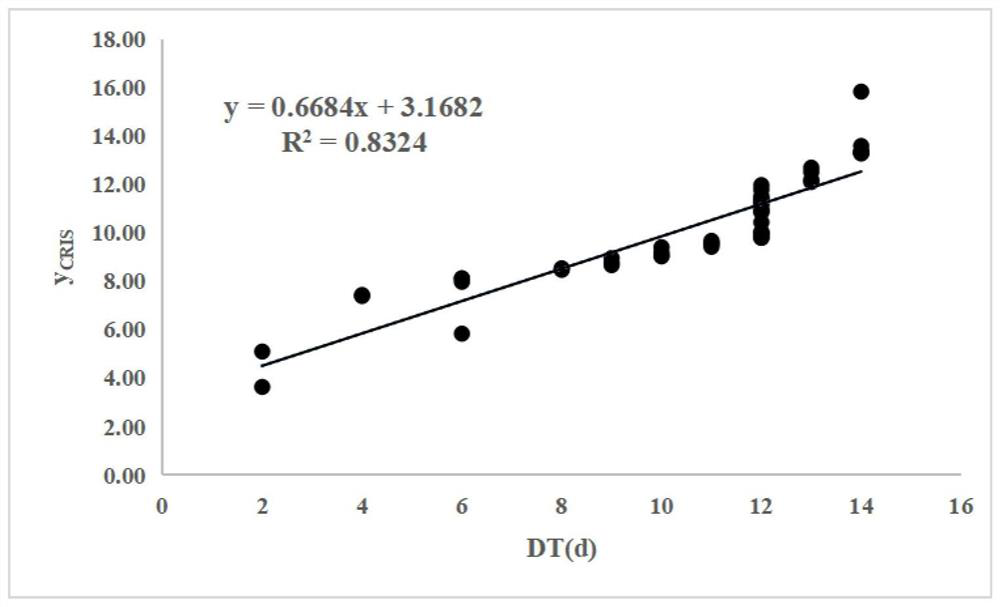
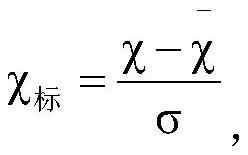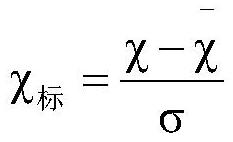Patents
Literature
38 results about "Bivalve mollusk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bivalves are a group of mollusks that includes clams, scallops, oysters, mussels, razor shells, cockles, venus shells, borers, trough shells and many others (some of which live in the deep sea and have yet to be identified). Bivalves are the second most diverse group of mollusks,...
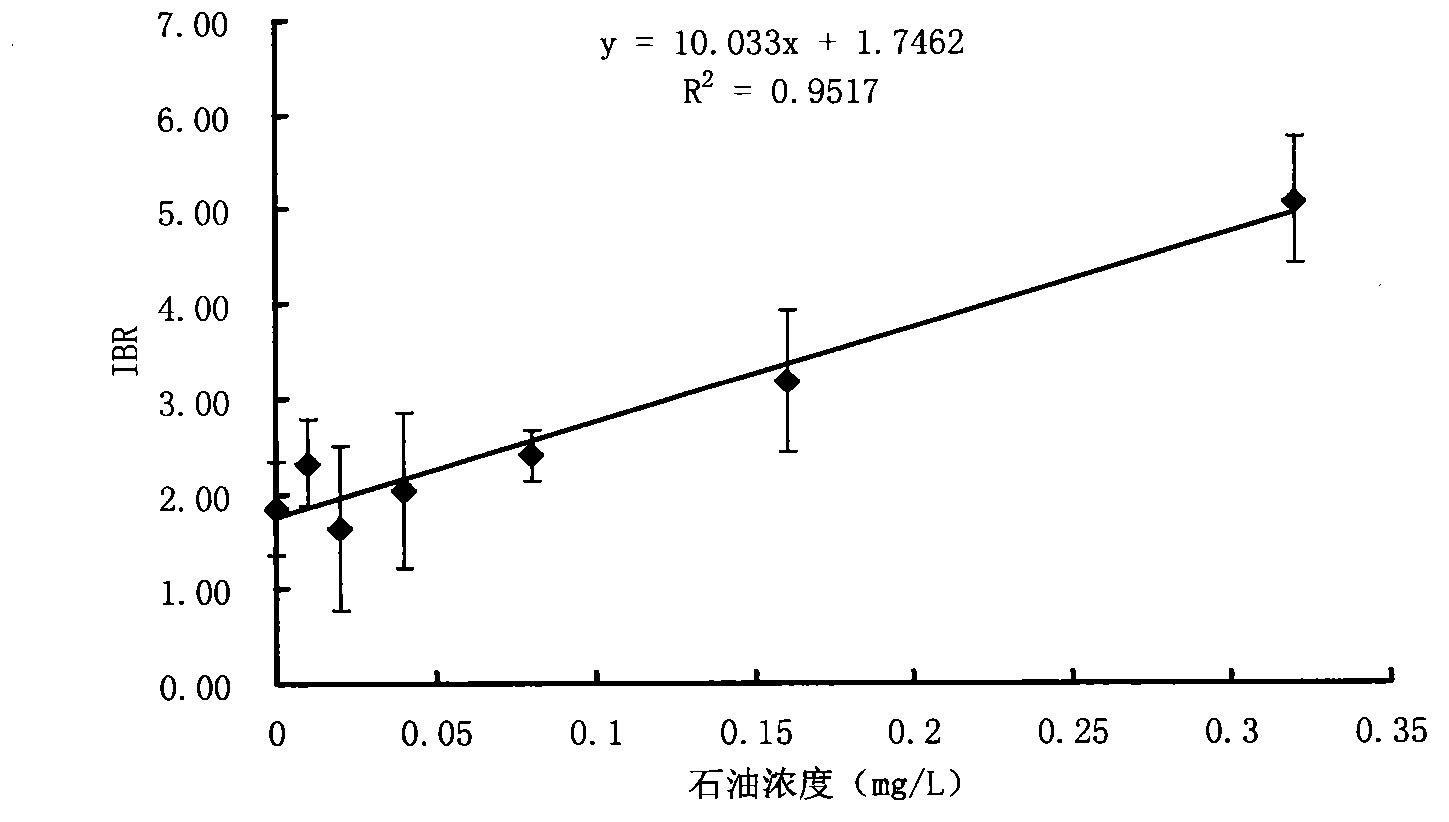
Shellfish monitoring method for ocean oil spill pollution base on integration biomarker method
InactiveCN103146805AReduced stabilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementShort-necked clamPeroxidase
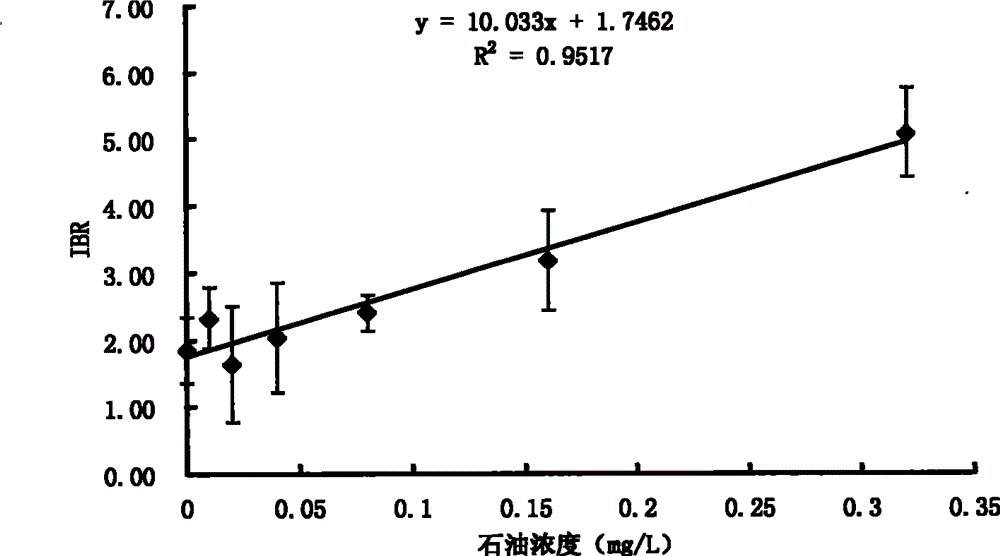
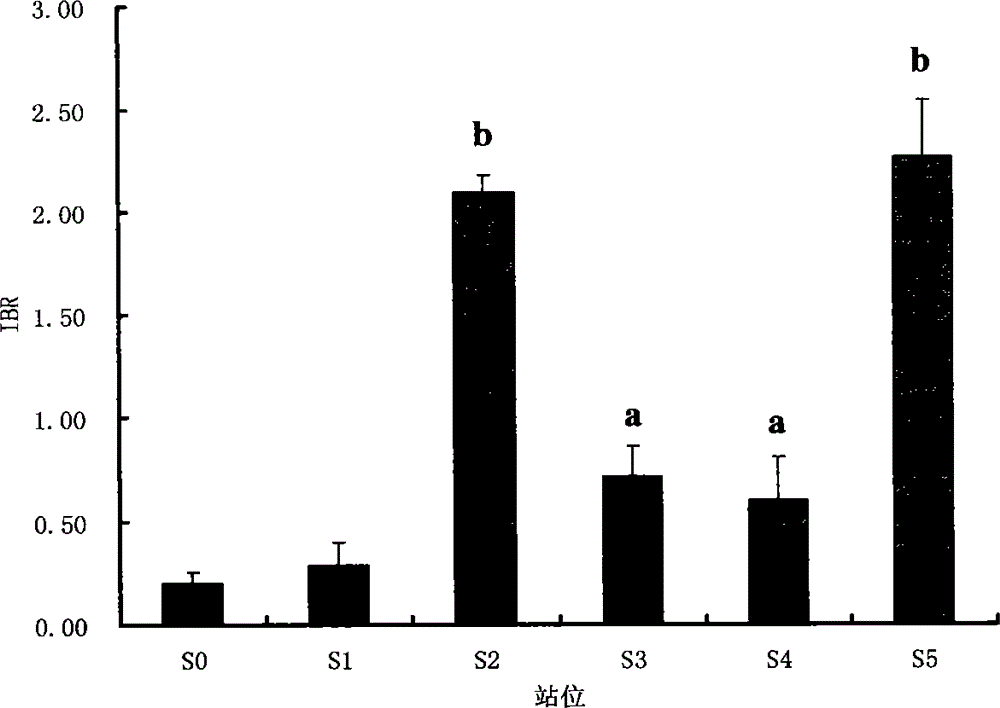
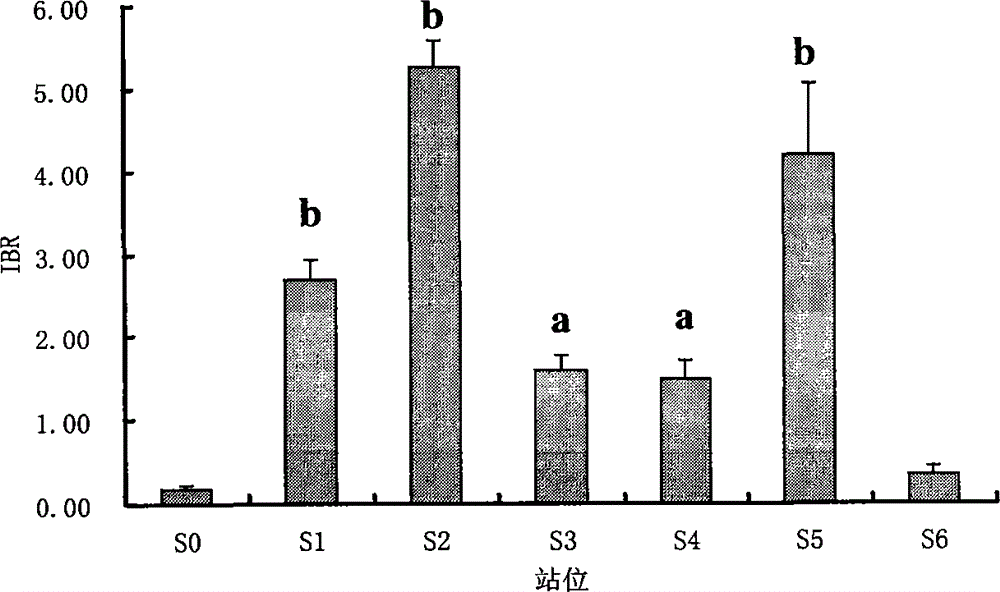
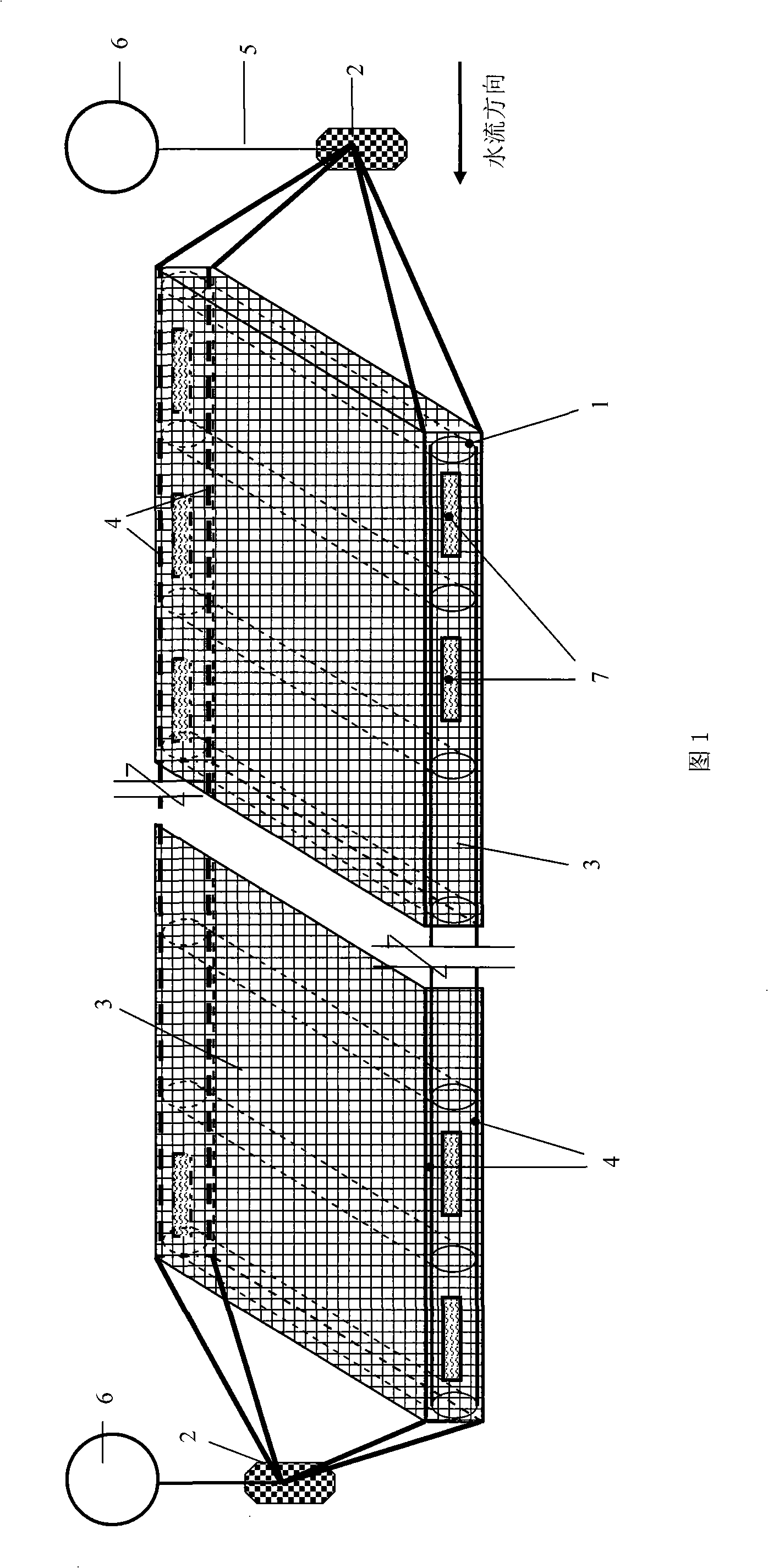
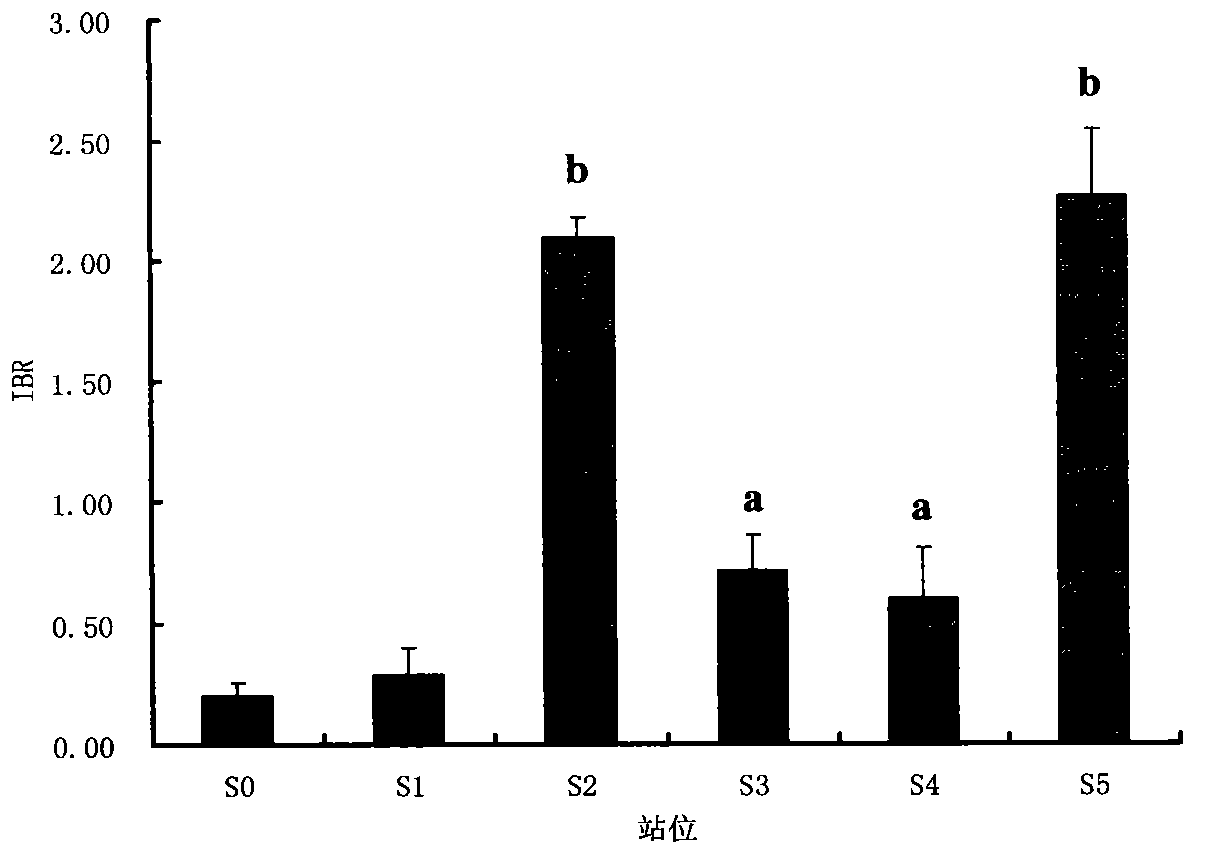
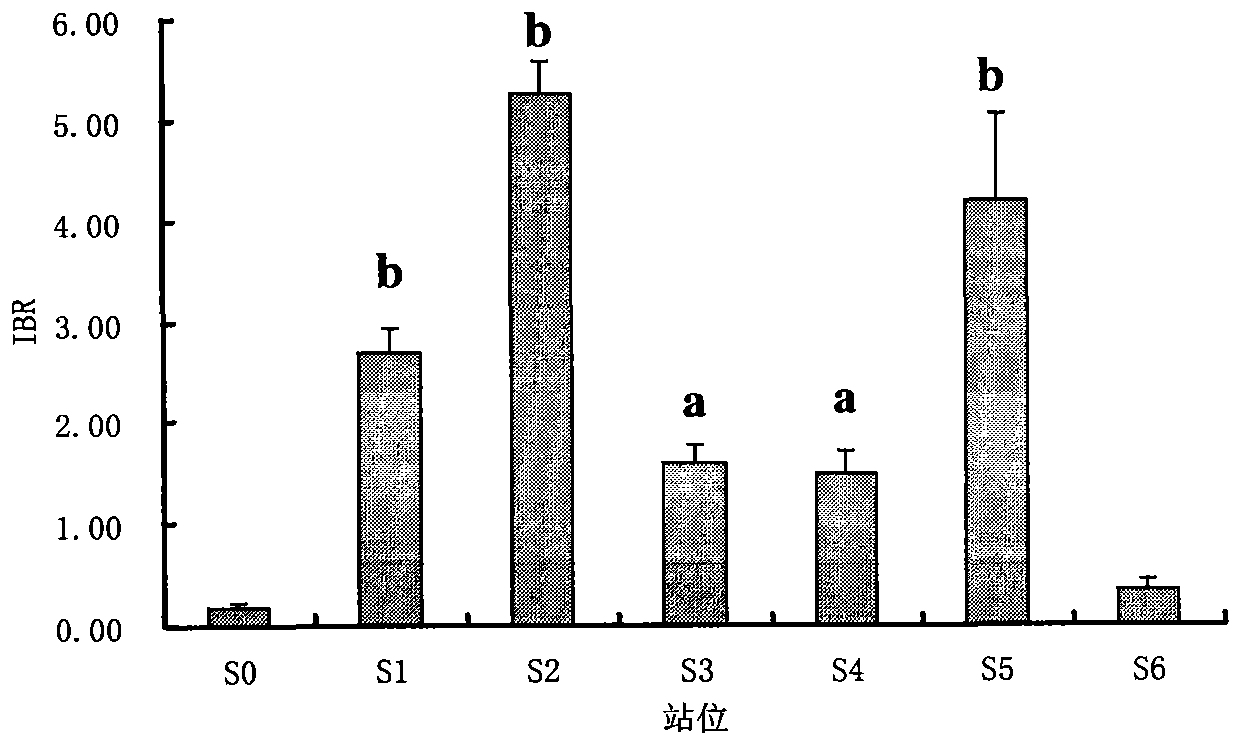
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological monitoring environment, and specifically relates to a shellfish monitoring method for ocean oil spill pollution. The shellfish monitoring method comprises the steps of utilizing typical bivalve mollusk such as short-necked clam and chlamys farreri in China to determine the shellfish visceral mass autioxidant enzyme activities including superoxide dismutase, glutathione glutathione S-transferase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase activity, integrating the enzyme activities so as to form an integration biomarker responding index (IBR), establishing a dose-effect relationship between the IBNNR and petroleum concentration, adopting a one-dimensional variance components method (ANOVA) to carry out notable difference analysis, determining the forcing degree of petroleum pollution on organisms, and finally judging pollution level of the ocean oil spill.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
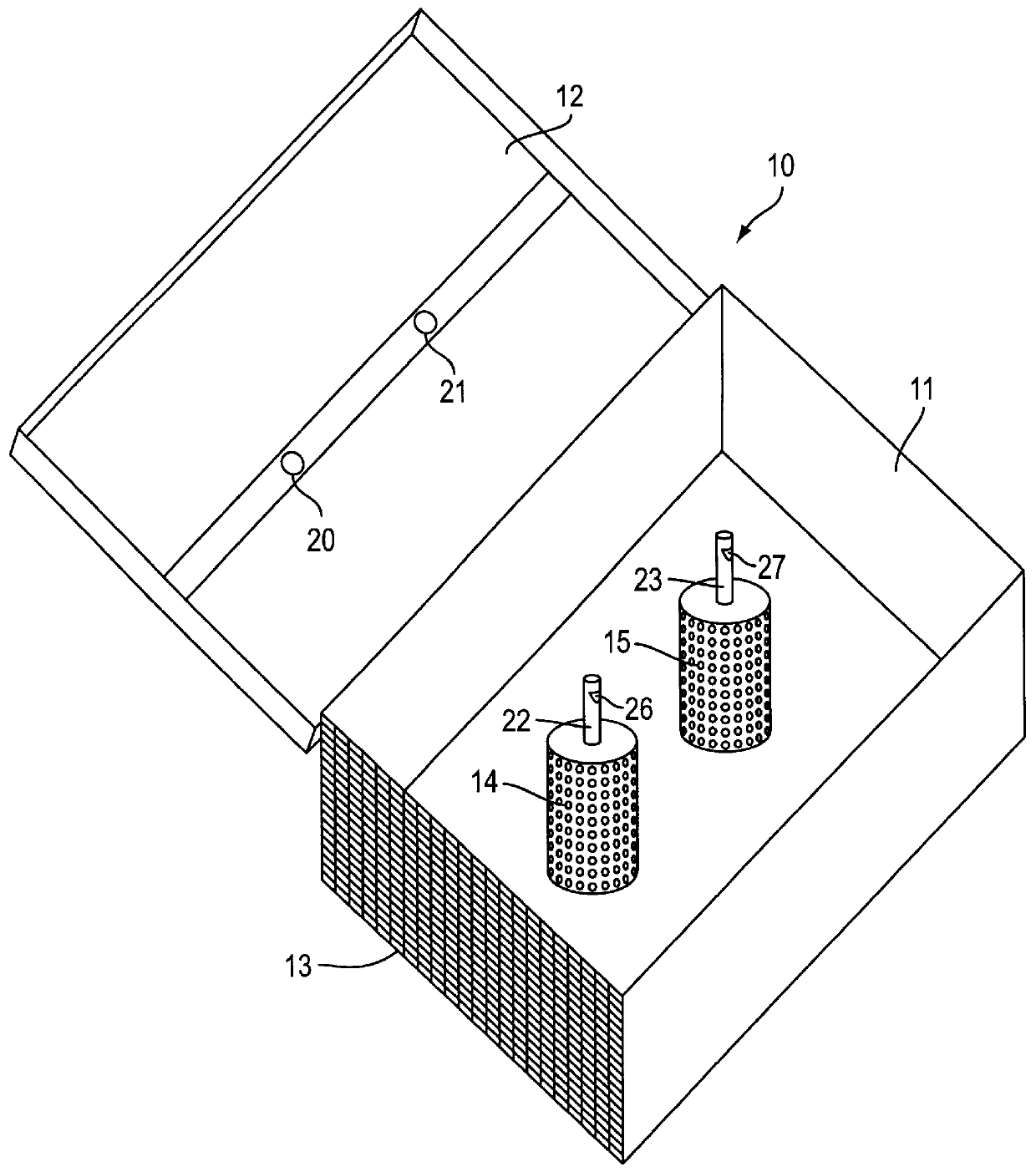
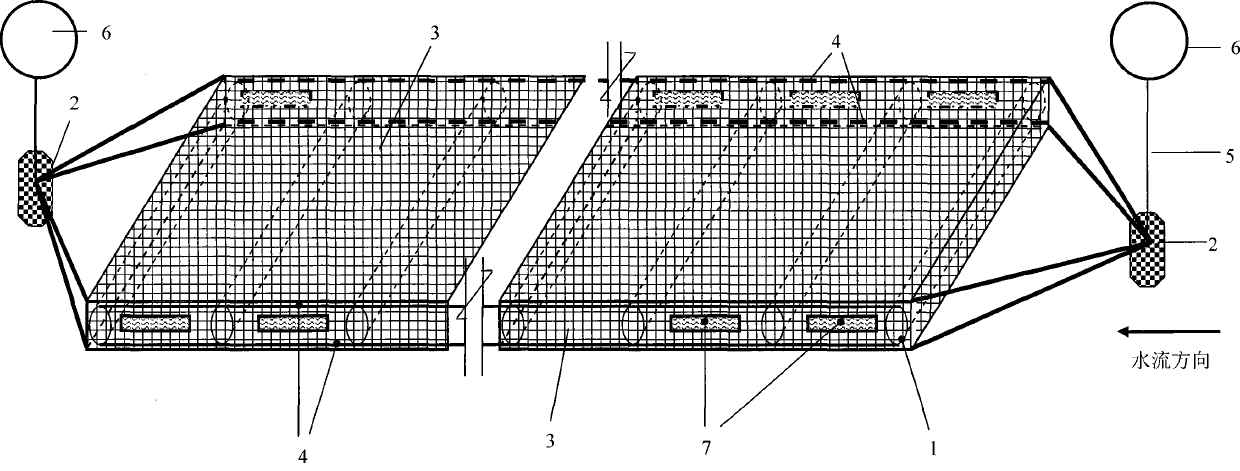
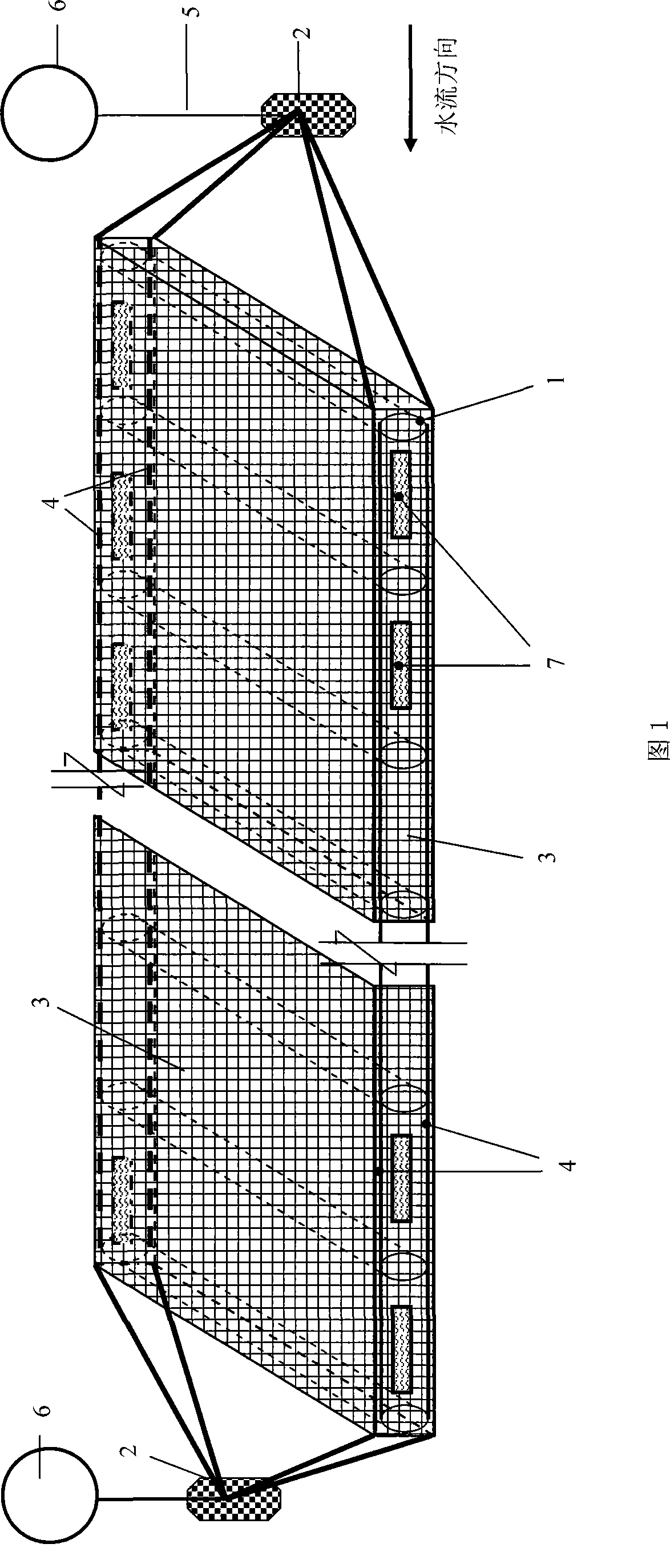
Bottom-seed sea water culture facilities suitable for sediment bottom sea area
ActiveCN101288385AChange design thinkingSuitable for survivalClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEngineeringSeawater
The invention relates to a bottom sowing-type mariculture facility which is suitable for the sea area with silt bottom, in particular to a bottom sowing-type raft frame and a net cage for marine bivalve mollusks, sea cucumbers or mixotrophic culture of marine bivalve mollusks and sea cucumbers. The facility is provided with a PVC pipe, a polyethylene rope for fixing the PVC pipe, a webbing, a stake or an anchor for fixing the facilities, a rope fixed on the stake or the anchor, and a fixable floating ball which is connected to the rope and floats on the surface of water; the PVC pipe is fixed on the polyethylene rope in parallel, the polyethylene rope is arranged in parallel, is perpendicular to the PVC pipe, is positioned at the upper side and the lower side of the two terminals of the PVC pipe and forms the structure similar to a 'soft ladder'; the 'soft ladder' is externally covered by the webbing, and a plurality of independent net cages are formed by combining the PVC pipe, the polyethylene rope and the webbing; the two ends of the undrawn 'soft ladder' are fixed at the bottom of the sea by the stake or the anchor respectively, and the floating ball is fixed at the two ends of the 'soft ladder' by the rope. The facility can effectively prevent the enemies and reduce the influence of storm and ocean current, thus being convenient for management and harvest and favorable to the comprehensive utilization of mariculture area.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of processing bivalve molluscs
InactiveUS6010397APrevent openingImprove tightnessBivalves processingFood preparationFruit juiceEngineering
PCT No. PCT / IE96 / 00030 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 19, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 19, 1997 PCT Filed May 14, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 36236 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 21, 1996A method of processing bivalve molluscs comprises filling a basket-like container (11) with the bivalve molluscs and vibrating the bivalve molluscs within the container (11), thereby inducing them to close tightly under stress and compacting them together. A lid (12) is closed to maintain the compact configuration of the bivalve molluscs, which are cooked by immersing the container into boiling seawater, before being removed and plunged into chilled water to halt the cooking process. The bivalve molluscs are then blast frozen. Because the shells of the bivalve molluscs are tightly closed and better compaction is achieved by vibrating the bivalve molluscs than by compressing them into the container (11), the shells are unable to open and the internal juices are retained within the shells throughout the cooking, chilling and freezing steps, thereby resulting in processed bivalve molluscs having greatly improved organoleptic qualities upon thawing.
