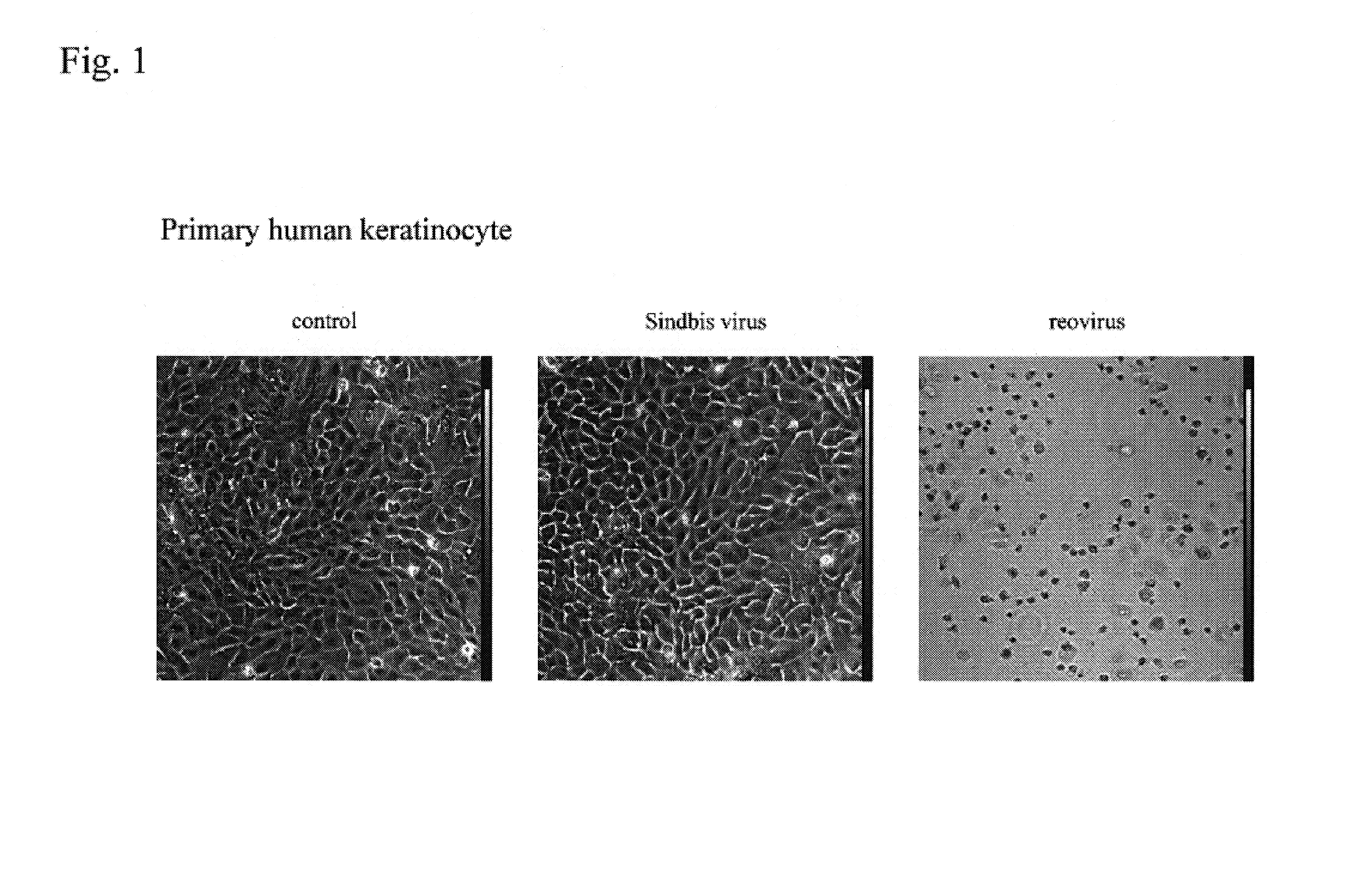
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Sindbis virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sindbis virus (SINV) is a member of the Togaviridae family, in the alphavirus subfamily. The virus was first isolated in 1952 in Cairo, Egypt. The virus is transmitted by mosquitoes (Culex spp.) SINV causes sindbis fever in humans and the symptoms include arthralgia, rash and malaise. Sindbis fever is most common in South and East Africa, Egypt, Israel, Philippines and parts of Australia. Sindbis virus is an "arbovirus" (arthropod-borne) and is maintained in nature by transmission between vertebrate (bird) hosts and invertebrate (mosquito) vectors. Humans are infected with Sindbis virus when bitten by an infected mosquito. SINV has been linked to Pogosta disease in Finland, Ockelbo disease in Sweden and Karelian fever in Russia.
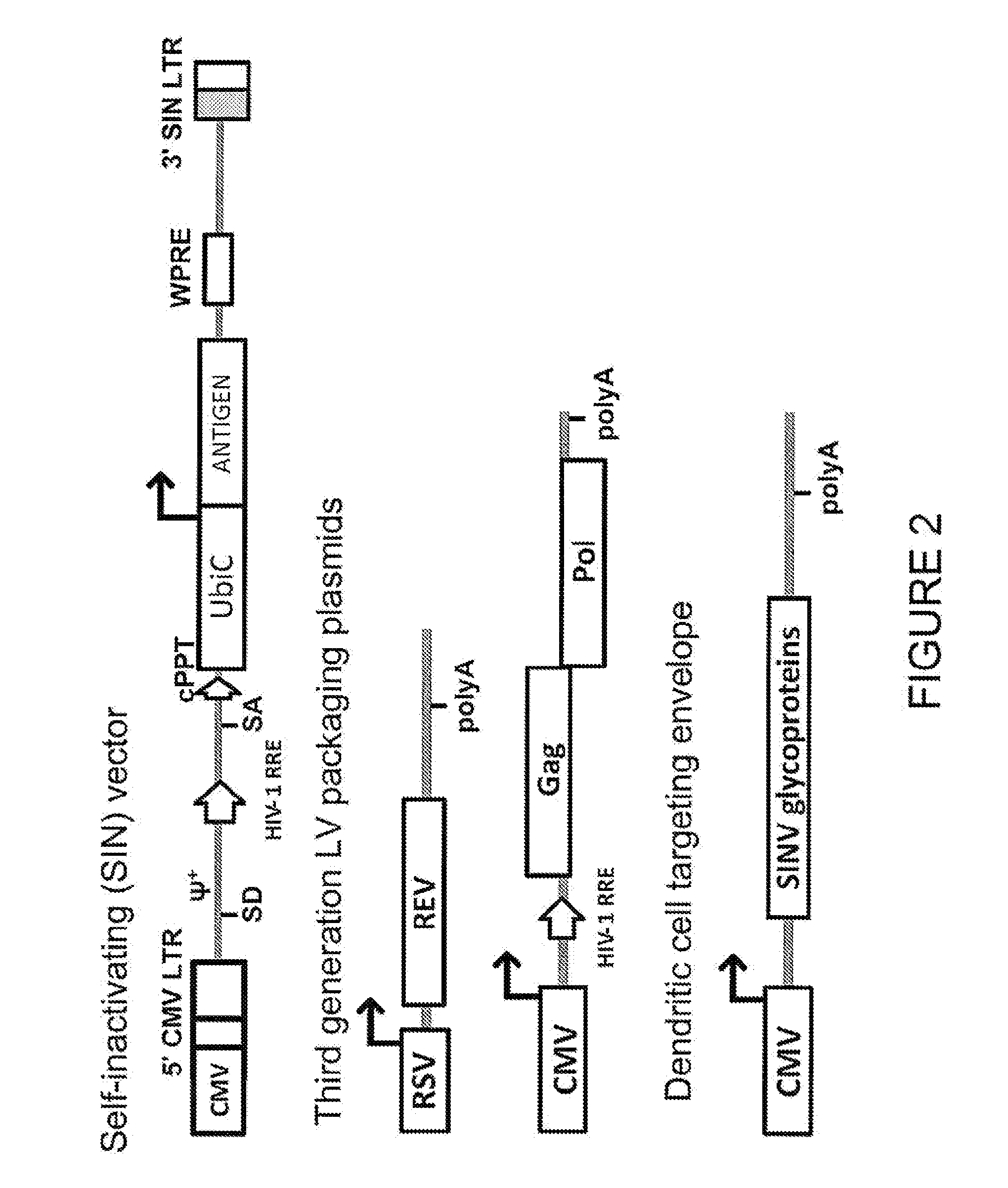
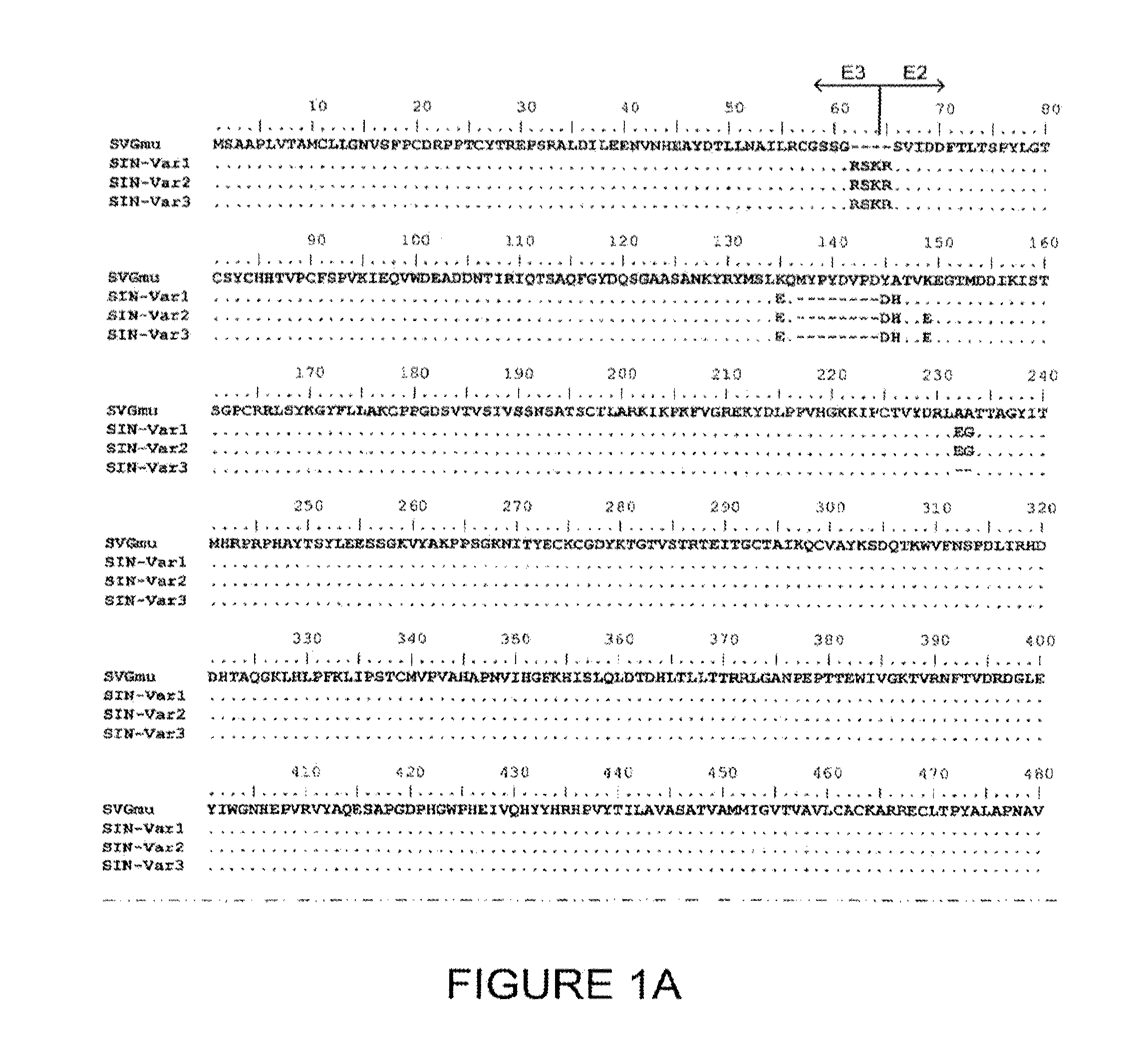
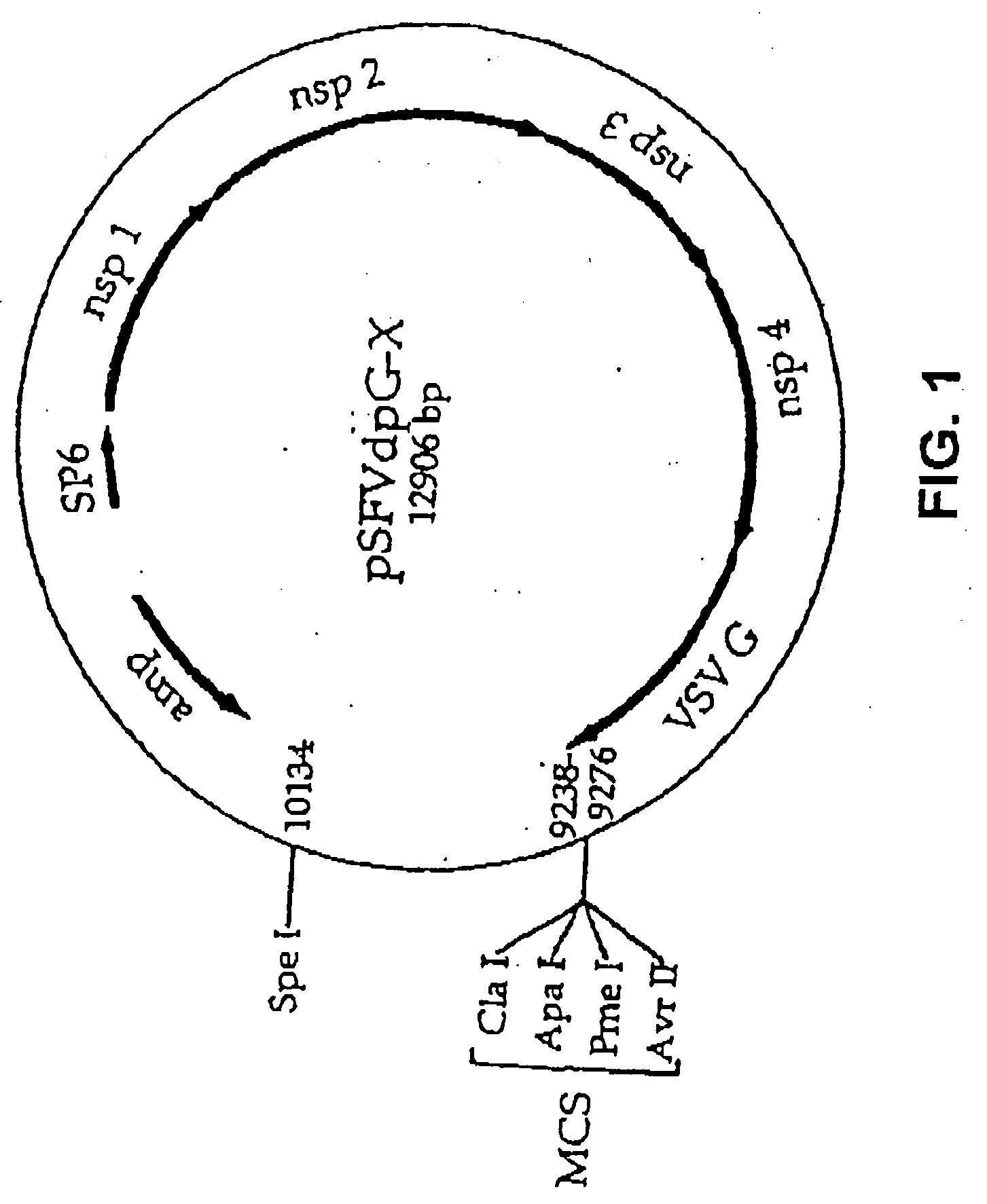
Lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with a sindbis virus envelope glycoprotein
InactiveUS20110064763A1Promote infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntiviralsDendritic cellSindbis virus
Lentiviral vector particles comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant and a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest are provided. A lentiviral vector particle comprising: (a) an envelope comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant; and (b) a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest; wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant facilitates infection of dendritic cells by the lentiviral vector particle, and wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant has reduced binding to heparan sulfate compared to a reference sequence (HR strain).
