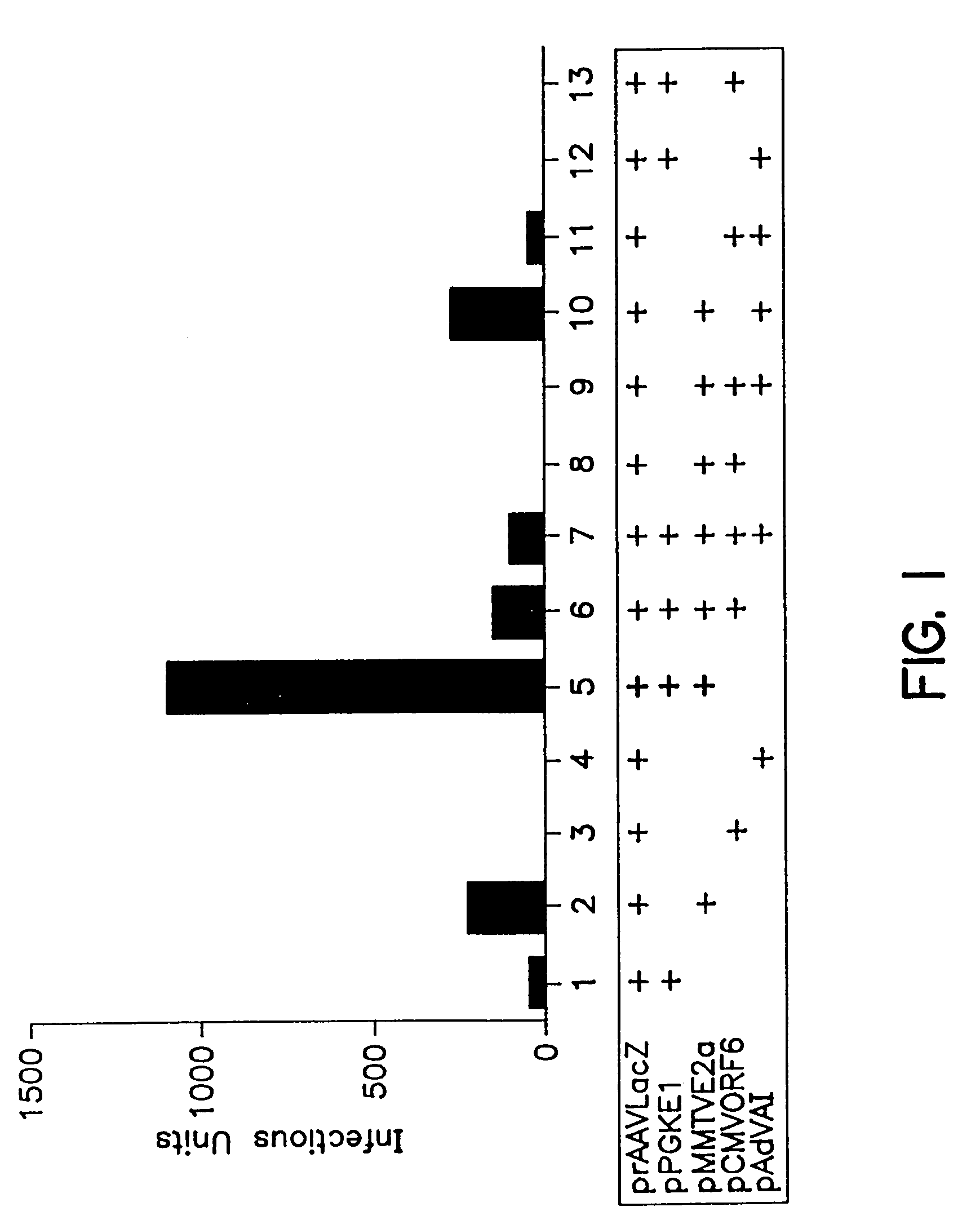
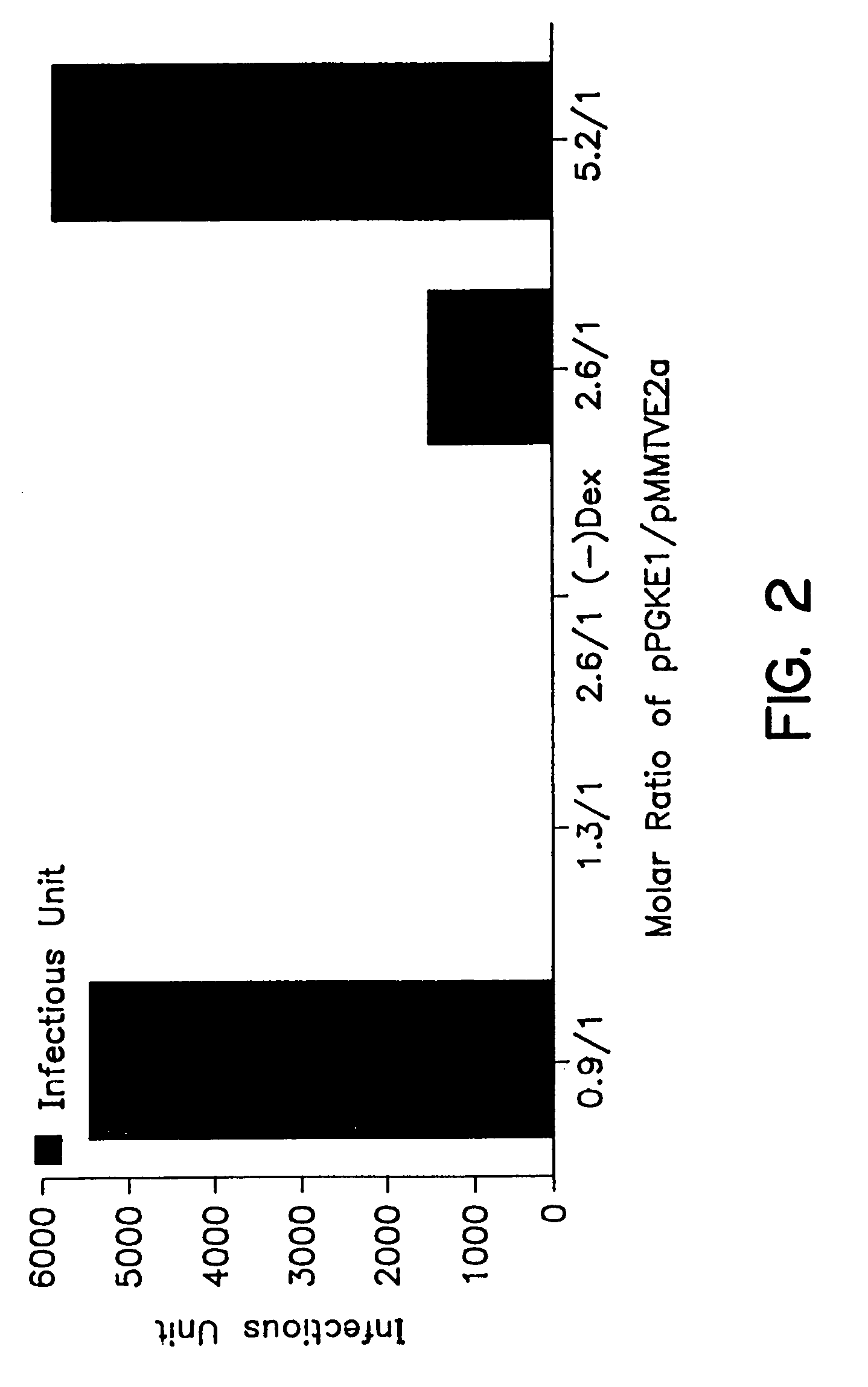
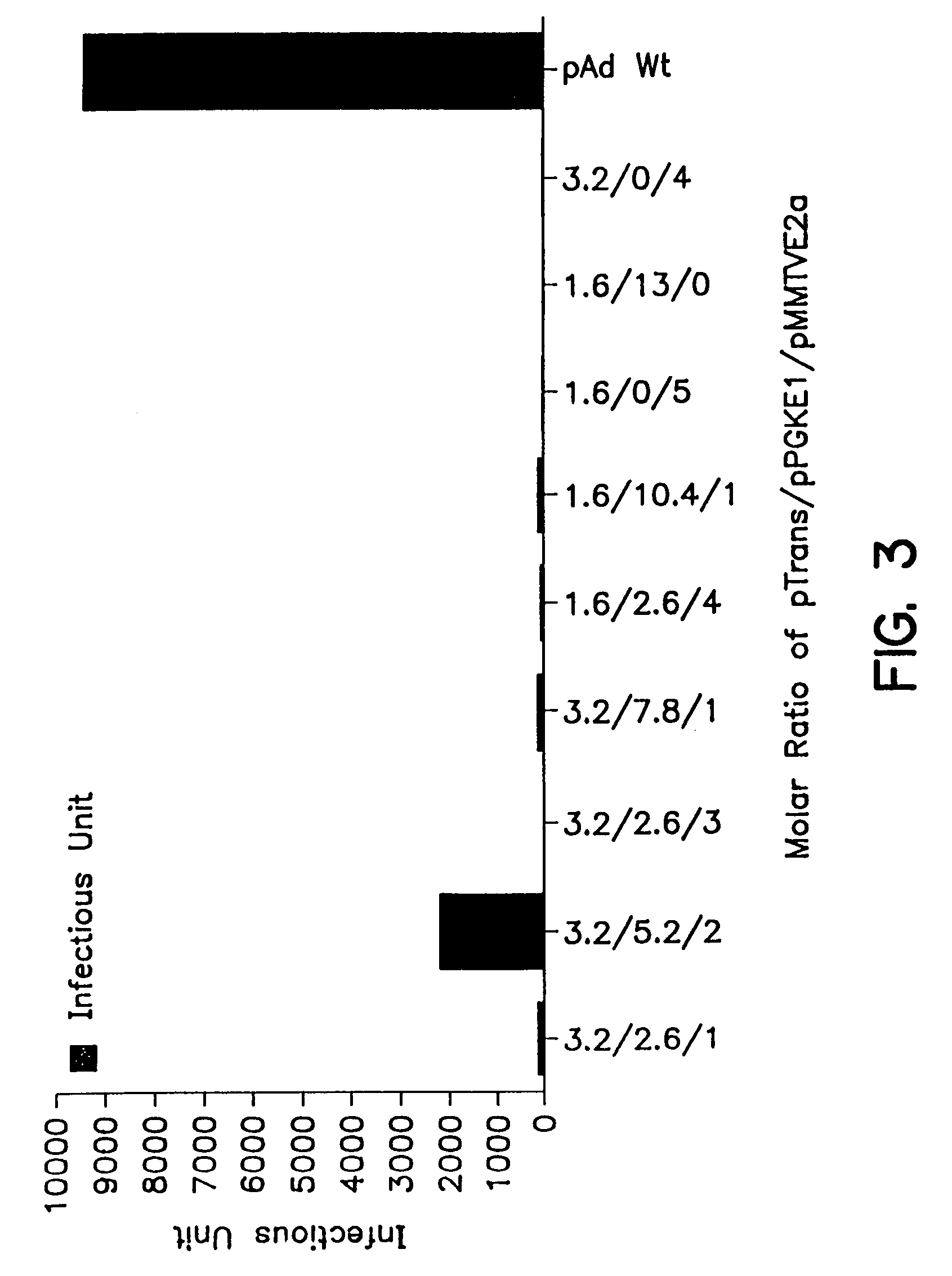
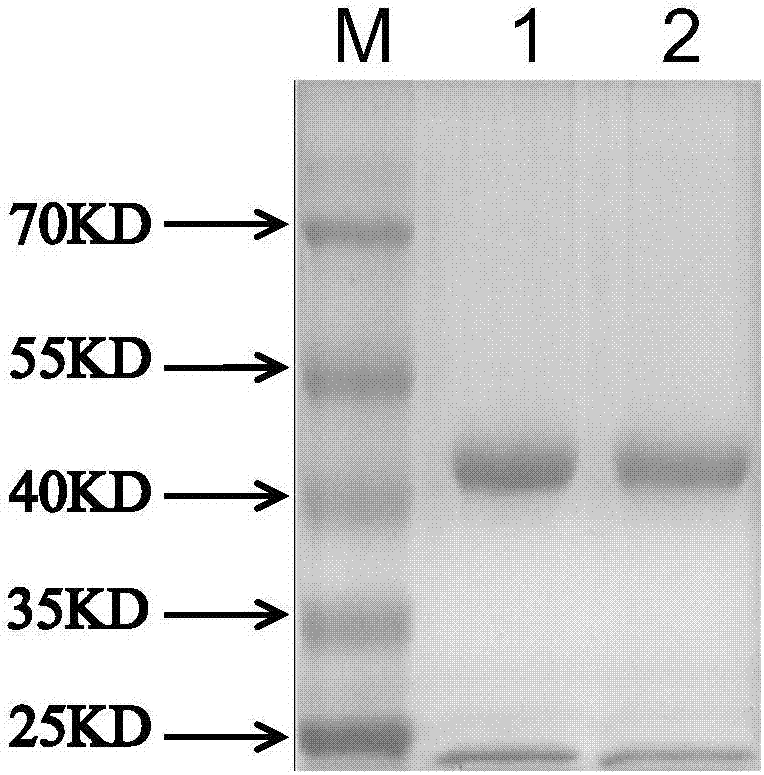
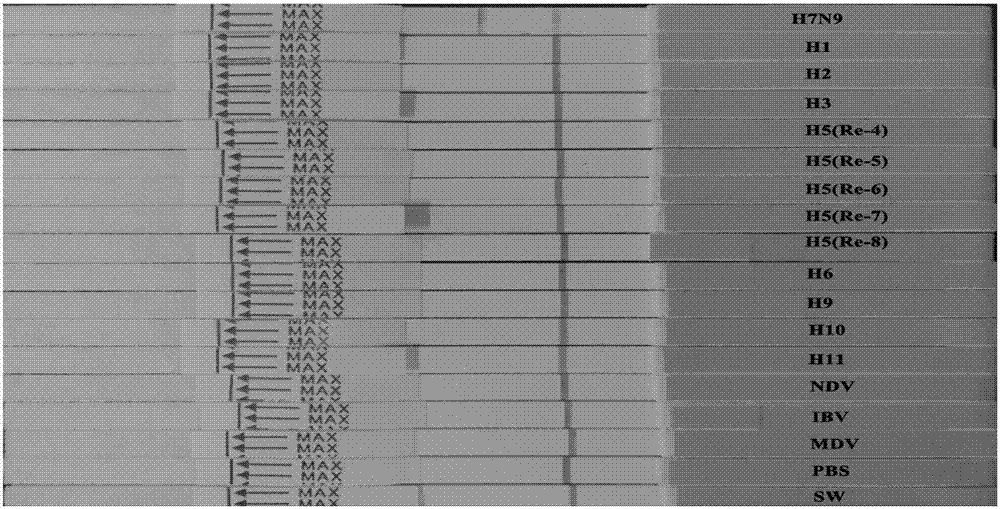
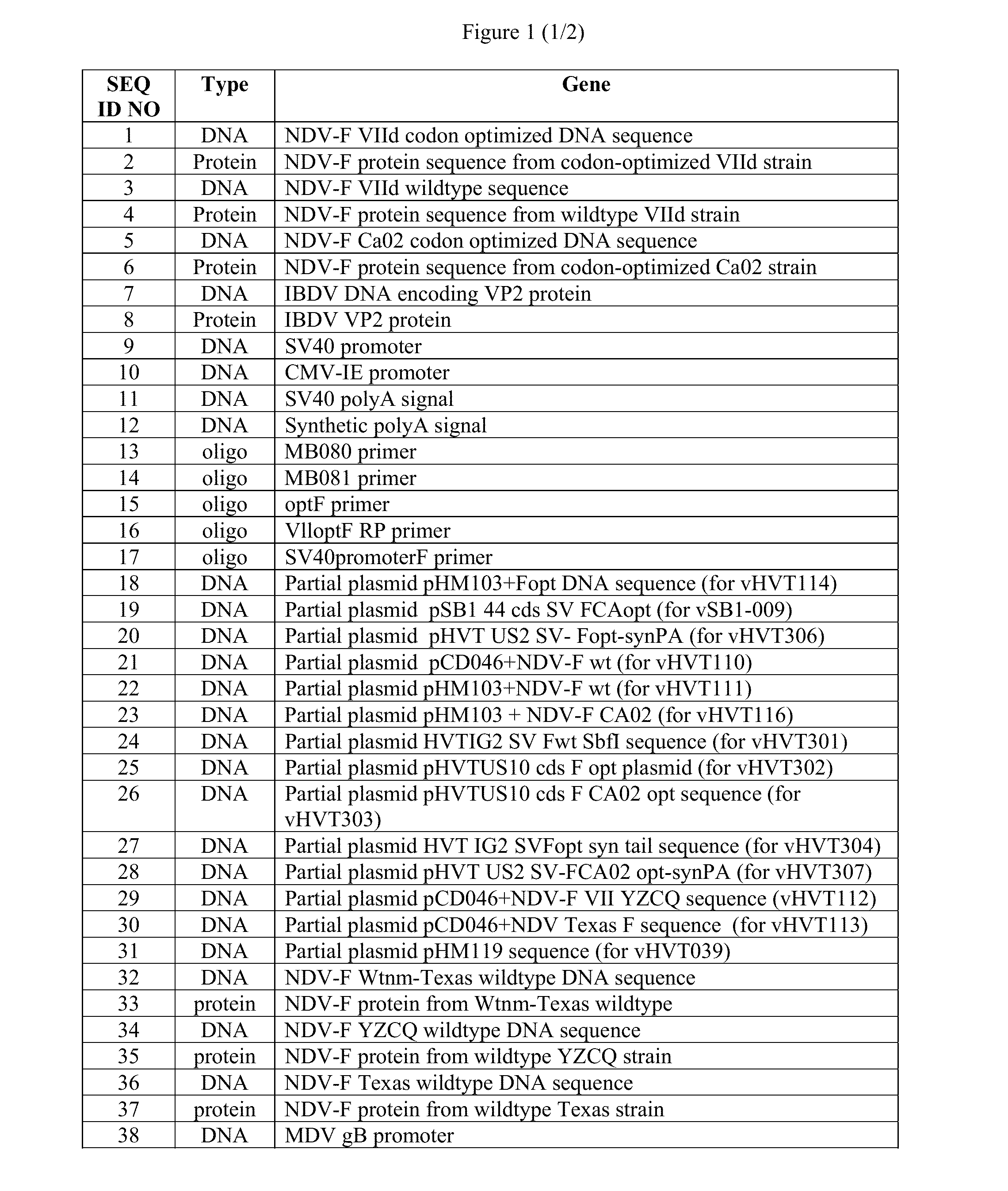
Patents
Literature
143 results about "Wild type virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wild-Type Virus. The naturally occurring, non-mutated strain of a virus. When exposed to antiretroviral (ARV) drugs, wild-type HIV can develop mutations that make the virus resistant to specific HIV drugs. Most people with HIV are initially infected with wild-type virus; however, some people become infected with mutated, drug-resistant strains of HIV.
