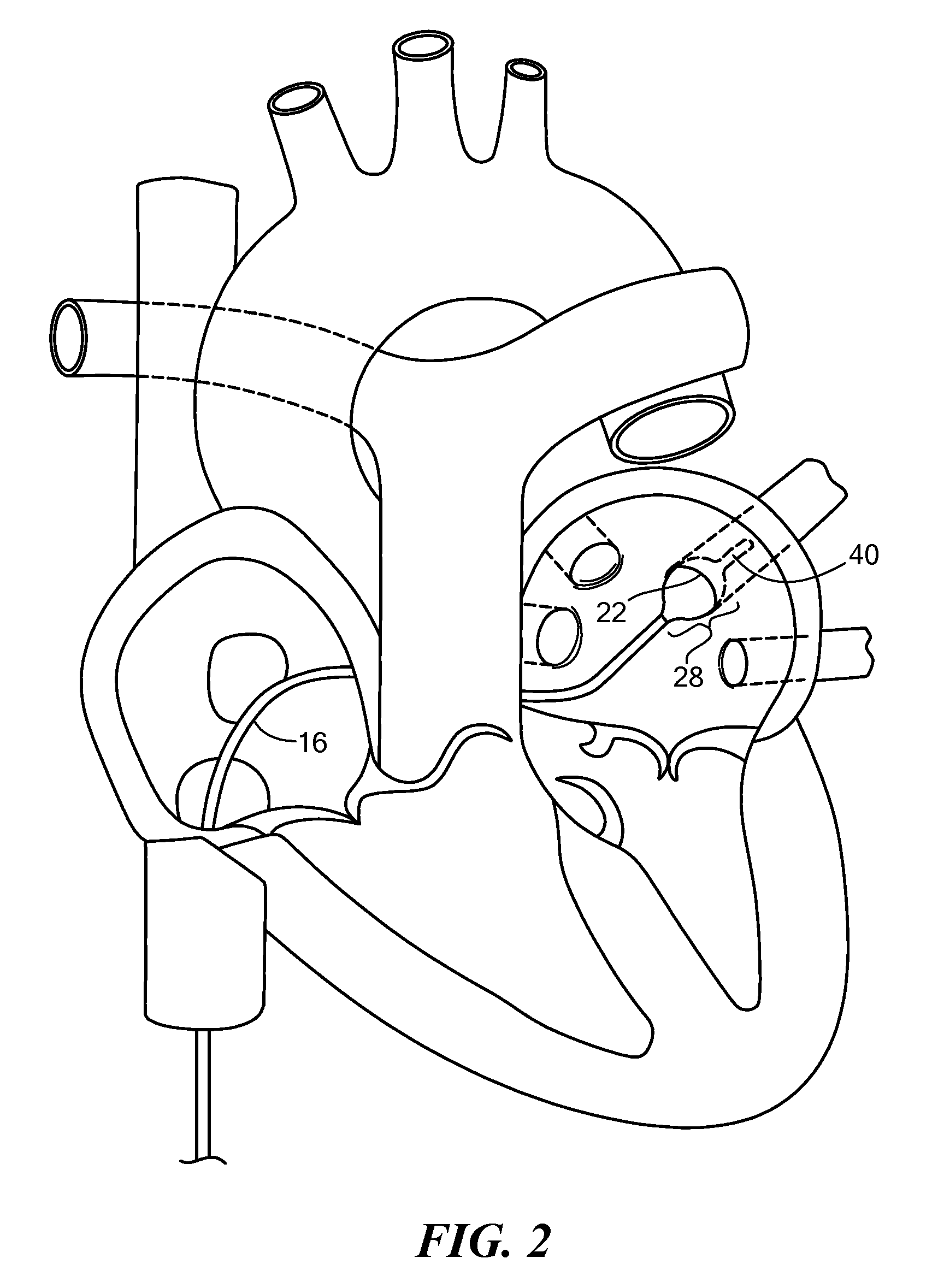Patents
Literature
165 results about "Radiofrequency ablation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
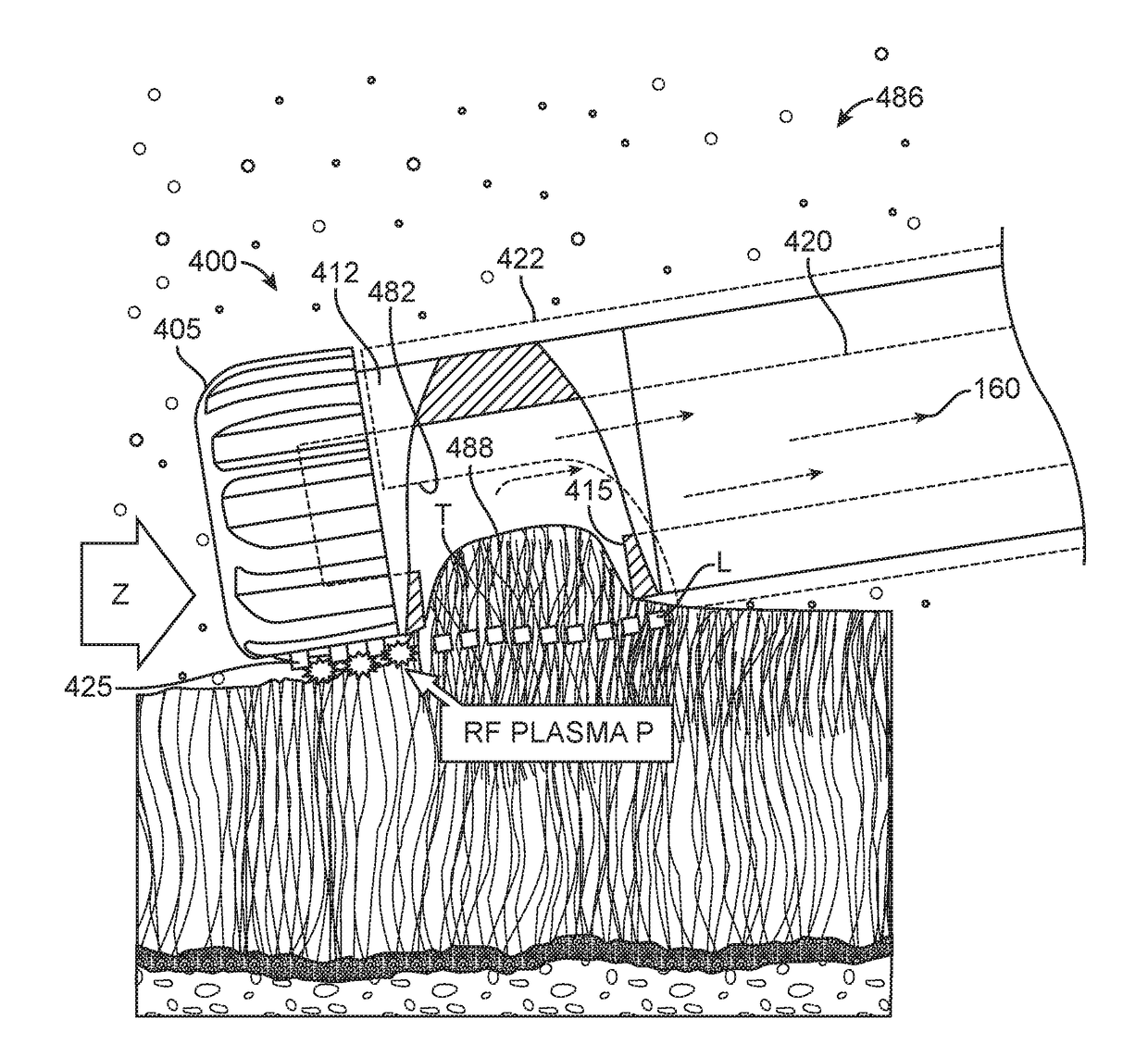
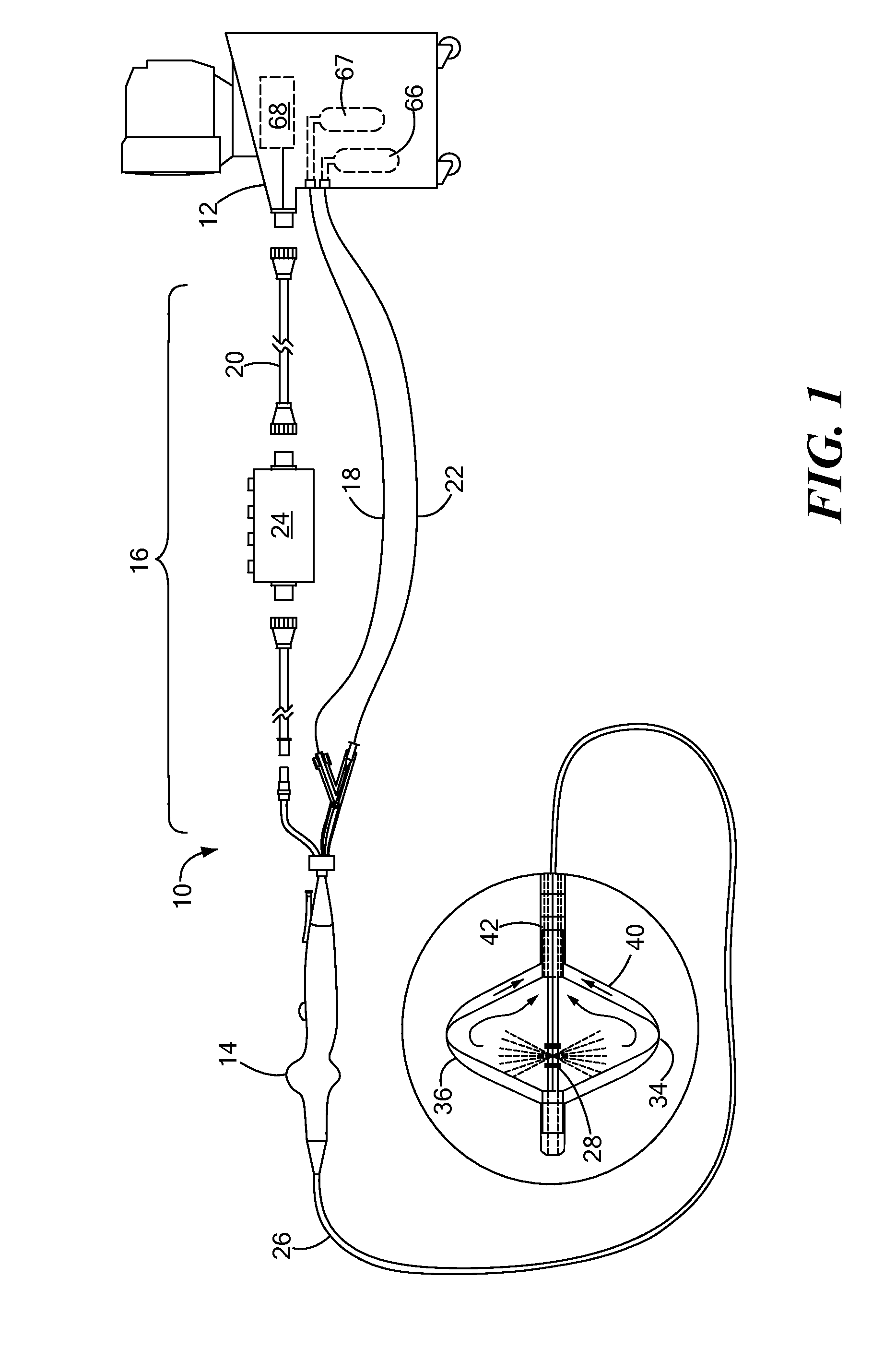
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor or other dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium frequency alternating current (in the range of 350–500 kHz). RFA is generally conducted in the outpatient setting, using either local anesthetics or conscious sedation anesthesia. When it is delivered via catheter, it is called radiofrequency catheter ablation.
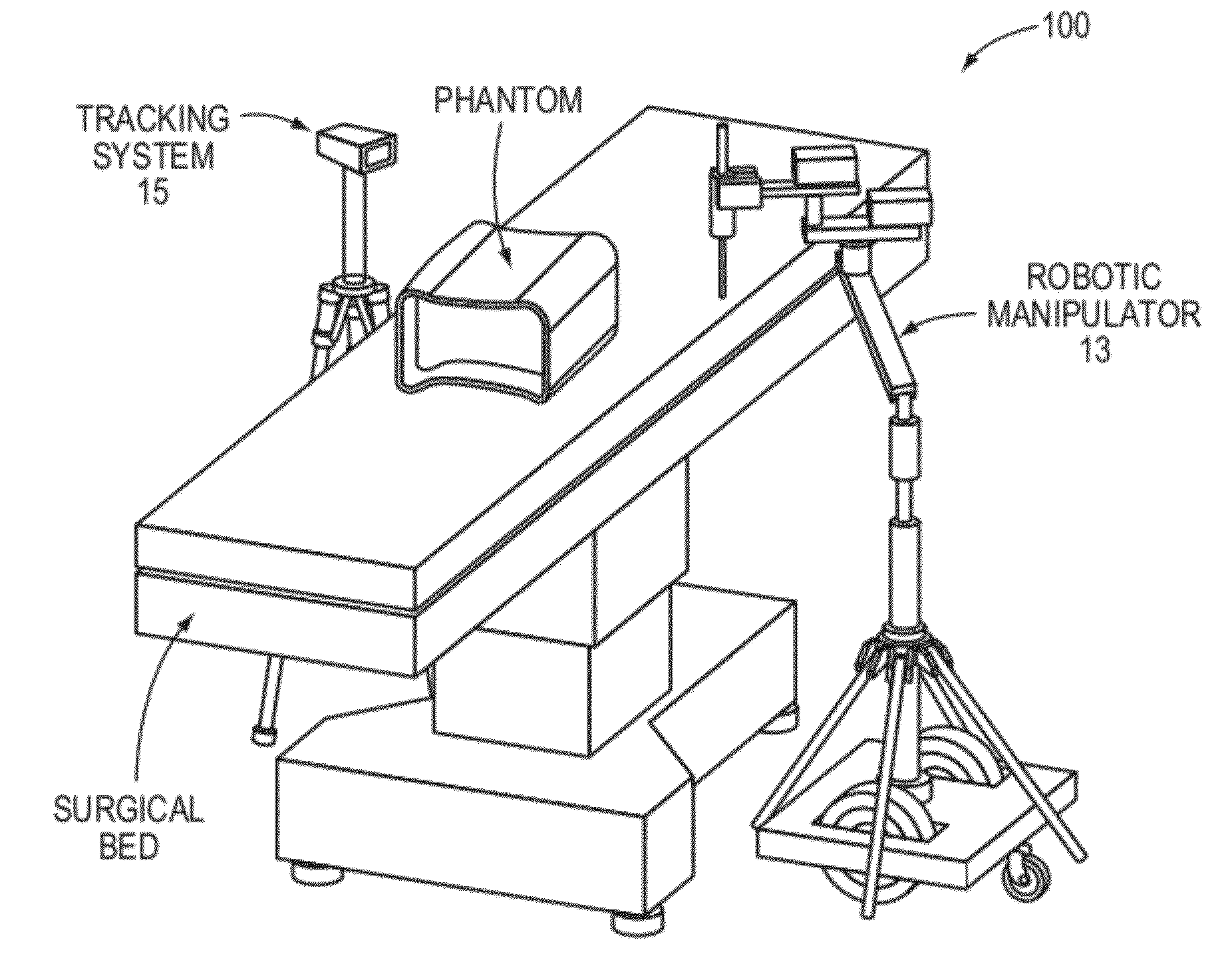
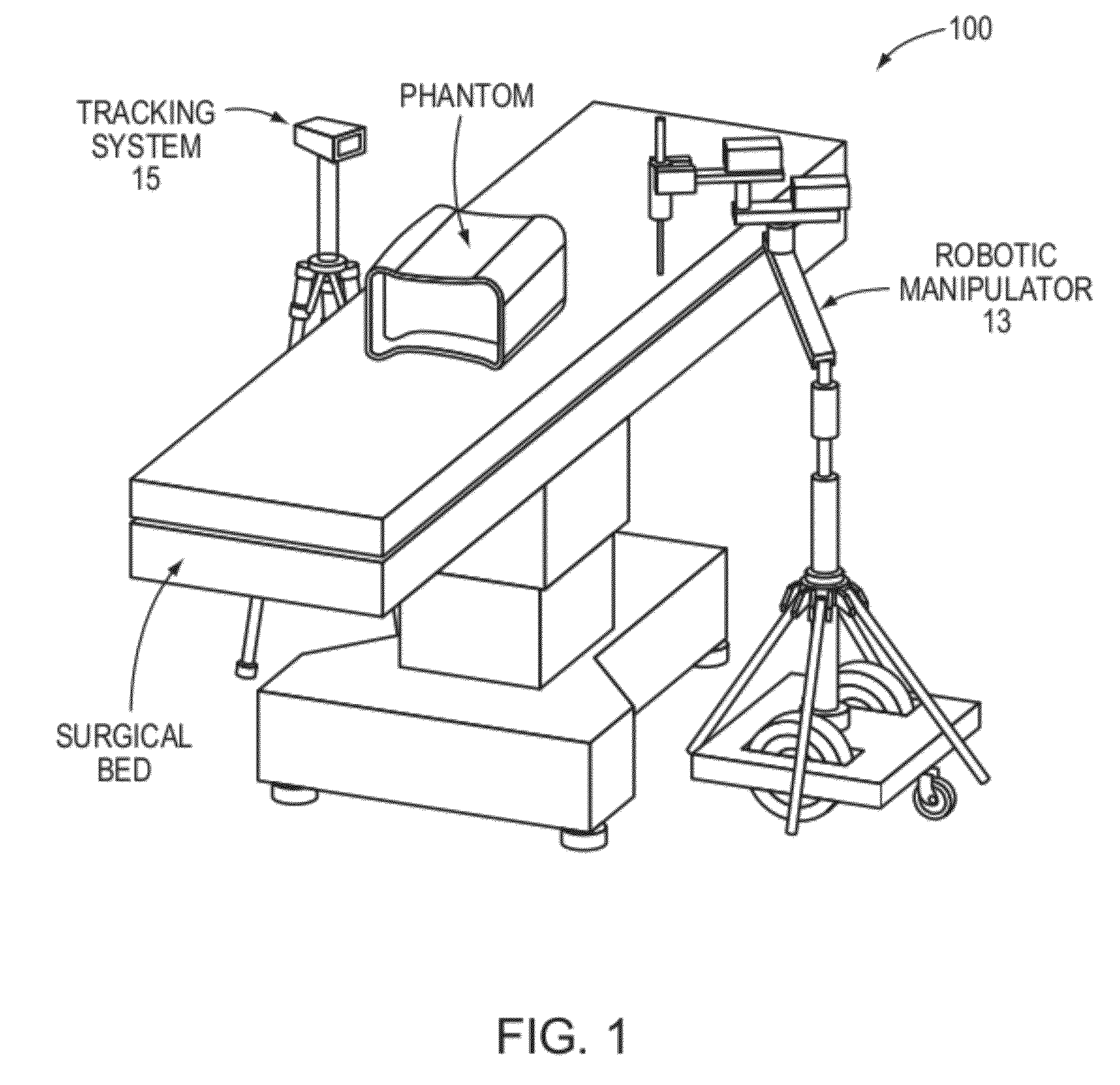
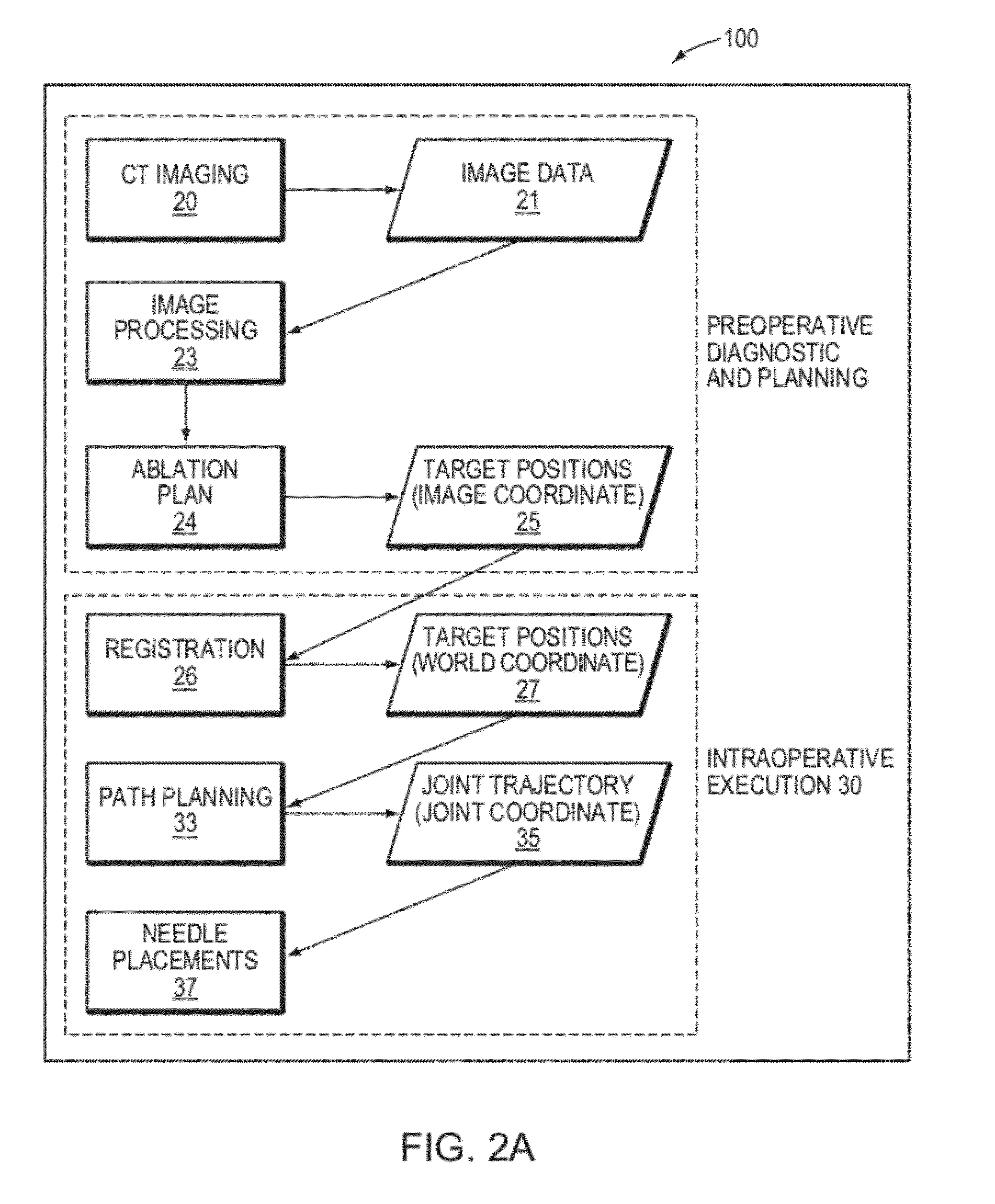
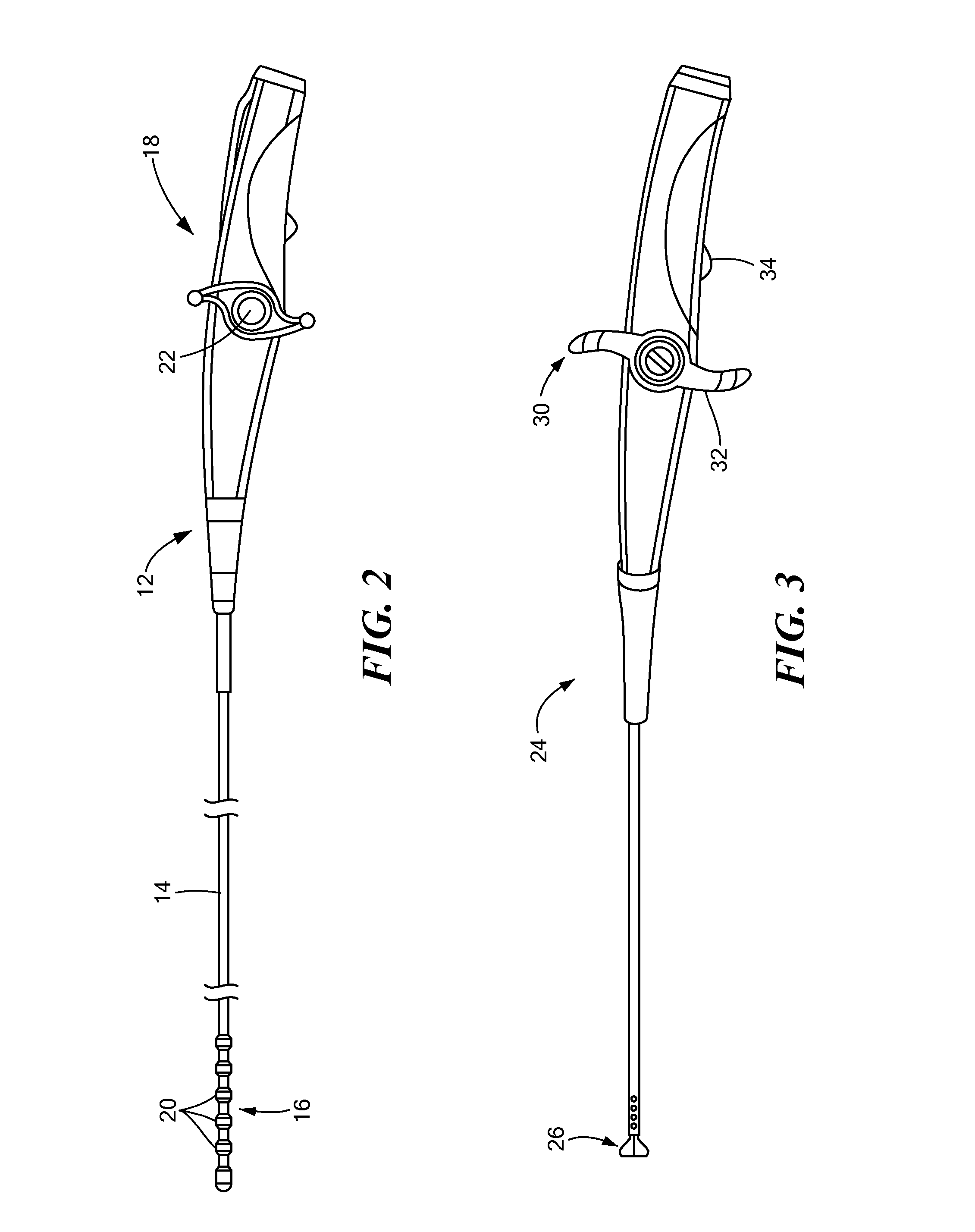
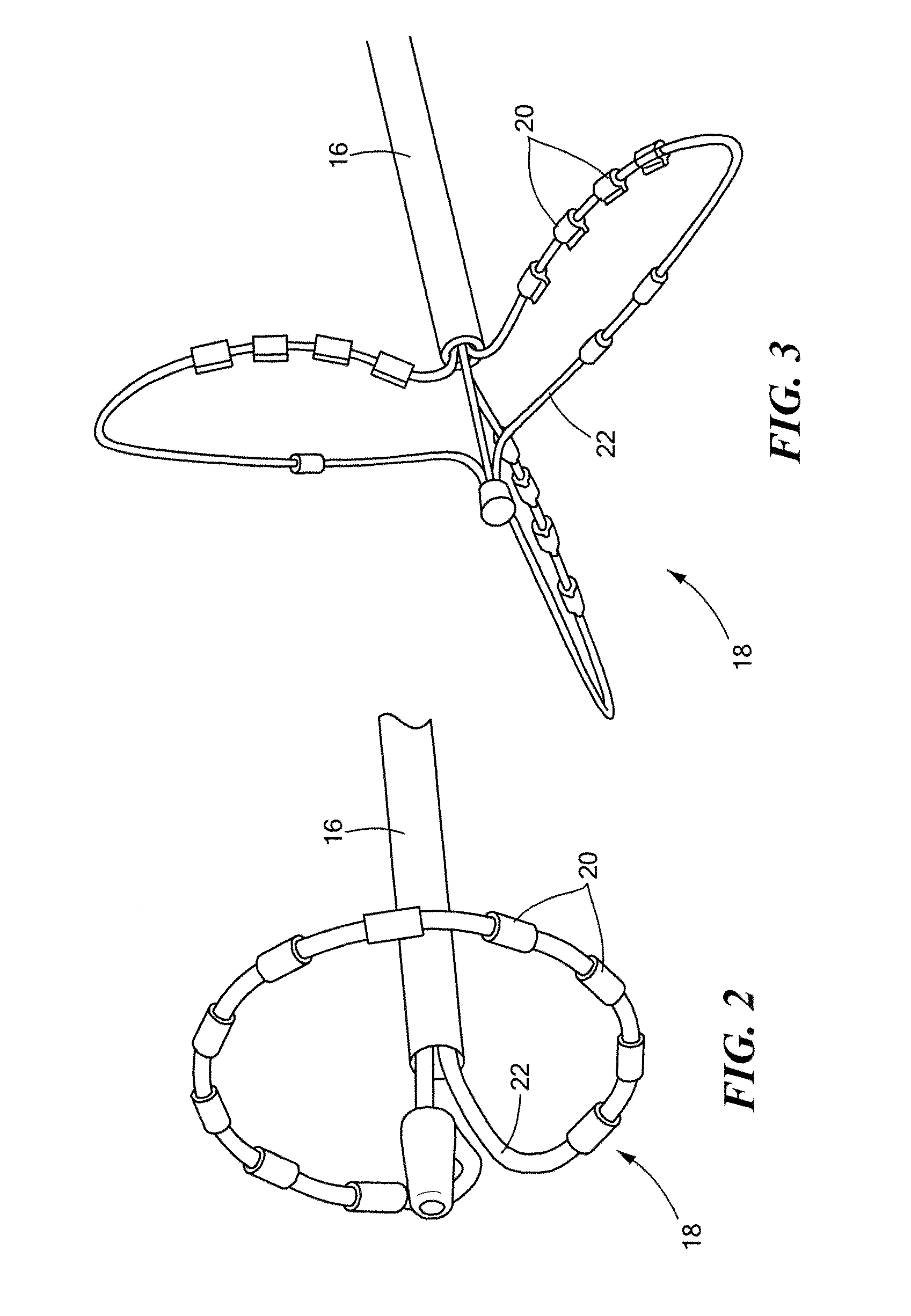
Transcutaneous robot-assisted ablation-device insertion navigation system
InactiveUS20120226145A1Easy to operateFacilitates potential expansionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesRadiofrequency ablationControl system design
A robotic system for overlapping radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in tumor treatment is disclosed. The robot assisted navigation system is formed of a robotic manipulator and a control system designed to execute preoperatively planned needle trajectories. Preoperative imaging and planning is followed by interoperative robot execution of the ablation treatment plan. The navigation system combines mechanical linkage sensory units with an optical registration system. There is no requirement for bulky hardware installation or computationally demanding software modules. Final position of the first needle placement is confirmed for validity with the plan and then is used as a reference for the subsequent needle insertions and ablations.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
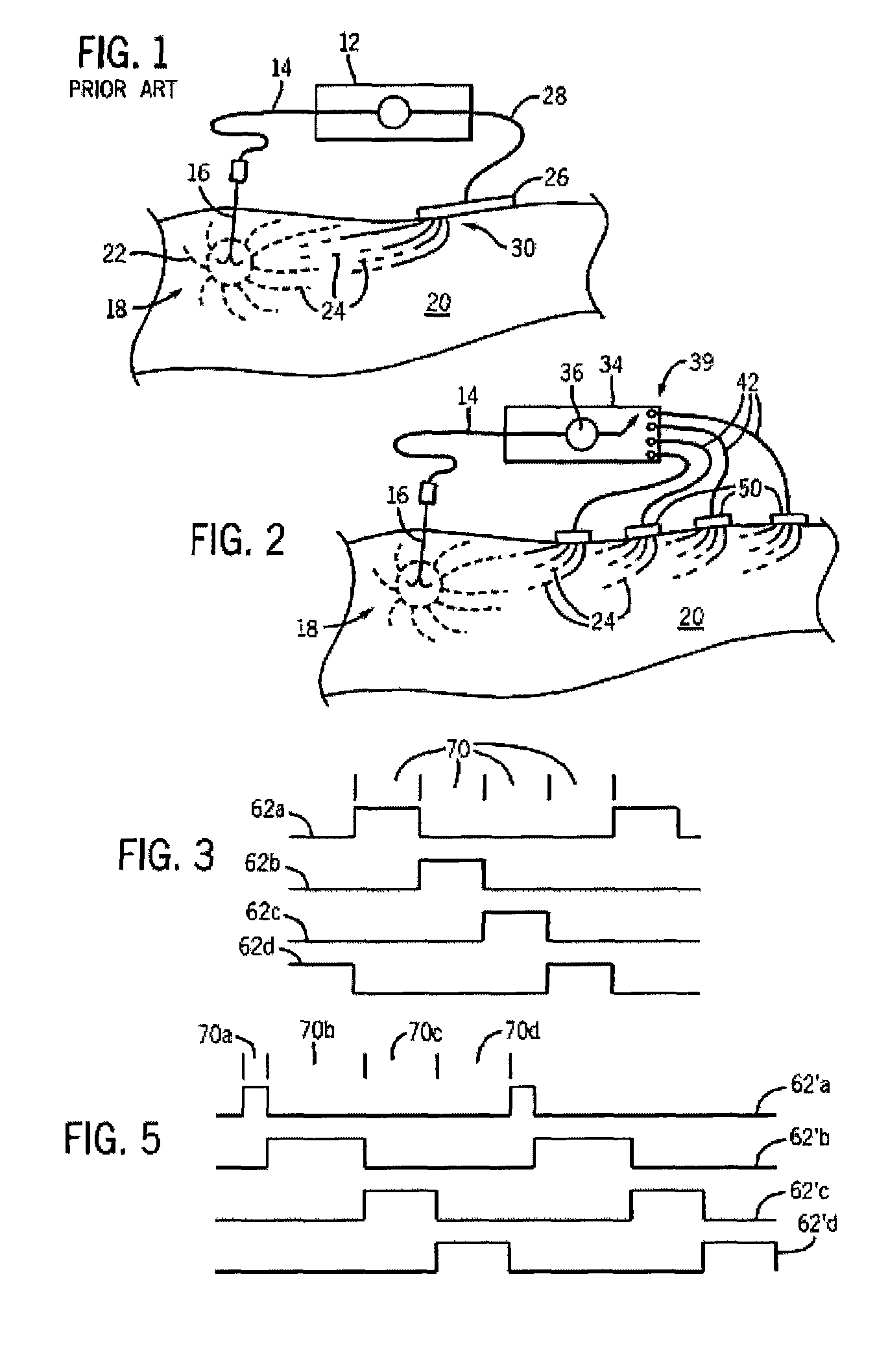
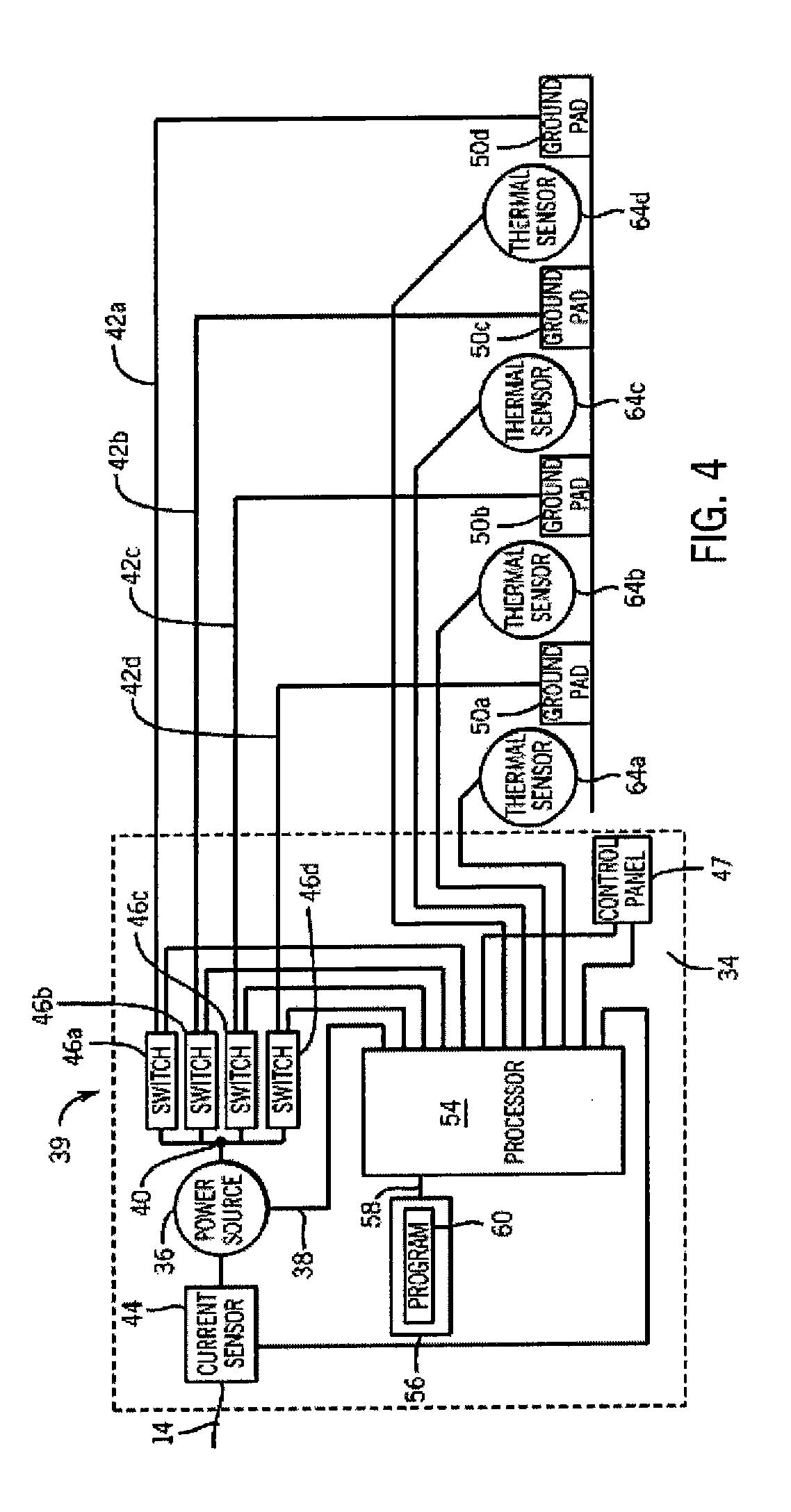
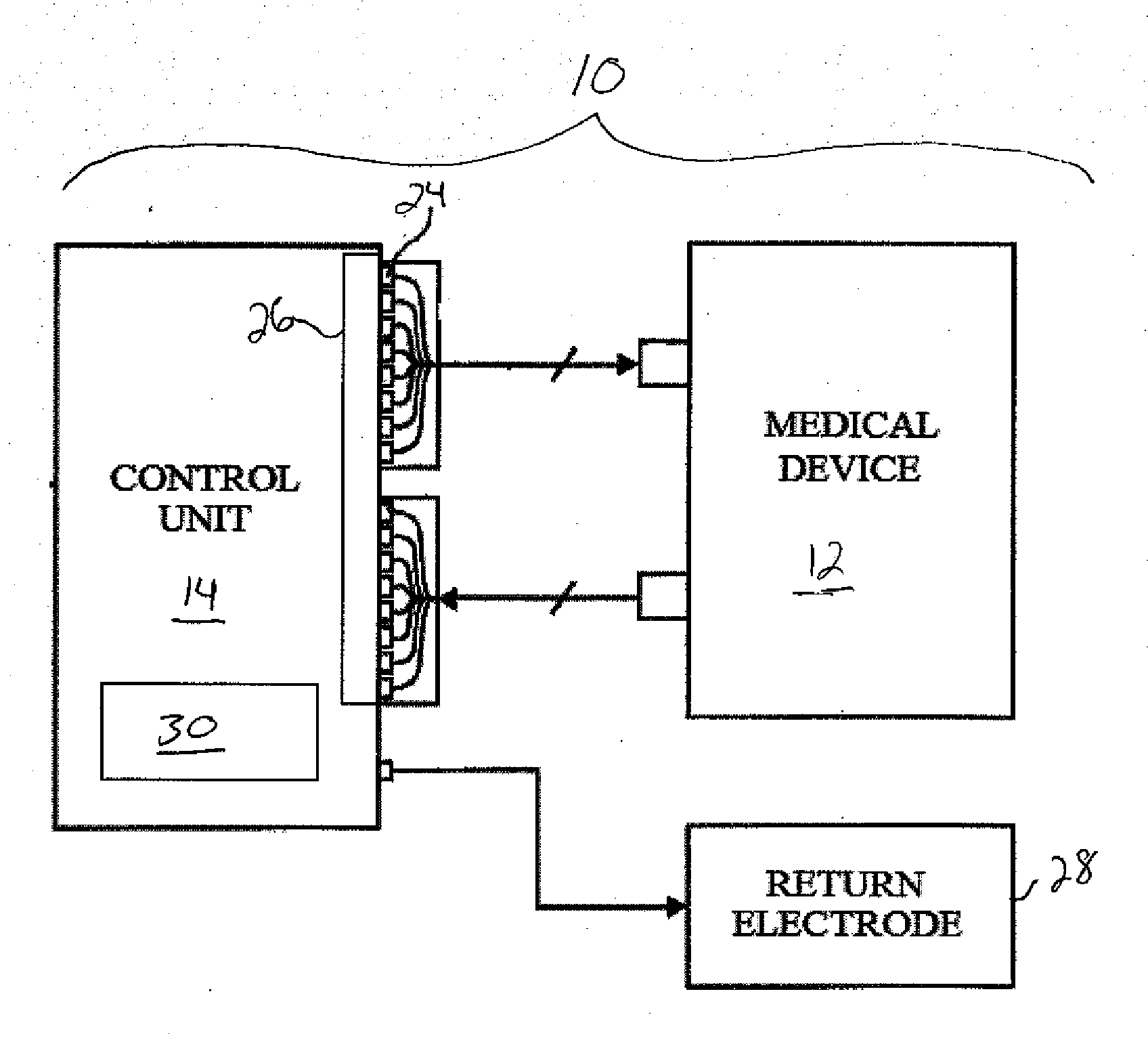
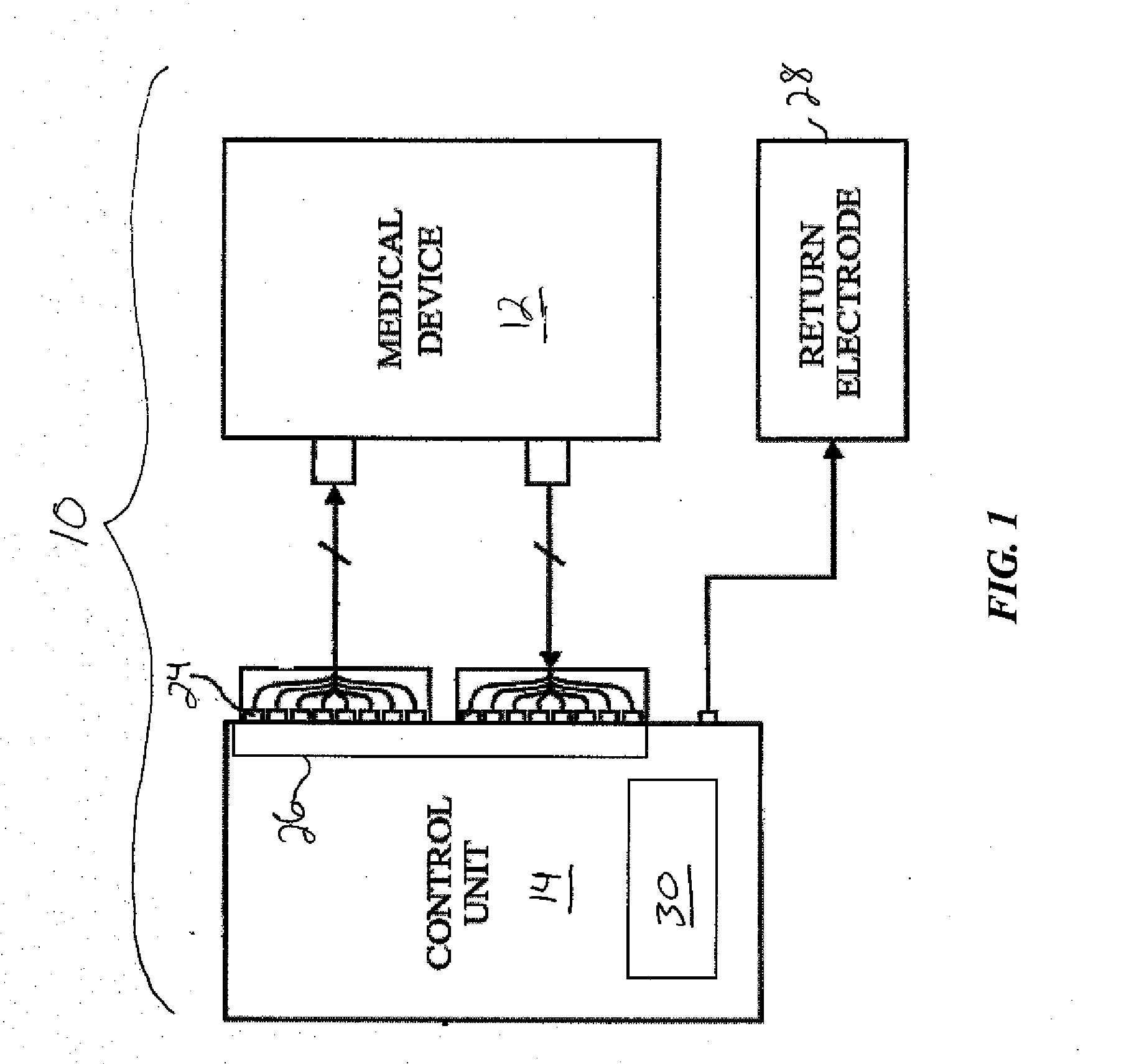
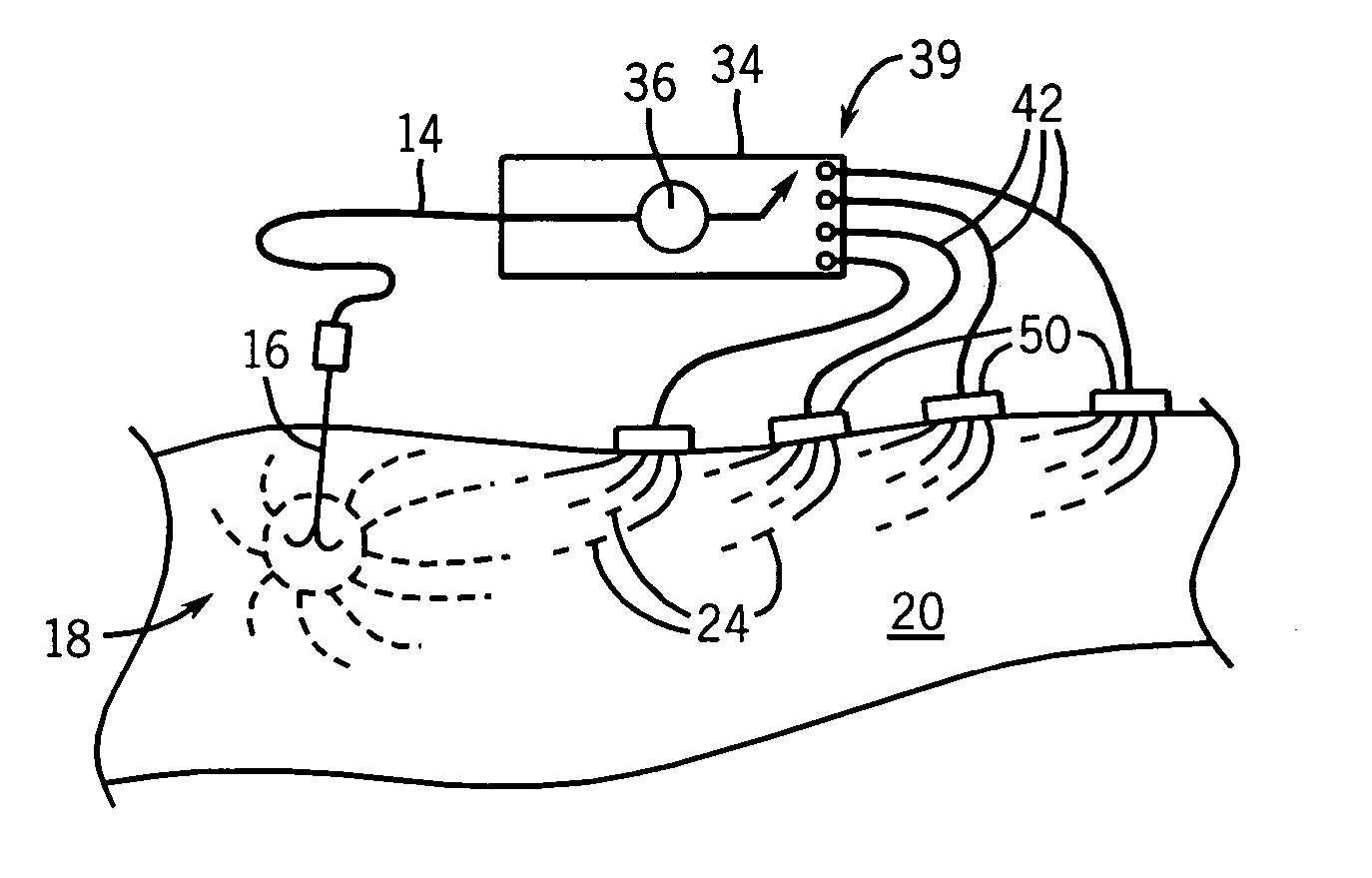
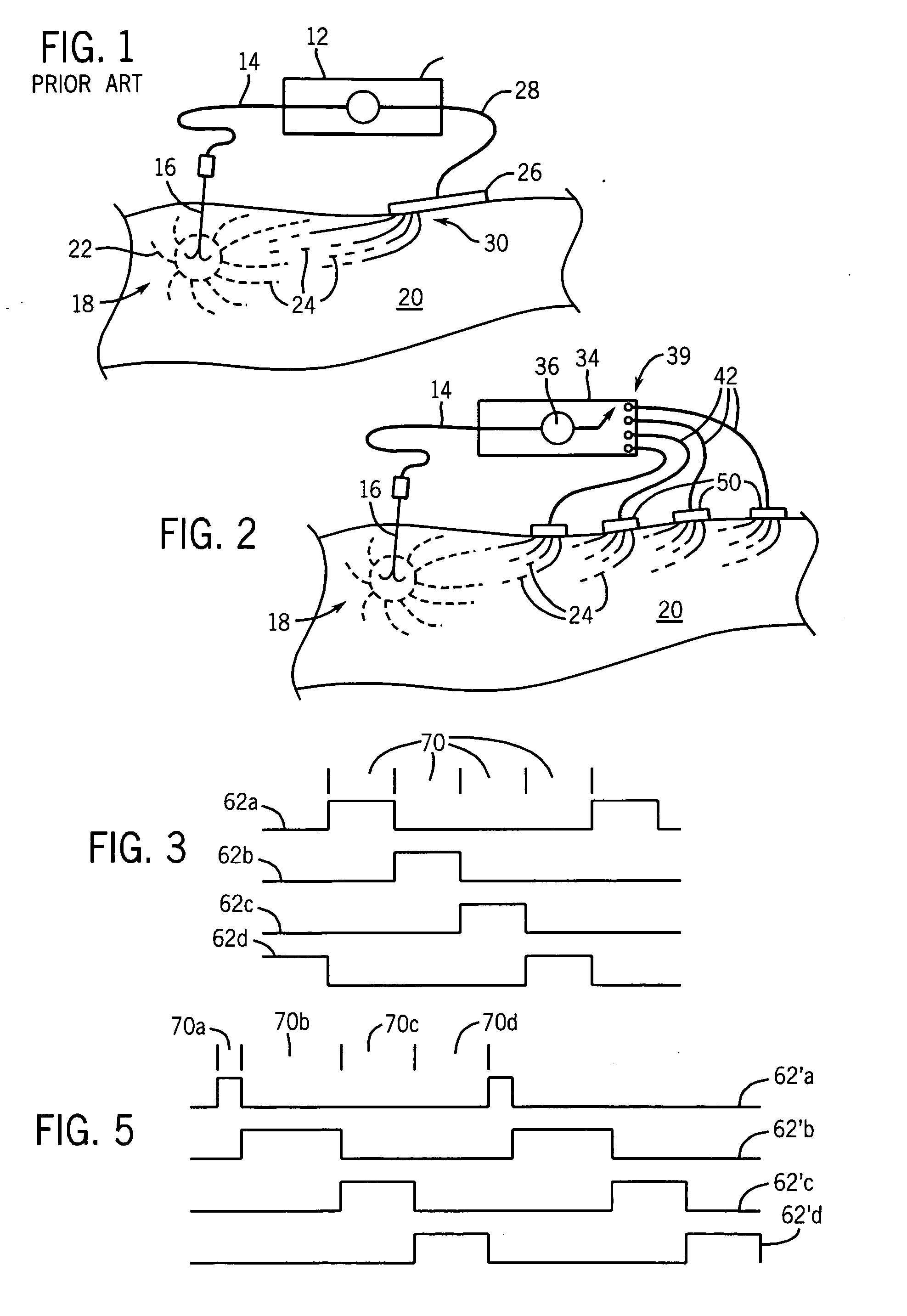
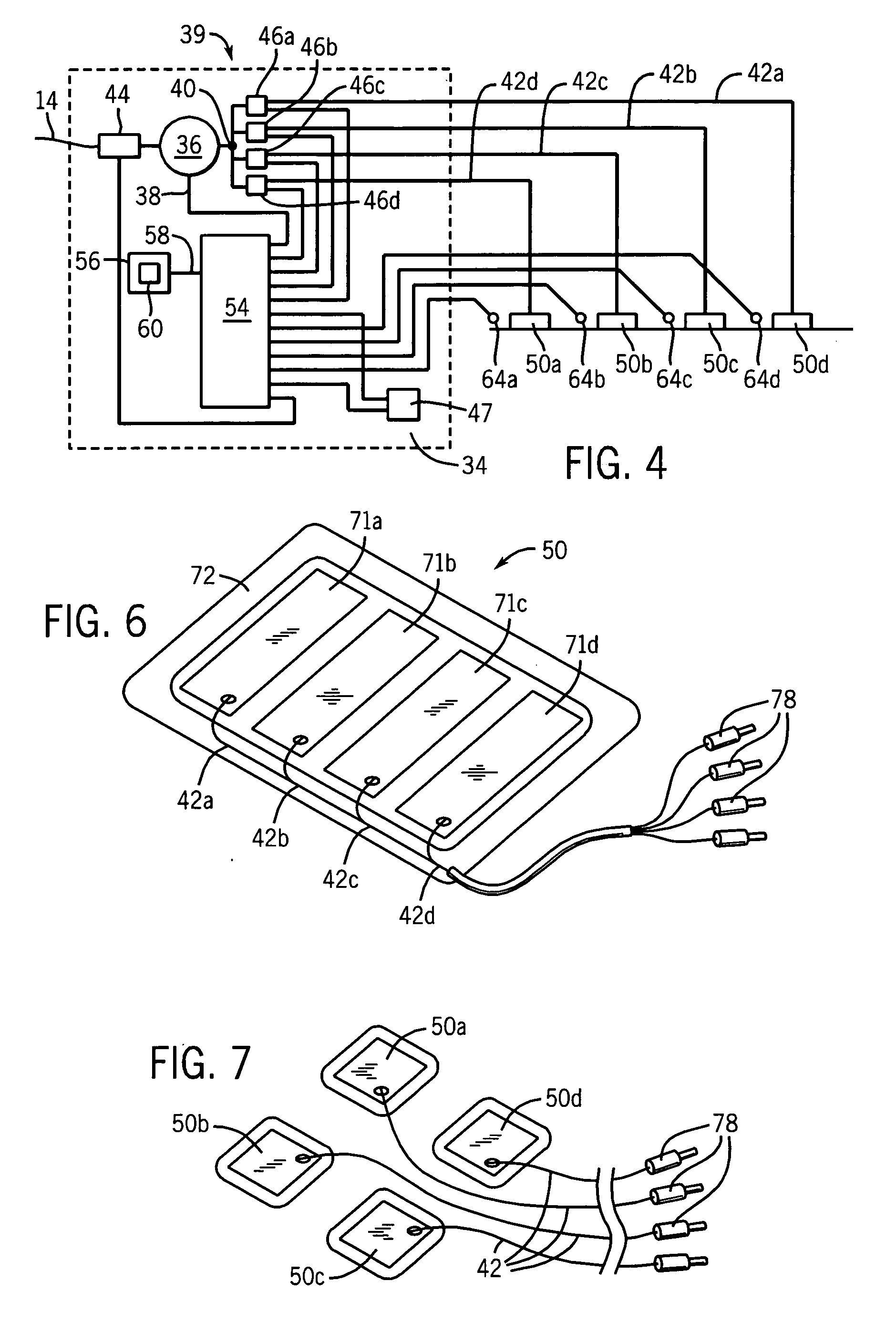
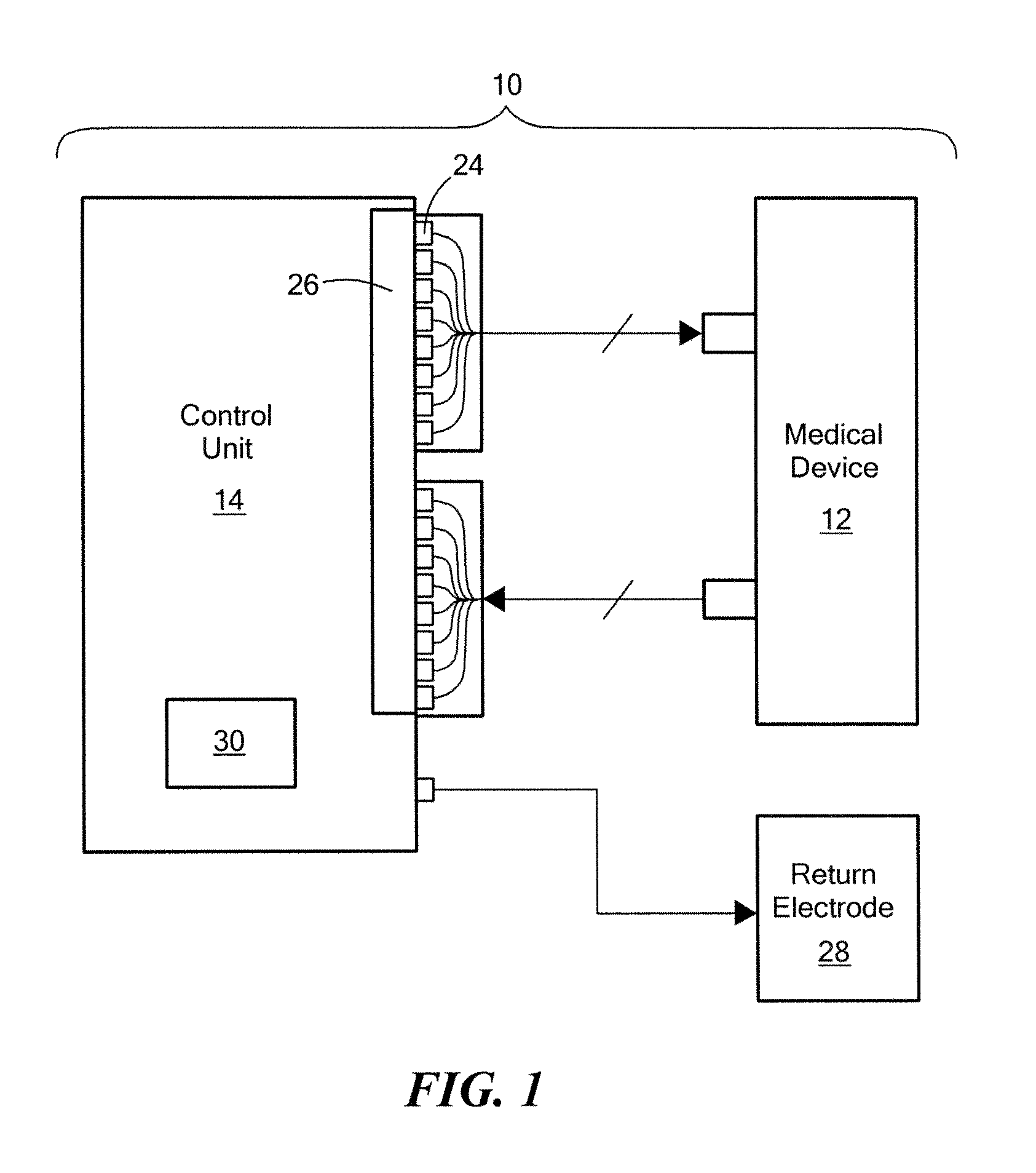
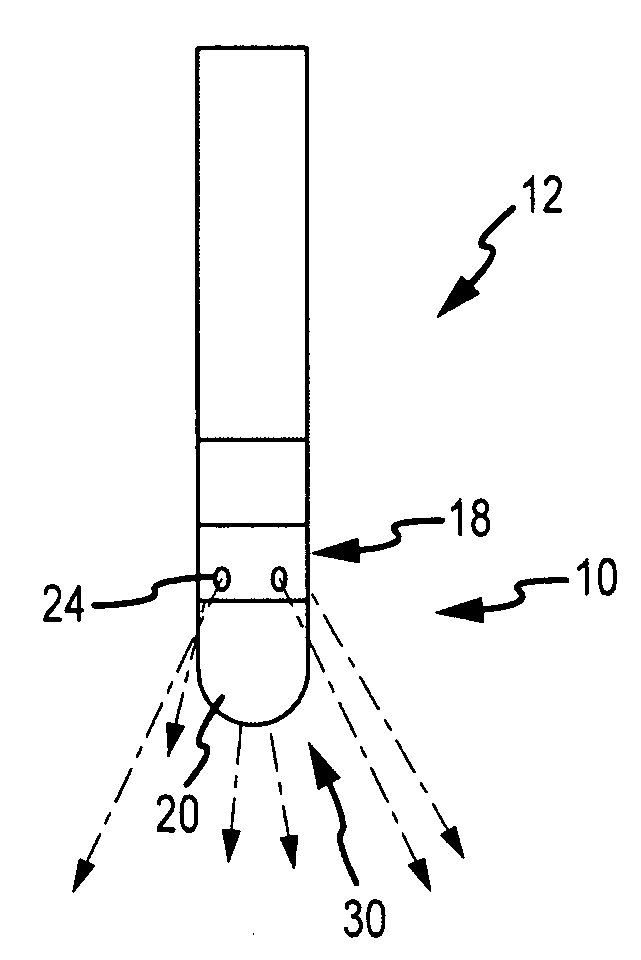
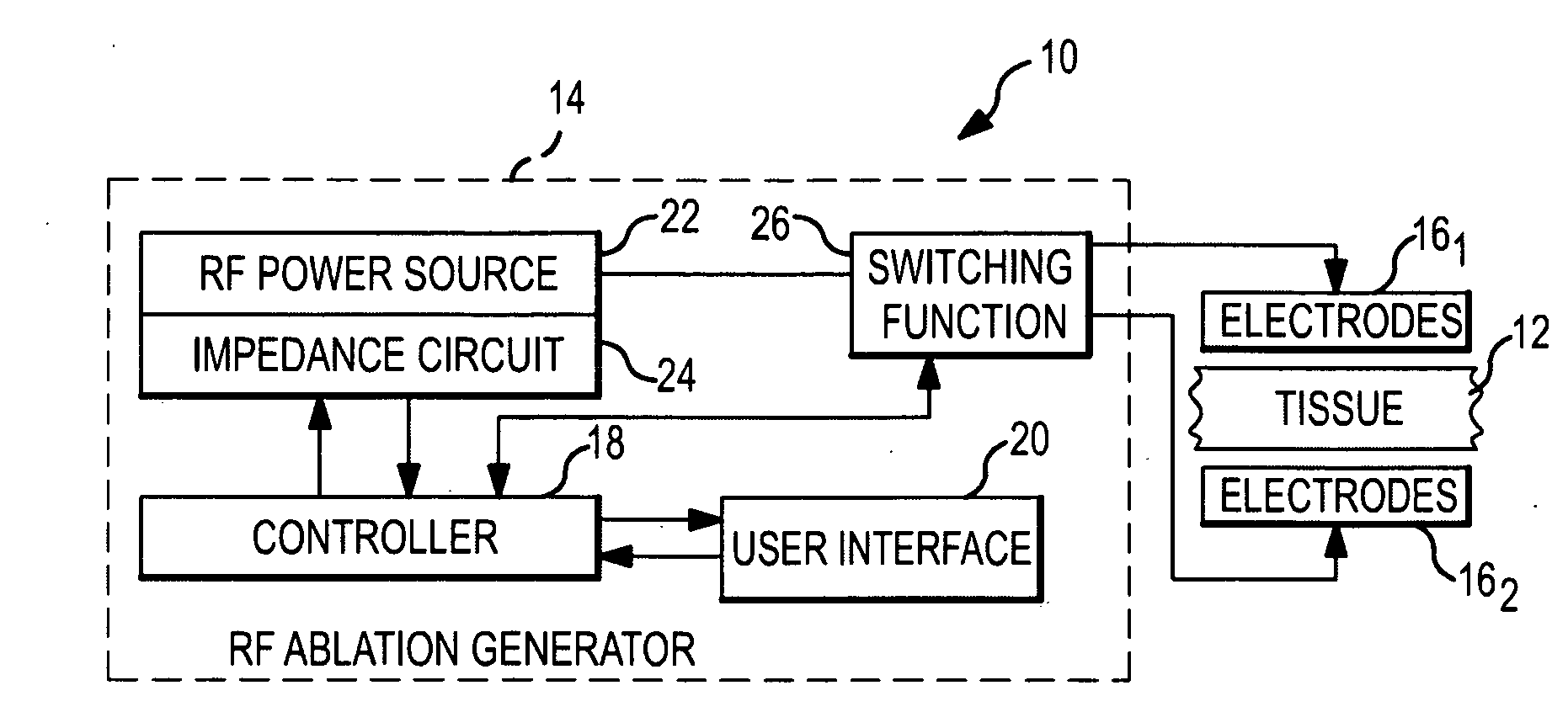