Owner:IMMUNE DESIGN CORP
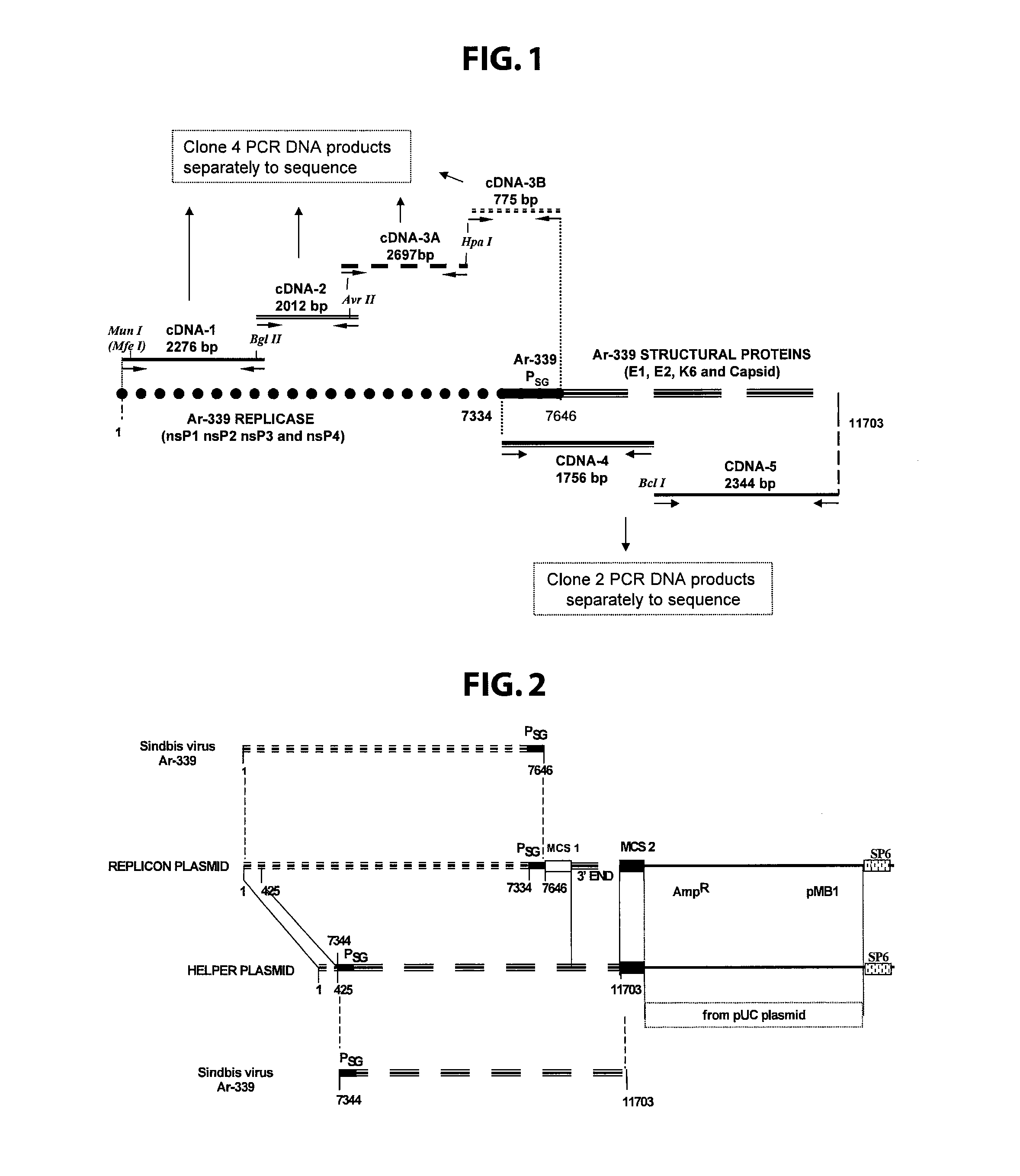
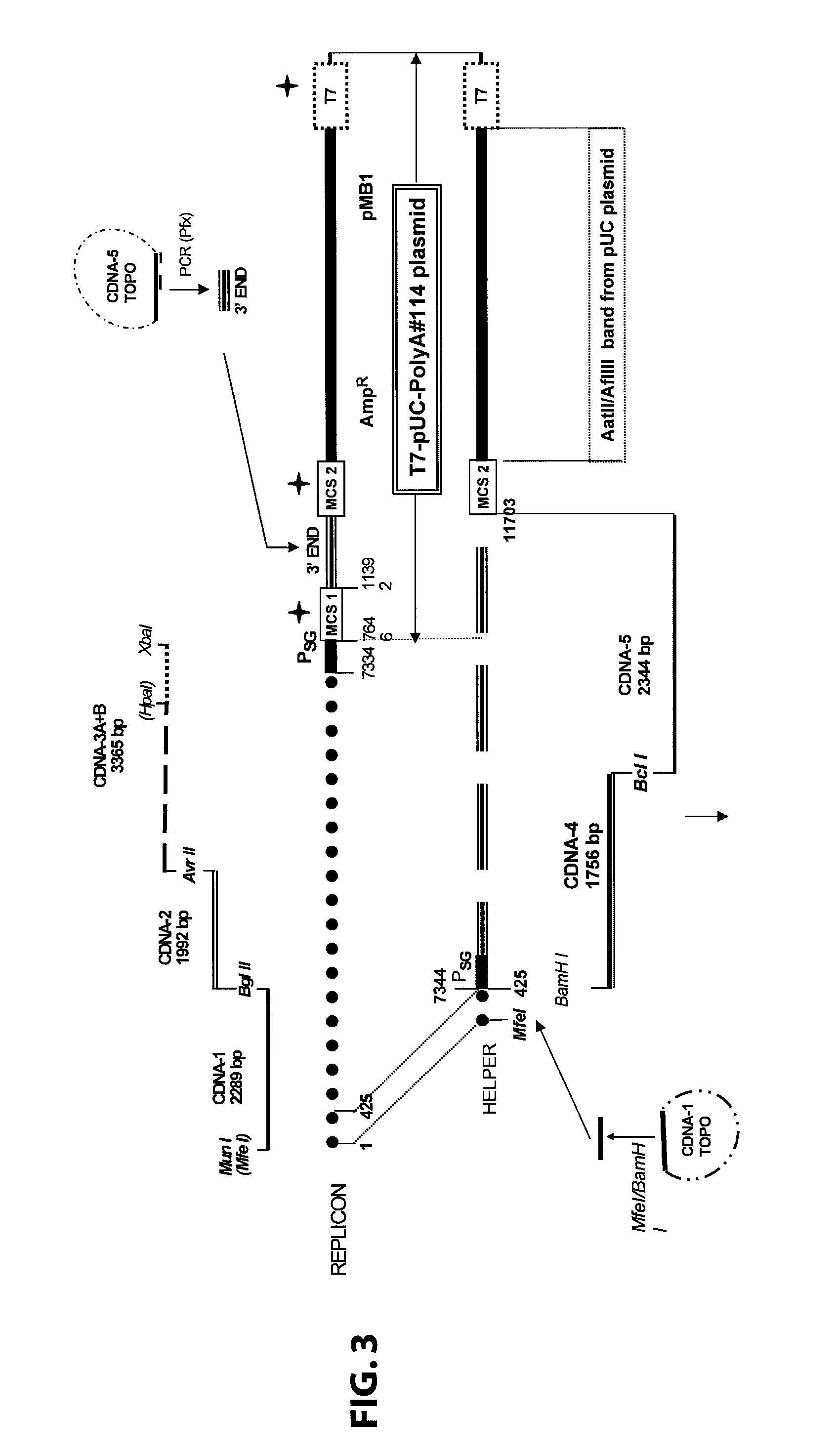
Defective sindbis viral vectors
ActiveUS8093021B2Suppressed abilityTargeted tumors more effectivelySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesMammalSindbis virus
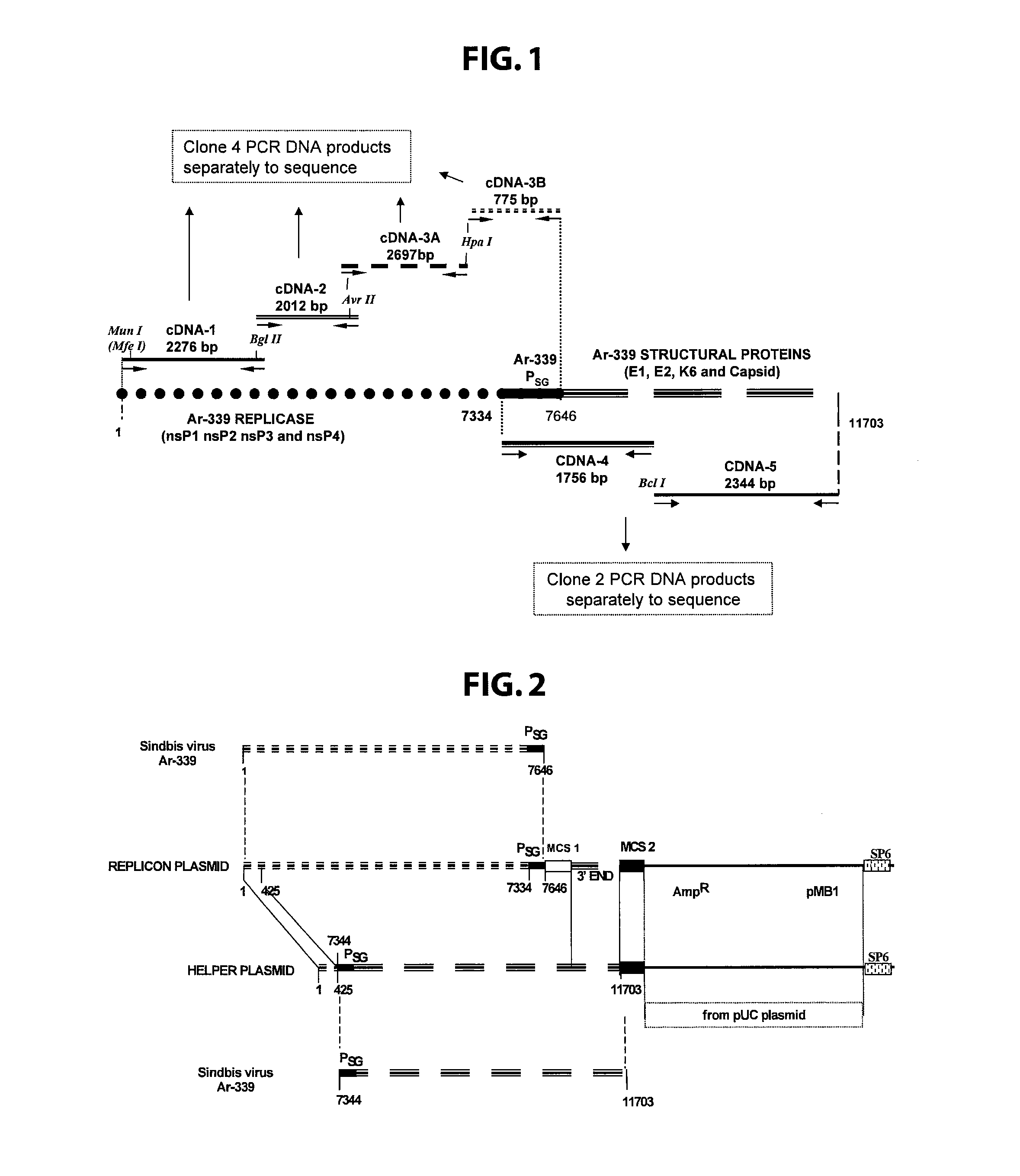
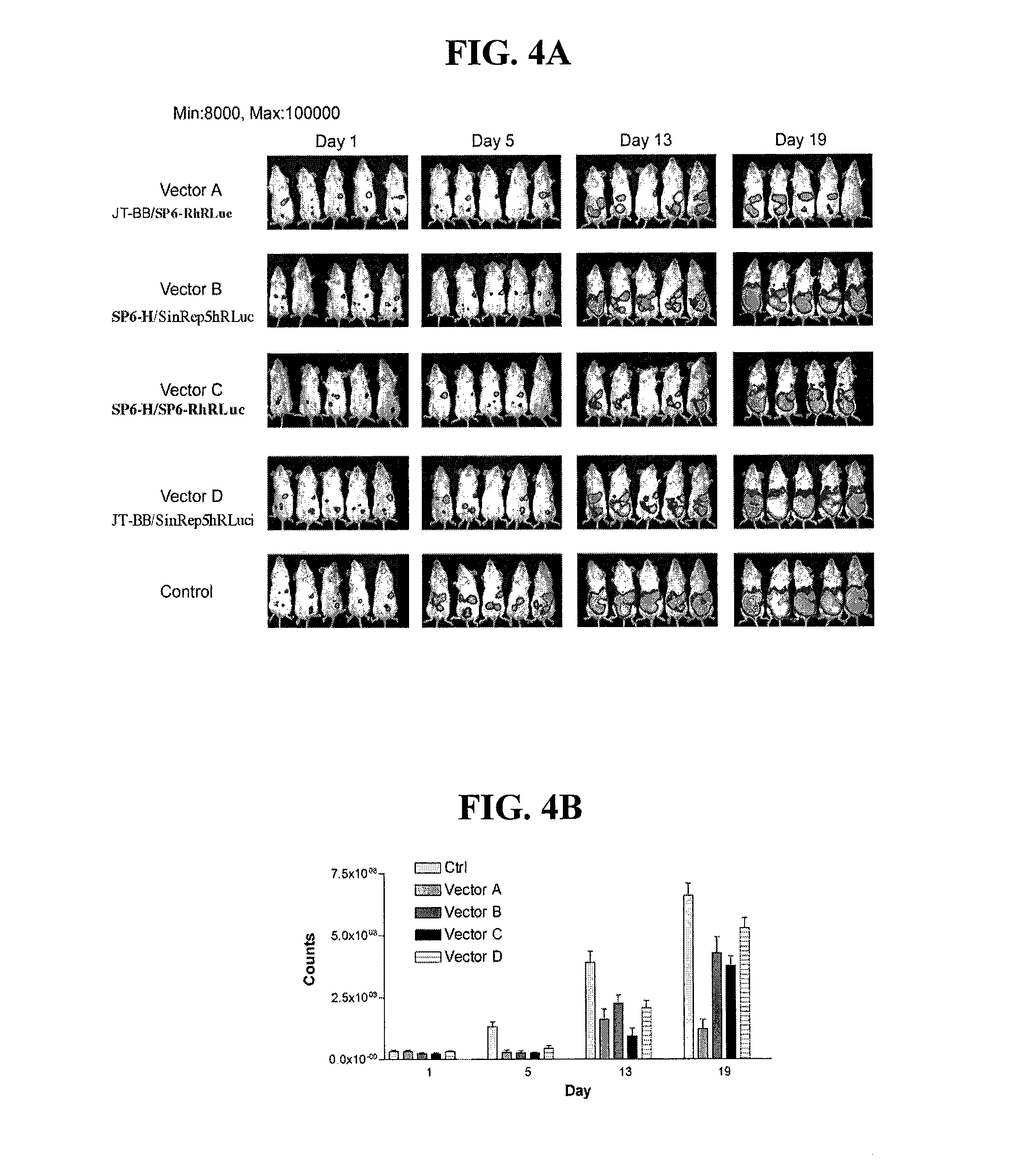
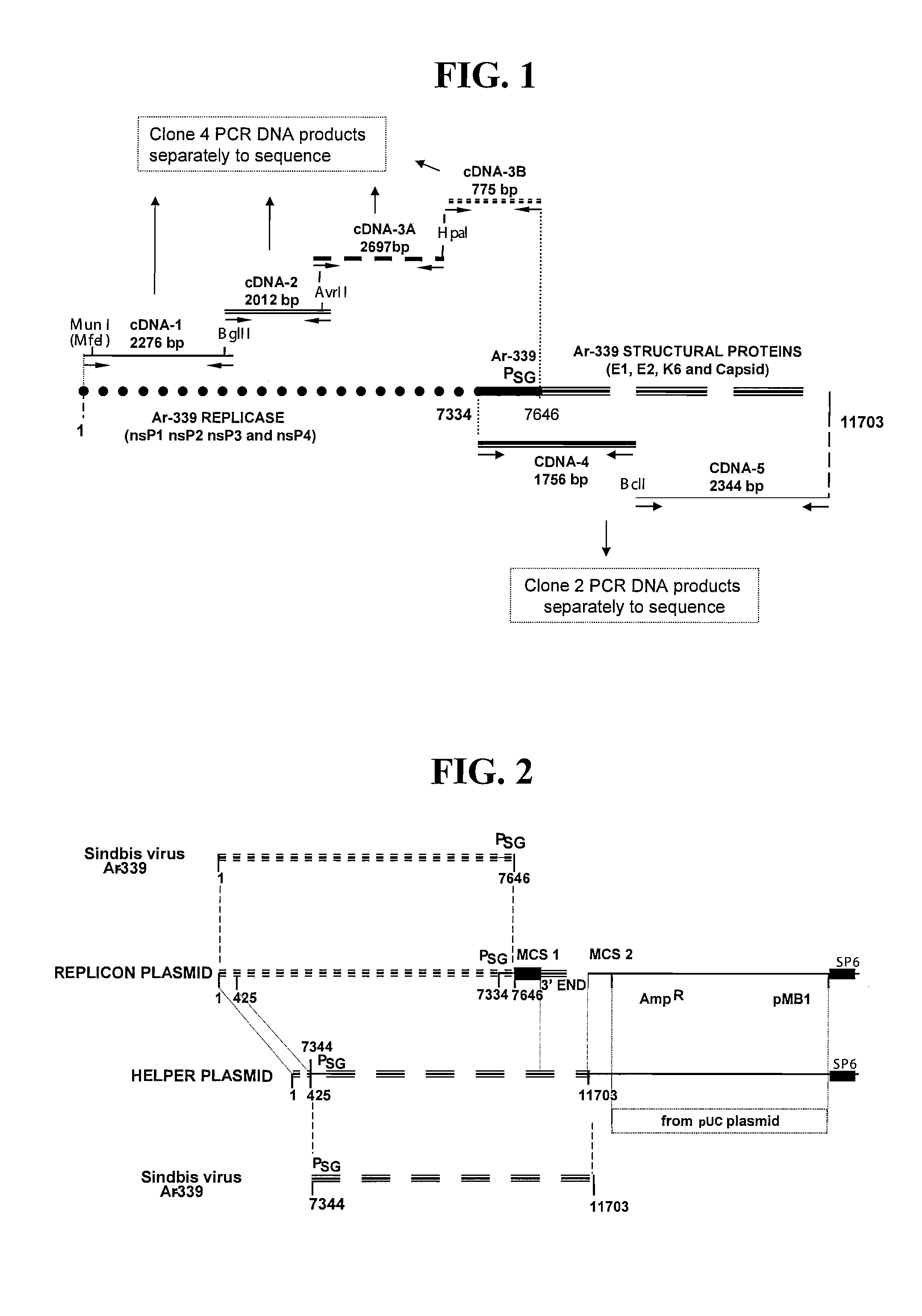
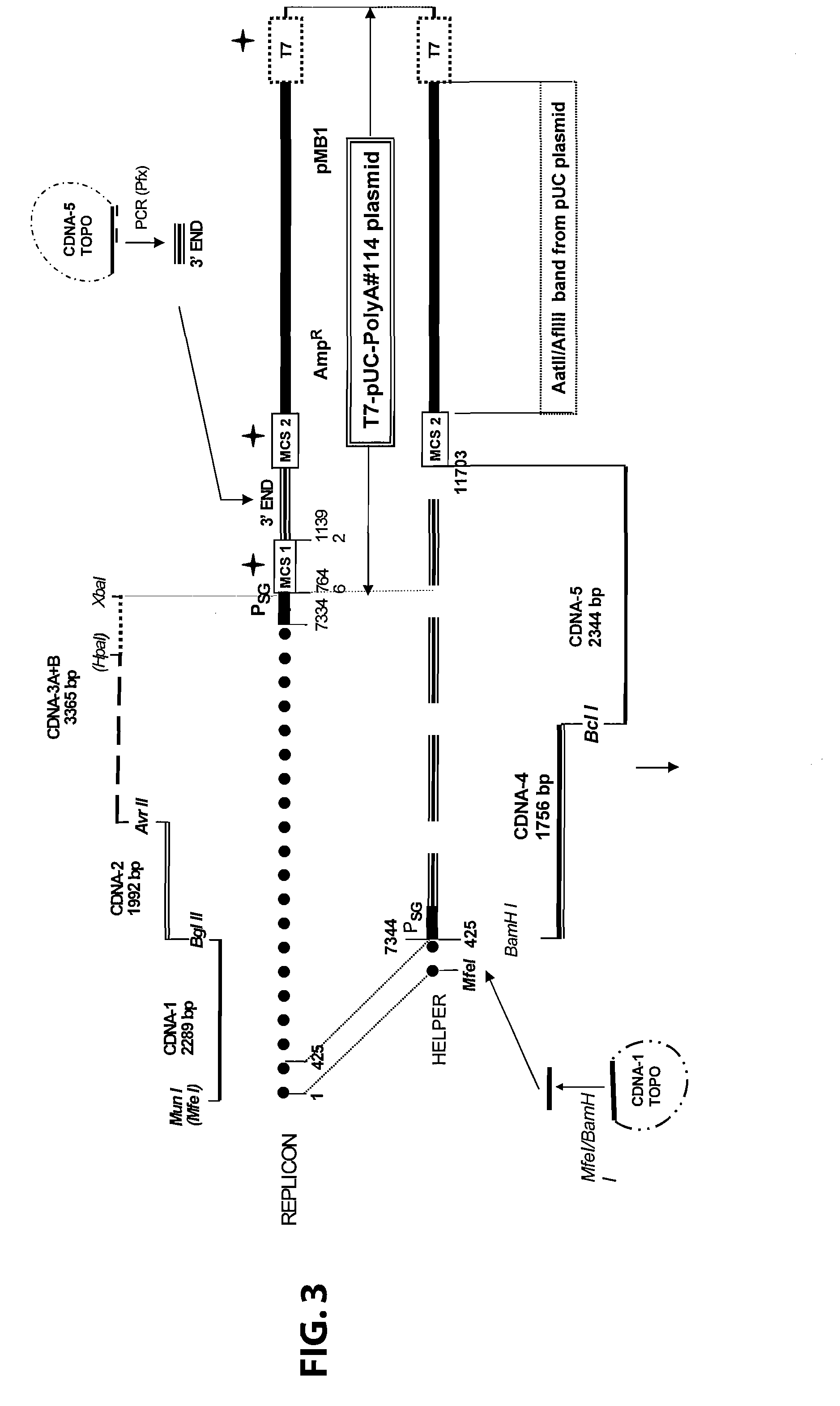
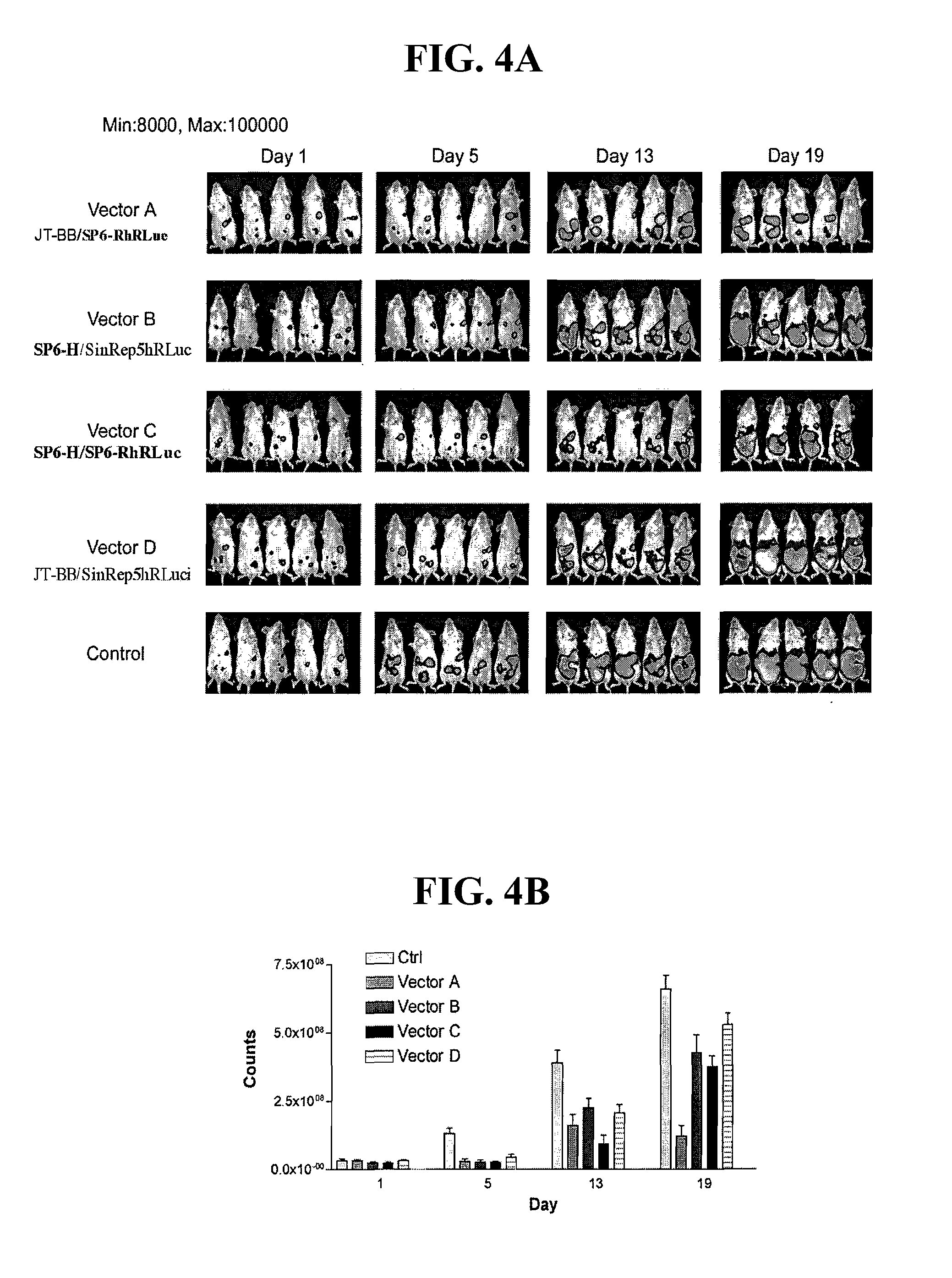
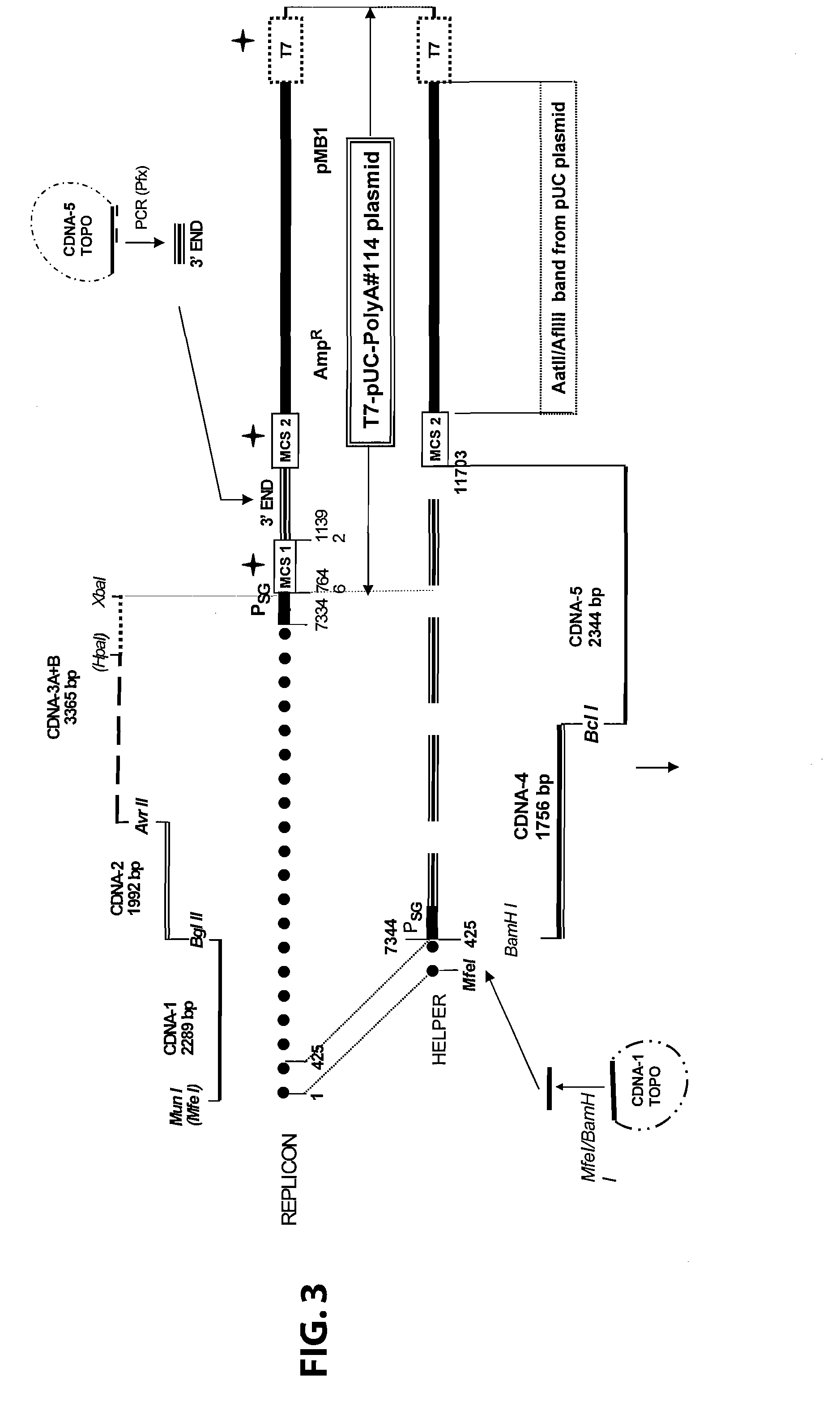
Disclosed herein are new defective Sindbis viral vectors made from a novel Helper plasmid, with differences in envelope proteins between JT vectors and consensus Sindbis virus sequences, and also between JT and Ar-339 vectors. Also disclosed are vectors produced using the plasmid, methods for producing the vectors, methods for treating mammals suffering from tumors and pharmaceutical formulations for use in the treatment methods.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Chimeric sindbis-western equine encephalitis virus and uses thereof
The present invention discloses a chimeric alphavirus comprising a Sindbis virus cDNA fragment, an Eastern equine encephalitis virus cDNA fragment, a Western equine encephalitis virus cDNA fragment or a combination thereof. The present also discloses the use of this chimeric alphavirus as vaccines and in serological and diagnostic assays.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Tumor therapy with alphavirus-based and high affinity laminin receptor-targeted vectors
