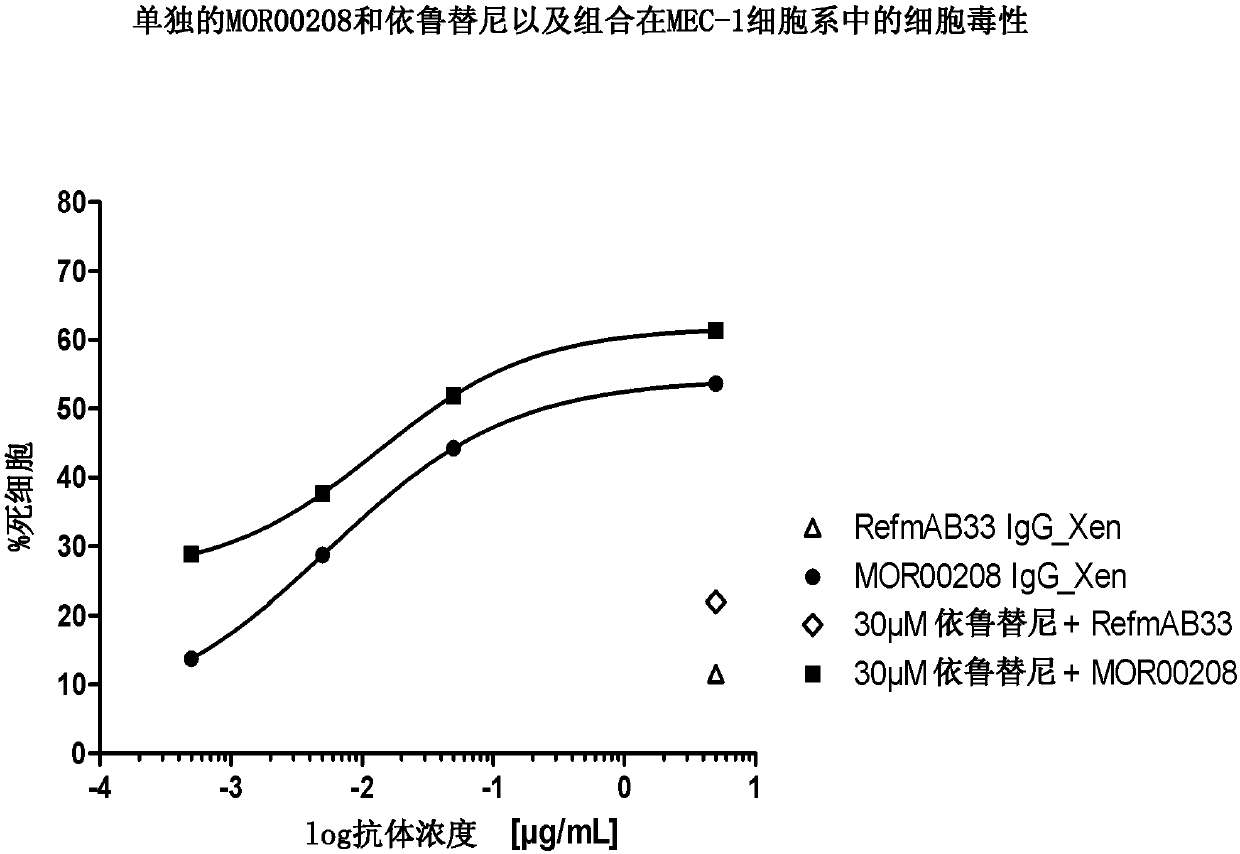
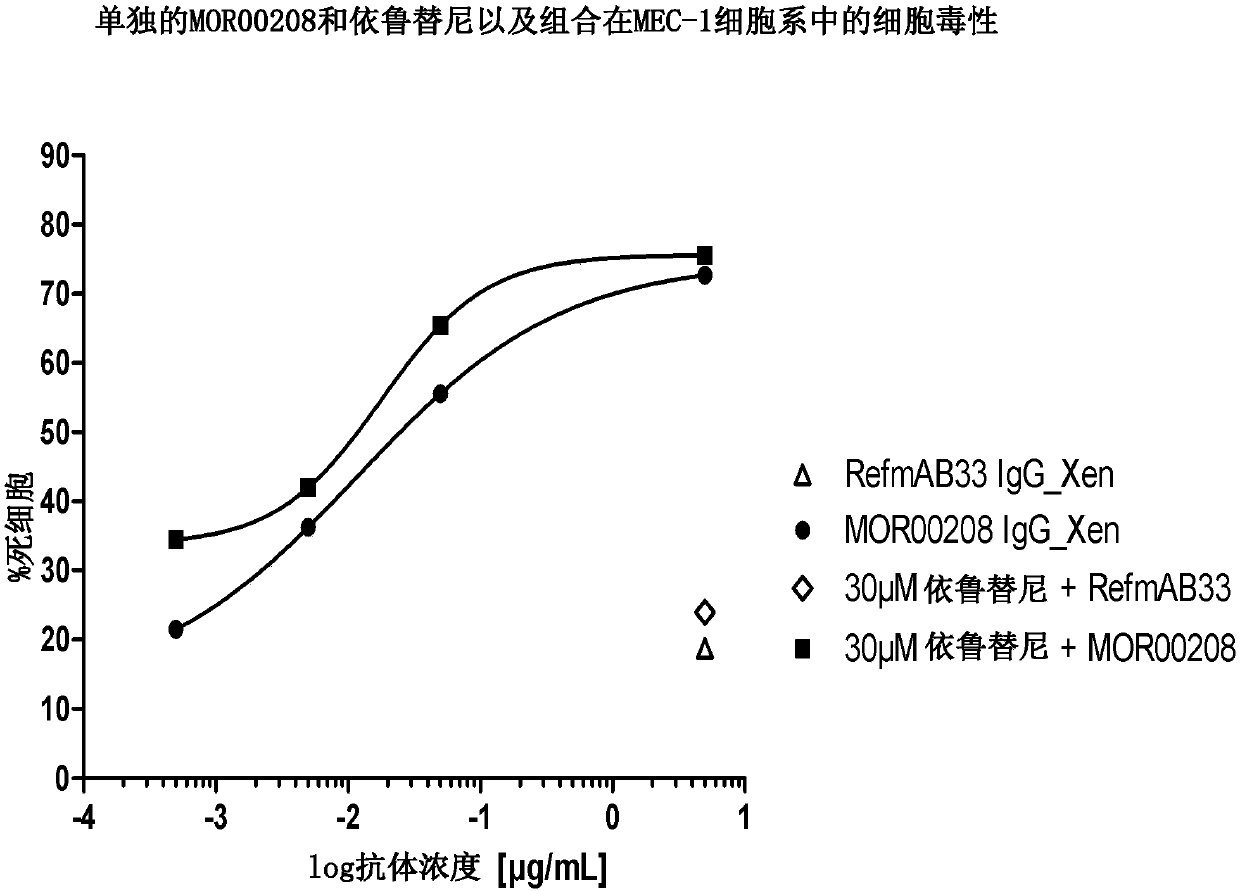
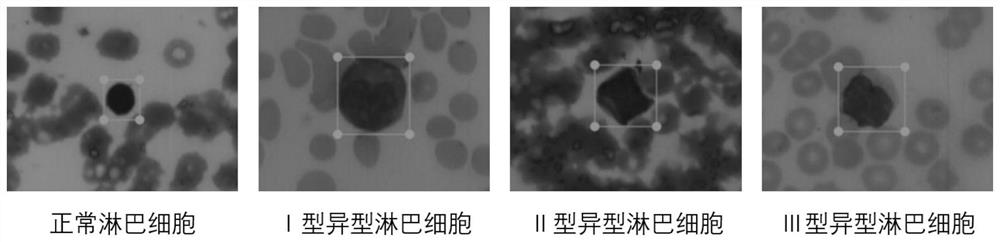
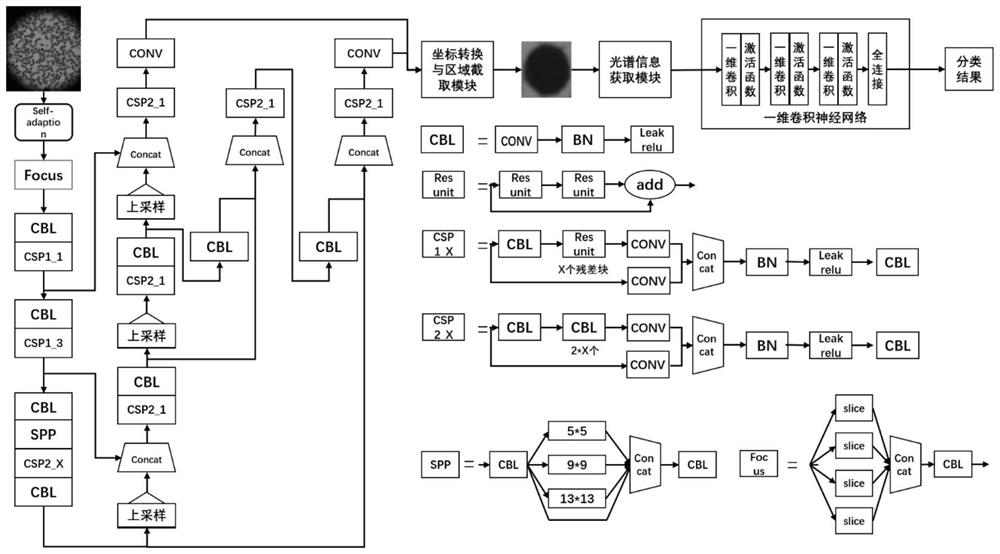
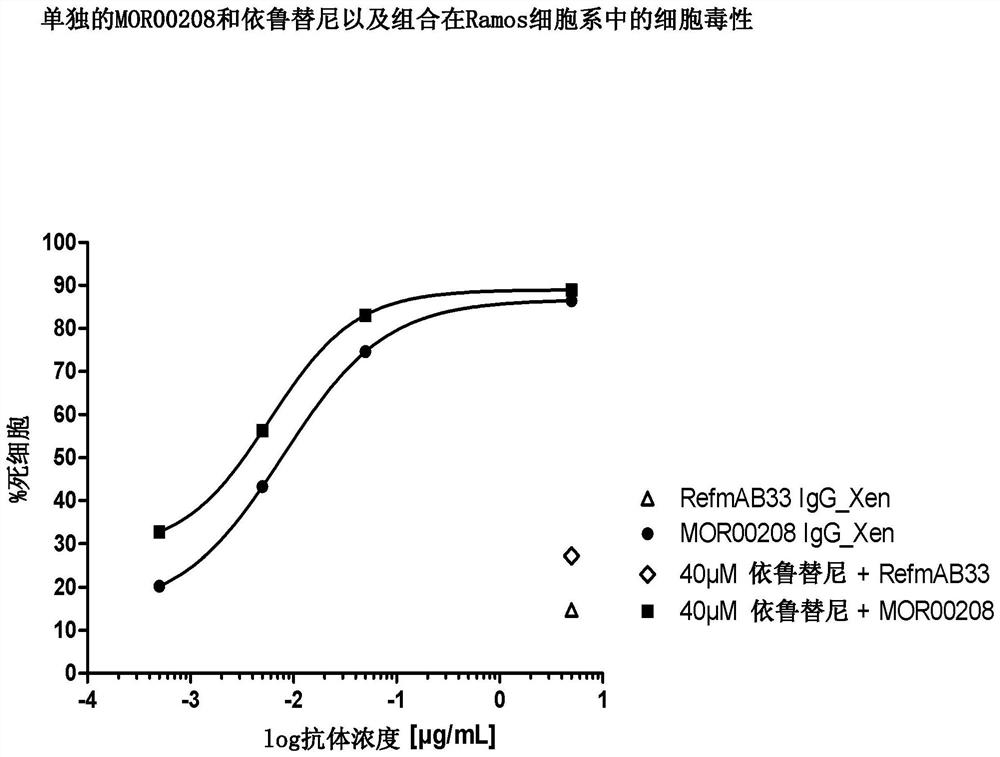
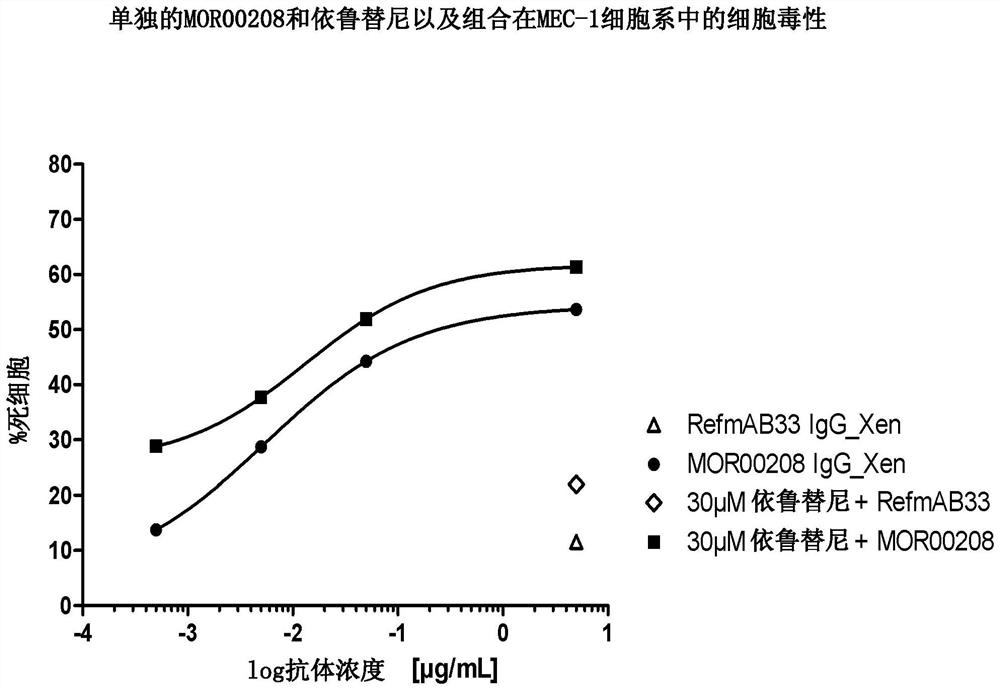
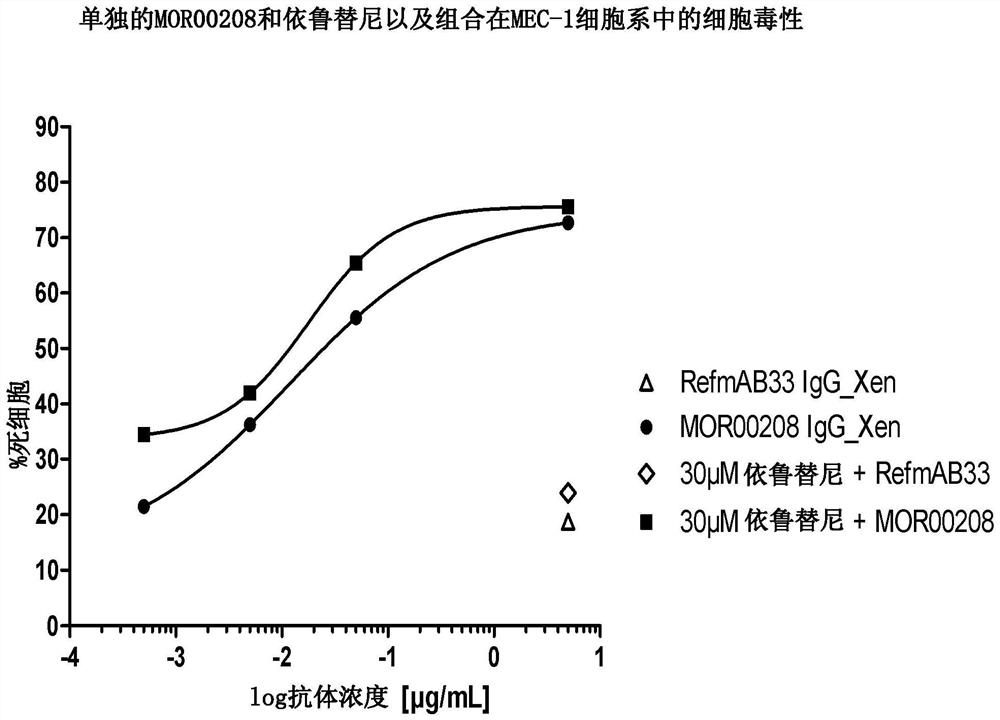
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Lymphoblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A lymphoblast is a modified naive lymphocyte with altered cell morphology. It occurs when the lymphocyte is activated by an antigen (from antigen-presenting cells) and increased in volume by nucleus and cytoplasm growth as well as new mRNA and protein synthesis. The lymphoblast then starts dividing two to four times every 24-hours for 3-5 days, with a single lymphoblast making approximately 1000 clones of its original naive lymphocyte, with each sharing the originally unique antigen specificity. Finally the dividing cells differentiate into effector cells, known as Plasma Cells (for B cells), Cytotoxic T cells, and Helper T cells.
