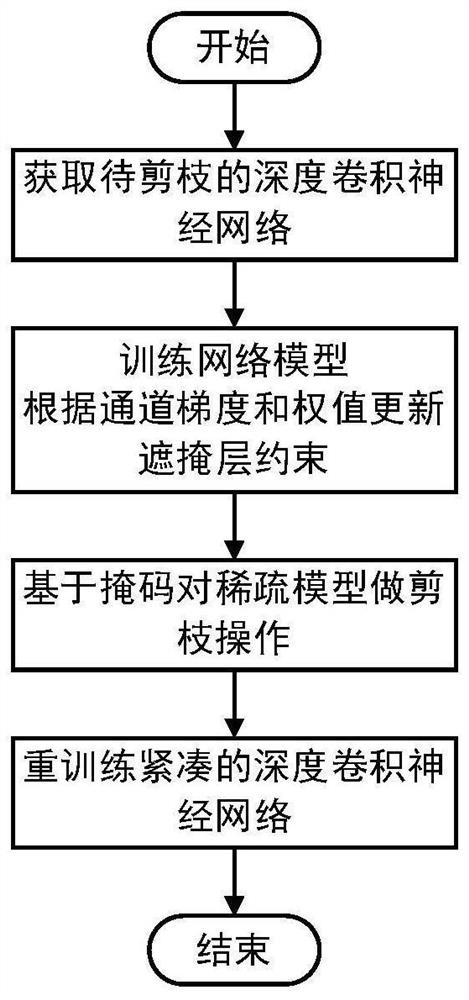
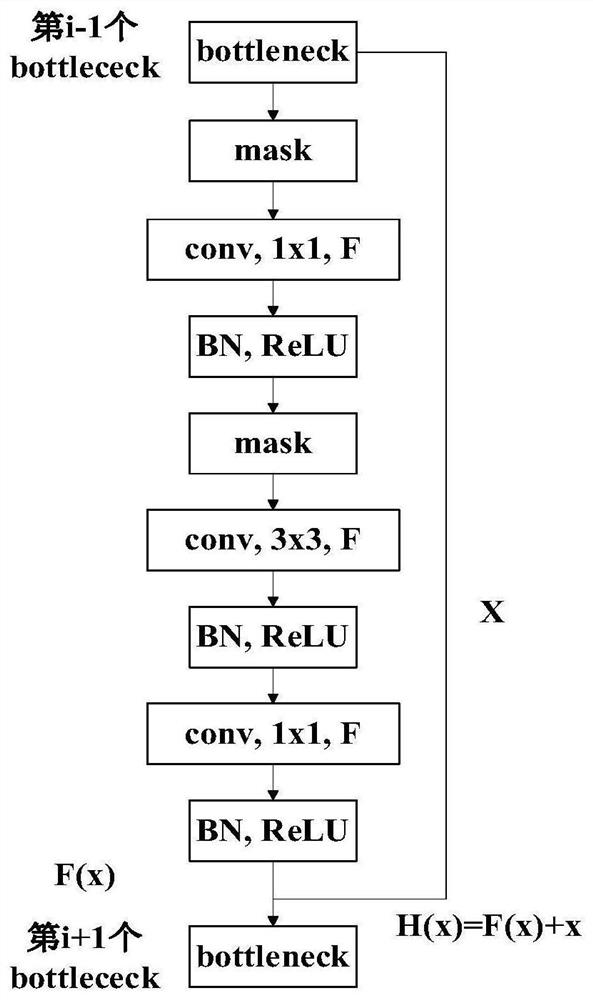
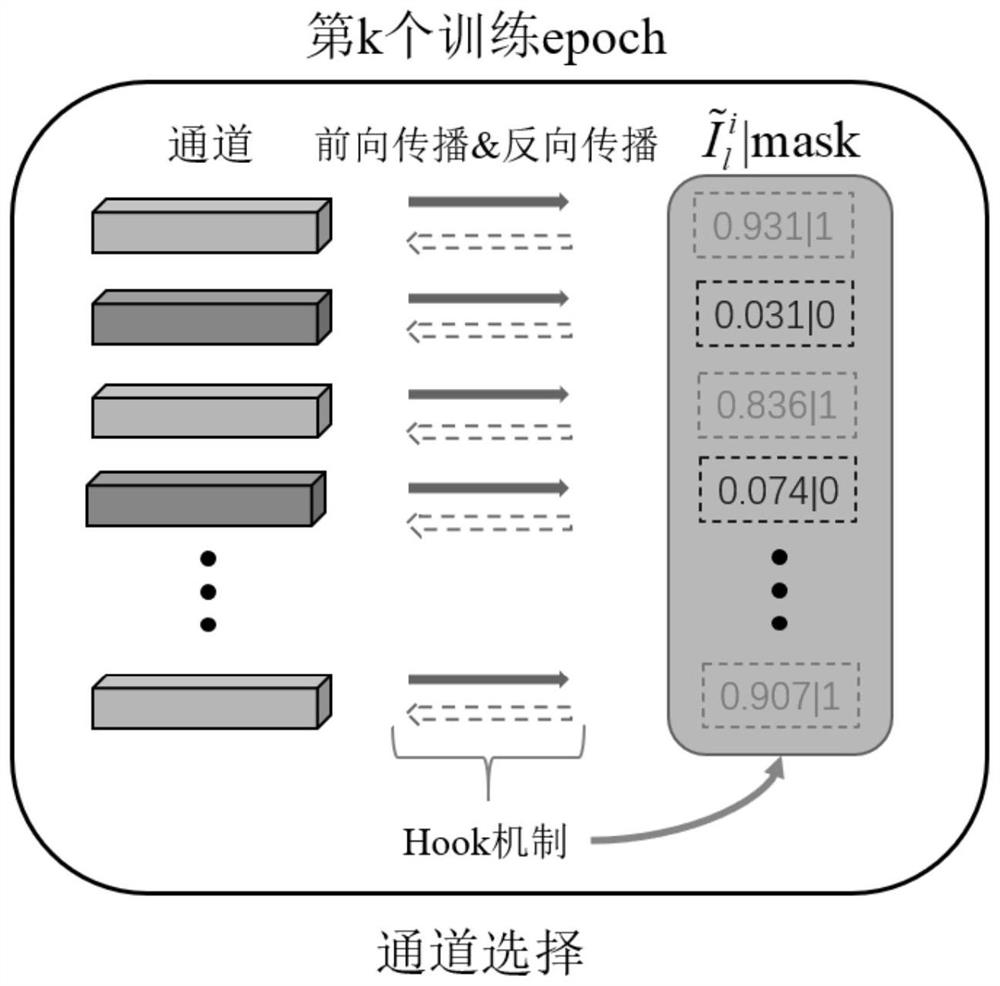
PendingCN112396179ATrim controllableImprove predictabilityNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a flexible deep learning network model compression method based on channel gradient pruning, and the method comprises the steps: 1, adding a masking layer constraint to an original network, and obtaining a to-be-pruned deep convolutional neural network model; wherein the absolute value of the product of the channel gradient and the weight serves as an importance standard toupdate the masking layer constraint of the channel to obtain a mask and a sparse model, 3, carrying out pruning operation on the sparse model based on the mask, and 4, retraining a compact deep convolutional neural network model. The invention further provides an application effect of the flexible deep learning network model compression method based on channel gradient pruning on an actual objectrecognition APP, the recognition speed of the model to the object after pruning is greatly improved, and the problem that the deep neural network model cannot be applied to the actual object recognition APP due to high storage space occupation and high memory occupation, high computing resources are occupied and cannot be deployed to embedded devices, smart phones and other devices are solved, and the application range of the deep neural network is expanded.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Graph regularization sparse coding-based magnetic resonance super-undersampled K data imaging method
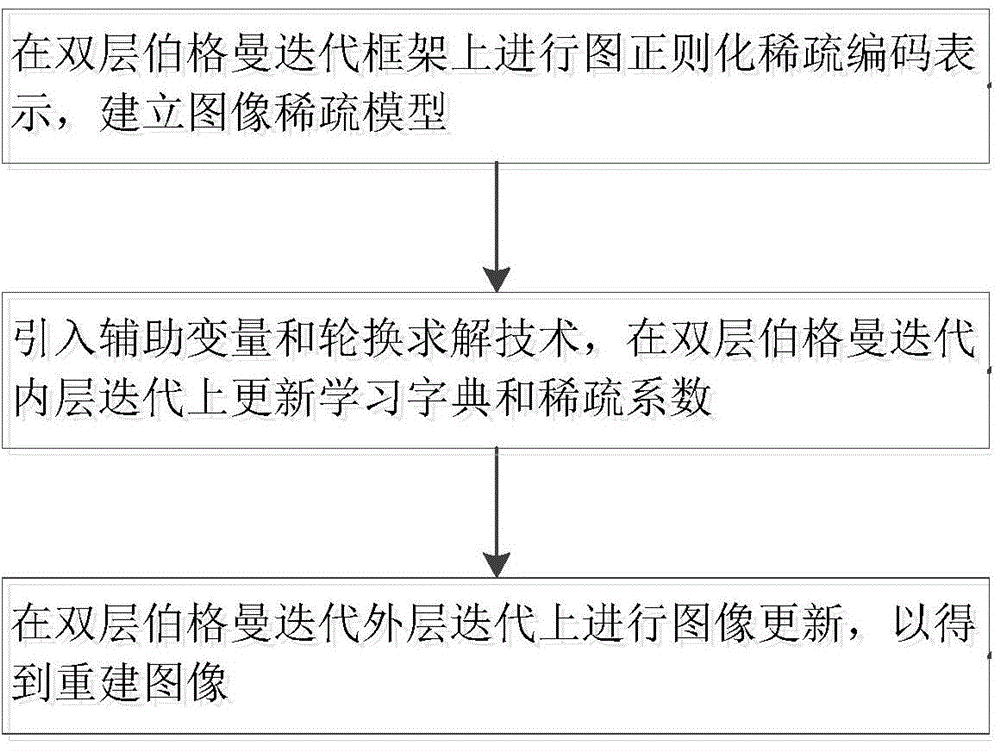
InactiveCN104574456AEfficient captureSparse means good2D-image generationDictionary learningGraph regularization
