Patents
Literature
33 results about "Pharmacogenetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
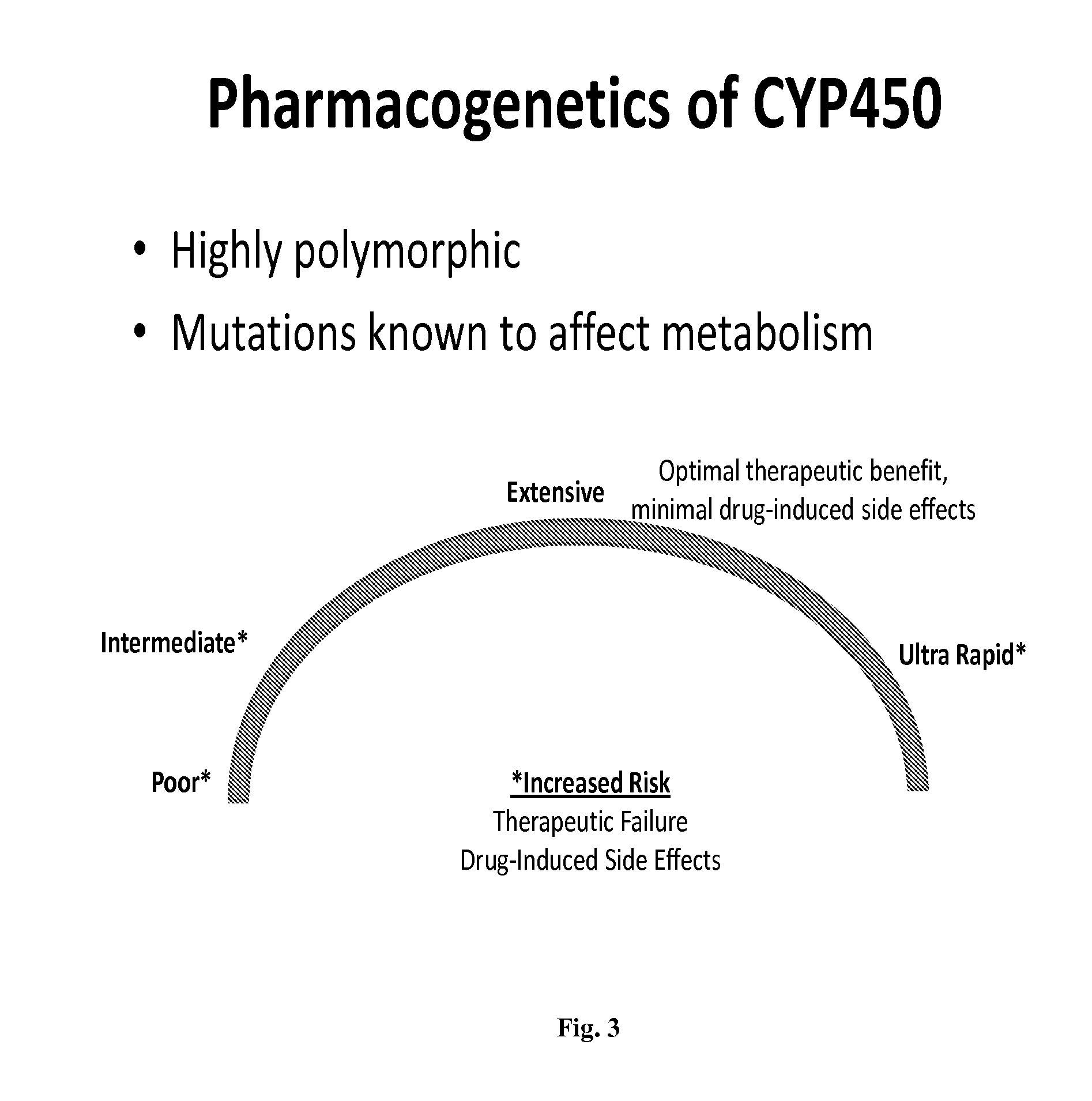
Pharmacogenetics is the study of inherited genetic differences in drug metabolic pathways which can affect individual responses to drugs, both in terms of therapeutic effect as well as adverse effects. The term pharmacogenetics is often used interchangeably with the term pharmacogenomics which also investigates the role of acquired and inherited genetic differences in relation to drug response and drug behavior through a systematic examination of genes, gene products, and inter- and intra-individual variation in gene expression and function. In oncology, pharmacogenetics historically is the study of germline mutations, whereas pharmacogenomics refers to somatic mutations in tumoral DNA leading to alteration in drug response.
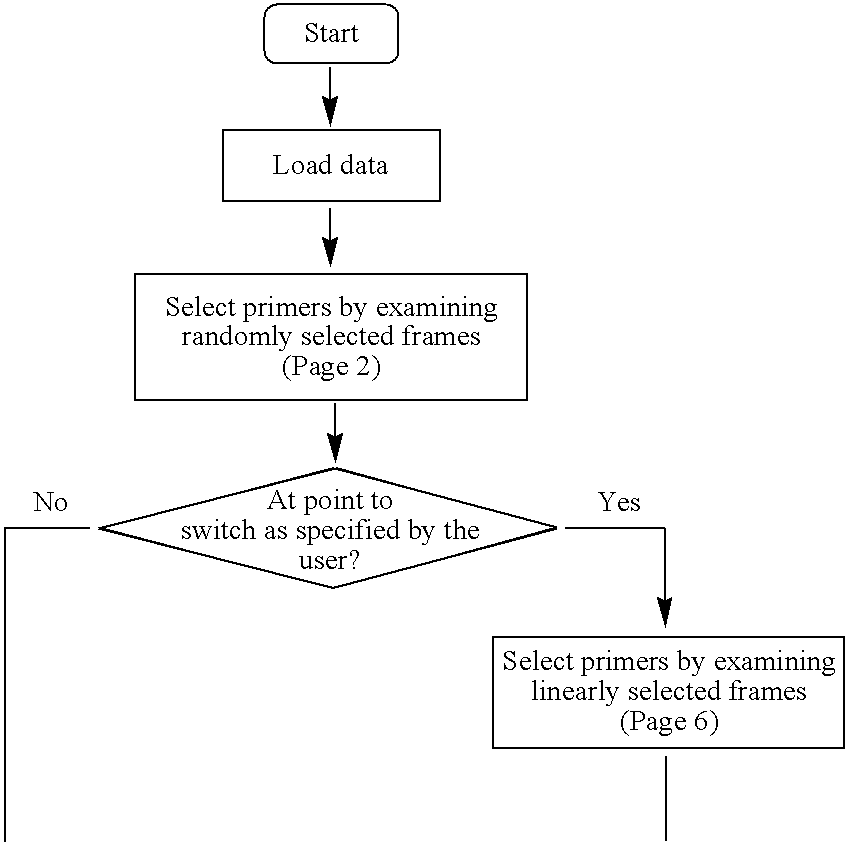
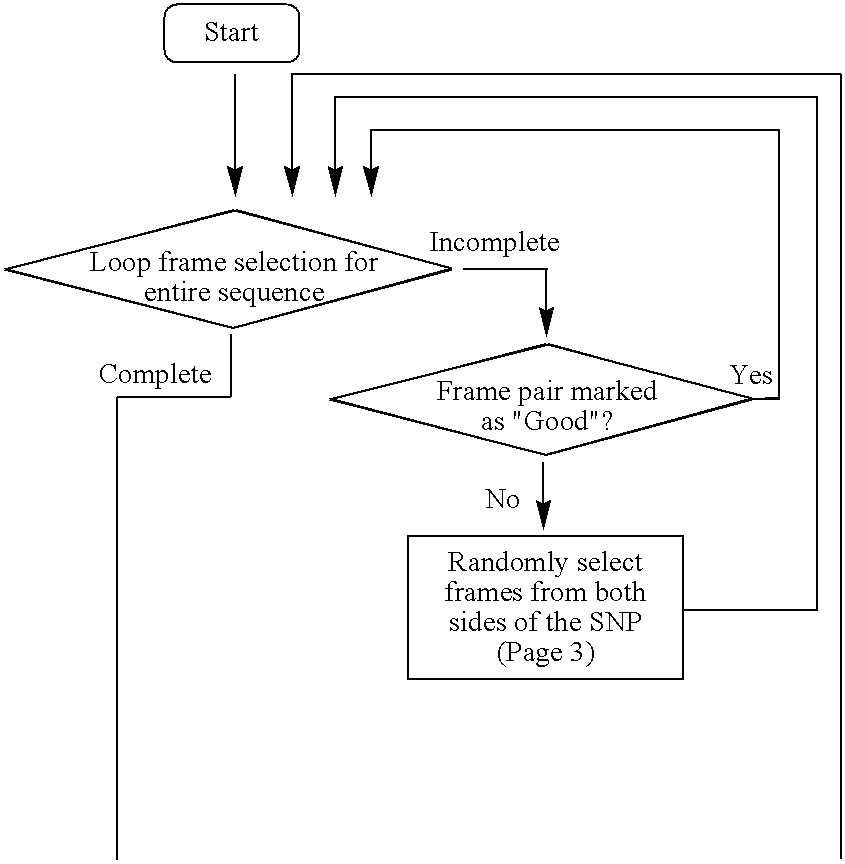
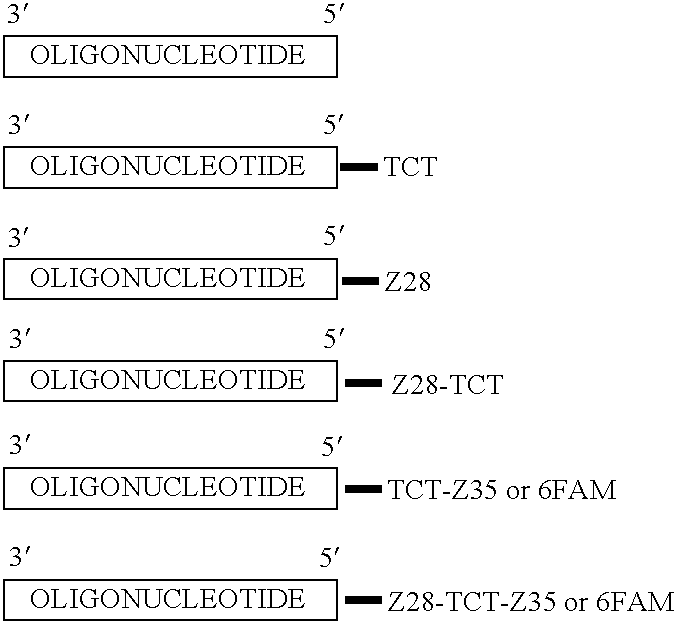
High throughput multiplex DNA sequence amplifications
InactiveUS20060281105A1Efficient and simultaneous amplificationMinimize formationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHigh throughput genotypingGenome scale
The present invention provides methods of designing PCR primers that allow the efficient and simultaneous amplification of a large number of different desired DNA fragments in a single multiplex PCR and minimize the formation of nonspecific extensions of undesired DNA fragments. The present invention allows a multiplex PCR to use at least 50 pairs of primers and produce at least 50 DNA fragments of interest. The present invention significantly broadens the application of multiplex PCR in the identification of multiple genes related to multifactorial diseases, the genome-scale detection of genetic alterations, the studies in large-scale pharmacogenetic reactions, the genotyping genetic polymorphism in a large population, the gene expression profiling in various samples, and high throughput genotyping technologies.
Owner:LI HONGHUA +1
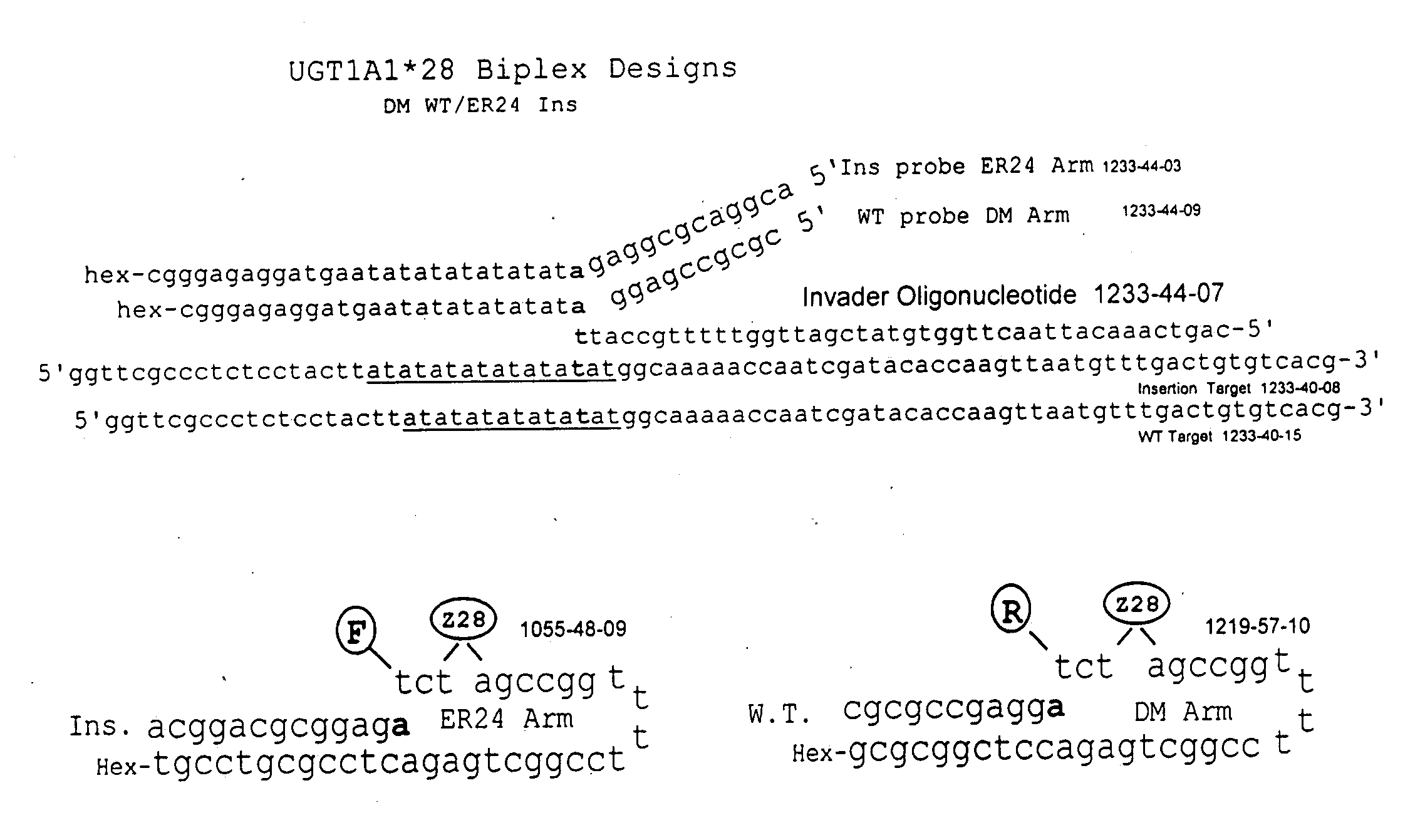
Pharmacogenetic DME detection assay methods and kits
InactiveUS20060160074A1Increase nucleic acid synthesis reaction rateHeating evenlySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug metabolismPharmacogenetics
The present invention relates to methods for detecting polymorphisms in enzymes related to drug metabolizm (Drug Metabolizing Enzymes or DMEs) such as uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) gene promoter, cytochrome p450, with a non-amplified oligonucleotide detection assays. The present invention also relates to pharmacogenetic DME detection assay kits.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
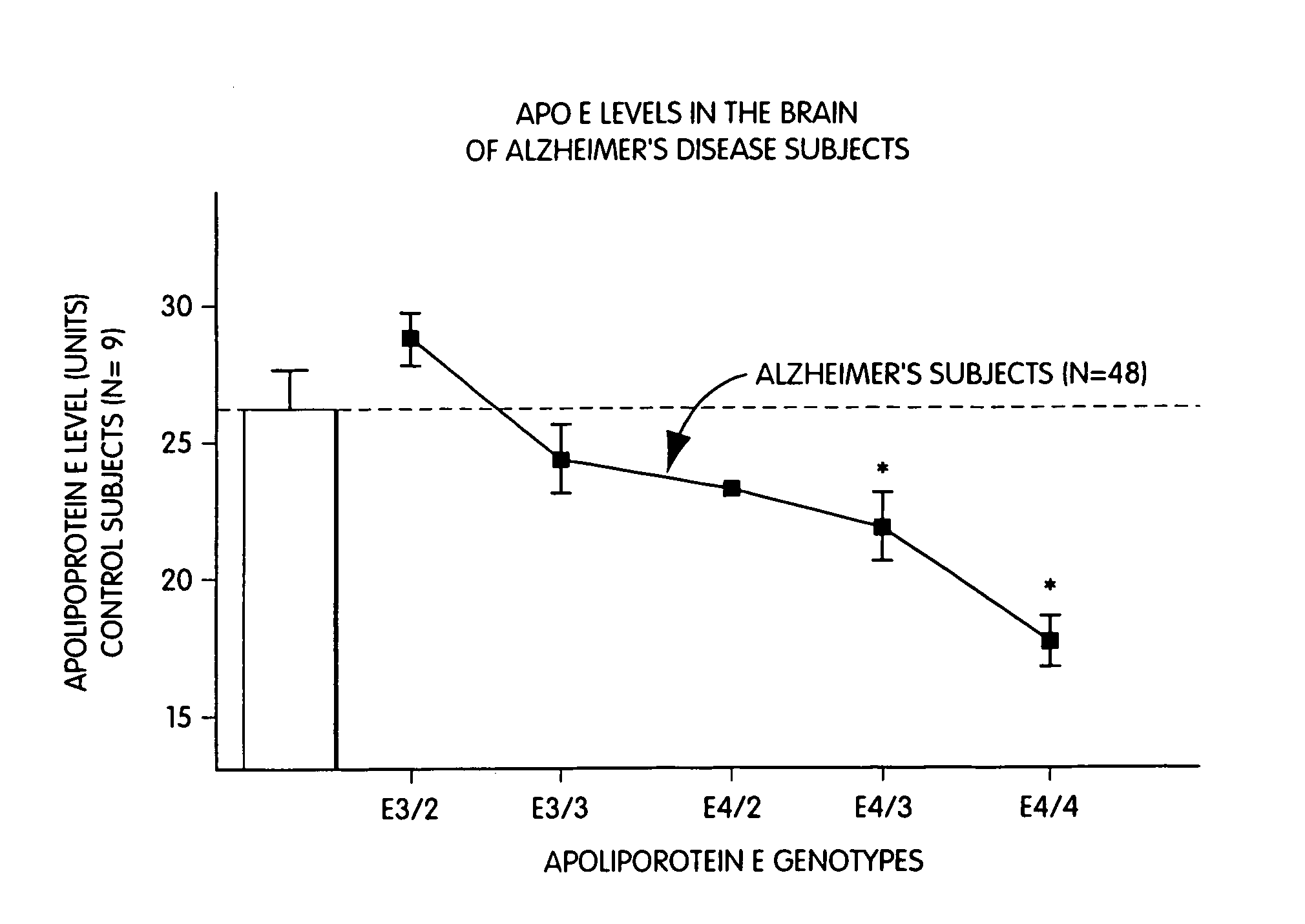
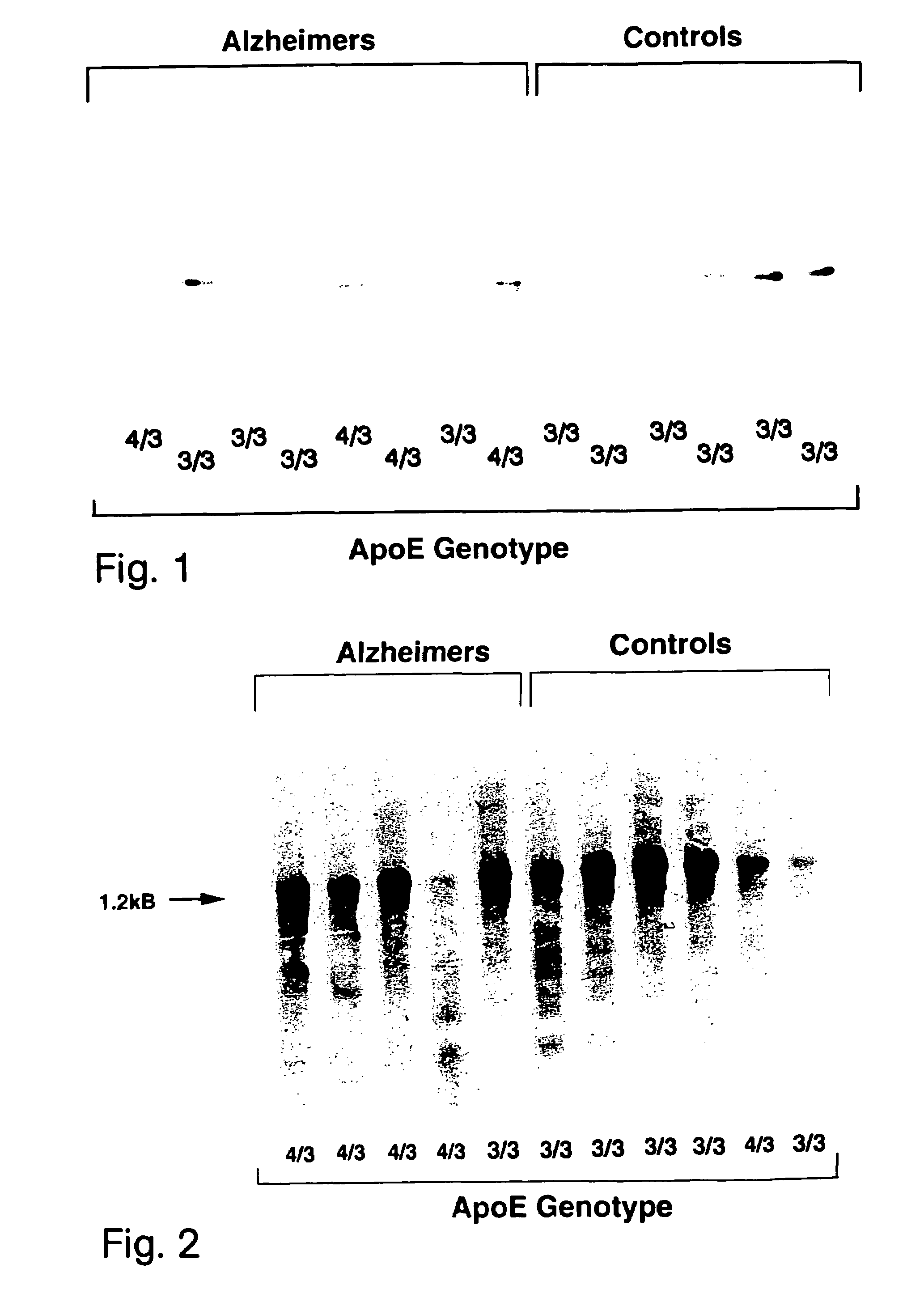
Pharmacogenetic methods for use in the treatment of nervous system diseases
InactiveUS7001736B1Quick cureData can be usedData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacogeneticsClinical trial
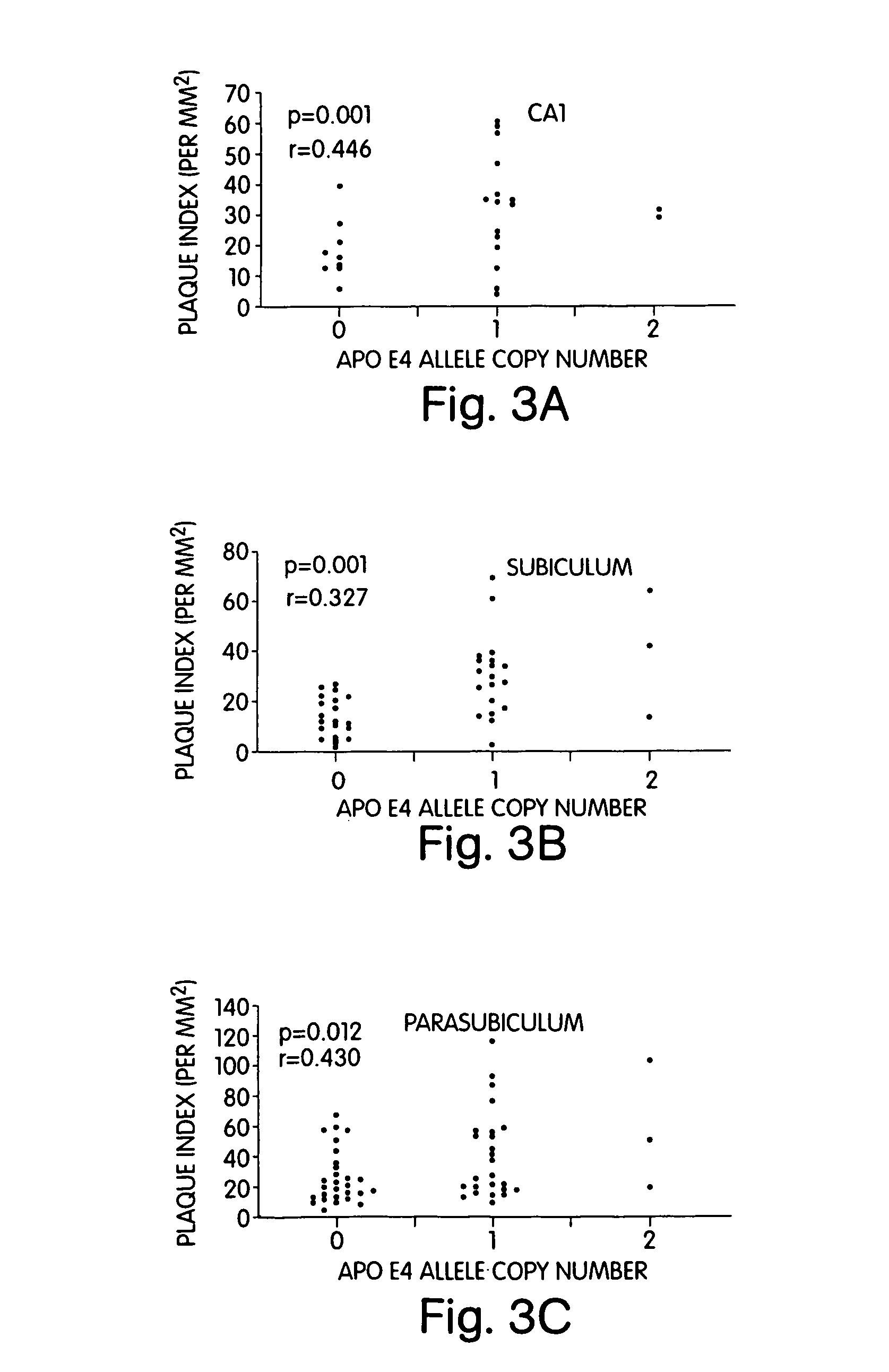
The present invention provides a method for the determining the appropriate therapy and / or prognosis for a patient diagnosed with a non-Alzheimer's disease (AD) neurological disease based upon the patient's apoE allele load. The invention also provides a method for the identification of human subjects with a non-AD neurological disease that are likely to respond in clinical trials that test pharmaceuticals useful in the treatment of neurological diseases.
