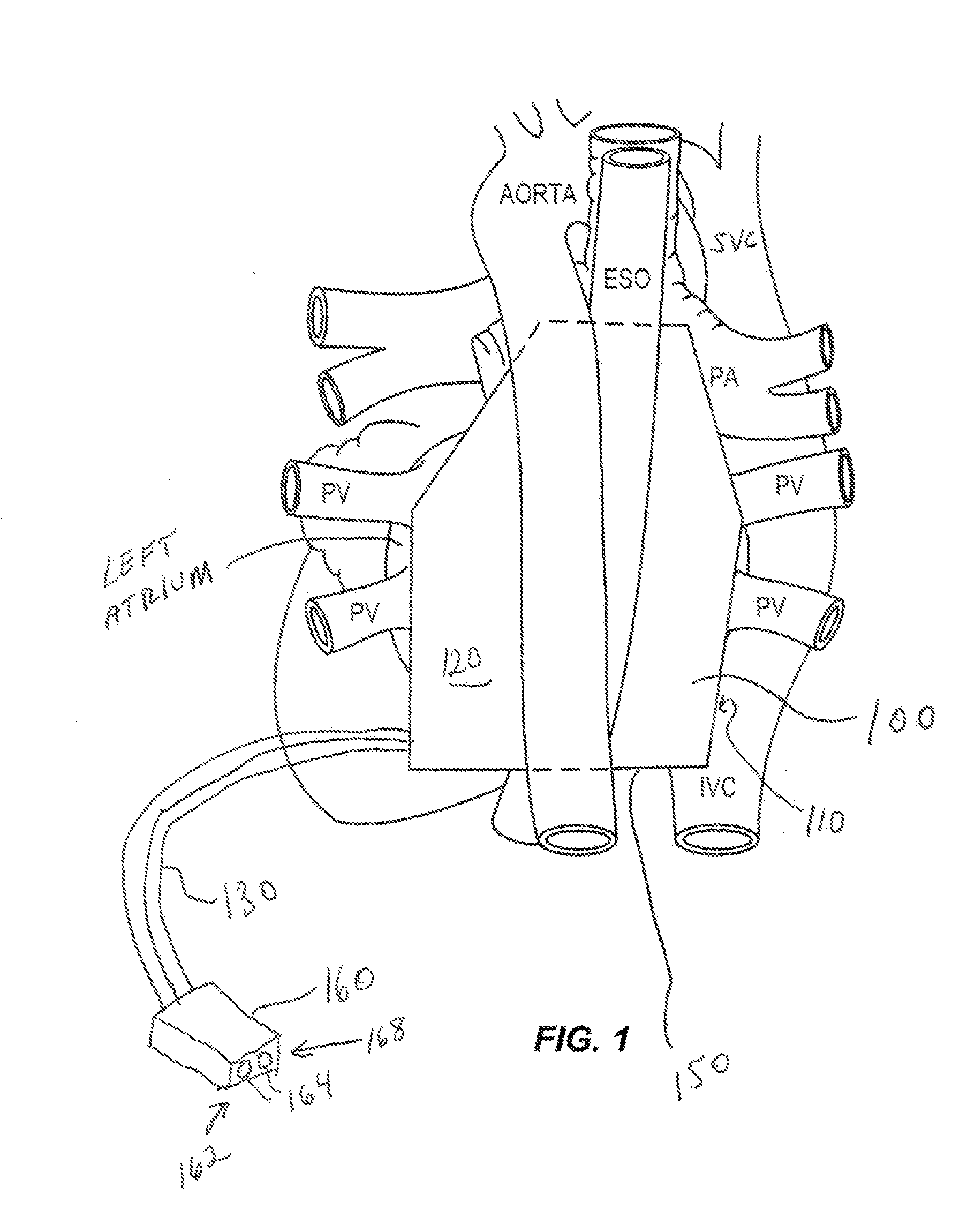
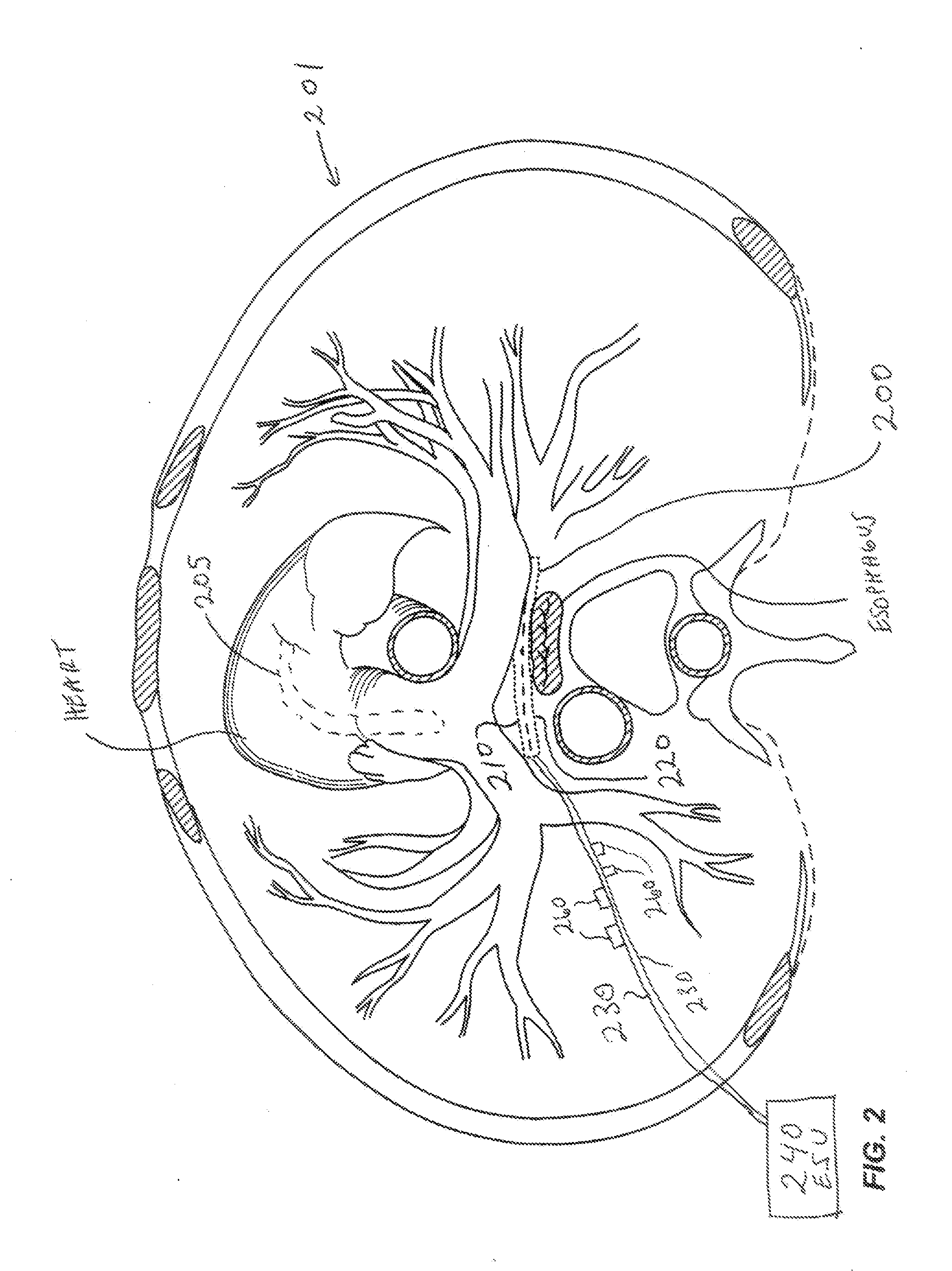
Patents
Literature
47 results about "Electrosurgical unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
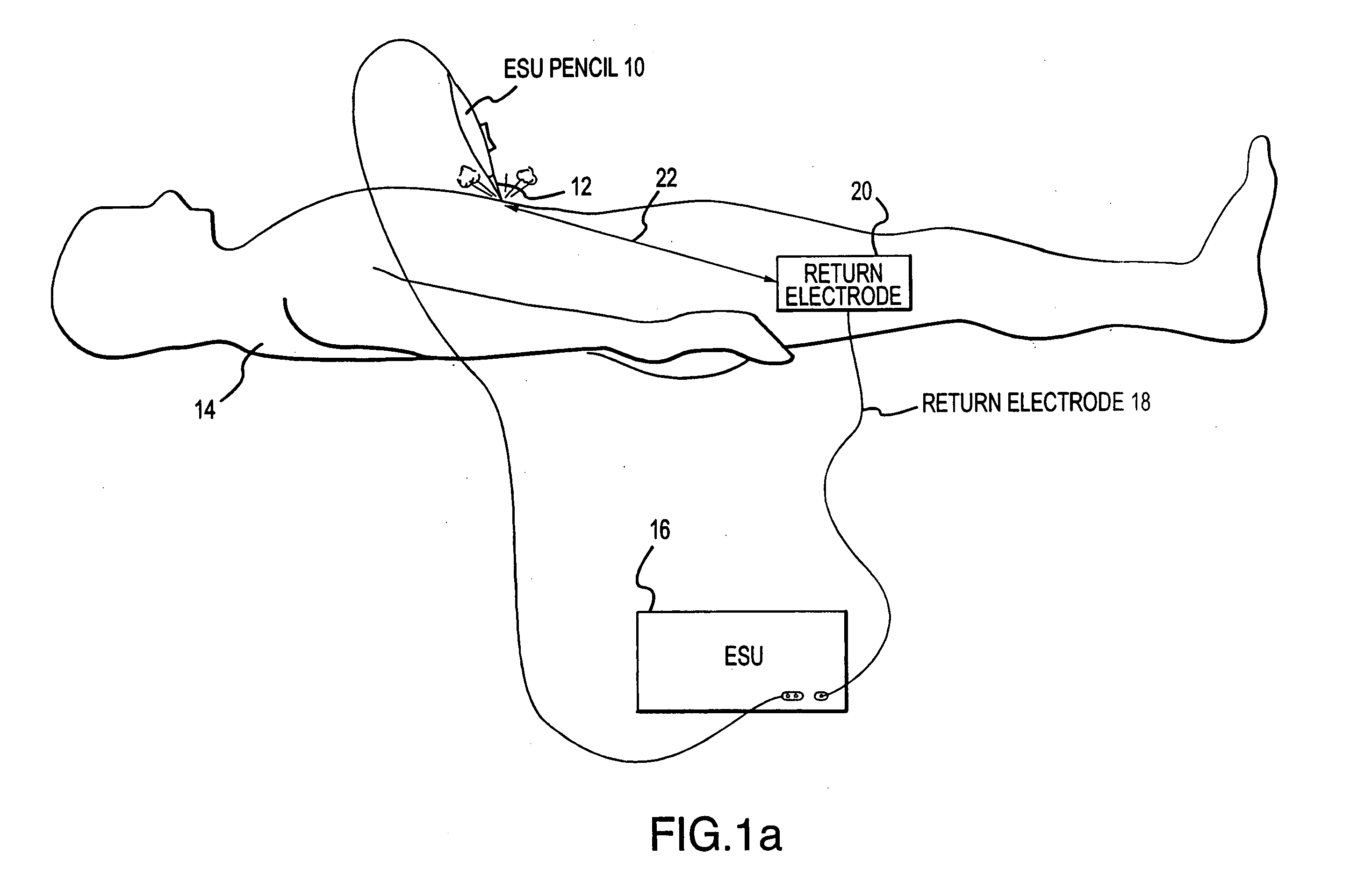
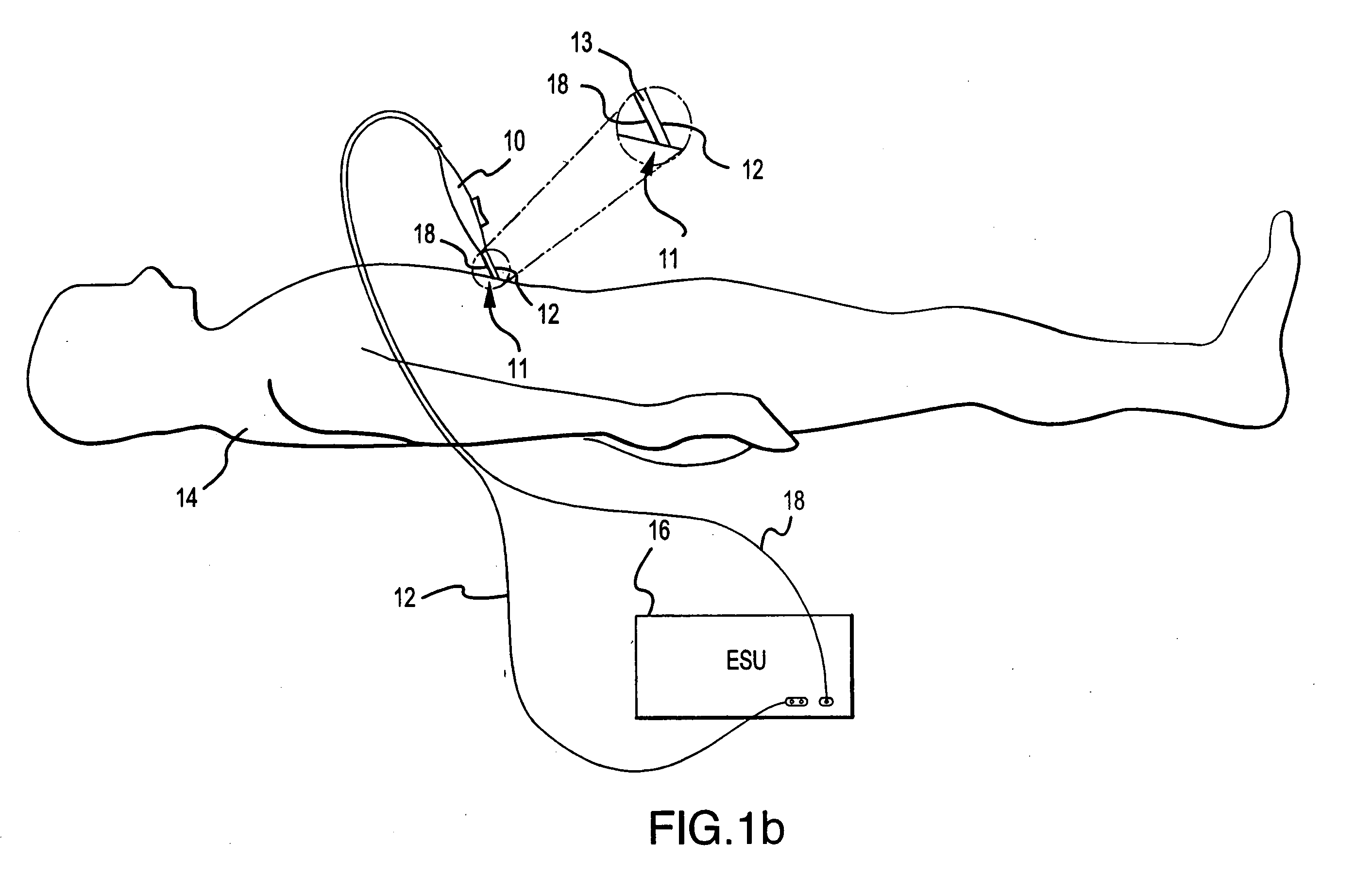
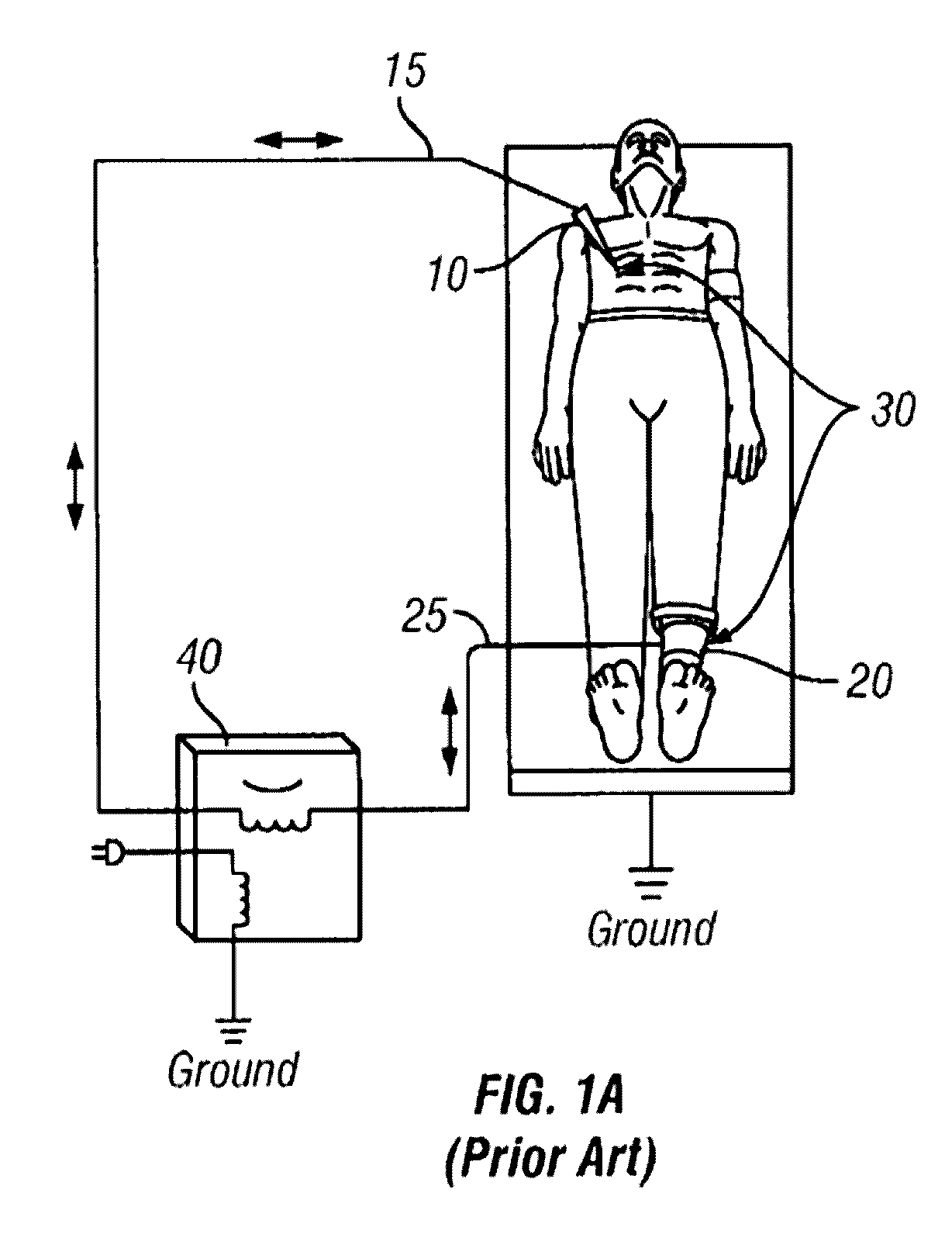
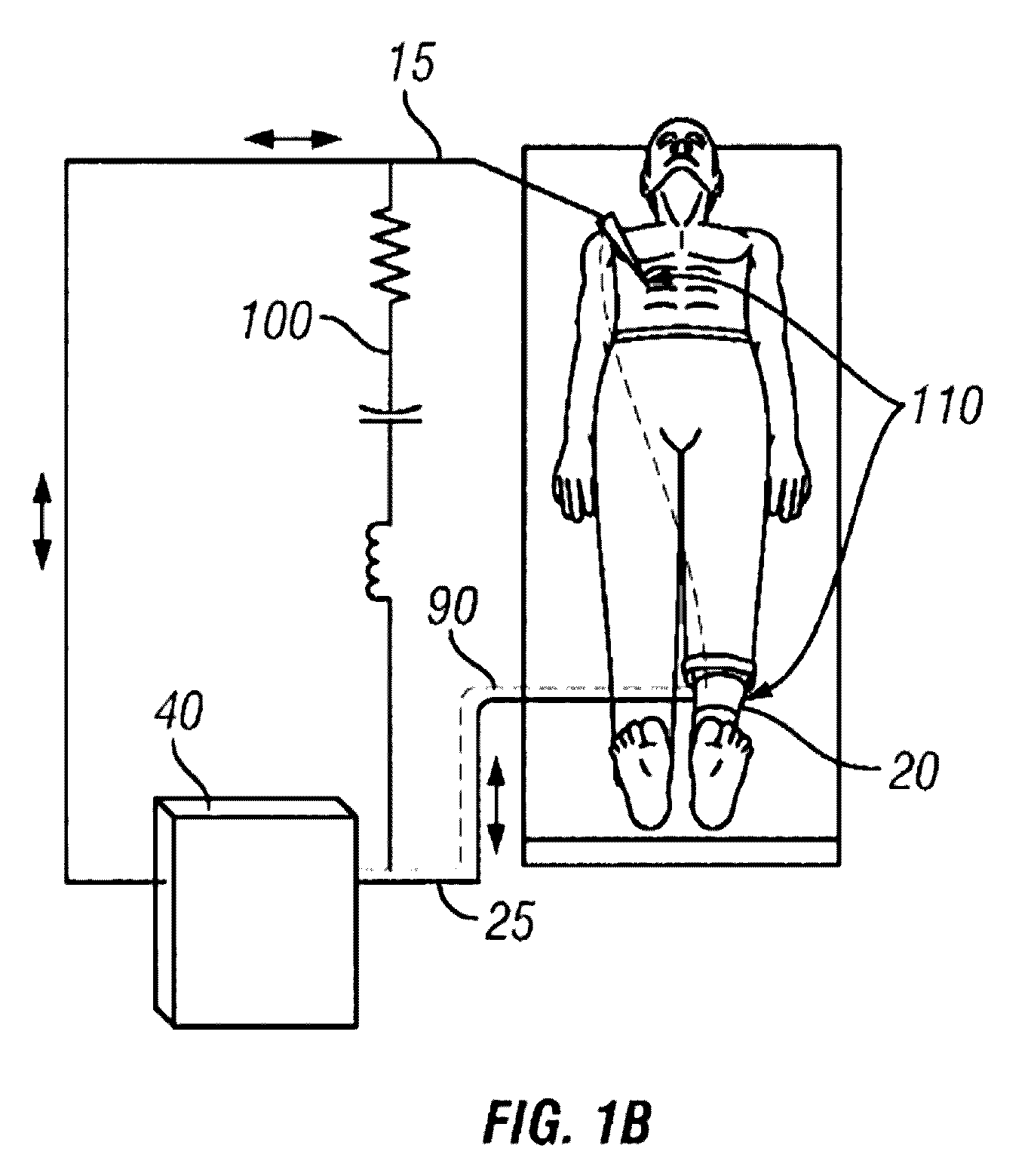
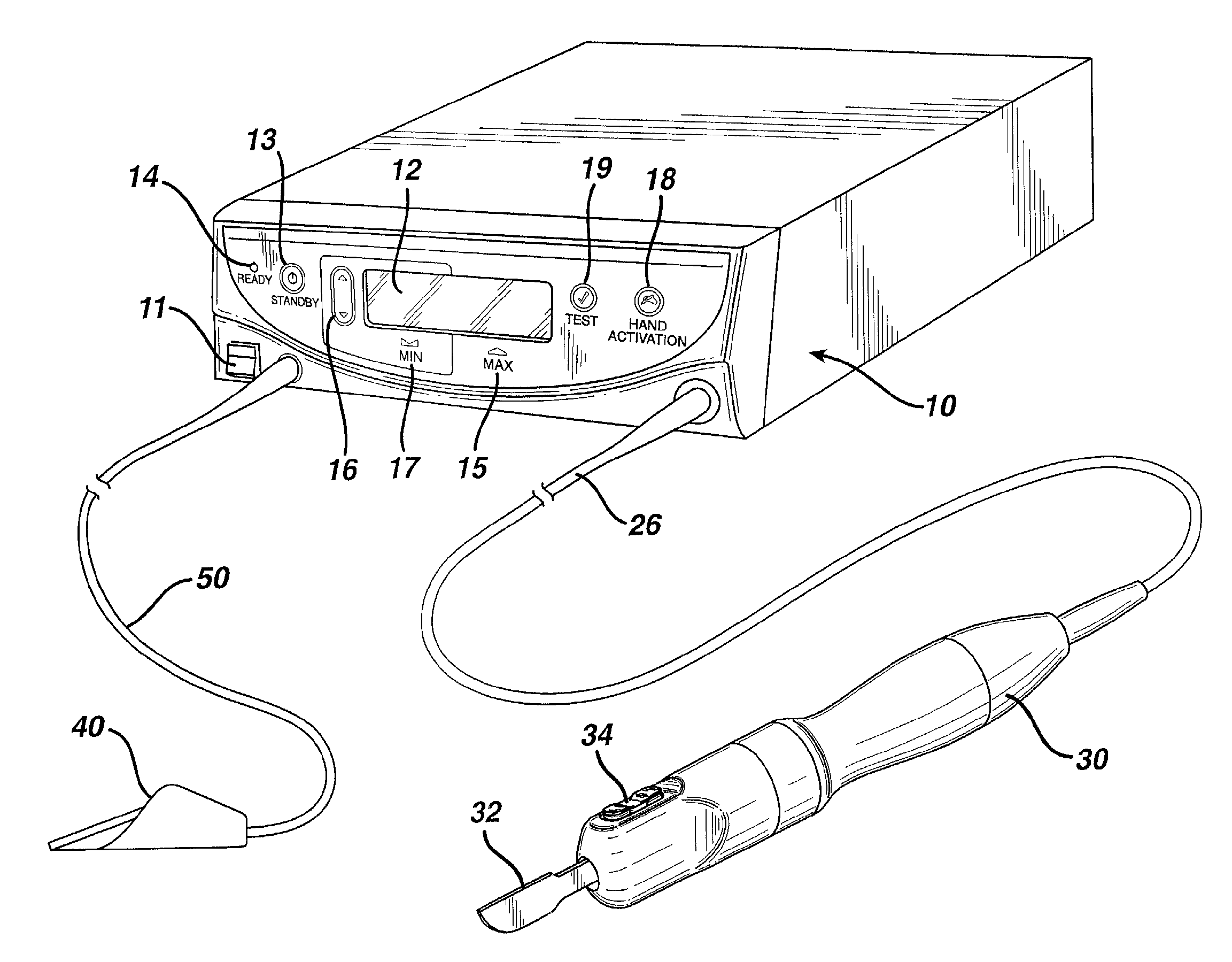
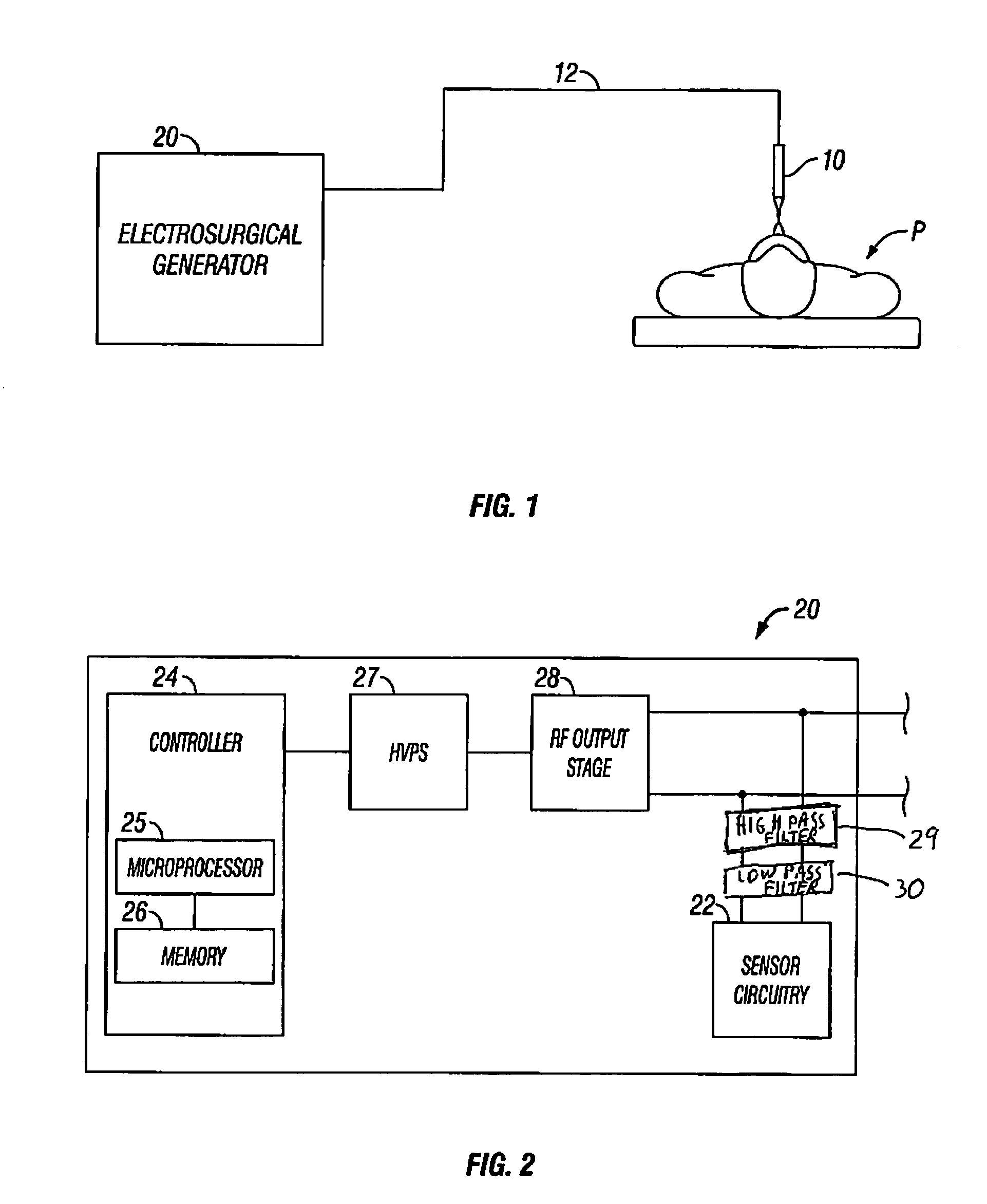
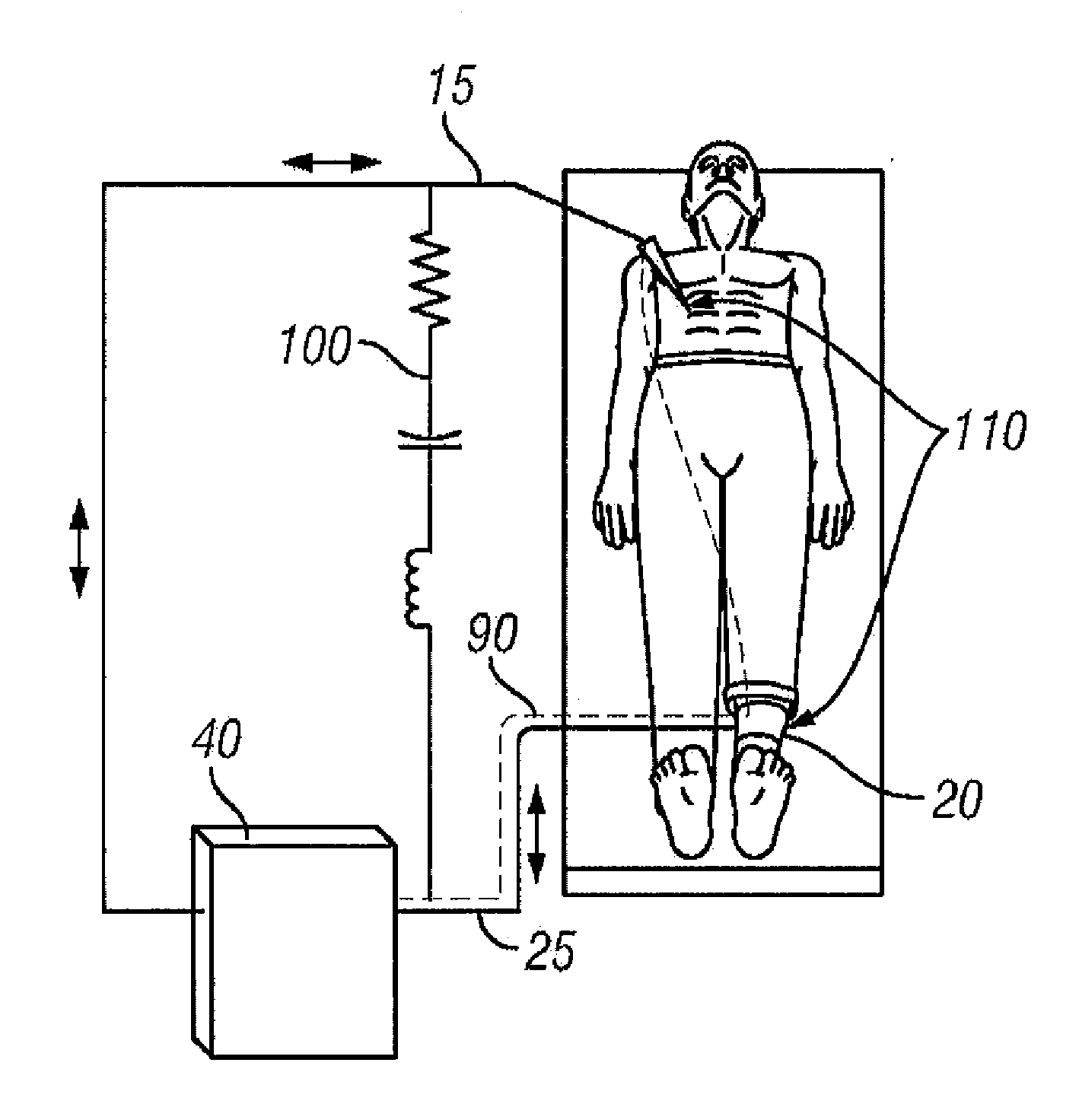
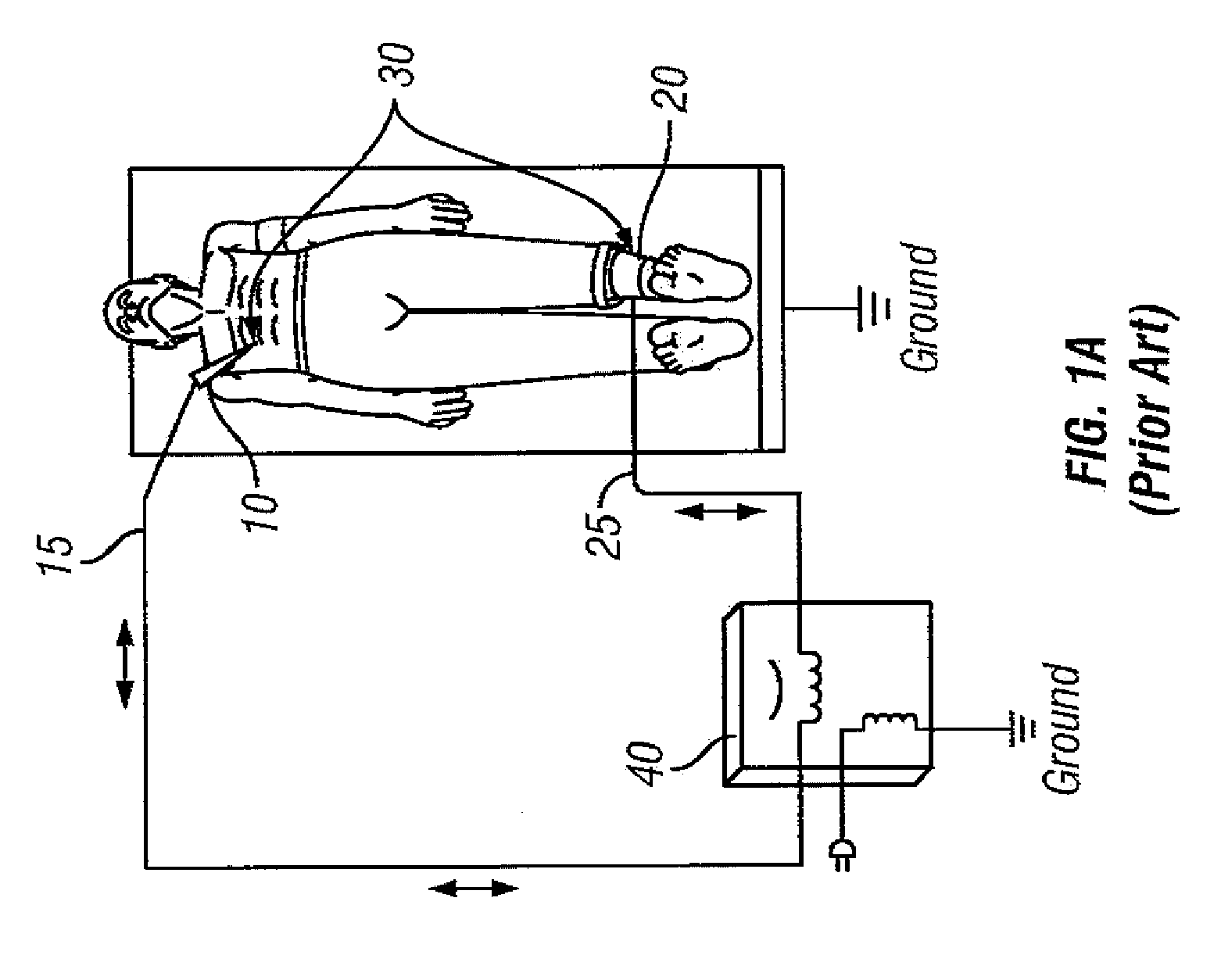
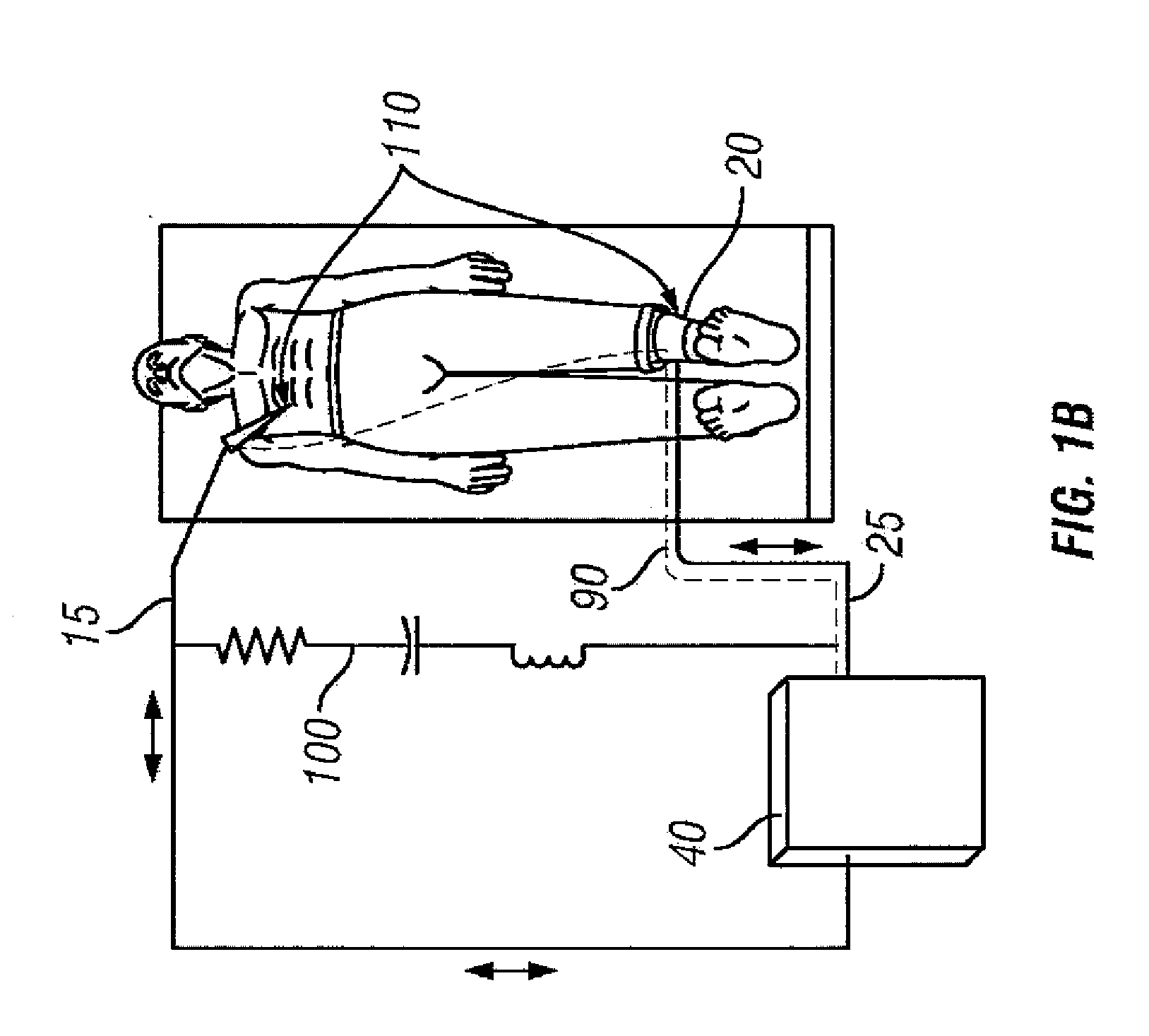
RF electrosurgery is performed using a RF electrosurgical generator (also referred to as an electrosurgical unit or ESU) and a handpiece including one or two electrodes—a monopolar or bipolar instrument.