The invention discloses a graph regularization sparse coding-based magnetic resonance super-undersampled K data imaging method which comprises the following steps: (a) performing graph regularization sparse coding expression on a double-layer Bergman iteration frame to obtain an image sparse model; (b) updating a learning dictionary and a sparse coefficient on the inner-layer iteration of double-layer Bergman iteration by introducing an auxiliary variable and an alternate solving technology; (c) performing image updating on the outer-layer iteration of the double-layer Bergman iteration to obtain an imaging result by utilizing a part of super-undersampled K data as constraints. According to the method, a proximity graph is established to code local structural data and dig geometric data constraints thereof by introducing adaptive dictionary learning into graph regularization sparse coding, so that image data can be sparsely expressed better; in addition, an image with more complex local geometric characteristics can be processed, a local image structure can be effectively captured, more image details can be recovered, and an obtained image result is higher in fidelity.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Blurred image blind restoration method based on mixed type Markov expert field
The invention discloses a blurred image blind restoration method based on a Gaussian scale mixed type Markov expert field. The method comprises the implementation steps that (1) modeling is carried out on noise, a restored image and a restored blurred kernel through a Gaussian model, the Gaussian scale mixed type Markov expert field and a sparse model based on an l1 norm respectively in a Bayes posterior probability model; (2) a Napierian logarithm is extracted from the obtained Bayes posterior probability model to obtain a problem to