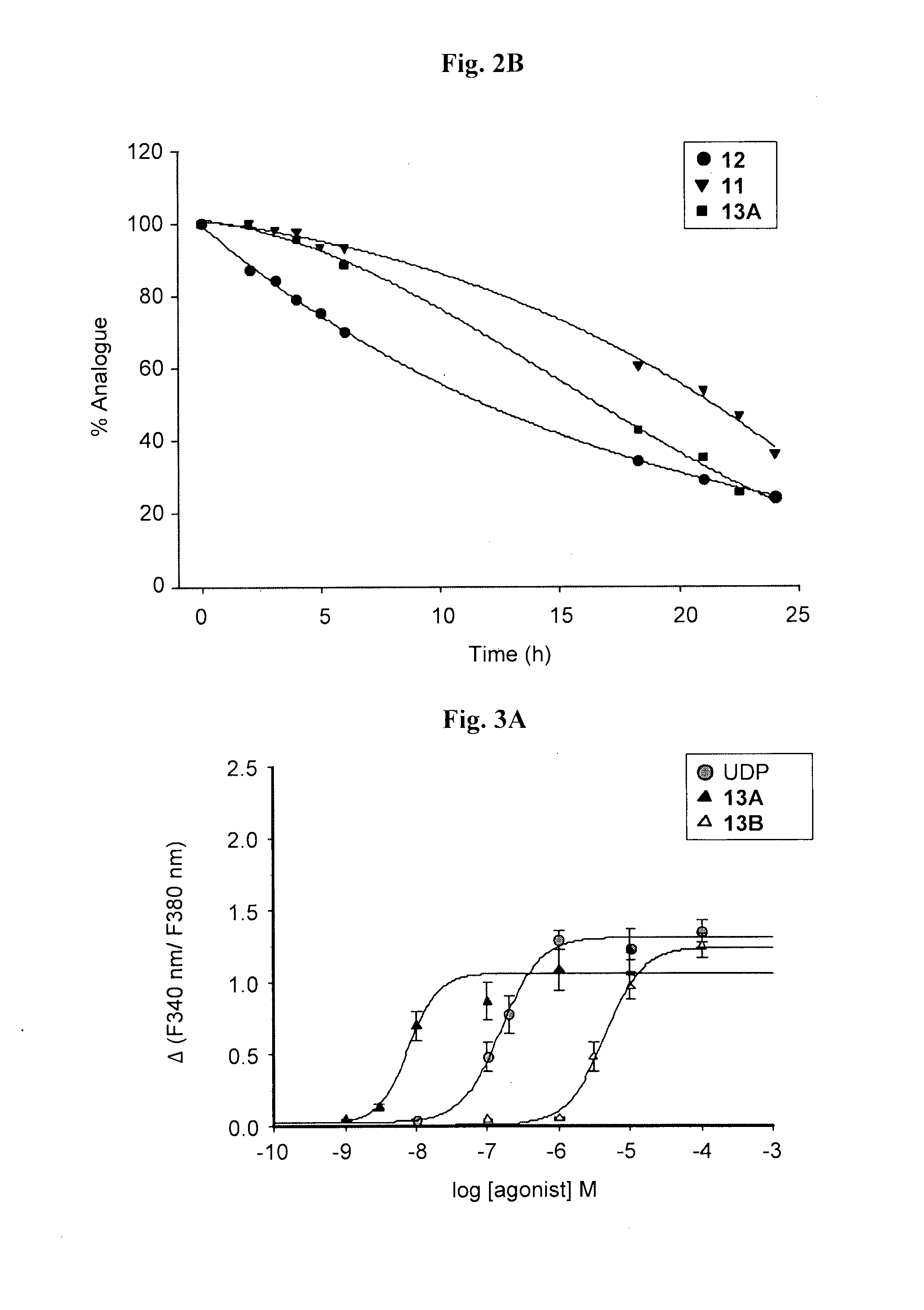
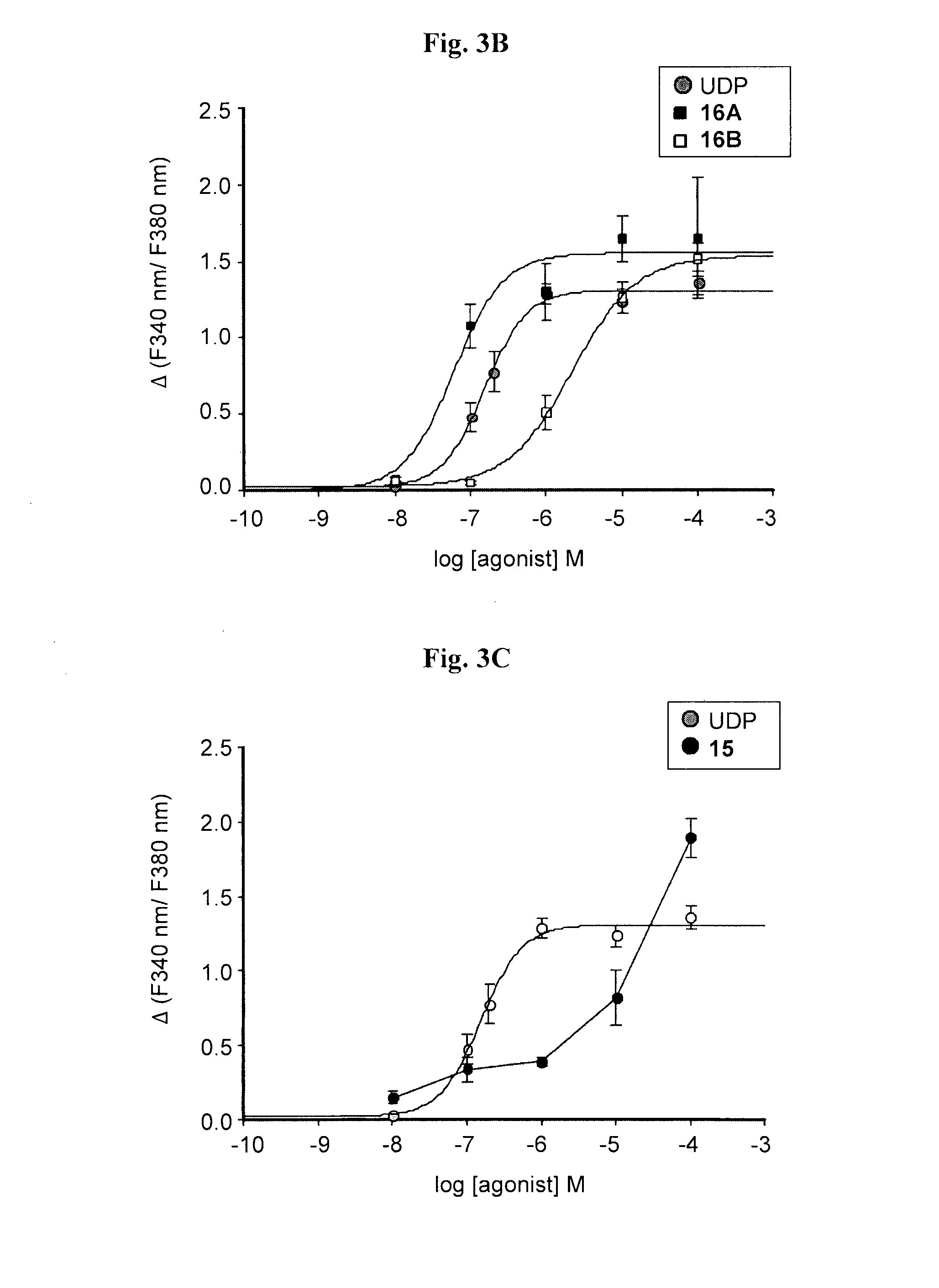
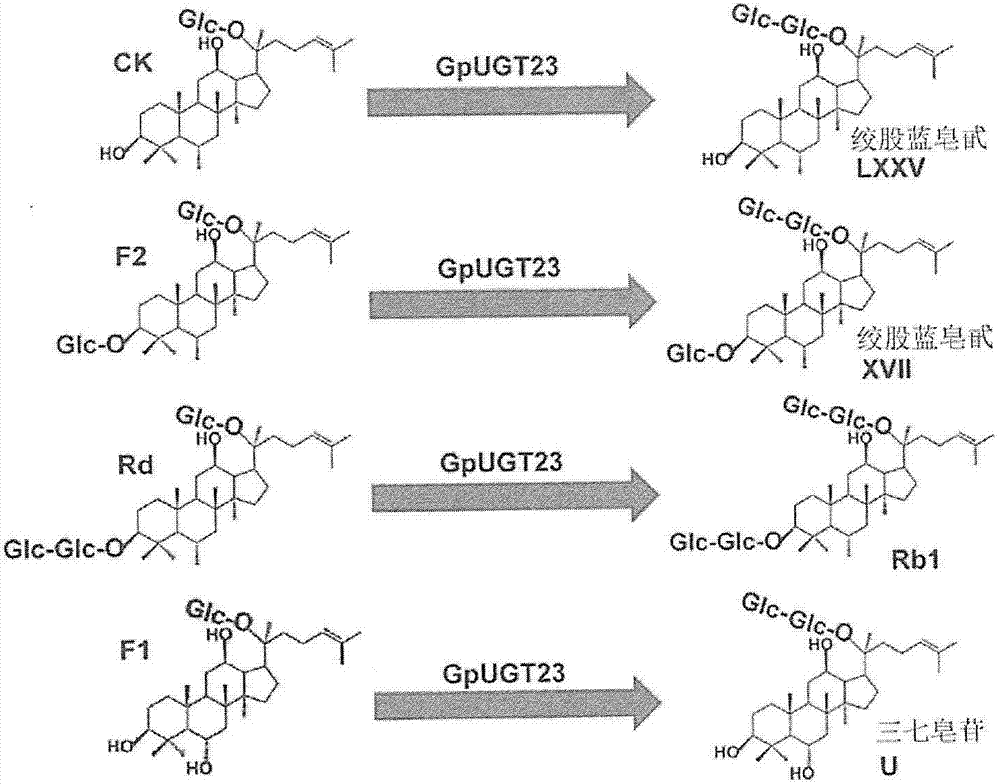
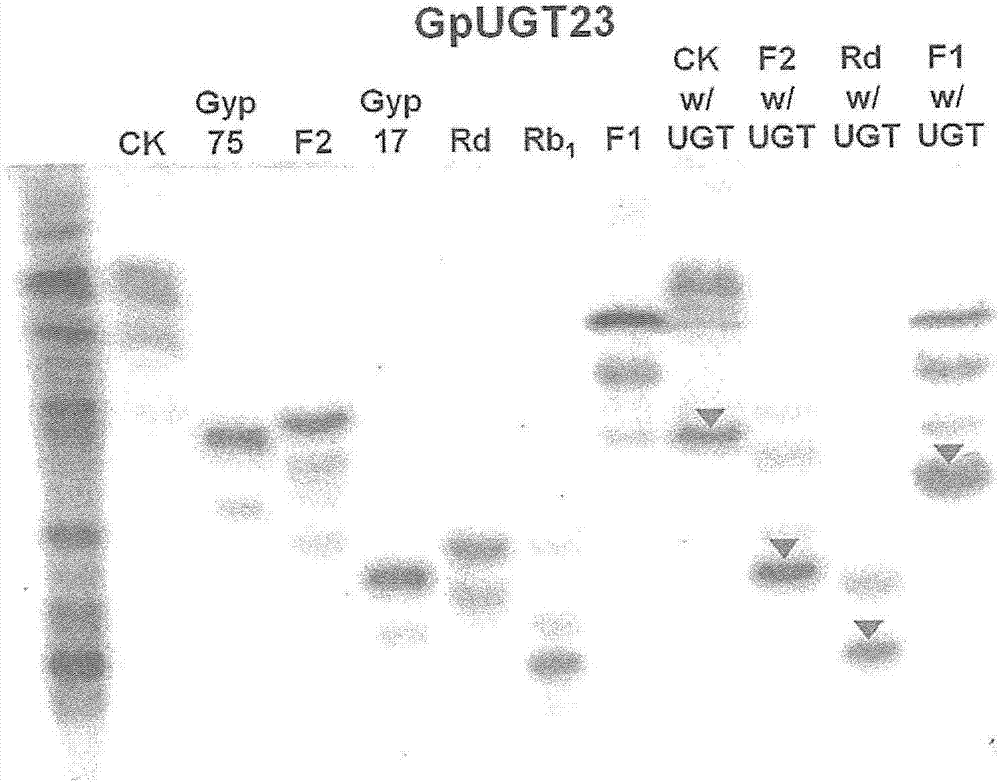
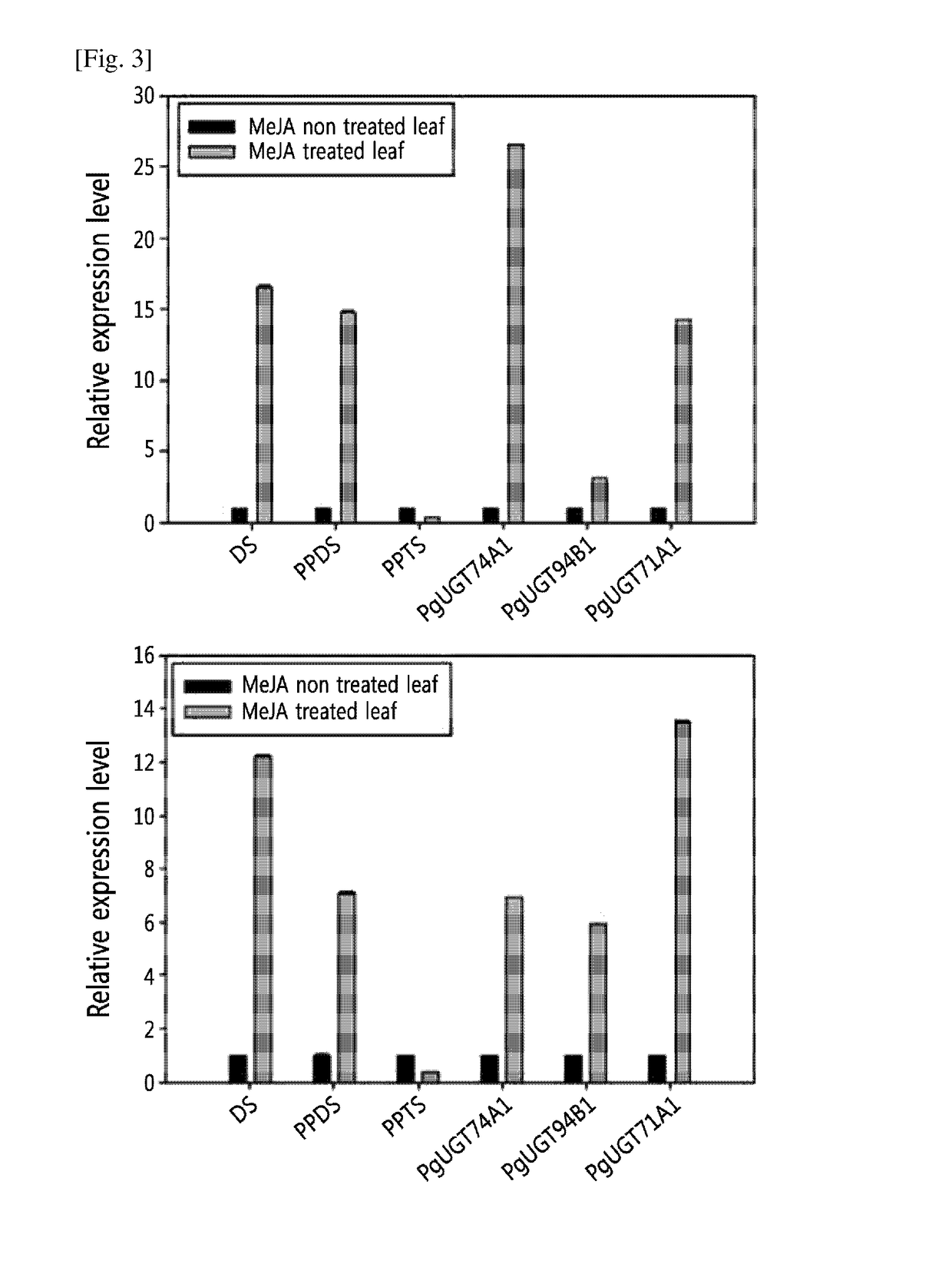
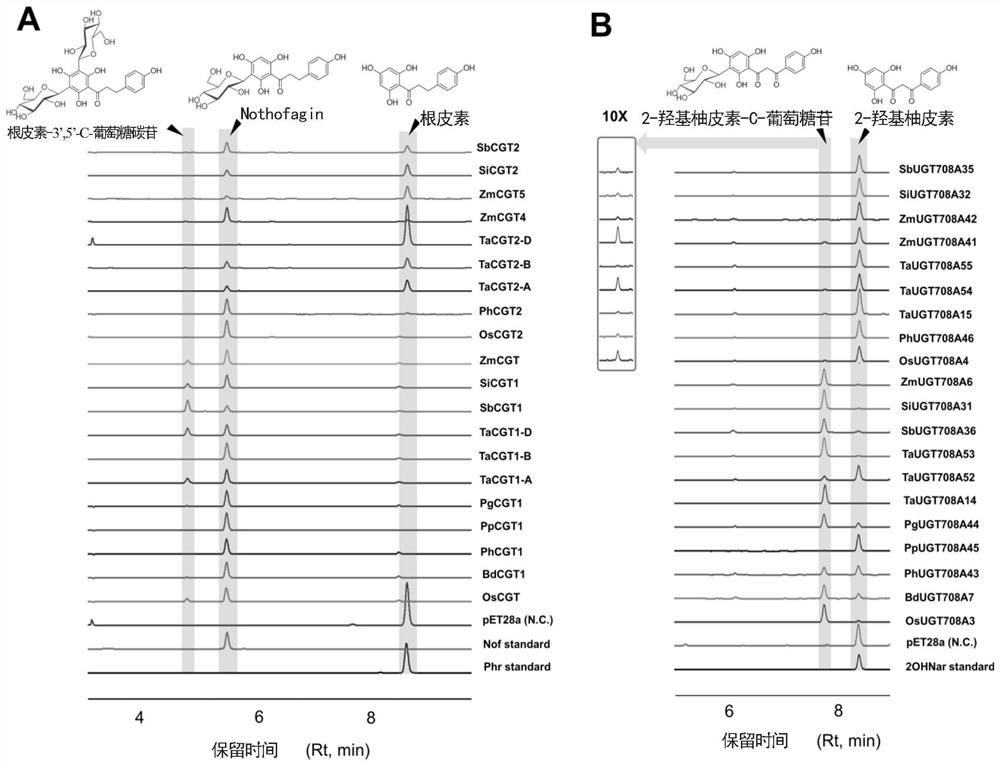
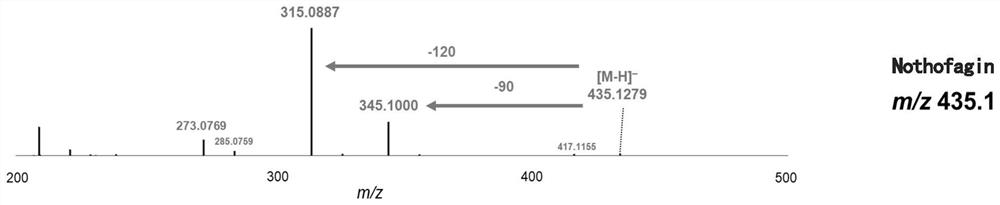
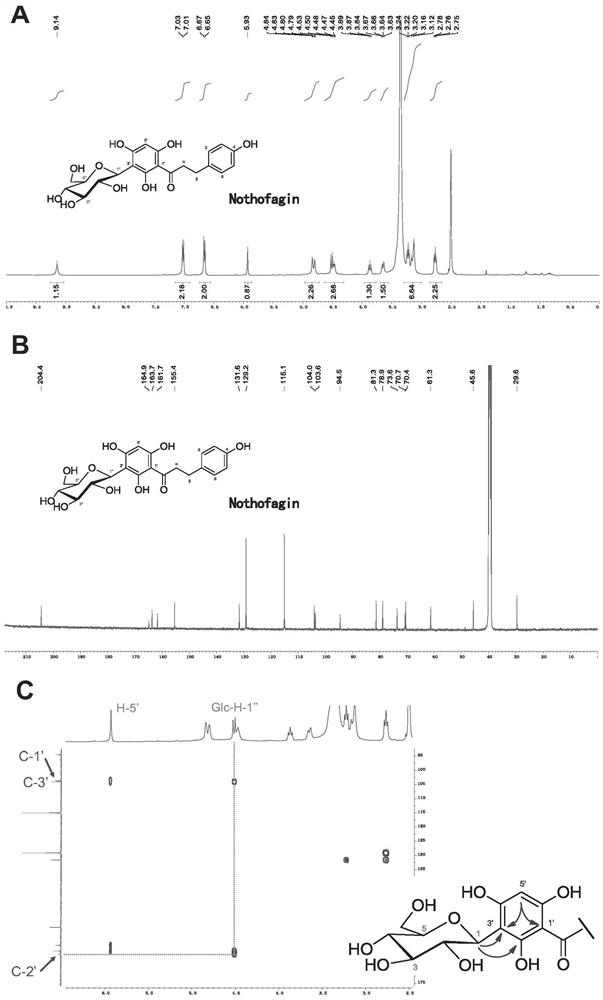
Patents
Literature
97 results about "Uridine diphosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
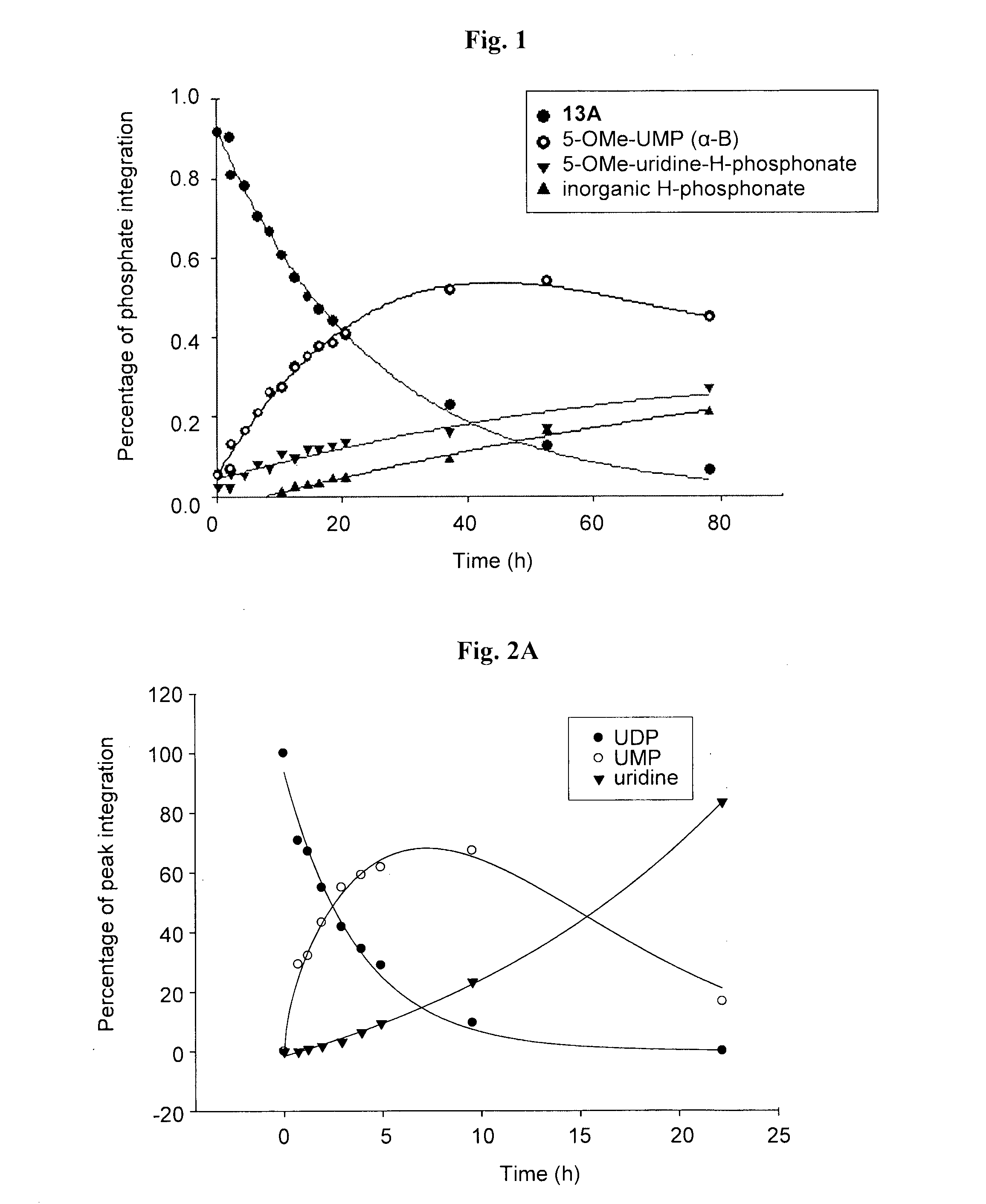
Uridine diphosphate, abbreviated UDP, is a nucleotide diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil.