Owner:NOVARTIS INT PHARM LTD
Method for treatment of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases and detecting the risk of the same
InactiveUS20070072798A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCysteine thiolateCoronary heart disease
This invention relates to the therapeutic, diagnostic and pharmacogenetic use of nucleic acids and proteins involved in human proteolytical system such as serine and cysteine proteases and their inhibitors and pharmaceutical agents and other therapies affecting these. This invention discloses methods for the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease (CHD), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), chronic CHD, arterial hypertension (HT) and cerebrovascular stroke and metabolic disorders such as the metabolic syndrome (MBO) and obesity and methods for detecting or diagnosing a risk of, or predisposition to the said diseases in a subject, for selecting treatment in a subject and for selecting subjects for studies testing cardiovascular, anti-diabetic and anti-obesity drugs, as well as to transgenic animals.
Owner:JURILAB
Diagnostics and Therapeutics of Neurological Disease
InactiveUS20080152589A1Improve accuracyFewer depressive episodesBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacogeneticsMedicine
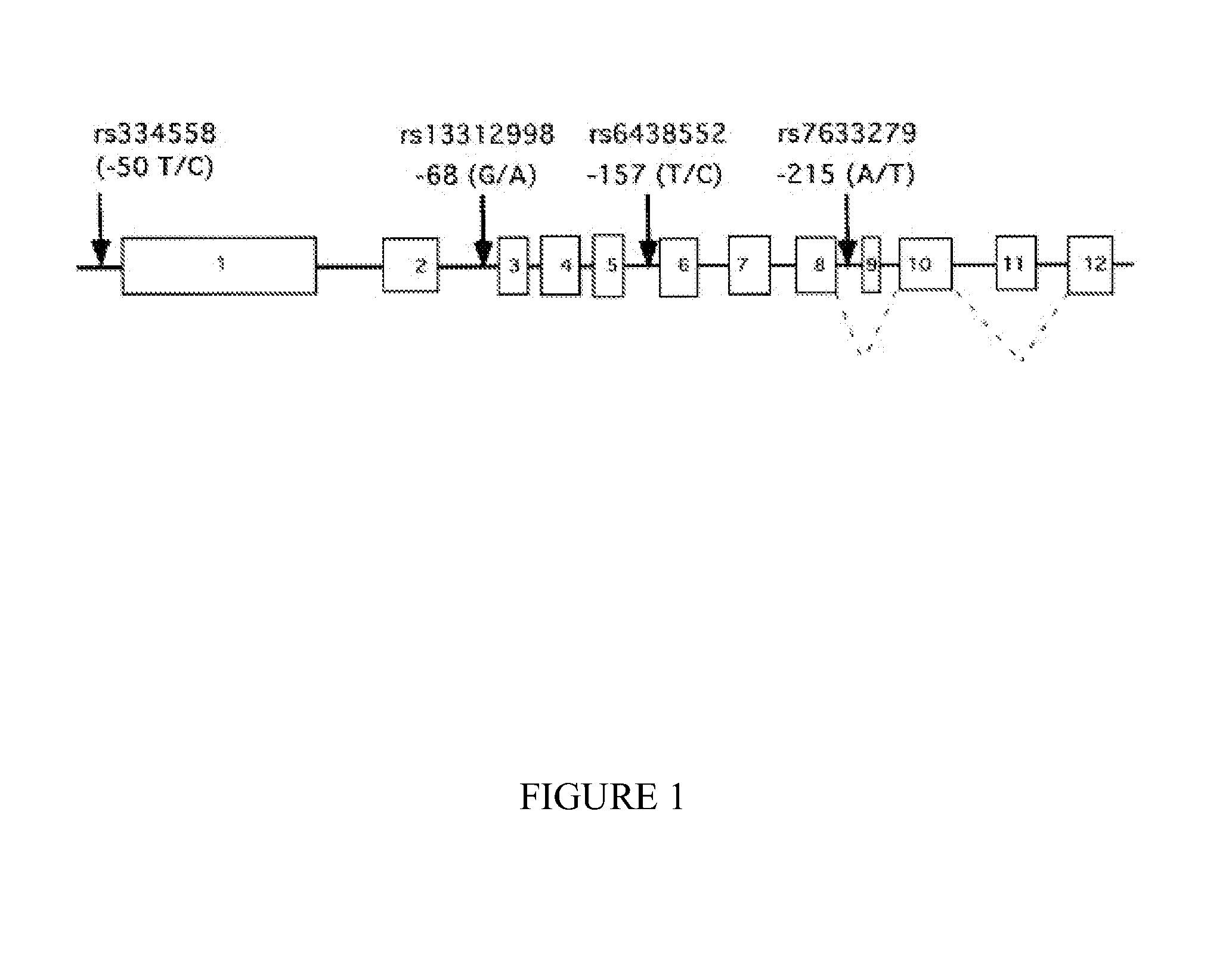
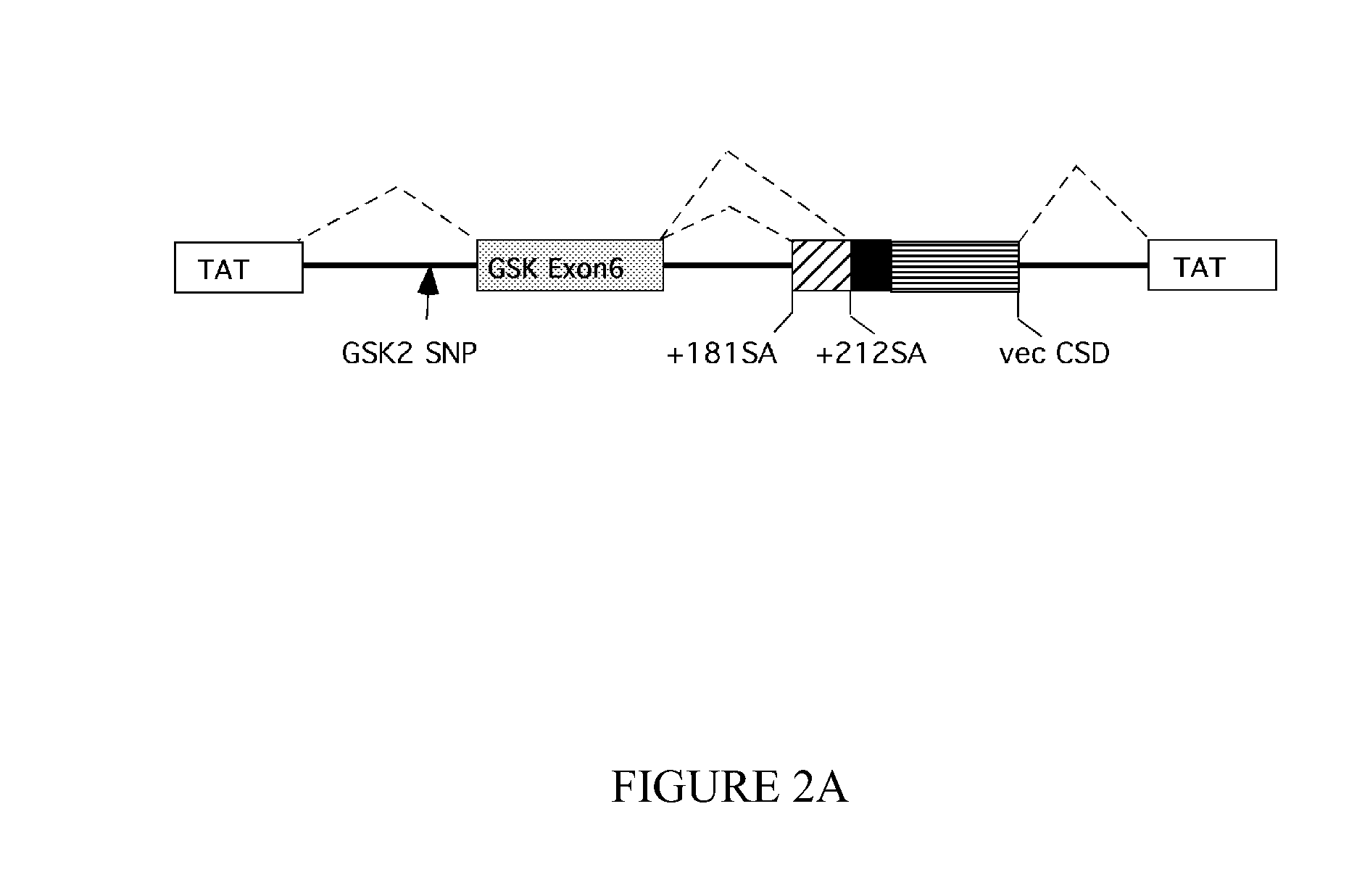
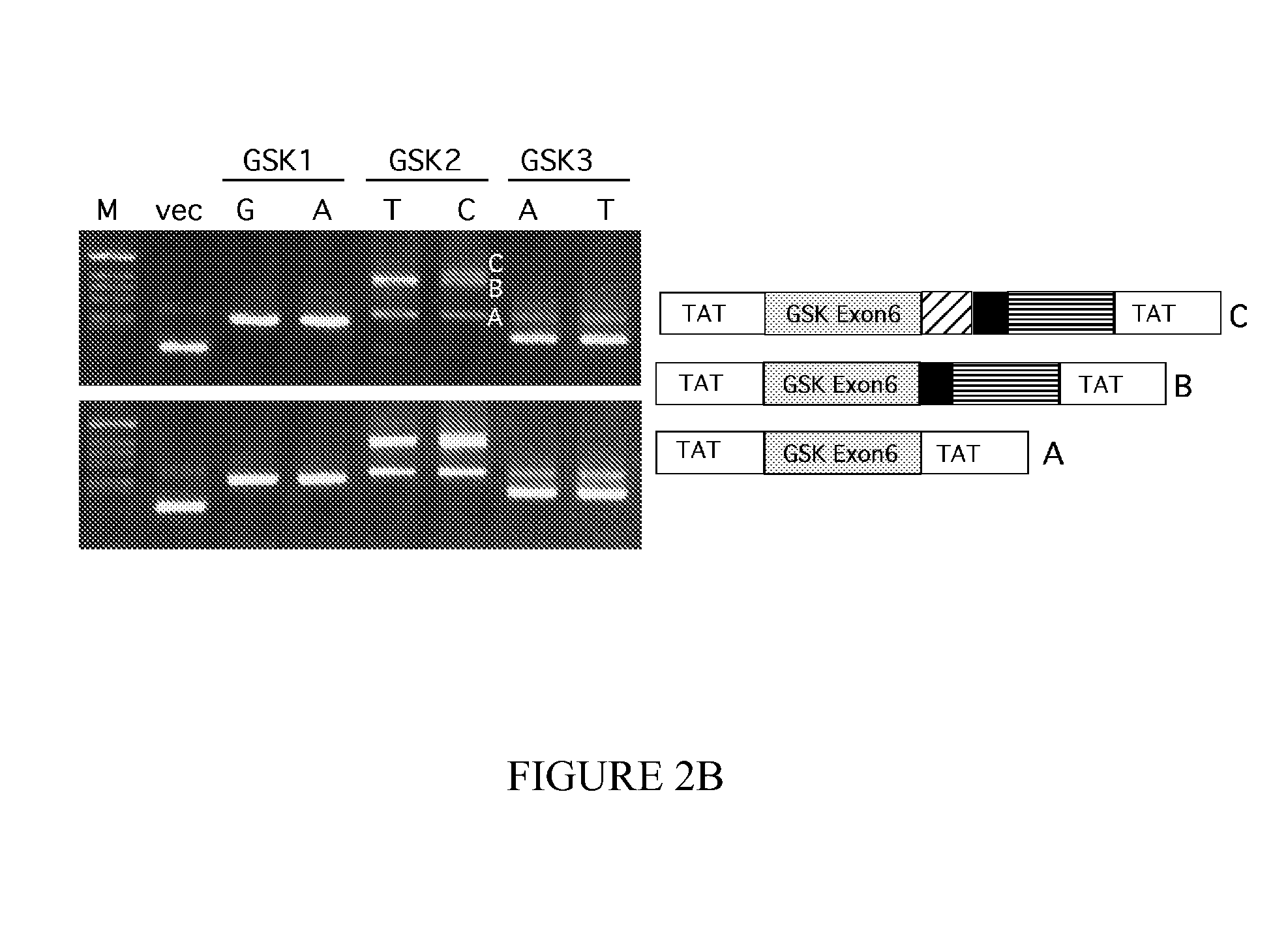
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing a neurological disease and / or for determining the predisposition of a subject to a neurological disease and / or for determining a subject at risk of developing a neurological disease, the method comprising detecting a marker in a glycogen synthase kinase 3β gene or expression product thereof and a microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) gene or expression product thereof. The present invention also provides pharmacogenetic methods, e.g., for identifying a subject that will respond to treatment with a therapeutic compound.
Owner:GARVAN INST OF MEDICAL RES OF C ST VINCENTS HOSPITAL
Methods and compositions relating to the pharmacogenetics of different gene variants
InactiveUS20090017452A1Reduce Toxicity RiskAddress bad outcomesMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacogeneticsGene product
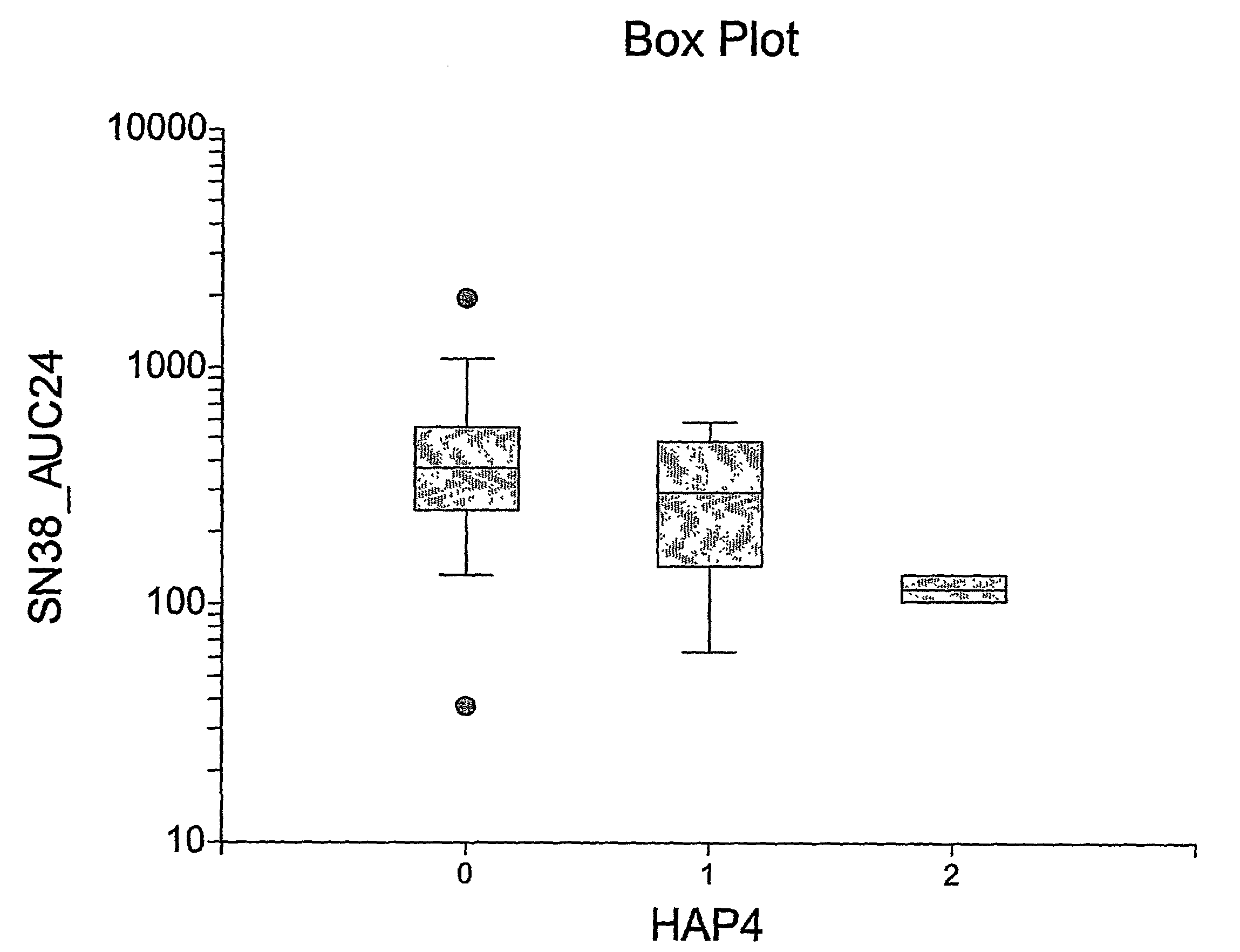
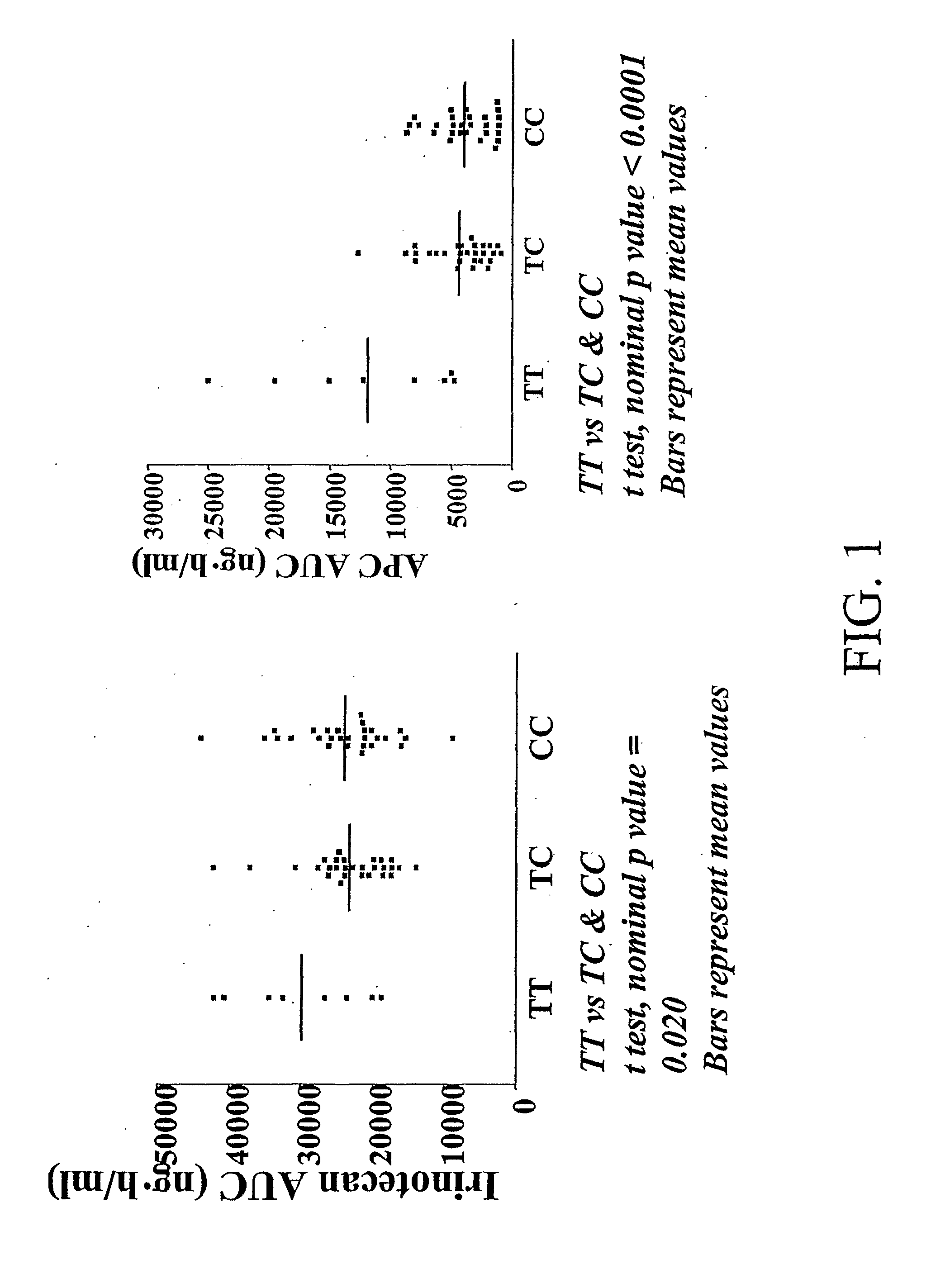
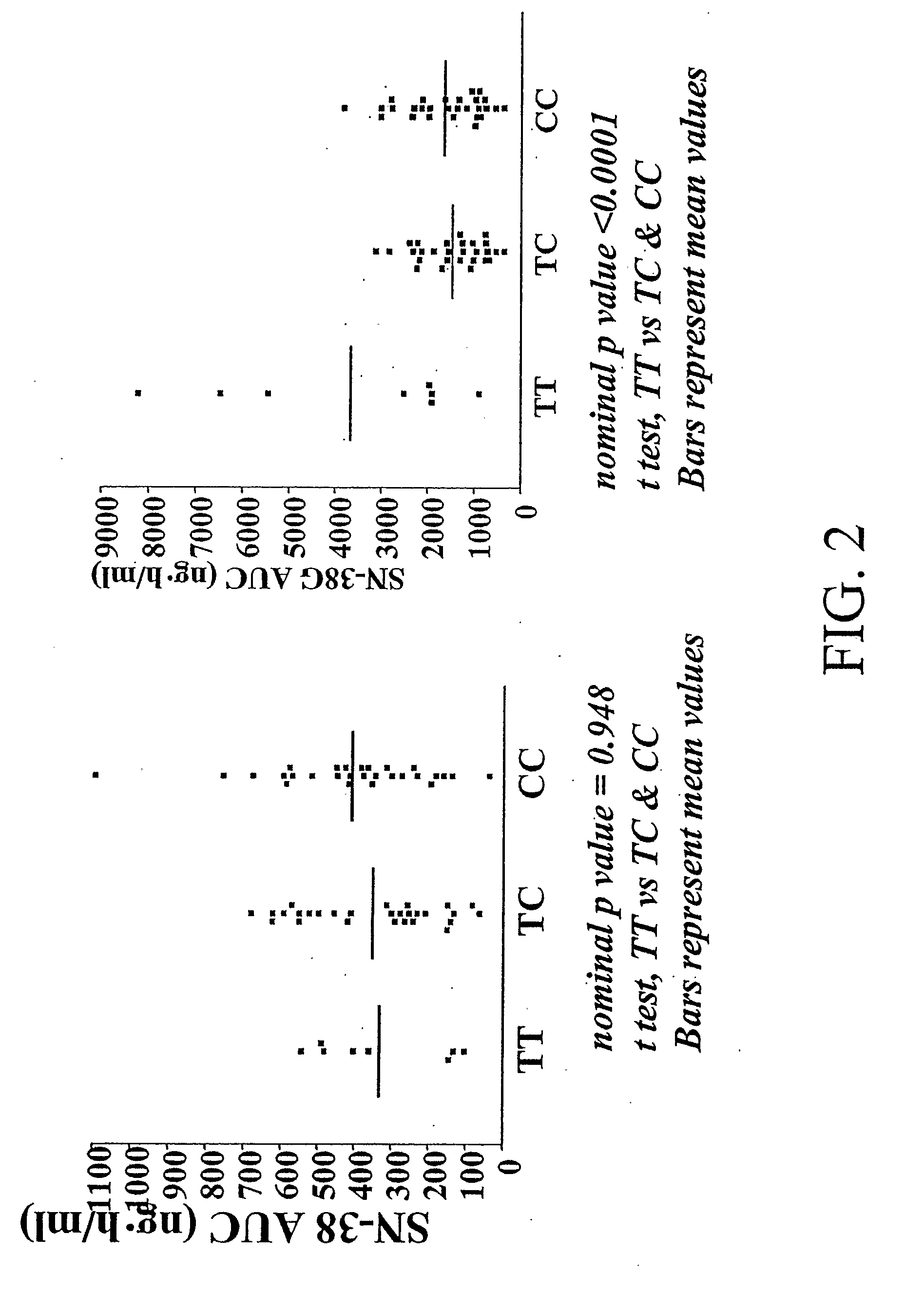
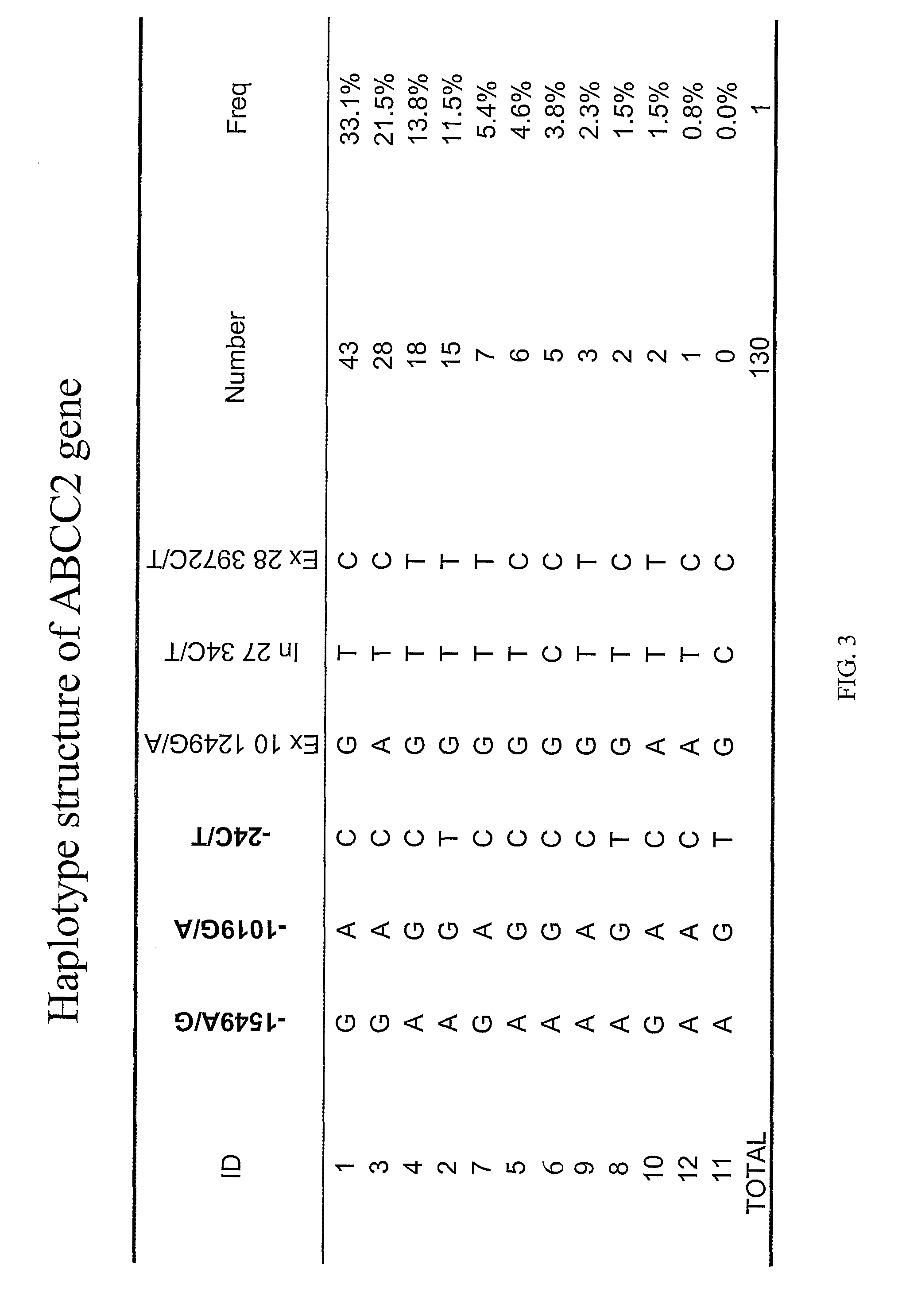
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for determining the presence or absence of polymorphisms within an ABCC2, UGT1A1, and / or SLCO1B1 gene and correlating these polymorphisms with activity levels of their gene products and making evaluations regarding the effect on their substrates, particularly those substrates that are drugs. In addition, there are methods and compositions of evaluating the risk of an individual for developing toxicity or adverse event(s) to an ABCC2, UGT1A1, and / or SLCO1B1 substrate. In some embodiments, the invention concerns methods and compositions for determining the presence or absence of ABCC2 3972C>T variant and predicting or anticipating the level of activity of ABCC2 and determining dosages of an ABCC2 drug substrate, such as irinotecan, in a patient. Such methods and compositions can be used to evaluate whether irinotecan-based therapy, or therapy involving other ABCC2 substrates, may pose toxicity problems if given to a particular patient or predicting their efficacy. Alterations in suggested therapy may ensue based on genotyping results.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