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for treating tumors using vectors that preferentially target tumor cells. In particular, the invention relates to Sindbis virus vectors which have a preferential affinity for high affinity laminin receptors (HALR). These vectors are efficiently targeted to tumors and have the ability to cause tumor necrosis.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
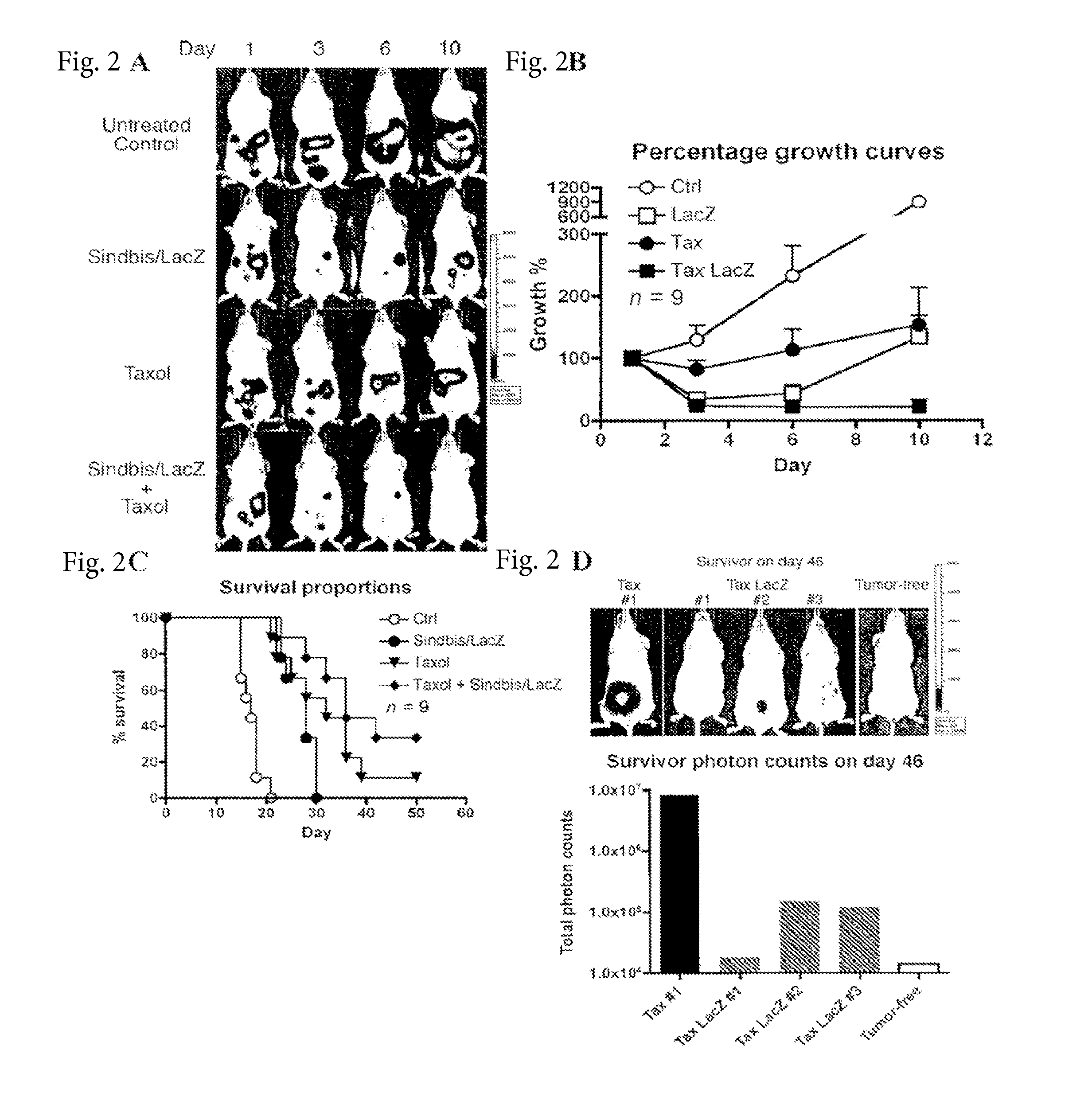
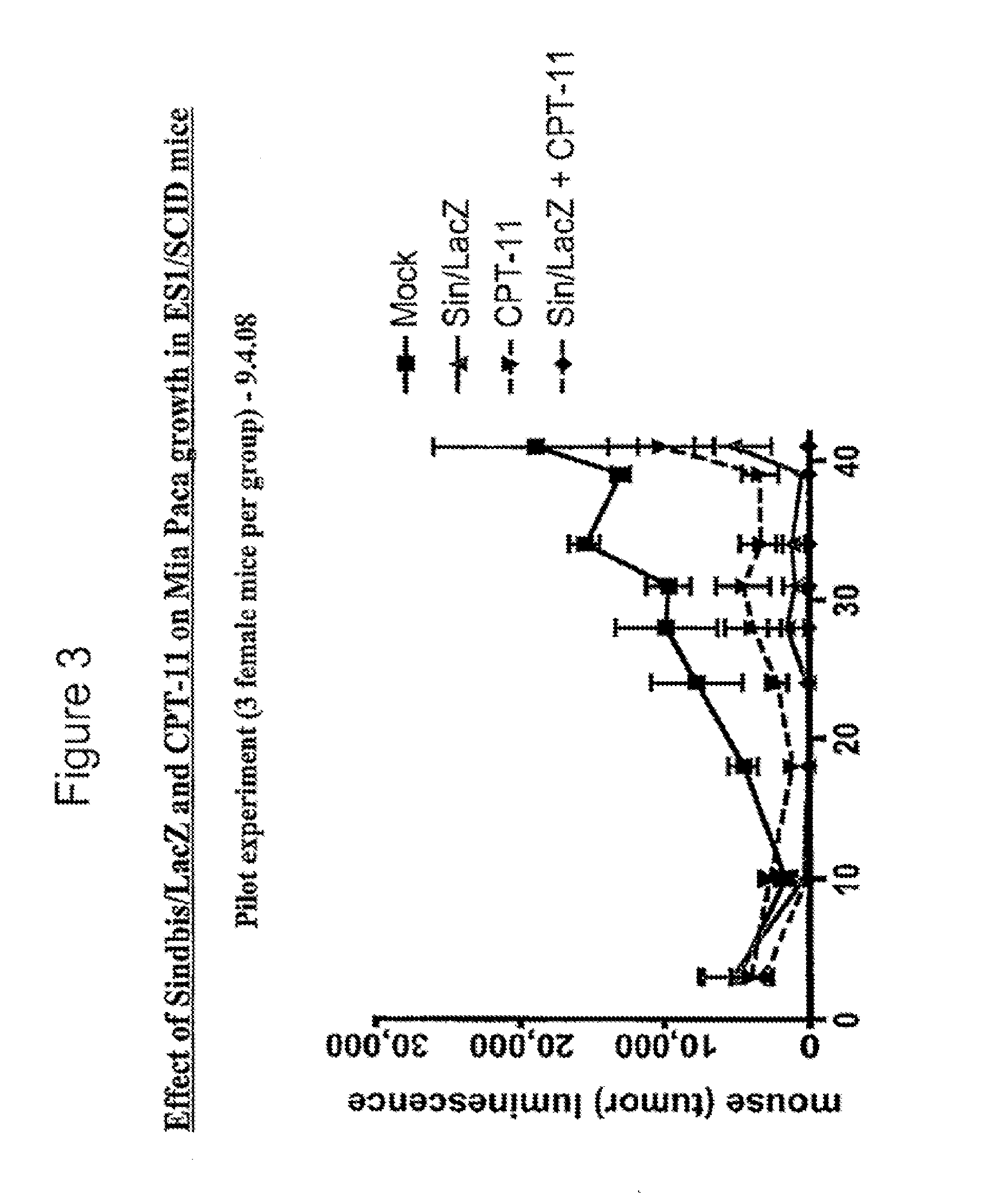
Tumor therapy with antitumor agents in combination with sindbis virus-based vectors
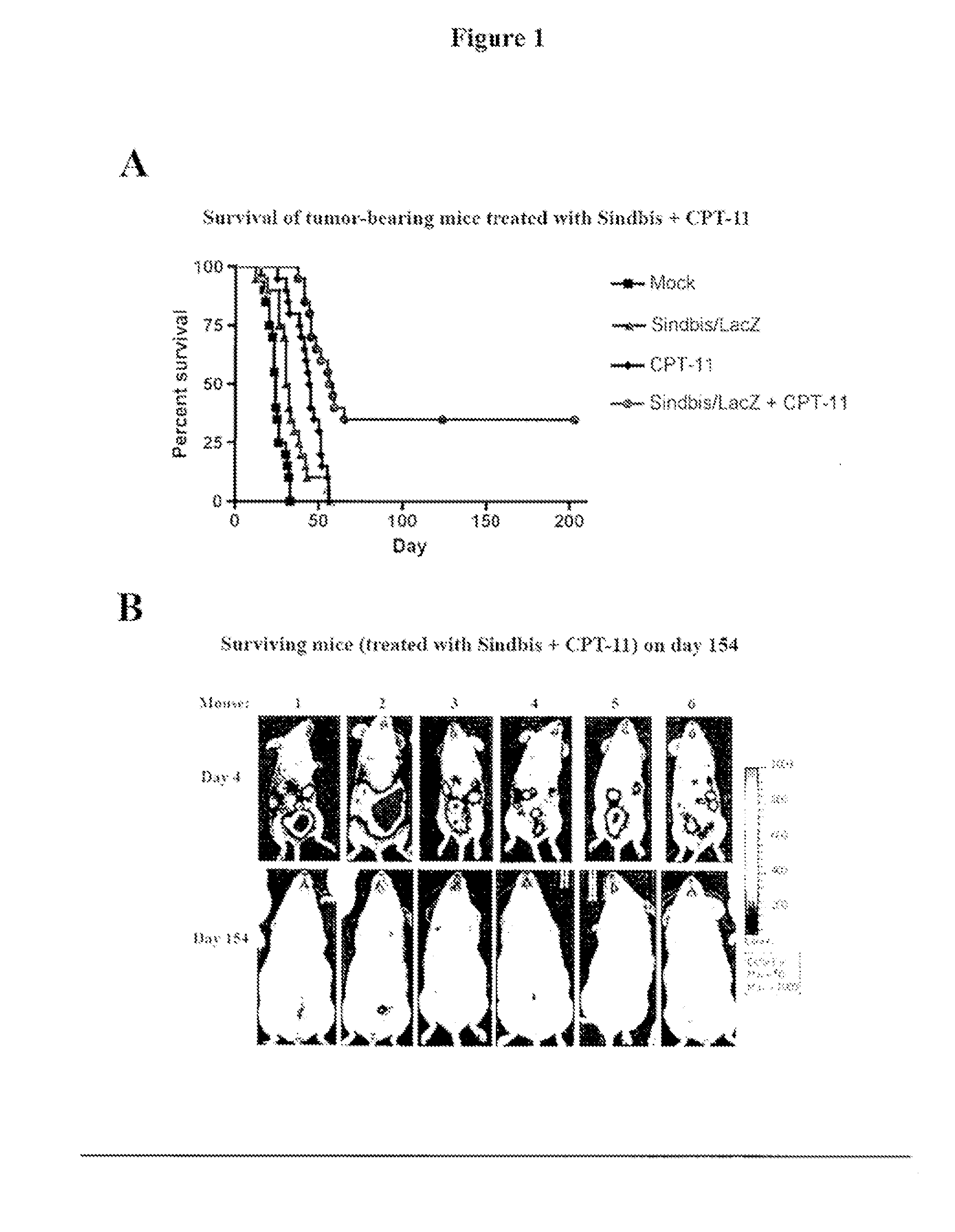
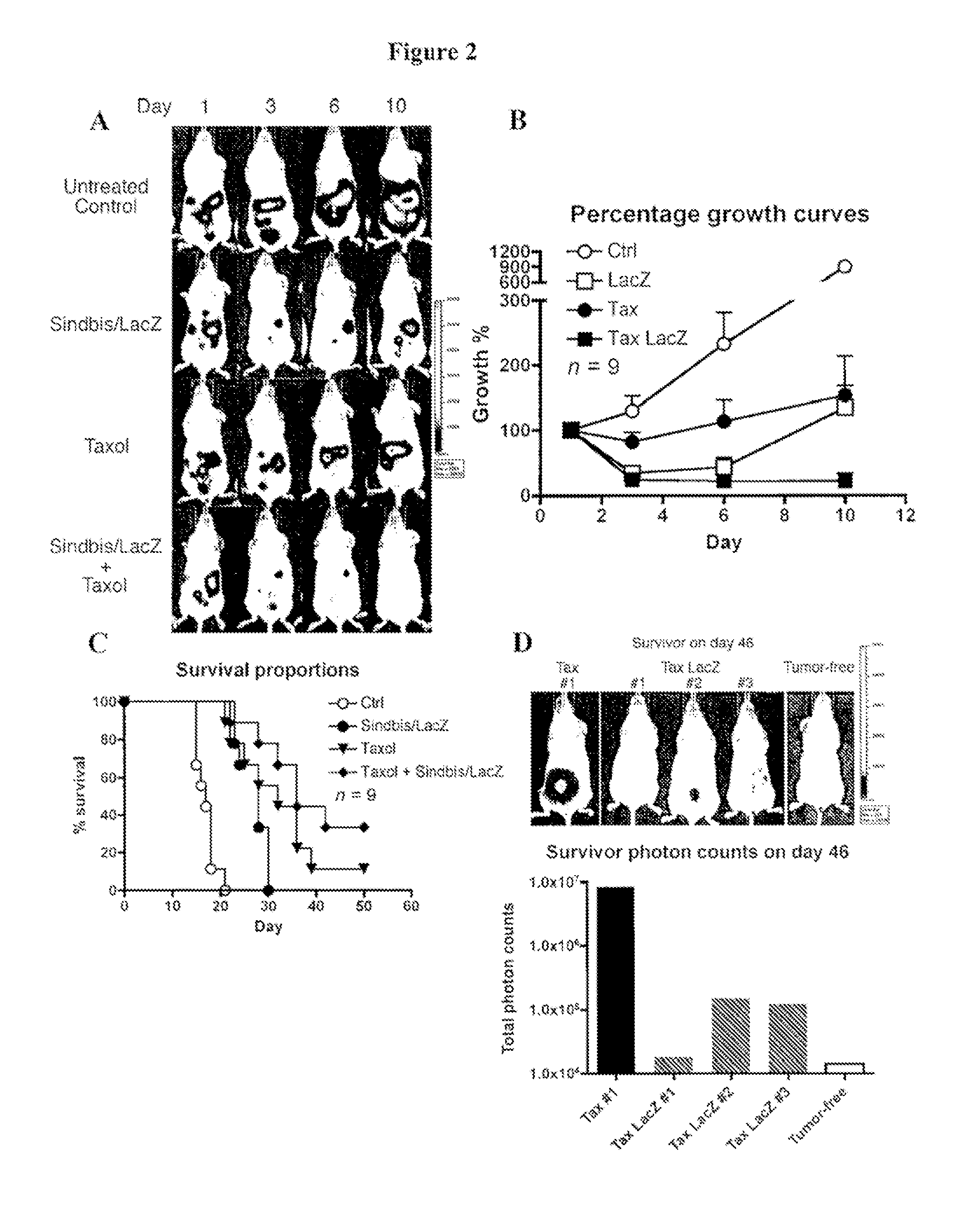
InactiveUS20110318430A1Improve survivalEfficient methodOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsSindbis virusTumor therapy
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Lentiviral Vectors Pseudotyped with a Sindbis Virus Envelope Glycoprotein
ActiveUS20120039932A1Promote infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsDendritic cellSindbis virus
Lentiviral vector particles comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant and a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest are provided. A lentiviral vector particle comprising: (a) an envelope comprising a Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein variant; and (b) a lentiviral vector genome comprising a sequence of interest; wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant facilitates infection of dendritic cells by the lentiviral vector particle, and wherein the E2 glycoprotein variant has reduced binding to heparan sulfate compared to a reference sequence (HR strain).