Radiofrequency ablation with independently controllable ground pad conductors
ActiveUS7736357B2Opportunities decreaseReducing maximum power outputSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationElectrical conductor
A radiofrequency ablation system provides multiple ground pads and active control of current flow through the ground pads to provide improved power sharing at the tissue near the ground pads reducing risk of patient skin burns for higher power ablation generators.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
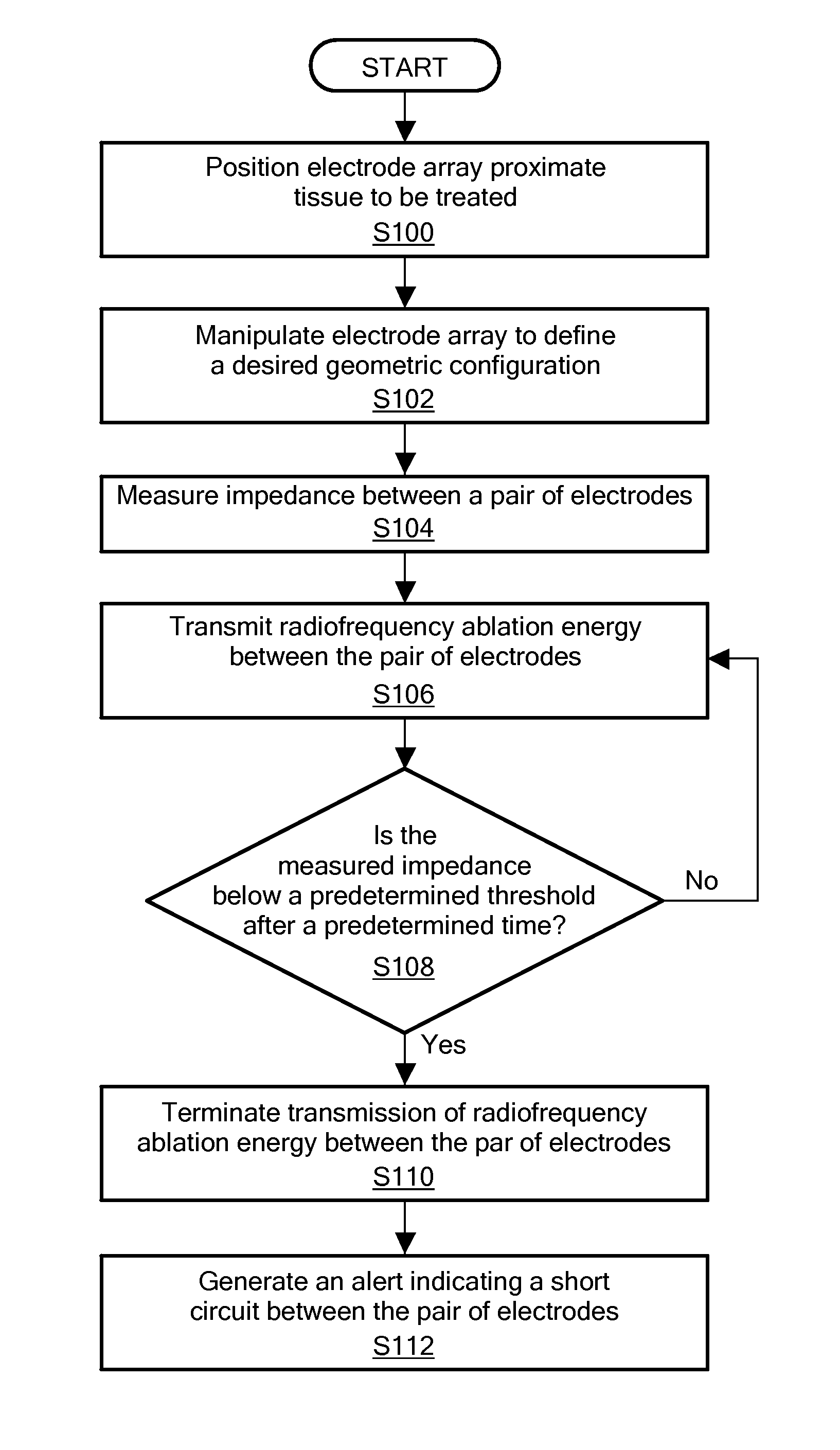
Detection of microbubble formation during catheter ablation
A method and system for detecting microbubble formation during a radiofrequency ablation procedure. The method includes measuring an impedance of a pair of electrodes, at least one electrode in the pair of electrodes being coupled to a treatment assembly of a medical device. Radiofrequency ablation energy is transmitted between the pair of electrodes. The transmission of radiofrequency ablation energy between the pair of electrodes is terminated when after a predetermined period of time the measured impedance in either of the electrodes in the pair of electrodes is a predetermined percentage above a measured minimum impedance and a measured power is above a predetermined power threshold. An alert is generated indicating at least one of the formation and release of microbubbles proximate the pair of electrodes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
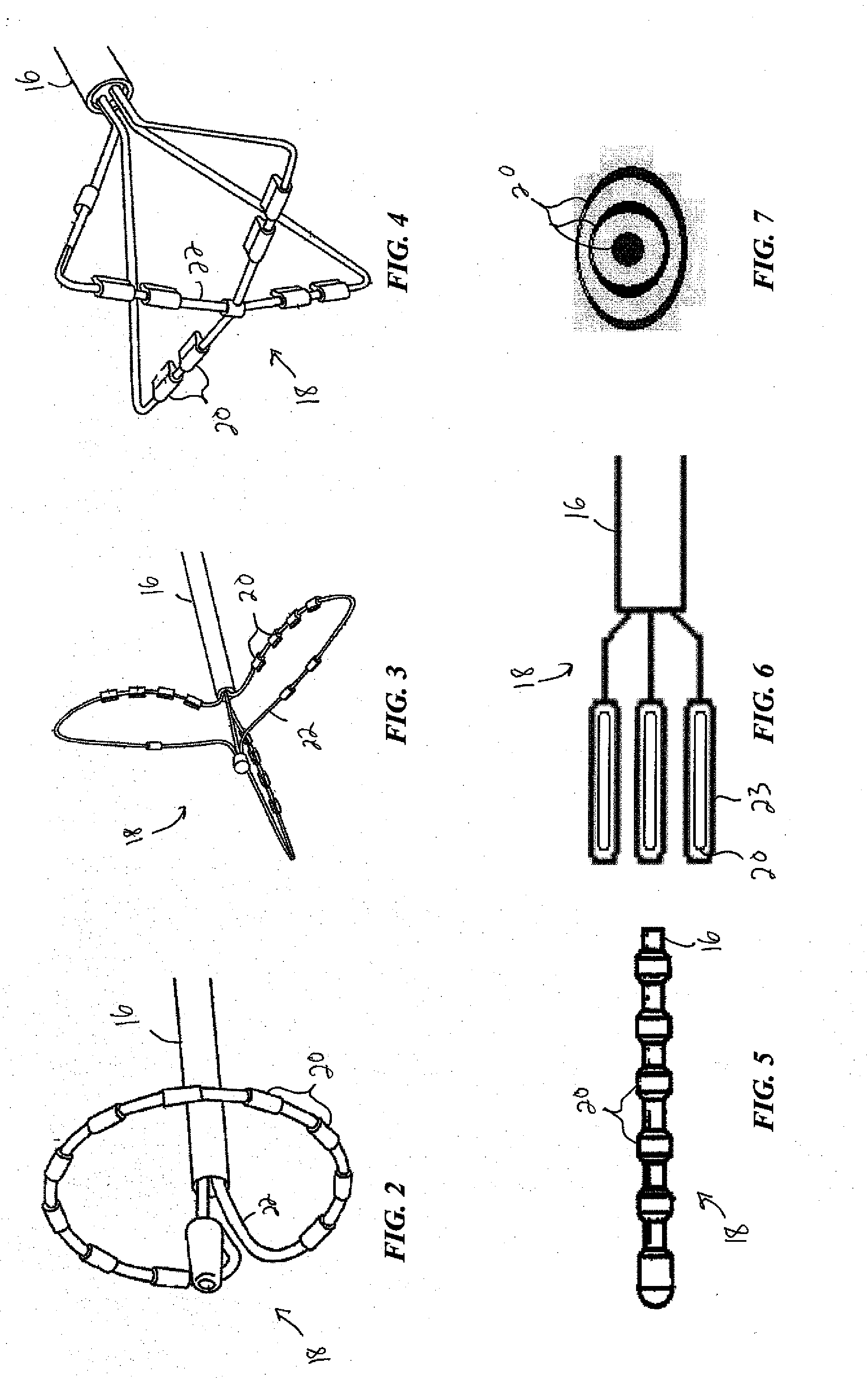
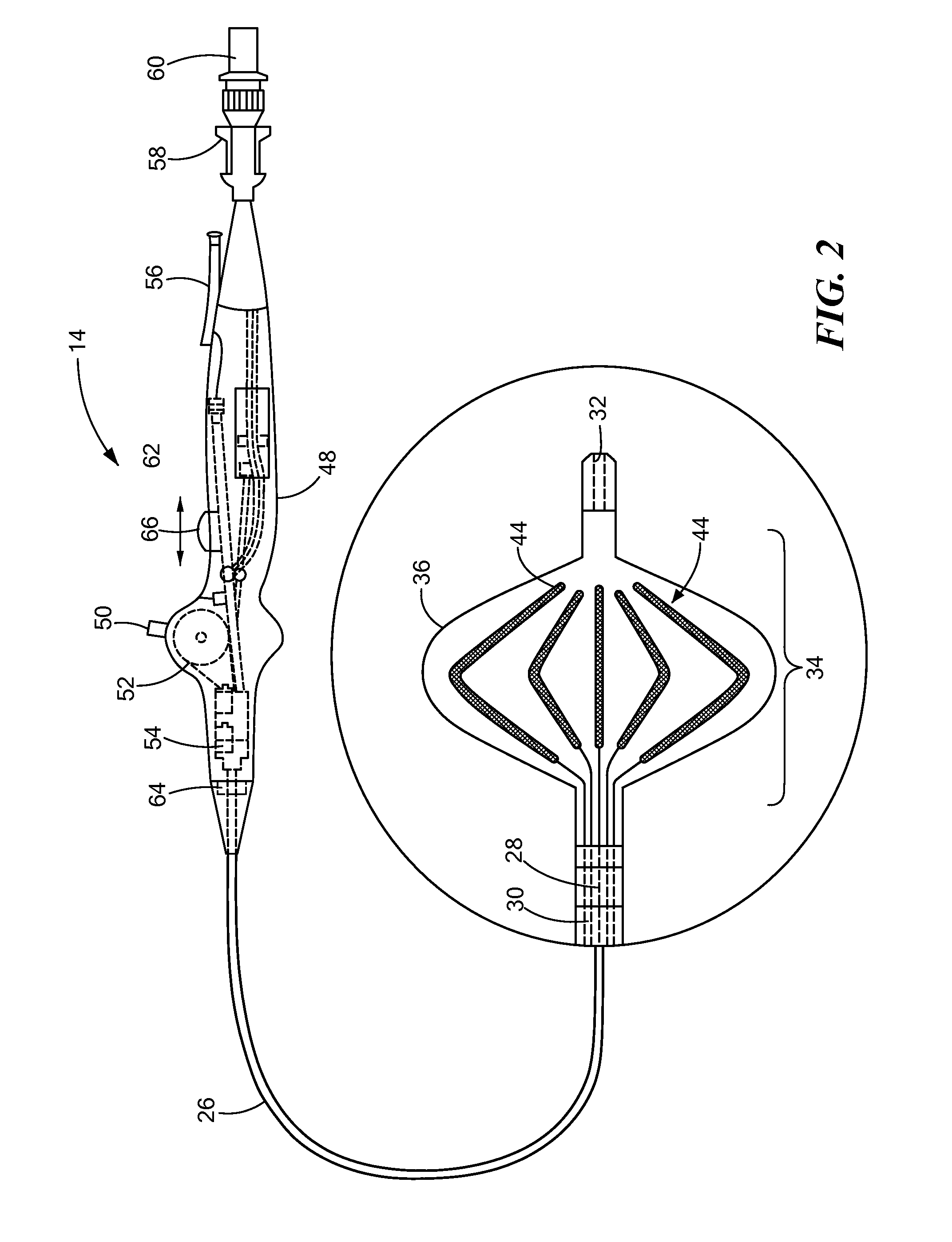
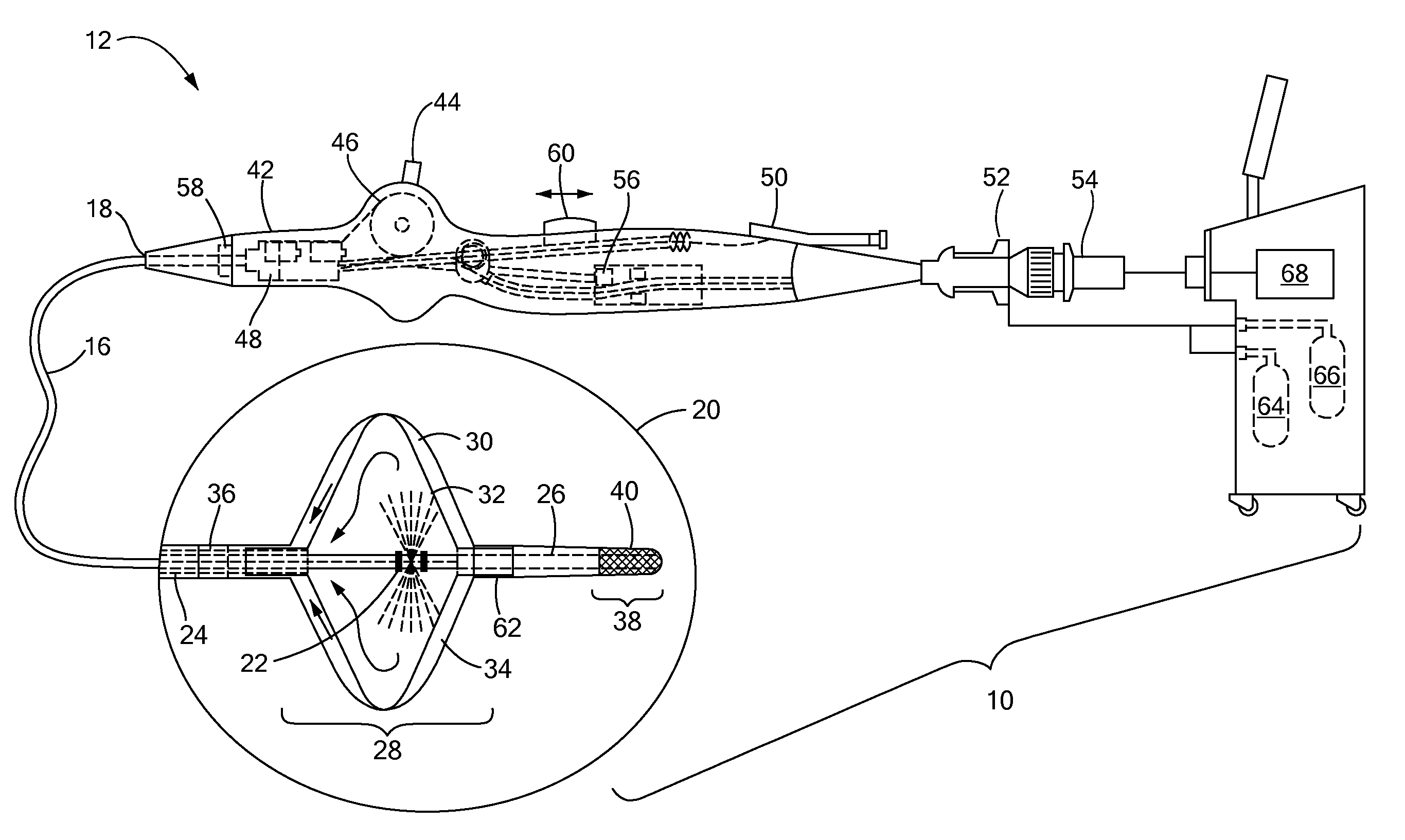
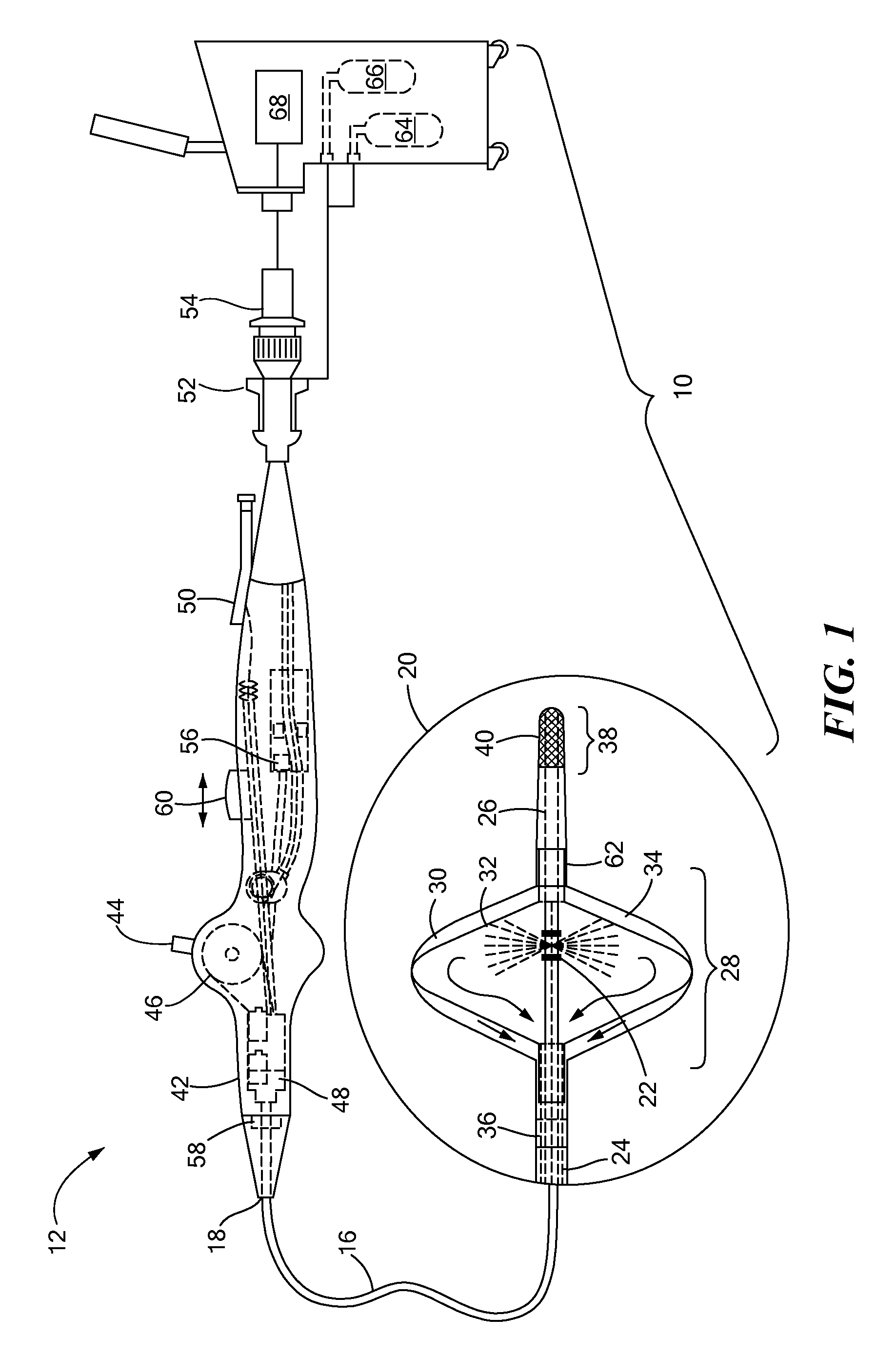
Multipolarity epicardial radiofrequency ablation
ActiveUS20120172859A1Increase rangeAdd depthSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesRadiofrequency ablationRadio frequency
A method of ablating an epicardial tissue region, including positioning a medical device adjacent the epicardial tissue region, the medical device having a first electrode, a second electrode, and a third electrode located in between the first and second electrodes; delivering an irrigation fluid to the tissue region; and ablating at least a portion of the tissue region by sequentially activating the third electrode in a monopolar radiofrequency delivery mode and activating the first and second electrodes in a bipolar radiofrequency delivery mode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Methods for inhibiting angiogenesis
