Patents
Literature
34 results about "Pseudorasbora parva" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The stone moroko (Pseudorasbora parva), also known as the topmouth gudgeon, is a fish belonging to the Cyprinid family, native to Asia, but introduced and now considered an invasive species in Europe and North America. The fish's size is rarely above 8 cm and usually 2 to 7.5 cm long.
Ecological breeding method of efficient polyculture of pseudorasbora parva, crab larva and loach
ActiveCN103749342AReduce wastePromote growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffPolycultureHazardous substance
The invention discloses an ecological breeding method of efficient polyculture of pseudorasbora parva, crab larva and loach. The method comprises the steps of: pond conditions, disinfection, breeding water preparation, grass planting, fry breeding, water level adjustment, water quality adjustment and control, feeding management, disease control, daily management and the like. The breeding method provided by the invention focus on the breeding of crab larvae; the pseudorasbora parva is mainly used as cleaners for residual feeds, so that the pollution to water quality can be greatly reduced, the water quality can be improved, the growth of crab larvae and loaches is promoted, and meanwhile, blue-green algae outbreak in the crab larva pond can be biologically controlled by the polyculture of the pseudorasbora parva; the loaches play a role in loosening the soil, and eliminates hazardous substances in the soil in time, so as to avoid the water quality becoming bad due to the high temperature in summer, in addition, loaches do not need additional feeding and management, are beneficial supplement to the breeding of the crab larvae, and thus the pond benefit is greatly increased.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
Method for controlling early-bred of odontobutis potamophila
InactiveCN103843709AShort reproductive cycleClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLive foodPseudorasbora parva
The invention discloses a method for controlling early-bred of odontobutis potamophila. The method comprises the following steps: screening parent fishes, and controlling water temperature during a parent fish rearing process, so that the gonad development of the odontobutis potamophila is promoted; and meanwhile, carrying out enriching broodstock through feeding live food such as pseudorasbora parva and freshwater shrimp, and setting an artificial spawning nest, so that the gonad maturity in advance of the odontobutis potamophila is promoted, the breeding cycle is shortened, and odontobutis potamophila spawning and hatch equipment is recycled. In addition, odontobutis potamophila fries (sold on February) early bred through the method is at least more than three months than fries (sold on May-June) bred normally, so that the fish growth cycle can be prolonged, and the economic benefit of fishes is increased.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for artificially inducing parent pseudorasbora parva gonad synchronous development
ActiveCN103718994APromotes synchronous developmentAvoid deformitiesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTemperature controlPseudorasbora parva
The invention discloses a method for artificially inducing parent pseudorasbora parva gonad synchronous development. The method comprises the steps of parent fish selecting, parent fish breeding, parent fish gonad synchronous development and the like. According to the method, through gradual temperature control, gradual lighting adjustment and appropriate feed putting, the purpose of promoting pseudorasbora parva gonad synchronous development is achieved, the problem of sperm and egg malformation caused by rapid environment changes is avoided, the brood rate and the fertility rate are improved and a technical basis is provided for pseudorasbora parva artificial breeding.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
Method for detecting genotoxic agent in water by utilization of Pseudorasbora parva
