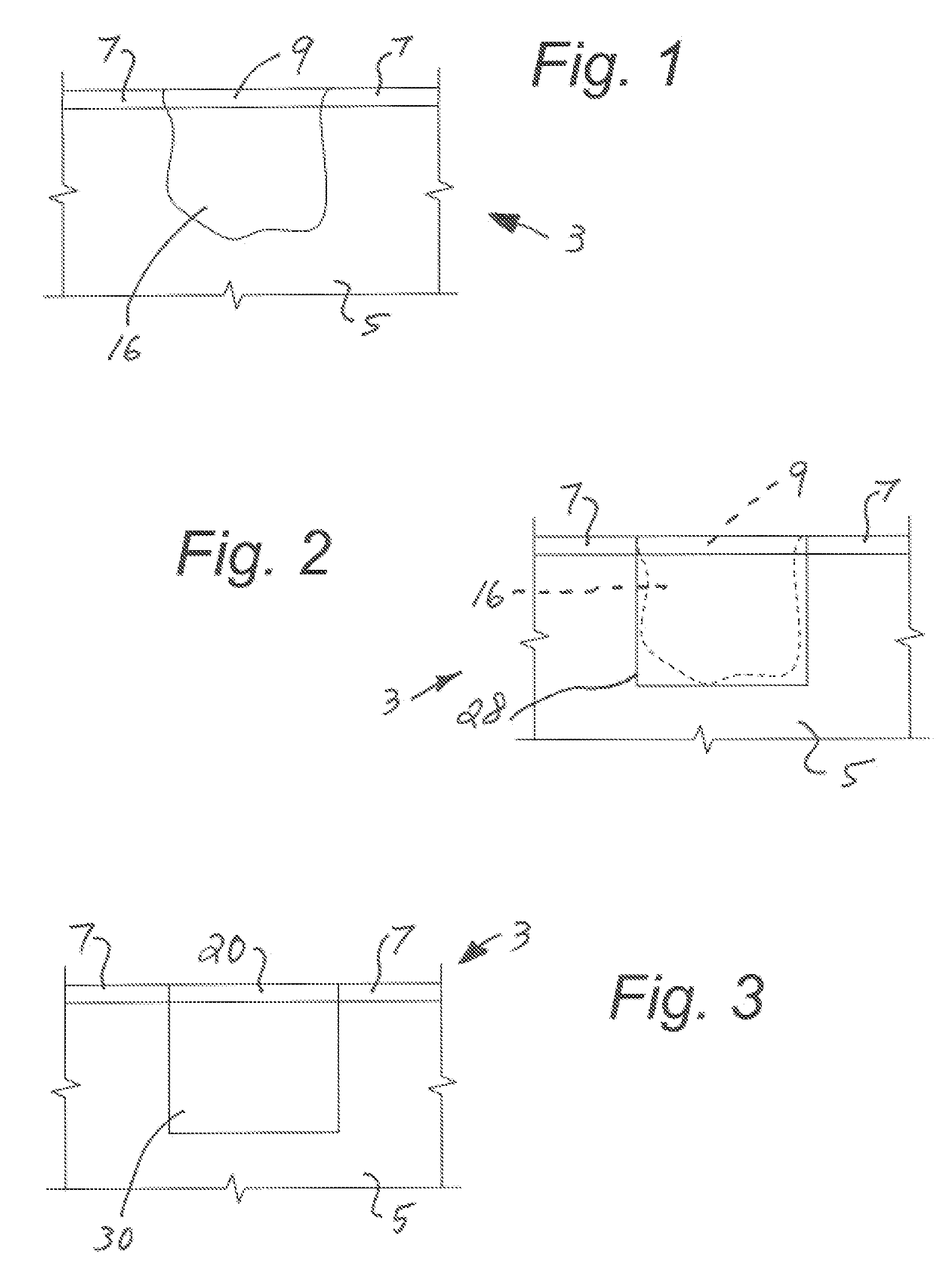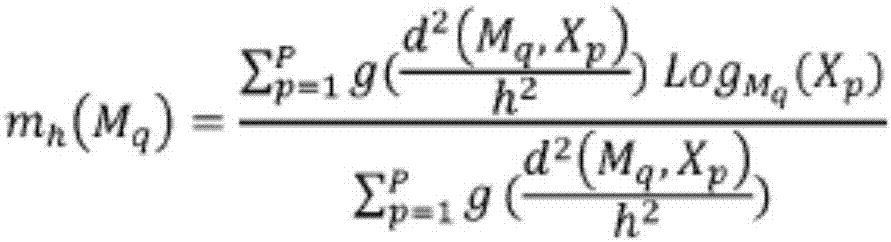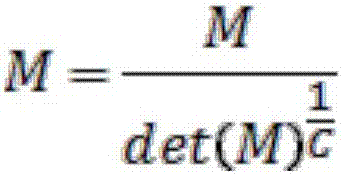Patents
Literature
66results about How to "Successful treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
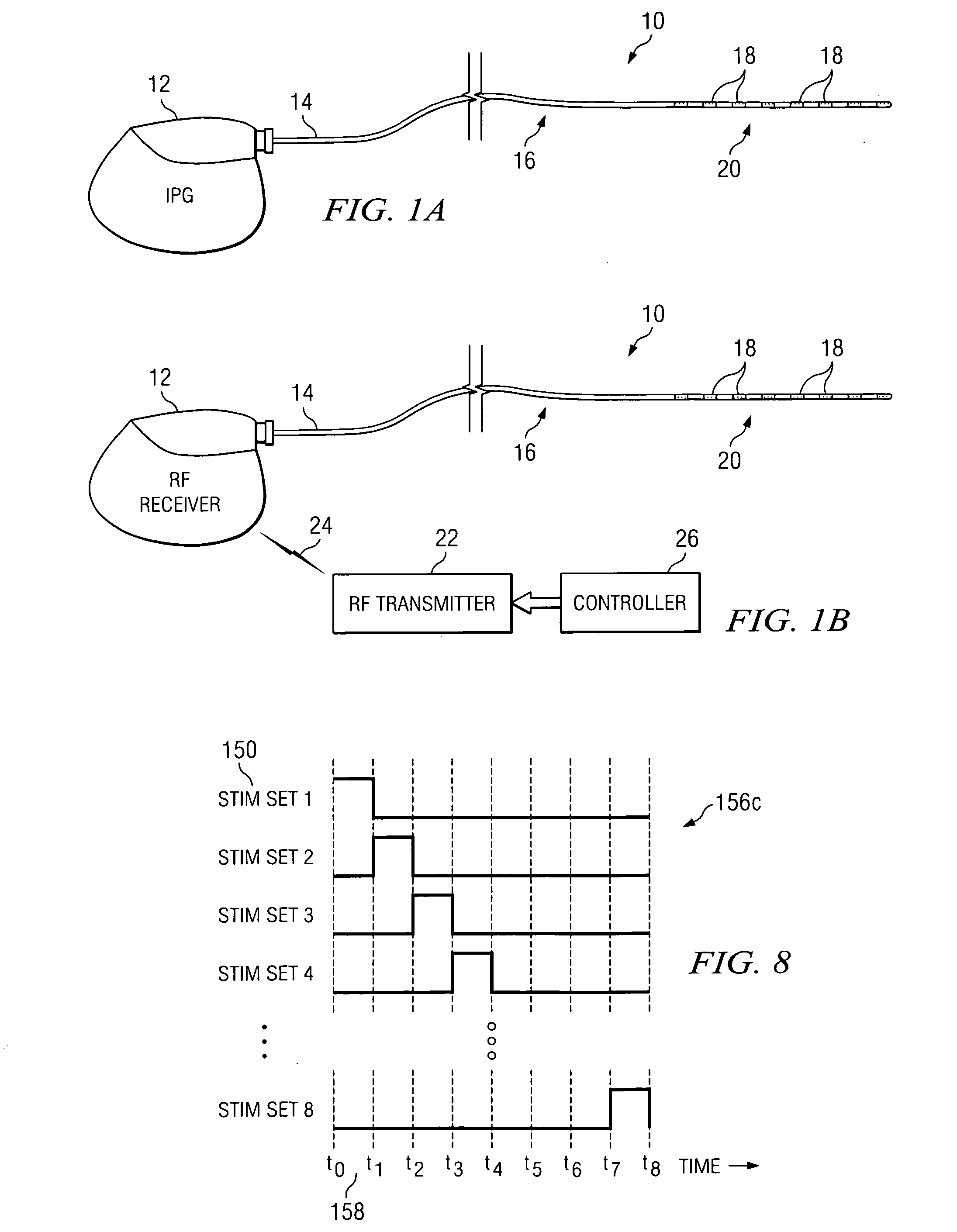
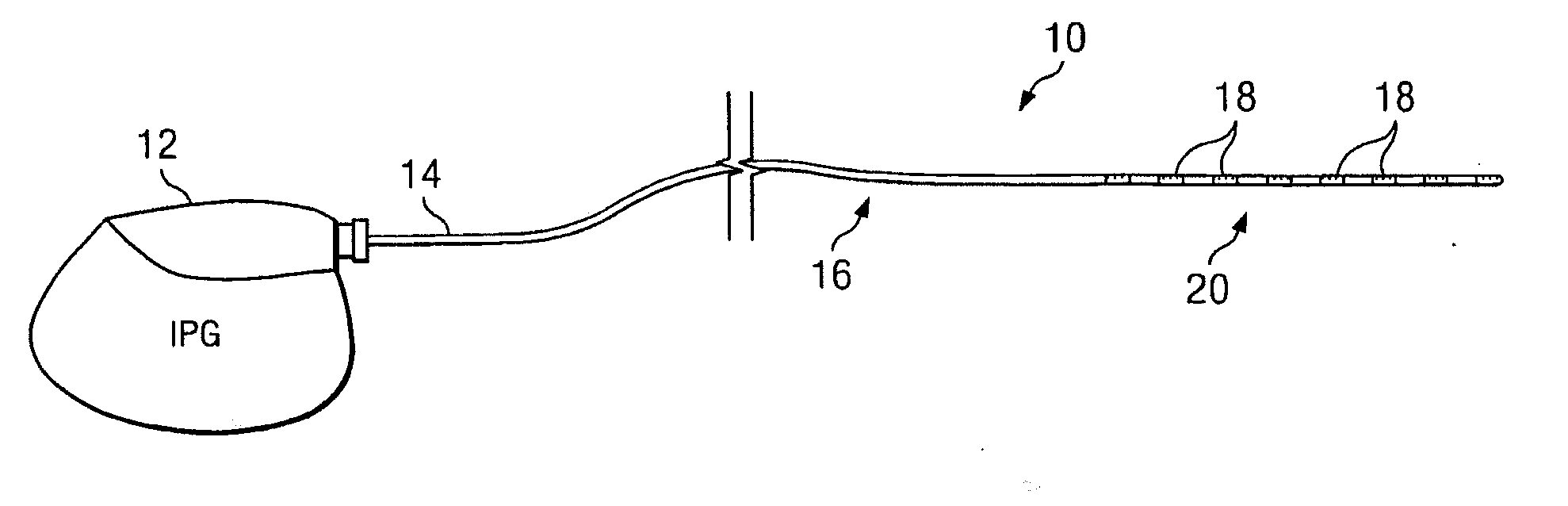
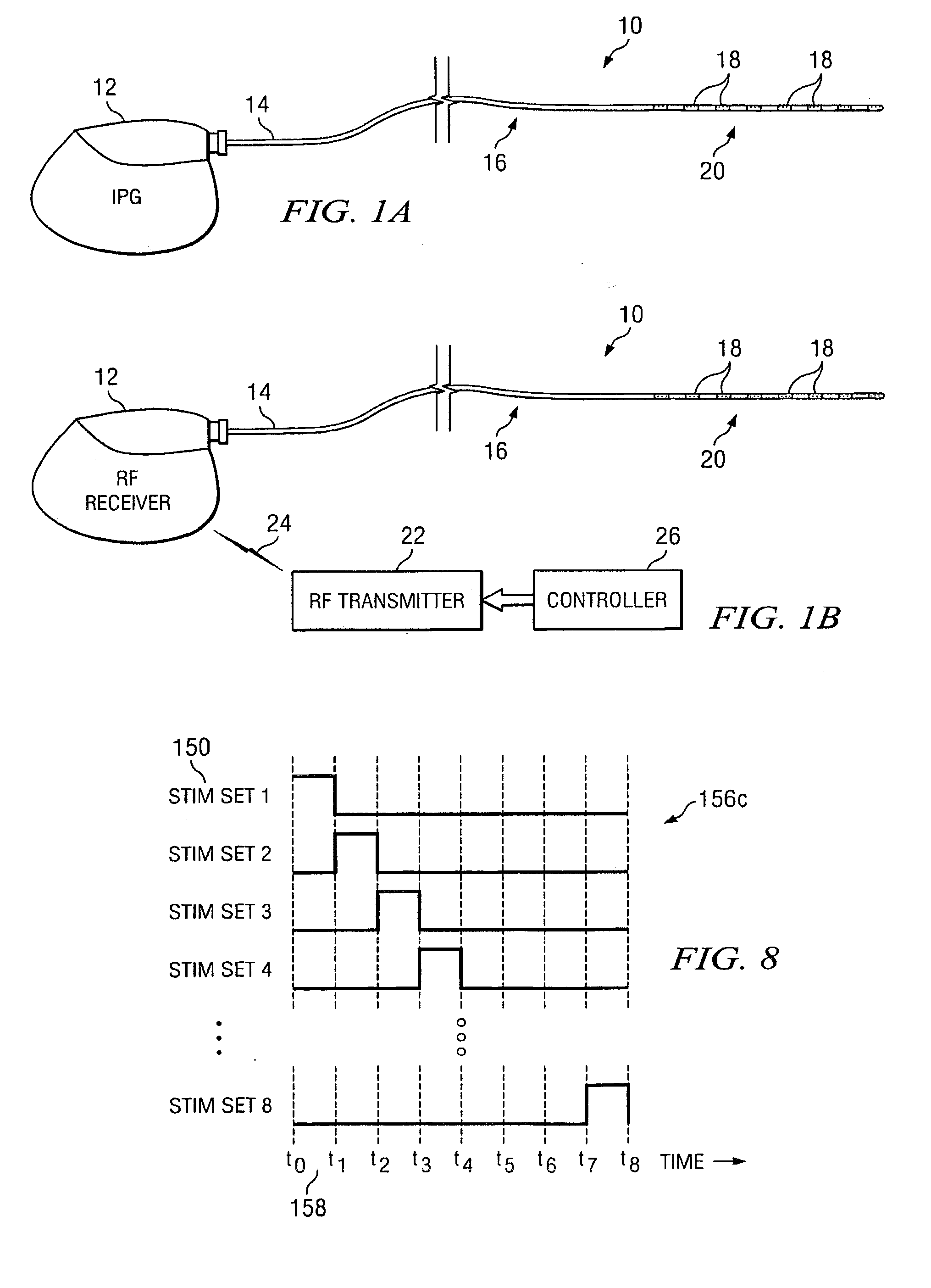
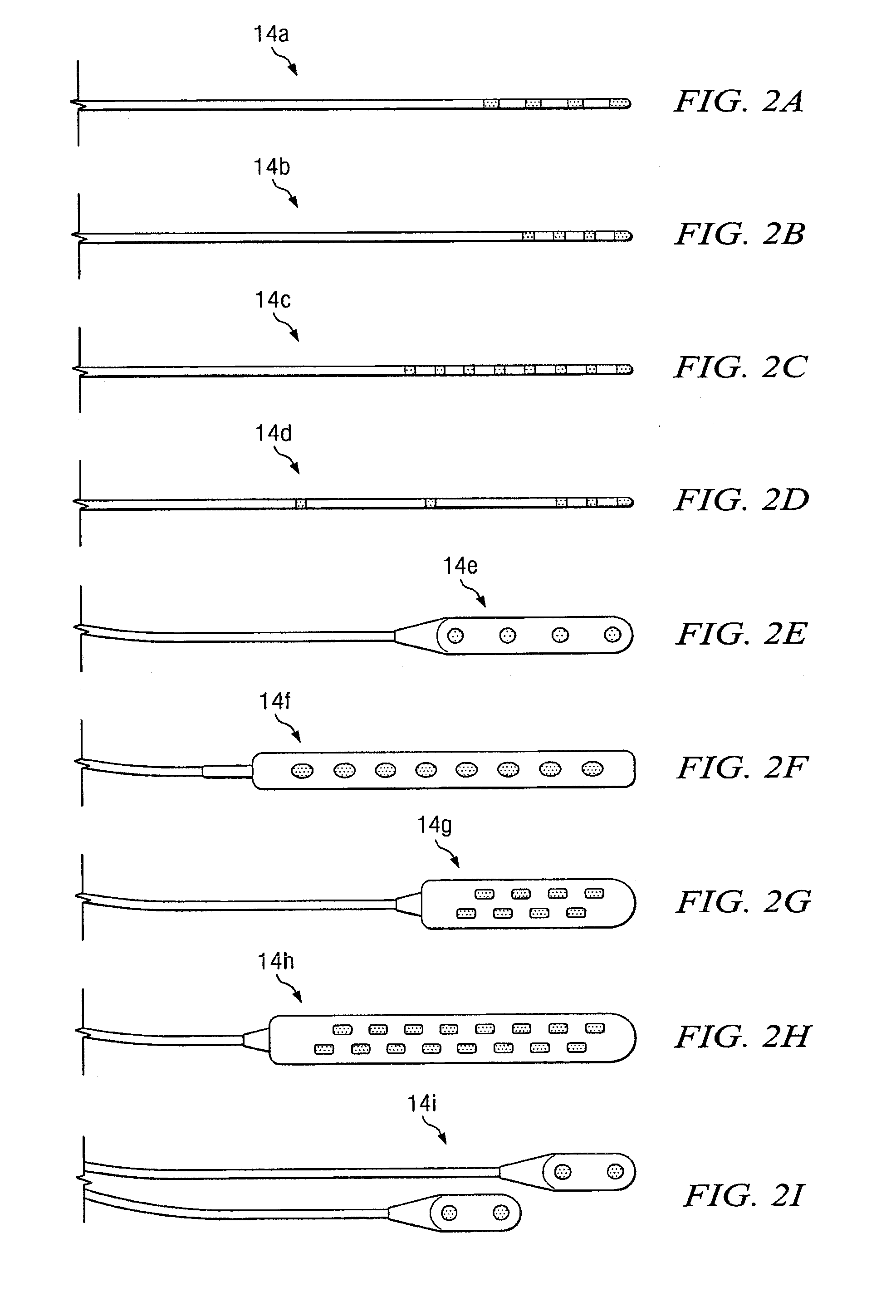
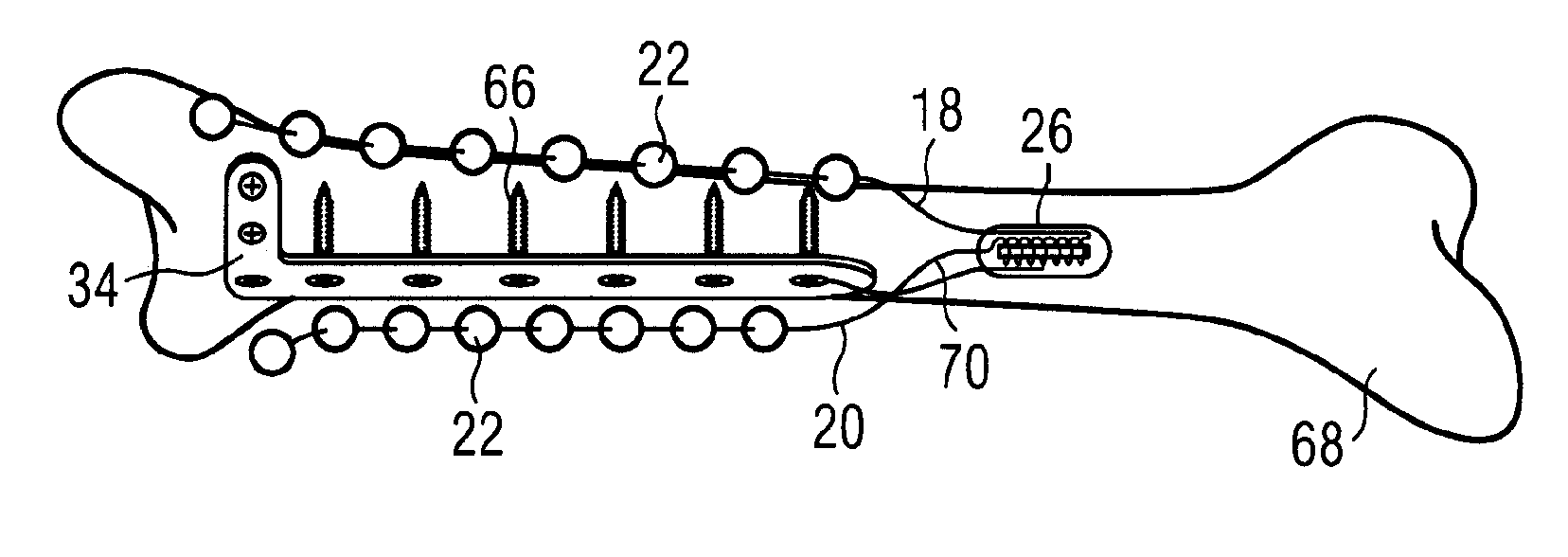
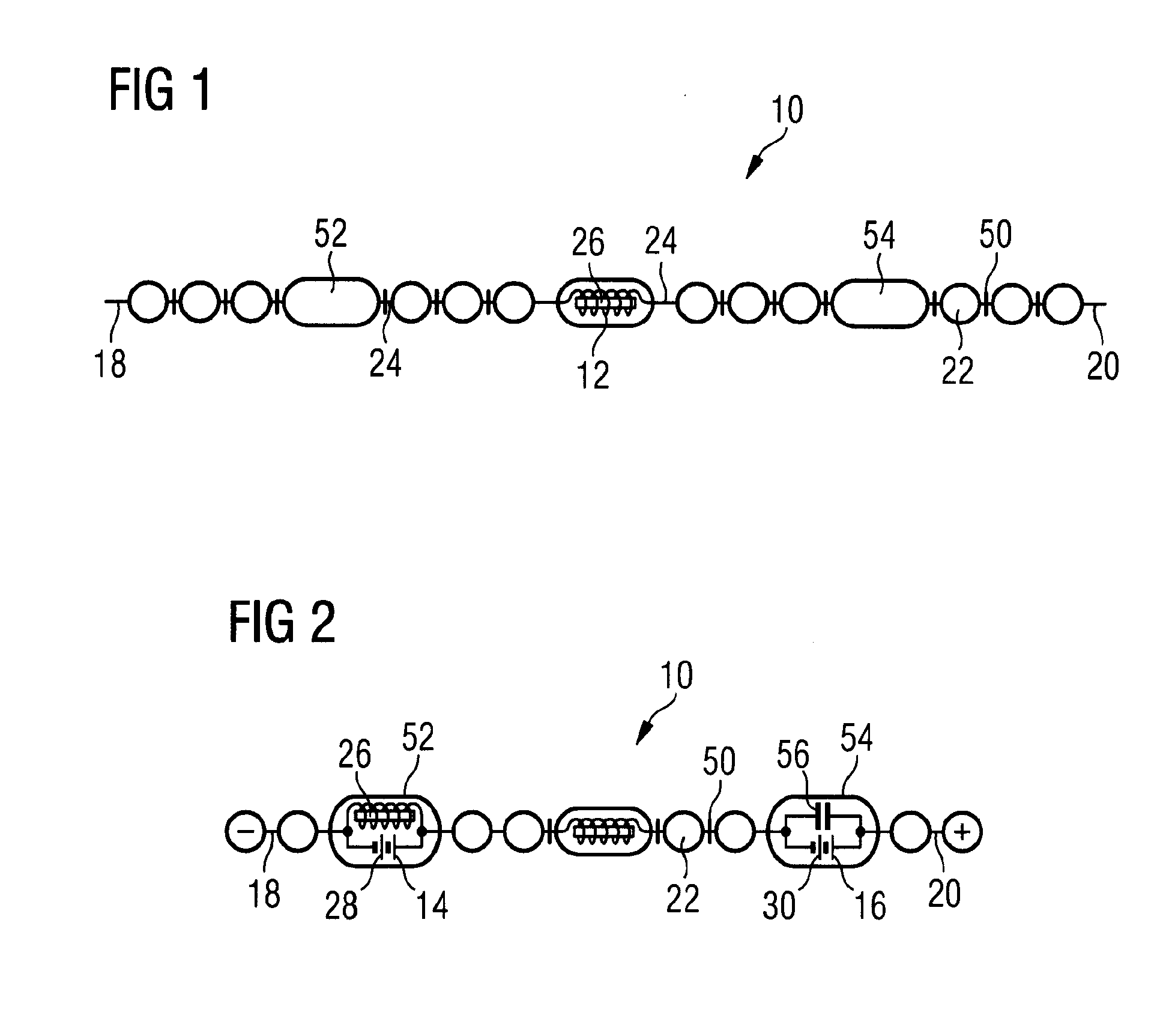
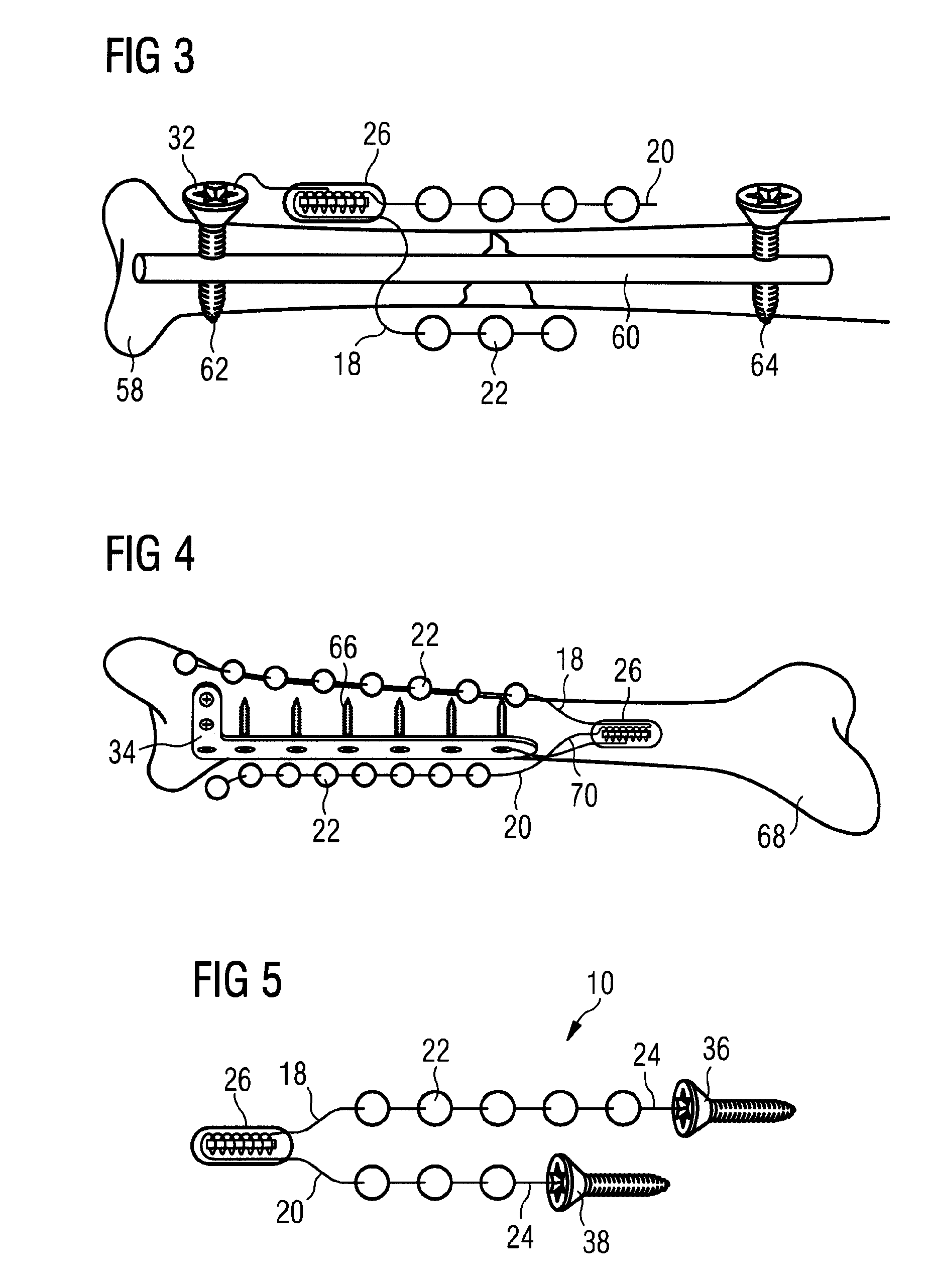
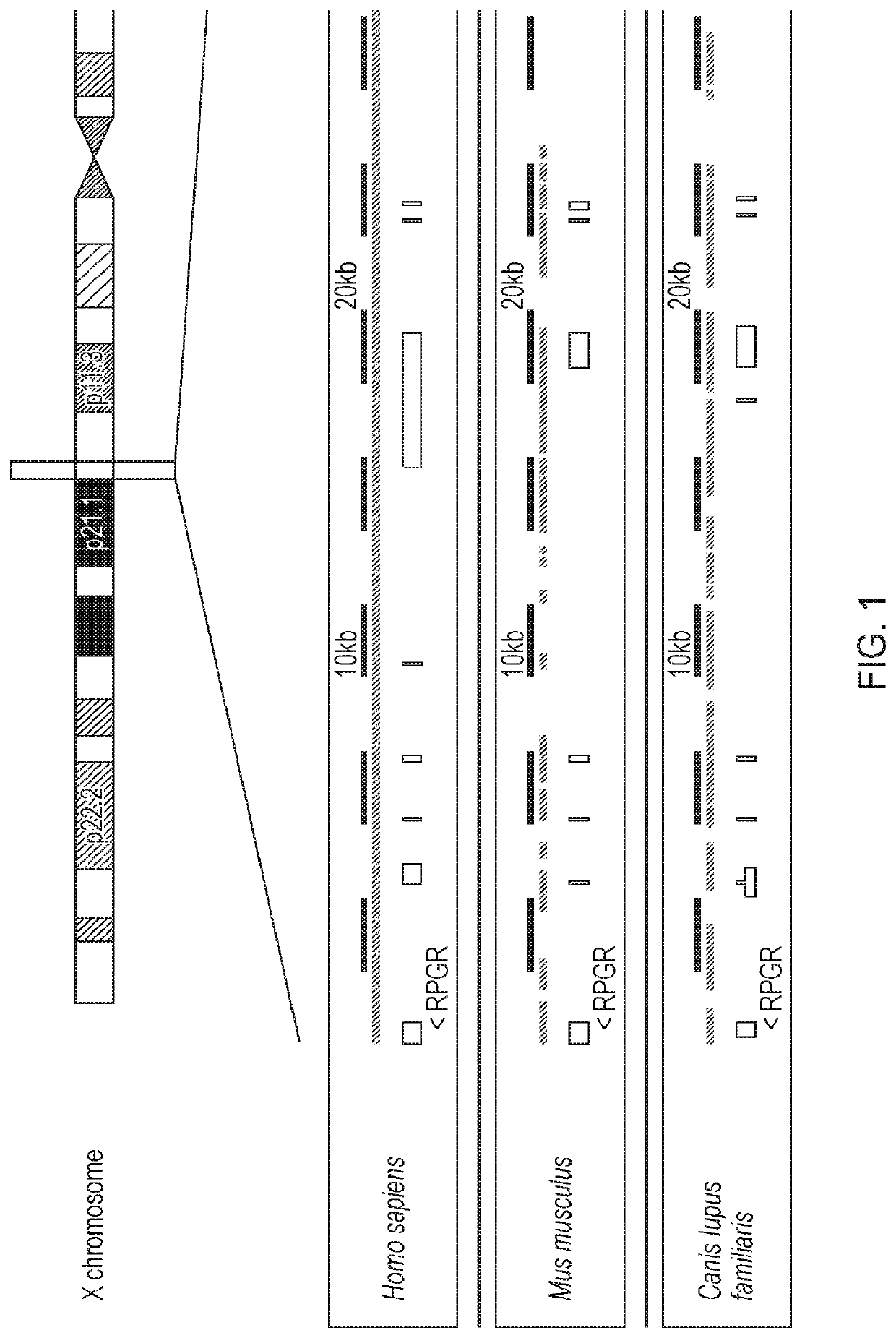
System and method for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerves to treat low back pain
ActiveUS7324852B2Reduce and eliminate and disadvantageReduce and eliminate problemSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesProximatePeripheral neuron
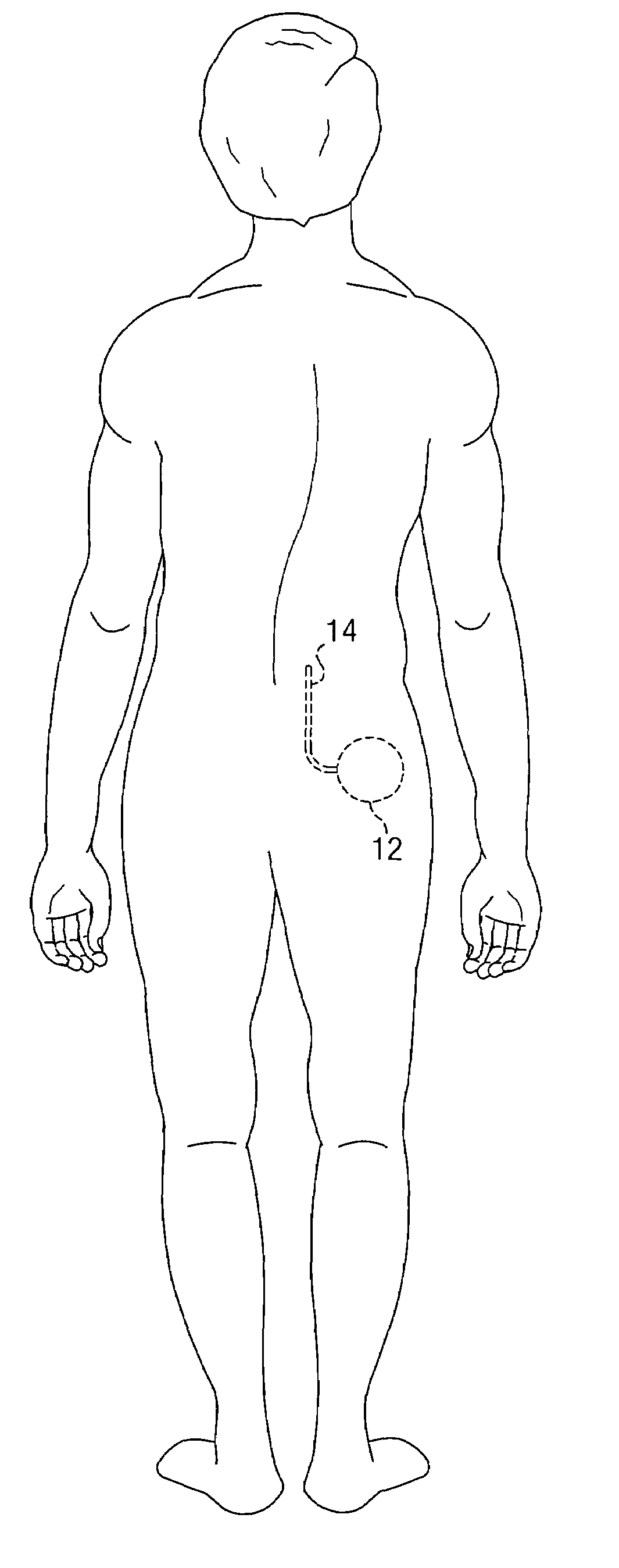
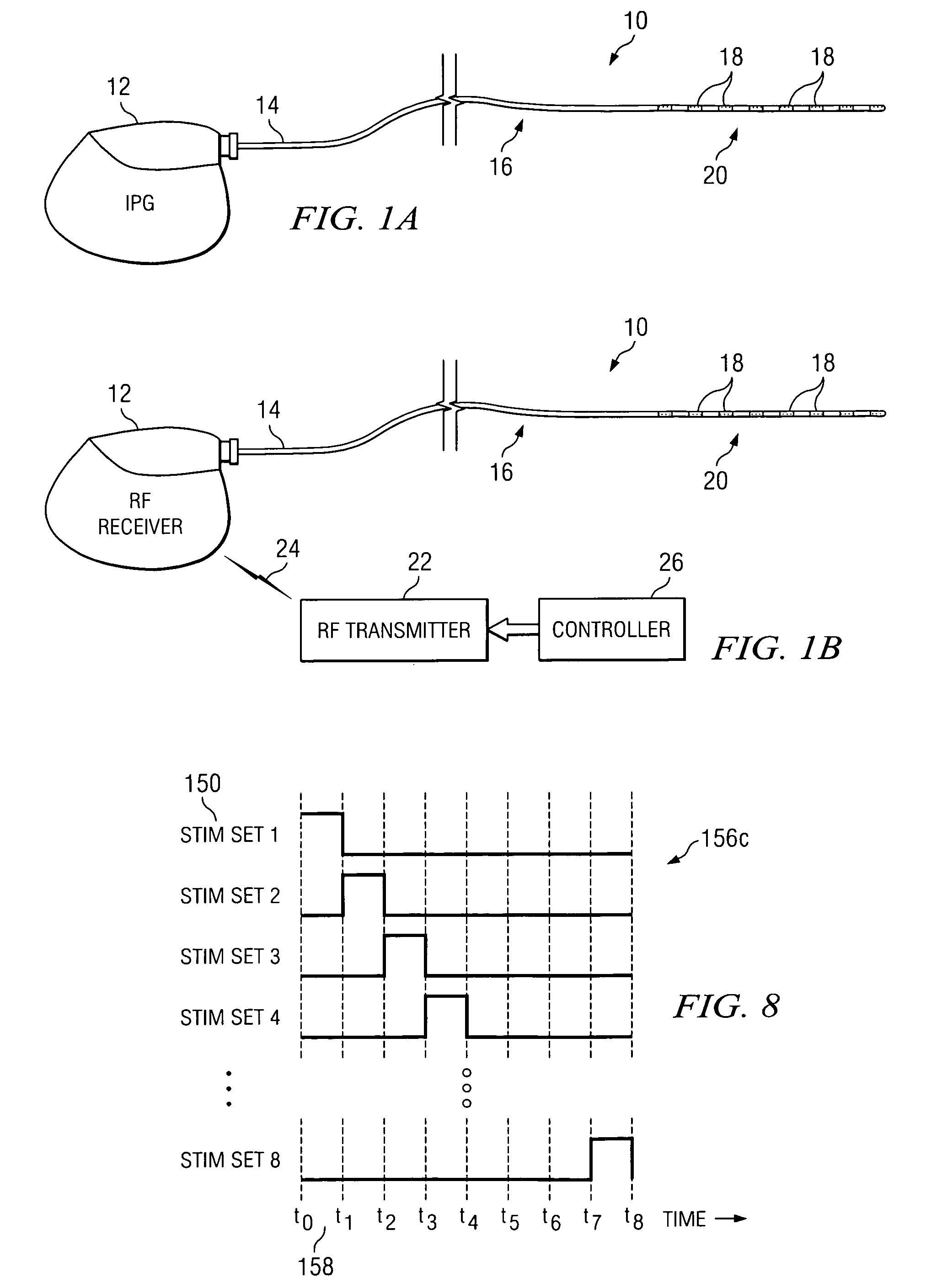
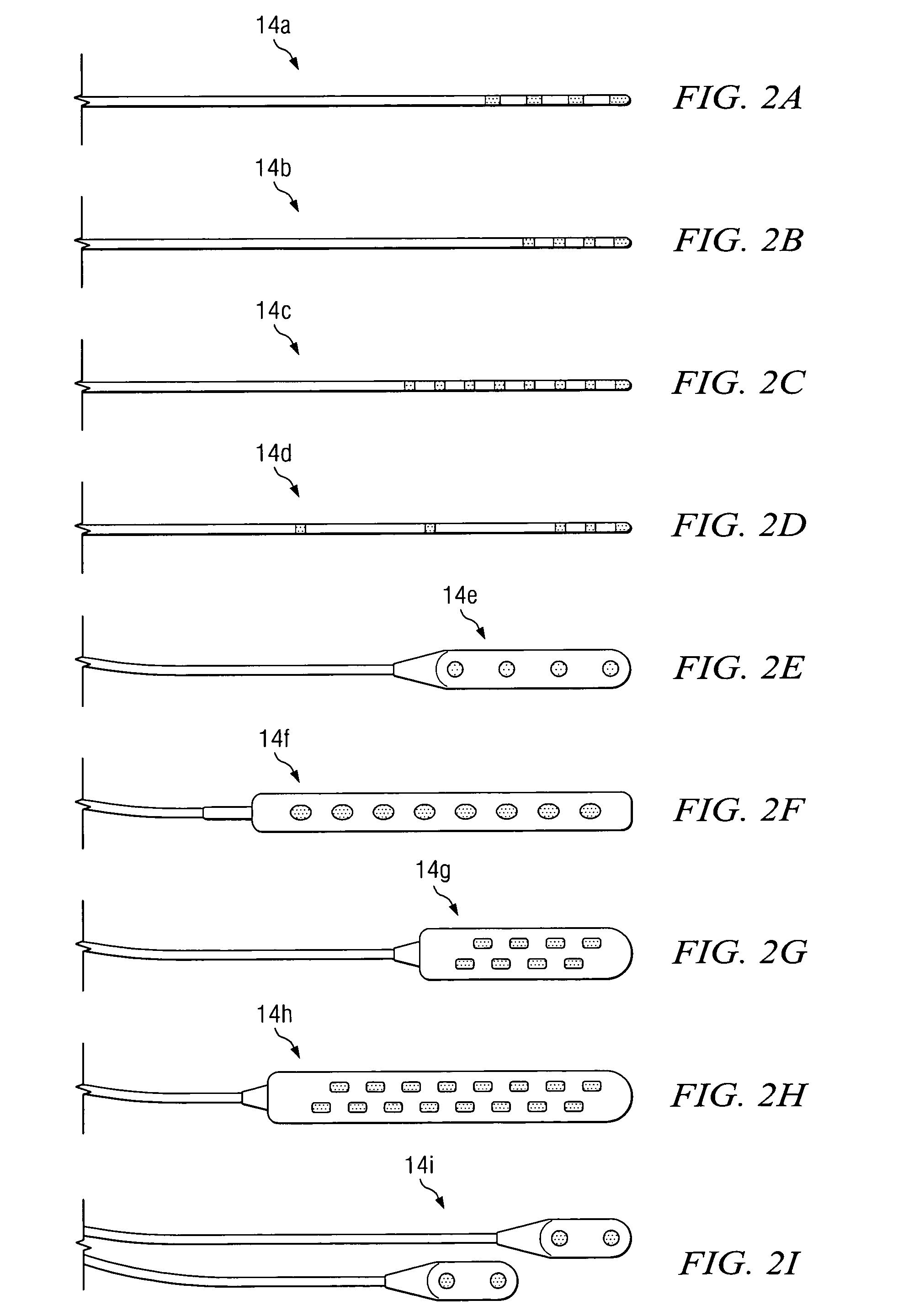
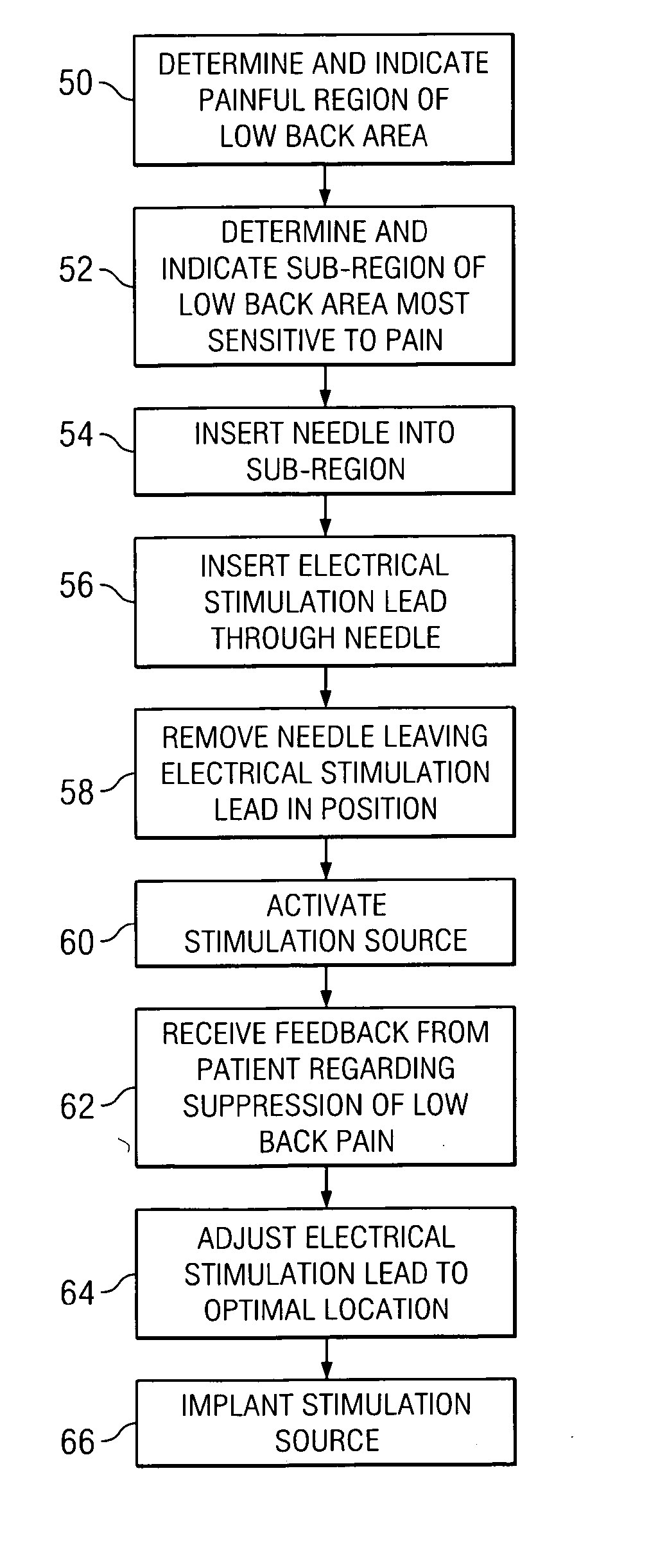
According to one embodiment, a system for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerve fibers to treat low back pain is provided. The system includes stimulation electrodes adapted to be implanted in tissue proximate a network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating a painful region of the low back area and to deliver electrical stimulation pulses to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area. The system also includes a stimulation source adapted for implantation into the person's body and operable to generate electrical stimulation pulses for transmission to the electrodes for delivery to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area to relieve pain in the painful region of the low back area.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV +1
Inhibition of migration inhibitory factor in the treatmente of diseases involving cytokine-mediated toxicity
InactiveUS6080407AIncreased mortalityEnhance macrophage killingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAutoimmune diseaseMigration Inhibitory Factor
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting the release and / or biological activity of migration inhibitory factor (MIF). In particular, the invention relates to the uses of such compositions and methods for the treatment of various conditions involving cytokine-mediated toxicity, which include, but are not limited to shock, inflammation, graft versus host disease, and / or autoimmune diseases.
Owner:BAXALTA GMBH
System and method for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerves to treat low back pain
ActiveUS20050240243A1Reduce and eliminate and disadvantageReduce and eliminate problemSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesProximateAnesthesia
According to one embodiment, a system for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerve fibers to treat low back pain is provided. The system includes stimulation electrodes adapted to be implanted in tissue proximate a network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating a painful region of the low back area and to deliver electrical stimulation pulses to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area. The system also includes a stimulation source adapted for implantation into the person's body and operable to generate electrical stimulation pulses for transmission to the electrodes for delivery to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area to relieve pain in the painful region of the low back area.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV +1
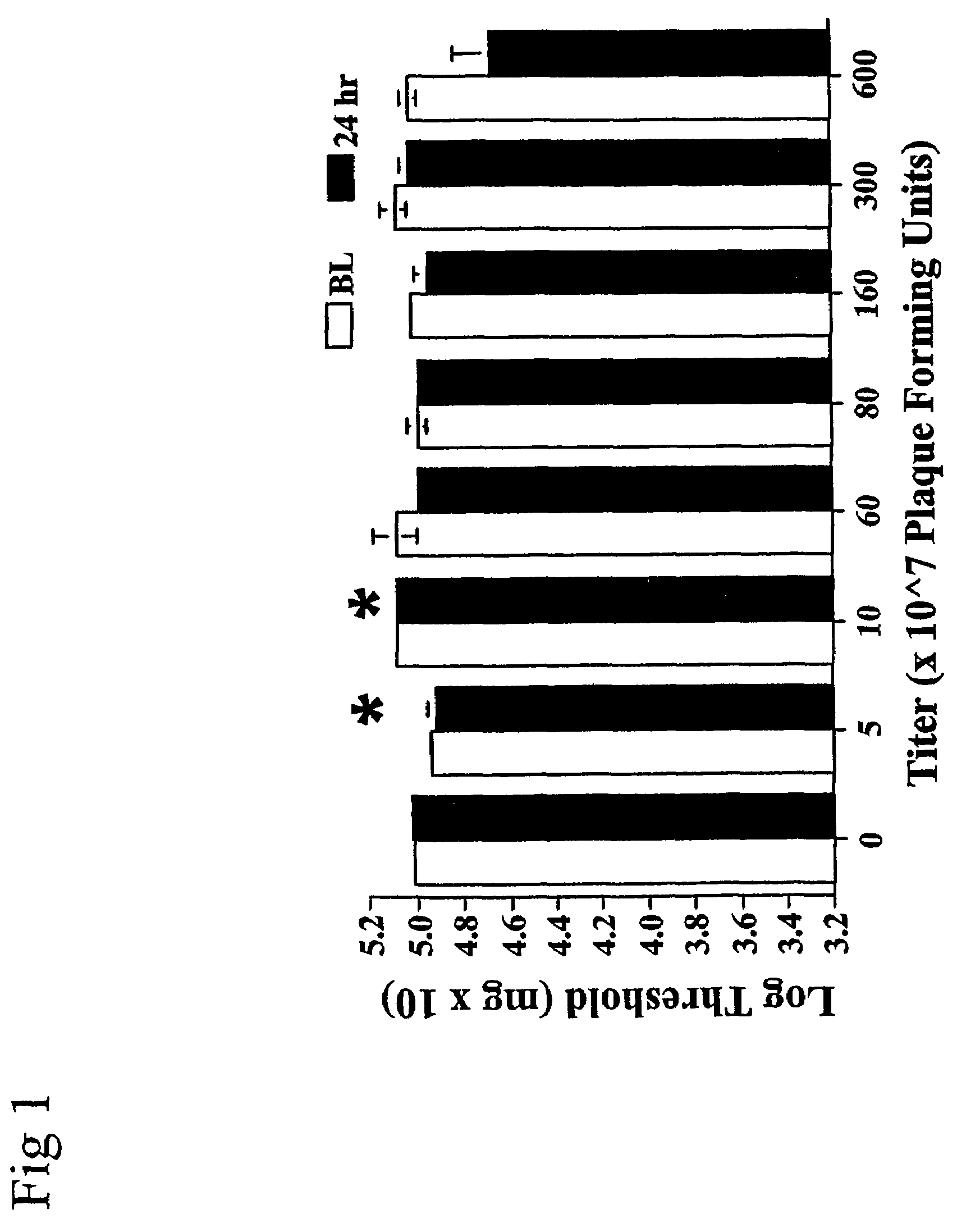
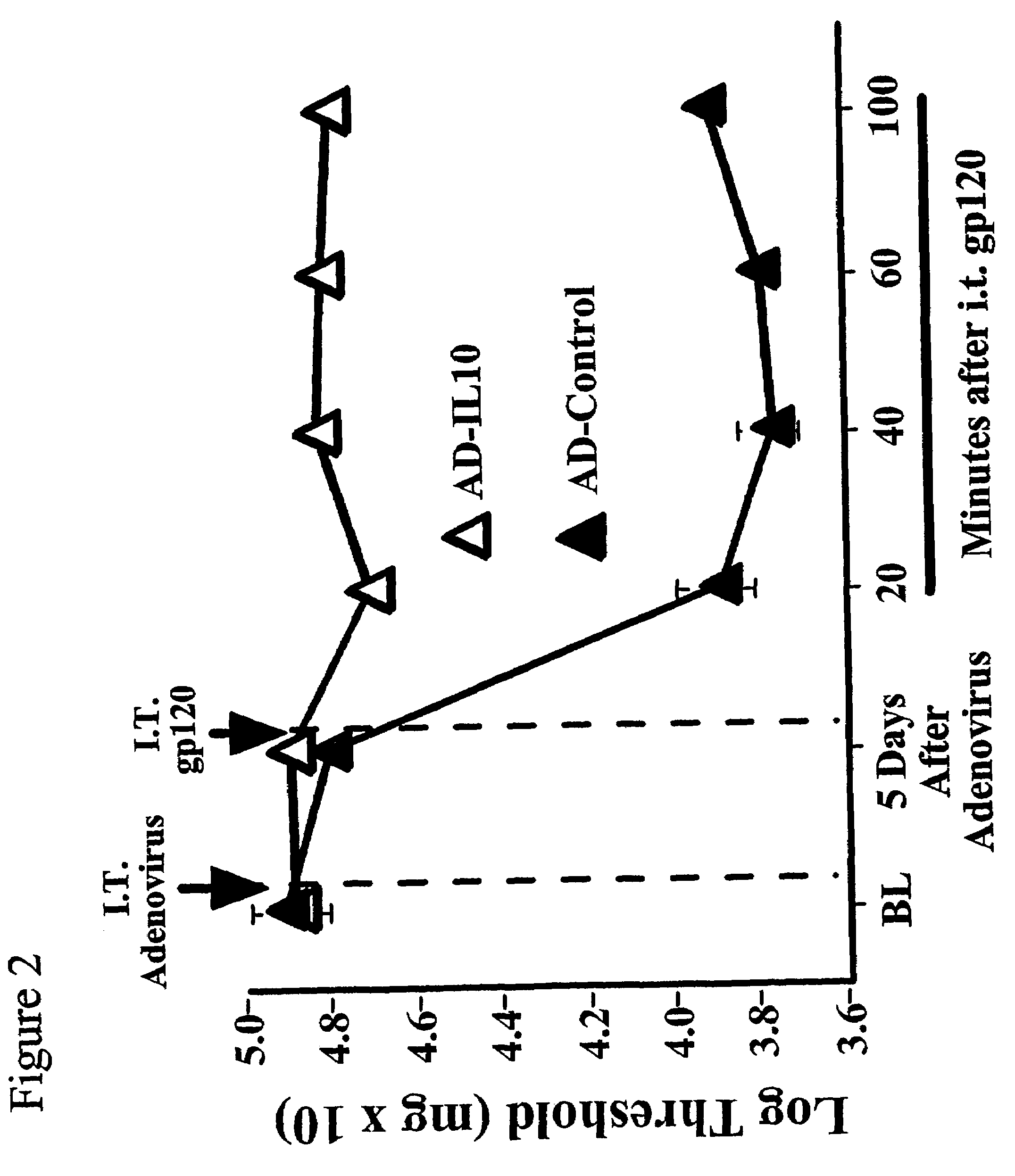
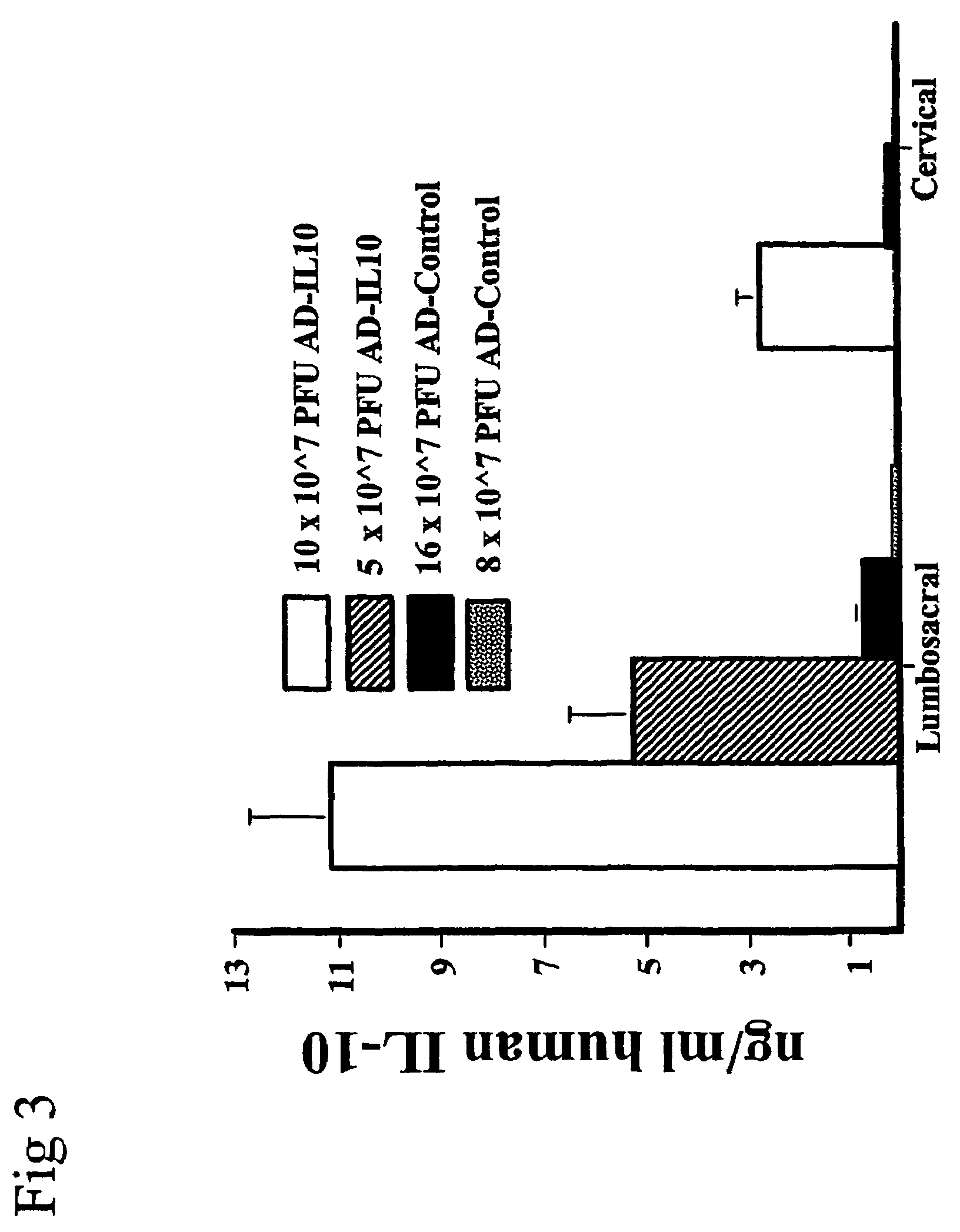
Methods for treating neuropathic pain by administering IL-10 polypeptides
ActiveUS7261882B2Avoid painSuccessful treatmentVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsNervous systemProtein composition
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
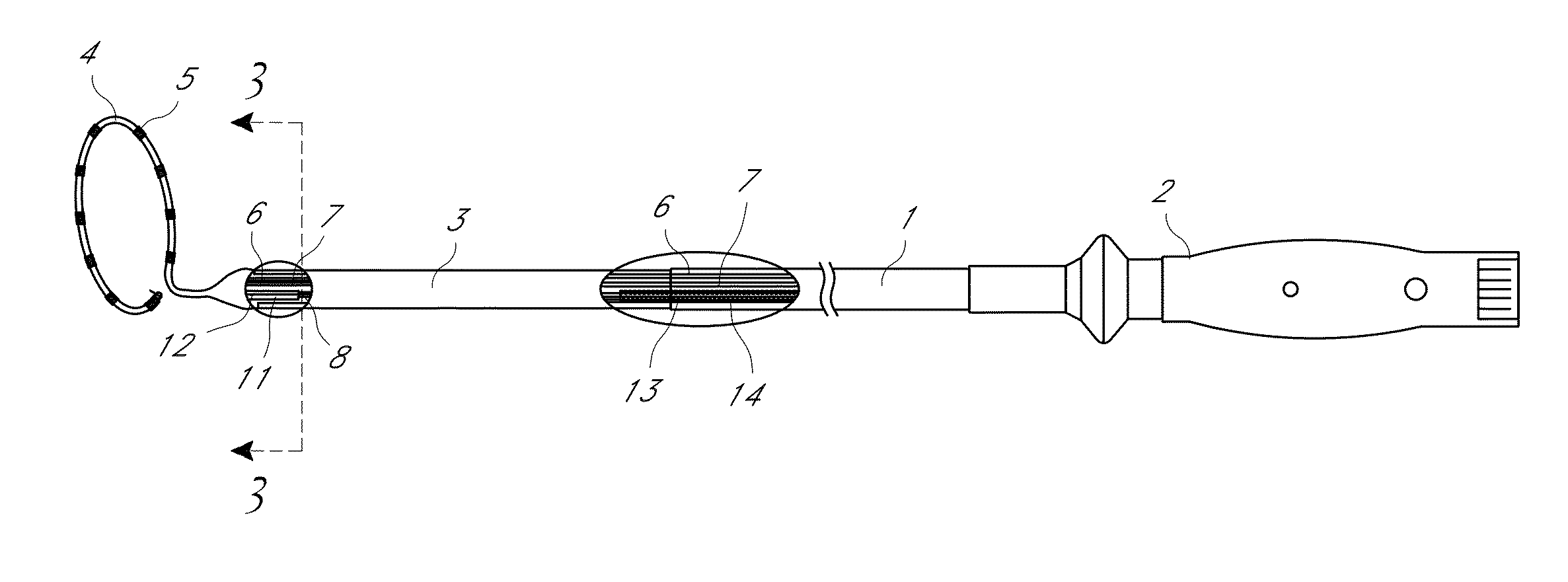
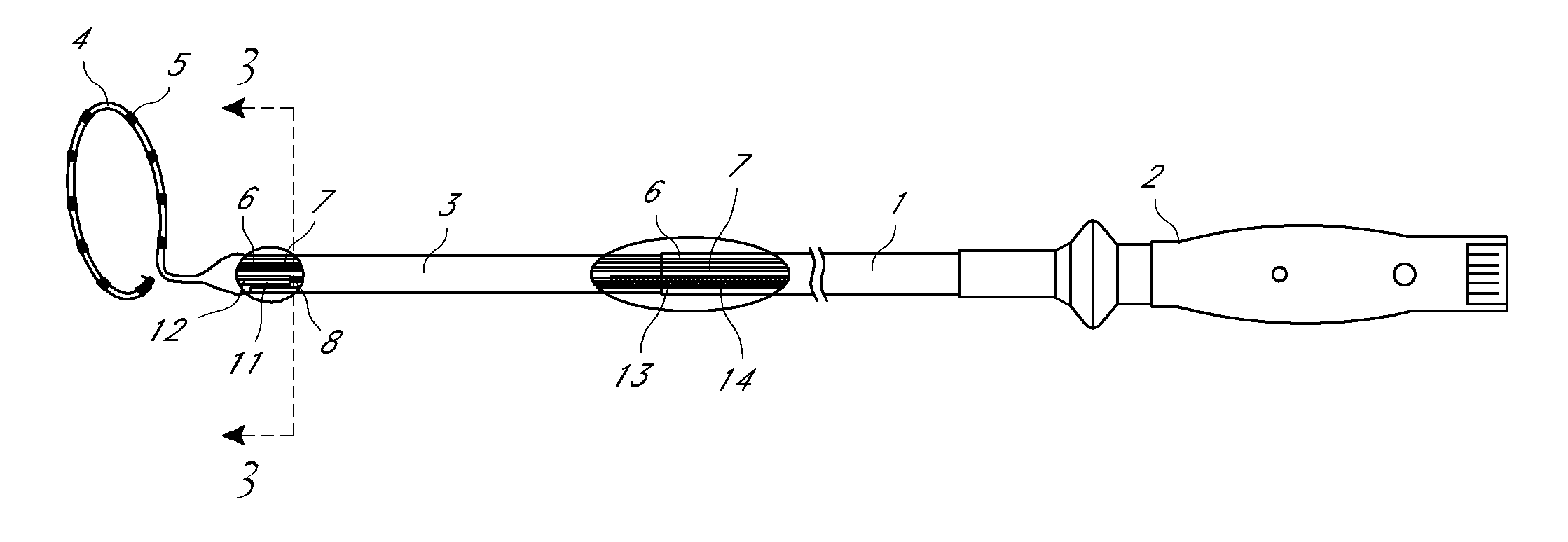
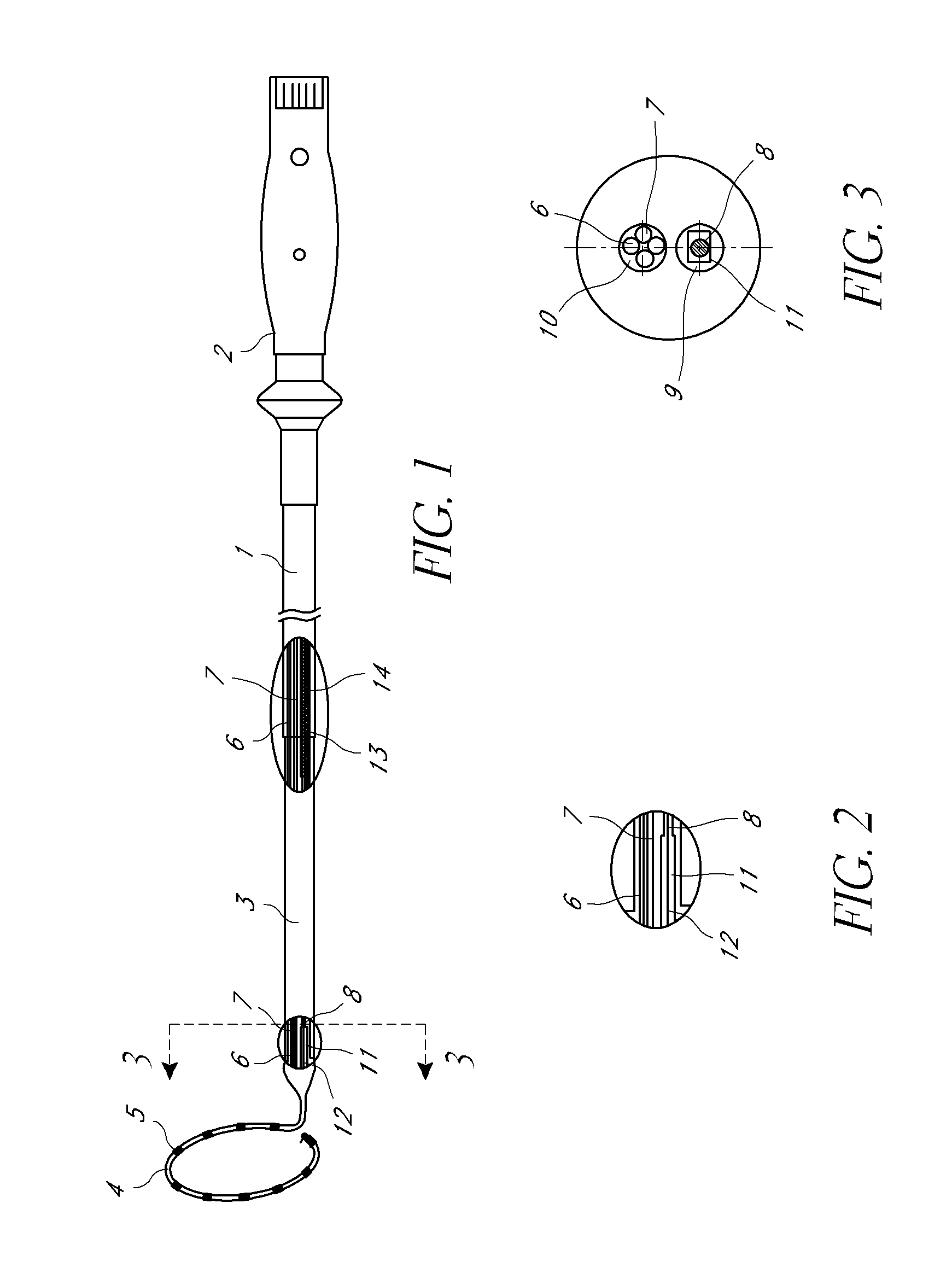
Multi-pole synchronous pulmonary artery radiofrequency ablation catheter
InactiveUS20140180277A1Avoid heating bloodEasy to operateUltrasound therapyInternal electrodesOperative timeLung
A multi-pole synchronous pulmonary artery radiofrequency ablation catheter, wherein an adjustment apparatus is arranged on a control handle; a catheter body is hollow, and a cavity is arranged therein; a lead wire, a temperature sensing wire and a pull wire are arranged in the cavity; one end of the catheter body is flexible, and the flexible end is connected to an annular ring; the annular ring is provided with an electrode group with each electrode connected to the lead wire and temperature sensing wire; the lead wire and temperature sensing wire go through the catheter body and are electrically connected to the control handle. The device uses cold saline perfusion method to protect the vascular intima and possesses advantages of simple operation, short operation time and controllable precise ablation. The device can be used to treat pulmonary hypertension with pulmonary denervation.
Owner:PULNOVO MEDICAL WUXI
Microfluidic systems and methods for transport and lysis of cells and analysis of cell lysate
InactiveUS7419575B2Improve throughputConsiderable utilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSludge treatmentCellular componentLysis
Microfluidic systems and methods are disclosed which are adapted to transport and lyse cellular components of a test sample for analysis. The disclosed microfluidic systems and methods, which employ an electric field to rupture the cell membrane, cause unusually rapid lysis, thereby minimizing continued cellular activity and resulting in greater accuracy of analysis of cell processes.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
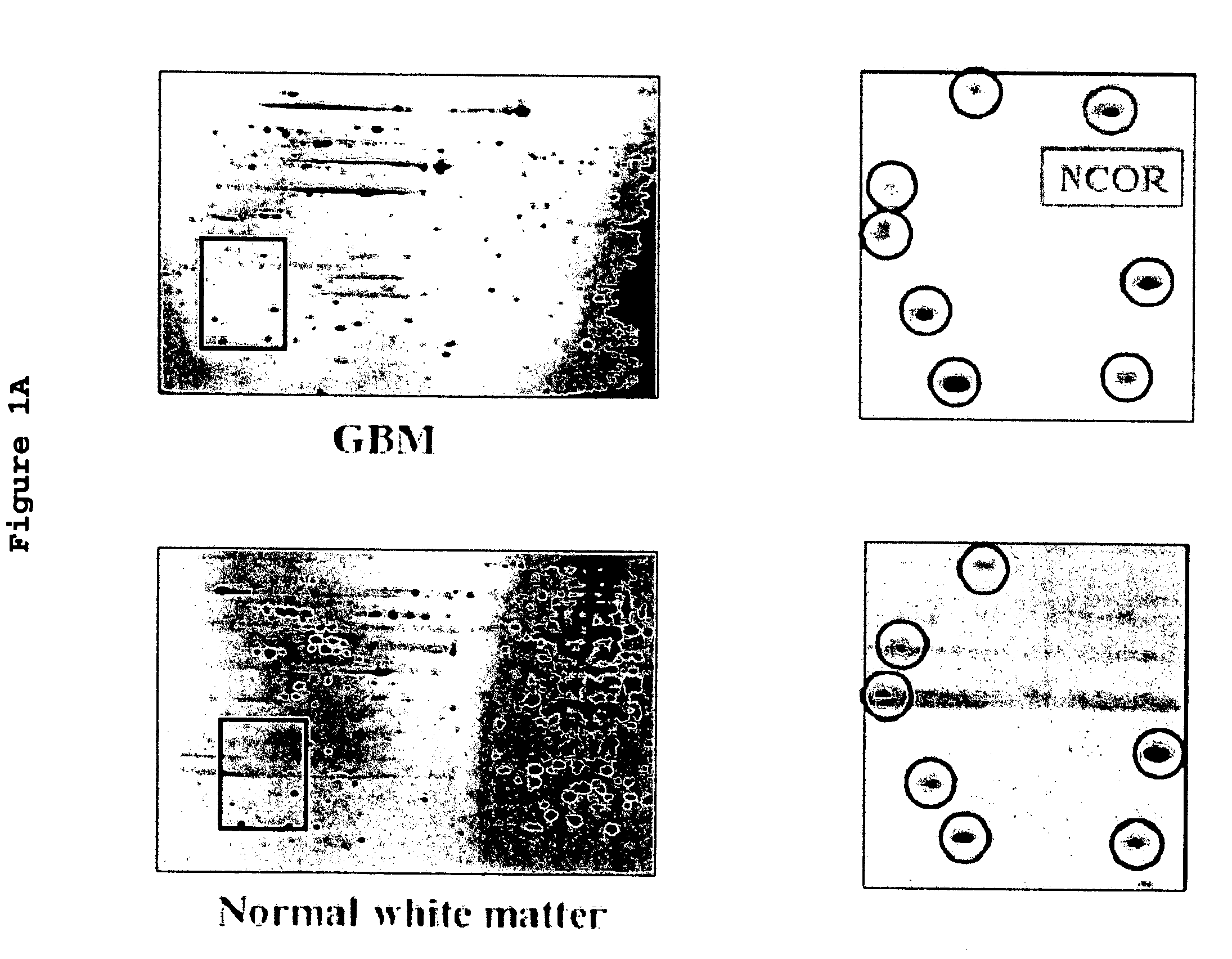
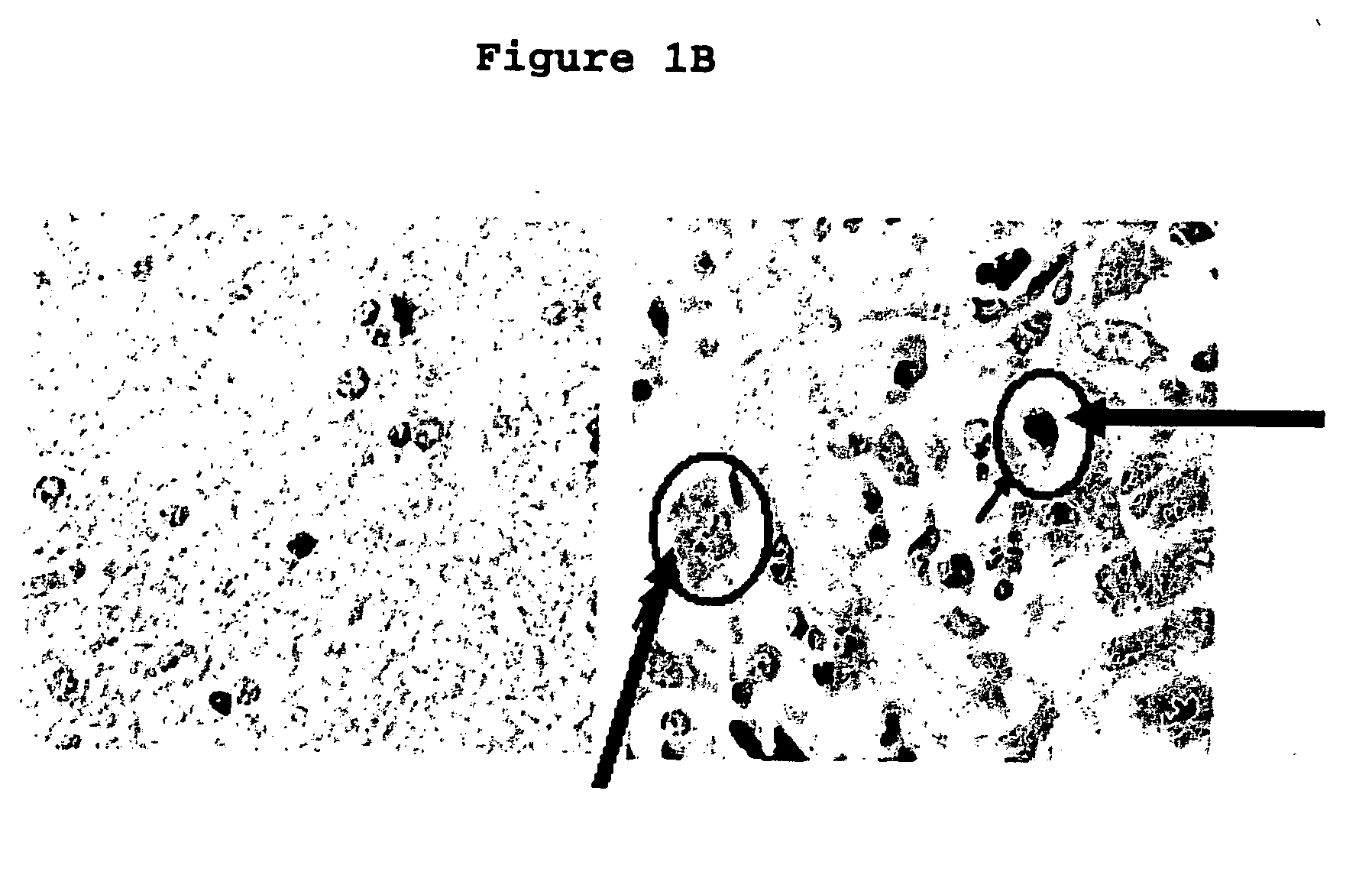
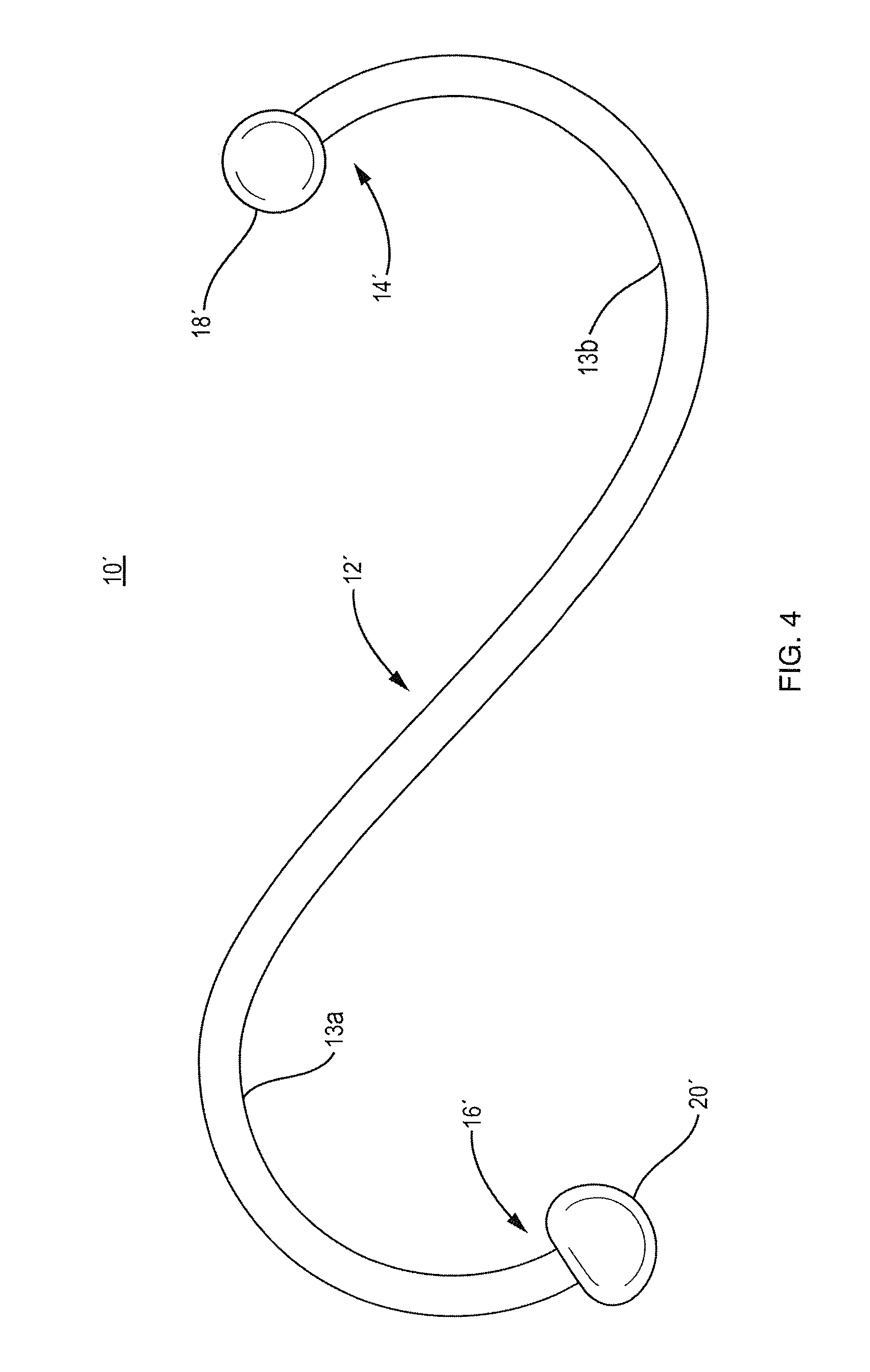
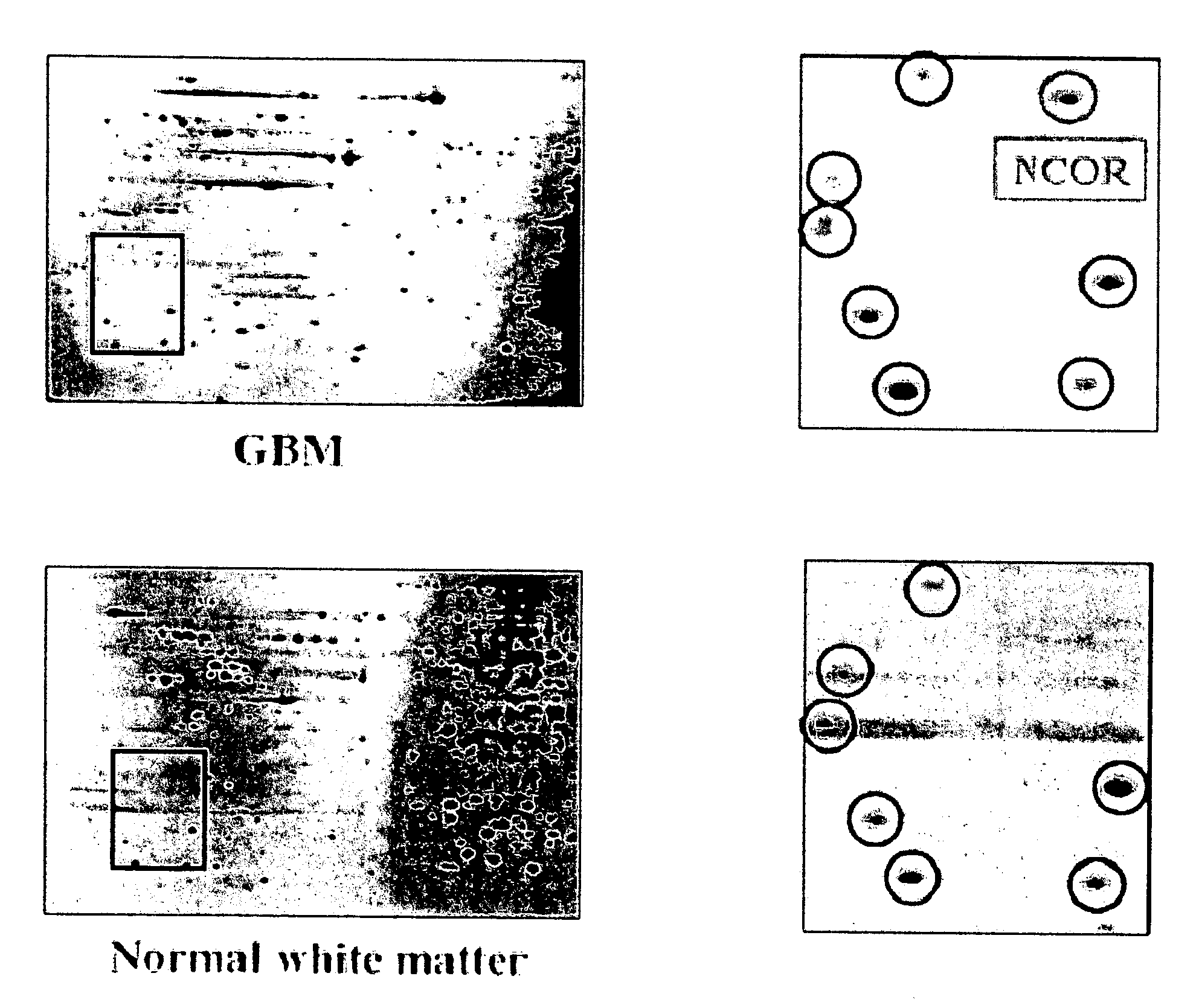
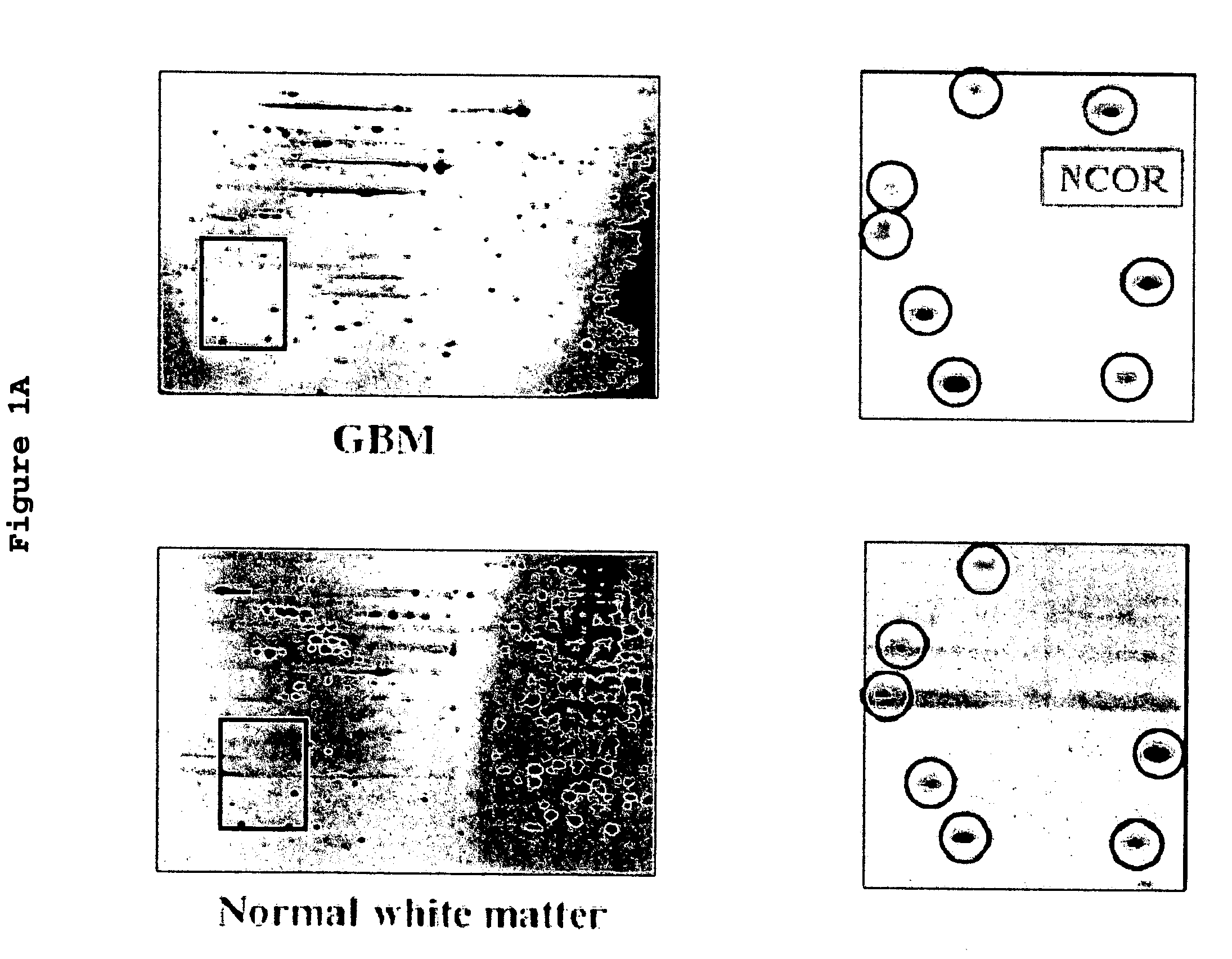
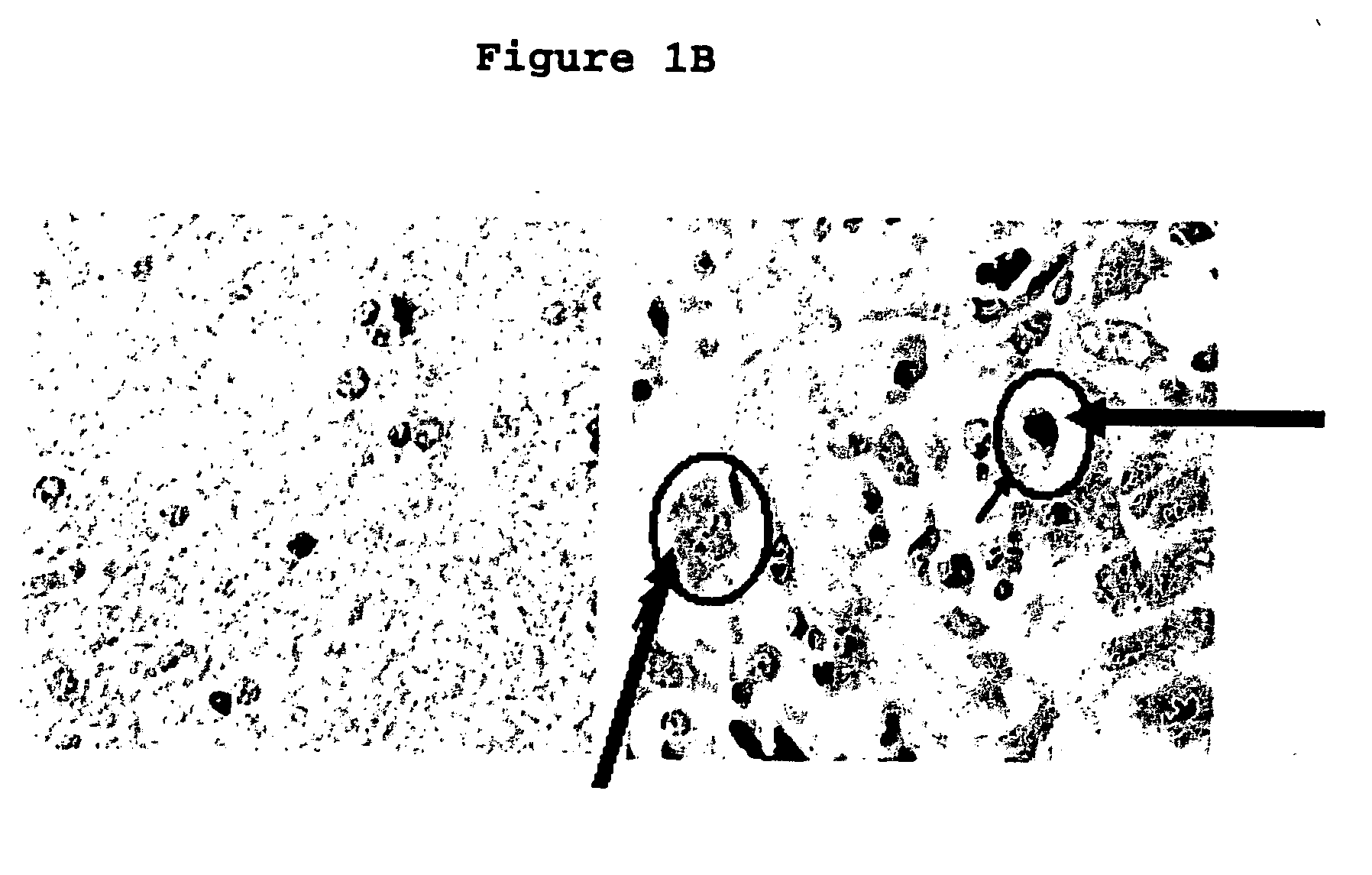
Use of phosphatases to treat tumors overexpressing N-CoR
InactiveUS20090018142A9Great likelihoodSuccessful treatmentOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthRetinoid receptor