be optimized; (3) the restored image and the restored blurred kernel are initialized through a blurred image and a Gaussian blurred kernel respectively, and a maximum number of iterations is set; (4) in a certain iteration, the obtained restored blurred kernel is fixedly optimized, and the restored image is optimized; (5) the obtained restored image is fixedly optimized, and the restored blurred kernel is optimized; (6) if the number of iterations is smaller than the maximum number of iterations, the step (4) and the step (5) are repeatedly executed; (7) a regularization coefficient in the step (4) is adjusted, and the known blurred image is restored through the final restored blurred kernel obtained in the step (6). According to the method, the high-quality restored image can be obtained through a single blurred image.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
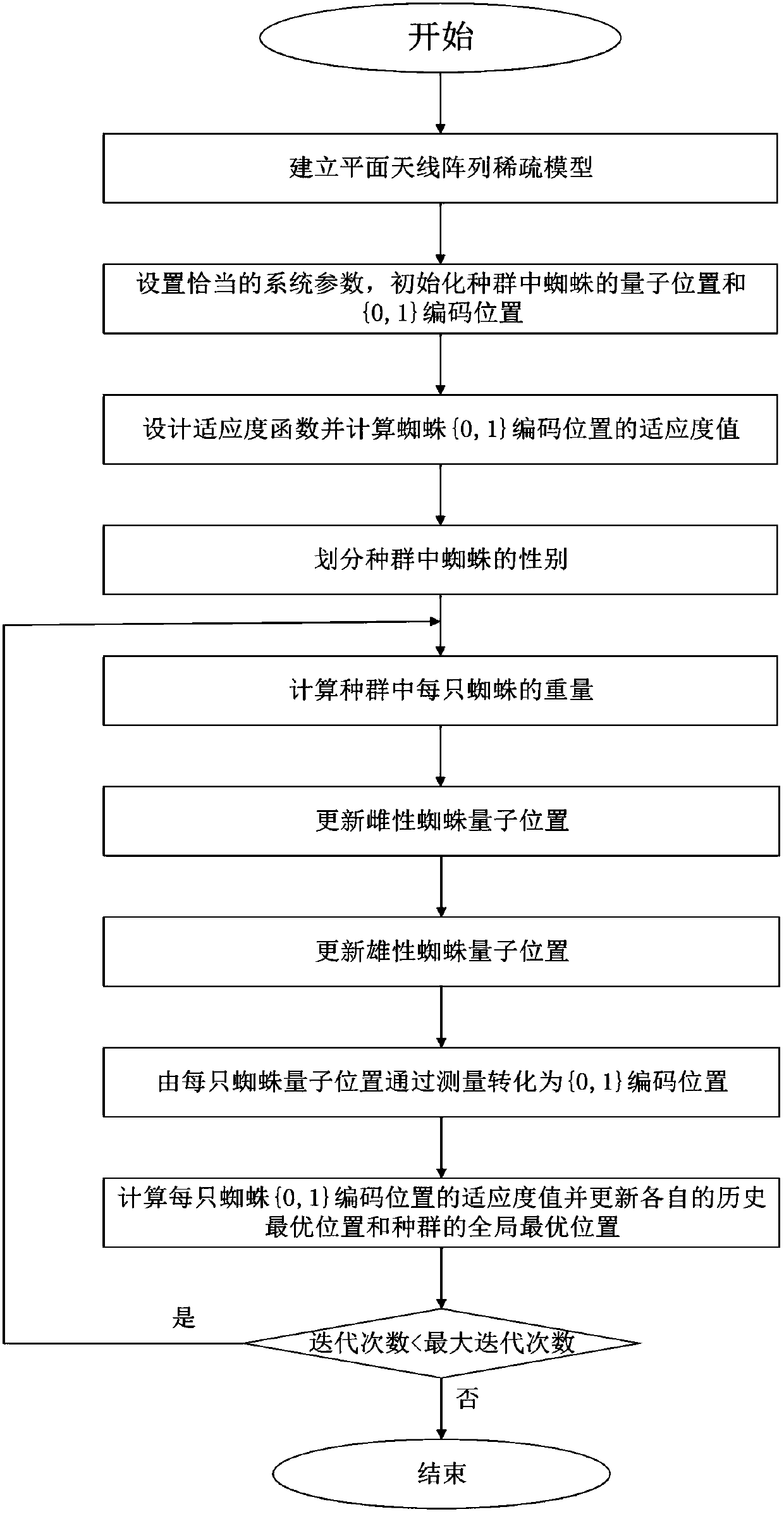
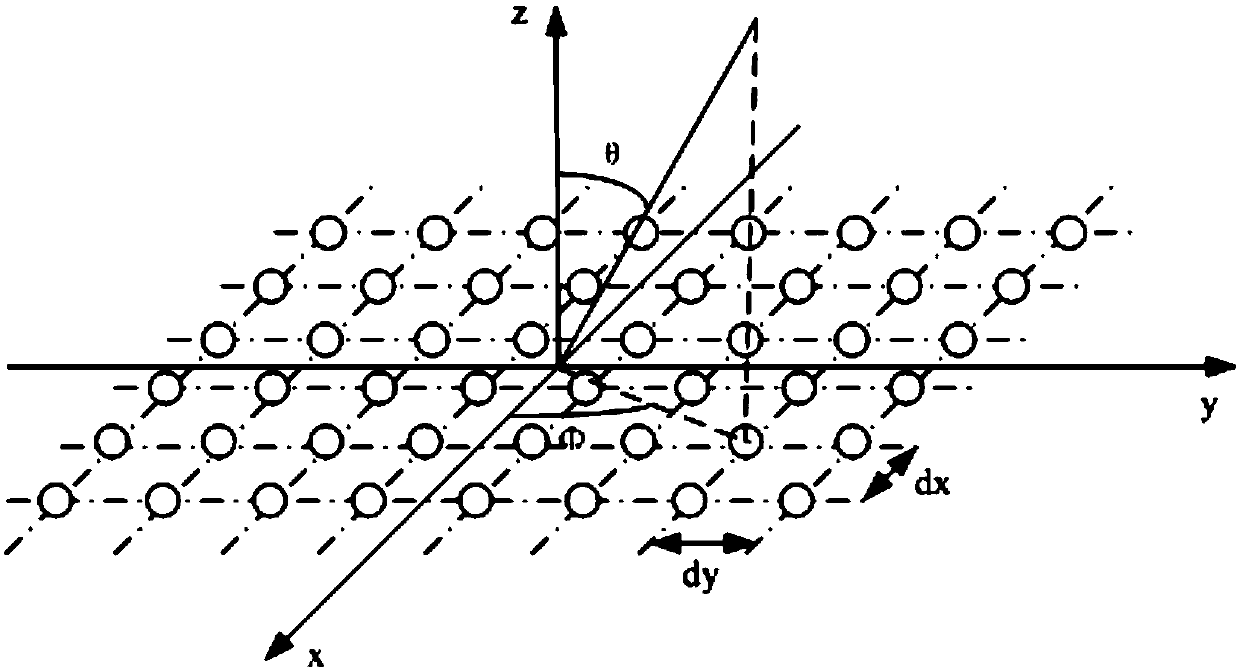
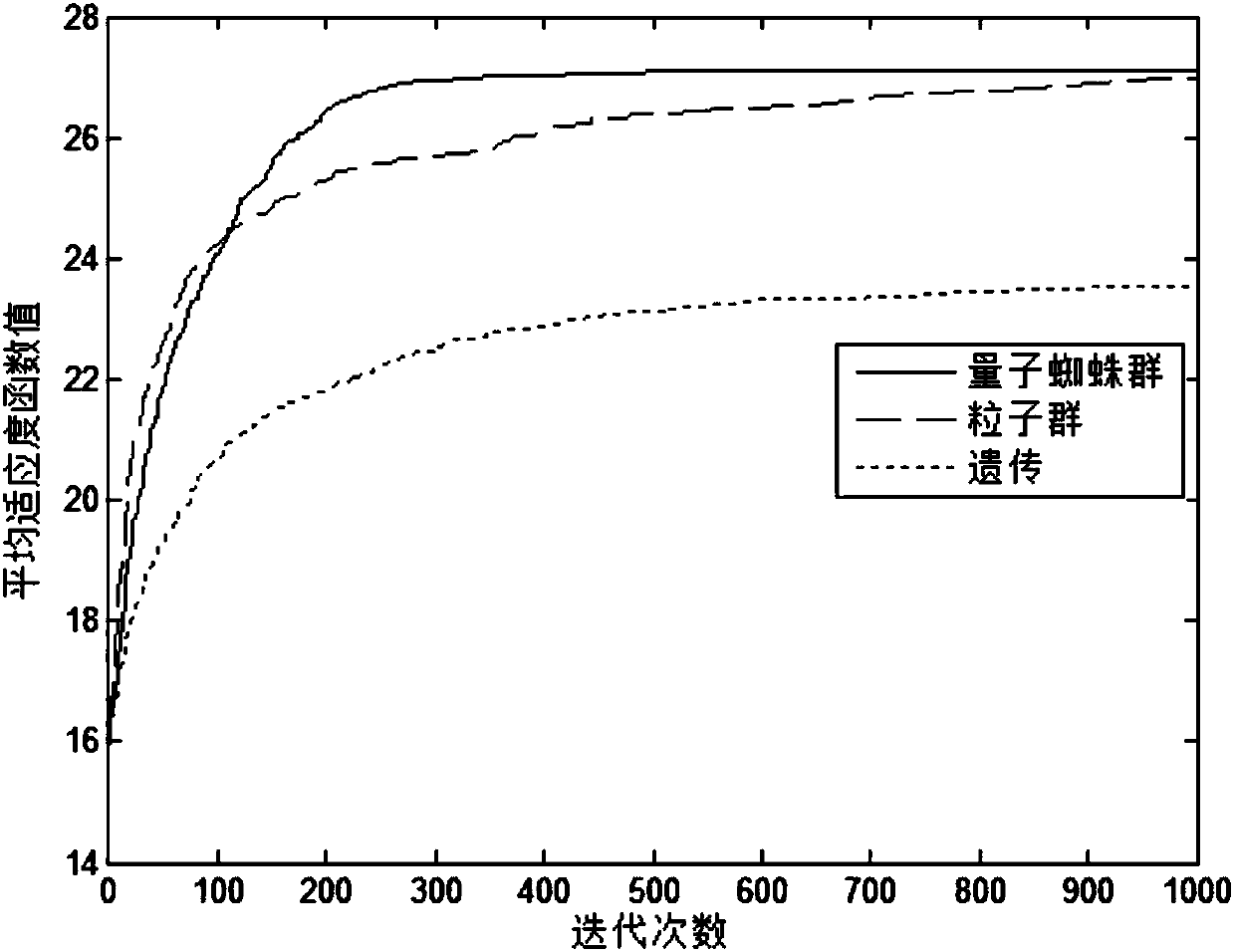
Planar antenna array sparse method based on quantum spider population evolution mechanism
ActiveCN107302140ASolving sparse problems with discrete variablesImprove the theory of evolution mechanismAntenna arraysArtificial lifeSparse methodsPlanar antenna array
The invention provides a planar antenna array sparse method based on a quantum spider population evolution mechanism. The planar antenna array sparse method comprises the steps of 1, establishing a planar antenna array sparse model; 2, setting system parameters; 3, performing evaluation on advantages and disadvantages of each spider coding position in a population by a fitness function, and taking the optimal position of the fitness function as the global optimal position of the whole population; 4, dividing genders of spiders in the population; 