InactiveCN105510543AFully assess health risksComprehensive assessment of health risksMaterial analysis by optical meansTesting waterPositive controlToxicant
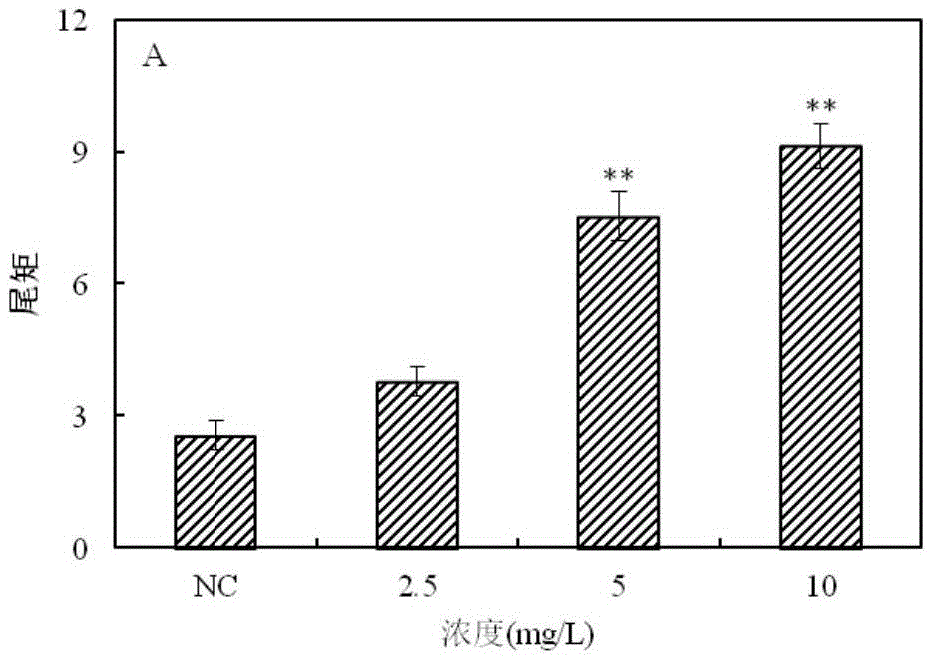
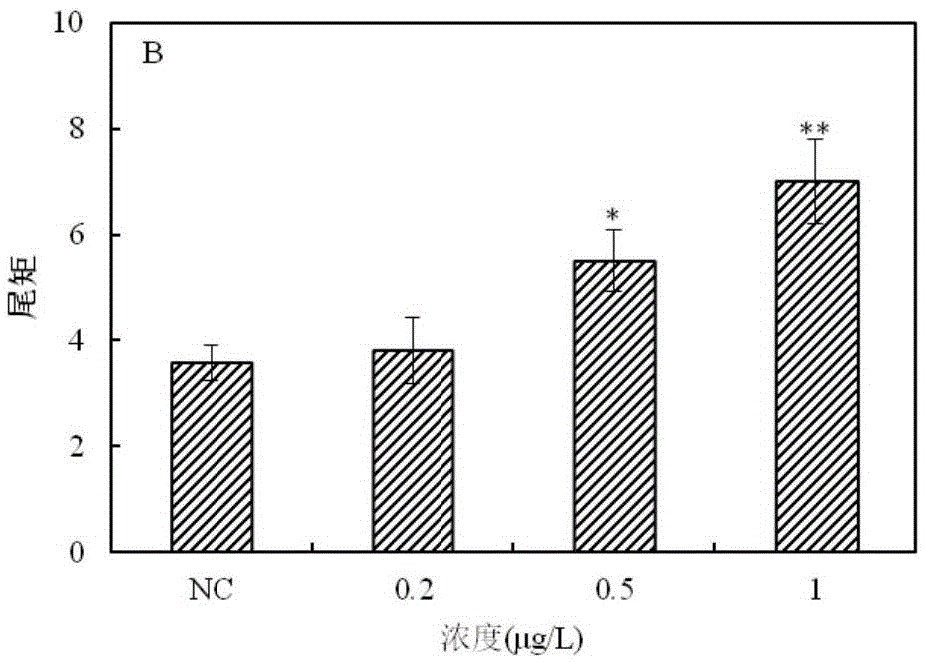
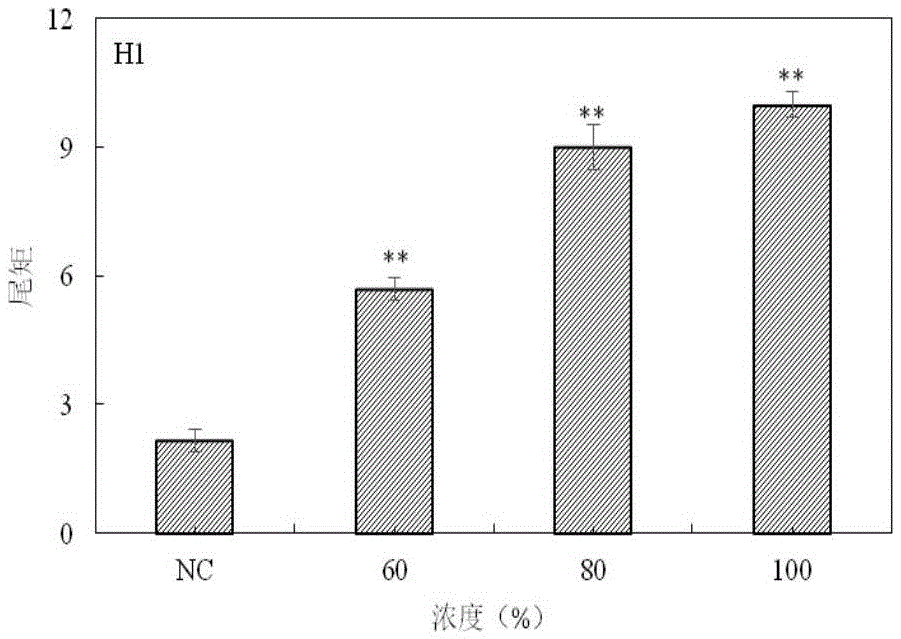
The invention provides a method for detecting a genotoxic agent by the utilization of Pseudorasbora parva and belongs to the field of chemicals safety evaluation and environmental monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: (1) processing Pseudorasbora parva by exposure treatment by the use of a water sample to be tested; and (2) carrying out single cell gel electrophoresis assay by using hepatic cells of Pseudorasbora parva processed after exposure treatment, detecting and counting cell tail length, DNA content and tail moment, and drawing a dose-effect curve. Through comparison between the result and a blank control and a positive control and through the dose-effect relationship, genetic toxicity of the test sample is determined. The detection method of the invention can sensitively and rapidly determine genetic toxicity of chemicals. The invention provides a China native species-based detection method for chemicals genetic toxicity evaluation and environmental genetic toxicity monitoring.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Strengthening breeding method of parent fishes of pseudorasbora parva
ActiveCN103718996ASolve quality problemsSolve the survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPseudorasbora parvaBroodstock
The invention discloses a strengthening breeding method of parent fishes of pseudorasbora parva. The method includes the steps of parent fish selection, pond selection and treatment, parent fish strengthening breeding, water temperature adjustment, daily management and the like. According to the strengthening breeding method, gonad development of the parent fishes of the pseudorasbora parva can be stimulated, and the success rate of parent rearing maturity is improved; meanwhile rapid growth of the parent fishes is promoted, the survival rate of the parent fishes is improved, the problem that the parent quality and the survival rate of the pseudorasbora parva are hard to guarantee is effectively solved, and the method lays a technical foundation for artificial breeding of the pseudorasbora parva in China and has important significance for industrialization exploitation of the pseudorasbora parva.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
Method for breeding or odontobutis obscurus
ActiveCN104026051AHarm reductionImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaChorionic gonadotropinsOvary
The invention discloses a method for breeding odontobutis obscurus. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing parent breeding of the odontobutis obscurus with freshwater shrimp and pseudorasbora parva as baits; secondly, selecting mixture of chorionic gonadotropin, an luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogue and maleic acid European ketone as an oxytocic, matching female odontobutis obscurus with male odontobutis obscurus according to the ratio of 1:1.2 and placing the matched odontobutis obscurus into a spawning pond; thirdly, controlling the water temperature for spawning at 19-21DEG C, placing (n+2) spawning nests in the spawning pond, wherein n is the number of the female odontobutis obscurus; fourthly, after spawning, taking meshes to which fish roes are attached from the spawning nests, lapping the meshes on PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) incubating tubes, enabling each mesh to correspond to one air stone, and transferring the meshes to an incubating frame for continuously incubating in two days before the fish roes break through membranes until incubating fries; fifthly, continuously culturing for one week with living food of daphnia pulex larvae and moina as initial feed. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the fertilization rate, the hatching rate and fry survival rate of the odontobutis obscurus are improved.