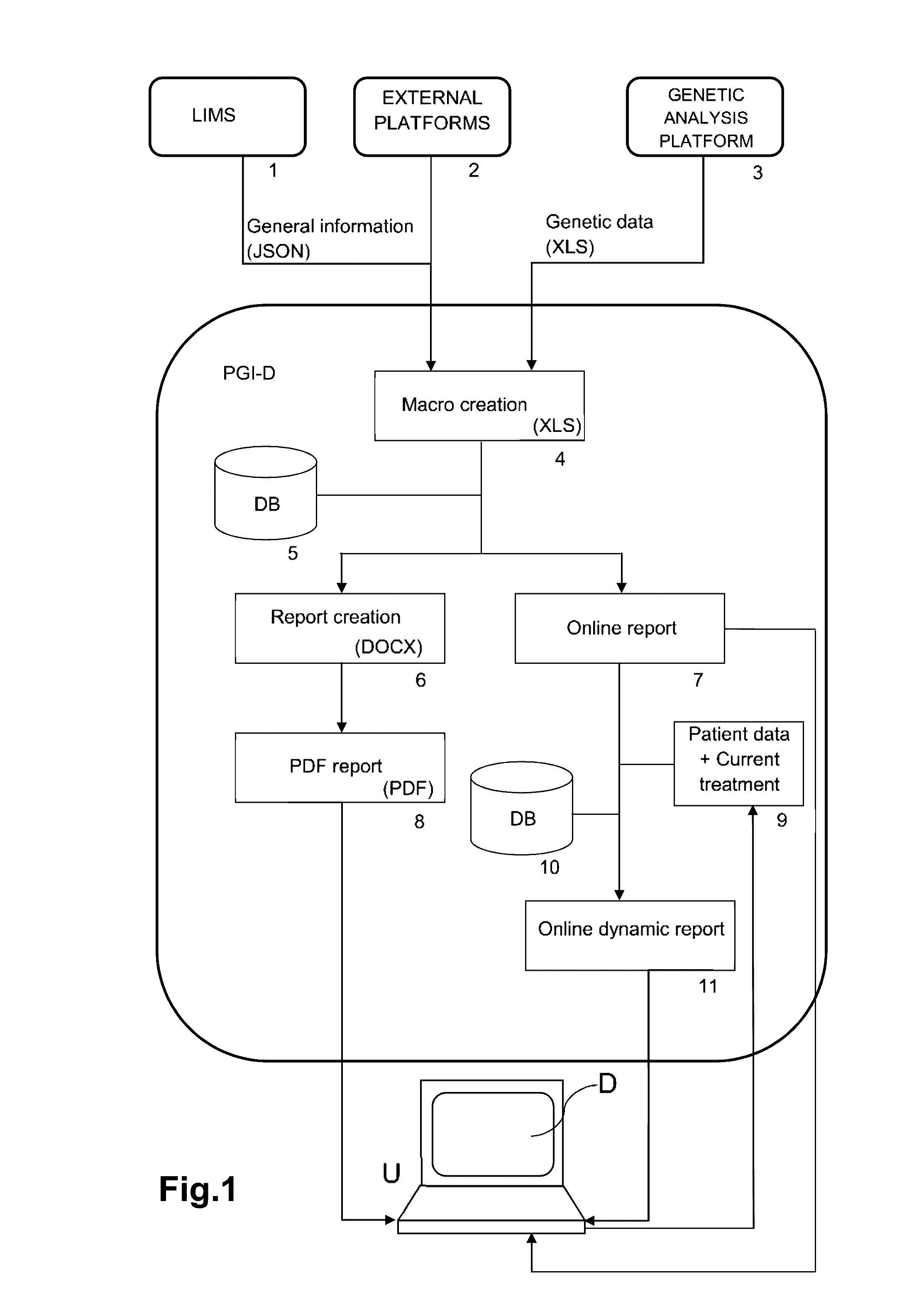
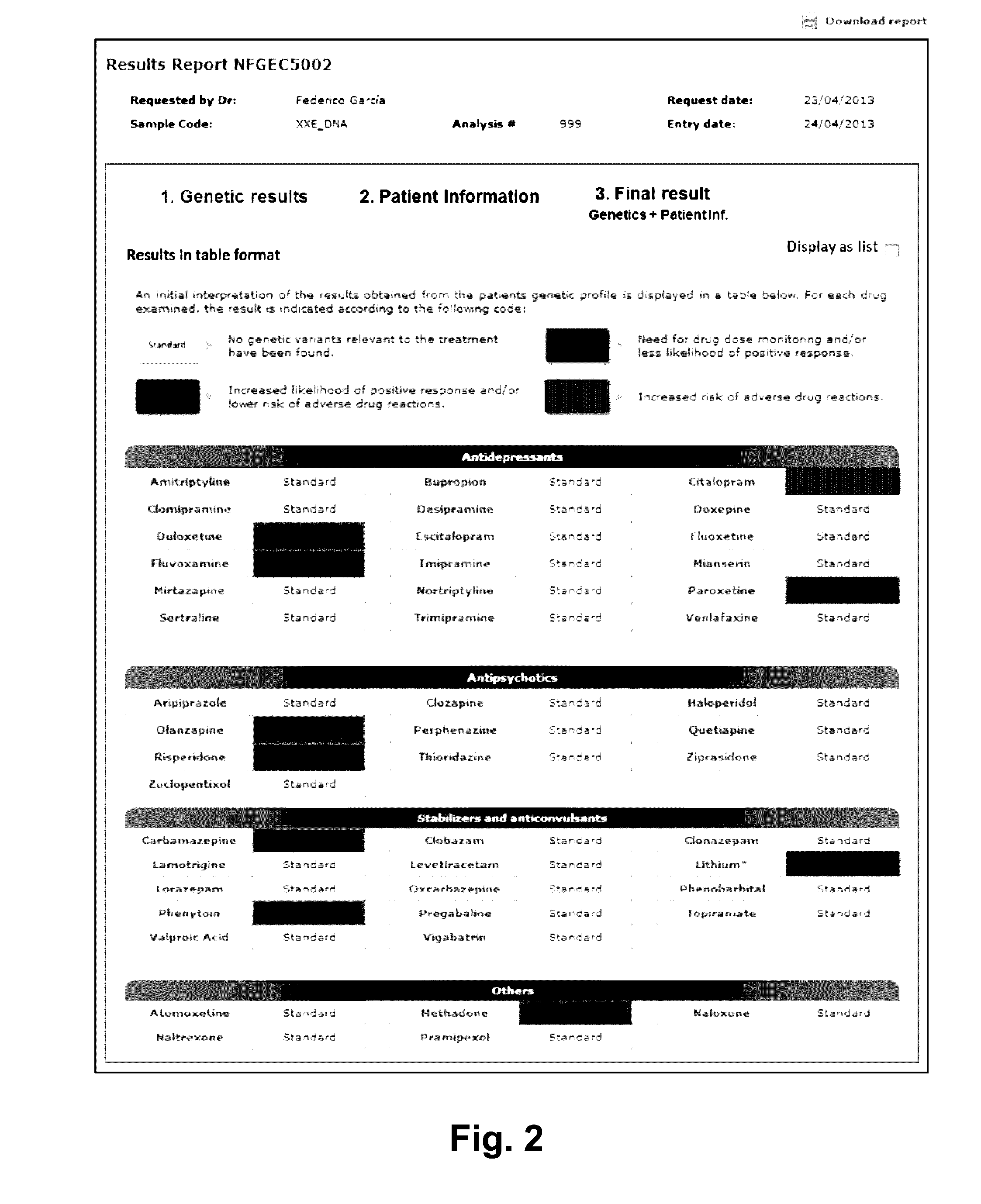
Web-based computer-aided method and system for providing personalized recommendations about drug use, and a computer-readable medium
ActiveUS20160314251A1Quality improvementReduce usageChemical property predictionDrug and medicationsPersonalizationComputer aid
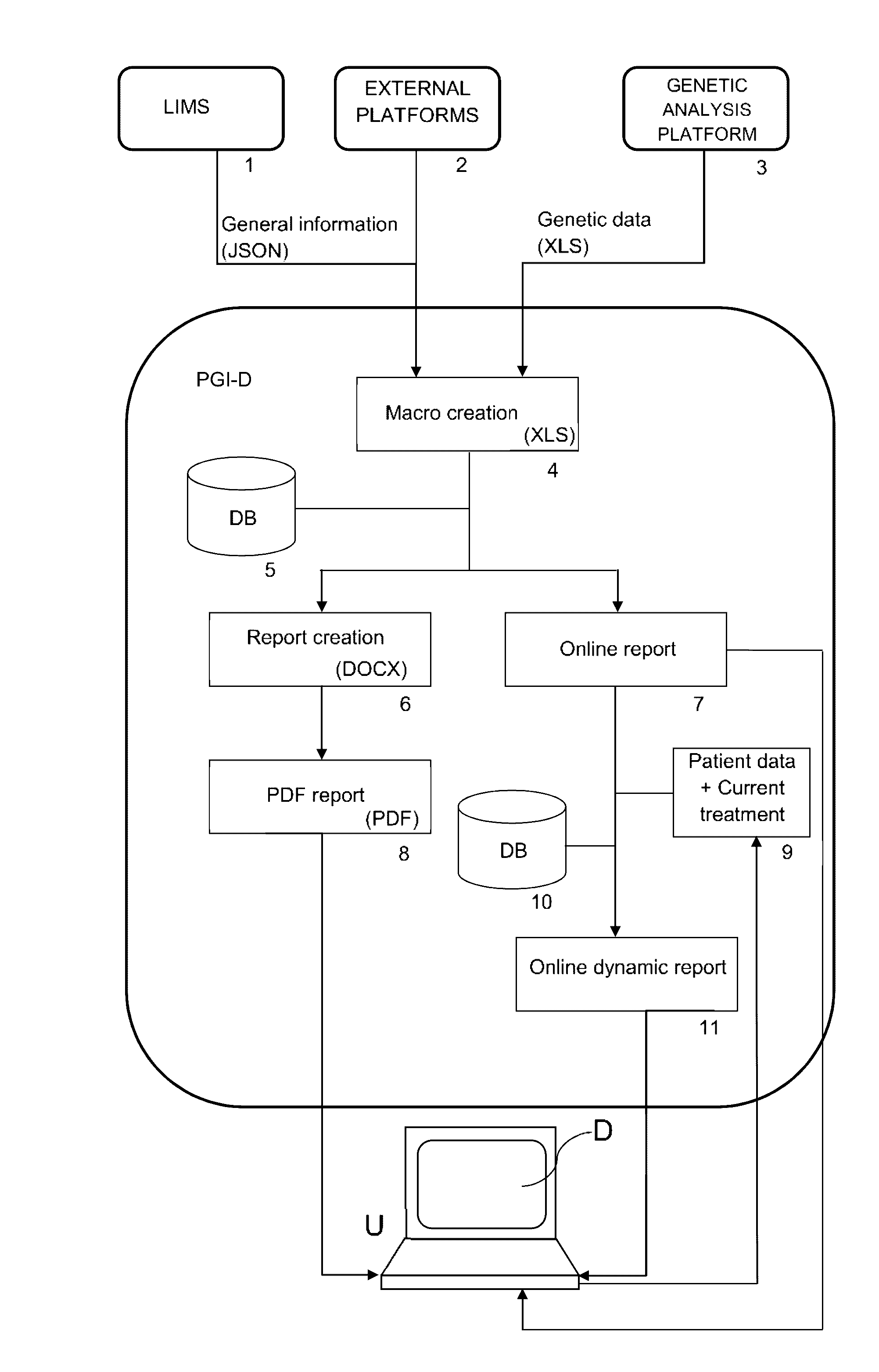
The present invention relates to a web-based computer-aided method and a system for providing personalized recommendations about drug use, based on pharmacogenetic information regarding genes and genetic variants associated to metabolism and genes and genetic variants which are not associated to metabolism, and which comprises automatically generating and displaying, by means of a graphical user interface (GUI) of a dynamic webpage, the personalized recommendations highlighting the ones associated to the highest adverse drug reactions.The present invention also relates to a computer-readable medium which contains program instructions for a computer to perform the method for providing personalized recommendations about drug use of the invention.The present invention also relates to a web-based computer-aided method and a system for generating a dynamic webpage, and a further computer-readable medium which contains program instructions for a computer to perform the method for generating a dynamic webpage.
Owner:BIOTICS
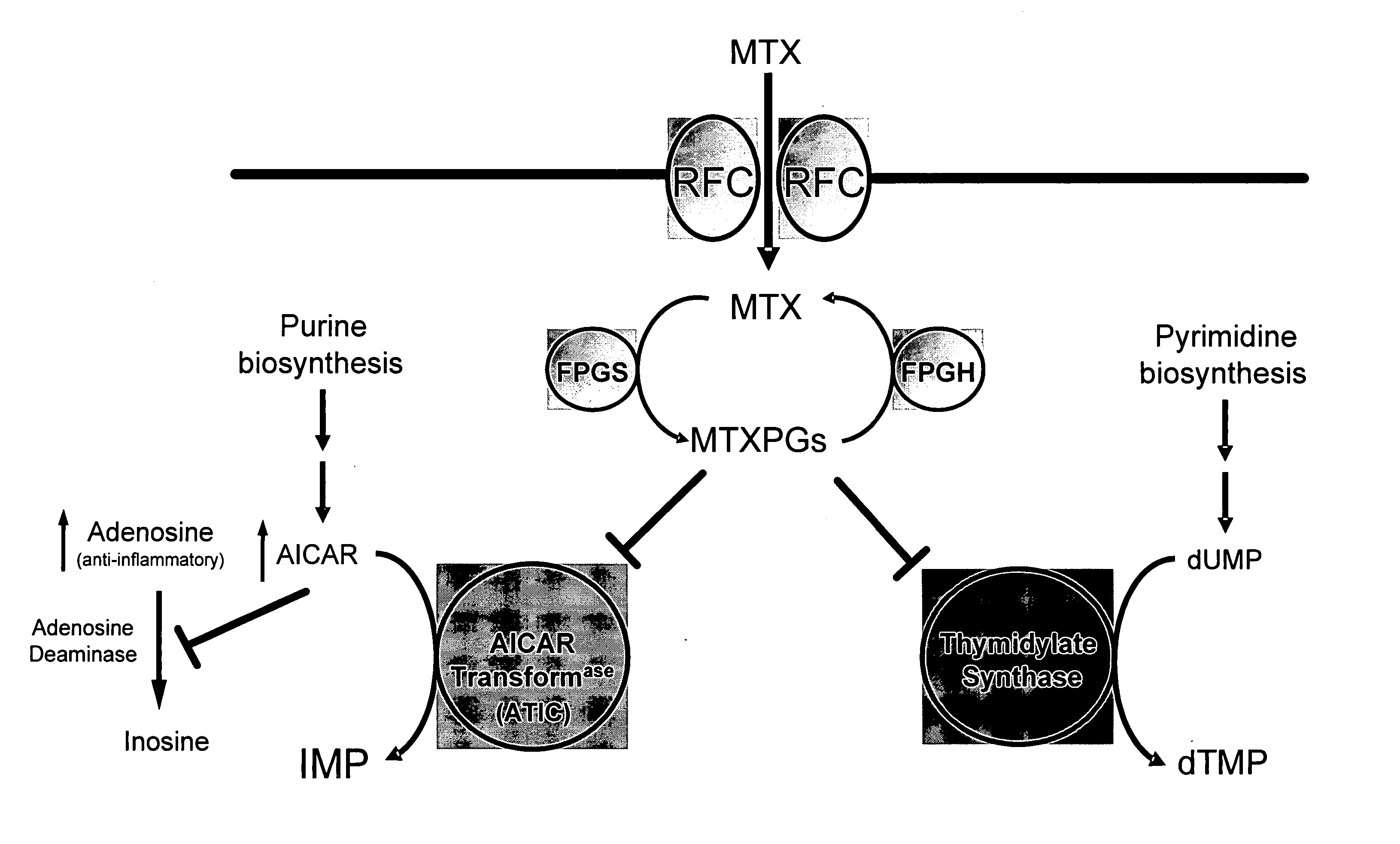
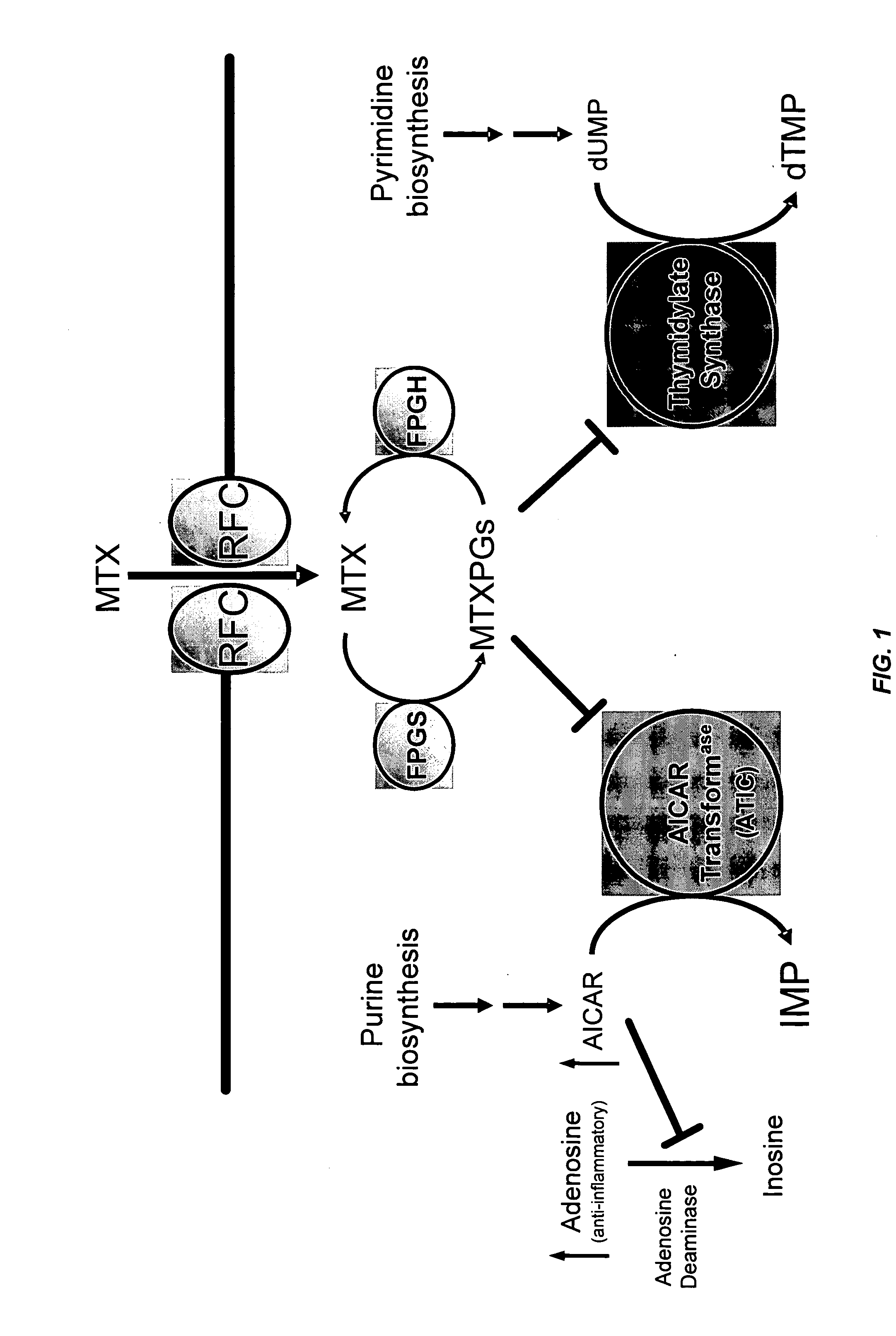
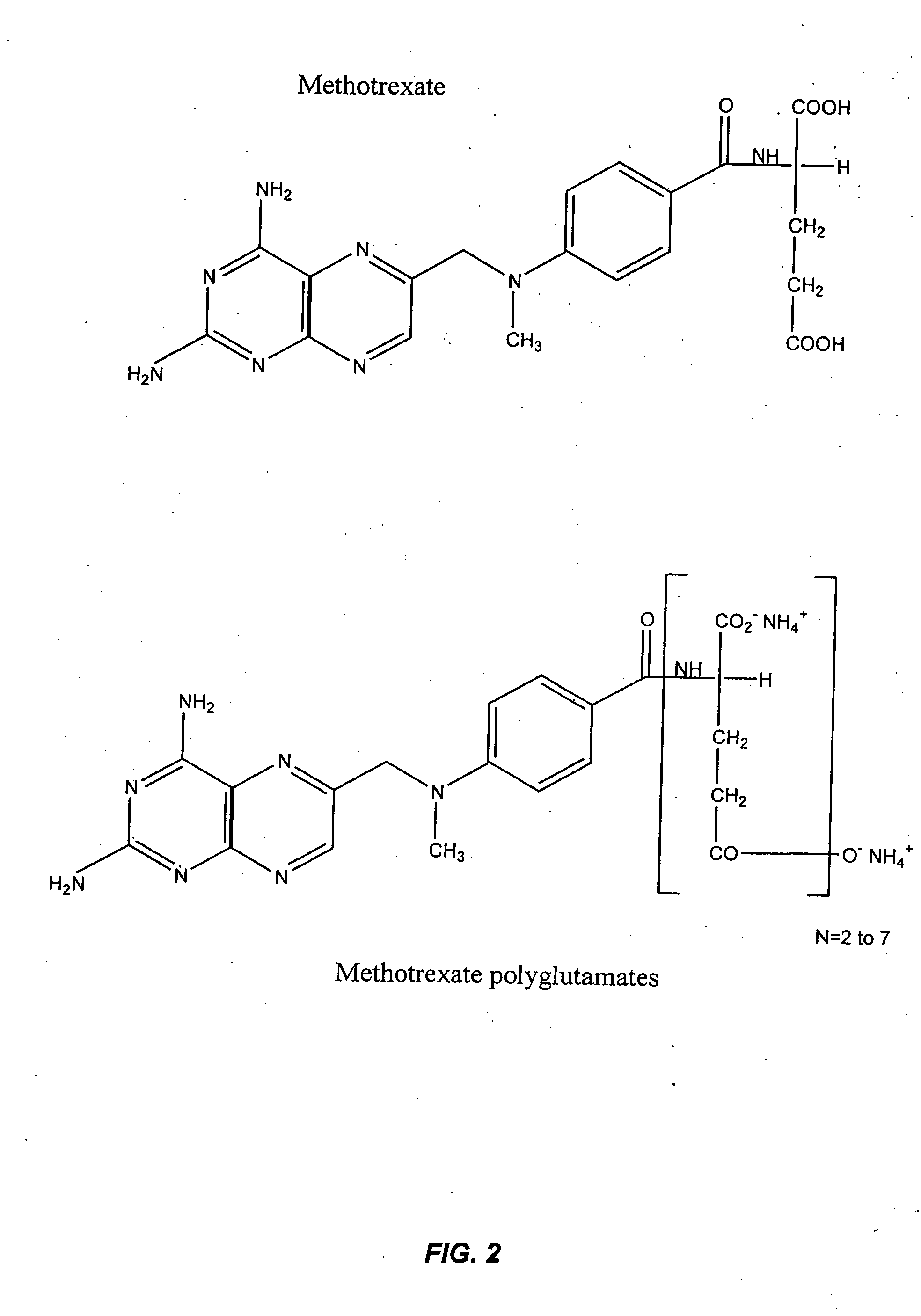
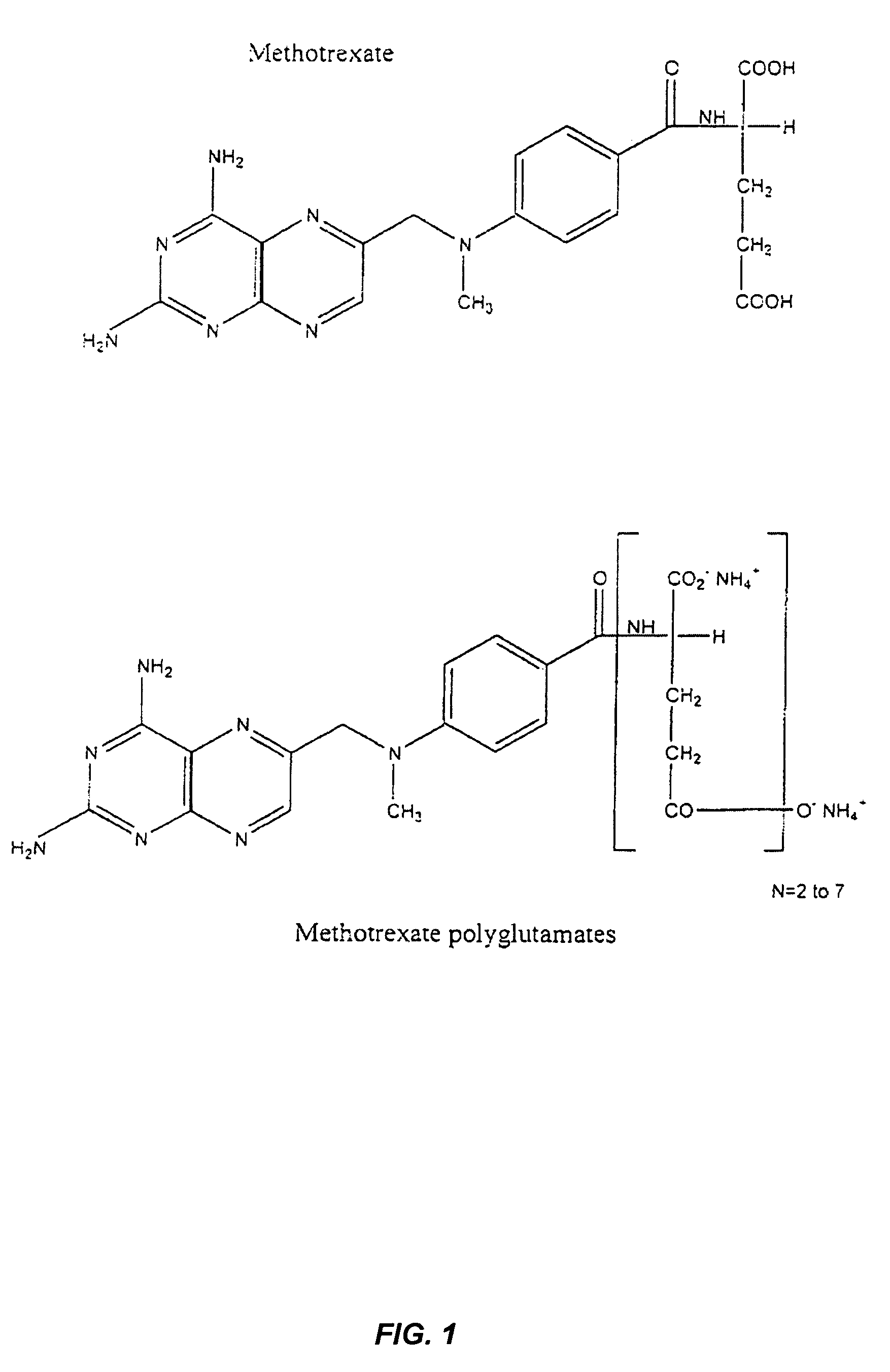
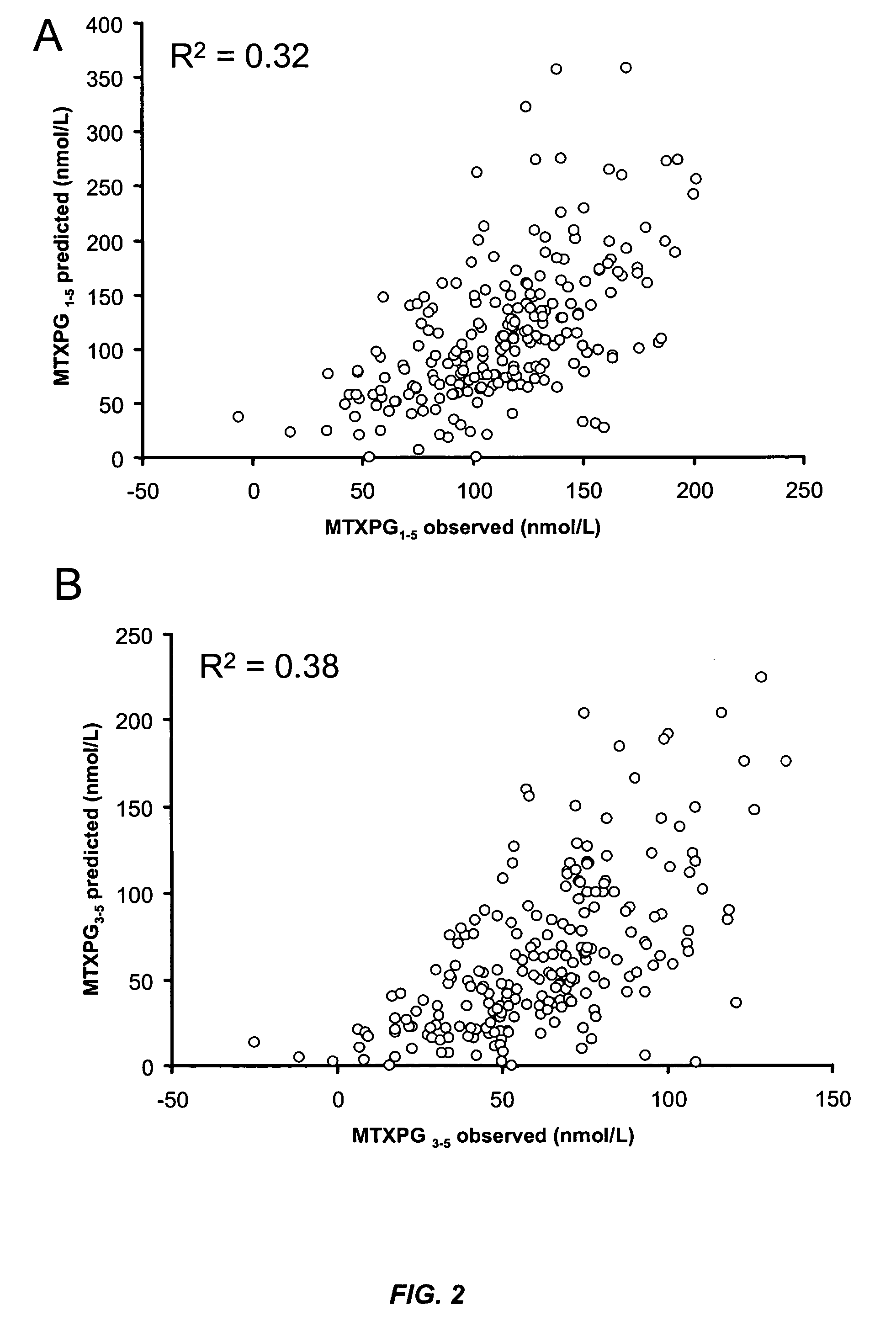
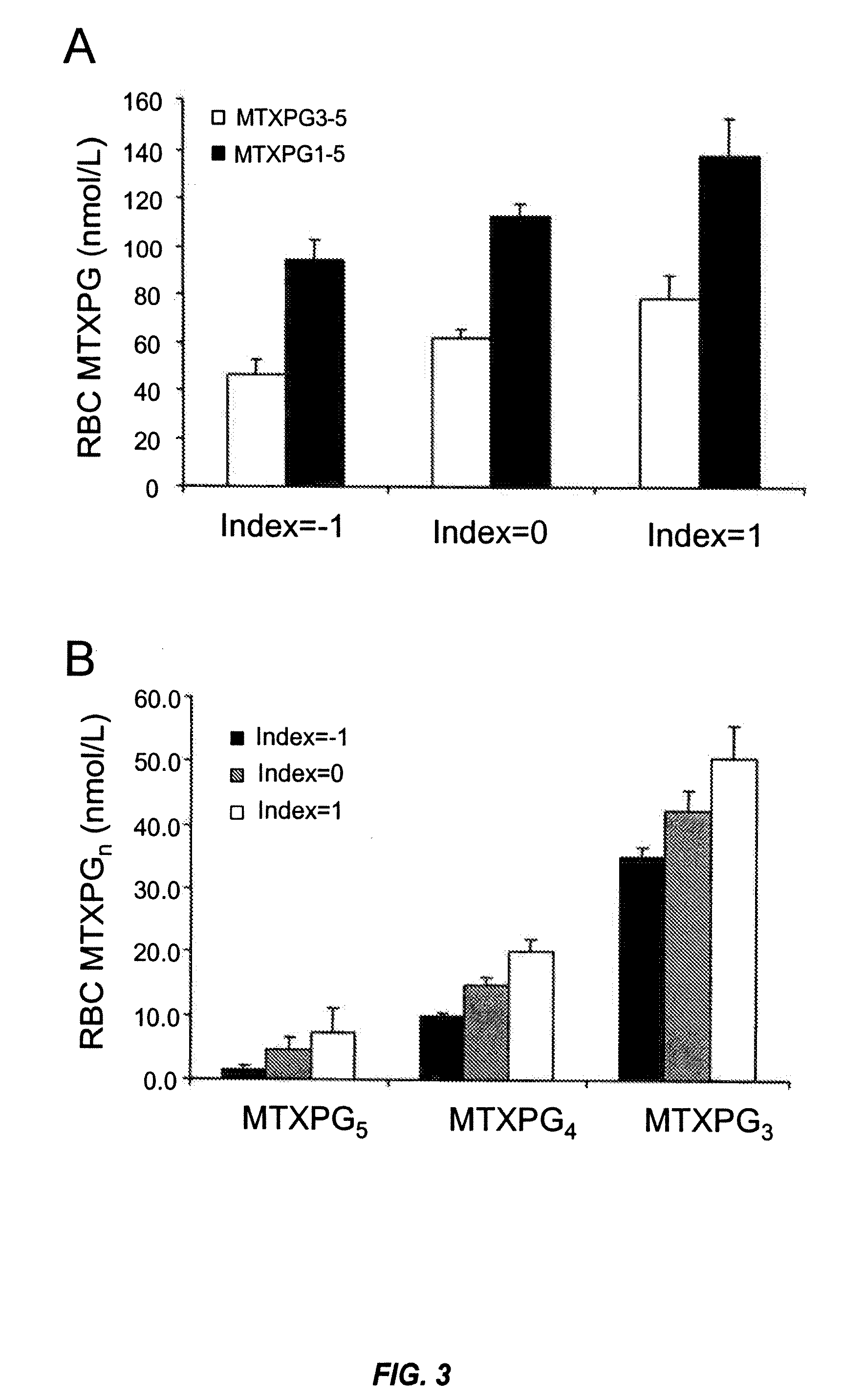
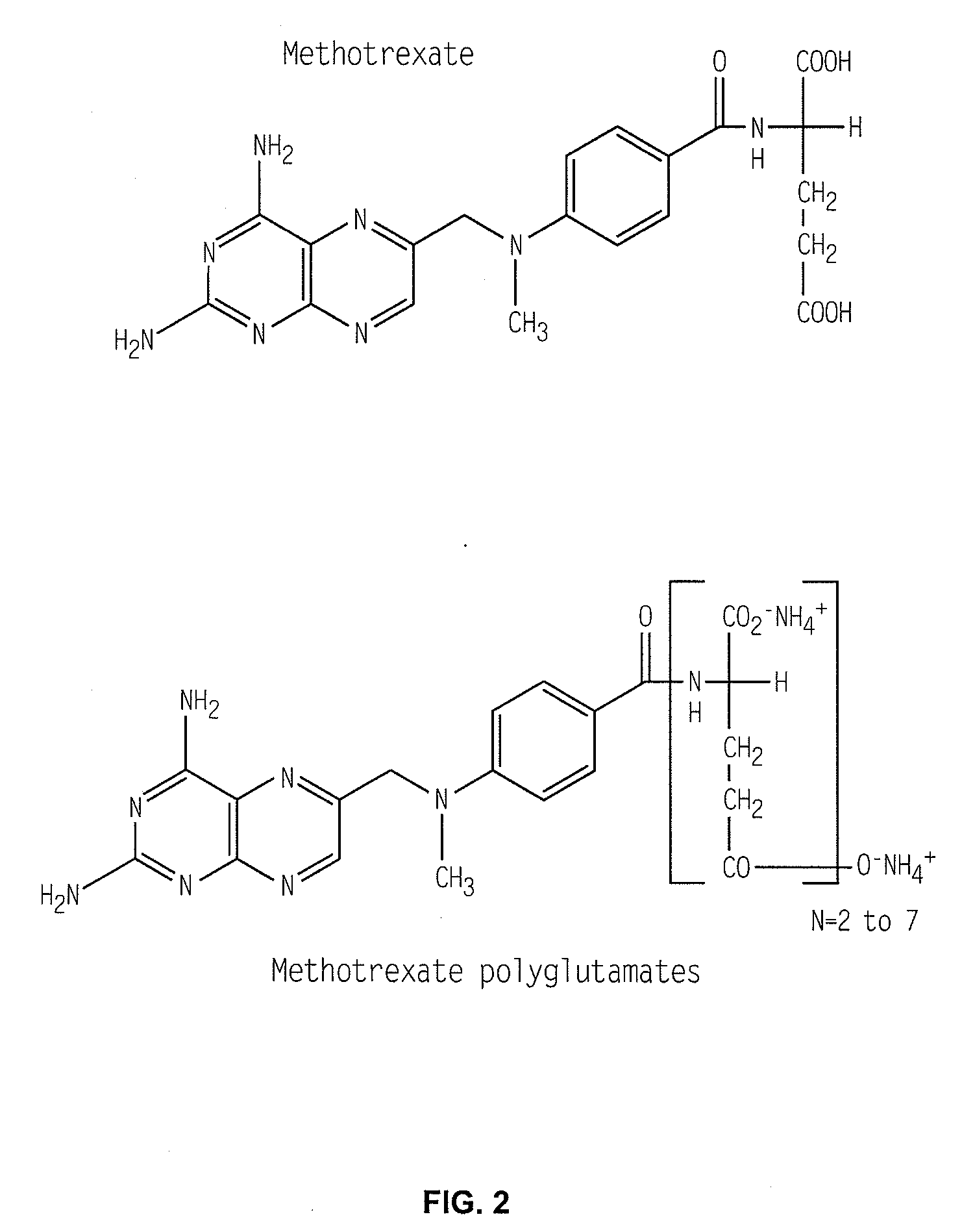
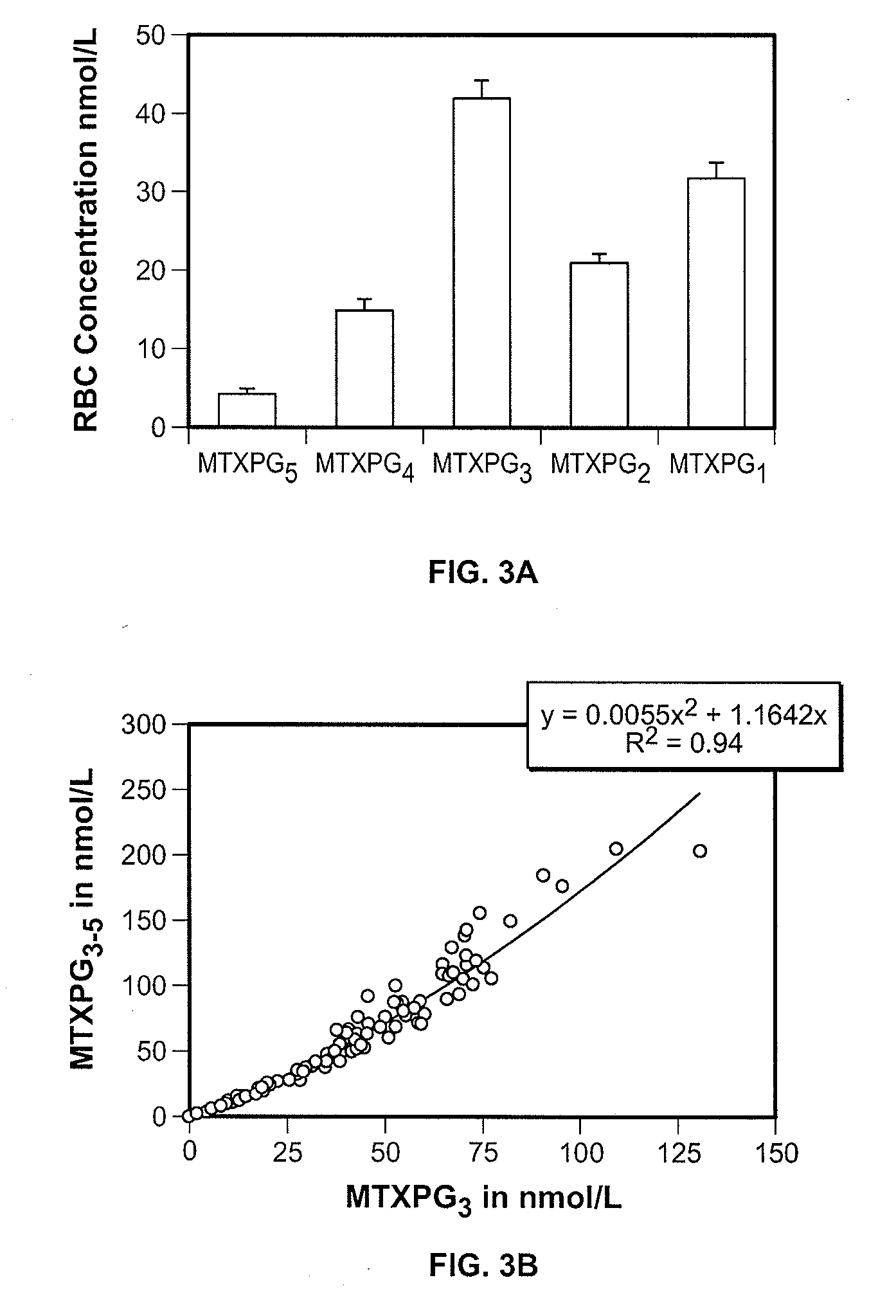
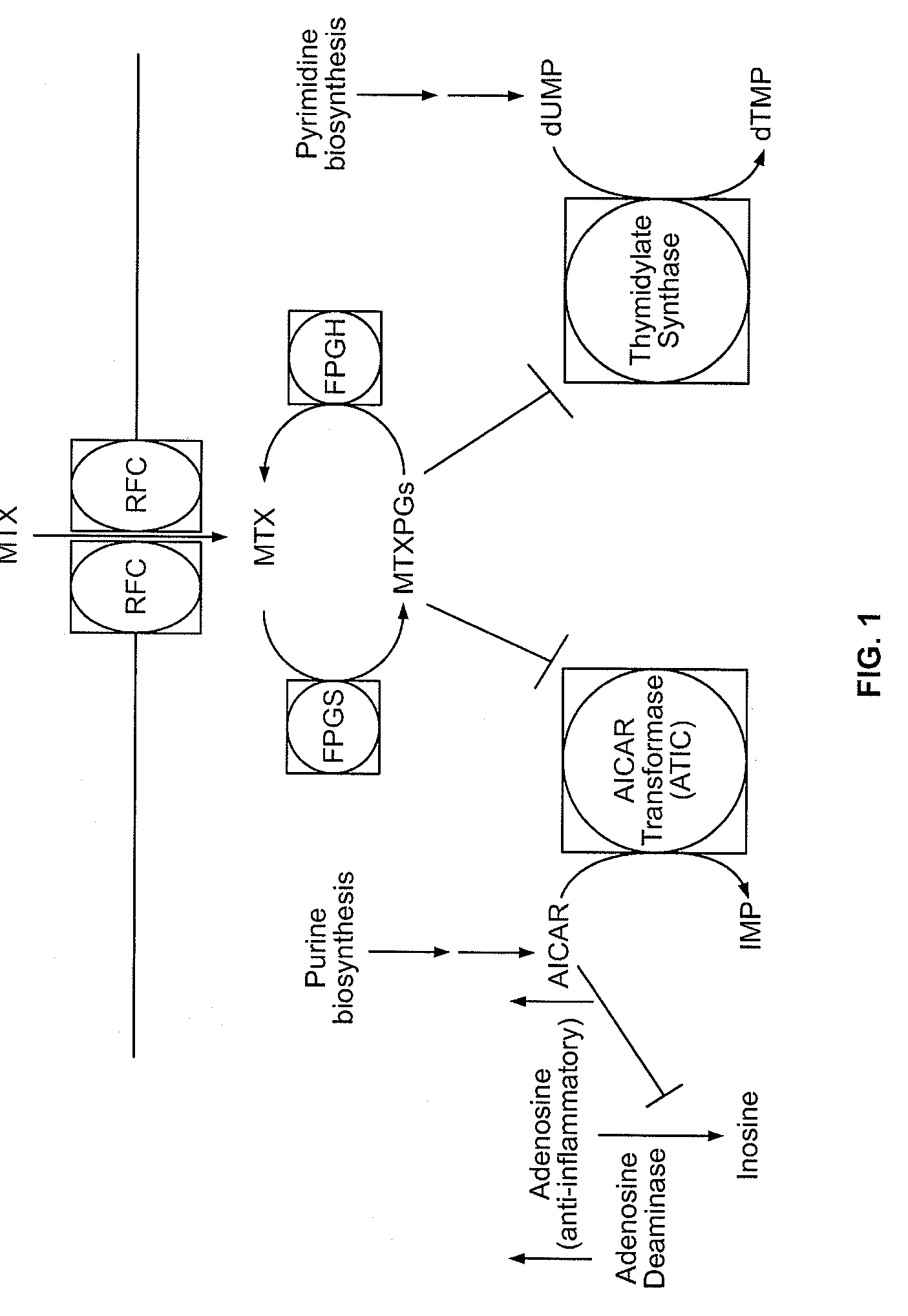
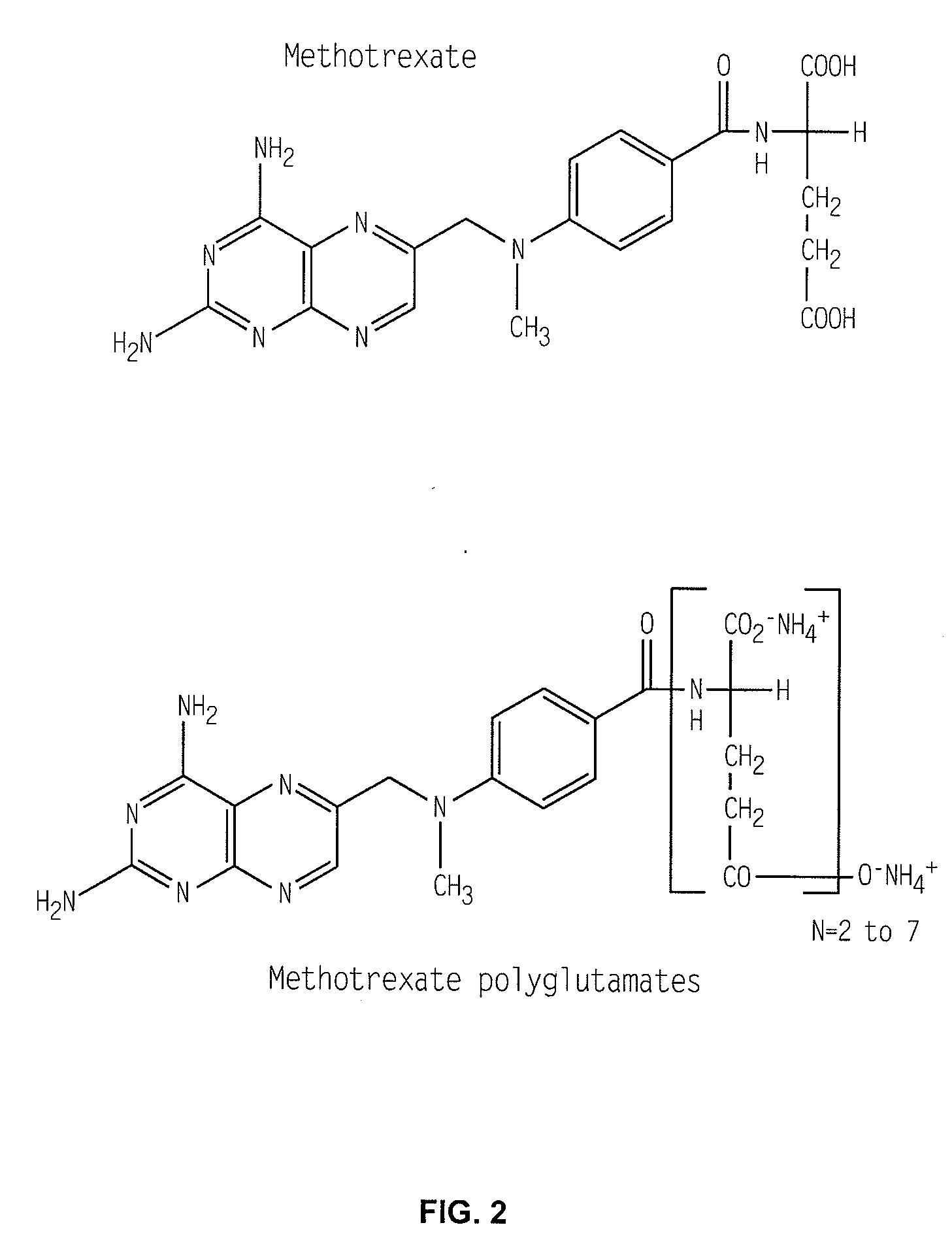
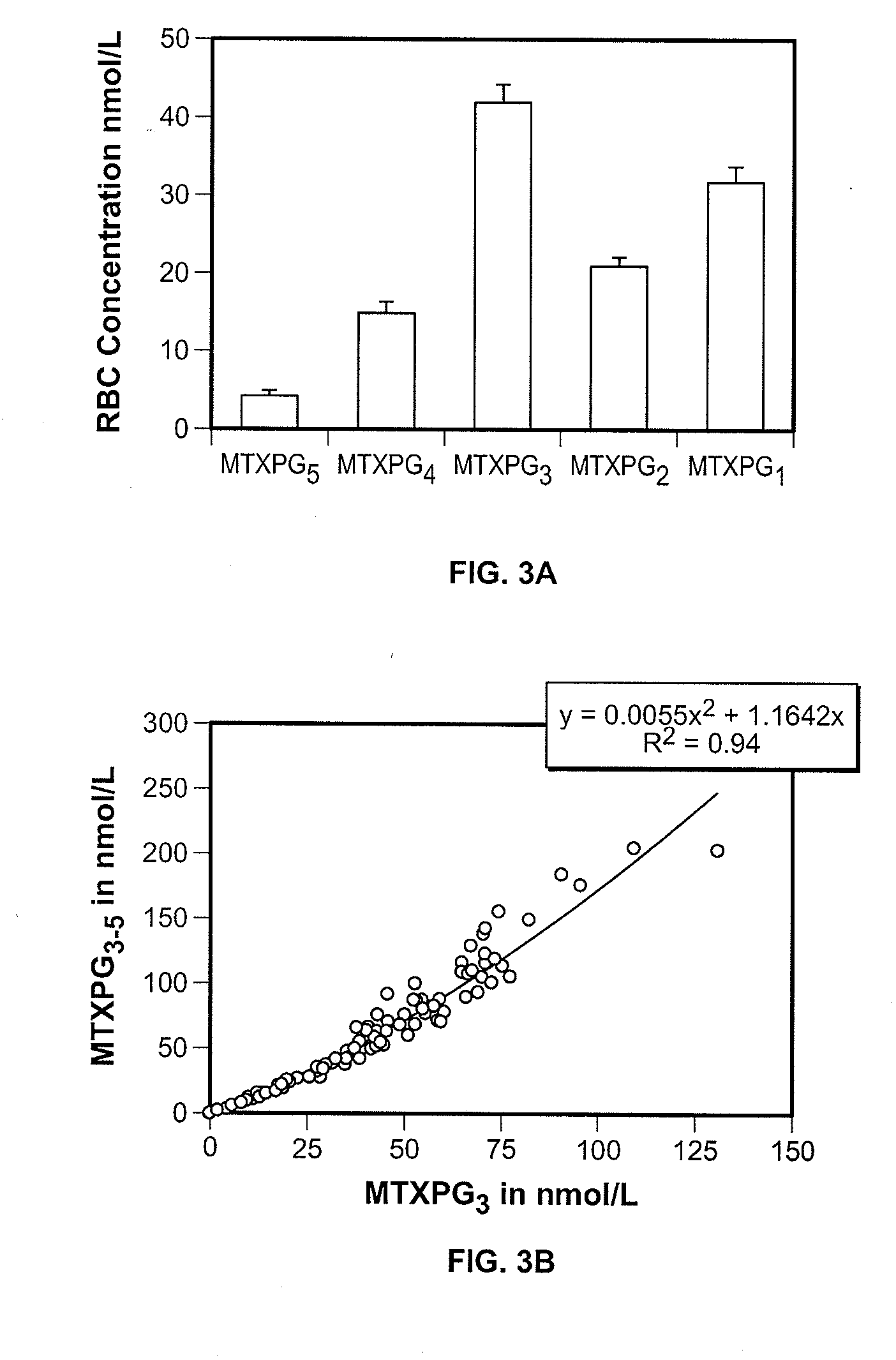
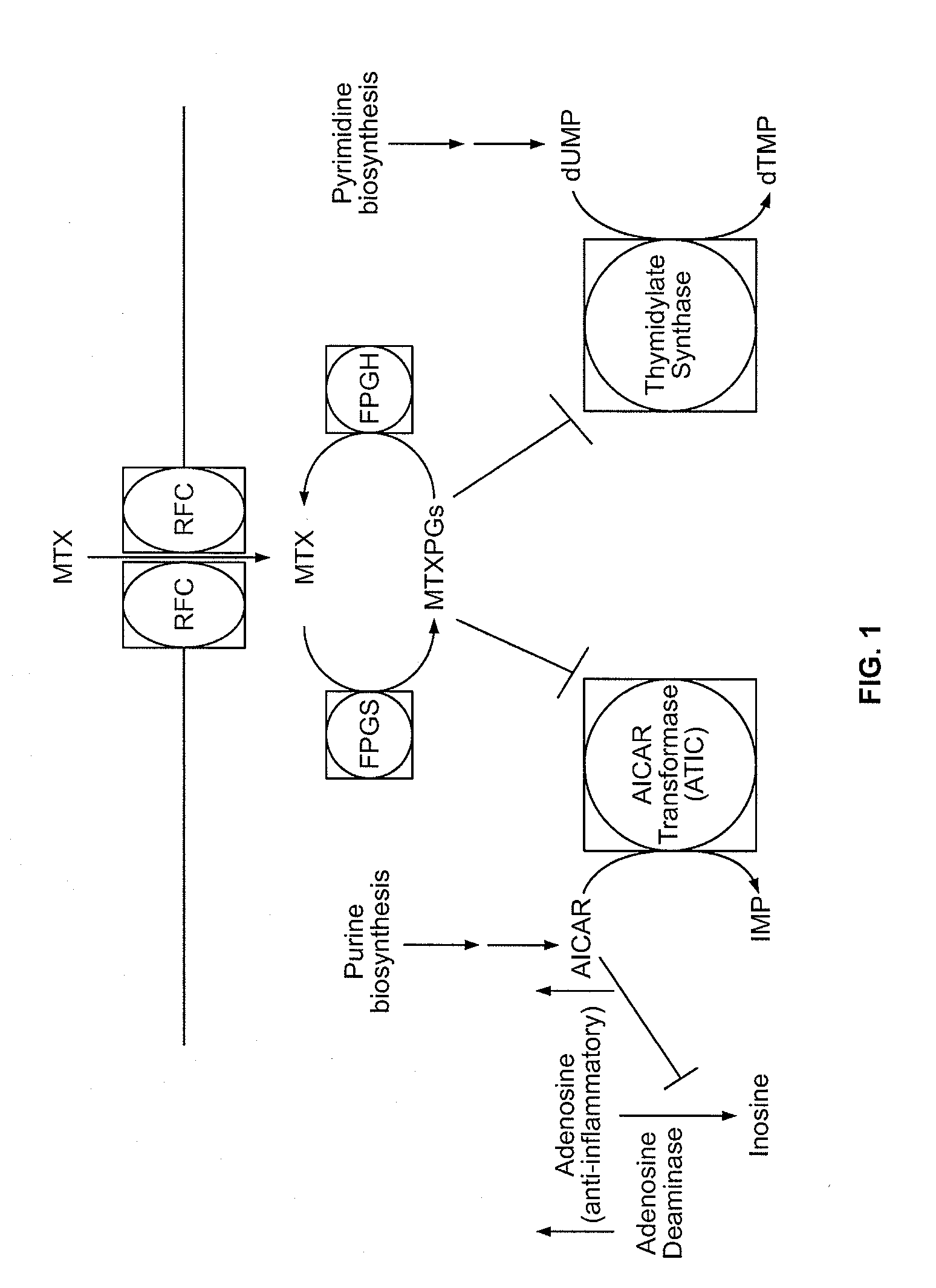
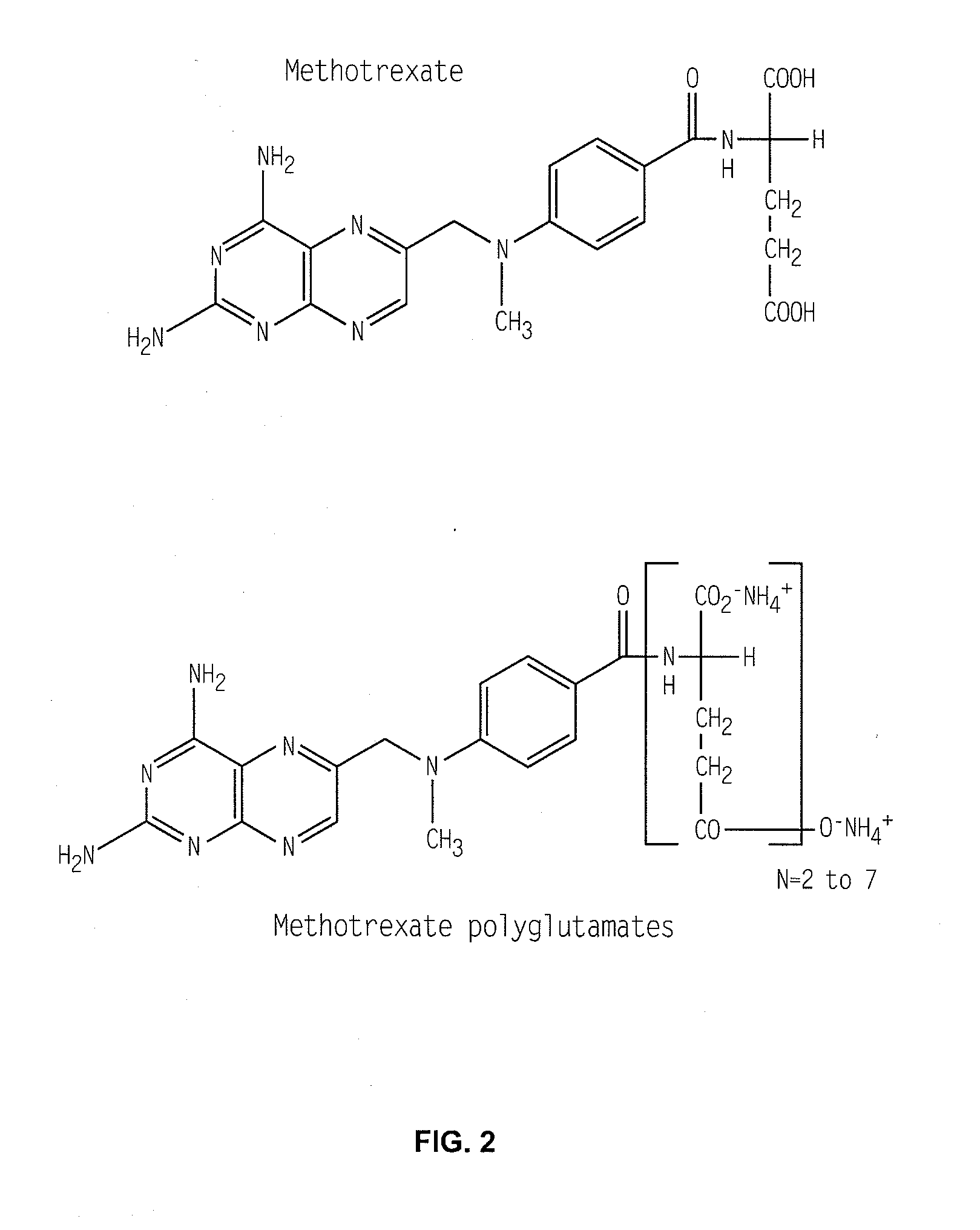
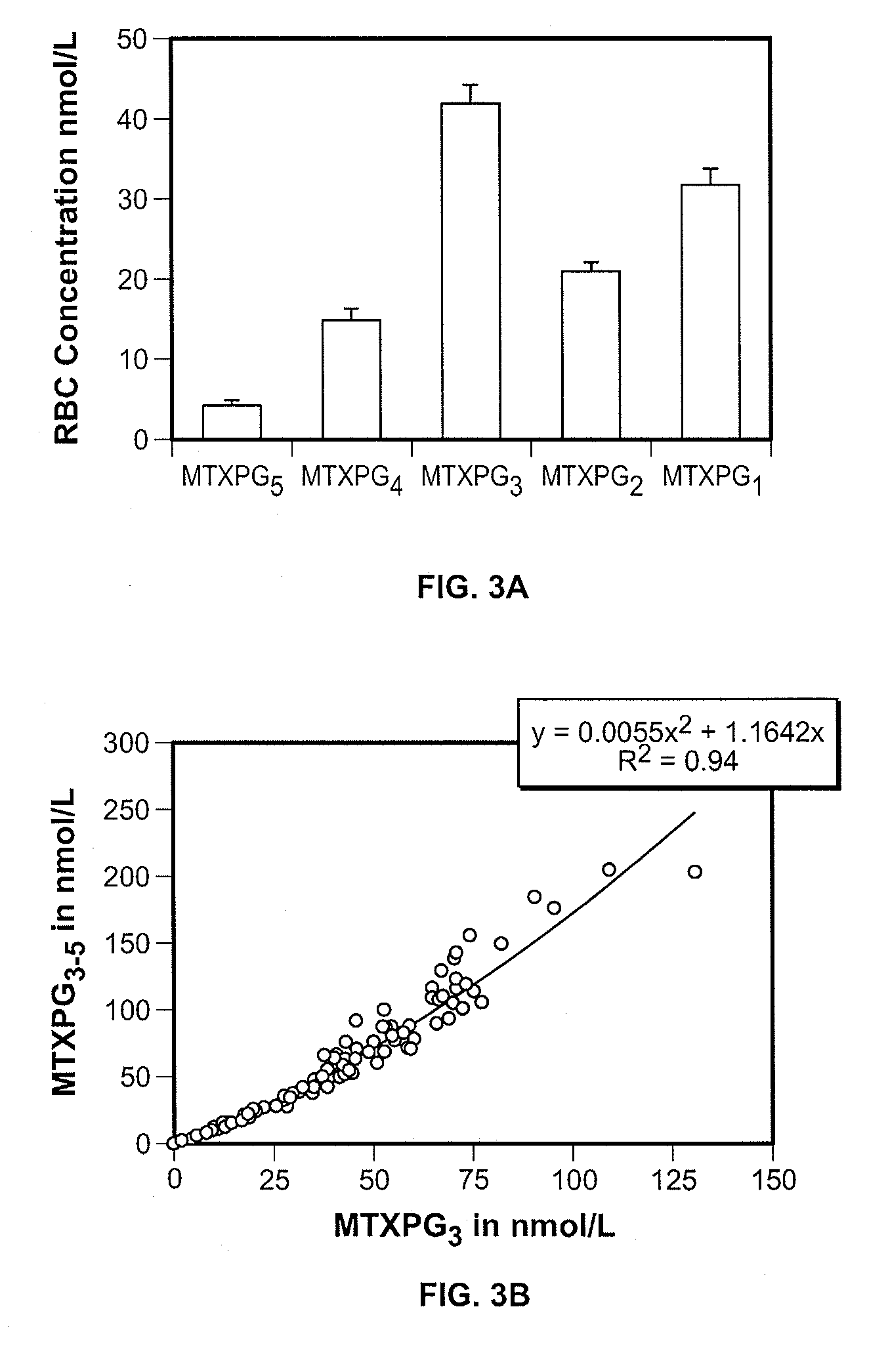
Methods for optimizing clinical responsiveness to methotrexate therapy using metabolite profiling and pharmacogenetics
The present invention provides methods for optimizing clinical responsiveness to chemotherapy in an individual through genotypic analysis of polymorphisms in at least one gene. The methods of the present invention may further comprise determining the level of at least one long-chain methotrexate polyglutamate (MTXPG) in a sample obtained from the individual. The present invention also provides methods for generating a pharmacogenetic index for predicting clinical responsiveness to chemotherapy in an individual through genotypic analysis of polymorphisms in at least one gene. In addition, the present invention provides methods for optimizing therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy in an individual by calculating the level of at least one long-chain MTXPG in a sample obtained from the individual.