Compositions and methods for helper-free production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
InactiveUS6953690B1Efficient productionIncrease the number ofBiocideGenetic therapy composition manufactureMammalWild type
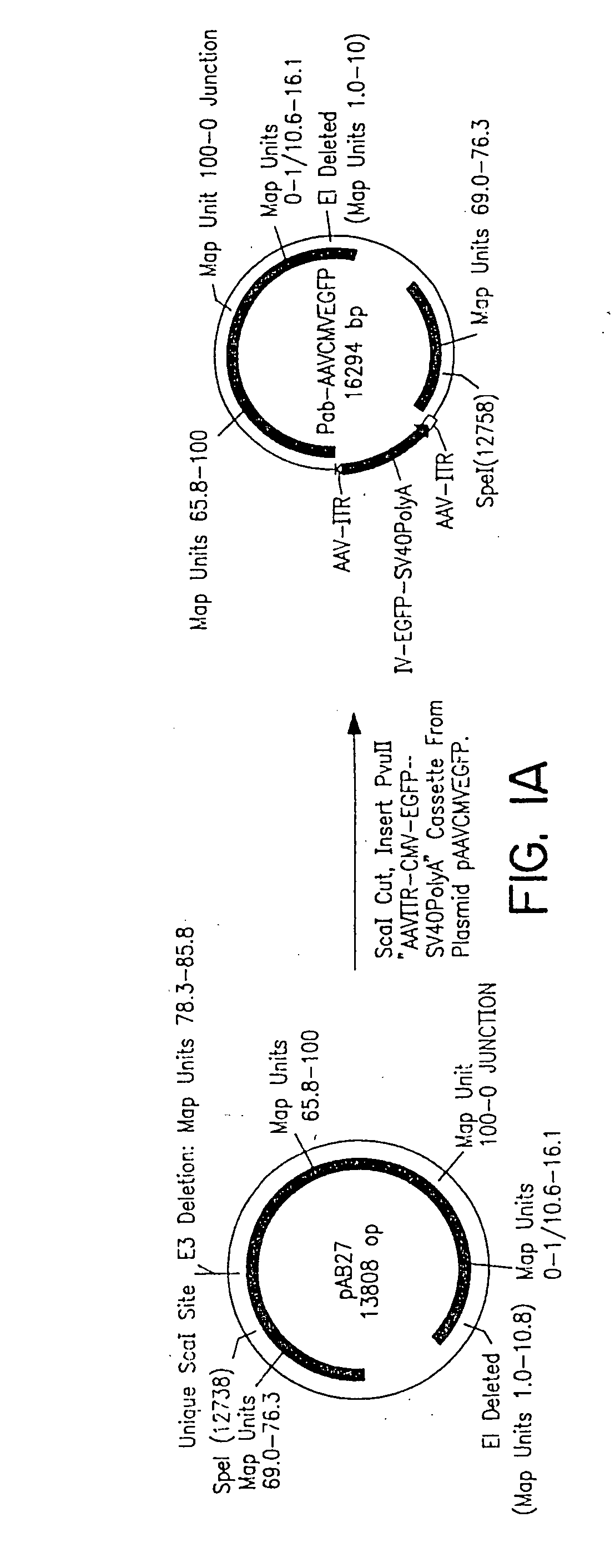
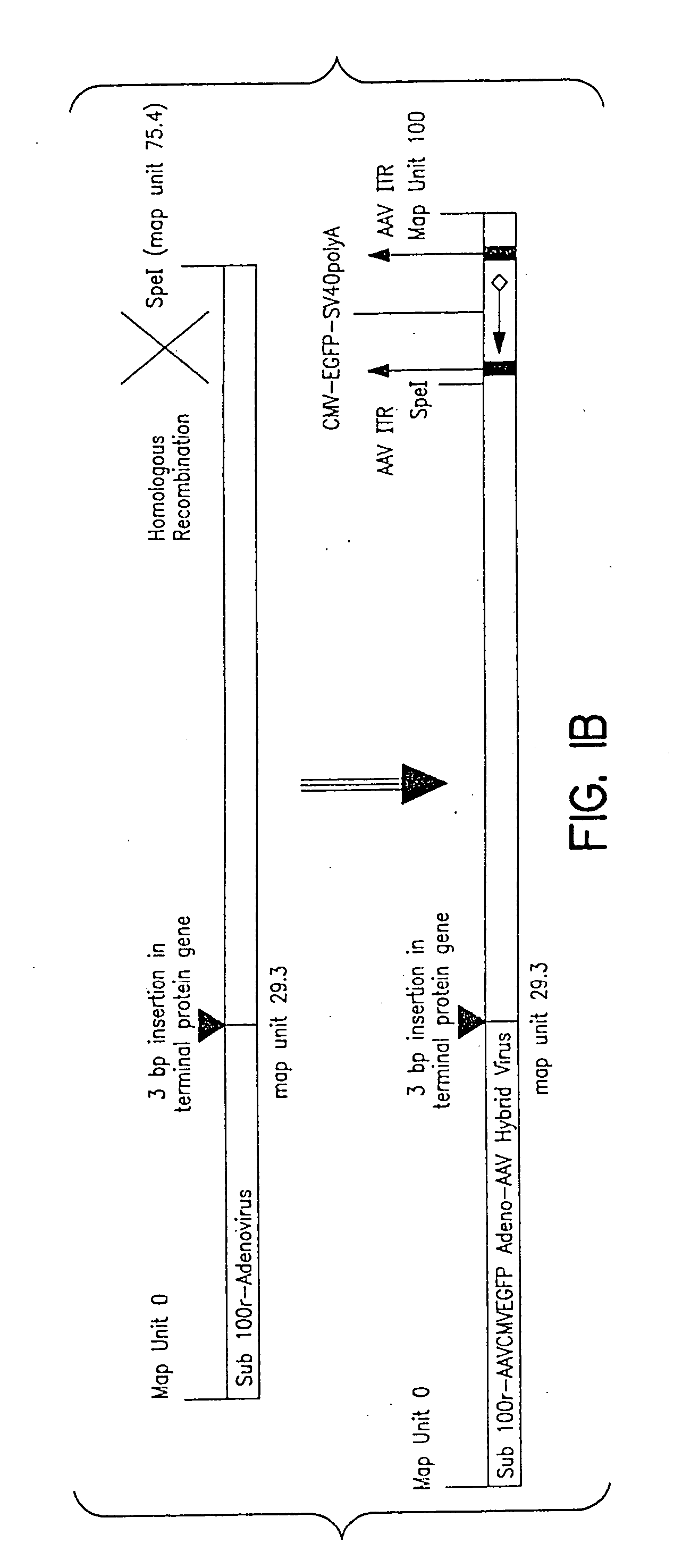
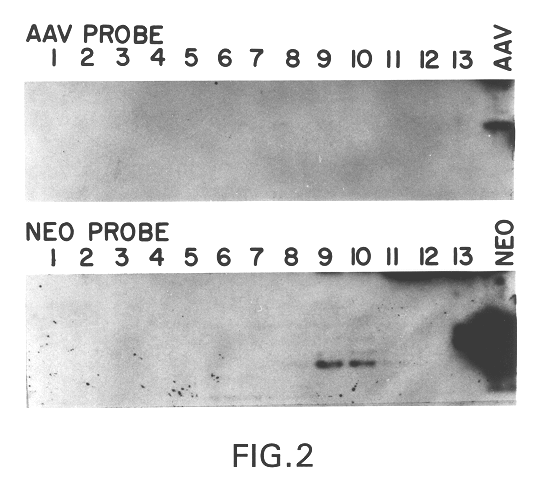
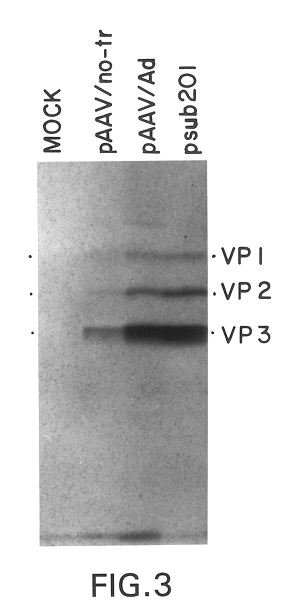
A method for producing recombinant adeno-associated virus in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wild-type virus involves culturing a mammalian host cell containing a transgene flanked by adeno-associated virus (AAV) inverse terminal repeats and under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, an AAV rep sequence and an AAV cap sequence under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, and the minimum adenovirus DNA required to express an E1a gene product, an E1b gene product and an E2a gene product, and isolating therefrom a recombinant AAV which expresses the transgene in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wildtype AAV. This method obviates a subsequent purification step to purify rAAV from contaminating virus. Also provided are various embodiments of the host cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Compositions and methods for helper-free production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Packaging cell
A virus-producing cell sustaining the ability to produce viruses at high titer is successfully constructed by expressing the virus structural gene under the regulation of EF1α promoter. In this virus-producing cell, the virus structural gene is ligated to a selection marker gene via IRES and domains other than the protein coding domain are eliminated from the DNA encoding virus structural proteins. Thus, reduction of the titer due to cell passages can be prevented and emergence of wild type viruses caused by unfavorable recombination of the virus genome can be inhibited.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Reverse genetic operation system of New castle disease LaSota vaccine strain and its applciation
The present invention is reverse genetic operation system of Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain and its application. The system includes one transcription plasmid including the genome cDNA sequence of the low virulent vaccine strain; one or several transcription aiding plasmids including the cDNA sequence coding the nucleoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain, the cDNA sequence coding the phosphoprotein of the low virulent vaccine strain and the cDNA sequence coding the large polymerase protein of the low virulent vaccine strain; and the host cell of the Newcastle disease Lasota low virulent vaccine strain. Wild viral strain is obtained by means of the reverse genetic operation system. The present invention lays firm foundation for further development of Newcastle disease virus live carrier vaccine and Newcastle disease virus related research.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Human papilloma virus 18 L1 (HPV18L1) polynucleotide sequence and its expression vector, host cell and use
ActiveCN102719453AHigh yieldLow costFungiViral antigen ingredientsSynthetic nucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a human papilloma virus 18 L1 (HPV18L1) polynucleotide sequence and its expression vector, host cell and use and especially relates to an amino acid sequence of an HPV L1 capsid protein, a synthetic nucleotide sequence for coding the amino acid sequence, a recombinant expression vector containing the synthetic nucleotide sequence, and a hansenula polymorpha expression host strain containing the synthetic nucleotide sequence. The invention also relates to a use of an HPV18L1 protein composed of the amino acid sequence and derivatives of the amino acid sequence in preparation of vaccines. Through modification of a nucleotide sequence of a gene of an HPV18L1 wide-type virus, a recombinant HPV18L1 capsid protein can be highly expressed in a hansenula polymorpha expression system and thus hansenula polymorpha expression system-based industrial production of an HPV18L1 capsid protein is realized. Compared with the existing eukaryotic expression systems, the HPV18L1 polynucleotide sequence and its expression vector and host cell have advantages of higher yield and lower cost.