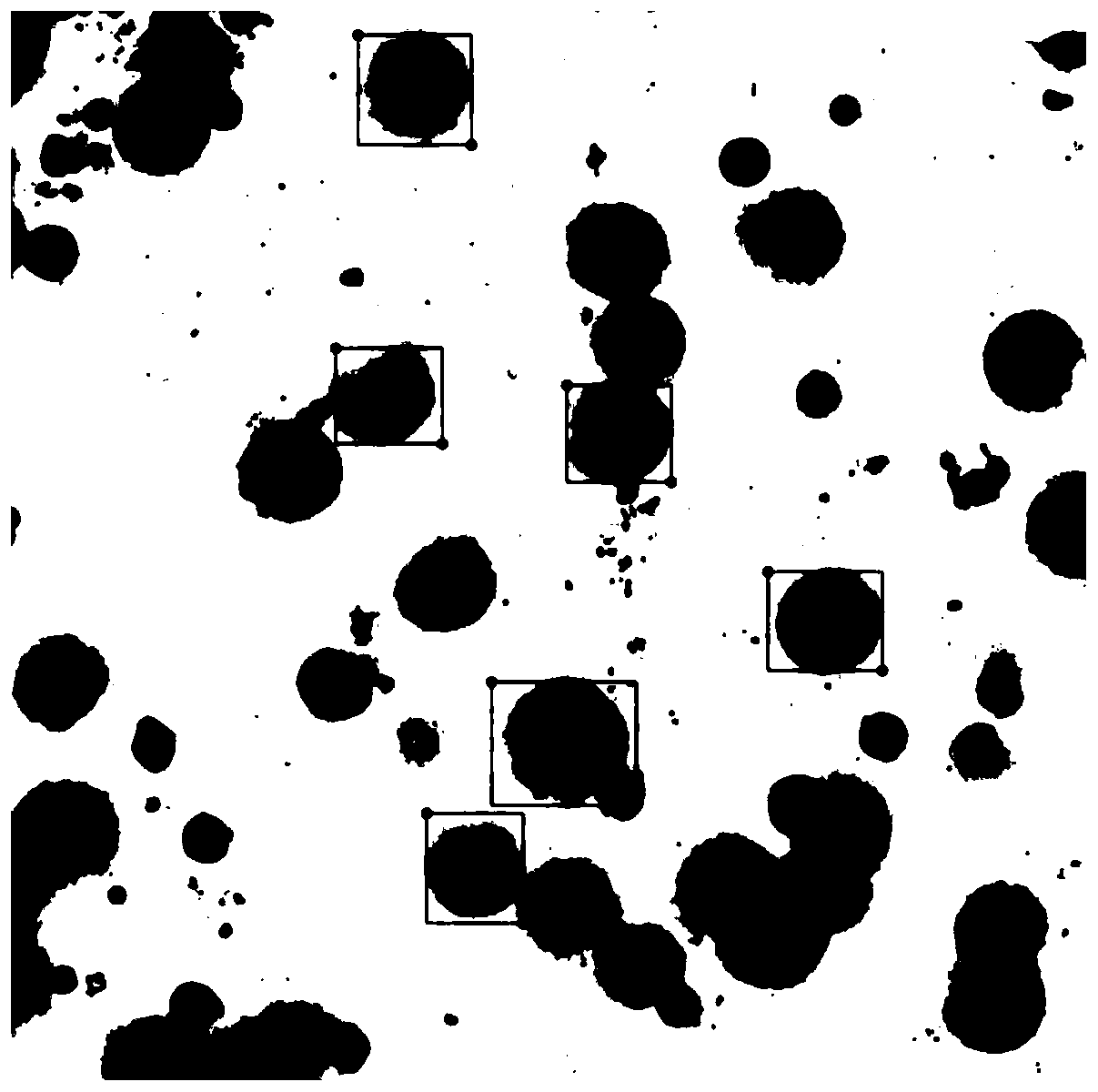
Blood analyzer and method for determining existence and nonexistence of lymphoblasts in blood sample
InactiveUS20100248247A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayFluorescence
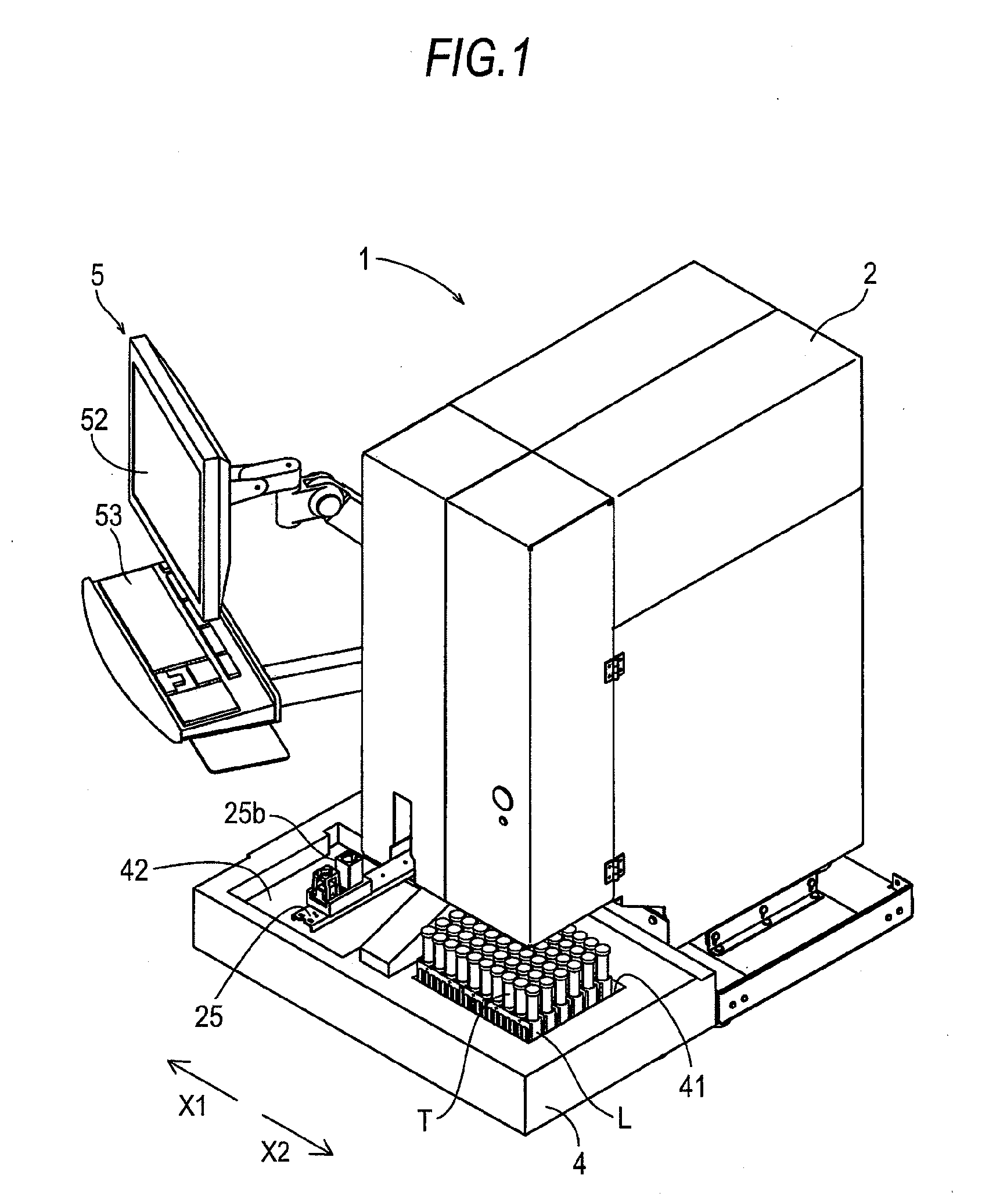
The invention provides a blood analyzer comprising a blood sample supply section, a sample preparation section for preparing an assay sample by mixing the blood sample with a nucleic acid-staining fluorescent dye, a light source for irradiating the assay sample, an optical detecting section for receiving fluorescence emitted from the irradiated assay sample and a controller for performing operations comprising detecting a cell group comprising lymphoblasts on the basis of the fluorescence received by the optical detecting section, and outputting an information on an appearance of the lymphoblasts in the blood sample, as well as a method for determining the existence and nonexistence of lymphoblasts in a blood sample.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
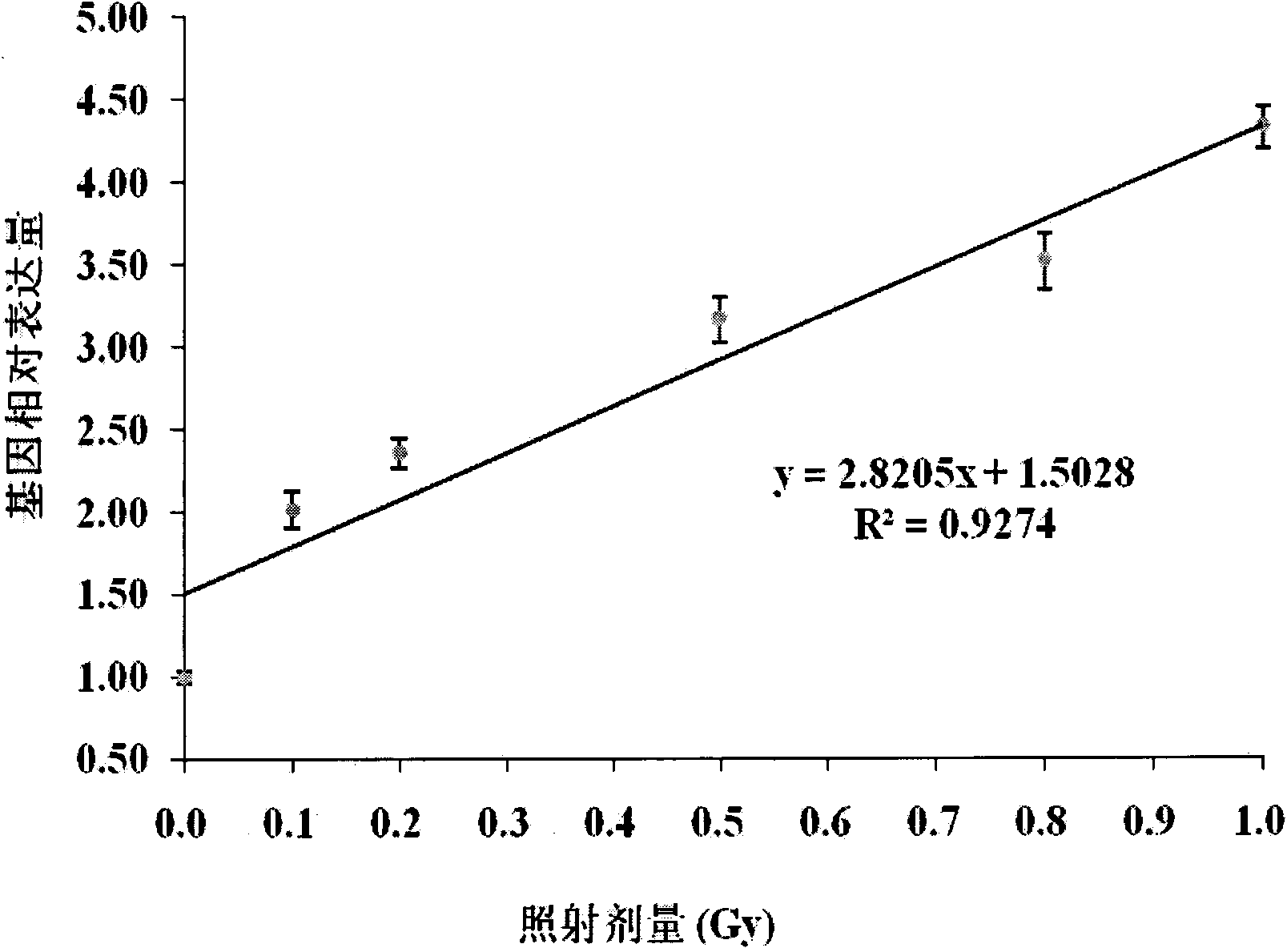
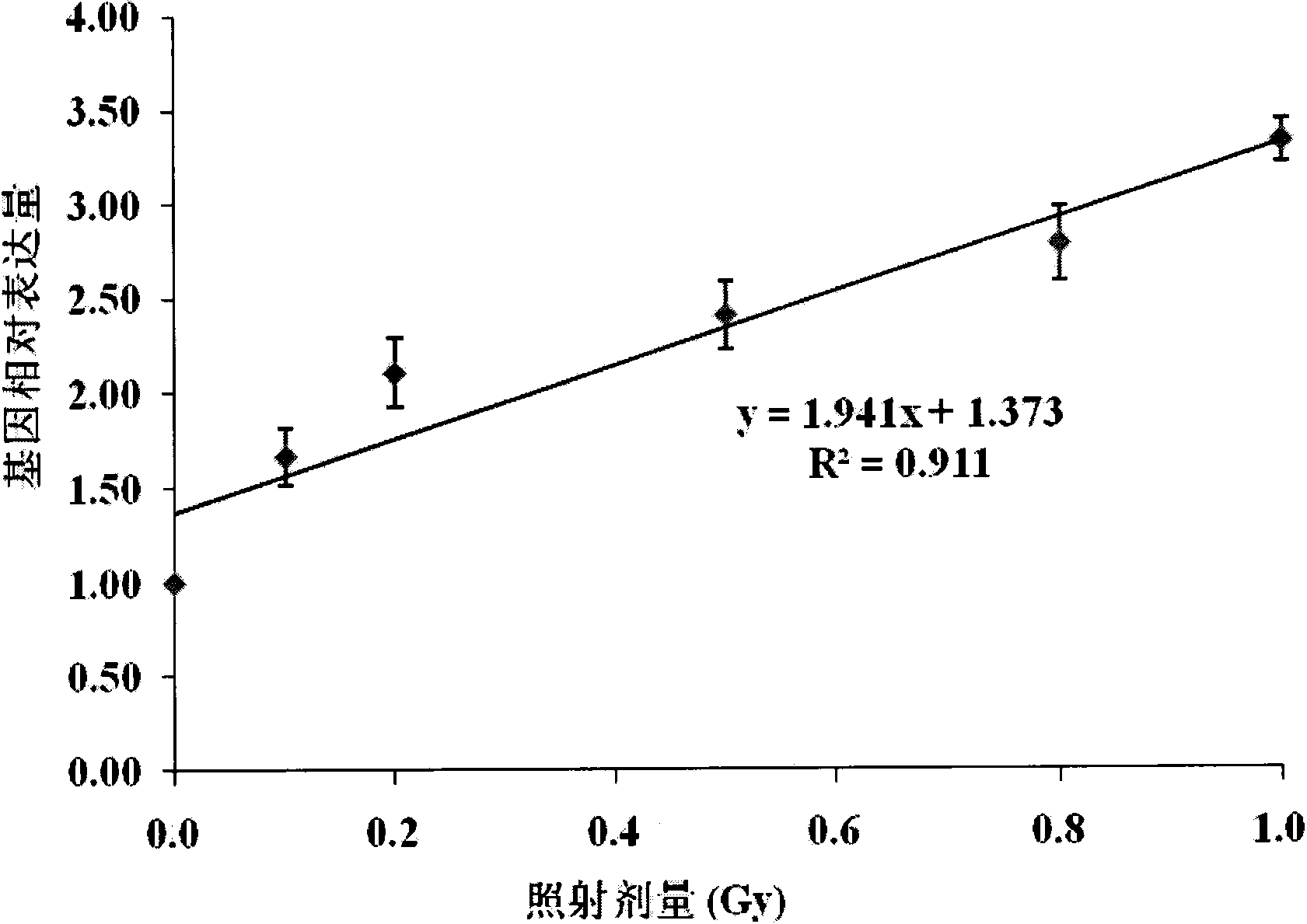
Application of cyclin G1 as low-dose ionizing radiation biodosimeter
InactiveCN103642904AHigh sensitivityQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementIonizationPeripheral blood lymphocyte
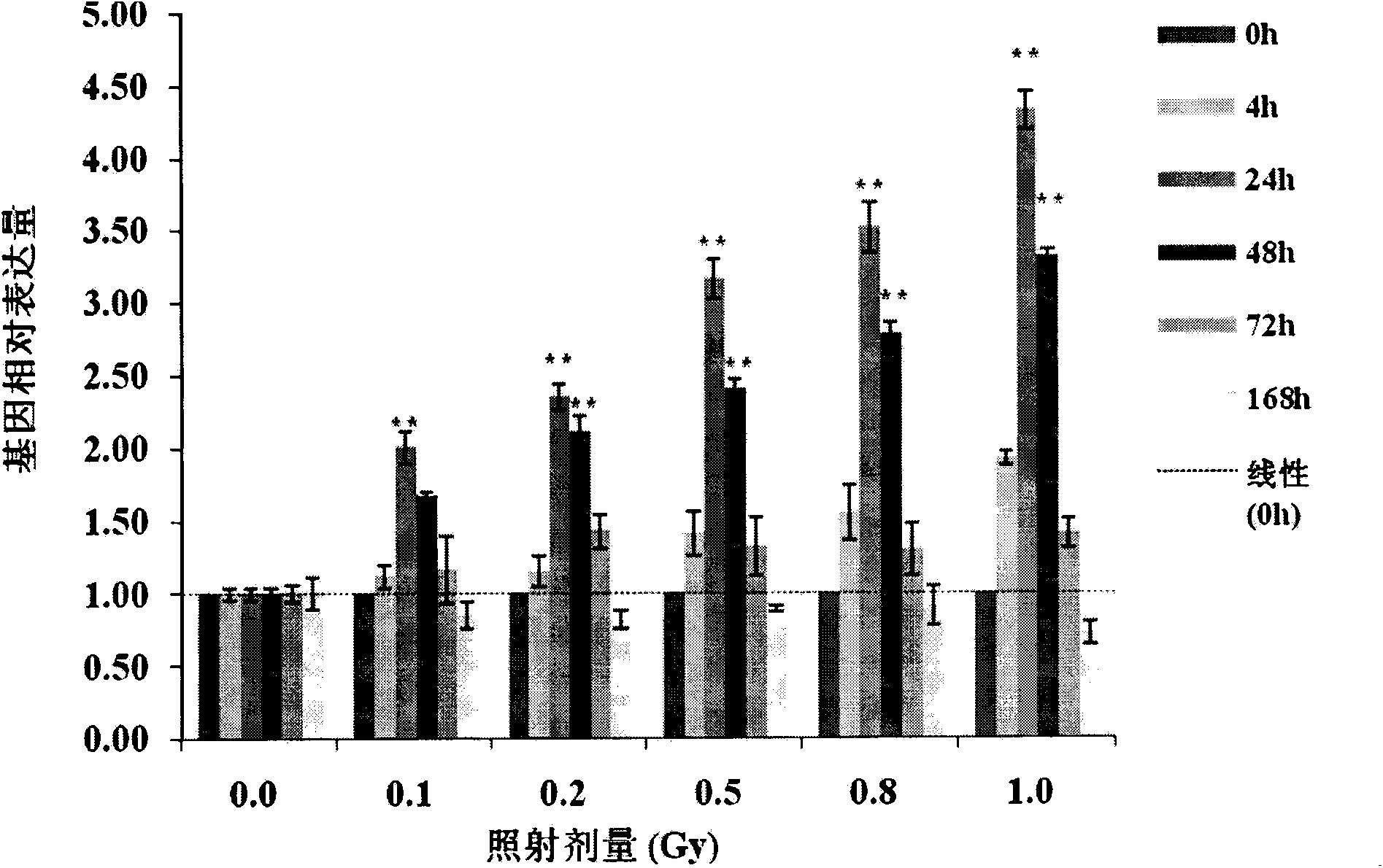
The invention belongs to an ionizing radiation biodosimeter, and concretely relates to an application of a cyclin G1 (CCNG1) gene as the ionizing radiation biodosimeter. After low-dose ionizing radiation of a human lymphoblast and the radiation of mammals, the increase of the expression level of the mRNA of the CCNG1 gene in a peripheral blood lymphocyte is directly proportional to the applied ionizing radiation dose, there is a certain dose-effect relation, and a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method is adopted 24h and 48h after the radiation to realize the fast and simple quantitative detection, so the CCNG1 can be used as a biodosimeter of a low-dose ionizing radiation range, and the dose of the low-dose ionizing radiation to the human bodies and the mammals can be evaluated through a CCNG1 gene expression quantitative-analysis method.