Owner:IMMUNE DESIGN CORP
Novel helper plasmid, defective sindbis viral vectors and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20100120897A1Improve survivalSuppressed abilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesMammalSindbis virus
Disclosed herein are new defective Sindbis viral vectors made from a novel Helper plasmid, with differences in envelope proteins between JT vectors and consensus Sindbis virus sequences, and also between JT and Ar-339 vectors. Also disclosed are vectors produced using the plasmid, methods for producing the vectors, methods for treating mammals suffering from tumors and pharmaceutical formulations for use in the treatment methods.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Defective sindbis viral vectors
ActiveUS7303898B2Suppressed abilityTargeted tumors more effectivelyBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseMammalSindbis virus
Disclosed herein are new defective Sindbis viral vectors made from wild type Ar-339 Sindbis virus, with differences in replicase and envelope proteins between JT vectors and consensus Sindbis virus sequences, and also between JT and Ar-339 vectors. Also disclosed are plasmids used for the production of the vectors, methods for producing the vectors, methods for treating mammals suffering from tumors and pharmaceutical formulations for use in the treatment methods.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for carrying out virus inactivation on pig fibrinogens through freeze-drying and heating
ActiveCN102210854BLower requirementReduce the risk of infectionPowder deliveryFibrinogenFiberFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for carrying out virus inactivation on pig fibrinogens through freeze-drying and heating. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out pretreatment on pig plasmas so as to obtain a concentrated pig fibrinogen solution; adding a group protectant into the concentrated solution; adjusting the pH value of the obtained mixture to 7.5-8.5; enabling the obtained mixture to pass a filter with a bore diameter of 0.2mu m; carrying out aseptic filling, freeze-drying and capping seal on the obtained solution by using 2.5mL perfume bottle so as to obtain a freeze-dried pig fibrinogen product; and carrying out heat preservation on the freeze-dried pig fibrinogen product 139-141 hours at a temperature of 63-67 DEG C so as to carry out hot air viral inactivation. The method disclosed by the invention is verified by National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (No.624 [2008] of NICPBP), through adding Sindbis viruses and PPV viruses to carry out verification, the inactivation effect is remarkable. In the method, through using a simple and feasible freeze-drying product virus inactivating method, the requirements for drying and sterilizing aseptic environments are reduced, the risk of animal-based virus infection in pig fiber products is reduced, and the influence (arising from the traditional virus inactivation) on the bioactivities such as proteins and the like of a product is avoided.
Owner:浙江赛灵特医药科技有限公司
Pharmaceutical composition for treatment of cancers
ActiveUS20050031594A1Shrink tumorEffective treatmentBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAbnormal tissue growthCytopathic effect
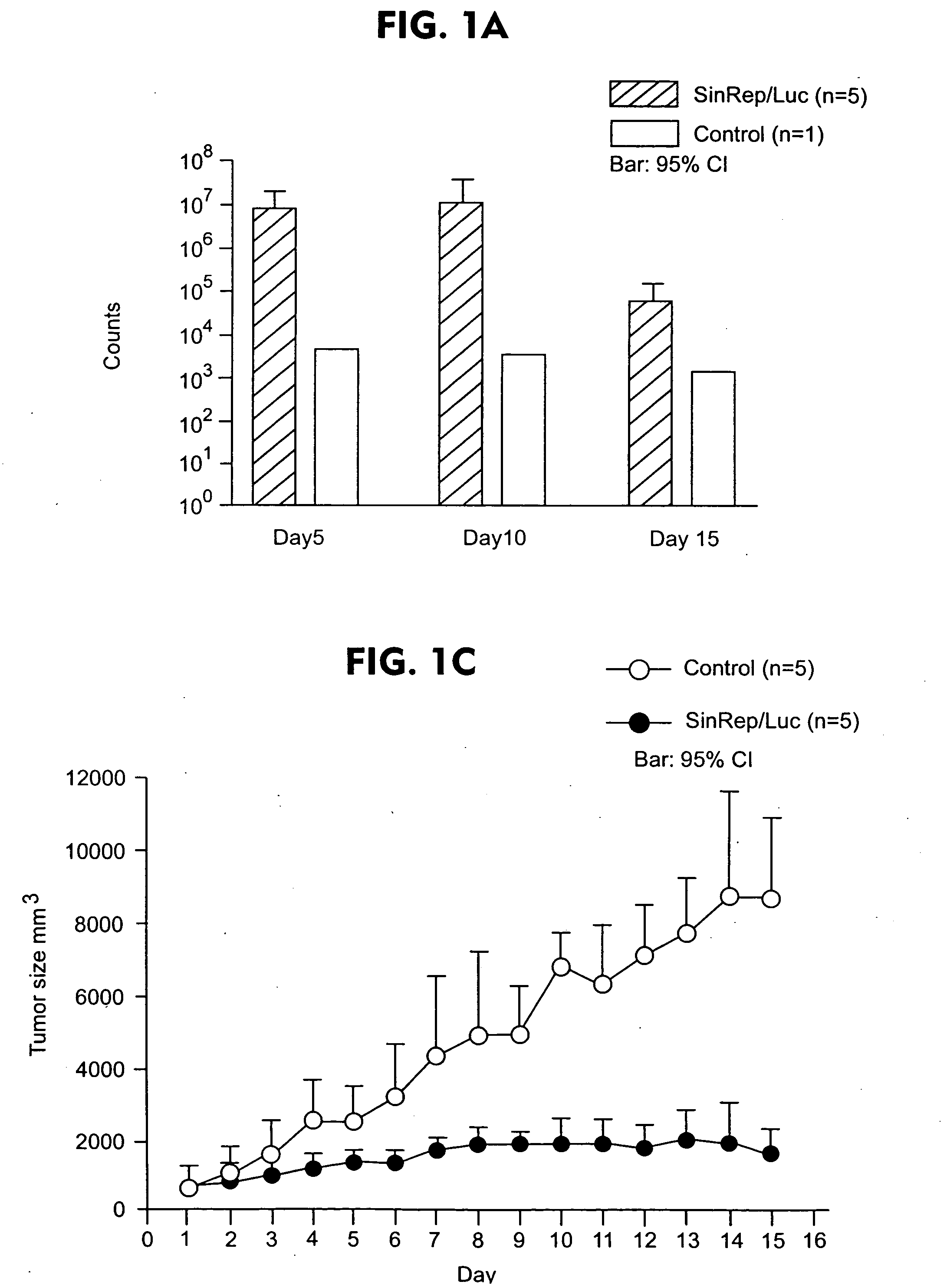
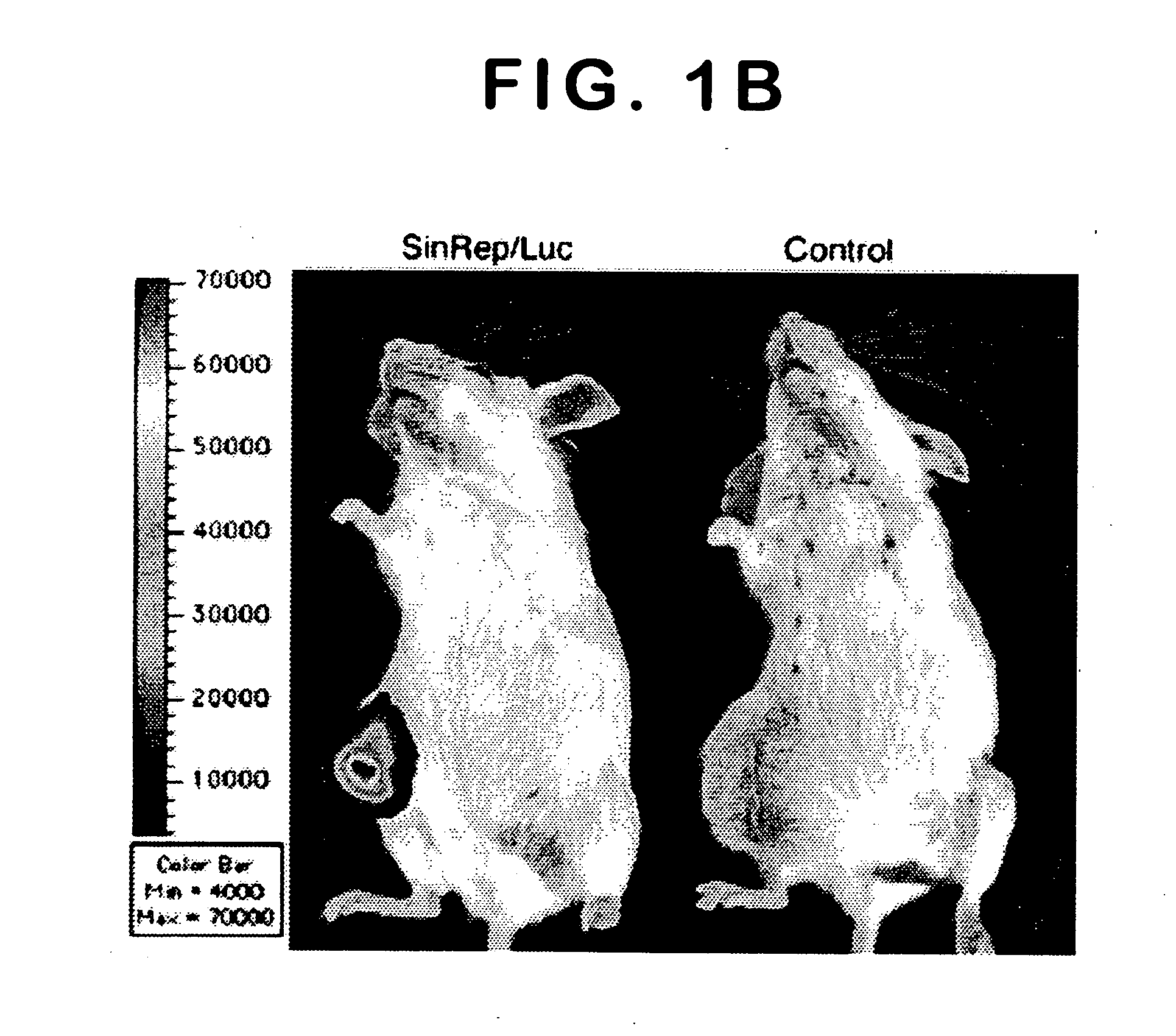
An object of the present invention is to find a new oncolytic virus and to utilize it for treatment of cancers. The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of cancers containing Sindbis virus as an active ingredient, a method for treatment of cancers, which comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of Sindbis virus to a mammal having cancers, a method for identifying cancers, which comprises introducing Sindbis virus into an animal, thereby detecting a Sindbis virus protein or Sindbis virus RNA in vital tissues of the above animal, a method of identifying cancers, which comprises introducing into an animal Sindbis virus having a reporter gene incorporated therein, thereby, detecting the product of said reporter gene in vital tissues of said animal, and a method of identifying cancers, which comprises detecting a increase in antibody titer to the Sindbis virus protein or the product of the reporter gene in the aforementioned animals. It is confirmed that Sindbis virus has cytopathic effects upon various cancer cell lines in vitro, and that reduction in tumor size or disappearance of tumor takes place in vivo. Therefore, Sindbis virus is effective for treatment of cancers. In addition, Sindbis virus shows selective proliferation in a tumor, and is effective for identification or diagnosis for cancers within the living body.
Owner:SHINO YUJI +3
Method for preparing mouse nerve growth factor and method for preparing mouse nerve growth factor for injection
ActiveCN101613394AGuaranteed biological activityEffective filteringPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic solventUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for preparing a mouse nerve growth factor (NGF) and a method for preparing a mouse nerve growth factor for injection. The method for preparing the mouse nerve growth factor adopts 100KD and 5KD of ultrafiltration membrane filtration and pasteurization processes on the basis of the conventional process, can effectively filter a macromolecular virus, can further inactivate potential viruses, such as pseudo rabies viruses (PRV), Sindbis viruses, encephalomyo-carditis (EMC) viruses and the like by pasteurization at the same time, does not introduce any pollutant, such as a foreign organic solvent, a detergent and the like, and can keep high purity, high specific activity and high safety of the mouse nerve growth factor.
Owner:SINOBIOWAY BIOMEDICINE
Chimeric chikungunya virus and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110171249A1Avoid infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesSindbis virusChikungunya fever
The present invention discloses a chimeric Chikungunya virus comprising a heterologous alphavirus cDNA fragment and a Chikungunya virus cDNA fragment. The heterologous alphavirus may include but is not limited to Sindbis virus, Eastern equine encephalitis virus or Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. The present invention also discloses the use of this chimeric Chikungunya virus as vaccines and in serological and diagnostic assays.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Pharmaceutical composition for treatment of cancers
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of cancers containing Sindbis virus as an active ingredient, a method for treatment of cancers, which comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of Sindbis virus to a mammal having cancers, a method for identifying cancers, which includes introducing Sindbis virus into an animal, thereby detecting a Sindbis virus protein or Sindbis virus RNA in vital tissues of the above animal, a method of identifying cancers, which includes introducing into an animal Sindbis virus having a reporter gene incorporated therein, thereby, detecting the product of the reporter gene in vital tissues of the animal, and a method of identifying cancers, which includes detecting a increase in antibody titer to the Sindbis virus protein or the product of the reporter gene in the aforementioned animals.