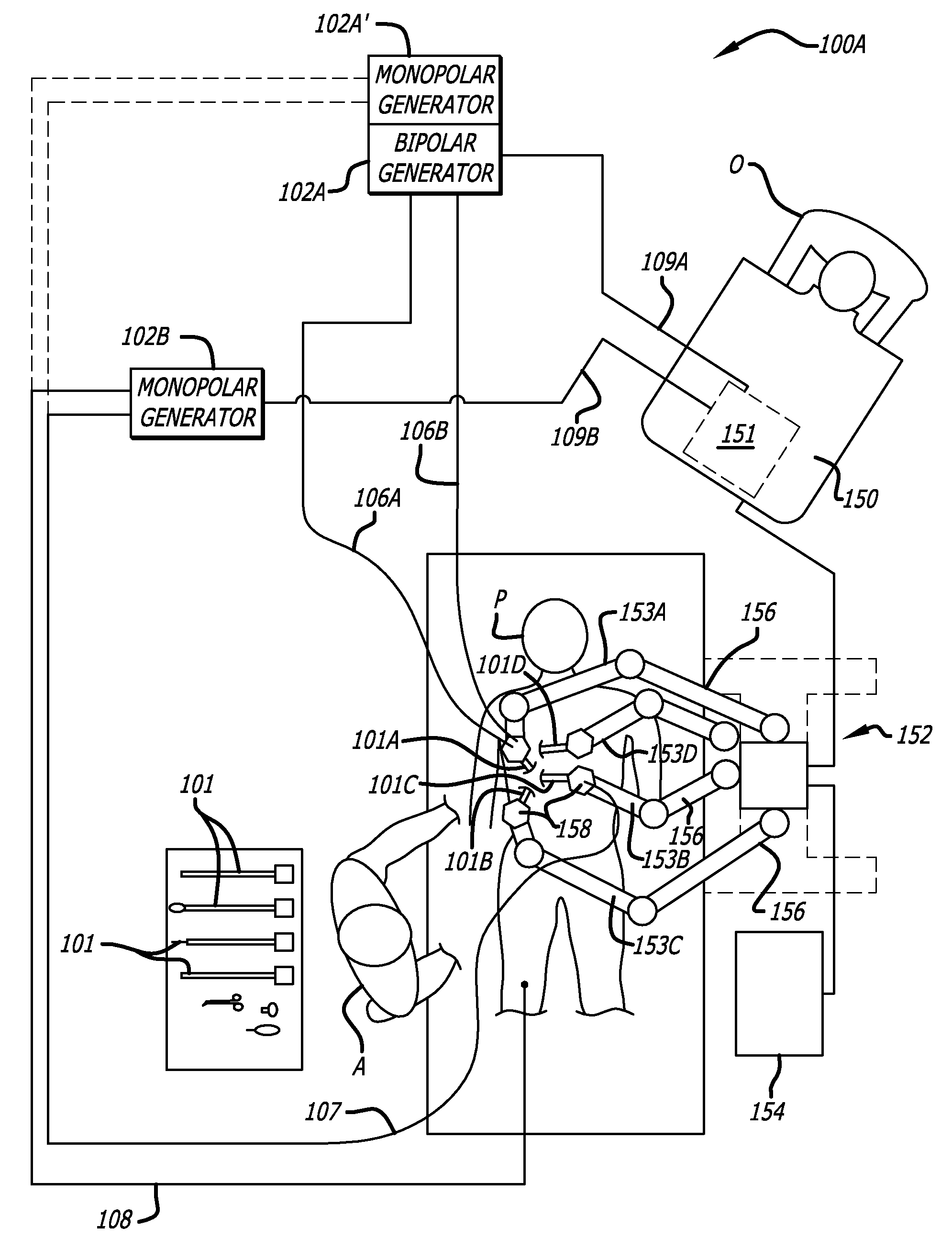
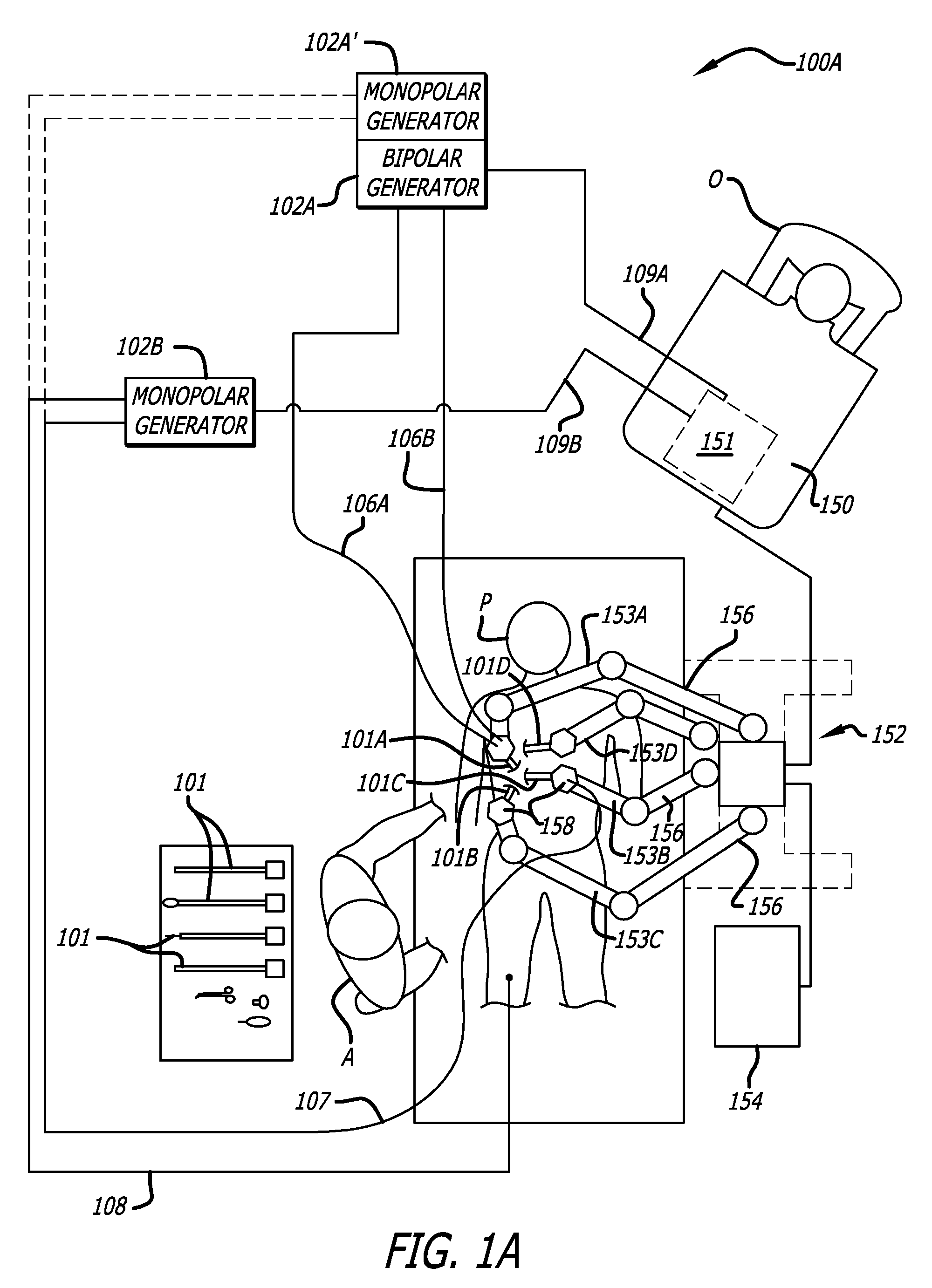
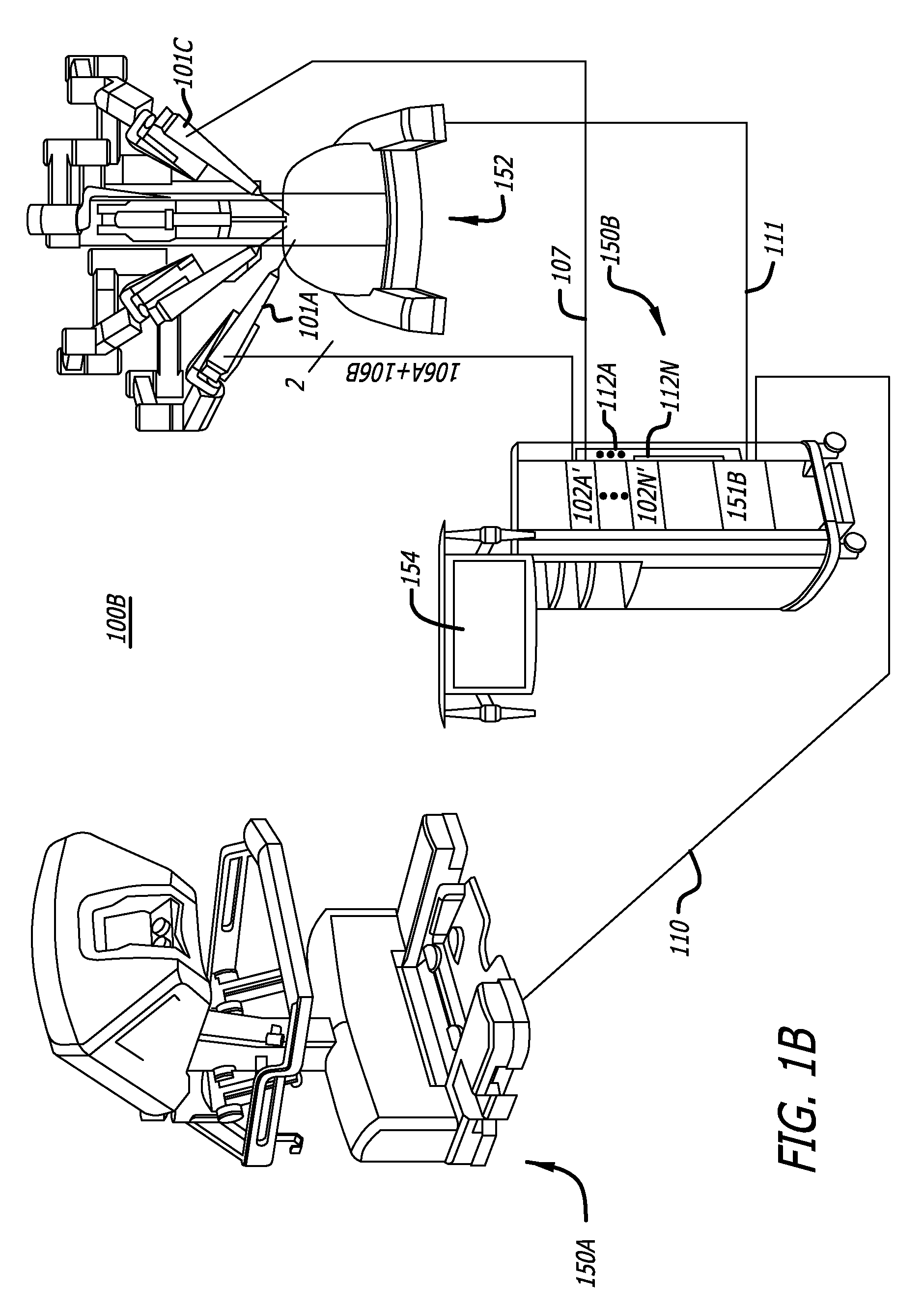
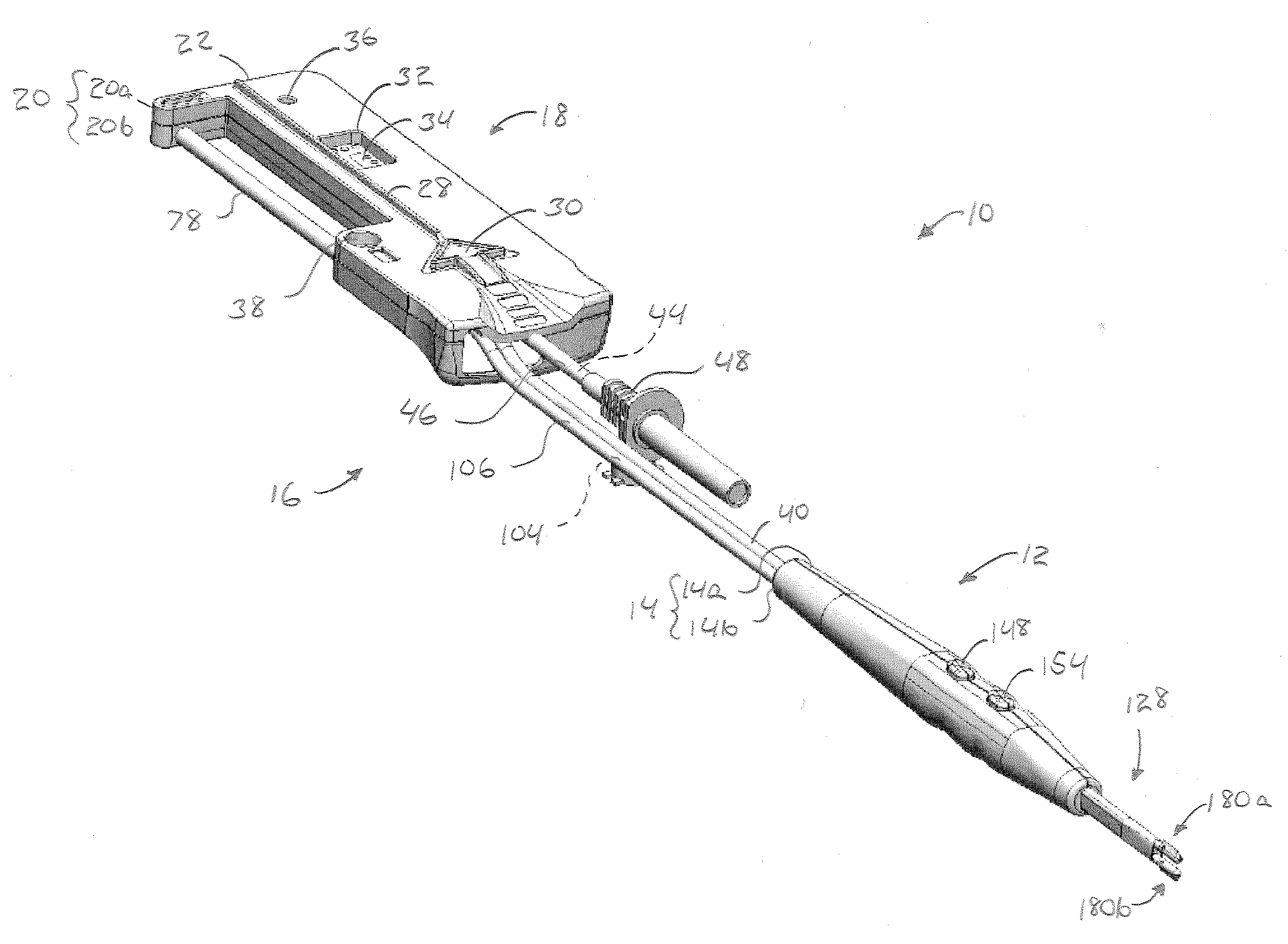
Adaptable integrated energy control system for electrosurgical tools in robotic surgical systems
A method for a minimally invasive surgical system is disclosed including reading first tool information from a storage device in a first robotic surgical tool mounted to a first robotic arm to at least determine a first tool type; reading equipment information about one or more remote controlled equipment for control thereof; comparing the first tool information with the equipment information to appropriately match a first remote controlled equipment of the one or more remote controlled equipment to the first robotic surgical tool; and mapping one or more user interface input devices of a first control console to control the first remote controlled equipment to support a function of the first robotic surgical tool.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
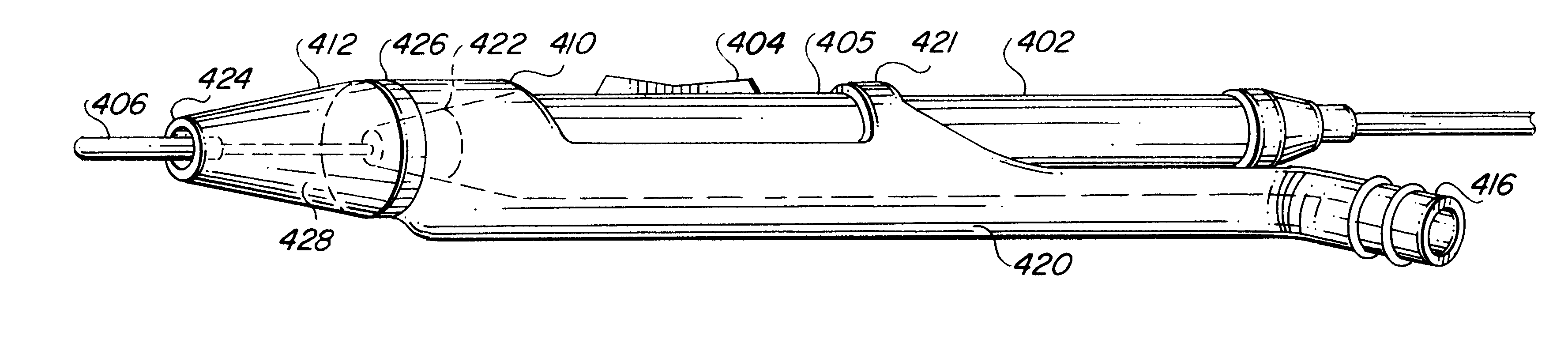
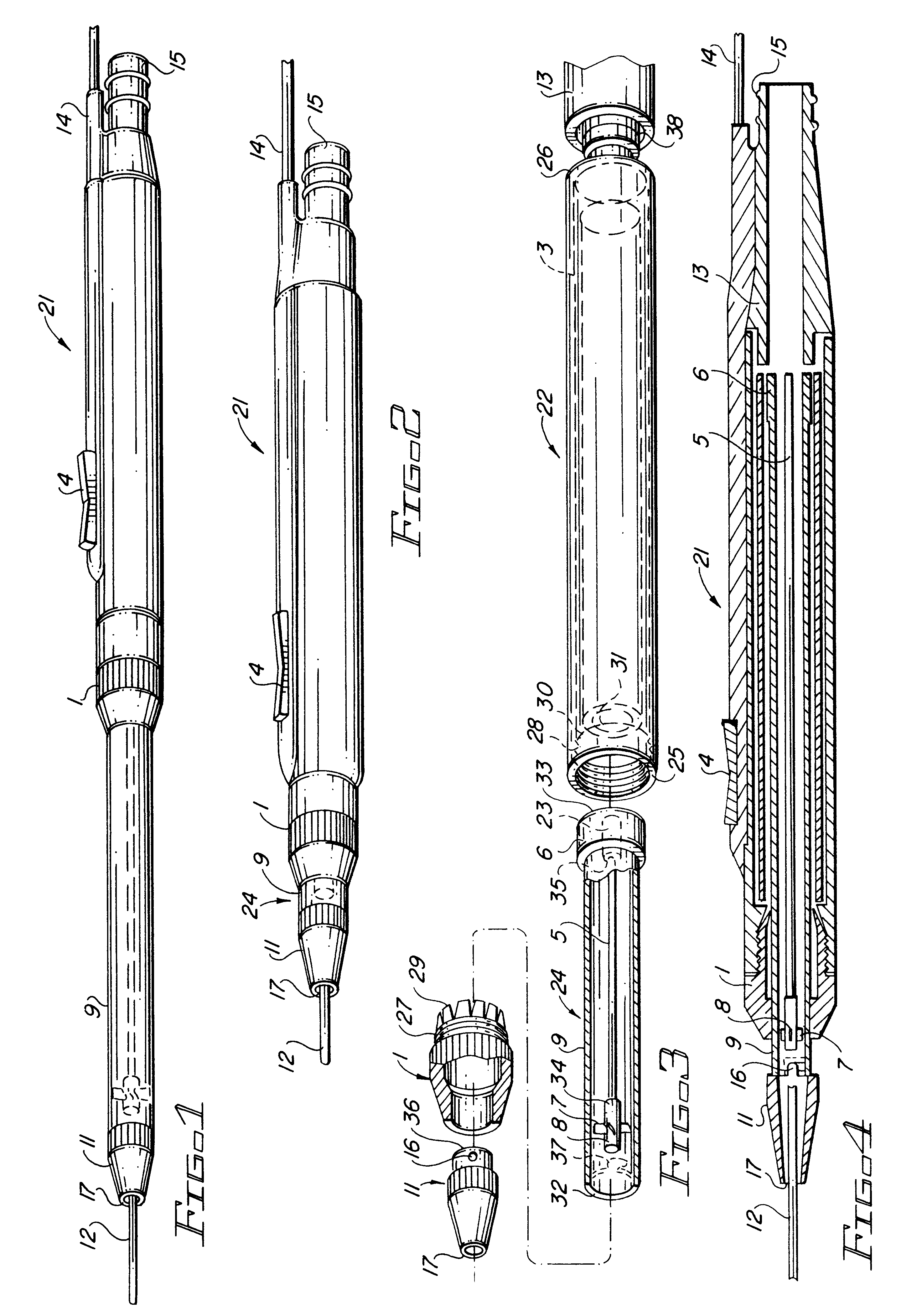
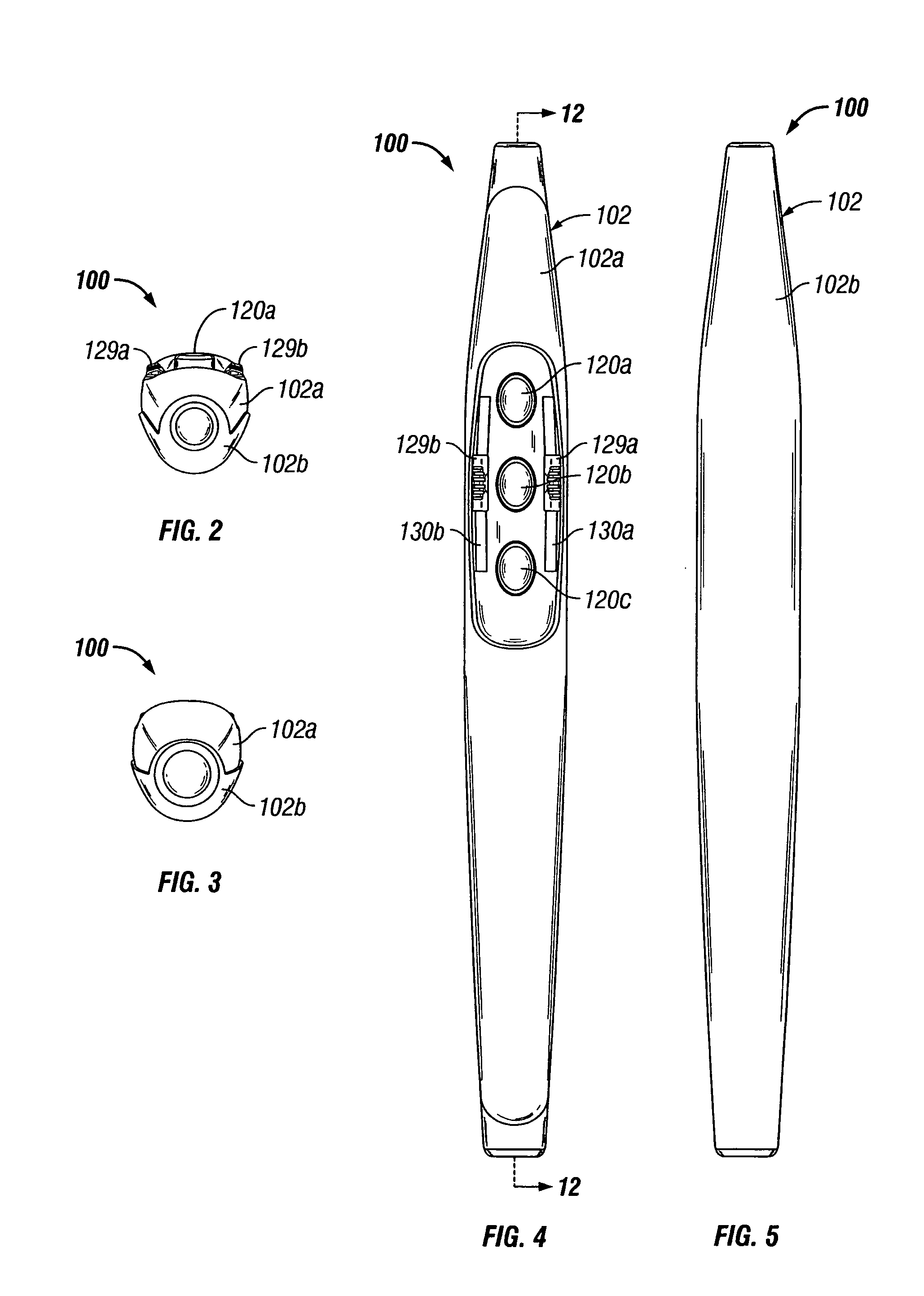
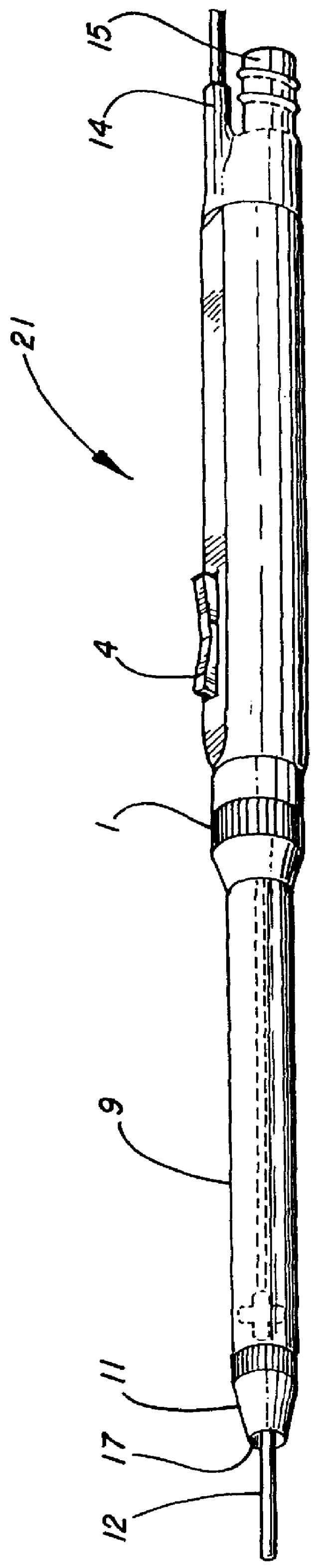
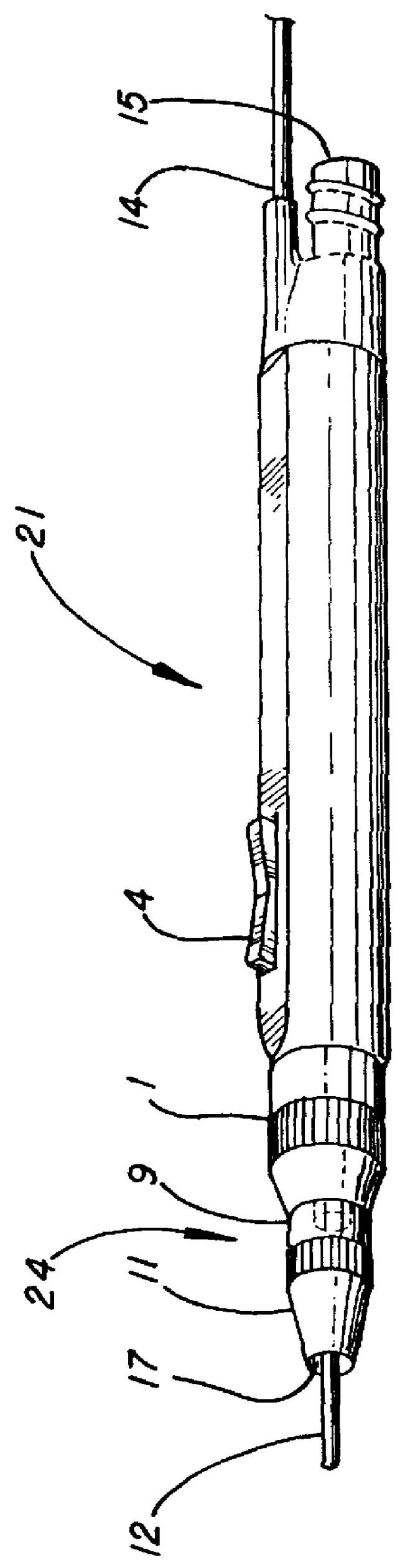
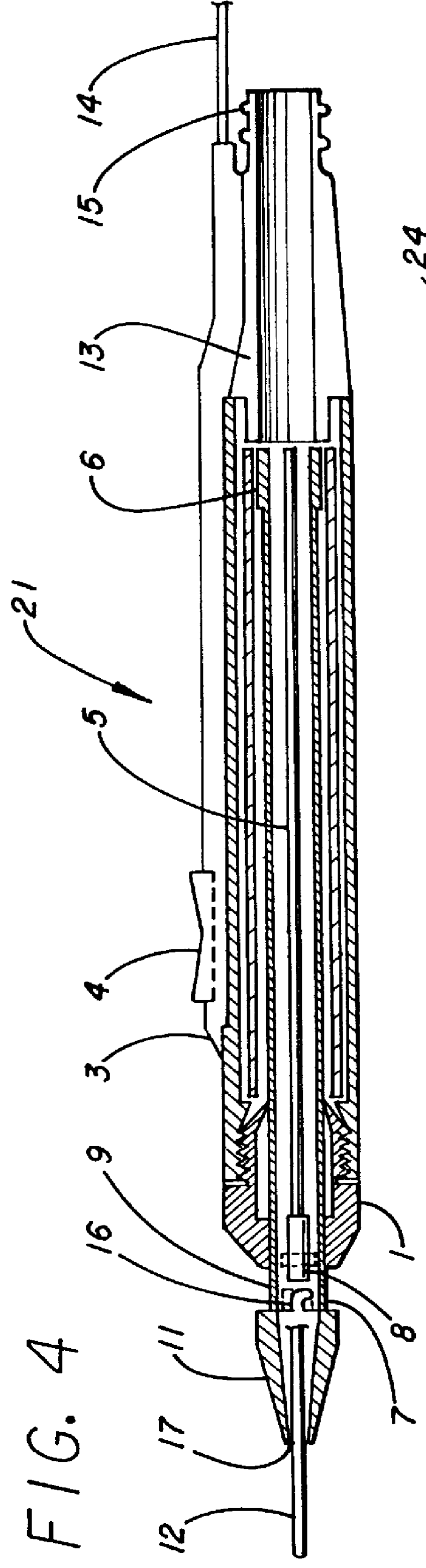
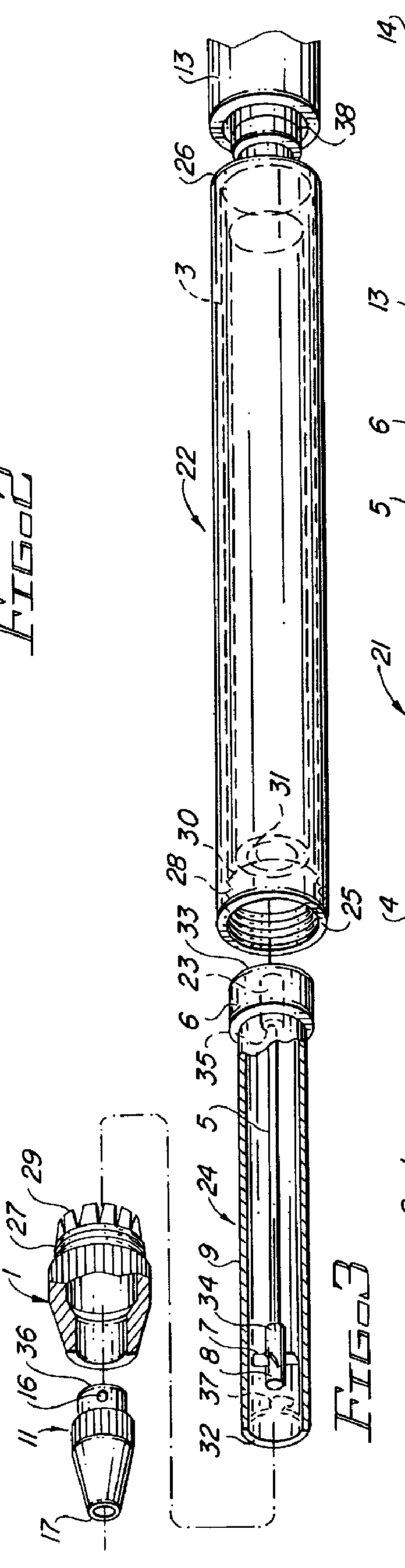
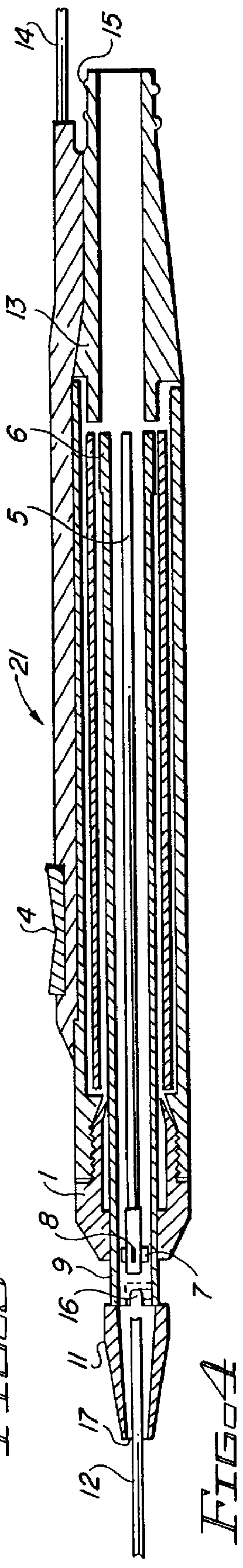
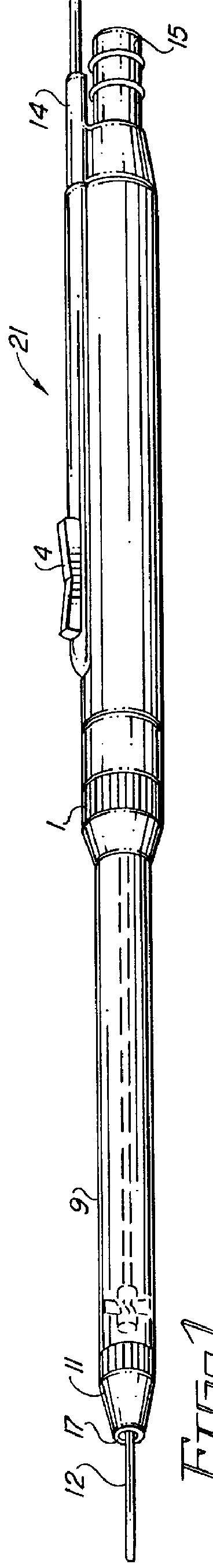
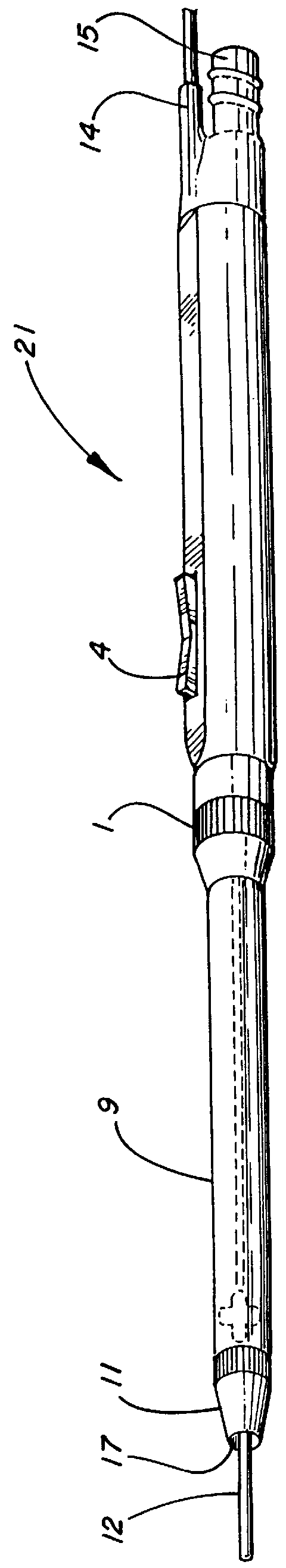
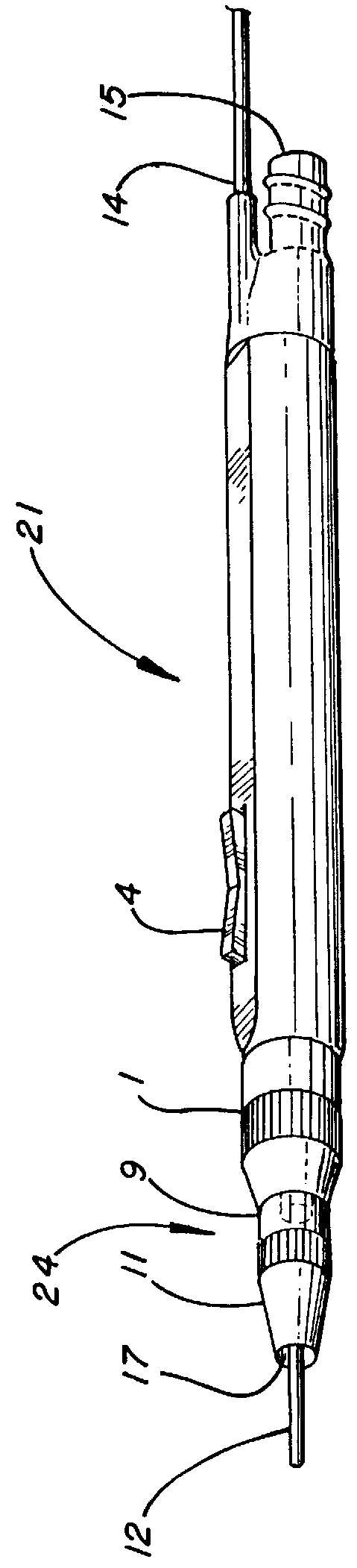
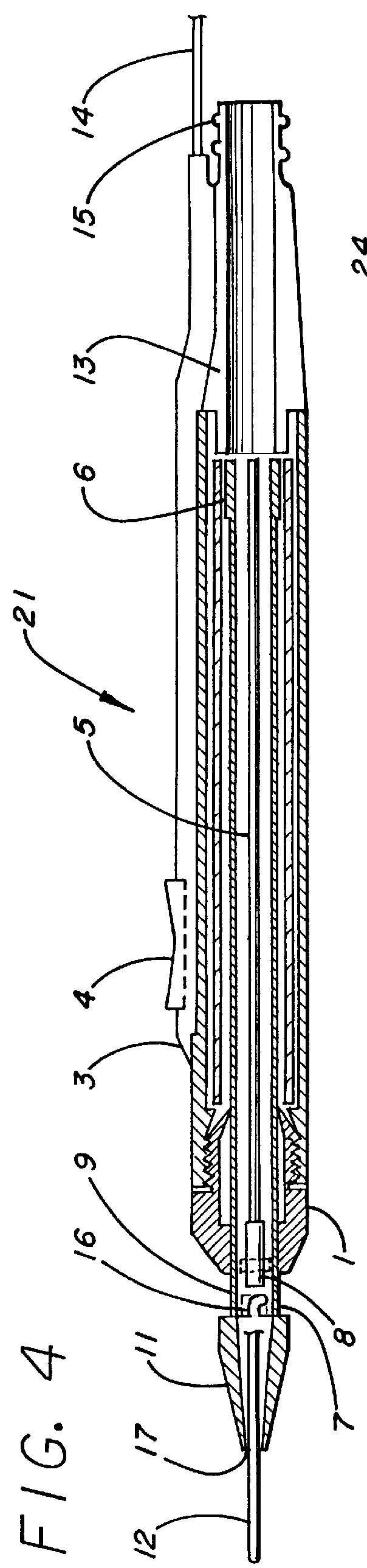
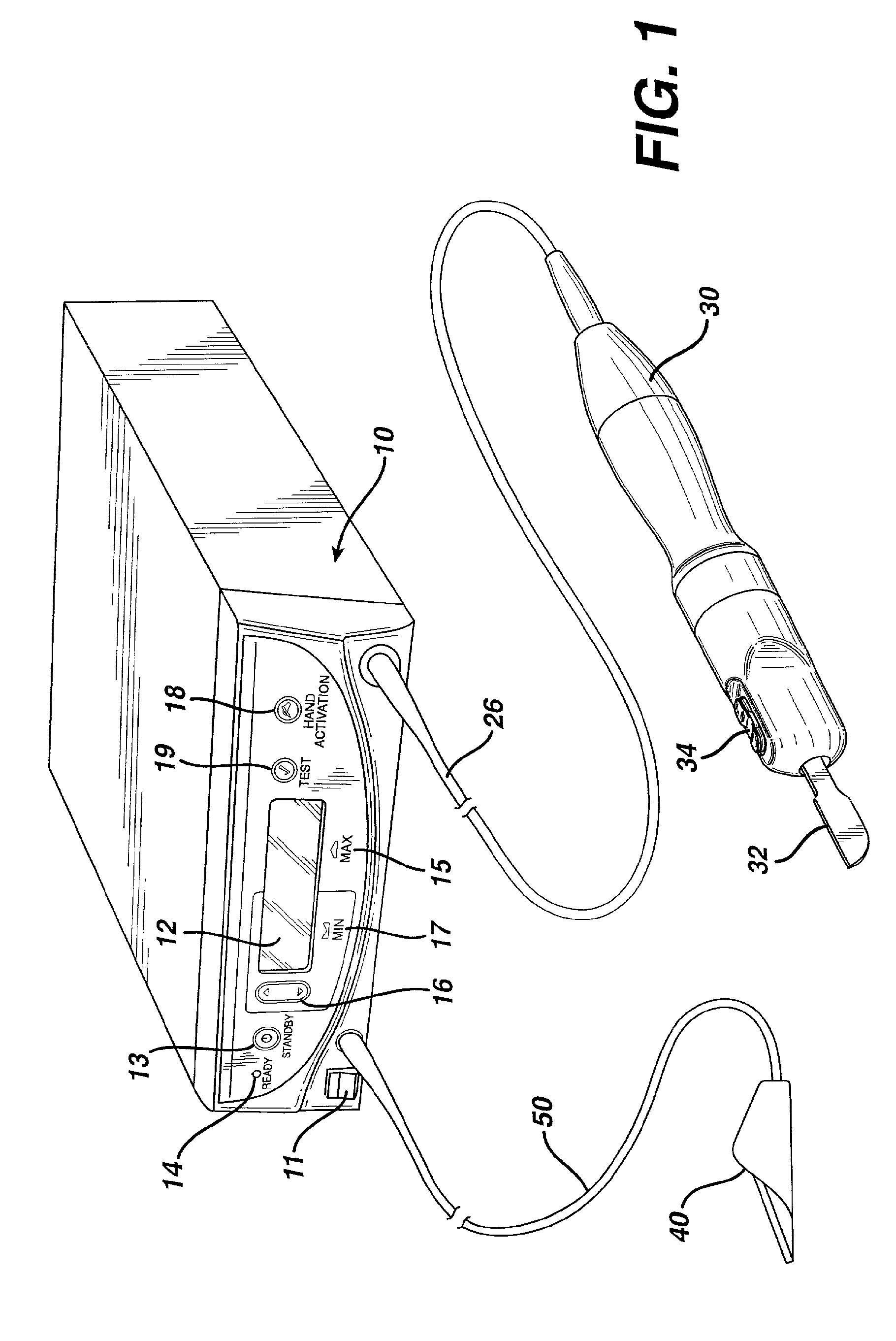
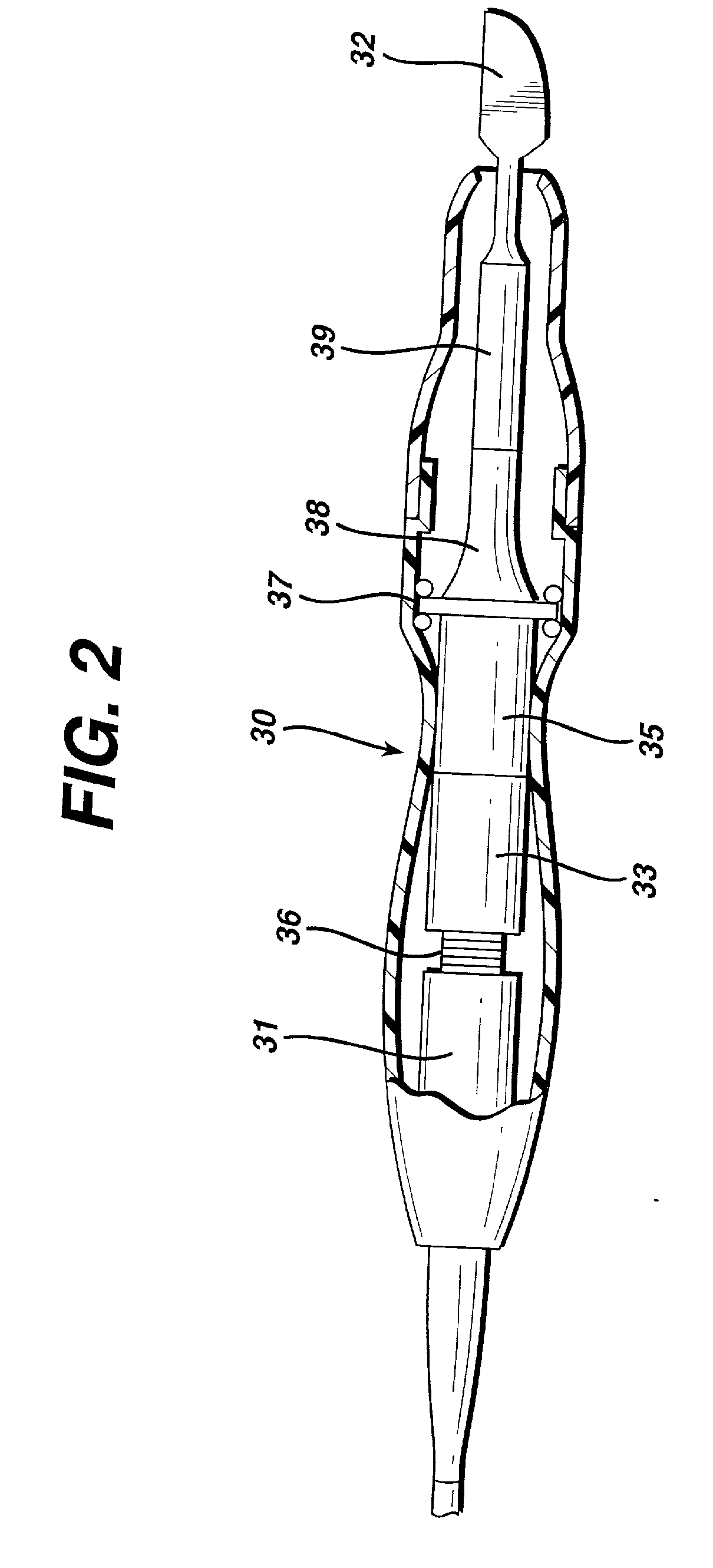
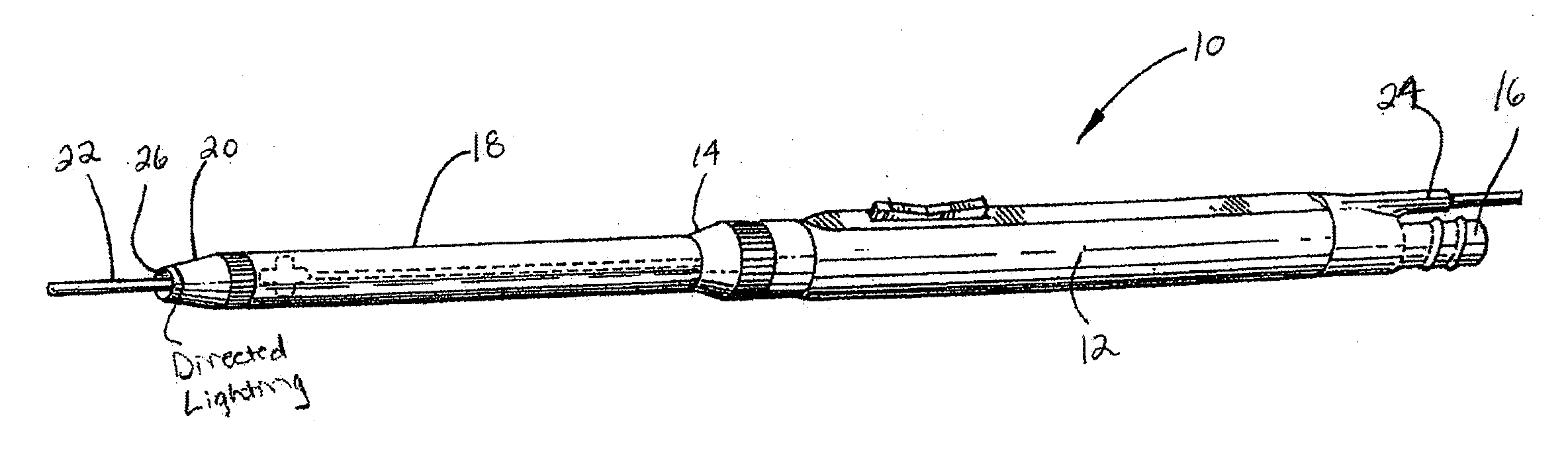
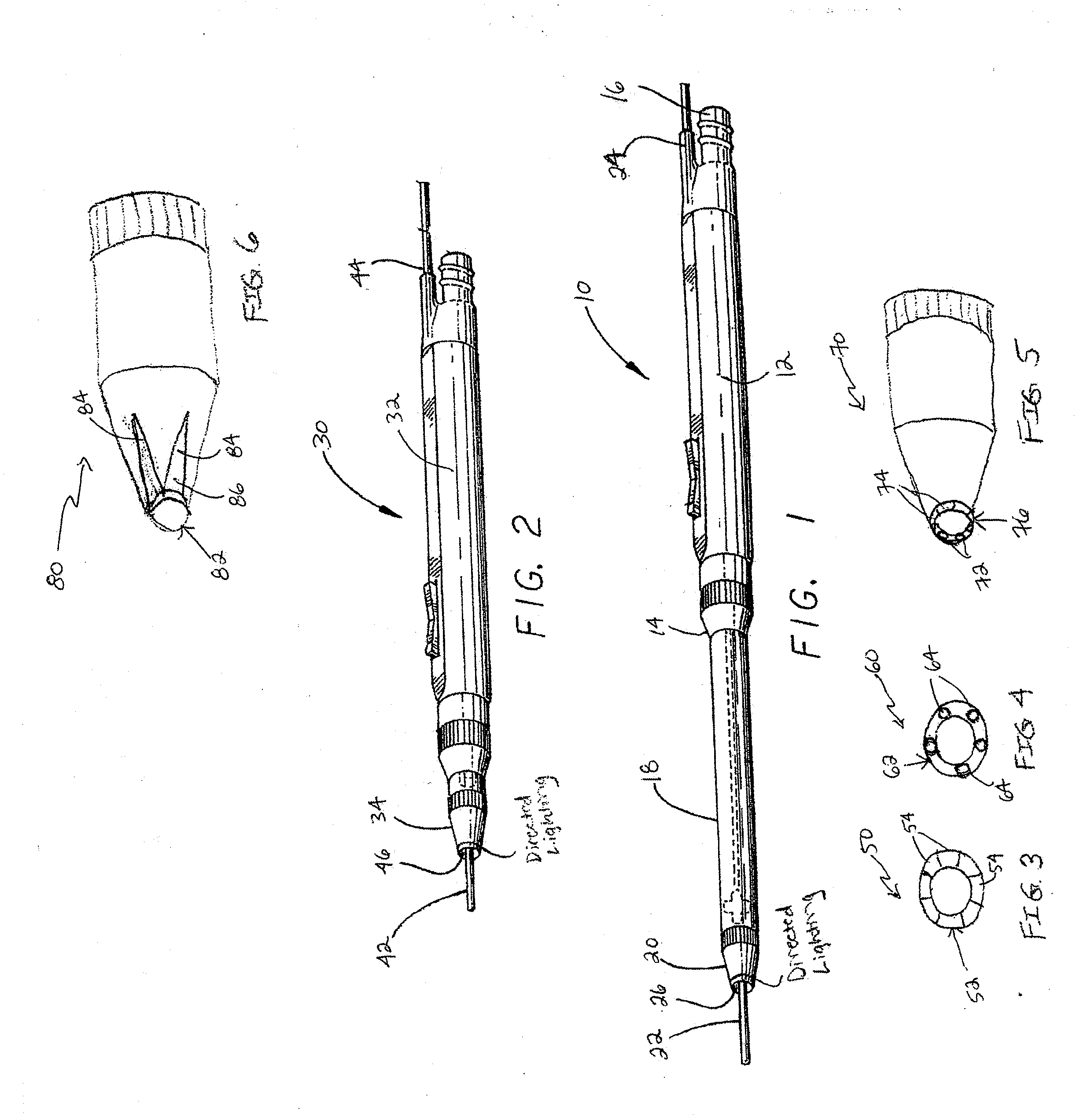
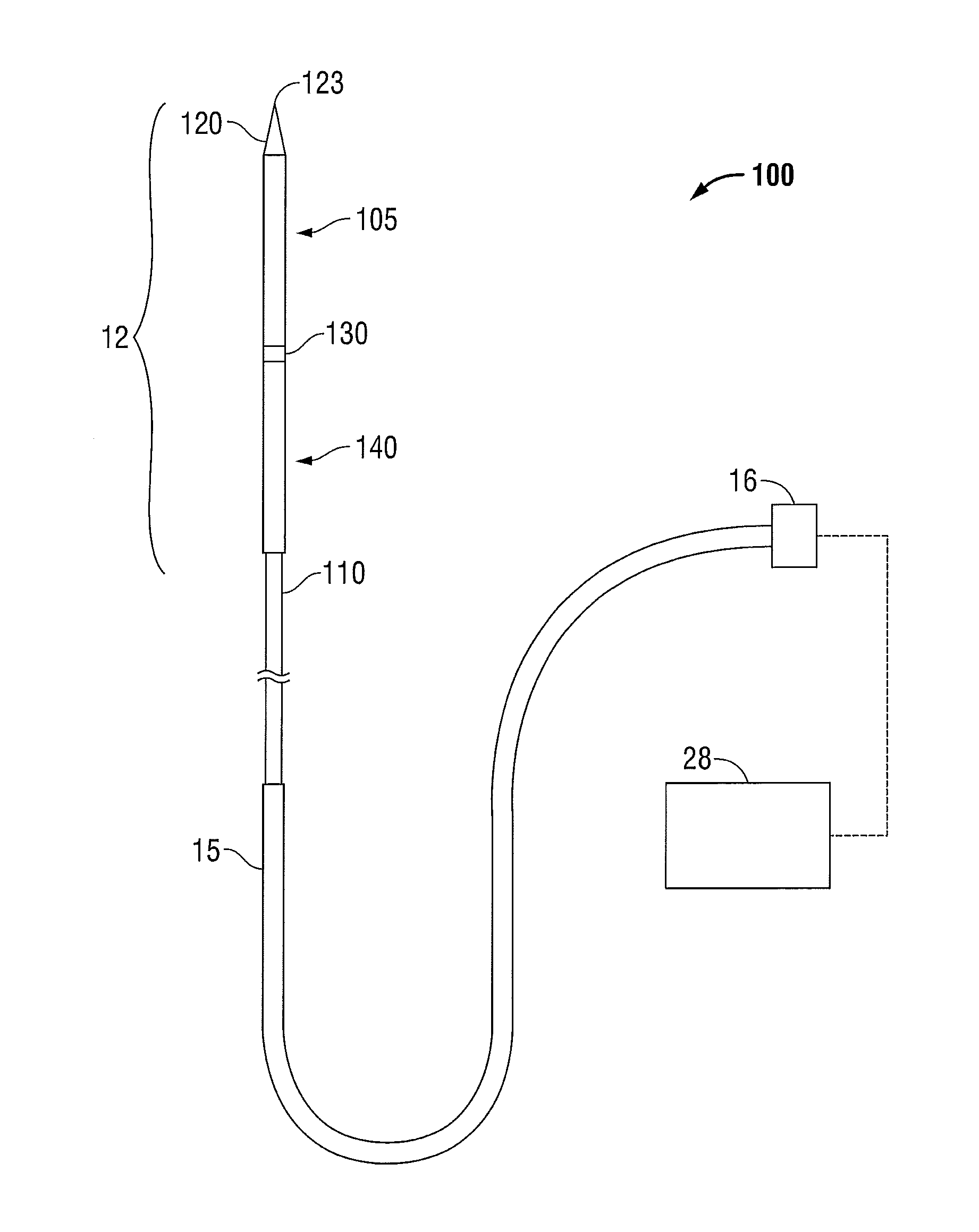
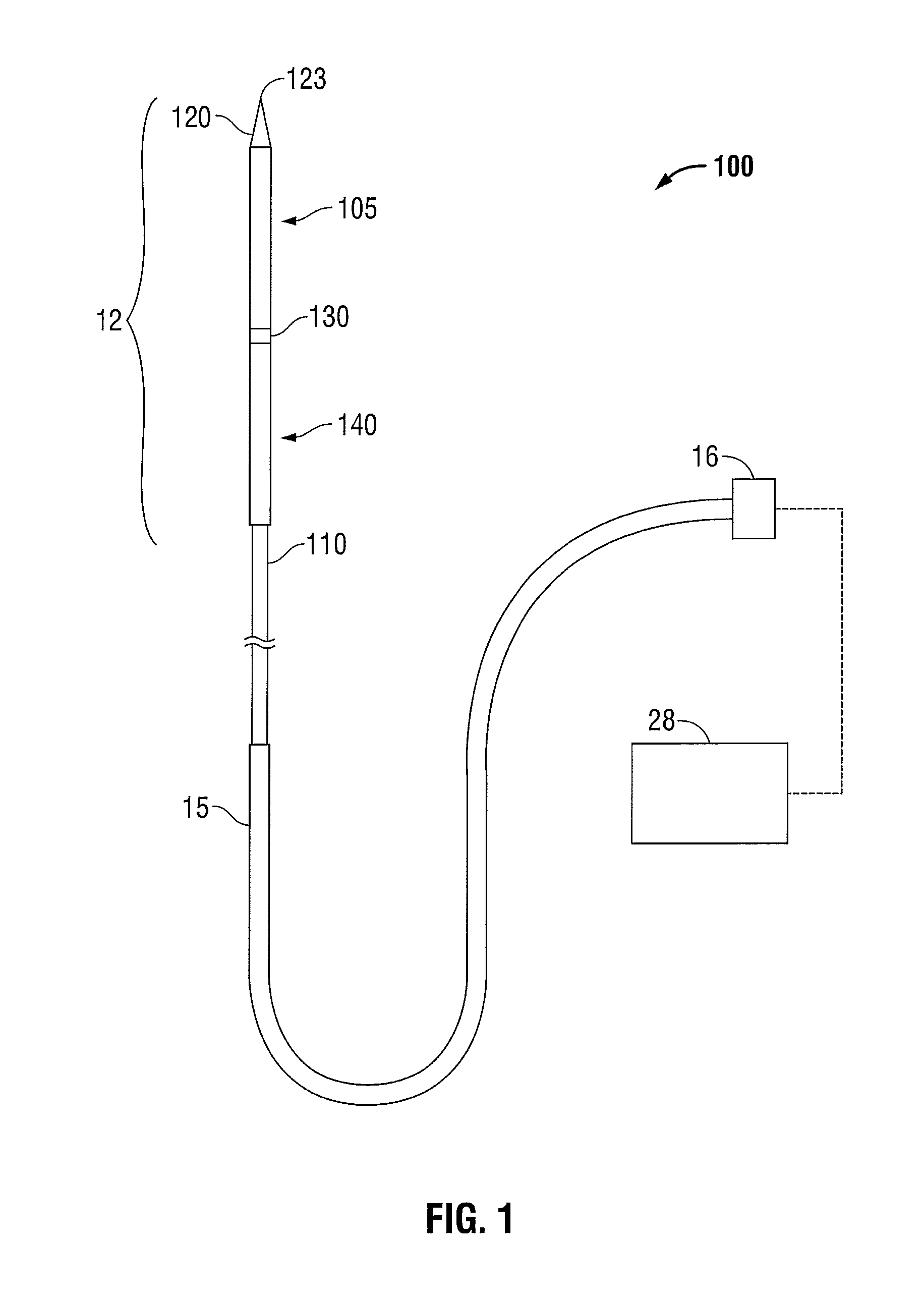
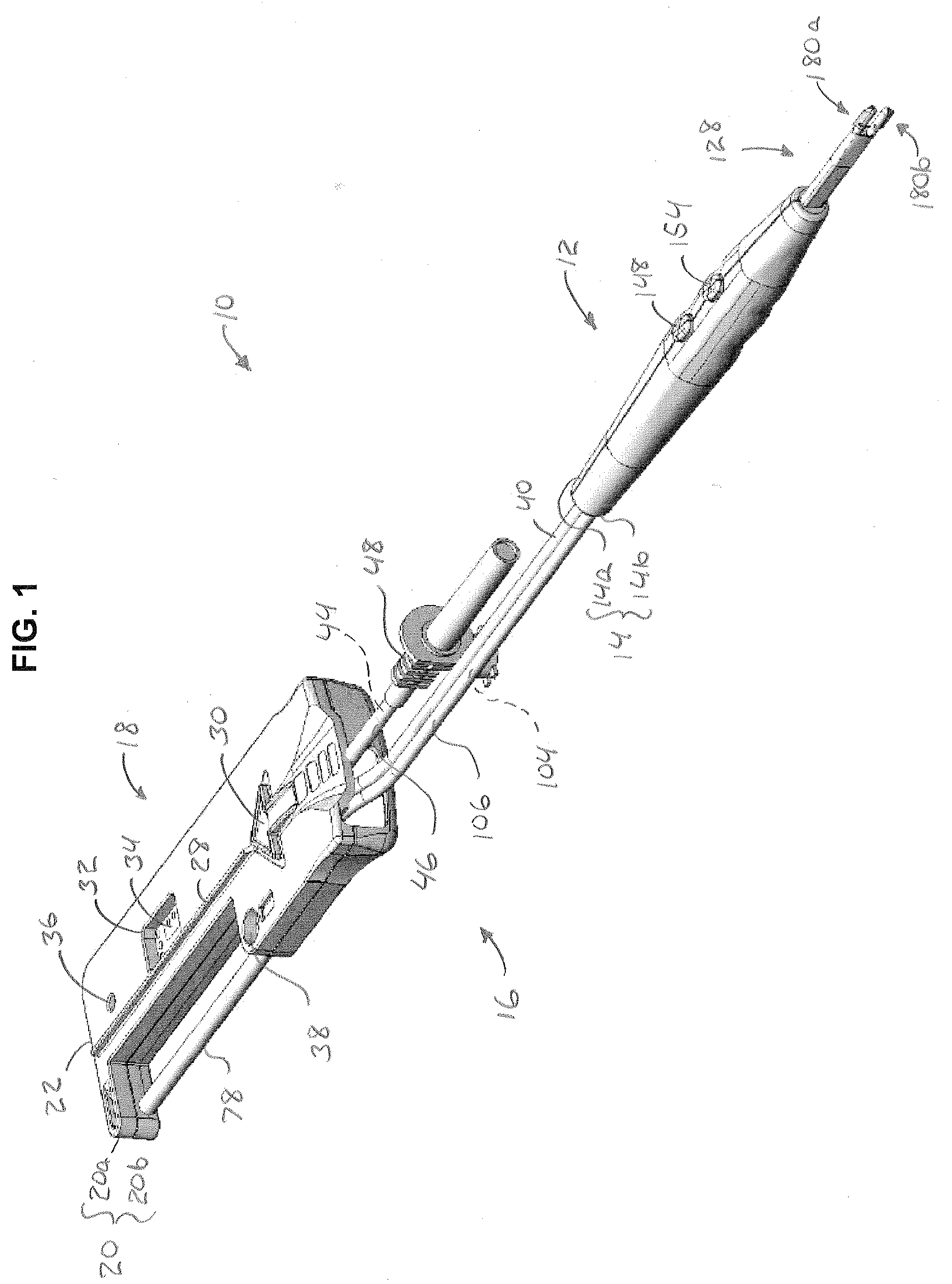
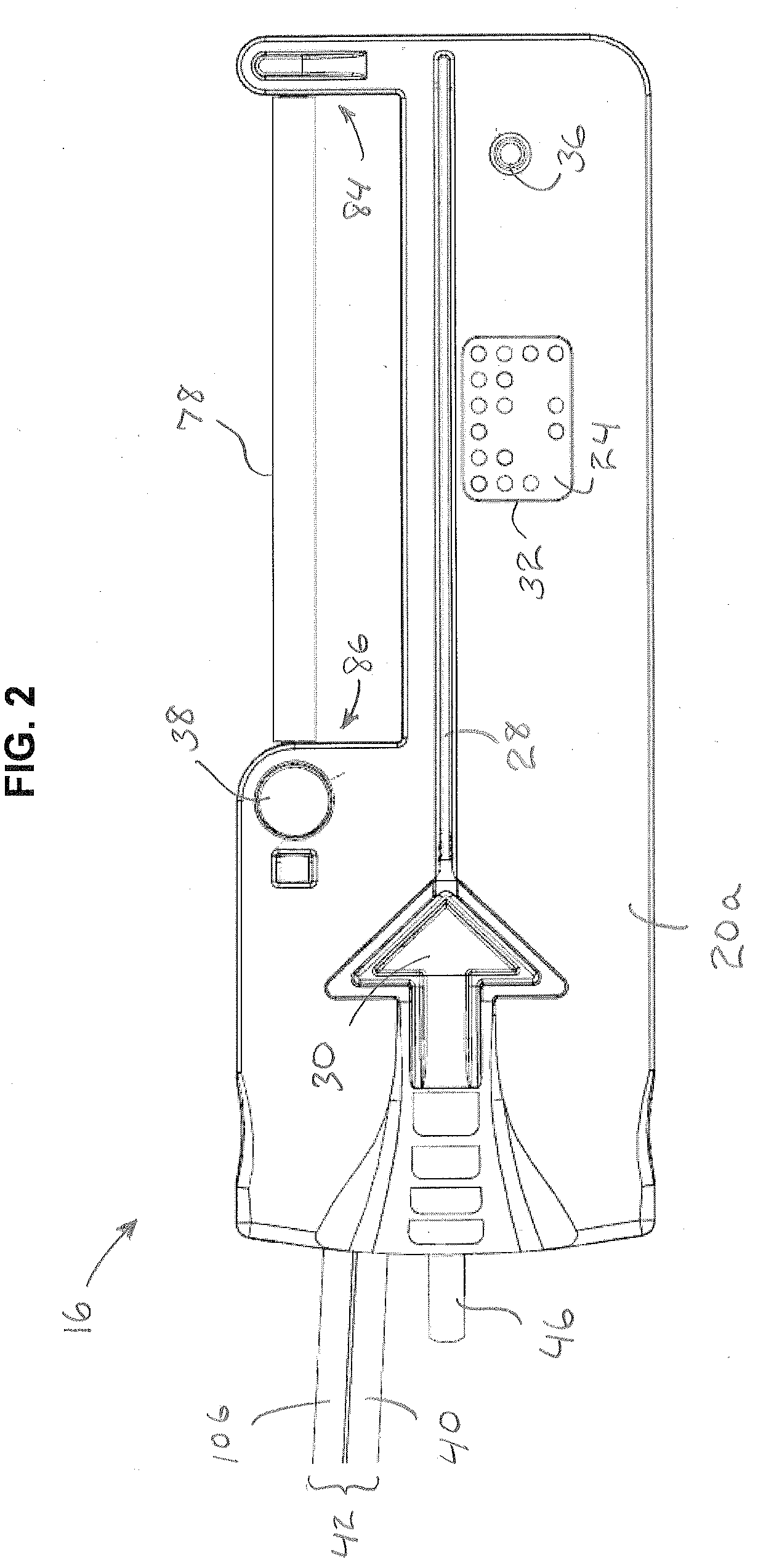
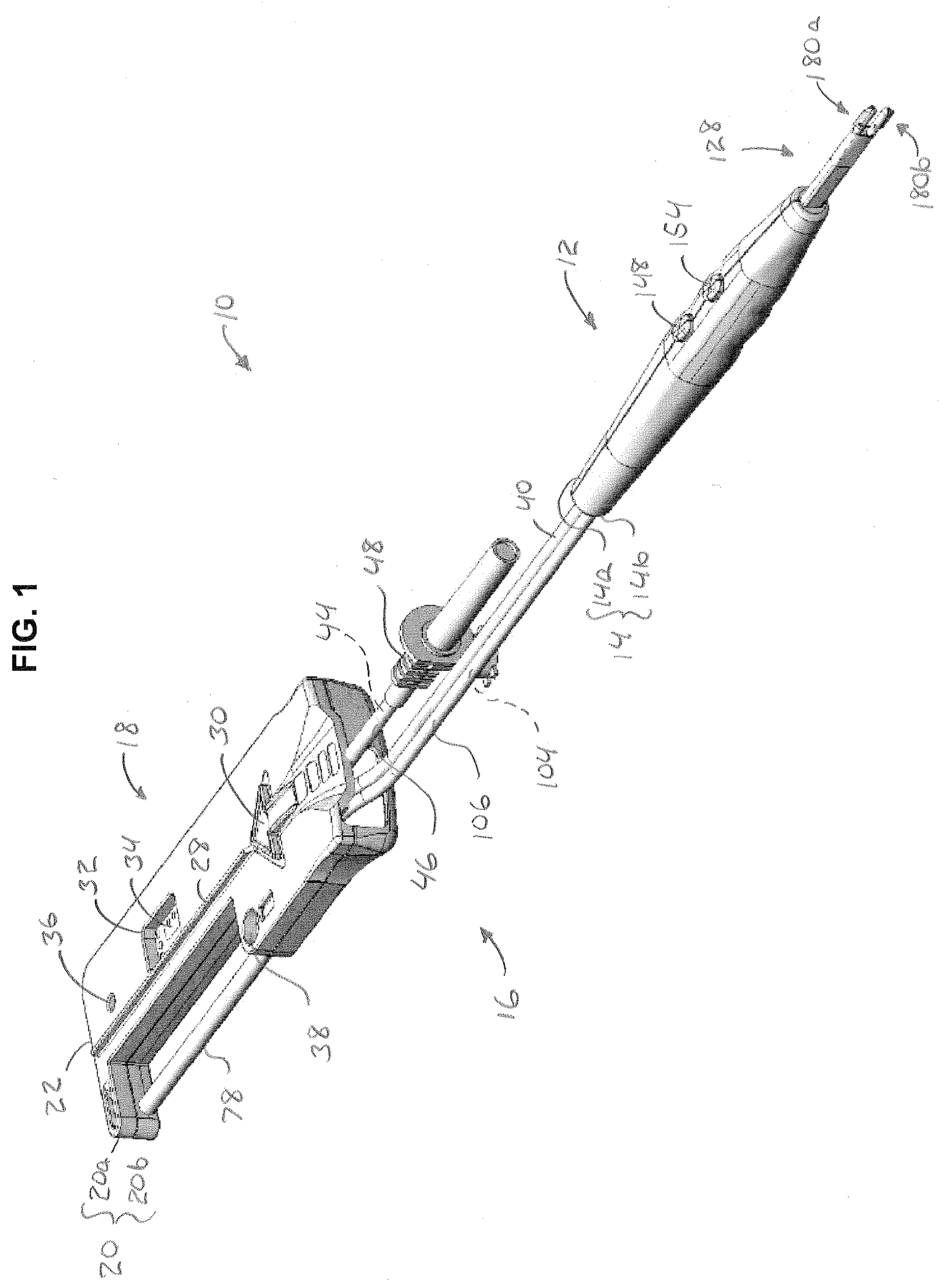
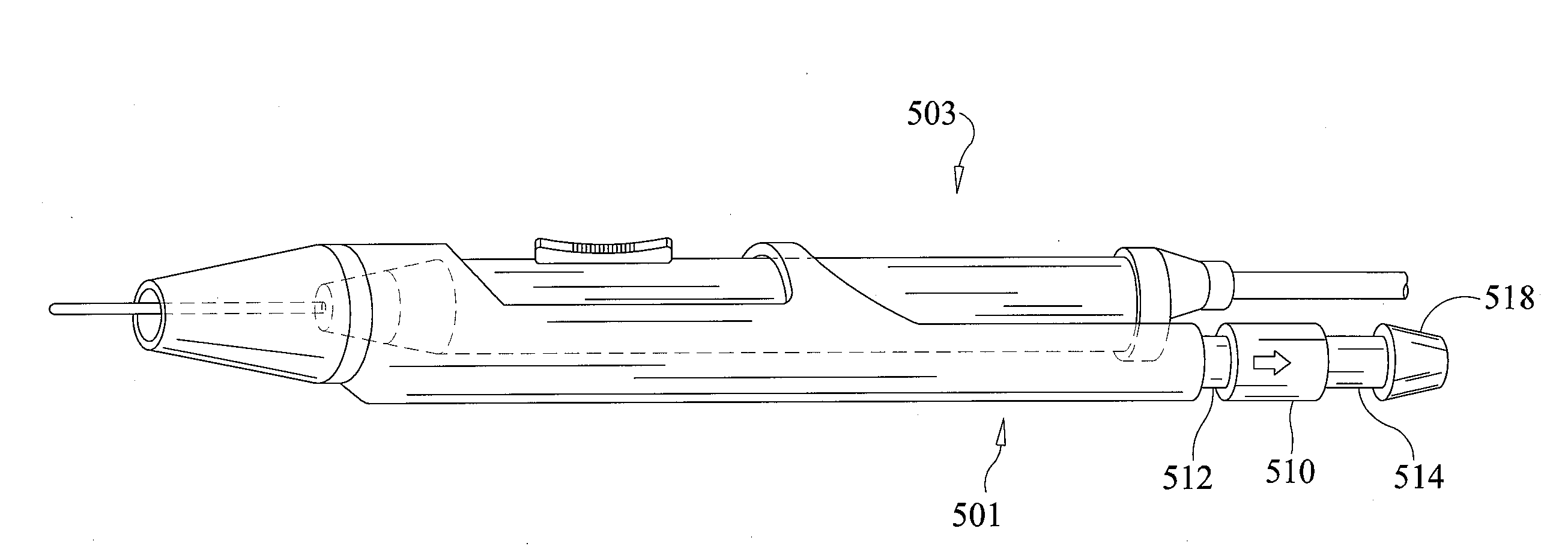
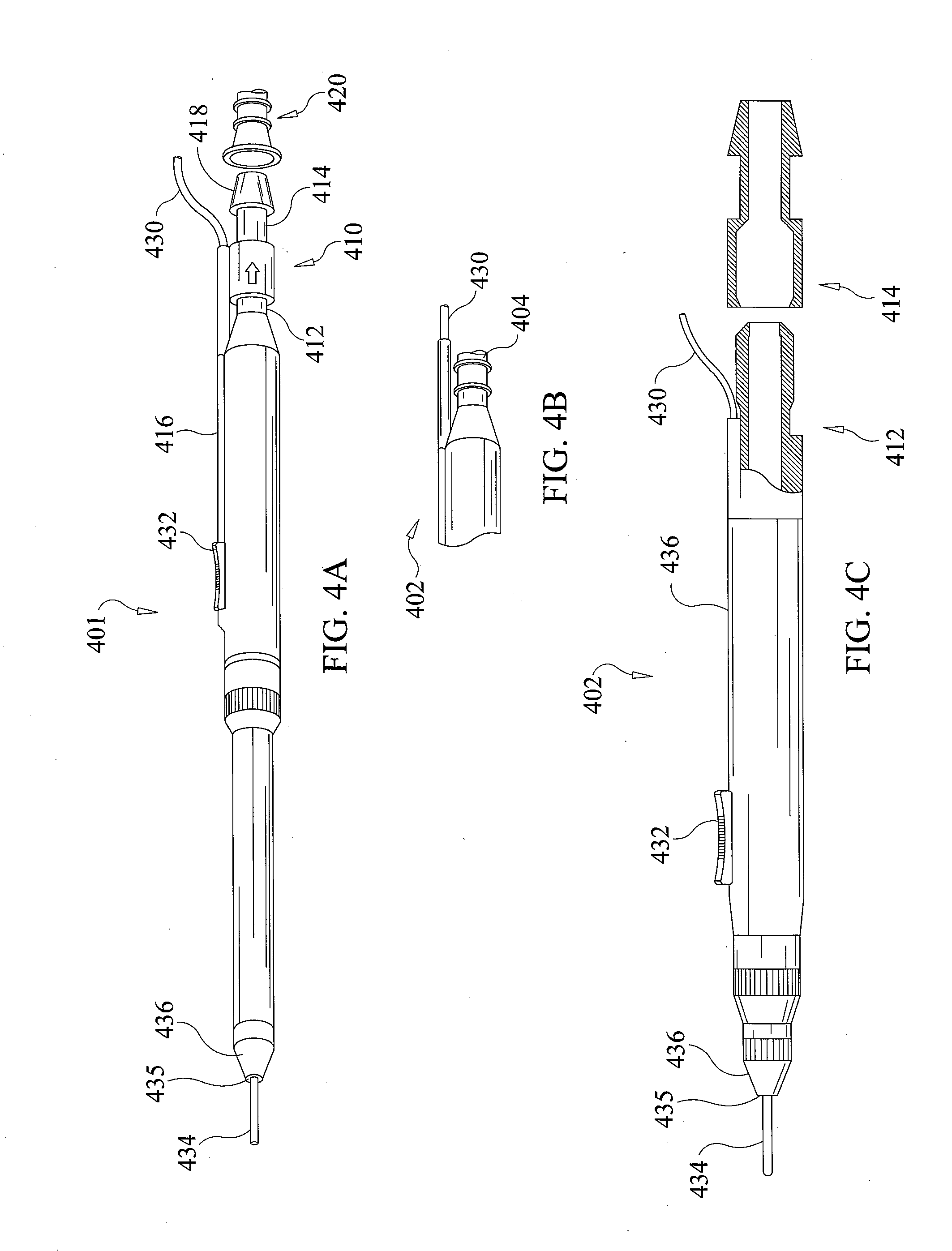
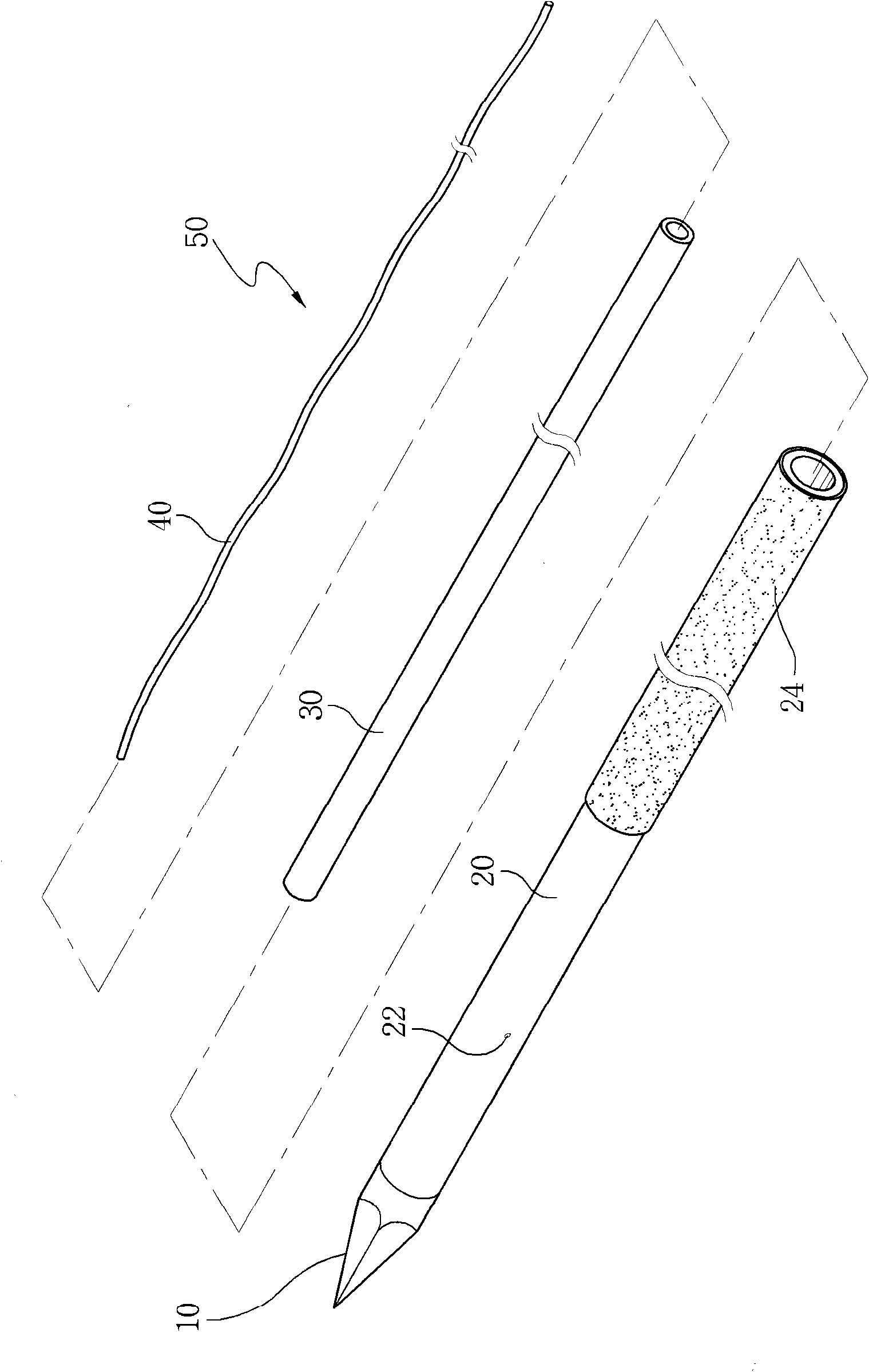
Electro-surgical unit pencil apparatus and method therefor
InactiveUS6458125B1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesArgon beamElectrosurgical unit
An electro-surgical unit (ESU) pencil apparatus is disclosed in which an improved handpiece enables the surgeon to vary the length of working electrode without having to use cutting electrodes of varying lengths. This is achieved by installing the electrode in an assembly that may, as desired by the surgeon, be extended from, or retracted into, the body of the ESU pencil apparatus. Means are provided for supplying uninterrupted RF supply to the electrode tip and uninterrupted smoke evacuation for the ESU pencil apparatus as the electrode assembly is expanded or retracted. Additionally, means are provided for locking the electrode assembly at the desired length, so that it does not move during the operation. The ESU pencil apparatus is also adapted for use with an ESU-argon beam coagulator pencil.
Owner:IC MEDICAL INC
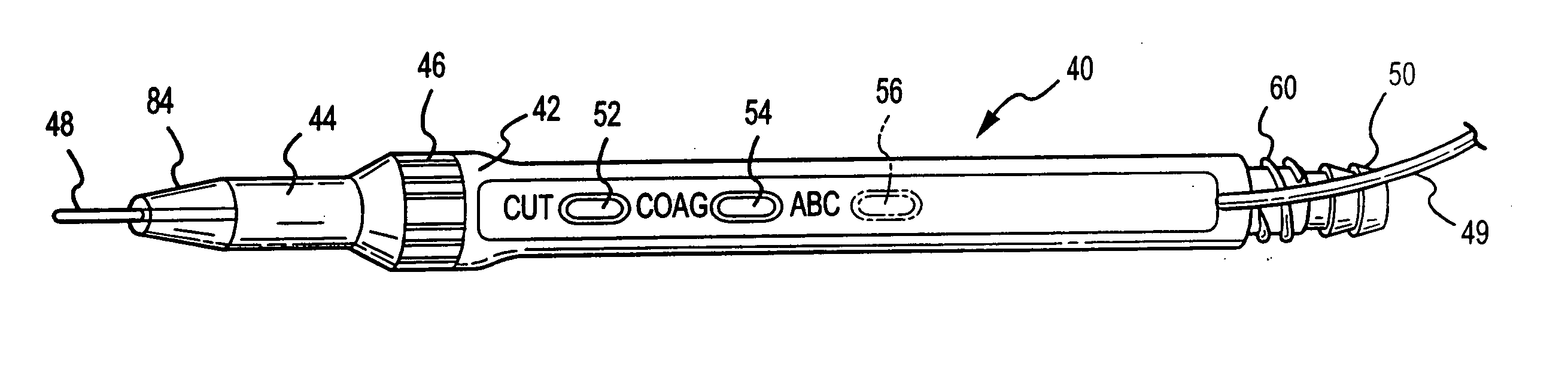
Electrosurgical pencil with advanced es controls