Owner:盐城市盐都区水产养殖场
Odontobutis obscurus large-size fry artificial classification separate culture method
PendingCN109496926AAchieve indoor cultivationImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater filterOxygen
The invention relates to an odontobutis obscurus large-size fry artificial classification separate culture method. The method comprises the steps that 1, a net cage is arranged in an indoor culture groove, oxygen increasing heads are arranged on the periphery of the indoor culture groove, a water pushing device is arrange on one side, and a water filtering device is arranged on the other side; 2,newly hatched larvae of odontobutis obscurus are put in the net cage of the culture groove; 3, the culture water depth is controlled to be 0.3+ / -0.6 m, the water temperature is controlled to be 22-28DEG C, and sewage suction and water replenishing are conducted every afternoon; 4, after hatching is conducted for 3 d, cladocerans and copepods obtained after filtering through a 60-mesh sieve serveas initial feed, after 7 d, bait mainly adopts limnodrilus and secondarily adopts the cladocerans and the copepods, and after 14 d, while the limnodrilus is used for feeding, loach and newly hatched larvae of pseudorasbora parva are additionally put; 5, after hatching is conducted for about 10 d, by taking the head width as the standard, odontobutis obscurus artificial classification separate culture is conducted, and hereafter, specification screening and classification are conducted every 10 d. Accordingly, indoor odontobutis obscurus large-size fry culture is achieved, after culture is conducted for about 50 d, for the odontobutis obscurus, the average overall length reaches about 20 cm, the head width is about 3.3 mm, and the pond survival rate reaches 90%.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
Special high-protein feed for snakehead fishes
InactiveCN103859221ANutritional balancePromote growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffFish pasteAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a special high-protein feed for snakehead fishes. The feed comprises an extruded feed and frozen fish paste, wherein the extruded feed comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 50%-55% of imported fish meal, 20%-25% of bean pulp, 2%-3% of yeast powder, 5%-7% of spiral seaweeds, 8%-10% of fish oil, 5%-8% of corn powder, 1%-2% of a vitamin premix and 1%-2% of a microelement premix; the frozen fish paste comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 30%-40% of pseudorasbora parva, 25%-35% of abbottina rivularis, 20%-30% of carp fries and the balance of other wild trash fishes. According to the mode, the feed is balanced in nutrition and high in protein content; the snakehead fishes are completely fed with the feed, so that the water body pollution can be alleviated, the growth of the snakehead fishes can be promoted, the meat quality of the snakehead fishes can be improved, and especially the immunity of the snakehead fishes is improved, the yield-per-mu of the snakehead fishes is increased, and the economic benefit of snakehead fish farming is remarkably increased.
Owner:SUZHOU YANGCHENGHU MODERN AGRI INDPARK SPECIAL AQUACULTURE
Artificial large-scale breeding method of pseudorasbora parva
ActiveCN108371124AArtificial reproductionAchieve concentrated inseminationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPseudorasbora parvaObserved Survival
The invention discloses an artificial large-scale breeding method of pseudorasbora parva. The method comprises the steps of parent selection, manufacturing of spawning induction feed, separate spawning induction of parents, insemination, incubation and the like. By means of the artificial large-scale breeding method of pseudorasbora parva, artificial breeding of pseudorasbora parva can be achieved; through the design of a specially-made spawning pond, it can be effectively guaranteed that the parents do not eat roes, and the survival rate is increased by around 2 times compared with that of the prior art; meanwhile, through the treatment of hormones before spawning induction, the gonads of the parents can be synchronously mature, and centralized insemination is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Cement pond net cage incubation method for pseudorasbora parva
ActiveCN103749341AImprove disease resistanceImprove hatchabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPseudorasbora parvaEconomic benefits
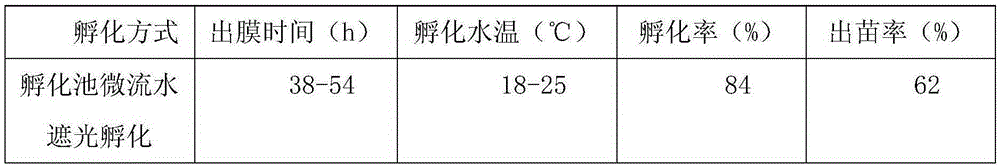
The invention discloses a cement pond net cage incubation method for pseudorasbora parva. The method comprises the steps of: source and cultivation of parent fishes, spawning pond and incubation facilities, induced spawning and ovulation, incubation and the like. The method provided by the invention can improve the disease resistance of pseudorasbora parva fry and enhance incubation rate, survival rate and emergence rate, is simple in operation, small in investment and large in output, provides technical base for the intensification, industrialization, large scale and quality of the pseudorasbora parva fry, and has enormous economic benefits.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
Takifugu obscures, coilia nasus schlegel and trionyx sinensis three-dimensional ecological breeding
ActiveCN110074019AImprove water utilizationReduce investmentClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTrionyxGenus Trionyx
The invention relates to the field of aquaculture, in particular to a takifugu obscures, coilia nasus schlegel and trionyx sinensis three-dimensional ecological breeding method, which comprises sevensteps of pond preparation, stocking of coilia nasus schlegel fingerlings and takifugu obscures, stocking of pseudorasbora parva and silver carps, bait feeding, daily management, and net pulling for catching. The invention fully utilizes the water space of a takifugu obscurus parent breeding pond, increases yield of the coilia nasus schlegel and trionyx sinensis under the conditions of not increasing the input, not reducing the takifugu obscures parent breeding density, and not affecting the takifugu obscurus parent gonad development, improves the water utilization rate of the pond, reduces theproduction cost, improves the economic benefit, reduces the feed cost, improves the quality of the trionyx sinensis, and makes the water quality of the pond more stable; the method of the invention is easy to operate and can be easily accepted and promoted.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Mixed-culture method for macrobrachium nipponense and pseudorasbora parva
InactiveCN107897058AEnsure diversityIncrease profitFood processingClimate change adaptationAquatic animalWater quality
The invention proposes a mixed-culture method for macrobrachium nipponense and pseudorasbora parva. The method comprises the following steps: 1) selecting a pond; 2) disinfecting the pond: putting water with a depth of 0.5-1m into the empty pond obtained in the step 1), throwing quick lime for disinfection, planting aquatic plants, hanging a decomposed microbial organic fertilizer at the edge of the pond, placing a shielding substance, and adjusting the water temperature, dissolved oxygen and pH value of the pond to obtain a cultivation pond; 3) throwing young macrobrachium nipponense and fry;and 4) performing breeding management: from a first week to a seventh week, performing feeding for 2 times every day, wherein boiled primary feed is thrown; and after an eighth week, performing feeding according to a water temperature, wherein traditional Chinese medicine feed is thrown, improving the water quality every 3-5 days, and throwing young grass carps and bellamya quadrata. The culturemethod provided by the invention fully utilizes culture resources, maintains the water quality, reduces small trash fishes in the fish pond, enriches the product structure of aquatic animals, reducesthe risk of production, greatly improves the utilization ratio of the feed, and increases the yield of the aquatic animals.