Pharmacogenetic DME detection assay methods and kits
InactiveUS20060160074A1Increase nucleic acid synthesis reaction rateHeating evenlySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug metabolismPharmacogenetics
The present invention relates to methods for detecting polymorphisms in enzymes related to drug metabolizm (Drug Metabolizing Enzymes or DMEs) such as uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) gene promoter, cytochrome p450, with a non-amplified oligonucleotide detection assays. The present invention also relates to pharmacogenetic DME detection assay kits.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
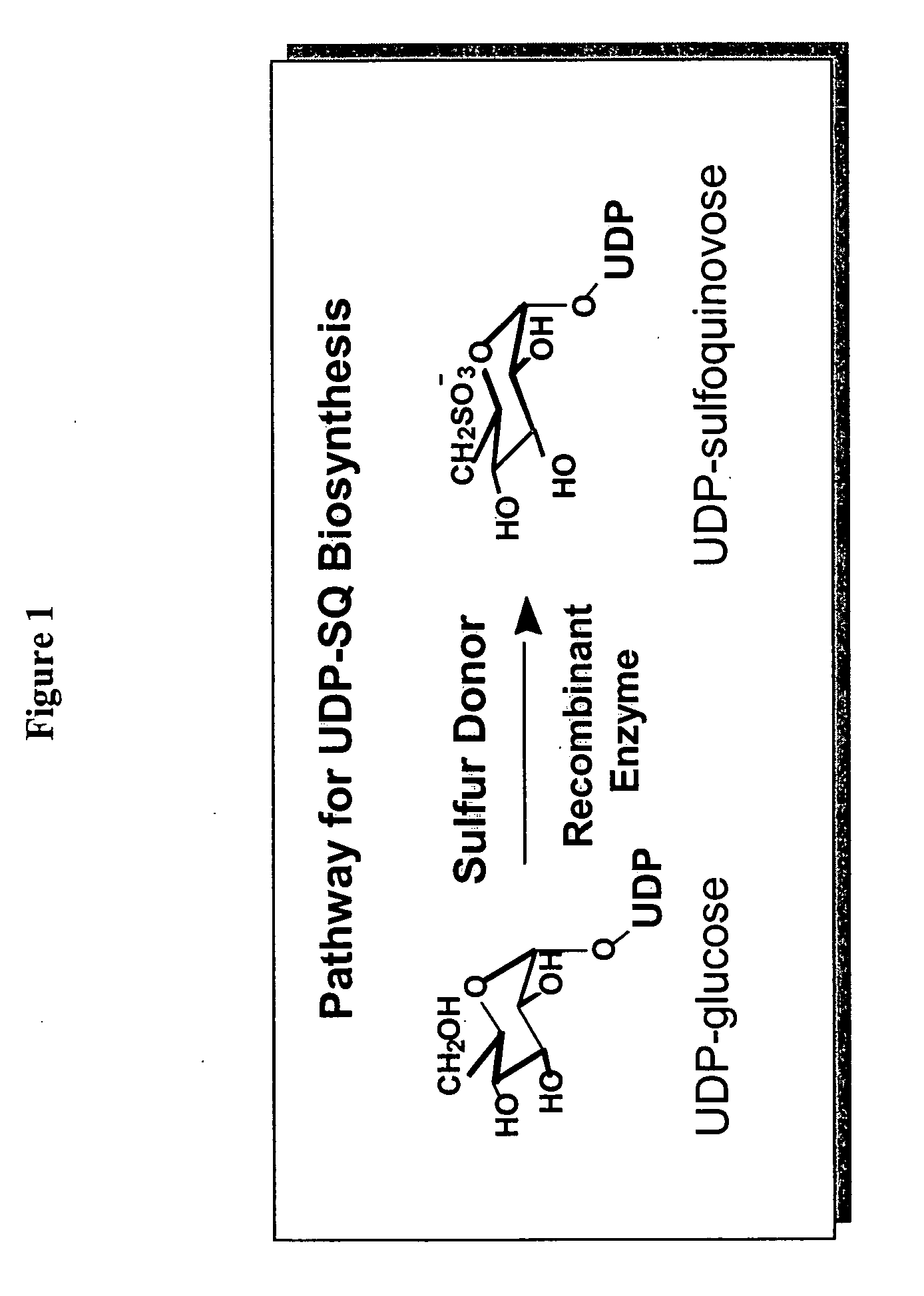
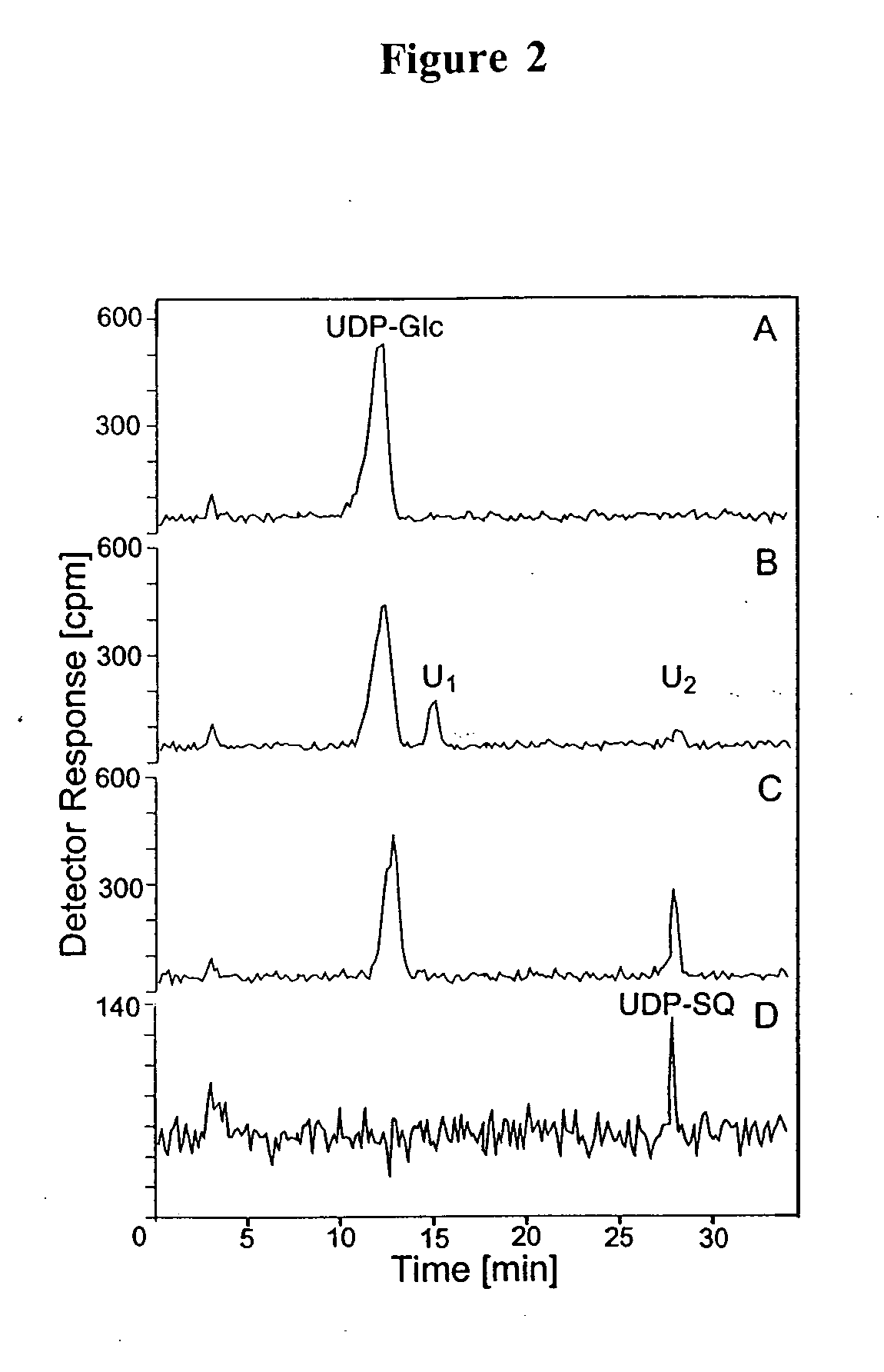
Compositions and methods for the synthesis and subsequent modification of uridine-5'-diphosphosulfoquinovose (UDP-SQ)
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods related to the synthesis and modification of uridine-5′-diphospho-sulfoquinovose (UDP-SQ). In particular, the methods of the present invention comprise the utilization of recombinant enzymes from Arabidopsis thaliana, UDP-glucose, and a sulfur donor to synthesize UDP-SQ, and the subsequent modification of UDP-SQ to form compounds including, but not limited to, 6-sulfo-α-D-quinovosyl diaclyglycerol (SQDG) and alkyl sulfoquinovoside. The compositions and methods of the invention provide a more simple, rapid means of synthesizing UDP-SQ, and the subsequent modification of UDP-SQ to compounds including, but not limited to, SQDG.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
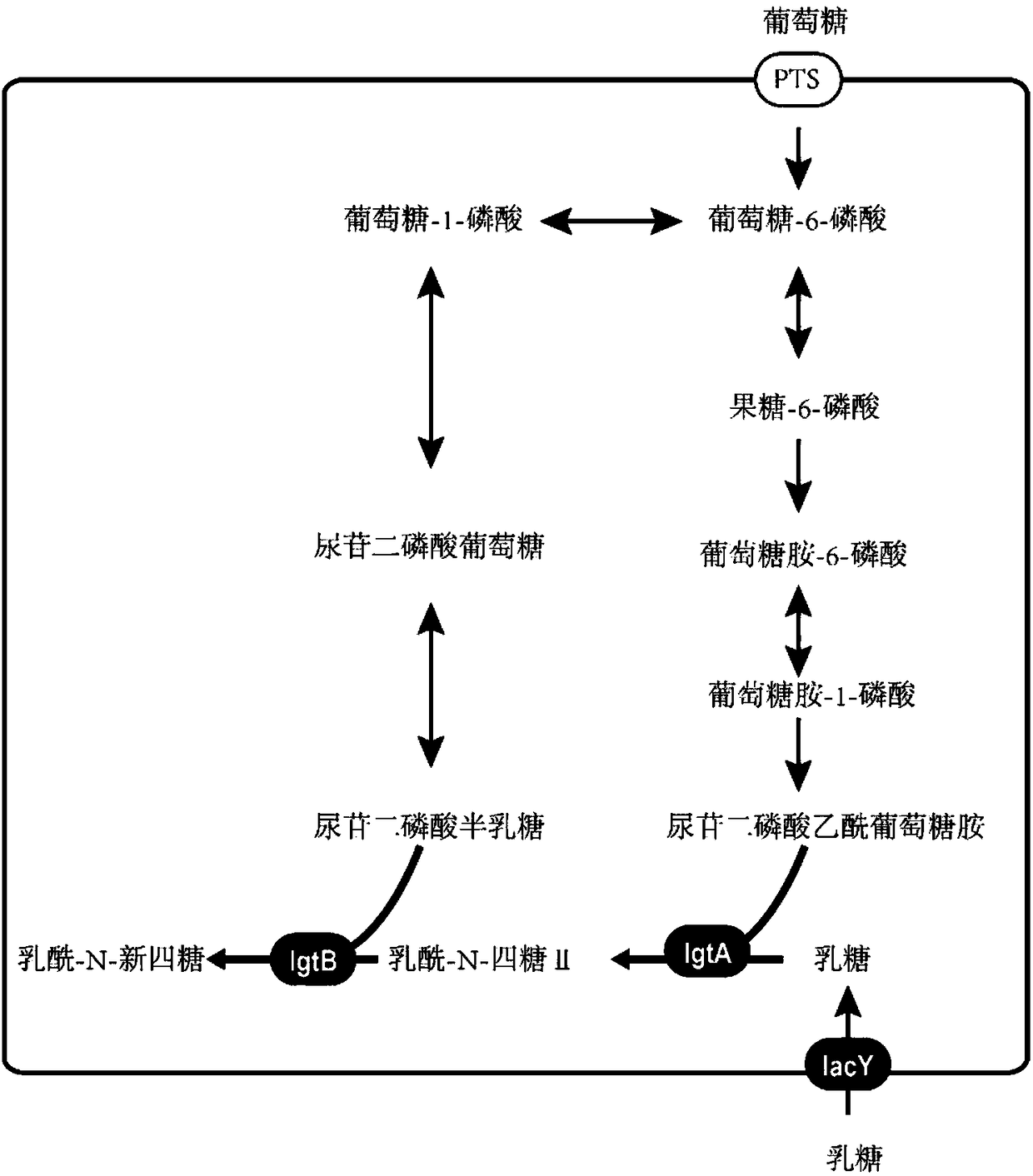
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lactyl-N-neotetraose and construction method and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis
The invention provides recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lactyl-N-neotetraose. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is integrated with lactose permease genes in a recombinant manner on bacillus subtilis 168 genome and converts plasmids which contain beta-1,3-N-glucoaminotransferase genes and beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase gene in bacillus subtilis 168. Uridine diphosphate galactose and acetylglucosamine uridine diphosphate in a metabolic pathway of the bacillus subtilis are used as precusor substances, lactose only needs to be added exogenously and is transferred into cells under theeffect of lactamase to synthesize the lactyl-N-neotetraose which is secreted to ectoenzyme. The accumulation amount of the lactyl-N-neotetraose synthesized by the recombinant bacillus subtilis reaches 1071 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for production of the lactyl-N-neotetraose through further metabolic engineering modified bacillus subtilis.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
Novel catalytic system for preparing rare ginsenosides and application thereof
ActiveCN105087739AHigh catalytic efficiencyReduce use costFungiBacteriaSucrose synthetaseProtopanaxadiol
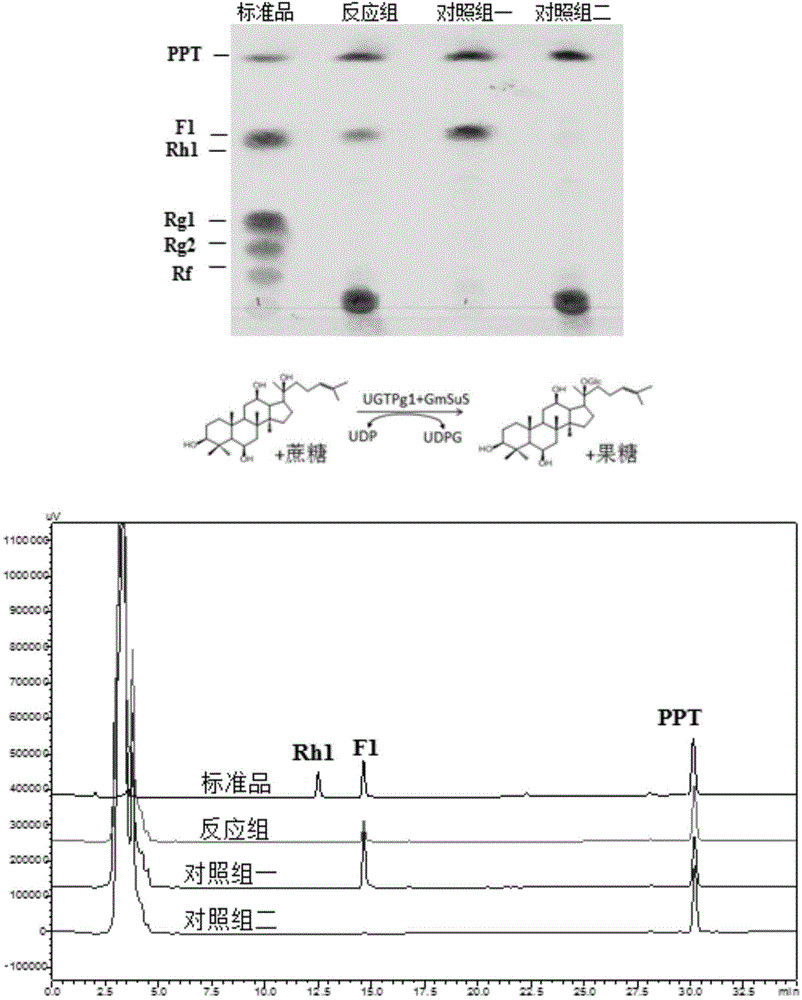
The invention discloses a co-catalytic reaction system for preparing rare ginsenosides. The co-catalytic reaction system comprises glycosyltransferase GT (a); sucrose synthase SUS (b); uridine diphosphate UDP (c); and saccharose (d). Experiments show that in the presence of the saccharose and little UDP, an enzyme combination composed of the glycosyltransferase and the saccharose is capable of replacing an in-vitro reaction system to synthesize UDP sugar, one of expensive materials for the rare ginsenosides, and efficiently and economically converting substrates such as protopanoxadiol or protopanaxatriol into the rare ginsenosides, wherein the UDP is about 1 / 4 of the UDP sugar in price and is 1% of its original dosage; thus, preparation cost of the rare ginsenosides is greatly saved, and large-scale commercial preparation of the ginsenosides is better facilitated.