InactiveUS20060079538A1Facilitate clinical managementFacilitate continued complianceBiocideAnimal repellantsPhotodynamic therapyRadiofrequency ablation
The invention relates generally to methods for inhibiting angiogenesis. More particularly, methods for inhibiting angiogenesis comprise selectively inhibiting phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3Kδ) activity in endothelial cells. The methods may comprise administration of one or more cytotoxic therapies including but not limited to radiation, chemotherapeutic agents, photodynamic therapies, radiofrequency ablation, anti-angiogenic agents, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ICOS CORP +1
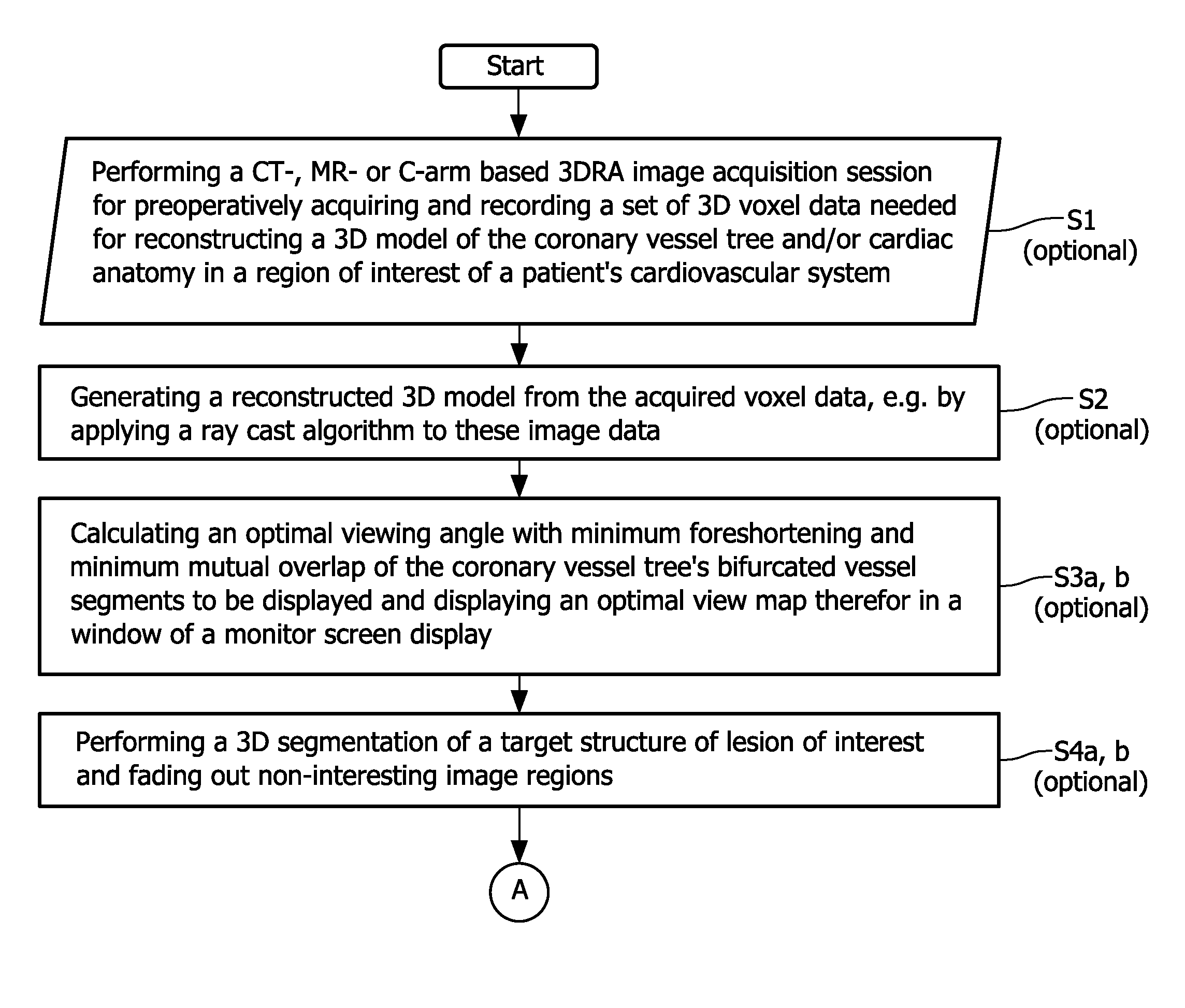
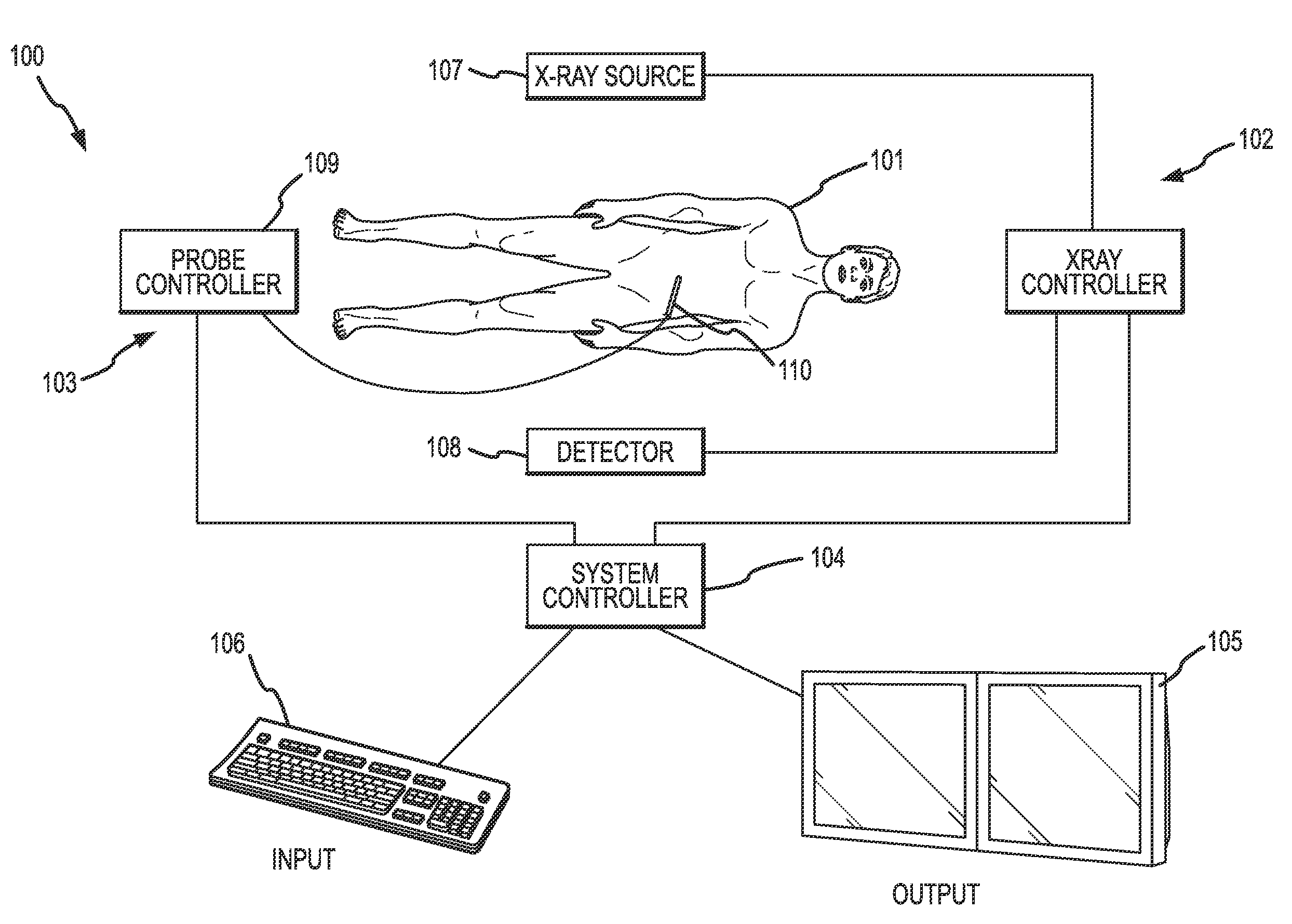
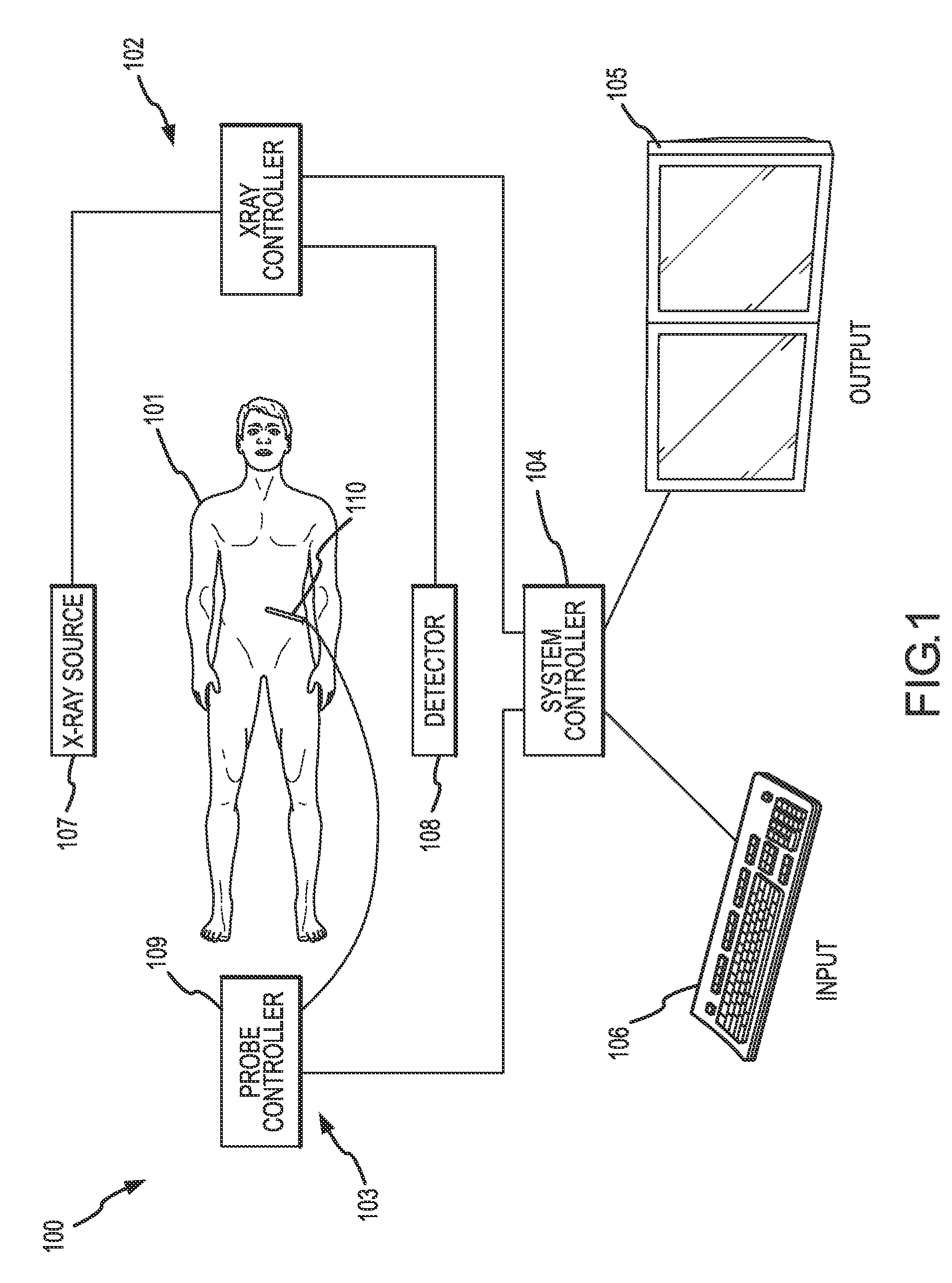
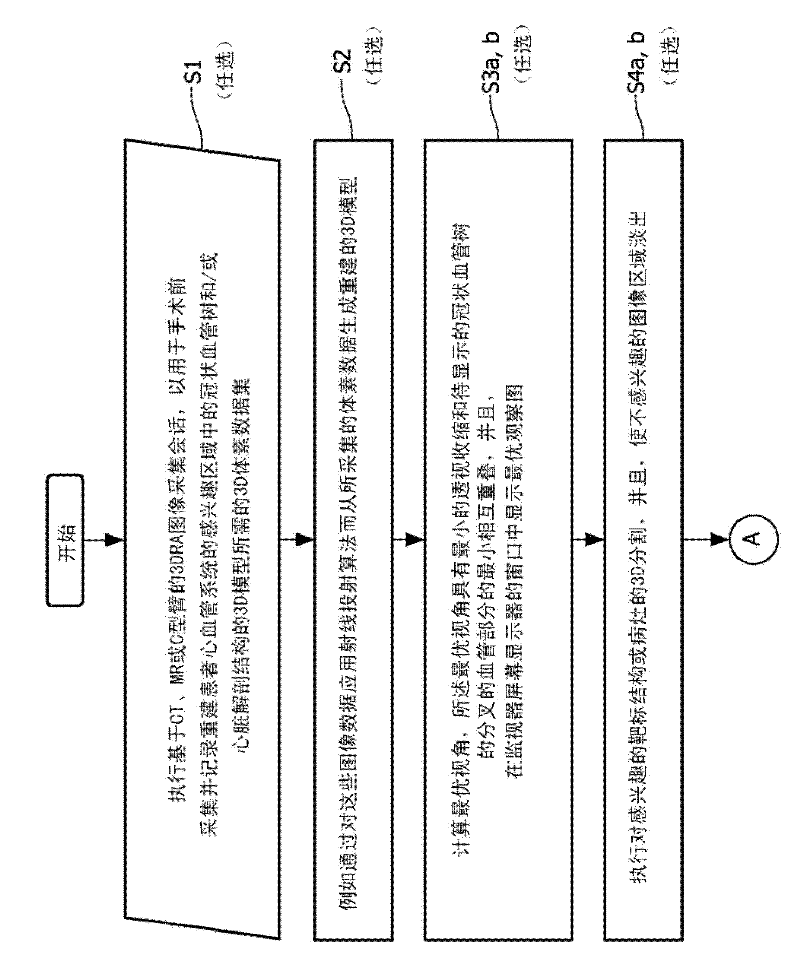
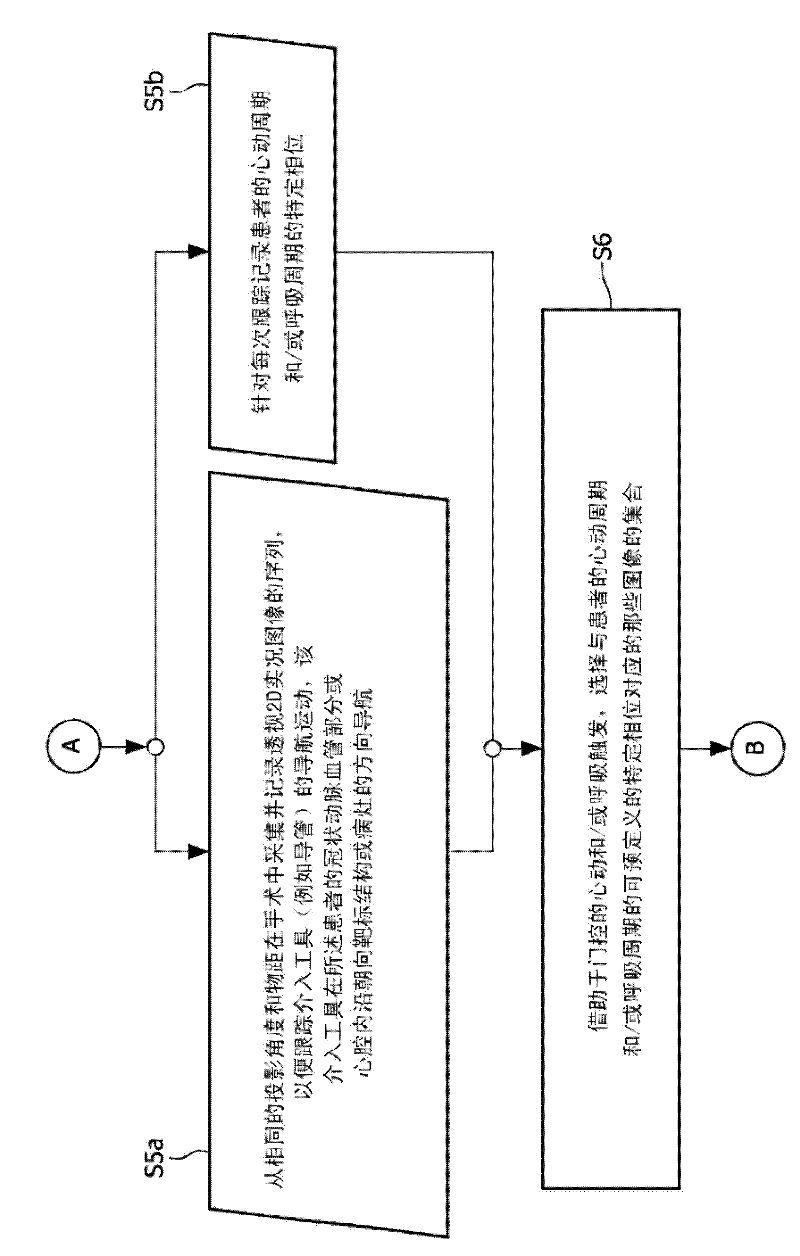
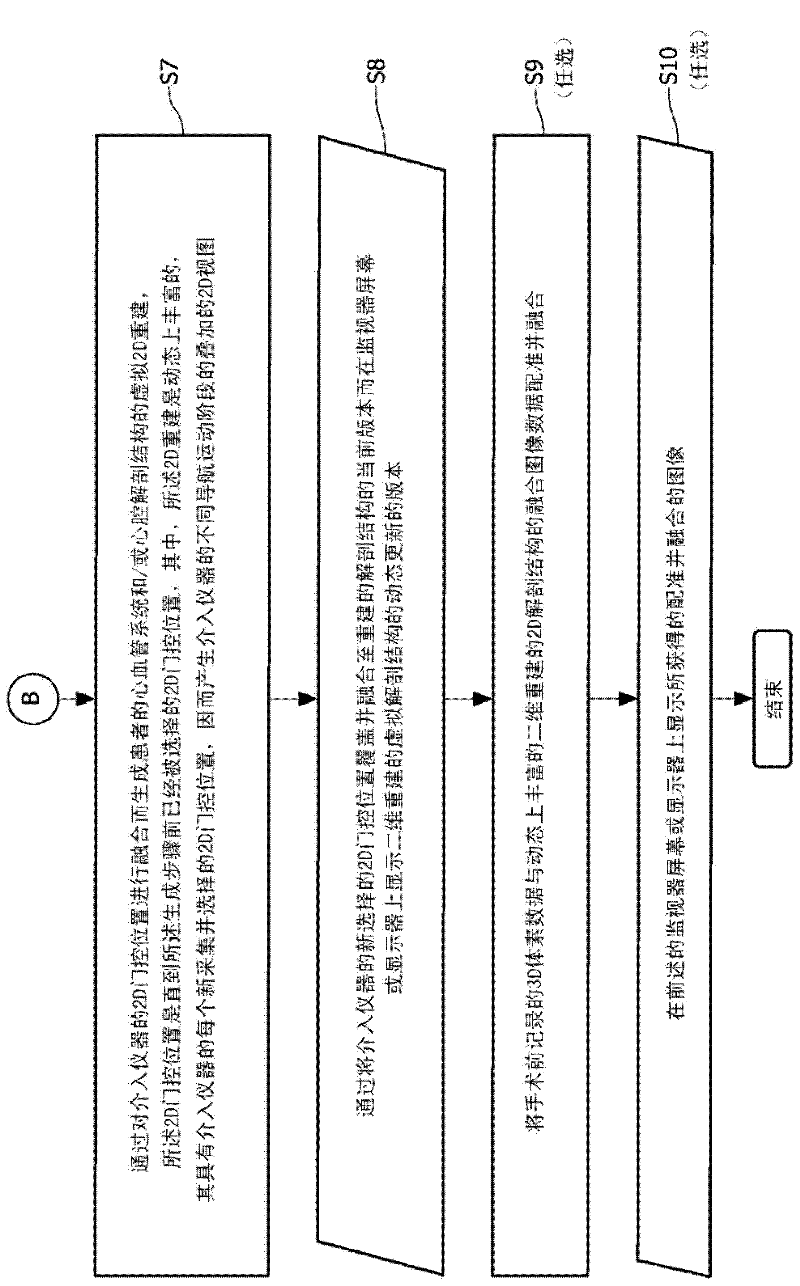
Cardiac and or respiratory gated image acquisition system and method for virtual anatomy enriched real time 2d imaging in interventional radiofrequency ablation or pace maker replacement procecure
ActiveUS20110201915A1Improve accuracyReduce inaccuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodePacemaker Placement
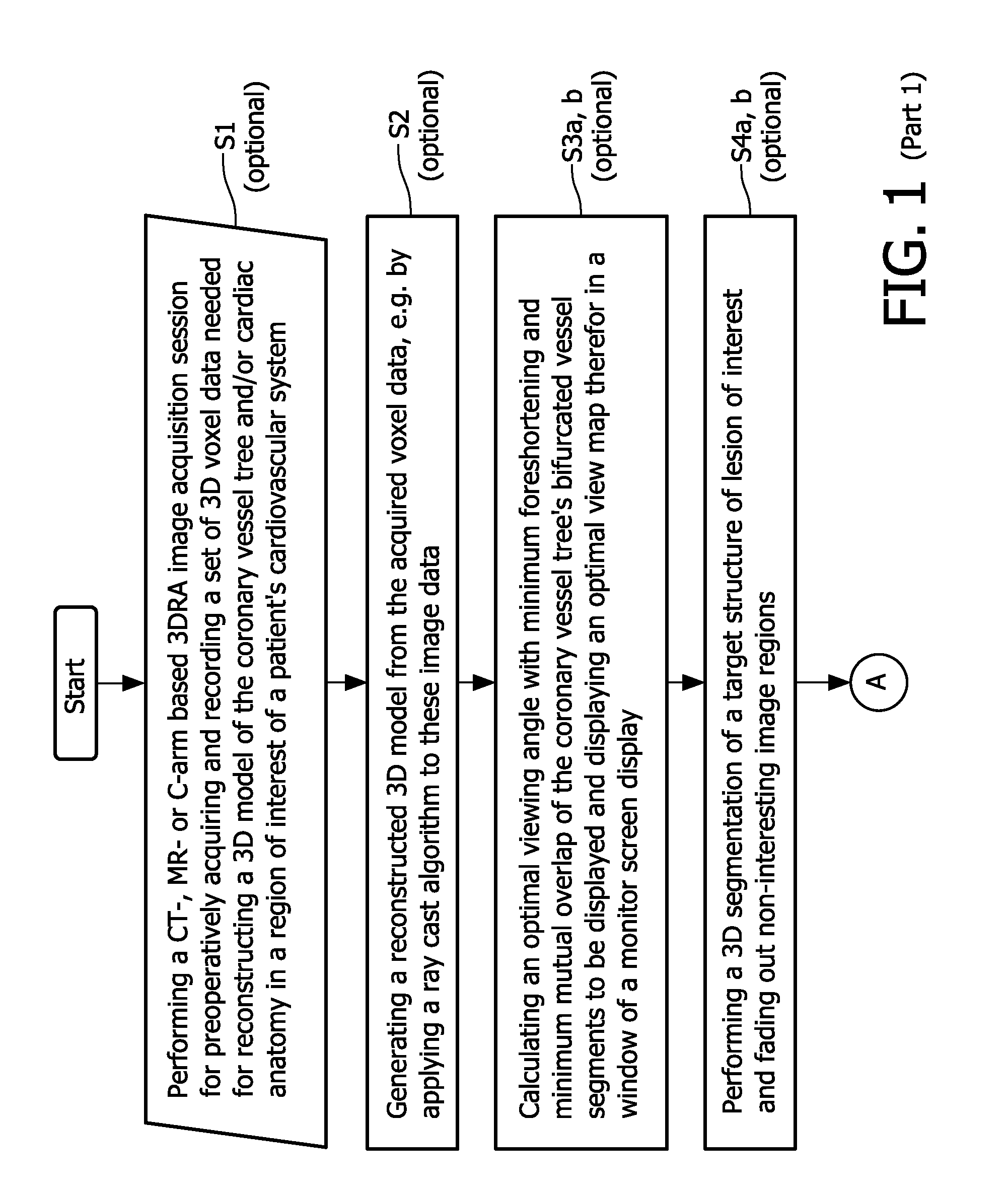
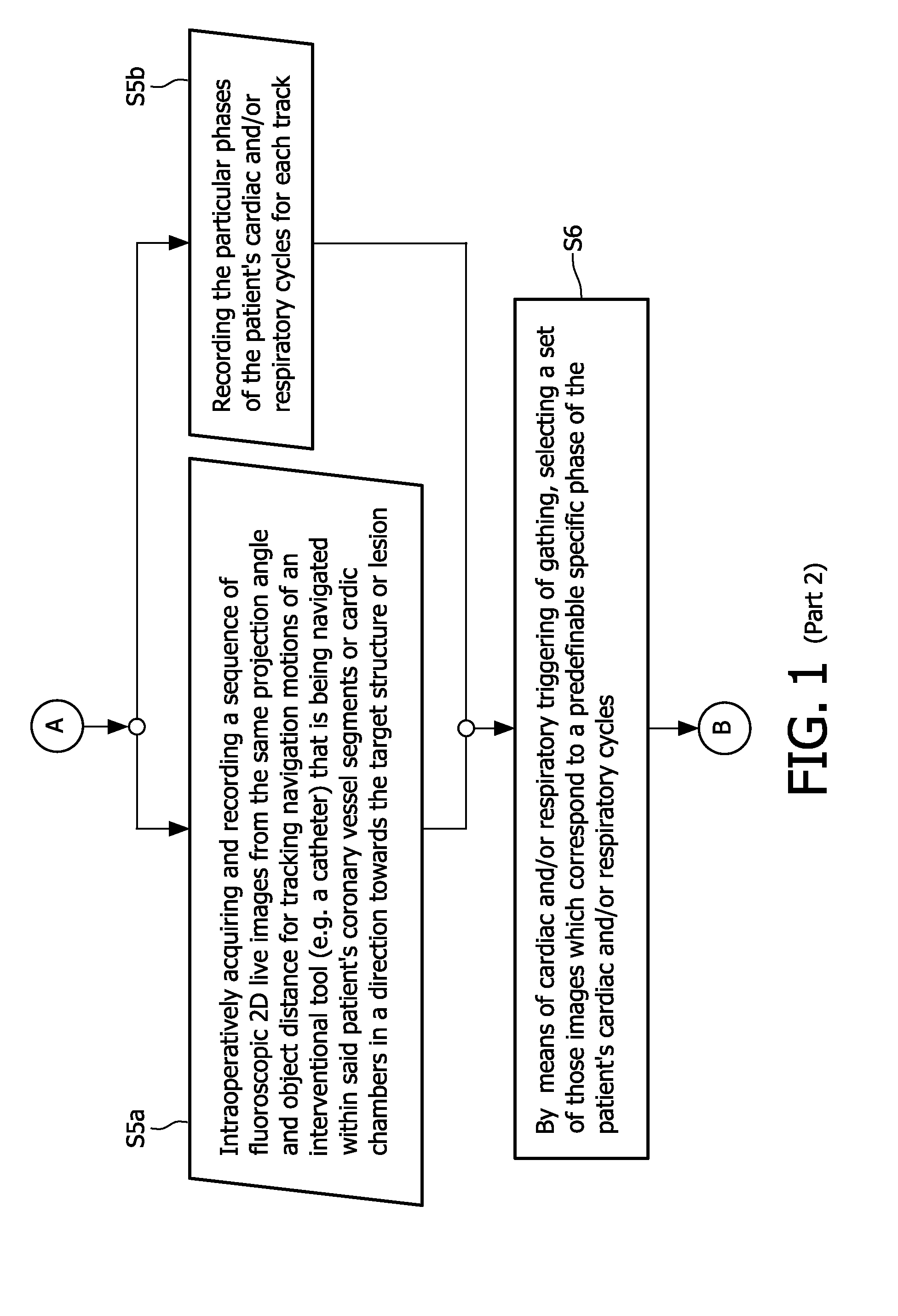
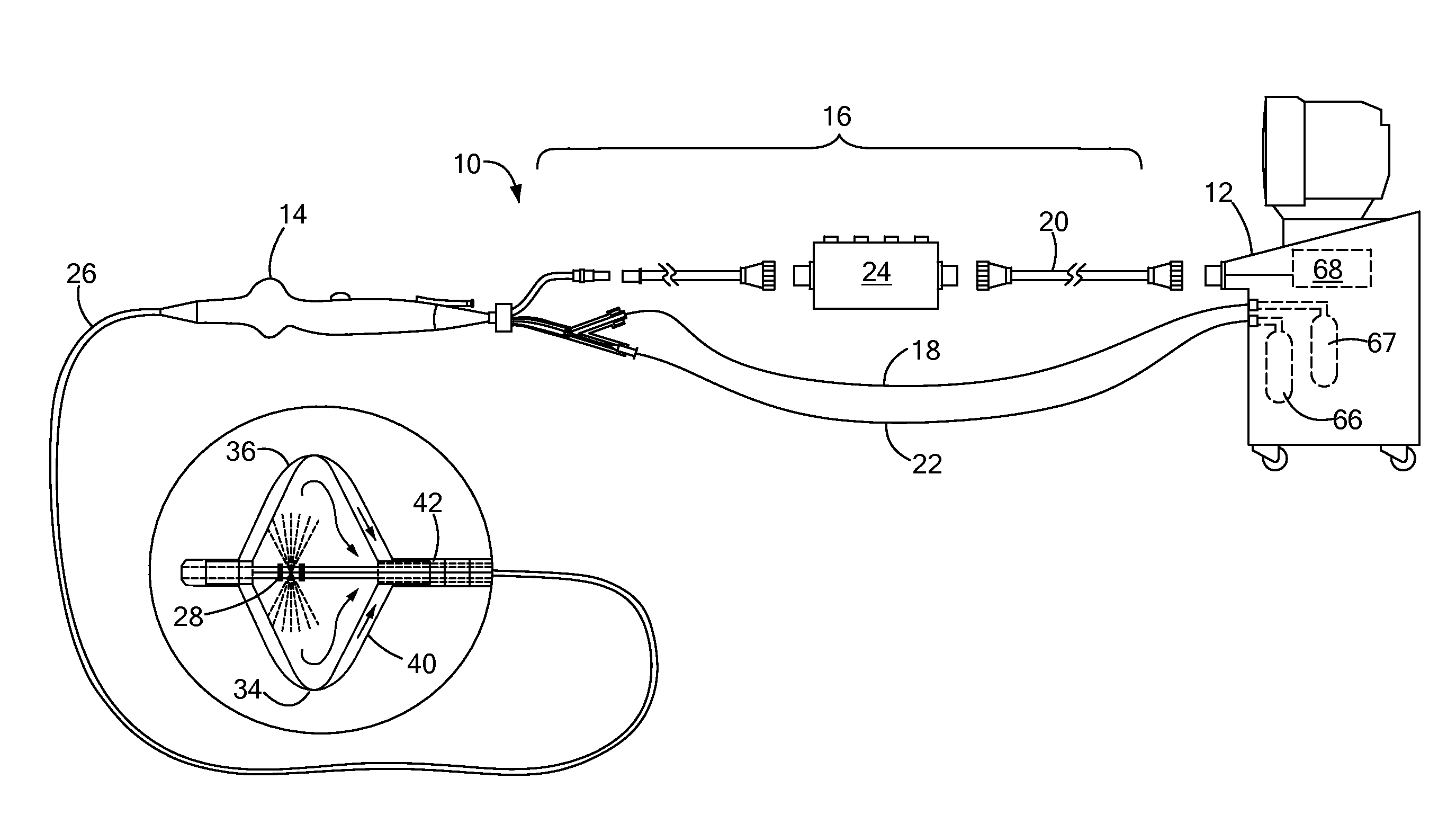
The present invention refers to the field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) and, more specifically, to image-guided radio frequency ablation and pacemaker placement procedures. For those procedures, it is proposed to display the overlaid 2D navigation motions of an interventional tool intraoperatively obtained from the same projection angle for tracking navigation motions of an interventional tool during an image-guided intervention procedure while being navigated through a patient's bifurcated coronary vessel or cardiac chambers anatomy in order to guide e.g. a cardiovascular catheter to a target structure or lesion in a cardiac vessel segment of the patient's coronary venous tree or to a region of interest within the myocard. In such a way, a dynamically enriched 2D