An electrosurgical system is provided that includes an electrosurgical generator; and an electrosurgical pencil selectively connectable to the electrosurgical generator. The electrosurgical pencil includes an elongated housing; at least one electrocautery end effector removably supportable within the housing and extending distally from the housing, the electrocautery end effector being connected to the electrosurgical generator; and at least one voltage divider network supported on the housing. The at least one voltage divider network is electrically connected to the electrosurgical generator and controls at least one of the intensity of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil and the mode of electrosurgical energy being delivered to the electrosurgical pencil. The voltage divider network generates a plurality of characteristic voltages which are measurable by the electrosurgical generator and which electrosurgical generator in turn transmits a corresponding waveform duty cycle at a particular intensity to the electrocautery end effector of the electrosurgical pencil.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Multifunctional telescopic monopolar/bipolar surgical device and method therefore
InactiveUS20050113825A1Eliminate needSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesBipolar electrosurgeryEndoscopic surgery
A multifunctional telescopic monopolar / bipolar electrosurgery pencil is disclosed for use with an electrosurgery unit (ESU). The monopolar / bipolar electrosurgery pencil includes a bipolar electrode having an insulator sandwiched between an active electrode and a return electrode wherein the bipolar electrode is connected to a handpiece capable of alternately effectuating cutting and coagulation with the bipolar electrode. The monopolar / bipolar electrosurgery pencil is capable of functioning as both a monopolar and bipolar device and can be used for open and closed laparoscopic and endoscopic procedures. Telescopic means for adjusting the length of the bipolar electrode is also provided as are means for smoke evacuation and suction / irrigation. The multifunctional telescopic monopolar / bipolar device can also be adapted for use with an ESU argon beam coagulator.
Owner:IC MEDICAL
Connection of a bipolar electrosurgical hand piece to a monopolar output of an electrosurgical generator
InactiveUS9532827B2Instrument handpiecesSurgical instruments for heatingActive componentBipolar electrosurgery
A method and apparatus for operatively connecting a bipolar electrosurgical hand piece to a monopolar output of an electrosurgical unit wherein active components simulate expected impedance characteristics of monopolar return electrodes connected to a patient.
Owner:NUORTHO SURGICAL
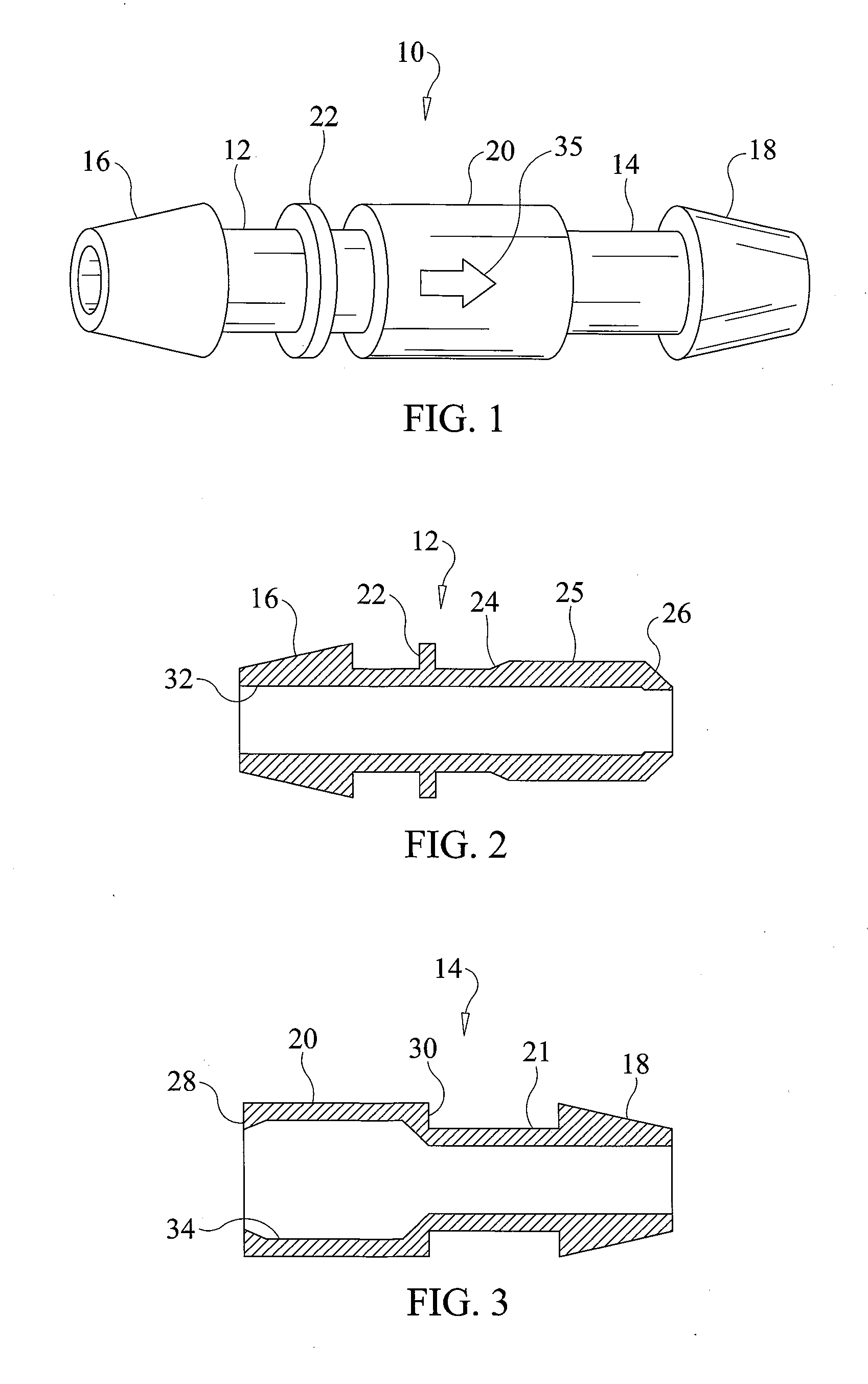
Removable shroud for receiving a pencil used in electro-surgery
InactiveUS6099525ASurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesElectrosurgical unitBiomedical engineering
A removable shroud for use with an electro-surgical unit pencil. The removable shroud includes a handpiece with a lumen therein; an elongated load-bearing support bearing a receiving surface on a top of the handpiece for cradling the electro-surgical unit pencil thereon; and a tapered nozzle, adapted to hold a distal end of the electro-surgical unit pencil therein when the pencil rests on the receiving surface, located at a distal end of the handpiece and having the lumen open into an interior of the tapered nozzle.
Owner:IC MEDICAL
Electro-surgical unit-argon beam coagulator pencil apparatus and method for operating same