Owner:SYNBIOTECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
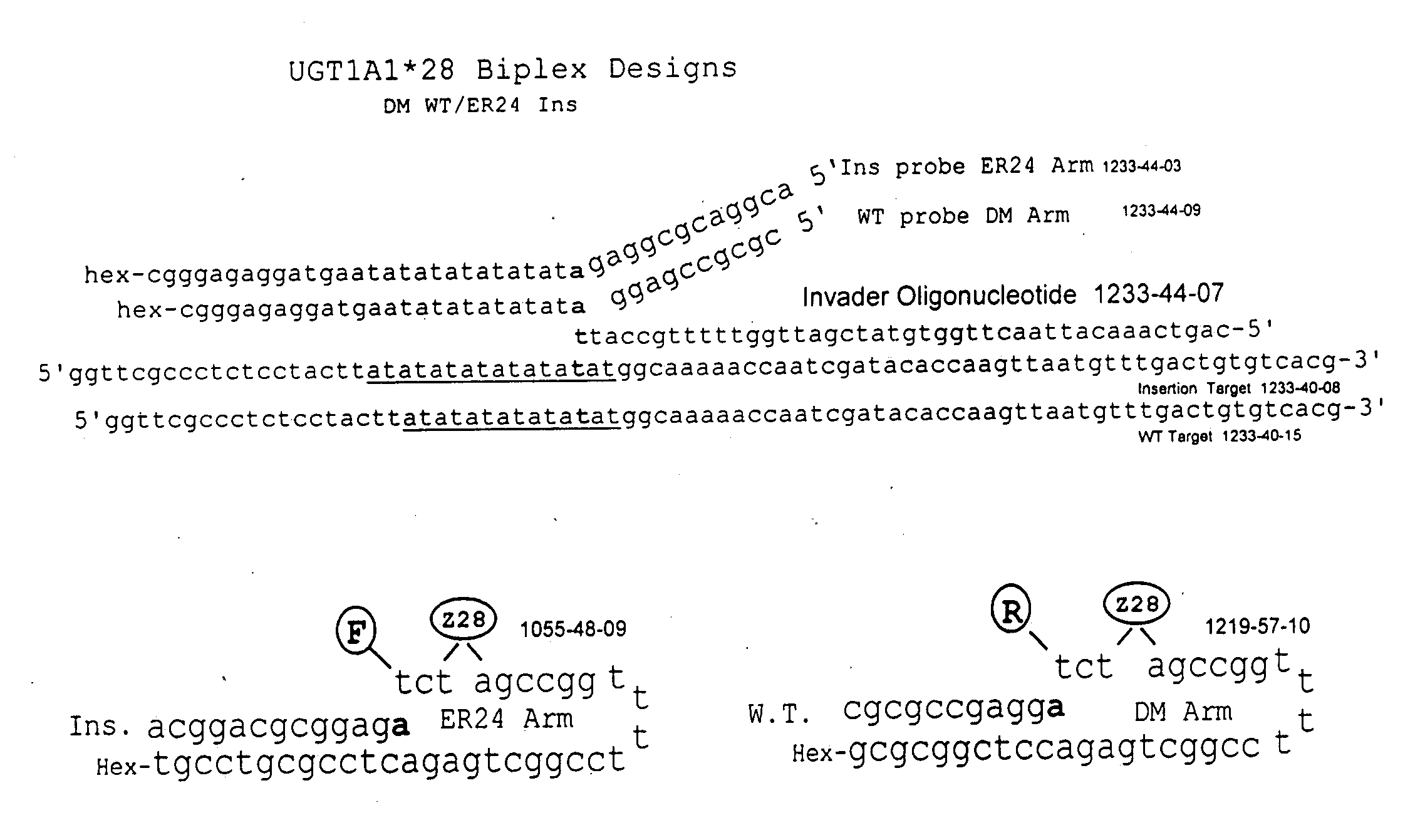
Methods and compositions for analysis of UGT1A1 alleles
InactiveUS20080032305A1Facilitate drug therapyConvenient treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug metabolismNucleic acid detection
The present invention relates to methods for detecting polymorphisms in enzymes related to drug metabolizm (Drug Metabolizing Enzymes or DMEs) such as uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) gene promoter, with nucleic acid detection assays. The present invention also relates to detection assay kits.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase, coding gene thereof and use thereof
InactiveCN101698839AIncrease the lengthImprove qualityMicroorganismsIsomerasesIsomeraseUridine diphosphate
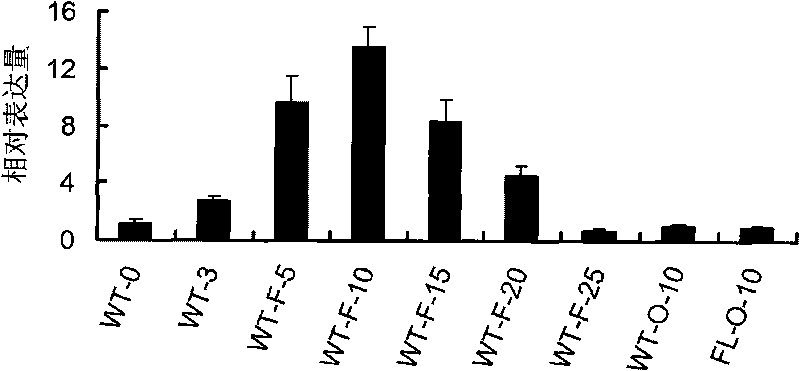
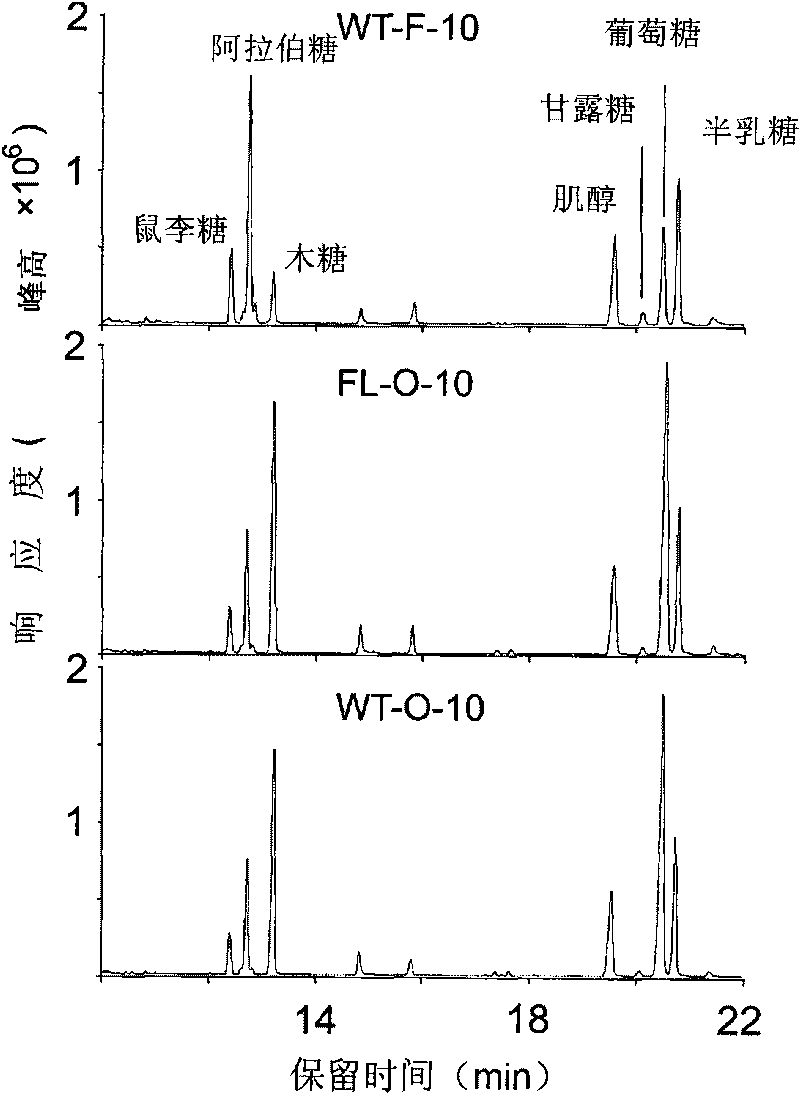
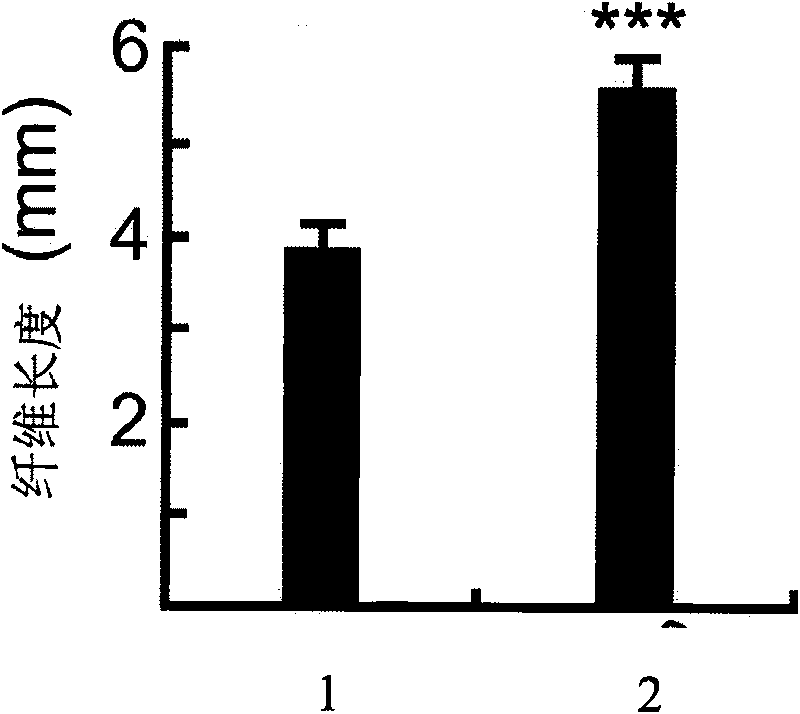
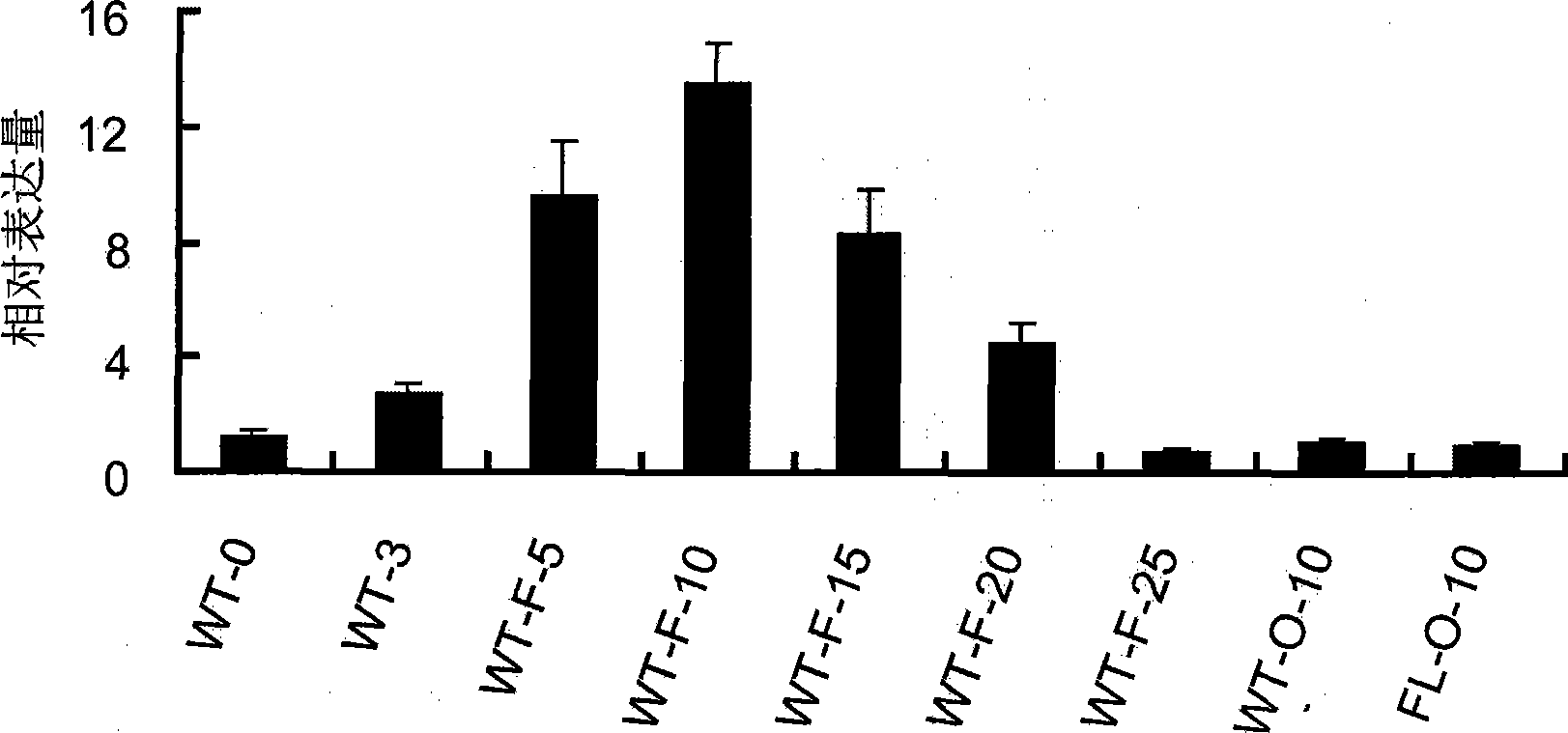
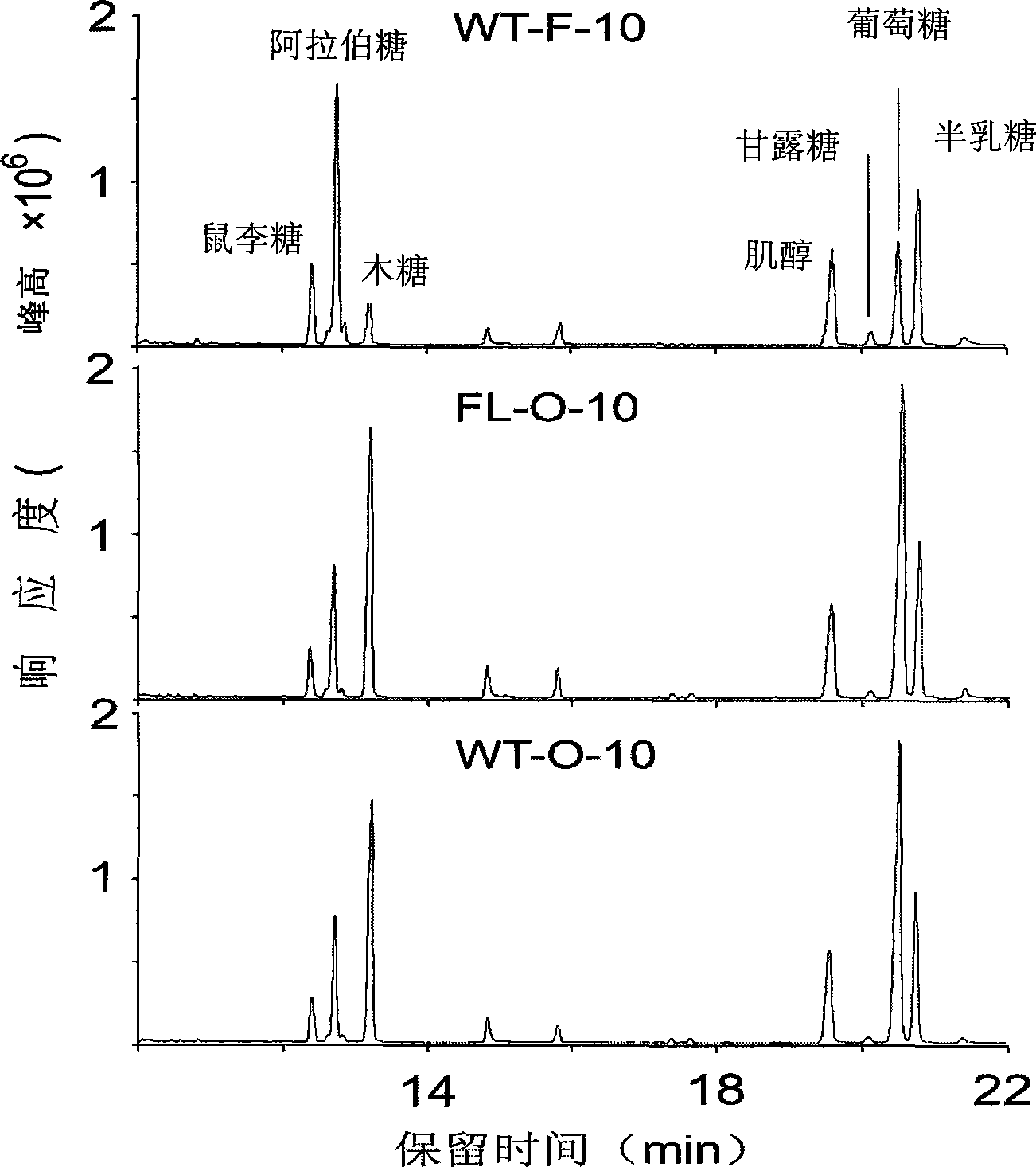
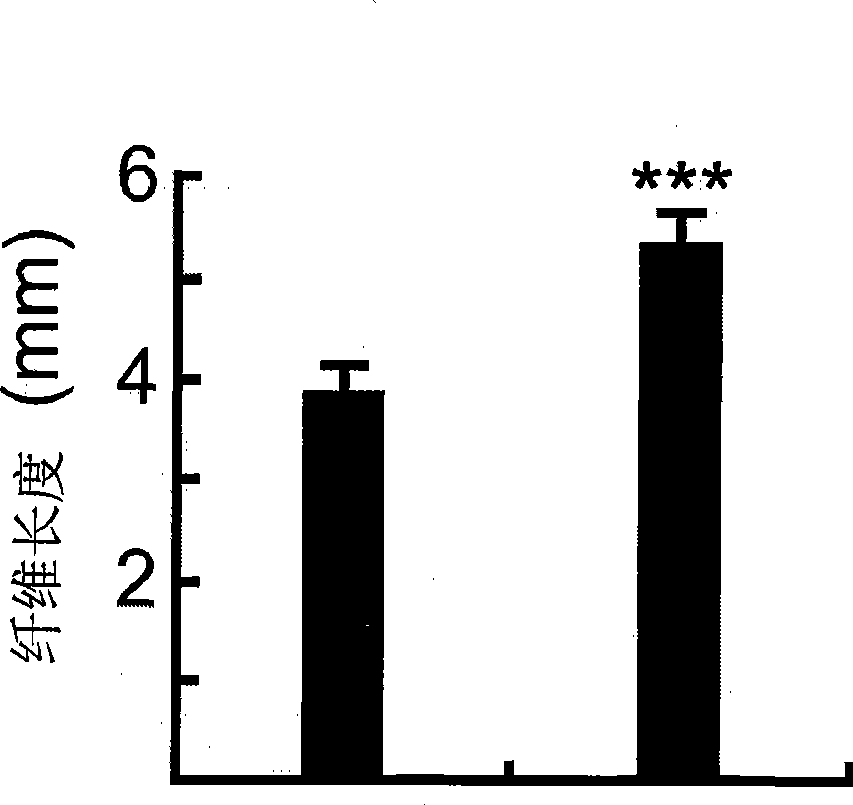
The invention discloses a uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase, a coding gene thereof and use thereof. The uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase is a protein a or a protein b, wherein the protein a has an amino acid sequence represented by the No.2 sequence in a sequence table; and the protein b is derived from the protein a by substituting and / or losing and or adding one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence represented by the No.2 sequence in the sequence table and is related to the synthesis of the uridine diphosphate arabinose. The invention also discloses a coding gene for coding the protein. The coding gene of the uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase can be introduced into cotton to lengthen cotton fibers and improve the quality and yield of cotton fibers. The uridine diphosphate xylose isomerase and the coding gene thereof have great economic values and application prospects.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
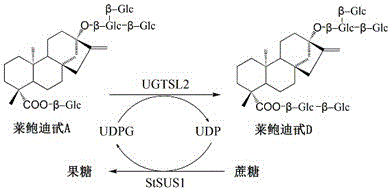
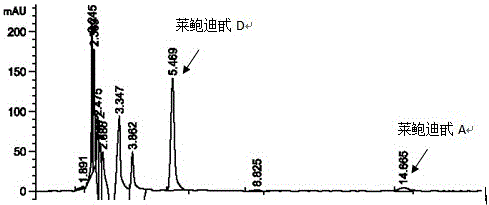
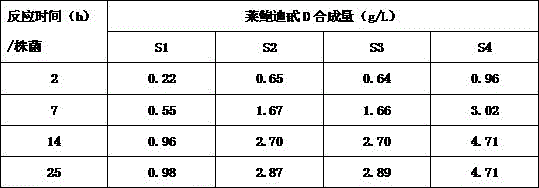
Recombinant bacterium and application of recombinant bacterium to generation of rebaudioside D by catalyzing rebaudioside A
ActiveCN106754595AAvoid separation and purificationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetaseRebaudioside D
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium and application of the recombinant bacterium to the generation of rebaudioside D by catalyzing rebaudioside A. The recombinant bacterium contains a tomato-derived glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene and a potato-derived sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene; the tomato-derived glycosyltransferase UGTSL2 gene is cloned between NdeI and XhoI sites of pRSFDuet-1 to construct a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2; then the potato-derived sucrose synthase StSUS1 gene is cloned between NcoI and EcoRI sites of the pRSFDuet-SL2 to construct a recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1; the recombinant plasmid pRSFDuet-SL2-SUS1 is transferred into a host cell to obtain the recombinant bacterium. After the recombinant bacterium is subjected to induction expression, the recombinant bacterium is added into a reaction mixture to catalyze the rebaudioside A to generate the rebaudioside D; in reaction, crude enzyme liquid obtained by crushing the recombinant bacterium is utilized and separation and purification of an enzyme are avoided; lyophilized powder does not need to be produced; UDP (Uridine Diphosphate) or UDP-glucose and any cell penetration agent or other chemical reagents do not need to be added into a reaction solution, so that the recombinant bacterium has a better environment-friendly property. The yield of the rebaudioside D can reach 10.8g / L.