Owner:SHINO YUJI +3
Method for carrying out virus inactivation on pig fibrinogens through freeze-drying and heating
ActiveCN102210854ALower requirementReduce the risk of infectionPowder deliveryFibrinogenFiberFreeze-drying
Owner:浙江赛灵特医药科技有限公司
Defective sindbis viral vectors
ActiveUS20070020236A1Suppressed abilityTargeted tumors more effectivelyBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAbnormal tissue growthMammal
Disclosed herein are new defective Sindbis viral vectors made from wild type Ar-339 Sindbis virus, with differences in replicase and envelope proteins between JT vectors and consensus Sindbis virus sequences, and also between JT and Ar-339 vectors. Also disclosed are plasmids used for the production of the vectors, methods for producing the vectors, methods for treating mammals suffering from tumors and pharmaceutical formulations for use in the treatment methods.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
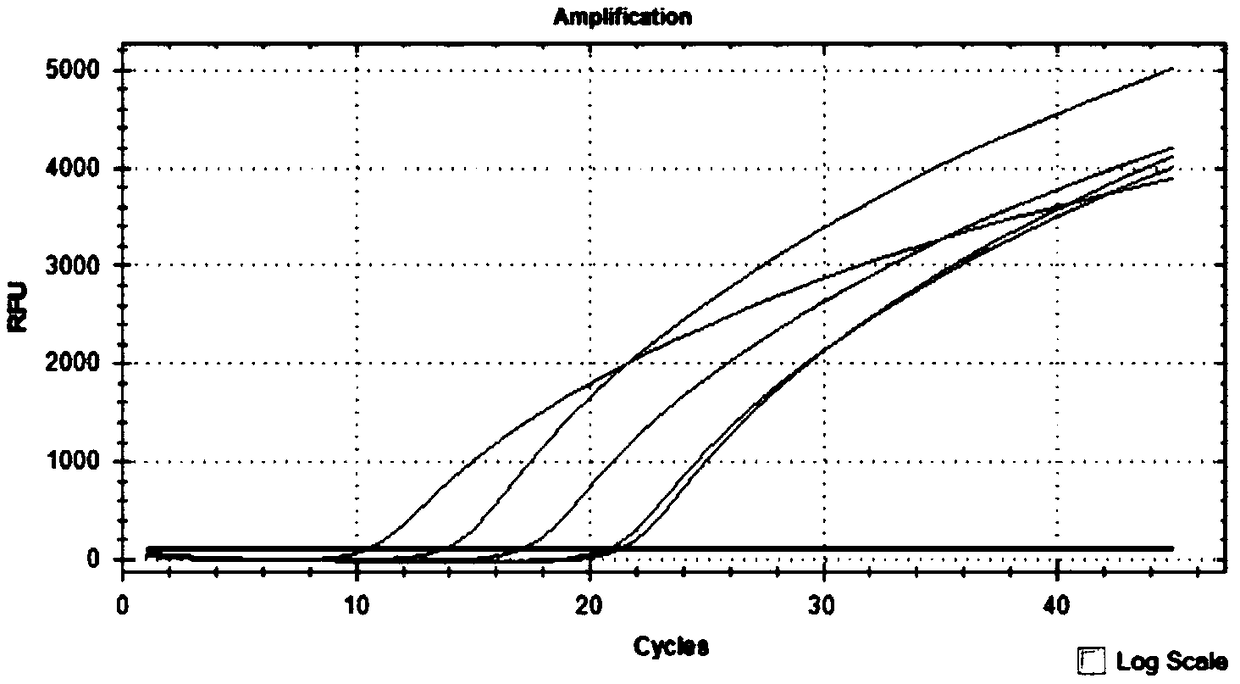
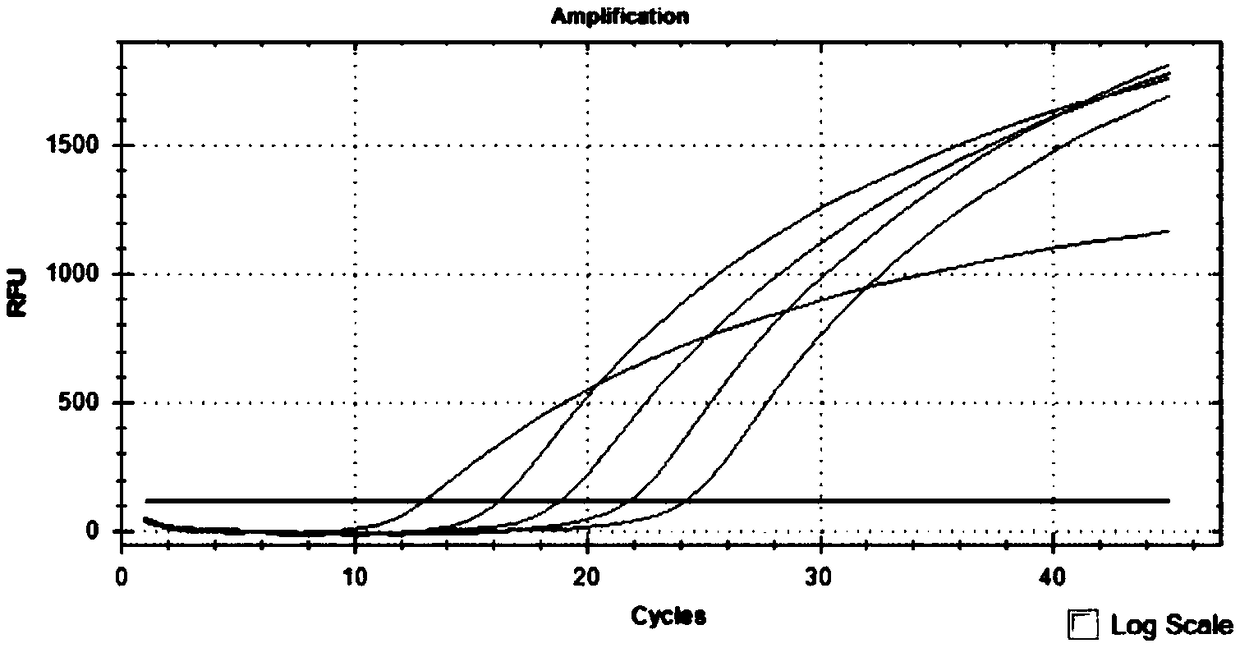
Primer probe group and kit for combined detection of Sindbis virus and Getah virus based on dual fluorescence PCR method
ActiveCN108950080AHighly conservativeImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerSindbis virus
The invention discloses a primer probe group and kit for combined detection of Sindbis virus and Getah virus based on a dual fluorescence PCR method. The primer probe group contains specific primers and probes aiming at the Sindbis virus as well as primers and probes aiming at the Getah virus, wherein the specific primers aiming at the Sindbis virus include a forward primer and a reverse primer, the nucleotide sequence of the forward primer aiming at the Sindbis virus is represented by SEQ ID No.1, and the nucleotide sequence of the reverse primer aiming at the Sindbis virus is represented bySEQ ID No.2; and the specific primers aiming at the Getah virus include a forward primer and a reverse primer, the nucleotide sequence of the forward primer aiming at the Getah virus is represented bySEQ ID No.3, and the nucleotide sequence of the reverse primer aiming at the Getah virus is represented by SEQ ID No.4. The primer probe group and the kit utilizing the primer probe group can be usedfor effectively detecting the Sindbis virus and the Getah virus, and the detection sensitivity can reach 1*10<3>copies / ml, so that the detection blanks of the Sindbis virus and the Getah virus in theprior art are effectively overcome, and the primer probe group and the kit have high industrial utilization values.
Owner:广东省疾病预防控制中心 +1
Recombinant alphavirus vectors and methods of using same
InactiveUS20080096274A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesTherapeutic proteinSindbis virus
The present invention describes nucleic acid segments, recombinant alphavirus vectors, and recombinant alphavirus particles that include a Sindbis viral vector. The Sindbis viral vector includes a nucleic acid segment encoding a fusion protein comprising a Sindbis virus nonstructural protein and a protein or peptide of interest, wherein the production of the fusion protein does not affect viral replication or infection. The protein or peptide of interest may be a marker, diagnostic, or therapeutic protein or peptide. Methods of using such recombinant alphavirus particles to kill tumor cells is also described herein.
Owner:OKLAHOMA THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF
Chimeric sindbis-western equine encephalitis virus and uses thereof
ActiveUS8748591B2Avoid infectionBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAssayEastern equine encephalitis virus
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method of preparing a treatment product, treatment product and a plasmid construct
InactiveUS20050256067A1Raise transfer toSuccessful treatmentBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus-like particleSindbis virus
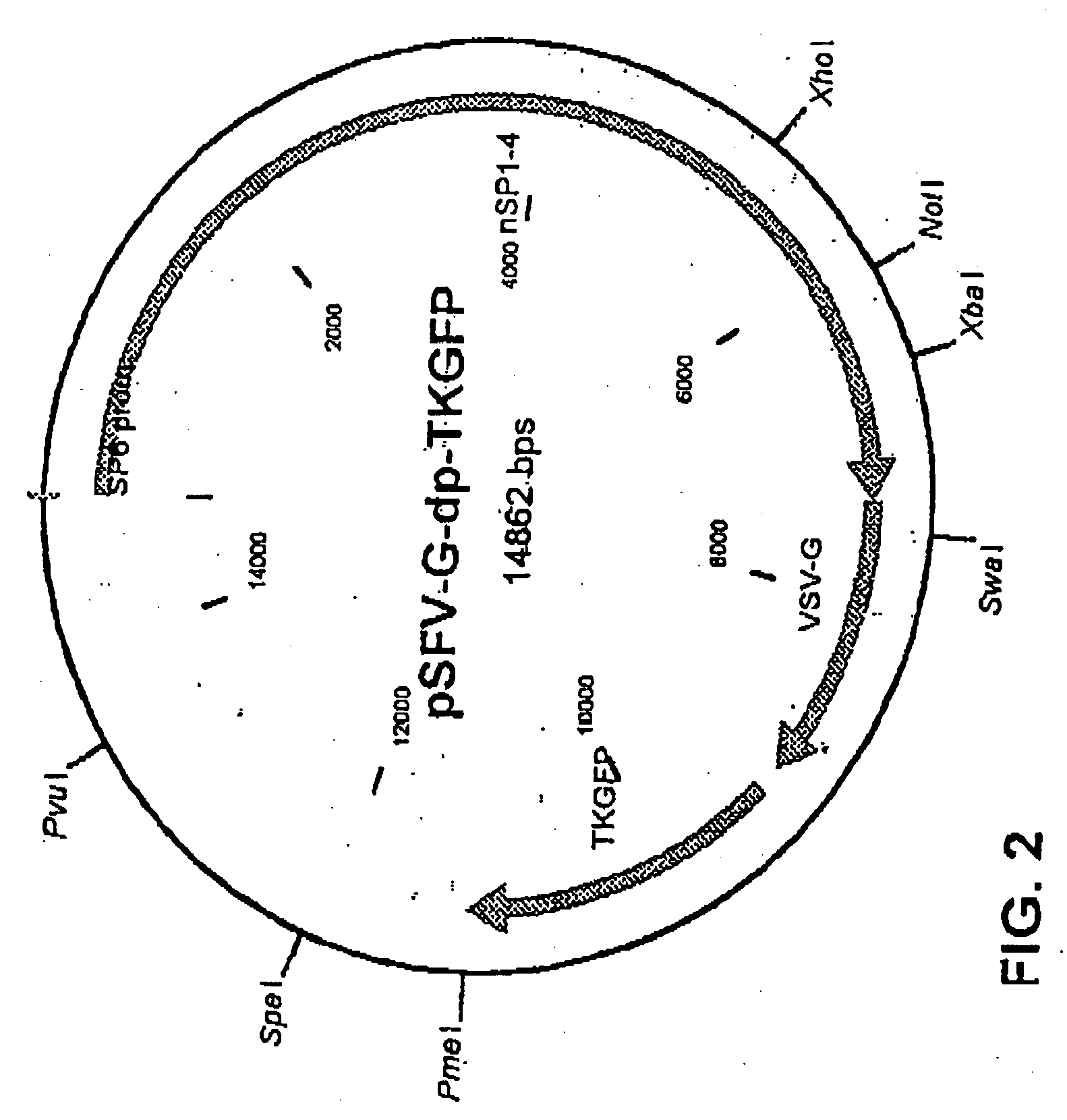