Owner:EXAGEN INC
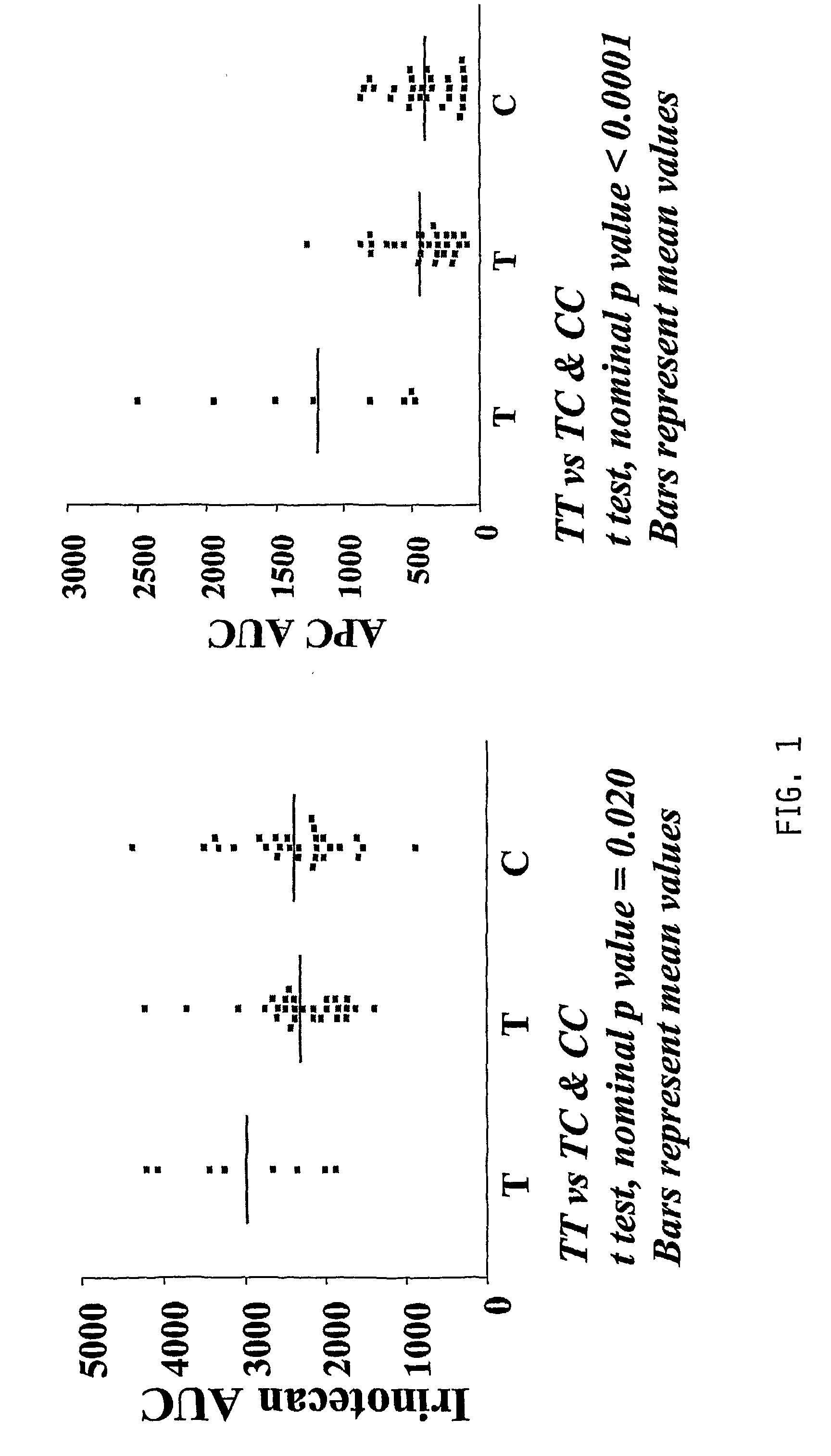
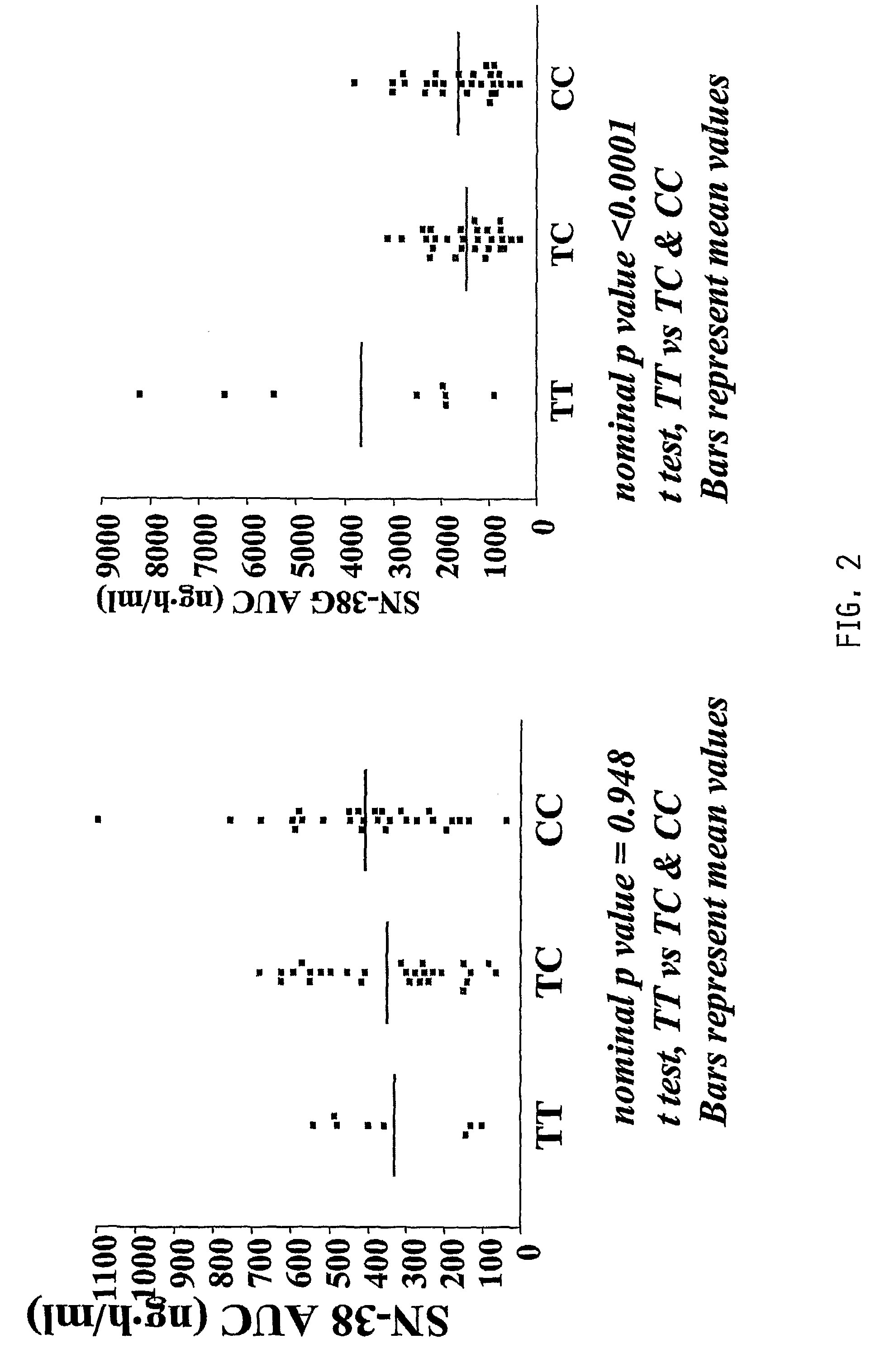
Methods and compositions relating to pharmacogenetics of different gene variants in the context of irinotecan-based therapies
InactiveUS20090247475A1Reduced cytotoxic activityIncrease and reduce chance of responseBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacogeneticsSLCO1B1
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for determining the presence or absence of polymorphisms within an ABCC2, UGT1A1, and / or SLCO1B1 gene and correlating these polymorphisms with activity levels of their gene products and making evaluations regarding the effect on their substrates, particularly those substrates that are drugs. In addition, there are methods and compositions of evaluating the risk of an individual for developing toxicity or adverse event(s) to an ABCC2, UGT1A1, and / or SLCO1B1 substrate. In some embodiments, the invention concerns methods and compositions for determining the presence or absence of ABCC2 3972C>T variant and predicting or anticipating the level of activity of ABCC2 and determining dosages of an ABCC2 drug substrate, such as irinotecan, in a patient. Such methods and compositions can be used to evaluate whether irinotecan-based therapy, or therapy involving other ABCC2 substrates, may pose toxicity problems if given to a particular patient or predicting their efficacy. Alterations in suggested therapy may ensue based on genotyping results.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Cell-Based Materials and Methods for Defining Pharmacogenetic Differences in Drug Metabolism
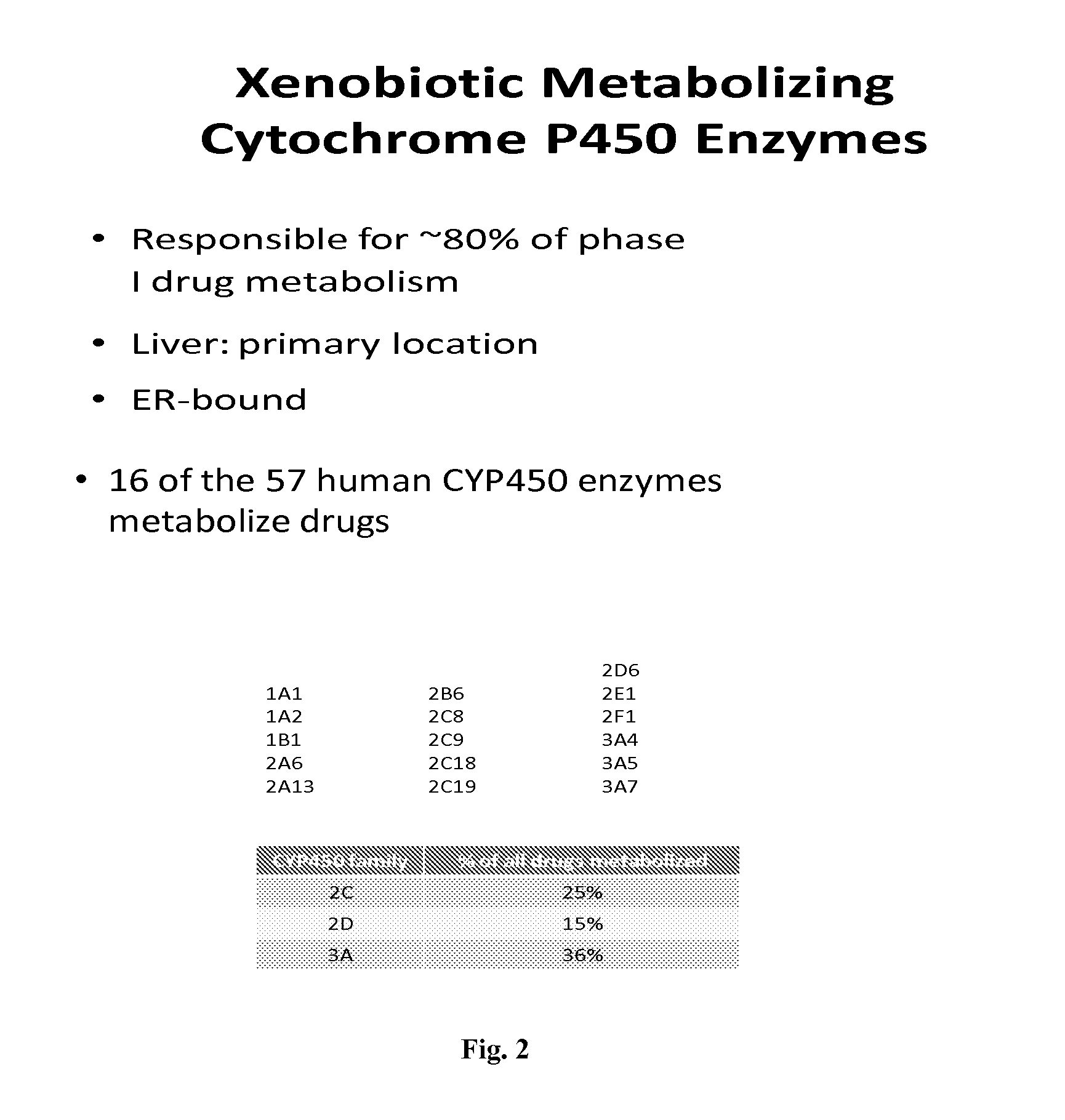
Cell lines harboring a range of polymorphisms using recombinant cytochrome P450 or other chemical-metabolizing enzymes in a parent cell line that is minimally expressing or devoid of its own cytochrome P450 protein or other chemical-metabolizing enzymes of interest can be placed into an array format to enable high throughput screening of one or more chemicals for CYP450 or other enzyme-dependent metabolism (FIG. 9). Processing of the cells can be automated, done en-masse through use of an array having a substrate upon which a plurality of cell lines with exogenous chemical-metabolizing enzymes are coupled, and both relative and quantitative metabolism rates determined using mass spectrometry over time. Thus, methods are disclosed to measure, for example, the effects of cytochrome P450 polymorphisms on clinical drug metabolism in a high throughput manner for drug development and genetically personalized diagnostics and treatment regimens.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for determining the haplotype of a human BRCA1 gene
InactiveUS6951721B2Reduce the possibilityEasy to identifySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseasePharmacogenetics
Methods for identifying functional allele profiles of a given gene are disclosed. Functional allele profiles comprise the commonly occurring alleles in a population, and the relative frequencies at which such alleles of a given gene occur. Functional allele profiles are useful in treatment and diagnosis of diseases, for genetic and pharmacogenetic applications and for evaluating the degree to which the gene(s) are under selective pressure.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS +1
Pharmacogenetic detection chip for cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases and its application
InactiveCN101067152ASmall toxicityGood curative effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVascular diseasePharmacogenetics
The present invention relates to gene polymorphism detecting chip, and discloses one kind of pharmacogenetic detecting chip for cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases and comprising solid carrier and probe. The probe can hybridize with the nucleotide sequence and / or its complementary sequence of the gene related to cardiac and cerebral vascular disease pharmacogenetics. The present invention also discloses the method of using the chip in detecting the gene related to cardiac and cerebral vascular disease pharmacogenetics. The detecting chip of the present invention makes it possible for the medical staff to obtain cardiac and cerebral vascular disease pharmacogenetics of the patient for predicting clinical medicine treatment and individualized treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOCHIP +1
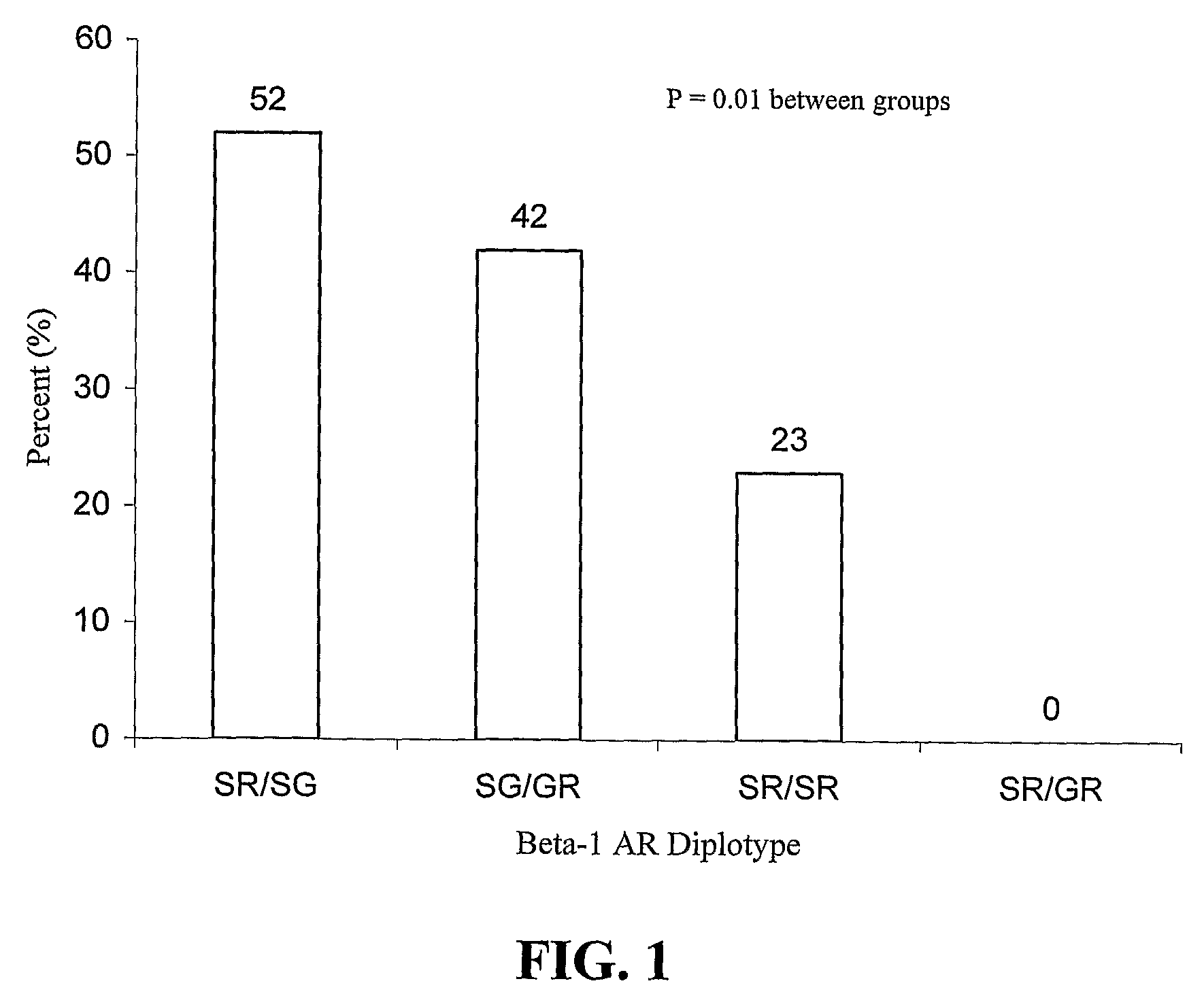
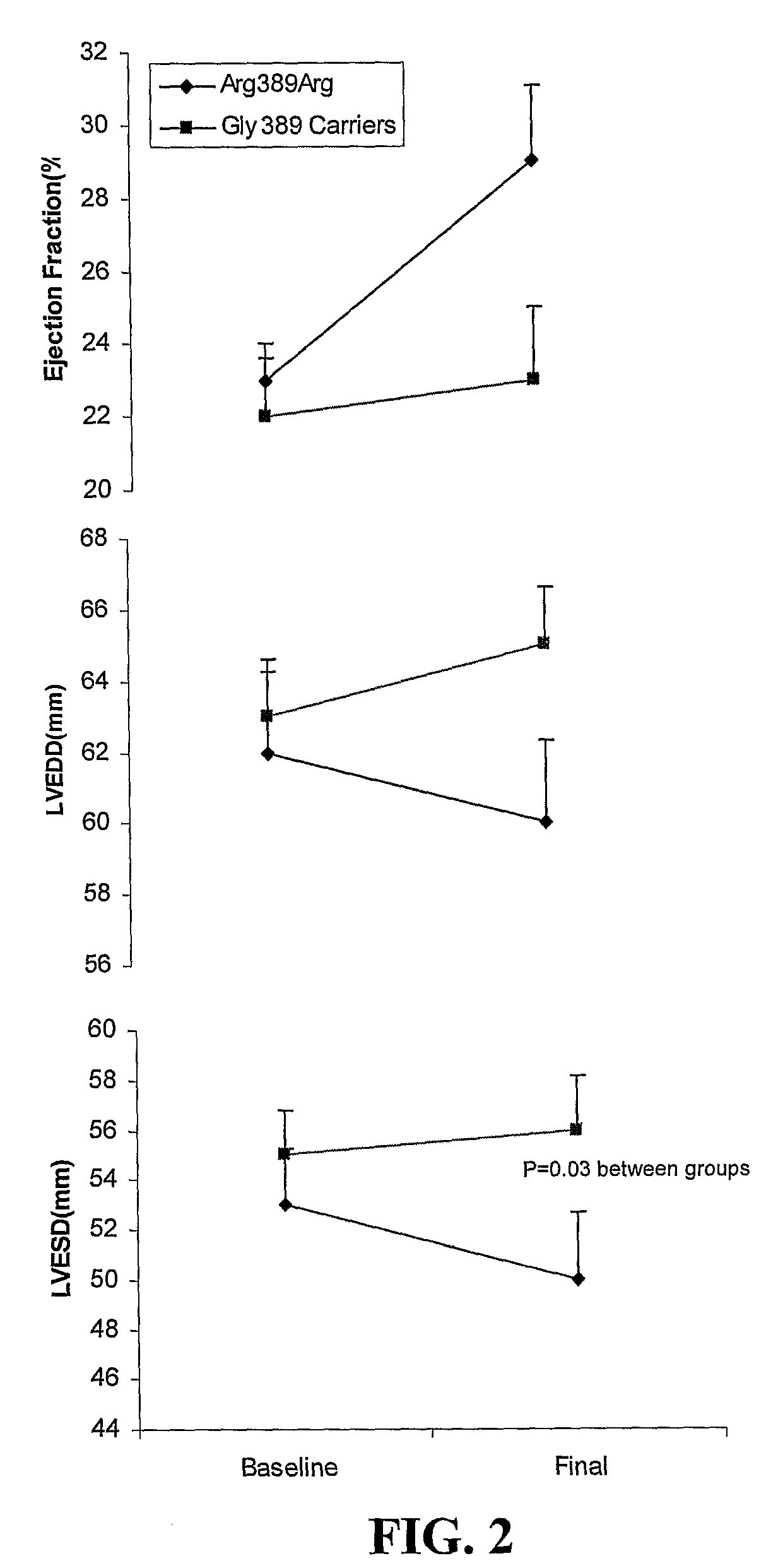
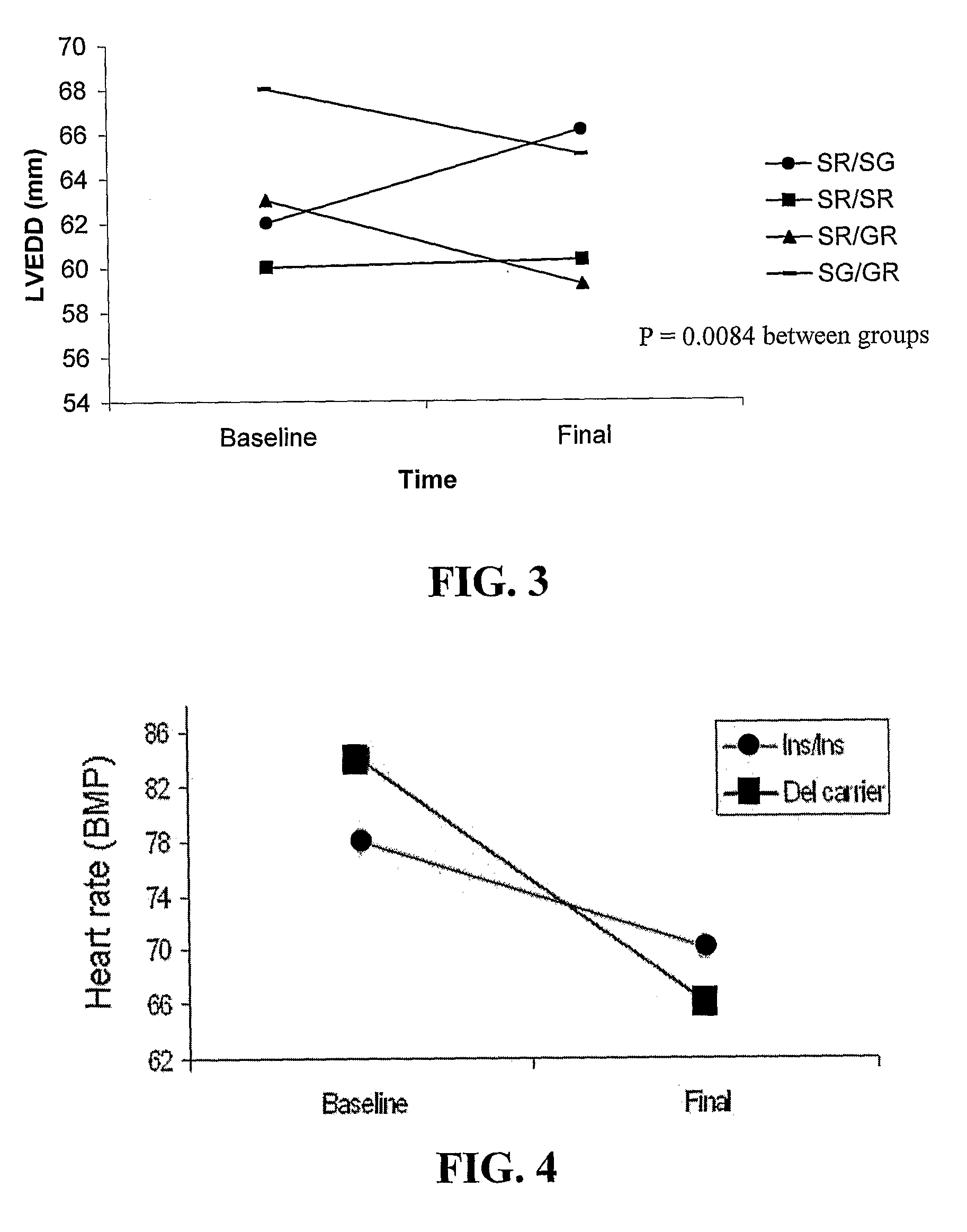
B-Blocker Pharmacogenetics in Heart Failure
InactiveUS20080269346A1Reduce riskPromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePharmacogeneticsTolerability
Polymorphisms in the beta-1 adrenergic receptor that (1) affect tolerability to beta-blocker treatment or (2) influence responsiveness to beta-blocker treatment are disclosed. Additionally, methods of predicting that an individual would obtain clinical improvement in left ventricular function as a result of β-blocker therapy or identifying at least one individual that would obtain a clinical improvement in left ventricular function as a result of β-blocker therapy are provided. Methods of treating patients characterized by such polymorphisms are also illustrated.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
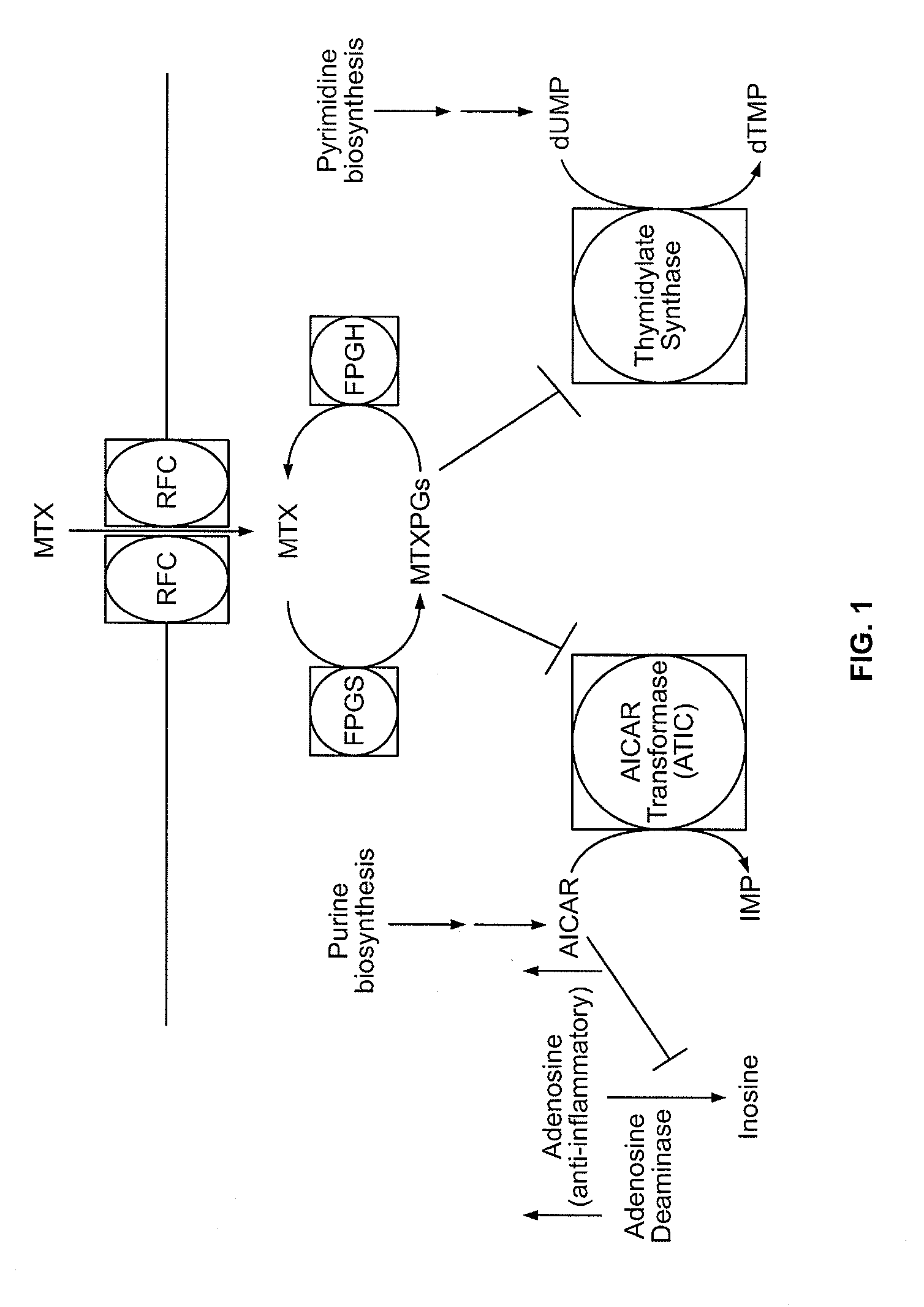
Methods for predicting methotrexate polyglutamate levels using pharmacogenetics
The present invention provides methods for determining a level of methotrexate polyglutamates (MTXPGs) in an individual undergoing methotrexate (MTX) therapy and for optimizing dose efficacy of MTX therapy in an individual by genotyping the individual at a polymorphic site in at least one folate pathway gene (e.g., a reduced folate carrier (RFC-1) gene, a gamma glutamyl hydrolase (GGH) gene, etc.). Methods are also provided for determining a level of MTXPGs in an individual undergoing MTX therapy and for optimizing dose efficacy of MTX therapy in an individual by generating a pharmacogenetic index based upon the genotype of the individual at a polymorphic site in an RFC-1 gene and / or a GGH gene.
Owner:EXAGEN INC
Detecting kit for polymorphism of warfarin pharmacogenetics genes CYP2C9 and VKORC1