InactiveUS6149648ASurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesElectrosurgeryArgon beam
An electro-surgical unit (ESU)-Argon beam coagulator pencil apparatus and method for operating the same is disclosed where the ESU-Argon beam coagulator pencil apparatus includes a telescoping device which is coupled to a cutting means, a coagulation means, and a smoke evacuation means. This apparatus enables a surgeon to vary the length of the cutting or coagulation means without interrupting the smoke evacuation means of the device. A locking means may also be included to lock the cutting and / or coagulation means at a desired length.
Owner:IC MEDICAL INC
Electro-surgical unit pencil apparatus having a removable shroud
InactiveUS6142995ASurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesCatheterEngineering
An electro-surgical unit pencil apparatus having a removable shroud adaptably fitted over an external surface of a surgical pencil is presented where the pencil apparatus includes a conduit located within the shroud having a tapered portion surrounding the surgical pencil and in communication with the distal end of the shroud. An external conduit may be coupled to the proximal opening of the shroud and smoke evacuation means may be coupled to the external conduit for exhausting smoke from the shroud. The conduit includes an open proximal end, an open distal end, and a generally semi-circular shaped hollow interior, a handpiece holder located near a top outer surface of the conduit, and a nozzle member attached near the distal end of the conduit.
Owner:IC MEDICAL
Ultrasonic surgical system
InactiveUS20100125292A1Inconsistent performanceLower capability requirementsSurgerySurgical operationDigital signal processing
An ultrasonic surgical system utilizes a digital control system to generate ultrasonic drive current for transducers that are located in a hand piece and are attached to a surgical scalpel or blade in the hand piece so as to vibrate the blade in response to the current. The digital control includes a digital signal processor (DSP) or microprocessor; a direct digital synthesis (DDS) device; a phase detection logic scheme, a control algorithm for seeking and maintaining resonance frequency; and design scheme that allows to regulate current, voltage, and power delivered to an ultrasonic thereby a device. Such system allows the power versus load output curve to be tailored to a specific hand piece, which improves efficiency and reduces heat. Further, the components of the digital system are much less sensitive to temperature variations, thereby allowing it to operate with narrow as needed frequency range around the desired resonance in order to avoid excitation of other resonances. Also, the digital system provides increased flexibility in locating the resonance frequency of the blade and running diagnostic tests. The start of a user initiated diagnostic test that requires movement of the blade is caused by operating two of the system switches, which guards against accidental operation of the blade which could be harmful if in contact with tissue and also generate false diagnostic results. In addition, the system has interlock with an Electrosurgical unit so that it is not effected by the electromagnetic interference generated by that unit.