Owner:XINGHUA GL STEVIA CO LTD
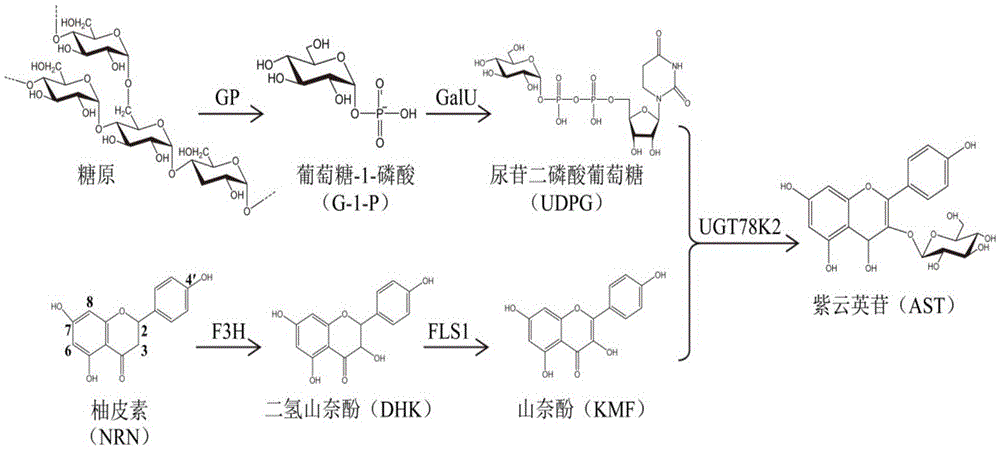
Method for enzymatically synthesizing astragalin
InactiveCN105463044AFew stepsMild operating conditionsFermentationEnzymatic synthesisDihydro-kaempferol
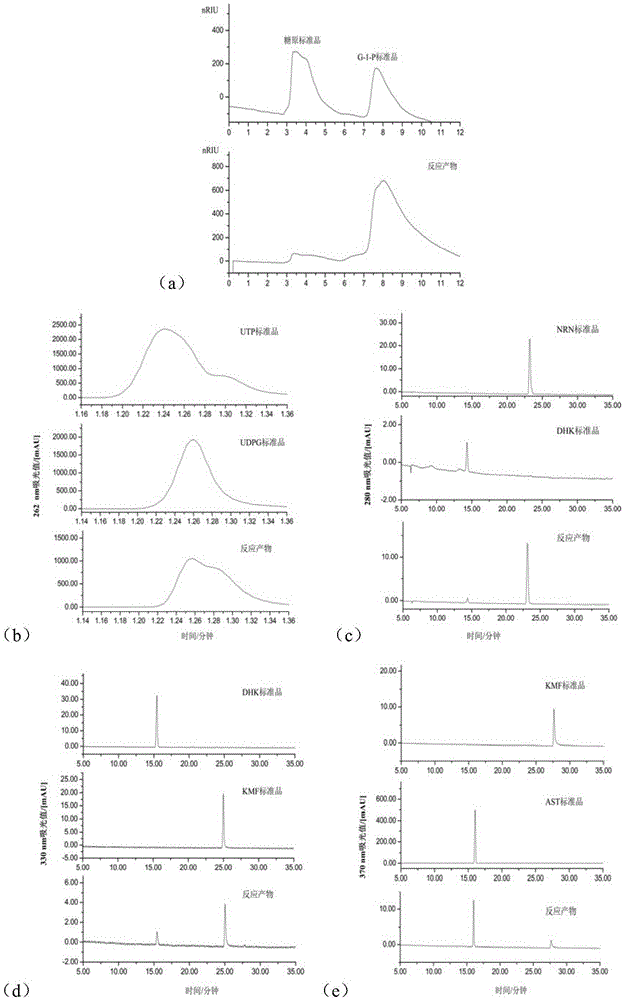
The invention provides a method for enzymatically synthesizing astragalin. The method comprises the following steps that 1, key enzymes needed in the synthesizing process of astragalin are cloned, expressed and purified, wherein the key enzymes comprise glycogen phosphorylase GP, glucose pyrophosphorylase GalU, flavanone-3-hydroxylase F3H, flavanone synthase FLS1 and flavonoid3-O-glucanotransferase UGT78K2; 2, glycogen Gn is synthesized into glucose-1-phosphoric acid G-1-P under the GP effect; 3, G-1-P is synthesized into uridine diphosphate UDPG under the GalU effect; 4, naringenin NRN is synthesized into dihydro kaempferol DHK under the F3H effect; 5, DHK is synthesized into kaempferol KMF under the FLS1 effect; 6, KMF and UDPG are synthesized into astragalin under the UGT78K2 effect. According to the method, few steps are adopted, the operation condition is mild, few side products are generated, the yield is large, pollution is avoided, and the production cost is remarkably reduced.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing uridine diphosphate
InactiveCN1962875AReduce the burden onShorten the timeMicroorganism based processesFermentationYeastPhosphoric acid
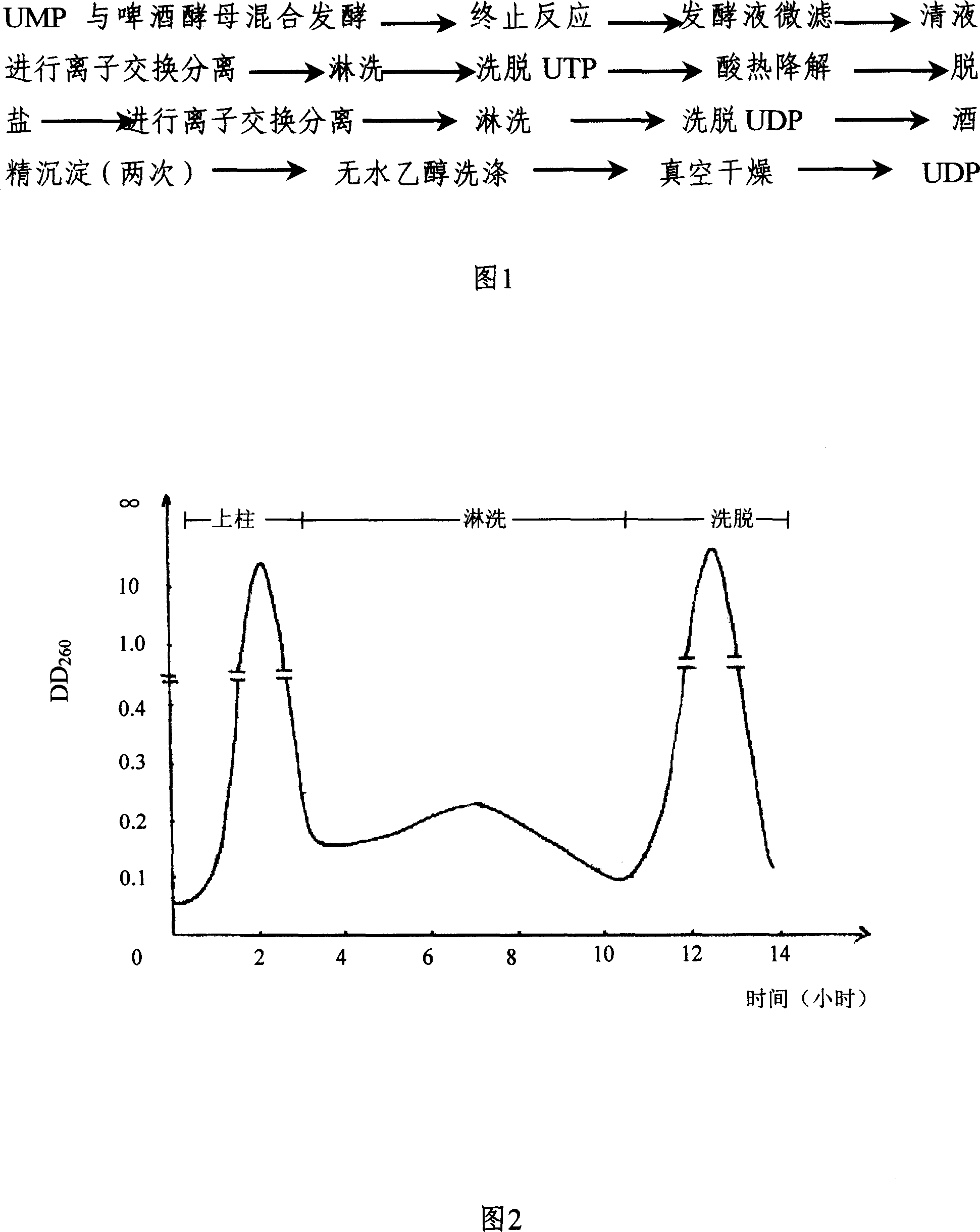
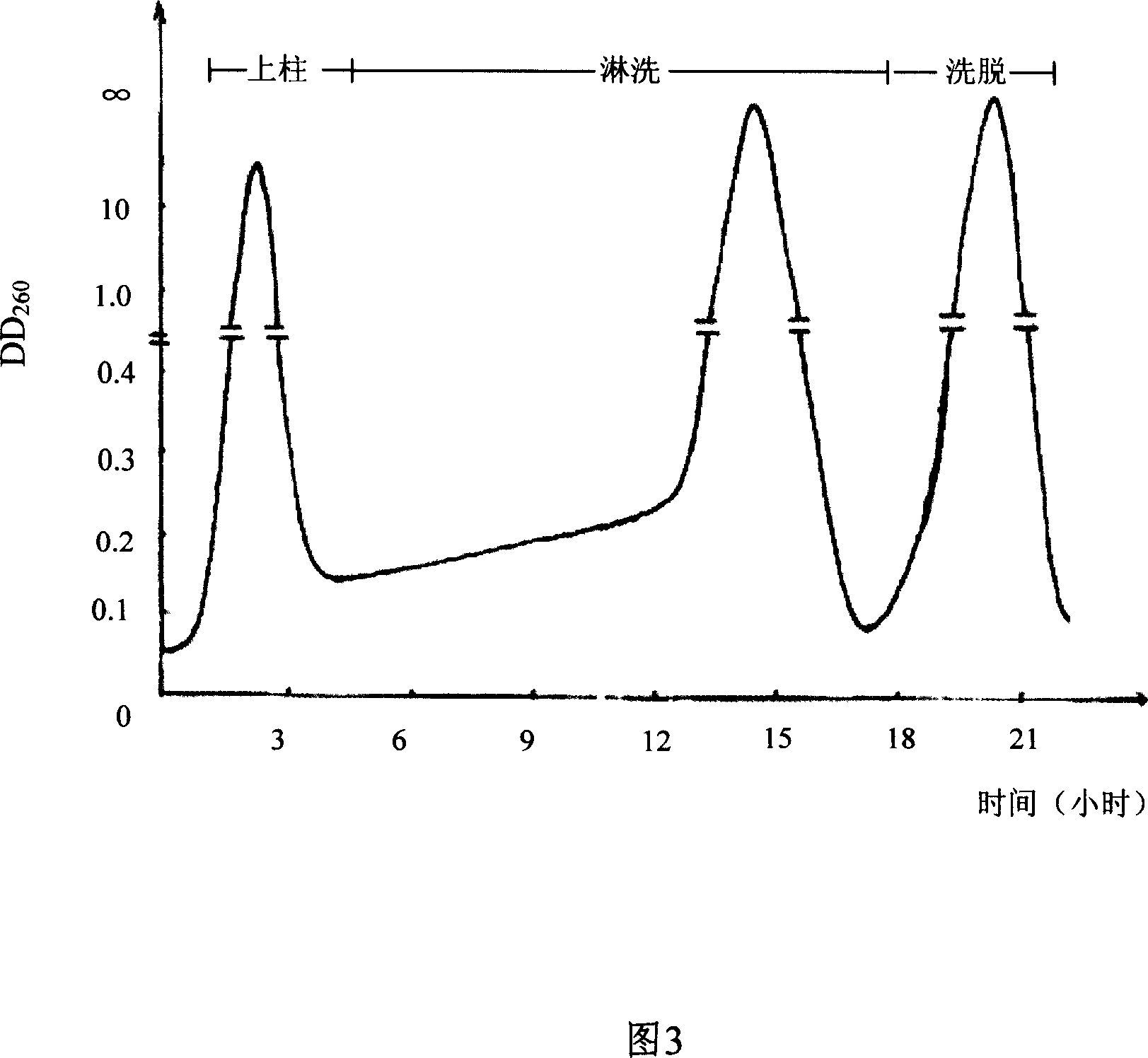
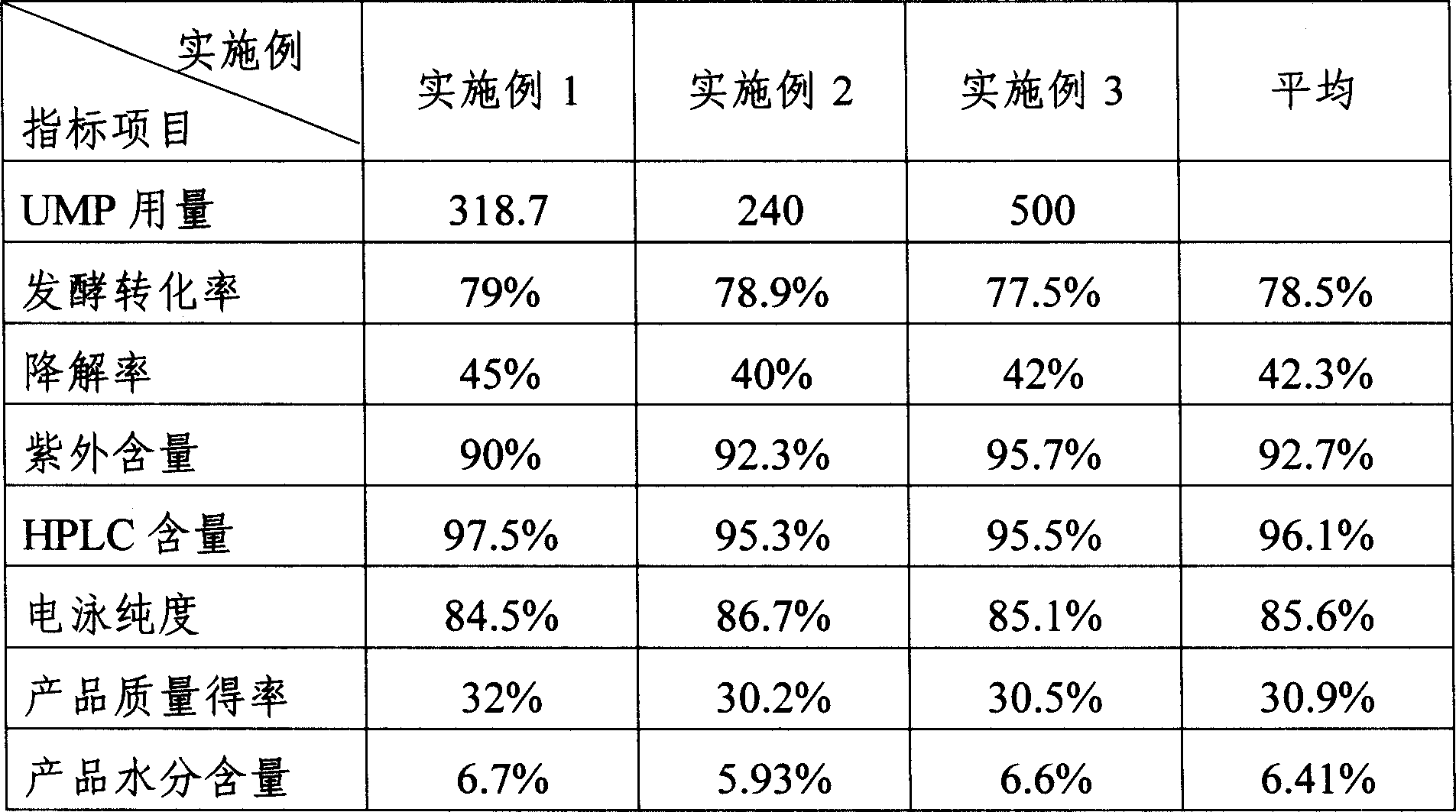
The invention discloses a preparing method of uridine diphosphite, which comprises the following steps: blending uridine monophosphate and beer yeast to ferment; terminating fermenting to obtain the ferment liquid of uridine triphosphate; predisposing ferment liquid; separating and purifying; proceeding acid heat to decompose purified uridine triphosphate; filtering; separating; refining. The invention shortens the predisposing time by two thirds and separating purifying time by one third, which makes receiving rate by over 30%.