Owner:GEARHIES INVESTMENTS
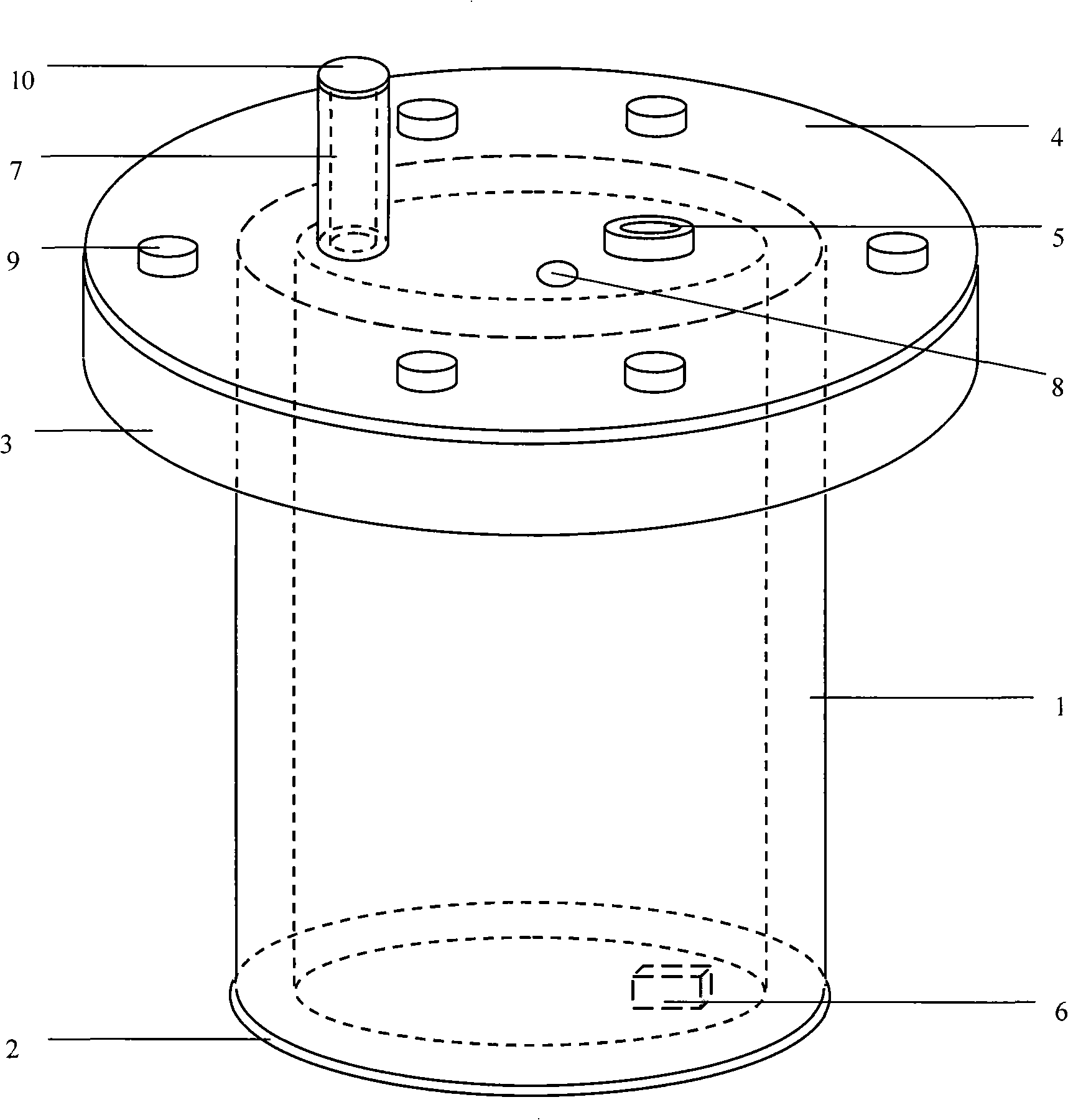
Device for conjunction measuring aquatic animal respiration apocatharsis
InactiveCN101254133AMeets requirements for measuring respiratory metabolismGood scientific research platformSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringAquatic animalFresh water organism
The invention relates to a device used for matching with the measurement for respiration and excretion of aquatic animals, in particular to an attachment used for matching with various dissolved oxygen probes to measure the respiration and the excretion of various aquatic animals such as fish, shrimps as well as crabs, bivalve mollusks, sea cucumbers, etc. living in freshwater or seawater. The device takes an organic glass slab-bottom at the bottom of a crude organic glass tube as a back cover to form a vessel; a concentric-circle organic glass flange provided with holes is sleeved on the upper end of the crude organic glass tube at the height parallel to a nozzle; an organic glass cover plate is arranged on the top of the organic glass flange to be used as an upper cover; a fine organic glass tube and a PVE tube cuff are arranged on the organic glass cover plate; the PVE tube cuff is inserted into the dissolved oxygen probes in a sealing way; a diving pump is arranged under the PVE tube cuff. The device solves the problems that the prior art cannot reflect the metabolic status of the aquatic animals factually and accurately, etc., and has the advantages of simple structure, low manufacturing cost, being easy to match with correlated instruments to detect accurately, etc.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface-active substance composition moireuphe and method for preparing the same and use thereof
ActiveCN101112393AEnsure enrichmentMake sure to removeRespiratory disorderMolluscs material medical ingredientsDecreased surfactantPhospholipid complex
The present invention relates to a surfactant moryoupe and the preparation method and the application of the surfactant, which pertains to the technical field of pharmaceutical industry. The composition is made by extraction, purification and other steps of the tissues of bivalves mollusks, the composition contains rich phospholipid complex of the seafood which is composed of polyunsaturated fatty acids, wherein, the composition includes plasmalogen, active short-chain peptides and amino acids etc. The composition of the present invention has the surface activity of the surfactant, which can be used for preparing the drugs for replacement, therapy during the lack of pulmonary surfactants; furthermore, the invention has no immunogenicity.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
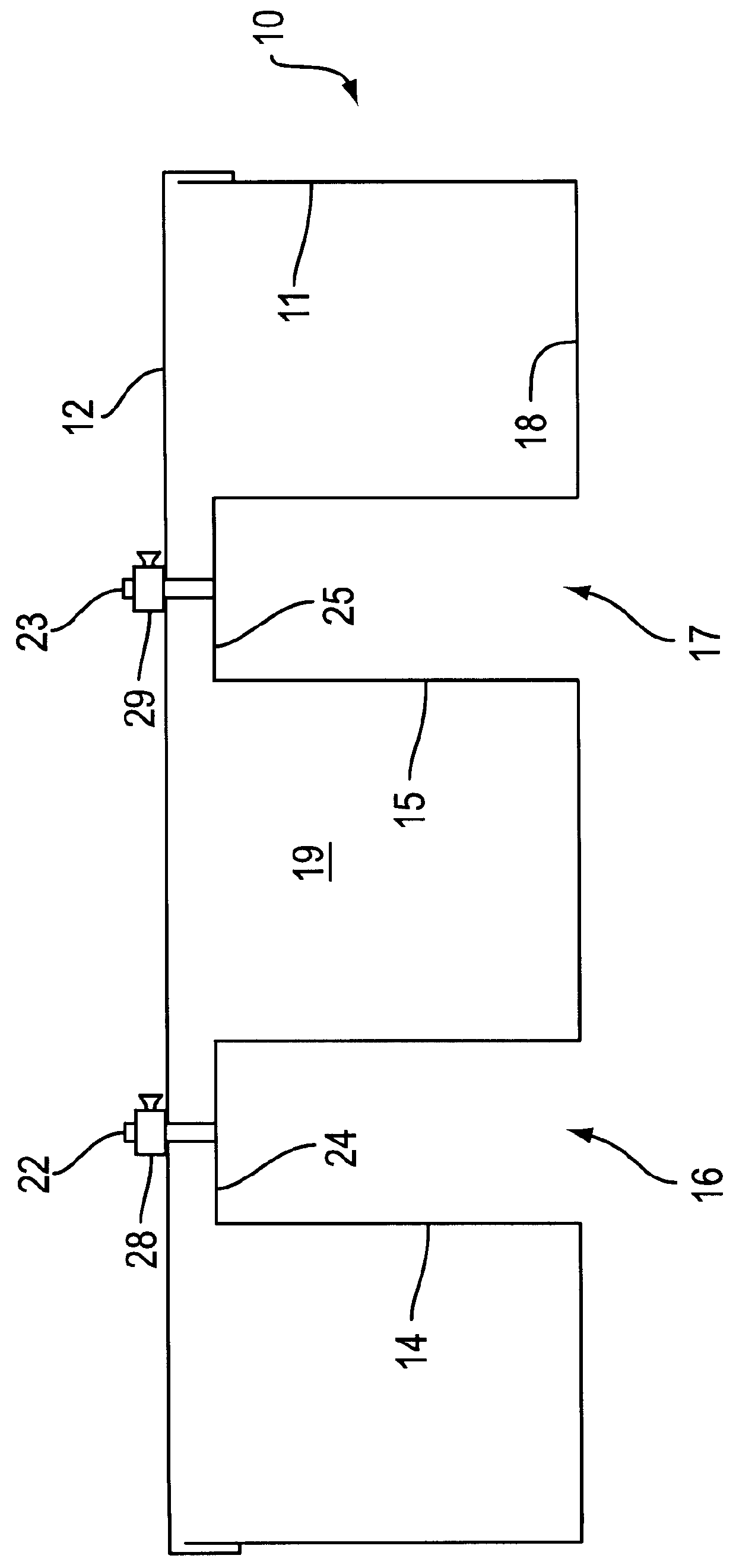
Experiment method and system for researches on seawater environmental stresses
InactiveCN105191844AAdjust the speed of changeChange speedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater storage tankInterference factor
The invention discloses an experiment method and system for researches on seawater environmental stresses. According to the experiment method, a mother solution of the seawater environmental stresses is added to a culture water tank with a drop method and is uniformly mixed with surrounding seawater through a mixing device, and the shellfish culture environment is changed gradually. The system comprises an environmental stress device for accommodating the mother solution of the environmental stresses and a culture device located below the environmental stress device, wherein the environmental stress device comprises an airtight water storage tank provided with a water inlet sealing screw cap above, the lower side of the airtight water storage tank is connected with a gas inlet pipe and a liquid outlet hose respectively, and a speed-changing knob is further arranged on the water outlet hose; the culture device is a culture water tank accommodating seawater, and an oxygen inflating device is further arranged at the bottom of the culture water tank; the mother solution is mixed to the culture water tank through the liquid outlet hose in a suspended dripping manner. With the adoption of the experiment method and the experiment device, the living environment of bivalve mollusks can be truly gradually changed, other interference factors are avoided, and the accuracy and the precision of the experimental researches on the seawater environmental stresses are improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
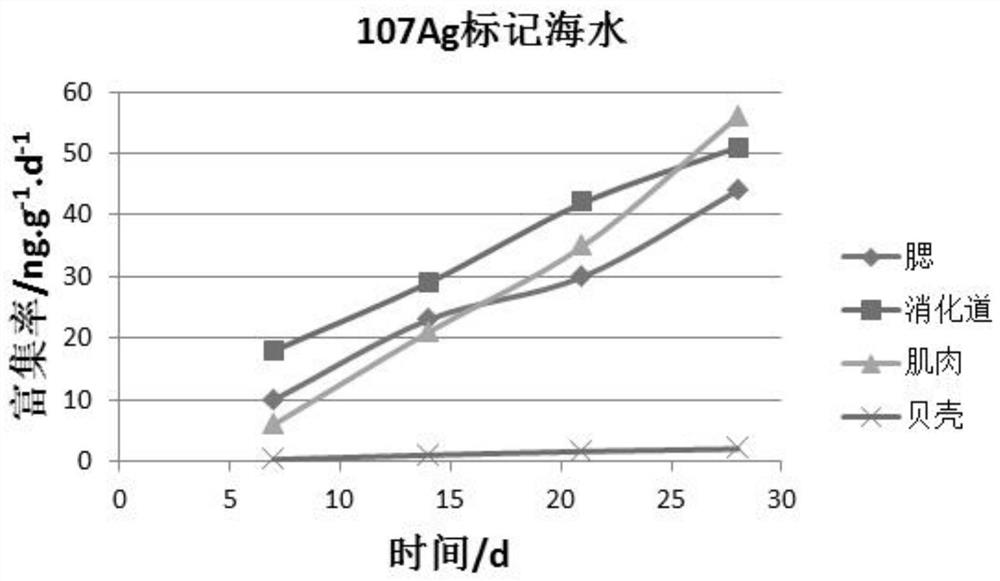
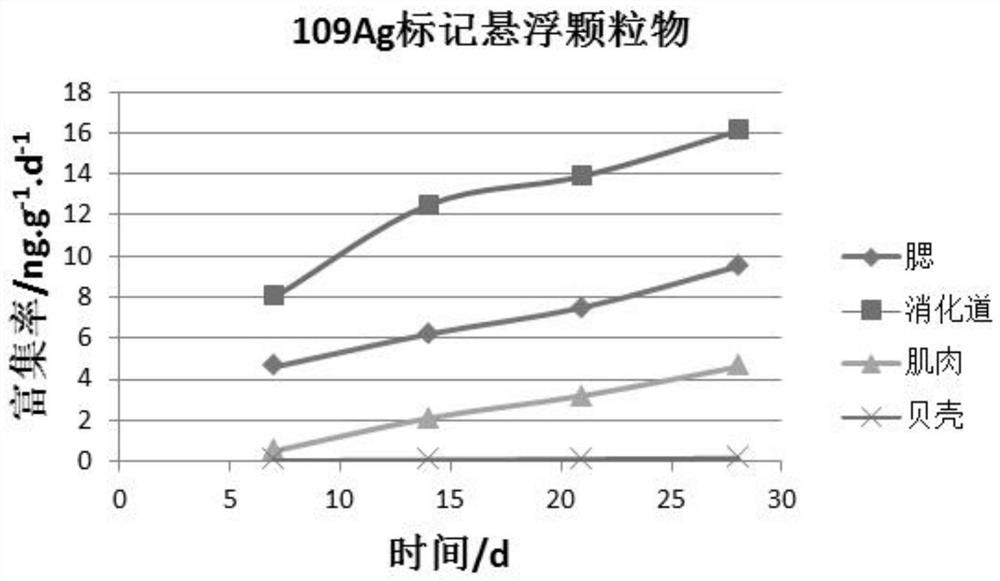
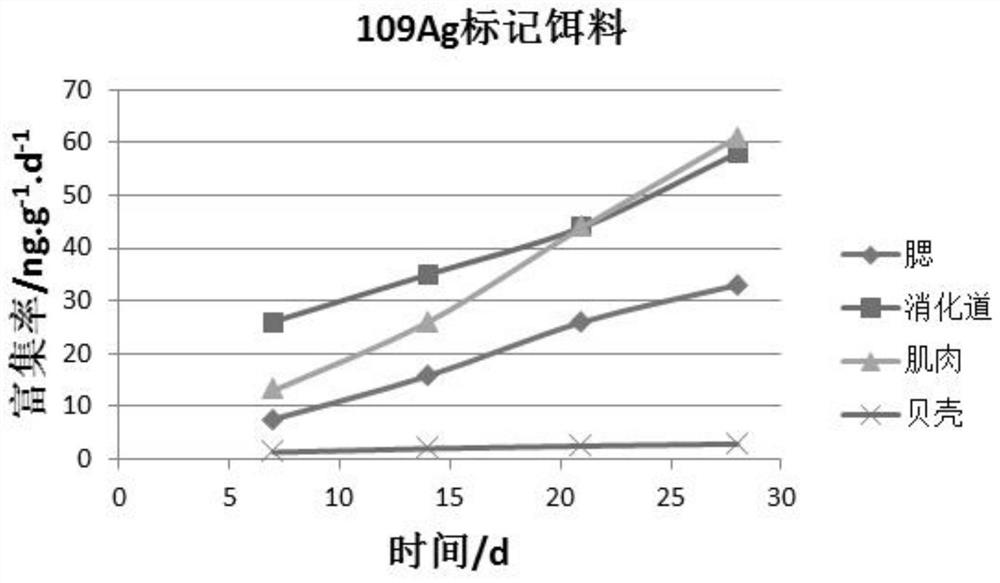
Method for tracing heavy metal enrichment path of suspended bivalve mollusks
ActiveCN111727915AOvercoming untraceable flawsClimate change adaptationPreparing sample for investigationBivalve shellSilver isotope
The invention discloses a method for tracing a heavy metal enrichment path of suspended bivalve mollusks. The method comprises the step of marking a selected medium with stable silver isotopes so as to obtain a marking medium, wherein the medium is a medium contained in a bivalve mollusk culture environment; and the stable silver isotopes comprise silver 107 and silver 109. According to a scheme provided by the invention, the silver stable isotopes (107Ag, 109Ag) are applied to tracing the adsorption and enrichment conditions of the suspended bivalve mollusks to the silver in different environmental media (seawater, suspended particulate matters and baits), so the source of the silver entering the suspended bivalve mollusks is obtained; meanwhile, the distribution conditions of the silverwith different sources in different tissues in the suspended bivalve mollusks are obtained. According to the scheme provided by the invention, the defect that traceability cannot be achieved by utilizing a single isotope is overcome; the silver stable isotopes which are simple in isotope composition and easily available are adopted as a tracer agent; and a technical support is provided for prevention and control of marine heavy metal silver pollution.