Owner:NAVY MEDICINE RES INST OF PLA
Blood analyzer and method for determining existence and nonexistence of lymphoblasts in blood sample
ActiveCN101852733APreparing sample for investigationScattering properties measurementsLymphoblastHematology analyzer
The invention provides a blood analyzer which enables the detection of lymphoblasts without the use of high-priced fluorescence-labeled antibodies. The blood analyzer comprises a blood sample supply section, a sample preparation section for preparing an assay sample by mixing the blood sample with a nucleic acid-staining fluorescent dye, a light source for irradiating the assay sample, an optical detecting section for receiving fluorescence emitted from the irradiated assay sample and a controller for performing operations comprising detecting a cell group comprising lymphoblasts on the basis of the fluorescence received by the optical detecting section (23), and outputting an information on an appearance of the lymphoblasts in the blood sample.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Combination therapy with anti-CD19 antibody and purine analog
ActiveCN103703027AOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsChronic lymphocytic leukemiaLymphocytes.immature
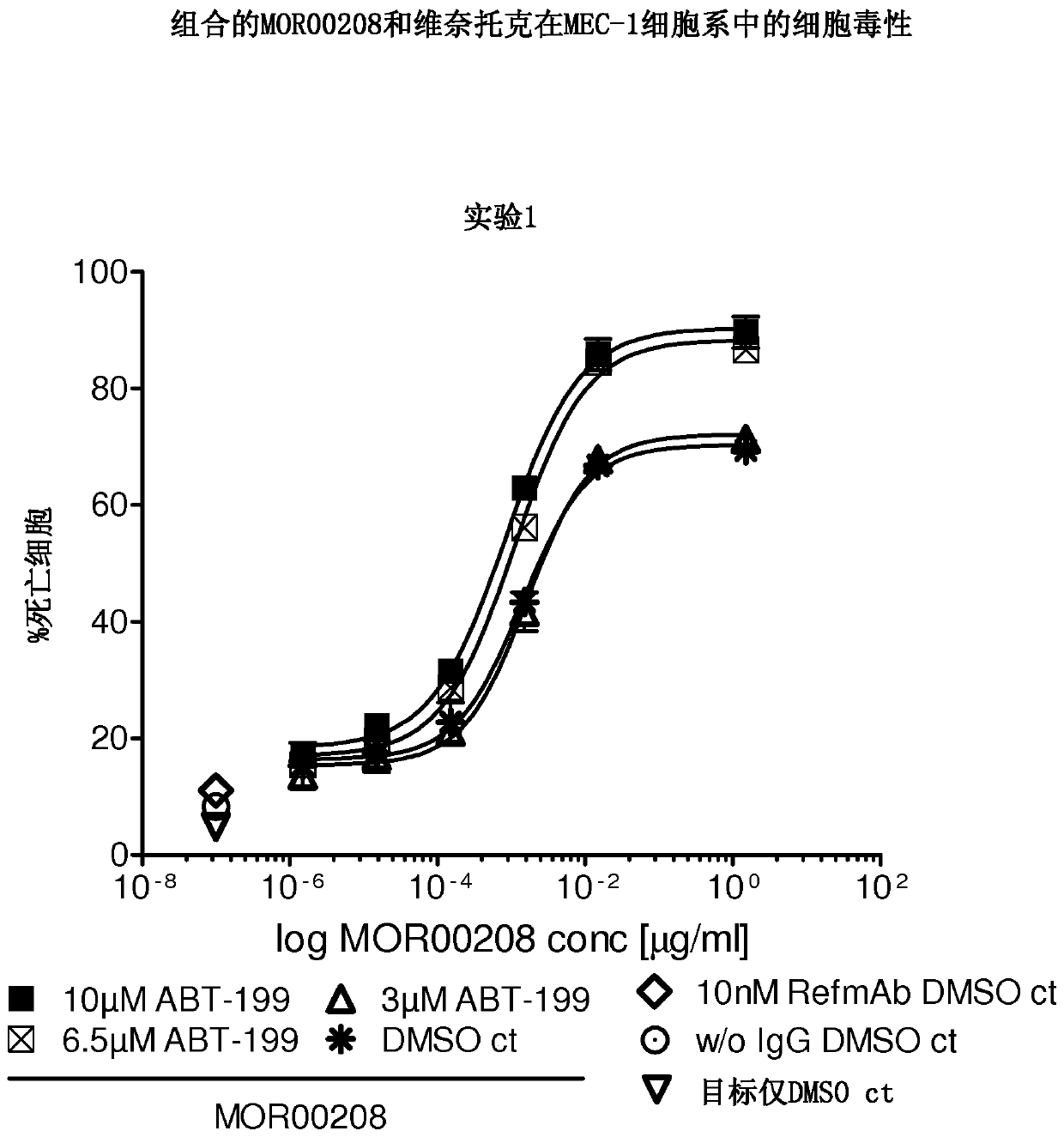
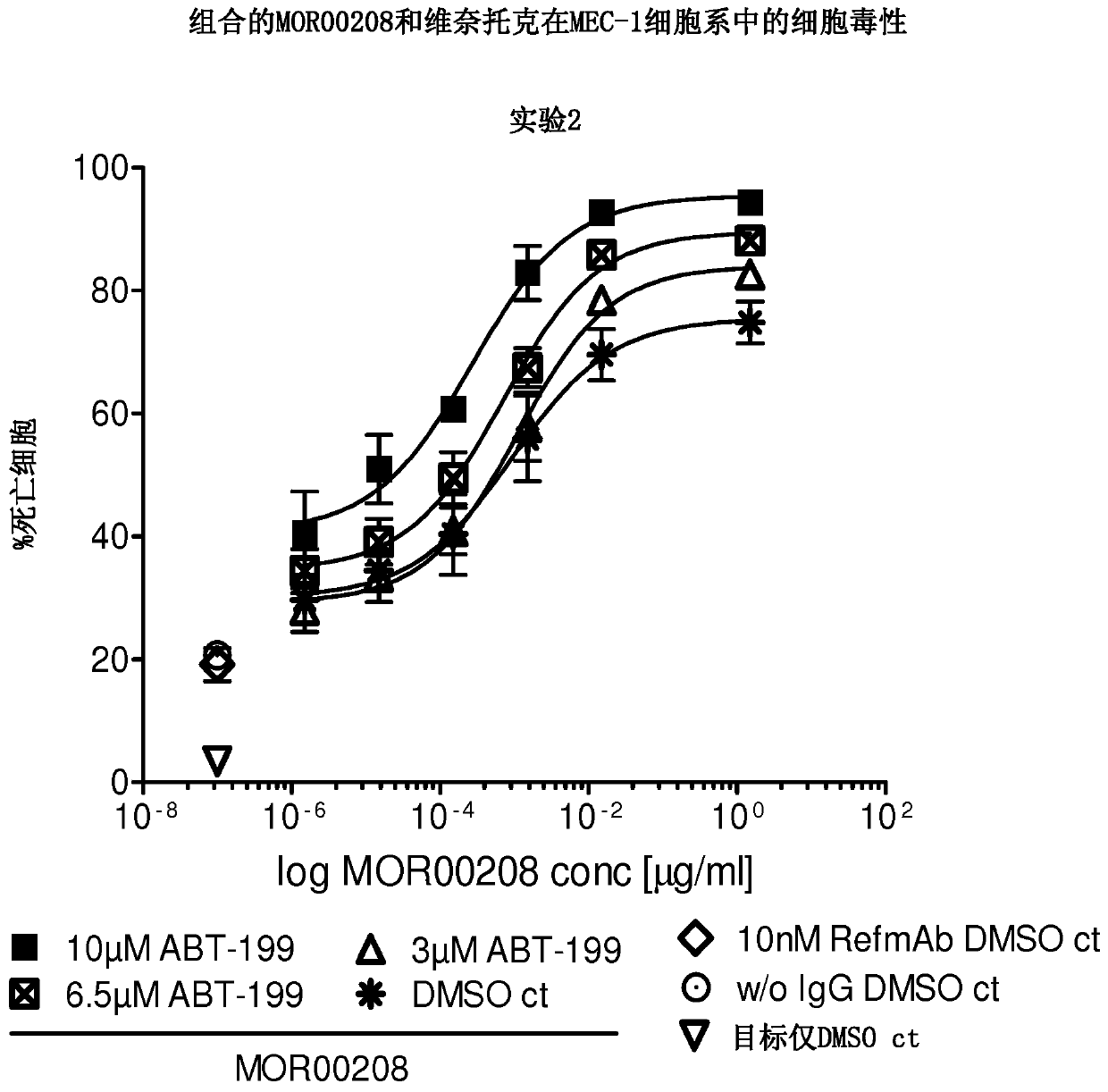
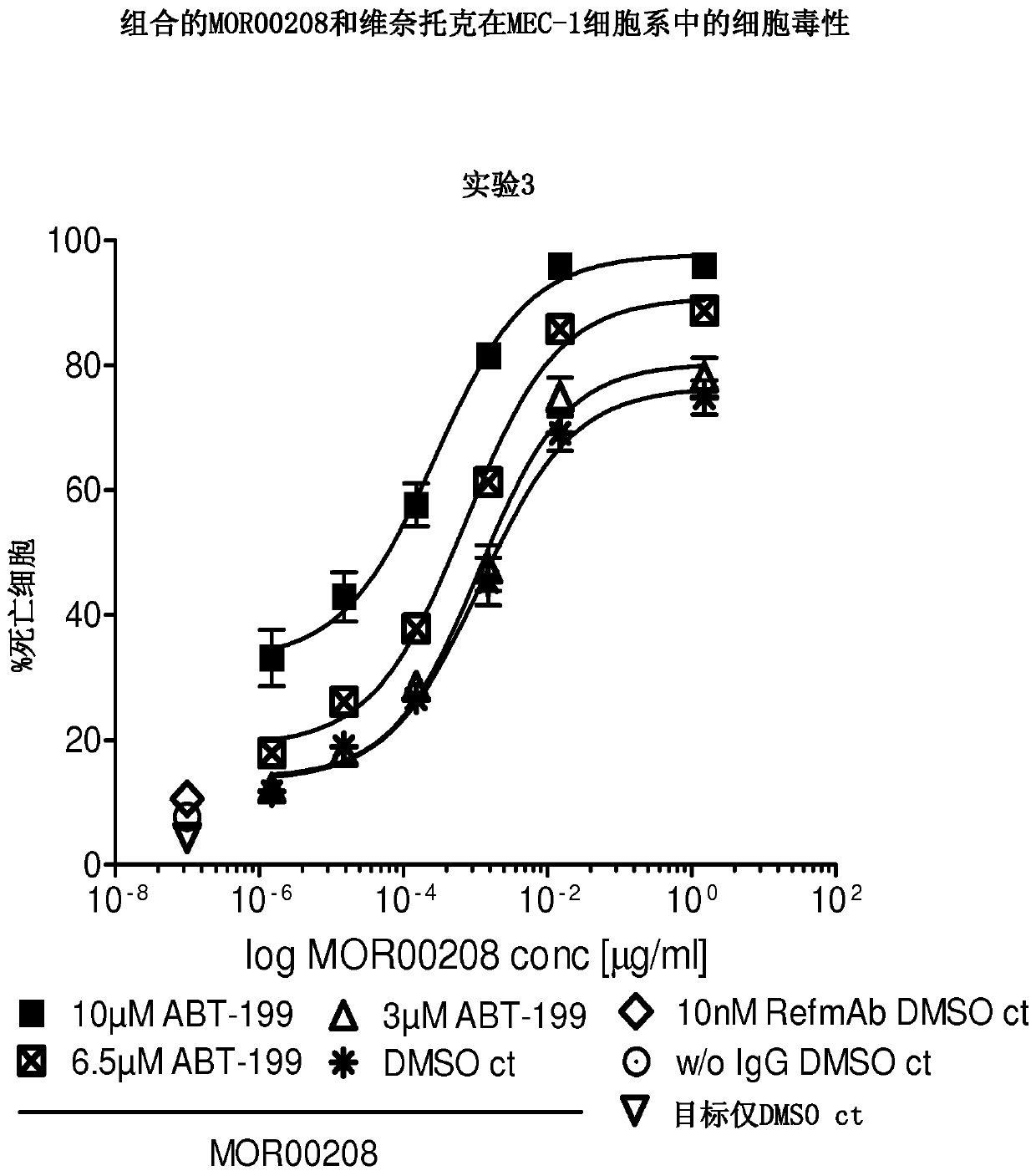
The disclosure describes a pharmaceutical combination of an anti-CD19 antibody and a purine analog for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia and / or acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
Methods for diagnosing bipolar and unipolar disorder
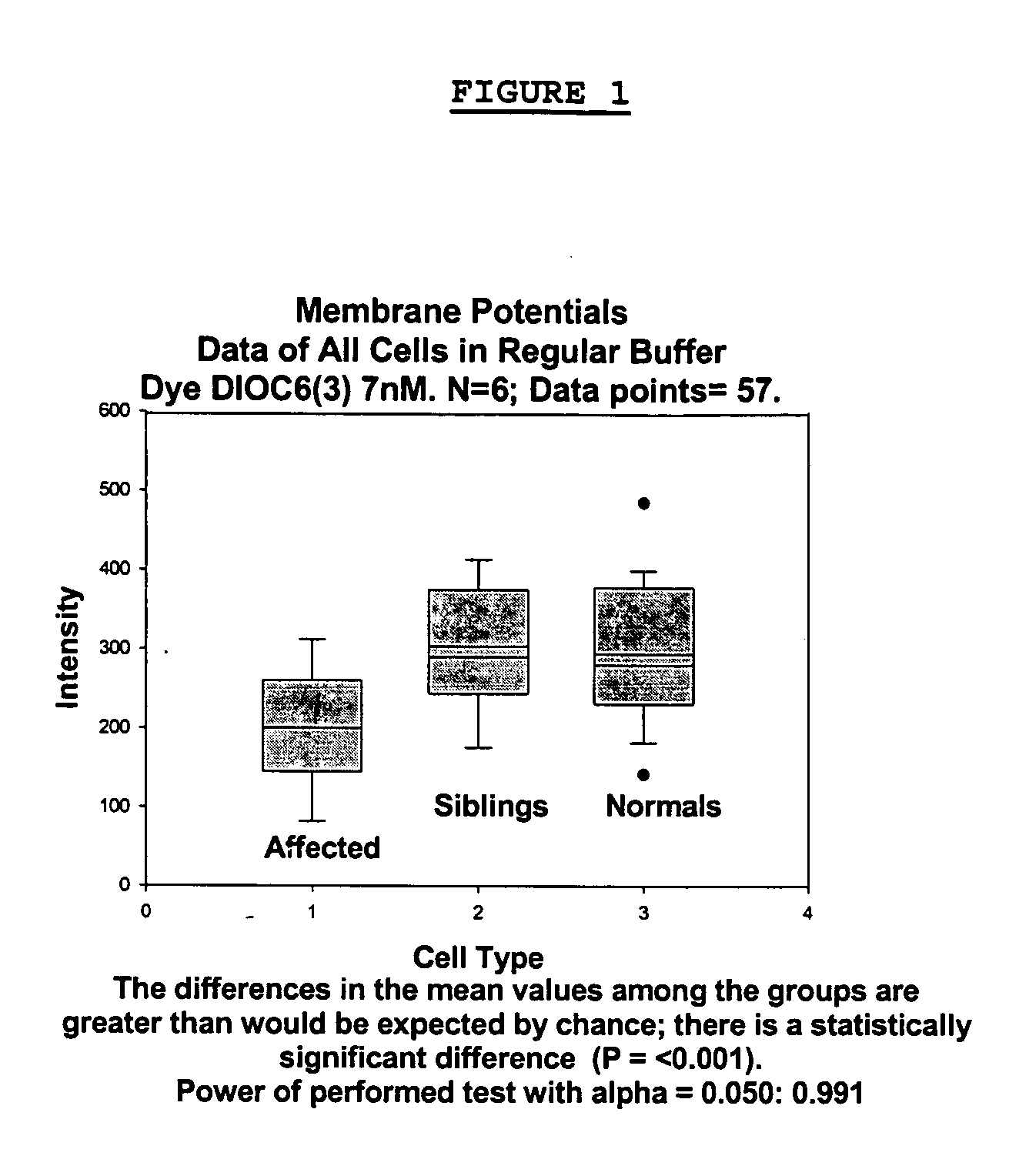
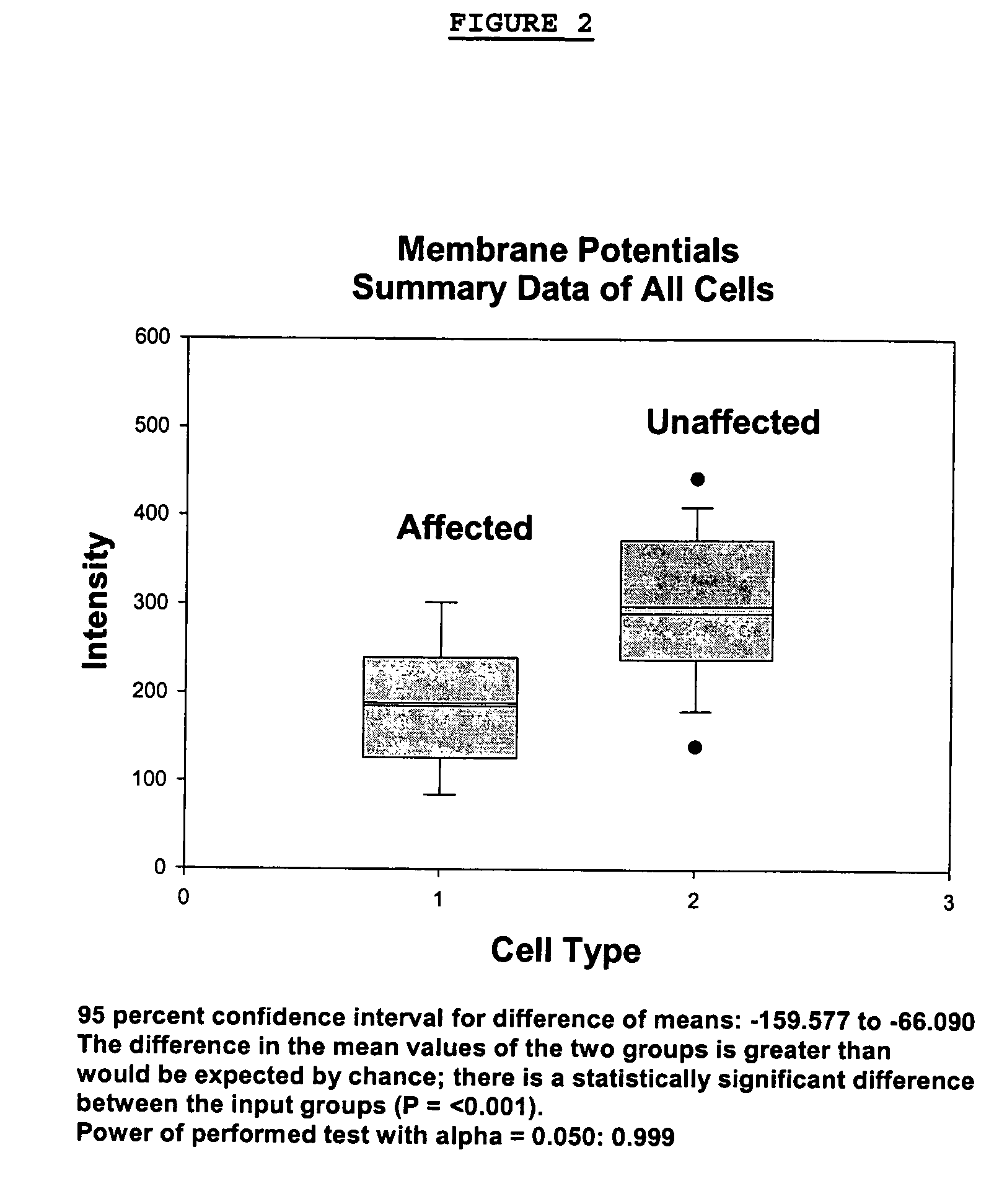
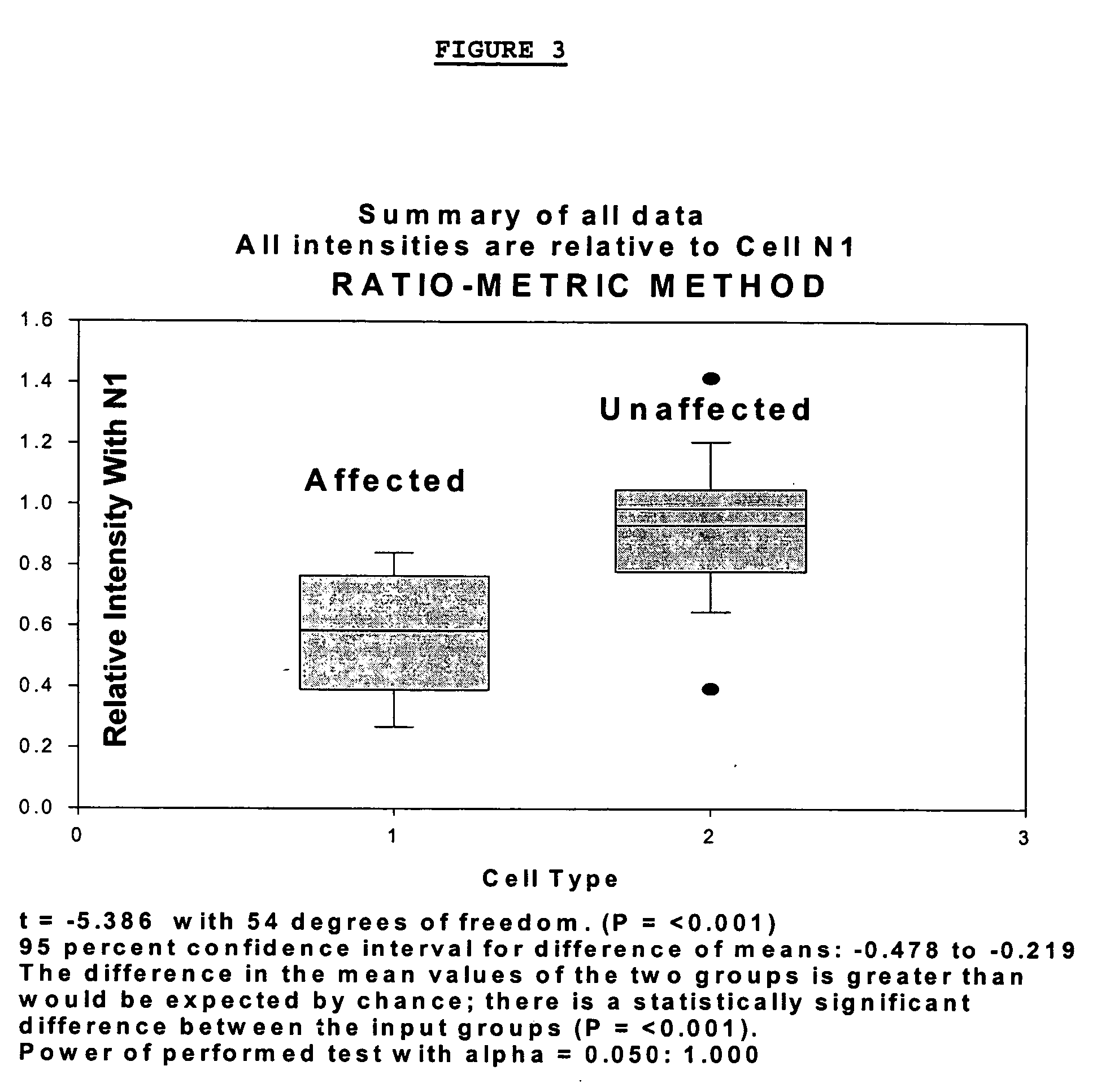
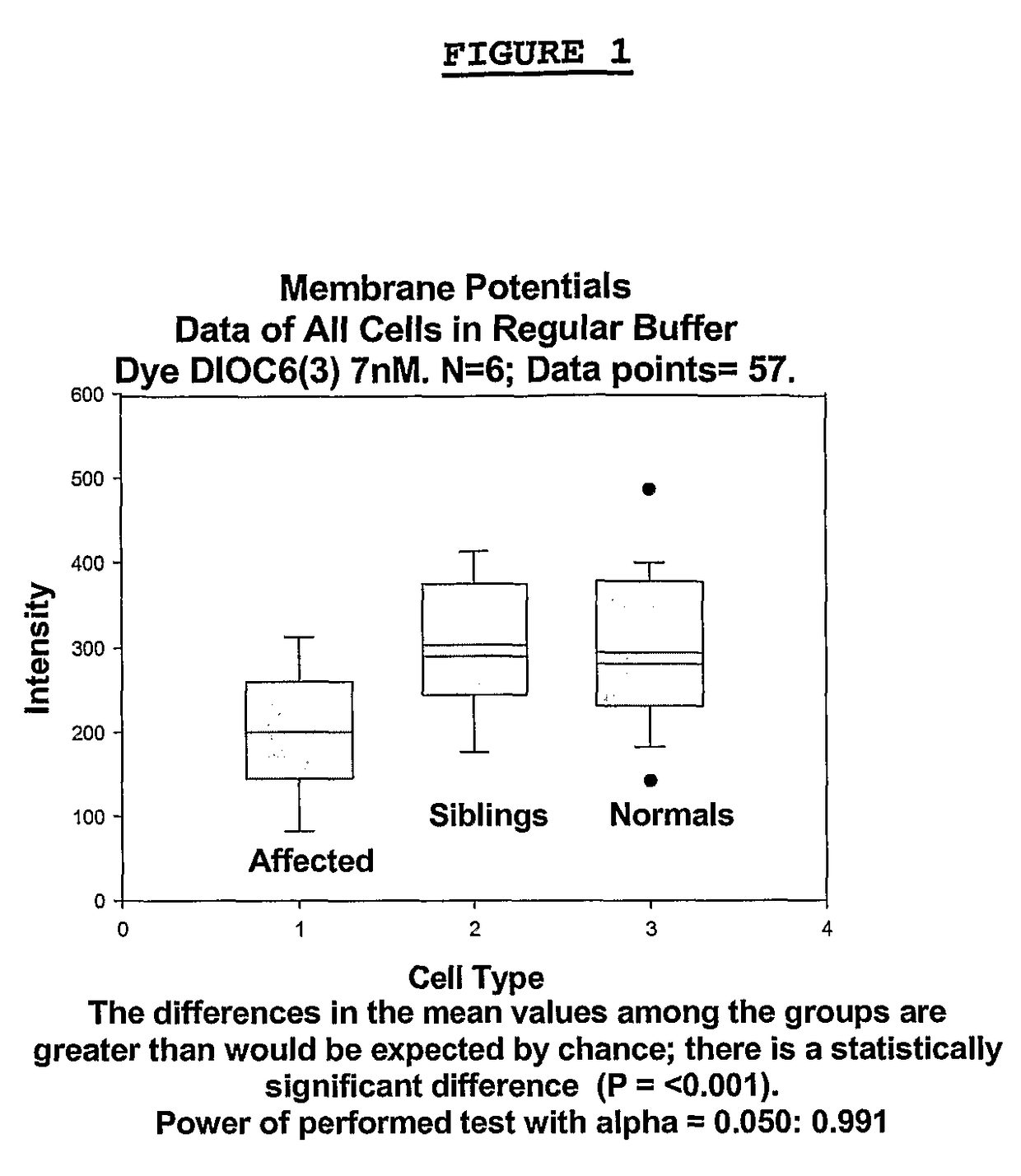
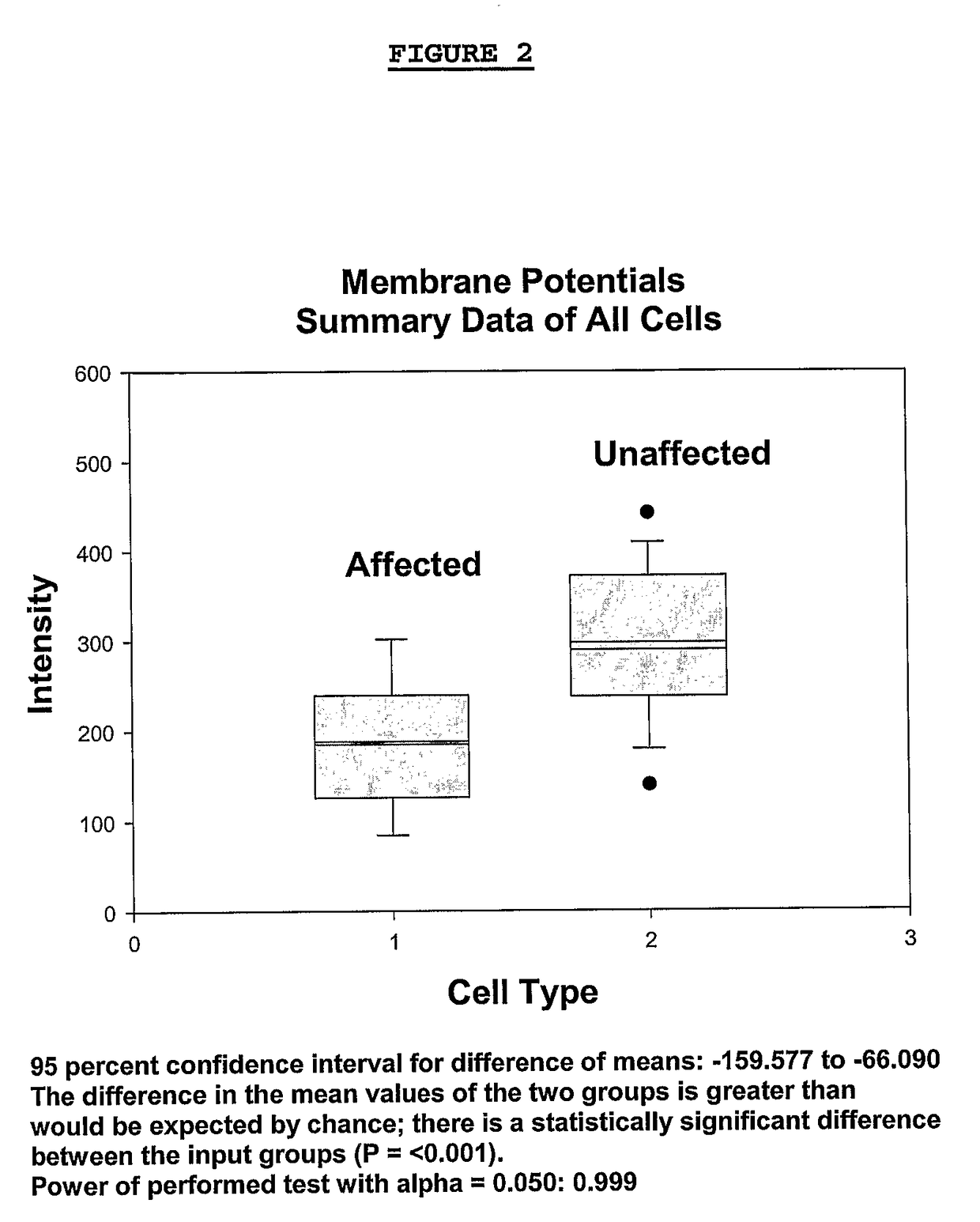
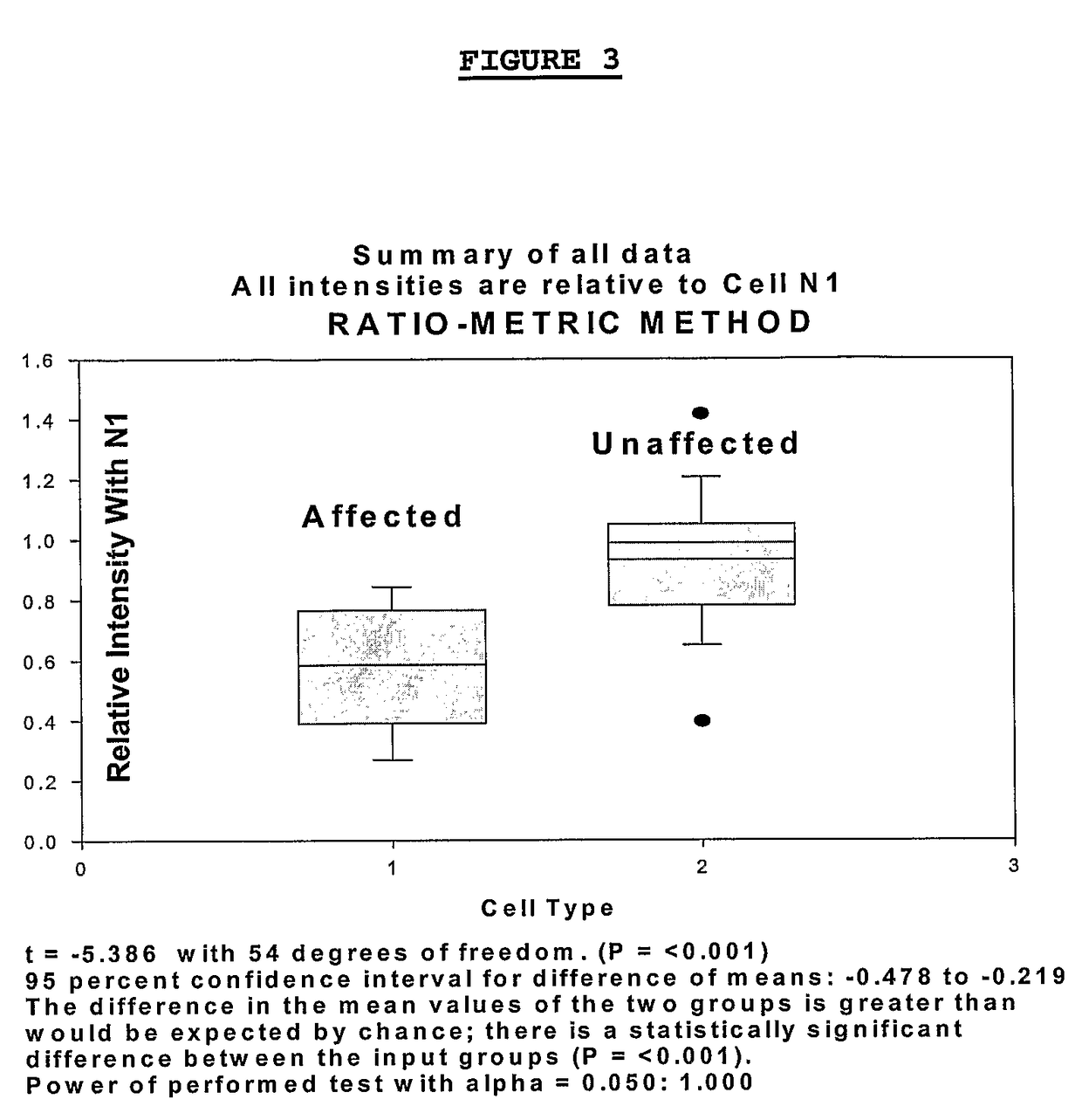
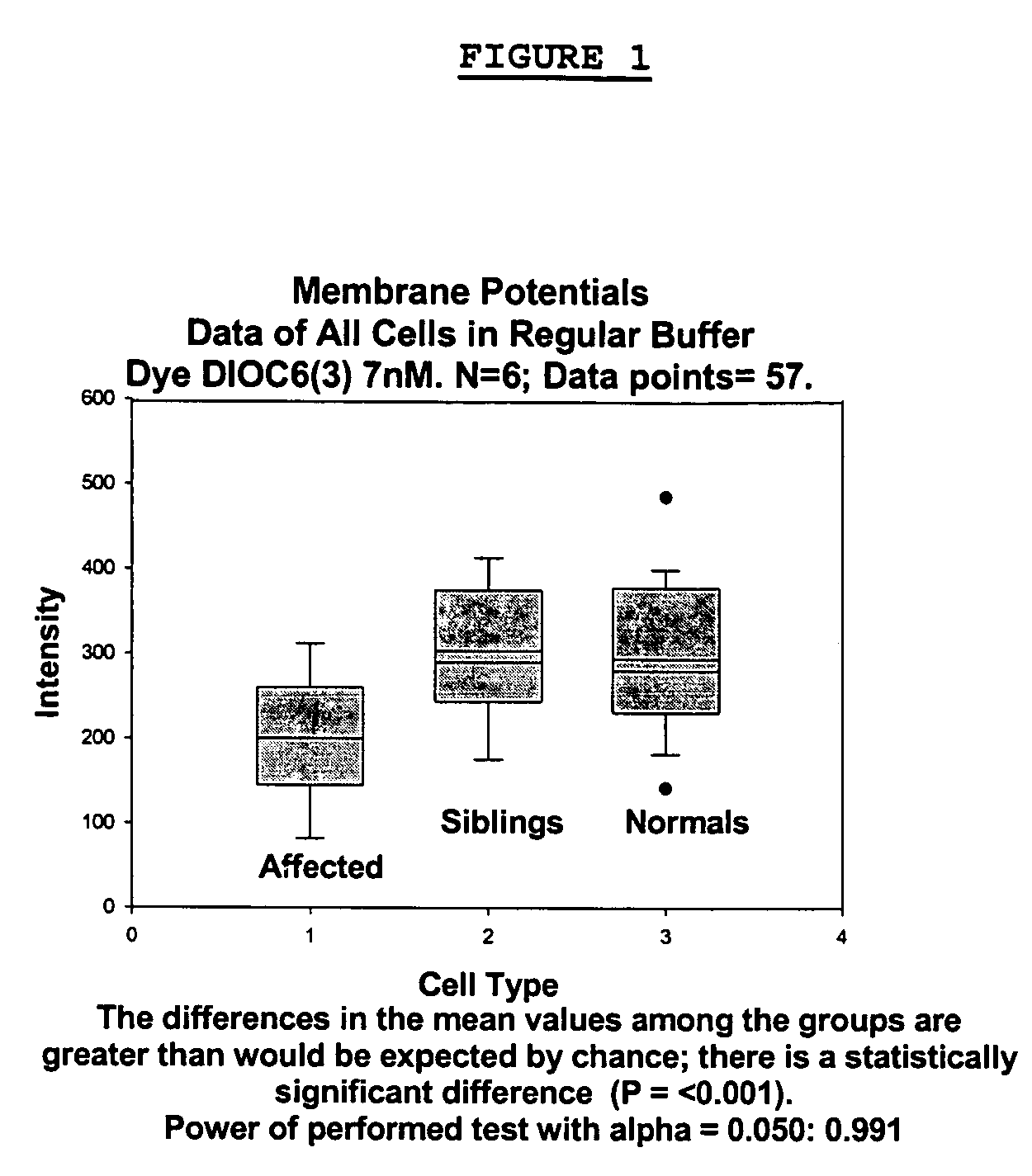