Owner:天津昕因达生物技术有限公司
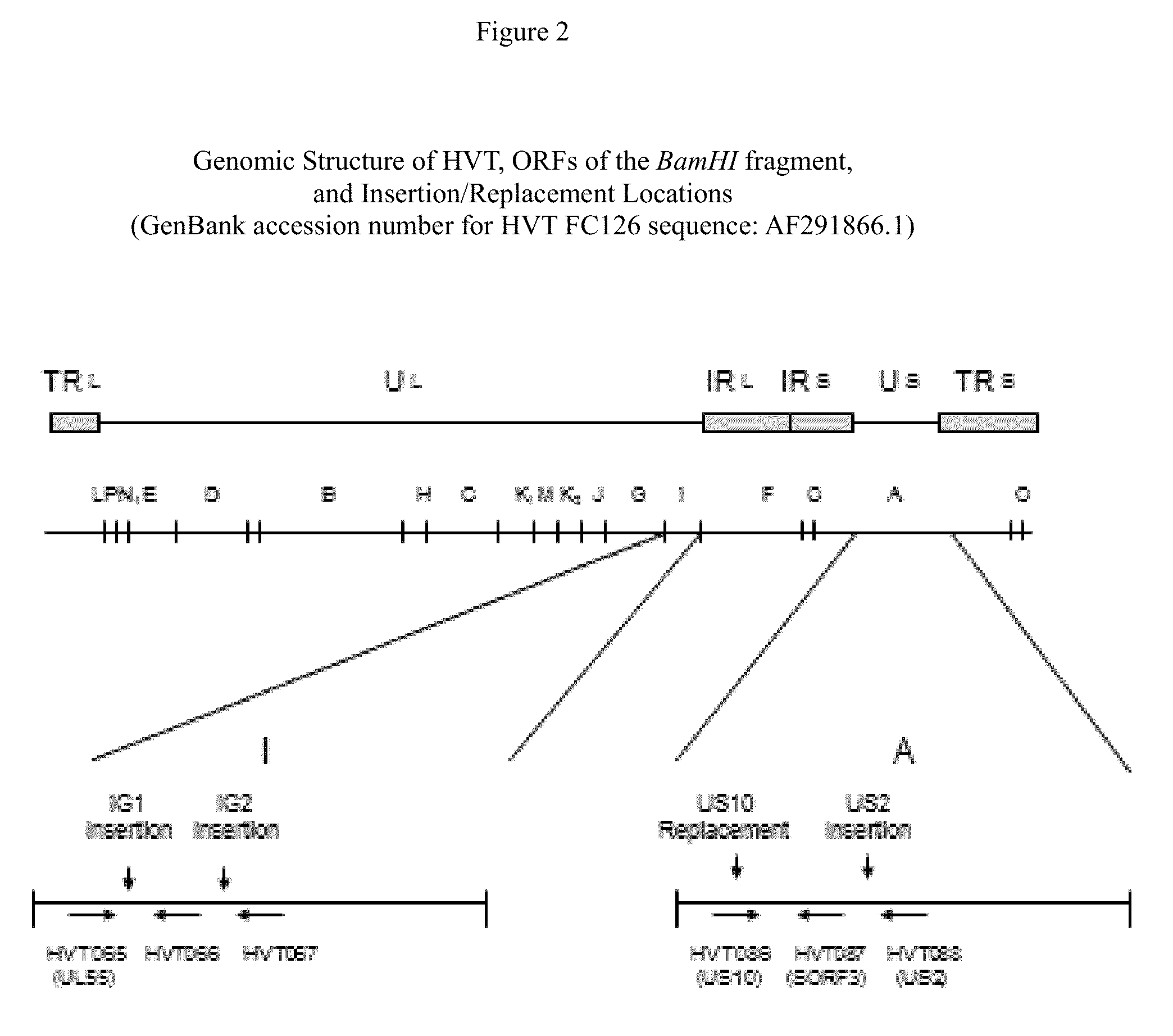
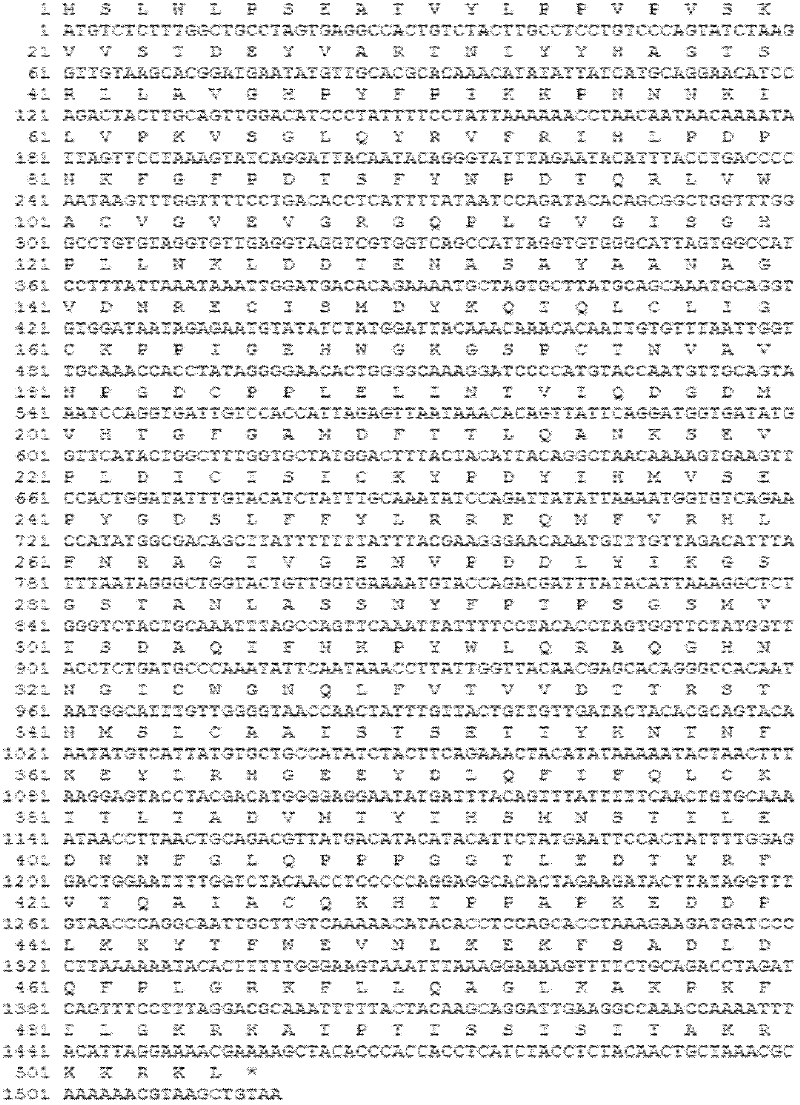
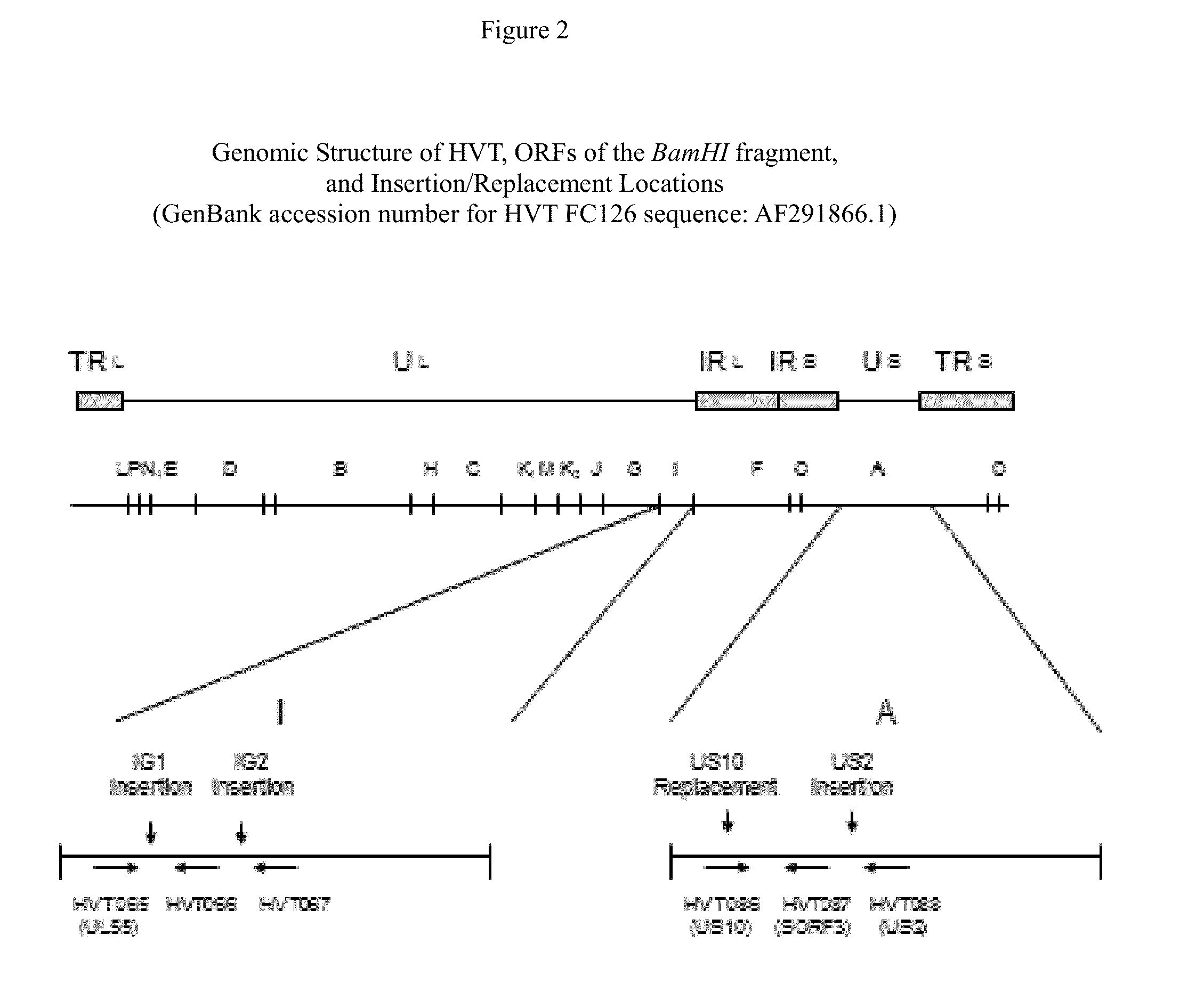
Recombinant HVT vectors expressing antigens of avian pathogens and uses thereof
ActiveUS9114108B2Effective protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigenFowl
The present invention provides recombinant herpesvirus of turkeys (HVT) vectors that contain and express antigens of avian pathogens, compositions comprising the recombinant HVT vectors, polyvalent vaccines comprising the recombinant HVT vectors and one or more wild type viruses or recombinant vectors. The present invention further provides methods of vaccination against a variety of avian pathogens and method of producing the recombinant HVT vectors.
Owner:MERIAL INC
HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence and expression vector, host cell and application thereof
InactiveCN102586287AHigh yieldLow costFungiViral antigen ingredientsHuman papillomavirusSynthetic nucleotide
The invention relates to an HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence, and an expression vector, a host cell and application of the HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence. The HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence comprises an amino acid sequence of recombinant human papillomavirus (HPV) L1 capsid protein, a synthetic nucleotide sequence coding the amino acid sequence, and a recombinant expression vector and a hansenula polymorpha expression host strain comprising the nucleotide sequence. The invention also relates to the application of HPV16L1 protein consisting of the amino acid sequence and derivatives of the HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence in preparing vaccine. According to the invention, by transforming the nucleotide sequence of HPV16L1 wild type virogene, the recombinant HPV16L1 capsid protein in a hansenula polymorpha system is efficiently expressed, and the HPV16L1 capsid protein can be industrially produced by using the hansenula polymorpha expression system; and compared with the conventional other eukaryotic expression systems, the hansenula polymorpha expression system has the advantages of high yield, low cost and the like.