Owner:自然资源部第四海洋研究所
Induction and extraction separation method of marine organism-sourced high-efficiency heavy metal removing agent shellfish metallothionein
ActiveCN104910273AReduce removal processReduce security impactPeptide preparation methodsMetallothioneinsAntidoteIon exchange
The invention discloses an induction and extraction separation method of marine organism-sourced high-efficiency heavy metal removing agent shellfish metallothionein. The induction and extraction separation method comprises following steps: (1) a selected bivalve mollusk is subjected to 2 to 7 days of temporary rearing in clean seawater, and dead ones are removed; (2) directional induction is carried out; (3) shells are open so as to collect shellfish meat, a buffer solution is added at a certain ratio, and an obtained extracted solution is subjected to thermal treatment so as to remove impurity protein; (4) the extracted solution is cooled, and is delivered through a screen so as to remove precipitates via filtering, an obtained supernate is subjected to multi-stage ultrafiltration and microfiltration, is delivered through a nanofiltration multielement film integrated purification system so as to remove macromolecules, and is subjected separation purification and concentration so as to obtain a MT crude product; and (5) the MT crude product is subjected to dextrangel and ion-exchange column chromatography combined-purification separation, and drying so as to obtain a high-purity marine organism-sourced MT product. The induction and extraction separation method is capable of increasing metallothionein content in shellfish effectively, and obtaining marine organism-sourced high-efficiency heavy metal antidote products which possess high efficiency removing effects on heavy metal, and are safer.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Method for purifying cadmium in bivalve mollusc
ActiveCN109042410AReduce purification costsEfficient purificationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaVitamin CPhosphopeptide
The invention relates to the technical field of purifying heavy metal in edible marine products, and discloses a method for purifying cadmium in bivalve mollusc, which comprises the following steps: adding nano calcium carbonate suspension, magnesium ion water solution, vitamin C and casein phosphopeptide into the water body cultivating the bivalve mollusc; replacing the water body every day, reading nano calcium carbonate suspension, magnesium ion water solution, vitamin C and casein phosphopeptide. According to the invention, the method is simple in operation, the purification cost is low and the operation time is short, the Cadmium ion residue in the edible bivalve bodies can be efficiently purified, and the product quality and flavor are not affected. According to the invention, when the bivalve mollusc polluted by Cadmium is treated by using the method, the removal rate of cadmium in the bivalve mollusk bodies can reach 36.5-38.4% after 7 days.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
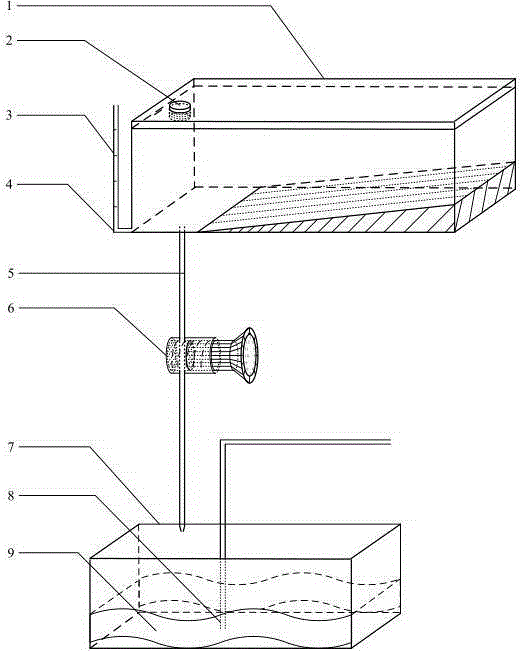
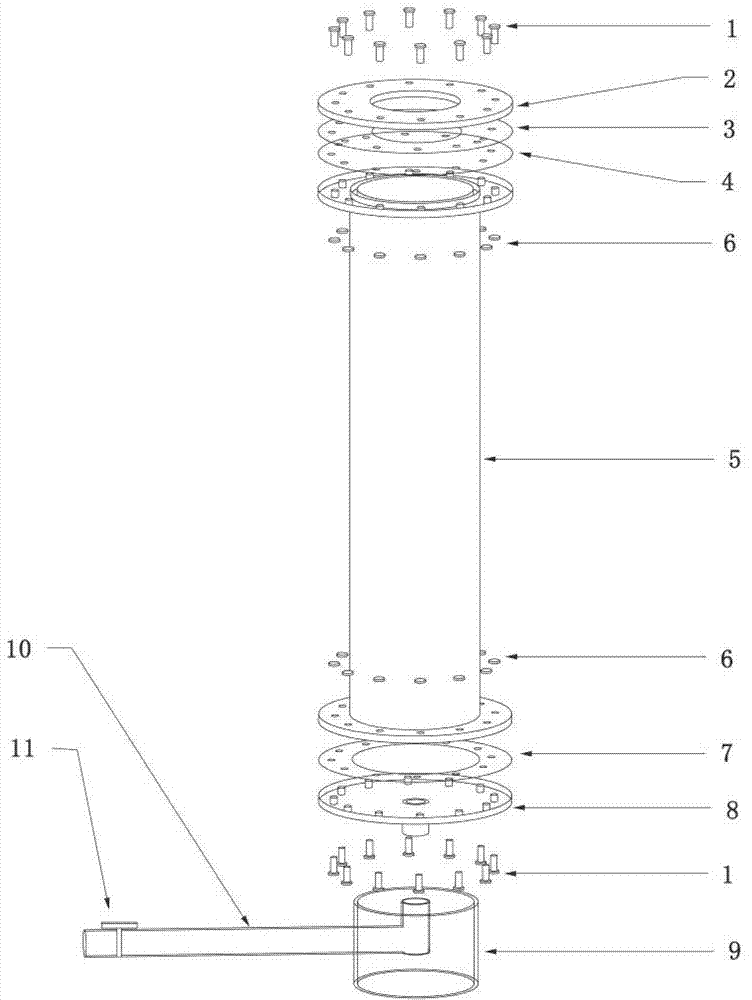
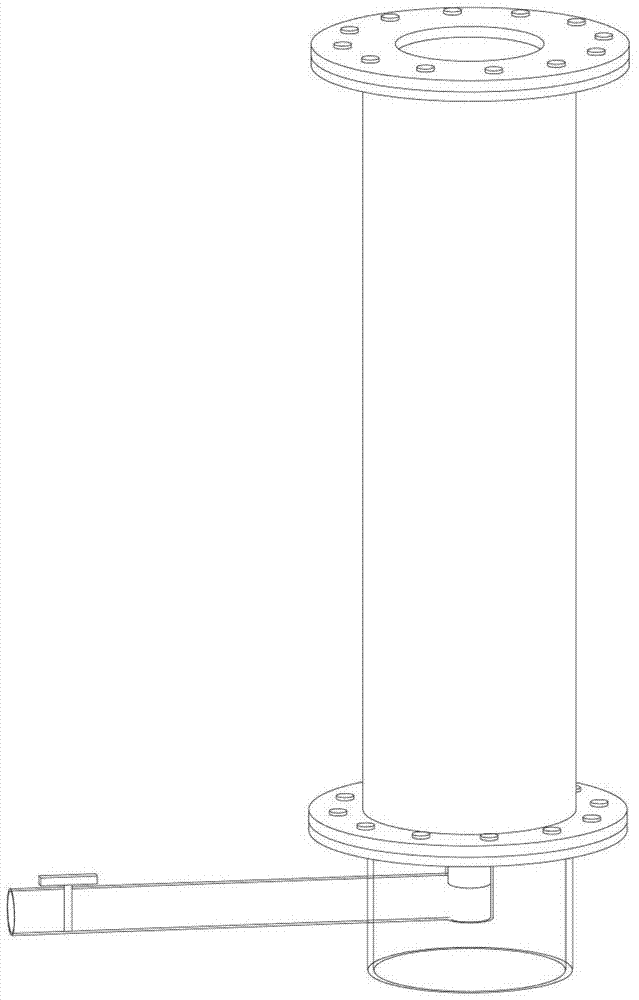
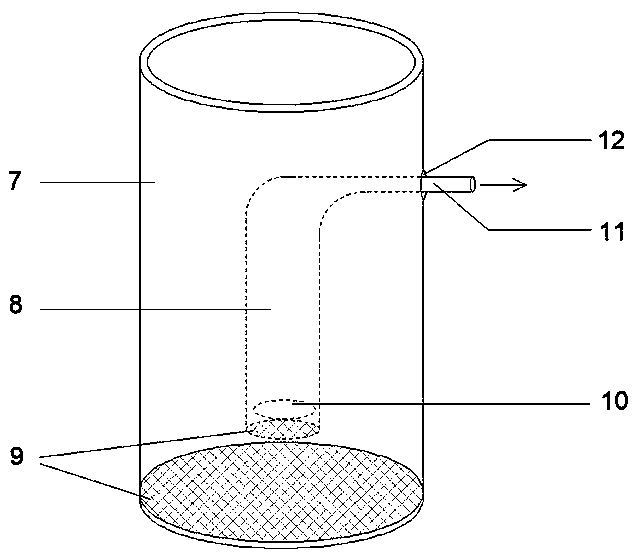
Culturing device and culturing method used for preventing atrina pectinata larva from floating and adhering
ActiveCN102884999APrevention of floating adhesionEvenly distributedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEngineeringOrganic glass
The invention relates to the production of aquaculture bivalve mollusk seeds and particularly relates to a culturing device and a culturing method used for preventing atrina pectinata larva from floating and adhering. The culturing device comprises an organic glass tube, a hollow plastic base and a plastic hose, flange pieces are arranged at the two ends of the organic glass tube and are respectively fixed with an upper-layer flange piece and a lower-layer flange piece by bolts, a connecting tube is arranged in the middle of the lower-layer flange piece, a hole is formed in the side wall of the hollow plastic base, the plastic hose passes through the hole to be connected with the connecting tube arranged in the middle of the lower-layer flange piece; boulting cloth and a silicon rubber gasket are arranged between the flange piece at one end of the organic glass tube and the upper-layer flange piece; and a silicon rubber gasket is arranged between the flange piece at the other end of the organic glass tube and the lower-layer flange piece. The culturing device designed by the invention is used for culturing the atrina pectinata larva, the larva floating and adhering rate is reduced by 94%-98%, the survival rate of the larva is more than 85%, the survival rate of the atrina pectinata larva is greatly increased, and the culturing efficiency of the atrina pectinata larva is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optimization feeding method for culturing shrimp
InactiveCN101053318APromote growthImprove conversion efficiencyClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffShrimp cultureZoology
An optimization feeding method for shrimp culture includes feeding according to the current feeding time and mode, its characteristcs are during the maturation period of shrimp to adopt natural animal baits and compound feeds by 2-4 :1 frequency or weight ratio to feed in turn; the said natural animal baits are sleeve-fishs, clamworms, minitype shrimps and crabs or bivalve mollusks which can be fed naturally by shrimp; the said compound feeds are juvenile shrimp or adult shrimp containing protein over 40 percent. To adopt this feeding mode of the present invention can promote shrimp growth, improve feed conversion efficiency and avoid feed resource waste caused by selectivity.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
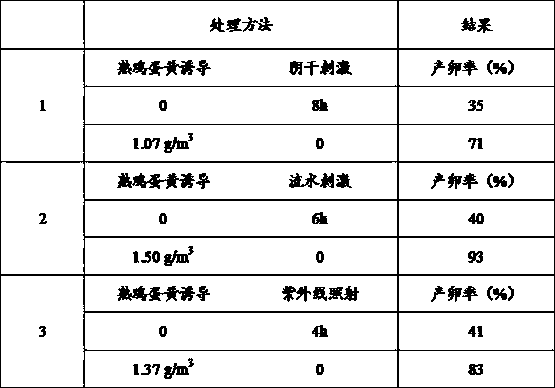
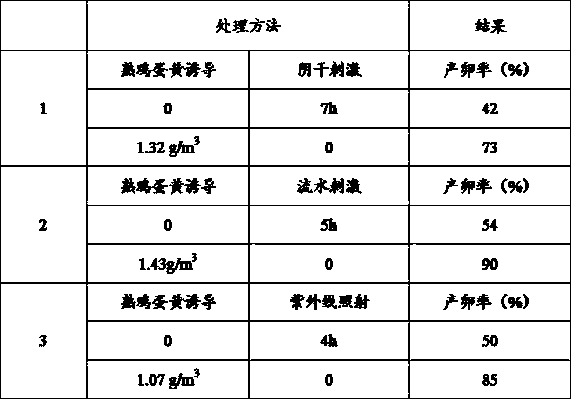
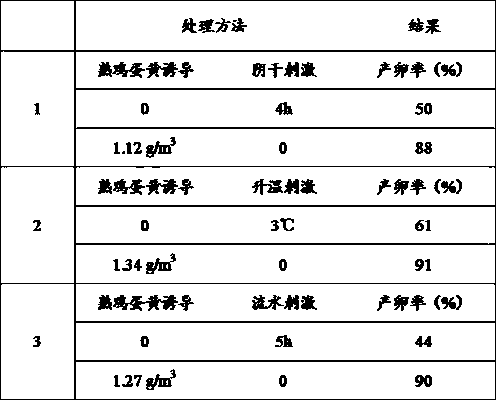
Inductive agent for inducing marine bivalve mollusk to produce eggs as well as application method thereof
ActiveCN108114001ALow costEasy to operateClimate change adaptationBird material medical ingredientsShort-necked clamAquatic product