5, calculating weight of each spider; 6, updating quantum positions of female spiders by adopting an analog quantum vector rotation door rotation based on the updated quantum vector rotary angle; 7, updating quantum positions of male spiders by adopting an analog quantum vector rotation door rotation based on the updated quantum vector rotary angle; 8, updating the respective historical optimal positions; and 9, judging whether the maximum number of iterations is reached or not. By adoption of the planar antenna array sparse method, the difficulty existing in multi-constraint planar array antenna sparsity is solved, and various requirements on the planar sparse array are satisfied.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
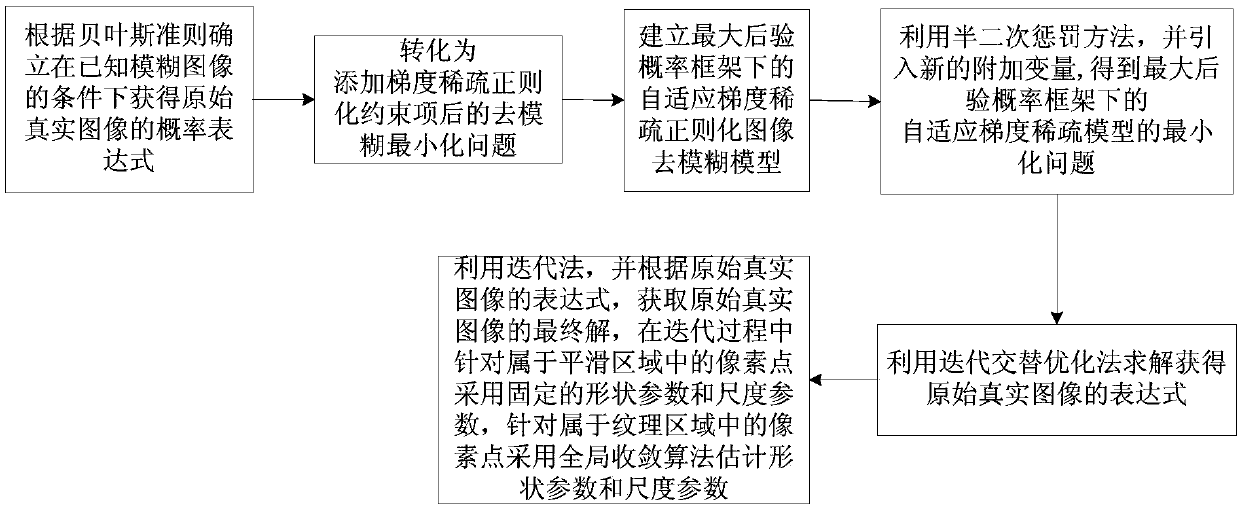
Non-blind deblurring method for blurred image based on adaptive gradient sparse model
ActiveCN107133923AAdapt to Texture ChangesHigh SNR valueImage enhancementPattern recognitionSparse model
The invention discloses a non-blind deblurring method for a blurred image based on an adaptive gradient sparse model. The non-blind deblurring method does not adopt a fixed shape parameter value or a fixed scale parameter value in gradient distribution estimation for an image, but adopts different shape parameter values and scale parameter values in allusion to different pixels, so that the method is enabled to well adapt to variations in image texture, and thus a restored image restored by using the method disclosed by the invention is enabled to have a high signal-to-noise ratio. Meanwhile, on the aspect of the subjective quality, a smooth region of the restored image does not have a noise point and appears smooth in a natural manner, a texture region of the restored image is clearer, and more excellent subjective visual quality