Owner:王昌华
Helper-free stocks of recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors
InactiveUS6489162B1Efficient yieldImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingWild typeViral vector
The present invention relates to a method for producing helper-free stocks of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) which can be used to efficiently and stably transduce foreign genes into host cells or organisms. The method comprises the cotransfection of eukaryotic cells with rAAV and with helper AAV DNA in the presence of helper virus (e.g. adenovirus or herpesvirus) such that the helper AAV DNA is not associated with virion formation. The crux of the invention lies in the inubility of the helper AAV DNA to recombine with rAAV vector, thereby preventing the generation of wild-type virus. In a specific embodiment of the invention, the vector comprises a recombinant AAV genome containing only the terminal regions of the AAV chromosome bracketing a non-viral gene, and the helper AAV DNA comprises a recombinant AAV genome containing that part of the AAV genome which is not present in the vector, and in which the AAV terminal regions are replaced by adenovirus sequences. In a further embodiment of the invention, cell lines are created which incorporate helper AAV DNA which can directly produce substantially pure recombinant AAV virus. The pure stocks of recombinant AAV produced according to the invention provide an AAV viral expression vector system with increased yield of recombinant virus, improved efficiency, higher definition, and greater safety than presently used systems.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
PCV2 virus-like particles as well as preparation method thereof and splitting and VLP assembly buffer liquor
ActiveCN104073473AHigh expressionImprove solubilityInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPorcine circovirus
The invention discloses PCV2 virus-like particles as well as a preparation method thereof and splitting and VLP assembly buffer liquor. Based on an autonomous optimization design, a PCV2 nucleocapsid protein gene which is suitable for efficiently expressing in a prokaryotic expression system is artificially synthesized, a full-length gene sequence of the PCV2 nucleocapsid protein gene is expressed by an escherichia coli prokaryotic expression system, and the virus-like particles are efficiently and autonomously assembled by utilizing soluble nucleocapsid protein of the full-length gene sequence under a special condition. An innovation point of the invention is that PCV2VLPs are obtained by utilizing the prokaryotic expression system instead of adopting the conventional method for obtaining VLPs through an eukaryotic expression system; the method is low in cost, simple and efficient, and suitable for large-scale industrial application; moreover, an innovative buffer liquor formula integrating double functions, which not only can promote thallus splitting, but also can be suitable for self-assembling of VLPs, is also applied; besides, the PCV2 virus-like particles obtained in the invention are very highly similar with wild type virus in outline and good in immunogenicity, and can be applied to developing a subunit vaccine and a drug delivery carrier with utilization potentiality of porcine circovirus.
Owner:湖南派智生物科技有限公司
Anti-bacterium antivirus guanidine salt star-shaped polymer, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103497275AOptimal Control StructureControllable Molecular WeightBiocideDisinfectantsFunctional monomerPolymer science
The invention discloses an anti-bacterium antivirus guanidine salt star-shaped polymer, a preparation method and applications thereof, and the arm number, structure and molecular weight of the star-shaped polymer are controllable. The polymer is prepared by the following steps: adopting a core-first method, taking brominated beta-cyclodextrin as an initiator, guanidine salt oligomer containing carbon-carbon double bonds as the functional monomers, and then carrying out atom transfer radical polymerization so as to obtain the target product, wherein the structure and molecular weight of the polymer can be modulated according to the application needs. The polymer and the preparation method thereof improve the molecular weight of the polymer, achieve chain amplification effect, increase the density of effective functional groups having an anti-bacterium effect, effectively solve the problems of contamination on other products caused by leakage of anti-bacterium agents and nondurable anti-bacterium effect, and eliminate the potential dangers caused by leaked anti-bacterium agents on human health. Furthermore, the polymer has a prominent function, which other guanidine salt polymers do not have, of killing wild type viruses and bacteria such as gland virus, influenza virus, and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Use of viruses and virus-resistant microorganisms for controlling microorganism populations
InactiveUS20060153811A1Controlling and reducing and eliminating populationEffectively control and reduce and eliminateBiocideViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsMicroorganismWild type
A lytic virus specific for a target strain of a microorganism and substantially free of undesirable genes may be utilized in processes including control of populations of microorganisms. The virus may include a host-range mutant, or “h-mutant.” A method for generating virus includes growing virus-resistant variants of a target strain of a microorganism in the presence of viruses that are specific for the target strain. Only h-mutant viruses will proliferate. Wild-type virus-resistant and virus-resistant variants of a microorganism are also disclosed, as are methods generating such variants. Methods for controlling target strain microorganisms include introducing virus into a treatment site where control of a population of a target strain microorganism is desired or introducing virus-resistant variants of a microorganism into treatment sites where the presence of the microorganism is desired.
Owner:OMNILYTICS INC
Recombinant gallid herpesvirus 3 (mdv serotype 2) vectors expressing antigens of avian pathogens and uses thereof
The present invention provides recombinant Gallid herpesvirus 3 (MDV-2) vectors that contain and express antigens of avian pathogens, recombinant Gallid herpesvirus 3 (MDV-2) vectors that contain a mutated gC gene, compositions comprising the recombinant Gallid herpesvirus 3 (MDV-2) vectors, polyvalent vaccines comprising the recombinant Gallid herpesvirus 3 (MDV-2) vectors and one or more wild type viruses or recombinant vectors. The present invention further provides methods of vaccination against a variety of avian pathogens and method of producing the recombinant Gallid herpesvirus 3 (MDV-2) vectors.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH +1
Oncolytic virus vaccine and medicine for treating tumors by combining oncolytic virus vaccine with immune cells
ActiveCN111286493AEffective treatmentHigh cure rateSsRNA viruses negative-senseMammal material medical ingredientsTumor therapyOncology
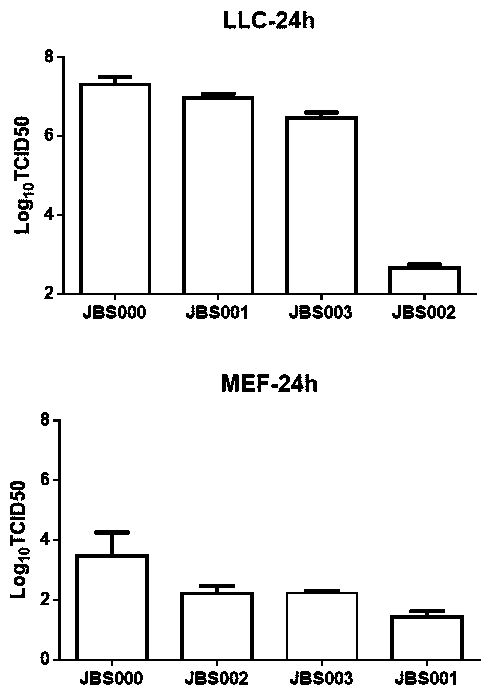
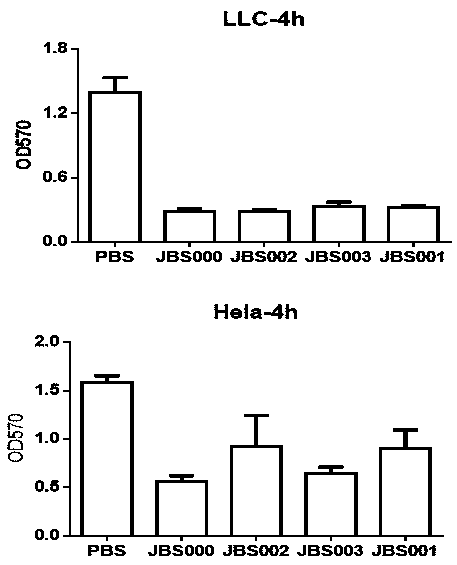
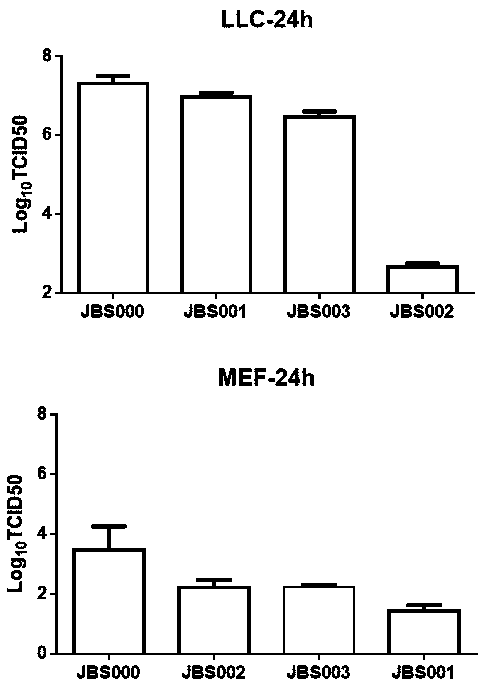
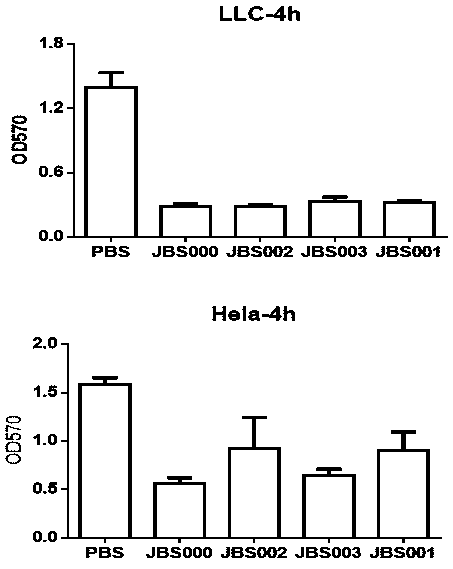
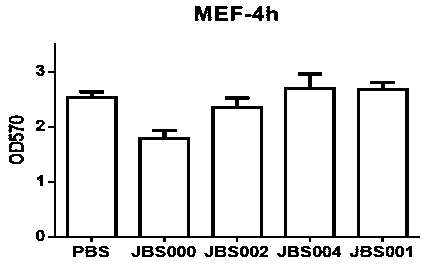
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to an oncolytic virus vaccine and a medicine for treating tumors by combining the oncolytic virus vaccine with immunecells. The invention provides a brand-new oncolytic virus attenuated strain by carrying out site-specific mutagenesis on the VSV wild type virus matrix protein M. The gene sequence of the matrix protein M is shown as SEQ ID NO 3. The attenuated strain can be independently used as a drug for treating tumors, and is superior to wild type viruses and other known attenuated strains in safety and curerate. On the basis of the oncolytic virus attenuated strain, NY-ESO-1 is inserted into the attenuated strain, and the invention further provides a vaccine capable of being applied to tumor treatment.The vaccine is high in cure rate and high in biological safety. On the basis of the vaccine, the vaccine and TCR-T cells are combined for application, and a medicine capable of efficiently treating various tumors is provided. On a mouse lung cancer model, the cure rate can reach the surprising rate of 95 percent.