Owner:WIENER EITAN T +1
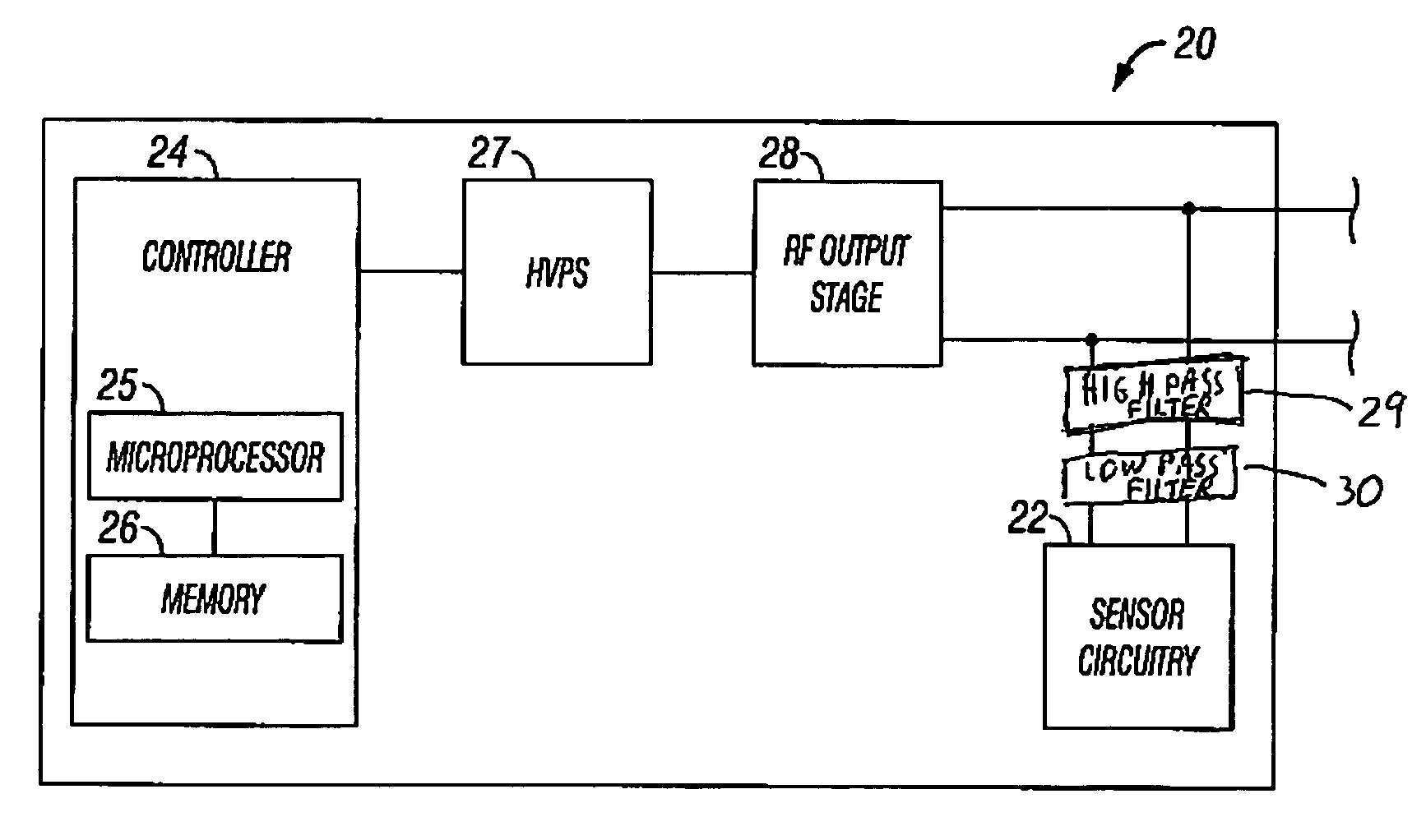
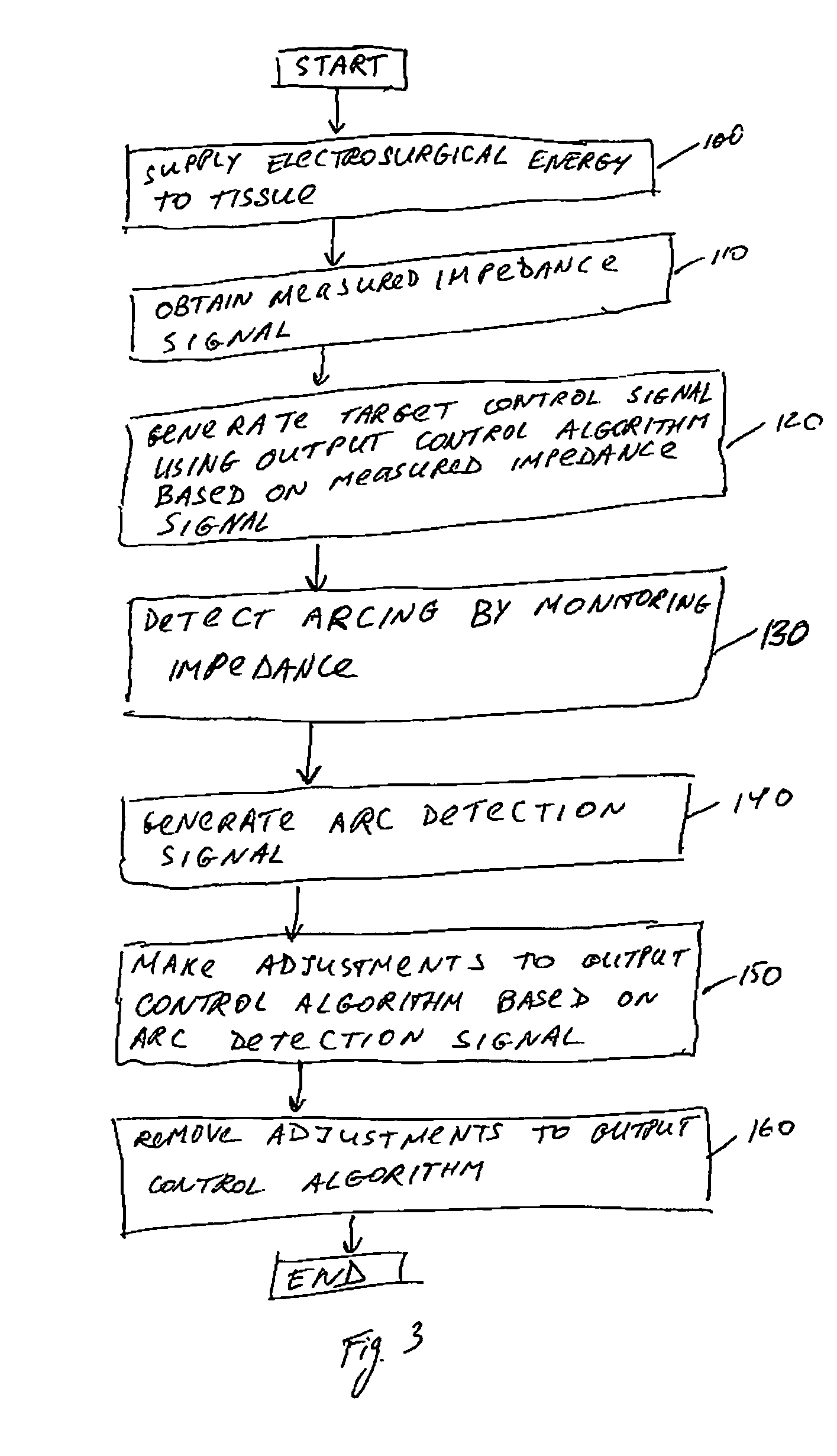
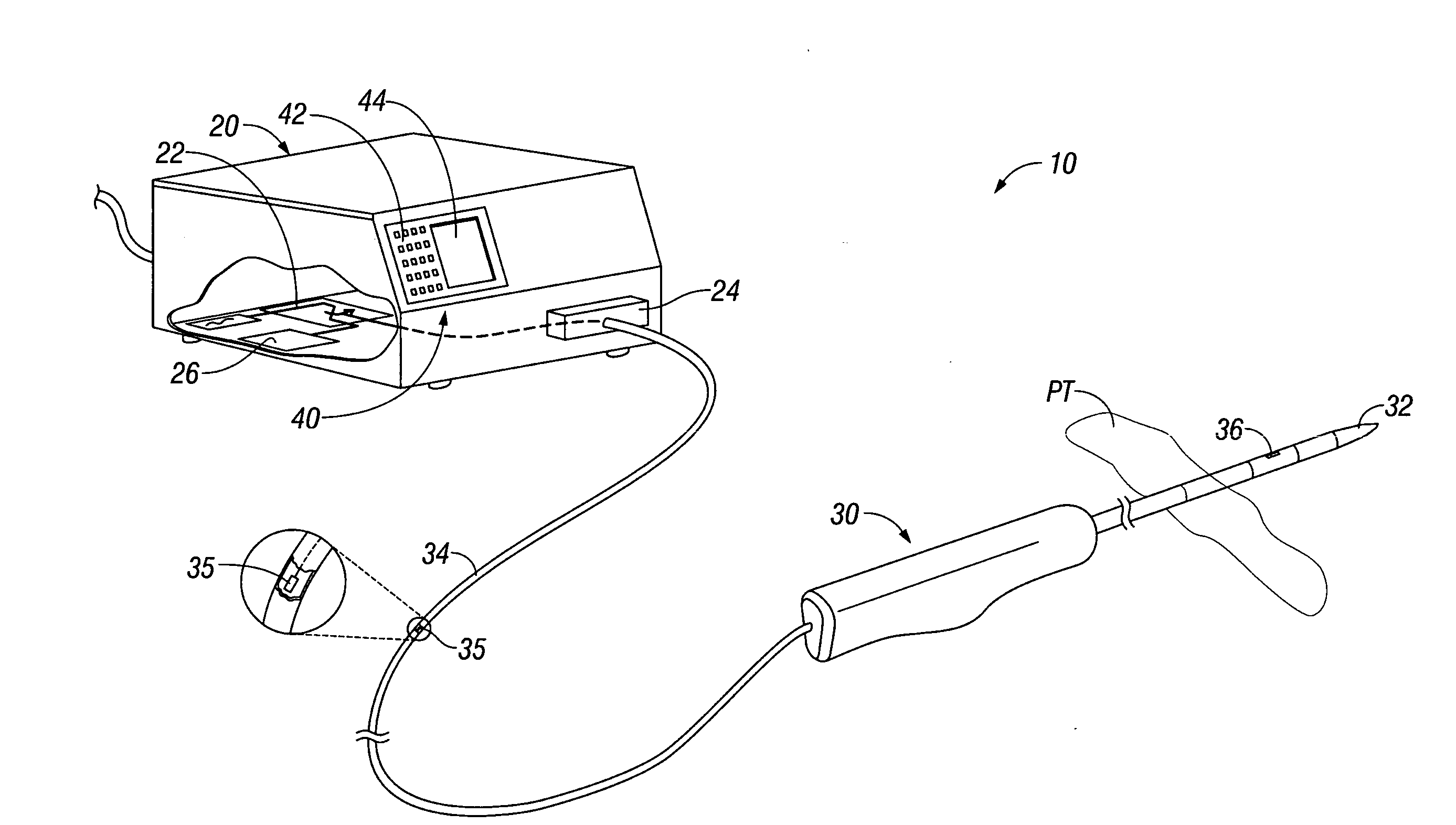
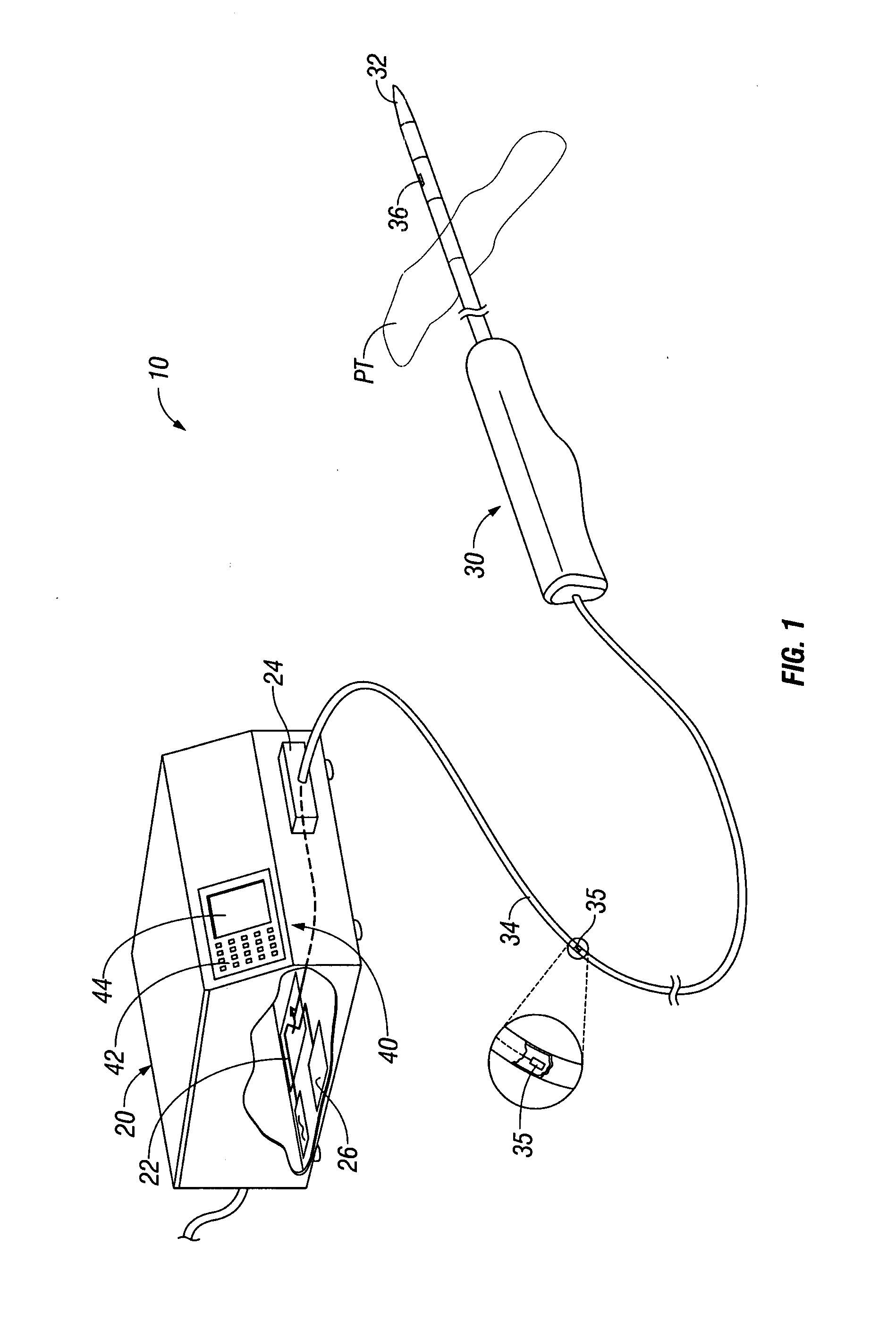
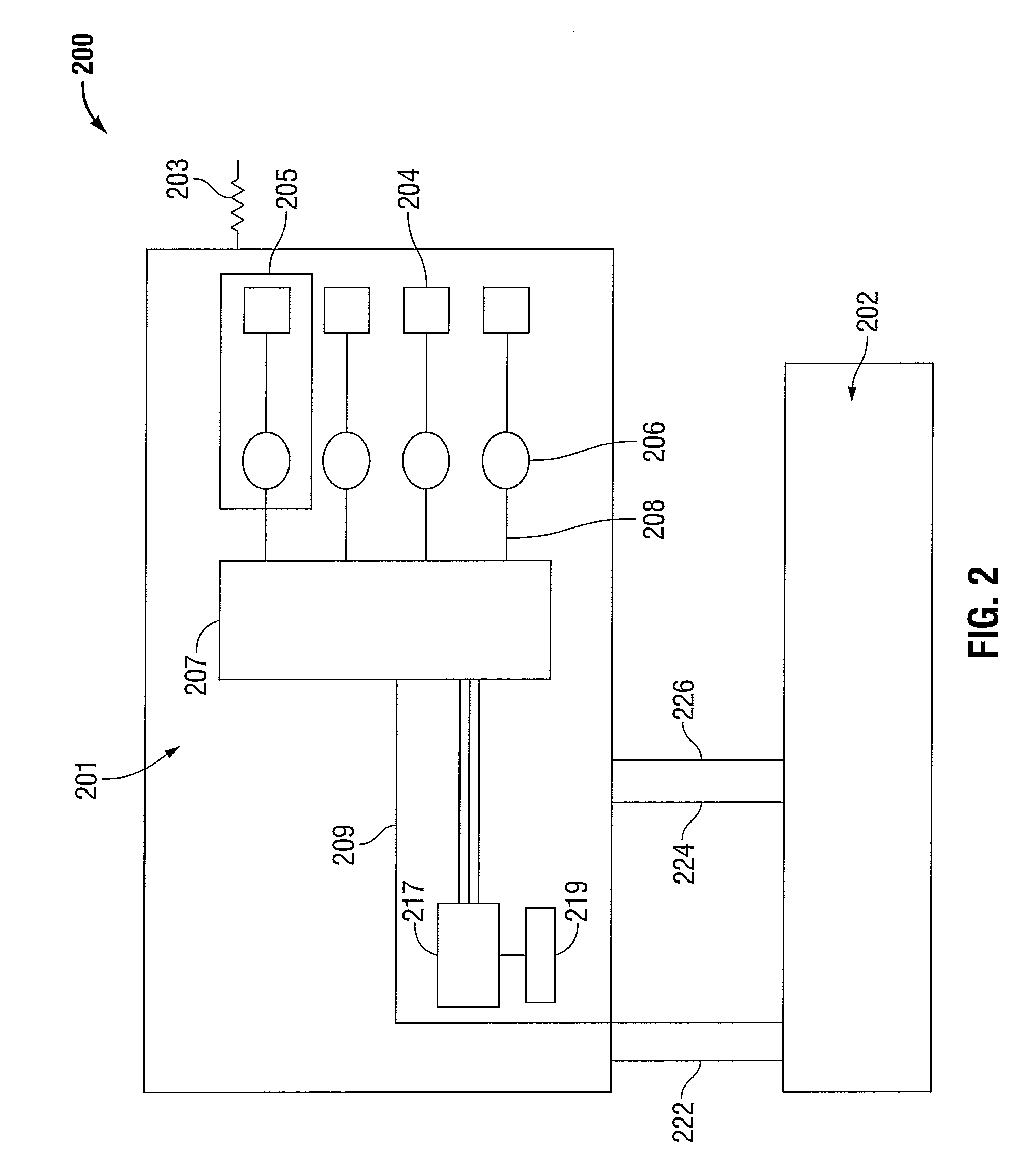
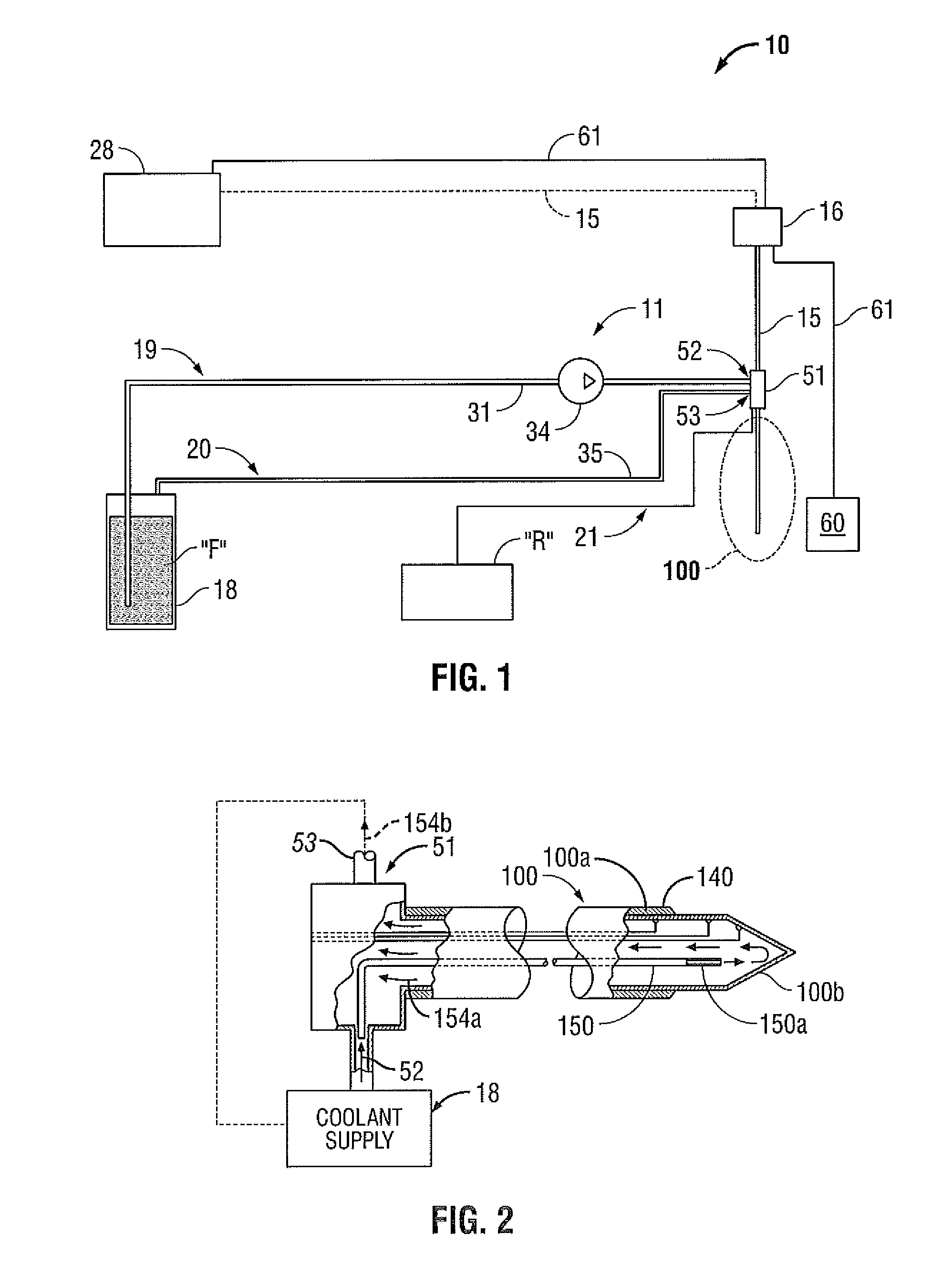
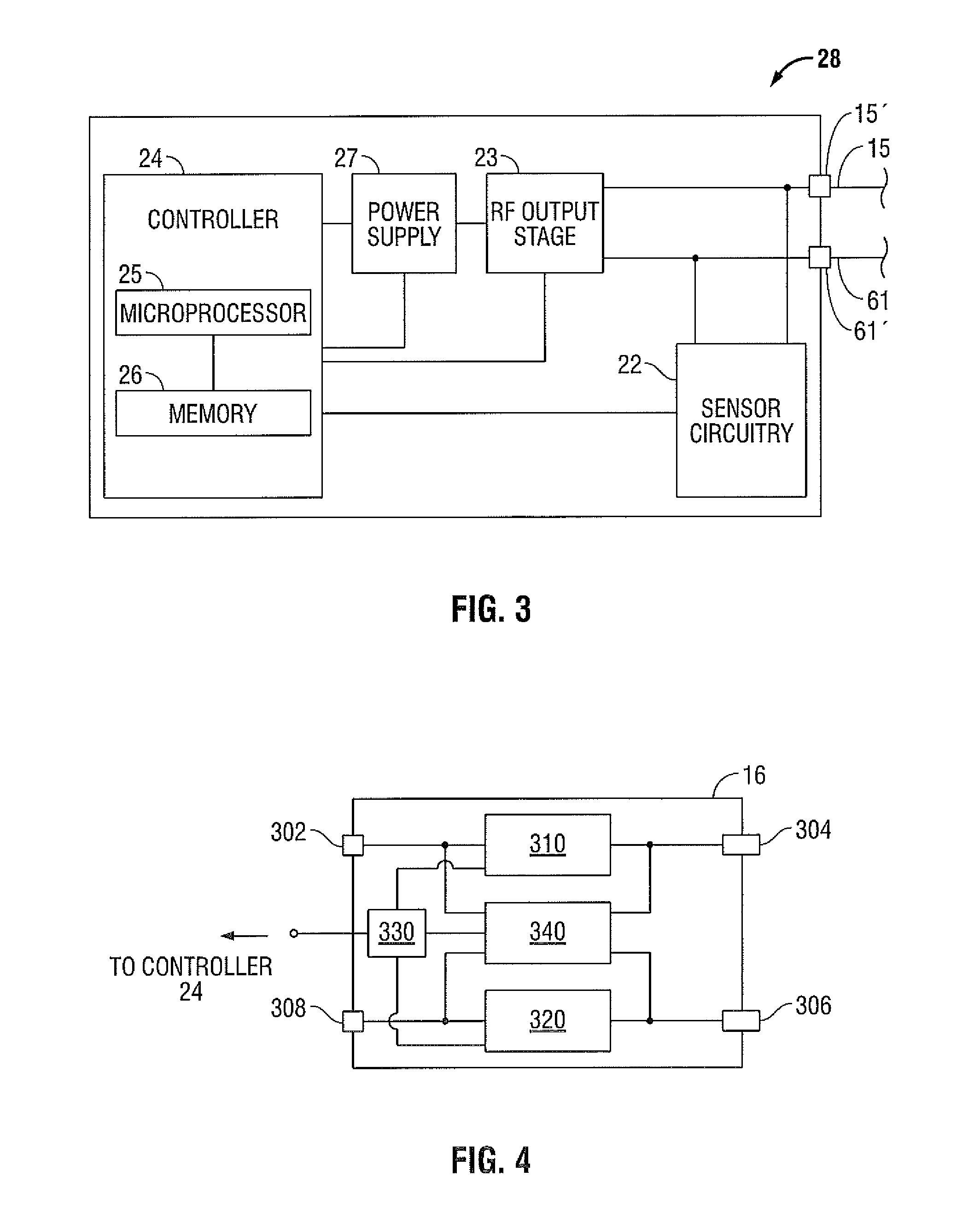
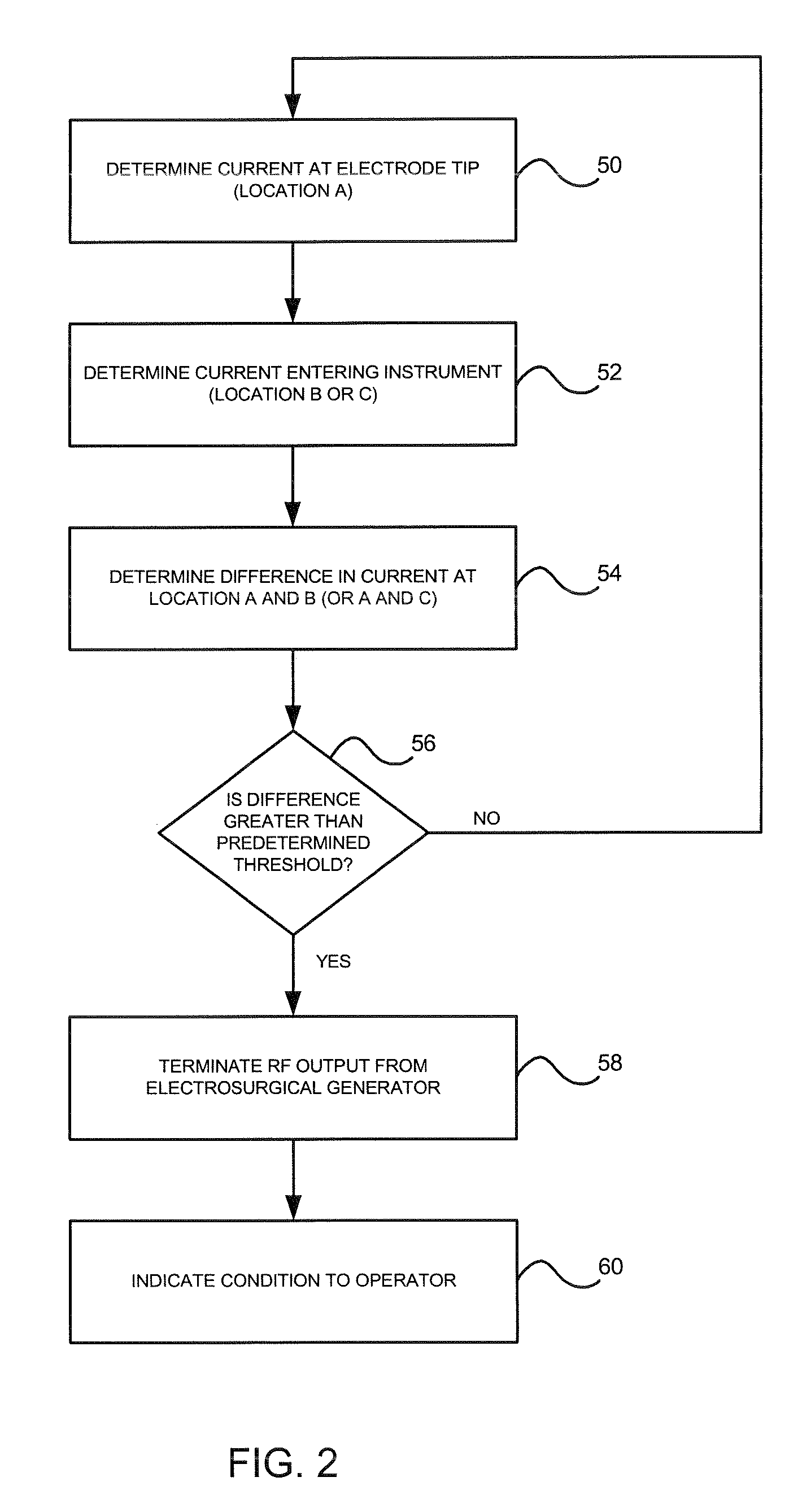
Arc based adaptive control system for an electrosurgical unit
A system and method for performing electrosurgical procedures are disclosed. The system includes an electrosurgical generator adapted to supply electrosurgical energy to tissue in form of one or more electrosurgical waveforms having a crest factor and a duty cycle. The system also includes sensor circuitry adapted to measure impedance and to obtain one or more measured impedance signals. The sensor circuitry is further adapted to generate one or more arc detection signals upon detecting an arcing condition§. The system further includes a controller adapted to generate one or more target control signals as a function of the measured impedance signals and to adjust output of the electrosurgical generator based on the arc detection signal. An electrosurgical instrument is also included having one or more active electrodes adapted to apply electrosurgical energy to tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Reflective power monitoring for microwave applications
ActiveUS20080319434A1ElectrocardiographySurgical instruments for heatingMicrowave applicationsEngineering
A system and method for supplying microwave energy to tissue for microwave therapy includes an electrosurgical generator having an output for coupling to a surgical instrument. The electrosurgical generator includes a microwave energy source and a controller for controlling the operation of the electrosurgical generator. The surgical instrument, coupled to the electrosurgical generator, includes a microwave antenna for delivering microwave energy from the microwave energy source. The controller of the electrosurgical generator is operable for causing the electrosurgical generator to apply at least two pulses of microwave energy.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