Owner:HEFEI KANGQINGYUAN BREEDING CO LTD
Spicy minced fish meal and method for making same
The invention discloses a spicy minced fish meal and a method for making the spicy minced fish meal, wherein the spicy minced fish meal is made from fresh trash fish, peanut, sesame, dried chili, ginger powder, salad oil, table salt, monosodium glutamate, chicken powder and pepper. The spicy minced fish meal made by the method provided by the invention is bright in color and luster, fresh in taste, moderate in flavor, and sweet in flavor, and thereby being a good mating dish for principal food such as pancake and sesame seed cake. The method for making the spicy minced fish meal is capable of taking full advantage of small fresh wild trash fishes such as shishamo, pseudorasbora parva and abbottina rivularis for making delicious food so that the utilization rate of the small wild trash fishes is increased; and the method has easily available raw materials, is simple and convenient, and is low in cost and obvious in benefit.
Owner:微山利民现代渔业科技有限公司
Pseudorasbora parva fodder
The invention discloses pseudorasbora parva fodder. The pseudorasbora parva fodder is characterized by comprising, by weight, 5%-10% of fish meal, 15%-18% of soybean cake powder, 4%-7% of shrimp shell powder, 8%-13% of wheat shorts, 10%-15% of rice bran powder, 5%-8% of bran powder, 6%-15% of rapeseed dreg powder, 8%-10% of earthworm powder, 8%-12% of corn flour, 5%-8% of barley flour, 3%-5% of spirulina powder, 5%-8% of yeast powder, 0.3%-0.6% of decavitamin and 0.5%-1% of composite mineral salt. The pseudorasbora parva fodder has various nutritional ingredients, and compared with the mode that fodder such as bran and rice bran is fed independently, the nutritional ingredients of the pseudorasbora parva fodder are more comprehensive. The fodder can be stored and used conveniently, and the fodder further has the effect of protecting and treating fish diseases through high temperature sterilization. The fodder is good in palatability, easy to digest and high in absorption speed. Pseudorasbora parva is high in growth speed, high in disease resistance and high in breeding survival rate. Prey fishes which are sufficient in number and excellent in quality can be provided for breeding high-quality fishes such as mandarin fishes.
Owner:杨成胜
A method of artificially inducing the synchronous development of the gonads of the broodstock
ActiveCN103718994BPromotes synchronous developmentAvoid deformitiesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTemperature controlPseudorasbora parva
The invention discloses a method for artificially inducing parent pseudorasbora parva gonad synchronous development. The method comprises the steps of parent fish selecting, parent fish breeding, parent fish gonad synchronous development and the like. According to the method, through gradual temperature control, gradual lighting adjustment and appropriate feed putting, the purpose of promoting pseudorasbora parva gonad synchronous development is achieved, the problem of sperm and egg malformation caused by rapid environment changes is avoided, the brood rate and the fertility rate are improved and a technical basis is provided for pseudorasbora parva artificial breeding.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
Medicine for treating viral hemorrhagic disease of pseudorasbora parva
InactiveCN104288291AImprove immunityEffective treatmentAntiviralsPteridophyta/filicophyta medical ingredientsPseudorasbora parvaCyrtomium fortunei
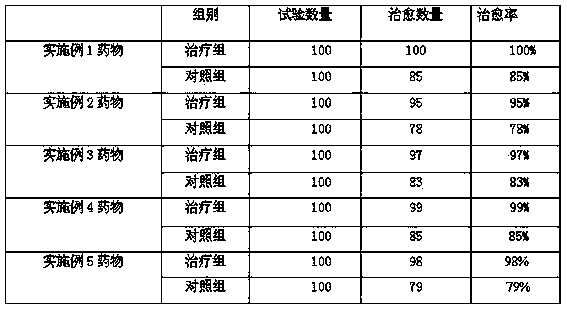
The invention discloses a medicine for treating viral hemorrhagic disease of pseudorasbora parva, and belongs to the technical field of a traditional Chinese medicine. The medicine is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of hairyvein agrimony, 5-10 parts of codonopsis pilosula, 10-20 parts of fingered citron, 2-8 parts of bark of eucommia, 5-10 parts of folium isatidis, 20-30 parts of honeysuckle, 10-20 parts of pterocarya stenoptera leaves, 2-8 parts of pseudo-ginseng, 6-16 parts of cyrtomium fortunei, 2-8 parts of radix sophorae subprostratae, 10-20 parts of raw radix paeoniae alba and 2-8 parts of cocklebur fruit. The