InactiveCN107447035AEasy to makeEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWarfarinPharmacogenetics
The invention discloses a detecting kit for polymorphism of warfarin pharmacogenetics genes CYP2C9 and VKORC1, belongs to the technical field of genetic test diagnosis, and is used for auxiliary determination of warfarin dosage of a patient. The kit disclosed by the invention comprises specific primers and specific probes which are used for detecting mutations at the sites rs1057910 and rs9923231; the specific primers comprise upstream primers and downstream primers; the specific probes comprise a positive probe and a negative probe; the specific primers and the specific probes of the rs1057910 are respectively the upstream primers as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.3, the downstream primers as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 and the SEQ ID NO.4, the positive specific fluorescent probe as shown in SEQ ID NO.5, and a negative specific fluorescent probe as shown in SEQ ID NO.6; and the detecting kit for the polymorphism of the warfarin pharmacogenetics genes CYP2C9 and VKORC1 can be used for individualized treatment of warfarin according to genetic genes, and has important significance in subsequent research.
Owner:苏州康吉诊断试剂有限公司
Methods for optimizing clinical responsiveness to methotrexate therapy using metabolite profiling and pharmacogenetics
The present invention provides methods for optimizing clinical responsiveness to chemotherapy in an individual through genotypic analysis of polymorphisms in at least one gene. The methods of the present invention may further comprise determining the level of at least one long-chain methotrexate polyglutamate (MTXPG) in a sample obtained from the individual. The present invention also provides methods for generating a pharmacogenetic index for predicting clinical responsiveness to chemotherapy in an individual through genotypic analysis of polymorphisms in at least one gene. In addition, the present invention provides methods for optimizing therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy in an individual by calculating the level of at least one long-chain MTXPG in a sample obtained from the individual.
Owner:CYPRESS BIOSCI +1
Methods for optimizing clinical responsiveness to methotrexate therapy using metabolite profiling and pharmacogenetics
The present invention provides methods for optimizing clinical responsiveness to chemotherapy in an individual through genotypic analysis of polymorphisms in at least one gene. The methods of the present invention may further comprise determining the level of at least one long-chain methotrexate polyglutamate (MTXPG) in a sample obtained from the individual. The present invention also provides methods for generating a pharmacogenetic index for predicting clinical responsiveness to chemotherapy in an individual through genotypic analysis of polymorphisms in at least one gene. In addition, the present invention provides methods for optimizing therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy in an individual by calculating the level of at least one long-chain MTXPG in a sample obtained from the individual.