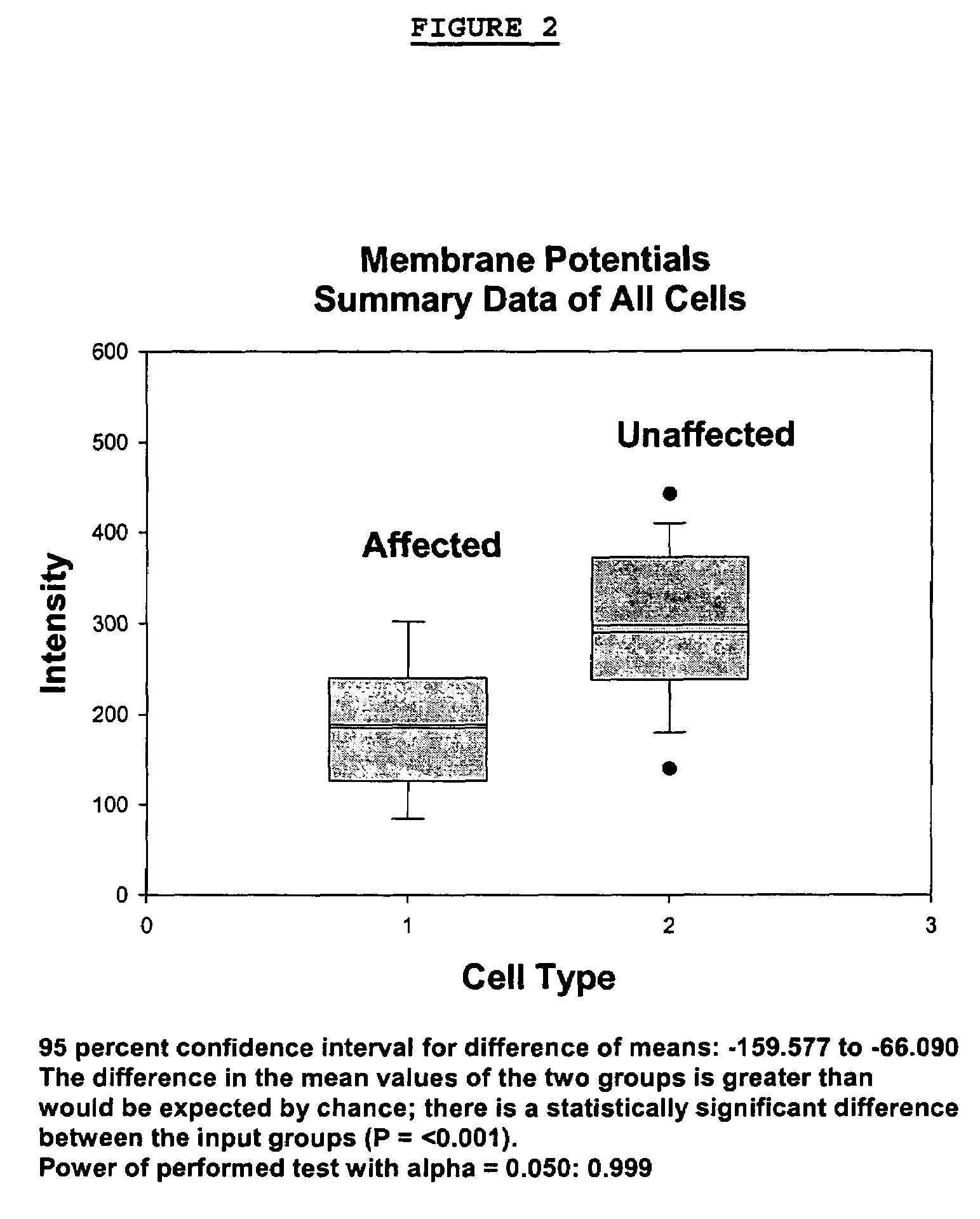
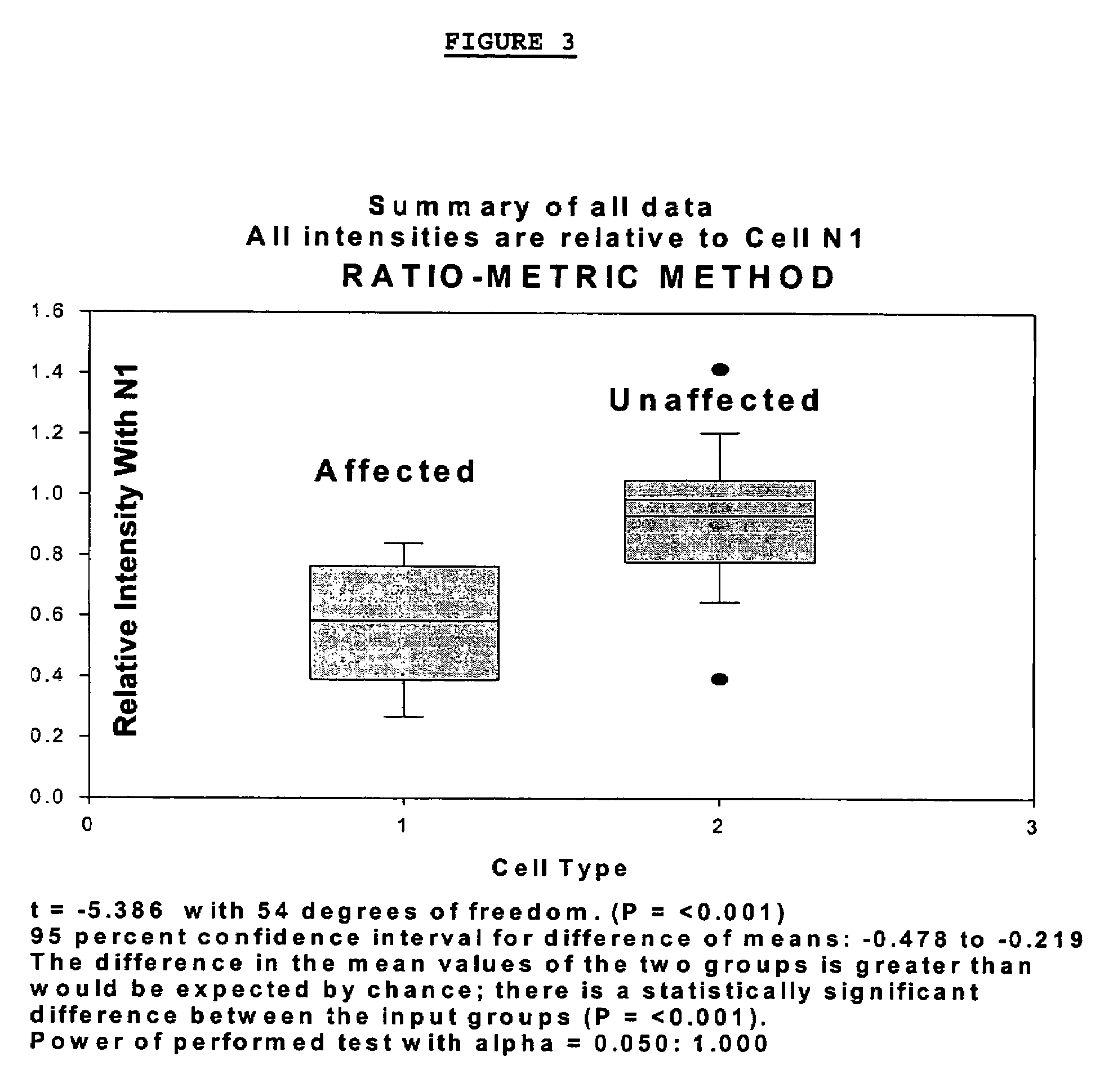
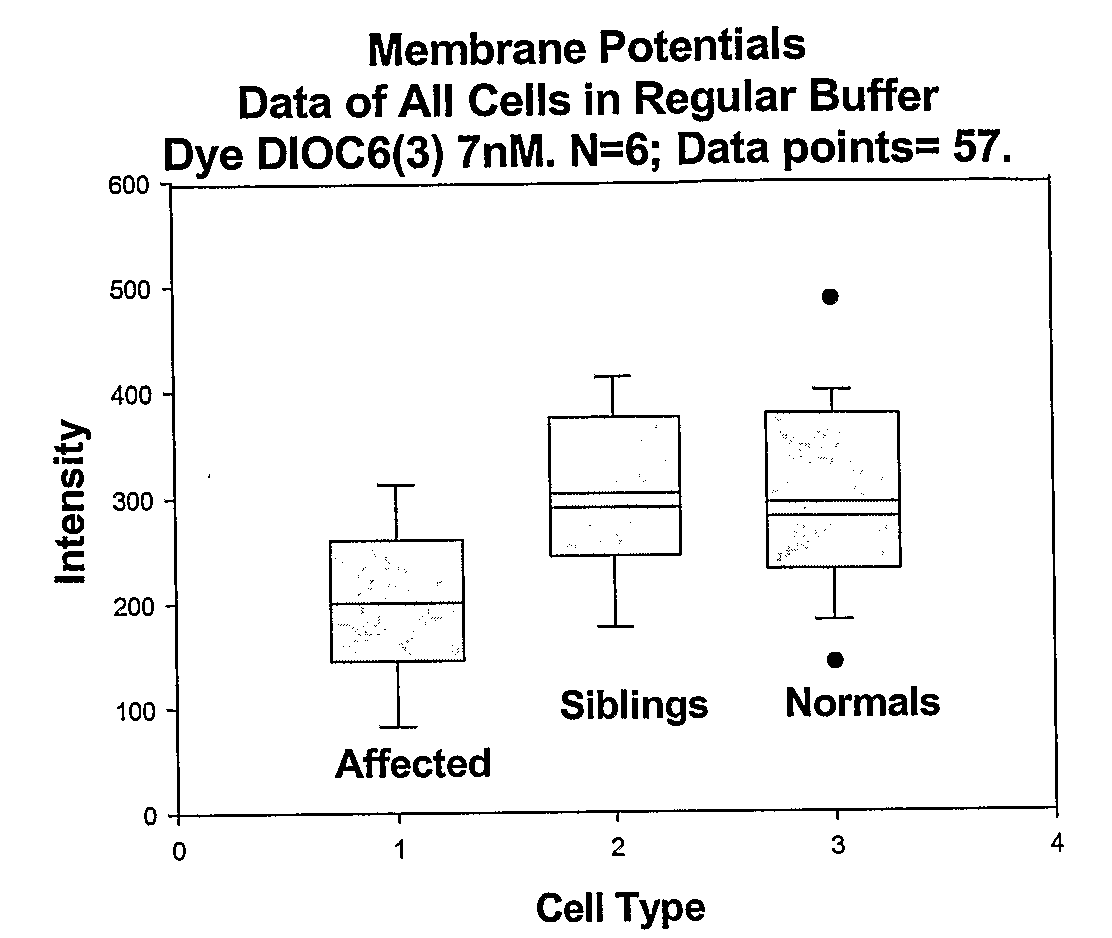
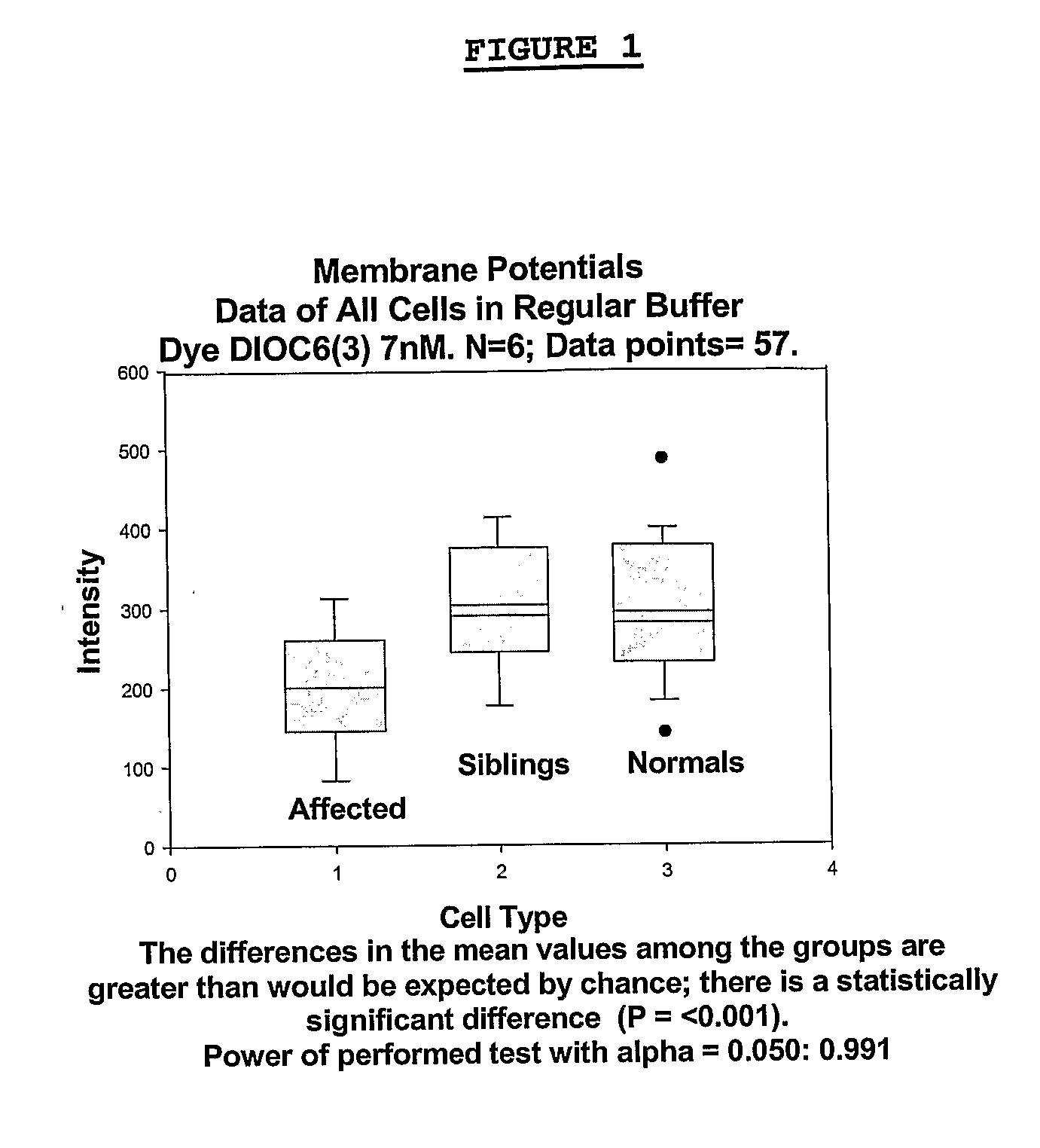
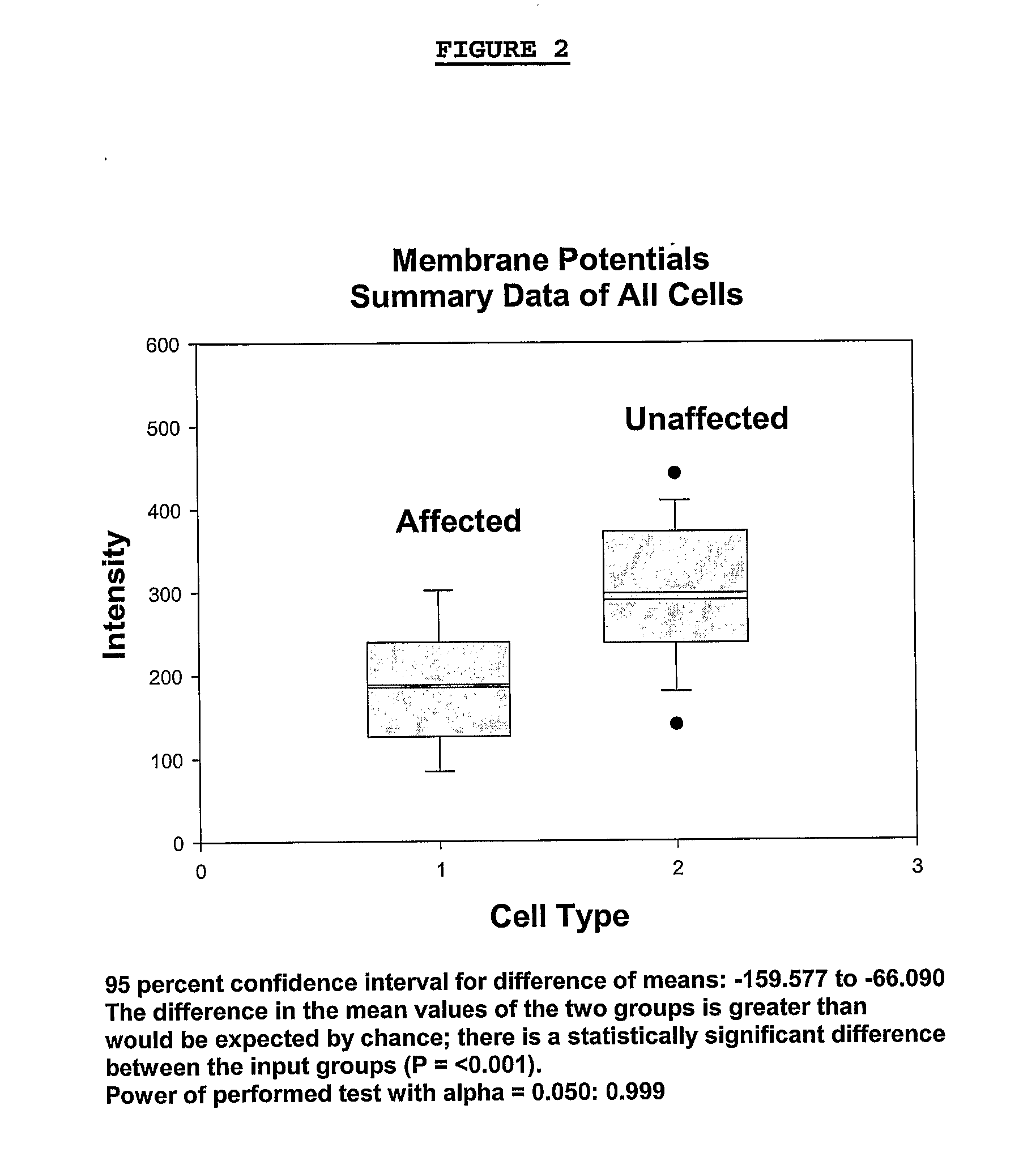
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for bipolar disorder. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from bipolar patients to those of people already known to have bipolar disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:FREE STATE DIAGNOSTICS
Mixture containing mix interferon-alpha hypotype
The invention discloses an IFN-Alpha subtype compound generated by lymphoblast, which is characterized in that the rarefied IFN-Alpha compound has higher specific activity, and can be used to cure cancer, virus and immunity diseases.
Owner:CYTOPHARM
Methods for diagnosing an attention-deficit/Hyperactivity disorder
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for bipolar I and bipolar II disorders. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from new patients to those of people already known to have bipolar I or bipolar II disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:PSYCHNOSTICS
Gene for identifying individuals with familial dysautonomia
InactiveUS7388093B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAutonomic bladder dysfunctionPhosphorylation
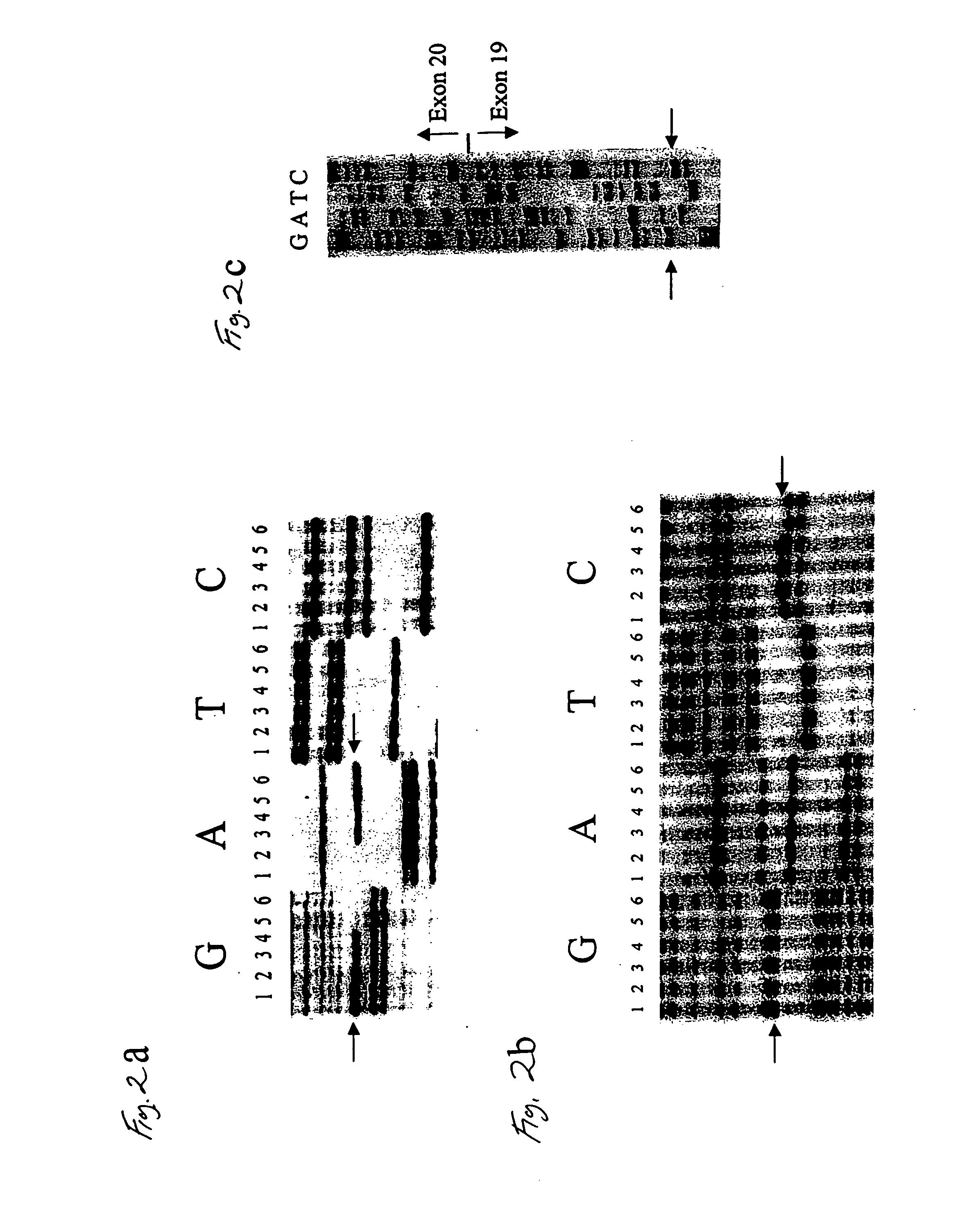
This invention relates to methods and compositions useful for detecting mutations which cause Familial Dysautonomia. Familial dysautonomia (FD; Riley-Day syndrome), an Ashkenazi Jewish disorder, is the best known and most frequent of a group of congenital sensory neuropathies and is characterized by widespread sensory and variable autonomic dysfunction. Previously, we mapped the FD gene, DYS, to a 0.5 cM region of chromosome 9q31 and showed that the ethnic bias is due to a founder effect, with >99.5% of disease alleles sharing a common ancestral haplotype. To investigate the molecular