medicine for treating viral hemorrhagic disease of pseudorasbora parva disclosed by the invention is reasonable in compatibility; the medicine, through an effect of supplementing each other by combining various raw materials according to scientific proportioning amounts, can be used for rapidly and effectively killing reoviruses and small RNA viruses of pseudorasbora parva, enhancing the immunity of the pseudorasbora parva, and rapidly and effectively treating hemorrhagic disease of the pseudorasbora parva; the cure rate is more than 95%; and the medicine disclosed by the invention is environment-friendly and free from pollution, resistance-free and harmless to a human body.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
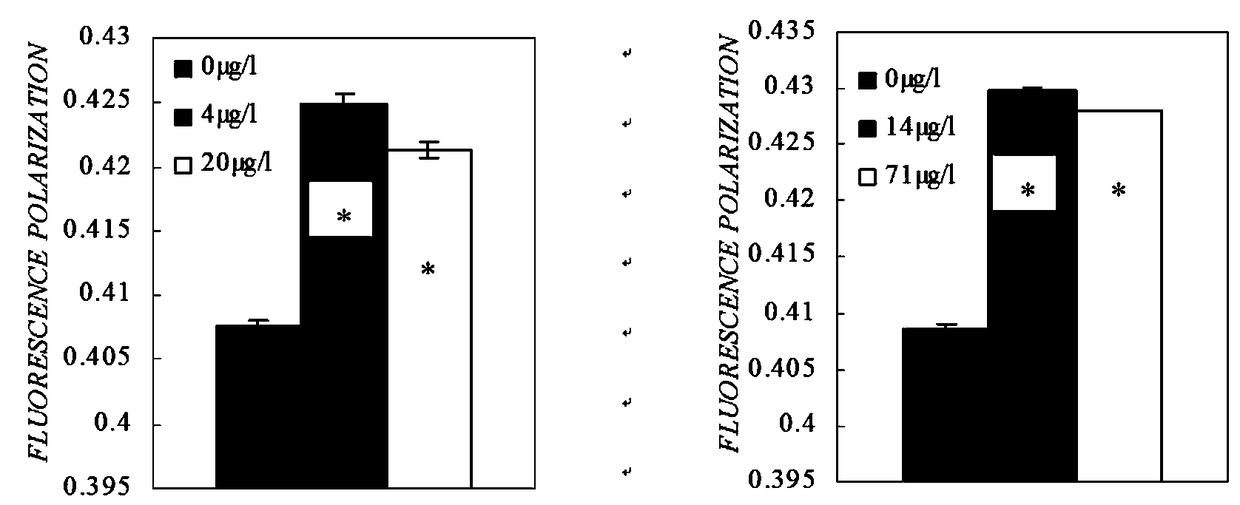
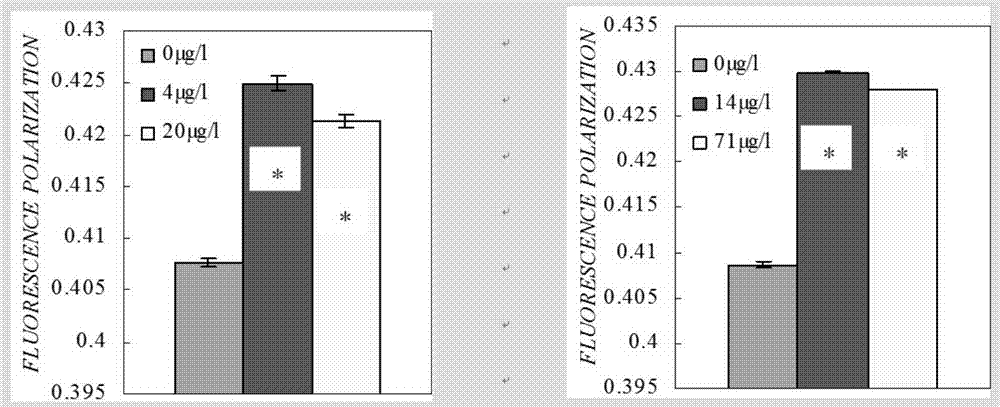
An In Vivo Test Method for Mitochondrial Membrane Fluidity in the Liver of Osprey carp
ActiveCN107449766BAvoiding pitfalls of ex vivo assays for mobilityTrue reflection of biological activityFluorescence/phosphorescenceInner mitochondrial membranePseudorasbora parva
The invention relates to testing of fluidity of fluidity of a mitochondrial membrane of the liver of fish, in particular to an in-vivo test method for the fluidity of the mitochondrial membrane of the liver of pseudorasbora parva. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, a fish body exposure experiment; S2, preparation of the mitochondrial membrane of the liver of the pseudorasbora parva; S3, preparation of a DPH solution; S4, marking of a DPH fluorescent probe of the mitochondrial membrane; S5, determination of the fluidity of the membrane; S6, determination of the content of protein in mitochondria. With the adoption of the in-vivo test method for the fluidity of the mitochondrial membrane of the liver of pseudorasbora parva, influence of an agent on the fluidity of the mitochondrial membrane of the fish is determined accurately and conveniently.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
A kind of method of controlling the early multiplication of sand pond snakehead in rivers
InactiveCN103843709BShort reproductive cycleClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBroodstockLive food
The invention discloses a method for controlling early-bred of odontobutis potamophila. The method comprises the following steps: screening parent fishes, and controlling water temperature during a parent fish rearing process, so that the gonad development of the odontobutis potamophila is promoted; and meanwhile, carrying out enriching broodstock through feeding live food such as pseudorasbora parva and freshwater shrimp, and setting an artificial spawning nest, so that the gonad maturity in advance of the odontobutis potamophila is promoted, the breeding cycle is shortened, and odontobutis potamophila spawning and hatch equipment is recycled. In addition, odontobutis potamophila fries (sold on February) early bred through the method is at least more than three months than fries (sold on May-June) bred normally, so that the fish growth cycle can be prolonged, and the economic benefit of fishes is increased.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Feed for improving immunity of pseudorasbora parva in rearing stage
InactiveCN112244181AEffectively Provides Disease ResistanceImprove immunityFood processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture, in particular to a feed capable of improving immunity of pseudorasbora parva in a rearing stage. The feed comprises a base material and anadditive, the base material comprises fishbone dust, water flea powder, soybean meal, milk powder, pine needle powder, dandelion powder, radix puerariae and radix bupleuri, fishbone dust and water flea powder, the soybean meal provides daily required capacity for the pseudorasbora parva, the milk powder, the pine needle powder, the dandelion powder, radix puerariae and radix bupleuri can effectively improve the disease resistance of fishes, the additive comprises monocalcium phosphate, zinc lactate, compound enzymes, methionine and lysine, and the immunity of the pseudorasbora parva is enhanced while vitamins and minerals of the pseudorasbora parva are supplemented.