is acquired. The image is divided into the smooth region and the texture region, a fixed shape parameter and a fixed scale parameter are directly adopted for pixels belonging to the smooth region, a global convergence algorithm is adopted for pixels belonging to the texture region to estimate the shape parameter and the scale parameter, and a better estimation result can be acquired under less data.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Robust sparse recovery STAP method and system based on alternating direction method of multipliers
ActiveCN106501785AEnhanced inhibitory effectEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsSparse model
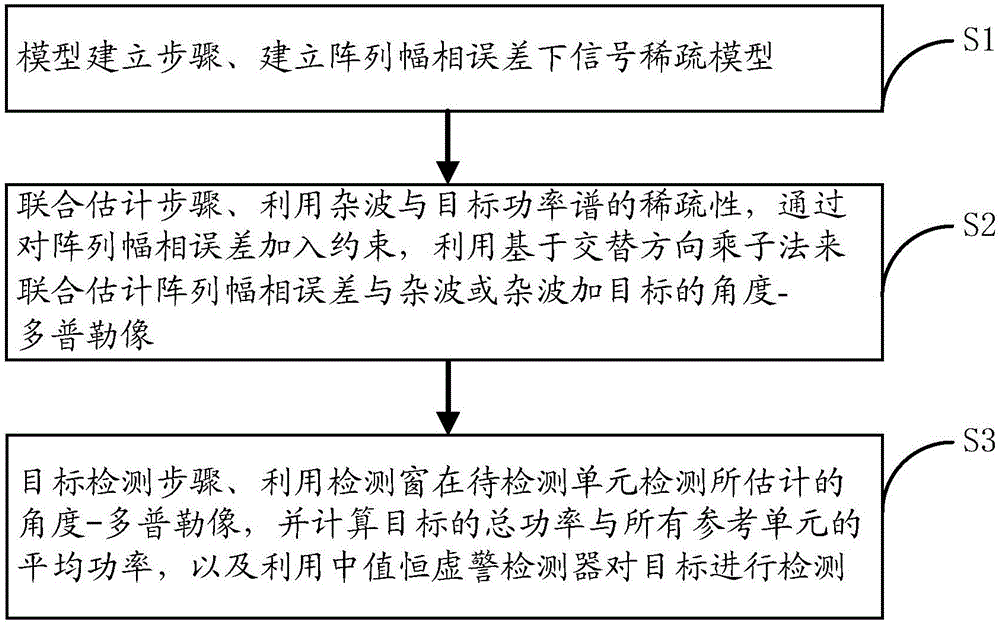
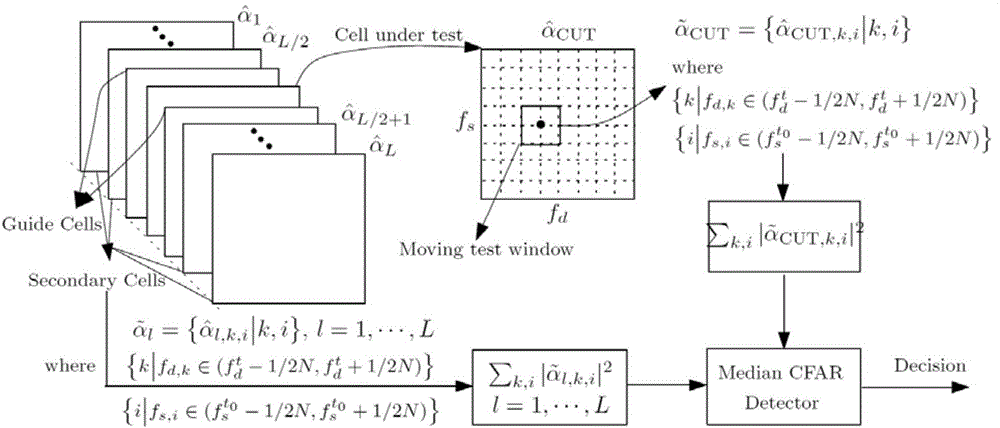
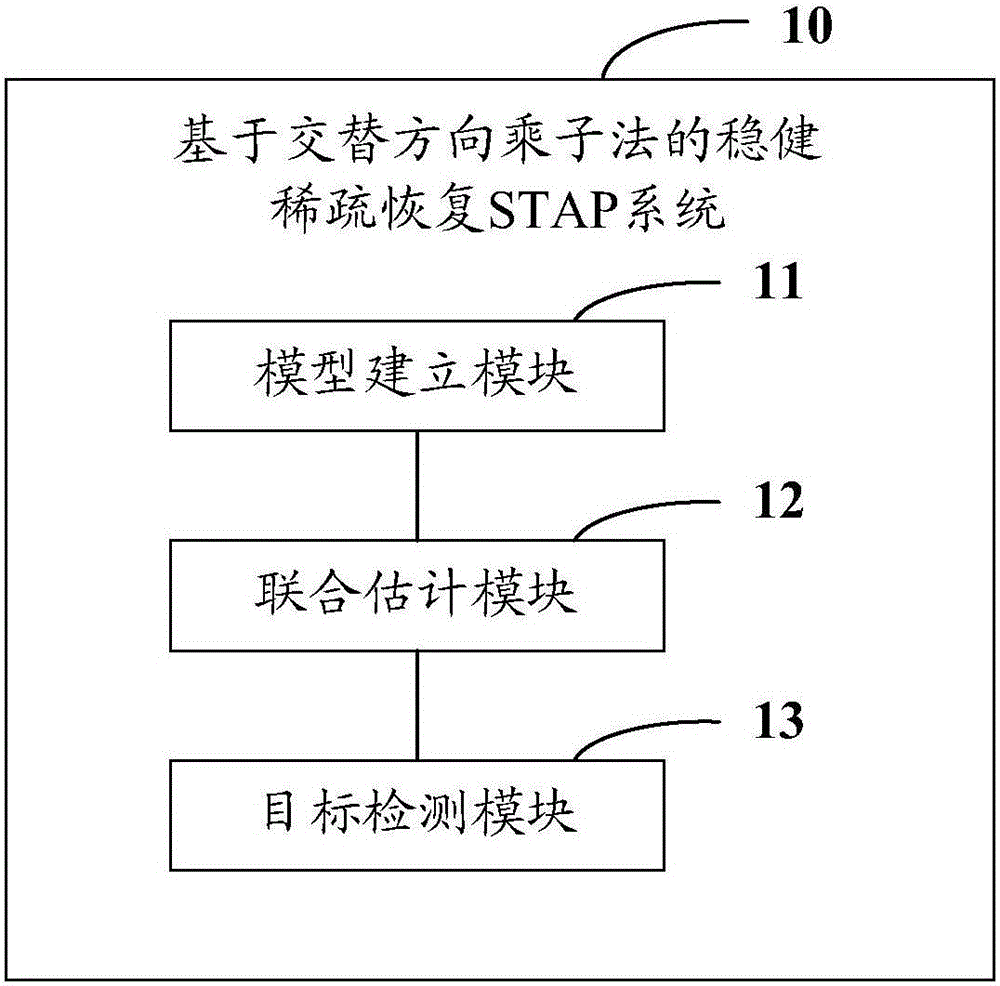
The invention provides a robust sparse recovery STAP method based on alternating direction method of multipliers (ADM), wherein the method comprises: a model establishing step of establishing a signal sparse model under an array amplitude phase error; a joint estimation step of jointly estimating the angle-Doppler image of the array amplitude phase error and the clutter or clutter and target by using the sparsity of the clutter and a target power spectrum, by adding constraint to array amplitude phase error, and by using the ADM; and a target detection step of detecting the estimated angle-Doppler image at a detection unit to be detected by using a detection window, computing the total power of the target and the average power of all reference units, and detecting the target by using a median value false alarm detector. The invention also provides a robust sparse recovery STAP system based on ADM. The method and system can overcome the influence of the performance degradation caused by the array amplitude phase error, and further improve the radar system clutter suppression and target detection capability.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Image fusion method based on joint sparse model