basis of FD, we sequenced the minimal candidate region and cloned and characterized its 5 genes. One of these, IKBKAP, harbors two mutations that can cause FD. The major haplotype mutation is located in the donor splice site of intron 20. This mutation can result in skipping of exon 20 in the mRNA from FD patients, although they continue to express varying levels of wild-type message in a tissue-specific manner. RNA isolated from patient lymphoblasts is primarily wild-type, whereas only the deleted message is seen in RNA isolated from brain. The mutation associated with the minor haplotype in four patients is a missense (R696P) mutation in exon 19 that is predicted to disrupt a potential phosphorylation site. Our findings indicate that almost all cases of FD are caused by an unusual splice defect that displays tissue-specific expression; and they also provide the basis for rapid carrier screening in the Ashkenazi Jewish population.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Protein which induces interferon-gamma production by immunocompetent cell
A protein of human cell origin, which induces the IFN-gamma production by immunocompetent cells and has the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 near or at the N-terminus. It can be produced from human cells such as lymphoblasts, lymphocytes, monoblasts, monocytes, myeloblasts, myelocytes, granulocytes and macrophages, and used for preventing and / or treating IFN-gamma susceptive diseases.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
Methods for diagnosing a bipolar disorder and unipolar disorder
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for a bipolar disorder. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from bipolar patients to those of people already known to have a bipolar disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:FREE STATE DIAGNOSTICS
Methods For Diagnosing Bipolar Disorders and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