Owner:周晚叔
A special feed for high-protein black fish
InactiveCN103859221BNutritional balancePromote growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffFish pasteFish oil
The invention discloses a special high-protein feed for snakehead fishes. The feed comprises an extruded feed and frozen fish paste, wherein the extruded feed comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 50%-55% of imported fish meal, 20%-25% of bean pulp, 2%-3% of yeast powder, 5%-7% of spiral seaweeds, 8%-10% of fish oil, 5%-8% of corn powder, 1%-2% of a vitamin premix and 1%-2% of a microelement premix; the frozen fish paste comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 30%-40% of pseudorasbora parva, 25%-35% of abbottina rivularis, 20%-30% of carp fries and the balance of other wild trash fishes. According to the mode, the feed is balanced in nutrition and high in protein content; the snakehead fishes are completely fed with the feed, so that the water body pollution can be alleviated, the growth of the snakehead fishes can be promoted, the meat quality of the snakehead fishes can be improved, and especially the immunity of the snakehead fishes is improved, the yield-per-mu of the snakehead fishes is increased, and the economic benefit of snakehead fish farming is remarkably increased.
Owner:SUZHOU YANGCHENGHU MODERN AGRI INDPARK SPECIAL AQUACULTURE
A kind of spicy fish paste powder and preparation method thereof
Owner:微山利民现代渔业科技有限公司
Dried fish and production method thereof
InactiveCN107712689AFull of nutritionHigh in calciumFood ingredient functionsMonosodium glutamatePotato starch
The invention relates to dried fish and belongs to the field of food processing. Aiming at solving the technical problems, the invention provides a production method of the dried fish; the specific method comprises the following steps: a, taking fresh pseudorasbora parva and removing internal organs; washing and putting the fish into beer and pickling for 0.2h to 0.5h; b, taking out the pseudorasbora parva from the beer and roasting the pseudorasbora parva at the temperature of 50 DEG C to 70 DEG C for 40s to 70s; taking out the pseudorasbora parva and covering the pseudorasbora parva with flour paste; putting the pseudorasbora parva into mixed oil and frying for 30s to 60s; fishing out the pseudorasbora parva and draining to prepare the dried fish, wherein the flour paste is prepared by uniformly mixing potato starch, wheat flour, egg white, salt, monosodium glutamate, pepper, chicken essence and Chinese prickly ash according to the weight ratio of 100 to (10 to 20) to (50 to 60) to (8 to 10) to (5 to 8) to (2 to 4) to (5 to 8) to (1 to 3) and the mixed oil is obtained by uniformly mixing peanut oil, rapeseed oil and lard oil according to the weight ratio of 1 to 1 to (0.3 to 0.5). The dried fish provided by the invention has abundant nutrients; especially, the content of calcium is greatly improved.
Owner:成都市新津活活饭店
A kind of strengthened cultivation method of broodstock of wheat ear fish
ActiveCN103718996BSolve quality problemsIncrease success rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPseudorasbora parvaBroodstock
The invention discloses a strengthening breeding method of parent fishes of pseudorasbora parva. The method includes the steps of parent fish selection, pond selection and treatment, parent fish strengthening breeding, water temperature adjustment, daily management and the like. According to the strengthening breeding method, gonad development of the parent fishes of the pseudorasbora parva can be stimulated, and the success rate of parent rearing maturity is improved; meanwhile rapid growth of the parent fishes is promoted, the survival rate of the parent fishes is improved, the problem that the parent quality and the survival rate of the pseudorasbora parva are hard to guarantee is effectively solved, and the method lays a technical foundation for artificial breeding of the pseudorasbora parva in China and has important significance for industrialization exploitation of the pseudorasbora parva.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
A kind of hatching method of net cage in cement pond of wheat ear fish
ActiveCN103749341BImprove disease resistanceImprove hatchabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseasePseudorasbora parva
The invention discloses a cement pond net cage incubation method for pseudorasbora parva. The method comprises the steps of: source and cultivation of parent fishes, spawning pond and incubation facilities, induced spawning and ovulation, incubation and the like. The method provided by the invention can improve the disease resistance of pseudorasbora parva fry and enhance incubation rate, survival rate and emergence rate, is simple in operation, small in investment and large in output, provides technical base for the intensification, industrialization, large scale and quality of the pseudorasbora parva fry, and has enormous economic benefits.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
A kind of ecological breeding method for high-efficiency polyculture of wheat ear fish, juvenile crab and loach
ActiveCN103749342BReduce wastePromote growthFodderClimate change adaptationPolycultureHazardous substance
The invention discloses an ecological breeding method of efficient polyculture of pseudorasbora parva, crab larva and loach. The method comprises the steps of: pond conditions, disinfection, breeding water preparation, grass planting, fry breeding, water level adjustment, water quality adjustment and control, feeding management, disease control, daily management and the like. The breeding method provided by the invention focus on the breeding of crab larvae; the pseudorasbora parva is mainly used as cleaners for residual feeds, so that the pollution to water quality can be greatly reduced, the water quality can be improved, the growth of crab larvae and loaches is promoted, and meanwhile, blue-green algae outbreak in the crab larva pond can be biologically controlled by the polyculture of the pseudorasbora parva; the loaches play a role in loosening the soil, and eliminates hazardous substances in the soil in time, so as to avoid the water quality becoming bad due to the high temperature in summer, in addition, loaches do not need additional feeding and management, are beneficial supplement to the breeding of the crab larvae, and thus the pond benefit is greatly increased.