reconstruction of the patient's anatomy is obtained while moving the interventional instrument. By applying a cardiac and / or respiratory gating technique, it can be provided that the 2D live images are acquired during the same phases of the patient's cardiac and / or respiratory cycles. Compared to prior-art solutions which are based on a registration and fusion of image data independently acquired by two distinct imaging modalities, the accuracy of the two-dimensionally reconstructed anatomy is significantly enhanced.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
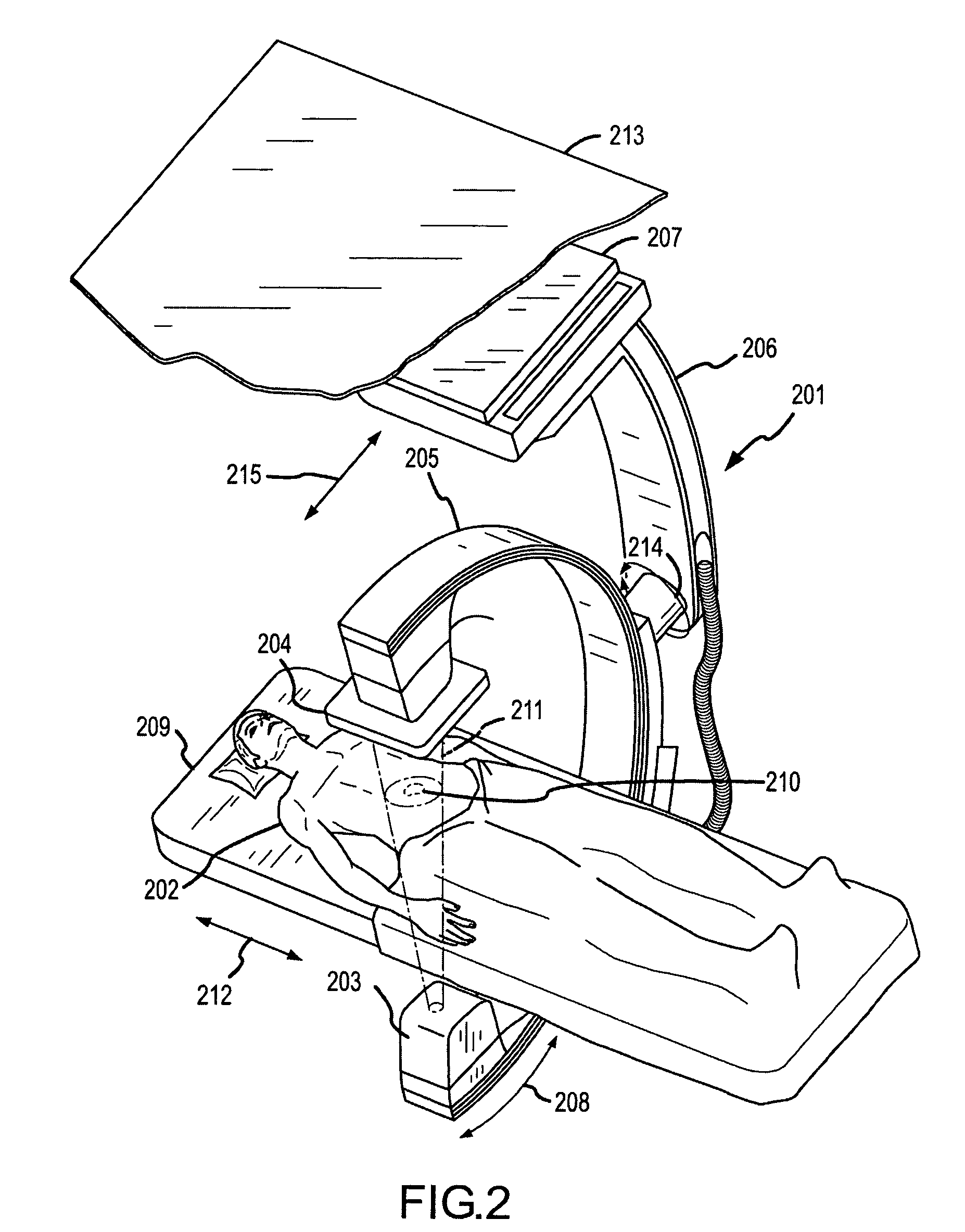
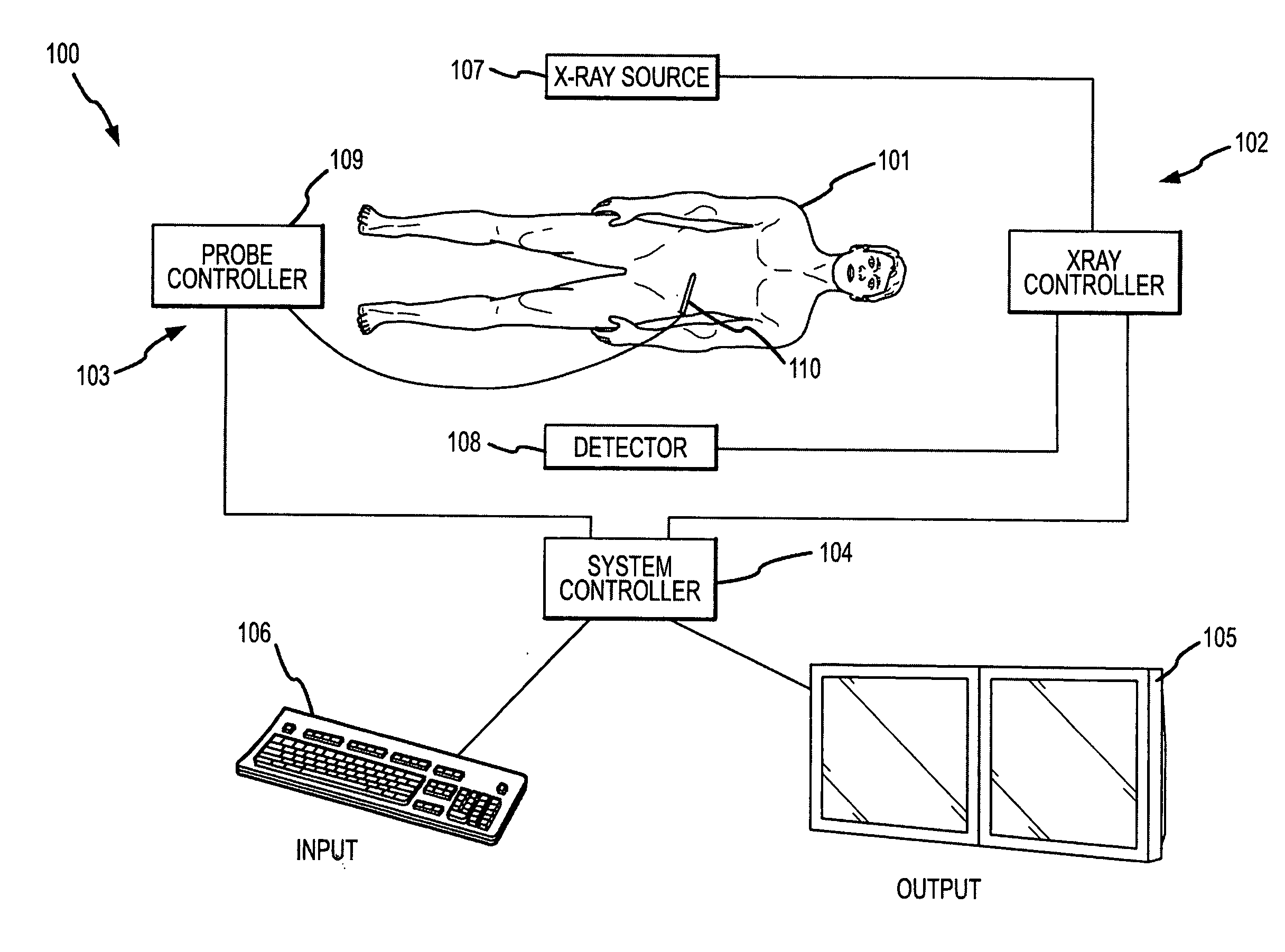
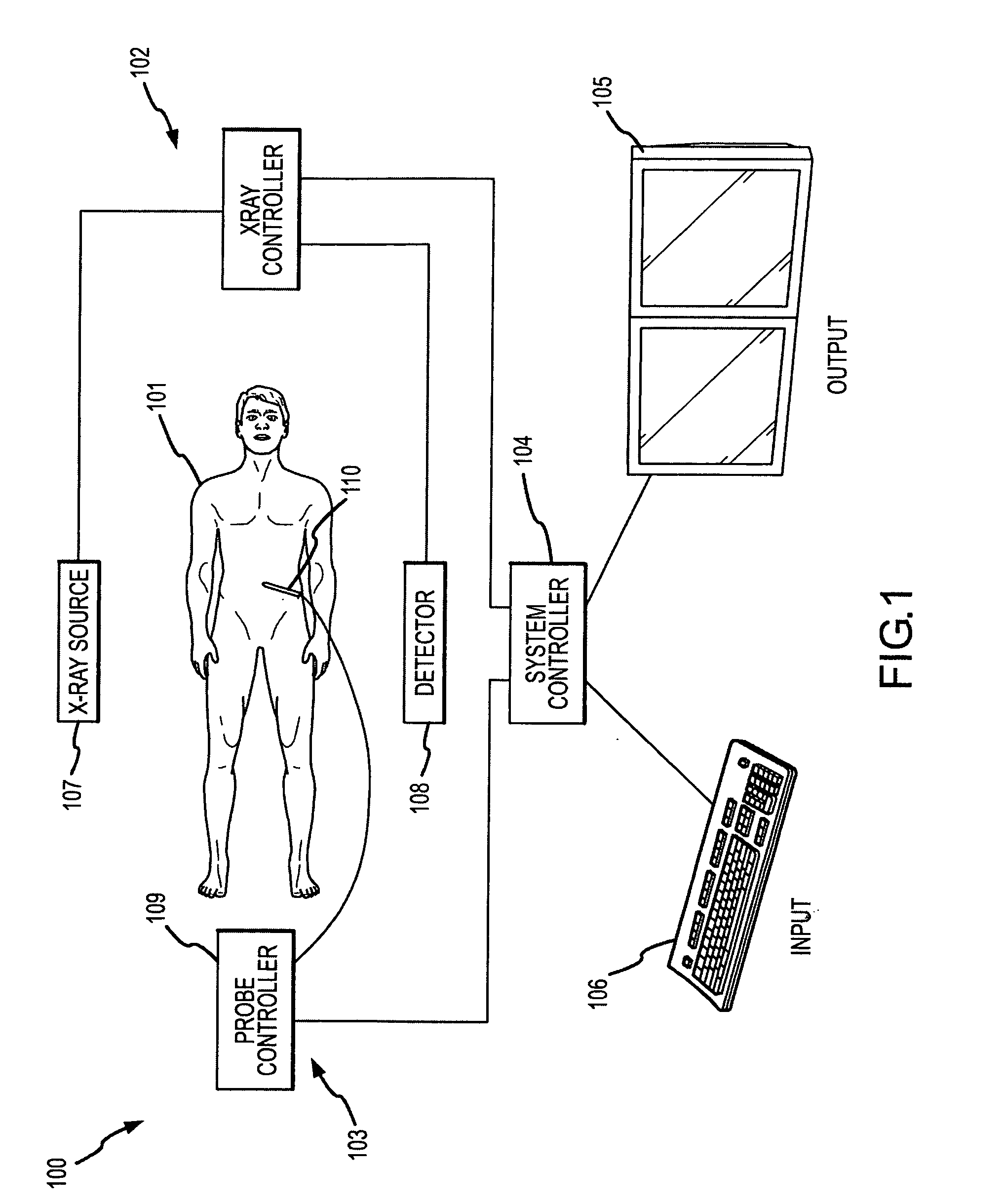
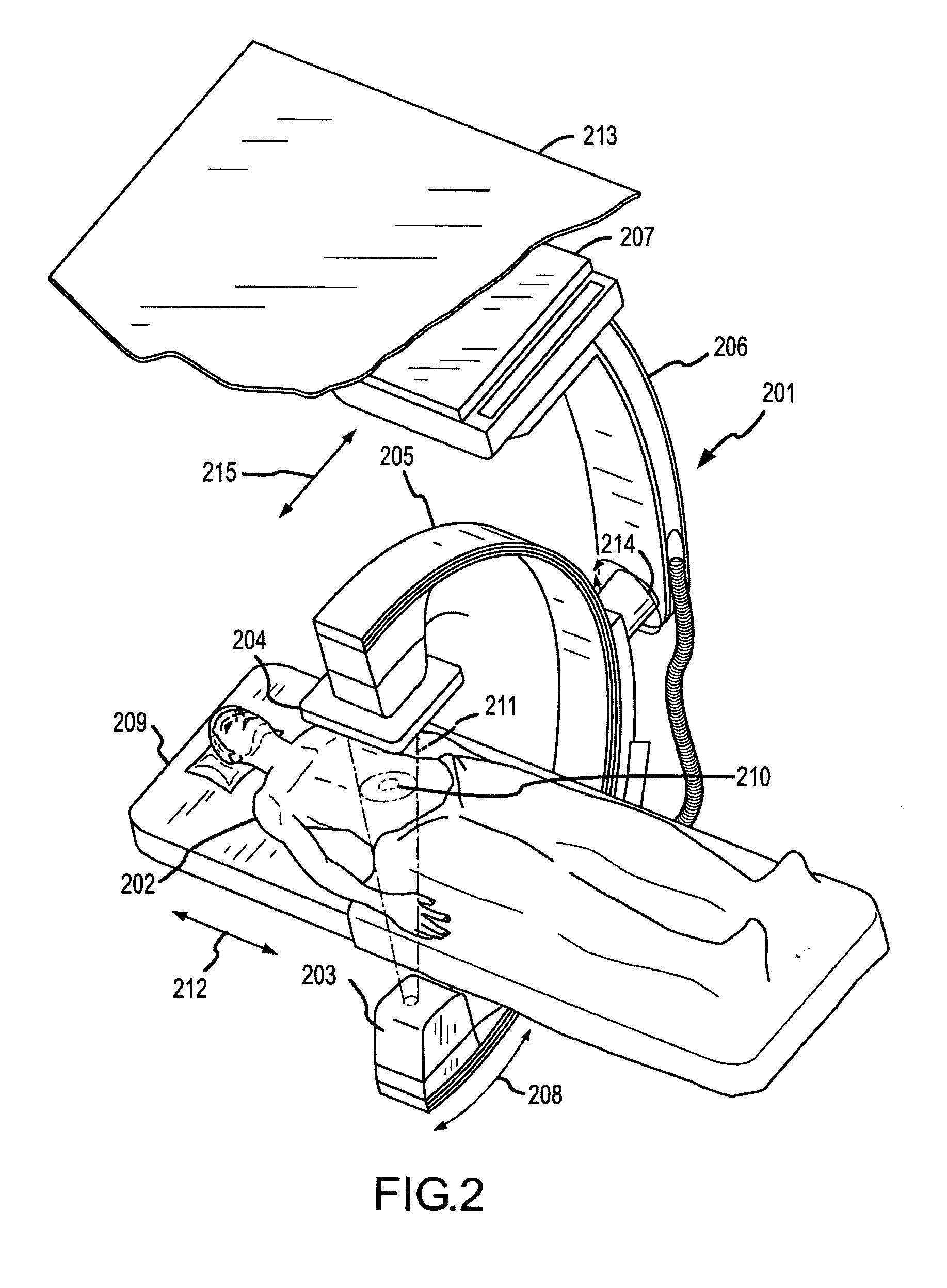
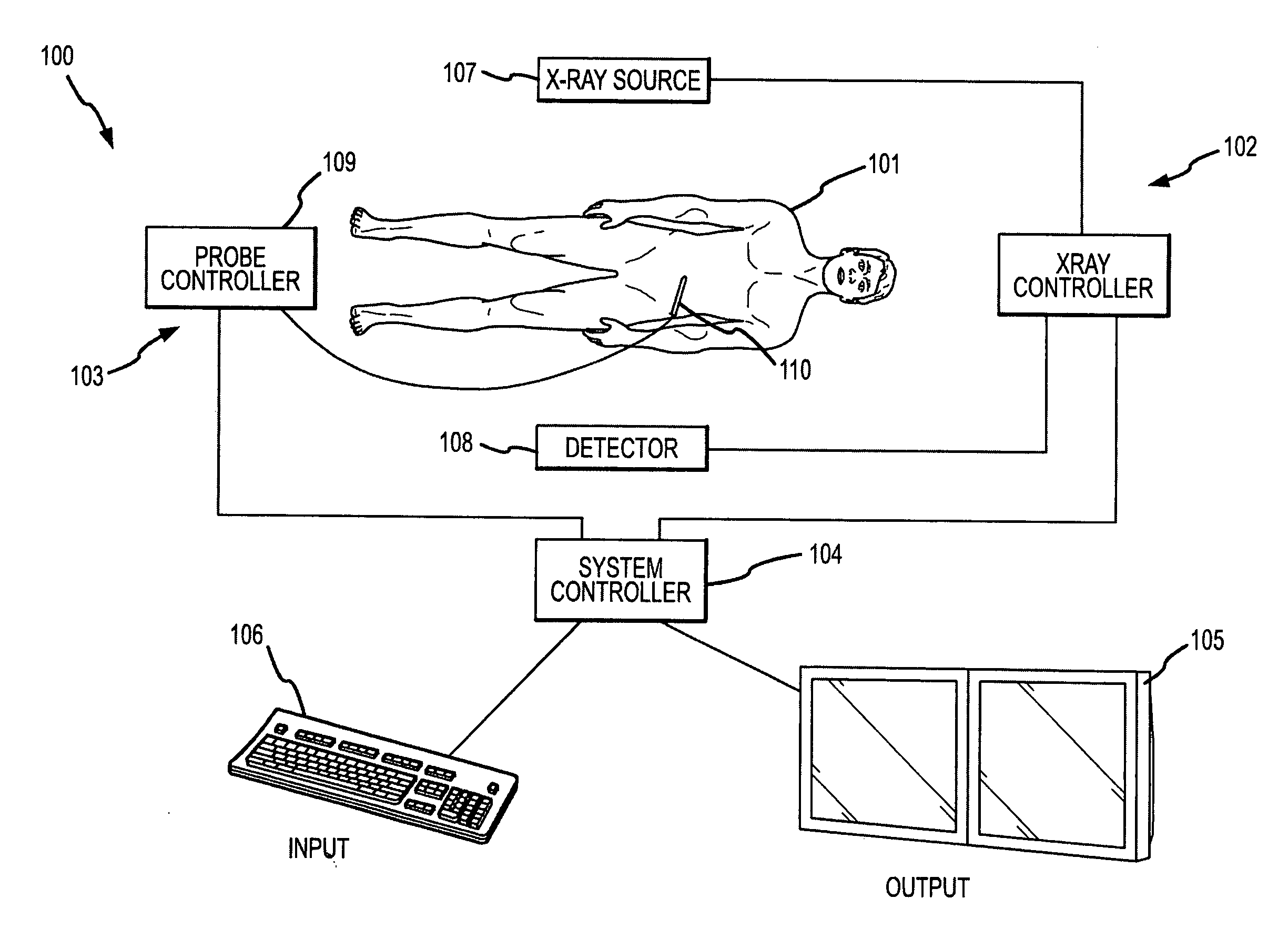
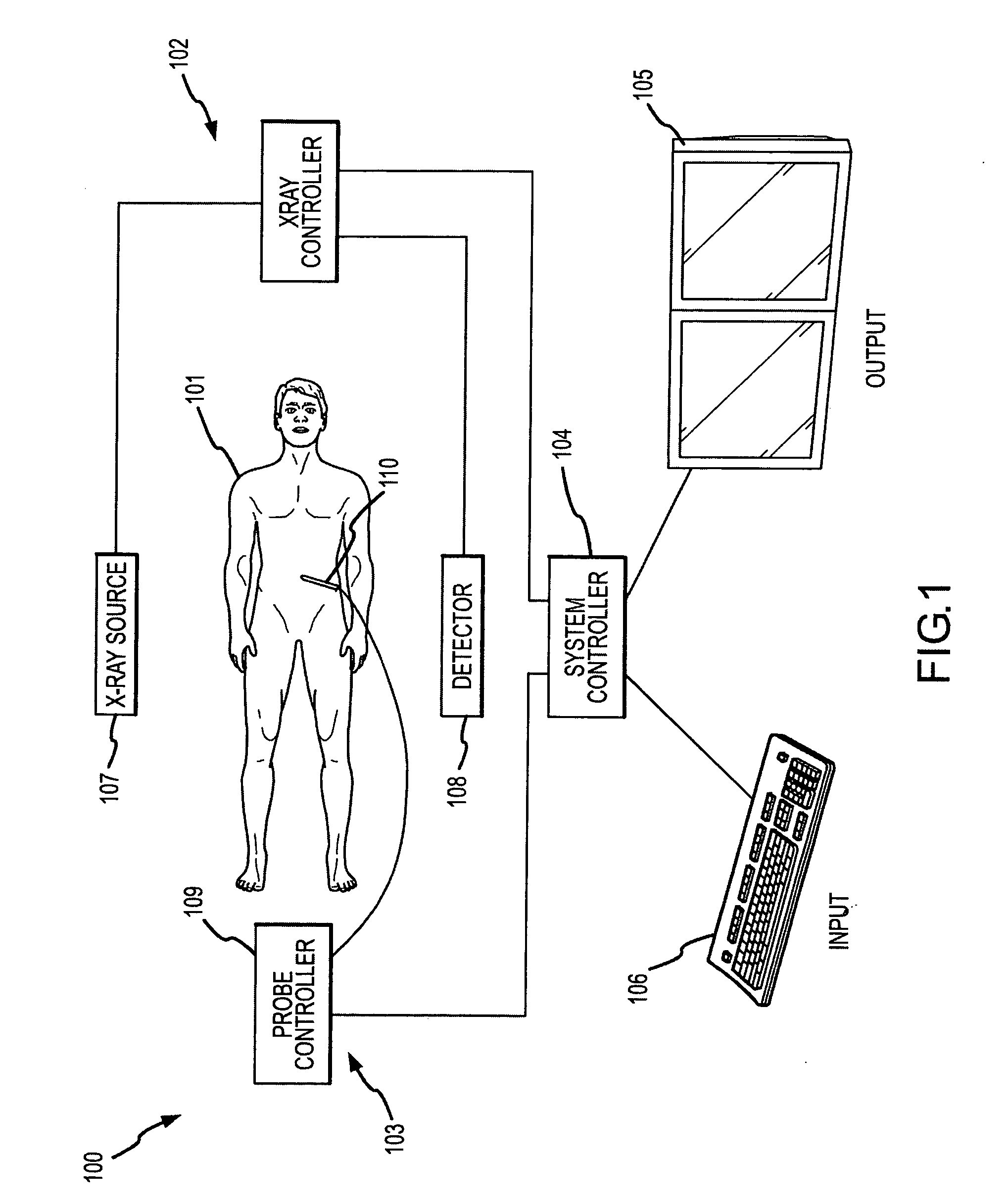
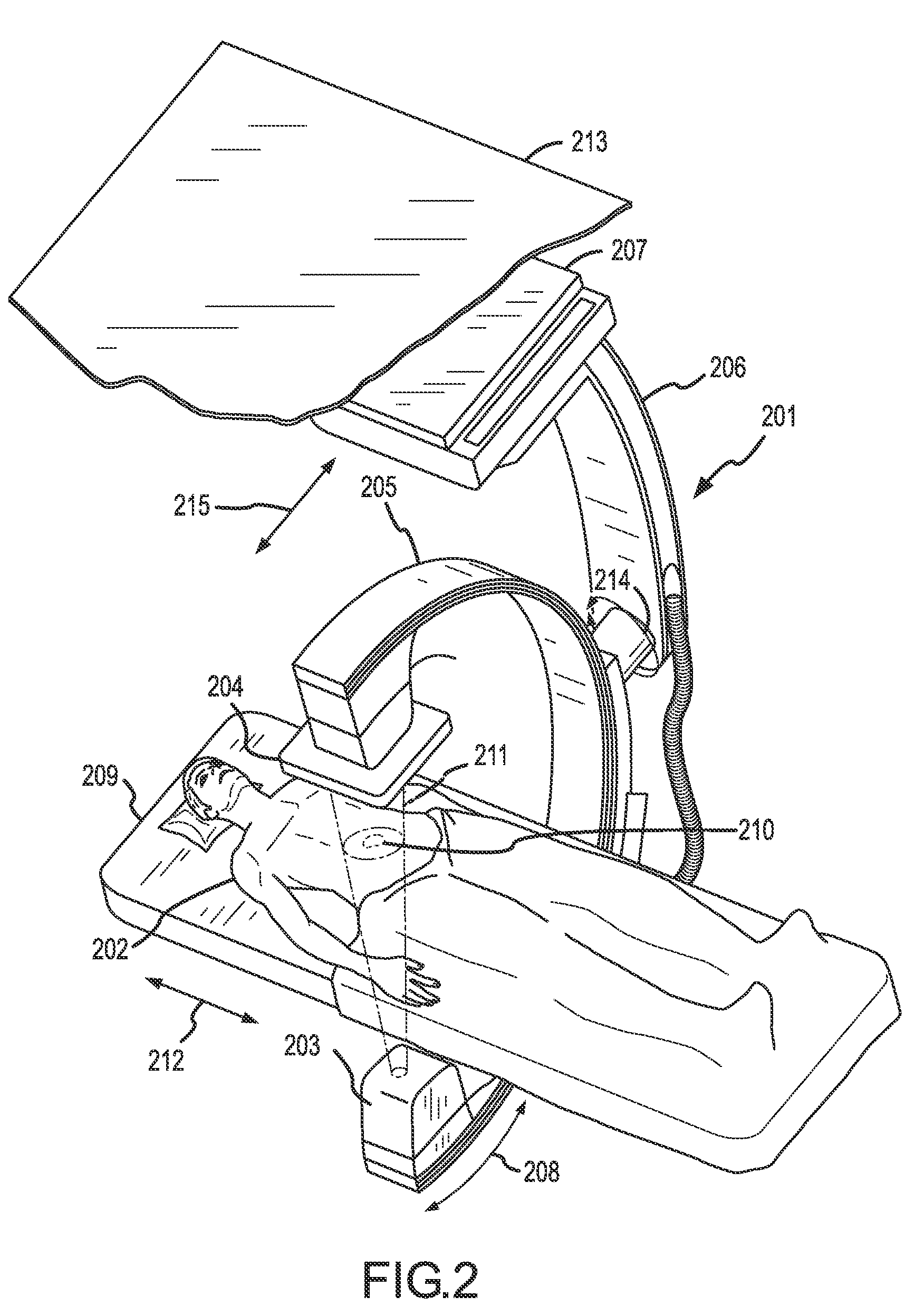
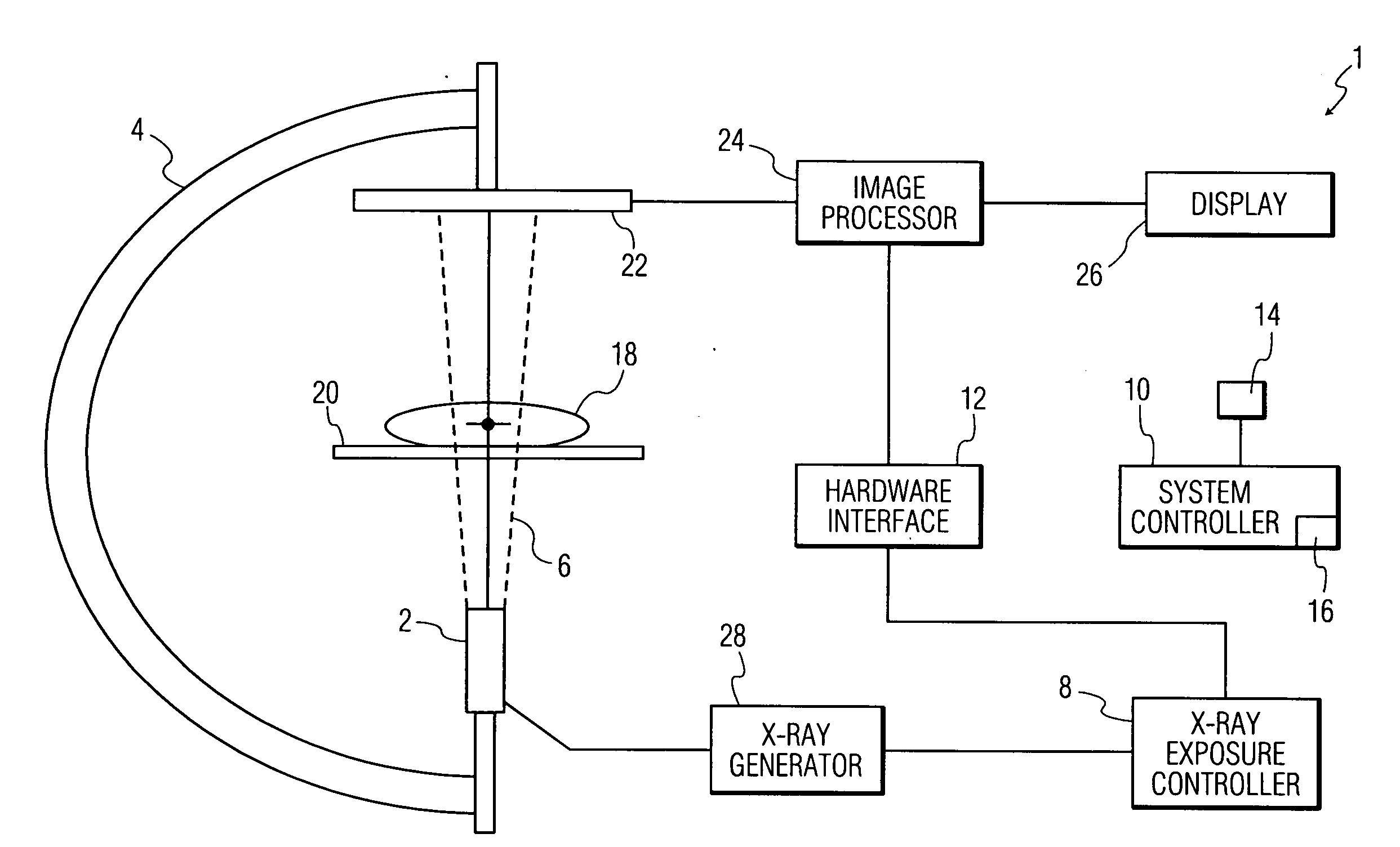
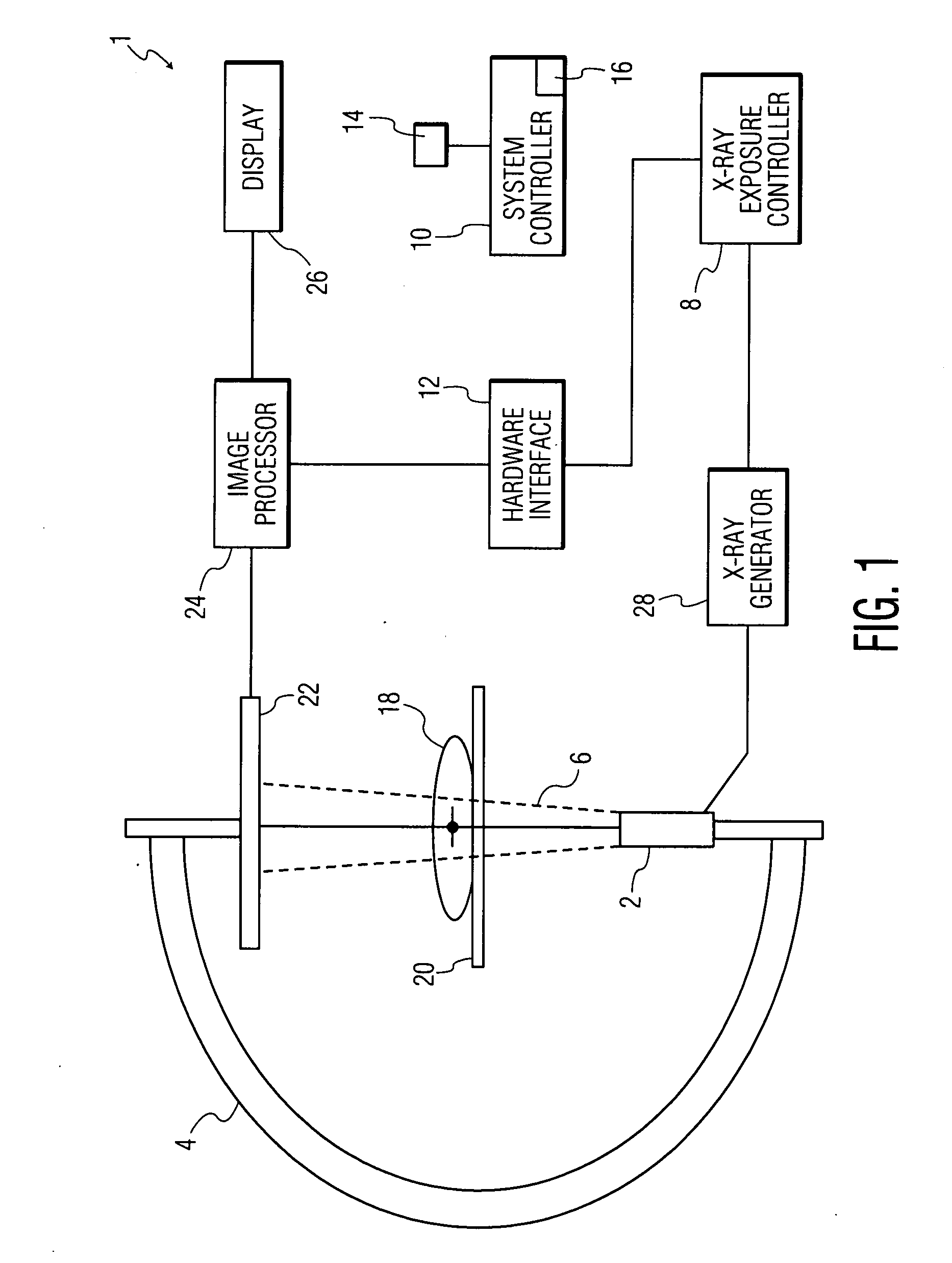
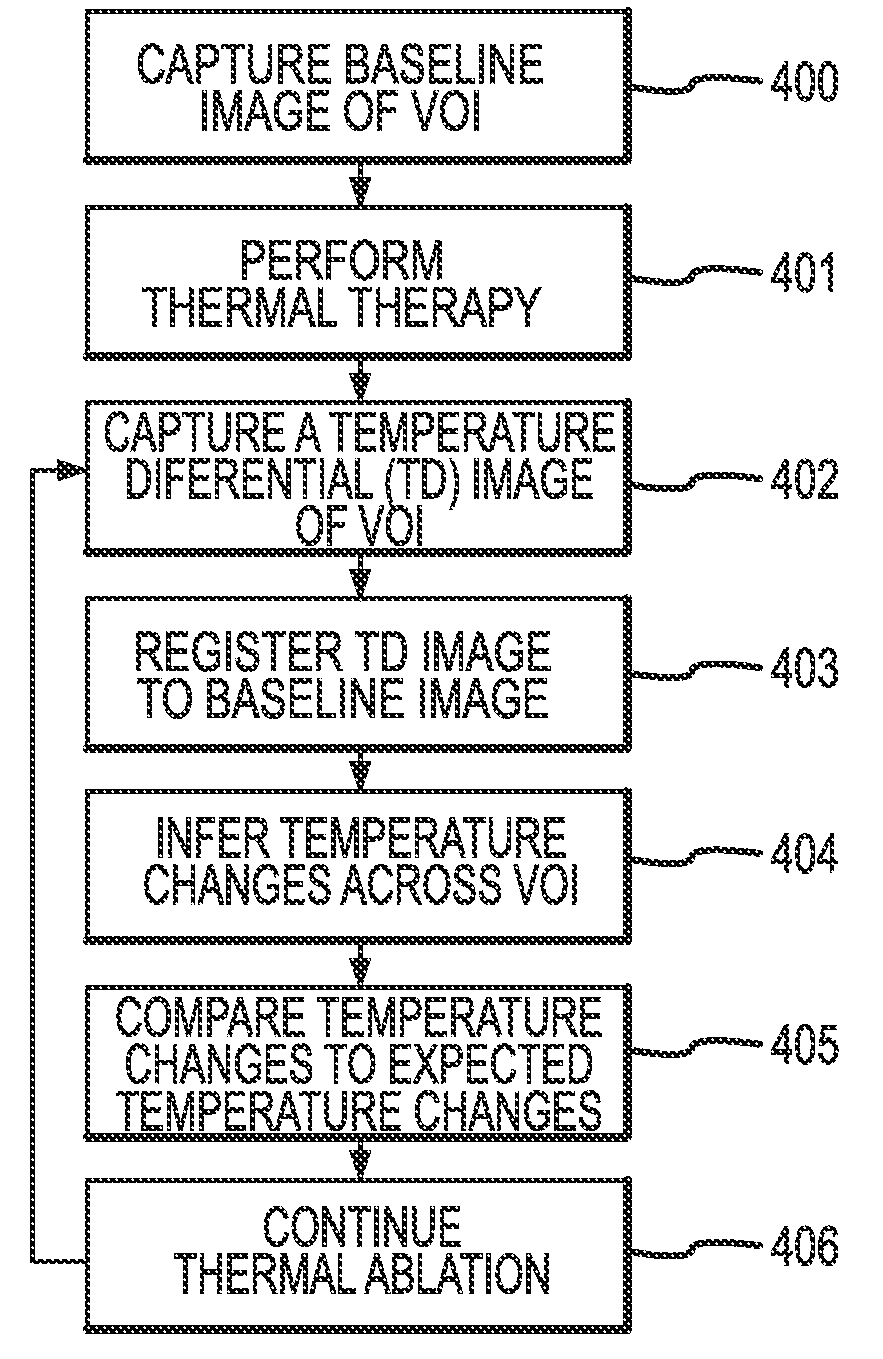
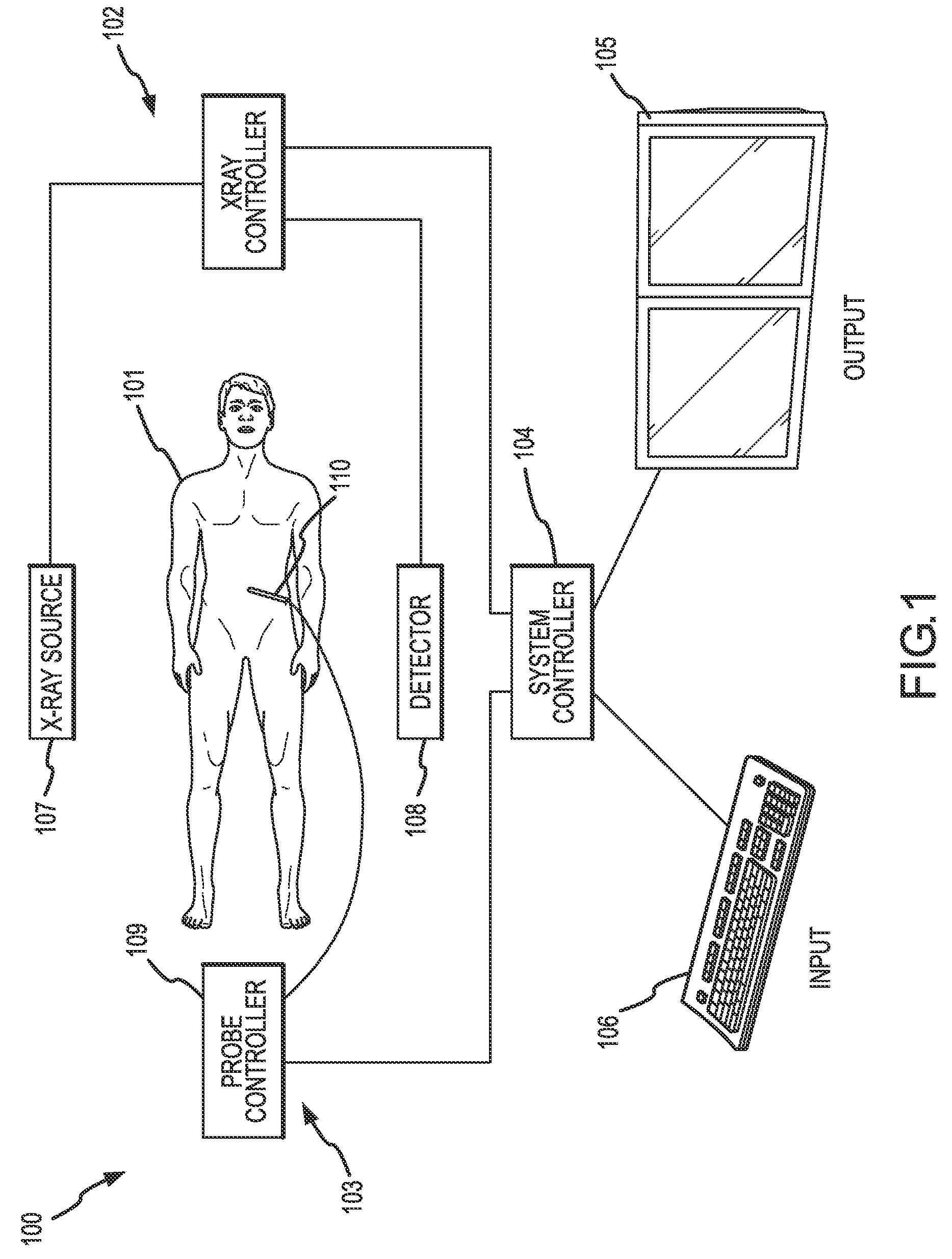
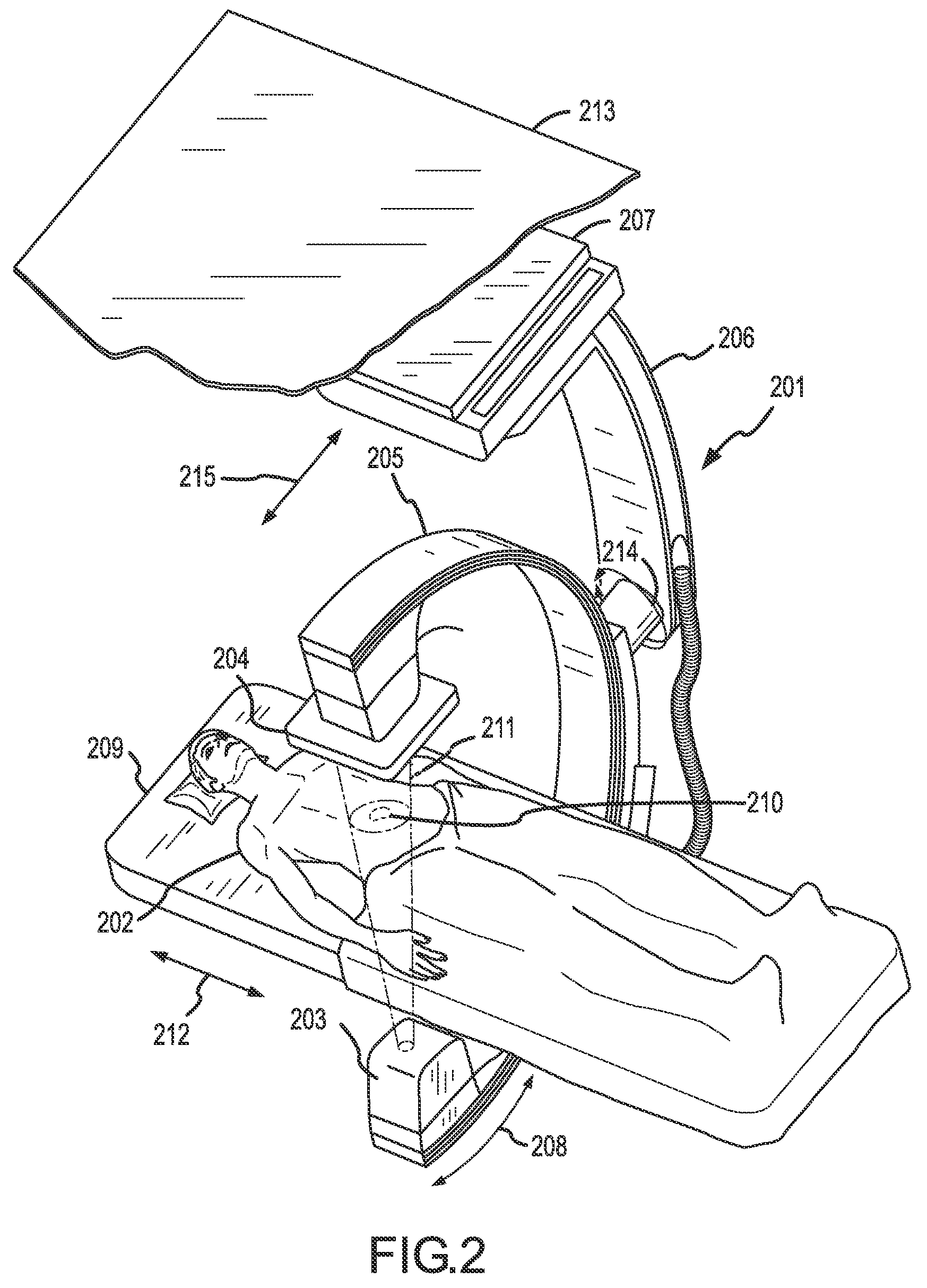
Methods for planning and performing thermal ablation
ActiveUS7871406B2Shorten the timeMovement is minimized and eliminatedUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingIntermediate imageRadiofrequency ablation
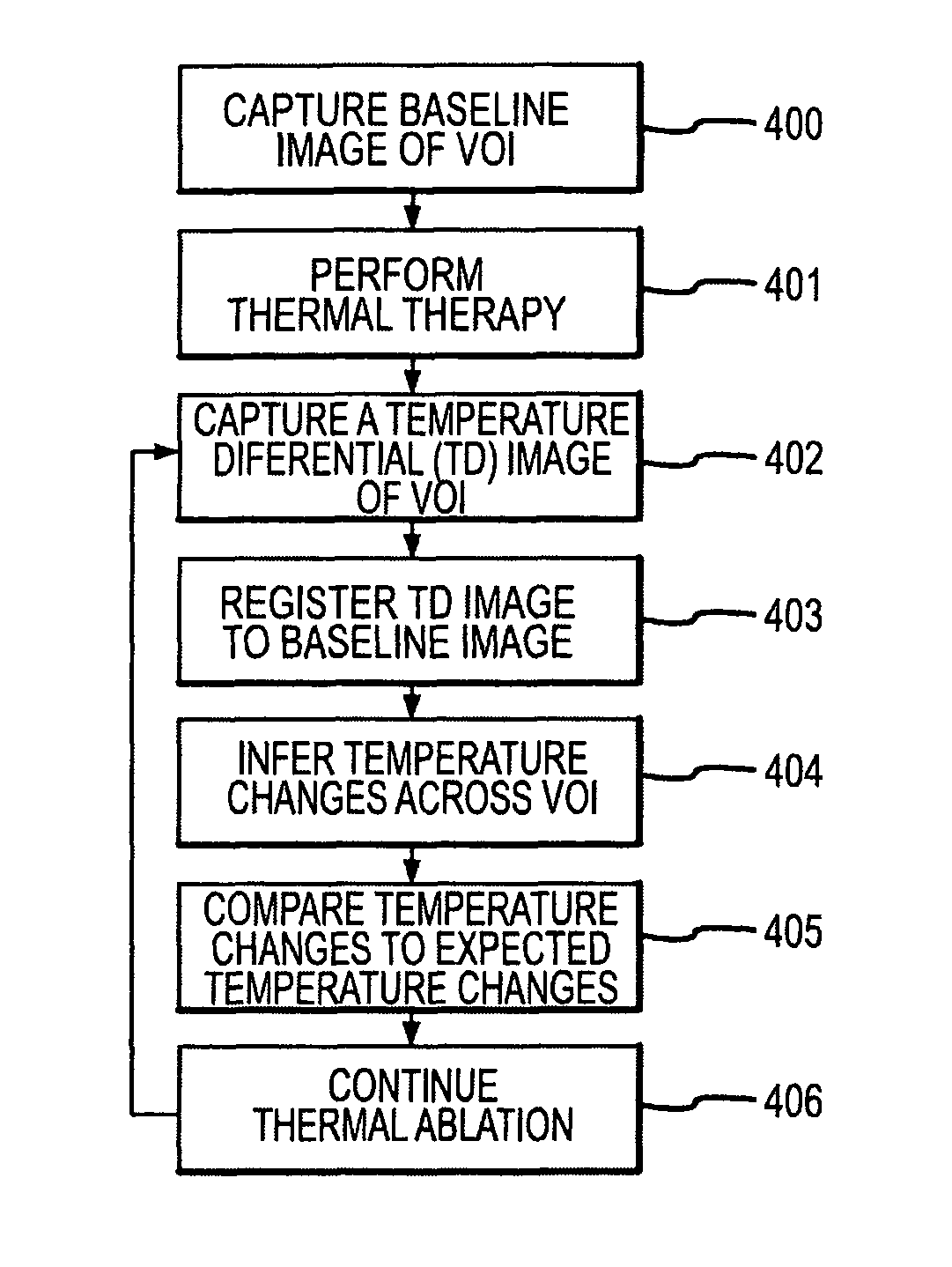
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC
Apparatus for planning and performing thermal ablation
InactiveUS20080033417A1Maintain positionShorten the timeUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsData setRadiofrequency ablation
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:ABLA TX +1
Method for planning, performing and monitoring thermal ablation
InactiveUS20080033419A1Shorten the timeMovement is minimized and eliminatedUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsRadiofrequency ablationData set
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC +1
Radiofrequency ablation with independently controllable ground pad conductors
ActiveUS20070049919A1Opportunities decreaseReducing maximum power outputSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationElectrical conductor