InactiveUS20080160554A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsBipolar mood disorderLymphoblast
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for bipolar I and bipolar II disorders. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from new patients to those of people already known to have bipolar I or bipolar II disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:PSYCHNOSTICS
Artificial intelligence identification method for peripheral hemolymph micronucleus cell image
PendingCN111458269AHigh speedImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionLymphoblast
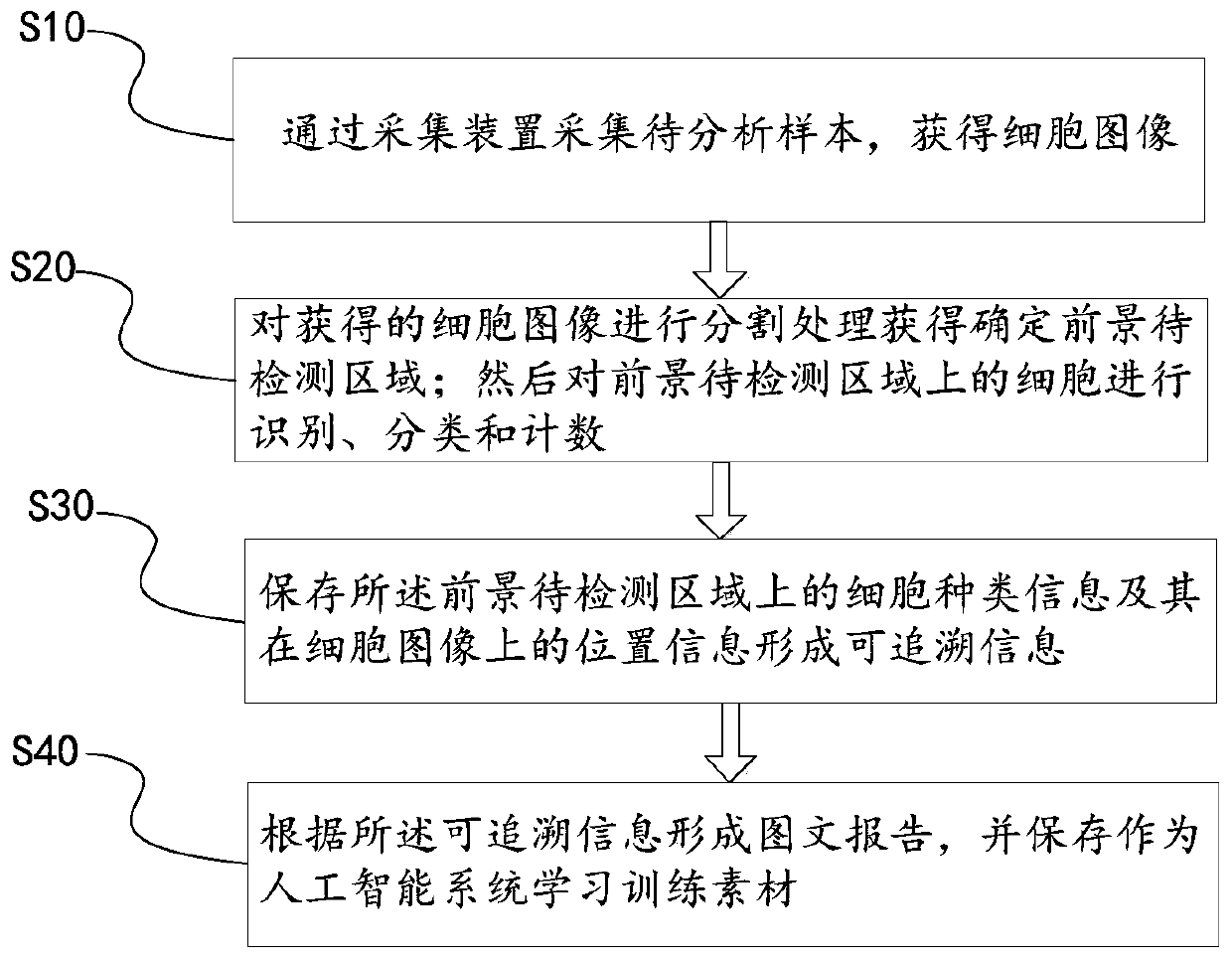
The invention provides an artificial intelligence identification method for a peripheral hemolymph micronucleus cell image, and the method comprises the steps: collecting a to-be-analyzed sample through a collection device, and obtaining a cell image; carrying out segmentation processing on the obtained cell image to obtain a foreground to-be-detected area; identifying, classifying and counting the cells on the foreground to-be-detected area; storing the cell type information on the foreground to-be-detected area and the position information of the foreground to-be-detected area on the cell image to form traceable information; and forming an image-text report according to the traceable information, and storing the image-text report as an artificial intelligence system learning training material. According to the artificial intelligence identification method for the peripheral hemolymph micronucleus cell image provided by the invention, automatic identification and classification of specific images of lymphoblasts, micronucleus cells and nude nuclei of peripheral blood can be realized. Compared with an existing microscope artificial microscopic examination method, the statistical accuracy is higher, and the detection speed is remarkably increased.
