Truncated guinea pig l-asparaginase variants and methods of use
A technology of asparaginase and variants, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of antibody inactivation and clearance, restricted use, reduced effectiveness, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
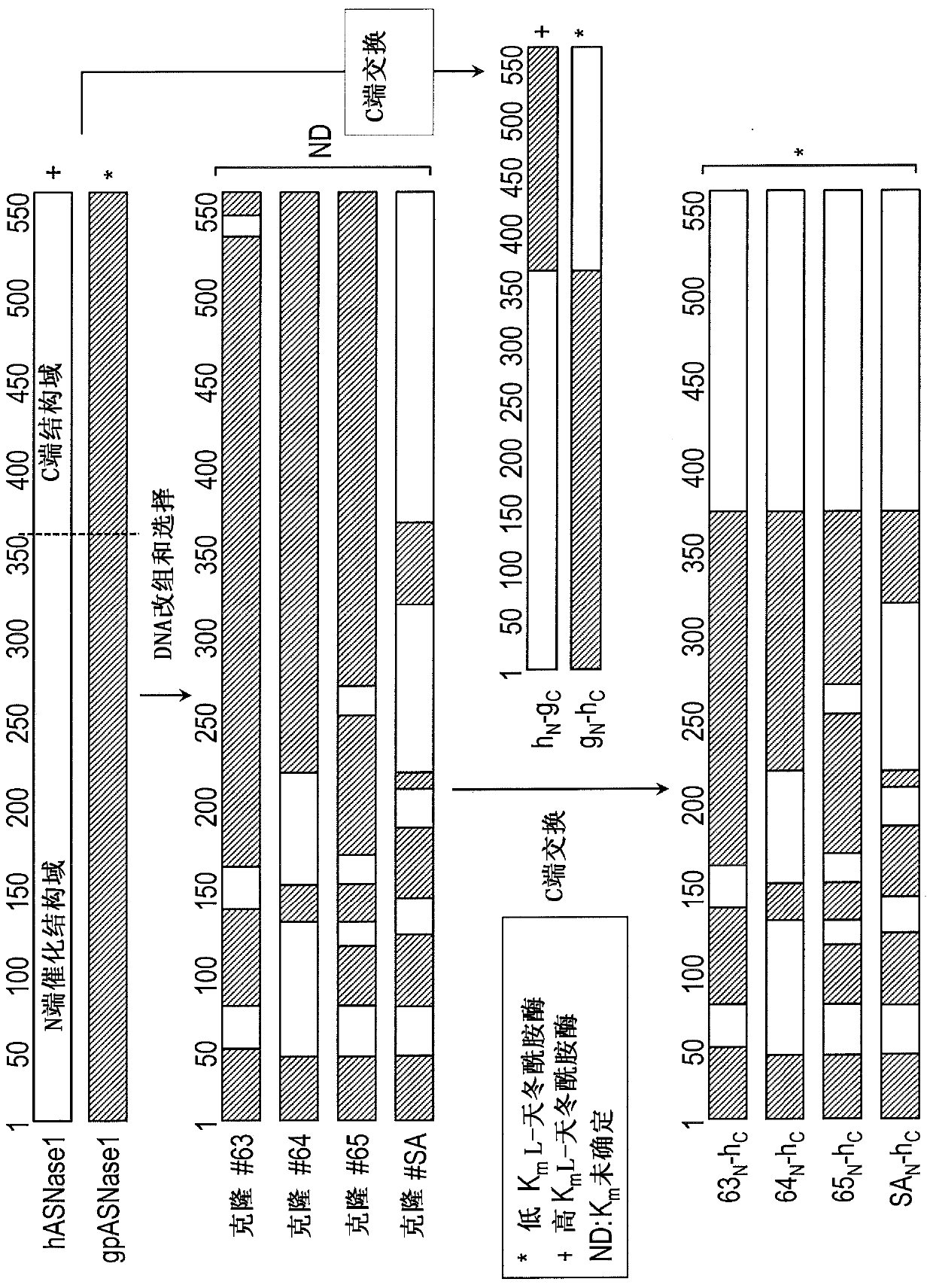
[0056] Example 1: Production of active C-terminally truncated GpA
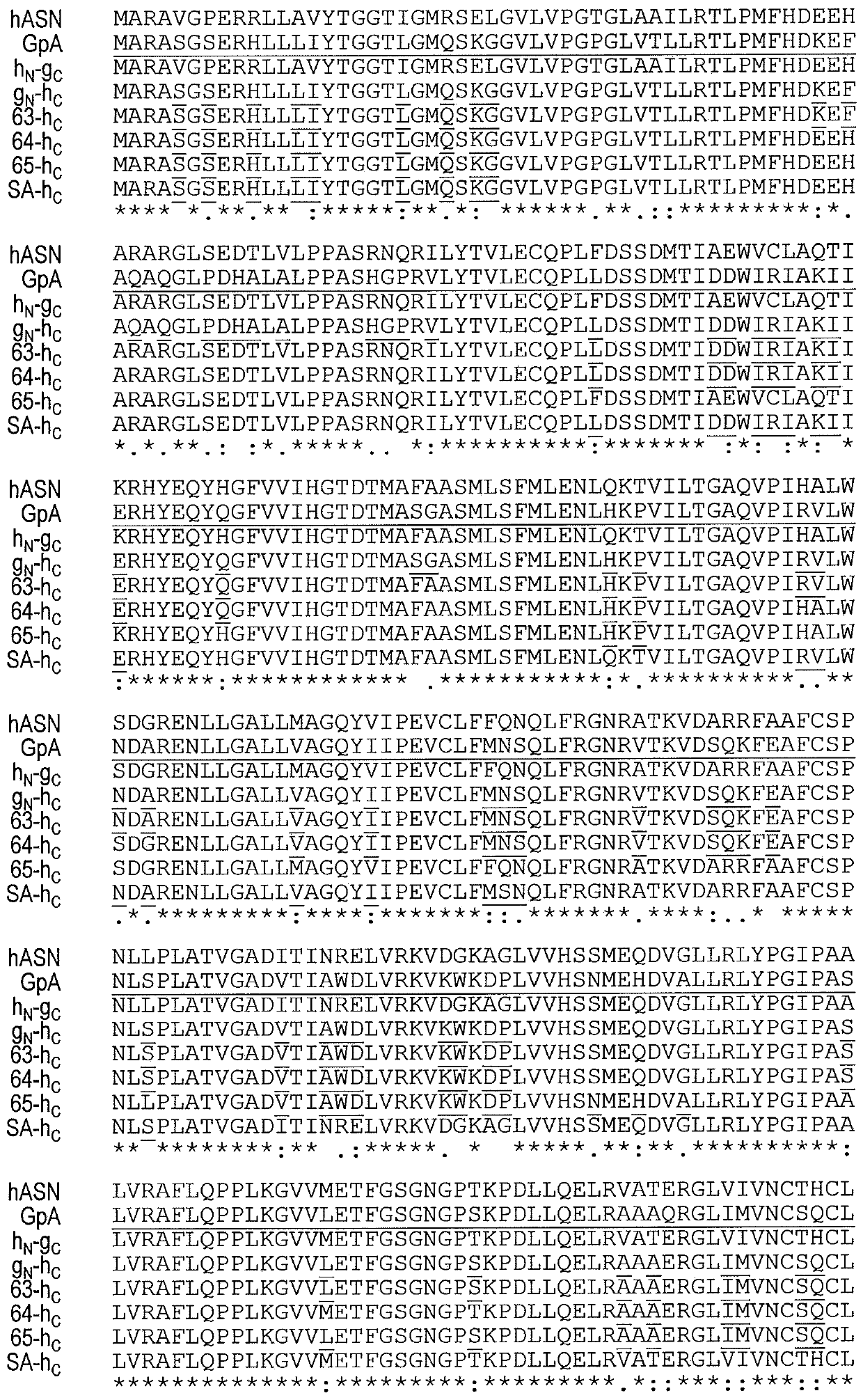
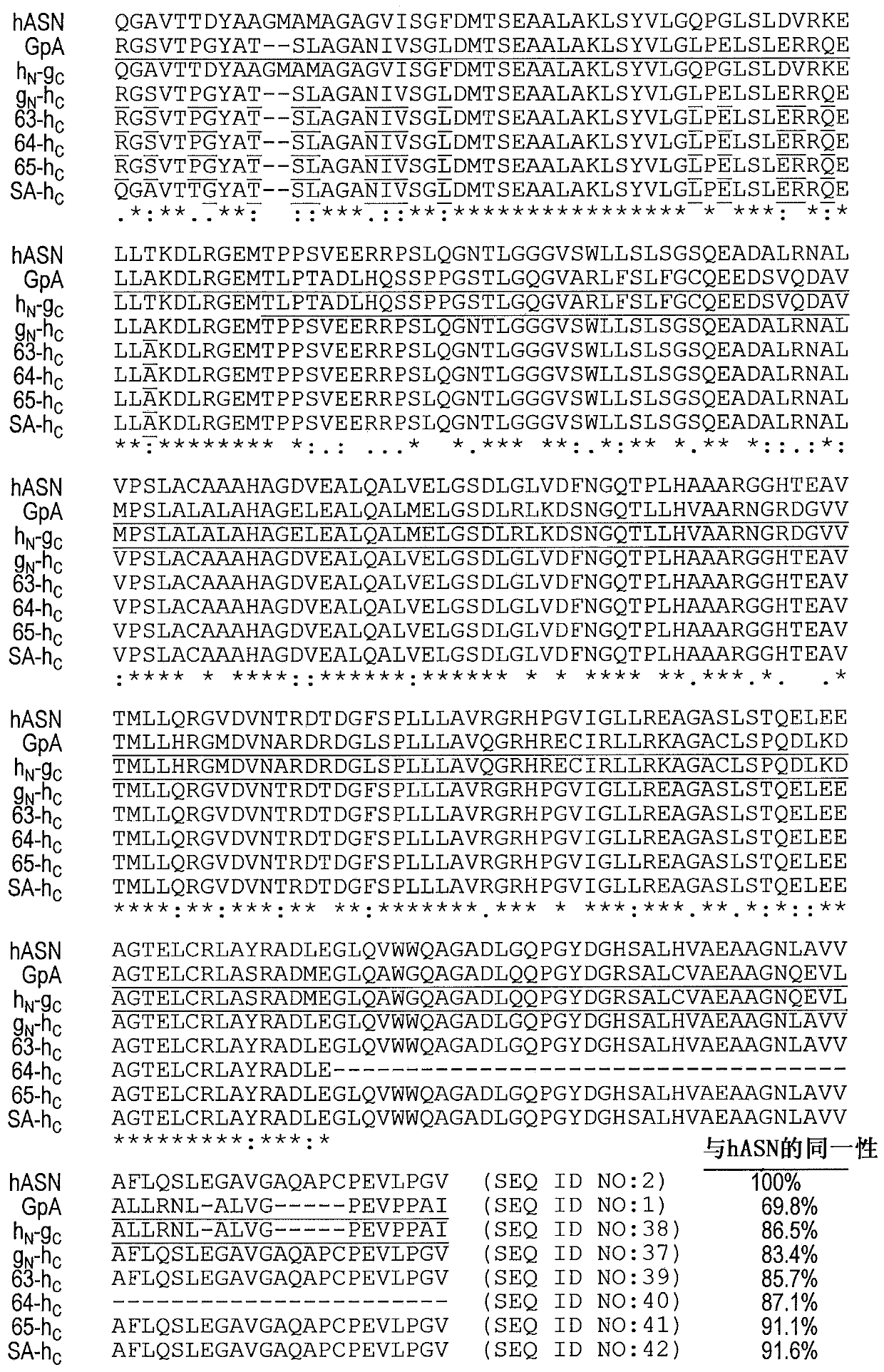
[0057] Mammalian L-asparaginase such as human L-asparaginase (hASNase1; UNIPROT accession number Q86U10; SEQ ID NO: 2) and guinea pig L-asparaginase (gpASNase1 or GpA; UNIPROT accession number HOWOT5; SEQ ID NO : 1) Contains two domains: an N-terminal domain of ~360 residues in which the L-asparaginase activity resides, and a C-terminal domain of ~200 residues whose function is unknown. For comparison, clinically relevant bacterial L-asparaginases from Escherichia coli and Erwinia chrysanthemi are approximately 350 amino acid residues in length and do not contain this C-terminal domain.