The method of the invention for preparing a treatment product is characterized by using a starting plasmid based on a virus belonging to the Togaviridae stock from which the genes encoding capsid proteins of the virus have been deleted. An RNA encoding virus-like particles (VLP-RNA) is prepared by manipulating the staring plasmid by connecting to it a spreading enabling gene and a treatment gene. The invention is furthermore concerned with such a treatment product and a plasmid construct encoding virus-like particles, which is prepared from the Sindbis virus in which the capsid protein of the virus has been substituted by a spreading enabling gene and a treatment gene. Example of spreading enabling gene is a gene encoding vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSV-G). A particular example of treatment product is Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase linked to GFP, said product being Spicude / Reporter construct
Owner:WAHLFORS JARMO +1
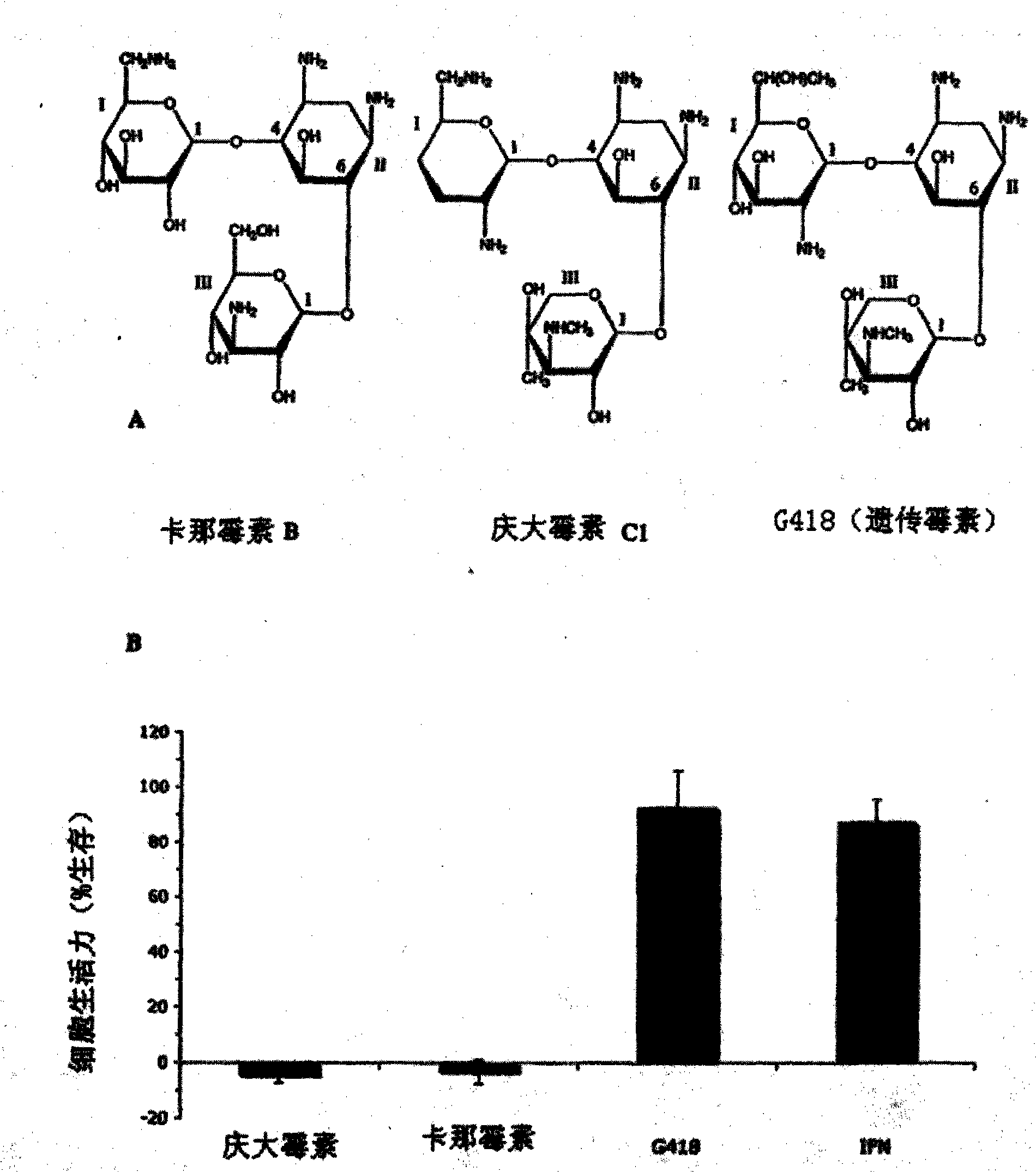
2-Amino-2,7-dideoxy-alpha-D-glycero-D-gluco-heptopyranosyl Inhibitors of Positive Sense Single-Stranded RNA Envelope Viruses
InactiveUS20090010880A1Avoid spreadingReduce infectivityBiocideSugar derivativesSingle-Stranded RNABovine Viral Diarrhea Viruses
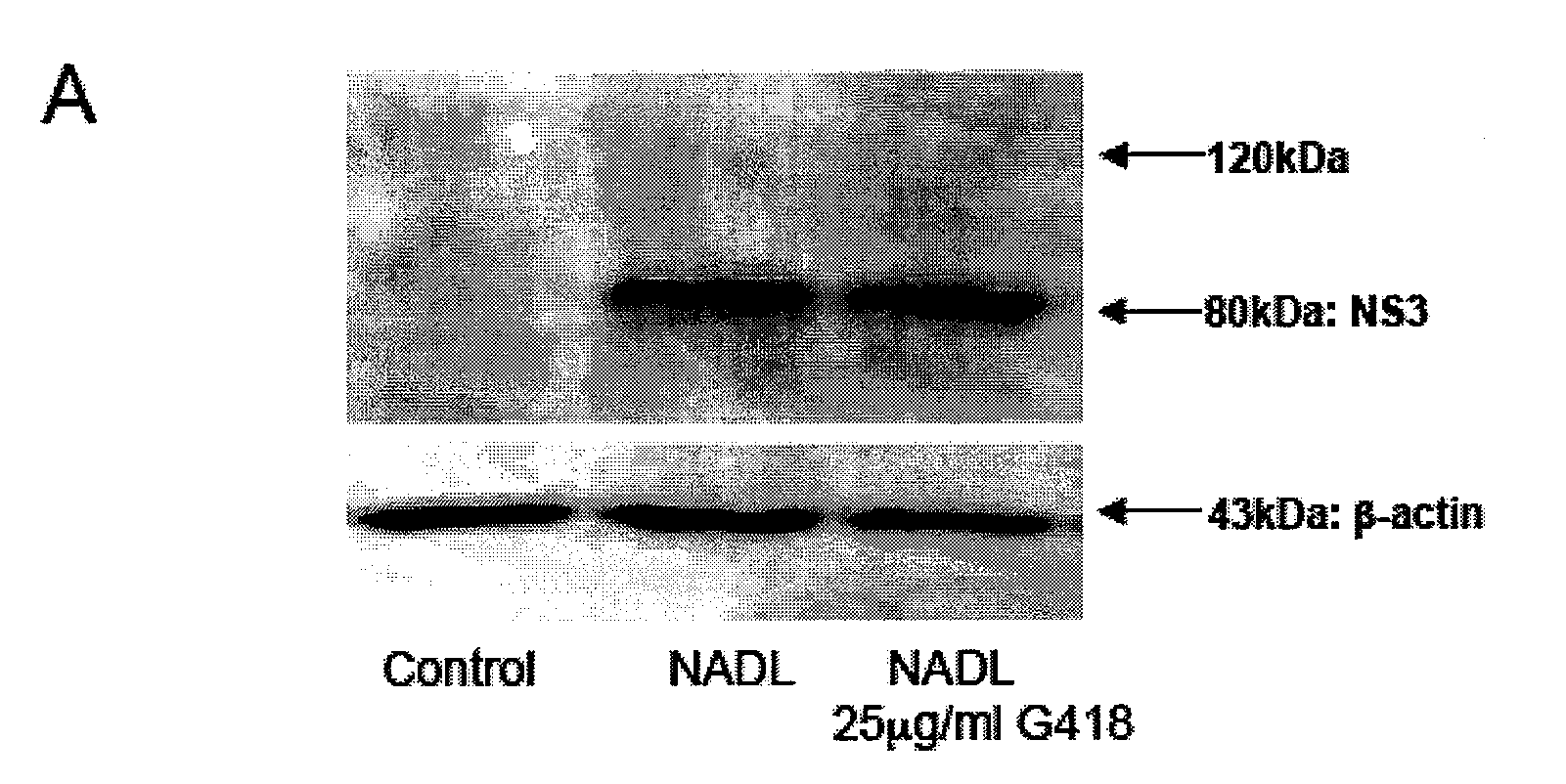
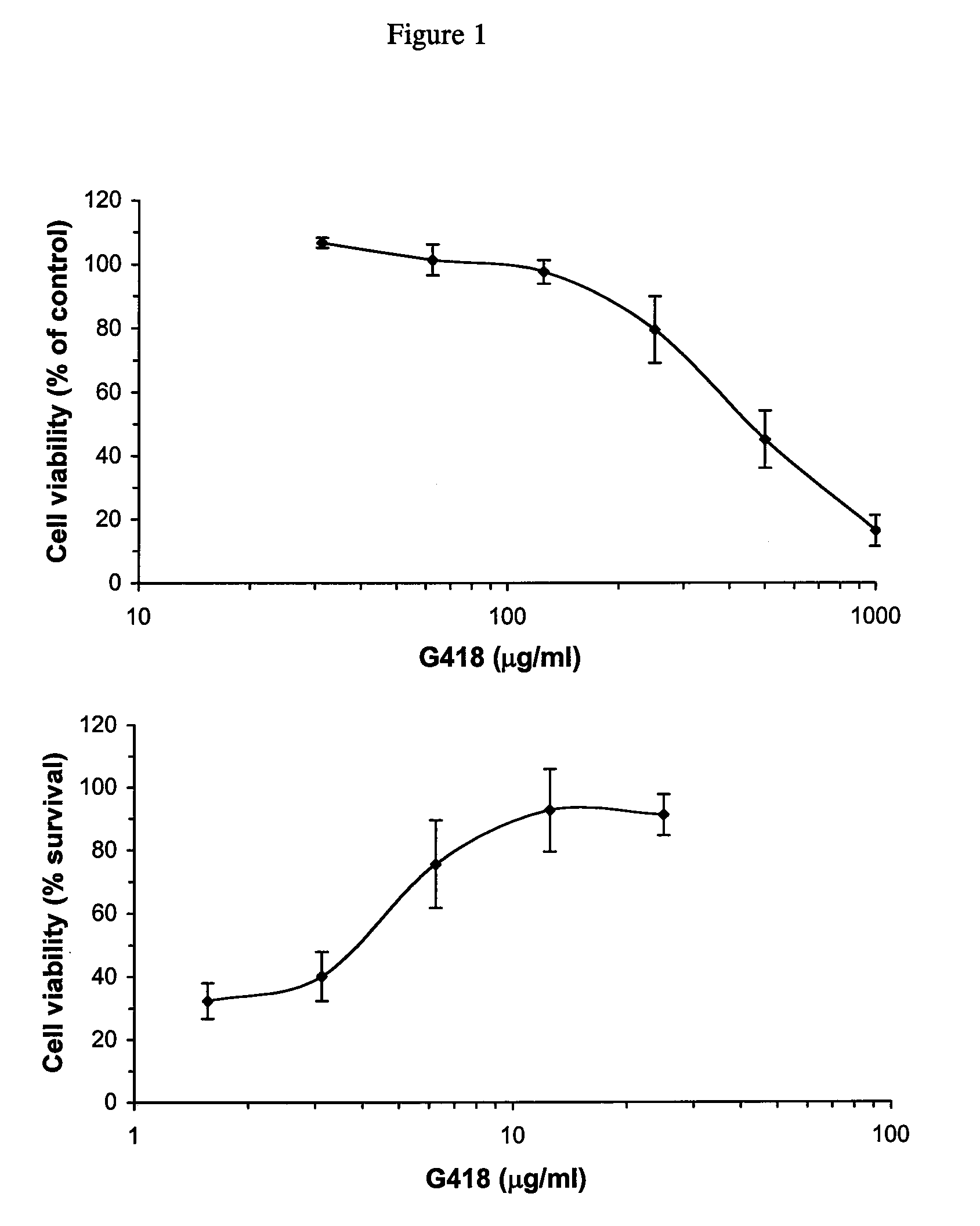
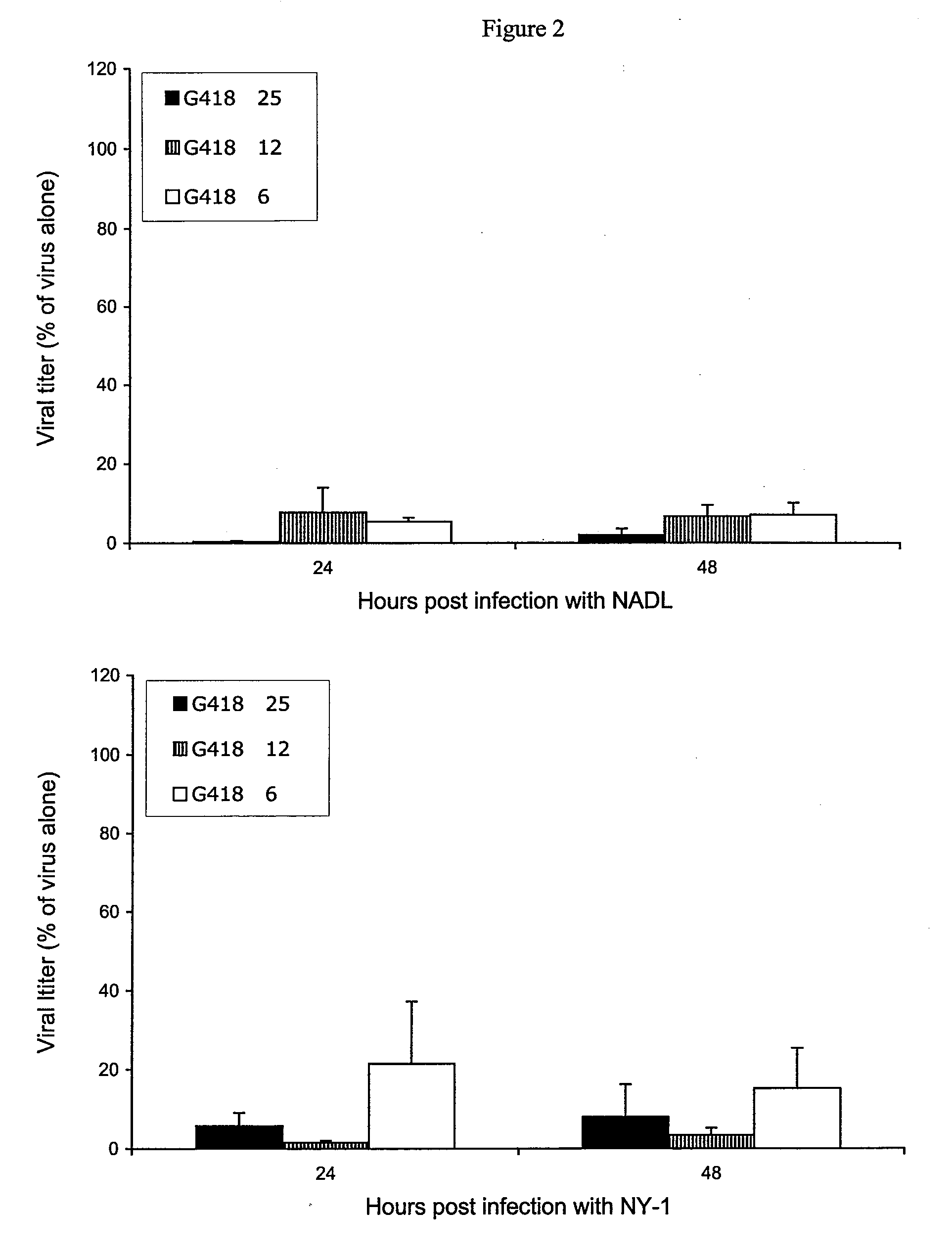
The present invention is directed to compounds, compositions and methods comprising the aminoglycoside moiety represented by Formula II for treating and preventing the spread of positive sense single-stranded RNA envelope viral infections. One embodiment of the present invention uses geneticin or its analogs, including 2-amino-2,7-dideoxy-alpha-D-glycero-D-gluco-heptopyranose, as the antiviral agent. The compounds, compositions and methods of the present invention are applicable to infections resulting from Hepatitis C virus, West Nile virus, Yellow Fever virus, Dengue virus, Bovine Viral Diarrhea virus, Equine Arteritis virus, and / or Sindbis virus.
Owner:INST FOR HEPATITIS & VIRUS RES
Method for preparing tetanus human immune globulin by double virus inactivation
InactiveCN102603891AReduce transmissionReduced viral titerAntibacterial agentsSerum immunoglobulinsDiseaseAnti virus
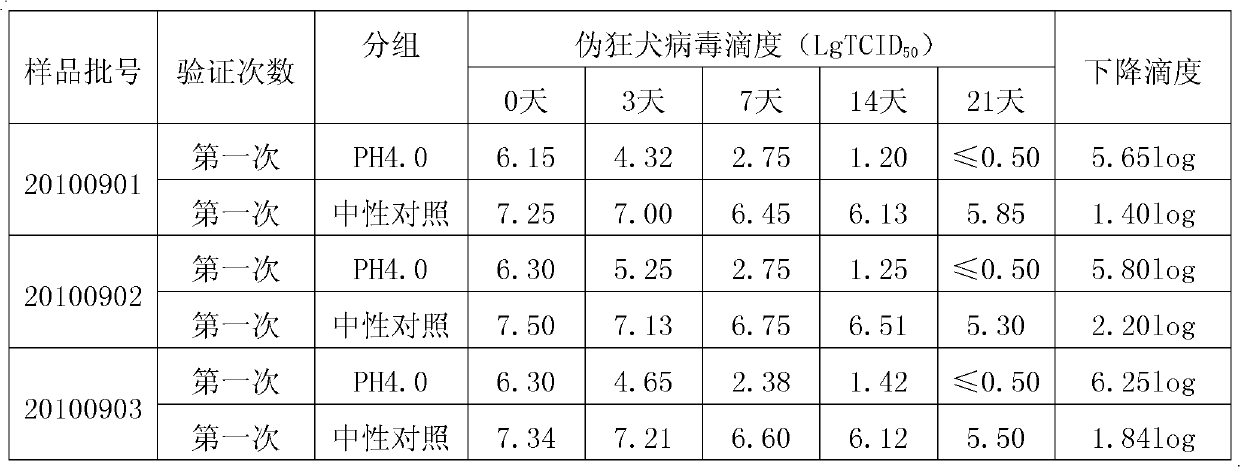
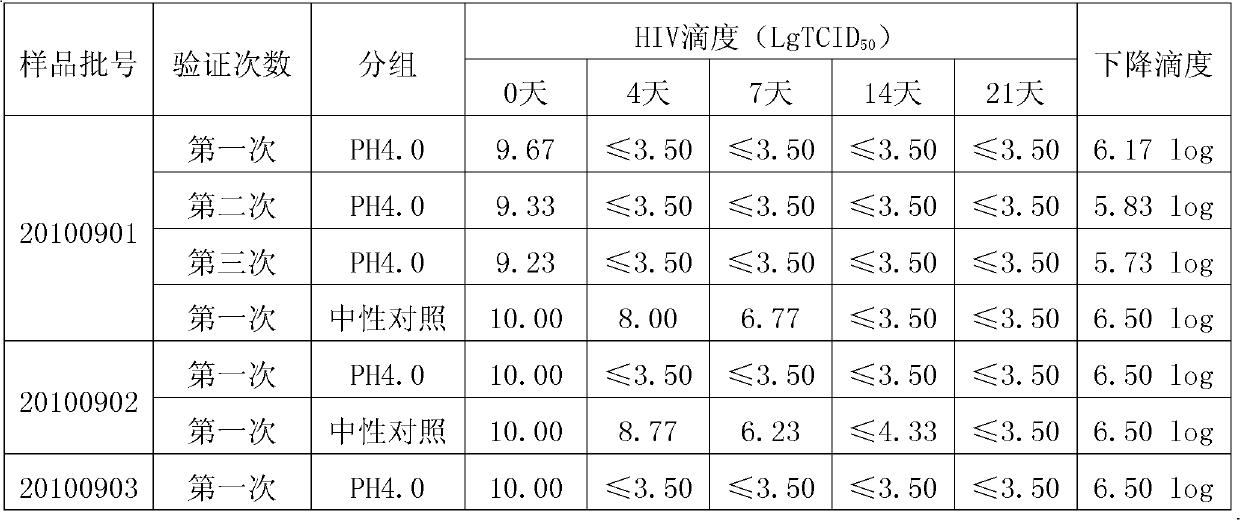
The invention discloses a method for preparing tetanus human immune globulin by double virus inactivation. The method comprises separating and purifying blood plasma from healthy people containing high-potency tetanus antibody by a low-temperature ethanol protein-separating method, and inactivating virus at the pH value of 4.0 after incubation at 23-25 DEG C for 21 days and treating with DV50 nanometer anti-virus membrane for double virus inactivation. The method of the invention has the beneficial effects that the tetanus human immune globulin prepared by double virus inactivation can greatly reduce disease transmitted by blood products, and the quality of products fully complies with the requirement of Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China. Through a test using the pseudorabies virus, Sindbis virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus titer (TCID50) can be decreased by at least 4.00log. The safety and reliability of the products are ensured. The tetanus human immune globulin is particularly suitable for people allergic to tetanus antitoxin (TAT).
Owner:新疆德源生物工程有限公司
Sindbis virus vector and virus particles thereof, and application of Sindbis virus vector and virus particles thereof in neural circuit
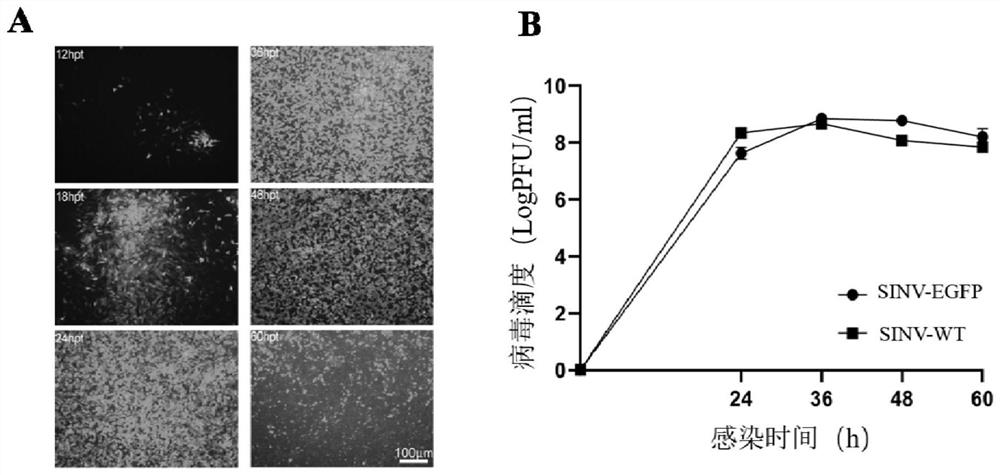
PendingCN113817774AWith visualizationShorten the timeSsRNA viruses positive-senseIn-vivo testing preparationsNucleotideViral Vaccine
The invention discloses a Sindbis virus vector and virus particles thereof, and application of the Sindbis virus vector and virus particles thereof in a neural circuit. The Sindbis virus particles carrying a green fluorescent protein gene are successfully prepared by transfecting cells with the Sindbis virus vector with a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1. The virus particles can infect a plurality of cells in vitro, can replicate and proliferate after infection, and can carry out forward cross-multistage-synapse propagation in a mouse cranial neural circuit; and the virus particles have a wide application value in the aspects of cranial neural circuit marking and tracing, marking of non-human primate nerve cells, establishment of a drug screening platform, research and development of pharmaceutical virus inhibition action mechanisms, viral vaccines and diagnostic reagents, establishment of animal models, analysis of virus replication and pathogenesis mechanisms and the like.