Owner:厦门汉舒捷医疗科技有限公司
Method of separating multipotent adult progenitor cells from umbilical cord blood
InactiveCN1920010AReduce the impactEfficient separationBlood/immune system cellsCell phenotypeProgenitor
The invention discloses the method for separating pluripotent ancestral cell from umbilical cord blood, comprising the following steps: using lymphoblast to separate umbilical cord blood monocyte, culturing for 3 days at culture medium with 8-15% bovine serum, throwing away cell which is not sticked on wall, replacing the culture medium with 2-5% bovine serum, bFGF, EGF, PDGF-BB, MCDB-201, ascorbic acid, anaflogistico and ITS addition agent, culturing, passage purifying, and separating. The method has the advantages of high separation rate. The cell phenotype, cell periodic time and evoked differentiation ability are the same.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
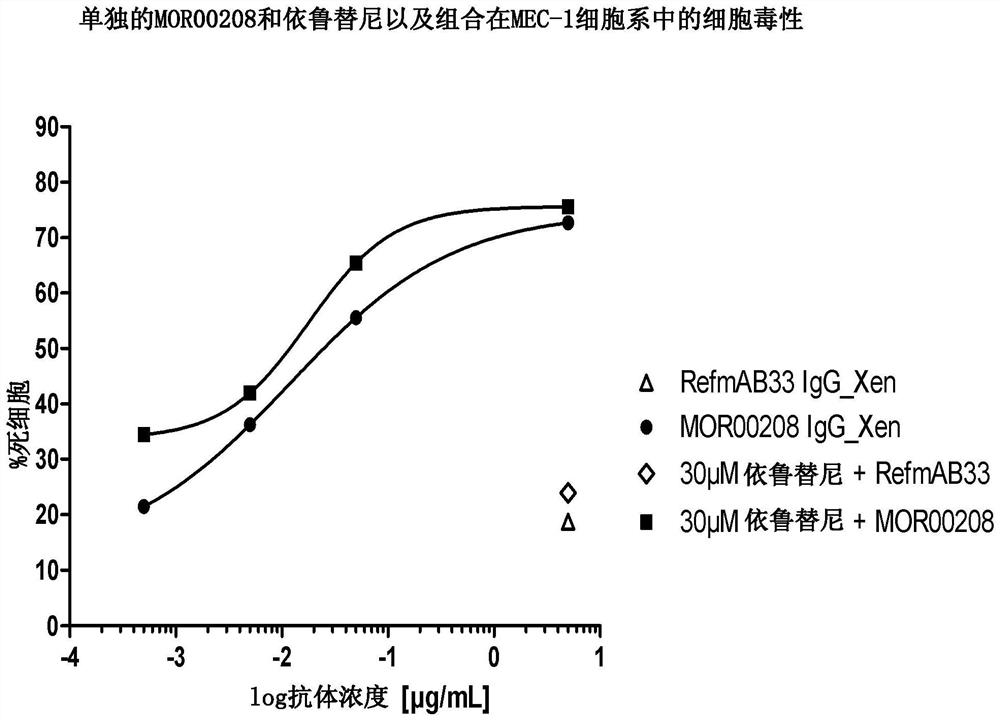
Combination Of An Anti-Cd19 Antibody And A Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor And Uses Thereof
ActiveCN107660151AOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesLymphoblast
The present disclosure describes a pharmaceutical combination of an anti-CD19 antibody and a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia and / or acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
Heterotypic lymphocyte typing method based on YOLOv5 and microscopic hyperspectral image
ActiveCN114300099ASmall amount of calculationImprove accuracyGenetic modelsMedical automated diagnosisColor imageLymphoblast
The invention provides a heterotypic lymphocyte typing method based on YOLOv5 and a microscopic hyperspectral image. The heterotypic lymphocyte typing method is improved on the basis of a standard YOLOv5 network structure. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a lymphocyte pseudo-color image by using gray images corresponding to 461, 548 and 698 nm, and finishing automatic positioning of lymphocytes by facing synthesized image information through an improved YOLOv5 network; using the relative position information of a lymphocyte prediction frame in an improved YOLOv5 network identification result to obtain an average spectrum value, using the average spectrum value as input, and using a one-dimensional convolutional neural network to realize typing identification of the heterotypic lymphocytes; and constructing the heterotypic lymphocyte typing model. By improving the standard YOLOv5 network structure, the network calculation amount is reduced, the accuracy of small target positioning is improved, the idea of first positioning and then recognition is put forward, the detection efficiency of lymphocytes is improved, and typing recognition of heterotypic lymphocytes is achieved.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Method for separating Pig-a gene mutant cells from cells cultured in vitro
PendingCN110885778AImprove separation efficiencyEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsBiological preparation purgeLymphocytic cellImmunofluorescence
The invention discloses a method for separating Pig-a gene mutant cells from cells cultured in vitro and application of the Pig-a gene mutant cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing an anti-GPI anchorage protein antibody marked by an immunofluorescent dye, magnetic beads resisting the immunofluorescent dye and the cells; and (2) separating cells marked by the magnetic beads from cells not marked by the magnetic beads, wherein the cells marked by the magnetic beads being Pig-a gene mutation negative cells, and the cells not marked by the magnetic beads being Pig-a gene mutation positive cells. The method provided by the invention has higher separation efficiency for removing cells, such as the Pig-a positive cells pre-stored in human lymphoblastic TK6 cells, can separate10 million cells within 15 minutes, and is simple to operate and low in cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOSTAR BIO TECH
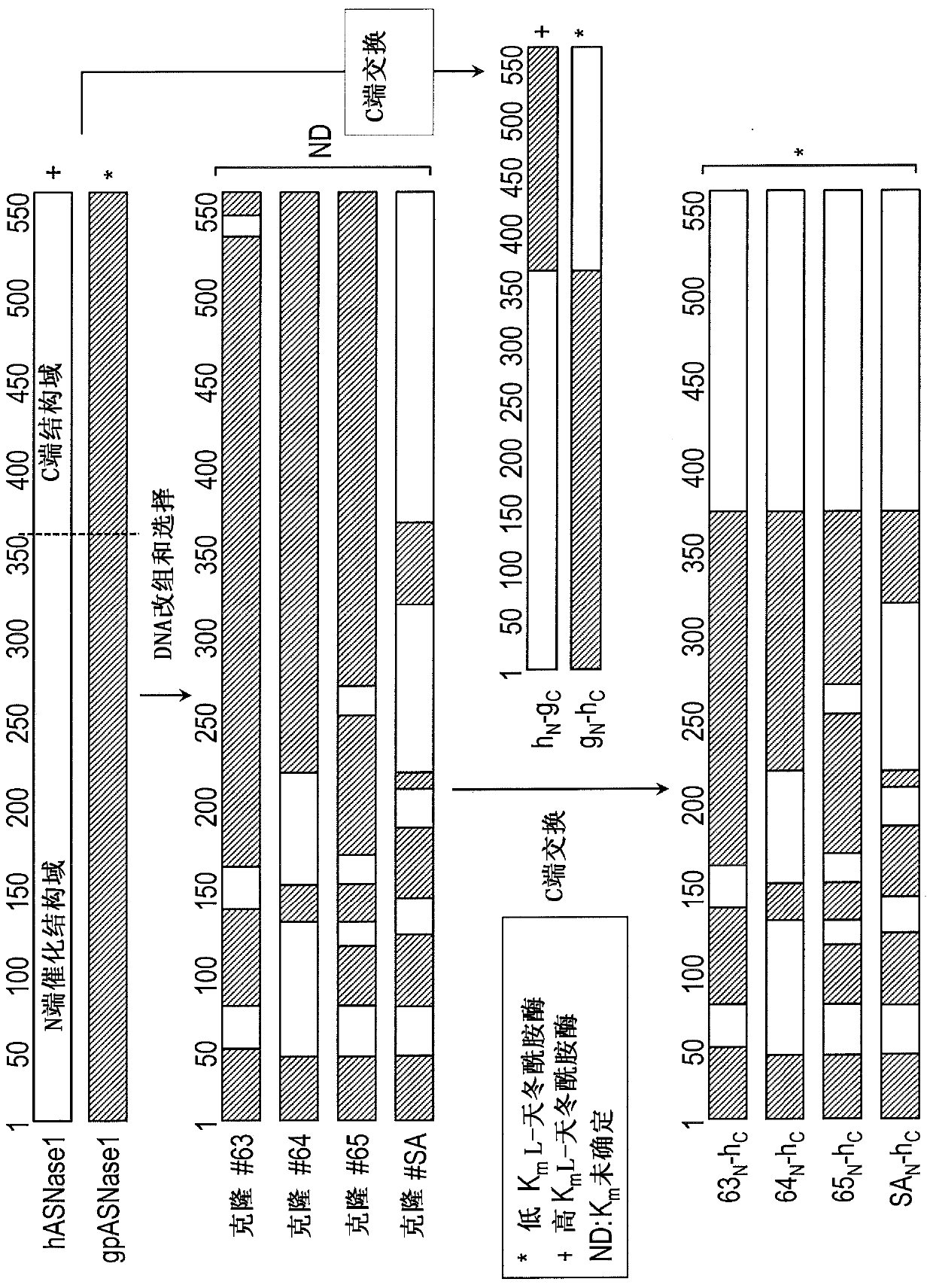
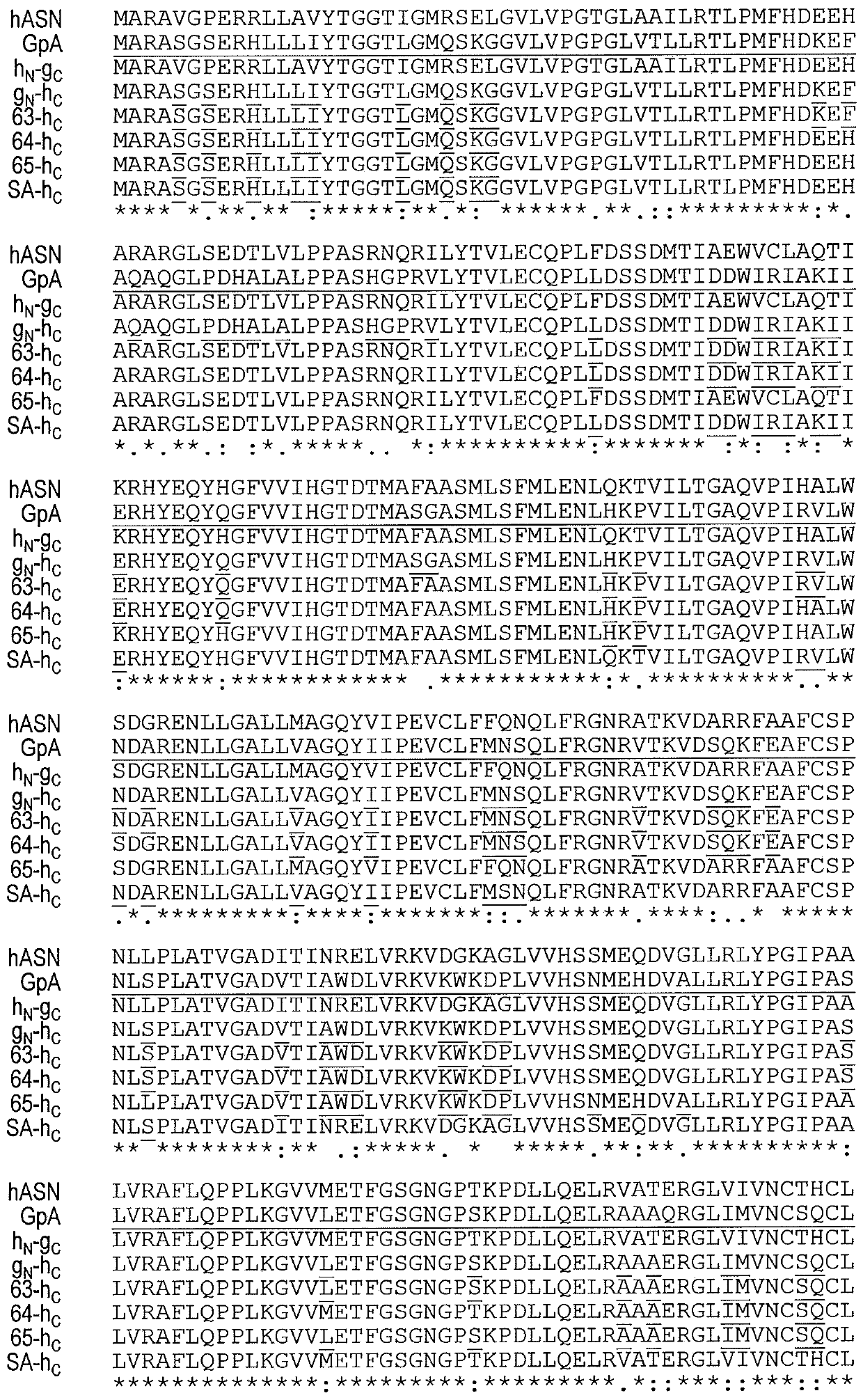
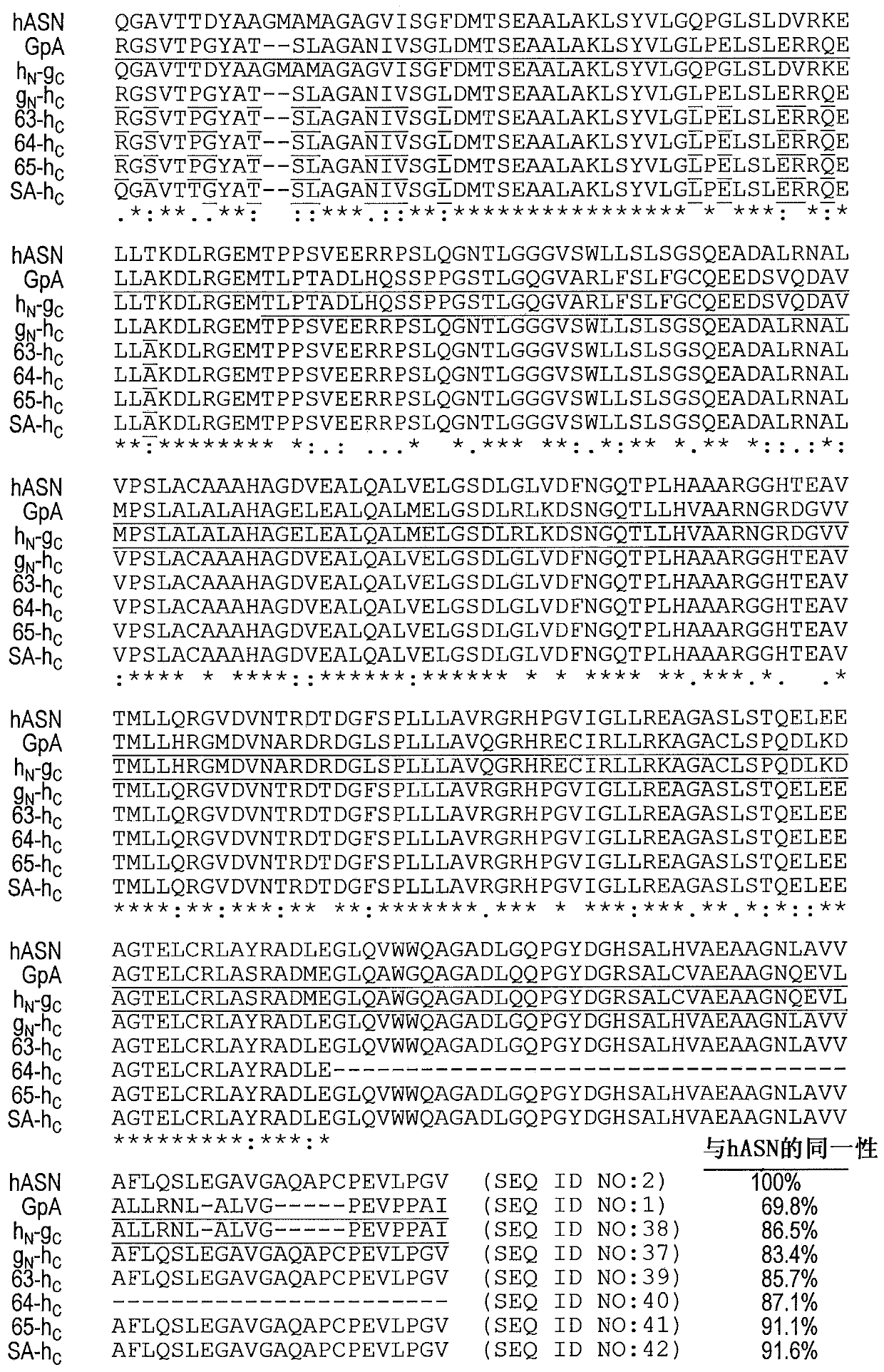
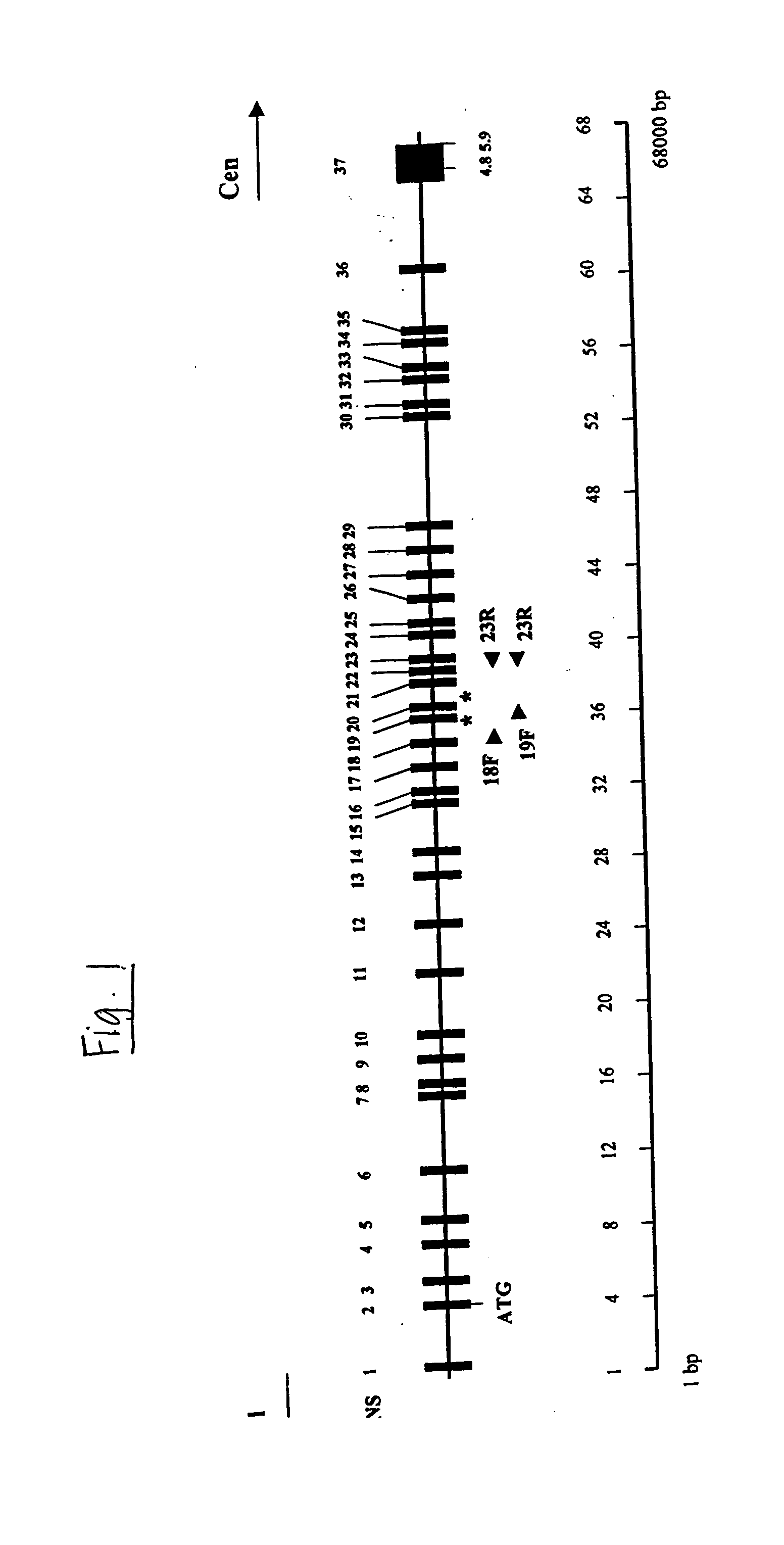
Truncated guinea pig l-asparaginase variants and methods of use
Variant guinea pig L-asparaginases which are truncated and humanized are described as are fusion proteins containing the L-asparaginase and use of the L- asparaginases in the treatment of cancers suchas acute lymphoblastic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Human peripheral blood lymphocyte culture medium
ActiveCN110669730AThe cultivation effect is stablePromote proliferationCulture processBlood/immune system cellsSodium bicarbonateLymphoblast
The invention belongs to the technical field of cell culture mediums, and discloses a human peripheral blood lymphocyte culture medium. The human peripheral blood lymphocyte culture medium mainly comprises the following components: RPMI 1640 culture medium powder, sodium bicarbonate, HEPES free acid, gentamycin sulphate, heparin sodium, mercaptoethanol, glutamine, calcium ions, iron ions, titaniumions and phytohemagglutinin. The human peripheral blood lymphocyte culture medium can contain or be free of serum or protein components, and the culture medium mainly uses certain specific metal ionsto promote cell proliferation. According to the culture medium, the composition is clear, the performance is stable, the cost is low, proliferation and division of lymphoblasts in human whole blood can be effectively promoted, and the high lymphocyte transformation rate and a high lymphocyte division index are achieved.