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Apparatus and method for treating myofascial trigger points
InactiveUS20120271345A1High pressureConvenient treatmentDevices for pressing relfex pointsSurgeryMassageSkeletal muscle
A device and method for the application of pressure to a location where muscle pain exists, including at a trigger point. The device and method provide gradual, uniform and systematic progression of pressure and release. The device and method enable the application of pressure in a manner that allows a patient to tolerate the pressure without tensing the relevant muscles and / or causing the locus of pain to become hyperirritable and painful. The device and method also enable the gradual selectable increase in that applied pressure while still preventing the tense response from the patient so that the optimal or desired amount of focused pressure is tolerated. The device enables progressive deep tissue massage in systematic and progressive steps that enhances the treatment of myofascial trigger points in skeletal muscles and other forms of muscle pain. The device includes a plurality of terminal configurations that differ in hardness and / or dimensions.
Owner:CLIPPER PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL SERVICES
Use of phosphatases to treat tumors overexpressing N-CoR
InactiveUS20080214569A1Great likelihoodSuccessful treatmentOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor growthAbnormal tissue growth
This invention provides a method of treating a patient suffering from a tumor overexpressing N—CoR comprising administering to the patient a phosphatase ligand, alone or in combination with a retinoid receptor ligand, a histone deacetylase ligand, or both, in amounts effective to treat the patient. This invention also provides a method of inhibiting tumor growth in a patient suffering from a tumor overexpressing N—CoR. This invention further provides a method of identifying a compound or a mixture of compounds capable of inducing differentiation of cells of a tumor overexpressing N—CoR. This invention still further provides a method of determining the likelihood of successfully treating a subject suffering from a tumor overexpressing N—CoR. This invention also provides a method of assessing the likelihood that a patient is suffering from a tumor overexpressing N—CoR. This invention yet also provides a method of assessing the likelihood that a patient previously suffering from and treated for a tumor overexpressing N—CoR has suffered a recurrence of a tumor overexpressing N—CoR. Finally, this invention provides analogous methods for use on glioblastoma multiforme.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
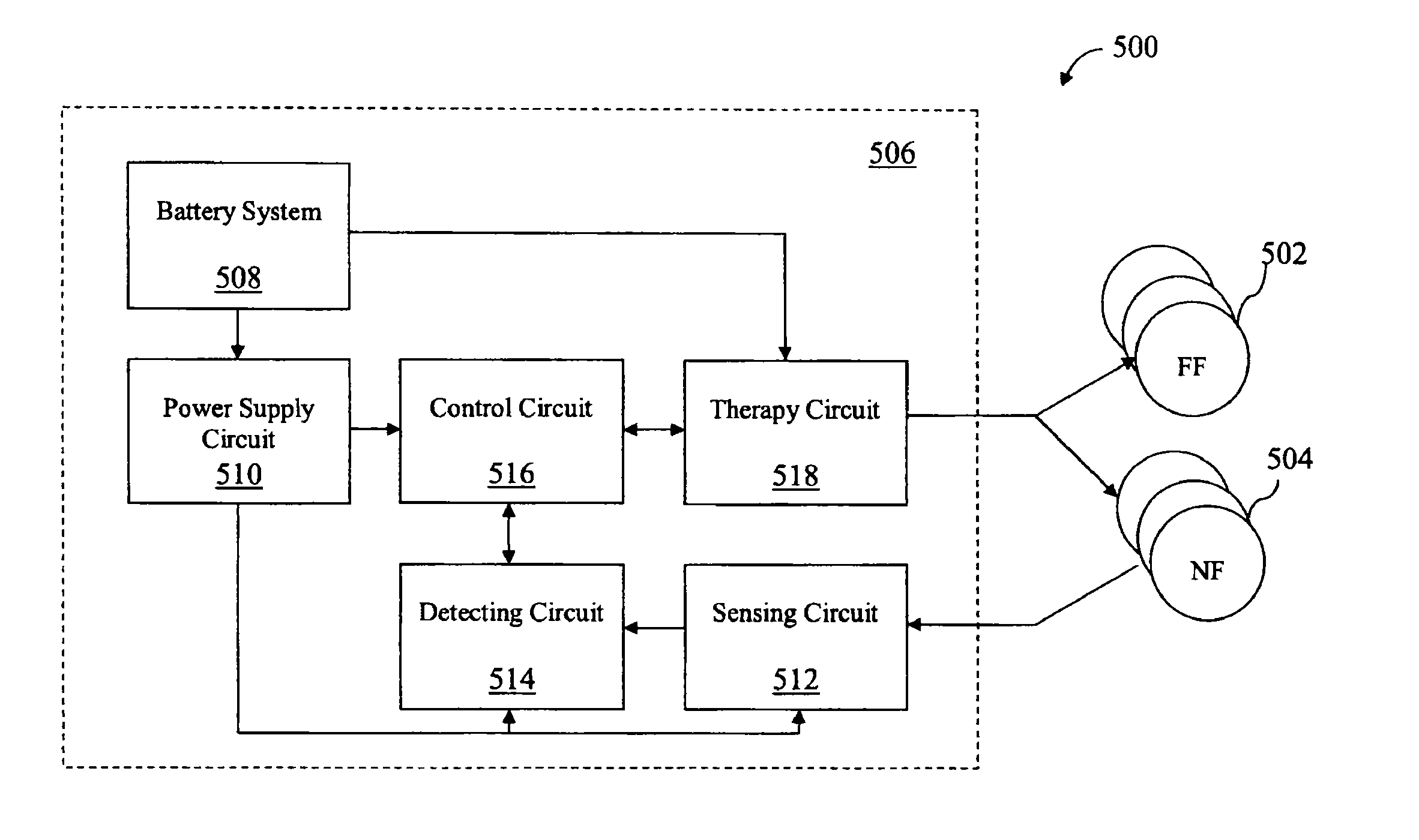
Methods and devices for three-stage ventricular therapy
ActiveUS8874208B2Exceeding pain thresholdSuccessful treatmentHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaProximate
Methods and apparatus for a three-stage ventricular cardioversion and defibrillation therapy that treats ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation at low energy levels. An implantable therapy generator adapted to generate and selectively deliver a three-stage ventricular therapy and at least two leads operably each having at least one electrode adapted to be positioned proximate the ventricle of the patient. The device is programmed to deliver a three-stage therapy via both a far-field configuration and a near-field configuration of the electrodes upon detection of a ventricular arrhythmia. The three-stage therapy includes a first stage for unpinning of one or more singularities associated with the ventricular arrhythmia, a second stage for anti-repinning of the one or more singularities, both of which are delivered via the far-field configuration of the electrodes, and a third stage for extinguishing of the one or more singularities associated delivered via the near-field configuration of the electrodes.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
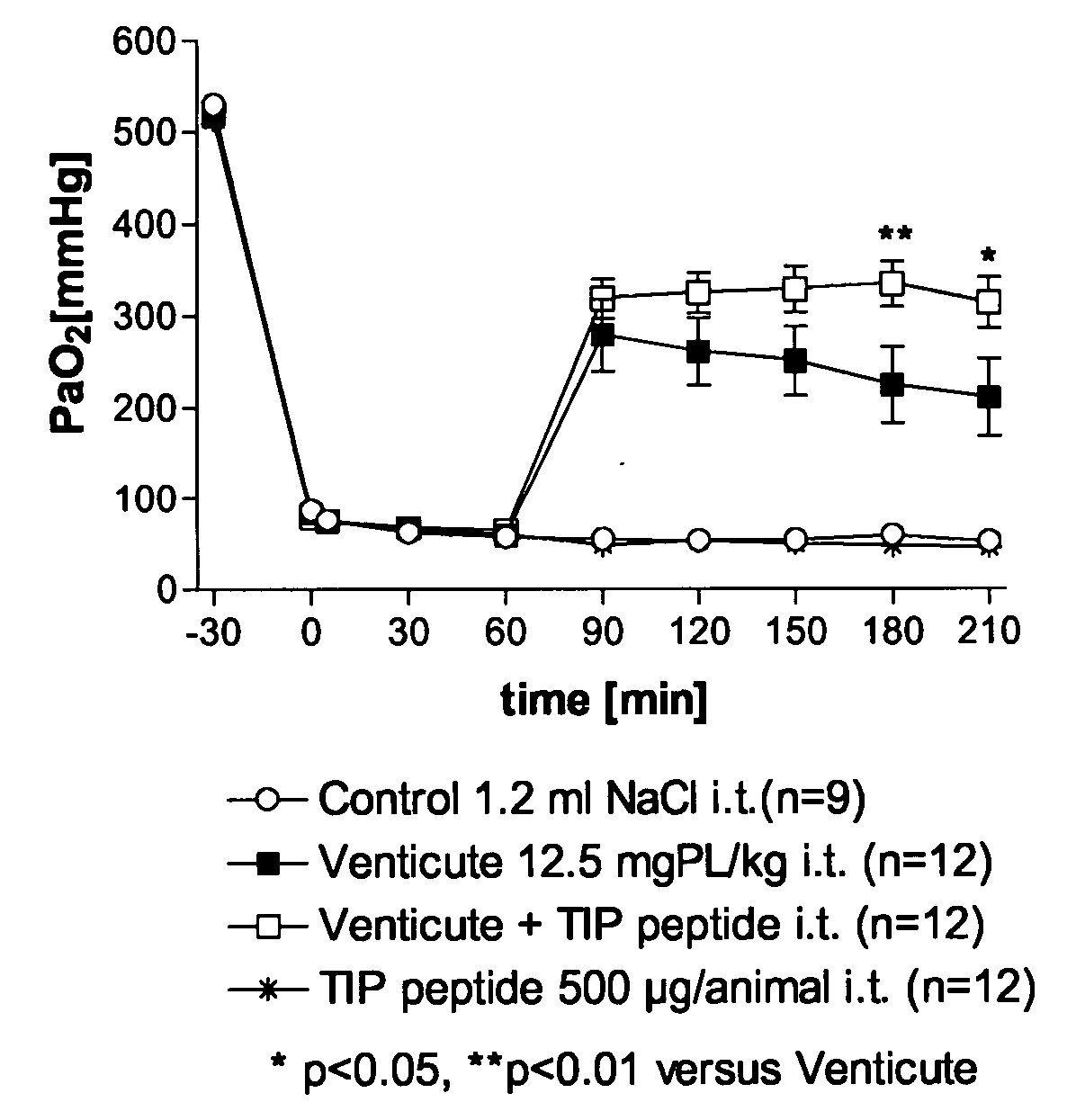
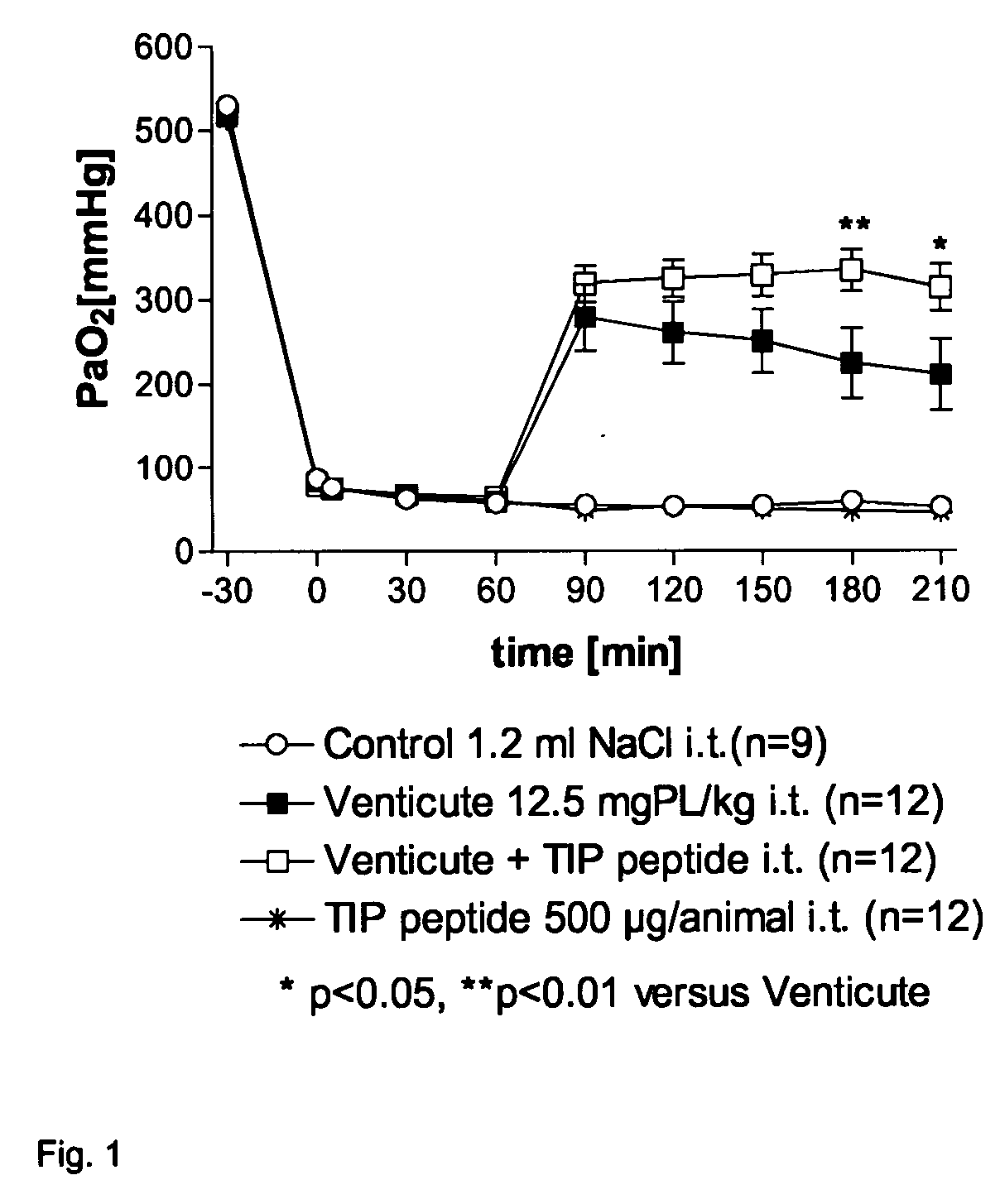
Composition Comprising a Pulmonary Surfactant and a Tnf-Derived Peptide
InactiveUS20070299003A1Convenient treatmentPatient compliance is goodPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCyclic peptide ingredientsDiseaseDecreased surfactant
The invention relates to the combination of a pulmonary surfactant and a TNF-derived peptide and its use for the treatment of respiratory disease.
Owner:TAKEDA GMBH
Pulmonary artery ablation catheter
InactiveUS20150057599A1Successful treatmentReduce pressureUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyBlood vesselOperative time
A multi-pole synchronous pulmonary artery radiofrequency ablation catheter, wherein an adjustment apparatus is arranged on a control handle; a catheter body is hollow, and a cavity is arranged therein; a lead wire, a temperature sensing wire and a pull wire are arranged in the cavity; one end of the catheter body is flexible, and the flexible end is connected to an annular ring; the other end of the catheter body is connected to the control handle; one end of the pull wire is connected to the flexible end, and the other end of the pull wire is connected to the adjustment apparatus on the control handle, the tension of the pull wire is adjusted through the adjustment apparatus to achieve radian control of the flexible end; a shape memory wire is arranged in the annular ring, one end of the shape memory wire extends to the end of the annular ring and the other end of the shape memory wire passes through the root of the annular ring and is fixed on the flexible end of the catheter body; the annular ring is provided with an electrode group with each electrode connected to the lead wire and temperature sensing wire; the lead wire and temperature sensing wire go through the catheter body and are electrically connected to the control handle. The device uses cold saline perfusion method to protect the vascular intima and possesses advantages of simple operation, short operation time and controllable precise ablation. The device can be used to treat pulmonary hypertension with pulmonary denervation.