Owner:JOINT BIOSCIENCES (SH) LTD
Type-A foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) marking vaccine and construction method thereof
ActiveCN104826098AImproving immunogenicityGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsWild typeAdemetionine
The invention discloses a type-A foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) marking vaccine and a construction method thereof. The seed virus of the disclosed marking vaccine is an A / rV-2 virus with a gene fragment as shown in SEQ ID NO:3; the amino acid sequence encoded according to the gene fragment is as shown in a sequence table as follows: SEQ ID NO:4; and the amino acid sequence is obtained by deleting amino acids from the 104th position to 115th position of a type-3A FMD virus protein. An animal infected by the FMD marking virus constructed by using the construction method is remarkably different from an animal infected by a wild-type virus on the aspect of serology; and an FMD marking vaccine immunized pig has favorable immunogenicity. Therefore, the type-A FMD virus constructed by using the method disclosed by the invention can be used for developing a differential diagnosis (DIVA) vaccine which is used for preventing and controlling the current type-A FMD in China.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and building method thereof
InactiveCN102329783AFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeUridine diphosphate
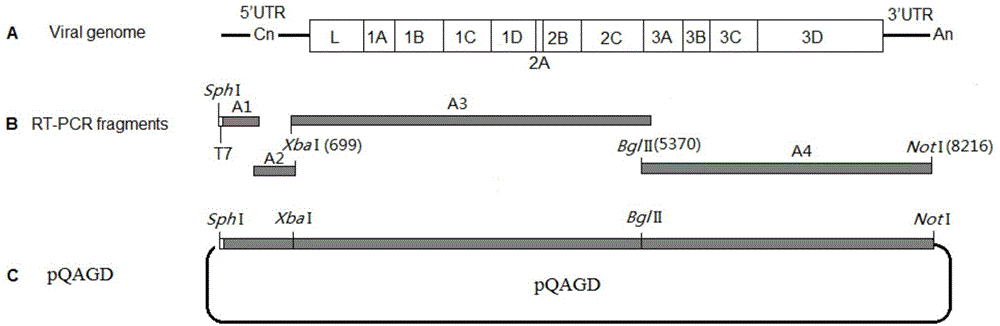
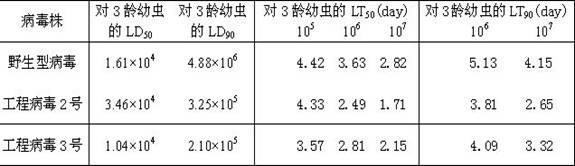
The invention discloses a prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and a building method thereof, in particular relates to a prodenia litura gene engineering virus used for carrying out deficiency and recombination on a wild type virus (SpltMNPV II) by utilizing a gene engineering method. The genome of the virus is deficient in an egt gene, namely an ecdysteroid UDP (uridine diphosphate) glucosyltransferase gene; and at the site of the deficient egt gene, a BmKITa1 gene controlled by a wild type virus, namely an early gene-1(ie-1) starter, and a marker gene, namely an enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene, which is controlled by the wild type virus, namely a polyhedron gene (ph) starterare inserted. The prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of faster insecticidal speed, less dosage effect and better field application effect compared with the wild type virus. Compared with the prior art, the prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 provided by the invention has less dosage effect and lower LT50 at low dose (105 polyhydral bodies / larva).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Recombinant Hvt Vectors Expressing Antigens Of Avian Pathogens And Uses Thereof
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM ANIMAL HEALTH USA INC
Duck tembusu virus E truncated protein and application
ActiveCN107656066AStrong specificityHigh compliance rateSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesYolkDisk diffusion susceptibility test
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of animal virology and animal infectious diseases, and particularly discloses a duck tembusu virus E truncated protein and application. Protein of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2 is used as a coating antigen, a duck tembusu virus serum detection kit which is prepared from a hybridoma cell strain under the accession number CCTCC NO: C2017169 is used for detecting duck serum and an egg yolk antibody which are infected by wild type virus, and has good specificity; and the sensitivity is high, and after being diluted to be 1: 12800, duck tembusu virus positive serum can still be positive when detected. Compared with the traditional agar diffusion test, the duck tembusu virus E truncated protein is high in coincidence rate, simple and convenient to operate, short in detection time and suitable for simultaneously detecting a large number of samples.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Lentiviral gene transfer vector, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101705246AIncrease productionIncrease nuclear inputViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionLarge fragmentWild type
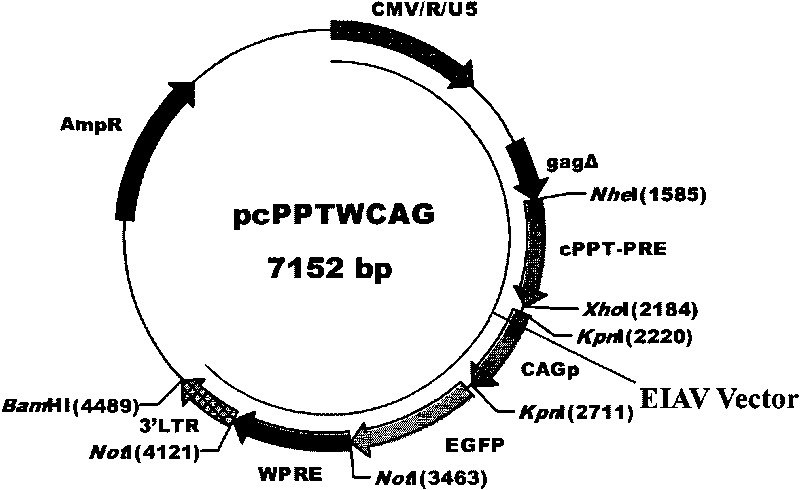
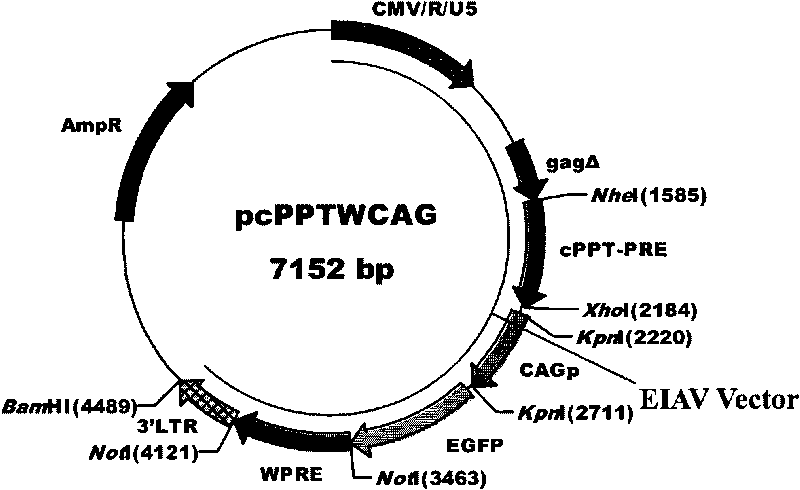
The invention discloses an equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV) gene transfer vector, a constructed method and an application thereof. The vector of the invention comprises a CMV / R / U5 promoter, a 5' non-translated region homing sequence, a partial 5' gag gene coding region sequence, a central polypurine sequence, an Rev reaction element of EIAV, a CMVIE / chicken beta-actin promoter, a reporter gene, WPRE of WHBV, a polyclone locus, a poly (A) signal before EIAV 3'LTR, complete 3'LTR and partial sequence of eukaryon expression vector. The vector of the invention possesses common advantages of lentiviral vector, lacks auxiliary genes of all the wild-type virus, can carry one or a plurality of selected genes to transmit to target cells, can insert with target DNA sequence with large fragments and can lead the foreign genes and reporter genes to express at a high level in the cells.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Novel influenza virus A mammalian cell adapted strain and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105985413ADoes not increase lethalityVirus peptidesMicroorganism based processesMutated proteinWild type
The invention discloses a novel influenza virus A mammalian cell adapted strain and preparation and application thereof and particularly provides PR8 virus strain mutant protein and a recombinant PR8 virus strain containing the PR8 virus strain mutant protein, wherein the PR8 virus strain mutant protein can greatly improve the growing ability of an influenza virus A strain PR8 on mammalian cells (particularly Vero cells), after K at the site 86 of NS2 protein of the PR8 virus strain is mutated into R, the growing ability of the obtained virus strain on the Vero cells is improved by 20-100 times compared with that of a wild PR8 virus strain, and the pathogenicity of the adapted strain on a living body is not enhanced. Therefore, the influenza virus A strain containing the mutant protein can serve as a high-yield vaccine seed strain on mammalian cells.