The invention relates to an aquaculture method of shells, in particular to an inductive agent for inducing marine bivalve mollusk to produce eggs as well as an application method thereof. The application method comprises the following steps: taking cooked egg yolk liquid obtained through bolting-silk treatment as the inductive agent, splashing the inductive agent in a parent shellfish pool uniformly according to the concentration, being 1.0 to 1.5 g / m<3>, of the cooked egg yolk under the conditions that the water temperature is 20 to 30 DEG C, the salinity is 25 to 35 and the pH value is 7.5 to 8.3, treating for 0.5 to 1 hour, performing pool separation according to a siphonage method after the parent shellfishes lay eggs, fully filling the pool with water again, and diluting the concentration of cooked egg yolk. Compared with other stimulation methods, the method has the following advantages: the egg producing efficiency can be increased by 30 to 50 percent and the egg producing efficiency of the parent shellfishes can be effectively improved. The inductive agent can be applied to various marine bivalve mollusk such as hard-shelled clam, clam, short-necked clam, cyclina sinensis gmelin, bay scallop, chlamys farreri and patinopecten yessoensis.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
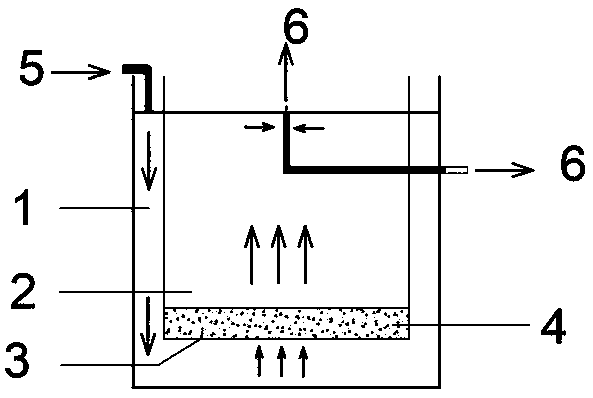
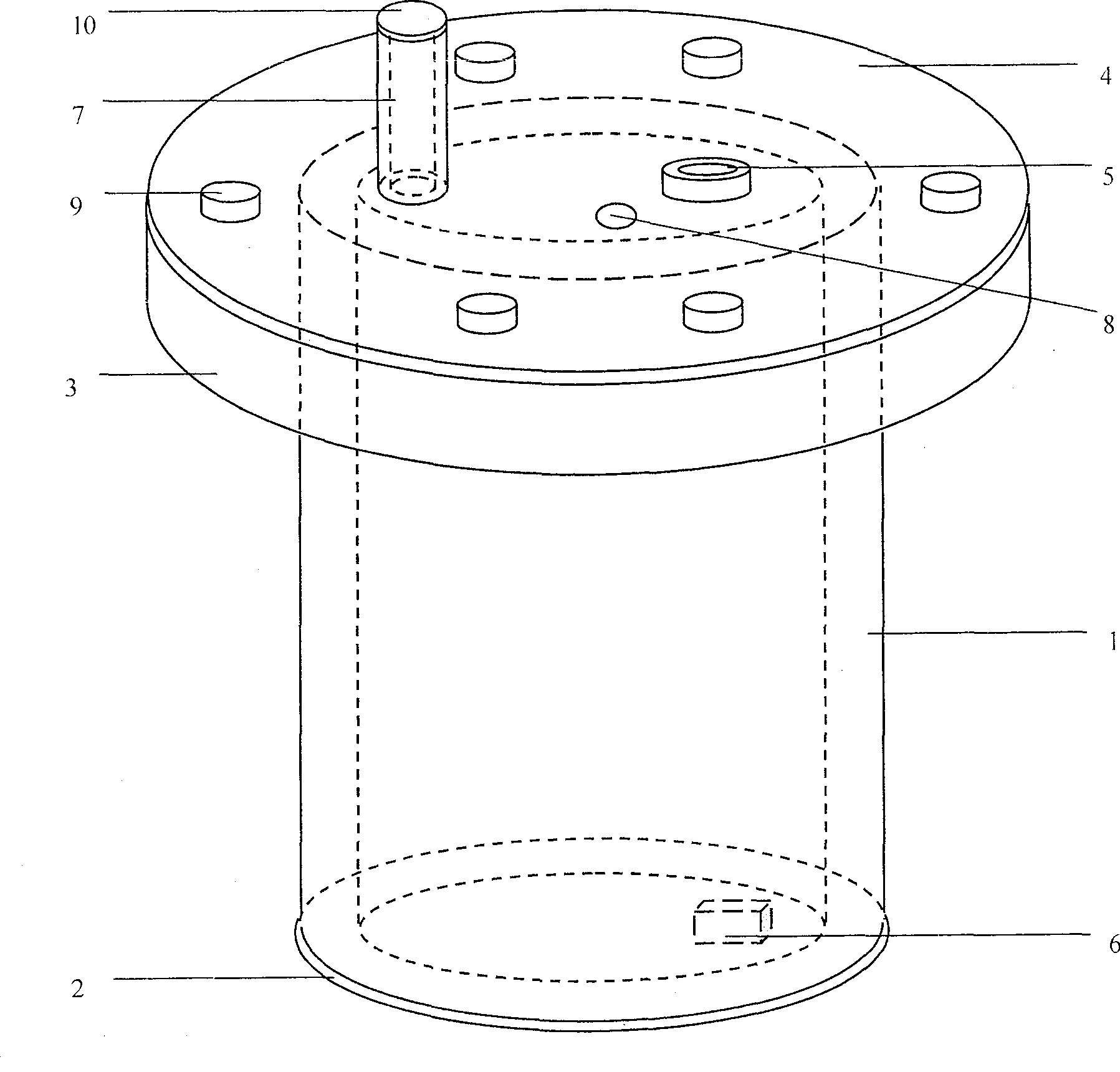
Sealed inflatable upwelling culture device for intermediate culture of bivalve mollusks and culture method thereof
PendingCN109169442AImprove survival rateFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaElectricityEngineering
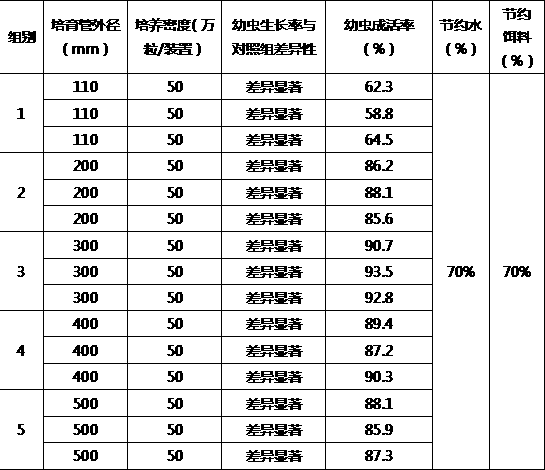
The invention provides a sealed inflatable upwelling culture device for intermediate culture of bivalve mollusks. The device includes a culture pipe, a negative pressure pipe, filter nets, an inflatorand a water outlet pipe, wherein the culture pipe is the outermost layer of the whole device, a bottom end of the culture pipe is provided with the filter mesh, an upper end side wall of the culturepipe is provided with a water outlet hole, the negative pressure pipe is placed in the culture pipe, a bottom end of the negative pressure pipe is provided with the filter net, one end of the water outlet pipe is connected with the negative pressure pipe, the other end of the water outlet pipe is placed at the water outlet hole of the culture pipe, and the inflator is placed on the filter net inside the negative pressure pipe. The culture device is advantaged in that through the culture method, water and electricity resources are greatly saved, the growth rate of juvenile mollusks is 20% to 50% higher than the traditional method, the survival rate is over 90%, and the seawater and the bait can be saved more than 70%.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene editing method for electrotransfected bivalve mollusks
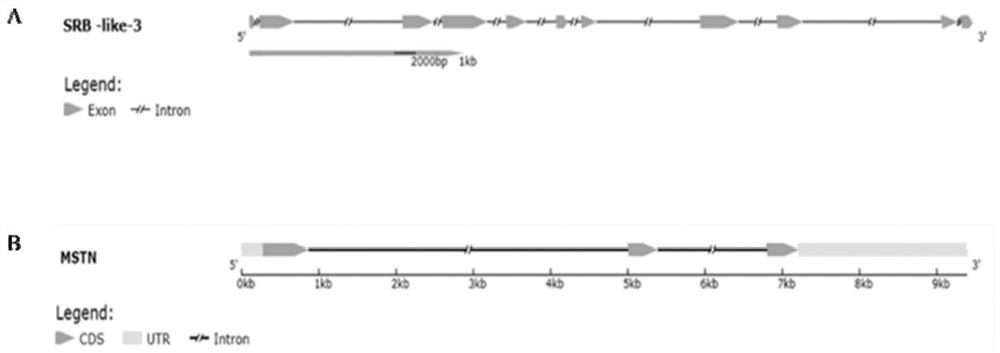
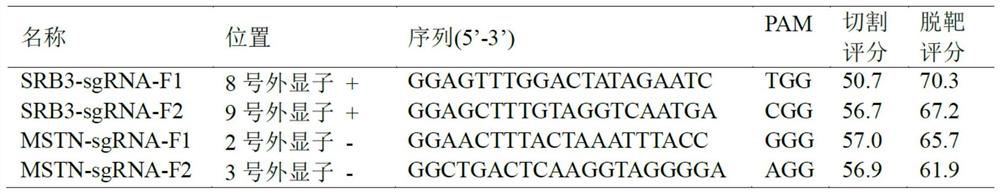
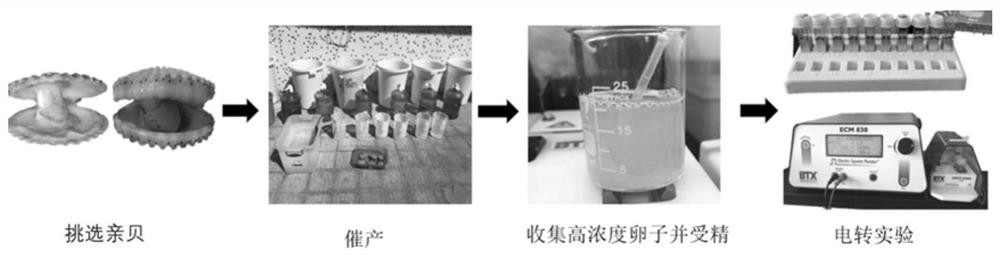
PendingCN114164232AEasy to operateSimple equipment requirementsHydrolasesInvertebrate cellsBivalve shellZoology
The invention belongs to the field of marine biology application, particularly relates to the field of shellfish molecular genetic breeding, and relates to an electrotransfection bivalve shellfish gene editing method, the concentration of recombinant plasmids is kept to be greater than or equal to 2 mu g / mu l, sgRNA and Cas9 protein are mixed into RNP (sgRNA and Cas9 protein complex) according to the volume ratio of 2: 1, the working concentration of the sgRNA is greater than or equal to 50 ng / mu l, the working concentration of the Cas9 is greater than or equal to 250 ng / mu l, the working concentration of the sgRNA is greater than or equal to 50 ng / mu l, and the working concentration of the Cas9 is greater than or equal to 250 ng / mu l; an electrotransfection method is applied to bivalve mollusk gene editing, the electric pulse condition is that the pulse interval is 1s, the number of pulses is 2, the electrode distance is 4mm, pulse voltage and pulse time are changed, the pulse voltage range is 50V-500V, and the pulse time is 100 microseconds-1ms. The method disclosed by the invention can provide a basis for bivalve gene function verification and gene breeding application, and has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low cost, easiness in popularization and the like.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Shellfish monitoring method for ocean oil spill pollution base on integration biomarker method
InactiveCN103146805BReduced stabilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementShort-necked clamPeroxidase
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for processing breeding water of tortoises
InactiveCN101843223AProtect environmentImprove cleanlinessClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquaculture industryMolgula
The invention relates to a method for processing breeding water of tortoises, which adopts a biological cleaning mode by a biologic chain principle. Fresh water fry and fresh water snail mollusk and / or bivalve mollusk are bred in a breeding pond of tortoises, and the breeding water of tortoises can be cleaned by a food chain formed by excrement of the tortoises, food residues, the fresh water fry, the fresh water snail mollusk and / or the bivalve mollusk. The body length of the fresh water fry is less than 10 centimeters; the breeding density of the fresh water fry is 1-25 fish fry per square meter, and the fresh water fry can be one of or more than one of scaled fish fry, carp fry, grass carp fry, chub fry and goldfish fry. The fresh water snail mollusk can be one of or more than one of mudsnail, Shankeng snail and sand snail. The fresh water bivalve mollusk is clam. The method for processing breeding water of tortoises has the advantages of easy realization, easy operation, environmental protection and low processing cost, accords with new requirements of new agricultural and sideline aquaculture for green ecology, and is suitable for the technical field of tortoise breeding.