A radiofrequency ablation system provides multiple ground pads and active control of current flow through the ground pads to provide improved power sharing at the tissue near the ground pads reducing risk of patient skin burns for higher power ablation generators.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Multipolarity epicardial radiofrequency ablation
ActiveUS20140296850A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesRadiofrequency ablationRadio frequency
A method of ablating an epicardial tissue region, including positioning a medical device adjacent the epicardial tissue region, the medical device having a first electrode, a second electrode, and a third electrode located in between the first and second electrodes; delivering an irrigation fluid to the tissue region; and ablating at least a portion of the tissue region by sequentially activating the third electrode in a monopolar radiofrequency delivery mode and activating the first and second electrodes in a bipolar radiofrequency delivery mode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
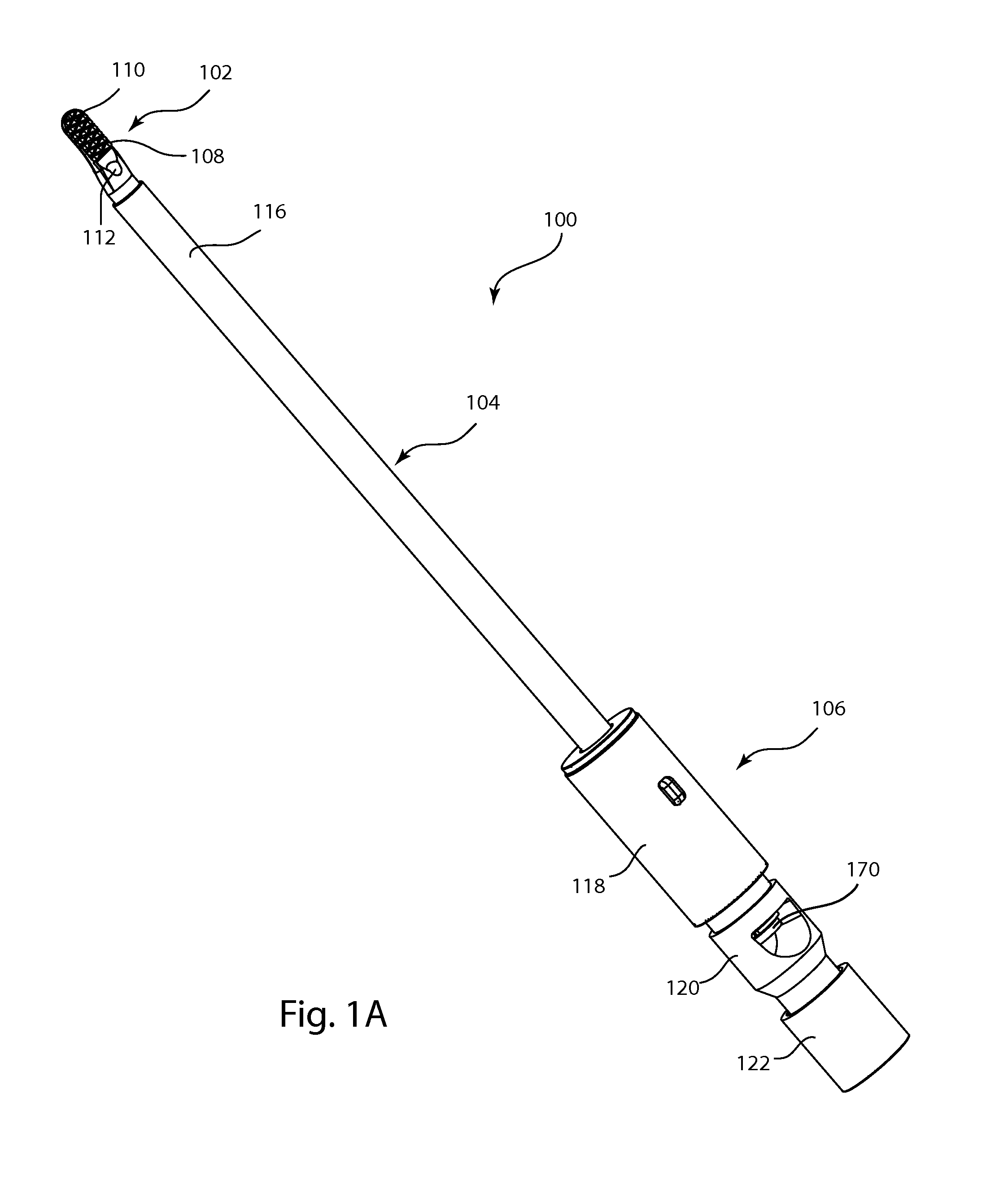
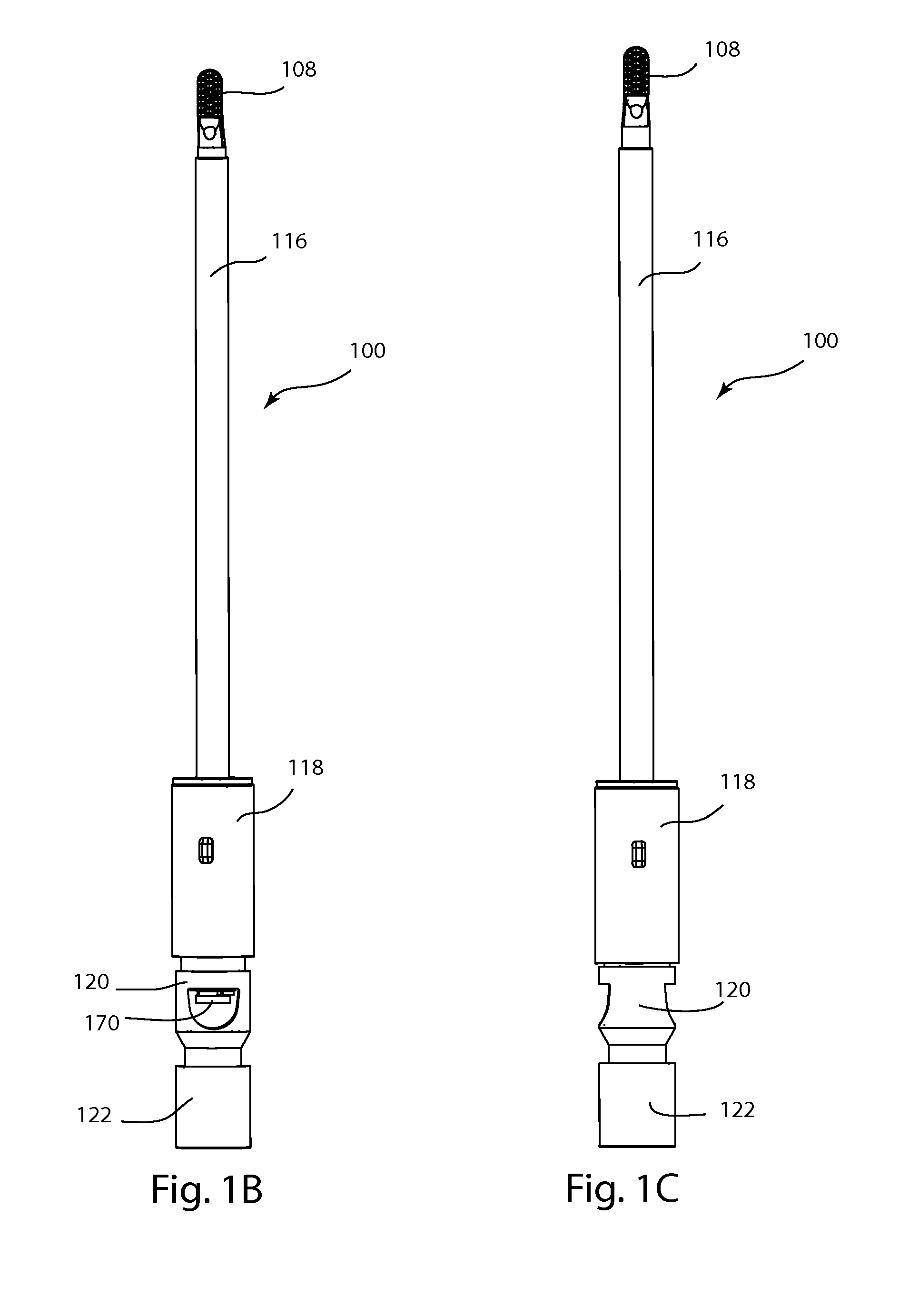
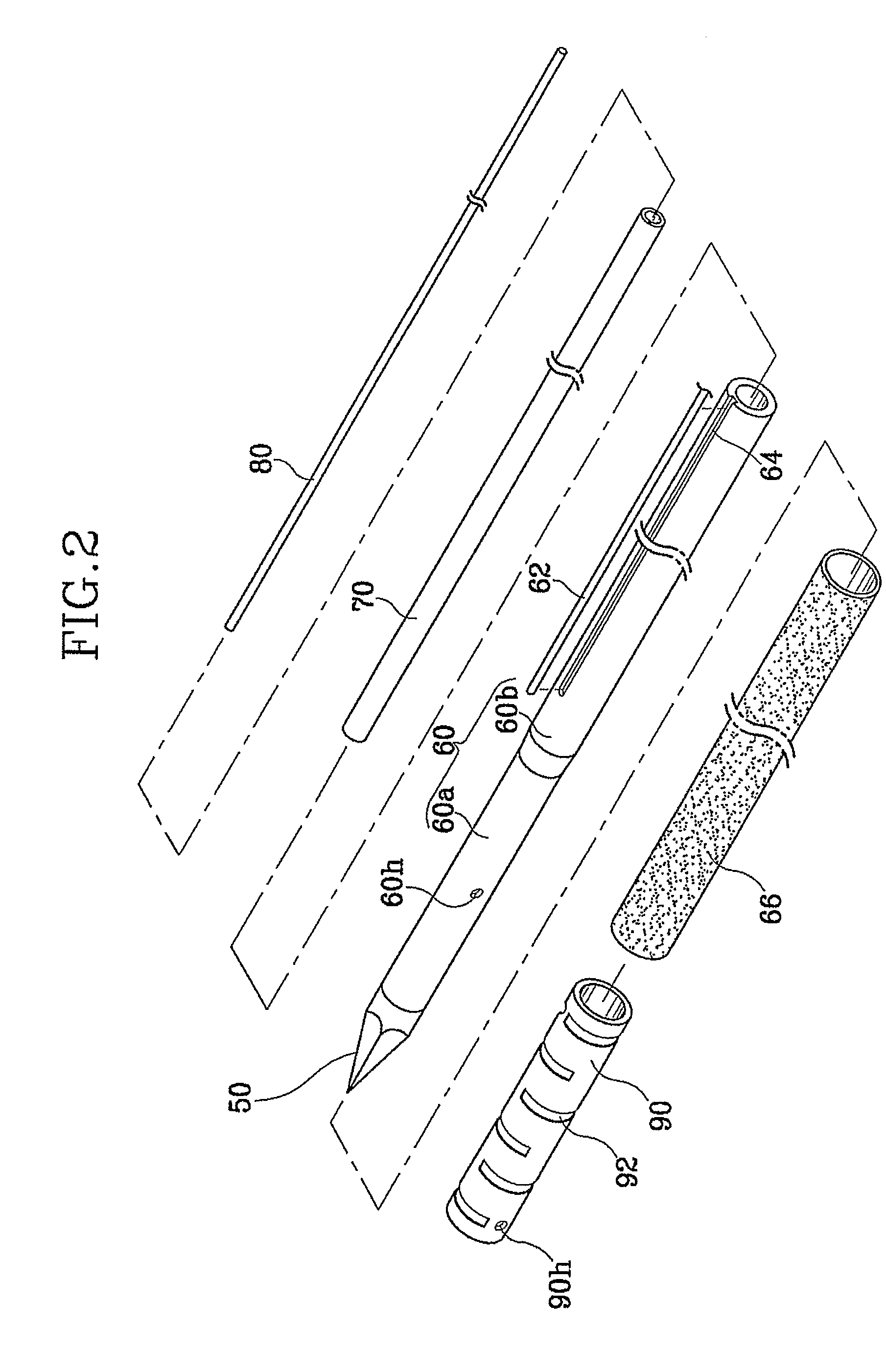
Electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation
ActiveUS20090287206A1Easy to liftMaximized economicallySurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationElectrosurgery
The present invention relates to an electrode for an electrosurgical unit for the use in ablating and necrosing a living tissue by RF electric energy. The present invention provides an electrode for an electrosurgical unit, including: a hollow electrode formed in an elongated hollow tube shape, a non-insulating region of a predetermined length being formed on one side of which, an insulating region being formed on an outer surface of which other than the non-insulating region; a saline solution circulation structure that supplies pressurized saline solution for cooling a living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode from the outside of the living tissue to the inside of the hollow electrode, and discharges the pressurized saline solution from the inside of the hollow electrode to the outside of the living tissue; and one or more saline solution discharge holes formed in the non-insulating region of the hollow electrode to discharge some of the circulating pressurized saline solution to the living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode.