Owner:中国科学院深圳理工大学筹
Chimeric sindbis-eastern equine encephalitis virus and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100247565A1Avoid infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsSindbis virusSerology
The present invention discloses a chimeric alphavirus comprising a Sindbis virus cDNA fragment and an Eastern equine encephalitis virus cDNA fragment. The present also discloses the use of this chimeric alphavirus as vaccines and in serological and diagnostic assays.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF TEXAS SYST THE
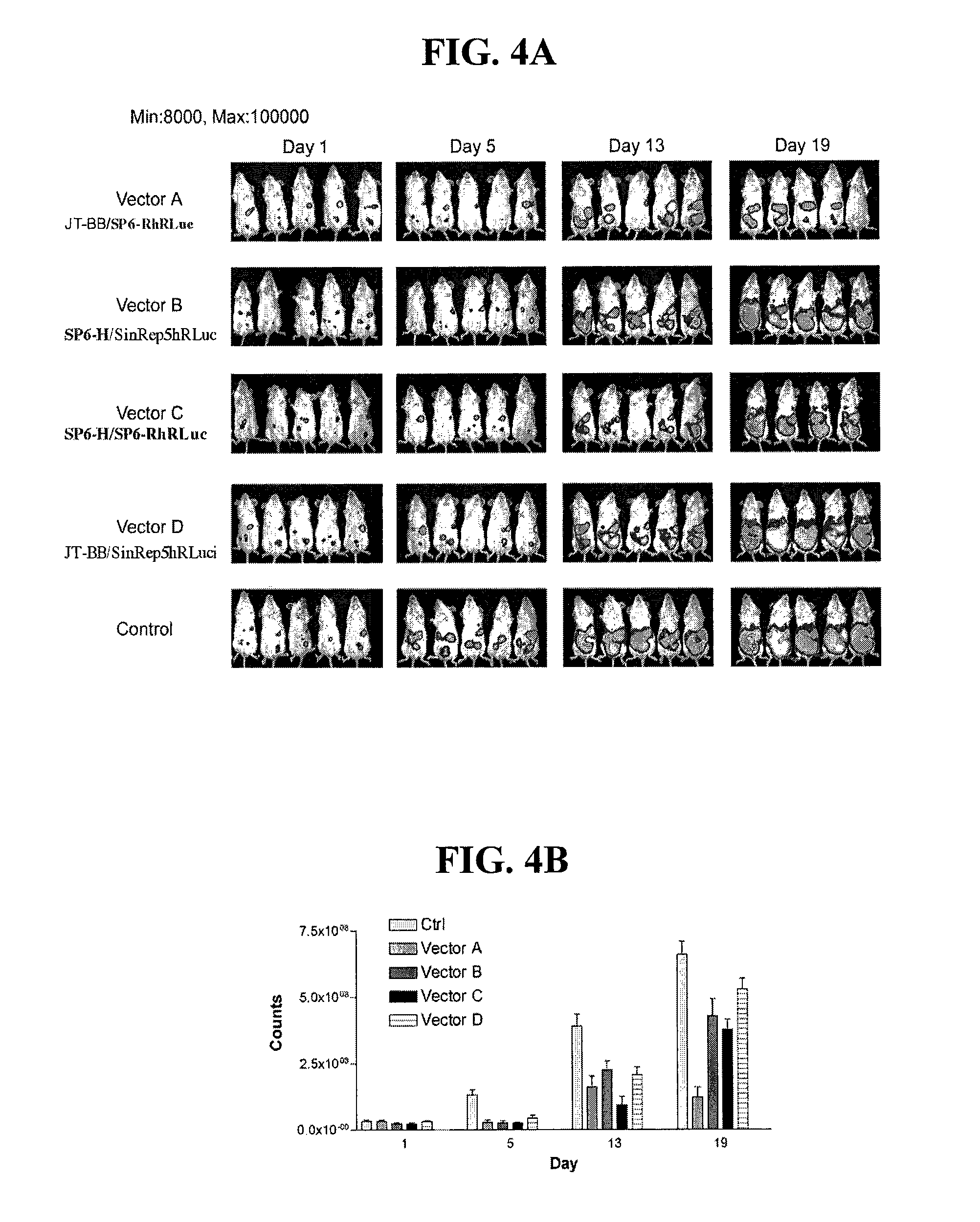
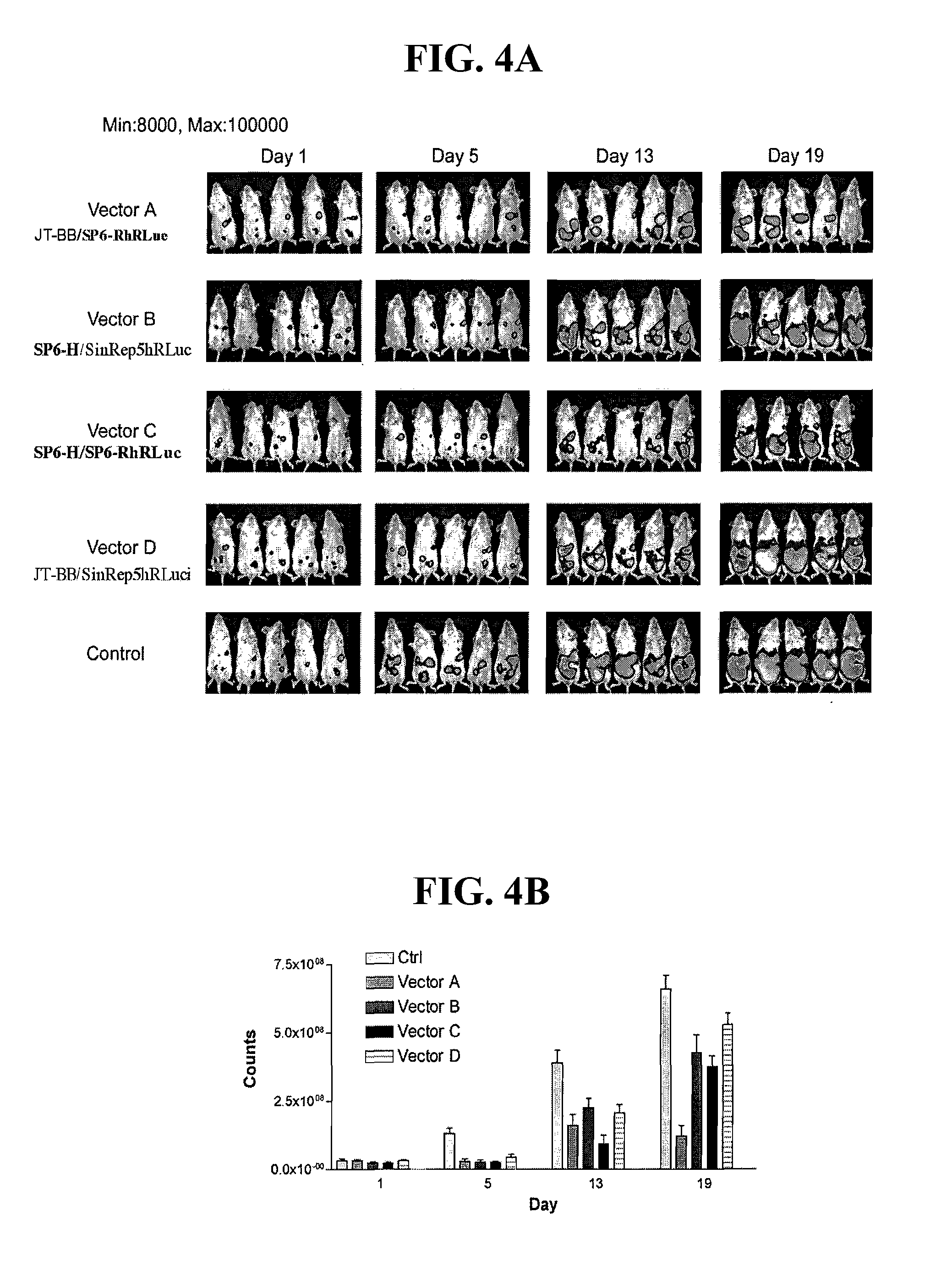
Method for detecting cancer cells and monitoring cancer therapy
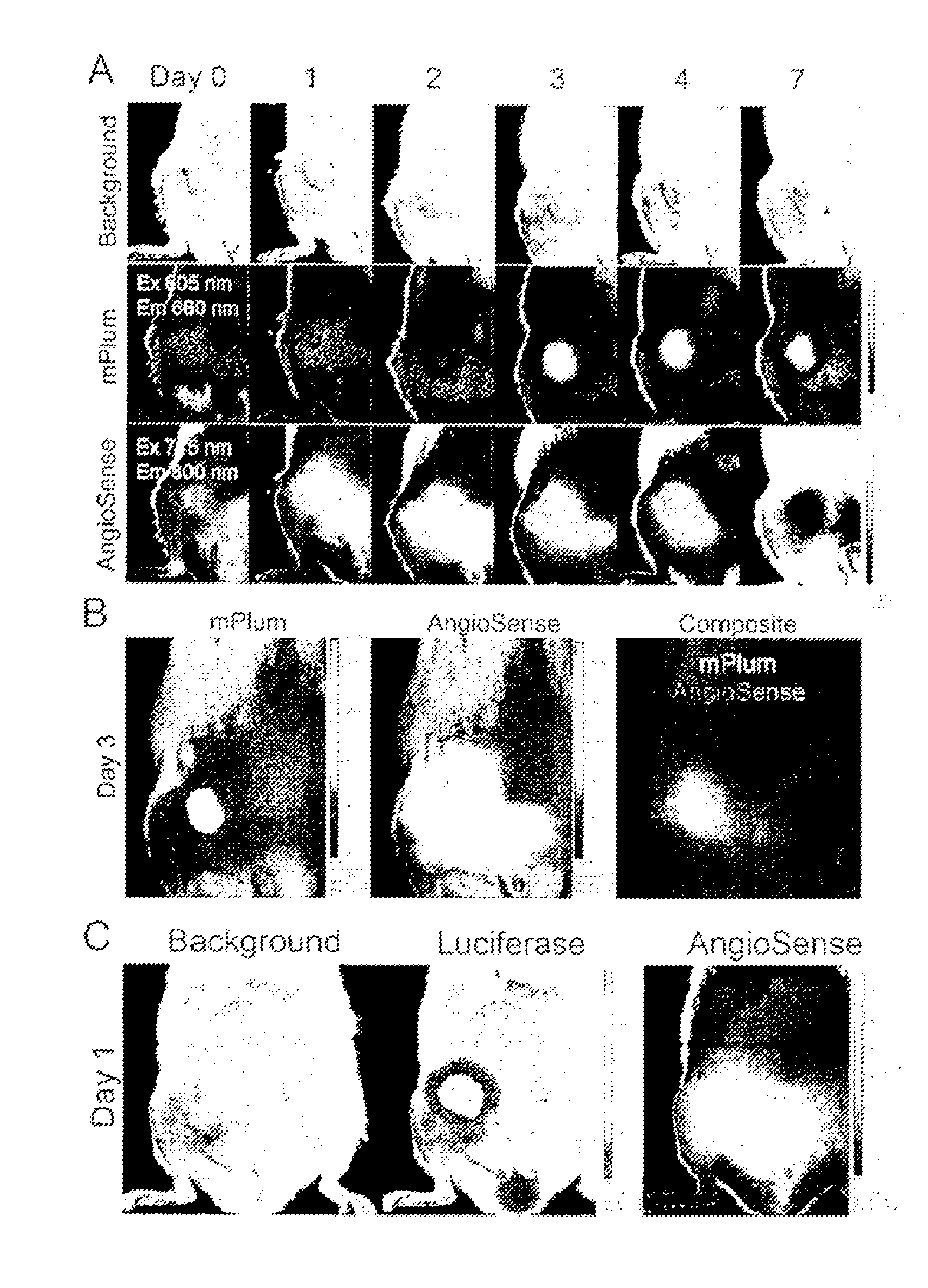
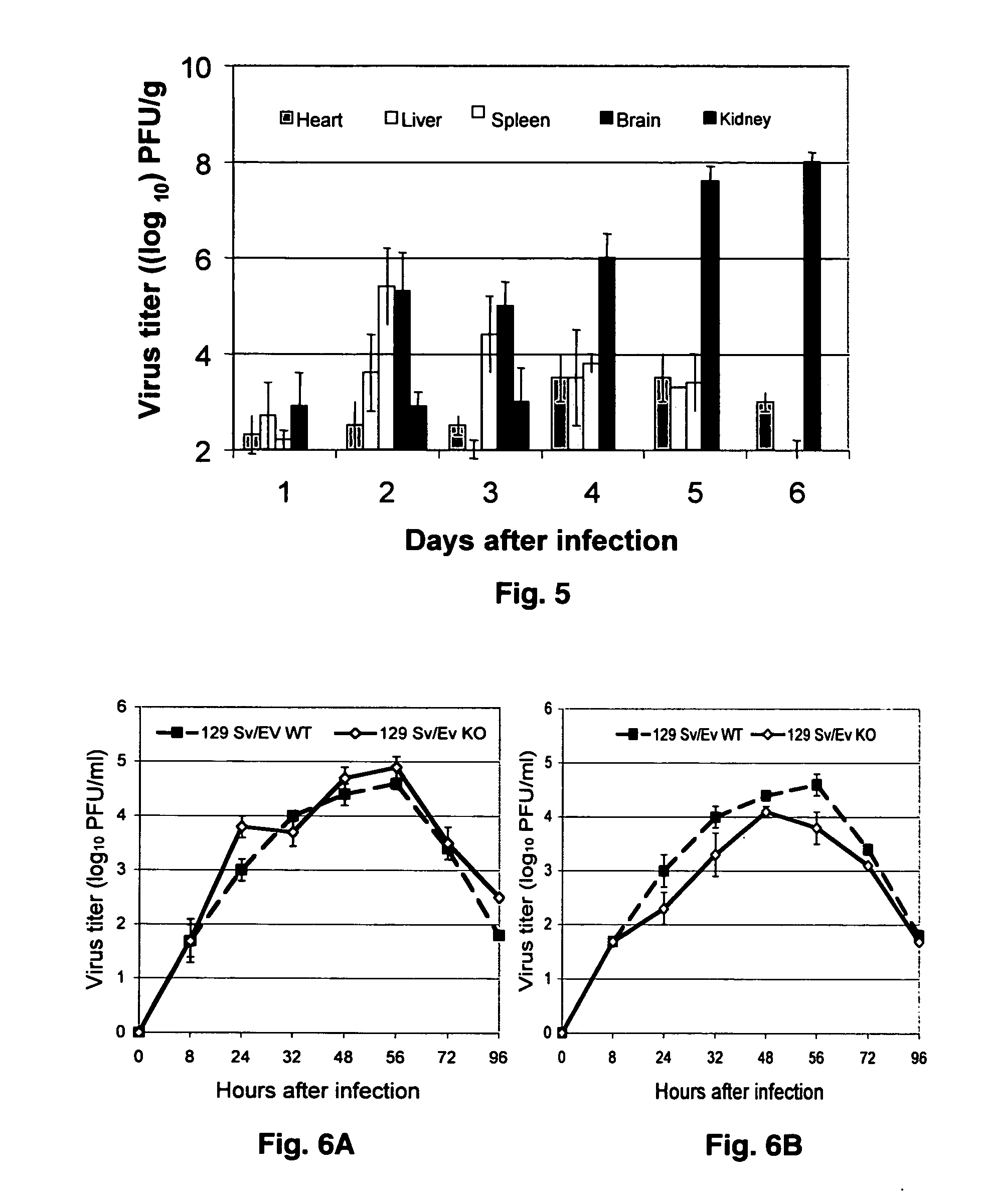
Disclosed herein are methods for identifying cancer cells and monitoring anti-cancer therapy in the body of a mammal by systemically delivering Sindbis viral vectors. The vector can specifically target and identify tumor cells in mice growing subcutaneously, intraperitoneally, intrapancreatically, or in the lungs. These findings demonstrate the remarkable specificity of the Sindbis vector system that is relatively safe and can specifically target tumor cells throughout the body via the bloodstream.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
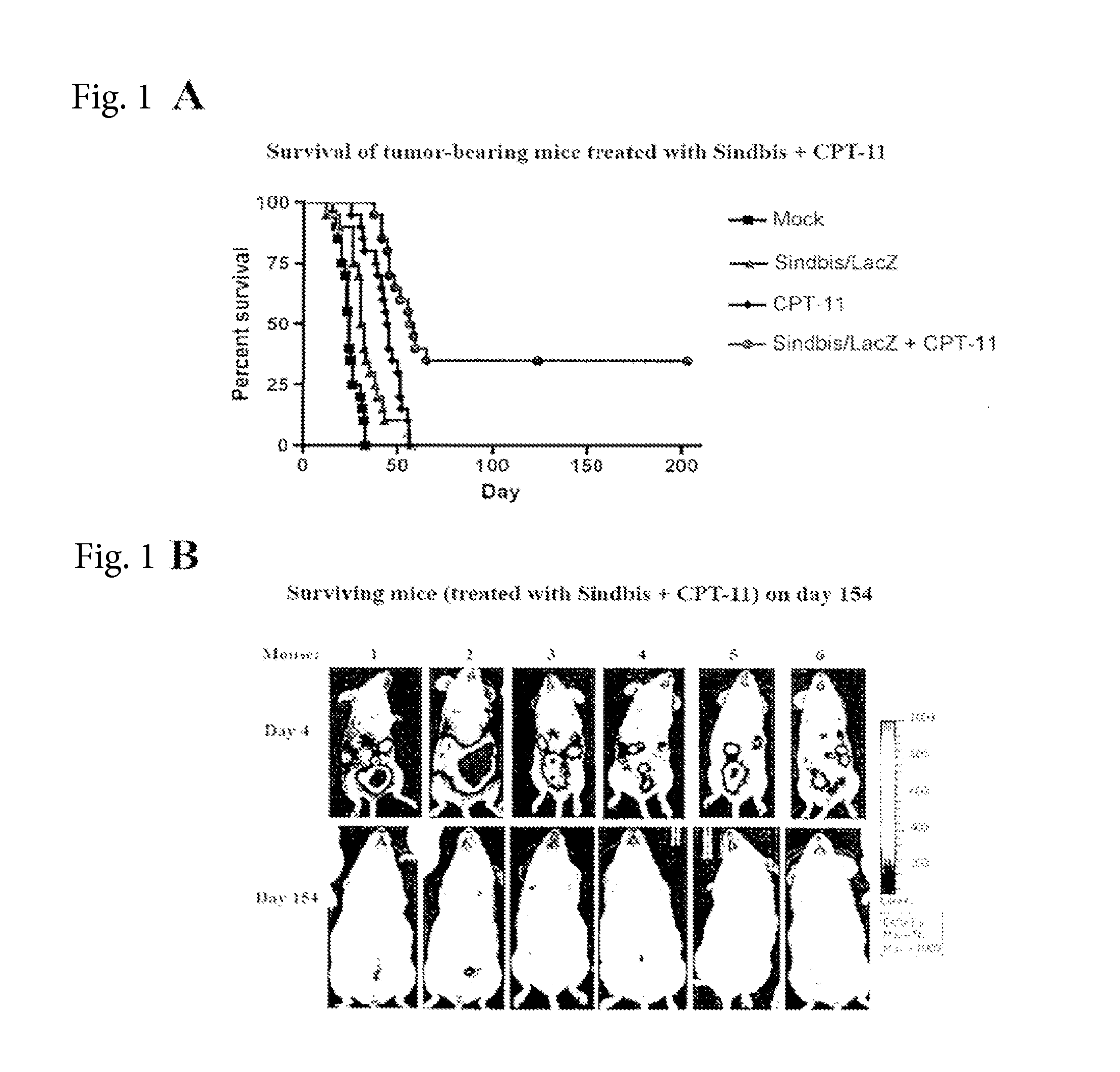
Tumor Therapy With Antitumor Agents In Combination With Sindbis Virus-Based Vectors
InactiveUS20160008431A1Improve survivalEfficient methodHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsTumor therapySindbis virus
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
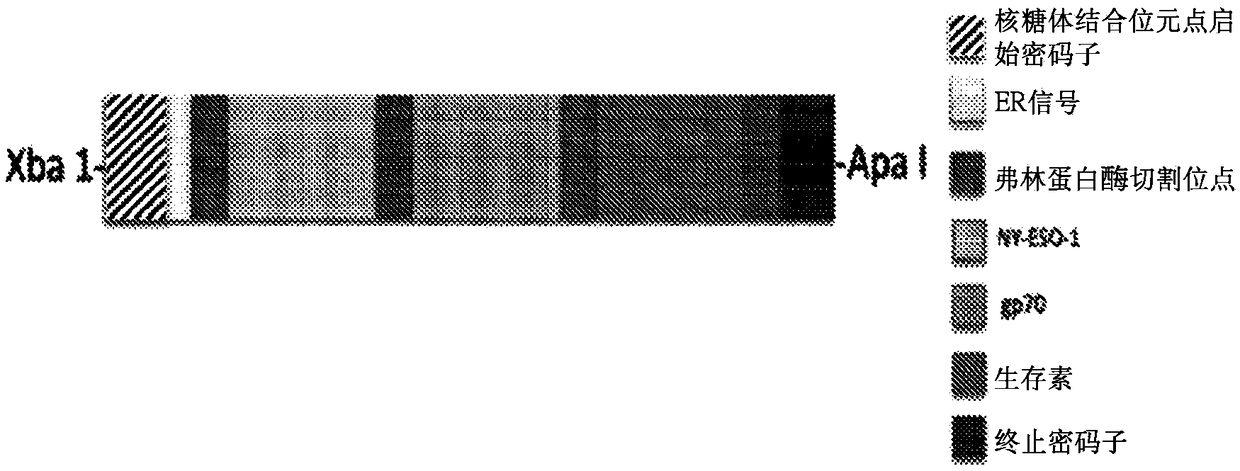
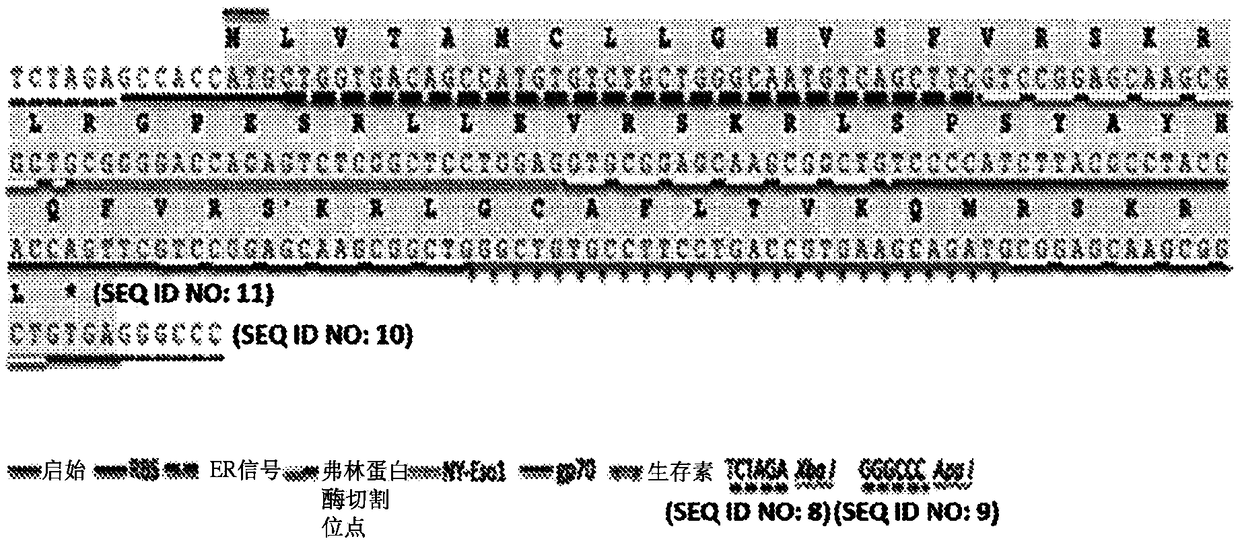
Virus vectors expressing multiple epitopes of tumor associated antigens for inducing antitumor immunity
InactiveCN109415416ATumor rejection antigen precursorsSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntitumor immunityAntigen epitope
Provided are polynucleotides and viral vectors, particularly, alphavirus vectors such as Sindbis viral vectors, which encode multiple, e.g., two or more, epitopes of at least one tumor associated antigen in which each epitope is separated by a processing or enzyme cleavage site. The multiple epitopes of the two or more tumor associated antigens encoded by the described polynucleotides and viral vectors may be the same or different. Methods of treating mammalian subjects having a cancer or tumor expressing the tumor associated antigen epitopes are provided, in which the viral vectors encoding the multiple epitopes, as well as other immunostimulatory or immunomodulatory components, generate an anti-cancer or anti-tumor immune response in which high levels of effector T cells increase the survivability of tumored mammalian subjects and result in epitope spreading, thus providing a further enhancement of the immune response.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
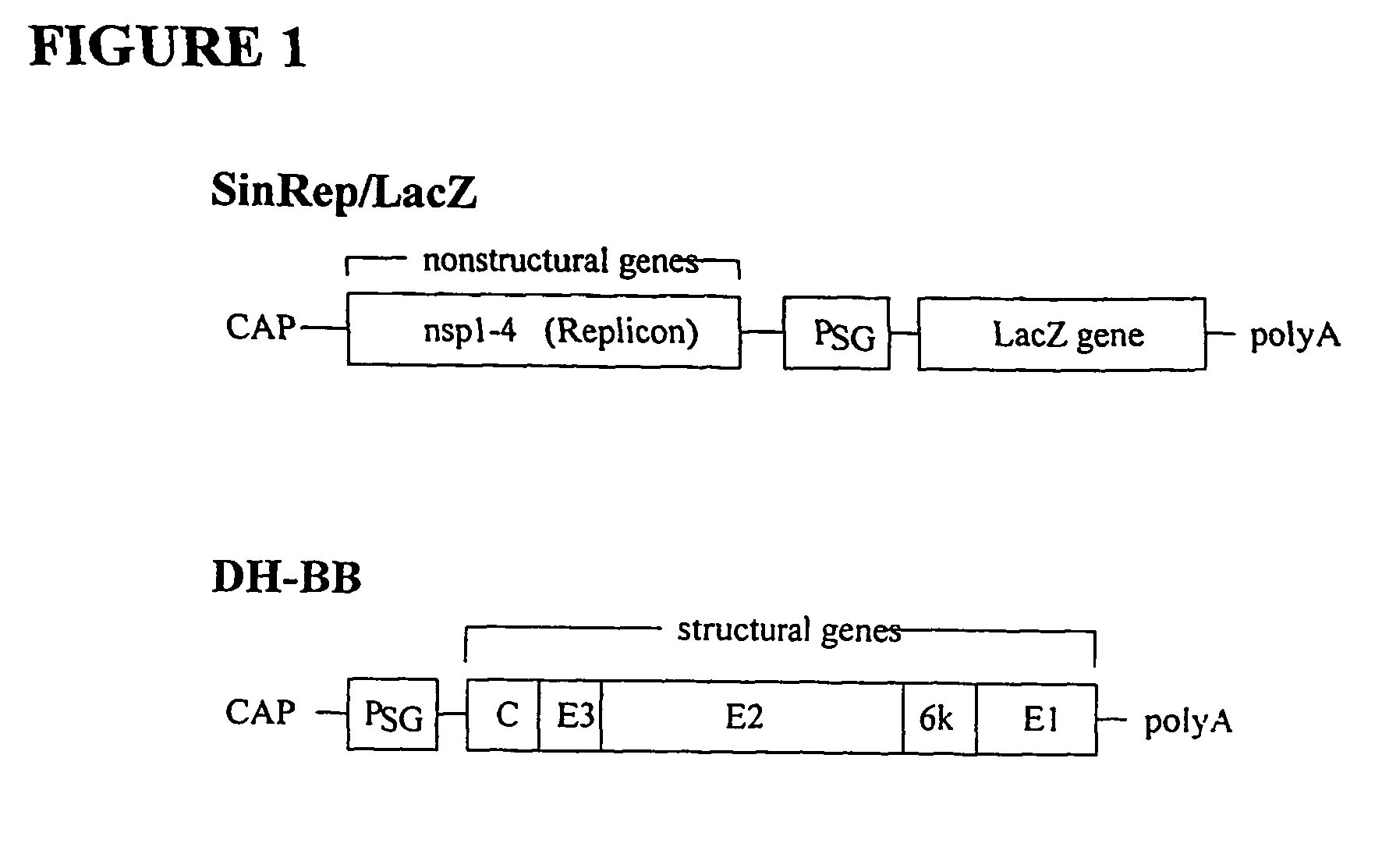
Sindbis virus overall length plasmid type carrier and its structuring method
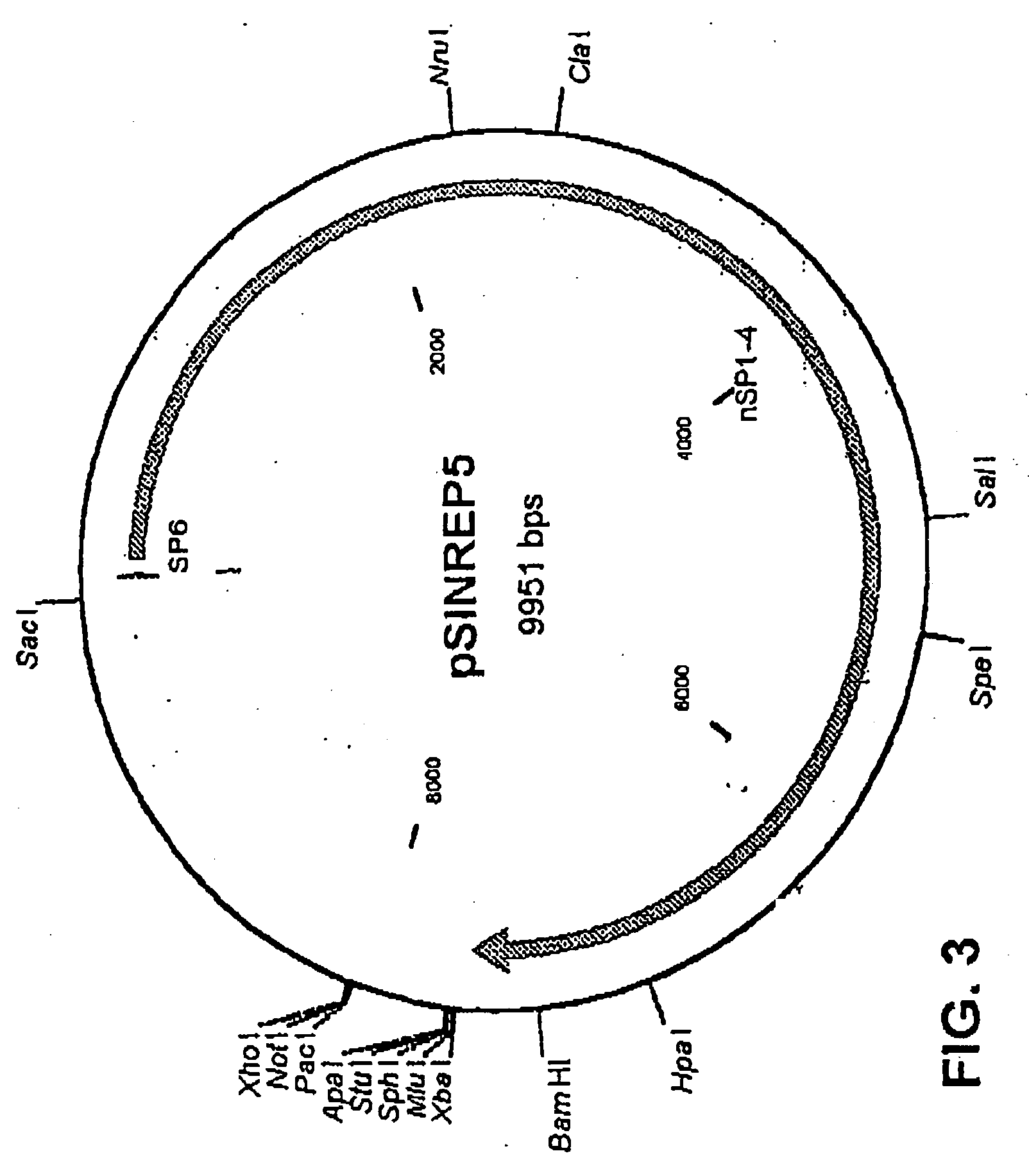
InactiveCN107254488AEasy to operateSimple and fast operationSsRNA viruses positive-senseVectorsSindbis virusDna transfection
The invention discloses a Sindbis virus overall length plasmid type carrier and its structuring method. The Sindbis virus overall length plasmid type carrier is an expression carrier recombined and structured by a main carrier PsinRep5 and an assistant carrier DH-BB and ESP promoter; firstly, ESP promoter is lead in a main carrier PsinRep5 of the Sindbis virus, and then inserted to DH-BB structure protein gene to obtain the Sindbis virus overall length plasmid type carrier pSinRep 5-DB-ESP; the carrier can directly transfect DNA to the cell, thus the operation of the virus carrier for expressing an exogenous gene is greatly simplified, thus the carrier can be applied to gene expression and also transformation of other viruses; the structuring method has the advantages of being simple in operation, good in safety, able to avoid appearance of recombined wild virus, low in cost, and convenient to popularize and apply.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