Owner:惠州李艺金钱龟生态发展有限公司
Method for inducing oviposition and spermiation of bivalve mollusks
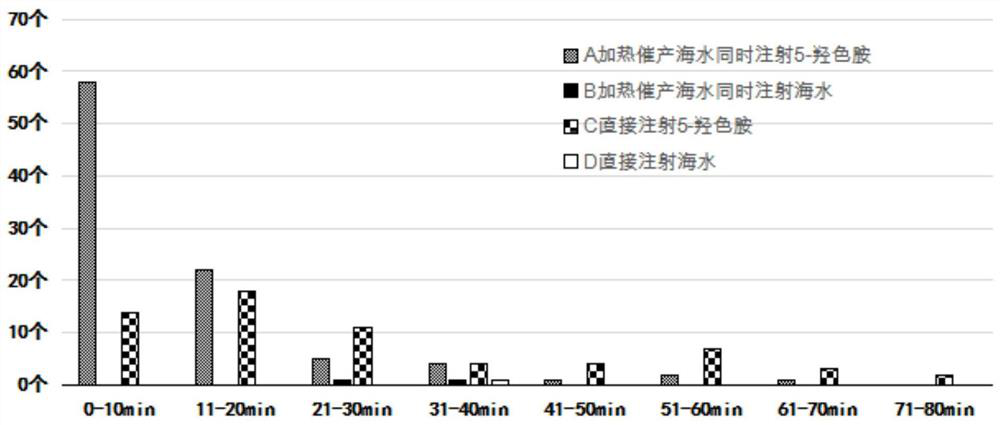
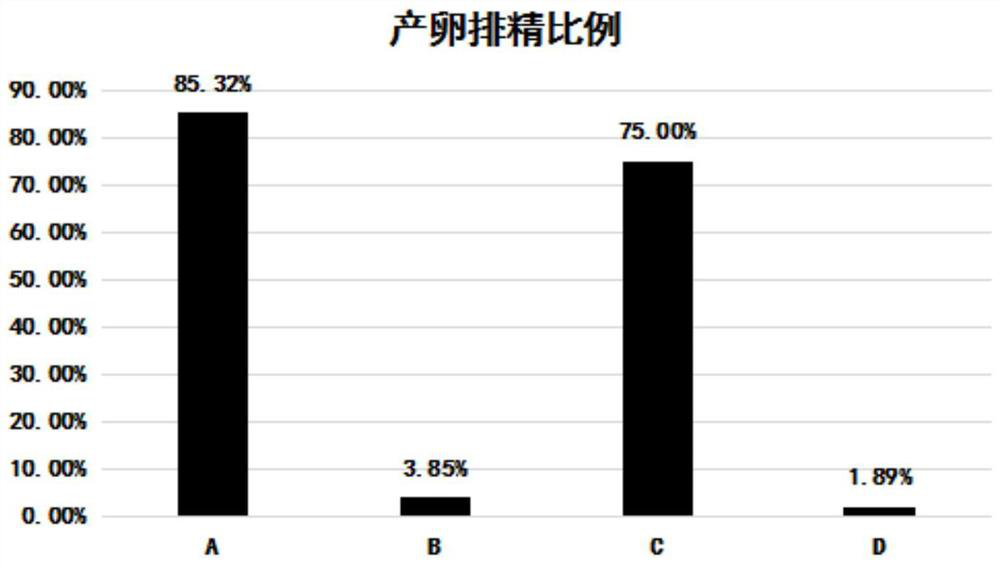
PendingCN113068642AAvoid cross infectionEjaculation and egg production are in stepClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBivalve shellZoology
The invention relates to a method for inducing oviposition and spermiation of bivalve mollusks, and belongs to the field of aquaculture. The method for inducing oviposition and spermiation of the bivalve mollusks comprises the following specific steps of preparing 5-hydroxytryptamine with the concentration of 2mM by using filtered seawater; adding pure filtered seawater into a container in advance and increasing the temperature by 3-8 DEG C compared with the normal culture temperature for later use; selecting parent mollusks with mature gonads, cleaning, putting into a disc-shaped container, and adding the filtered seawater which is half of the width of the parent mollusks until the mollusks are opened; injecting the prepared 5-hydroxytryptamine solution into the gonads of the parent mollusks, and then putting the parent mollusks into the prepared container to wait for oviposition and spermiation. Within 30 minutes, the oviposition and spermiation rate of the parent mollusks is 75% or above; compared with a traditional method, the method for inducing oviposition and spermiation of the bivalve mollusks is not limited by time, and cross infection between families can be completely eradicated; meanwhile, spermiation and oviposition are consistent in step and short in duration time, and manual continuous attention to oviposition and spermiation is avoided.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Water monitoring system using bivalve mollusks
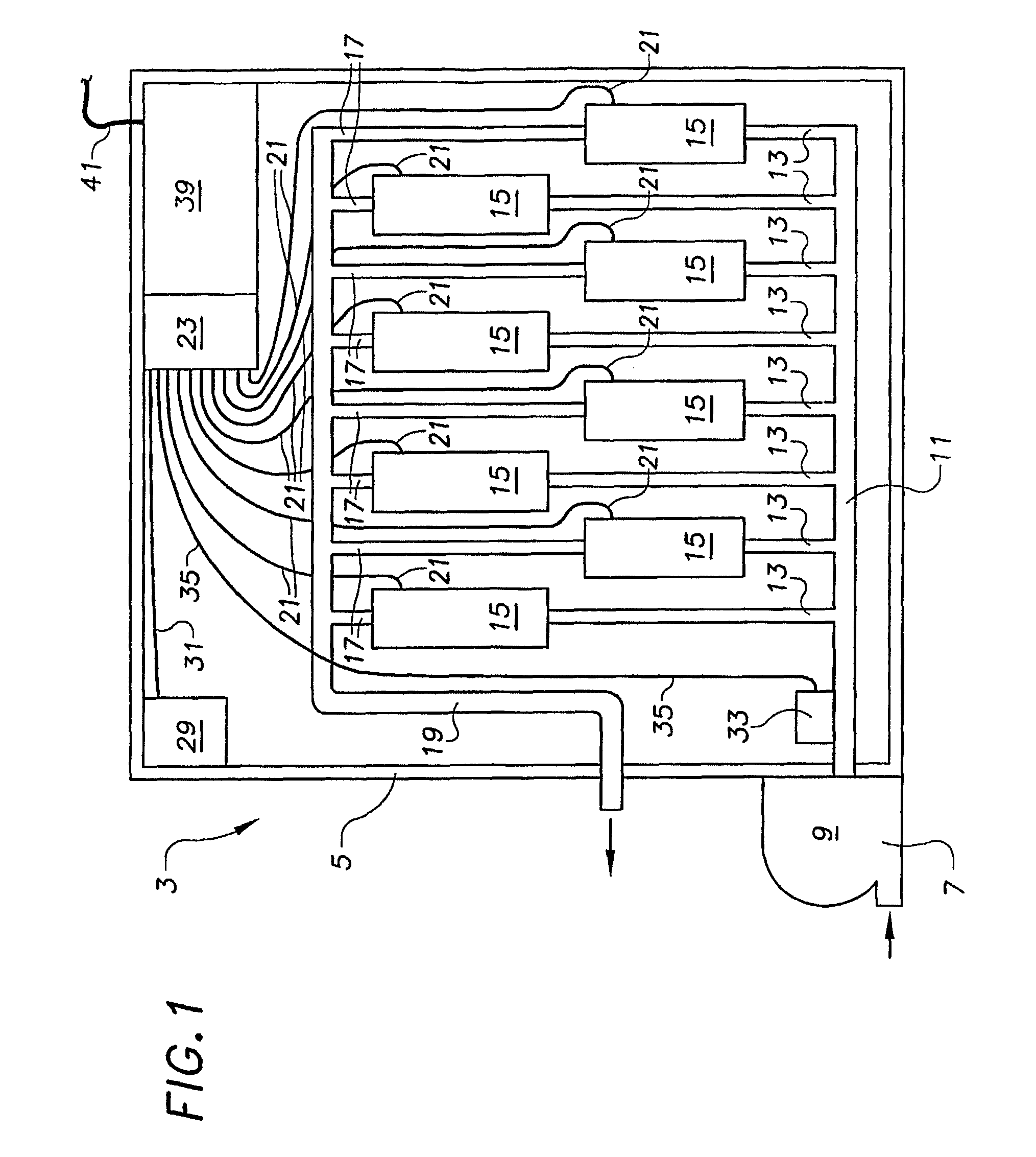
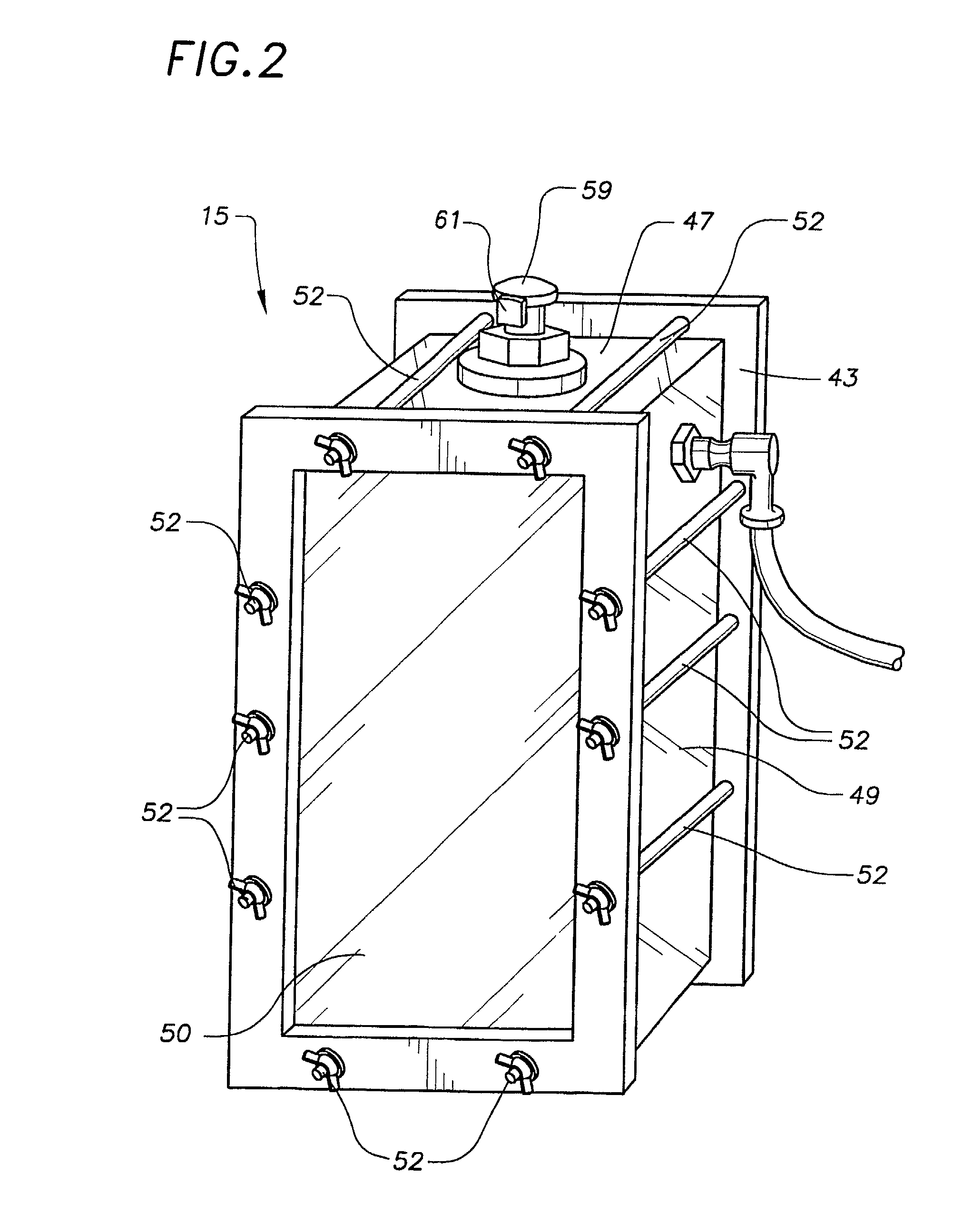
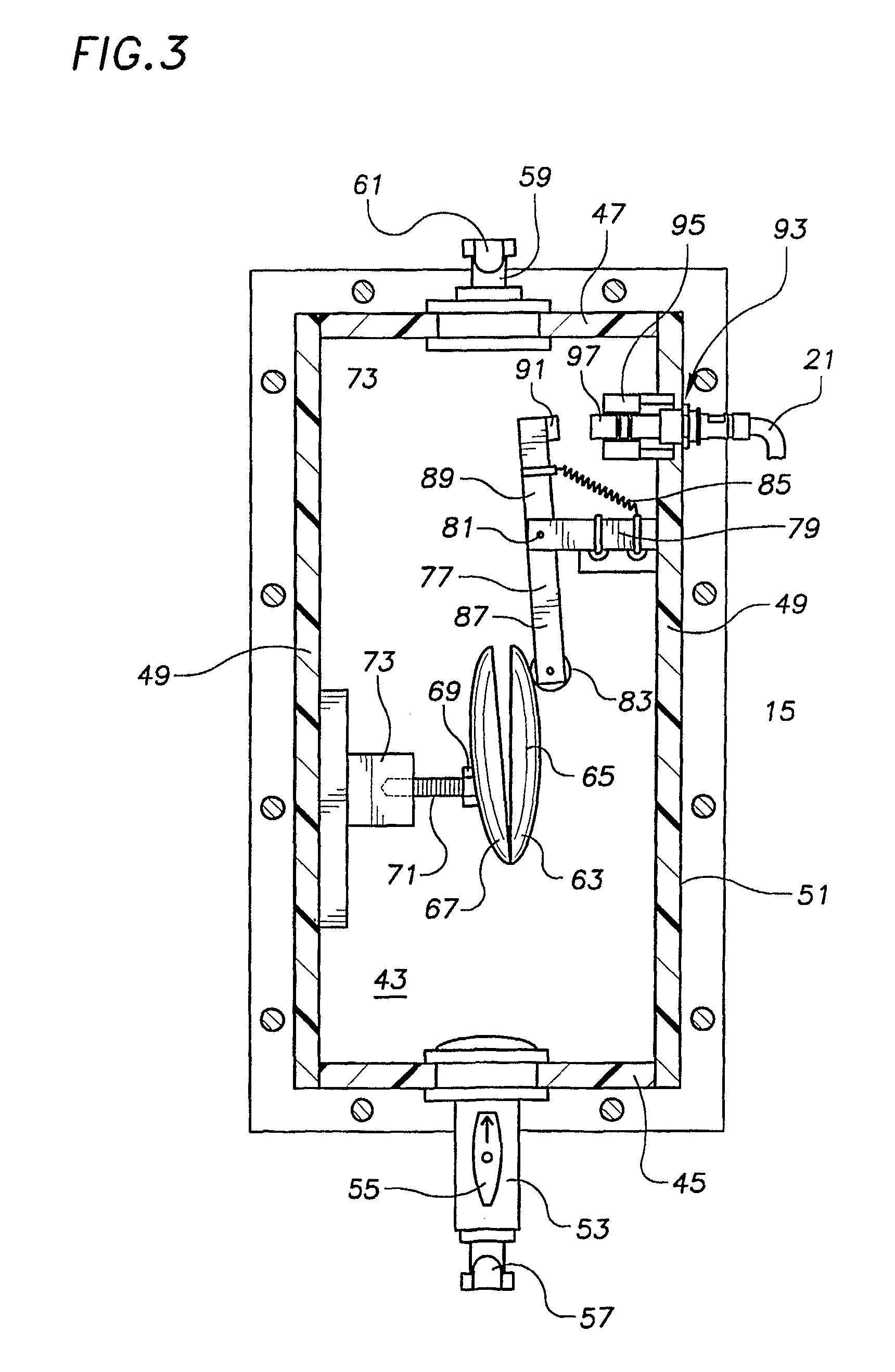
InactiveUS7330794B2High precisionEasy to installTesting/calibration apparatusPollution detectorsToxicantMonitoring system
A toxicant detection system comprises at least one watertight chamber containing a mollusk. Water to be screened is introduced into the chamber. The mollusk is preferably supported on a mounting structure which facilitates quick mounting of the mollusk in the device, comprising a releasable element affixed to the shell of the mollusk, e.g., a bolt which is screwed into a nut affixed to the mollusk's shell. A sensing apparatus is provided which includes a movable member supported in the chamber so that it engages the shell of the mollusk, and moves when the shell opens and closes. The sensing apparatus detects the position of the mollusk shell based on the position of the movable member. The sensing apparatus preferably includes a Hall effect transducer which co-acts with a magnet carried on the movable member. The system allows for accurate readings of the small movements of the mollusk shell which aid in detecting toxicants, and also provides for installation of mollusks of varying sizes, without the need to move components of the standard configuration of the chamber. Methods and systems for detecting or identifying a toxicant in water being screened are also described.