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
A kind of biological indicator method for the efficacy of copper sulfate in aquaculture ponds by using wheat ear fish
ActiveCN104502578BDrug sensitive and stableEasy to operateBiological testingMortality ratePlant disease
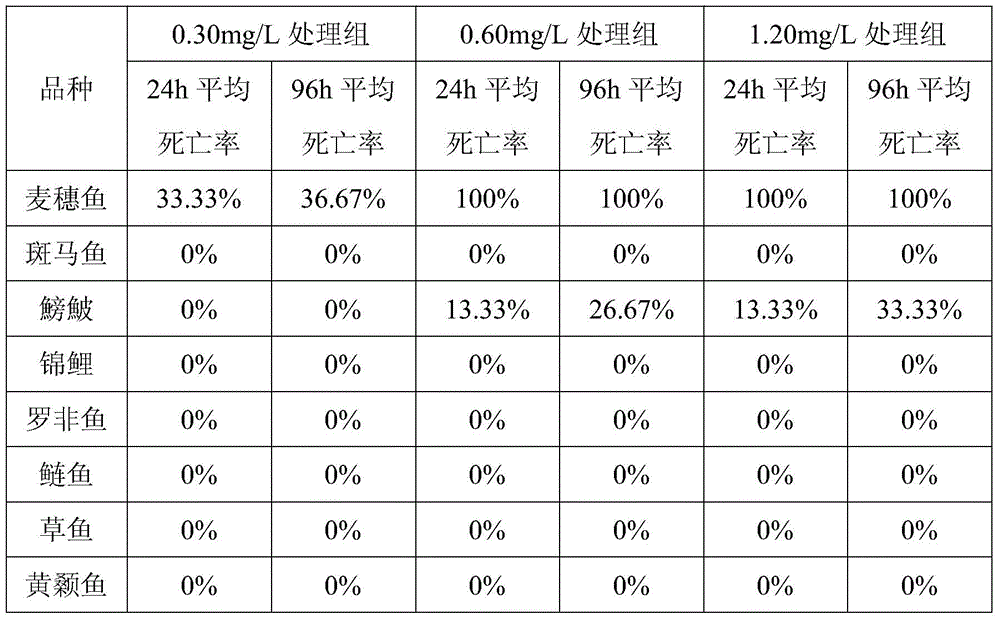
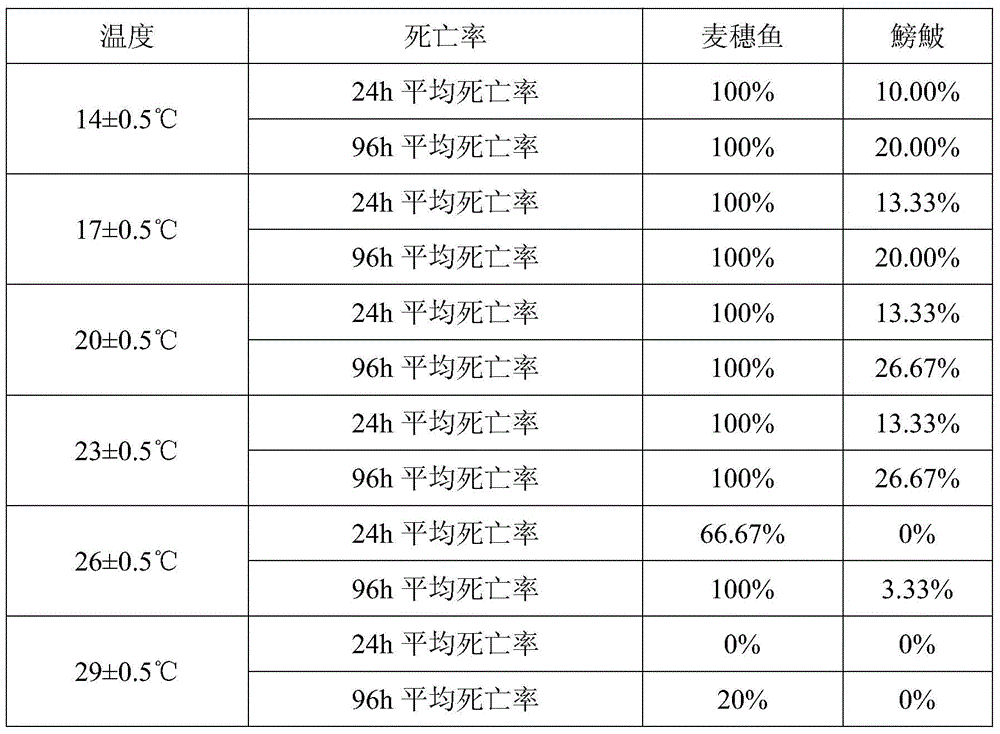
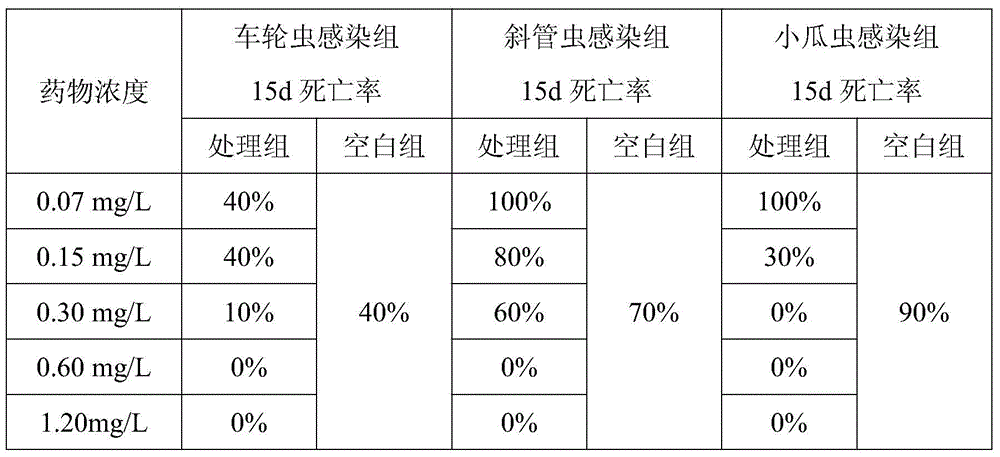
The invention discloses a biological indicator method using pseudorasbora parva for indication of drug effect of copper sulfate in a culture pond, and belongs to the technical field of aquaculture disease control, the pseudorasbora parva is used as a biological indicator for indication of drug effect situation of the copper sulfate in the culture pond using a copper sulfate-containing reagent by observation and statistics of abnormal behavior and mortality of the pseudorasbora parva, so that rational drug use and production can be guided. The biological indicator method is simple and practical, low in price, fast and accurate, and easy to produce and manage.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A kind of ecological breeding method for efficient polyculture of river crab, freshwater shrimp and wheat ear fish
ActiveCN103718993BImprove recovery rateAct as a scavengerBiocideClimate change adaptationScavengerPolyculture
The invention discloses an ecological breeding method for efficient polyculture of river crabs, freshwater shrimps and pseudorasbora parva. The method comprises preparing conditions of a pond, constructing escape-preventing facilities, airing and sterilizing the bottom of the pond, applying fertilizer to the pond, planting water plants, putting in snails, putting in fingerlings, regulating and controlling water quality, throwing in feed and the like. According to the ecological breeding method, the situation that siniperca chuatsi feed on freshwater shrimps in the breeding mode of shrimps, crabs and siniperca chuatsi in the past is avoided, so that the output of the freshwater shrimps is increased greatly, and the recapture rate of the freshwater shrimps is high; the pseudorasbora parva play a role as a scavenger by feeding on residual feed, so that water quality pollution is reduced greatly, water quality is improved, and the growth of river crabs, freshwater shrimps and pseudorasbora parva is boosted. According to the ecological breeding method, the output and quality of river crabs, freshwater shrimps and pseudorasbora parva are improved remarkably, death rate is lowered, feed waste is reduced, breeding cost is lowered, breeding benefit is improved, income of fishermen is increased, and efficiency improvement of the fishery industry is realized.
Owner:南京宁渔种业研究院有限公司
A kind of intensive aerobic cultivation method of wheat ear carp fry