Owner:RF MEDICAL
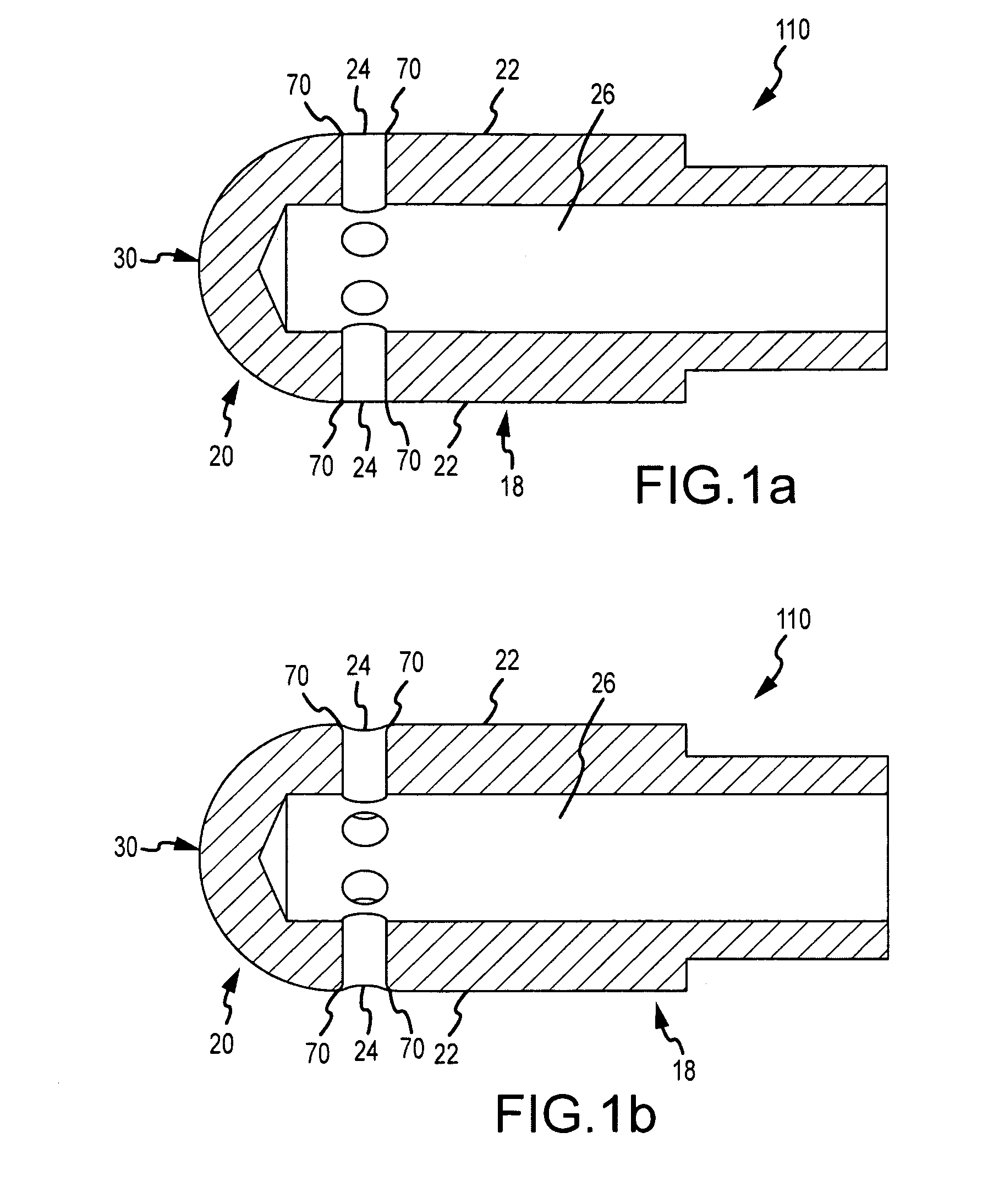
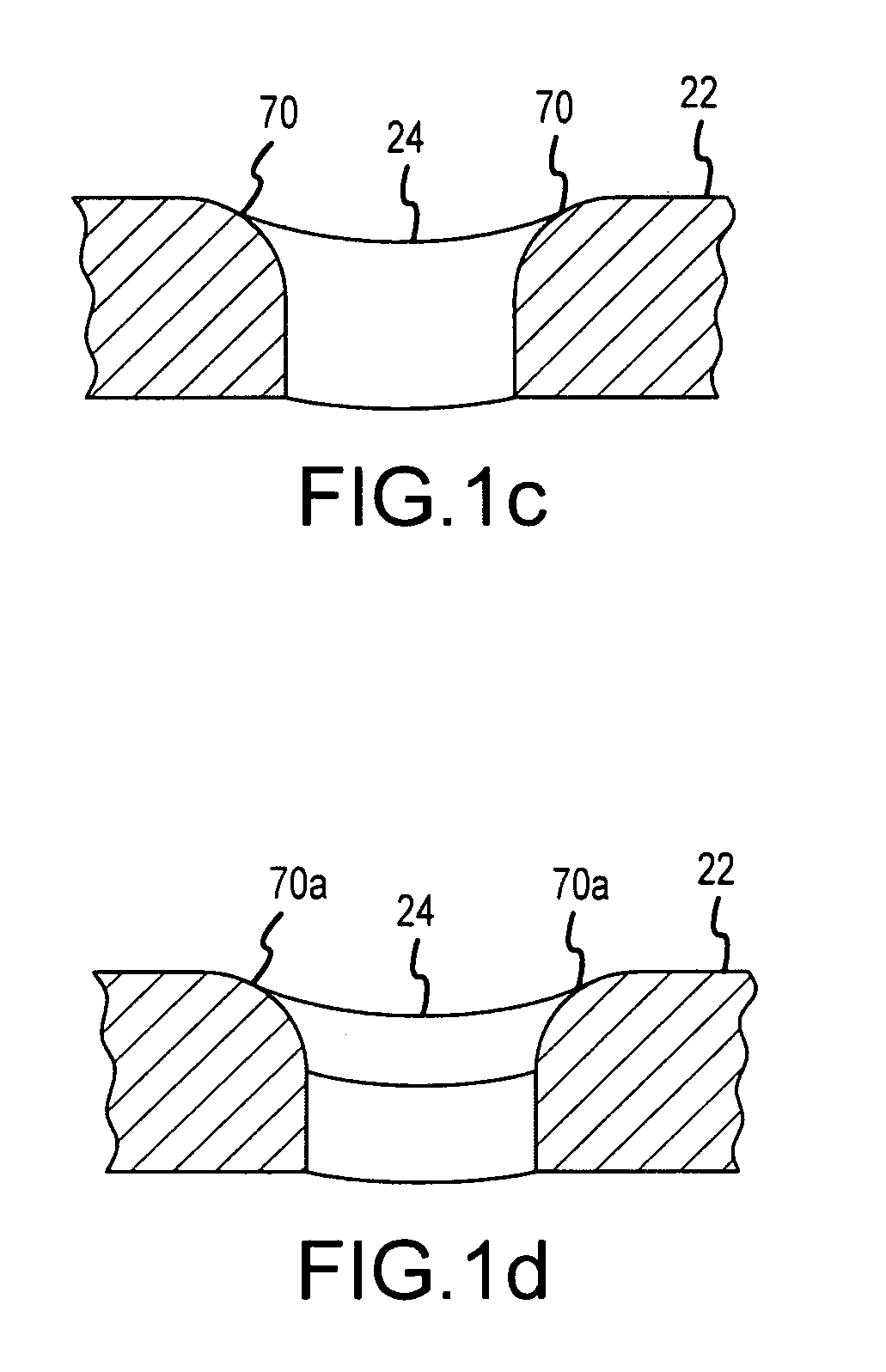
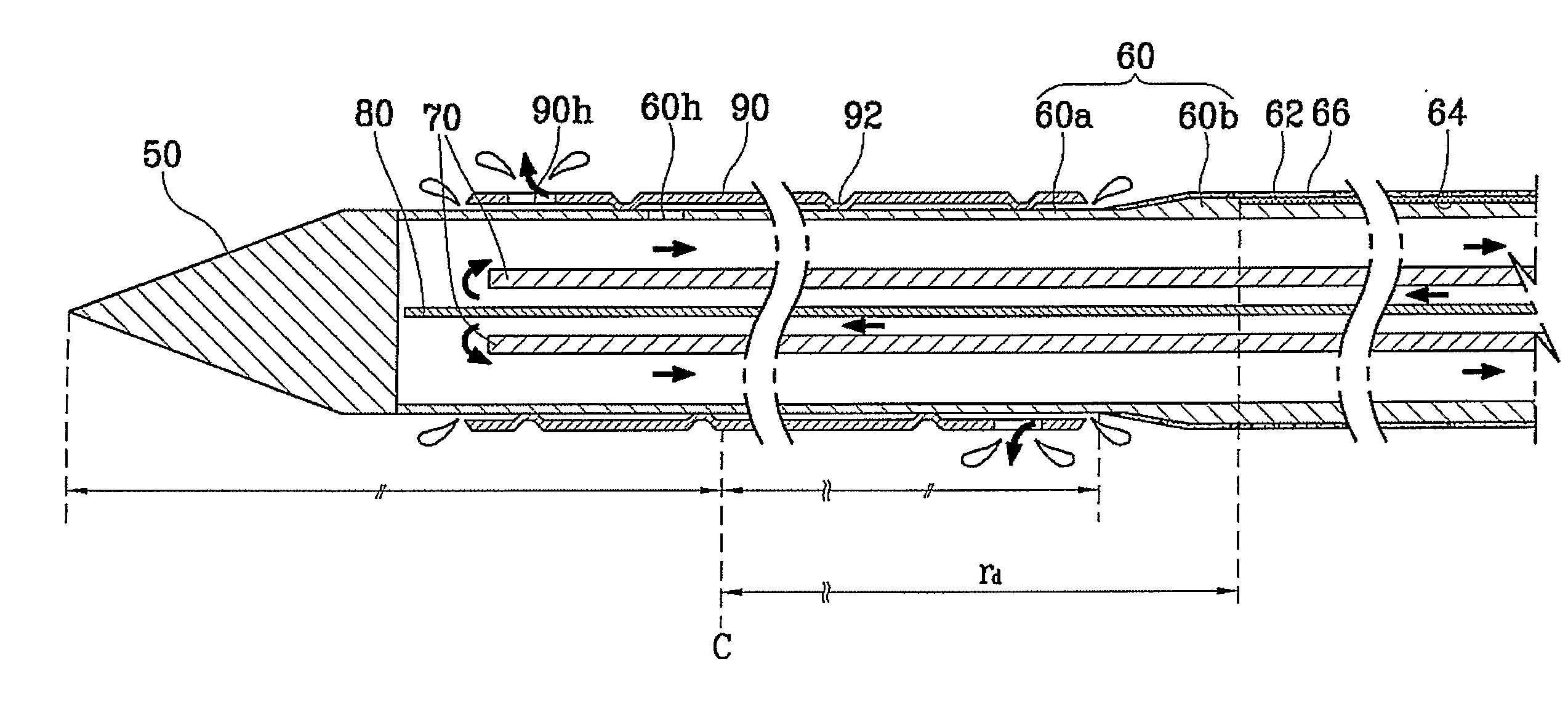
Irrigated ablation electrode having smooth edges to minimize tissue char
ActiveUS20090177193A1Tissue char is minimizedMinimize coagulationSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationCatheter electrode
The invention relates to ablation catheter electrodes that solve in part the problem of tissue charring during radiofrequency ablation. The electrode assemblies of the invention include passageways that lead from the inner lumen of the assemblies to the surface of the assemblies, wherein the passageways have a smooth conjunction with the outer surface. These smooth conjunctions comprise rounded edges or are camfered. In the case of rounded edges, the rounded edges can have fixed radii of about 0.002″ to about 0.008″.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
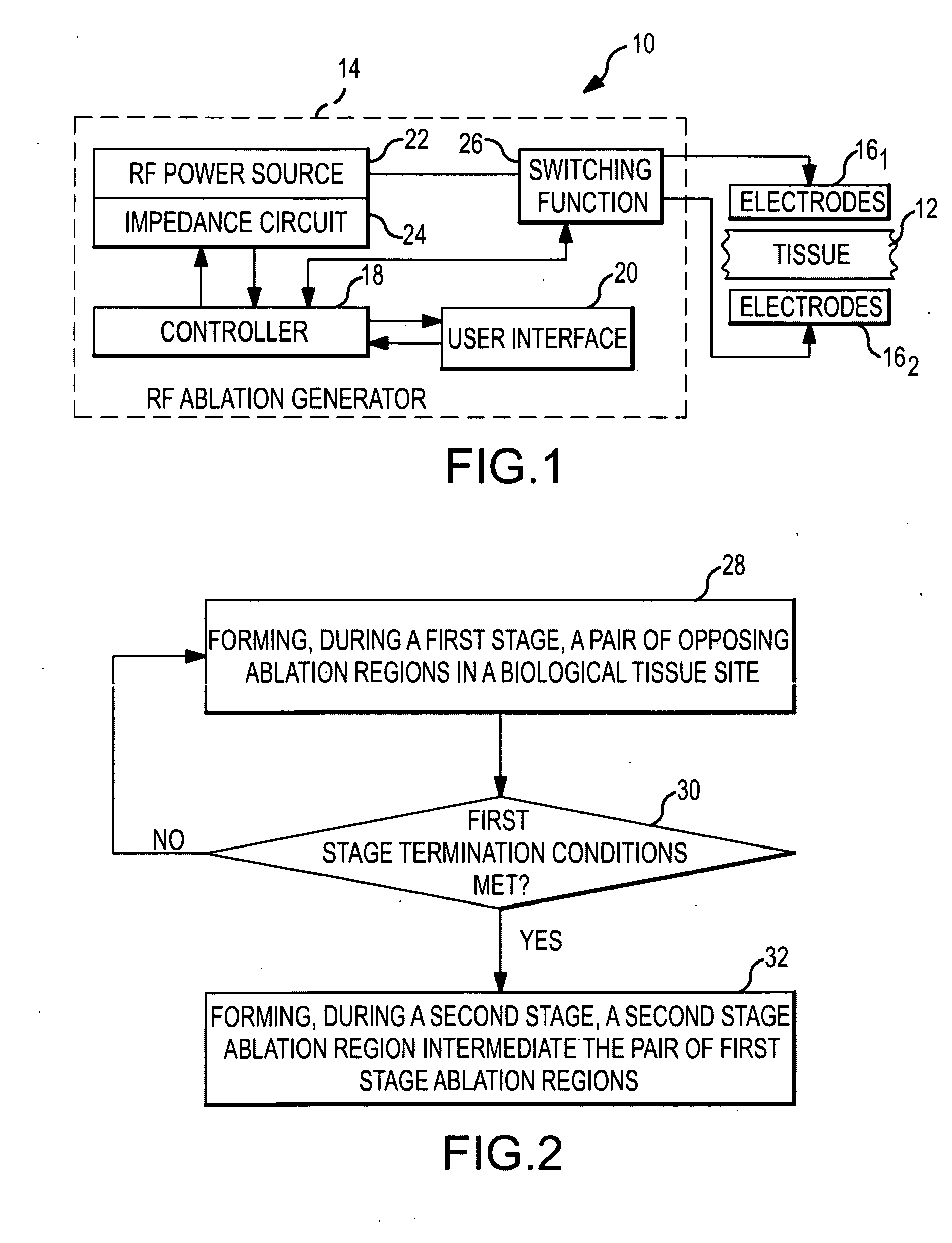
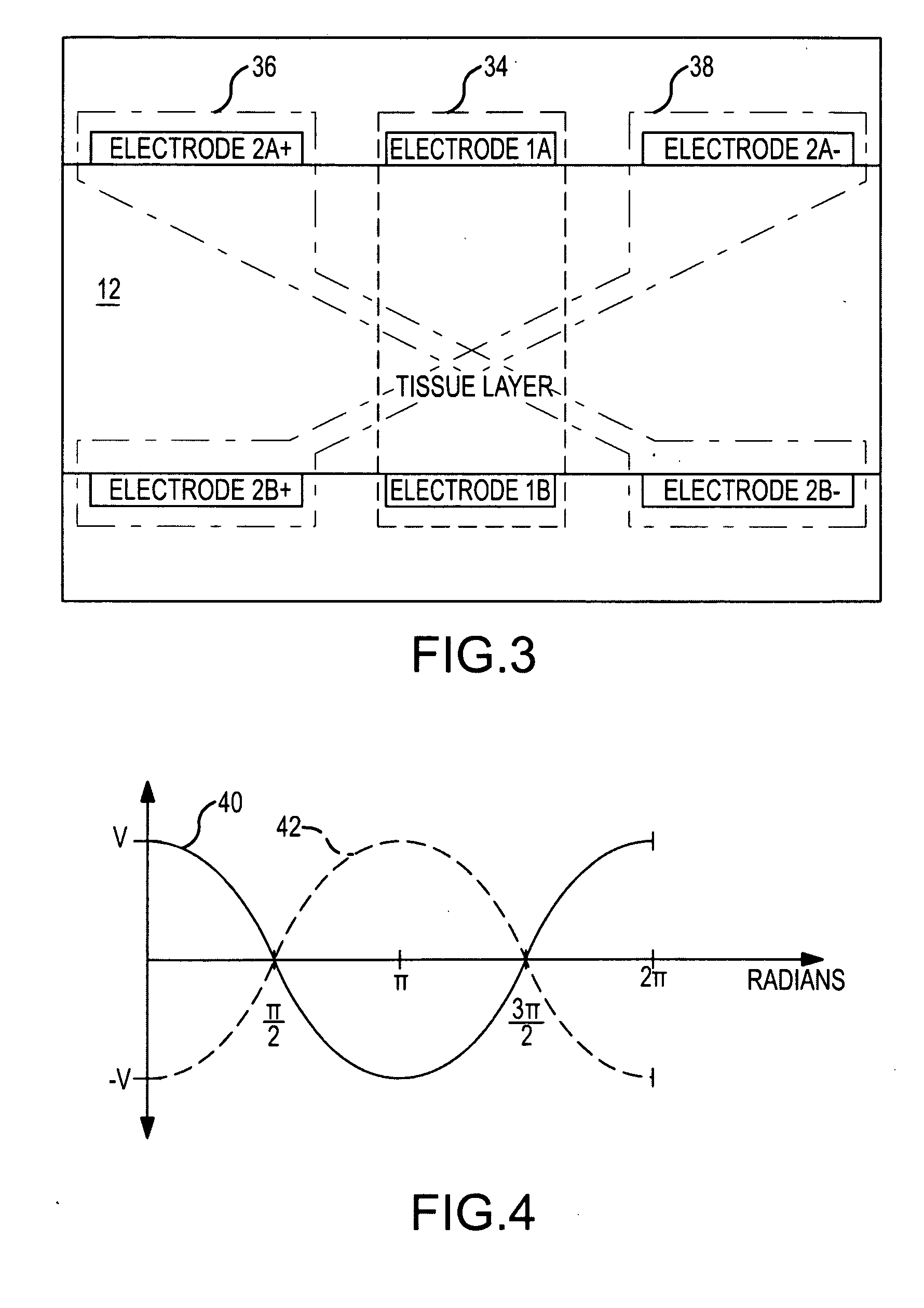
Method and apparatus for radiofrequency ablation with increased depth and/or decreased volume of ablated tissue
ActiveUS20100274238A1Add depthLower the volumeSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsRadiofrequency ablationAblation radiofrequency
A method of ablating a tissue site includes at least two stages. A first stage involves conducting bipolar ablation between a first pair of electrodes situated in an opposing arrangement on opposing sides of the tissue site to form a pair of opposing first stage ablation regions extending from respective sides of the tissue towards the center. A second stage involves conducting bipolar ablation between a second pair of electrodes situated in a diametrical arrangement with respect to the first stage ablation regions, which forms a second stage ablation region intermediate the pair of first stage ablation regions. The second stage completes the ablation through the entire depth of the tissue site. Since the overall process can accommodate incomplete ablation during the first stage, lower power, reduced ablation times or both may be used during the first stage, avoiding overheating and with a decrease in ablated tissue volume.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Intermittent short circuit detection on a multi-electrode catheter
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Methods and apparatuses for planning, performing, monitoring and assessing thermal ablation
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided. Methods of assessing the post-ablation status of the patient and performance of the system are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC
Arthroscopic devices and methods
ActiveUS20170224368A1Inhibit inflammationEasy to viewExcision instrumentsSurgical instruments for heatingMotor driveRadiofrequency ablation
A medical device includes an elongated sleeve having a longitudinal axis, a proximal end and a distal end. A cutting member having sharp edges formed from a wear-resistant ceramic material is carried at the distal end of the elongated sleeve. A motor drive is coupled to the proximal end of the elongated sleeve to rotate the sleeve at cutting member at high speed to cut bone and other hard tissue. An electrode is carried in a surface portion of ceramic cutting member for cautery or radiofrequency ablation of tissue when the sleeve and cutting member are is a stationary position.
Owner:RELIGN CORP
Reciprocating surgical instrument
A surgical rasping and / or shaving system functions in multiple orthopedic applications, including but not limited to shoulder, knee, hip, wrist, ankle, spinal, or other joint procedures. The system may comprise a tissue removal member with a rasping and / or shaving head which may be low profile and offer a flat cutting / rasping / shaving surface, or with a cutting head with at least one cutting edge. The tissue removal member is configured to be driven by an attached hub that translates a rotational movement into a reciprocating motion. Suction for removal of bone fragments or other tissues is provided through an opening spaced apart from or adjacent to the rasping surface. A radiofrequency ablation (RF) electrode may be carried on the system to provide ablation or coagulation of soft tissues.