Owner:HANGZHOU GENE META MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
Method of separating multipotent adult progenitor cells from umbilical cord blood
InactiveCN100453640CEfficient separationObvious separation success rate advantageBlood/immune system cellsCell phenotypeProgenitor
The invention discloses the method for separating pluripotent ancestral cell from umbilical cord blood, comprising the following steps: using lymphoblast to separate umbilical cord blood monocyte, culturing for 3 days at culture medium with 8-15% bovine serum, throwing away cell which is not sticked on wall, replacing the culture medium with 2-5% bovine serum, bFGF, EGF, PDGF-BB, MCDB-201, ascorbic acid, anaflogistico and ITS addition agent, culturing, passage purifying, and separating. The method has the advantages of high separation rate. The cell phenotype, cell periodic time and evoked differentiation ability are the same.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Gene for identifying individuals with familial dysautonomia
InactiveUS20050204409A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAutonomic bladder dysfunctionProgenitor
This invention relates to methods and compositions useful for detecting mutations which cause Familial Dysautonomia. Familial dysautonomia (FD; Riley-Day syndrome), an Ashkenazi Jewish disorder, is the best known and most frequent of a group of congenital sensory neuropathies and is characterized by widespread sensory and variable autonomic dysfunction. Previously, we mapped the FD gene, DYS, to a 0.5 cM region of chromosome 9q31 and showed that the ethnic bias is due to a founder effect, with >99.5% of disease alleles sharing a common ancestral haplotype. To investigate the molecular basis of FD, we sequenced the minimal candidate region and cloned and characterized its 5 genes. One of these, IKBKAP, harbors two mutations that can cause FD. The major haplotype mutation is located in the donor splice site of intron 20. This mutation can result in skipping of exon 20 in the mRNA from FD patients, although they continue to express varying levels of wild-type message in a tissue-specific manner. RNA isolated from patient lymphoblasts is primarily wild-type, whereas only the deleted message is seen in RNA isolated from brain. The mutation associated with the minor haplotype in four patients is a missense (R696P) mutation in exon 19 that is predicted to disrupt a potential phosphorylation site. Our findings indicate that almost all cases of FD are caused by an unusual splice defect that displays tissue-specific expression; and they also provide the basis for rapid carrier screening in the Ashkenazi Jewish population.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Traditional Chinese medicinal preparation for treating malignant tumors
InactiveCN105213967ANo discomfortEasy medicationAmphibian material medical ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsDiseaseCinnabar
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal preparation for treating malignant tumors. The traditional Chinese medicinal preparation is prepared by combing such traditional Chinese medicines as rhizoma sparganii, curcuma zedoary, fritillaria cirrhosa, edible tulip, trametes robiniphila murr, fructus camptothecae acuminatae, ganoderma lucidum spore powder, saffron crocus, cinnabar, semen strychni, indigo naturalis, rheum officinale, dragon's blood, oldenlandia diffusa, natural calculus bovis, musk, antelope horn, scorpion, centipede, bombyx batryticatus, geckos, pangolin, blood amber, tortoise-plastron glue, colla cornus cervi and the like. On the basis of a synergistic effect generated from the combined medicinal materials which combine tonification and purgation and supplement each other, the traditional Chinese medicinal preparation is not only relatively strong in effect of inhibiting tumor cells, but also capable of better improving immunity of patients, promoting transformation of lymphoblast, enhancing functions of a reticuloendothelial system, promoting the generation of immune globulins and improving disease resistance of the patients. Due to the technical scheme, the traditional Chinese medicinal preparation, compared with the prior art, has the advantages of being simple to take, low in toxic and side effects, unique in curative effect and the like, and the traditional Chinese medicinal preparation is capable of treating both symptoms and root causes.
Owner:郑文修
Combination of anti cd19 antibody with a bcl-2 inhibitor and uses thereof
PendingCN109890418AOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLymphocytic cellAntiendomysial antibodies
The present disclosure describes a pharmaceutical combination of an anti-CD19 antibody and a BCL-2 inhibitor for the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia and / or acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
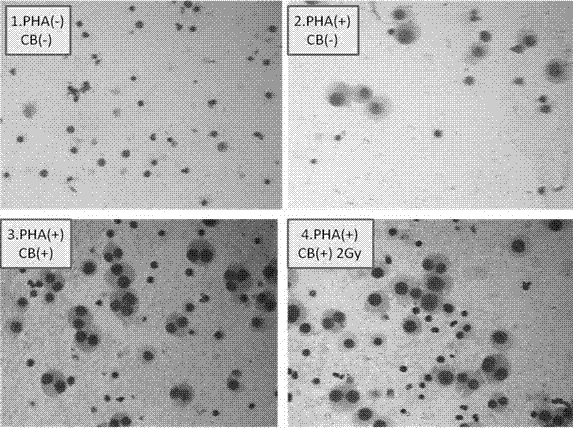
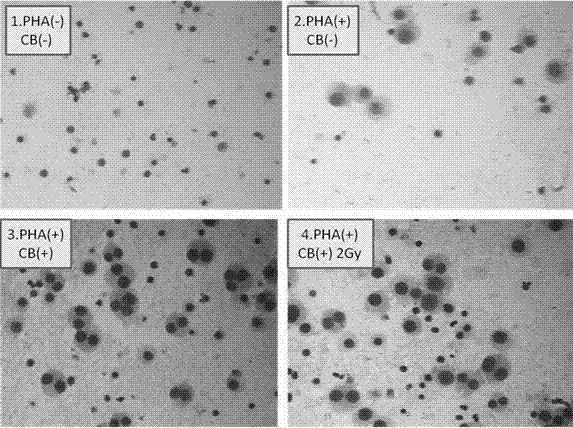
Method for detecting lymphocyte transformation by utilizing medicament cytochalasins B
InactiveCN102505039AReduce experiment costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphocyte transformationLymphoblast
The invention relates to the technical field of medical detection, and particularly relates to a method for detecting lymphocyte transformation by utilizing a medicament cytochalasins B. According to the invention, the principle that peripheral blood lymphocytes can be transformed into lymphoblasts which are divisive after being stimulated by phytohemagglutinin in vitro and the principle that the cytochalasins B can retard cell division but can not retard cell nucleus division are utilized, 2 Gyg ray irradiation is carried out on the peripheral blood of a human body for further realizing immunodepression, and PHA (phytohemagglutinin) stimulation is carried out and the cytochalasins B is added for treatment, so that the difference between the dikaryon rate of radiated lymphocytes and the dikayron rate of non-irradiated lymphocytes is detected. The result shows that transformed lymphocytes can form dikaryocytes, the dikaryon rate of the radiated lymphocytes can be obviously reduced, the immunity of radiated T lymphocytes can be obviously inhibited, and the dikaryon rate can better reflect the immune function of the lymphocytes. The method is intuitive, simple in operation, rapid, economical, and accurate in result during detection of indexes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Composition for improving number and lethality of autologous lymphocytes and application of composition
PendingCN112725272AEasy to quantify productionCulture processBlood/immune system cellsAntiendomysial antibodiesWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a composition for improving the number and lethality of autologous lymphocytes and application of the composition. The composition comprises an anti-human CD3 monoclonal antibody, interleukin, a composite nutrient composition, calf serum, heparin, colchicine and phytohemagglutinin P (PHA-P). The composition includes 150-250 ng of the anti-human CD3 monoclonal antibody, 500-1500 ng of the interleukin, 1500-2500 Ug of the composite nutrient composition, 0.8-1.2 mL of the serum, 20-28 Ug of the heparin and 500-1500 ng of the phytohemagglutinin. The culture solution prepared from the composition plays a positive role in production of typeface lymphocytes, and under the action of an anti-human CD3 monoclonal antibody, interleukin and phytohemagglutinin (PHA), the small lymphocytes can be stimulated to be converted into lymphoblasts and enter mitosis. After short-term culture, a large number of mitotic cells can be obtained through colchicine treatment, hypotonic treatment and immobilization, and quantitative production is facilitated.
Owner:山东凌曼生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of transfer factor for resisting avian influenza virus
PendingCN114681485ANo purification requiredImprove immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseMicroorganism based processesImmunopotencyLymphoblast
The invention relates to a method for preparing a specific transfer factor for resisting avian influenza virus in vitro. Chicken spleen or peripheral blood is used as a raw material to prepare a lymphocyte monolayer, then phytohemagglutinin and avian influenza virus are used for inducing and culturing lymphocytes, and the avian influenza virus resistant specific transfer factor is produced in vitro. The prepared specific transfer factor can be used for preventing and treating avian influenza, and can improve the immunity of chickens. The preparation method has the advantages of high specificity, low cost, good effect and the like, and is an ideal preparation method of the transfer factor for resisting the avian influenza virus.
Owner:DINGZHENG XINXING BIOTECH TIANJIN
Combinations of anti-cd19 antibodies and Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveCN107660151BOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesLymphoblast
The present disclosure describes pharmaceutical combinations of an anti-CD19 antibody and a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and / or acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
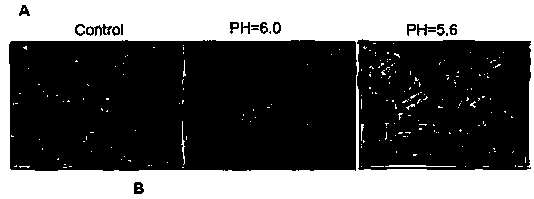
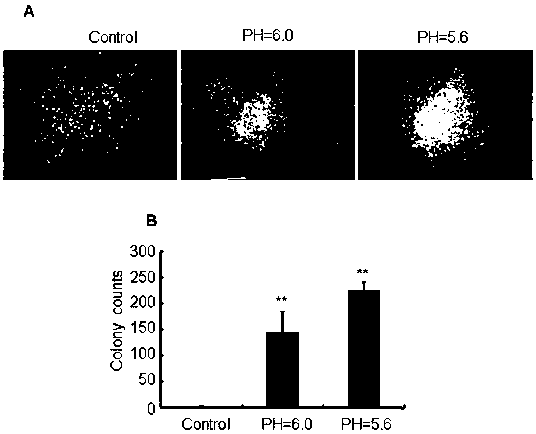
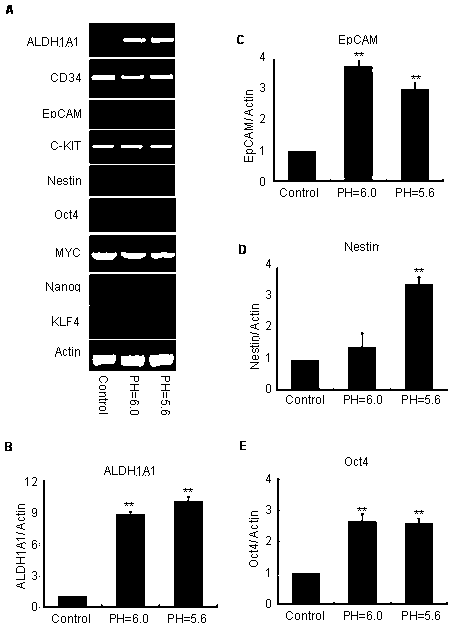
Research method for promoting lymphoblast without tumorigenicity to be dedifferentiated in lactic acid/acid environment so as to obtain tumorigenicity
ActiveCN110964696AHigh expressionPromotes dedifferentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processBiotechnologyLymphoblast
The invention discloses a research method for promoting lymphoblast without tumorigenicity to be dedifferentiated in a lactic acid / acid environment so as to obtain tumorigenicity. The research methodcomprises the steps of: cell culture, low-pH culture medium preparation, cell morphology detection, measurement of cell proliferation, a colony-forming experiment, RT-PCR, data analysis and the like.The method disclosed by the invention is convenient and accurate.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of anti-Newcastle disease transfer factor
PendingCN114681490ANo purification requiredImprove immunityAntiviralsBird material medical ingredientsImmunopotencyLymphoblast
The invention relates to a method for preparing an anti-Newcastle disease specific transfer factor in vitro. Chicken spleen or peripheral blood is used as a raw material to prepare a lymphocyte monolayer, then phytohemagglutinin and the Newcastle disease are used for inducing and culturing lymphocytes, and the anti-Newcastle disease specific transfer factor is produced in vitro. The prepared specific transfer factor can be used for preventing and treating the Newcastle disease, and meanwhile, the immunity of chickens can be improved. The preparation method has the advantages of high specificity, low cost, high yield, good effect and the like, and is an ideal preparation method of the Newcastle disease transfer factor.
Owner:DINGZHENG XINXING BIOTECH TIANJIN
Combination of anti-CD19 antibody and bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor and uses thereof
ActiveCN114601931AOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesLymphoblast
The present disclosure describes a pharmaceutical combination of an anti-CD19 antibody and a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and / or acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Owner:MORFOZIS AG
Preparation method of poultry specific transfer factors
Owner:TIANJIN ASIAN BIOENG
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com