Owner:PULNOVO MEDICAL WUXI
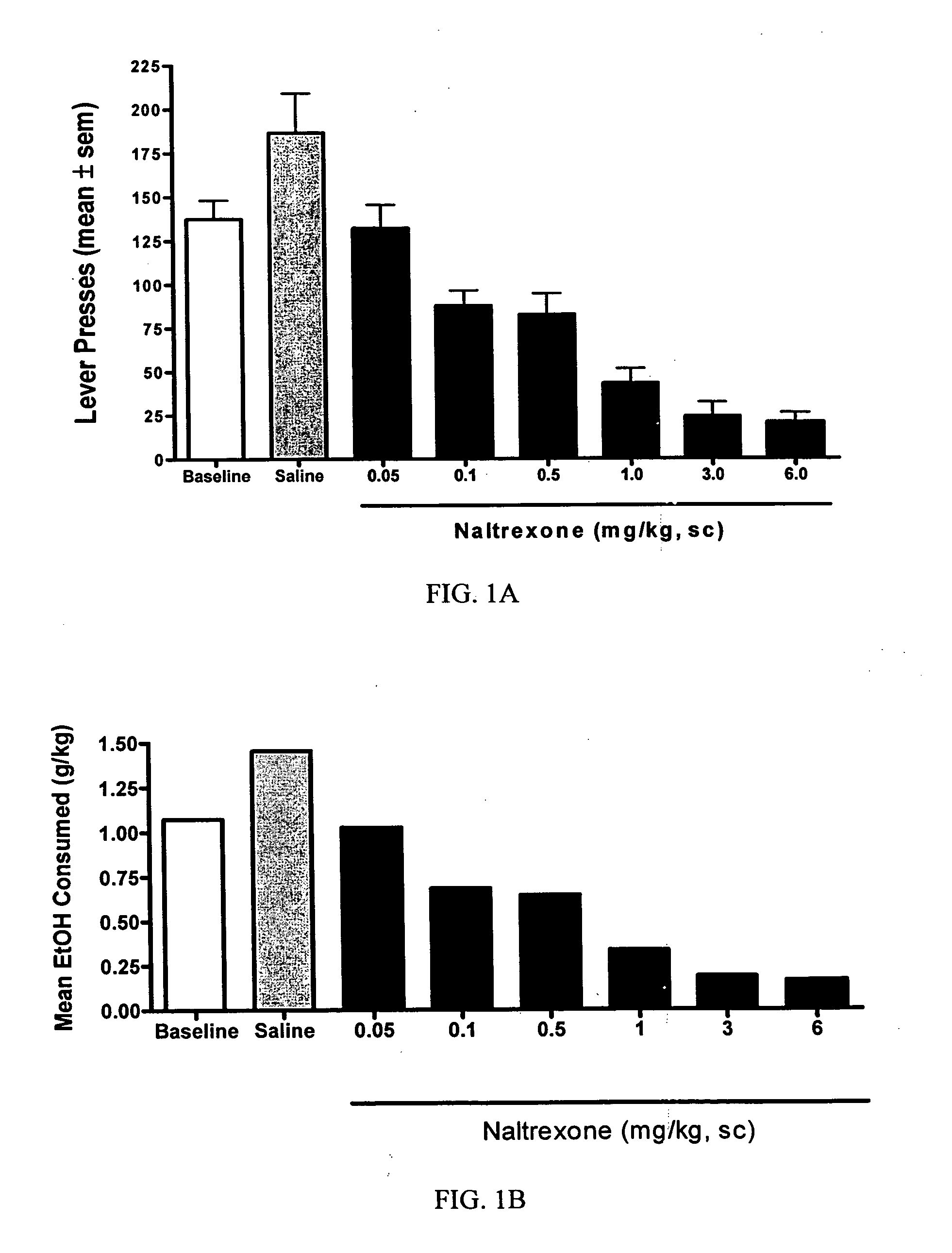
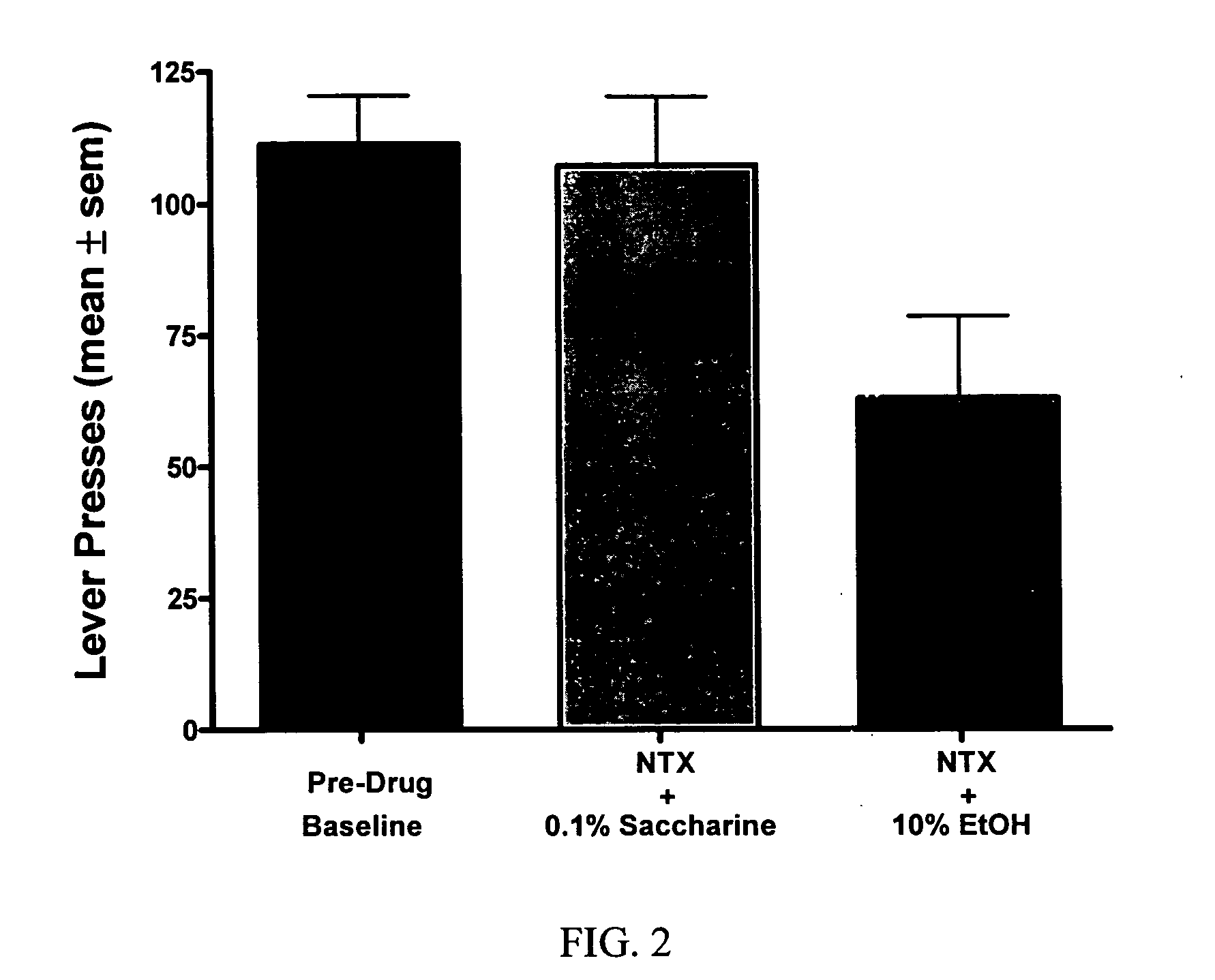
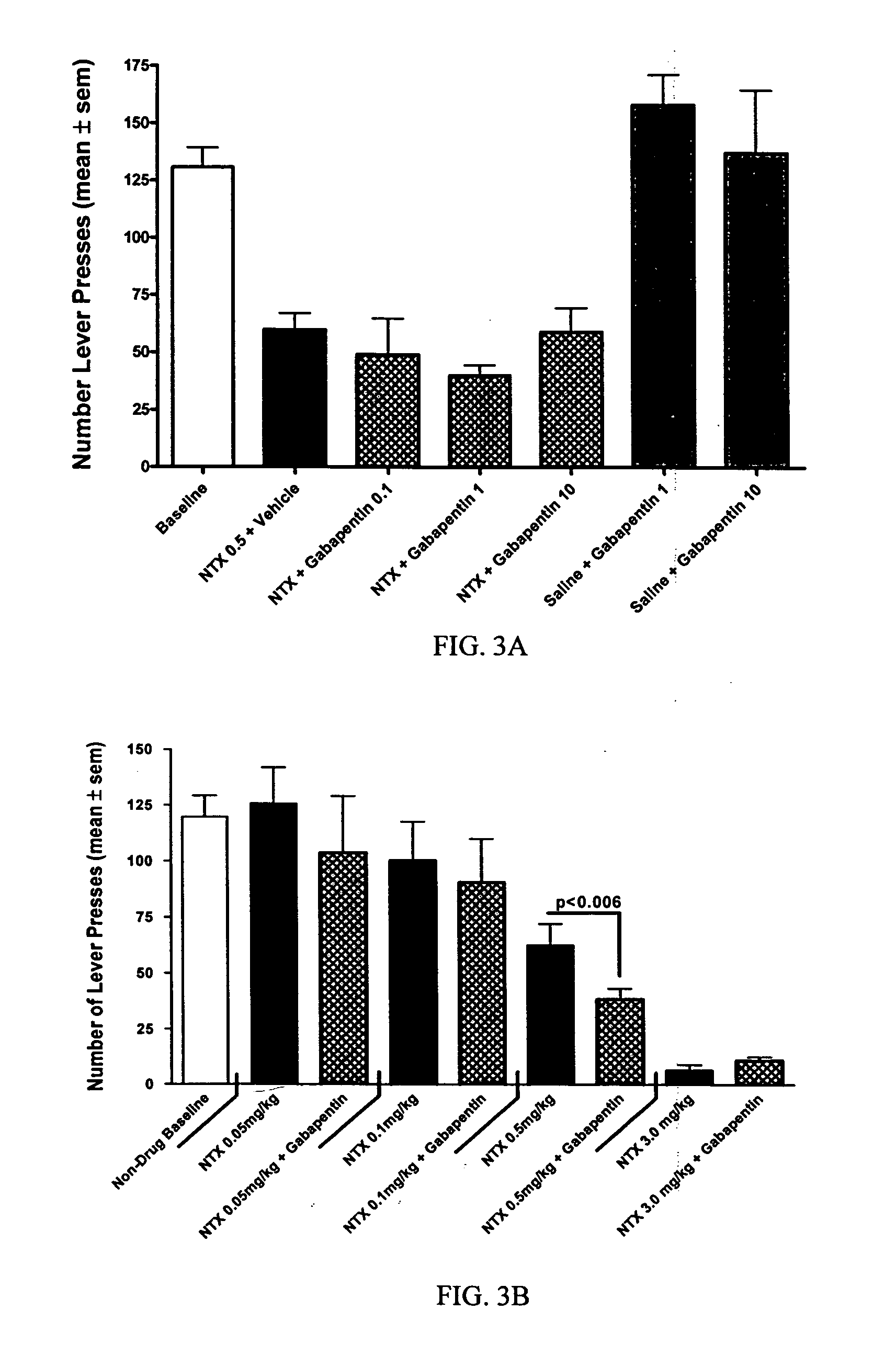
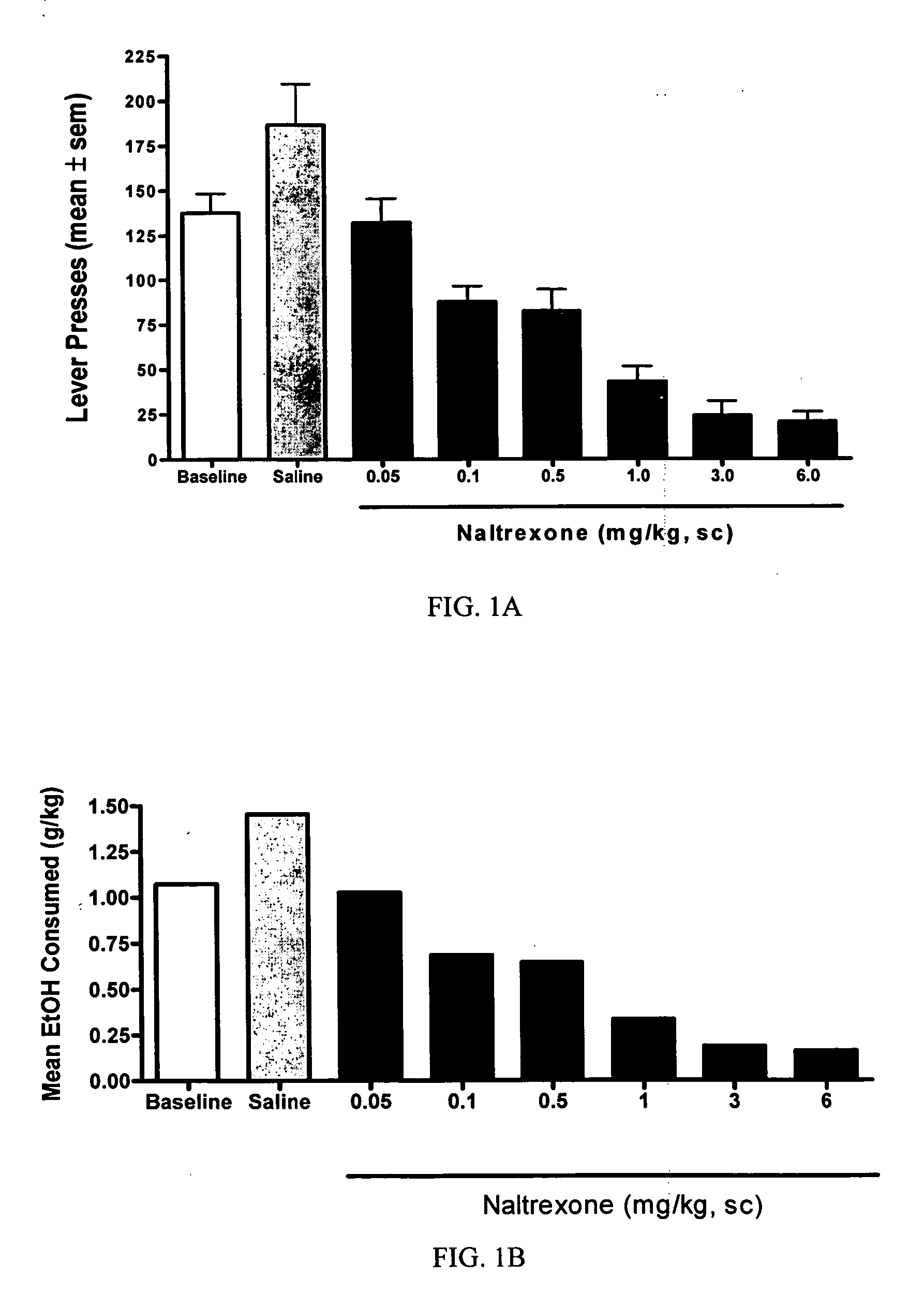
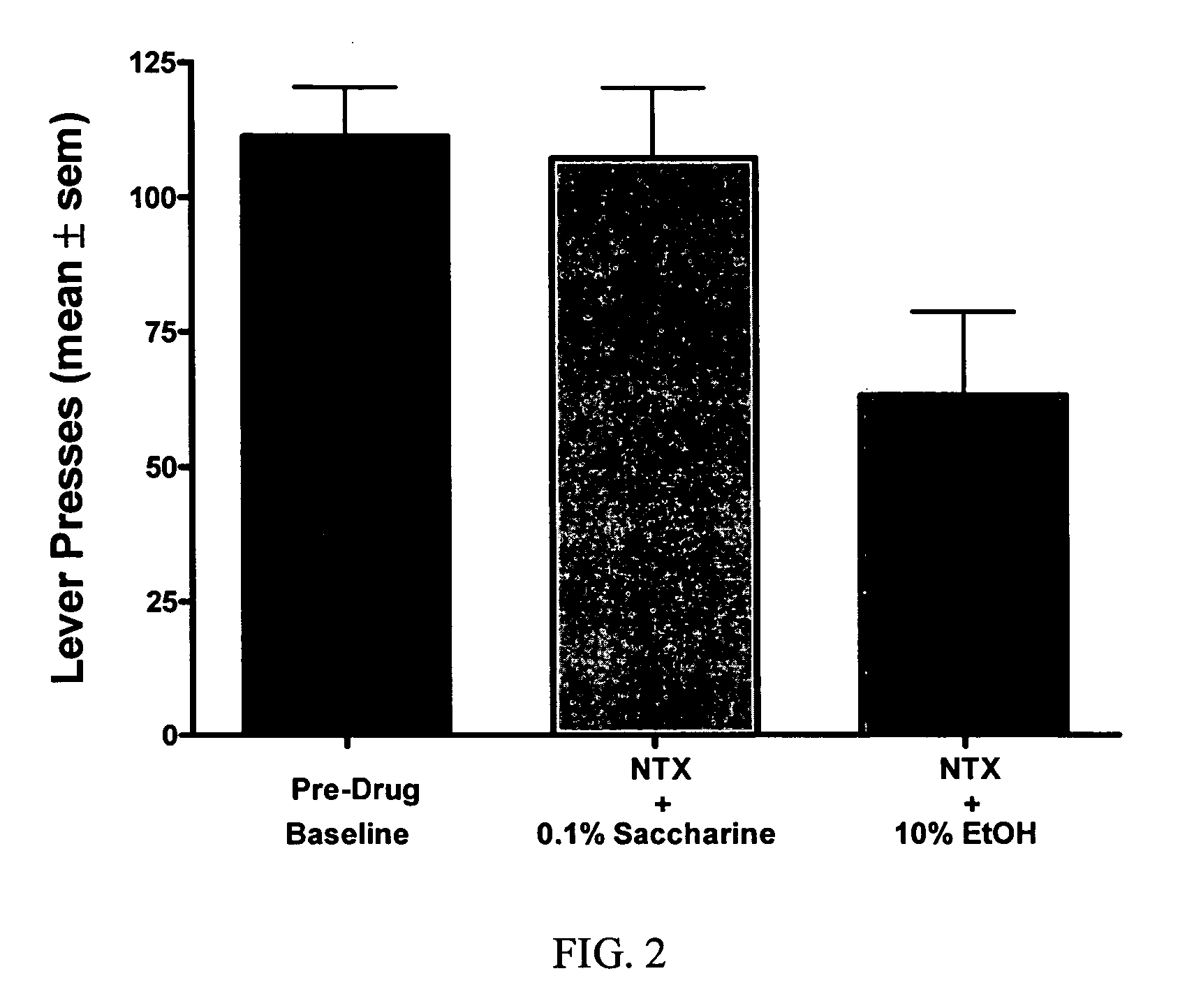
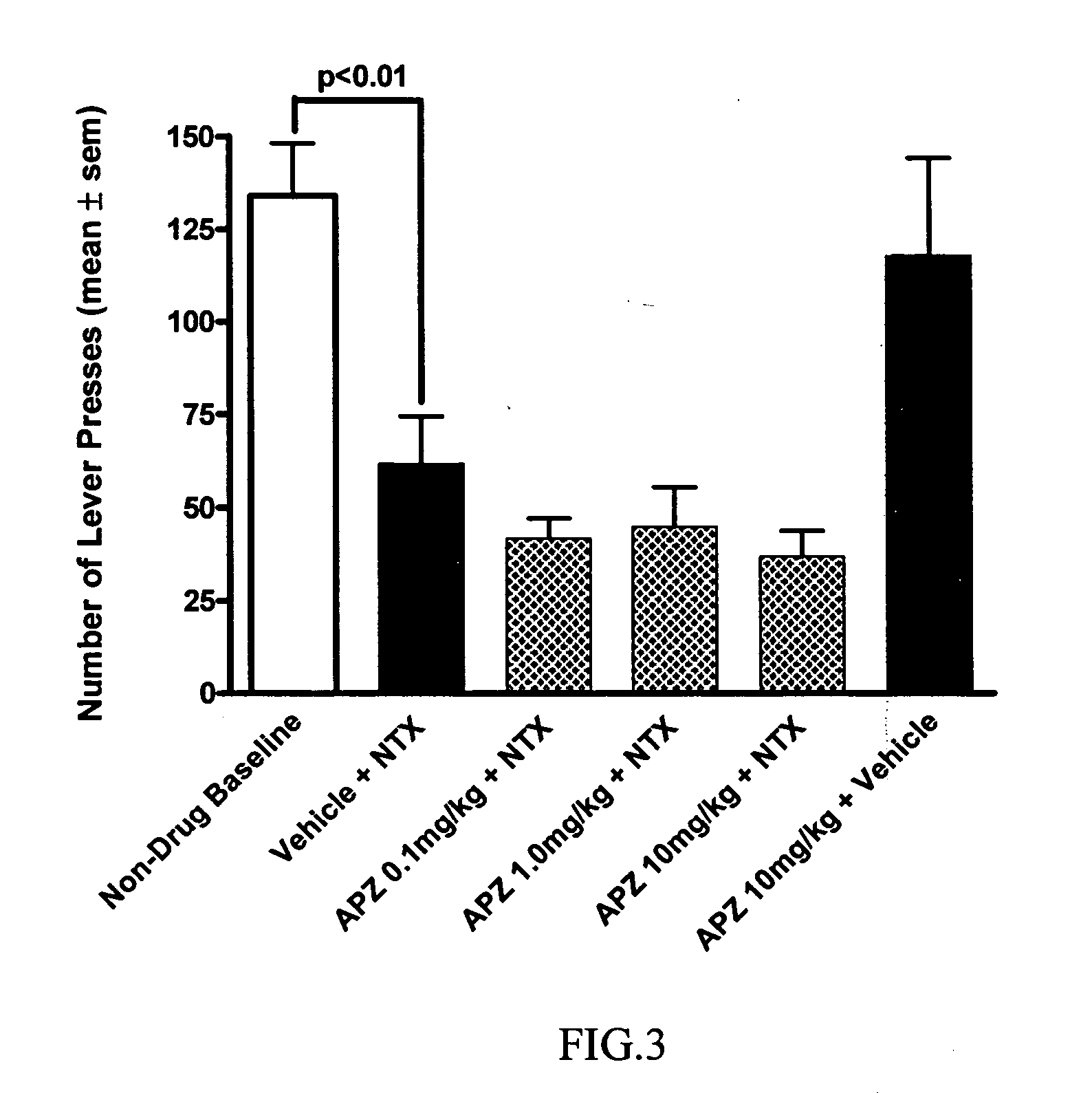
Methods for treating alcoholism
InactiveUS20050245461A1Reduce alcohol-related morbidityReduce consumptionBiocideNervous disorderOpioid antagonistDrug
In the treatment of alcoholism, co-treatment with an active agent capable of offsetting unwanted adverse clinical manifestations to the treatment itself, for example, negative drug adverse clinical manifestations, greatly increases patient compliance. Increasing patient compliance, in turn, creates a better success rate and decreased recidivism or relapse. The current invention combines the use of an opioid antagonist with at least one anticonvulsant for the treatment of alcoholism.
Owner:ALKERMES INC
System and method for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerves to treat low back pain
ActiveUS20080188906A1Reduce and eliminate and disadvantageReduce and eliminate problemSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesProximatePeripheral neuron
According to one embodiment, a system for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerve fibers to treat low back pain is provided. The system includes stimulation electrodes adapted to be implanted in tissue proximate a network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating a painful region of the low back area and to deliver electrical stimulation pulses to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area. The system also includes a stimulation source adapted for implantation into the person's body and operable to generate electrical stimulation pulses for transmission to the electrodes for delivery to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area to relieve pain in the painful region of the low back area.
Owner:BAROLAT GIANCARLO +2
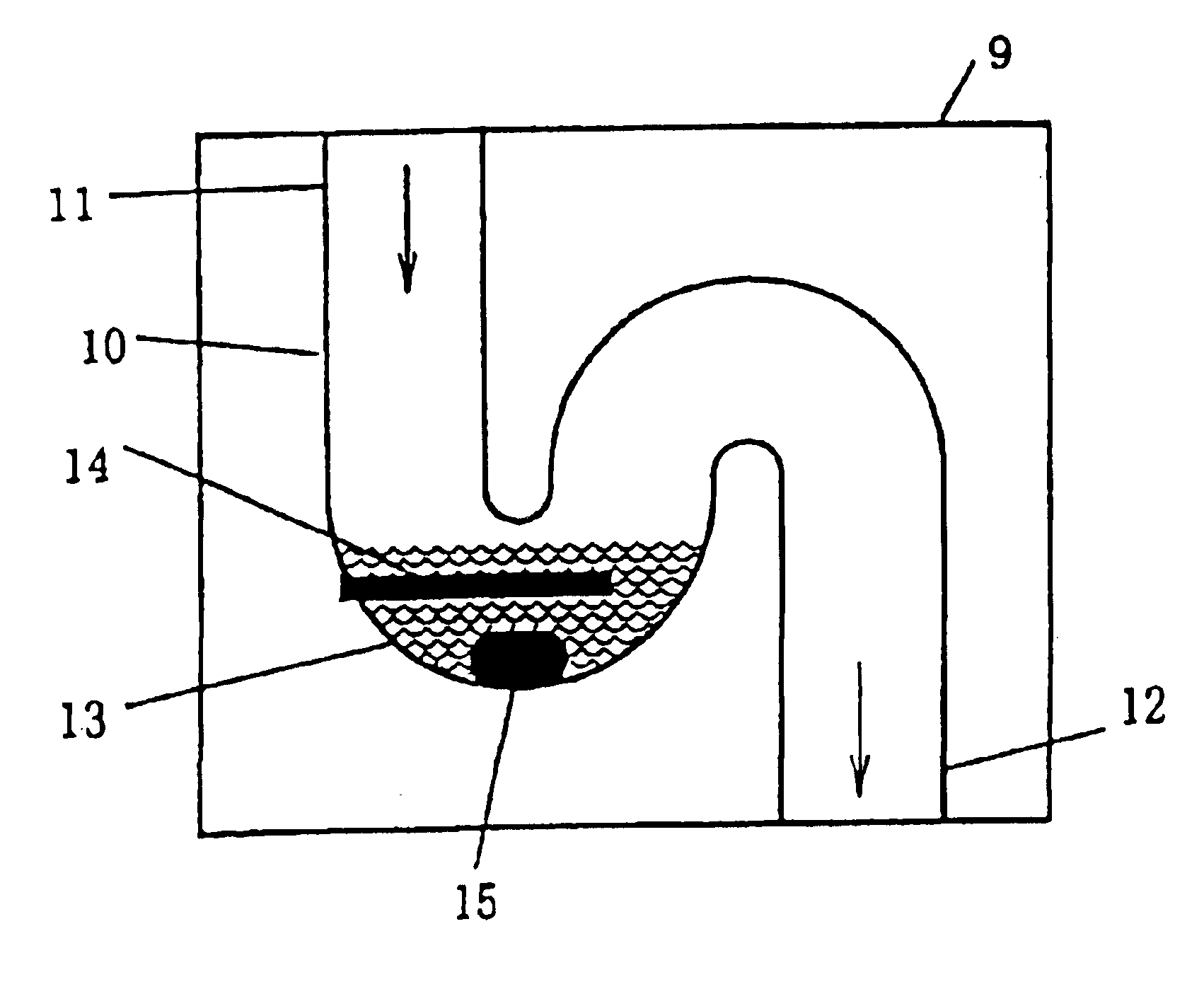
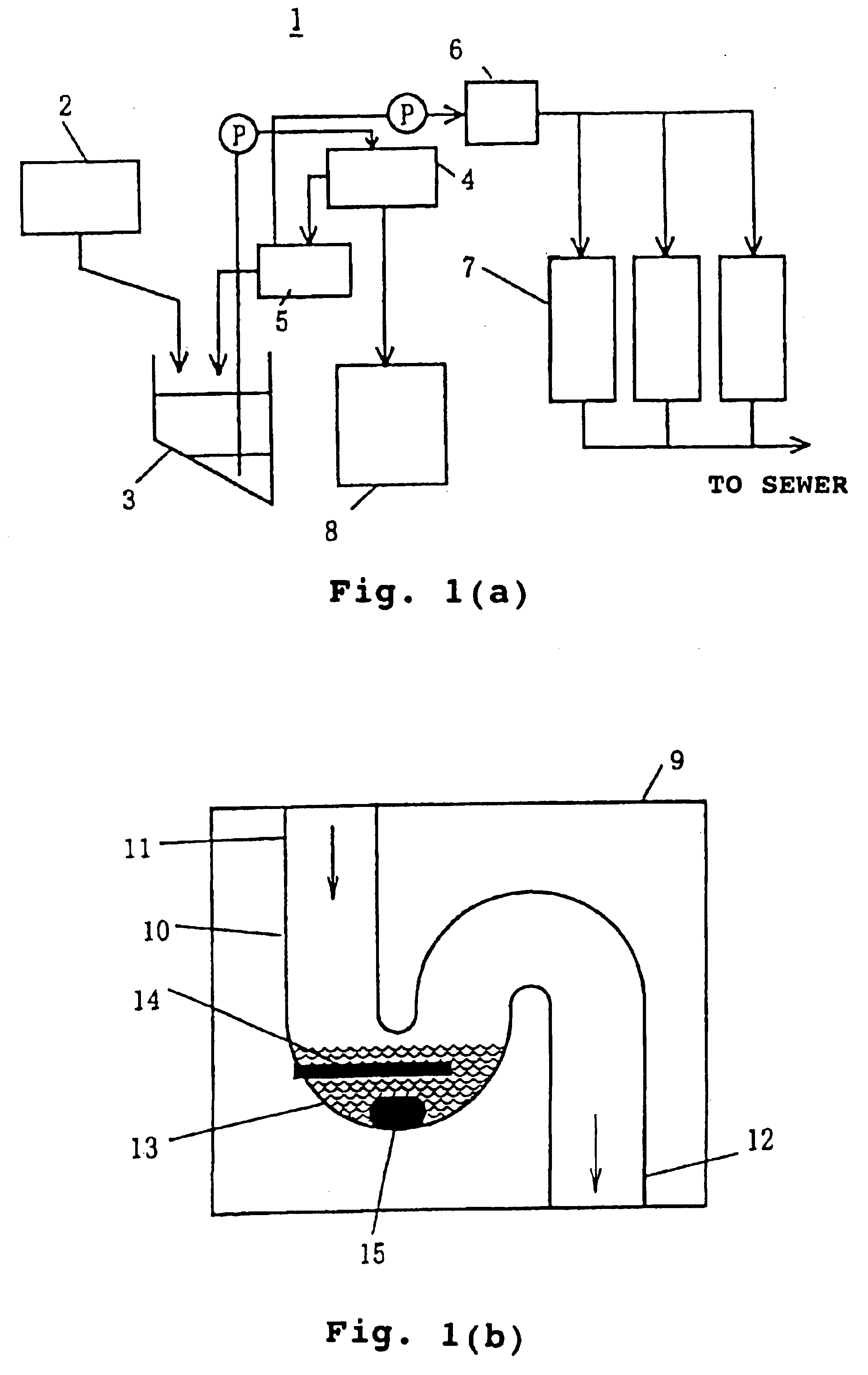
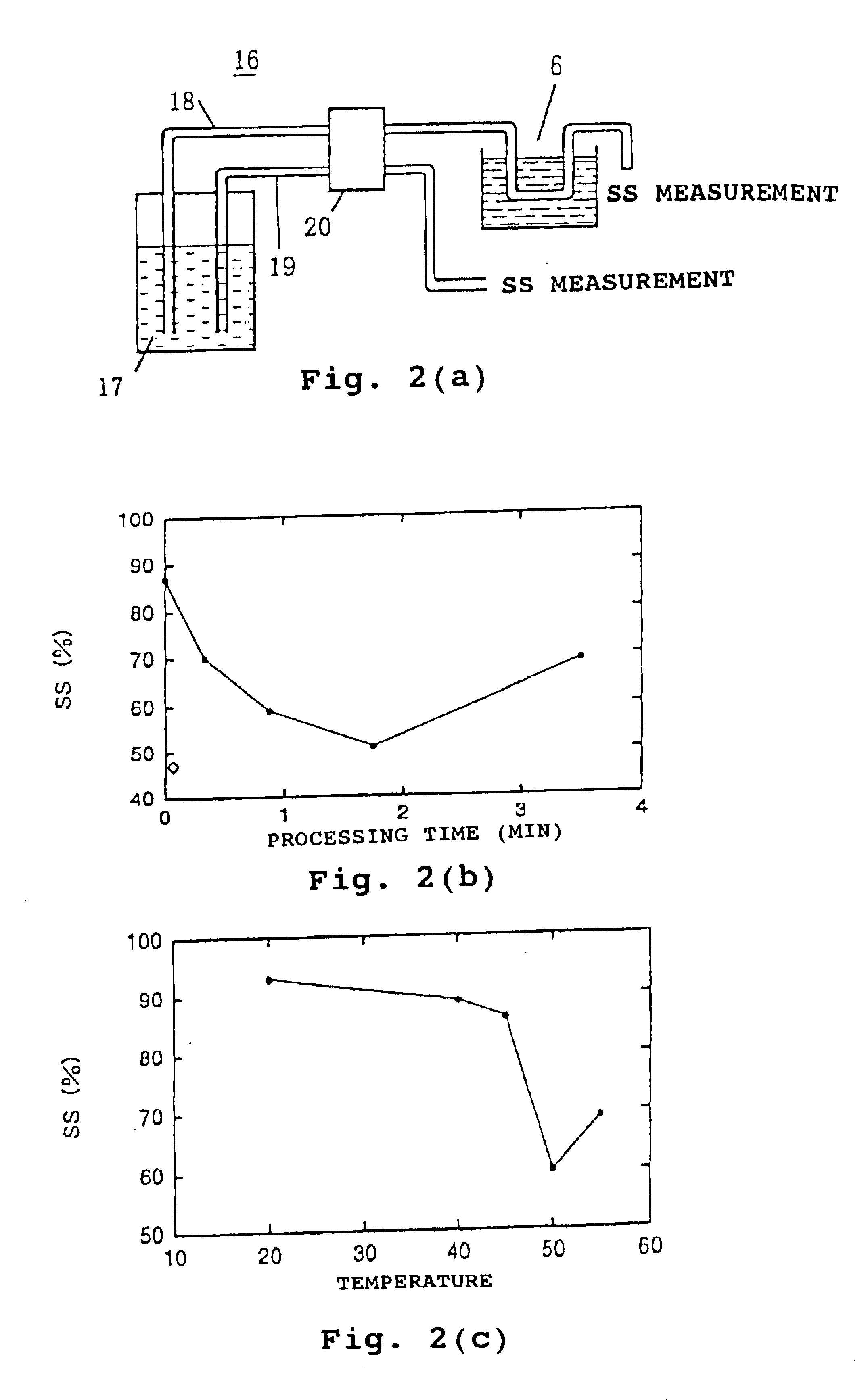
Heated ultrasonic treating device and treating method for suspended matter-containing liquid
InactiveUS6866780B2Avoid cloggingReduce SS (suspended solids)Liquid degasificationTreatment using aerobic processesEngineeringSuspended matter
A heated ultrasonic treating device (6) comprising a sump (13) through which suspended matter-containing liquid passes, a temperature-controllable heater (14) disposes in the sump (13), and a ultrasonic vibrator (15) disposed in the sump (13). The heated ultrasonic treating device (6) uses the ultrasonic vibrator (15) to apply ultrasonic waves while heating organic drain passing the sump (13) with the heater (14), thereby pulverizing suspended matters and reducing the amount of SS. In addition, a treating column, where pulverized suspended matter-containing liquid is aerobically treated by aerobic microorganisms, is prevented from efficiency lowering due to clogging.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Methods for treating alcoholism
InactiveUS20050245541A1Reduce consumptionReduce morbidityBiocideNervous disorderOpioid antagonistAlcoholisms
In the treatment of alcoholism, co-treatment with an active agent capable of offsetting unwanted adverse clinical manifestations to the treatment itself, for example, negative drug adverse clinical manifestations, greatly increases patient compliance. Increasing patient compliance, in turn, creates a better success rate and decreased recidivism or relapse. The current invention combines the use of an opioid antagonist with at least one dopamine D2 partial agonist for the treatment of alcoholism. Suitable dopamine D2 partial agonists are aripiprazole and (−)3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-n-propylpiperidine [(−)-3PPP].