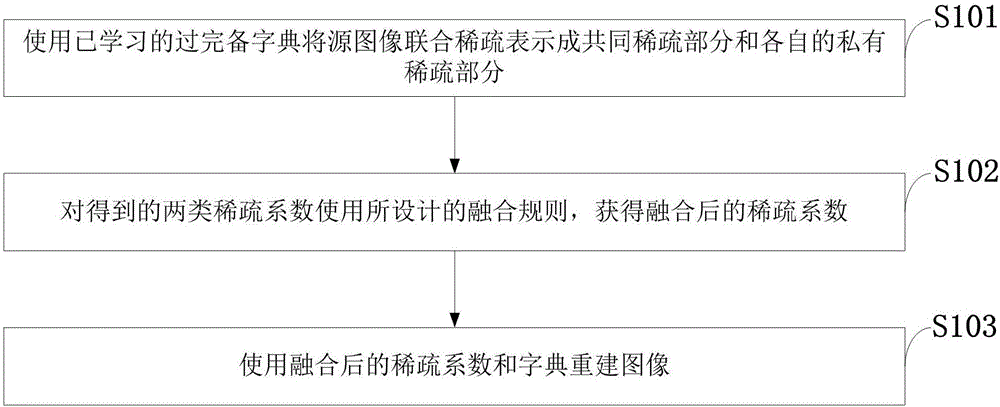
The invention discloses an image fusion method based on joint sparse model; the image fusion method comprises: using a learned over-complete dictionary to subject source images to joint sparse representation into a common sparse portion and respective private sparse portions; fusing the two types of sparse coefficients obtained through designed fusion rules so as to obtain a fused sparse coefficient; reconstructing an image with the fused sparse coefficient and the dictionary. Simulation experiment results show that the image fusion method provides improved fusion effect for infrared and visible light images.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Method and device for reconstructing dynamic magnetic resonance image and readable storage medium
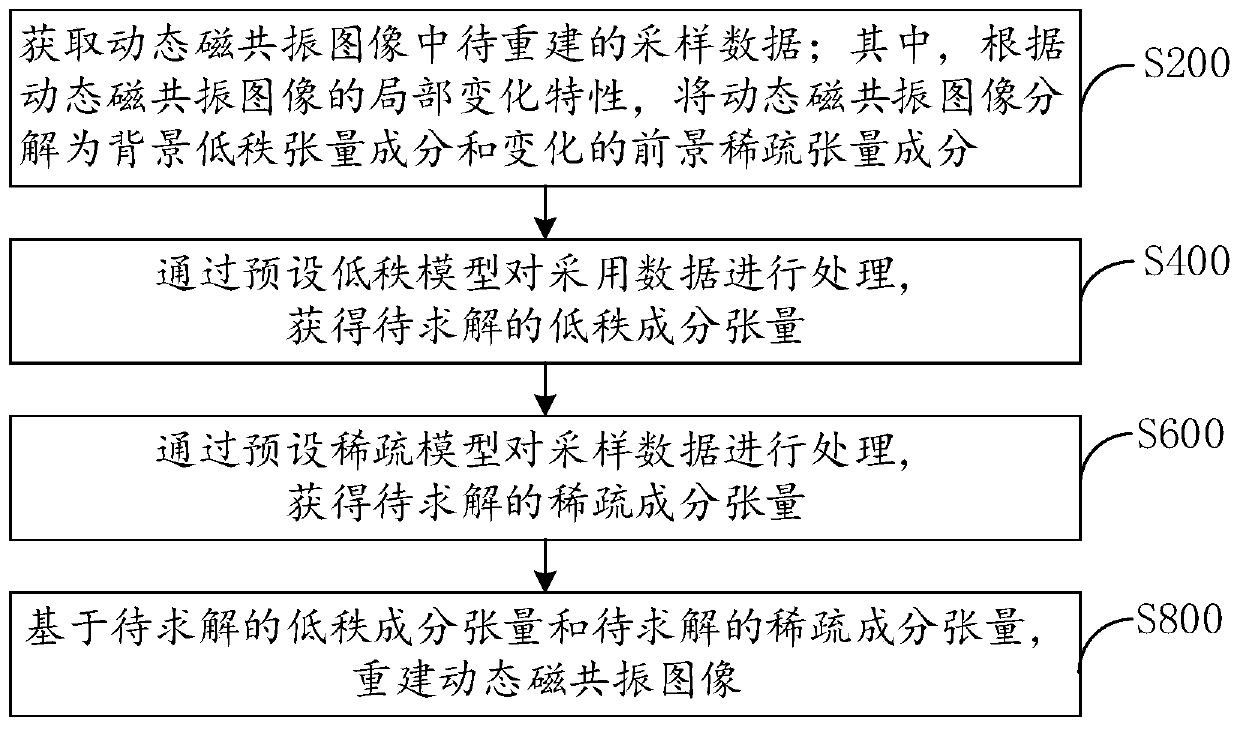
PendingCN109872376ATake full advantage of redundancy2D-image generationImaging processingSparse model
The invention discloses a method and device for reconstructing a dynamic magnetic resonance image and a readable storage medium, and relates to the technical field of image processing. The method forreconstructing the dynamic magnetic resonance image comprises the steps of obtaining to-be-reconstructed sampling data in the dynamic magnetic resonance image; Decomposing the dynamic magnetic resonance image into a background low-rank tensor component and a changed foreground sparse tensor component according to the local change characteristic of the dynamic magnetic resonance image; Processing the sampling data through a preset low-rank model to obtain a background