Owner:北京燕京中科生物技术有限公司
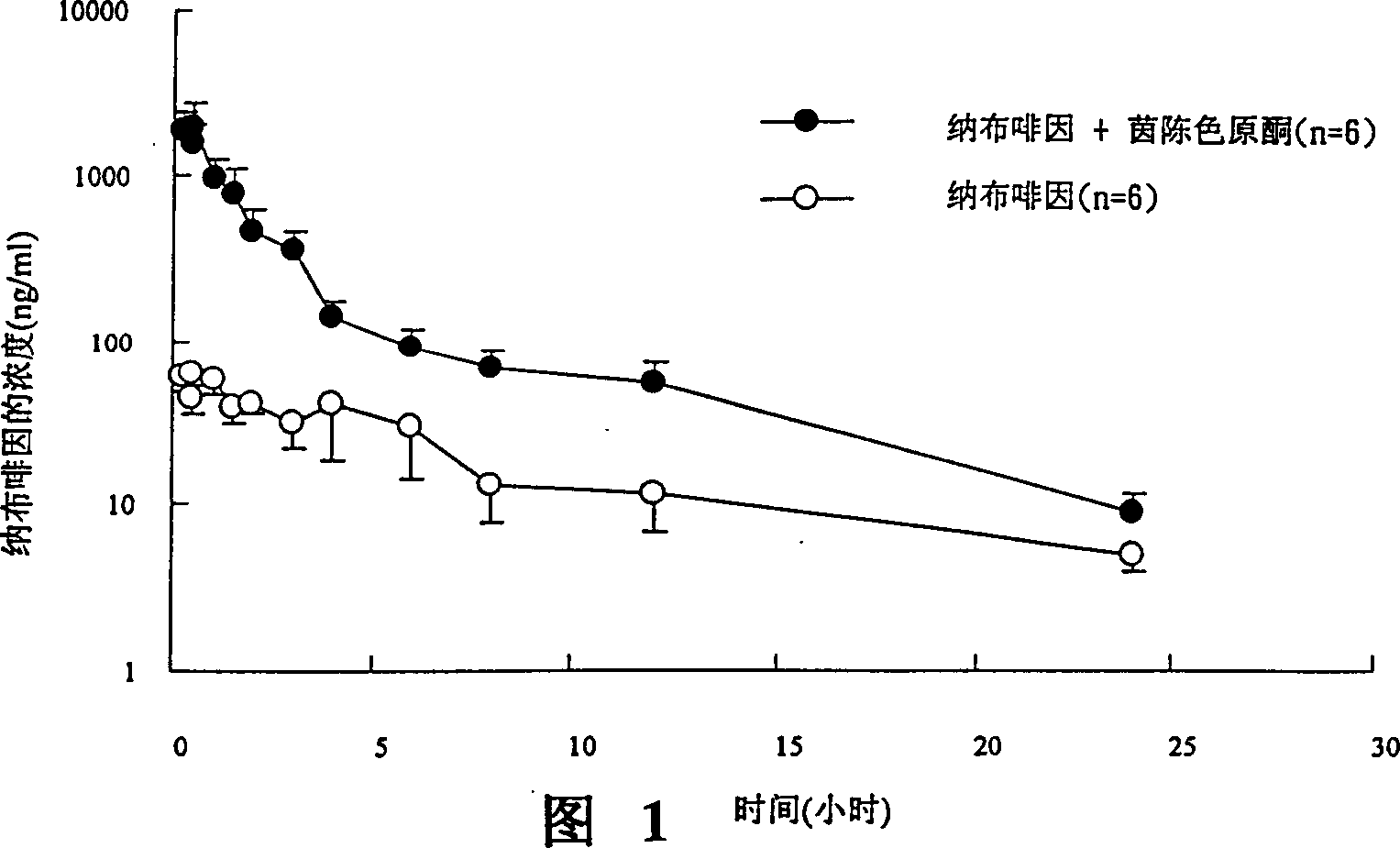
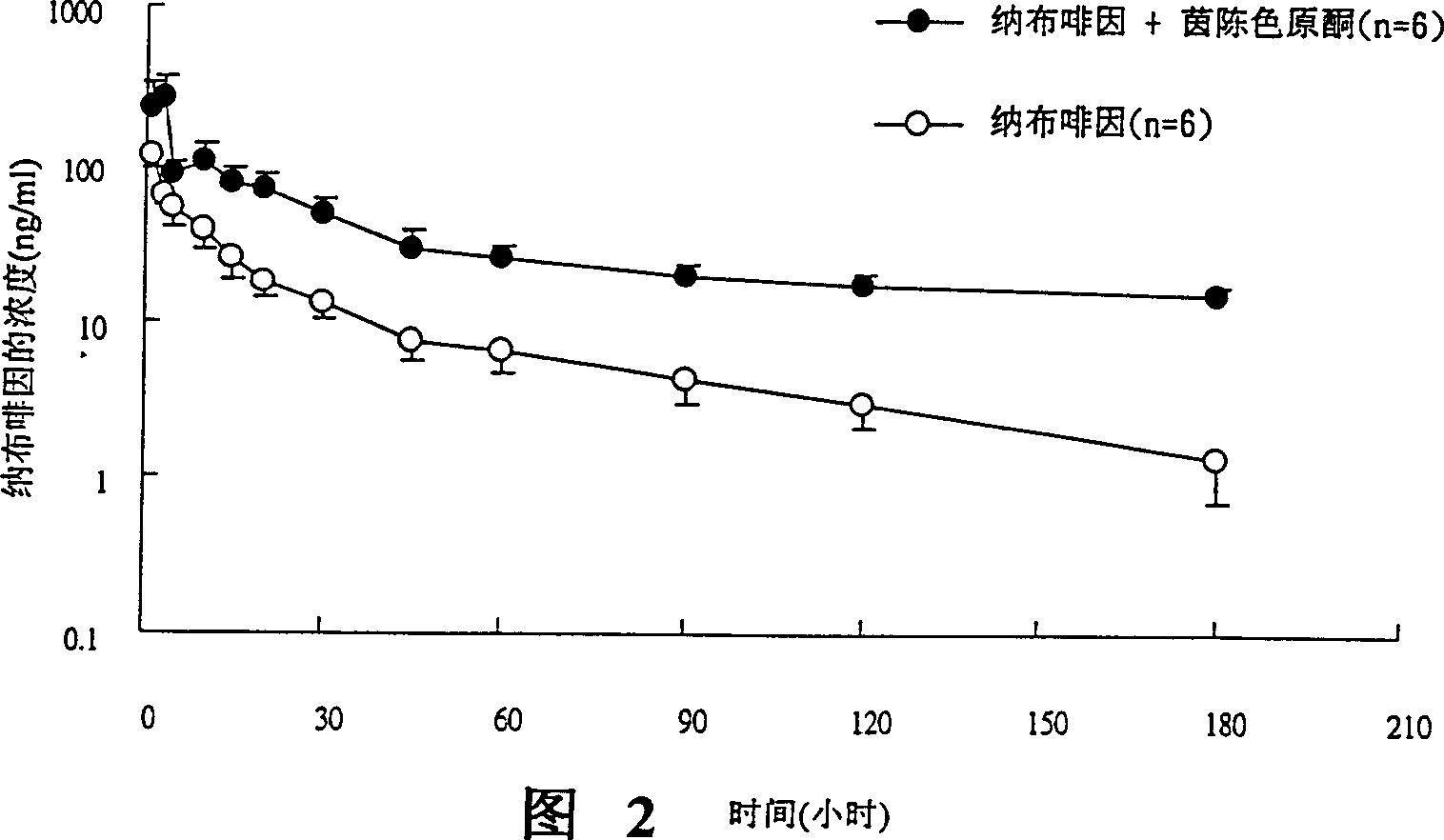
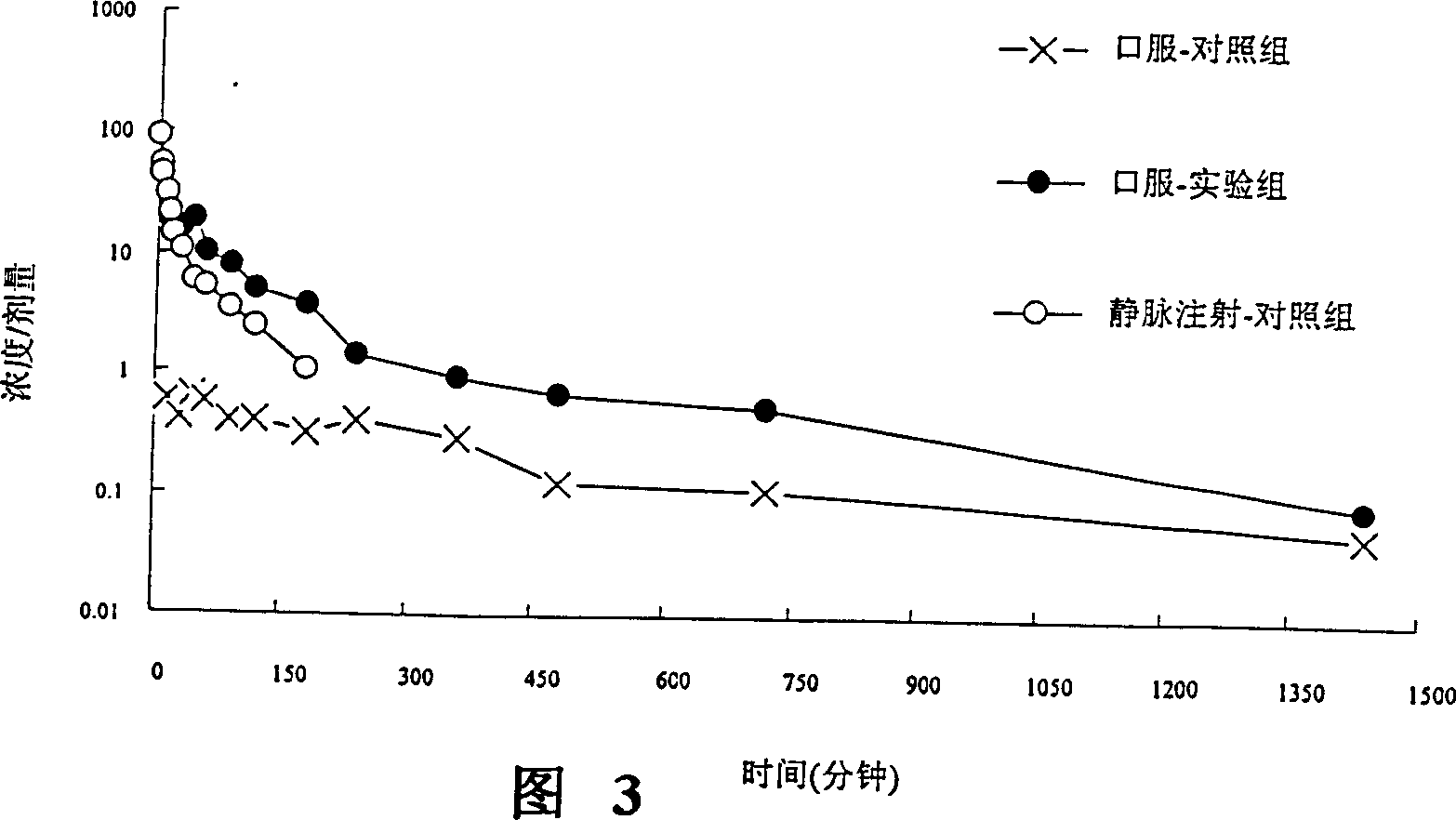
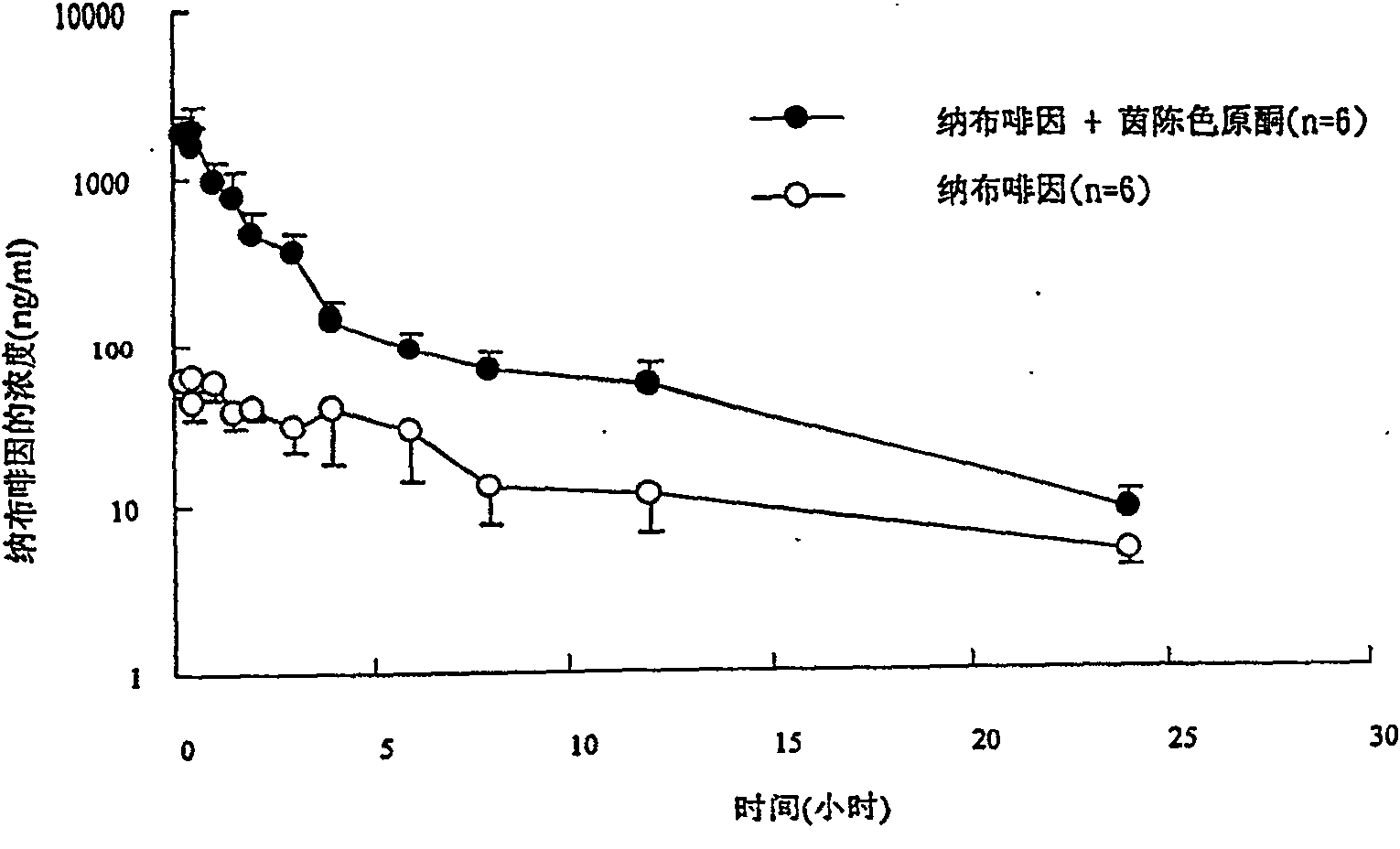
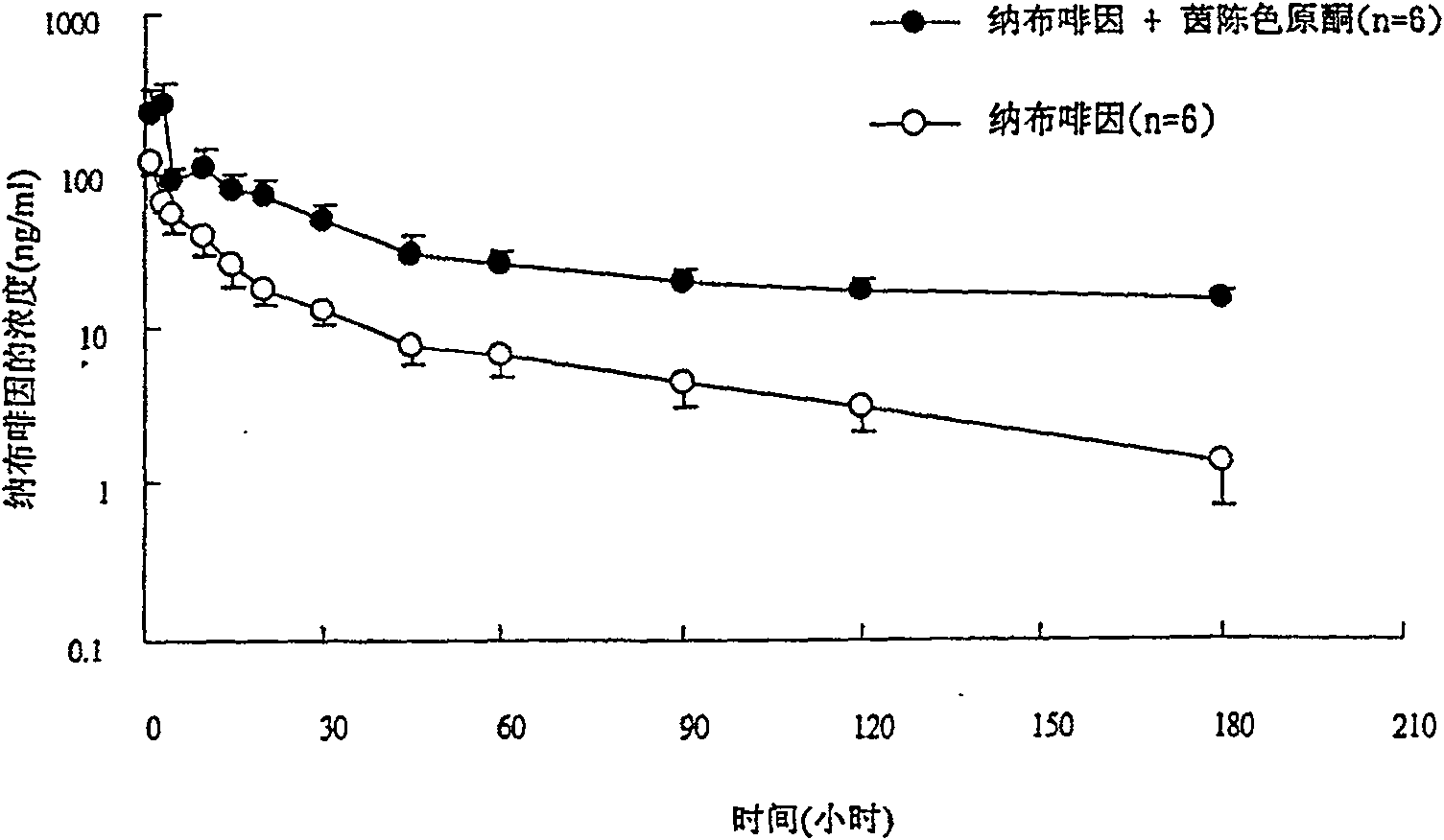
Inhibitor or promoter of uridinediphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 2B (UGT2B)
The present invention provides one kind of UGT2B inhibitor capable of raising the bioavailability of medicine. The UGT2B inhibitor is one or the composition of capillarisin, isorhamnetin, beta-naphthoflavone and other compounds and in the form of alkali or pharmaceutically acceptable salt. The present invention also provides one kind of UGT2B promoter capable of promoting the detoxication function of liver. The UGT2B promoter is one or the composition of nordihydroguaiaretic acid, wogonin, trans-cinnamicacid and other compounds and in the form of alkali or pharmaceutically acceptable salt.