Owner:ALKERMES INC
Methods for evaluating and treating waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
ActiveUS20160222465A1ResilienceSuccessful treatmentOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMacroglobulinemiaMacroglobulin
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Treatment of neurodegenerative diseases by targeting mirna
ActiveUS20130184331A1Successful treatmentIncrease of regenerationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDrugSynapse
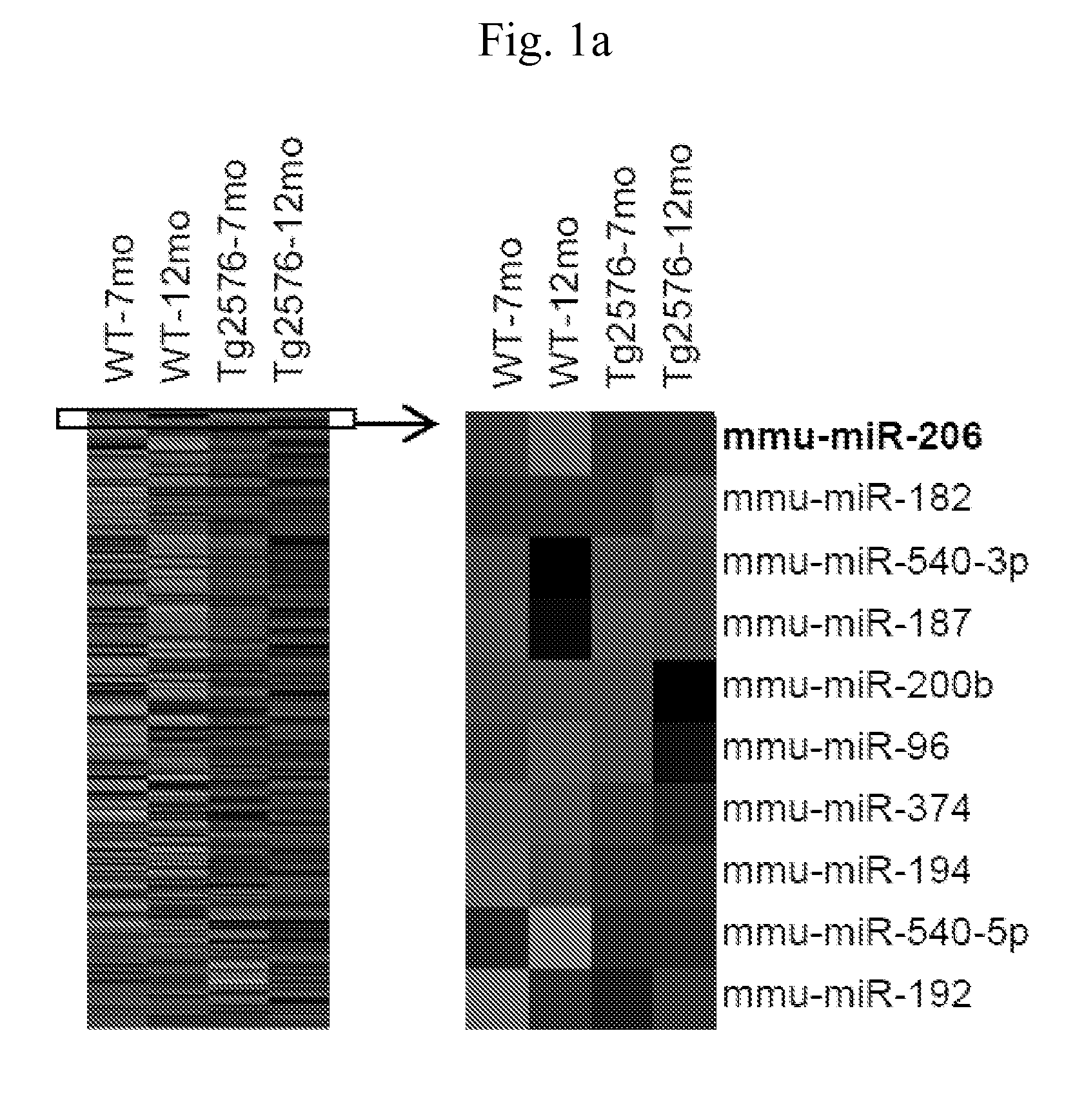
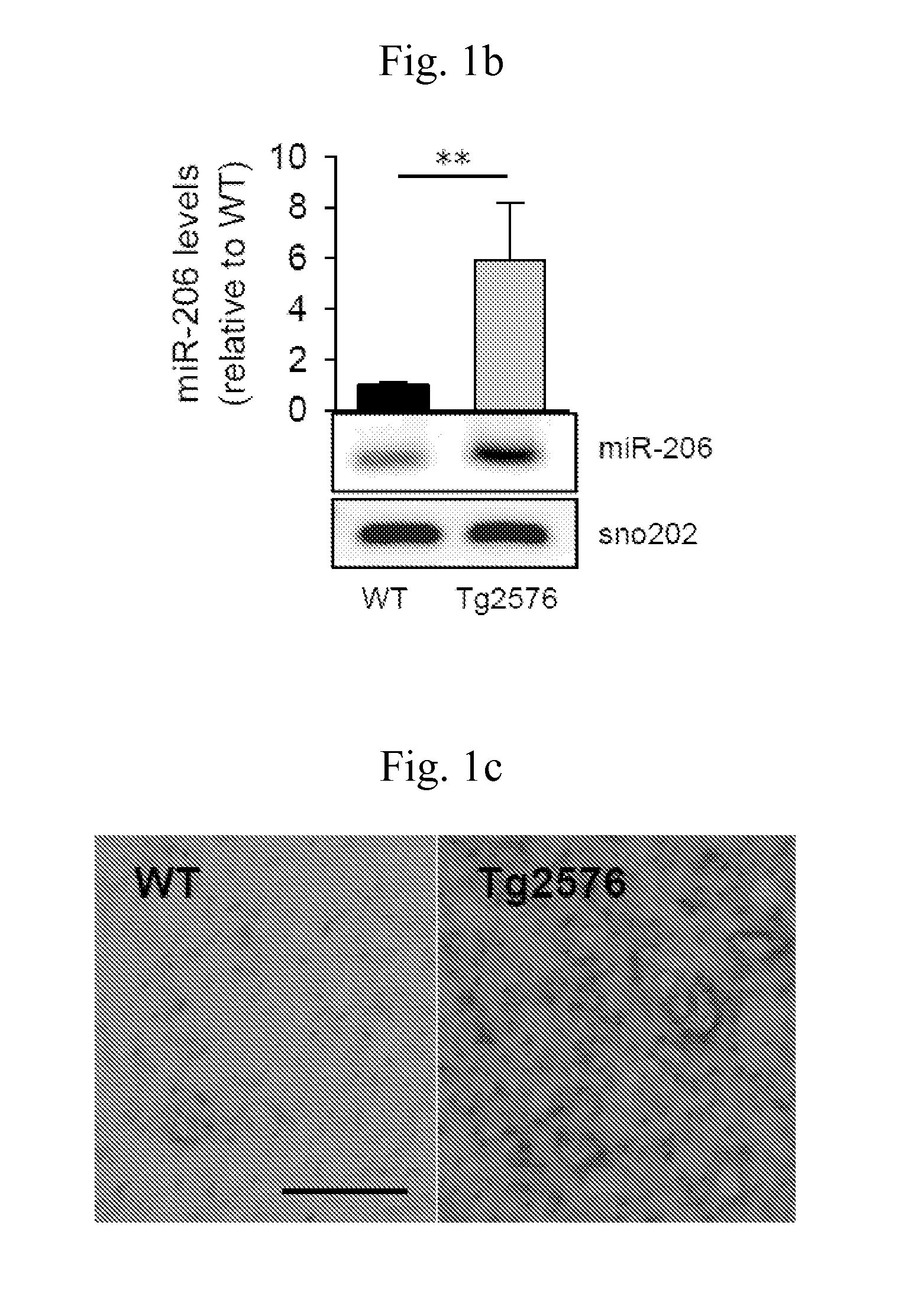
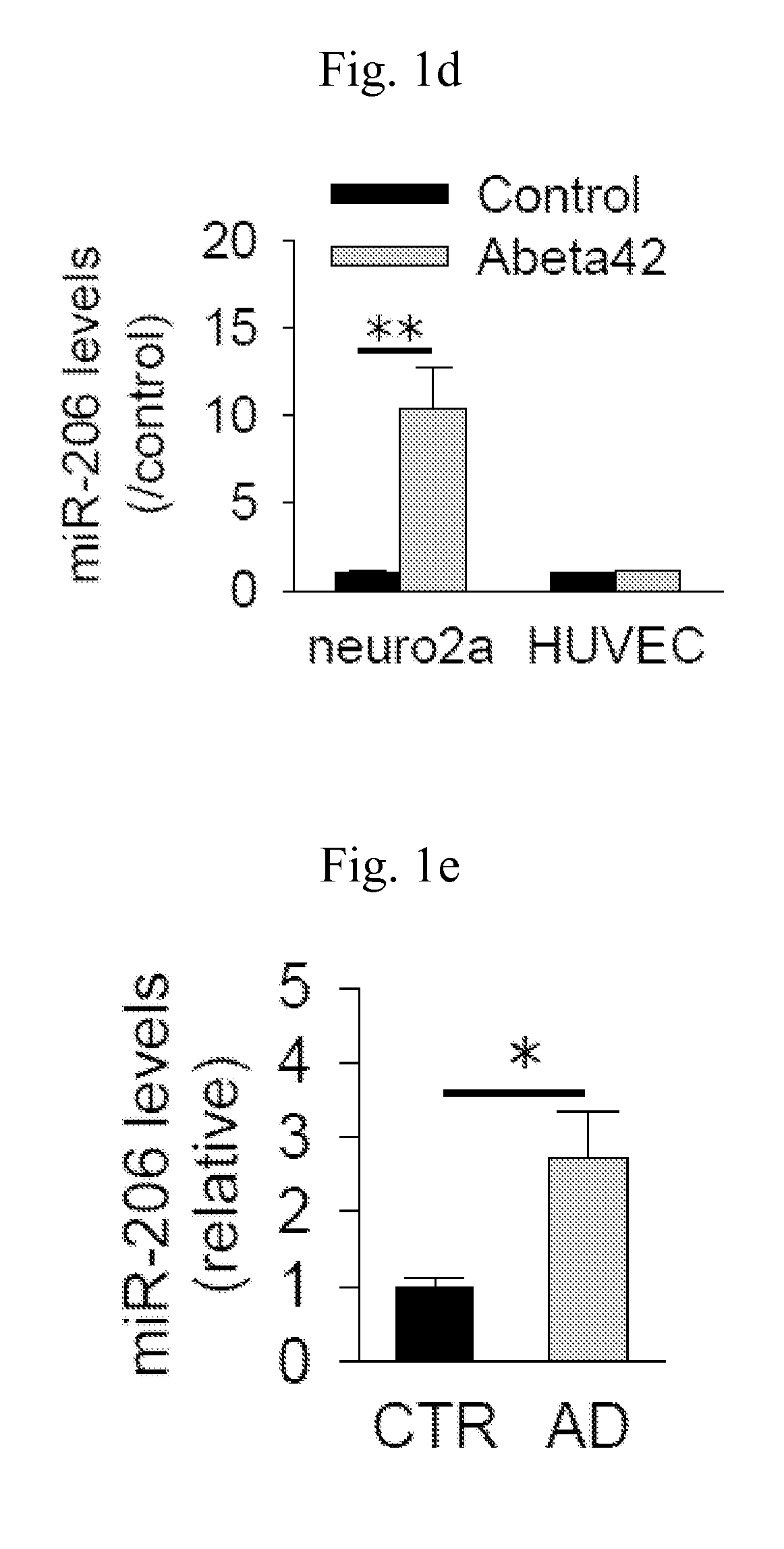
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases by targeting a specific miRNA. In addition, the present invention relates to a kit for diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases. A miR-206 target found in the present invention, which is highly expressed in both animal models of Alzheimer's disease and human brain samples, is a substantial treatment target selected without artifact errors. An antisense oligonucleotide of the present invention as an inhibitor for miR-206 suggests a successful result in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases by targeting miRNA. The antisense oligonucleotide of the present invention inhibits the function of miR-206 to greatly increase the levels of BDNF and IGF-1 and to increase the regeneration of synapses, thereby treating neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
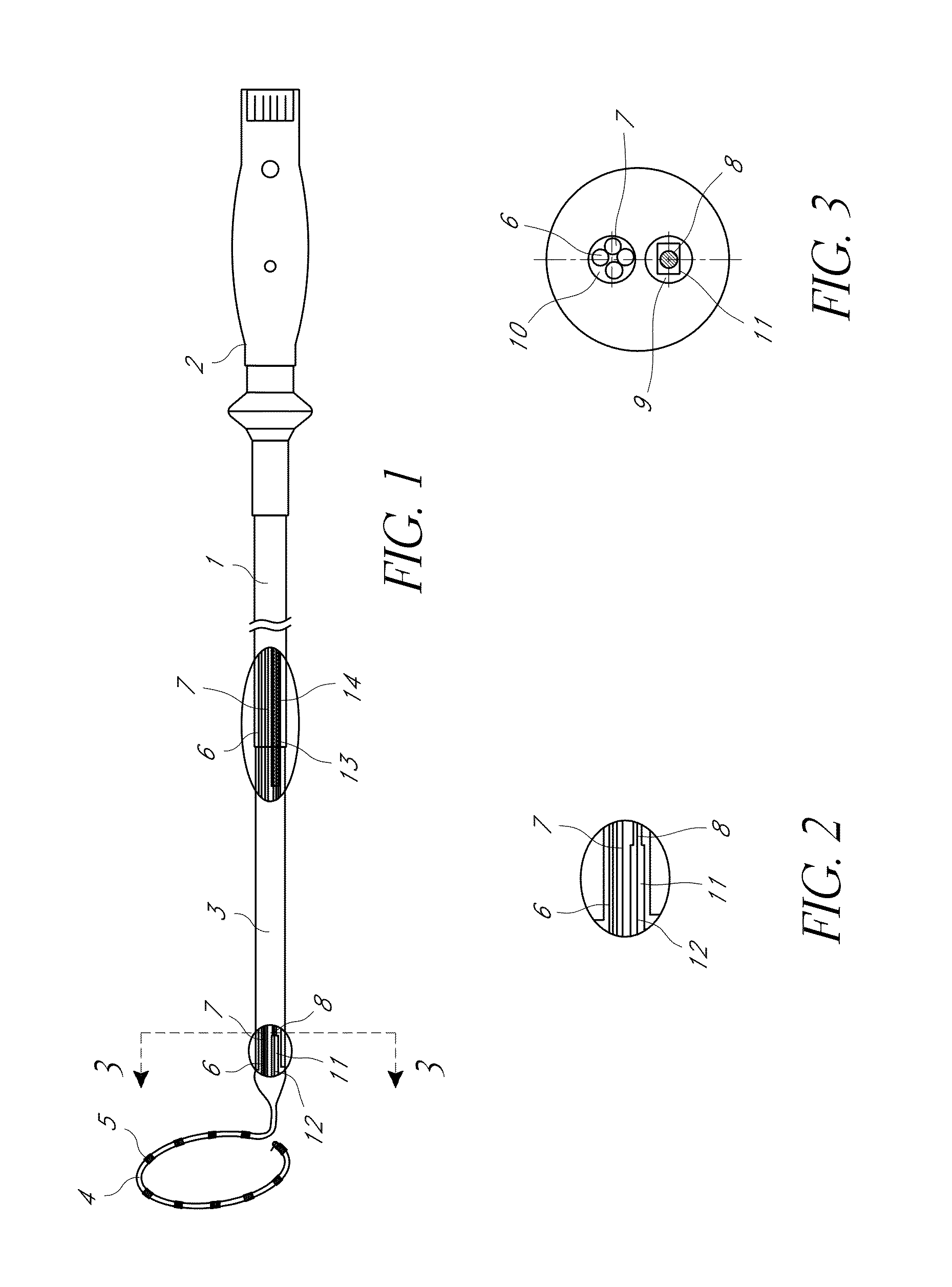
Multi-pole synchronous pulmonary artery radiofrequency ablation catheter
ActiveUS20180140347A1Decrease pulmonary artery pressureSuccessful treatmentElectrotherapyCatheterDenervationPulmonary artery
A multi-pole synchronous pulmonary artery radiofrequency ablation catheter may comprise a control handle, a catheter body and an annular ring. One end of the catheter body may be flexible, and the flexible end of the catheter body may be connected to the annular ring. The other end of the catheter body may be connected to the control handle. A shape memory wire may be arranged in the annular ring. One end of the shape memory wire may extend to an end of the annular ring and the other end of the shape memory wire may pass through a root of the annular ring and be fixed on the flexible end of the catheter body. The annular ring may be provided with an electrode group. The device possesses advantages of simple operation, short operation time and controllable precise ablation. The device can be used to treat pulmonary hypertension with pulmonary denervation.