Owner:INST PASTEUR OF SHANGHAI CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Adeno-Associated Virus with Site-Directed Mutagenesis and Site-Directed Modification and Preparation Method and Application Thereof
ActiveUS20160297855A1Improve aimingVirus peptidesWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsAdeno associate virusSite-directed mutagenesis
The present invention relates to an adeno-associated virus with site-directed mutagenesis and site-specific modification, and a preparation method and uses thereof. Specifically, the present invention uses genetic code expansion techniques to incorporate non-natural amino acid into an adeno-associated virus capsid protein VP1 or fragment thereof, thereby obtaining an adeno-associated virus with site-directed mutagenesis using the non-natural amino acid. The adeno-associated virus with site-directed mutagenesis is equivalent to a wild-type virus in terms of production, transduction and mobility, can couple with other functional molecules, such as targeting molecules, and can carry a functional gene in a normal manner, which indicates that the adeno-associated virus with site-directed mutagenesis can be used as a tool adeno-associated virus, and applied in various aspects associated with adeno-associated virus such as finding adeno-associated virus binding proteins or using as target genetic therapy vector.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Attenuated SARS and use as a vaccine
The present invention relates to nucleic acids encoding attenuated SARS-CoV viruses which are capable of producing a maximum viral titer in cell culture that is reduced at least by a factor of 2 when compared to the maximum viral titer of wild-type SARS-CoV virus in the same cell culture. According to a further aspect of the present invention, the nucleic acids encoding an attenuated SARS-CoV virus, are obtainable by a method comprising steps, wherein the genome of a SARS-CoV virus is modified by amending the sequence of the gene encoding the SARS-CoV E protein so that the nucleic acid cannot express a functional E protein. The present invention further relates to the viruses encoded by these nucleic acids as well as the medical use of the nucleic acids and of the viruses.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Preparation method of asymmetric virus nanoparticles
InactiveCN102321590AHave diversityControllableInactivation/attenuationDepsipeptidesProtein moleculesFunctionalized nanoparticles
The invention discloses a preparation method of asymmetric virus nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out gene modification on the virus capsid protein surface, so that the virus capsid protein simultaneously has coupled functional group and separate group; thoroughly mixing the modified virus capsid protein and wild type virus capsid protein while controlling the proportion of the two virus capsid proteins; and meanwhile, adding corresponding inorganic nanoparticles according to the total amount of the virus capsid protein to implement controllable assembly of the virus nanoparticles, thereby obtaining the asymmetric functionalized nanoparticles which are the goal product. The invention adopts biomacromolecule-protein as the nano material, and the biomacromolecule-protein can be easily modified and manually operated, and can be conveniently obtained massively. On the basis of the structural symmetry of the self-assemblable virus capsid protein, the two different protein molecules can be assembled in an oriented mode according to the previous design, and therefore, the assembly body has diversity and controllability; and the invention has the advantage of manageable reaction conditions, and can implement large-scale production.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Recombinant live attenuated foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) vaccine containing mutations in the L protein coding region
ActiveUS8846057B2Reduce severityReduce probabilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsNeutralizing antibodyAttenuated Live Vaccine
Previously we have identified a conserved domain (SAP, for SAF-A / B, Acinus, and PIAS) in the foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) leader (L) protein coding region that is required for proper sub-cellular localization and function. Mutation of isoleucine 55 and leucine 58 to alanine (I55A, L58A) within the SAP domain resulted in a viable virus that displayed a mild attenuated phenotype in cell culture, along with altered sub-cellular distribution of L and failure to induce degradation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa-B. Here we report that inoculation of swine and cattle with this mutant virus results in the absence of clinical disease, the induction of a significant FMDV-specific neutralizing antibody response, and protection against subsequent homologous virus challenge. Remarkably, swine vaccinated with SAP mutant virus are protected against wild type virus challenge as early as two days post-vaccination suggesting that a strong innate as well as adaptive immunity is elicited. This variant could serve as the basis for construction of a live-attenuated FMD vaccine candidate.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Anti-H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus monoclonal antibody epitope as well as screening method and application thereof
The invention provides an anti-H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus monoclonal antibody epitope as well as a screening method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of immunodetection. The screening method comprises the following steps: mixing wild type H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus liquid with a corresponding monoclonal antibody with a neutralizing property for incubation, and inoculating the mixture to an SPF chick embryo, so as to obtain allantoic fluid with a positive hemagglutination titer; and carrying out gradient dilution on the positive allantoic fluid, mixing the positive allantoic fluid with the monoclonal antibody for incubation, inoculating the mixture to the SPF chick embryo, determining a hemagglutination inhibition titer of the monoclonal antibody by selecting the allantoic fluid with the positive hemagglutination titer as an antigen, when the determined hemagglutination inhibition titer is lower than the hemagglutination inhibition titer of a wild type virus by 8log2, determining the positive allantoic fluid as an escape mutant of the wild type H7N9 subtype avian influenza virus, measuring an HA gene sequence of the positive allantoic fluid, and determining the epitope recognized by the monoclonal antibody. By virtue of the method, the specific epitope can be clearly screened; the method is simple, accurate and short in screening period.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Recombinant hvt vectors expressing antigens of avian pathogens and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140147457A1Effective protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigenVaccination
The present invention provides recombinant herpesvirus of turkeys (HVT) vectors that contain and express antigens of avian pathogens, compositions comprising the recombinant HVT vectors, polyvalent vaccines comprising the recombinant HVT vectors and one or more wild type viruses or recombinant vectors. The present invention further provides methods of vaccination against a variety of avian pathogens and method of producing the recombinant HVT vectors.
Owner:MERIAL INC
Genetically engineered virus of Chinese ballworm
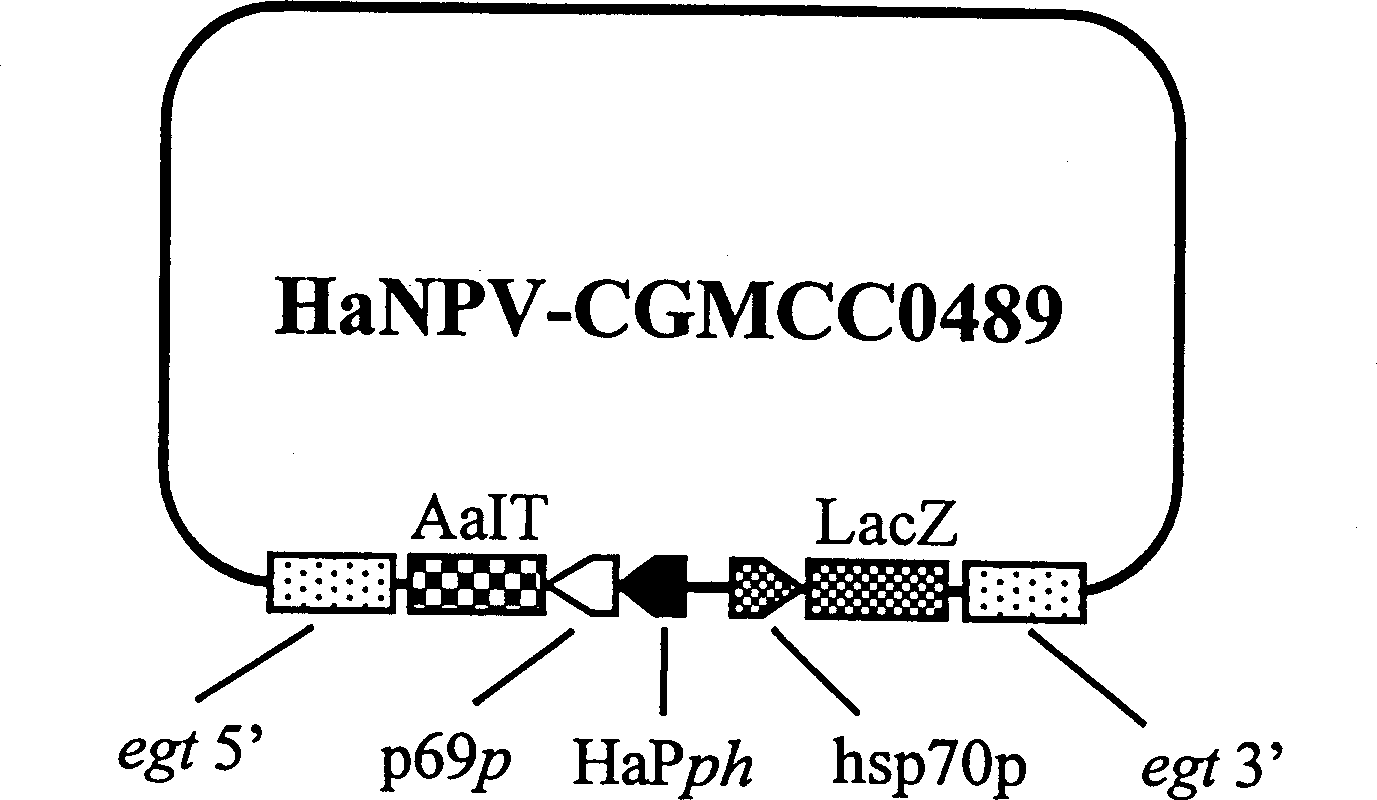
InactiveCN1109105CFast insecticideGood field application effectBiocideViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeEngineered genetic
A genetically engineered virus of Chinese ballworm is obtained by double recombination of wild virus. Its genome is deficient is egt gene. At the position deficient in egt gene, the insect-specific neurotoxic AaIT gene controlled by the promoters of Chinese ballworm virus' alkaline DNA binding protein gene (p6.9) and polyhedrin protein gene (ph) and the beta-galactosidase (LacZ) gene controlled by the promoter of heat shock protein gene (hsp70) are inserted. Its advantages are higher insecticiding speed and better application effect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Defective sindbis viral vectors
ActiveUS20070020236A1Suppressed abilityTargeted tumors more effectivelyBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAbnormal tissue growthMammal
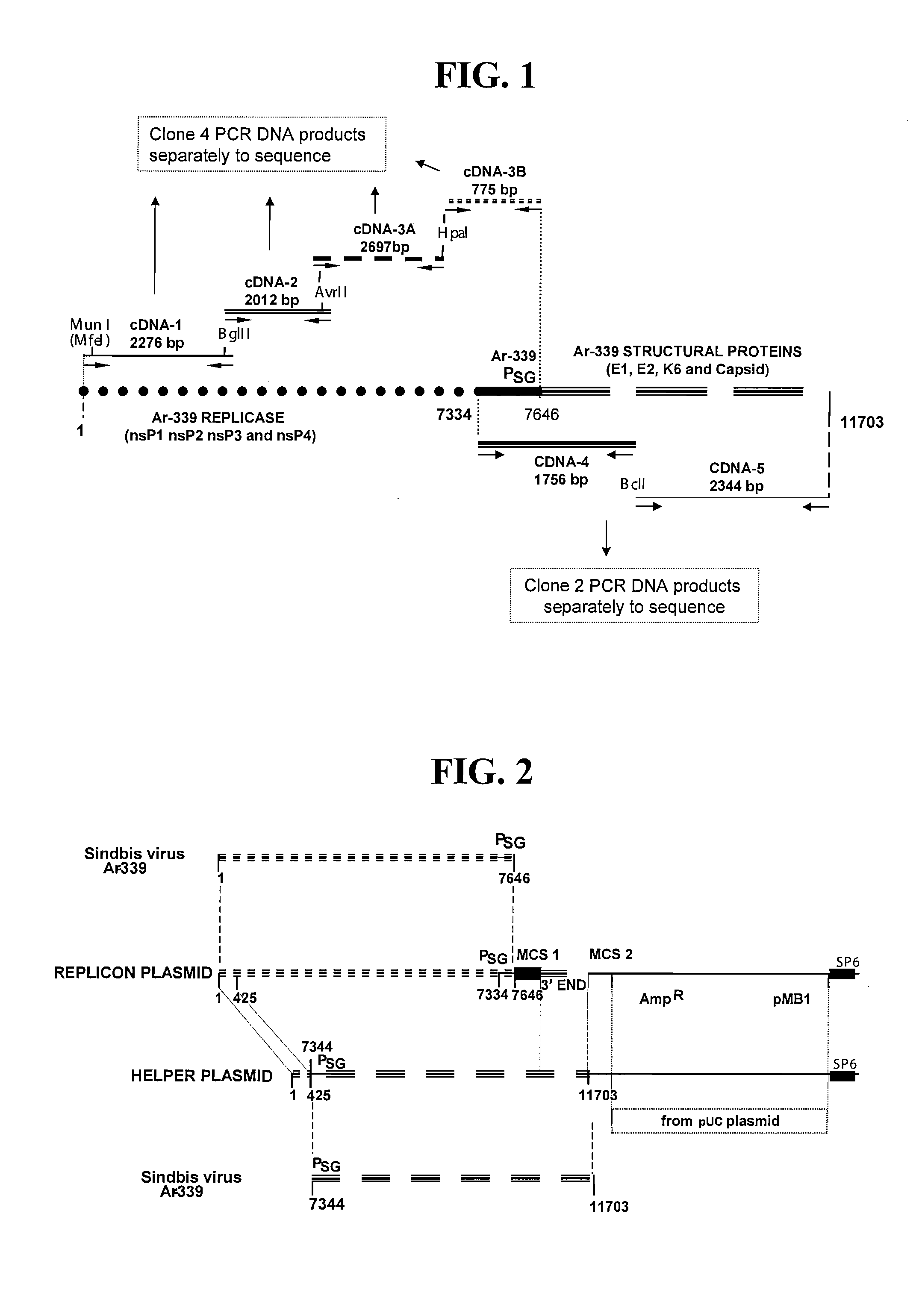
Disclosed herein are new defective Sindbis viral vectors made from wild type Ar-339 Sindbis virus, with differences in replicase and envelope proteins between JT vectors and consensus Sindbis virus sequences, and also between JT and Ar-339 vectors. Also disclosed are plasmids used for the production of the vectors, methods for producing the vectors, methods for treating mammals suffering from tumors and pharmaceutical formulations for use in the treatment methods.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
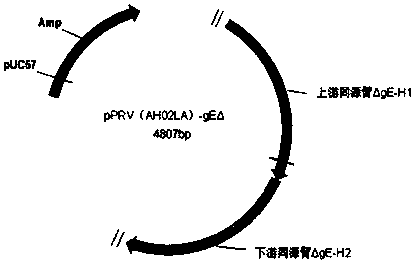
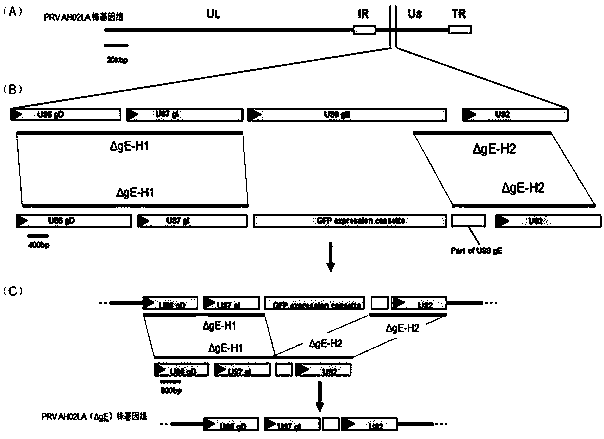
Pseudorabies virus (PRV) digene deletion attenuated strain and application thereof
ActiveCN107828741APrevent diseasePrevent detoxificationViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesProtective antigenWild type
The invention provides a pseudorabies virus (PRV) digene deletion attenuated strain and application thereof, and belongs to the field of vaccines for animal medicine. A preservation number of a PRV LA1206-80 strain is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.14329. The invention also provides application of the PRV digene deletion attenuated strain in preparation of a pseudorabies vaccine, and a recombinant vector live vaccine. A recombinant vector is obtained by inserting an exogenous protective antigen gene expression cassette into an attenuated strain genome. The live vaccine of the PRV LA1206-80 strain is absolutely safe to one-day-old neonatal piglets, can be used for early immunization of the neonatal piglets and blocks off infection of wild type viruses asearly as possible. The vaccine is inoculated to weaned PRV negative piglets, so that a high-efficiency protecting force can be quickly generated; particularly, the vaccine can prevent attacking and detoxify. By monitoring PRV gE and gB antibodies, purification on a PRV variant strain is greatly facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
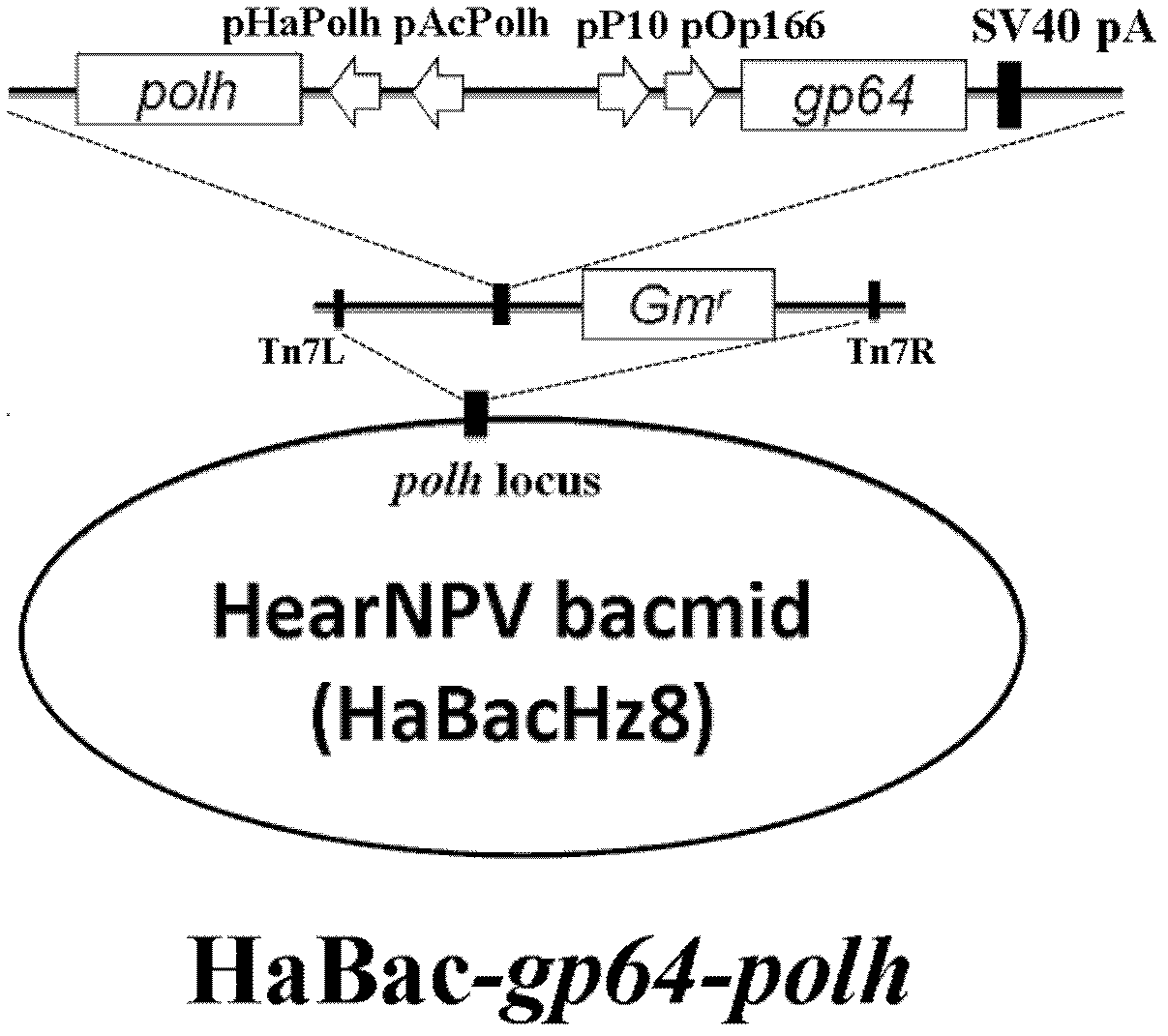
Construction method of novel gene engineering recombinant virus for expressing gp64 gene
InactiveCN102382803AEasy to insertHigh insecticidal activityMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesF proteinNovel gene
The invention relates to a method for implementing gene engineering genetic improvement on a gp64-free baculovirus of a genome by using a Bac-to-Bac system. The method comprises construction of a recombinant virus, amplification of a recombinant virus polyhedrosis and biological assay of the recombinant virus; and according to the construction strategy, a gp64 gene controlled by an autographa californica multiplenucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV) polyhedrosis virus gene promoter and a cyst membrane glycoprotein gene promoter of an orgyia pseudotsugata multiplenucleopolyhedrovirus (OpMNPV) polyhedrosis virus together and a helicoverpa armigera single nucleopolyhedrovirus (HearNPV) polyhedrin gene controlled by an AcMNPV polyhedrin gene promoter and a HearNPV polyhedrin gene promoter together are inserted into a polyhedrin gene site of HearNPV bacmid to construct a recombinant HearNPV bacmid for co-expressing two cyst membrane glycoproteins, namely GP64 and F proteins. The recombinant virus has better insecticidal activity and higher biological safety than a wild virus.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Tumor treatment drug
ActiveCN111467489AAdaptableHigh cure rateSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesTumor therapyTherapeutic effect
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to an oncolytic virus vaccine and a tumor treatment drug combing oncolytic virus vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor. A brand-new oncolytic virus attenuated strain is provided by site-directed mutagenesis of wild-type virus matrix protein M of VSV (vesicular stomatitis virus). The attenuated strain can be used asa drug alone to treat tumors, and has safety and cure rate higher than those of wild-type viruses and other known attenuated strains. On the basis of the oncolytic virus attenuated strain, a vaccinethat can be used in tumor treatment is also provided by inserting NY-ESO-1 into the attenuated strain. The vaccine has high cure rate and high biological safety. On the basis of the vaccine, the invention also combines the vaccine with the immune checkpoint inhibitor to provide the drug capable of efficiently treating various tumors. In mouse lung cancer models, the cure rate can be astonishing, up to 87.5%, and the treatment effect on large tumors is also good.
Owner:JOINT BIOSCIENCES (SH) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com