low-rank tensor component; Processing the sampling data through a preset sparse model to obtain a changed foreground sparse tensor component; Based on the background low-rank tensor component and the changed foreground sparse tensor component, the dynamic magnetic resonance image is reconstructed, and the data structure correlation of the dynamic magnetic resonance image data in the time dimension and the space dimension can be fully utilized.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Airborne radar space time adaptation processing method based on environment dynamic perception
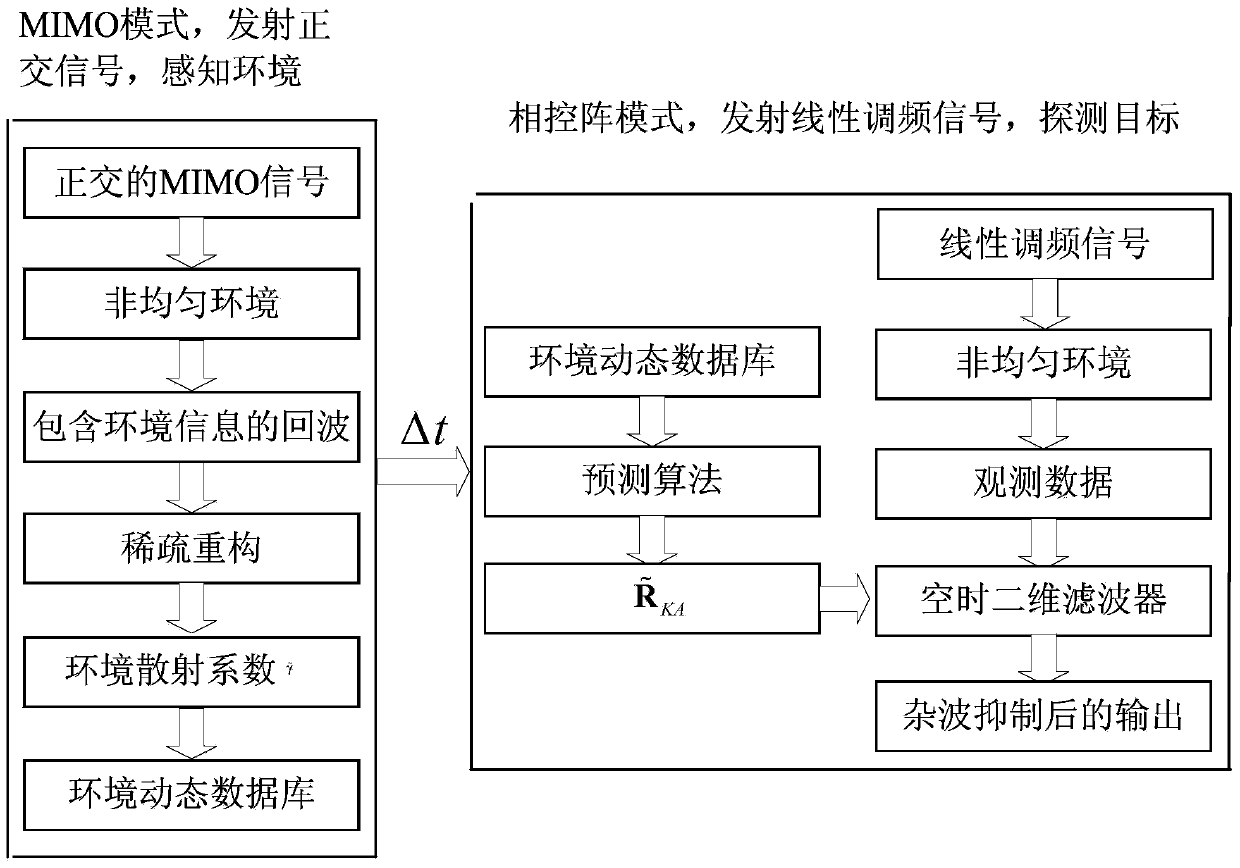
InactiveCN104215937AImproved clutter suppression performanceWave based measurement systemsPattern perceptionDiscretization
The invention belongs to the technical field of airborne radar space time adaptation processing, and particularly relates to an airborne radar space time adaptation processing method based on environment dynamic perception. The airborne radar space time adaptation processing method based on the environment dynamic perception includes concrete steps: setting a work mode of an airborne radar to be an MIMO (multiple input multiple output) mode, using a receiving array to receive a time domain return signal Y, and representing a clutter scattering coefficient vector in an airborne radar observation area as gamma; marking the position of a jth clutter block of an ith distance unit in the airborne radar observation area as Aij; building a sparse model, and representing a basis matrix corresponding to observation data Y after discretization as H; obtaining vector estimation of the clutter scattering coefficient vector gamma of the airborne radar observation area by solving the sparse model, setting the work mode of the airborne radar to be a phased array