Owner:INT EDUCATION FOUND
Uridine di- or tri-phosphate derivatives and uses thereof
The invention provides particular uridine di- and tri-phosphate derivatives, and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. These compounds are useful for treatment of diseases, disorders and conditions modulated by P2Y6 receptors, and particularly for lowering intraocular pressure and thereby treating ocular hypertension and / or glaucoma.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV +1
A novel glycosyltransferase derived from dolwoe and use thereof
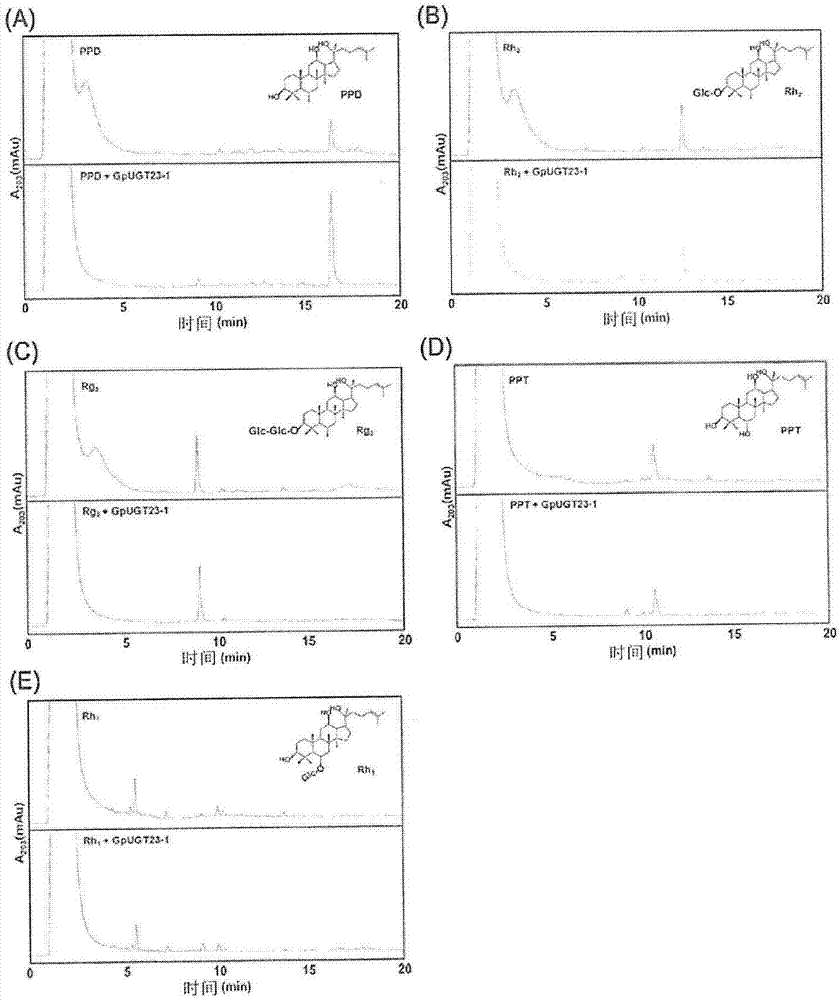
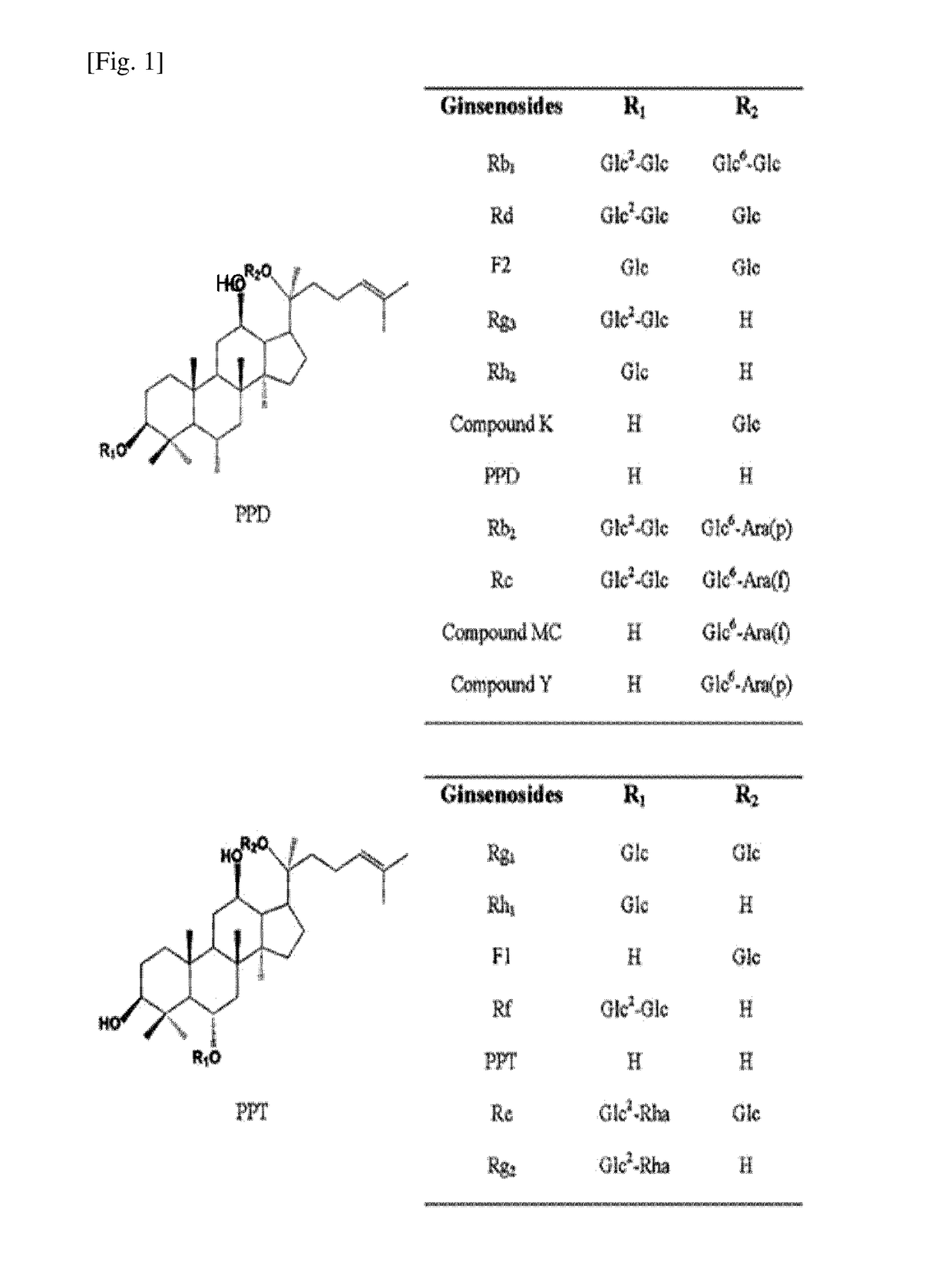
Provided are a novel UDP-glycosyltransferase (uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase) protein from Dolwoe (Gynostemma pentaphyllum) having glycosyltransfer activity for glucose linked by a glycosidic bond at the C-20 position of PPD (protopanaxadiol)-type or PPT (protopanaxatriol)-type ginsenoside, and use thereof.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids
ActiveCN105087454AImprove solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
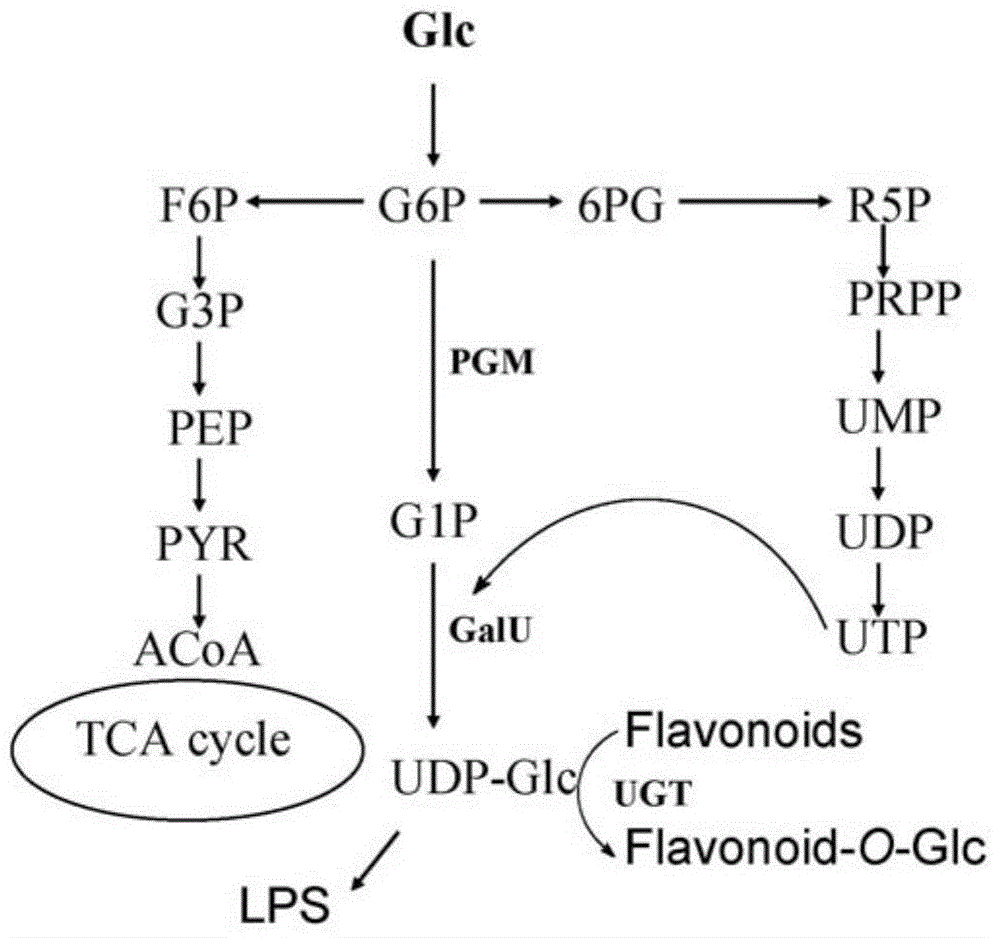
The invention relates to genetically engineered organisms, especially to microbes like Escherichia coli with activity in catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids, and provides a genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids. The genetically engineered bacterium is prepared by coexpression of three genes respectively coding phosphoglucomutase, uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase in a microbial cell and introduction of the functional enzyme genes into the cell through expression vectors. The genetically engineered bacterium induces expression of functional enzyme protein under the condition of addition of an inductive agent--isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) and is directly used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids; and the advantages of good cell growth, a short fermentation period and low cost are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
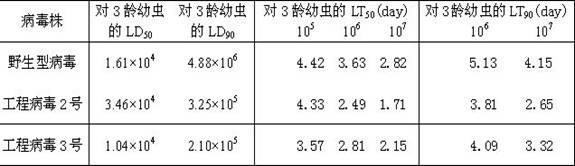
Prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and building method thereof
InactiveCN102329783AFast insecticideLow dose effectMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeUridine diphosphate
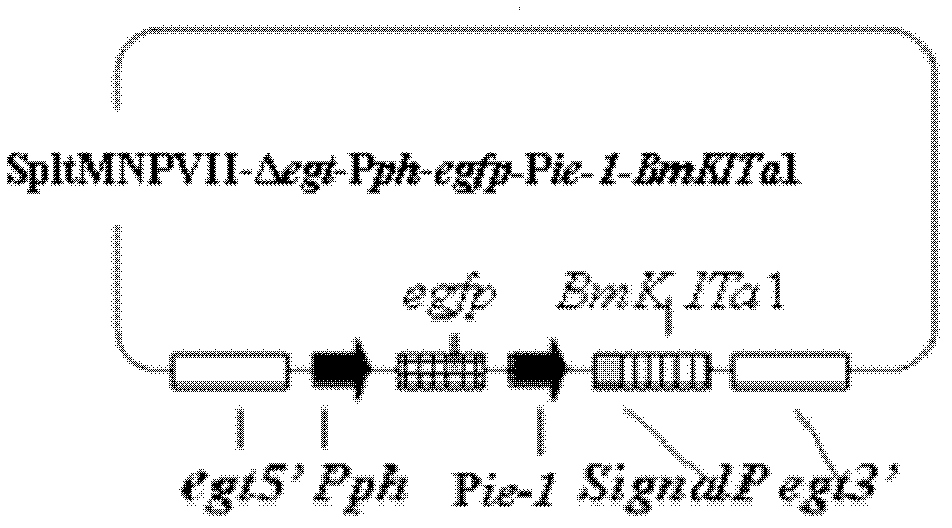
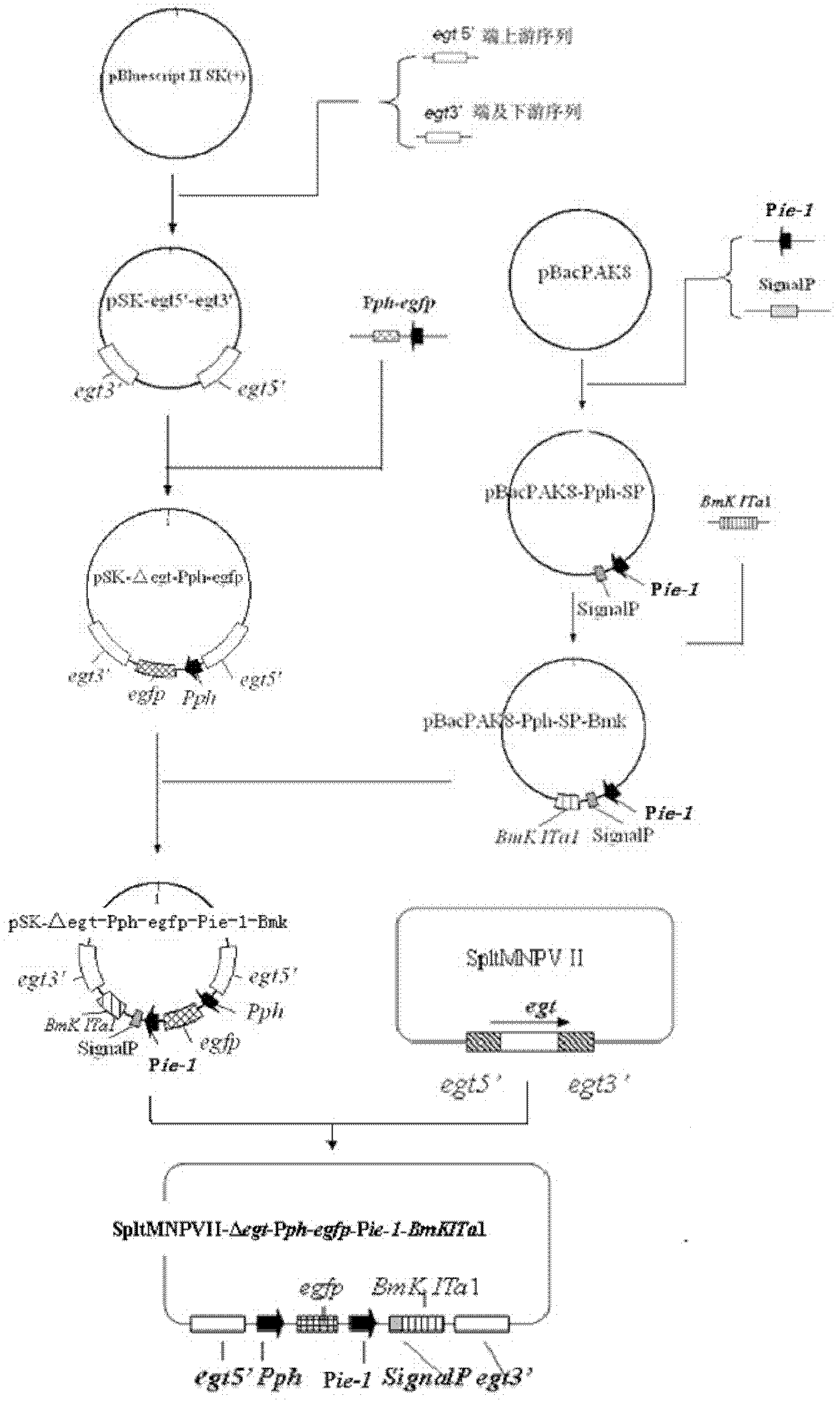
The invention discloses a prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 and a building method thereof, in particular relates to a prodenia litura gene engineering virus used for carrying out deficiency and recombination on a wild type virus (SpltMNPV II) by utilizing a gene engineering method. The genome of the virus is deficient in an egt gene, namely an ecdysteroid UDP (uridine diphosphate) glucosyltransferase gene; and at the site of the deficient egt gene, a BmKITa1 gene controlled by a wild type virus, namely an early gene-1(ie-1) starter, and a marker gene, namely an enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene, which is controlled by the wild type virus, namely a polyhedron gene (ph) starterare inserted. The prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of faster insecticidal speed, less dosage effect and better field application effect compared with the wild type virus. Compared with the prior art, the prodenia litura gene engineering virus No.3 provided by the invention has less dosage effect and lower LT50 at low dose (105 polyhydral bodies / larva).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
A novel method for glycosylation of ginsenoside using a glycosyltransferase derived from panax ginseng
The present invention relates to a uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glycosyltransferase protein which has glycosylation activity for a hydroxyl group at the C-20 position of a protopanaxadiol (PPD)- or protopanaxatriol (PPT)-type ginsenoside, and a method for glycosylation of UDP using the same.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
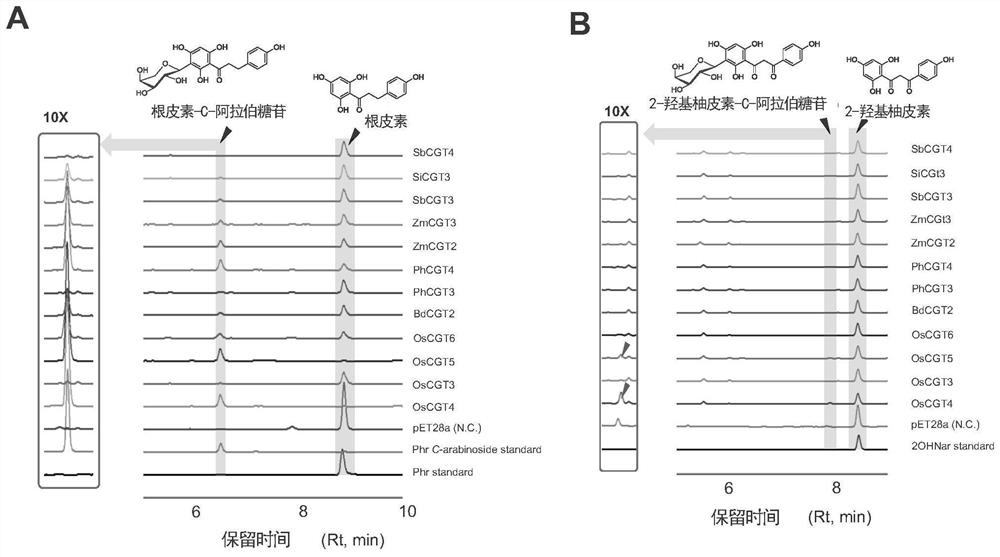
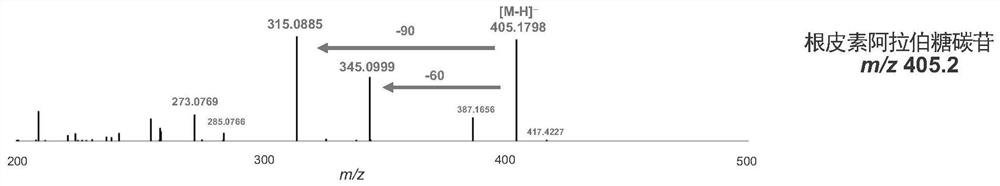
Novel C-glycoside glycosyl transferase and application thereof
The invention provides a group of novel uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glycosyl transferase, which is a C-glycoside glycosyl transferase. The glycosyl transferase can be used for specifically and efficiently catalyzing the carbon glycoside glucosylation of a dihydrochalcone (class) compound or a 2-hydroxyflavanone (class) compound, so that a class of carbon glycoside dihydrochalcone (class) compounds or a class of carbon glucoside-2-hydroxyflavanone (class) compounds are generated; and the carbon glucoside-2-hydroxyflavanone (class) compound is subjected to further dehydration reaction to form the flavone C-glycoside (class) compound. The invention also relates to application of the novel UDP glycosyl transferase to an artificially constructed recombinant expression system, and production of C-glycoside dihydrochalcone (class) compounds or flavone C-glycoside (class) compounds through fermentation engineering.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Difunctional C-glycoside glycosyltransferase and application thereof
The invention provides a group of novel uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glycosyltransferases. The group of novel uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glycosyltransferases are composed of a difunctional carbon glycoside arabinosyl transferase and a difunctional carbon glycoside glucosyl transferase. The glycosyltransferases can specifically and efficiently catalyze arabinoglycosylation and glucosylation of C-glycoside of a dihydrochalcone (dihydrochalcone-series) compound or a 2-hydroxyflavanone (hydroxyflavanone-series) compound, so C-glycoside dihydrochalcone-series and C-glycoside-2-hydroxyflavanone-series compounds are generated; and the C-glucoside-2-hydroxyflavanone-series compounds are subjected to further dehydration reaction to form the flavone C-glycoside-series compounds. The invention also relates to application of the novel UDP glycosyl transferases to an artificially constructed recombinant expression system, and production of C-glycoside dihydrochalcone and flavone C-glycoside compounds through fermentation engineering.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, method for constructing same and application of chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium
ActiveCN109486734AHigh molecular weightGood yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood additiveUridine diphosphate
The invention discloses a chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, a method for constructing the same and application of the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. Chondroitin synthetase genes and UDP (uridine diphosphate)-glucosamine isomerase genes are transferred into corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium. The chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, the method and the application have the advantages that the corynebacterium glutamicum is used as a host for the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, is a GRAS (generally recognized as safe) strain affirmed by the Food and Drug Administration of the America, does not secreteoptional endotoxin or exotoxin, is safe and can be applied to producing amino acid or food additives and the like for a long term, and chondroitin produced by the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium is high in molecular weight and good in yield; the chondroitin yield of preferable recombinant bacteria of the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium can reach 3.7 g / L, chondroitin products with high molecular weights can be produced by the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, and accordingly the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium has anexcellent industrial prospect and can be effectively applied to medicines and health protection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Kelp uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGPase) gene