Owner:PULNOVO MEDICAL WUXI
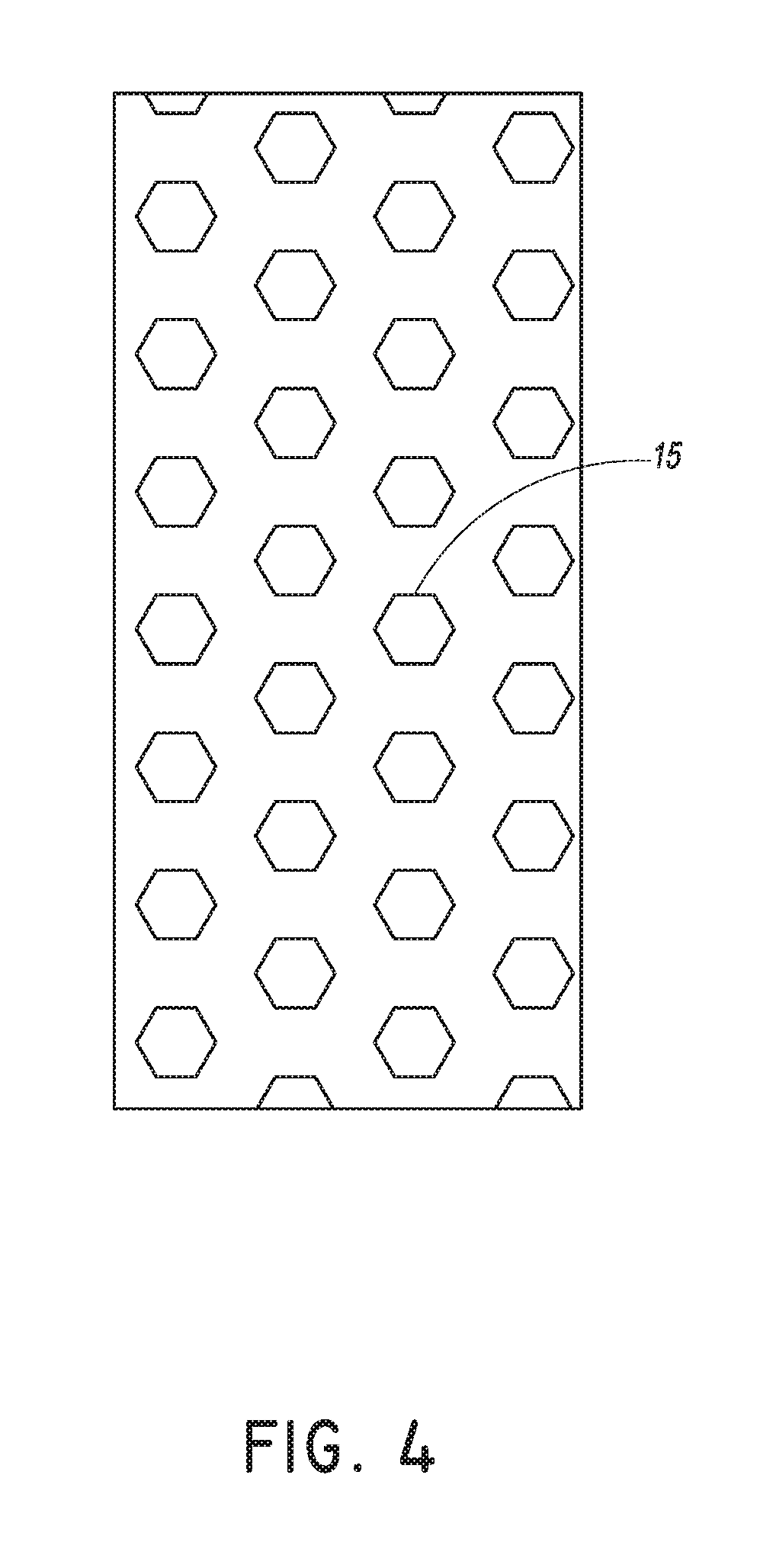
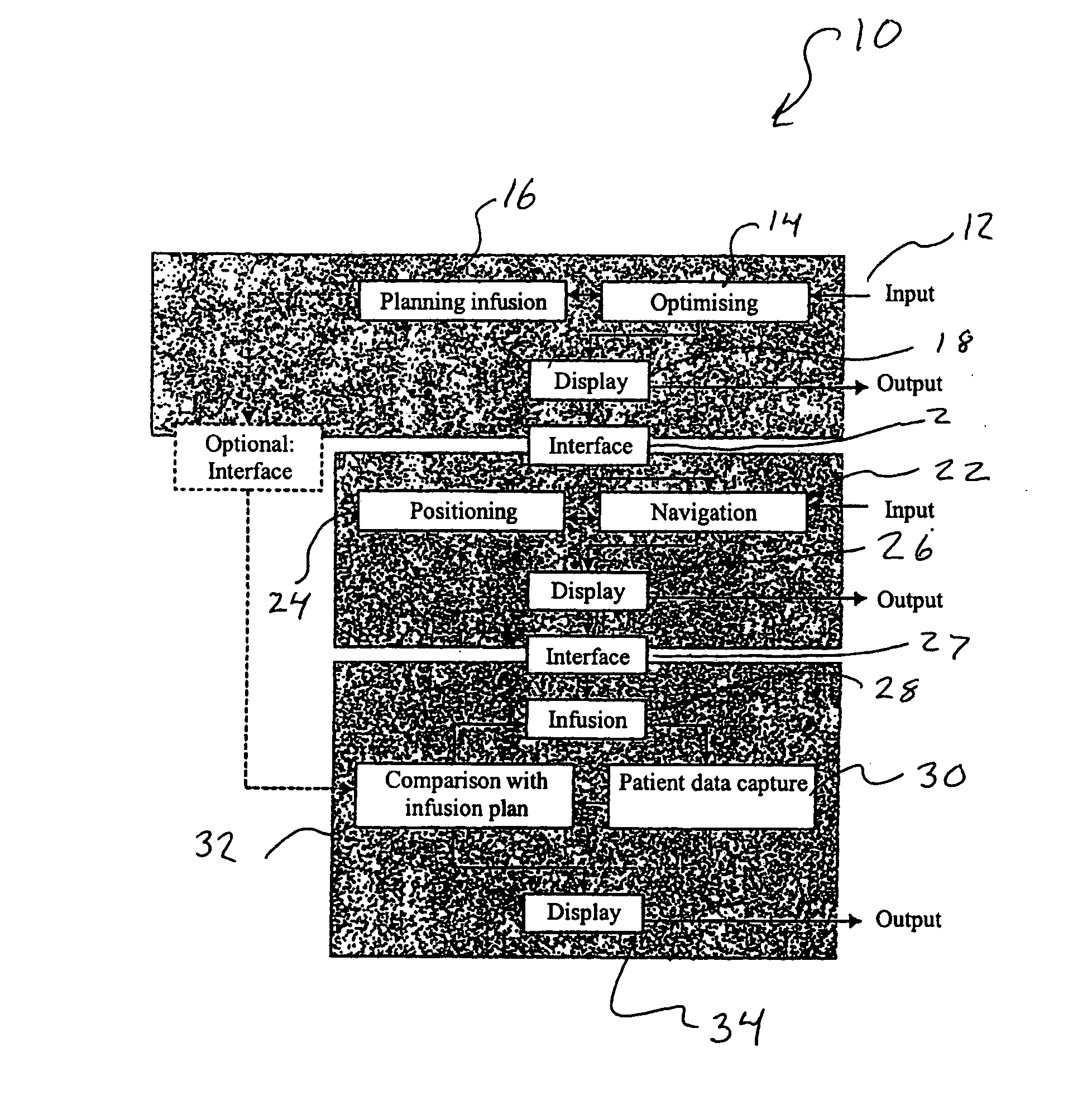
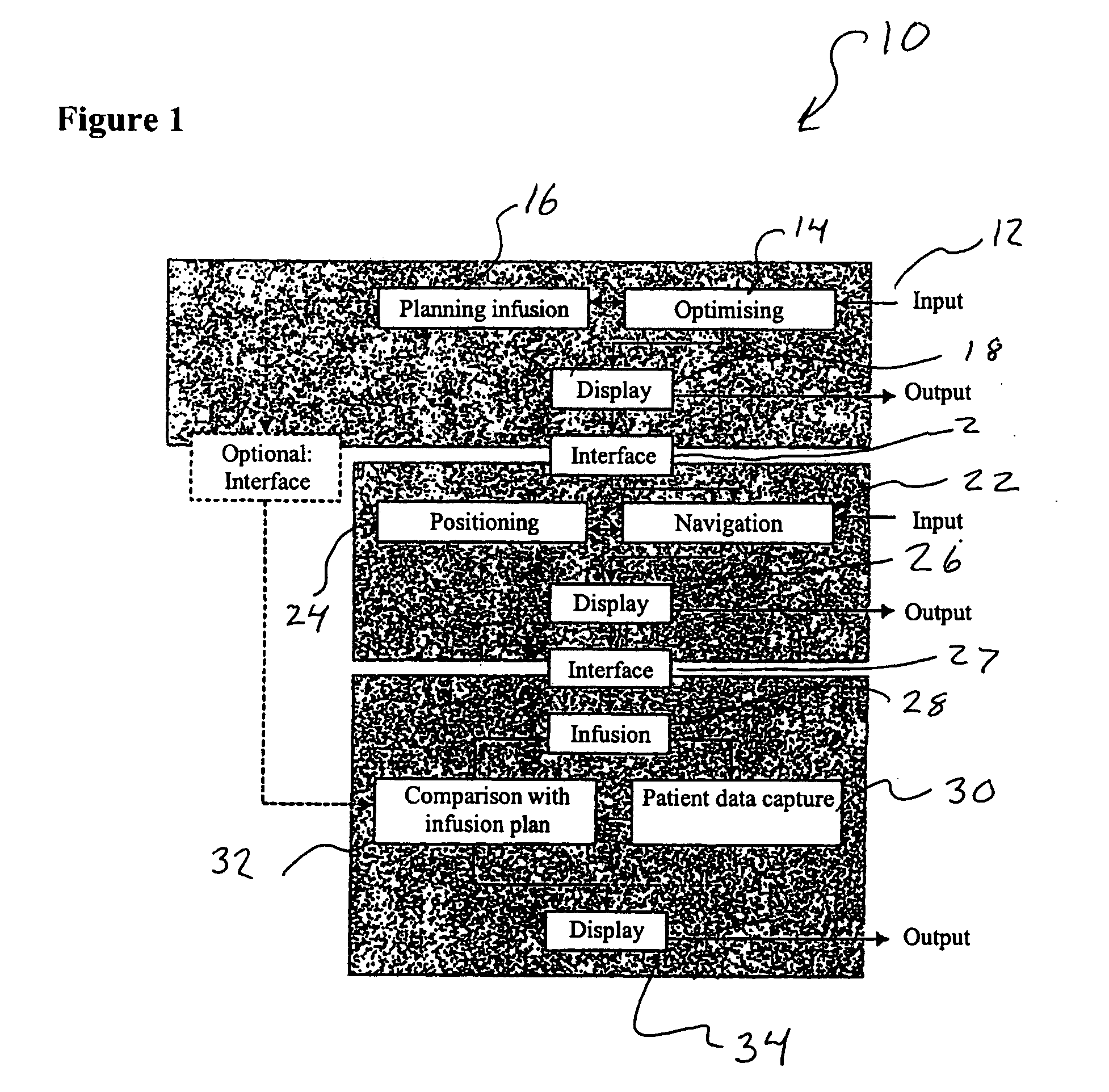
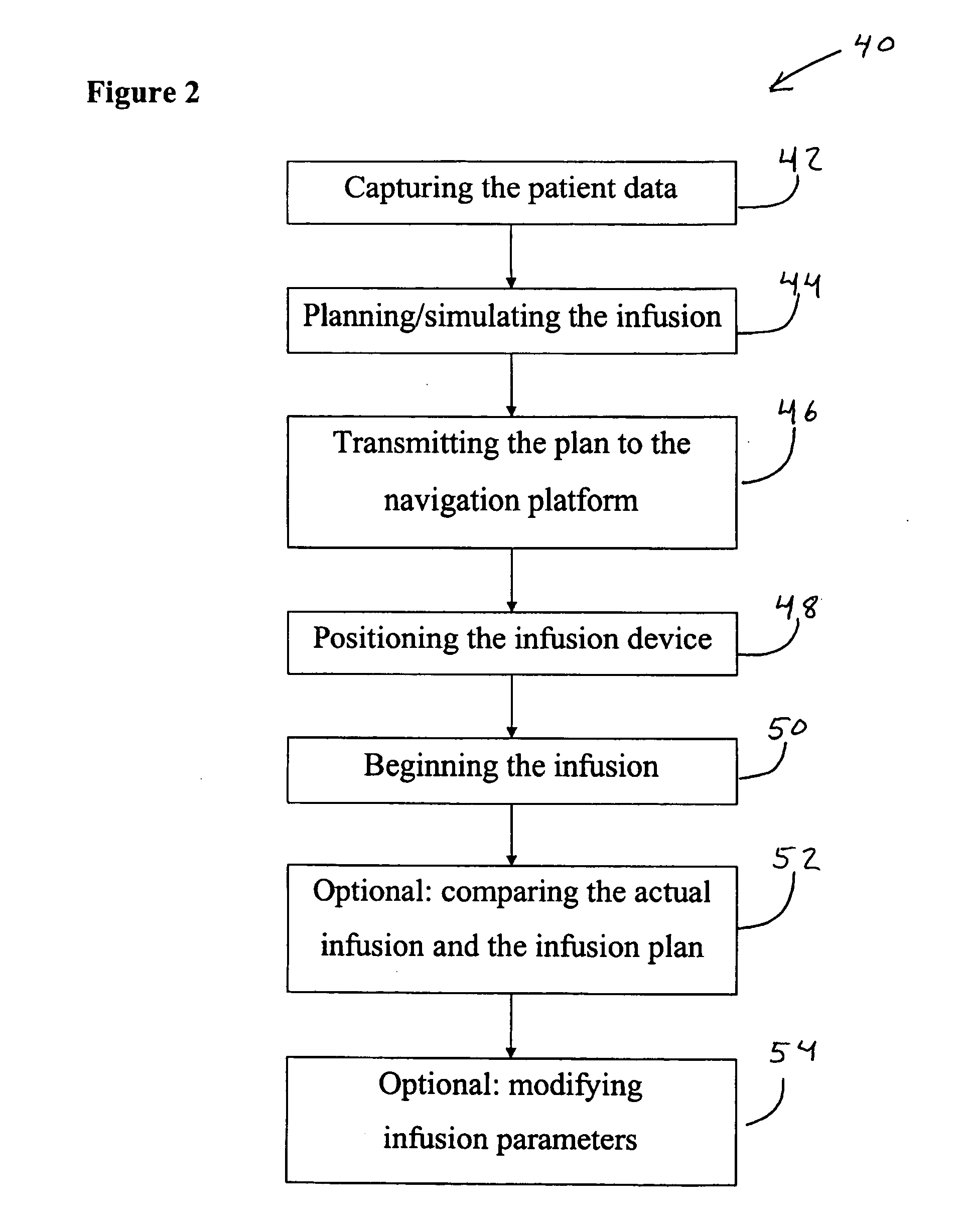
Method and device for planning a direct infusion into hepatic tissue
InactiveUS20070078338A1Decreased blood flowIncrease concentrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical simulationAdministered substancePatient data
A method for planning an infusion into hepatic tissue into a patient includes: obtaining anatomical and / or physiological patient data of the patient's liver or a region of the liver; determining at least one patient parameter from the patient data; planning the infusion using the anatomical patient data, physiological patient data, and / or at least one patient parameter, wherein planning includes determining how an administered substance is distributed in the tissue and / or how the administered substance influences physiological properties of the tissue; and determining a distribution and / or effectiveness of a therapeutic agent administered with the substance or after the substance.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Process for preparing colored mineral powders by thermal treatment
InactiveUS6022405ASuccessful treatmentReduce wearInorganic pigment treatmentRainbowThermal treatment
Disclosed is a system of natural colors consisting of thousands of colored powders of mineral origin and of materials in or on which pigments have been applied and, afterwards, submitted to at least one thermal treatment and / or irradiation. These natural colors cover the totality of the visible spectrum and offer a great variety of tones, tints and reflections from white to black, including all the rainbow colors. The powders of this system are obtained by mechanical, chemical, thermal and / or physical processes and are used alone or in combination. They are particularly useful to color materials and, more especially those used in the construction and architectural fields.
Owner:TOURANGEAU PAULETTE
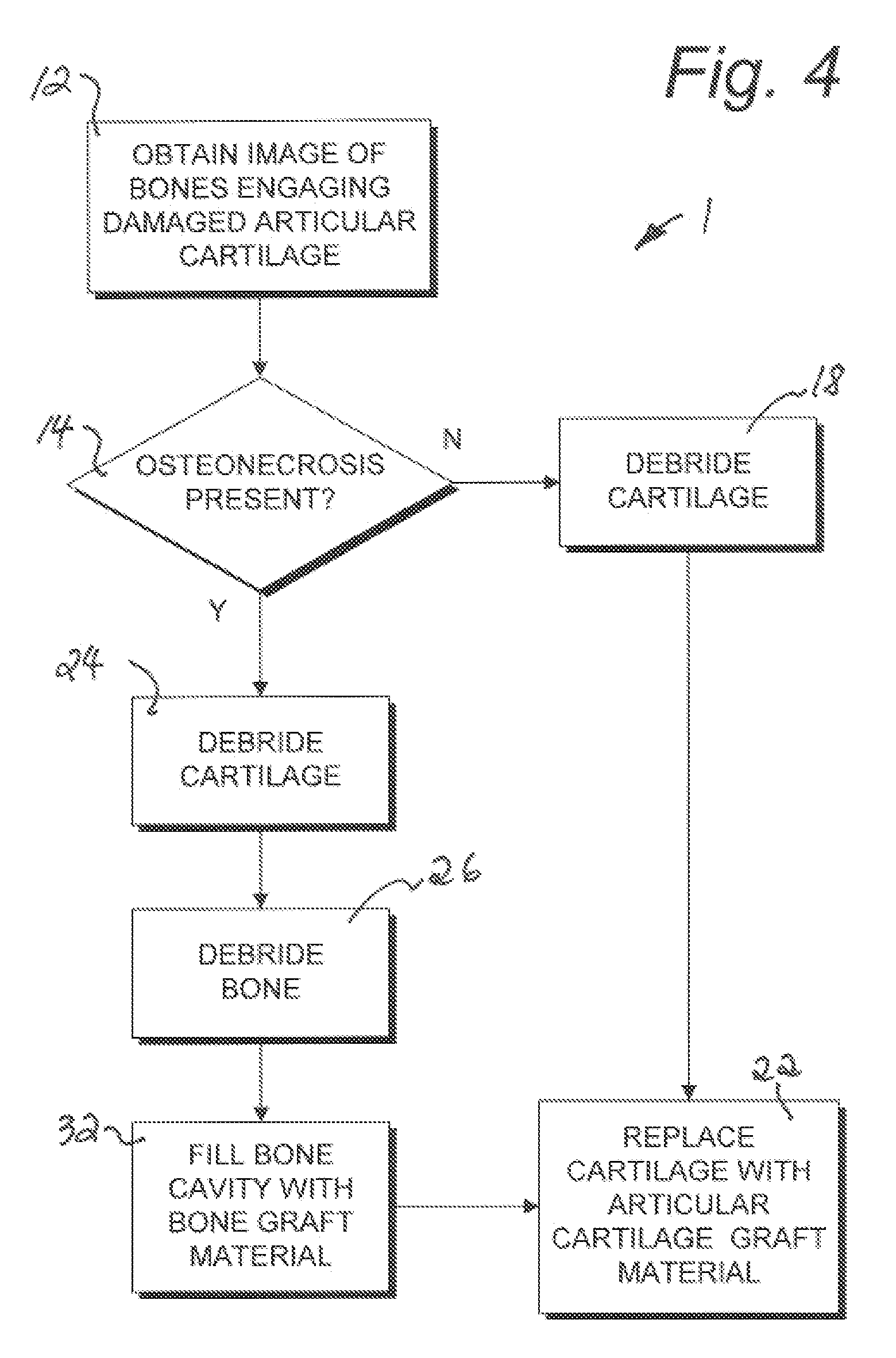
Articular cartilage treatment method
The present invention provides an method to alleviate a deteriorated condition at an articular joint site and for repair of damaged cartilage the method including the steps of imaging for the presence of osteonecrosis in the underlying bone, forming a cylindrical plug comprising articular cartilage and osteonecrotic bone using an endoscopic trephine, inspecting the removed cylindrical plug and the joint site for additional articular cartilage and osteonecrotic bone, selectively debriding osteonecrotic bone material associated with the bone cavity to achieve desired vascular characteristics for receiving a prepared bone graft material within the bone cavity, and overlying the received bone graft material with cartilage tissue at the cartilage tissue receiving surface.
Owner:BRANNON JAMES K
Scoring method based on improved signals analysis
InactiveCN107106069ASuccessful treatmentDiagnostics using spectroscopyMedical automated diagnosisAlgorithmStatistical physics
Owner:MENSIA TECH
Multi-pole synchronous pulmonary artery radiofrequency ablation catheter
ActiveUS20150201988A1Successful treatmentReduce pressureElectrotherapyCatheterCatheterPulmonary artery
A multi-pole synchronous pulmonary artery radiofrequency ablation catheter may comprise a control handle, a catheter body and an annular ring. One end of the catheter body may be flexible, and the flexible end of the catheter body may be connected to the annular ring. The other end of the catheter body may be connected to the control handle. A shape memory wire may be arranged in the annular ring. One end of the shape memory wire may extend to an end of the annular ring and the other end of the shape memory wire may pass through a root of the annular ring and be fixed on the flexible end of the catheter body. The annular ring may be provided with an electrode group. The device possesses advantages of simple operation, short operation time and controllable precise ablation. The device can be used to treat pulmonary hypertension with pulmonary denervation.
Owner:PULNOVO MEDICAL WUXI
Removal device
InactiveUS20200121342A1Successful treatmentMinimizes pressure differentialUrinary bladderAnti-incontinence devicesAnatomical structuresUrethral Diseases