[0058] One of the challenges with injectable biotherapeutics comes from the short half-life, which leads to poor bioavailability. Clearance is mainly caused by proteolysis, renal filtration or neutralization by the immune system. Larger foreign sequence molecules have a greater chance of being detected by the immune system ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2: Humanized GpA variants produced by directed evolution
[0065]overview. Directed evolution, or the process of mimicking natural evolutionary processes in the laboratory, is widely used to improve enzyme performance. See eg Dalby (2011) Curr. :91-100; Wang & Zhao (2012) Bioresour.Technol.115:117-125. Thanks to advances in library generation, screening techniques, and most importantly a better understanding of the mechanisms of natural protein evolution, large increases in evolved catalytic activity (relative to the starting point, and based on absolute k cat / K m value) (Fasan et al., (2008) J. Mol. Biol. 383:1069-80; Bar-Even et al., (2011) Biochemistry (Mosc.) 50:4402-10).
[0066] To overcome immunogenicity, a human-like L-asparaginase with kinetic properties close to that of type II E. coli L-asparaginase was generated by directed evolution approach. High sequence identity to hASNase1 but low K of gpASNase1 was identified using DNA family shuffling m...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3: Humanized GpA variants produced by a structured-based approach
[0106] As an alternative to DNA shuffling and domain swapping, a structure-based approach was taken to humanize and reduce the immunogenicity of the GpA enzyme. For this approach, a truncated GpA369 variant (SEQ ID NO: 5) was modified. The crystal structure of GpA was examined and predictions were made as to which residues at the surface of the enzyme could be mutated to the corresponding amino acids in hASNase1 and whose presence would not be detrimental to the activity or stability of the enzyme. The candidate surface residues were classified into three groups based on their likelihood of having a possible effect on the activity or stability of GpA (group 1, no effect; group 2, likely to have no effect; and group 3, with possible impact) (Table 6).
[0107] Table 6
[0108]
[0109]
[0110] 1 Reference sequence GpA369 (SEQ ID NO: 5).
[0111] 2 Corresponding residues in reference ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com