ActiveCN103710365AActive functionIn-depth understanding of the synthesis mechanismHydrolasesGenetic engineeringSucroseADAMTS Proteins
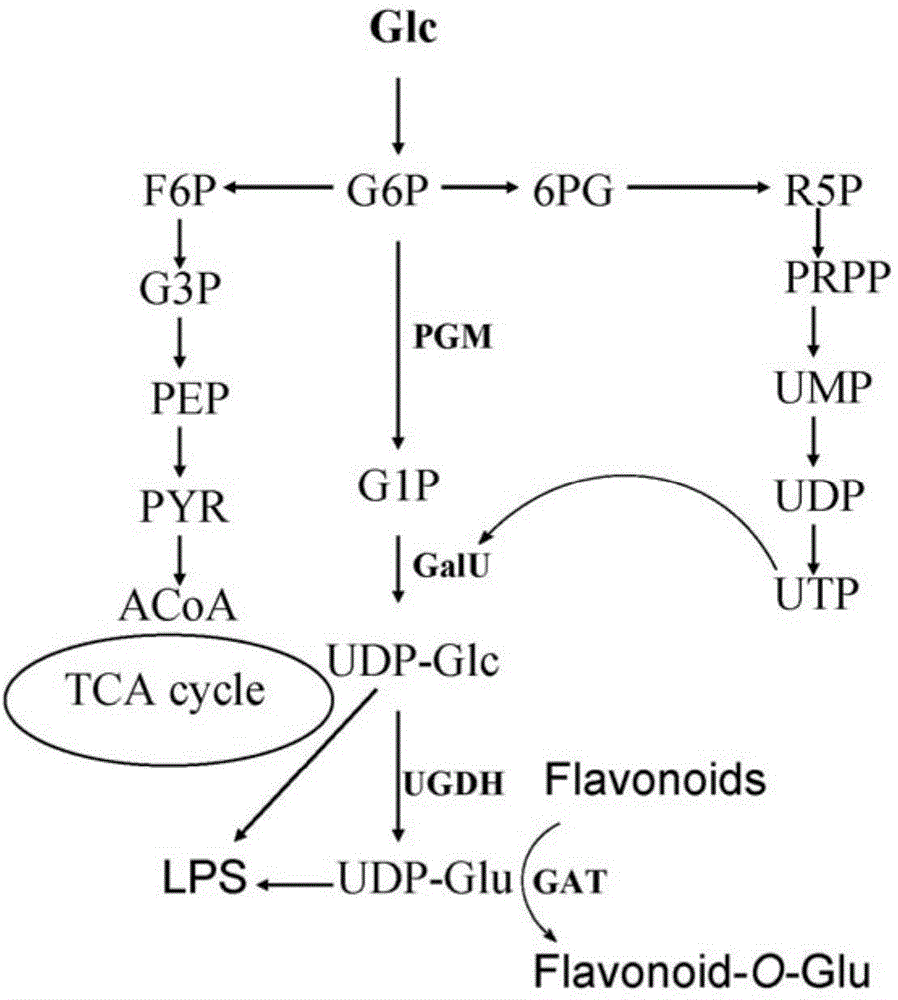
The invention relates to the field of a genetic engineering technology, and particularly relates to a kelp uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGPase) gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene and the amino acid sequence of the coding protein are SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 respectively. According to the invention, the gene sequence is cloned through the gene cloning technology, and a prokaryotic expression vector is established; and enzyme activity detection on recombinant protein proves that the gene has the function of catalyzing UDP-glucose and pyrophosphoric acid to form glucose-1-phosphoric acid and UTP and belongs to a key enzyme coding gene of the synthesis path of agar-agar, starch, cellulose, trehalose, sucrose and the like. The gene has an important application value in increasing the content of economic components including algae agar-agar, starch, cellulose, trehalose, sucrose and the like.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
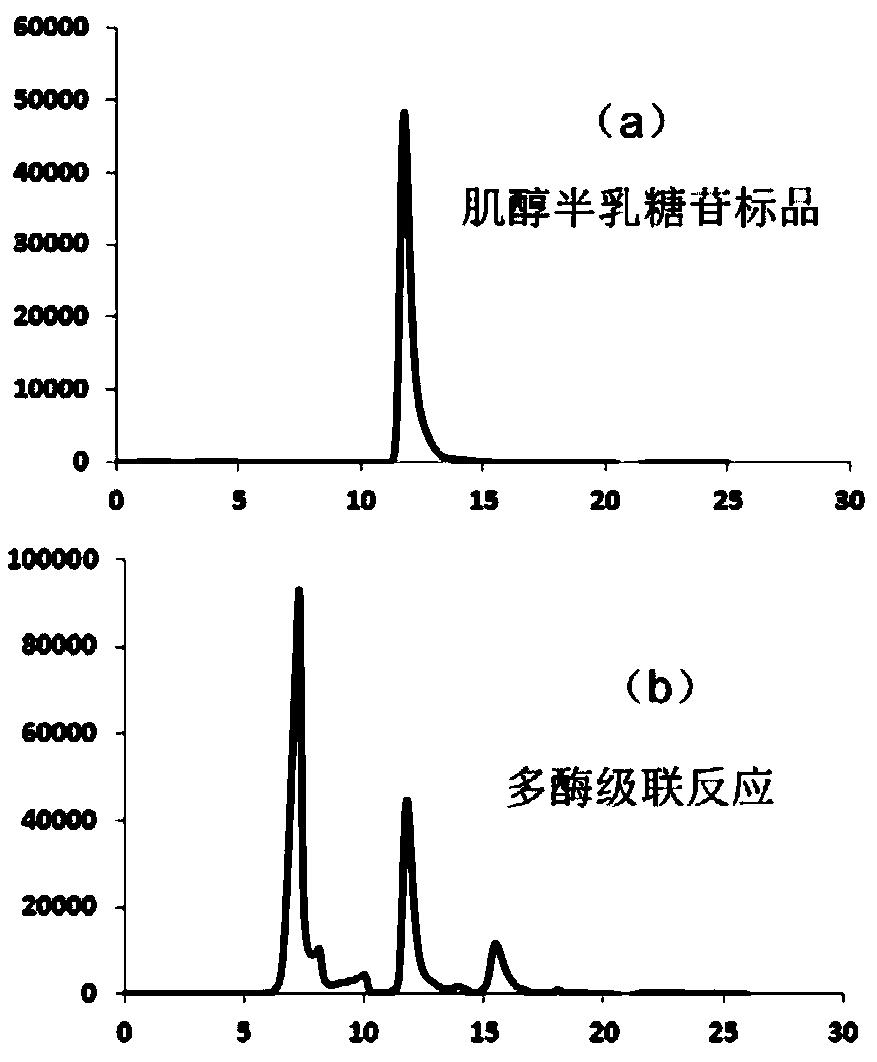
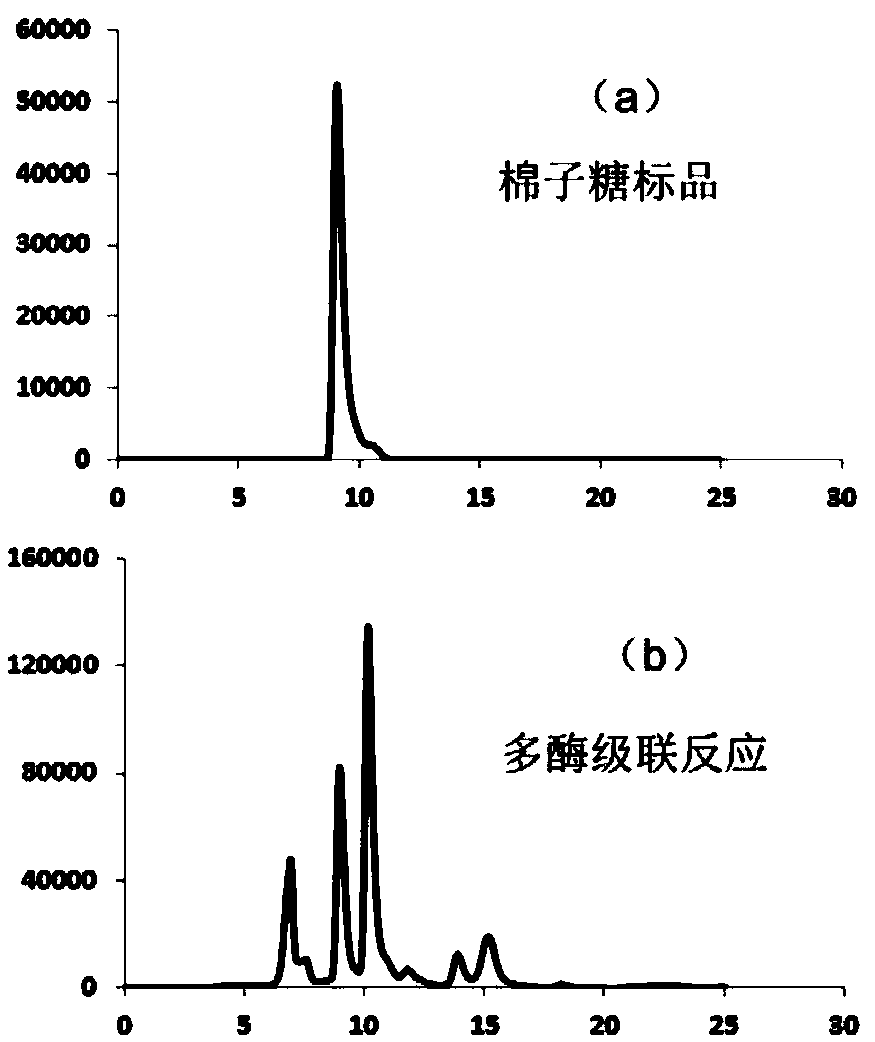
Method for synthesizing soybean oligosaccharides through biological catalysis
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing soybean oligosaccharides through biological catalysis. The method has the beneficial effects that that through establishing an in-vitro multi-enzyme cascade reaction system composed of sucrose synthetase, uridine diphosphate glucose 4-differential isomerase, inositol galactoside synthase, raffinose synthase and threonose synthase, sucrose is takenas a substrate to synthesize a single component or a mixed component in inositol galactoside, raffinose and threonose; the method realizes the recycling conversion of uridine diphosphate and inositol,and a crude enzyme solution added in the system contains a small amount of uridine diphosphate, so that the expensive uridine diphosphate can be avoided; the inositol galactoside yield reaches 50 g / L, the conversion rate is 70 percent, the raffinose yield reaches 20 g / L, the threonose yield reaches 10 g / L, and the obtained inositol galactoside, raffinose and threonose can be used in the fields offood, medicines and the like; the method disclosed by the invention is of great significance in the utilization of high attachment values of the sucrose and a biomass rich in the sucrose.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
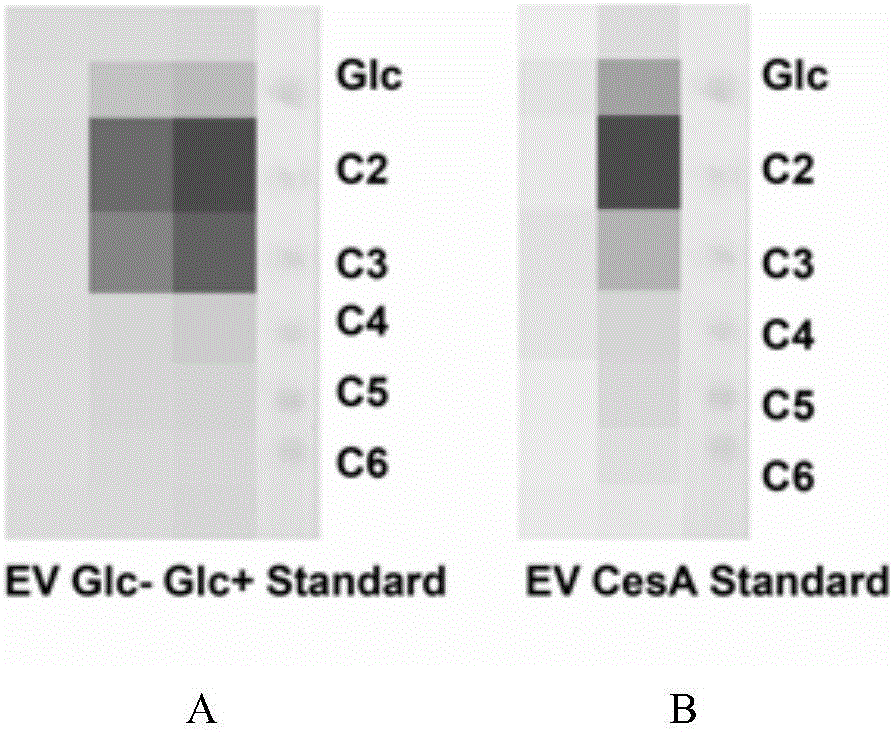
Cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein from phytophthora capsici, and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein from phytophthora capsici, and an encoding gene and application thereof. The PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention is the protein as shown in a sequence 2; the encoding gene of the protein is as shown in a sequence 1. An experiment proves that the protein PCCESA1 provided by the invention can catalyze substrate uridine diphosphate D glucose (UDPG) to generate cellobiose, and has significance on biosynthesis of main component cellulose of a cell wall of the phytophthora capsici; as an oomycetes cell wall plays an important role in maintaining oomycetes vital movement, including maintaining cell shapes, participating in host interaction and the like. Therefore, the cellulose synthase PCCESA1 protein provided by the invention provides technical support for the oomycetes cell wall, and provides a new molecular target for future bactericide research and development.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for measuring activity of beta-glucan synthase
InactiveCN102443621AImprove securityReduce experiment costMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsBeta-glucan synthesisSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a method for measuring the activity of beta-glucan synthase. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that the activity of the beta-glucan synthase is determined by detecting the amount of glucan consumed by synthesizing the beta-glucan synthase into beta-glucan with the glucan as an enzymatic reaction substrate and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid as a color developing agent under visible light. Compared with a traditional method for measuring the activity of the beta-glucan synthase by measuring the change of radioactive activity of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-[14C] glucan through a liquid scintillation counting instrument by using the UDP-[14C] glucan as a substrate, and the experiment cost is greatly reduced. In addition, no radioactive glucan is used as the substrate in the method, thus the safety of the experiment is high. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, simpleness and safety in operation, convenience, quickness and convenience for large-scale popularization and application. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely used for researching and developing saccharide and enzyme products.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids
ActiveCN105087453AImprove efficacyGood water solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetically engineered organisms, especially to microbes like Escherichia coli with activity in catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids, and provides a genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids. The genetically engineered bacterium is prepared by coexpression of four genes respectively coding phosphoglucomutase, uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase and uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase in a cell and introduction of the functional enzyme genes into the cell through expression vectors. The genetically engineered bacterium induces expression of functional enzyme protein under the condition of addition of an inductive agent--isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) and is directly used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids; and the advantages of good cell growth, a short fermentation period and low cost are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Oleanolic acid glucuronyltransferase and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN109266626ACatalyzes glycosylation reactionsPromote biosynthesisFermentationGlycosyltransferasesPlant genetic engineeringUridine diphosphate