Owner:AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
Optimization feeding method for culturing shrimp
InactiveCN101053318BPromote growthImprove conversion efficiencyClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffShrimp cultureZoology
An optimization feeding method for shrimp culture includes feeding according to the current feeding time and mode, its characteristcs are during the maturation period of shrimp to adopt natural animal baits and compound feeds by 2-4 :1 frequency or weight ratio to feed in turn; the said natural animal baits are sleeve-fishs, clamworms, minitype shrimps and crabs or bivalve mollusks which can be fed naturally by shrimp; the said compound feeds are juvenile shrimp or adult shrimp containing protein over 40 percent. To adopt this feeding mode of the present invention can promote shrimp growth, improve feed conversion efficiency and avoid feed resource waste caused by selectivity.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Early warning method for paralytic saxitoxin in bivalve mollusks
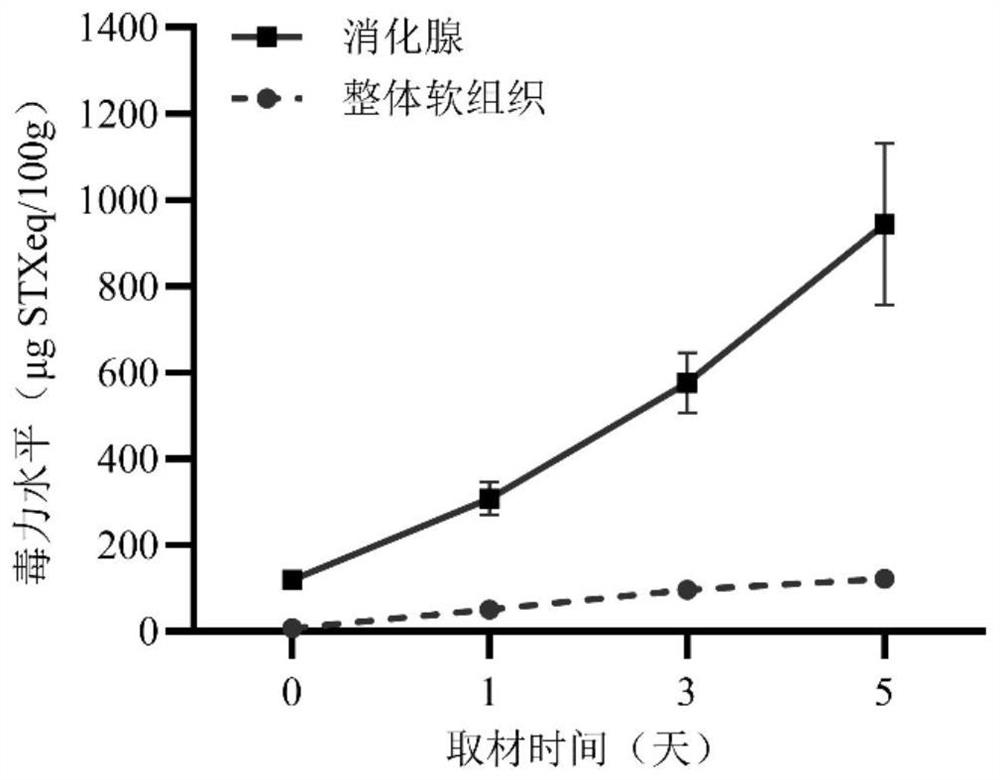
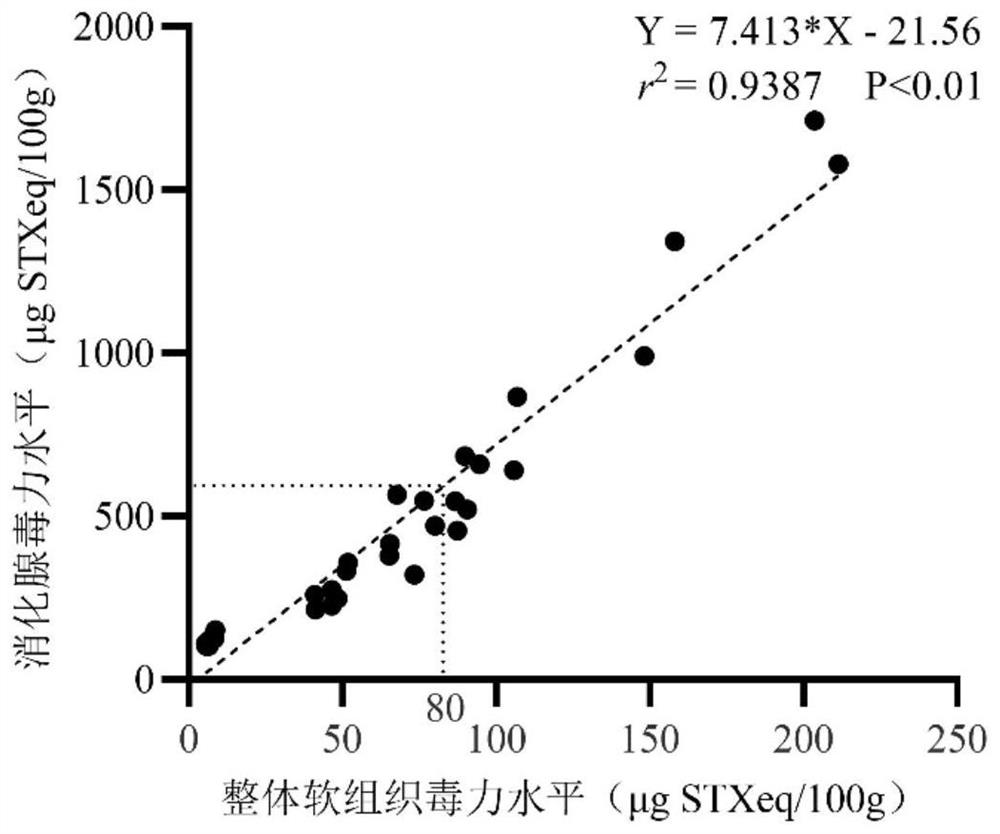
PendingCN114544819AExtract economic savingsEasy to homogenize and grindComponent separationClimate change adaptationAnimal scienceAdenosine
The invention provides an early warning method for paralytic saxitoxin in bivalve mollusks. Whether the risk that the content of paralytic saxitoxin exceeds the standard exists or not is determined by detecting the content of paralytic saxitoxin in digestive glands of the bivalve mollusks. According to the method, the digestive gland is used as a monitoring sample, in toxin extraction operation, compared with integral soft tissue used in a conventional detection method, homogenate grinding is easier, operation is easy and convenient, and time and labor are saved. The volume of a detection sample is smaller, and toxin extraction is more economical. The accumulation of the digestive adenosine toxin is quicker and the accumulation amount is high, so that the toxin is more easily and sensitively detected. Meanwhile, compared with monitoring of the toxic algae level in a water body and a shellfish organism biomarker, the digestive gland is used as a toxin monitoring sample, interference of other factors is small, and the shellfish toxin level can be reflected more directly.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Intelligent bivalve mollusk planktonic larva detection method based on deep learning
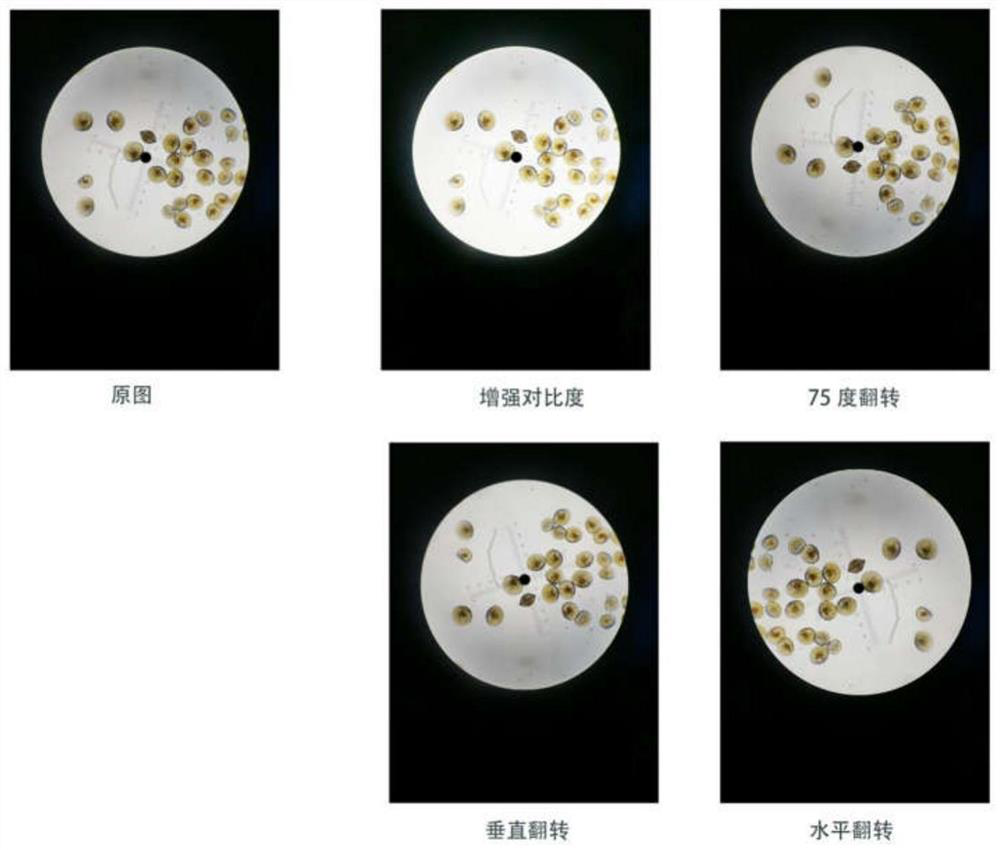
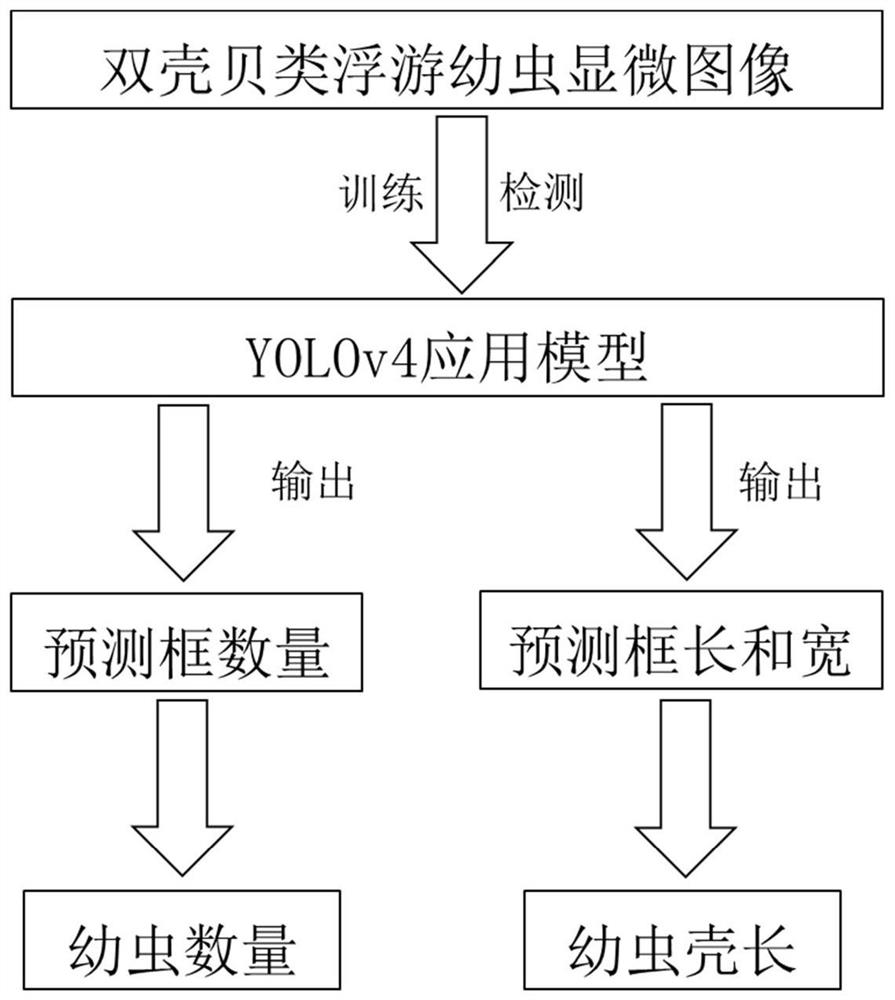
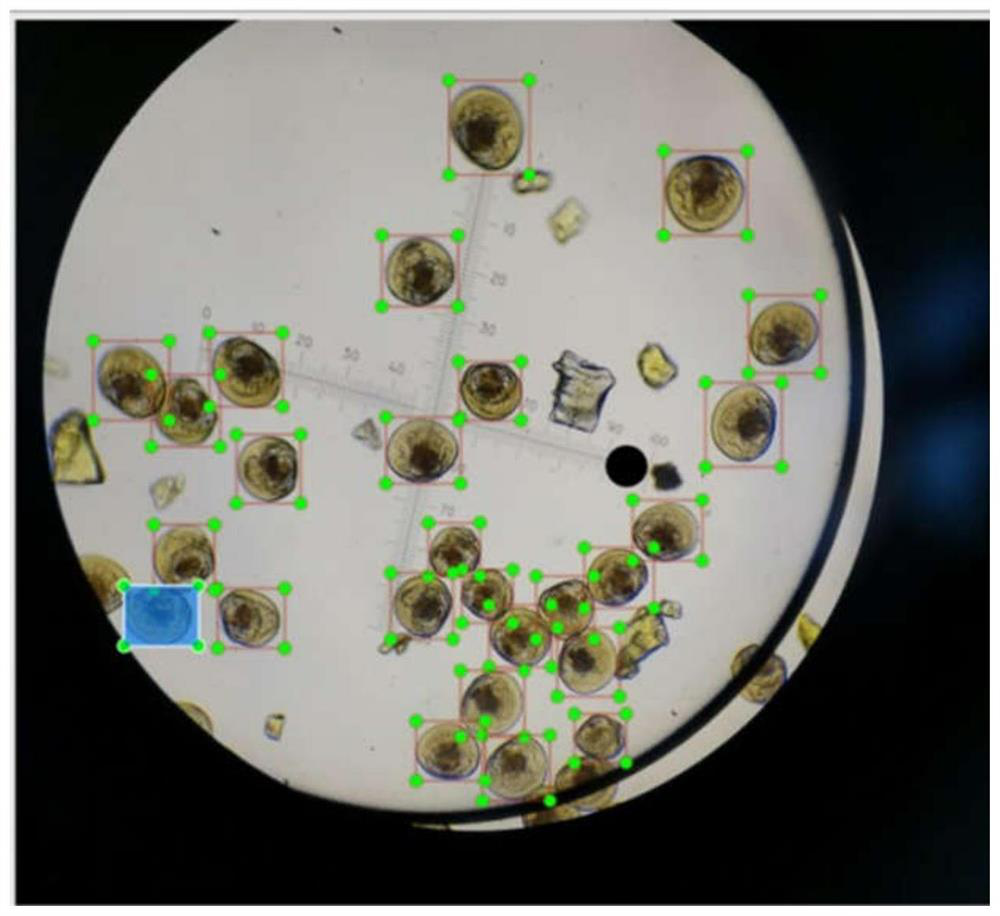
PendingCN114782373AImprove observation efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses an intelligent detection method for bivalve mollusk planktonic larvae based on deep learning. The intelligent detection method comprises the steps of bivalve mollusk planktonic larva microscopic image collection with ink dots, image preprocessing, planktonic larva data set making, application model training and obtaining and planktonic larva detection. According to the method, intelligent detection of the number and the shell length of bivalve planktonic larvae under the microscopic view is realized through a deep learning method, so that the workload and the working time of artificial microscopic observation of the larvae are reduced, and the working efficiency of larva observation in the aquatic product field is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bottom-seed sea water culture facilities suitable for sediment bottom sea area
ActiveCN101288385BChange design thinkingSuitable for survivalClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEngineeringSeawater
The invention relates to a bottom sowing-type mariculture facility which is suitable for the sea area with silt bottom, in particular to a bottom sowing-type raft frame and a net cage for marine bivalve mollusks, sea cucumbers or mixotrophic culture of marine bivalve mollusks and sea cucumbers. The facility is provided with a PVC pipe, a polyethylene rope for fixing the PVC pipe, a webbing, a stake or an anchor for fixing the facilities, a rope fixed on the stake or the anchor, and a fixable floating ball which is connected to the rope and floats on the surface of water; the PVC pipe is fixedon the polyethylene rope in parallel, the polyethylene rope is arranged in parallel, is perpendicular to the PVC pipe, is positioned at the upper side and the lower side of the two terminals of the PVC pipe and forms the structure similar to a 'soft ladder'; the 'soft ladder' is externally covered by the webbing, and a plurality of independent net cages are formed by combining the PVC pipe, the polyethylene rope and the webbing; the two ends of the undrawn 'soft ladder' are fixed at the bottom of the sea by the stake or the anchor respectively, and the floating ball is fixed at the two ends of the 'soft ladder' by the rope. The facility can effectively prevent the enemies and reduce the influence of storm and ocean current, thus being convenient for management and harvest and favorable tothe comprehensive utilization of mariculture area.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
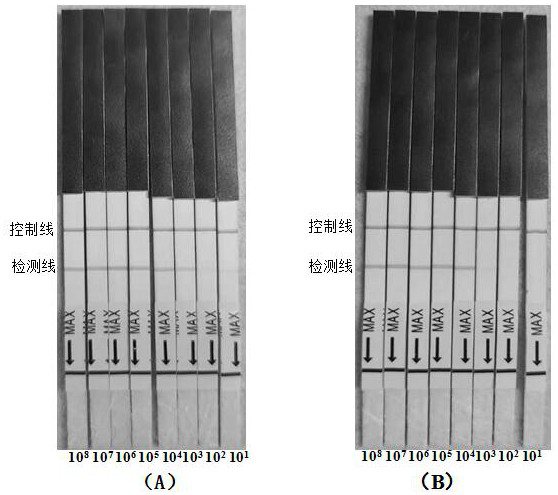
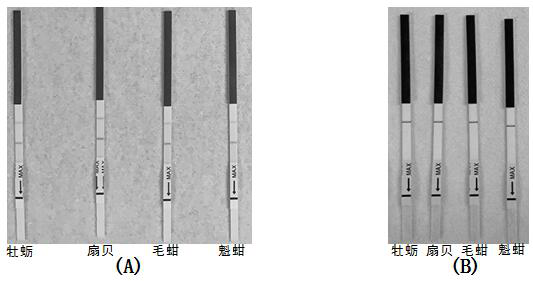
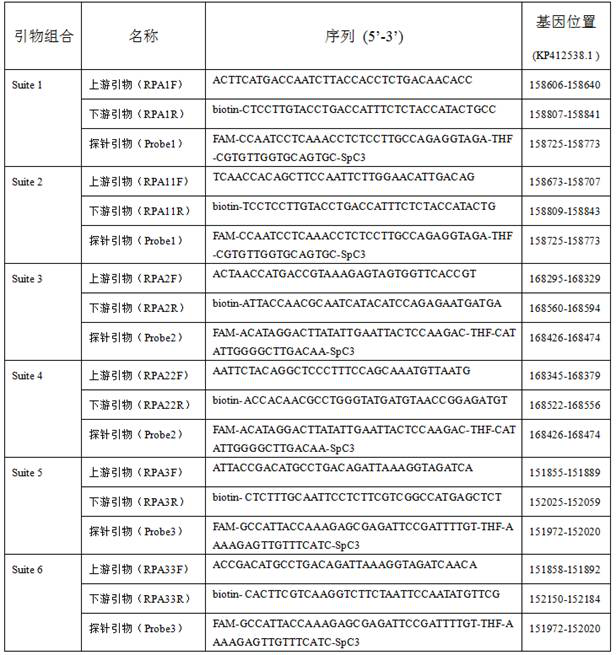
Universal rpa nucleic acid isothermal amplification primers, kits and applications for bivalve mollusk-infected herpes virus oshv-1
ActiveCN113293239BStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBivalve shellHerpes simplex virus DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of marine biology, and in particular relates to a universal RPA nucleic acid isothermal amplification primer, a kit and an application thereof for bivalve mollusks infected with herpes virus OsHV‑1. The primers are a set of amplification primers, consisting of upstream and downstream primers and probe primers; the upstream primers are shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the downstream primers are shown in SEQ ID NO.2; the probe primers are shown in SEQ ID NO.3 shown. The present invention designs general-purpose RPA amplification detection primers for 7 kinds of OsHV-1 mutant strains in currently known four kinds of bivalve hosts, and establishes a test strip RPA detection system and method for OsHV-1. On-site rapid screening and detection of OsHV‑1 is of great value and has broad market application prospects.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
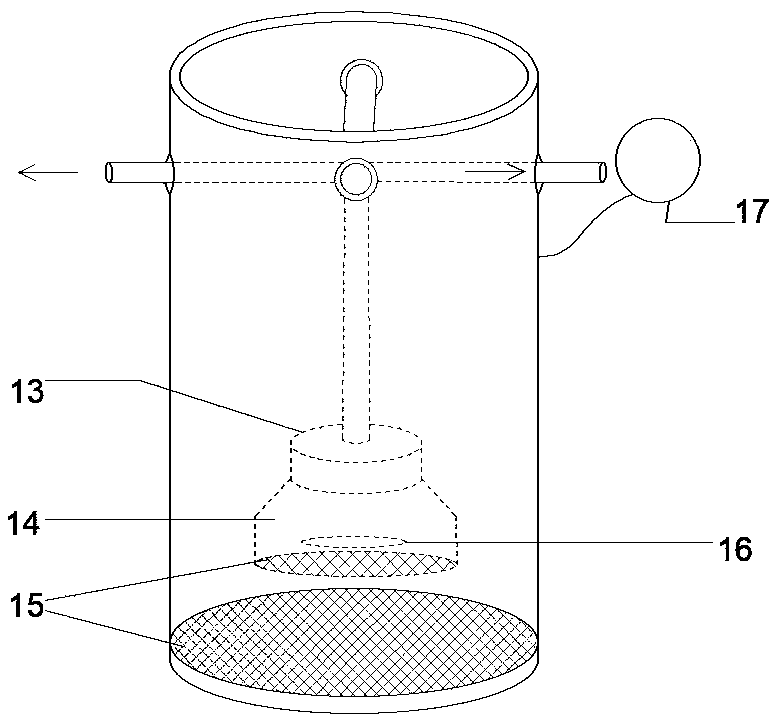
Open inflatable upwelling culture device for intermediate culture of bivalve mollusks and culture method thereof
PendingCN109169441AImprove survival rateFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaElectricityEngineering
The invention provides an open inflatable upwelling culture device for intermediate culture of bivalve mollusks. The device includes a culture pipe, filter nets and an inflator, wherein the culture pipe is the outermost layer of the whole device, two ends of the culture pipe are opened, the filter nets are two layers, the culture pipe is divided by the filter nets into an upper portion, a middle portion and a lower portion, the middle between the two layers of filter nets is the middle portion and is the culture area, the inflator is arranged at an upper end of the upper filter net, an upper end of the culture pipe is provided with a water outlet, and a lower end of the culture pipe is provided with a water inlet. The culture device is advantaged in that through the culture method, water and electricity resources are greatly saved, the growth rate of juvenile mollusks is 20% to 50% higher than the traditional method, the survival rate is over 90%, and the seawater and the bait can be saved more than 70%.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for obtaining shellfish shell cavity and measuring its volume
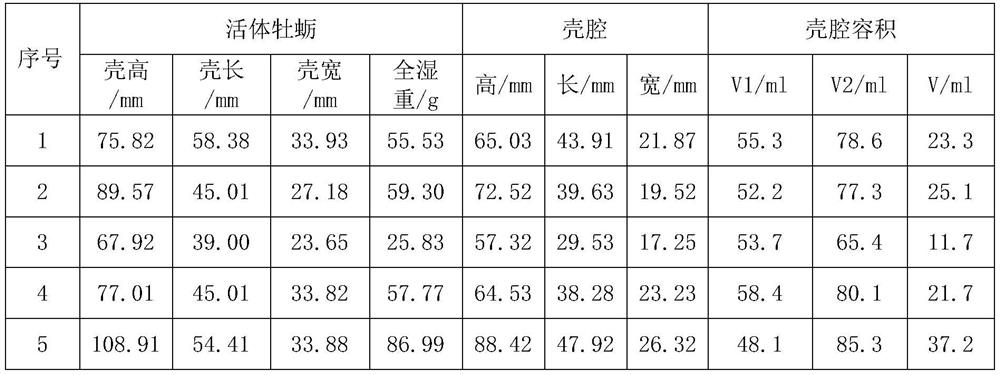
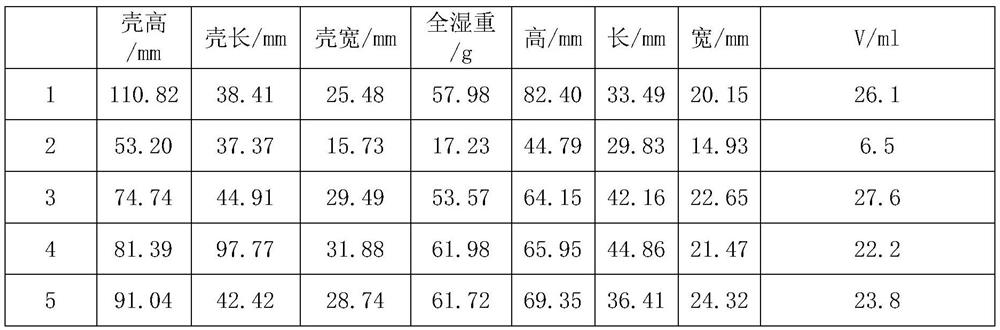
ActiveCN111771783BComplete formAccurately obtain shell cavity volumeClimate change adaptationMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsOysterBivalve shell