Owner:PROMETHEUS LAB
Methods for optimizing clinical responsiveness to methotrexate therapy using metabolite profiling and pharmacogenetics
Owner:PROMETHEUS LAB
Methods and kits for detecting risk factors for development of jaw osteonecrosis and methods of treatment thereof
Methods of and kits for determining the pharmacogenetic, pharmacokinetic and cellular basis of bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw (BONJ) involve associating particular proteins and particular single nucleotide polymorphisms with a risk for developing BONJ after receiving bisphosphonate treatment. Methods and kits for identifying the genetic basis for a patient's predisposition to BONJ, and methods of identifying patients who are prone to develop BONJ following bisphosphonate administration provide for the development of a tool for physicians to prescribe treatment protocols for BONJ patients based on the patients' genomes (“personal / tailored medicine”). A haplotype tagging SNP approach was used to analyze candidate genes involved in bone absorption and destruction and to examine the influence of genetic variants on the susceptibility of BONJ. Bone biomarkers of BONJ were examined using molecular cell techniques. The methods described herein can be used to identify differences in how patients are genetically predisposed to BONJ as well as genetic differences amongst patients that account for differences in how these patients clear bisphosphonate s from their systems. Determining such genetic differences provides for improved monitoring of the drugs used to treat BONJ, improved prevention of BONJ, and optimized treatment for patients having BONJ or predisposed to BOND.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Pharmaceutical composition for specifically regulating activity of hypothalamic ventral nucleus astrocyte and application of pharmaceutical composition
PendingCN113456646AUnique practicalityAvoid damageOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderChronic stressPharmacogenetics
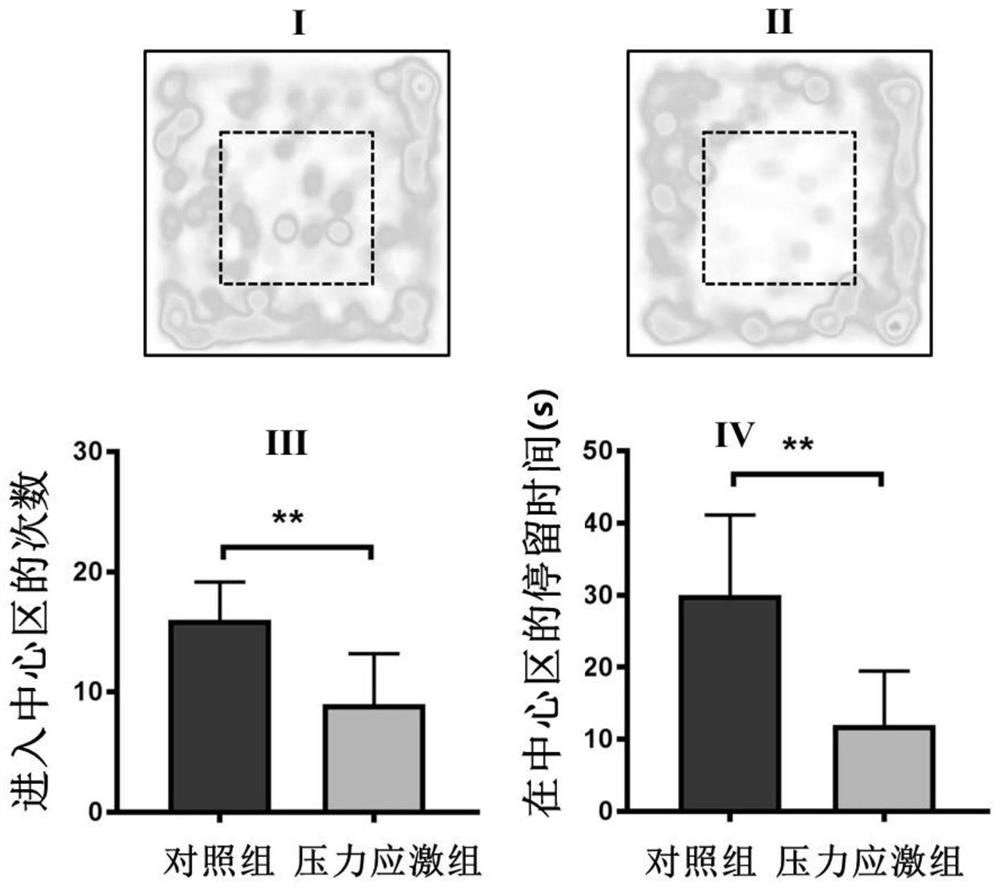
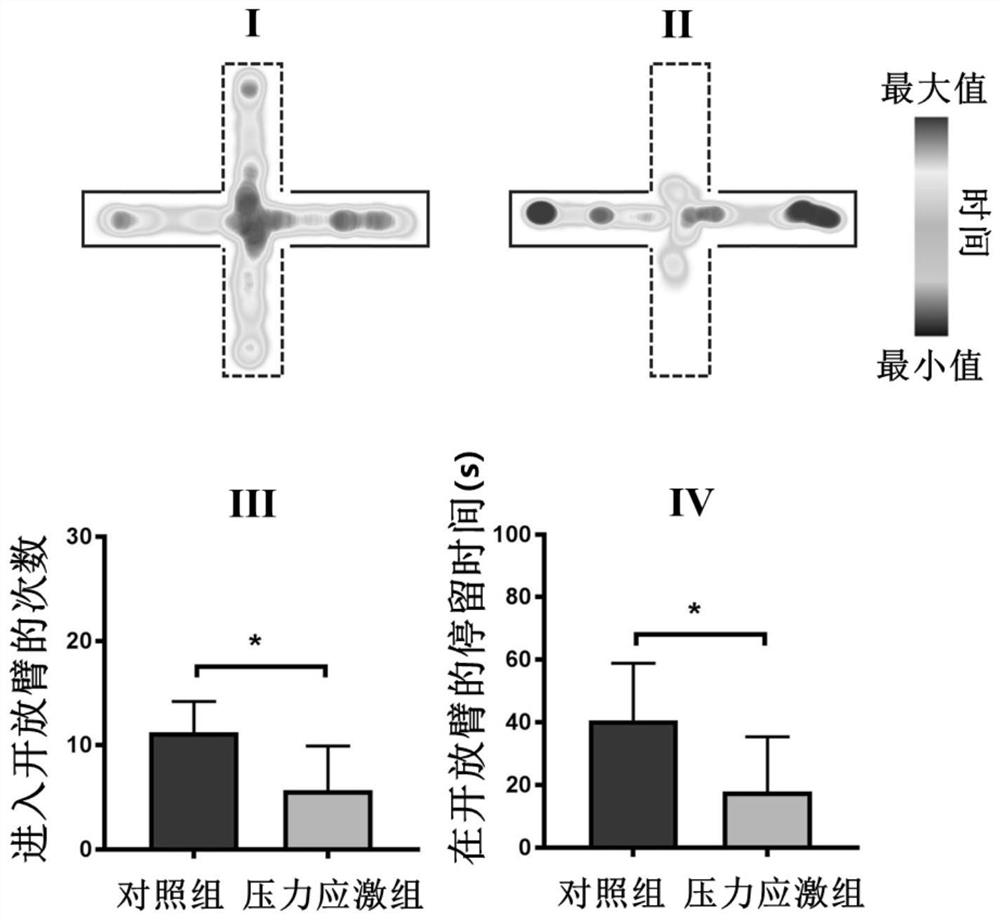
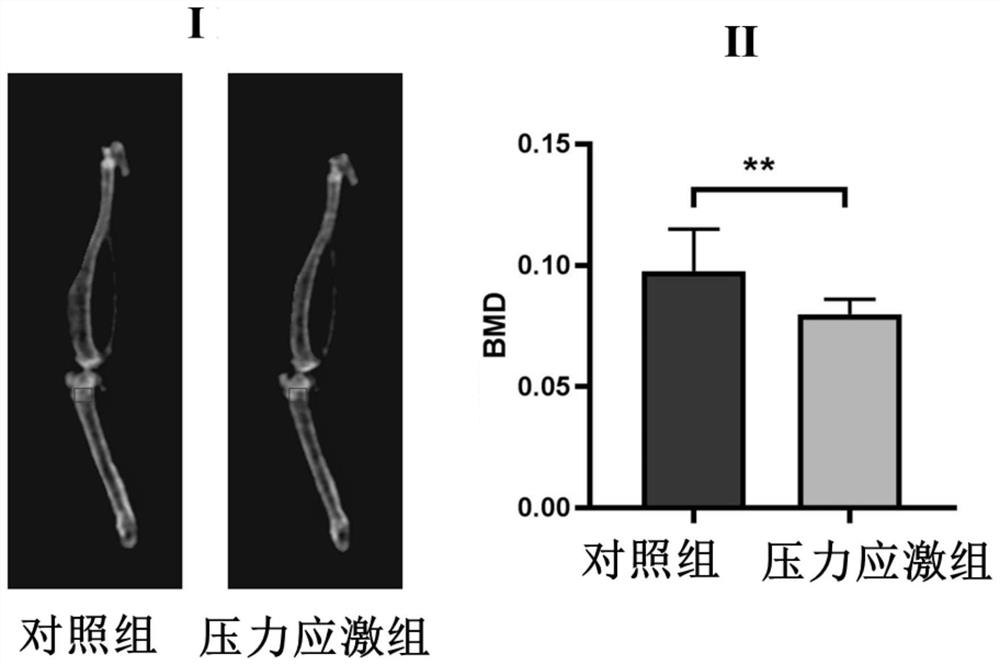
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for specifically regulating activity of hypothalamic ventral nucleus astrocytes and application of the pharmaceutical composition. The pharmaceutical composition comprises clozapine nitrogen oxide and a viral vector used for infecting the astrocytes; the viral vector comprises a pharmaceutical genetics regulatory element hM4Di or hM3Dq. The pharmaceutical composition can selectively activate a Gi pathway or a Gq pathway of astrocytes, and by means of the pharmaceutical composition. According to the invention, it is proved that anxiety-like behaviors and bone loss phenomena induced by chronic pressure stress can be intervened by selectively adjusting the activity of VMH astrocytes.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
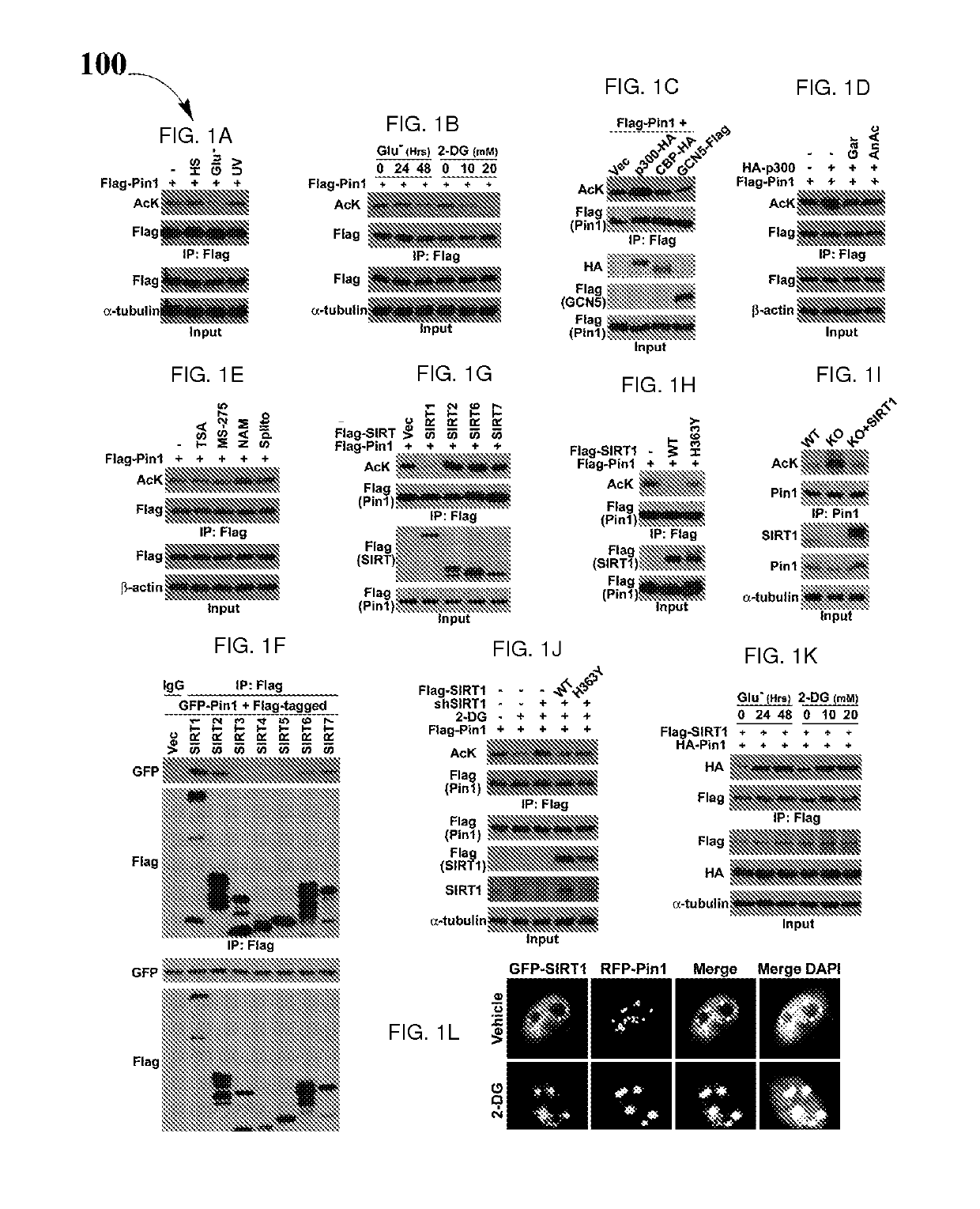
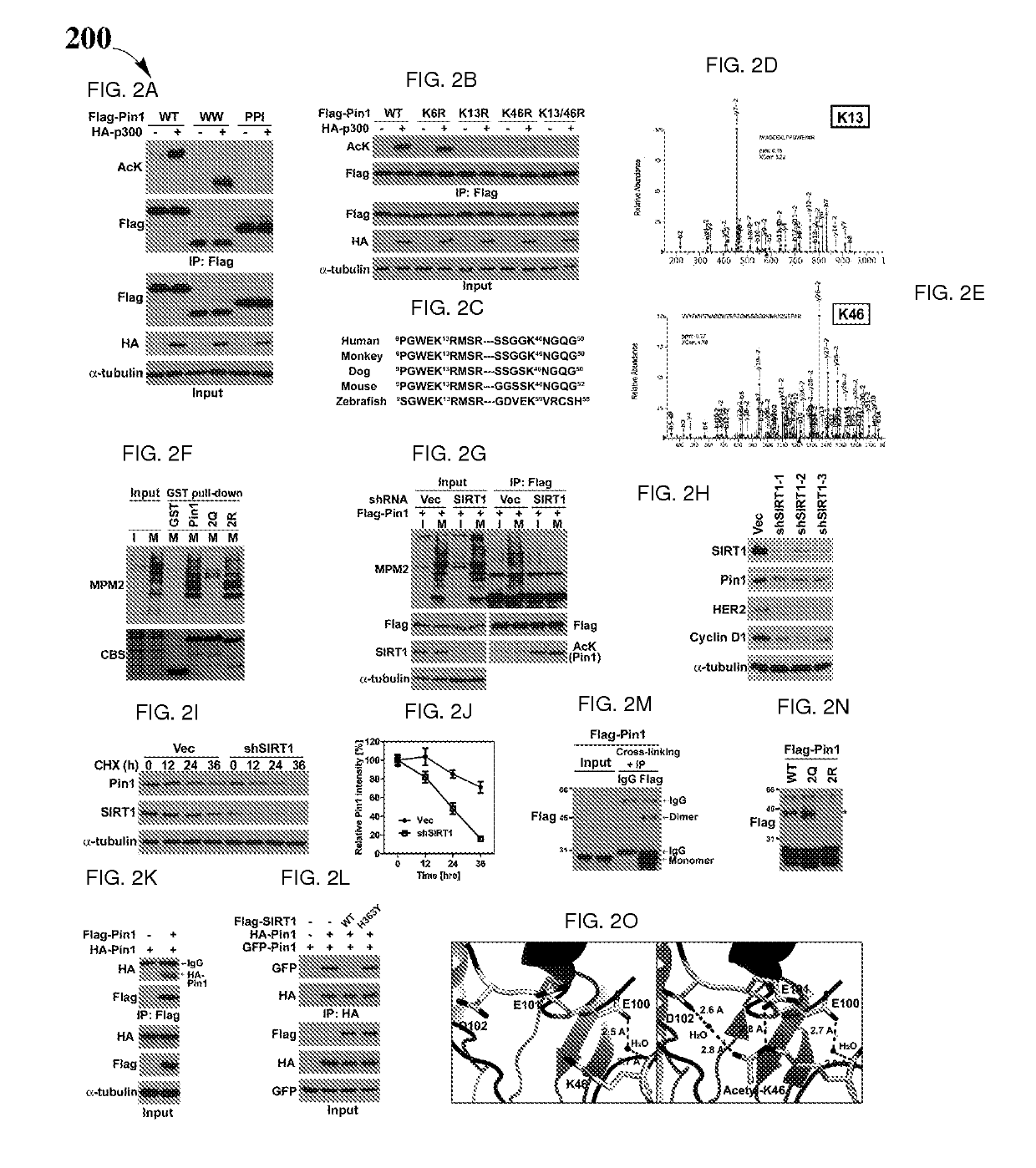
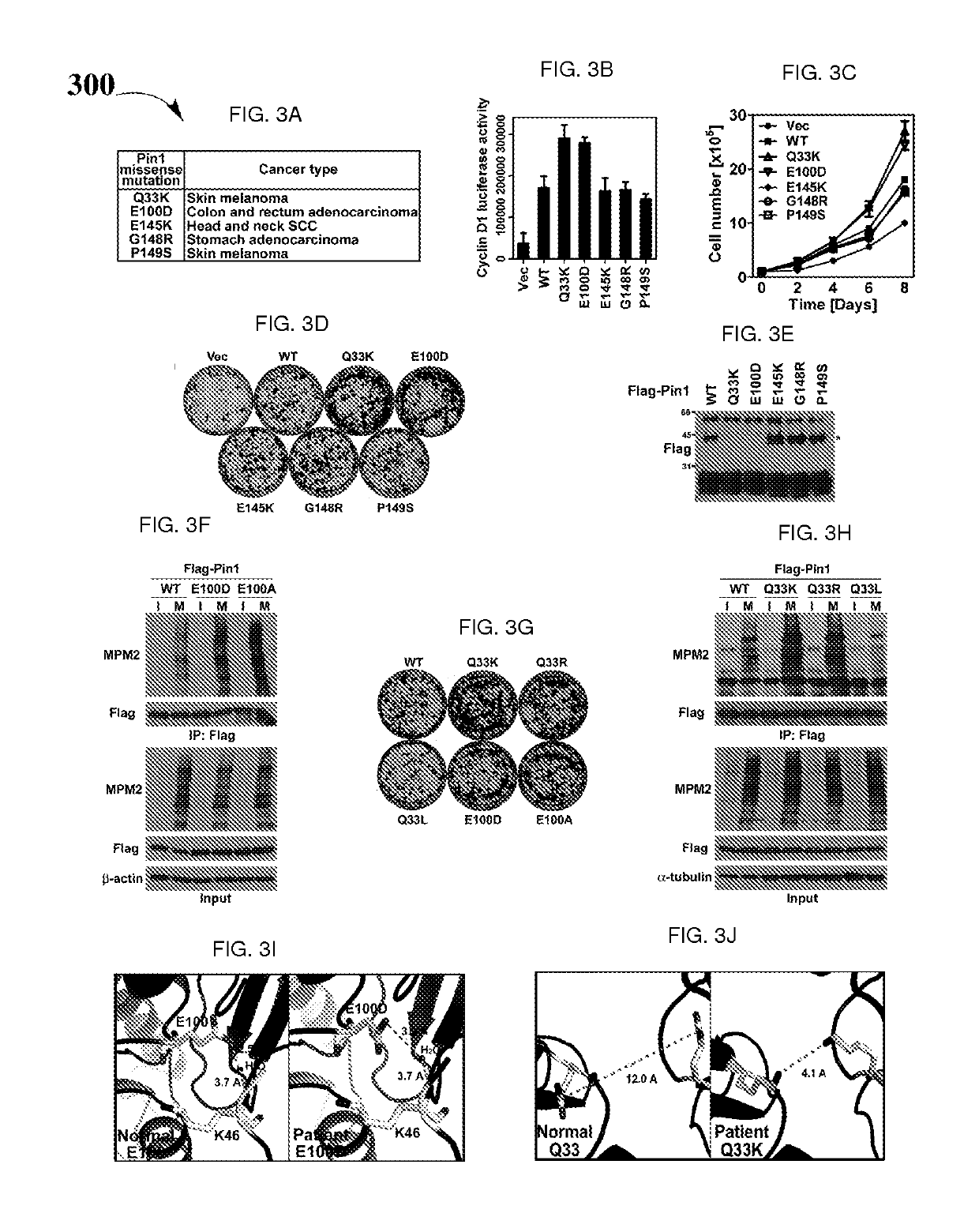
Biomarkers for Pin1-associated disorders
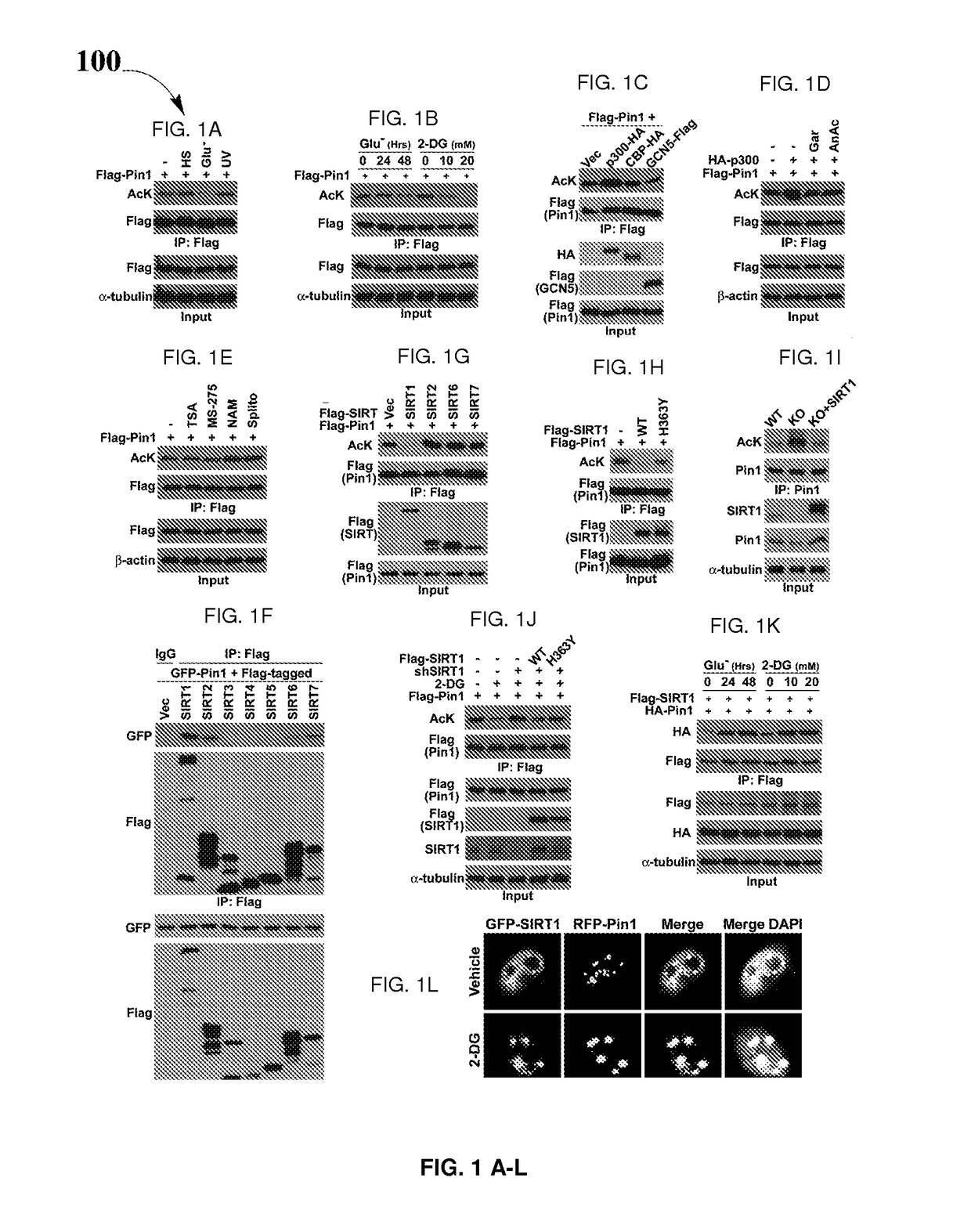
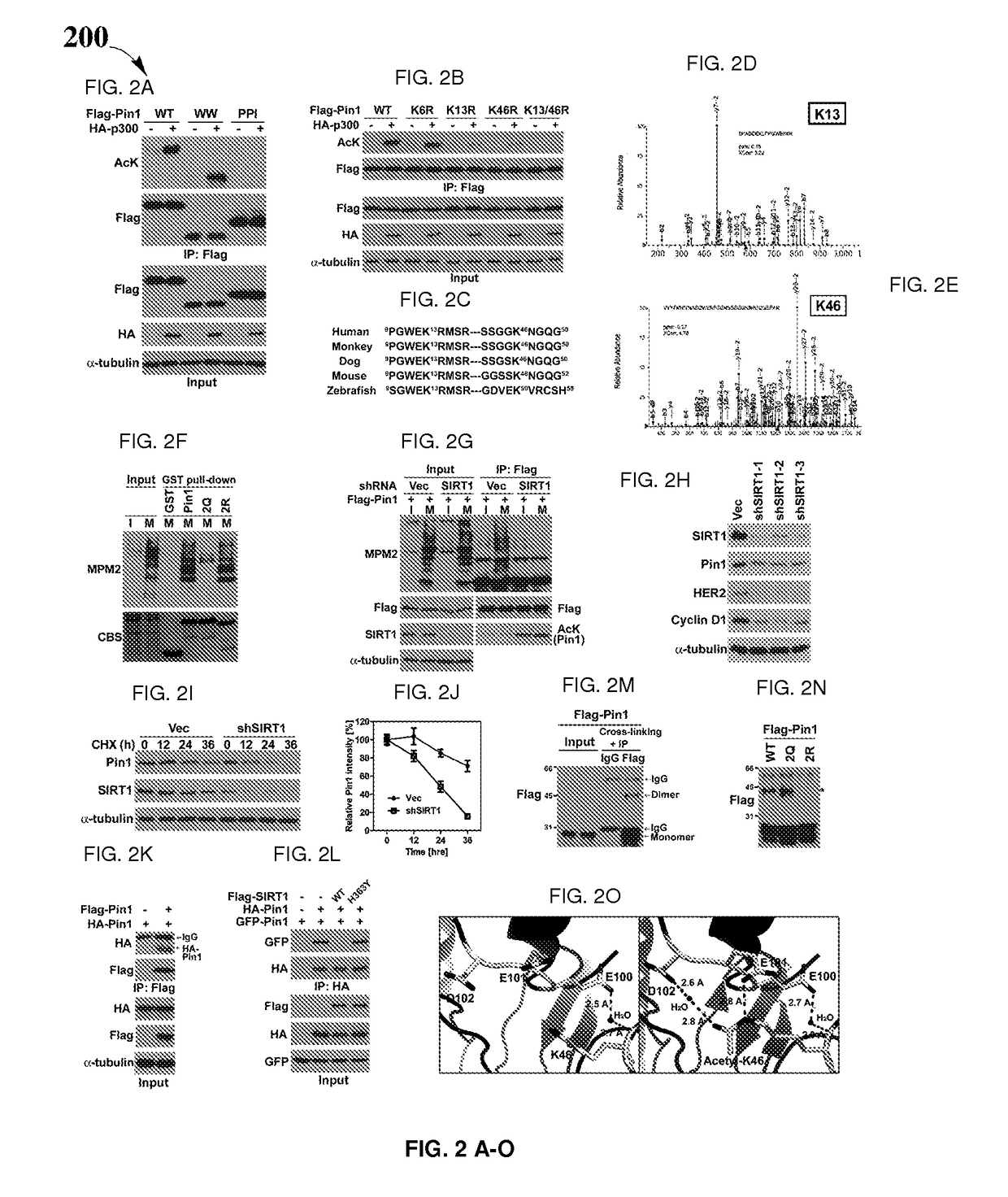
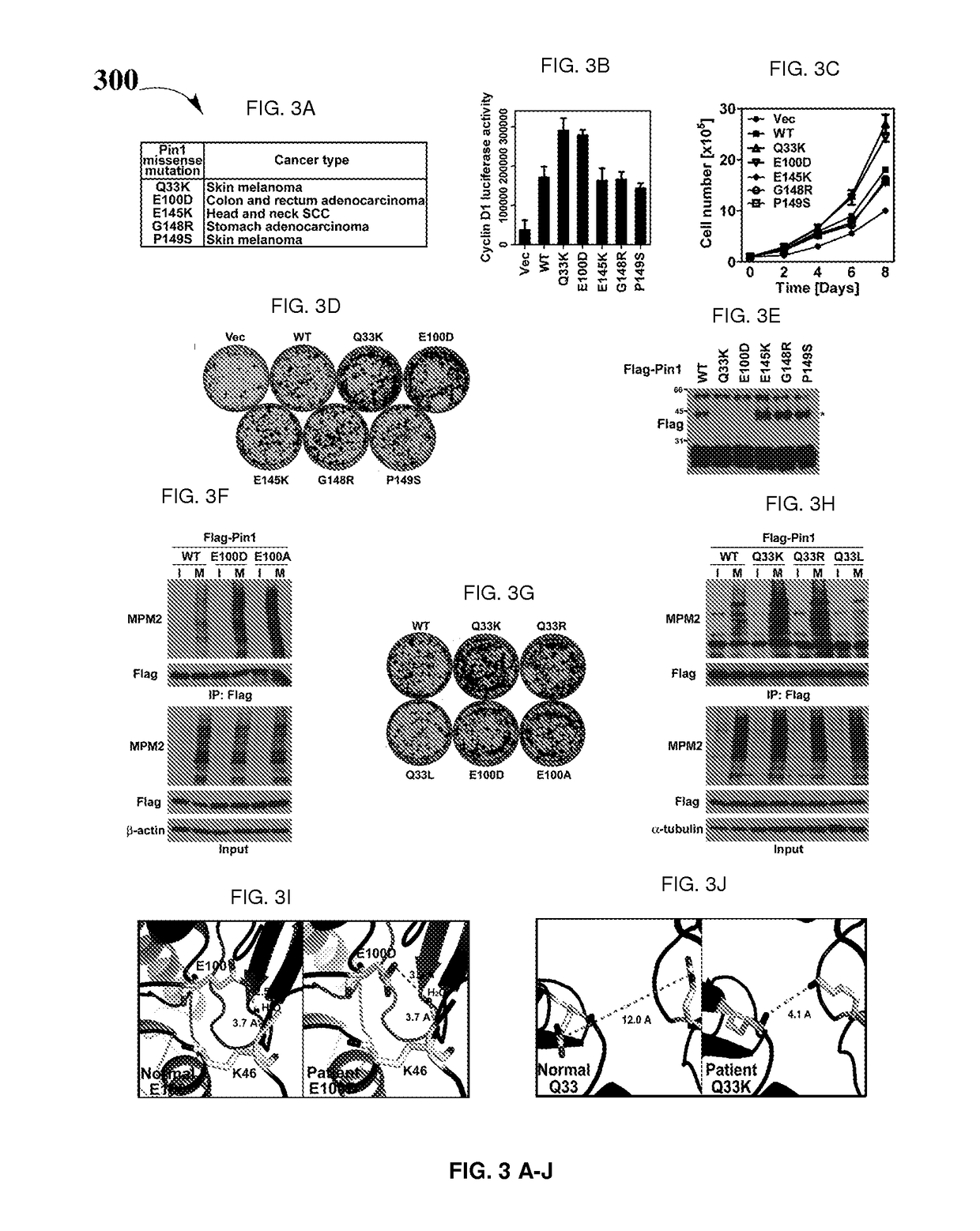
ActiveUS10351914B2Easy diagnosisHigh activityHydroxy compound active ingredientsAerosol deliveryDiseasePharmacogenetics
Biomarkers and driver mutations for diagnosis and prognosis of Pin 1-associated diseases are disclosed. In one embodiment, the methods for diagnosis of Pin 1-associated diseases may include detecting the level of Pin1 to stage abnormal cell growth, such as breast or prostate cancer. In another embodiment, the methods include evaluating the efficacy of a treatment of abnormal cell growth, such as cancer, by monitoring the levels of Pin1. In another embodiment, the methods include using driver mutations to determine the pharmacogenetics of abnormal cell growth, such as cancer. In the present disclosure, elevated active monomeric Pin1 levels may be detected by Pin1 biomarkers, which may include Pin1 Q33K or E100D driver mutations, Pin1 protein or transcript overexpression, dephosphorylation of Pin1 on Ser71, dephosphorylation of S16, phosphorylation of S65, phosphorylation of S138, deacetylation of Pin1 on K13 and deacetylation of K46, and / or desumoylation of Pin1 on K6 and desumolation of K63, among others.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
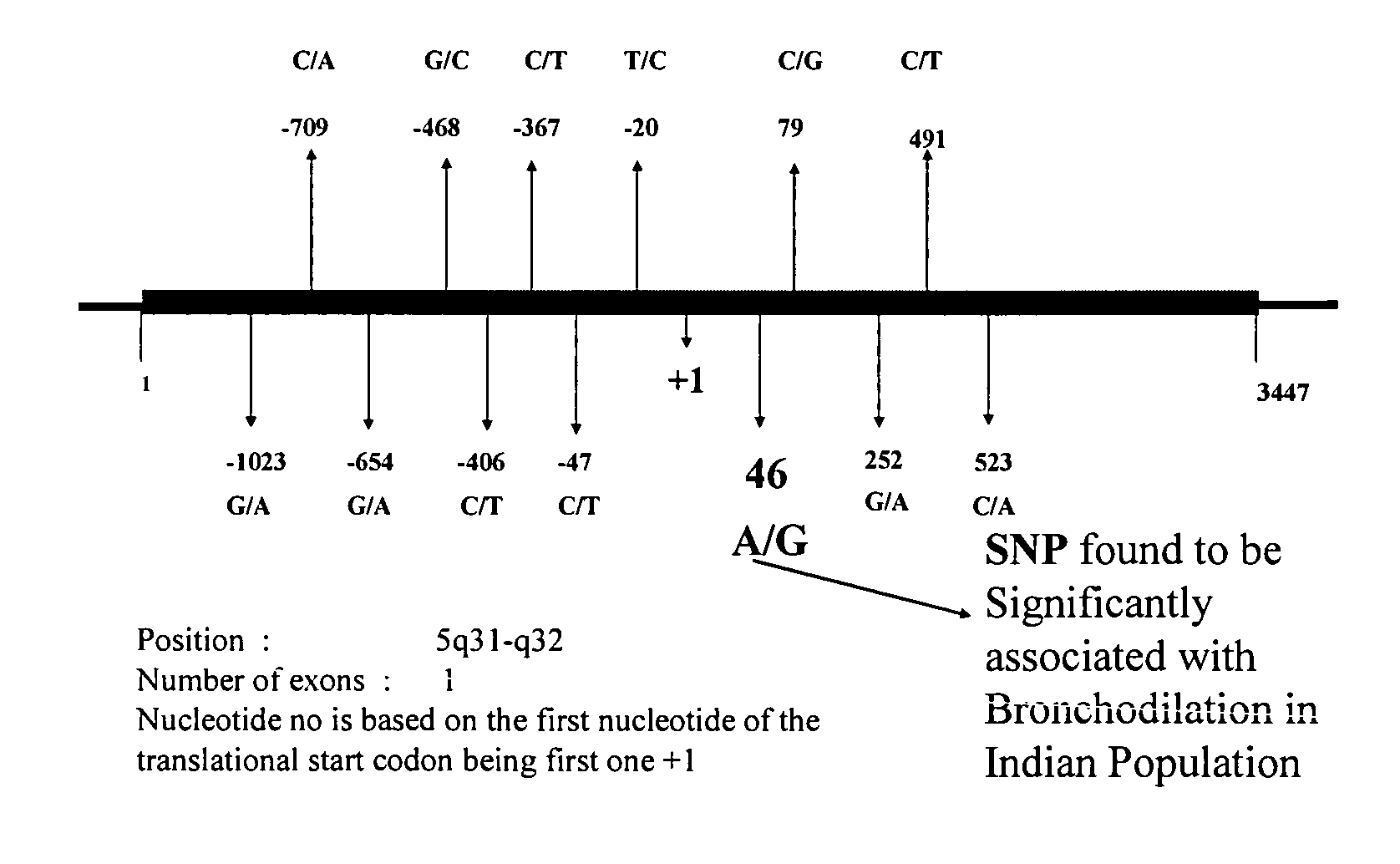
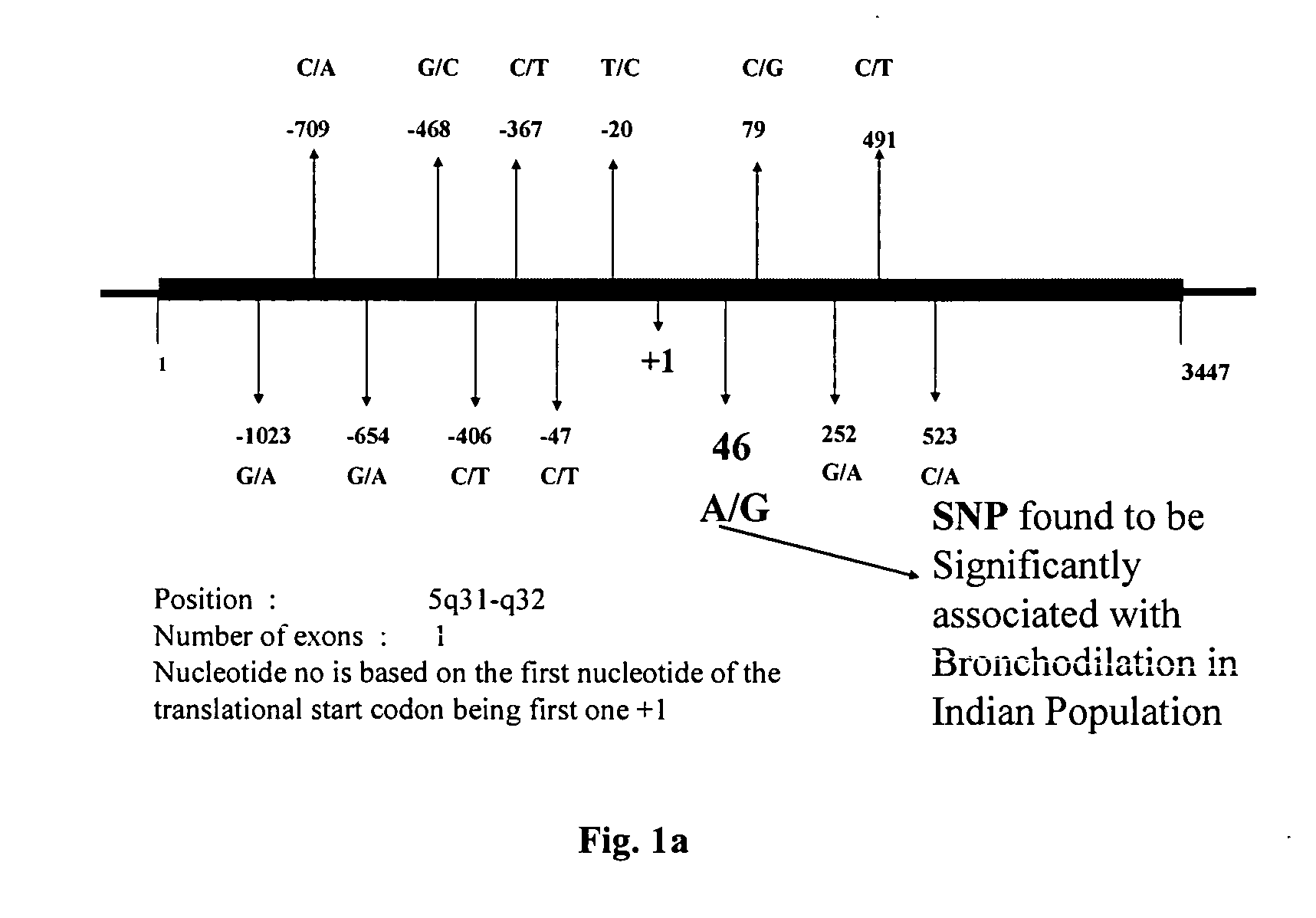
Method of detecting and predicting bronchodilatory response to beta agonist
InactiveUS20050255479A1Faster and specific methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacogeneticsPharmaceutical drug
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
Pharacogenetic method for prediction of the efficacy of methotrexate monotherapy in recent-onset arthritis
Pharmacogenetic methods for determining a predicting responsiveness to antifolate therapy for subjects that present with recent-onset undifferentiated arthritis. The methods are based on the determination of a set of clinical parameter values and determining a predicted responsiveness to antifolate therapy by correlating the parameter values with predefined responsiveness values associated with ranges of parameter values. Parameters values that are decisive for responsiveness to antifolate therapy may include polymorphisms in the methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (MTHFD1) gene as well as in three genes involved in the adenosine release pathway, the presence or absence of Rheumatoid factors, gender, pre- or postmenopausal status and / or smoking status.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZEIKENHUIS H O D N LUMC
Biomarkers for pin1-associated disorders
ActiveUS20170204466A1Easy diagnosisHigh activityHydroxy compound active ingredientsAerosol deliveryDiseasePharmacogenetics
Biomarkers and driver mutations for diagnosis and prognosis of Pin 1-associated diseases are disclosed. In one embodiment, the methods for diagnosis of Pin 1-associated diseases may include detecting the level of Pin1 to stage abnormal cell growth, such as breast or prostate cancer. In another embodiment, the methods include evaluating the efficacy of a treatment of abnormal cell growth, such as cancer, by monitoring the levels of Pin1. In another embodiment, the methods include using driver mutations to determine the pharmacogenetics of abnormal cell growth, such as cancer. In the present disclosure, elevated active monomeric Pin1 levels may be detected by Pin1 biomarkers, which may include Pin1 Q33K or E100D driver mutations, Pin1 protein or transcript overexpression, dephosphorylation of Pin1 on Ser71, dephosphorylation of S16, phosphorylation of S65, phosphorylation of S138, deacetylation of Pin1 on K13 and deacetylation of K46, and / or desumoylation of Pin1 on K6 and desumolation of K63, among others.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Interneuron-specific therapeutics for normalizing neuronal cell excitability and treating dravet syndrome