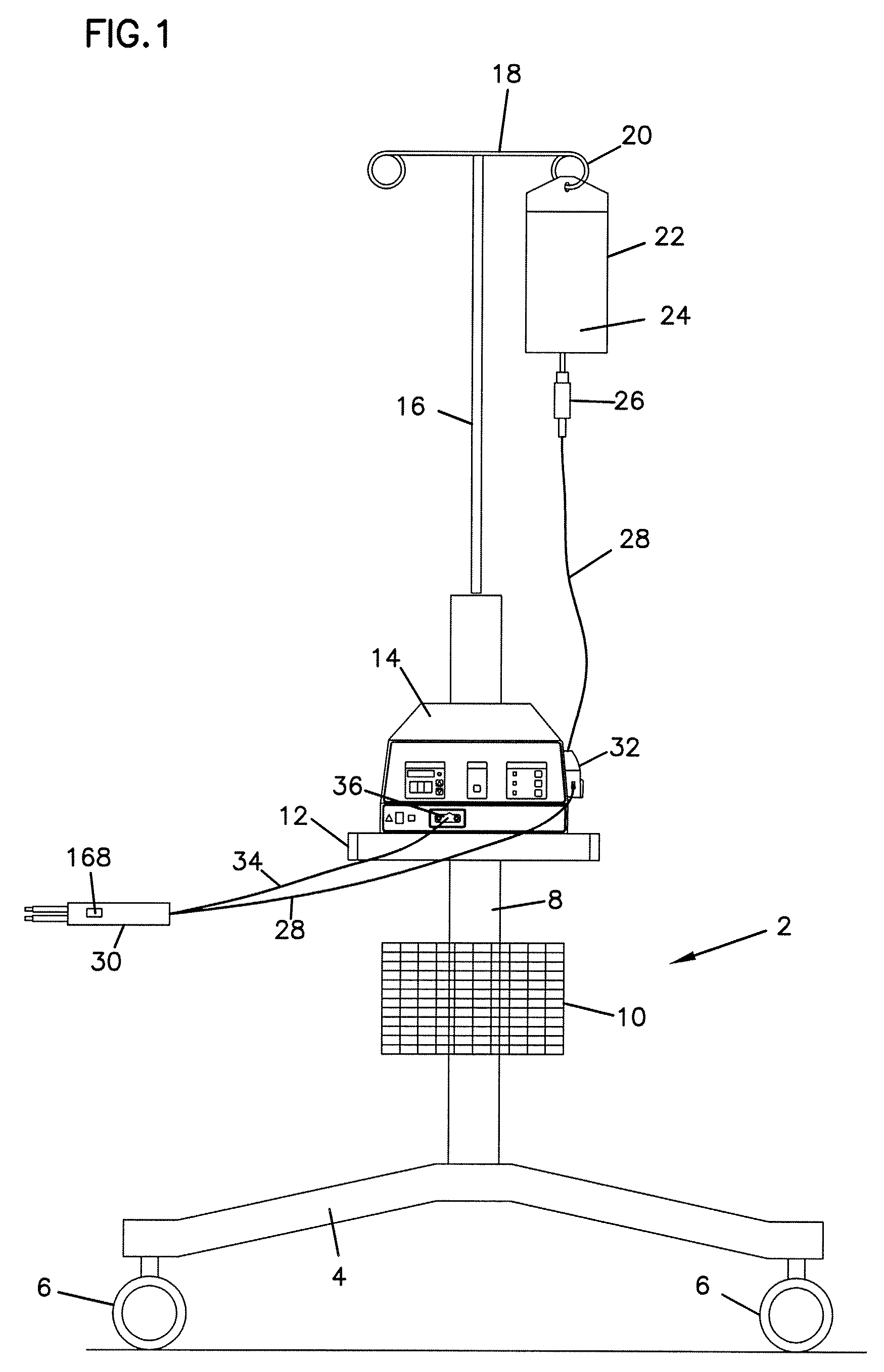
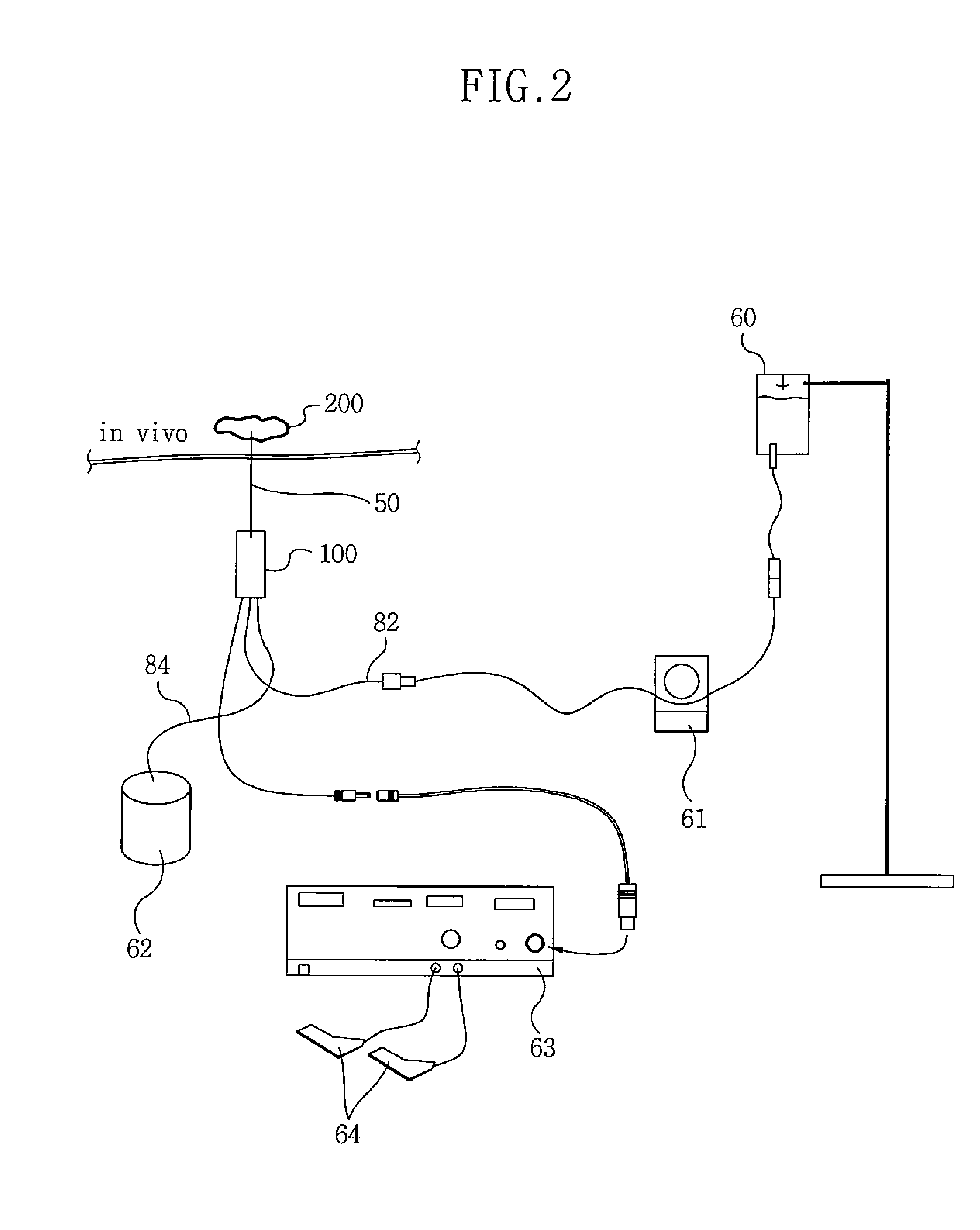
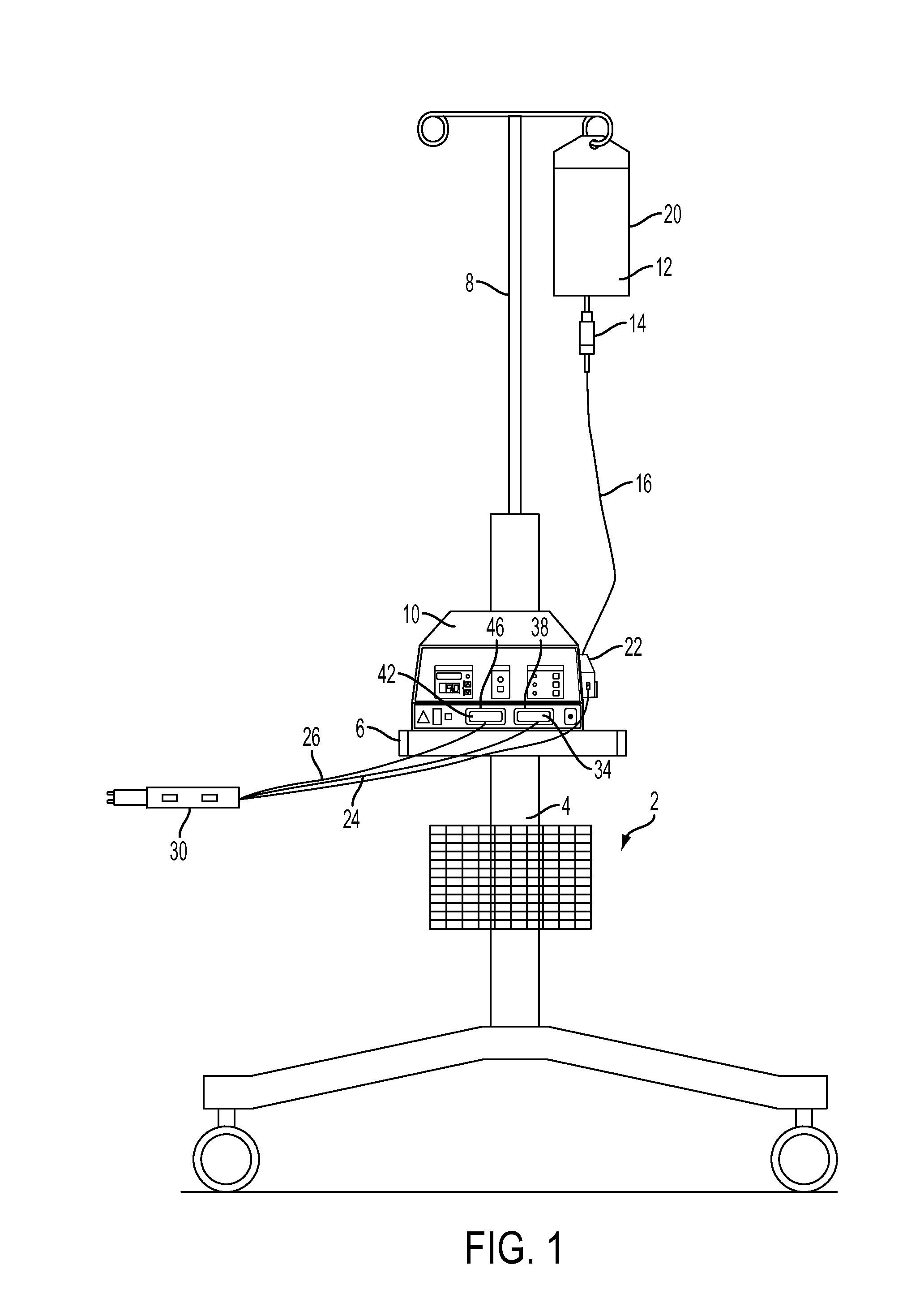
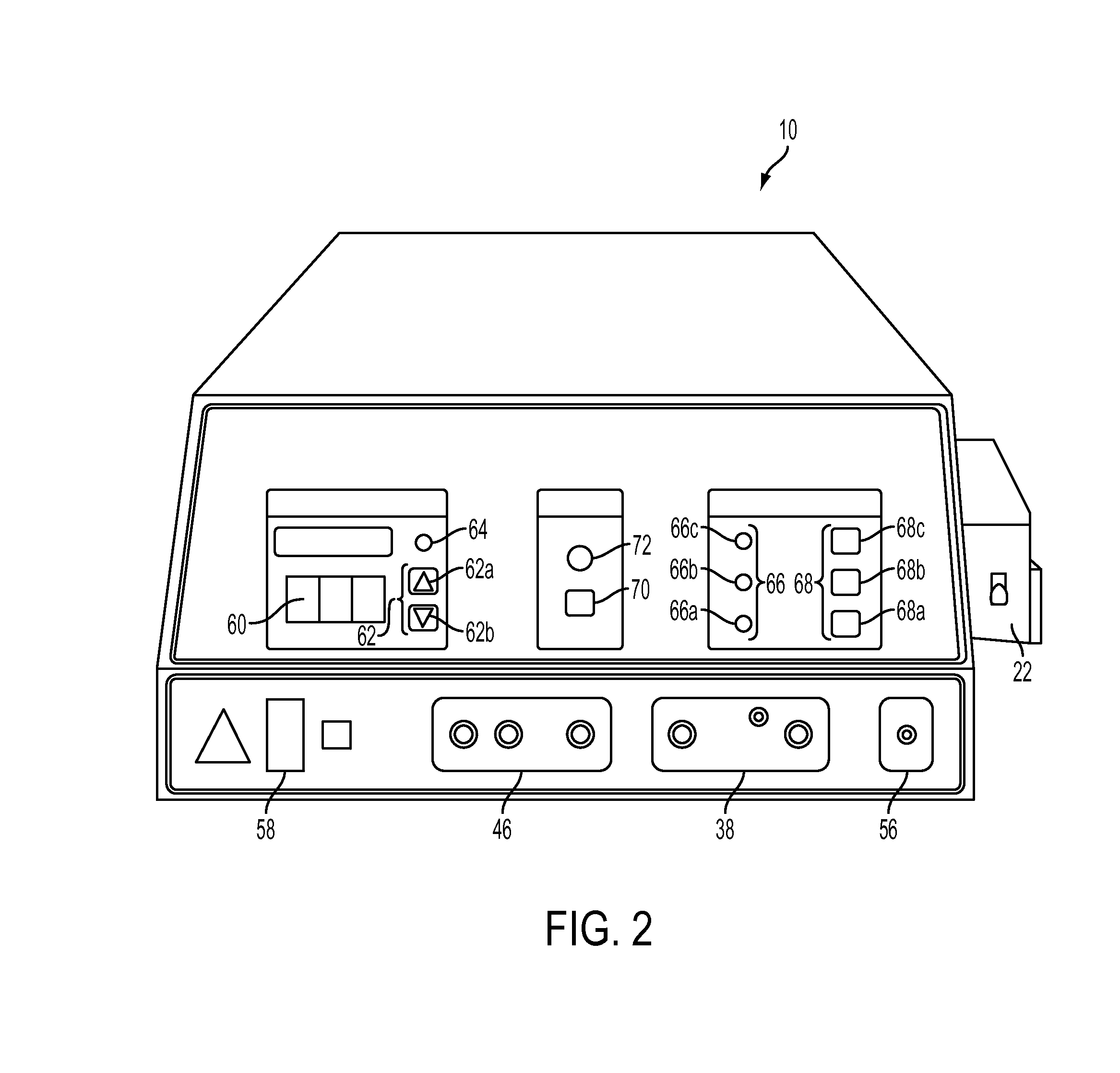
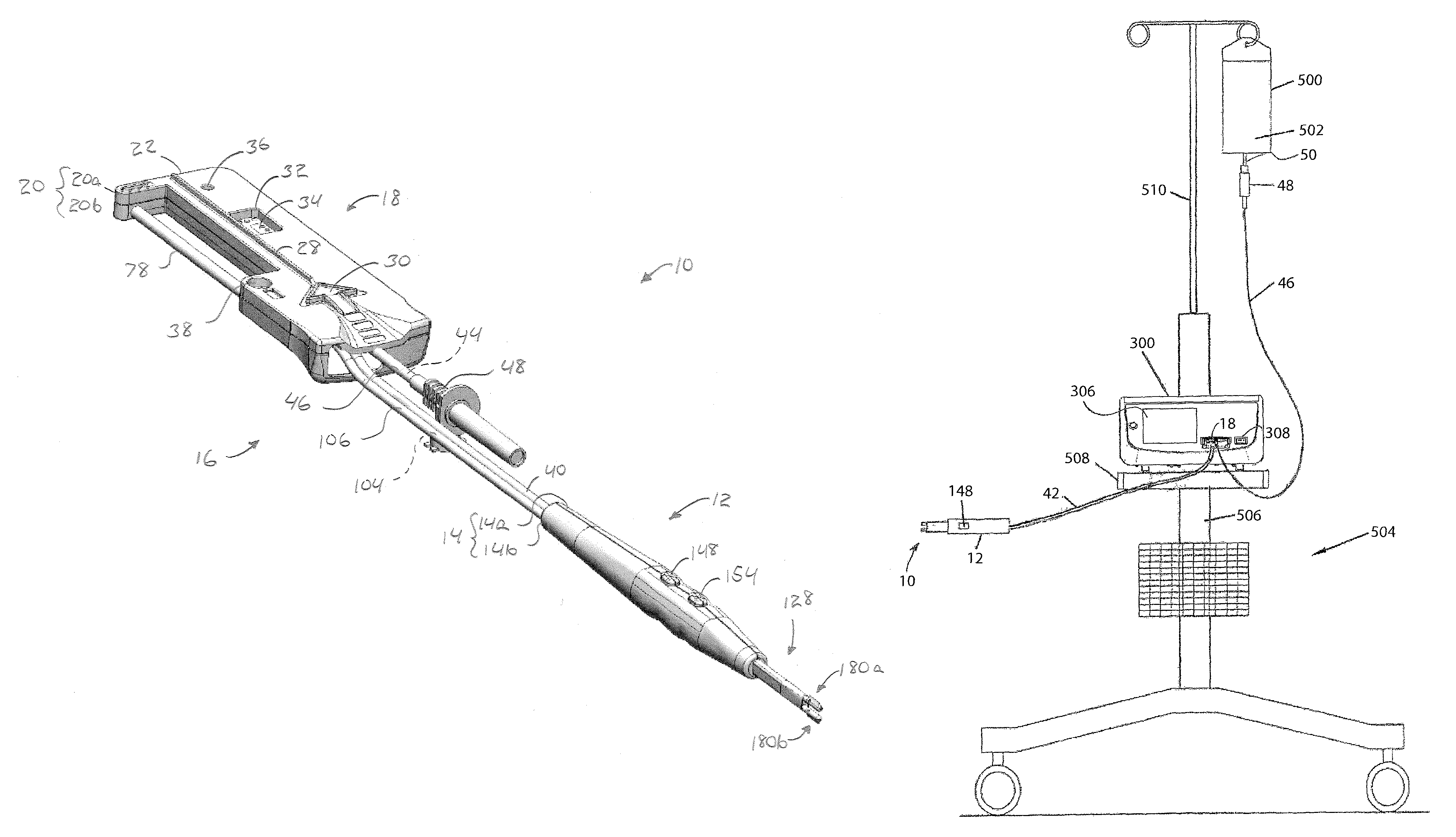
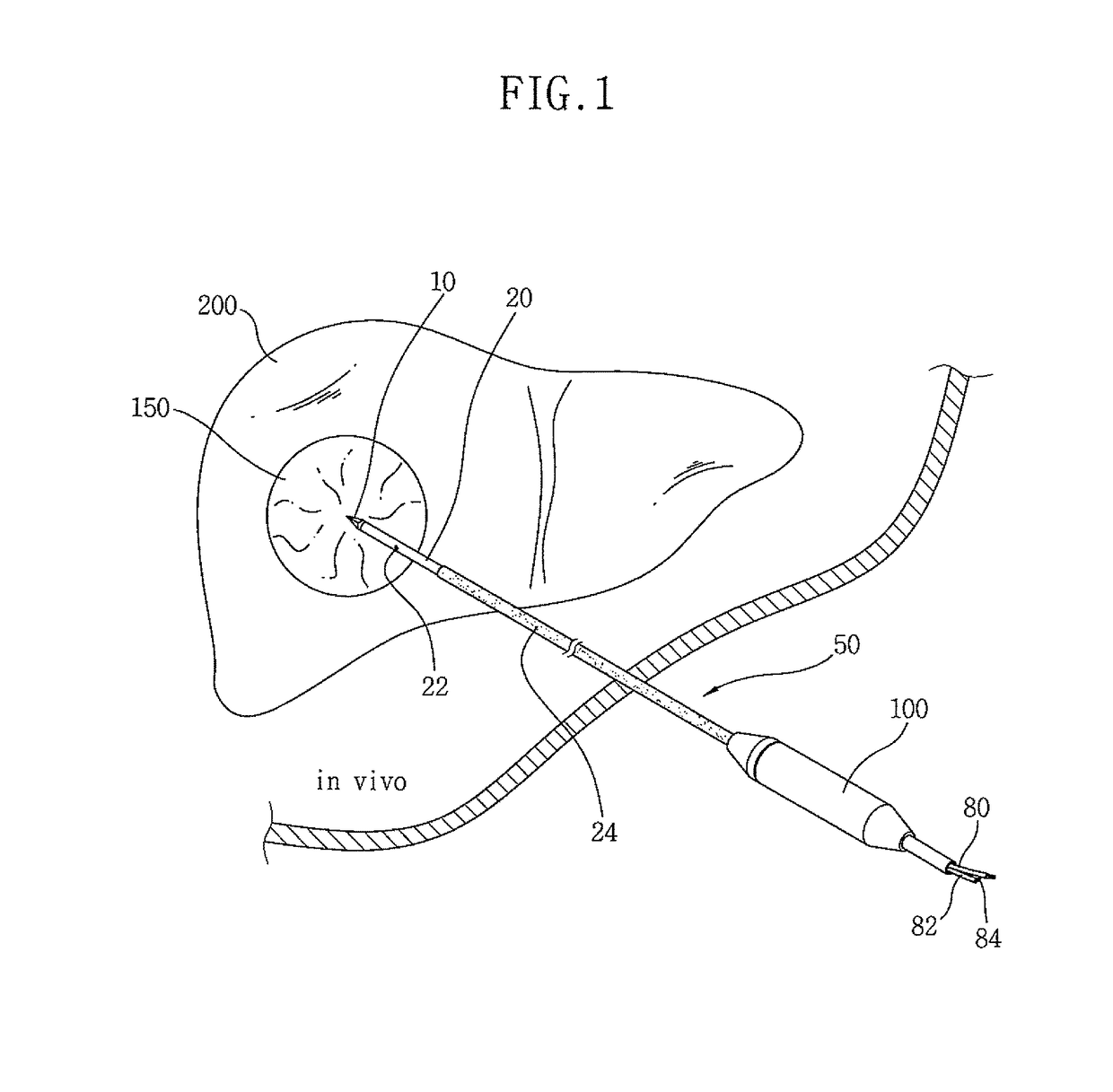
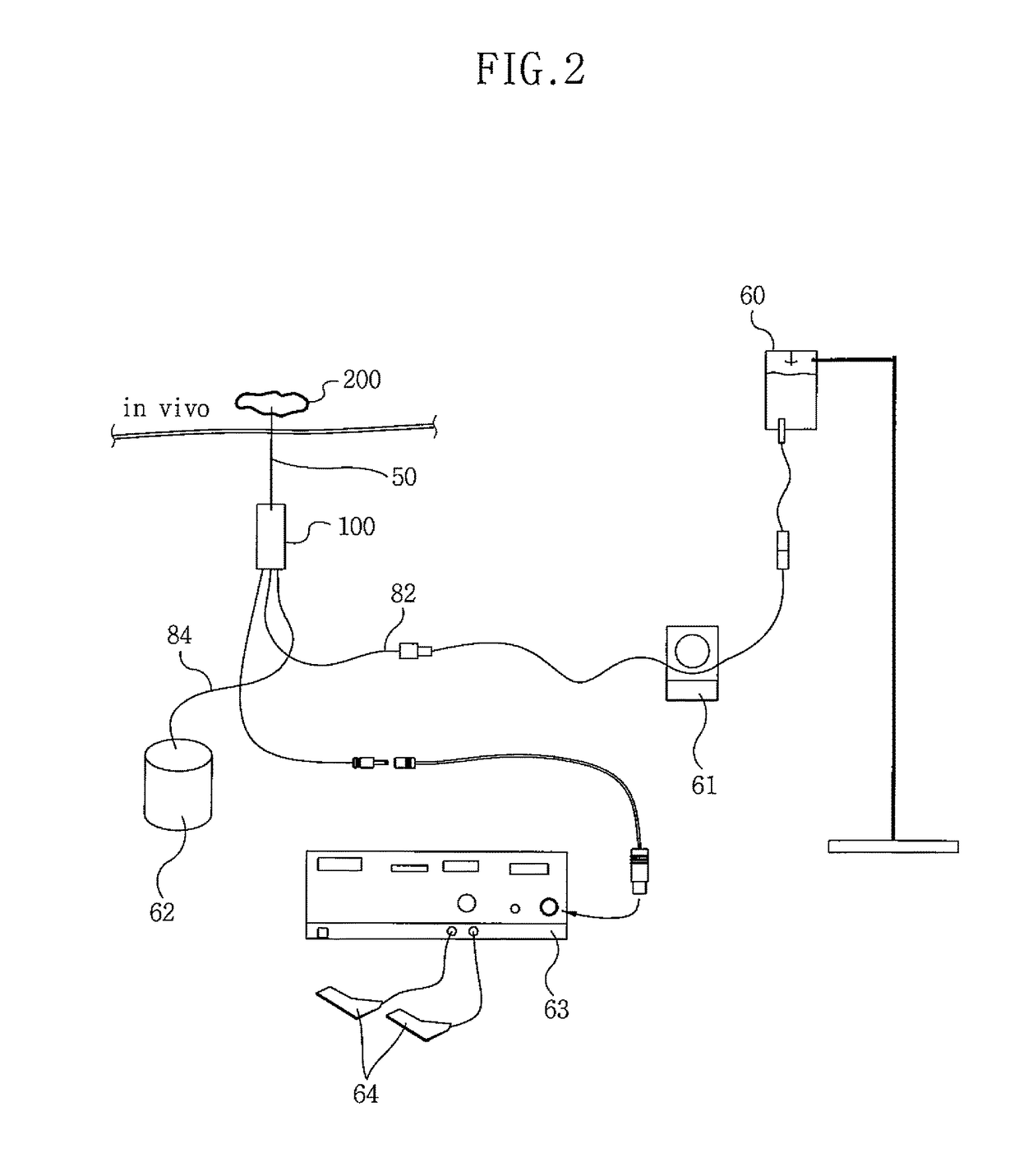
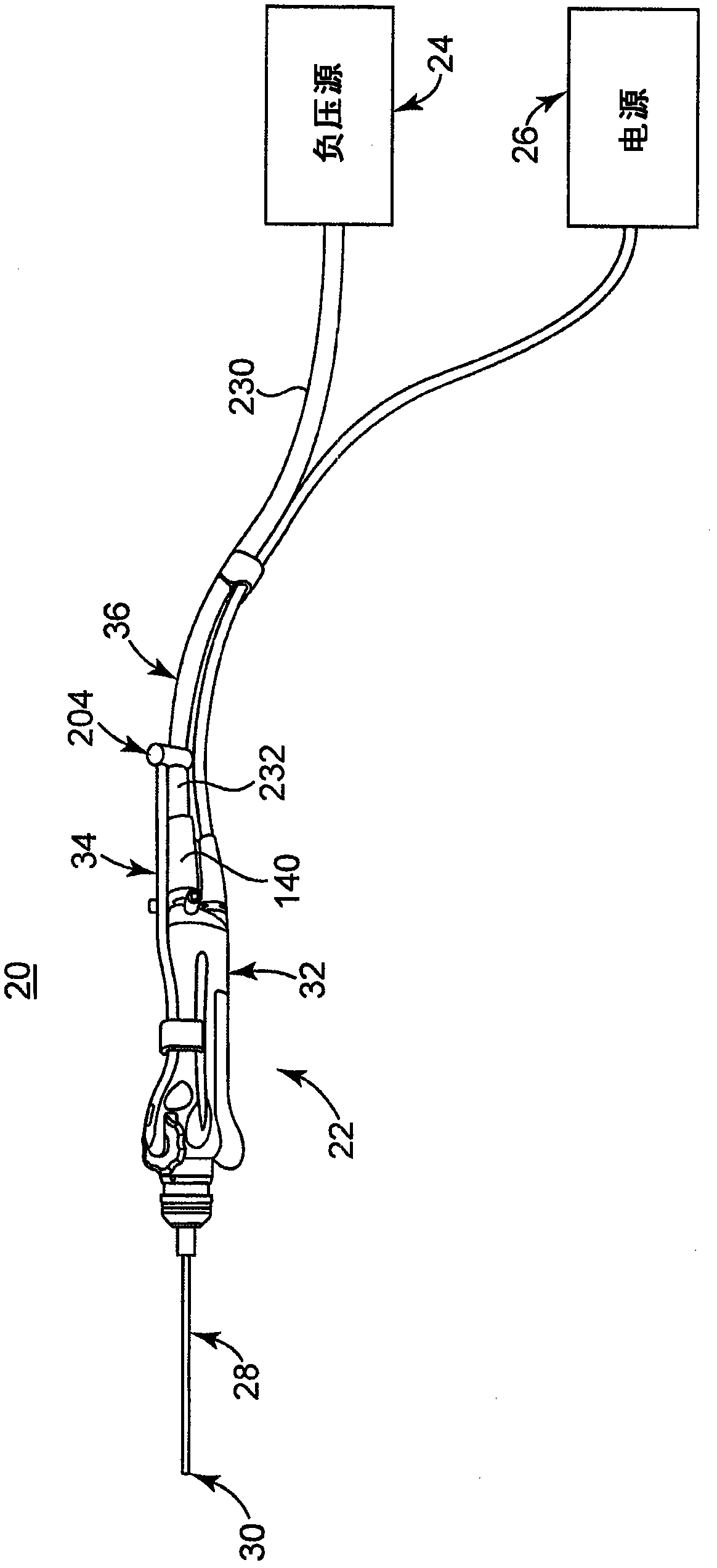
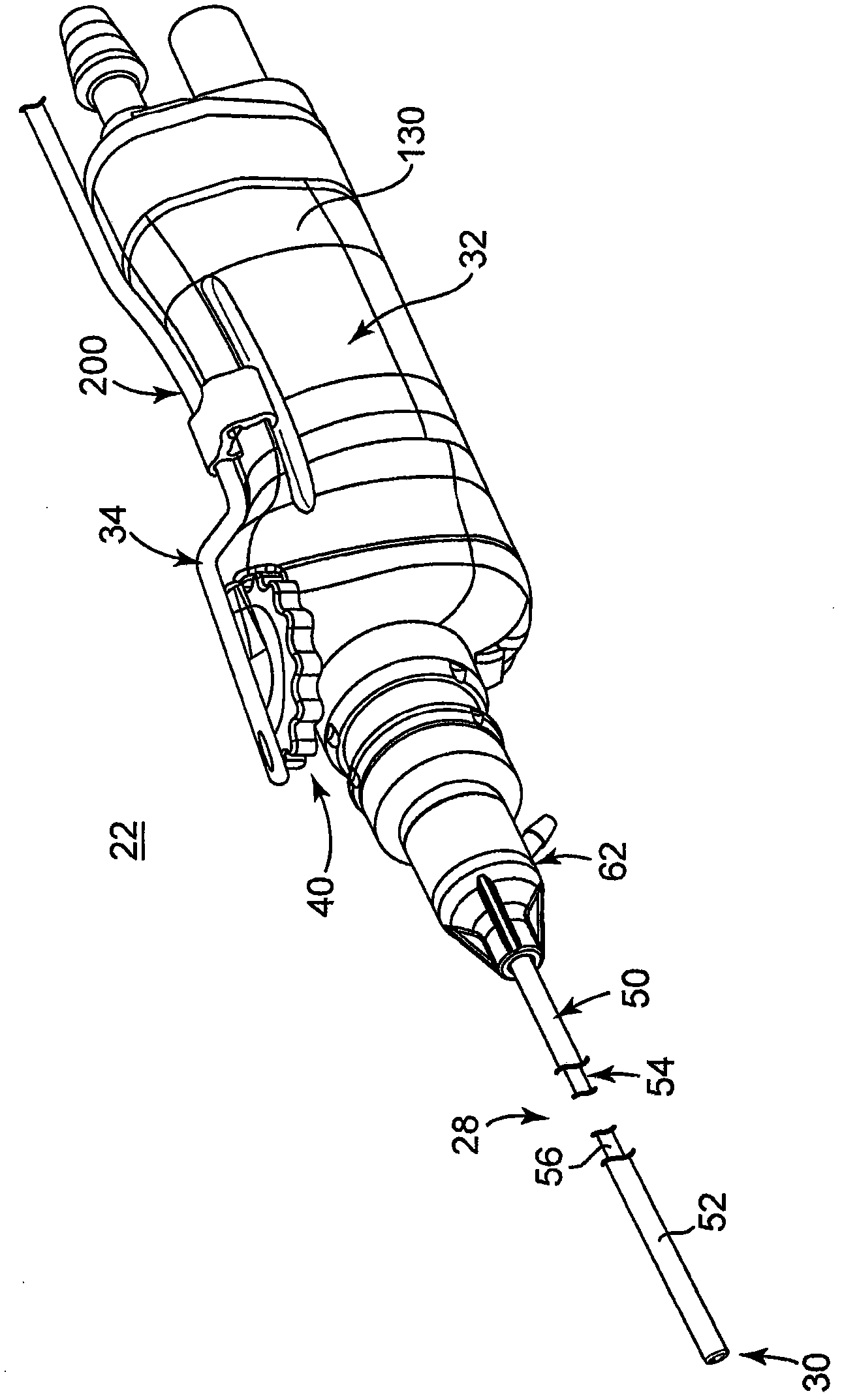
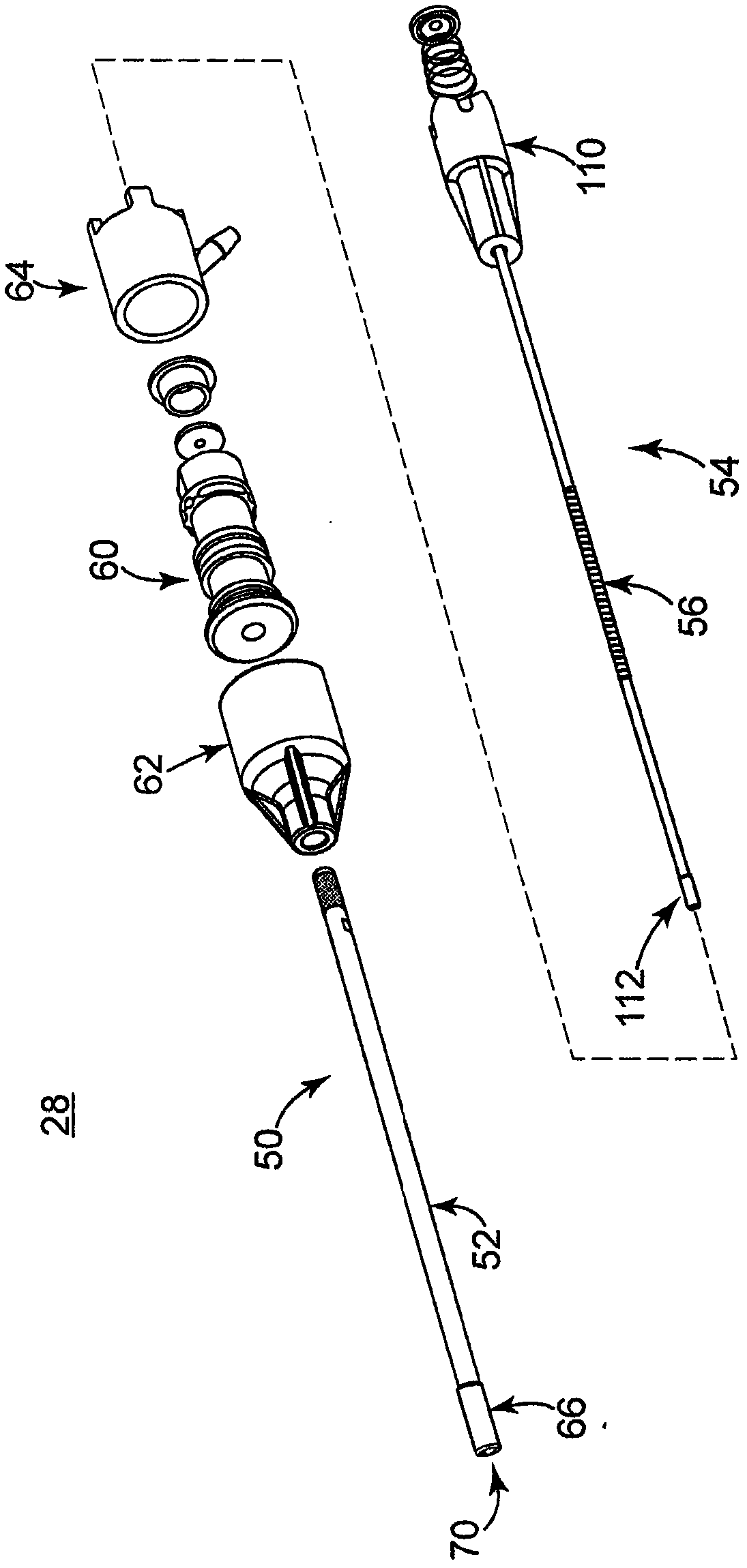
Fluid-assisted electrosurgical devices, electrosurgical unit with pump and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20060149225A1High trafficReduce trafficControlling energy of instrumentCatheterEngineeringElectrosurgical unit
The invention provides an electrosurgical unit comprising a radio-frequency power source and a pump, with the throughput of fluid expelled by the pump controlled by the RF power level setting and fluid flow rate setting. The invention also provides various electrosurgical devices which may be used with the electrosurgical unit. In one embodiment, the electrosurgical device comprises a first electrode tip spaced next to a second electrode tip with a portion of the first electrode tip facing the second electrode tip and a portion of the second electrode tip facing the first electrode tip, the first electrode tip and the second electrode tip both having a spherical distal end, and a fluid outlet arrangement to expel fluid onto the electrode tips solely at locations remote from the electrode tip portions facing each other.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
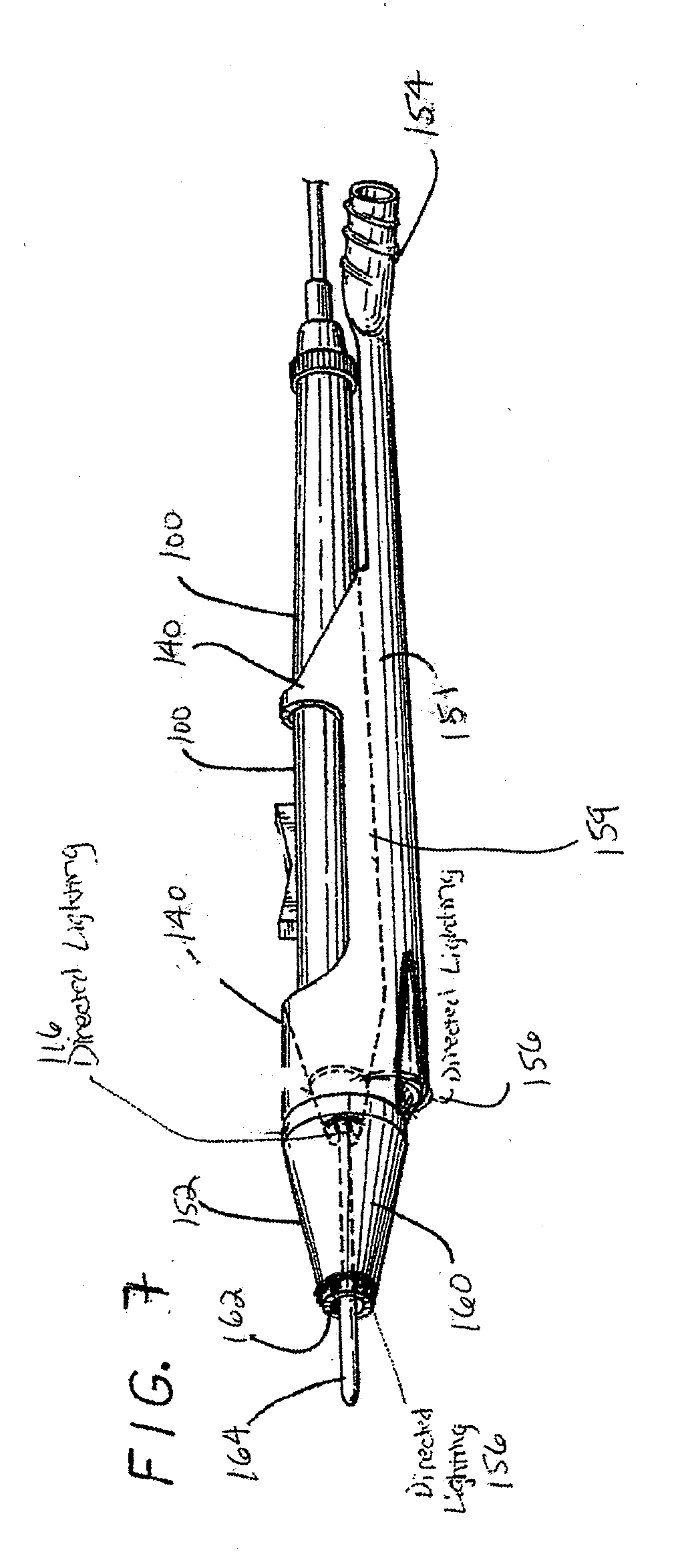
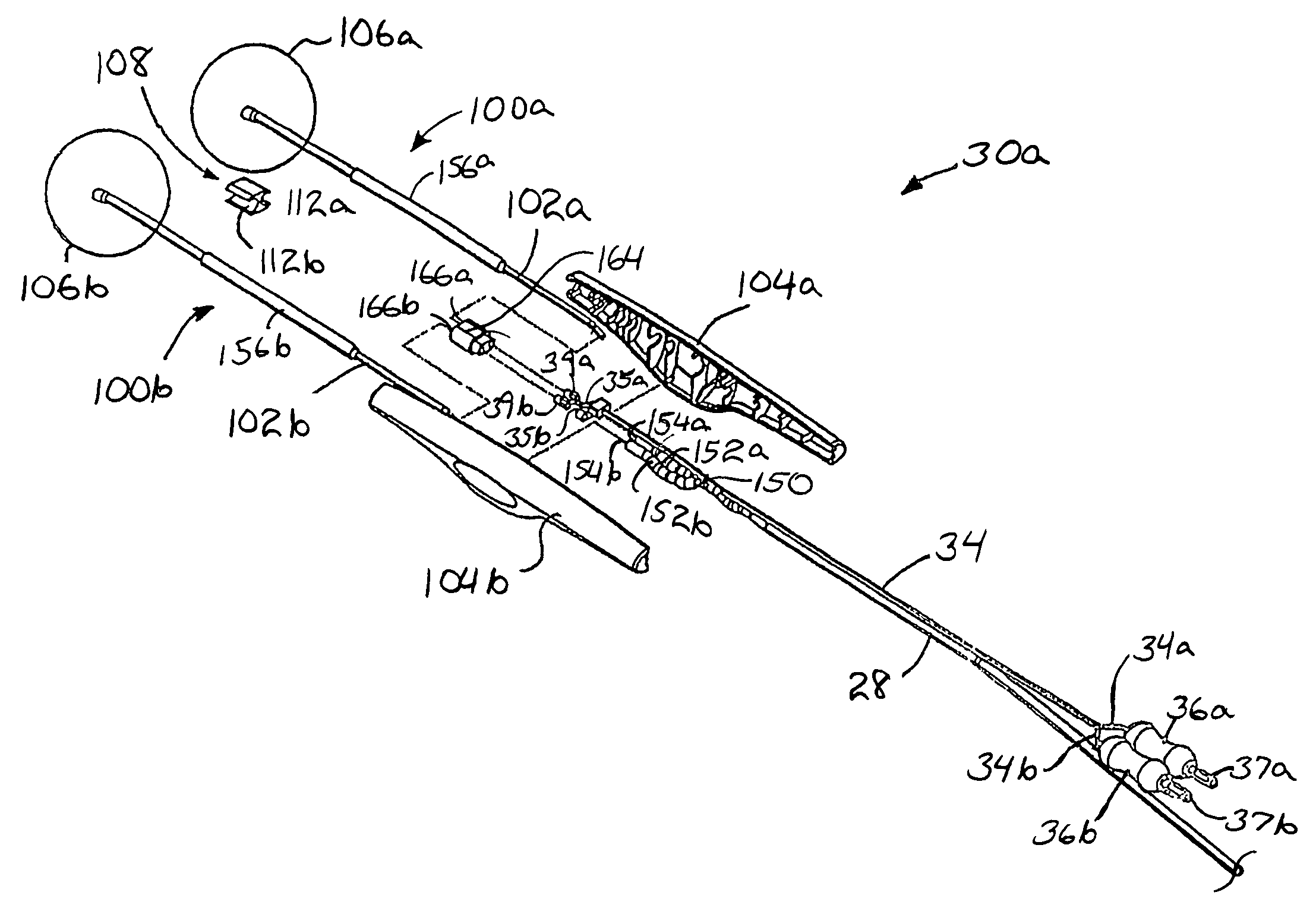
Electrosurgical unit pencil apparatus and shroud having directed illumination
An electrosurgery pencil having directed illumination and a removable shroud having directed illumination where the removable shroud is adapted to fit over an electrosurgery pencil.