The invention relates to an oleanolic acid glucuronyltransferase, a coding gene and an application thereof, belonging to the field of plant genetic engineering and biotechnology. The amino acid sequence of the oleanolic acid glucuronyltransferase of the present invention is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 or SEQ ID NO.4. A nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.5, SEQ ID NO.6, SEQ ID NO.7 or SEQ ID NO.8. The oleanolic acid glucuronyltransferase of the invention can specifically take uridine diphosphoglucuronic acid as a glycosyl donor and catalyze the glycosylation of oleanolic acid C-3 to produce oleanolic acid 3-O-beta-Glucuronic acid. This enzyme is the upstream step in the synthesis of oleanolic saponins, which is of great significance for the elucidation of the synthetic pathway of oleanolic saponins.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
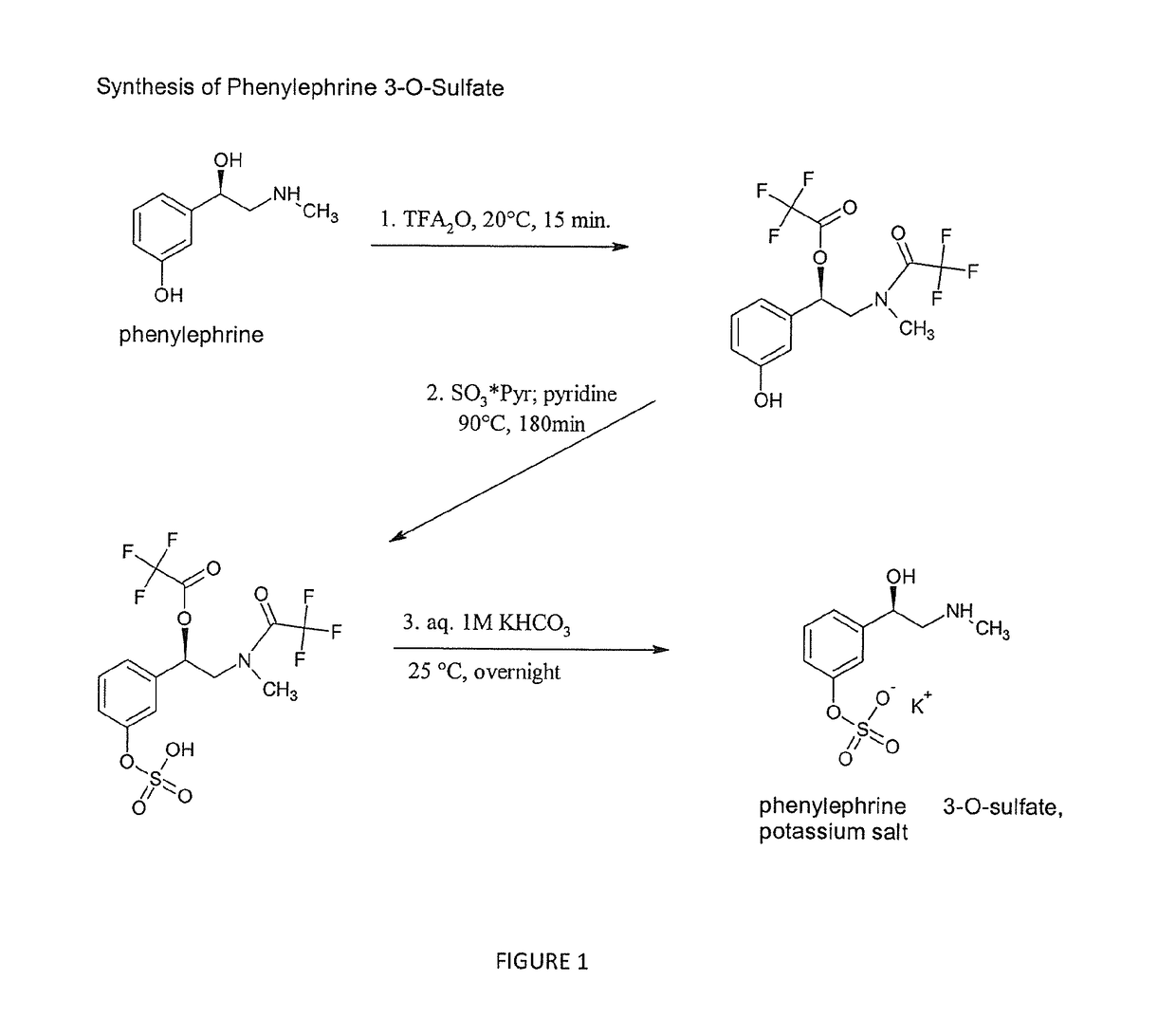
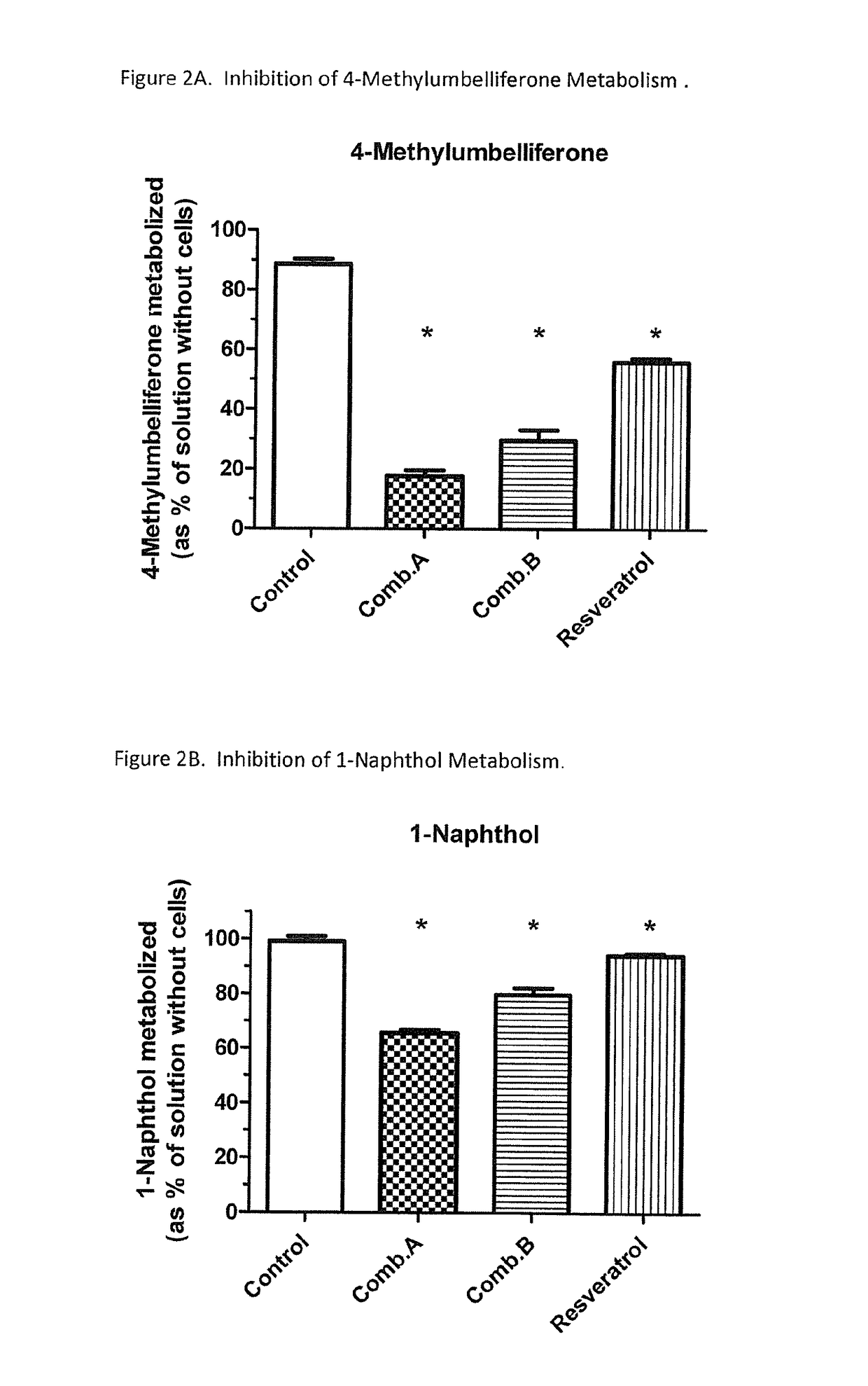
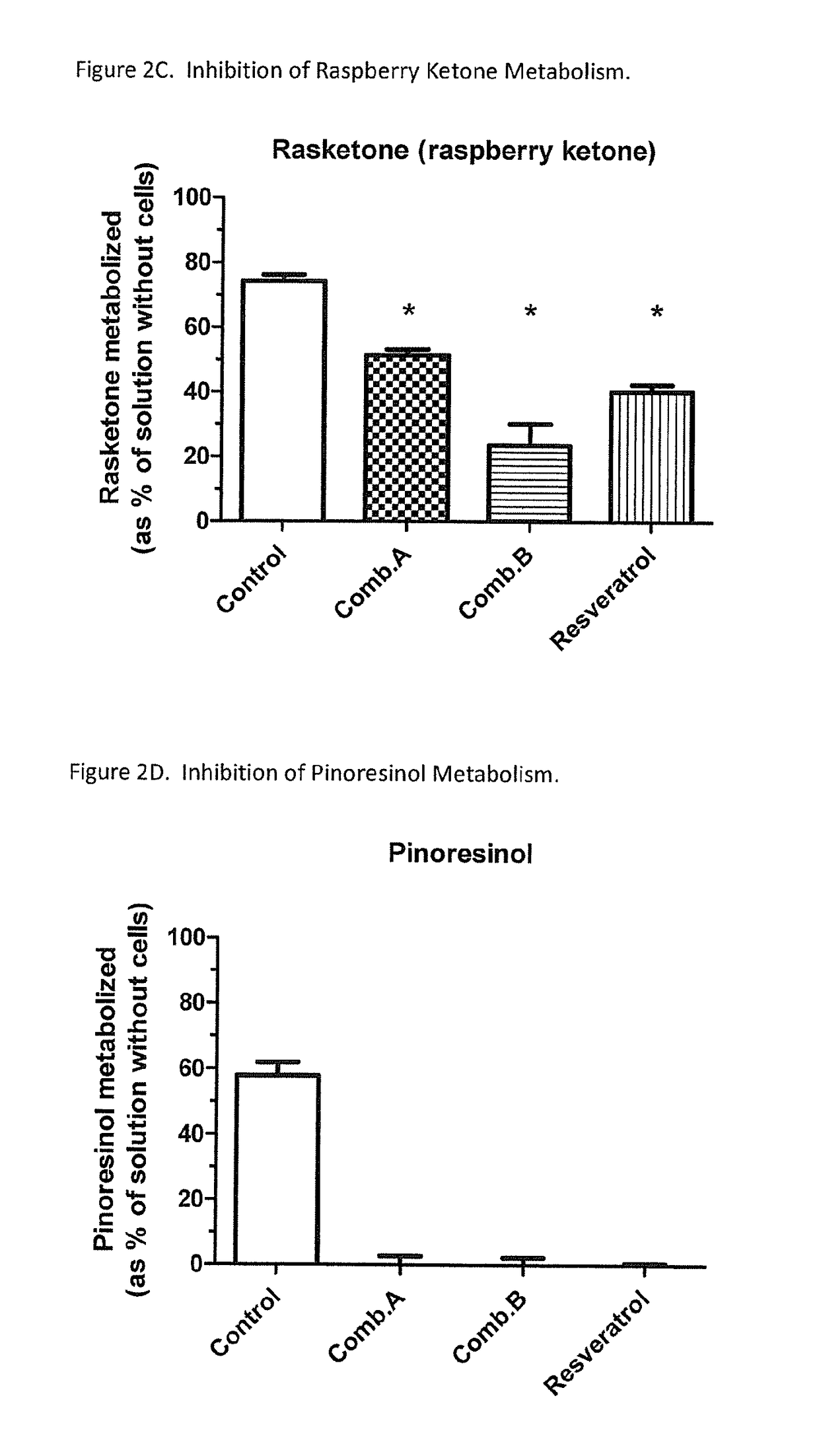
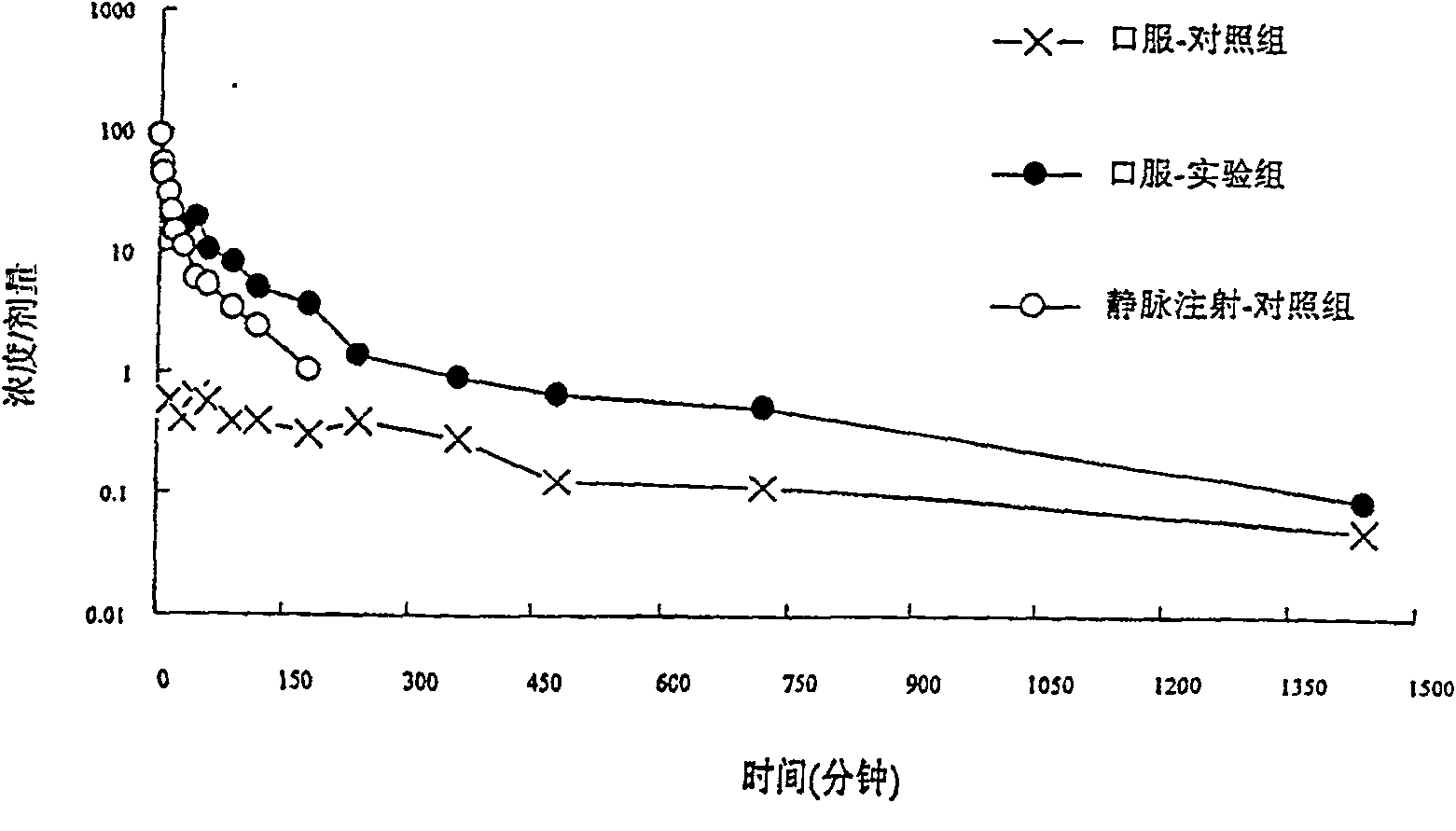
Selective metabolic approach to increasing oral bioavailability of phenylephrine and other phenolic bioactivities
ActiveUS9616033B2Promote absorptionReduced bioavailabilityHydroxy compound active ingredientsMetabolism disorderIntestinal structureUridine diphosphate
Presystemic metabolism in intestine of bioactives such as phenylephrine is avoided by administering a subject (human or animal) the bioactive (e.g., phenylephrine) in combination with one or more inhibitors of sulfation (e.g., sulfotransferase enzymes aka SULTs). This can also be enhanced be co-administering inhibitors of monoamine oxidases aka, MAOs, and uridine diphosphate glucoronysl transferases, aka UGTs. Preferably the inhibitors are GRAS compounds. The one or more inhibitor compounds inhibit the enzymes responsible for rapid presystemic metabolism, thus allowing the bioactives (e.g., phenylephrine) to be more readily absorbed intact into the circulatory system.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Uridine diphosphate-dependent glycosyltransferase enzyme
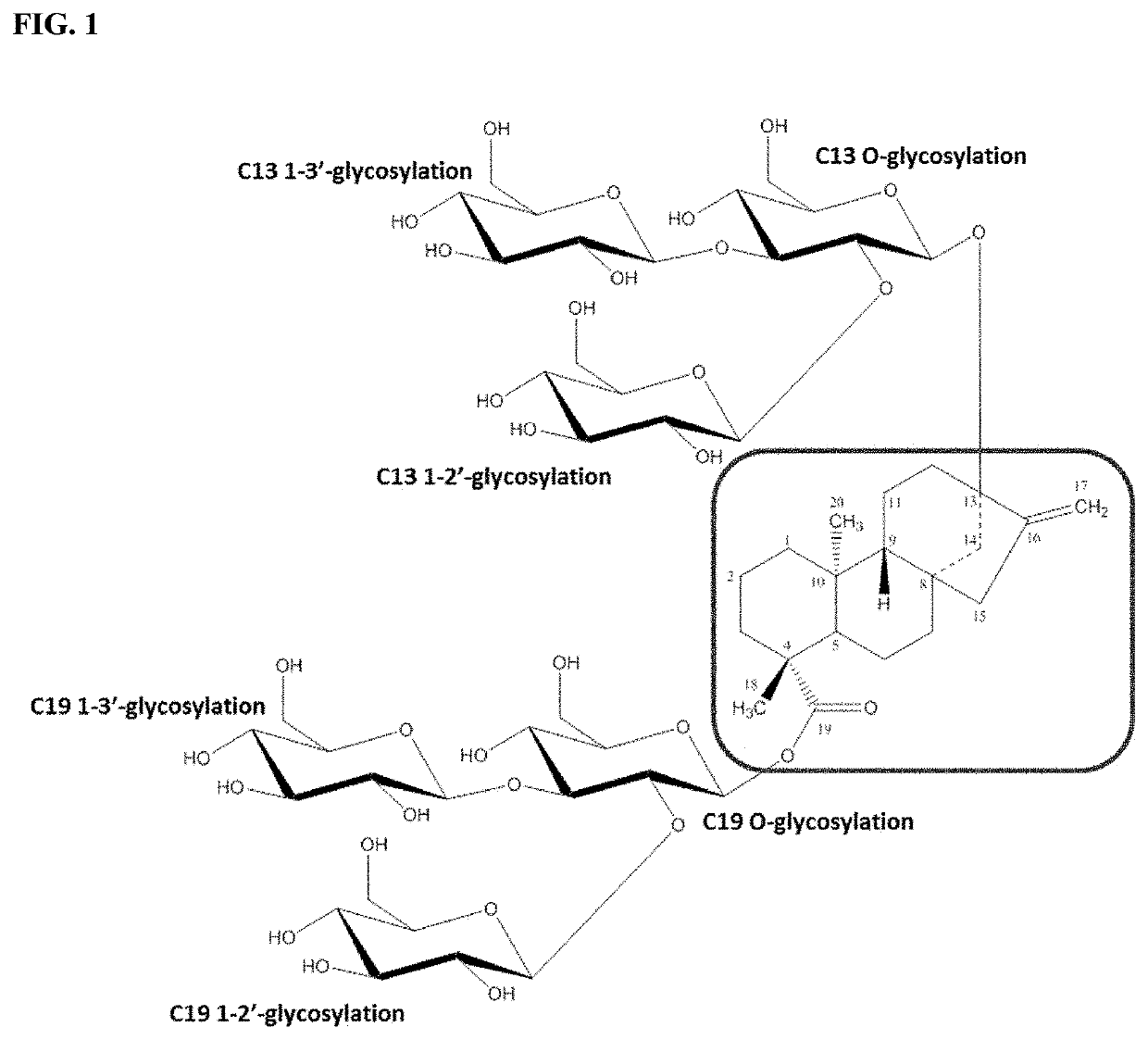
ActiveUS11168309B2High activitySpeed up the conversion processFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGlycosideGlycan
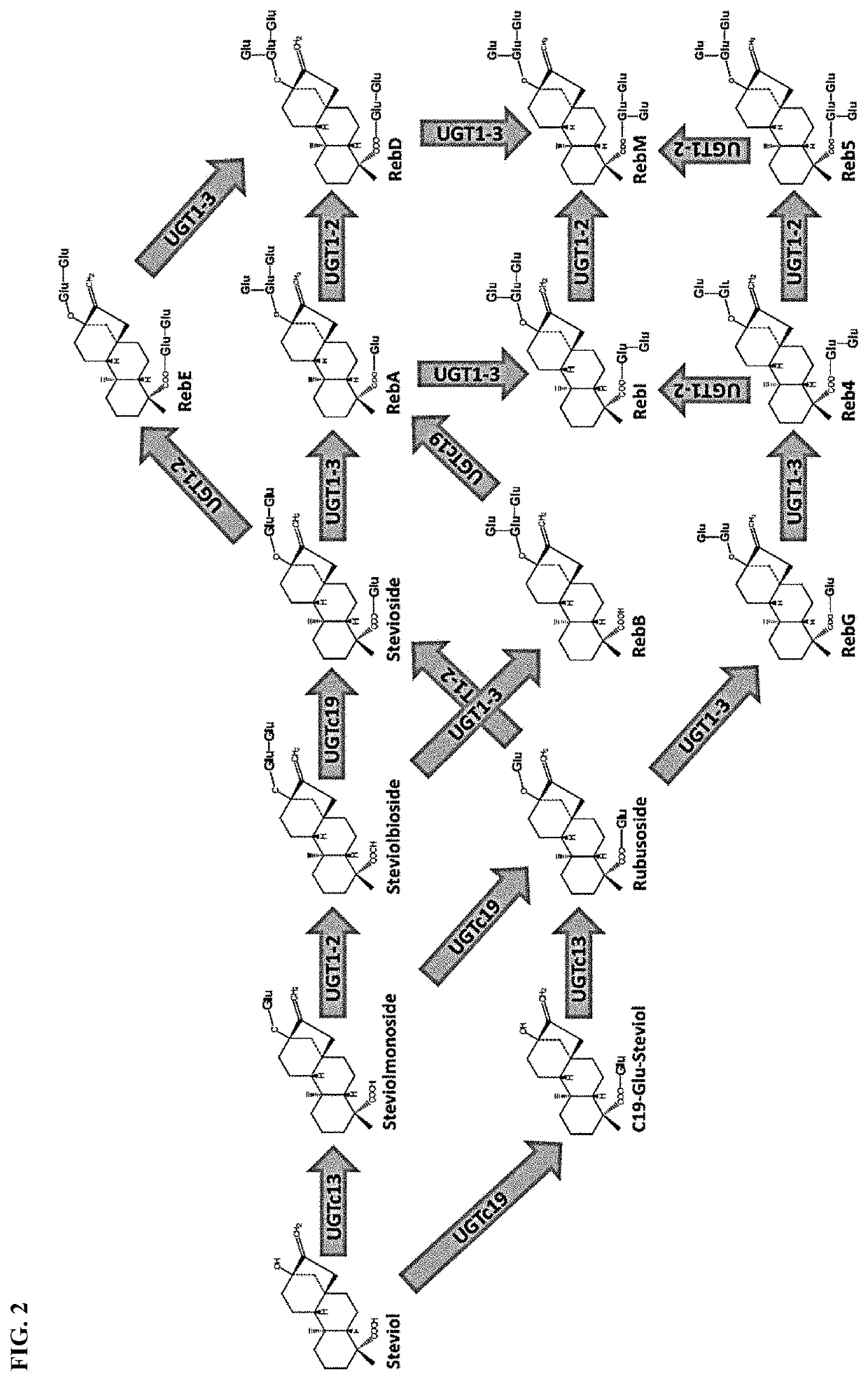
In various aspects, the present invention provides uridine diphosphate-dependent glycosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes capable of catalyzing the transfer of a monosaccharide moiety from a NDP-sugar to the 3′ carbon of a sugar moiety of a substrate, such as a terpenoid glycan, thereby functioning as a “1-3 UGT.” In other aspects, the invention provides polynucleotides encoding the 1-3 UGT, and host cells comprising the same. In still other aspects, the invention provides methods for preparing glycosylated substrates, including steviol glycosides, using the enzyme and host cells of this disclosure.
Owner:MANUS BIO INC
glmm gene knock-out bacterial strain as well as preparation method and application in sieving mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase inhibitors
InactiveCN101928691AIntegrity breachImprove efficacyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention discloses a glmM gene knock-out bacterial strain ML2009 (mycobacterium smegmatis), CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 3418, which is constructed by using phosphoglucomutase participating in the biosynthesis of key components in a mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall. The bacterial strain ML2009 can be used as a cell model for sieving phosphoglucomutase inhibitors with high flux, be used for sieving effective phosphoglucomutase inhibitors from a combined compound library, traditional Chinese medicine and natural products to prepare tuberculosis-resisting medicaments with high medicine effects; and in addition, in the cells of a human body, the synthesis approach of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-acetyl glucosamine is different from that of mycobacterium tuberculosis, no phosphoglucomutase exists in the UDP-acetyl glucosamine, therefore, the reaction catalyzed by the mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase does not exist in the cells of the human body so that the tuberculosis-resisting medicaments developed by using the phosphoglucomutase as a target enzyme are harmless to the human body, and the defect that the traditional antibacterial medicament also kill normal cells is overcome.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing rebaudioside A through double-enzyme fermentation catalysis
PendingCN111662942AReduce stepsHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSucrose synthetase
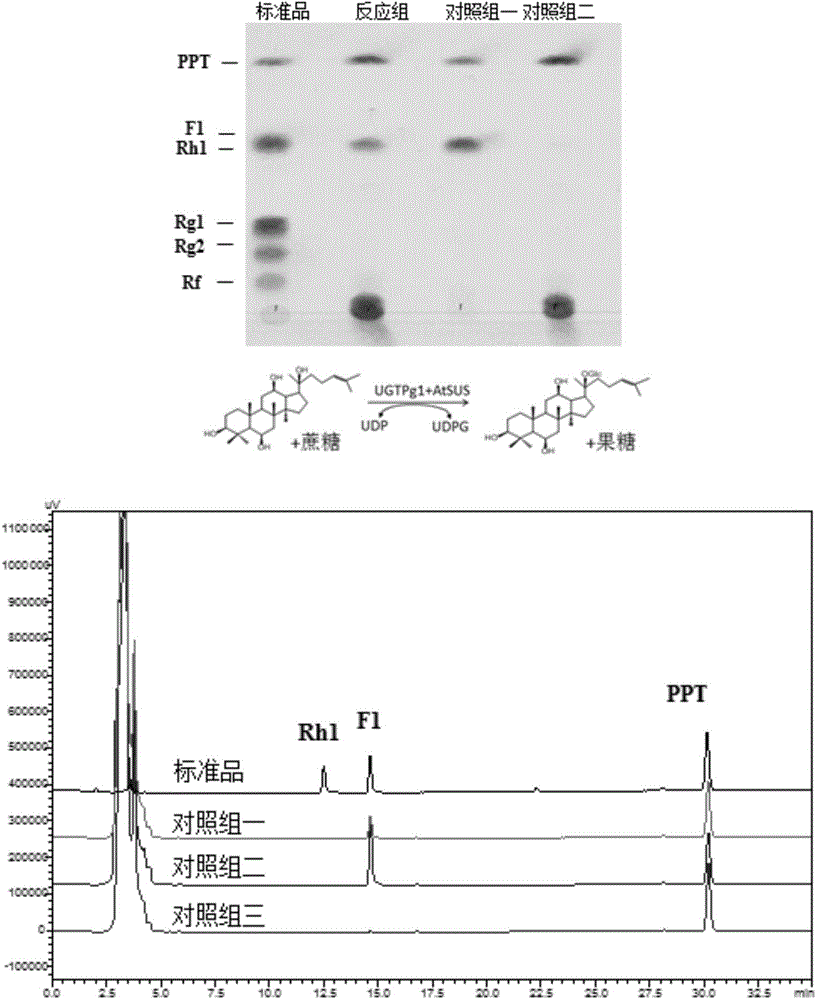
The invention relates to a method for producing rebaudioside A through double-bacterium fermentation catalysis. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) connecting a glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 gene and a sucrose synthase AtSUSY gene to a pUC18 plasmid vector, transferring the pUC18 plasmid vector to DH5alpha escherichia coli competent cells, inoculating an LB culture medium, and culturing at 25-37 DEG C and 200-250 rpm for 10-18 h; (2) inoculating to a seed tank according to the inoculum size of 0.5%-15%, and culturing for 5-16 h at the speed of 150-400rpm and the ventilation ratio of 0.1-1.5 V / V.min at the temperature of 25-37 DEG C; (3) inoculating into a fermentation tank according to the inoculum size of 1%-10%, and culturing for 20-40 h at the speed of 100-1,000 rpm, the ventilation ratio of 0.2-2 V / V.min and the pH of 6.6-8.5 at the temperature of 25-37 DEG C; (4) adding an inducer when the OD600 value reaches 20-100, wherein the concentration of the inducer is 0.1-1.5 mmol / L; (5) carrying out filter pressing, resuspending, crushing and filter pressing on the fermentation liquid to obtain a crude enzyme liquid; and (6) mixing stevioside, uridine diphosphate, a phosphate buffer solution and the crude enzyme solution according to a mass ratio of (40-100):(1-4):(400-600):(50-100), and performing reaction at 25-40 DEG C for 24-48 h. The method has the advantages that two crude enzyme solutions are obtained through one-time fermentation, and operation steps are few; the enzyme activity is high and the production cost is low.
Owner:ANHUI JINGHE IND
Uridine diphosphate-4-one-6-deoxyglucose heterogeneous reductase and coding gene thereof and application
The invention discloses uridine diphosphate-4-ketone-6-deoxyglucose isomerous reductase, and encoding genes and application thereof. The uridine diphosphate-4-ketone-6-deoxyglucose isomerous reductase is a) or b): a), proteins which are formed by amino acid sequences shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and b), proteins which are formed by the amino acid sequences shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more than one amino acid, related to synthesis of uridine diphosphate rhamnose and derived from the a). The invention also discloses the encoding genes for the proteins. After the encoding genes of the uridine diphosphate-4-ketone-6-deoxyglucose isomerous reductase are transferred into cotton, the fiber length of the cotton is increased and the quality and the yield of cotton fibers are improved. The uridine diphosphate-4-ketone-6-deoxyglucose isomerous reductase and the encoding genes of the uridine diphosphate-4-ketone-6-deoxyglucose isomerous reductase have large economic value and application prospect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Inhibitor or promoter of uridinediphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 2B (UGT2B)
ActiveCN100571696CNervous disorderHydrocarbon active ingredientsBeta-NaphthoflavoneUridine diphosphate
Owner:INT EDUCATION FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com