Provided are therapeutic virus vectors, particularly, recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors, designed to contain an enhancer sequence that specifically restricts expression of an effector gene (e.g., an SCN1A-encoding polynucleotide, Gq-DREADD-encoding polynucleotide, or PSAM-encoding polynucleotide) contained in the vector to PV-expressing GABAergic interneuron or to neuron cell populations in the brain. The rAAV vectors, compositions and methods thereof are useful for treating subjects afflicted with neuropathologies, seizures, pharmacologically-intractable forms of epilepsy including Dravet syndrome (DS), a form of infantile epilepsy associated with severe seizures, cognitive impairment and premature death, as the cause of DS involves loss of function of a sodium channel encoded by the SCN1A gene. The described vectors restore expression of effector genes to the appropriate interneuron or neuron cell populations with specificity and sensitivity, advantageously to address the root cause of the disease by restoring the excitation-inhibition balance by means of gene-therapy (with SCN1A) or pharmacogenetics.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Web-based computer-aided method and system for providing personalized recommendations about drug use, and a computer-readable medium
ActiveUS10943672B2Quality improvementReduce usageChemical property predictionDrug and medicationsPersonalizationEngineering
The present invention relates to a web-based computer-aided method and a system for providing personalized recommendations about drug use, based on pharmacogenetic information regarding genes and genetic variants associated to metabolism and genes and genetic variants which are not associated to metabolism, and which comprises automatically generating and displaying, by means of a graphical user interface (GUI) of a dynamic webpage, the personalized recommendations highlighting the ones associated to the highest adverse drug reactions.The present invention also relates to a computer-readable medium which contains program instructions for a computer to perform the method for providing personalized recommendations about drug use of the invention.The present invention also relates to a web-based computer-aided method and a system for generating a dynamic webpage, and a further computer-readable medium which contains program instructions for a computer to perform the method for generating a dynamic webpage.
Owner:BIOTICS
Markers useful in enrichment strategies for the treatment of osteoarthritis
PendingUS20220047674A1Low or no sensitivity to treatmentImprove welfarePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBiology
The present invention relates to pharmacogenetics, more specifically to strategies involving biomarkers associated with the clinical response to a compound before or during treatment of a cartilage disorder, such as osteoarthritis. The present invention more particularly relates to the combination of JSW measurements and level of specific proteins present in the blood, serum, synovial fluid or in the urine, which can be used in strategies such as patients' enrichment in clinical trials, patients' selection strategy before or during treatment or for adapting the treatment of a patient in the frame of treatments for cartilage disorder, such as osteoarthritis.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Polymorphic markers for pharmacogenetic HLA risk alleles
PendingUS20220228207A1Low assessed riskHigh assessed riskMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsAntigenWhite blood cell
We have identified panels of proxy single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that are highly predictive of particular HLA risk alleles, and concordant across multi-ethnic populations. Accordingly, methods are provided involving clinical DNA testing for HLA panel markers to assess risk for life-threatening adverse drug reactions associated with the human leucocyte antigen (HLA) alleles HLA-B*57:01, HLA-B*15:02, HLA-A*31:01 and HLA-B*58:01. Methods of treating a subject with a drug associated with an adverse drug reaction (ADR) are provided. Based on the assessed risk to a subject for developing an adverse drug reaction in response to a drug, appropriate administrations of the drug can be made. In some embodiments of the method, the drug is administered when there is a low assessed risk of ADR in the subject. Alternatively, when there is a high assessed risk of ADR in the subject, a reduced dosage of the drug, or no drug, can be administered.
Owner:SEMA4 OPCO INC
Methods and kits for detecting risk factors for development of jaw osteonecrosis and methods of treatment thereof
Methods of and kits for determining the pharmacogenetic, pharmacokinetic and cellular basis of bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the jaw (BONJ) involve associating particular proteins and particular single nucleotide polymorphisms with a risk for developing BONJ after receiving bisphosphonate treatment. Methods and kits for identifying the genetic basis for a patient's predisposition to BONJ, and methods of identifying patients who are prone to develop BONJ following bisphosphonate administration provide for the development of a tool for physicians to prescribe treatment protocols for BONJ patients based on the patients' genomes (“personal / tailored medicine”).
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
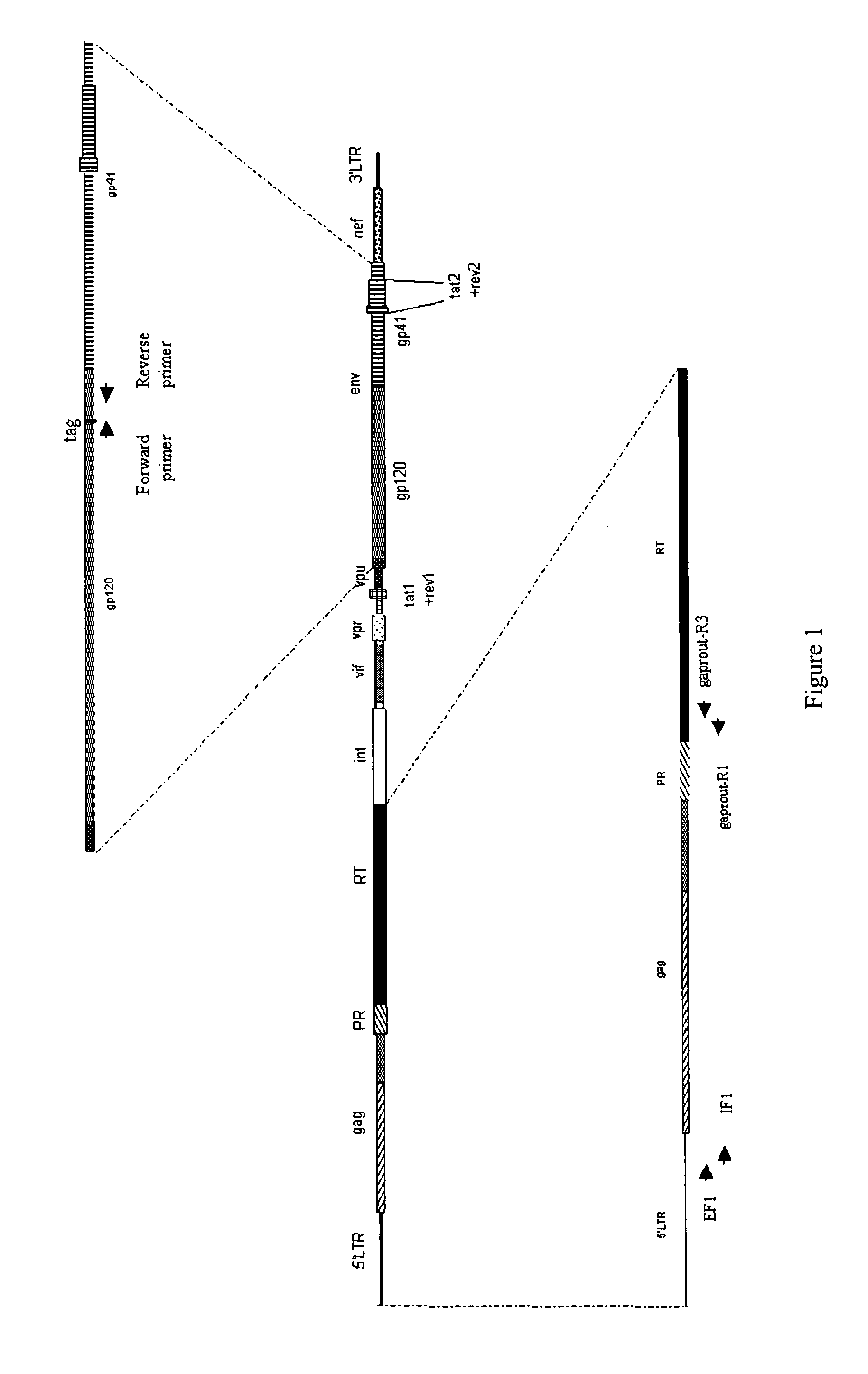
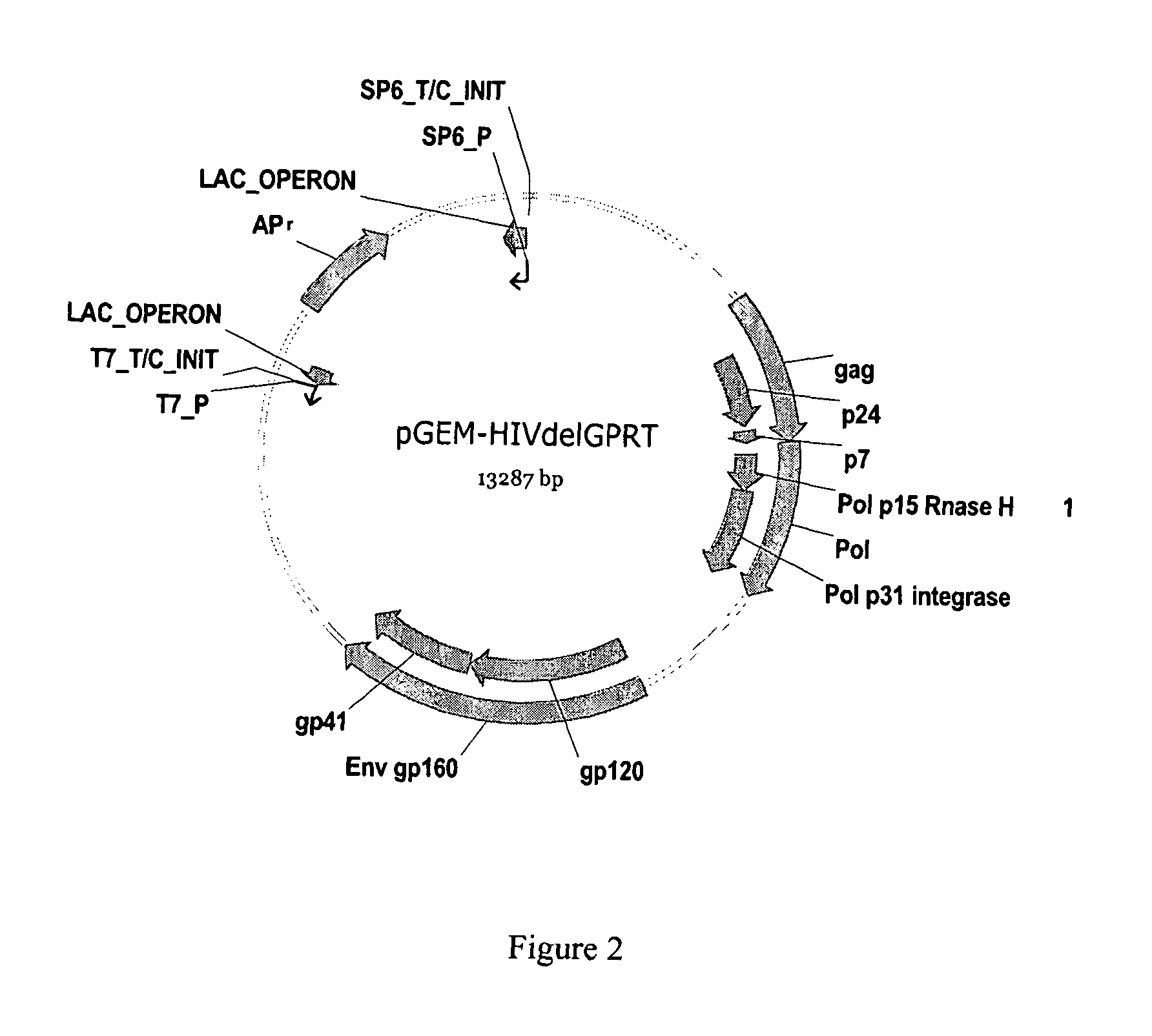
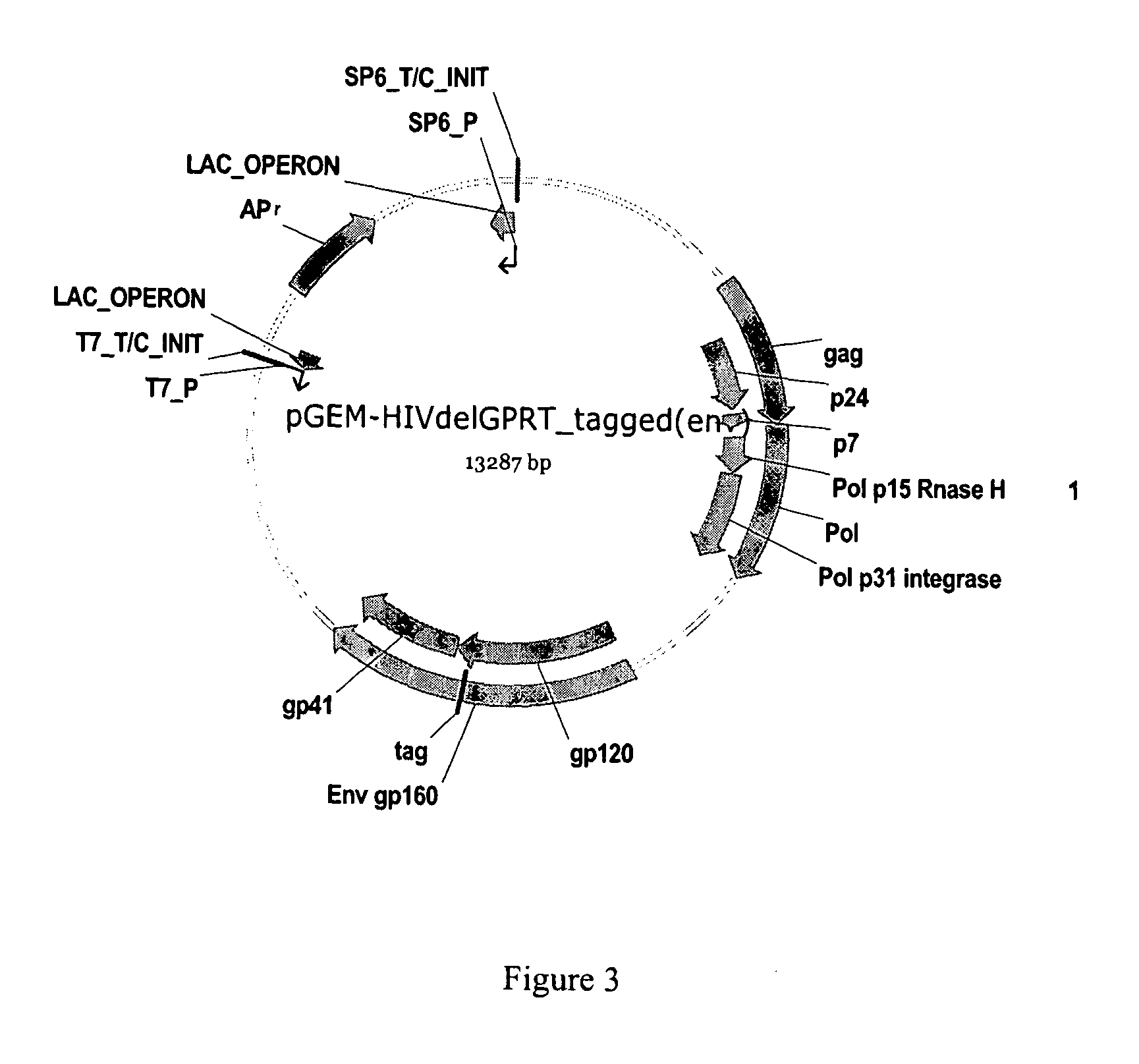
Methods, plasmid vectors and primers for assessing HIV viral fitness
ActiveUS8673551B2Eliminate the effects ofEliminates possible fitness effects of polymorphismsProtozoaMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacogeneticsViral fitness
The present invention relates to methods and means for the evaluation of HIV replicative capacity in a given environment. In particular, the invention provides a growth competition assay that can determine relative viral fitness using a recombinant tagged HIV-1 virus system. The methods rely on plasmid vectors, amplicons, primers and probes, and the generation of replication-competent viruses therefrom. Said methods and materials may find use in multiple fields including diagnostics, drug screening, pharmacogenetics and drug development.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com