Method and system for treating a patient using a compressible, pressure-attenuating device. According to one embodiment, the system is used to treat urinary tract disorders and comprises an access device, a delivery device, a pressure-attenuating device, and a removal device. The access device can be used to create a passageway to an anatomical structure, such as the patient's bladder. The delivery device can be inserted through the passageway created by the access device and can be used to deliver the pressure-attenuating device to the anatomical structure. The removal device can be inserted through the passageway created by the access device and can be used to view the bladder and / or to capture, to deflate and to remove the pressure-attenuating device.
Owner:SOLACE THERAPEUTICS
Method of preparing a treatment product, treatment product and a plasmid construct
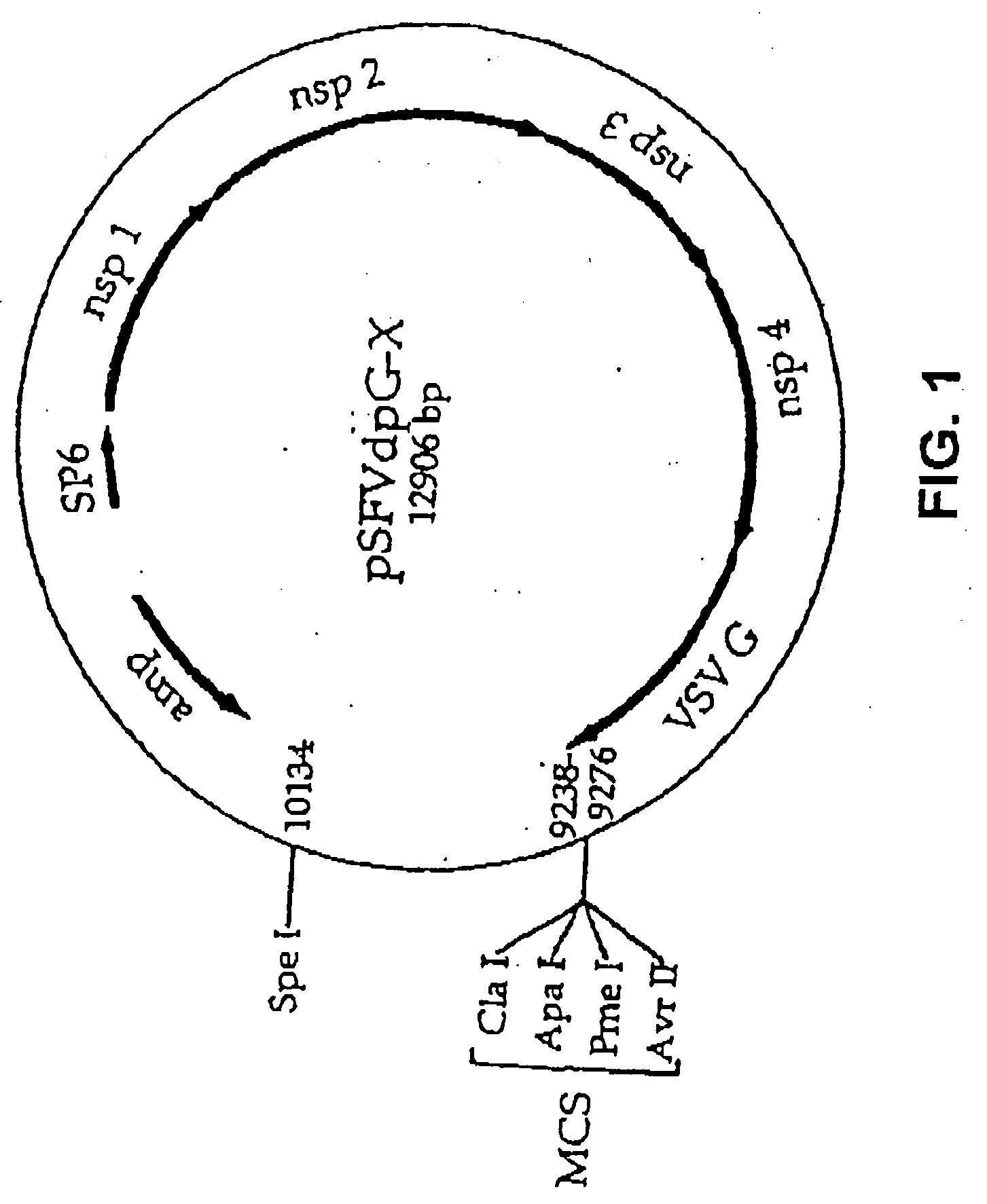
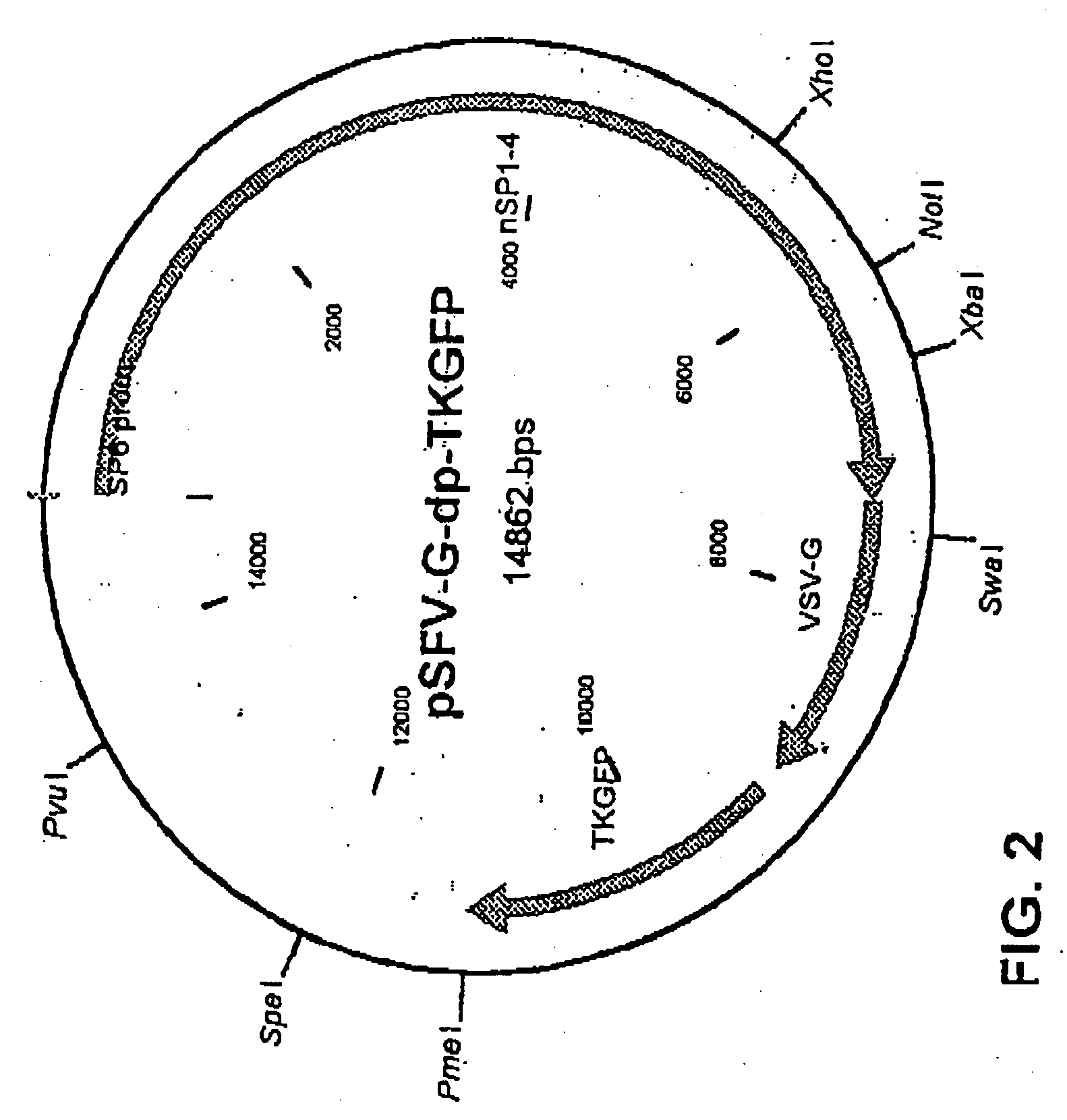
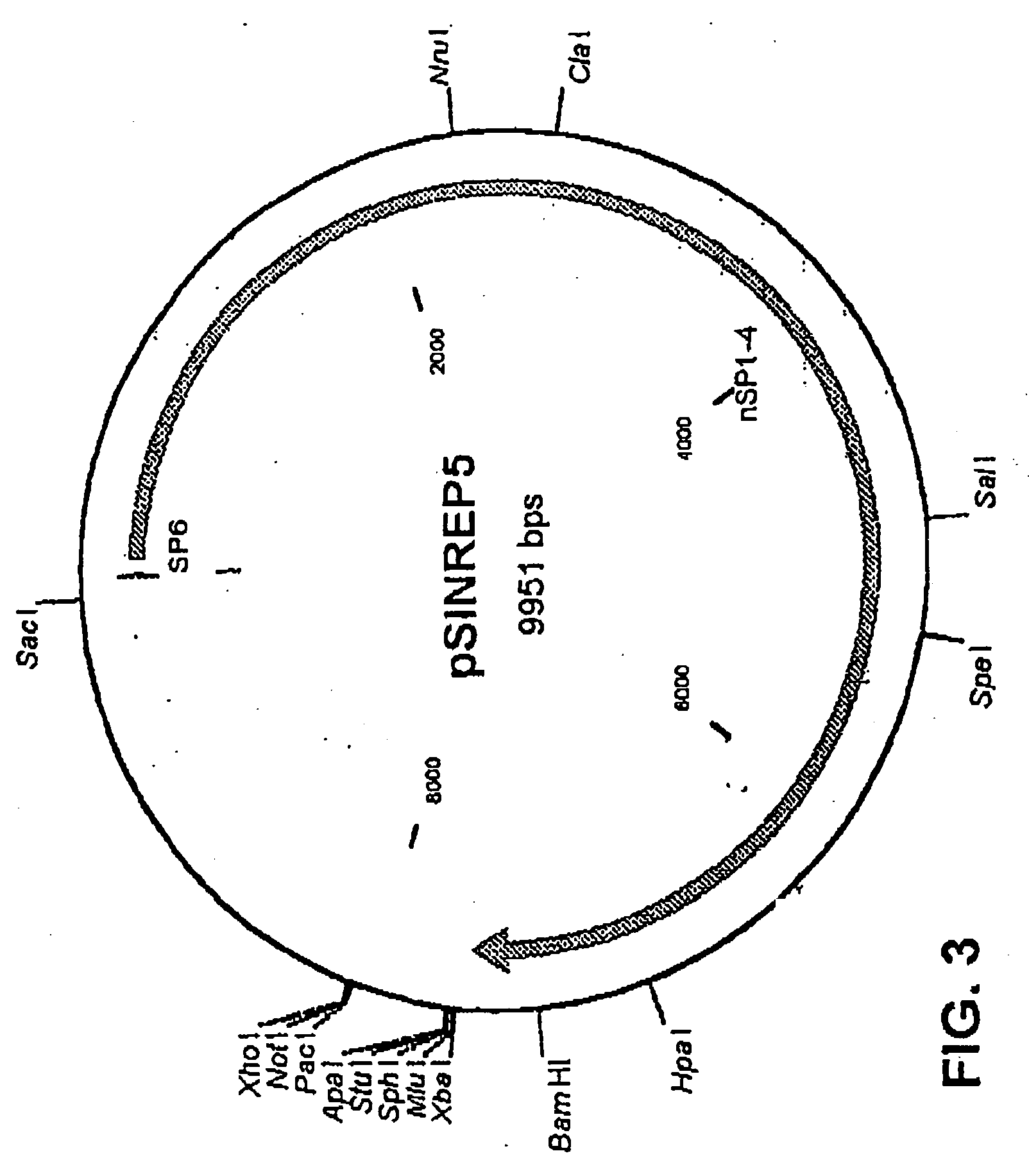
InactiveUS20050256067A1Raise transfer toSuccessful treatmentBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus-like particleSindbis virus
The method of the invention for preparing a treatment product is characterized by using a starting plasmid based on a virus belonging to the Togaviridae stock from which the genes encoding capsid proteins of the virus have been deleted. An RNA encoding virus-like particles (VLP-RNA) is prepared by manipulating the staring plasmid by connecting to it a spreading enabling gene and a treatment gene. The invention is furthermore concerned with such a treatment product and a plasmid construct encoding virus-like particles, which is prepared from the Sindbis virus in which the capsid protein of the virus has been substituted by a spreading enabling gene and a treatment gene. Example of spreading enabling gene is a gene encoding vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSV-G). A particular example of treatment product is Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase linked to GFP, said product being Spicude / Reporter construct
Owner:WAHLFORS JARMO +1
Method and substances for treating t-cell mediated autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20100004210A1Detect genetic susceptibilityHigh riskBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsDiseaseAutoimmune disease
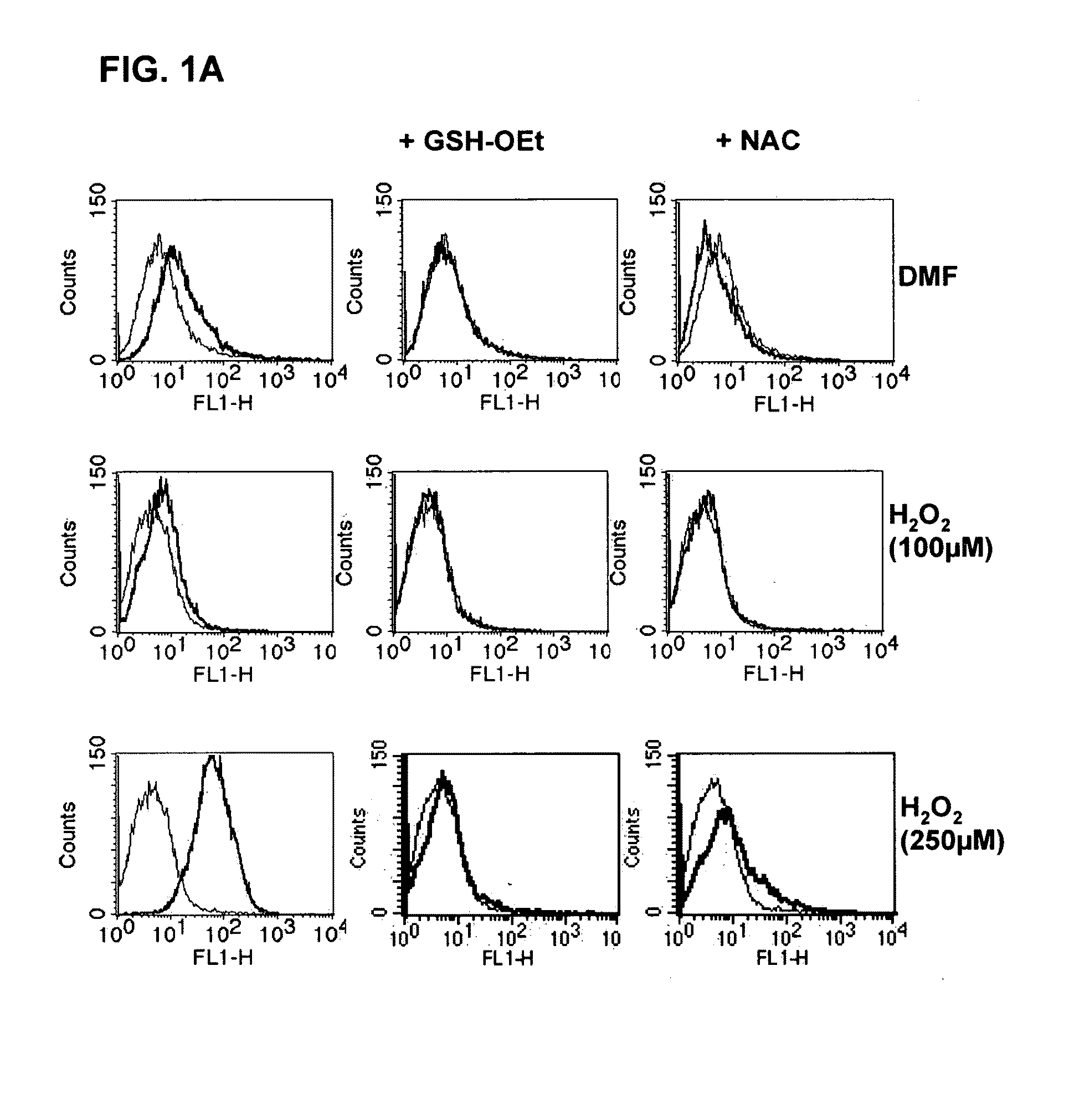
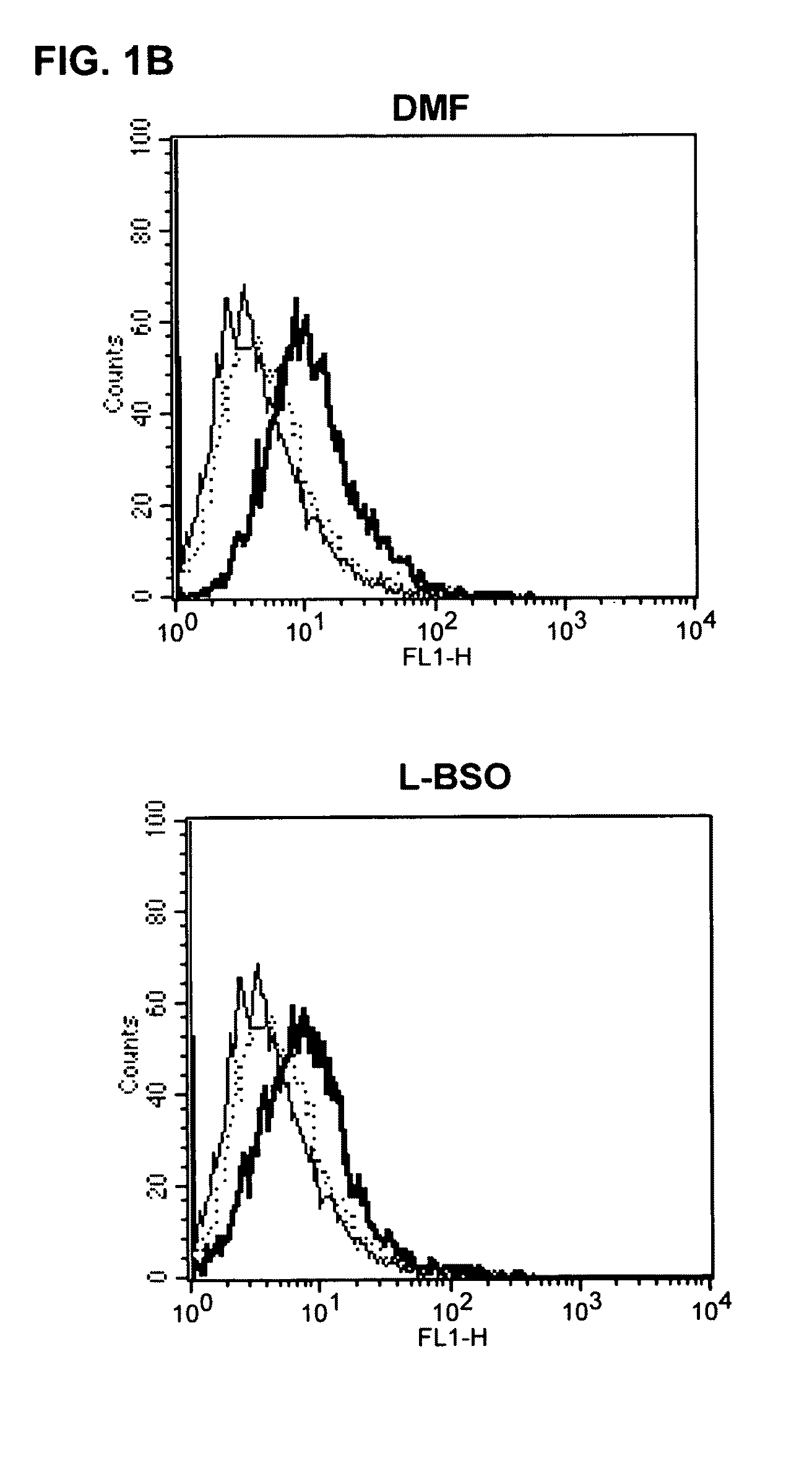
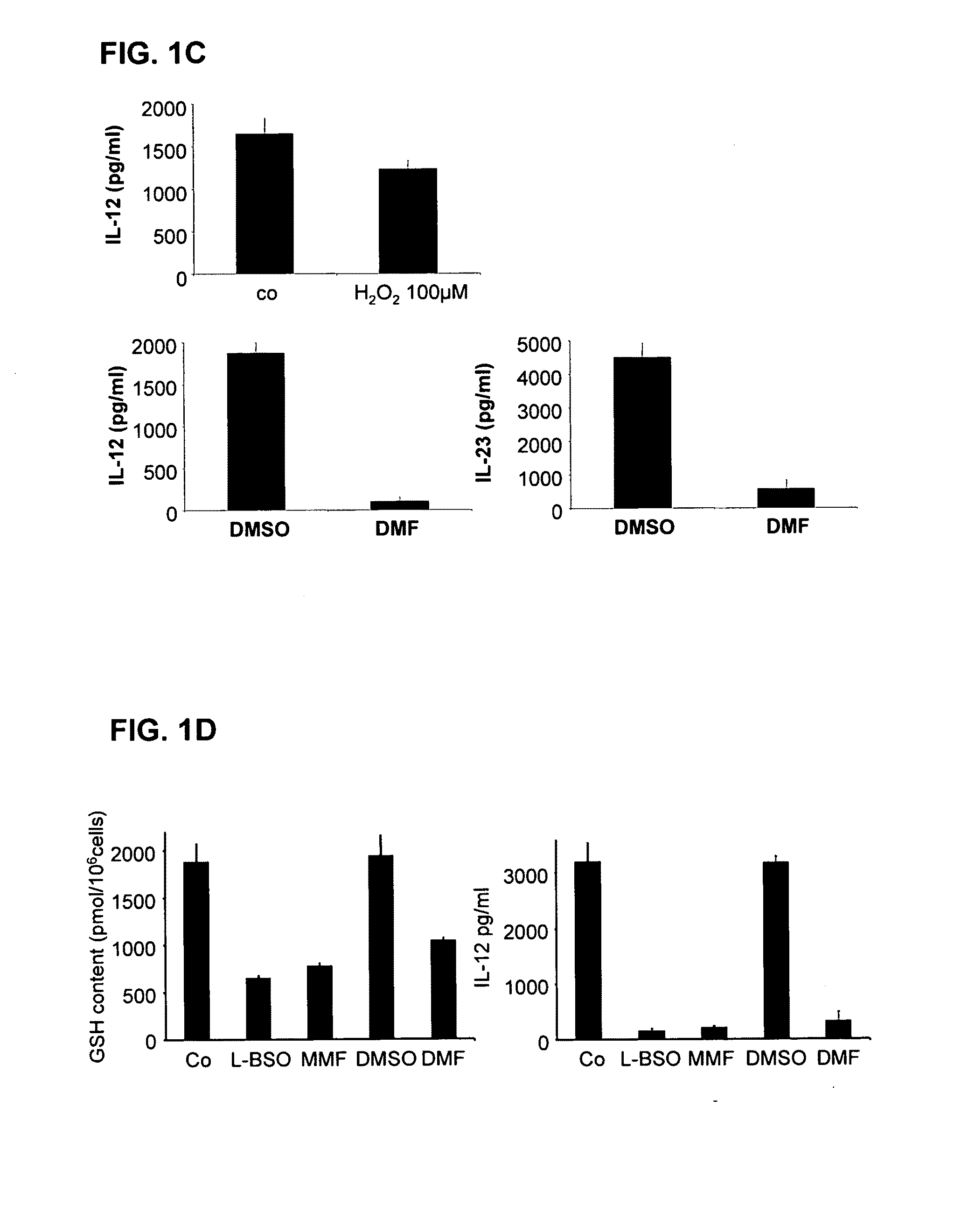
The invention relates to methods for treating T cell mediated autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis and multiple sclerosis, in a human in need thereof, wherein a therapeutically effective amount of a substance which lowers the cellular glutathione content is administered to the human.
Owner:UNIV TUBINGEN
Use of kgf in the treatment of menopausal disorders
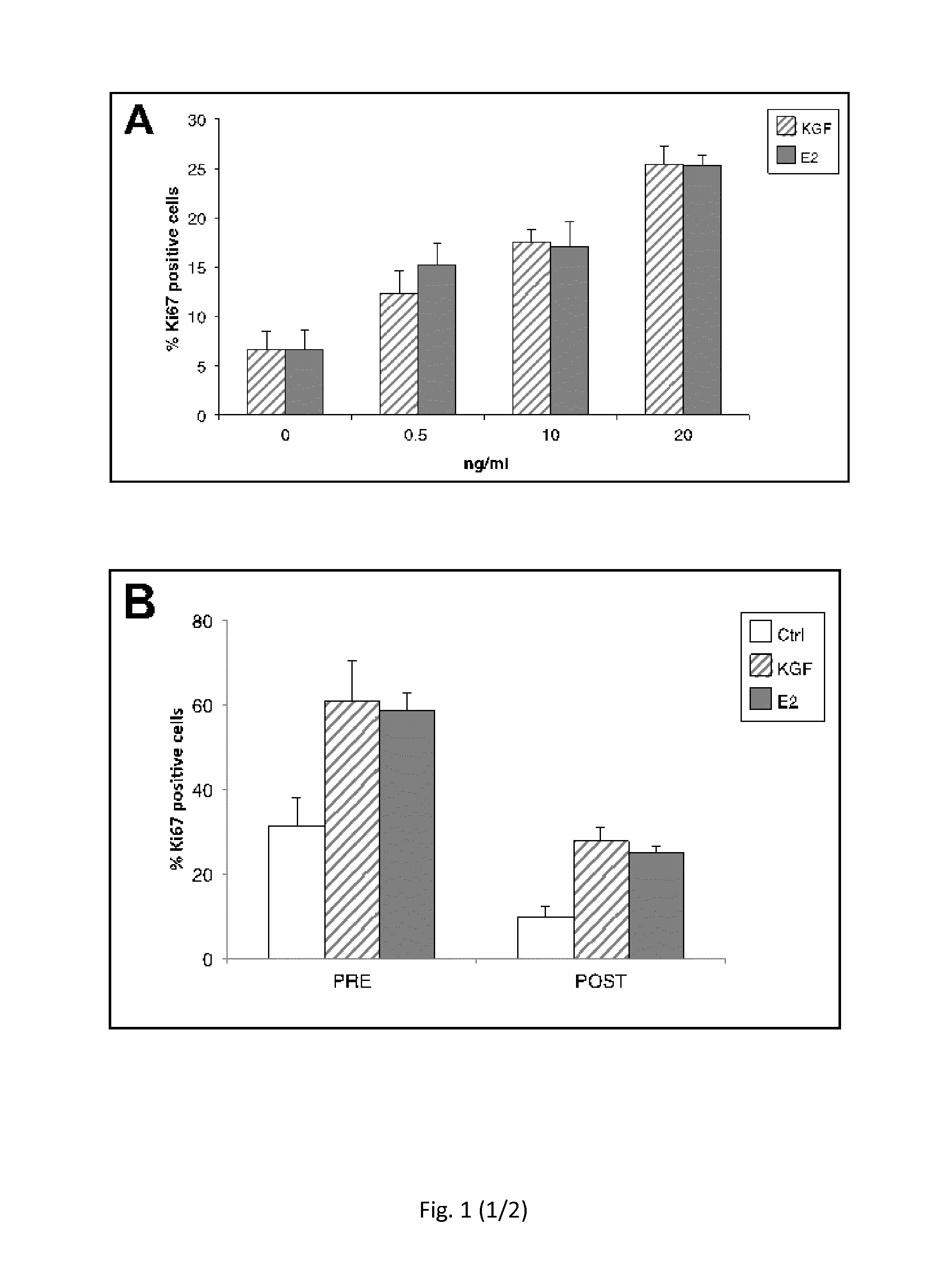
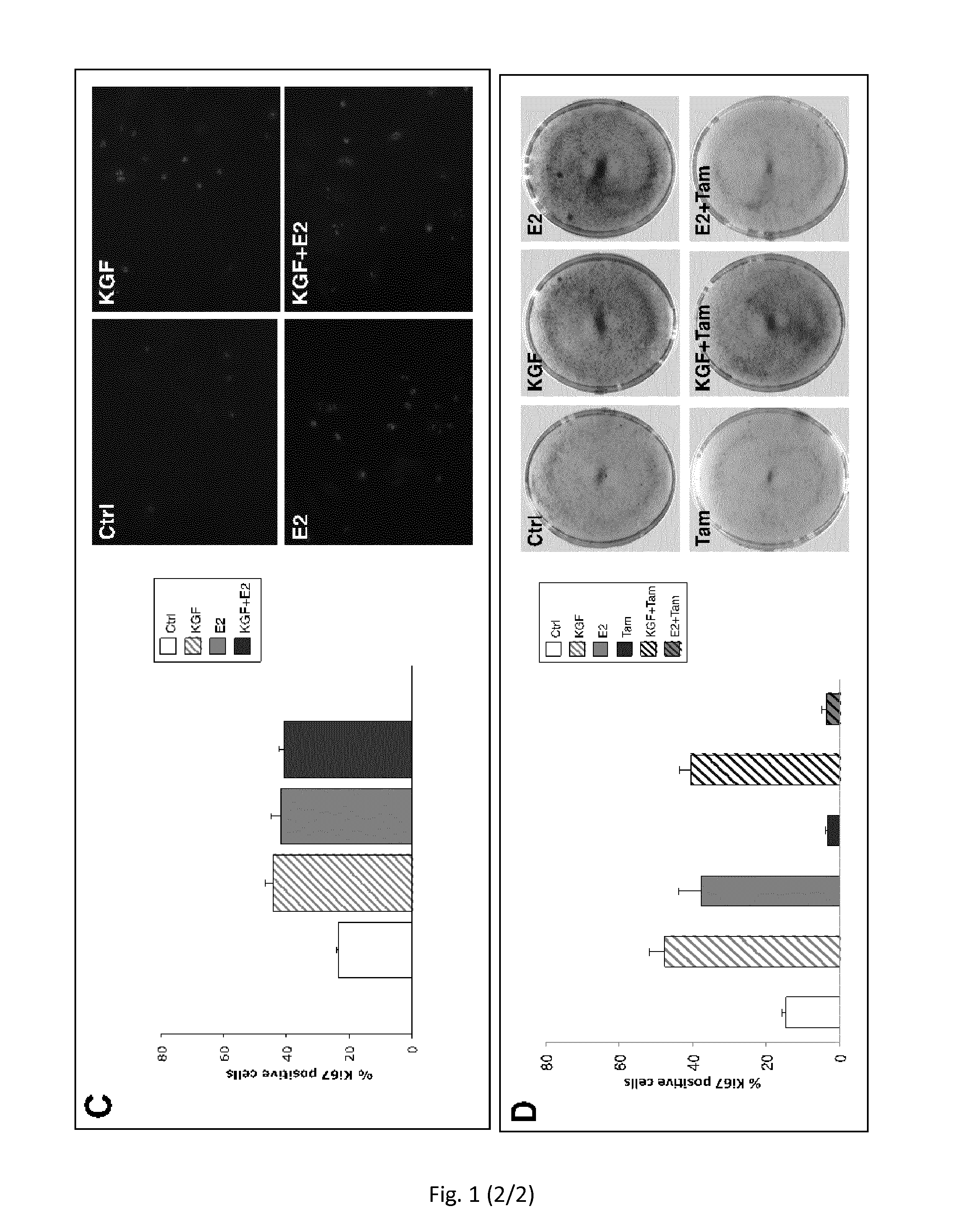
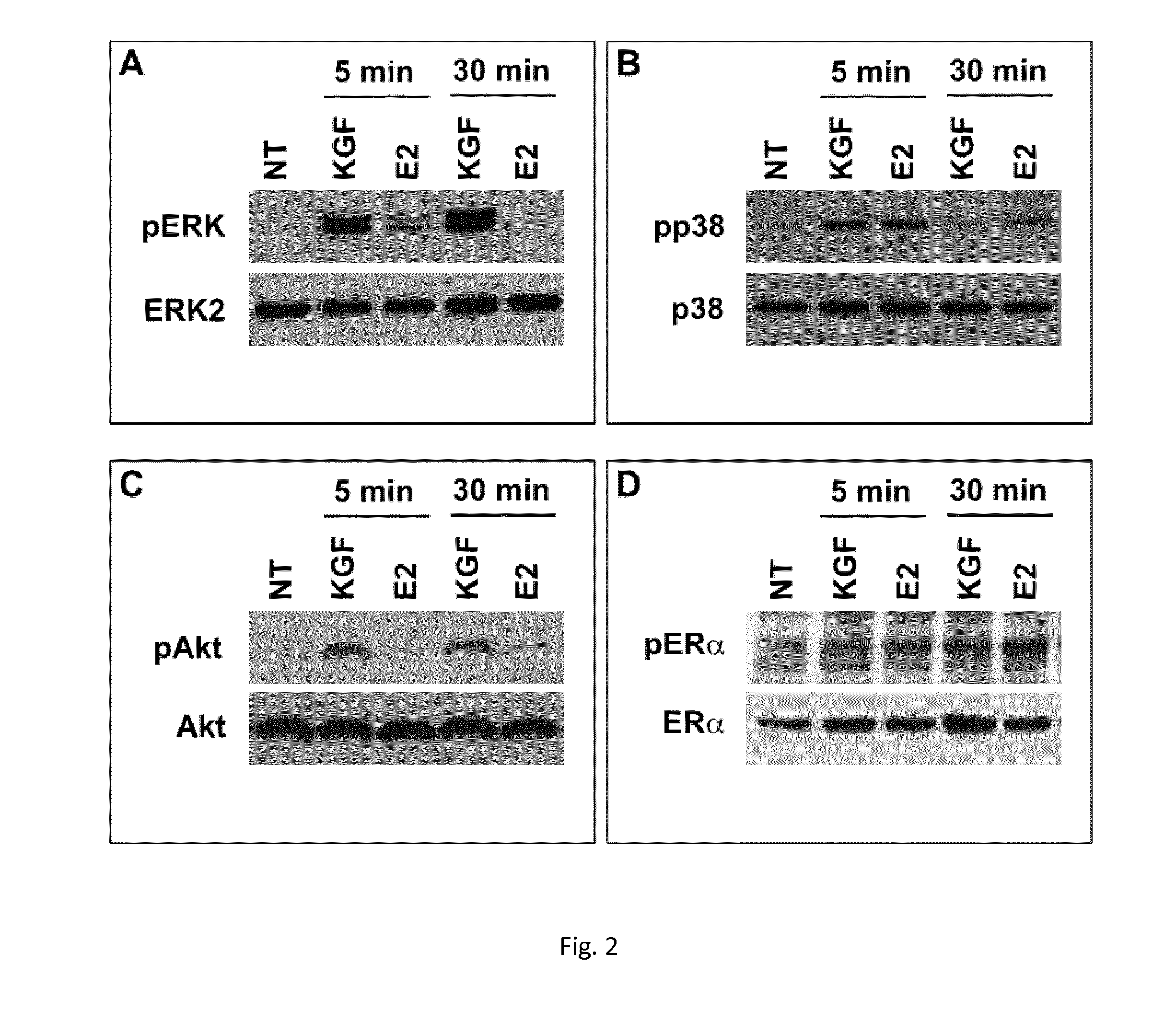
ActiveUS20150224172A1Less elasticMore fragileBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsVaginal PainRadical radiotherapy
The present invention relates to the use of keratinocyte growth factor (KGF / FGF7) and pharmaceutical compositions thereof in the treatment of vaginal atrophy, dysuria, vaginal pain and / or vaginal dryness induced by a post-menopausal state, by surgical intervention, by illness and / or by chemotherapy or radiotherapy treatments.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA
Device for Administering Drugs and for Influencing the Effects of Drugs
InactiveUS20120232330A1Positive influence on encouragement and differentiationStrong effectDental implantsLine/current collector detailsDrugElectromagnetic field
Owner:GEIGES BJARNE
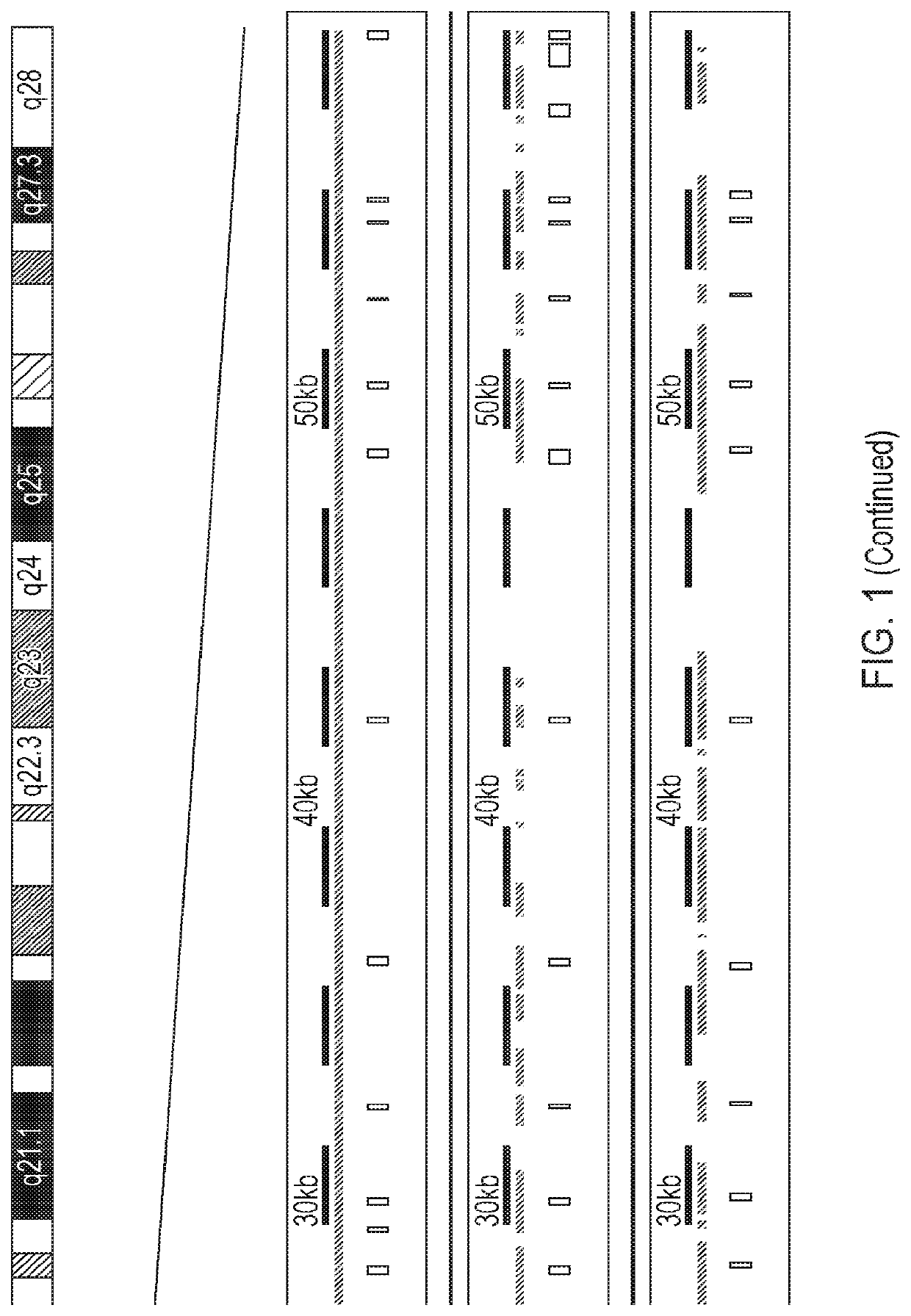
Treatment of retinitis pigmentosa
ActiveUS10836803B2Optimization orderPrevent and reduce occurrenceSenses disorderTransferasesRetinitis pigmentosaNucleotide
A polynucleotide comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding the retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator ORF15 isoform (RPGRORF15), wherein the RPGRORF15-encoding nucleotide sequence has been codon optimised to increase fidelity of replication of the sequence.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com