The invention relates to the field of aquatic biology, in particular to a method for accurately obtaining the shape of a bivalve shell cavity and measuring its volume. Filling the shell cavity of the bivalve mollusc to be treated with material, so that the filler fills and shapes the entire cavity; after compaction, the cavity filling material is taken out to obtain the complete shell cavity shape of the bivalve mollusk. The application of the method to obtain the morphology of the shellfish shell cavity in determining the volume of the shell cavity. The method can accurately obtain the shell cavity volume of the measured shellfish, and the method has universal applicability to bivalve shellfish, not only applicable to shellfish with regular shell shapes such as clams, but also to shellfish with irregular shell shapes such as oysters, and scallops, etc. The same applies to shellfish whose shell cavity cannot be completely closed.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for conjunction measuring aquatic animal respiration apocatharsis
InactiveCN100518687CMeets requirements for measuring respiratory metabolismGood scientific research platformSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringAquatic animalFresh water organism
The invention relates to a device used for matching with the measurement for respiration and excretion of aquatic animals, in particular to an attachment used for matching with various dissolved oxygen probes to measure the respiration and the excretion of various aquatic animals such as fish, shrimps as well as crabs, bivalve mollusks, sea cucumbers, etc. living in freshwater or seawater. The device takes an organic glass slab-bottom at the bottom of a crude organic glass tube as a back cover to form a vessel; a concentric-circle organic glass flange provided with holes is sleeved on the upper end of the crude organic glass tube at the height parallel to a nozzle; an organic glass cover plate is arranged on the top of the organic glass flange to be used as an upper cover; a fine organic glass tube and a PVE tube cuff are arranged on the organic glass cover plate; the PVE tube cuff is inserted into the dissolved oxygen probes in a sealing way; a diving pump is arranged under the PVE tube cuff. The device solves the problems that the prior art cannot reflect the metabolic status of the aquatic animals factually and accurately, etc., and has the advantages of simple structure, low manufacturing cost, being easy to match with correlated instruments to detect accurately, etc.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Technique for controlling myofibril in processing instant scallop
ActiveCN101779803BImprove the level of processing technologyImprove qualityFood preparationBiotechnologyMyofibril
The invention discloses a technique for controlling mesoplasm in processing instant scallop, which is a proper processing technique established aiming at the variation of myofibril of scallop through systematically studying the protein compositions of marine bivalve mollusk of pectinidae and the characteristics of the processing process. The technique comprises the following steps of: eviscerating the hot myofibril, the frozen myofibril or the directly fetched myofibril at 20-40 DEG C, immersing in 0.5-3% NaCl for 20-50 min, leachating for using; immersing molluse meat in spice soup with 1-2 times of mass at 50-70 DEG C for 0.5-5 h to achieve tasty effect and shaping the shape of protein tissue; and then slowly heating to be cured in the original spice soup; immersing the edible muscle parts of the fully cured mollusk in an envelope solution containing sodium alga acid and konjaku powder for 3-10 S, and then taking out and leachating; directly vacuuming and packaging the enveloped raw materials, or introducing nitrogen to package, or quickly freezing in an instant freezer to shape the state, and then rapidly vacuuming and packaging, or introducing nitrogen to package; directly freezing the packaged myofibril products for selling, or sterilizing at 90-120 DEG C for 30-60 min, freezing, storing in cold, or being ready for selling at the normal temperature.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Induction, extraction and separation process of shellfish metallothionein, a high-efficiency heavy metal removal agent from marine biological sources
ActiveCN104910273BReduce removal processReduce security impactPeptide preparation methodsMetallothioneinsAntidoteIon exchange
The invention discloses an induction and extraction separation method of marine organism-sourced high-efficiency heavy metal removing agent shellfish metallothionein. The induction and extraction separation method comprises following steps: (1) a selected bivalve mollusk is subjected to 2 to 7 days of temporary rearing in clean seawater, and dead ones are removed; (2) directional induction is carried out; (3) shells are open so as to collect shellfish meat, a buffer solution is added at a certain ratio, and an obtained extracted solution is subjected to thermal treatment so as to remove impurity protein; (4) the extracted solution is cooled, and is delivered through a screen so as to remove precipitates via filtering, an obtained supernate is subjected to multi-stage ultrafiltration and microfiltration, is delivered through a nanofiltration multielement film integrated purification system so as to remove macromolecules, and is subjected separation purification and concentration so as to obtain a MT crude product; and (5) the MT crude product is subjected to dextrangel and ion-exchange column chromatography combined-purification separation, and drying so as to obtain a high-purity marine organism-sourced MT product. The induction and extraction separation method is capable of increasing metallothionein content in shellfish effectively, and obtaining marine organism-sourced high-efficiency heavy metal antidote products which possess high efficiency removing effects on heavy metal, and are safer.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
A method for purifying cadmium in bivalve mollusk
ActiveCN109042410BReduce purification costsEfficient purificationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaVitamin CBivalve shell
The invention relates to the technical field of purifying heavy metal in edible marine products, and discloses a method for purifying cadmium in bivalve mollusc, which comprises the following steps: adding nano calcium carbonate suspension, magnesium ion water solution, vitamin C and casein phosphopeptide into the water body cultivating the bivalve mollusc; replacing the water body every day, reading nano calcium carbonate suspension, magnesium ion water solution, vitamin C and casein phosphopeptide. According to the invention, the method is simple in operation, the purification cost is low and the operation time is short, the Cadmium ion residue in the edible bivalve bodies can be efficiently purified, and the product quality and flavor are not affected. According to the invention, when the bivalve mollusc polluted by Cadmium is treated by using the method, the removal rate of cadmium in the bivalve mollusk bodies can reach 36.5-38.4% after 7 days.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for rapidly evaluating resistance of bivalve mollusks based on tension index
ActiveCN114158502AEfficient tension detectionImprove detection success rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaZooidCharales
The invention provides a method for quickly evaluating the resistance of bivalve mollusks based on a tension index, which is a method for detecting the tension index without damage on the basis of not influencing the activity of a tested individual and quickly evaluating the resistance of scallops based on the tension index. According to the method, efficient and lossless tension detection is carried out on the scallops, and the obtained four tension indexes including the total force, the shell closing time, the average force and the maximum force of the scallops serve as the basis for rapidly evaluating the scallop resistance. Compared with the traditional method, the method provided by the invention can realize nondestructive living body detection, and compared with a concentricity detection method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of being more stable, accurate, simple, convenient, high in detection success rate and the like. In addition, the tension of the adductor muscle of the scallop is used as an index for rapidly evaluating the resistance of the scallop for the first time. The method provided by the invention can provide reference for scallop resistance index determination, and provides technical support for subsequent breeding of scallop stress-resistant varieties.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com