Owner:IMDS CORPORATION
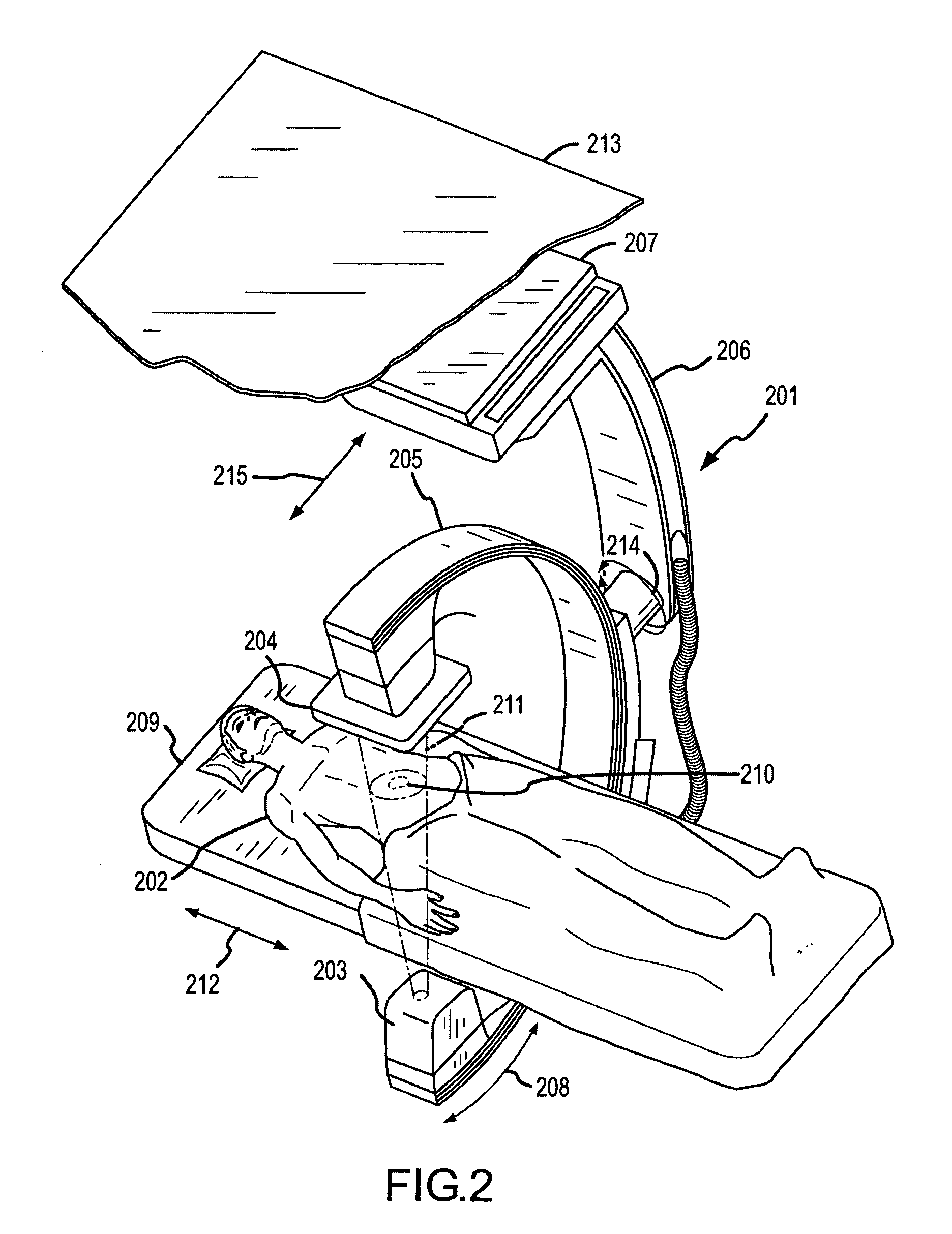
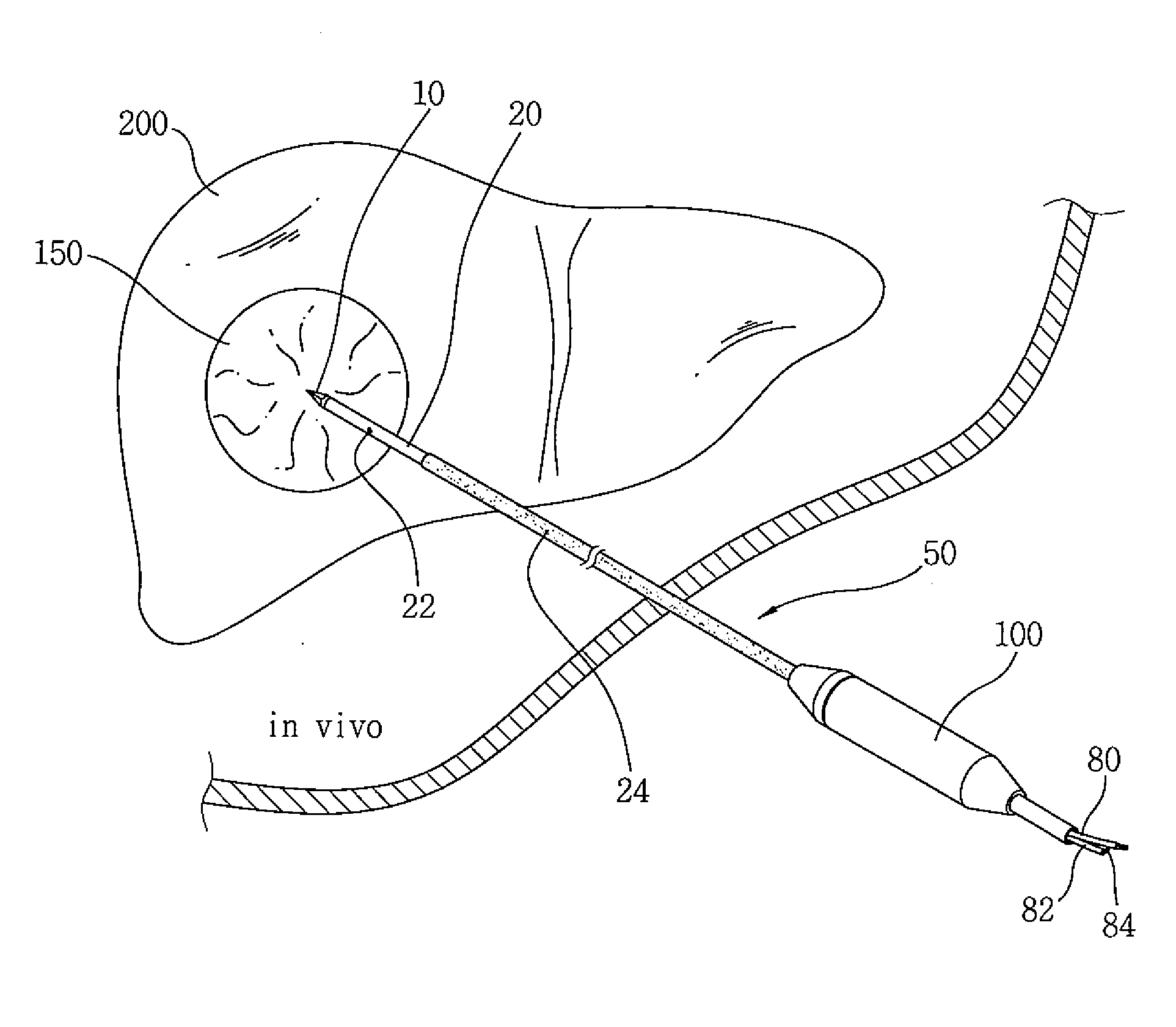
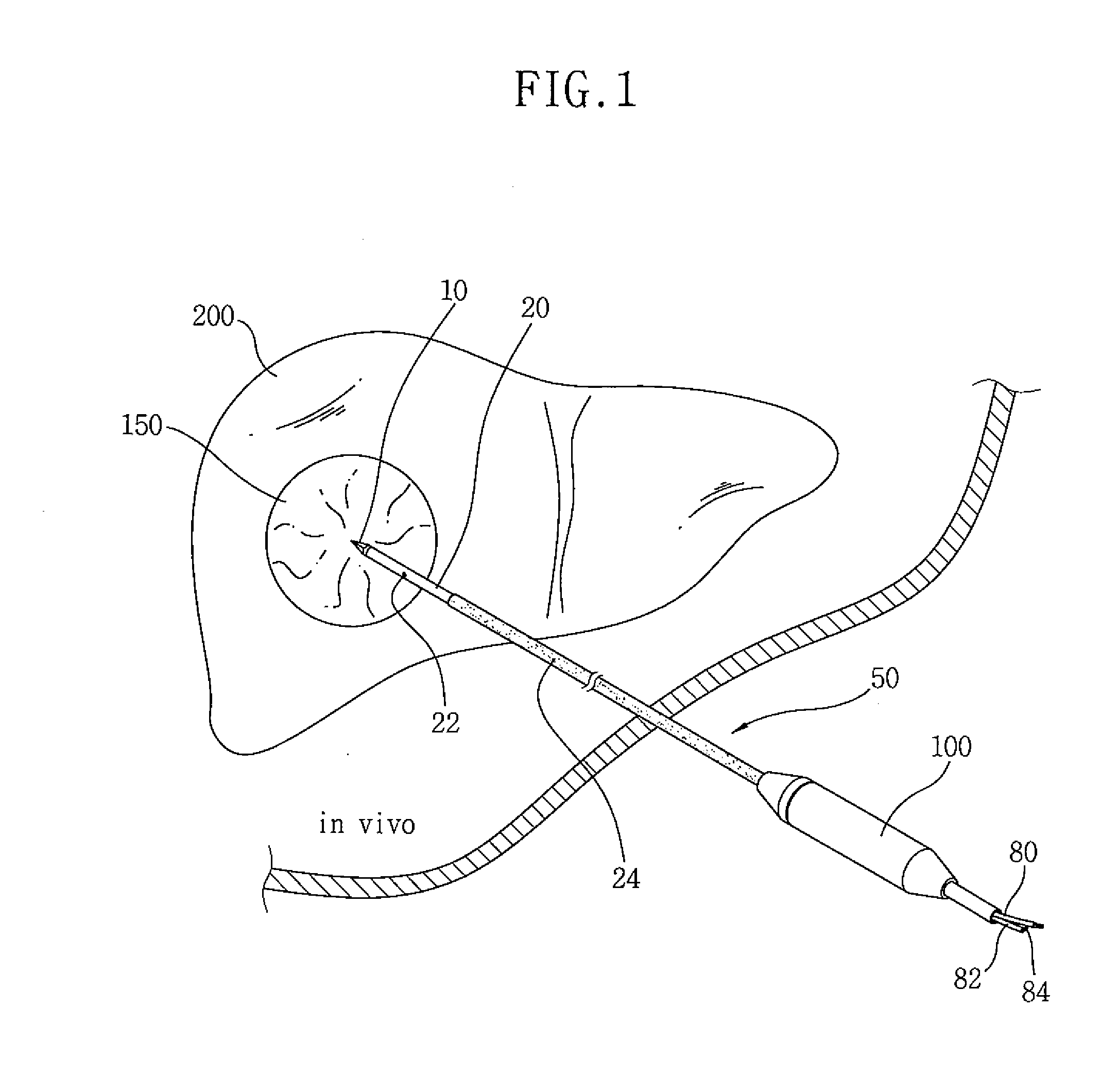
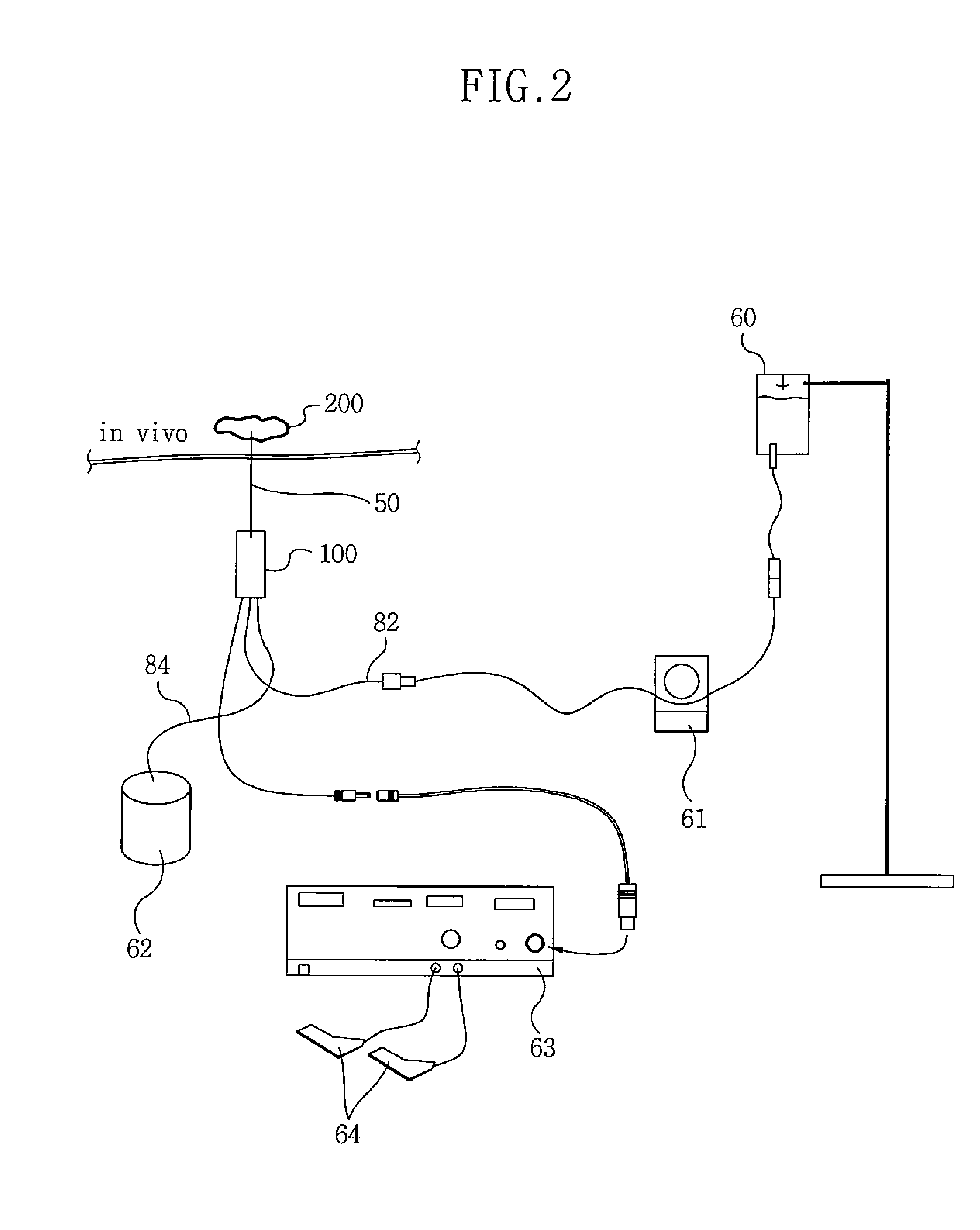
System and method for planning and guiding percutaneous procedures
InactiveUS20100111389A1Radiation/particle handlingHealth-index calculationRadiofrequency ablationExAblate
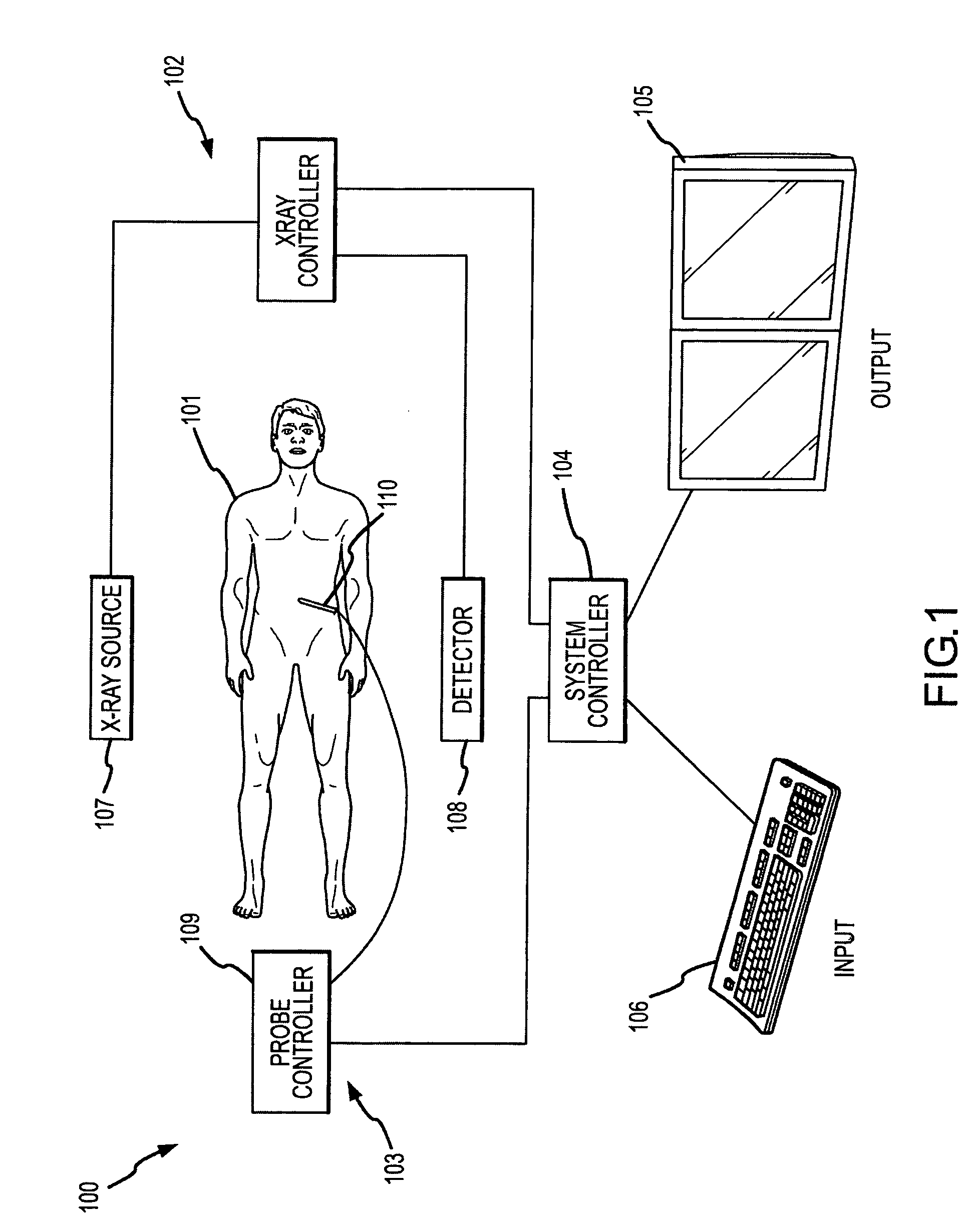
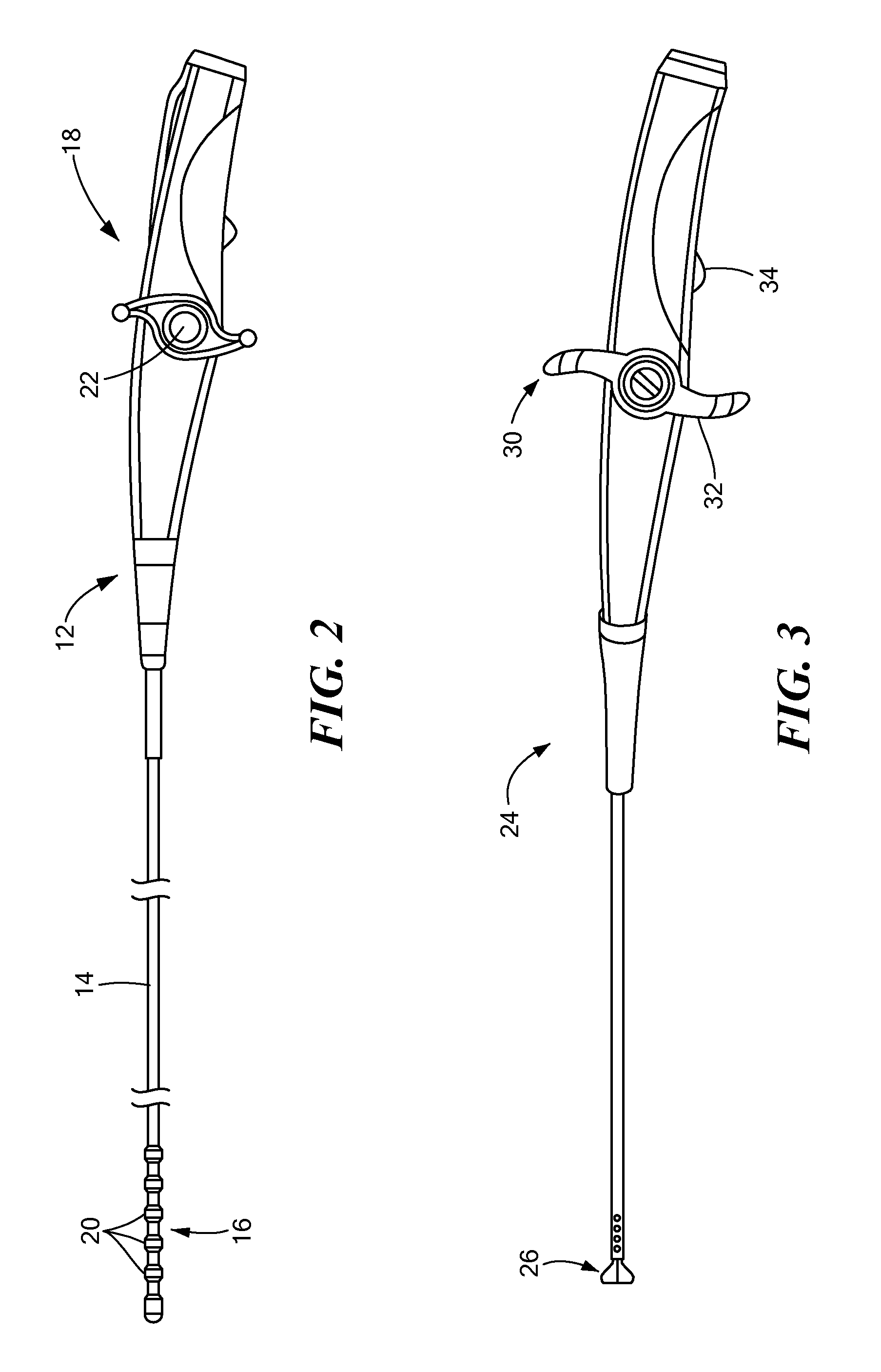
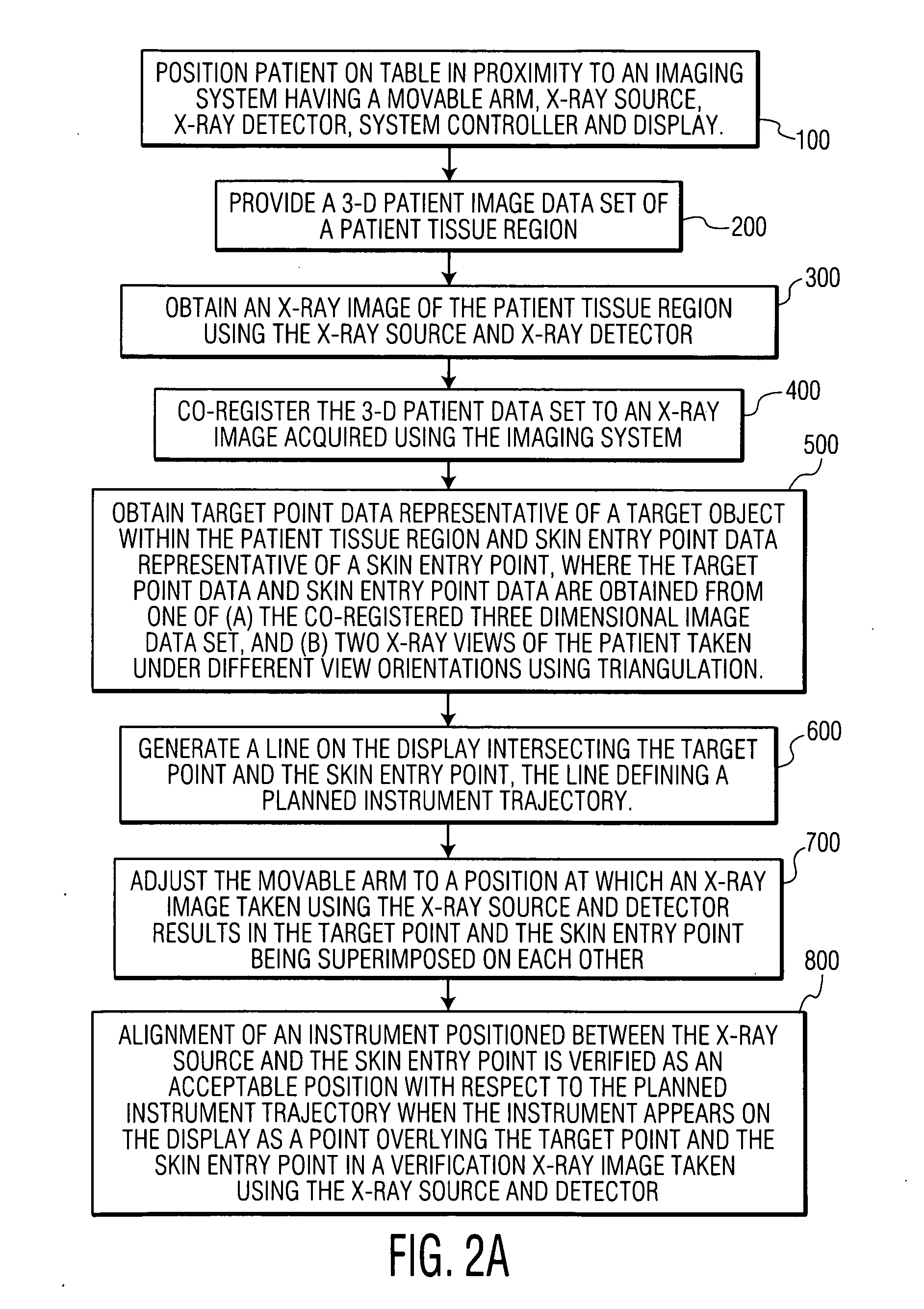
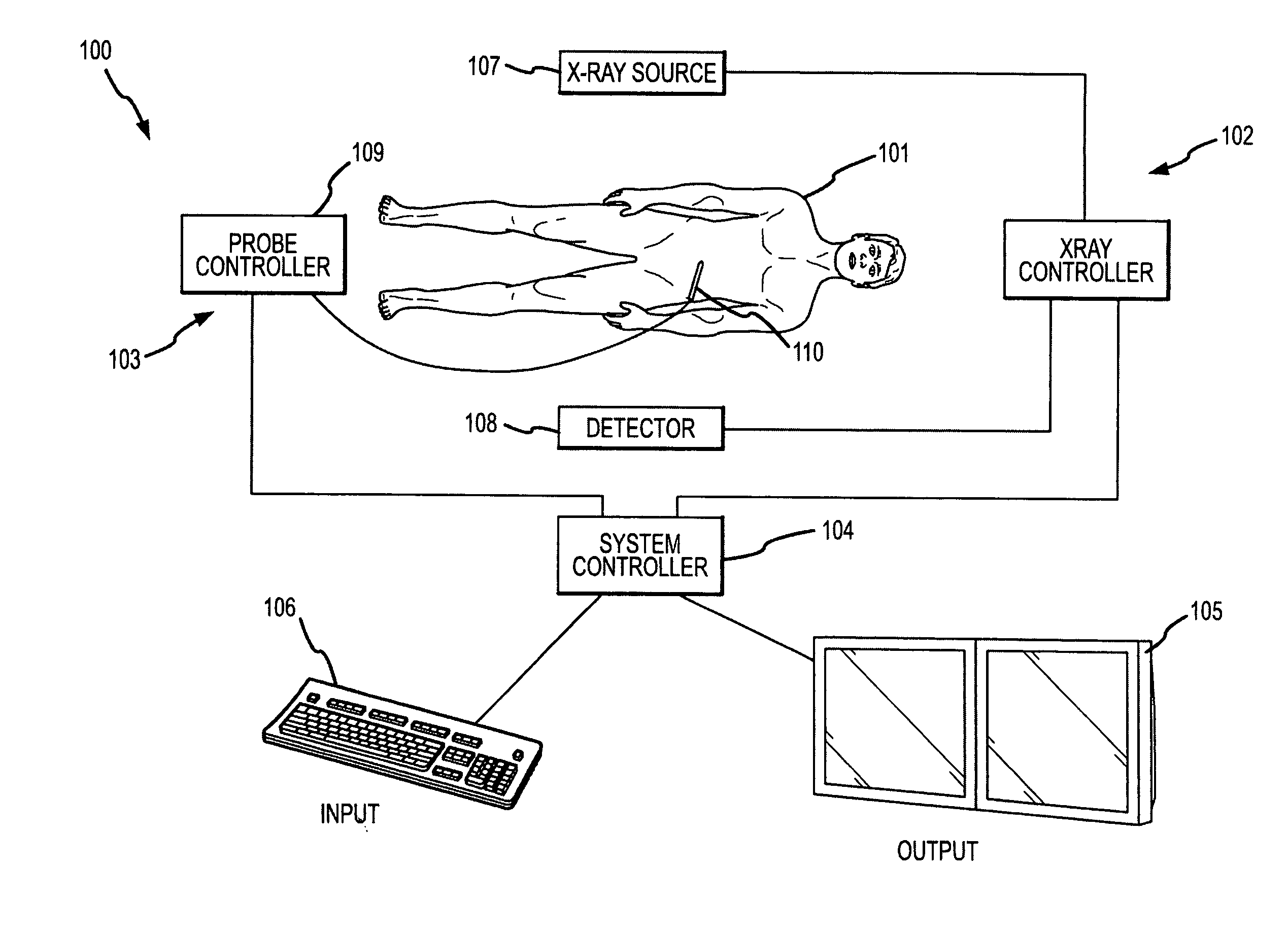
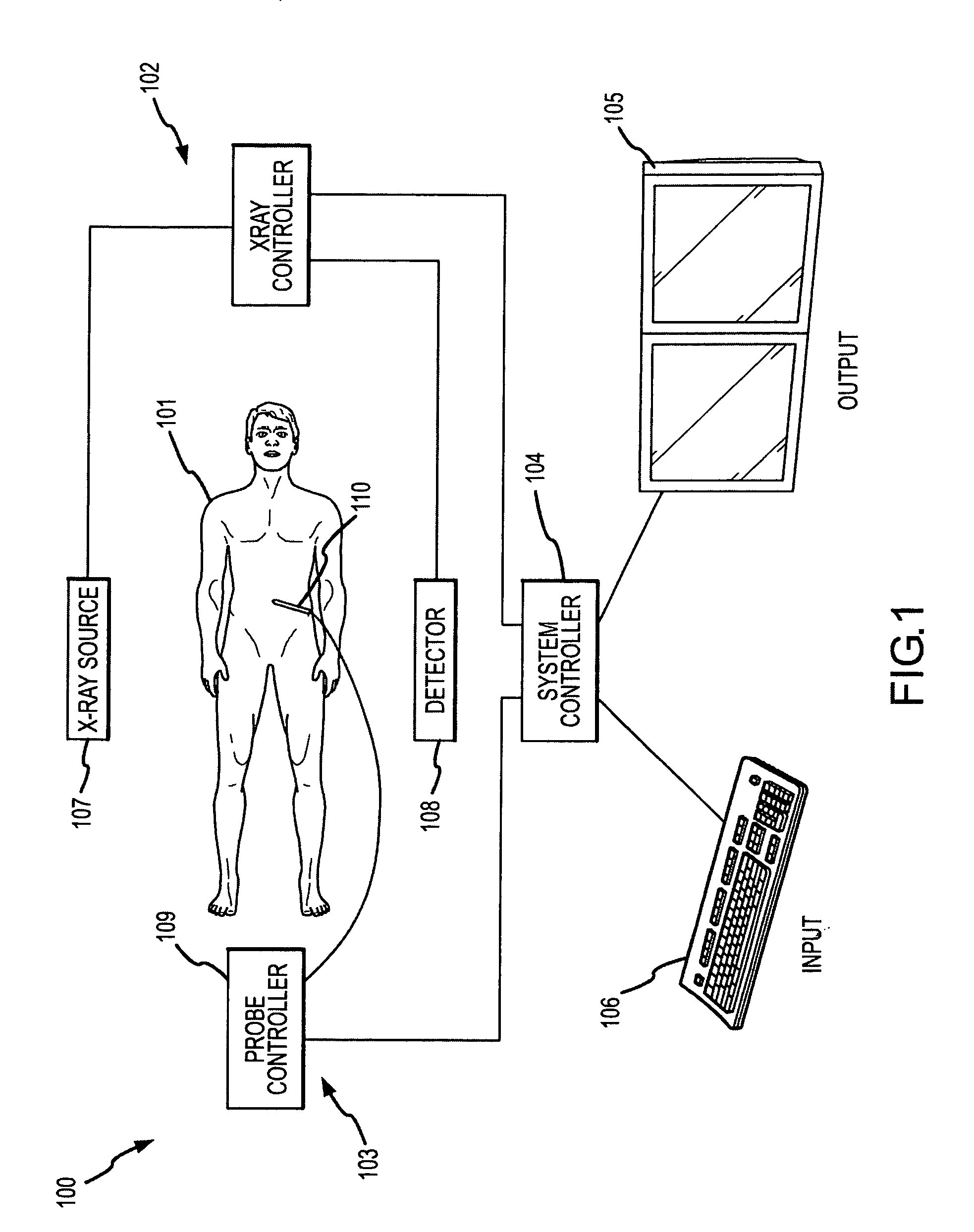
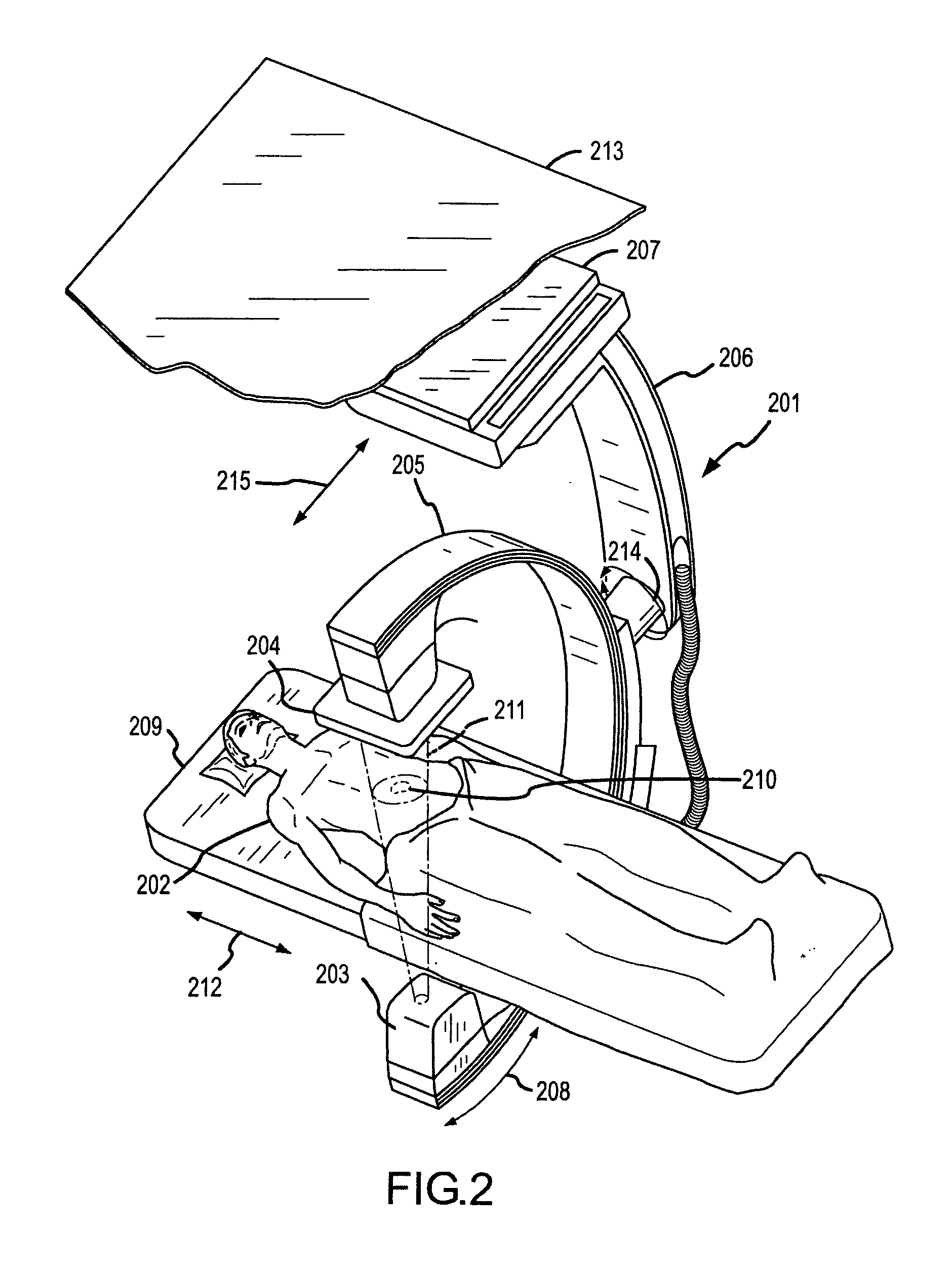
A system and method are disclosed for planning a percutaneous procedure and for guiding an instrument to engage a target within a patient's body. A patient 3-dimensional image data set is provided, within which a user selects a skin entry point and a target point. A line, or “planned path,” is generated between the points which is used to align a movable arm to achieve a “Bull's Eye View,” in which the two points are superimposed. The instrument is placed at the skin entry point and aligned using the Bull's Eye View along a desired trajectory that intersects the target. Initial alignment is verified using fluoroscopy. Progression fluoroscopic views are used during the insertion procedure to ensure the instrument remains on the planned path. When the instrument reaches the target, a procedure may be performed, such as a biopsy, a drainage procedure, a radiofrequency ablation, or other medical interventional procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +1
Methods for monitoring thermal ablation
InactiveUS20080033418A1Shorten the timeMovement is minimized and eliminatedUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsIntermediate imageRadiofrequency ablation
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:ABLA TX +1
Arthroscopic devices and methods
ActiveUS10022140B2Inhibit inflammationEasy to viewExcision instrumentsSurgical instruments for heatingMotor driveRadiofrequency ablation
A medical device includes an elongated sleeve having a longitudinal axis, a proximal end and a distal end. A cutting member having sharp edges formed from a wear-resistant ceramic material is carried at the distal end of the elongated sleeve. A motor drive is coupled to the proximal end of the elongated sleeve to rotate the sleeve at cutting member at high speed to cut bone and other hard tissue. An electrode is carried in a surface portion of ceramic cutting member for cautery or radiofrequency ablation of tissue when the sleeve and cutting member are is a stationary position.
