Bottom-seed sea water culture facilities suitable for sediment bottom sea area
A seawater culture and sediment bottom technology, applied in the fields of application, fish farming, climate change adaptation, etc., can solve the problems of low survival rate of cultured organisms, easy encounter of seedlings with predators, poor wind and wave resistance, etc., and achieve low cost , enhance the ability to resist wind and waves, and reduce the effect of impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
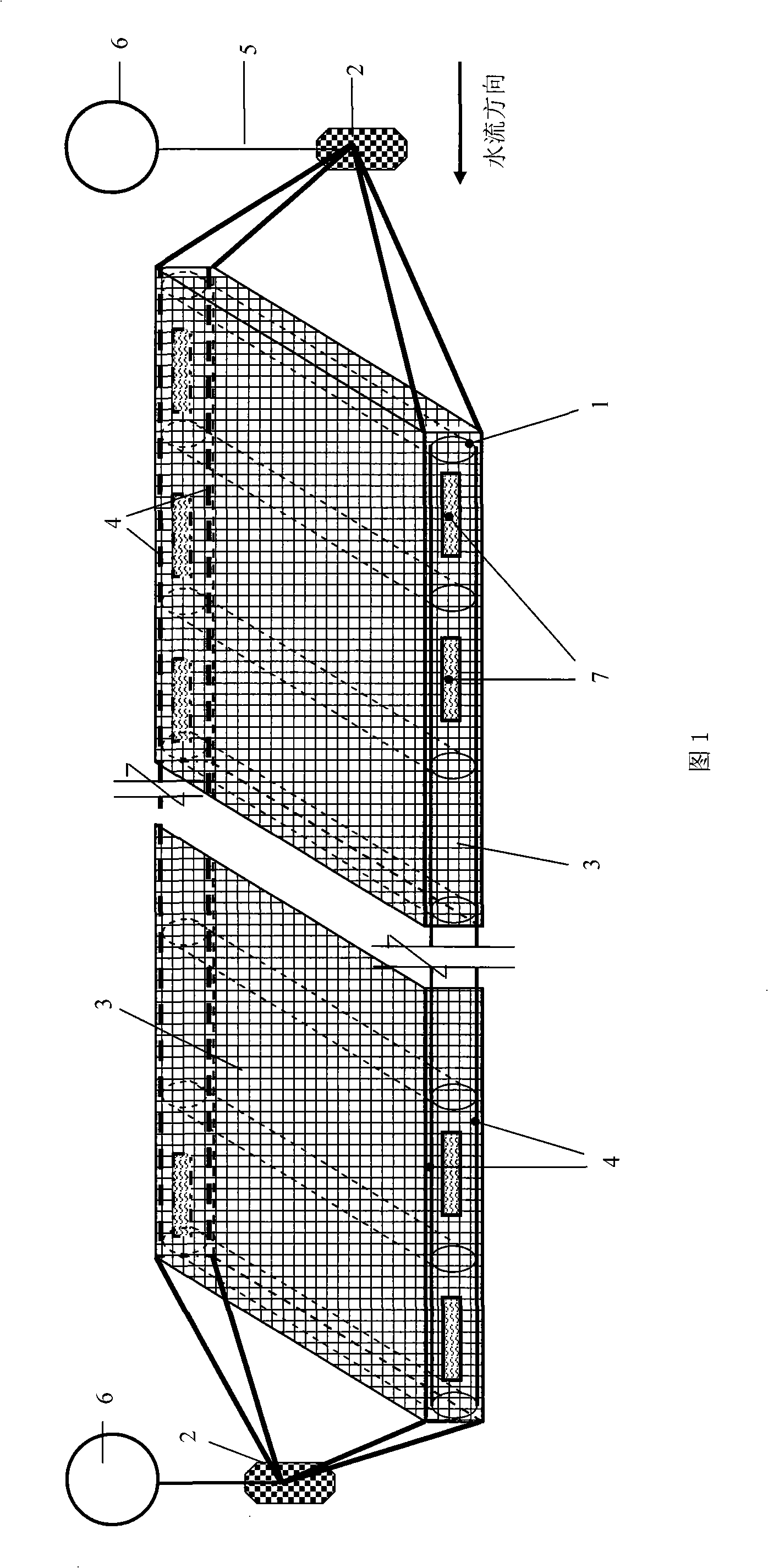
[0031] As shown in Figure 1-3, the bottom-seeding marine aquaculture facilities suitable for sediment-bottom sea areas are applied to the cultivation of scallops (chlamys farreri, bay scallops, scallops, etc.). A certain number of scallop seedlings are respectively placed in the breeding cages supported by the PVC pipe 1, polyethylene rope 4 and netting 3. Before putting the seedlings, the netting 3 is left at the opening 7, and the opening is closed after the seedlings are placed. 7 sutures. After the seedlings are released, the entire bottom-sowing breeding facility is fixed on the seabed by stakes or anchors 2, and ropes 5 are fixed at both ends of the facility. The upper end of the rope 5 is fixed with a floating ball 6, and the floating ball 6 floats on the sea surface, which is convenient for production management and harvesting .
Embodiment 2
[0033] The bottom sowing culture facility shown in Figure 1-3 is applied to sea cucumber cultivation. Put a certain amount of japonicus seedlings respectively in the breeding cages supported by PVC pipe 1, polyethylene rope 4 and net clothes 3. Before putting the seedlings, the net clothes 3 leave a mouth at the opening 7. After putting the seedlings, place them Opening 7 sutured. After the seedlings are released, the entire bottom-sowing breeding facility is fixed on the seabed by stakes or anchors 2, and ropes 5 are fixed at both ends of the facility. The upper end of the rope 5 is fixed with a floating ball 6, and the floating ball 6 floats on the sea surface, which is convenient for production management and harvesting .
Embodiment 3
[0035] The bottom sowing culture facility shown in Figure 1-3 is applied to the polyculture of shellfish. A certain amount of sea cucumbers and scallops (chlamys scallops, bay scallops, ezo scallops, etc.) seedlings with a suitable matching ratio are respectively placed in the breeding cages supported by PVC pipe 1, polyethylene rope 4 and netting 3, Before putting the seedlings, the net clothing 3 leaves a mouth at the opening 7, and the opening 7 is sewed up after the seedlings are put. After the seedlings are released, the entire bottom-sowing breeding facility is fixed on the seabed by stakes or anchors 2, and ropes 5 are fixed at both ends of the facility. The upper end of the rope 5 is fixed with a floating ball 6, and the floating ball 6 floats on the sea surface, which is convenient for production management and harvesting .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com