ActiveCN103718992BReduce competitionImprove work efficiencyBiocideClimate change adaptationPseudorasbora parvaEconomic benefits
Owner:TONGLING RUIPU PEONY IND DEV
Disinfectant for hatching codfish in cages
ActiveCN109511587BWill not cause secondary pollutionImprove hatchabilityBiocideClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention provides a disinfectant for cage hatching of Pseudorasbora parva, and belongs to the technical field of aquaculture. A preparation method comprises the following steps: culturing by inoculating endophyte in camphor to a PDA liquid medium containing sucrose octaacetate and sucrose stearate, sterilizing after fermentation, extracting a fermentation broth obtained, and concentrating toobtain a camphor endophyte metabolite; adding a sodium hypochlorite solution and cyanuric acid into a reaction kettle and simultaneously introducing chlorine gas, reacting and cooling and filtering toobtain sodium dichloroisocyanurate; and adding a citrate buffer, catalpol and casein into the camphor endophyte metabolite and the sodium dichloroisocyanurate, and uniformly mixing to obtain the disinfectant. The disinfectant of the invention has a killing rate of more than 99% on viruses, fungi and bacteria, has better stability, high solubility, longer duration of drug effect, causes no secondary pollution to the cultured water body, and helps improve hatching rate of fish eggs, and has little effect on the growth and meat quality of the advanced fry of Pseudorasbora parva.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
In-vivo test method for fluidity of mitochondrial membrane of liver of pseudorasbora parva
ActiveCN107449766AAvoiding pitfalls of ex vivo assays for mobilityTrue reflection of biological activityFluorescence/phosphorescenceMembrane fluidityPseudorasbora parva
The invention relates to testing of fluidity of fluidity of a mitochondrial membrane of the liver of fish, in particular to an in-vivo test method for the fluidity of the mitochondrial membrane of the liver of pseudorasbora parva. The method comprises steps as follows: S1, a fish body exposure experiment; S2, preparation of the mitochondrial membrane of the liver of the pseudorasbora parva; S3, preparation of a DPH solution; S4, marking of a DPH fluorescent probe of the mitochondrial membrane; S5, determination of the fluidity of the membrane; S6, determination of the content of protein in mitochondria. With the adoption of the in-vivo test method for the fluidity of the mitochondrial membrane of the liver of pseudorasbora parva, influence of an agent on the fluidity of the mitochondrial membrane of the fish is determined accurately and conveniently.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com