Owner:IC MEDICAL INC
Fluid-assisted electrosurgical devices, electrosurgical unit with pump and methods of use thereof
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
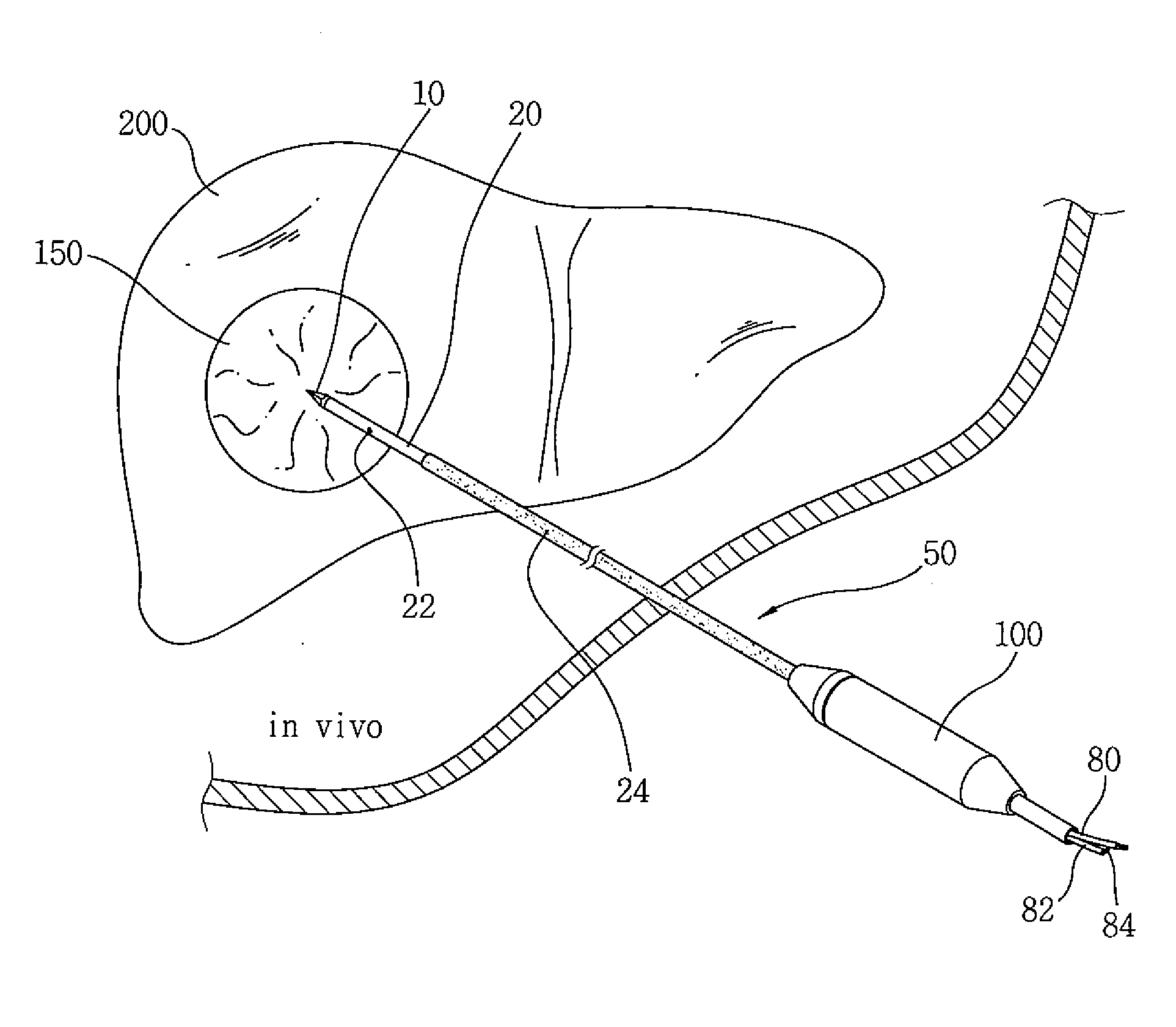
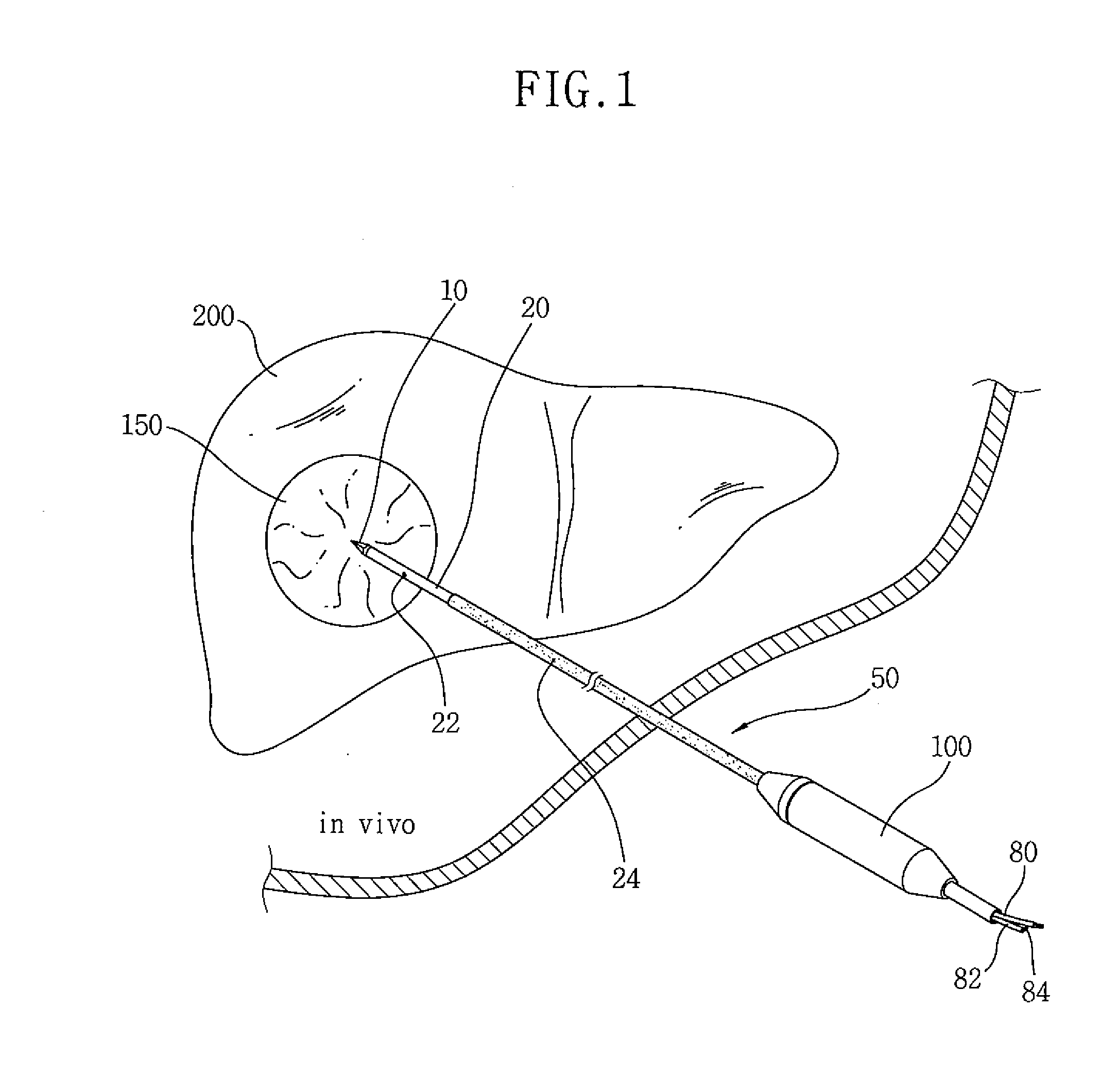
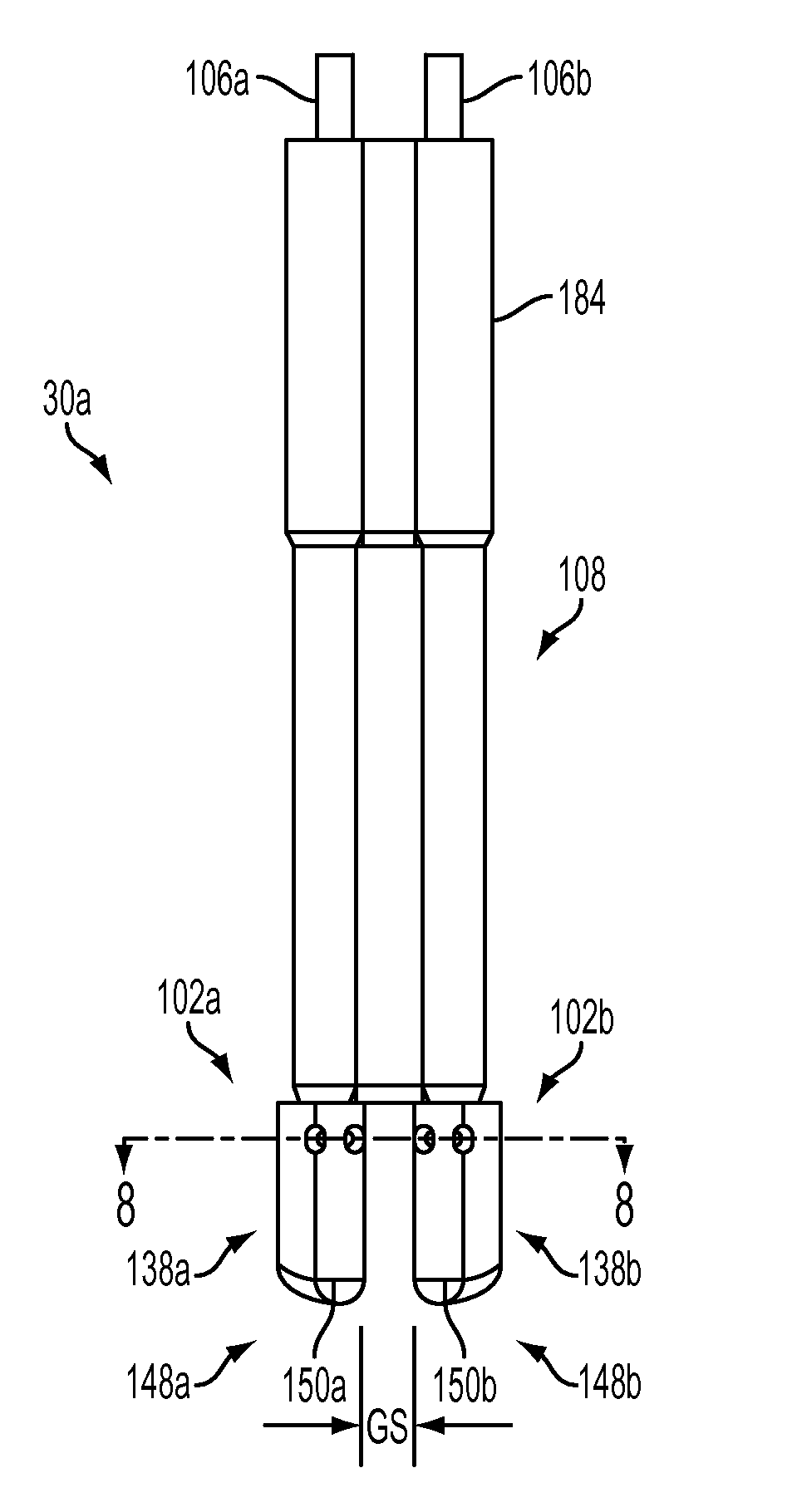
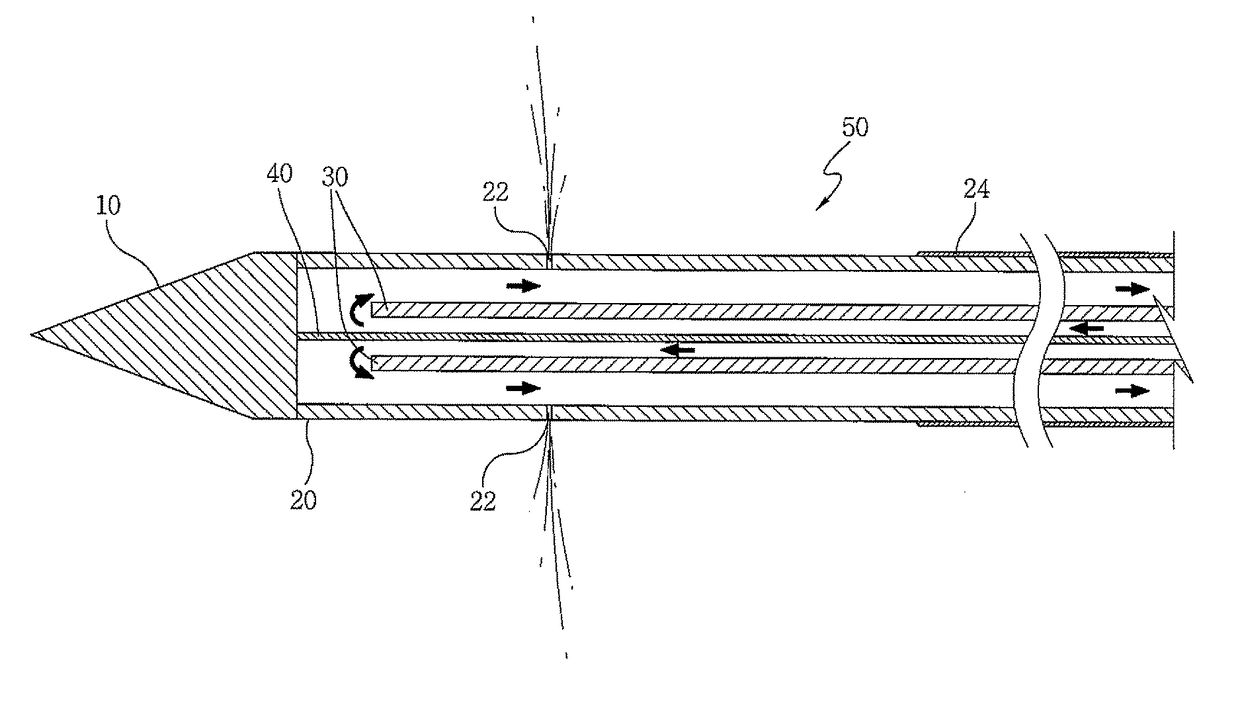
Electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation
ActiveUS20090287206A1Easy to liftMaximized economicallySurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationElectrosurgery
The present invention relates to an electrode for an electrosurgical unit for the use in ablating and necrosing a living tissue by RF electric energy. The present invention provides an electrode for an electrosurgical unit, including: a hollow electrode formed in an elongated hollow tube shape, a non-insulating region of a predetermined length being formed on one side of which, an insulating region being formed on an outer surface of which other than the non-insulating region; a saline solution circulation structure that supplies pressurized saline solution for cooling a living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode from the outside of the living tissue to the inside of the hollow electrode, and discharges the pressurized saline solution from the inside of the hollow electrode to the outside of the living tissue; and one or more saline solution discharge holes formed in the non-insulating region of the hollow electrode to discharge some of the circulating pressurized saline solution to the living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode.
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Fluid-assisted electrosurgical device
ActiveUS8632533B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesDistal portionElectrosurgical unit
The invention provides an electrosurgical device and methods of use thereof. The device comprises a first electrode, a second electrode and at least one fluid outlet. In one embodiment, the first electrode has a distal portion with an electrically conductive spherical surface, the second electrode has a distal portion with an electrically conductive spherical surface, and at least one of the first electrode and the second electrode have a blade portion.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
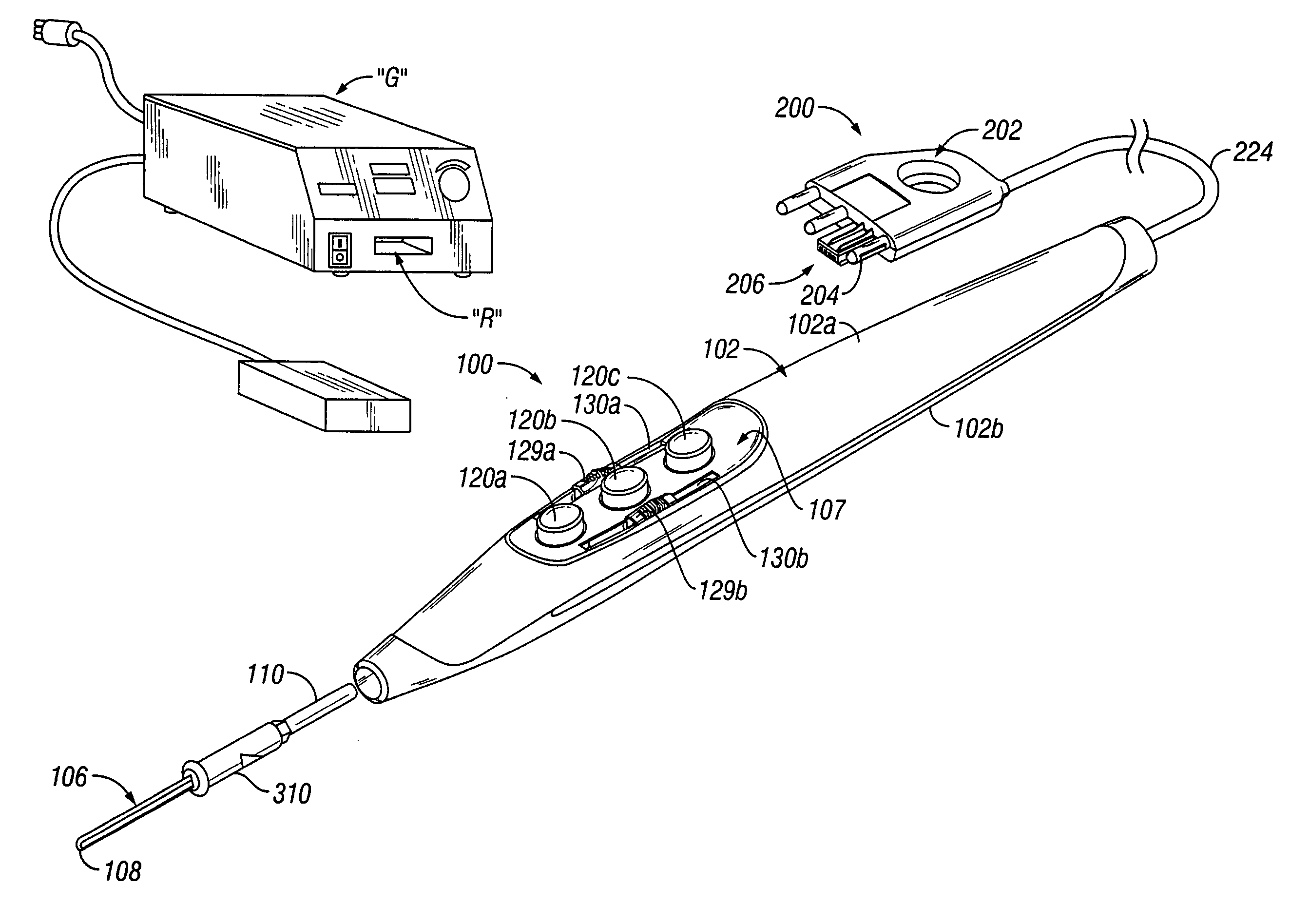
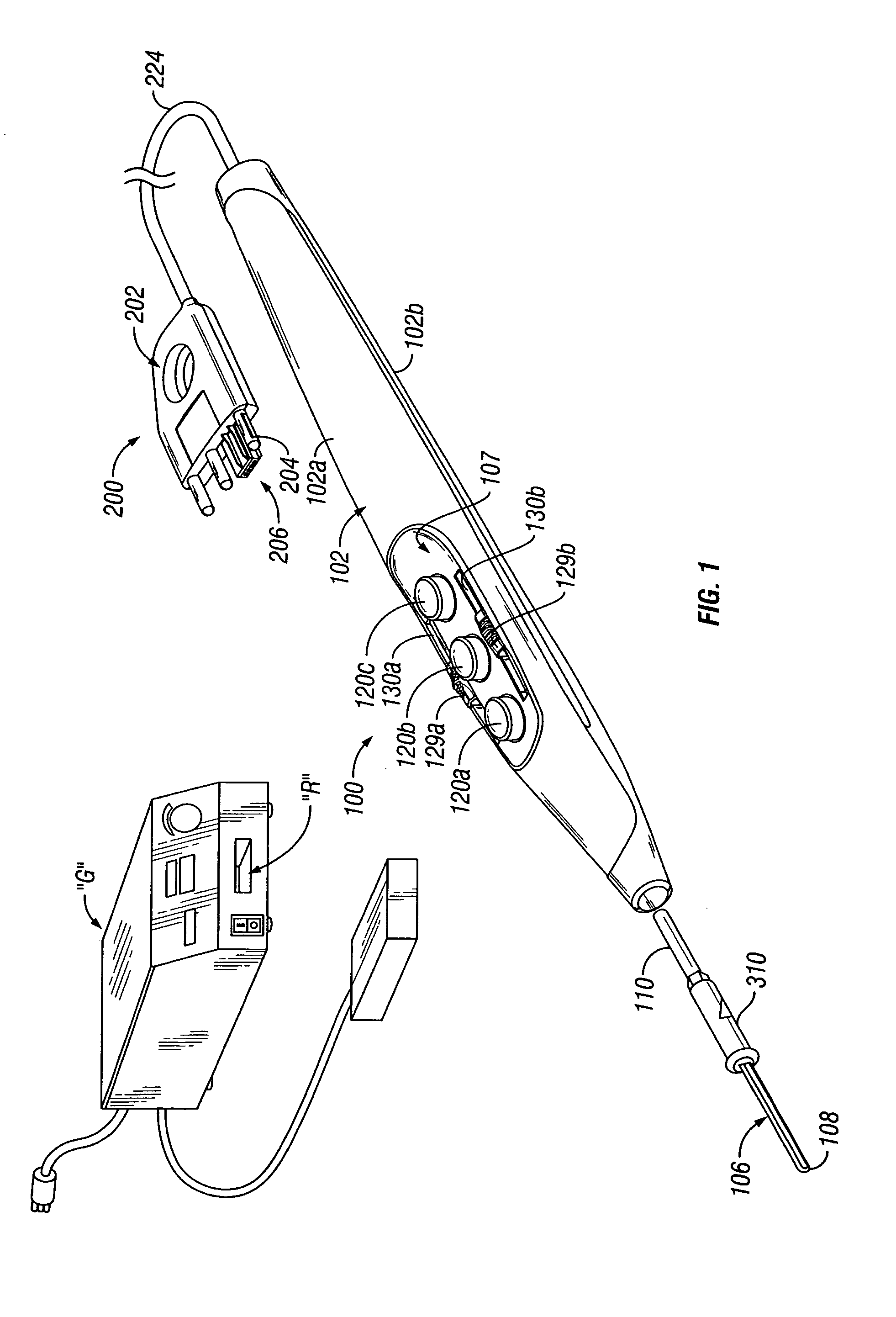
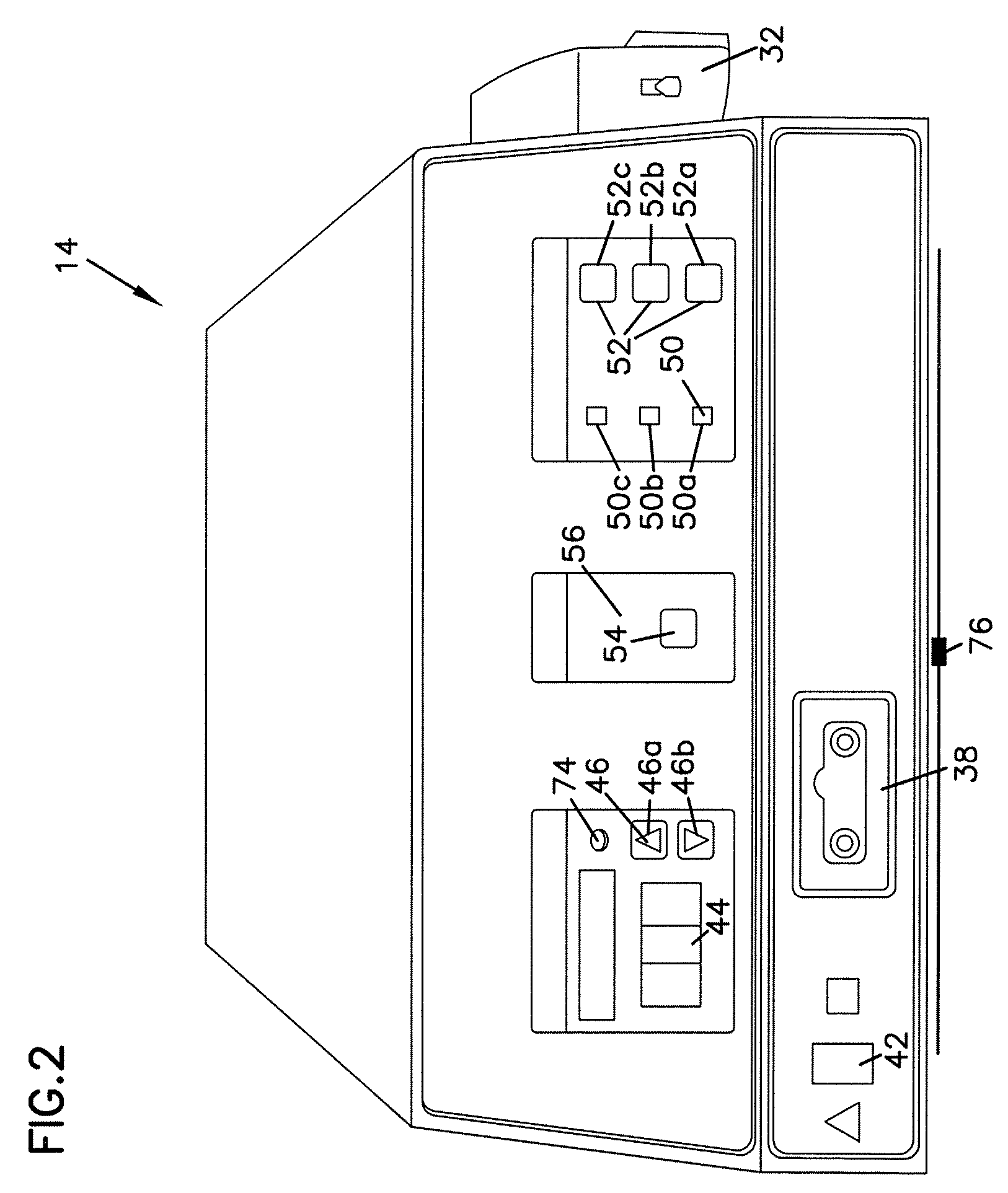
Electrosurgical Device Having a Multiplexer
An electrosurgical system includes an electrosurgical generator configured to provide electrosurgical energy to an electrosurgical device coupled thereto which, in turn, delivers electrosurgical energy to tissue. The electrosurgical device may include a plurality of sensors configured to detect one or more tissue properties and output a detected tissue property signal relating thereto. One or more multiplexers having a plurality of channels are electrically connected to each of the corresponding plurality of sensors. The multiplexer(s) may be configured to receive the detected tissue property signal from each sensor of the plurality of sensors and output at least one output signal along a signal line. The signal line is configured to connect to the electrosurgical generator to control a power output of the electrosurgical generator. A channel select algorithm is configured to automatically select channels from the plurality of channels.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Cartridge Assembly For Electrosurgical Devices, Electrosurgical Unit And Methods Of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20110125146A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesElectricityElectrosurgical unit
The invention provides a cartridge assembly to couple a tissue treatment device with an electrosurgical unit, with the cartridge assembly operable with a power delivery apparatus and a fluid delivery apparatus of the electrosurgical unit. The invention also provides an electrosurgical unit comprising a power delivery apparatus and a fluid delivery apparatus operable with the cartridge assembly and a system thereof.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
Cartridge assembly for electrosurgical devices, electrosurgical unit and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9345541B2Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesEngineeringElectrosurgical unit
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
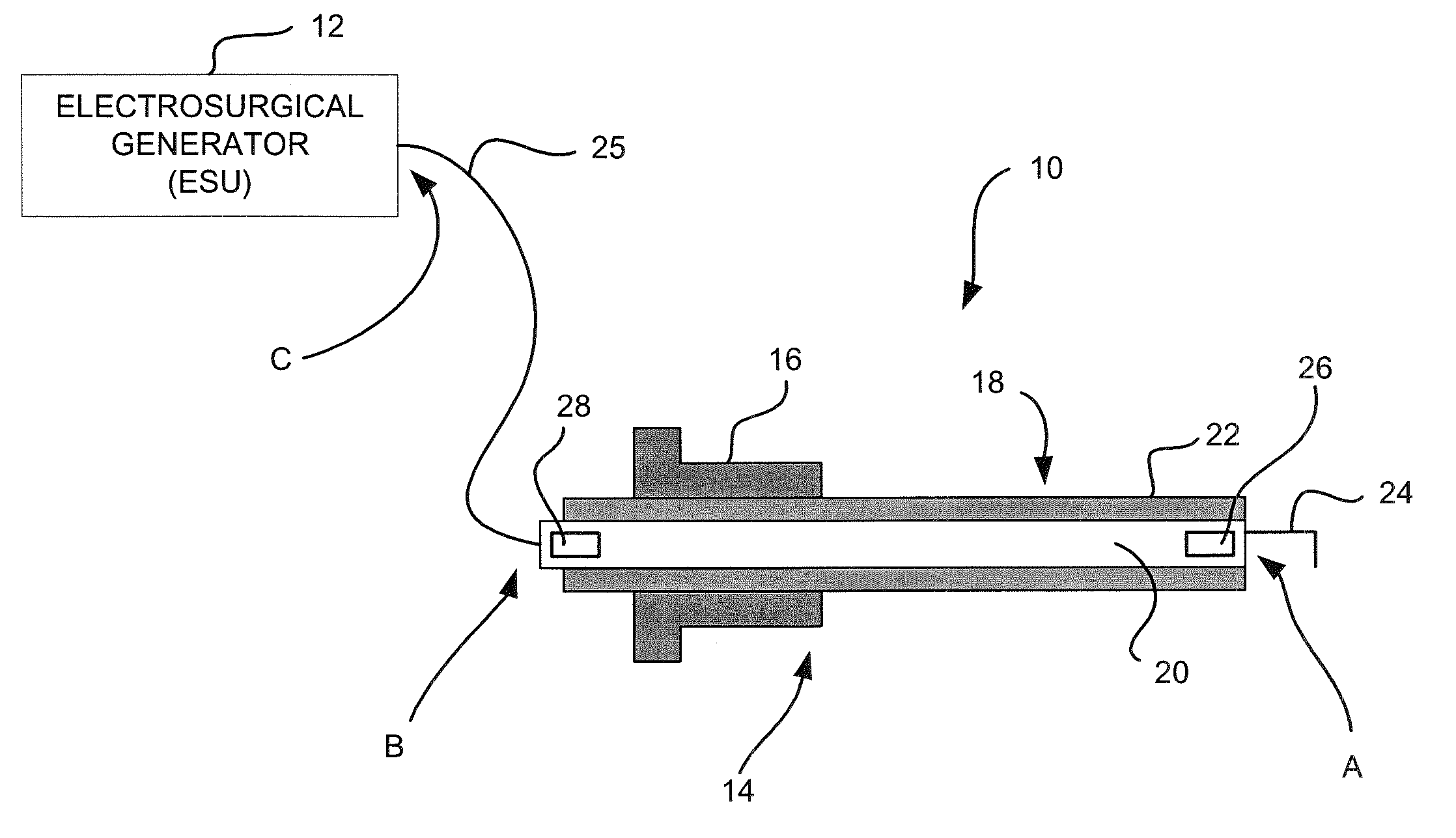
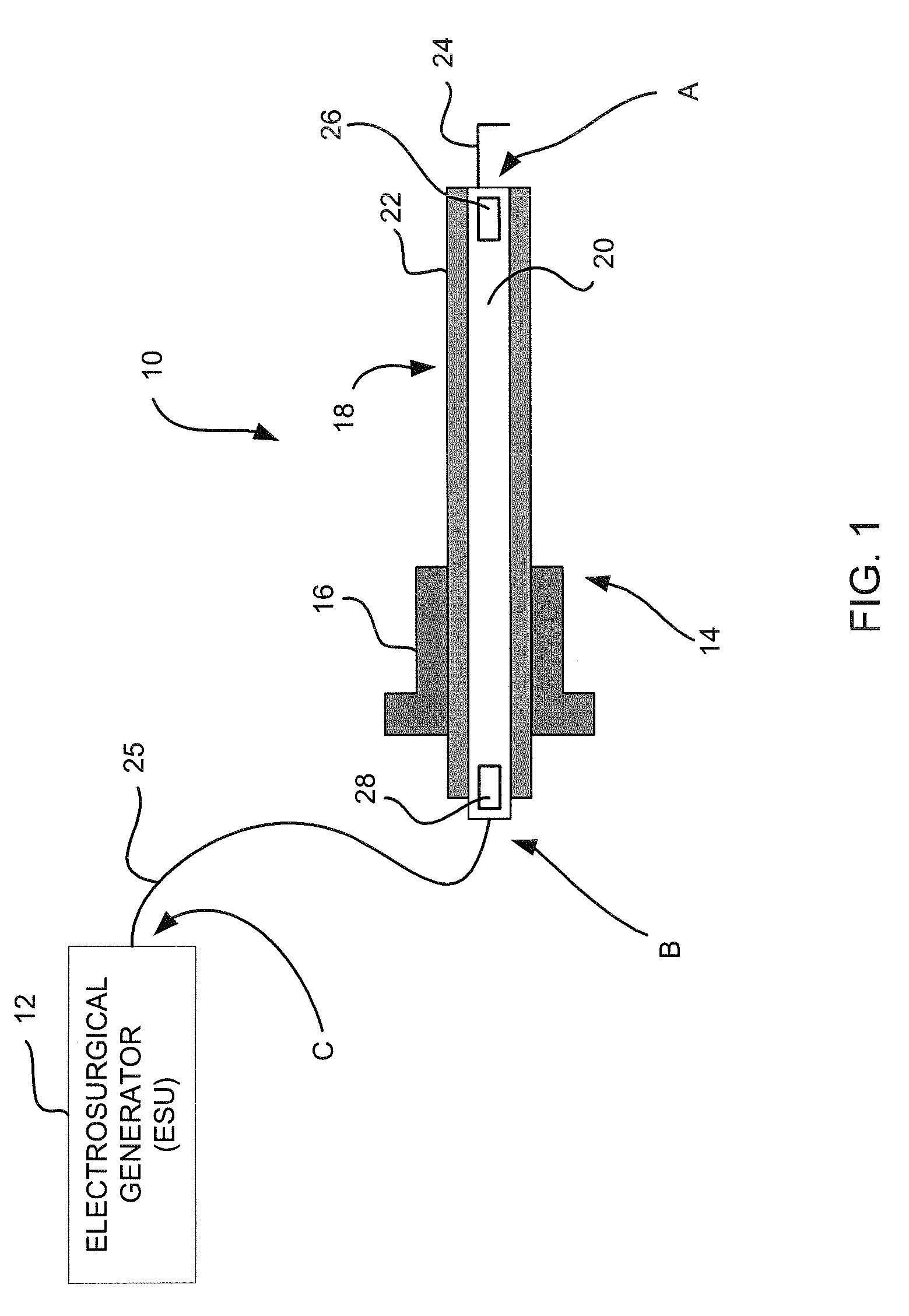
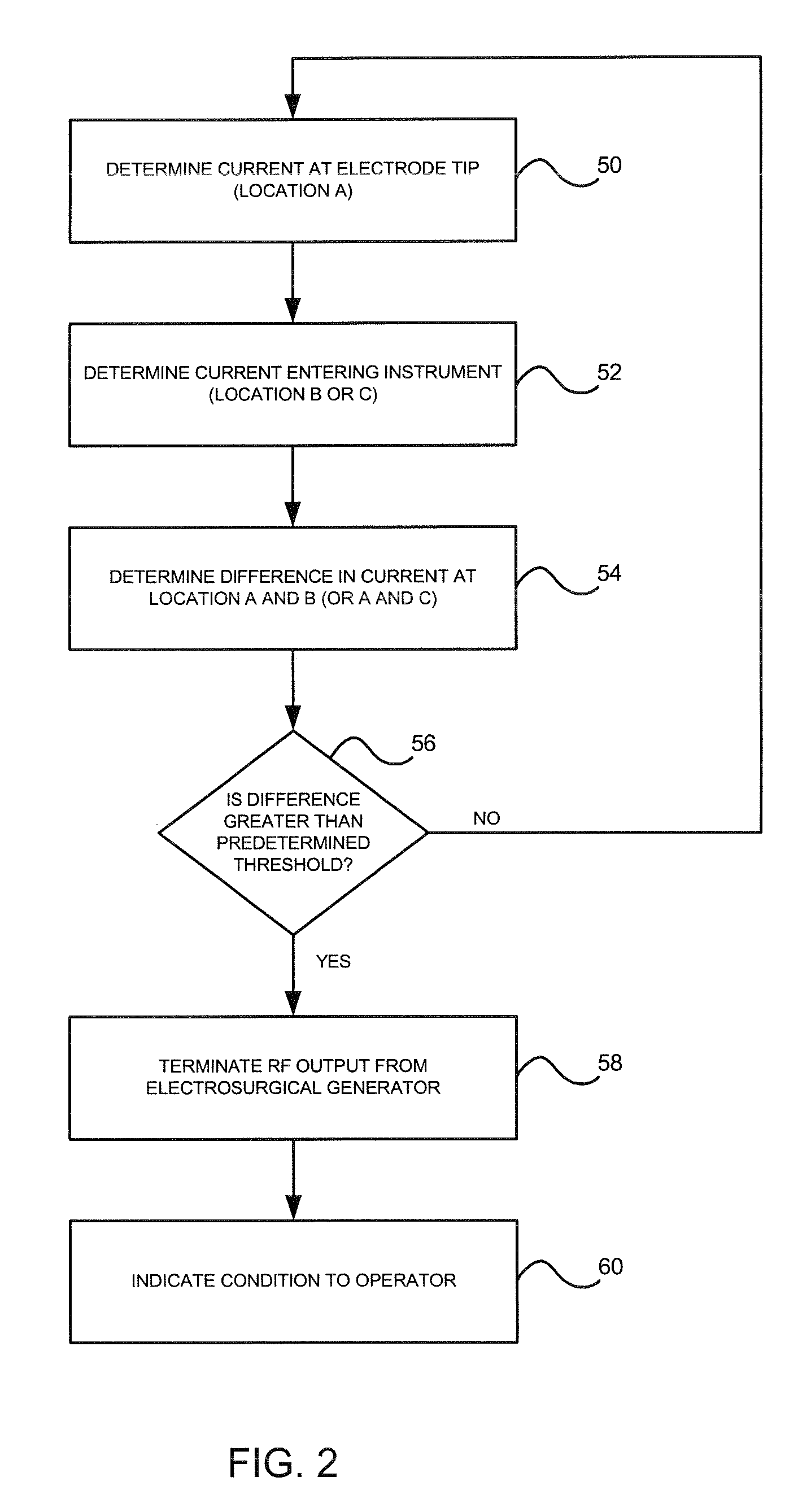
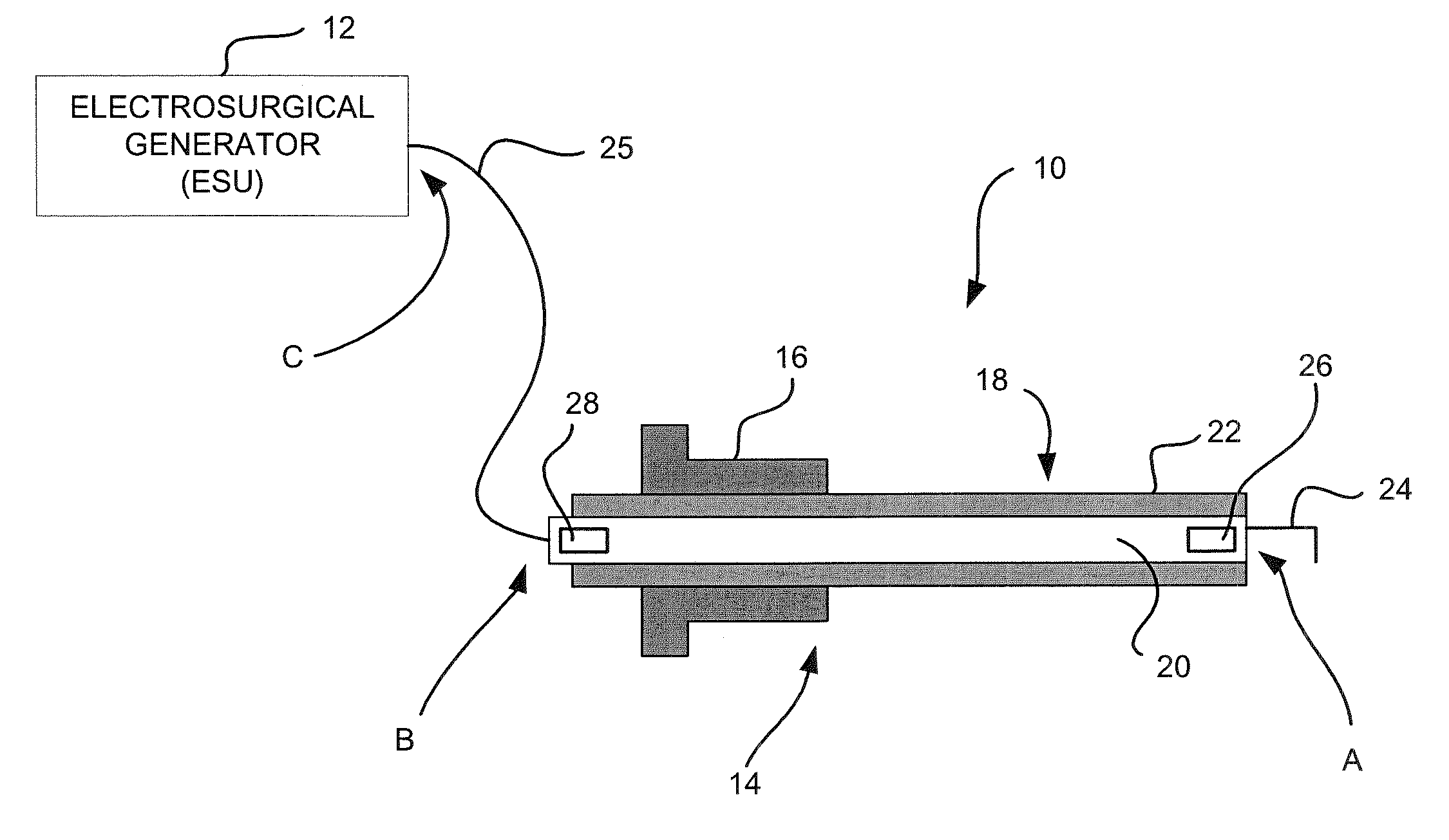
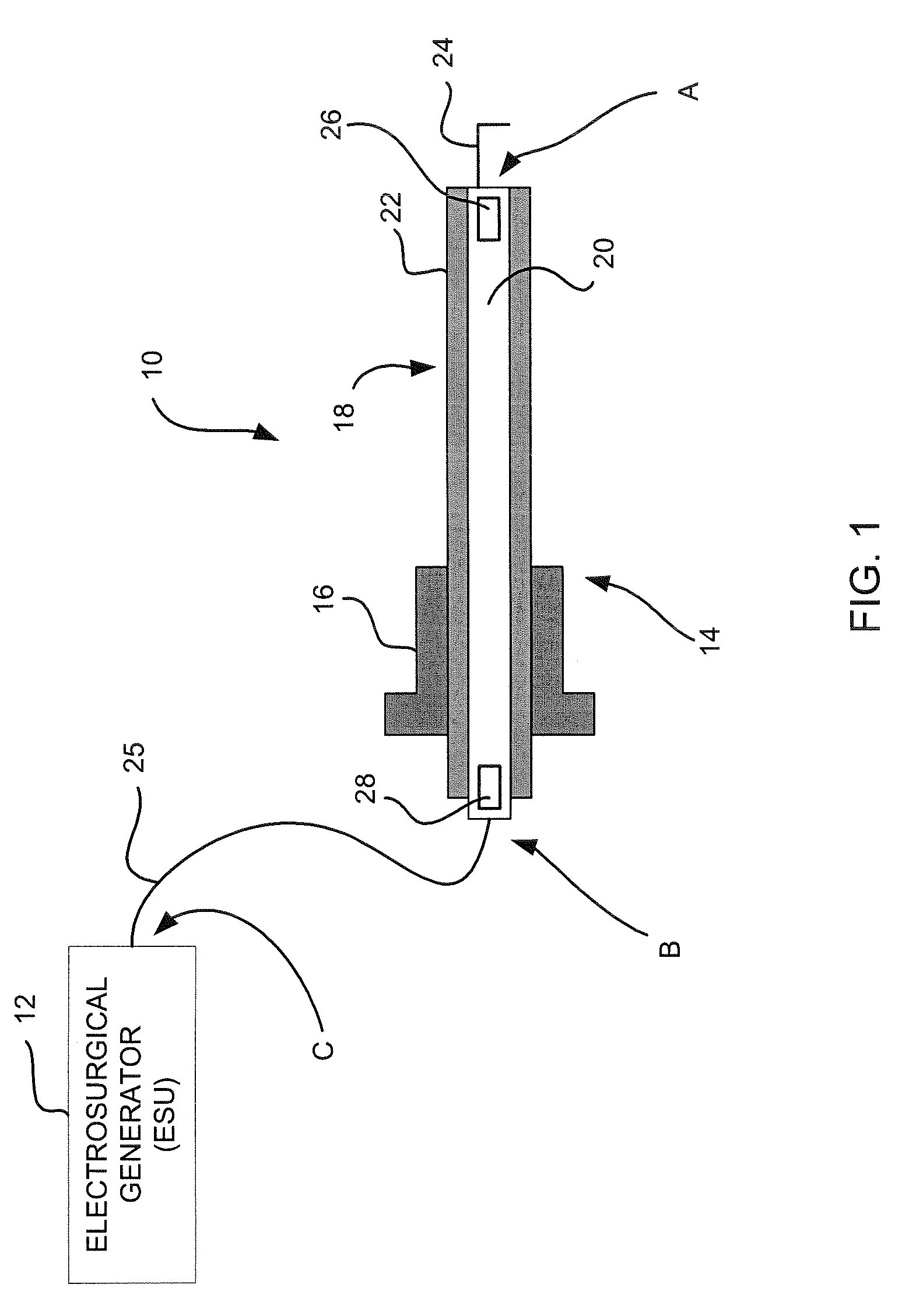
Laparoscopic electrosurgical electrical leakage detection
An electrical leakage detection method and system for use with laparoscopic electrosurgical instruments are provided. The present disclosure provides for an electrosurgical unit for providing electrosurgical energy at an active output thereof and for controlling the flow of the energy through the active output; an active electrode coupled to the active output for transmitting electrosurgical energy to a patient in an electrosurgical procedure; a first sensor disposed at a distal end of the active electrode and for outputting a first signal indicative of current measured at the distal end; a second sensor disposed at a proximal end of the active electrode and for outputting a second signal indicative of current measured at the proximal end; and a comparison circuit coupled to the first and second sensors for receiving the first and second signals and determining a difference value, the difference value being indicative of leakage current.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORPORATION
Electrosurgical devices, electrosurgical unit and methods of use thereof
Owner:MEDTRONIC ADVANCED ENERGY
Electrosurgical Generator to Ablation Device Adaptor
ActiveUS20120004703A1High voltage levelReduce the current levelElectrotherapySurgical needlesTransformerElectrosurgical unit
An electrosurgical system is provided that includes an electrosurgical generator configured to output a first electrosurgical waveform and a probe configured to deliver a second electrosurgical waveform to tissue. The system also includes an adapter coupled between the electrosurgical generator and the probe and operable to convert the first electrosurgical waveform to the second electrosurgical waveform. The adapter includes a step down transformer configured to convert the first electrosurgical waveform to the second electrosurgical waveform.
Owner:TRANSACTION HLDG L L C +1
Swivel device for improved surgical smoke evacuation
InactiveUS20140228839A1Maintains power and efficiency of vacuumPrevent leakageSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesOther medical devicesEngineeringElectrosurgical unit