mode so as to obtain the distance r'i between the clutter block on the position Aij and the airborne radar and an corresponding return signal arrival angle; obtaining a clutter covariance matrix of units with distance to be detected, and performing space time adaptation processing on a return signal which is received when the airborne radar works under the phased array mode.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
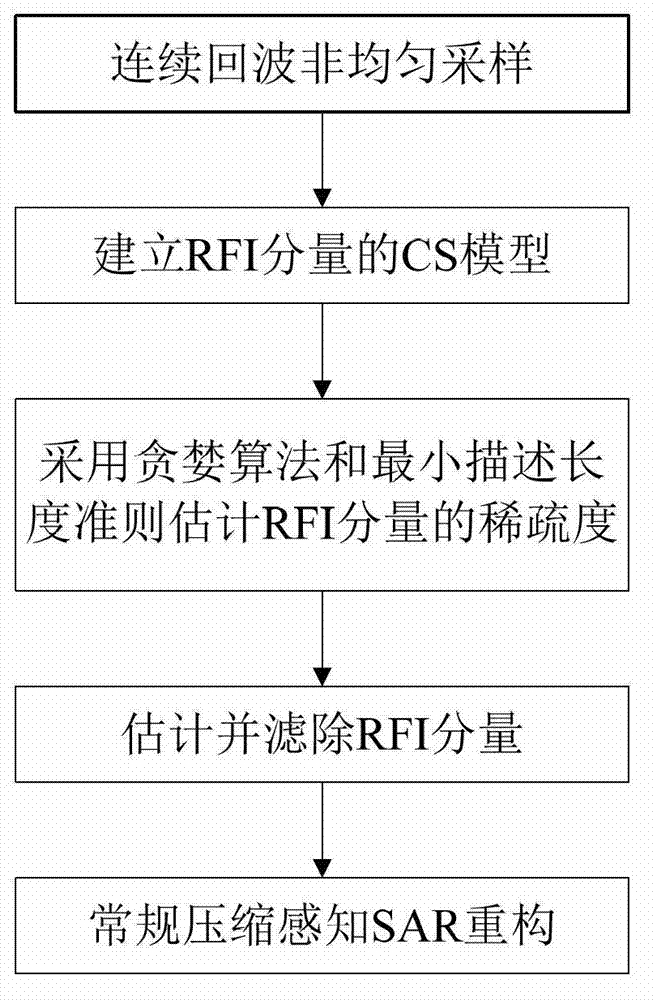
Compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method
InactiveCN103091665AApparent sparsenessEstimated sparsityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarMinimum description length
The invention provides a compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method. The method includes the following steps: (1) building a compressed sensing model of a radio frequency interference (RFI) signal based on an obvious sparse feature of a RFI component in frequency domain, (2) estimating sparseness of the RFI component by using a greedy algorithm to combine with minimum description length, (3) estimating a RFI signal component and filtering directly in time domain to an echo signal of each pulse, and (4) achieving imaging process by using an conventional compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) reconstructing algorithm. The compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar radio frequency interference suppression handling method is based on the sparse feature of the RFI component in the frequency domain and builds a RFI sparse model based on a compressed sensing theory, restrains narrow-band and broadband RFI signals effectively by using the iterative greedy algorithm to estimate and filter the RFI component in the echo signal.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com