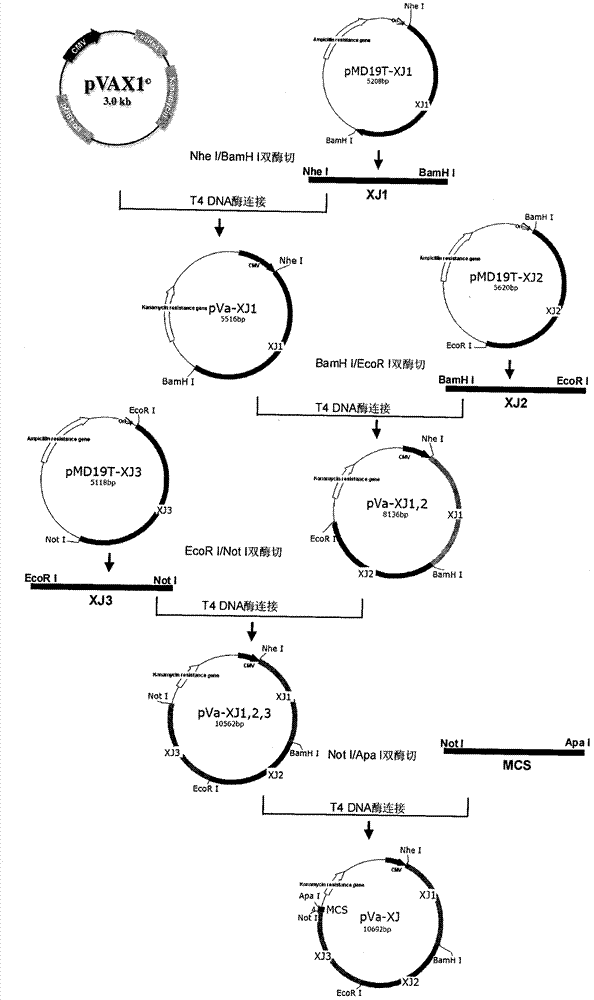
Sindbis virus XJ-160 defective replicon and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102816781AGood broad spectrumEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSindbis virusStructural protein
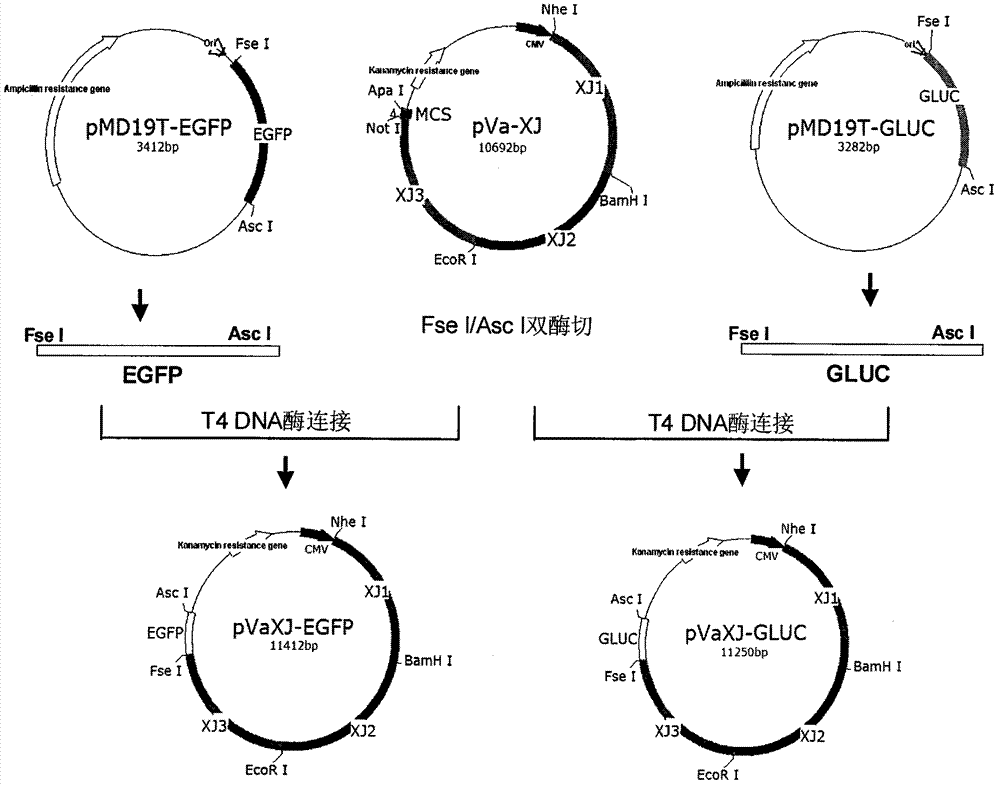
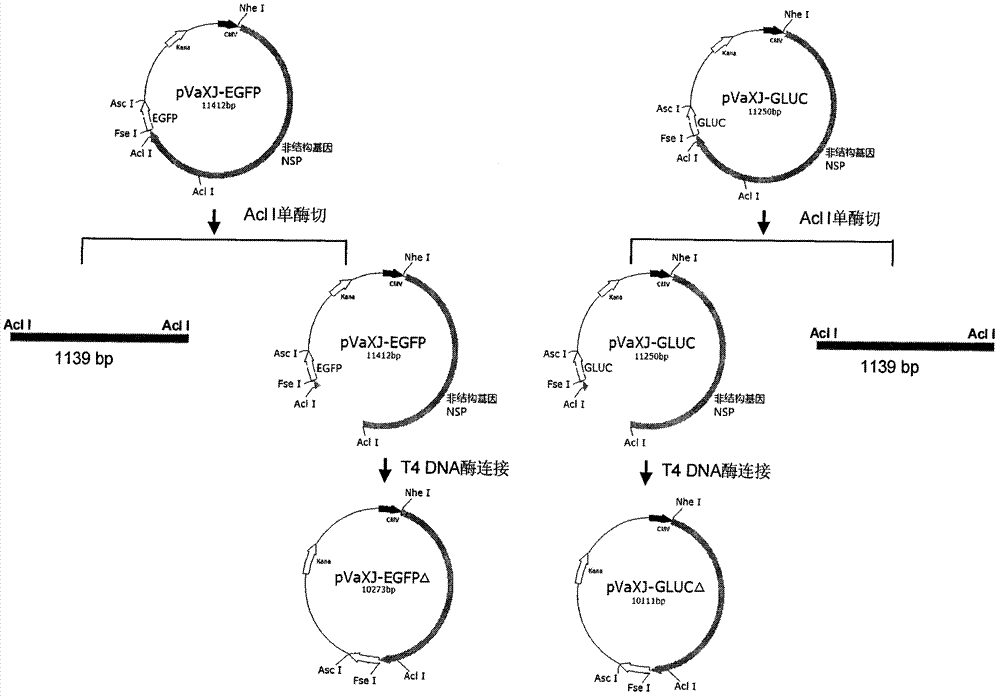
The invention provides a sindbis virus XJ-160 defective replicon and a construction method and application thereof. The construction method comprises the steps of constructing an XJ-160 virus particle type replicon carrier pVa-XJ, constructing XJ-160 particle type replicons pVaXJ-EGFP and pVaXJ-GLUC containing reporter genes, constructing a XJ-160 defective replicon, utilizing Acl I restriction enzyme to respectively perform single digestion of the VaXJ-EGFP and the pVaXJ-GLUC and constructing defective particles pVaXJ-EGFP delta and pVaXJ-GLUC delta with 1139 base deletions at the positions of non-structural genes. The mechanism of the construction method is that due to the partial absence of non-structural genes regions, a large amount of the reporter genes cannot be expressed normally after cells are introduced into the defective replicon, and non-structural protein expressed by virus can remedy and react on expression of the large amount of the reporter genes caused by the defective replicon when alphavirus infection exists in the cells. The sindbis virus XJ-160 defective replicon can detect multiple types of alphavirus, has not reaction on non-alphavirus and is high in specificity and sensitivity and can detect 1PFU virus. Operation is simple and quick, required instruments are few, sustainability is strong, the virus is not required to be killed in detection, and the sindbis virus XJ-160 defective replicon is suitable for quick identification of the alphavirus.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
2-amino-2,7-dideoxy-alpha-D-glycero-D-gluco-heptopyranosyl inhibitors of positive sense single-stranded RNA envelope viruses
InactiveCN101772347AReduce infectivitySugar derivativesCarbohydrate active ingredientsSingle-Stranded RNABovine Viral Diarrhea Viruses
The present invention is directed to compounds, compositions and methods comprising the aminoglycoside moiety represented by Formula (II) for treating and preventing the spread of positive sense single-stranded RNA envelope viral infections. One embodiment of the present invention uses geneticin or its analogs, including 2-amino-2,7-dideoxy-alpha-D-glycero-D-gluco-heptopyranose, as the antiviral agent. The compounds, compositions and methods of the present invention are applicable to infections resulting from Hepatitis C virus, West Nile virus, Yellow Fever virus, Dengue virus, Bovine Viral Diarrhea virus, Equine Arteritis virus, and / or Sindbis virus.
Owner:INST FOR HEPATITIS & VIRUS RES
A nucleic acid composition, kit and detection method for simultaneous detection of Sindbis virus, Getha virus and Yunnan orbivirus
ActiveCN112852999BReduce detection timesReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTest sampleSindbis virus
The application discloses a nucleic acid composition, a kit and a detection method for simultaneously detecting Sindbis virus, Getha virus and Yunnan orbivirus. The nucleic acid composition includes forward and reverse primers and probes against Sindbis virus, forward and reverse primers and probes against Getha virus, and forward and reverse primers and probes against Yunnan orbivirus. In addition to the above three sets of primers and probes, the kit also includes enzyme mixture and PCR reaction reagents. The present application also provides a method for simultaneous detection of the above three viruses. Firstly, the RNA of the test sample is extracted, and then the RNA is subjected to real-time fluorescent PCR reaction using the above kit, and finally the negative or positive of the sample to be tested is judged according to the intensity of the fluorescent signal. The application can simultaneously detect three viruses, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, good repeatability, simple operation, fast detection speed, easy interpretation of results and the like.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com