A swivel device includes an improved connection between an electro-surgical unit (ESU) pencil's smoke evacuation system and a vacuum tube. The swivel device includes a fixed member attached to a rotating member. The rotating member allows the stiff vacuum tube to twist and coil freely while preventing forced movement of the fixed member or the ESU pencil. The swivel device can be added to existing ESU pencils with smoke evacuation systems or it can be built into ESU pencils with smoke evacuation systems.
Owner:IC MEDICAL INC
Electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation
ActiveUS9833282B2Simple electrode structureEasy to liftSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingMedicineSaline solutions
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Connection of a bipolar electrosurgical hand piece to a monopolar output of an electrosurgical generator
InactiveUS20120095457A1Instrument handpiecesSurgical instruments for heatingBipolar electrosurgeryActive component
A method and apparatus for operatively connecting a bipolar electrosurgical hand piece to a monopolar output of an electrosurgical unit wherein active components simulate expected impedance characteristics of monopolar return electrodes connected to a patient.
Owner:NUORTHO SURGICAL
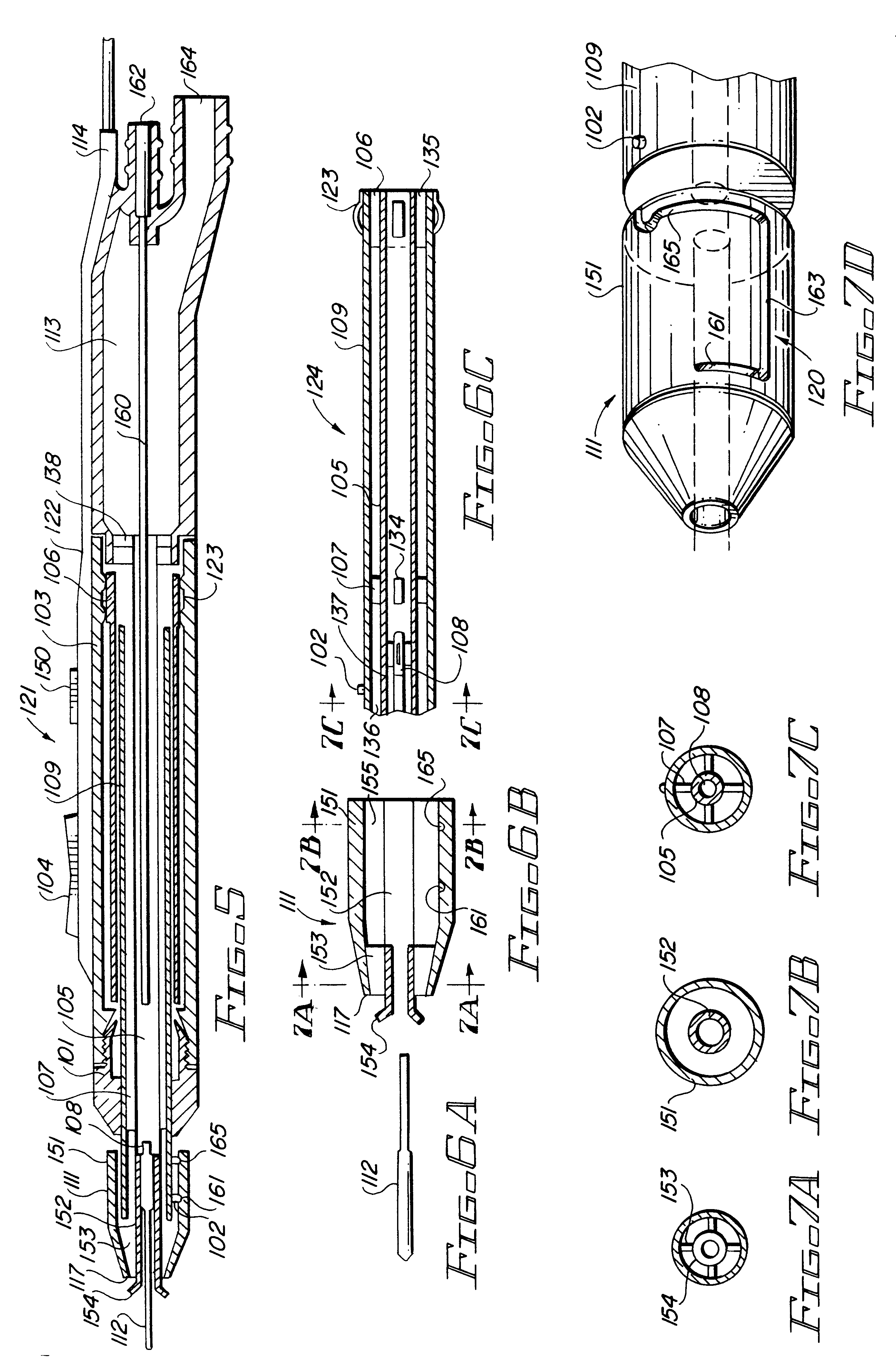
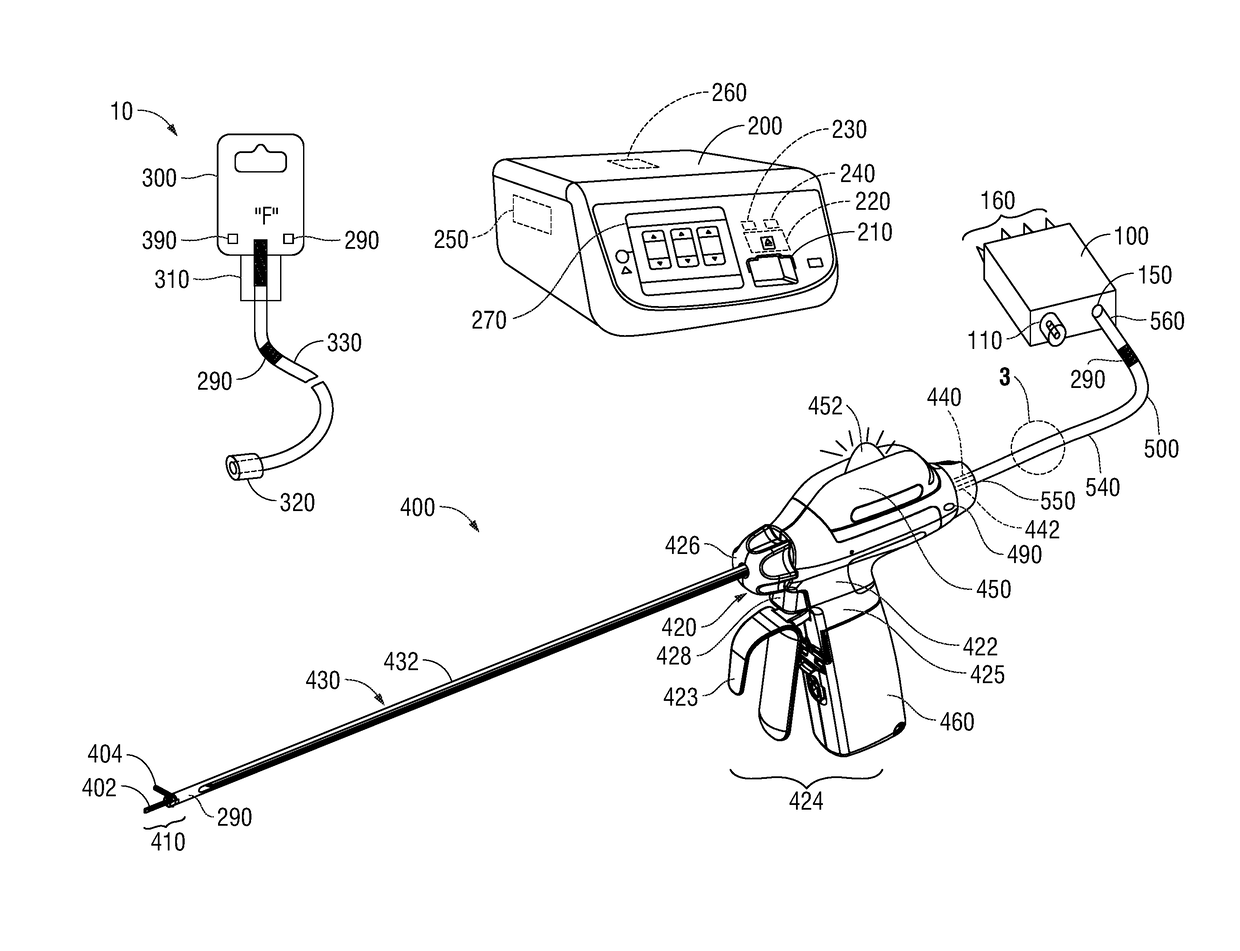
Devices, systems, and methods for establishing electrical and fluid connections to surgical instruments
A cartridge includes an electrical connection assembly, a first port, a second port, a pumping mechanism, a valve, and a fluid flow sensor. The electrical connection assembly is configured to electrically couple to an electrosurgical unit. The first port is configured to fluidly couple to a fluid source. The second port is configured to fluidly and electrically couple to a surgical instrument. The pumping mechanism is disposed between the first and second ports and is configured to draw fluid from the fluid source and pump the fluid to the surgical instrument. The valve is disposed between the first and second ports and is configured to selectively obstruct the flow of the fluid therethrough. The fluid flow sensor is disposed between the first and second ports and is configured to sense fluid flow therethrough. The fluid flow sensor is configured to electrically communicate with the electrosurgical unit.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electrode for radiofrequency tissue
ActiveCN101579257AExtended area of ablative necrosisSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingSaline solutionsElectrosurgical unit
The present invention relates to an electrode for an electrosurgical unit for the use in ablating and necrosing a living tissue by RF electric energy. The present invention provides an electrode for an electrosurgical unit, including: a hollow electrode formed in an elongated hollow tube shape, a non-insulating region of a predetermined length being formed on one side of which, an insulating region being formed on an outer surface of which other than the non-insulating region; a saline solution circulation structure that supplies pressurized saline solution for cooling a living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode from the outside of the living tissue to the inside of the hollow electrode, and discharges the pressurized saline solution from the inside of the hollow electrode to the outside of the living tissue; and one or more saline solution discharge holes formed in the non-insulating region of the hollow electrode to discharge some of the circulating pressurized saline solution to the living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode.
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Nerve monitoring during electrosurgery
A signal processing module includes an input module electronically coupled to a sensing probe (52) of a nerve integrity monitoring system (10). The probe senses electrical signals from a patient during operation of an electrosurgical unit (12). The input module receives an input signal from the probe. An EMG detection module is coupled to the input module and is adapted to detect conditions in the input signal. The conditions are classified as a function of a level of electromyographic activity. An output module, coupled to the EMG detection module, provides an indication of electromyographic activity in the input signal based on the detected conditions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Laparoscopic Electrosurgical Electrical Leakage Detection
An electrical leakage detection method and system for use with laparoscopic electrosurgical instruments are provided. The present disclosure provides for an electrosurgical unit for providing electrosurgical energy at an active output thereof and for controlling the flow of the energy through the active output; an active electrode coupled to the active output for transmitting electrosurgical energy to a patient in an electrosurgical procedure; a first sensor disposed at a distal end of the active electrode and for outputting a first signal indicative of current measured at the distal end; a second sensor disposed at a proximal end of the active electrode and for outputting a second signal indicative of current measured at the proximal end; and a comparison circuit coupled to the first and second sensors for receiving the first and second signals and determining a difference value, the difference value being indicative of leakage current.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORPORATION
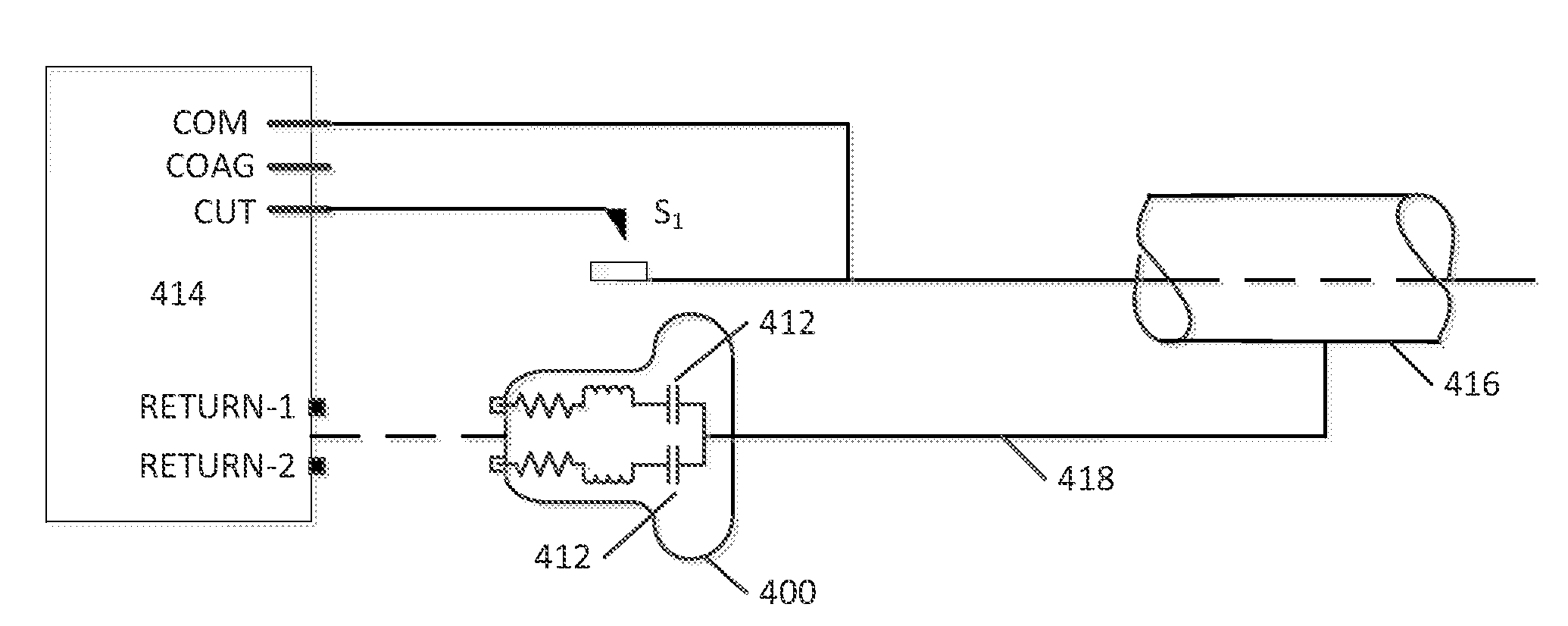
Indifferent electrode pad systems and methods for tissue ablation
InactiveUS20110238058A1Good effectEfficient use ofSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringElectrosurgical unit
Systems and methods for transmitting energy through patient tissue involve the use of an indifferent pad assembly in conjunction with an ablation probe. Systems may include an electrical surgical unit having a power output connector, a first power return connector, and a second power return connector. Systems may also include an ablation probe coupleable with the power output connector of the electrical surgical unit, and an indifferent pad assembly having a conductive mechanism coupled with an electrical and thermal insulator mechanism, and a wire assembly coupled with the conductive mechanism. The wire assembly can include a first connector coupleable with the first power return connector of the electrical surgical unit, and a second connector coupleable with the second power return connector of the electrical surgical unit.
Owner:ATRICURE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com