Owner:RELIGN CORP
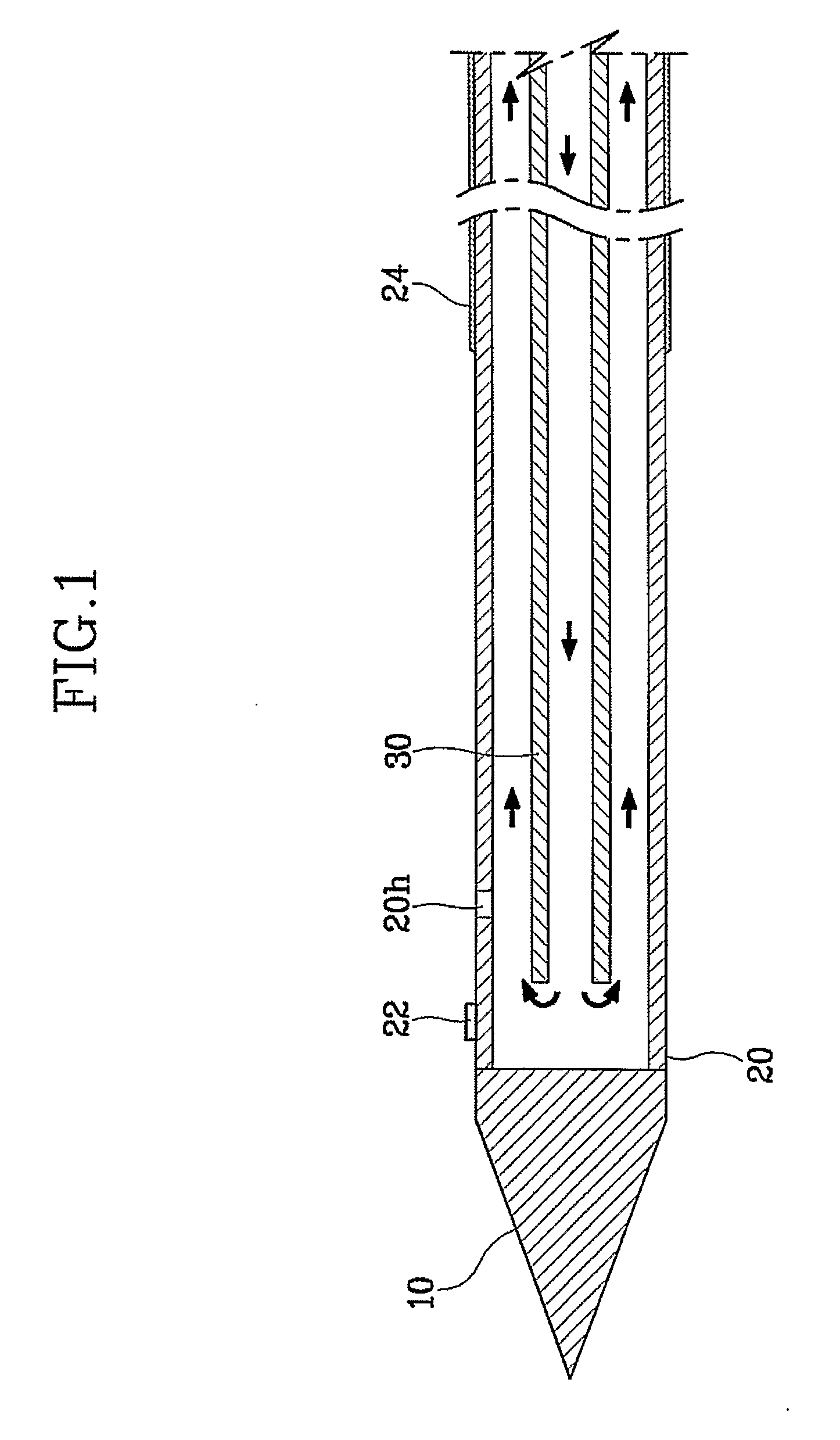
Cryogenic-radiofrequency ablation system
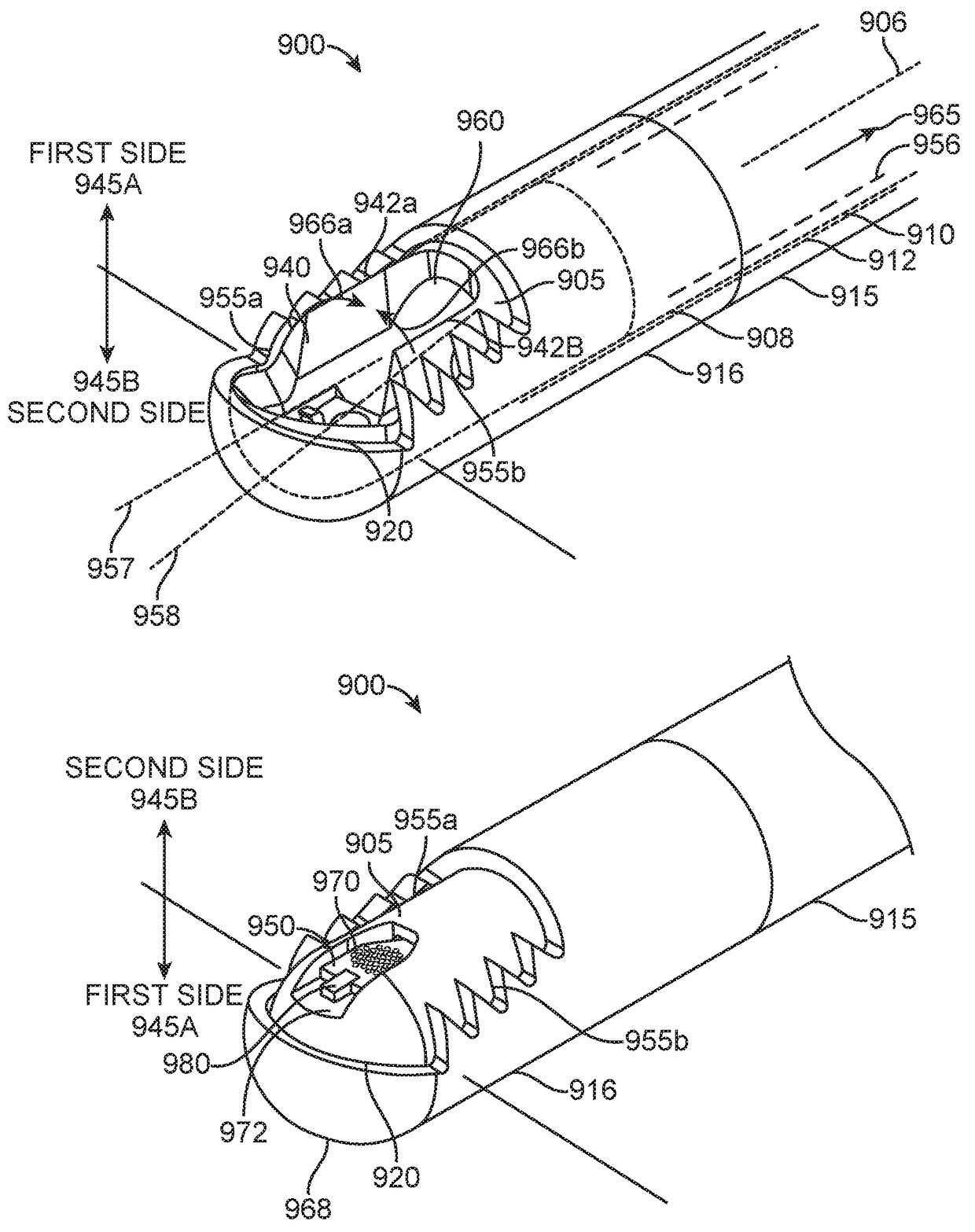
A medical treatment system, including a catheter body defining a fluid flow path therethrough; an expandable element disposed on the catheter body, the expandable element defining a cooling chamber therein in fluid communication with the fluid flow path; a plurality of electrodes disposed on the expandable element; a cryogenic fluid source in fluid communication with the fluid flow path; and a radiofrequency energy source in electrical communication with the plurality of electrodes. A method of treating a cardiac tissue site proximate an orifice, including substantially occluding the orifice with an expandable element; powering a plurality of electrodes coupled to the expandable element to reach a predetermined target temperature; circulating a coolant through the expandable element to freeze portions of the cardiac tissue site located between the plurality of electrodes; and ablating the non-frozen portions of the tissue site with the plurality of electrodes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Cryogenic balloon device with radiofrequency tip
ActiveUS9204916B2Fill in the blanksCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationElectroporation
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Method and system for interactive percutaneous pre-operation surgical planning
The success of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation mainly depends on the accuracy of the needle insertion, making it possible to destroy the whole tumor, while avoiding damages on other organs and minimizing risks of a local recurrence. This invention presents a simulated 3D environment for user to interactively place a treatment probe to a target position.
Owner:EDDA TECH
Cardiac- and/or respiratory-gated image acquisition system and method for virtual anatomy enriched real-time 2D imaging in interventional radiofrequency ablation or pacemaker placement procedures
ActiveCN102196768AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac cyclePacemaker Placement
The present invention refers to the field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) and, more specifically, to image-guided radio frequency ablation and pacemaker placement procedures. For those procedures, it is proposed to display the overlaid 2D navigation motions of an interventional tool intraoperatively obtained from the same projection angle for tracking navigation motions of an interventional tool during an image-guided intervention procedure while being navigated through a patient's bifurcated coronary vessel or cardiac chambers anatomy in order to guide e.g. a cardiovascular catheter to a target structure or lesion in a cardiac vessel segment of the patient's coronary venous tree or to a region of interest within the myocard. In such a way, a dynamically enriched 2D reconstruction of the patient's anatomy is obtained while moving the interventional instrument. By applying a cardiac and / or respiratory gating technique, it can be provided that the 2D live images are acquired during the same phases of the patient's cardiac and / or respiratory cycles. Compared to prior-art solutions which are based on a registration and fusion of image data independently acquired by two distinct imaging modalities, the accuracy of the two-dimensionally reconstructed anatomy is significantly enhanced.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Reciprocating surgical instrument
A surgical rasping system functional in multiple orthopedic applications, including but not limited to shoulder, knee, hip, wrist, ankle, spinal, or other joint procedures. The system may comprise a tissue removal member with a rasping head which may be low profile and offer a flat cutting / rasping surface, or with a cutting head with at least one cutting edge. The tissue removal member is configured to be driven by an attached hub that translates a rotational movement into a reciprocating motion. Suction for removal of bone fragments or other tissues is provided through an opening spaced apart from or adjacent to the rasping surface. A radiofrequency ablation (RF) electrode may be carried on the rasping system to provide ablation or coagulation of soft tissues.
Owner:MEDICINELODGE
Electrode for Radiofrequency Tissue Ablation
ActiveUS20080147060A1Surgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationTubes types
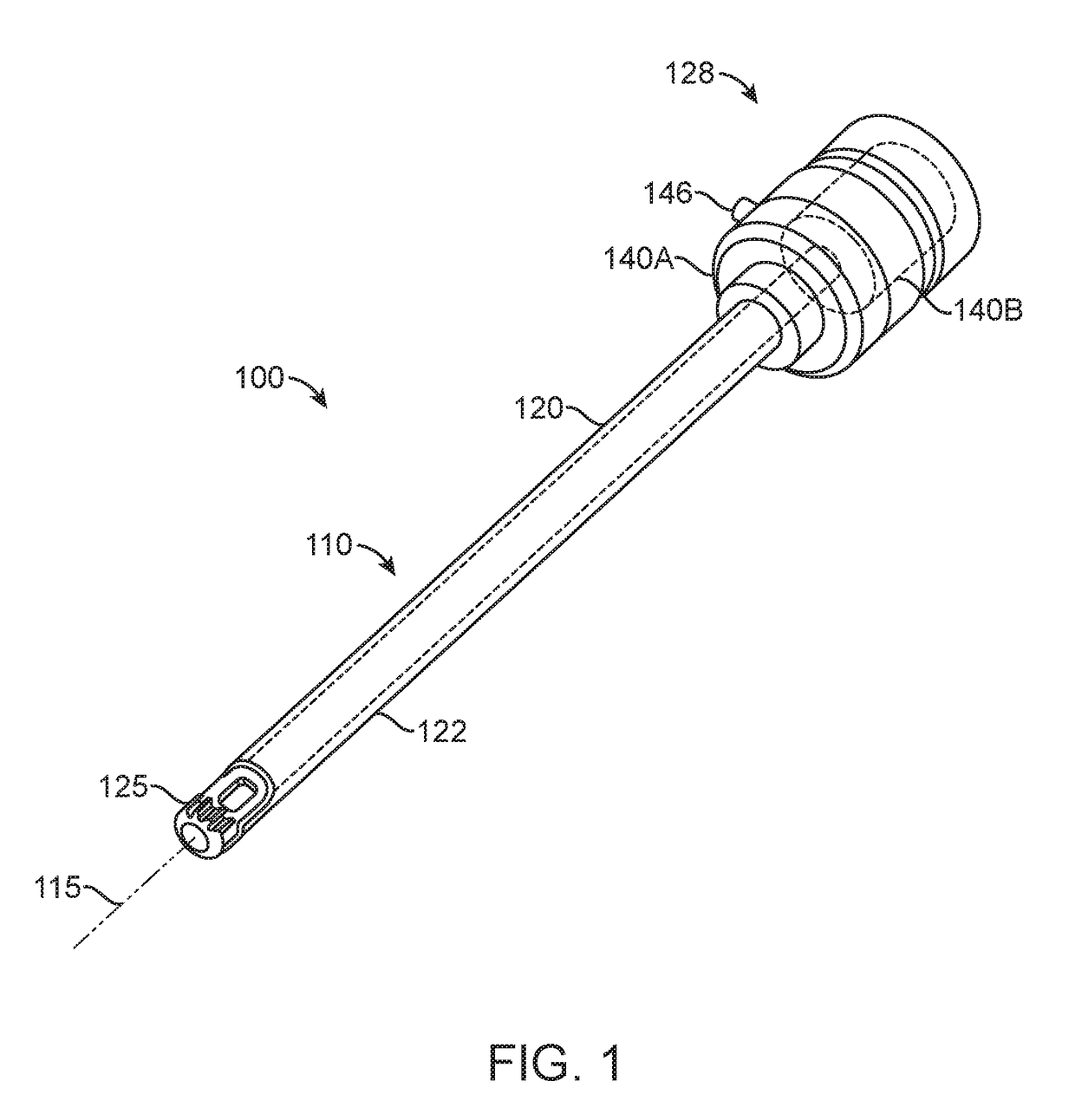
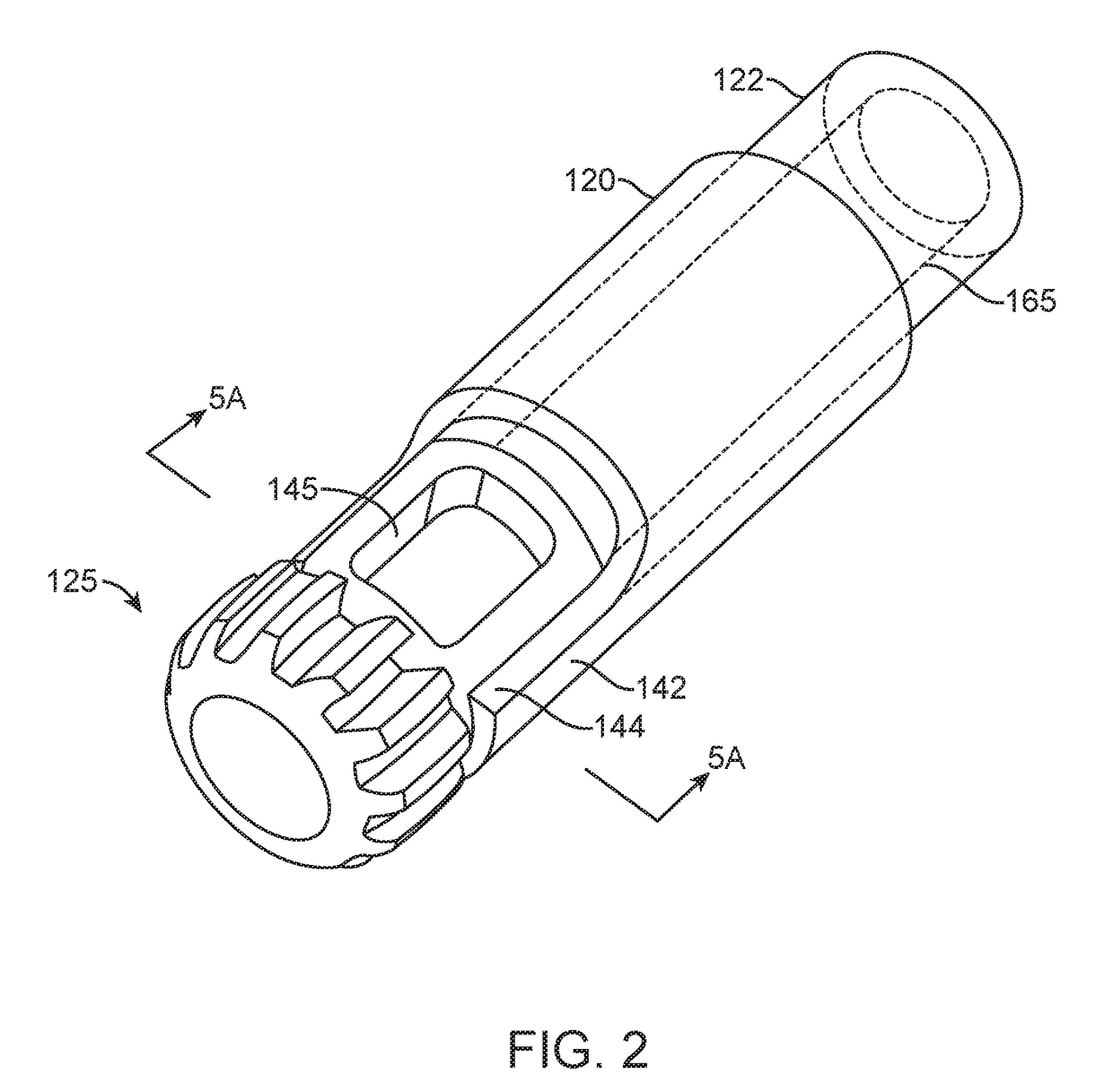
The present invention discloses an electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation which can coagulate and necrotize a tissue by radiofrequency electric energy. The electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation precisely coagulates and necrotizes a target part of the tissue by sensing a temperature of the tissue. The electrode includes a horn-shaped closed end sharpened to its one end, a hollow tube type electrode extended long in the length direction from the other end of the closed end, an insulation member installed on the outer circumference of the hollow electrode except for the part connected to the closed end, at least one temperature sensor installed on the outer circumference of the hollow electrode to be positioned inside the insulation member, for sensing an ambient temperature, and a control unit connected to the hollow electrode and the temperature sensor, for deciding coagulation and necrosis of the tissue according to the temperature sensed by the temperature sensor, and controlling the output supplied to the hollow electrode.
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Methods and apparatuses for performing and monitoring thermal ablation
ActiveUS8556888B2Shorten the timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyData setIntermediate image
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided. Methods of assessing the post-ablation status of the patient and performance of the system are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC
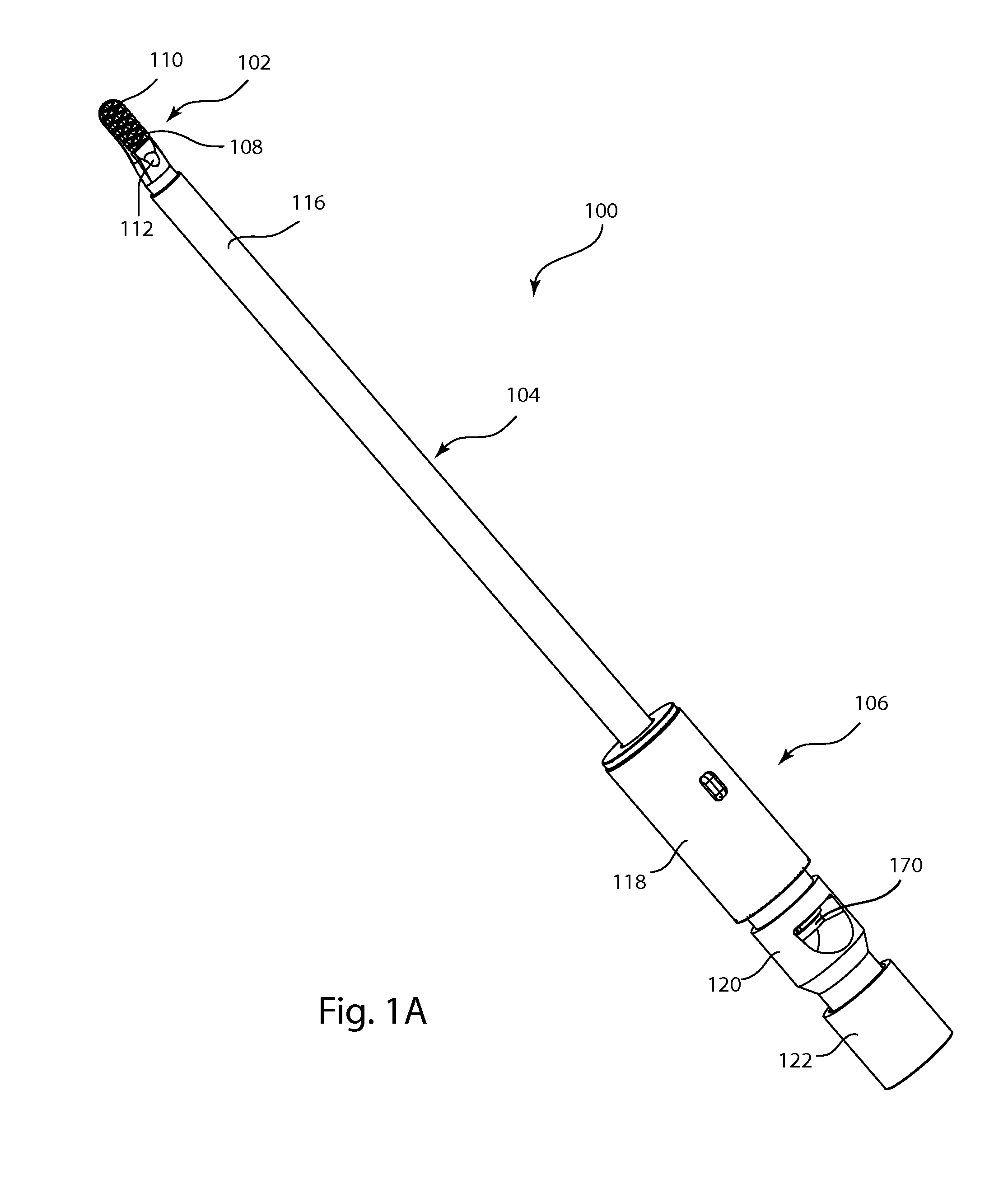
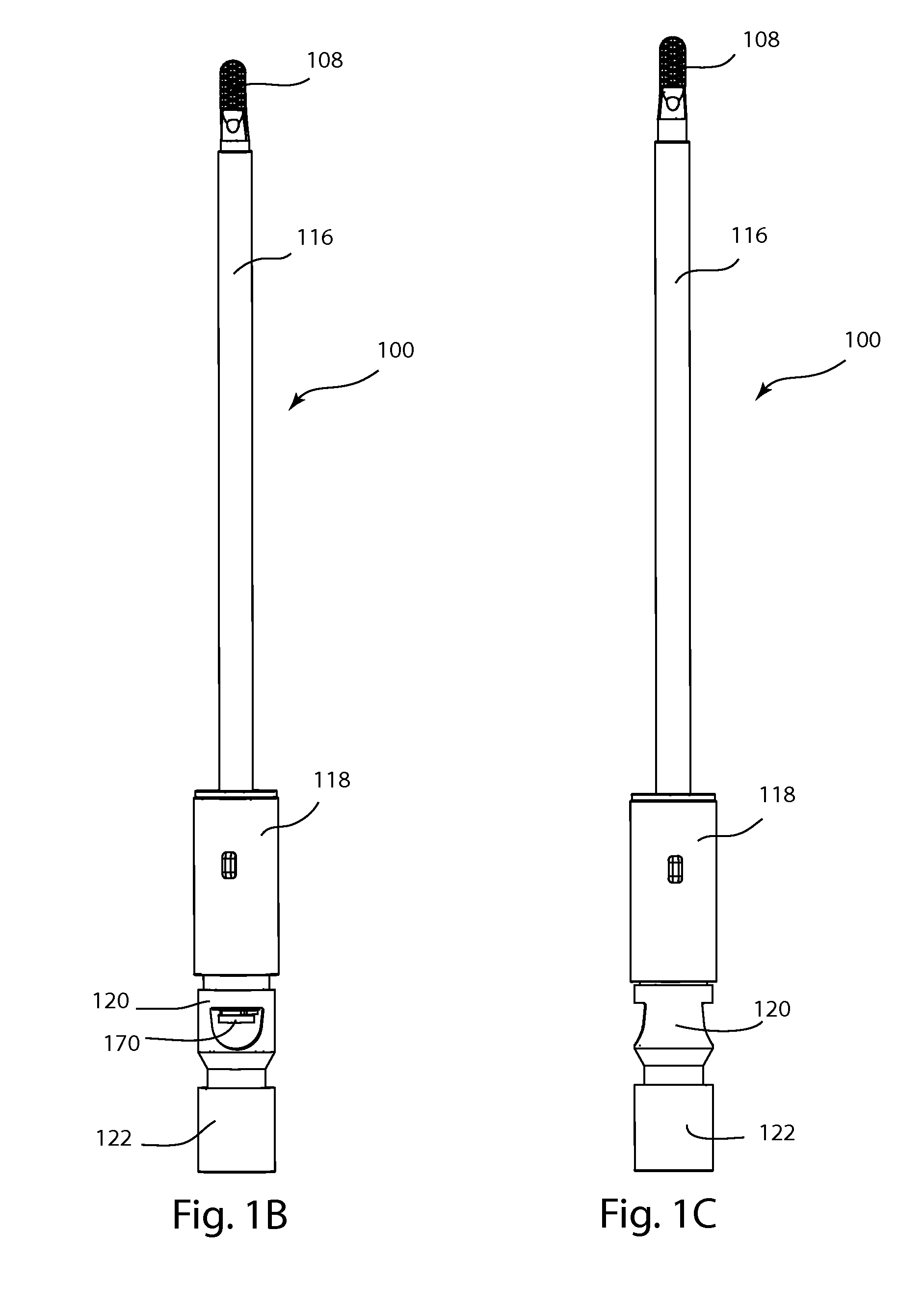
Ablation needle component and ablation system
PendingCN109833091AAvoid repeated puncturesAvoid damageSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationHypertrophic cardiomyopathy
The invention provides an ablation needle component and an ablation system. The ablation needle component comprises a hollow outer sleeve and an ablation needle, wherein the outer sleeve movably sleeves outside an electrode needle main body of the ablation needle and is connected with an ablation handle in a detached and rotating manner, so that the ablation needle can be separated from the outersleeve after an ablation operation is completed, the outer sleeve is still kept in a tissue, a channel is provided for other operations, such as biopsy, repeated puncture is avoided, damages on tissues are reduced, and the biopsy operation can be convenient and efficient. Furthermore, the ablation handle is in rotating connection with the outer sleeve, the electrode needle main body can be drivento rotate relative to the outer sleeve when the ablation handle rotates relative to the outer sleeve, which means that the outer sleeve and the electrode needle main body are not of an integral structure, and the outer sleeve can be kept standing still when the ablation needle should be rotated, so that damages on tissues can be reduced, and the rotating resistance is relatively small. Therefore,the ablation needle component and the ablation system are especially applicable to radiofrequency ablation treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Owner:HANGZHOU NUO CHENG MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
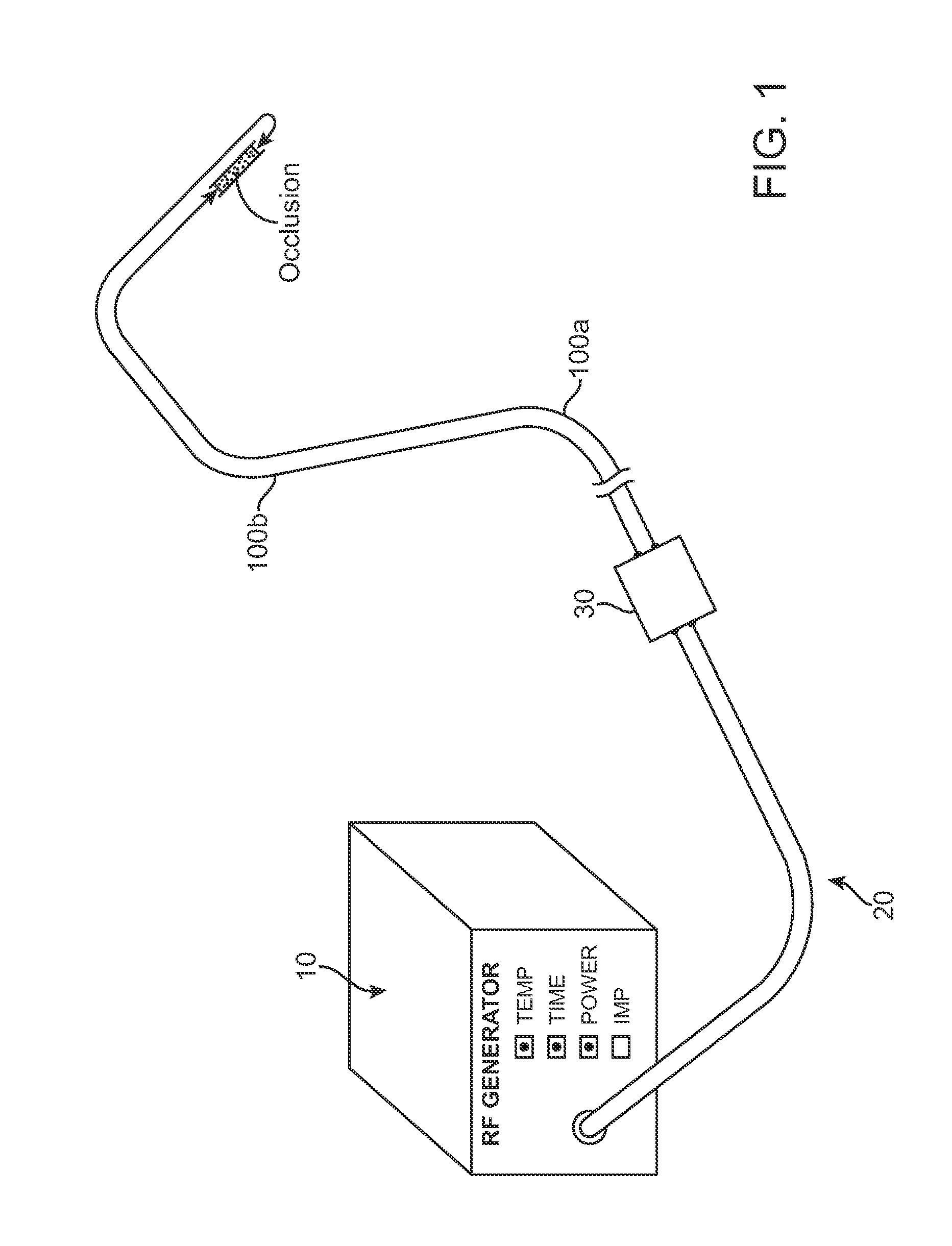
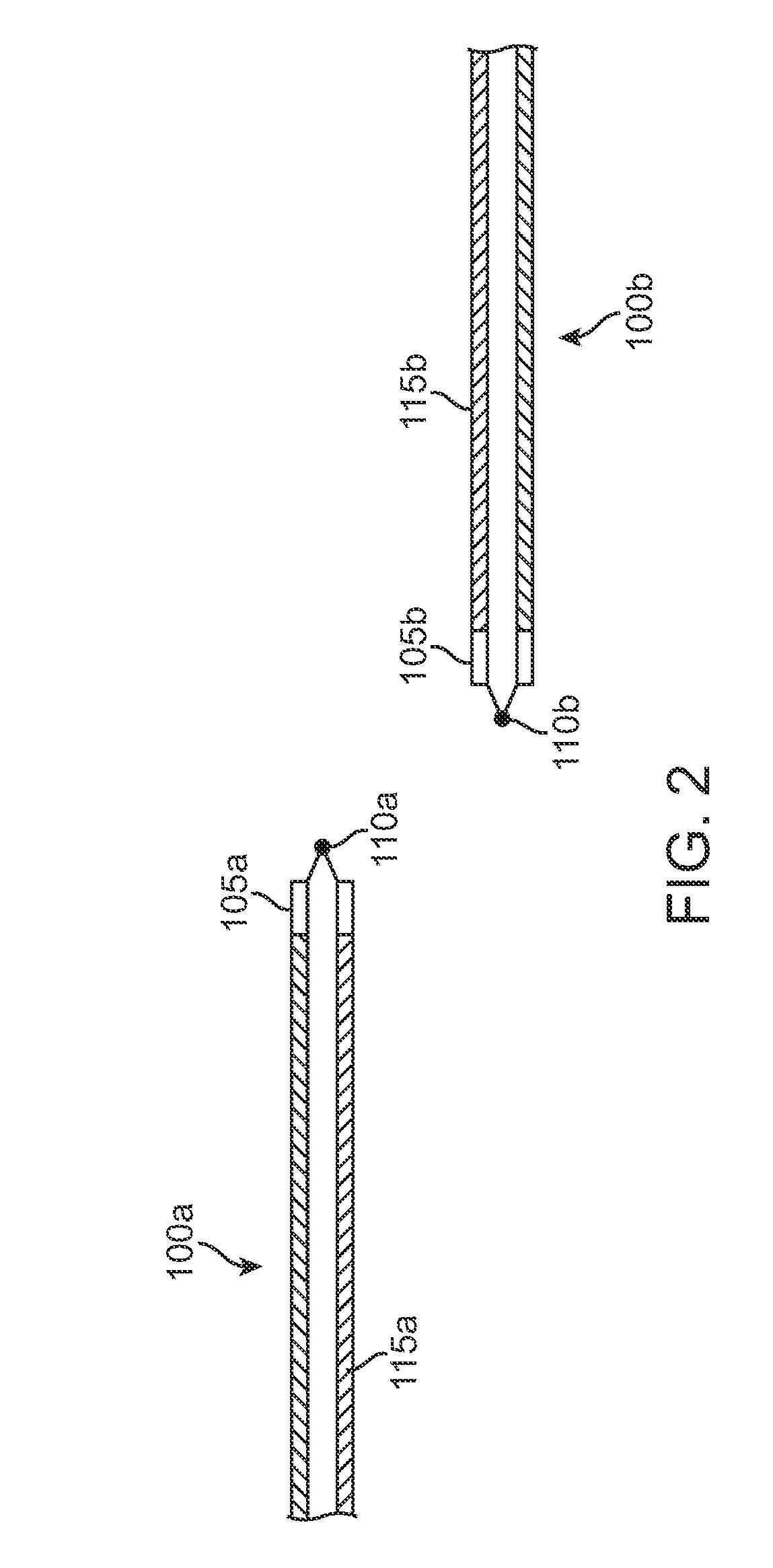
Recanalizing occluded vessels using radiofrequency energy
Owner:ASAHI MEDICAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com