Patents
Literature
39 results about "Interneuron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An interneuron (also called internuncial neuron, relay neuron, association neuron, connector neuron, intermediate neuron or local circuit neuron) is a broad class of neurons found in the human body. Interneurons create neural circuits, enabling communication between sensory or motor neurons and the central nervous system (CNS). They have been found to function in reflexes, neuronal oscillations, and neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain.
Method and system to control respiration by means of confounding neuro-electrical signals
A method to control respiration generally comprising generating a confounding neuro-electrical signal that is adapted to confound or (suppress) at least one interneuron that induces a reflex action and transmitting the confounding neuro-electrical signal to the subject, whereby the reflex action is abated. In one embodiment, the confounding neuro-electrical signal is adapted to confound at least one parasympathetic action potential that is associated with the target reflex action, e.g., bronchial constriction.
Owner:NEUROSIGNAL TECH
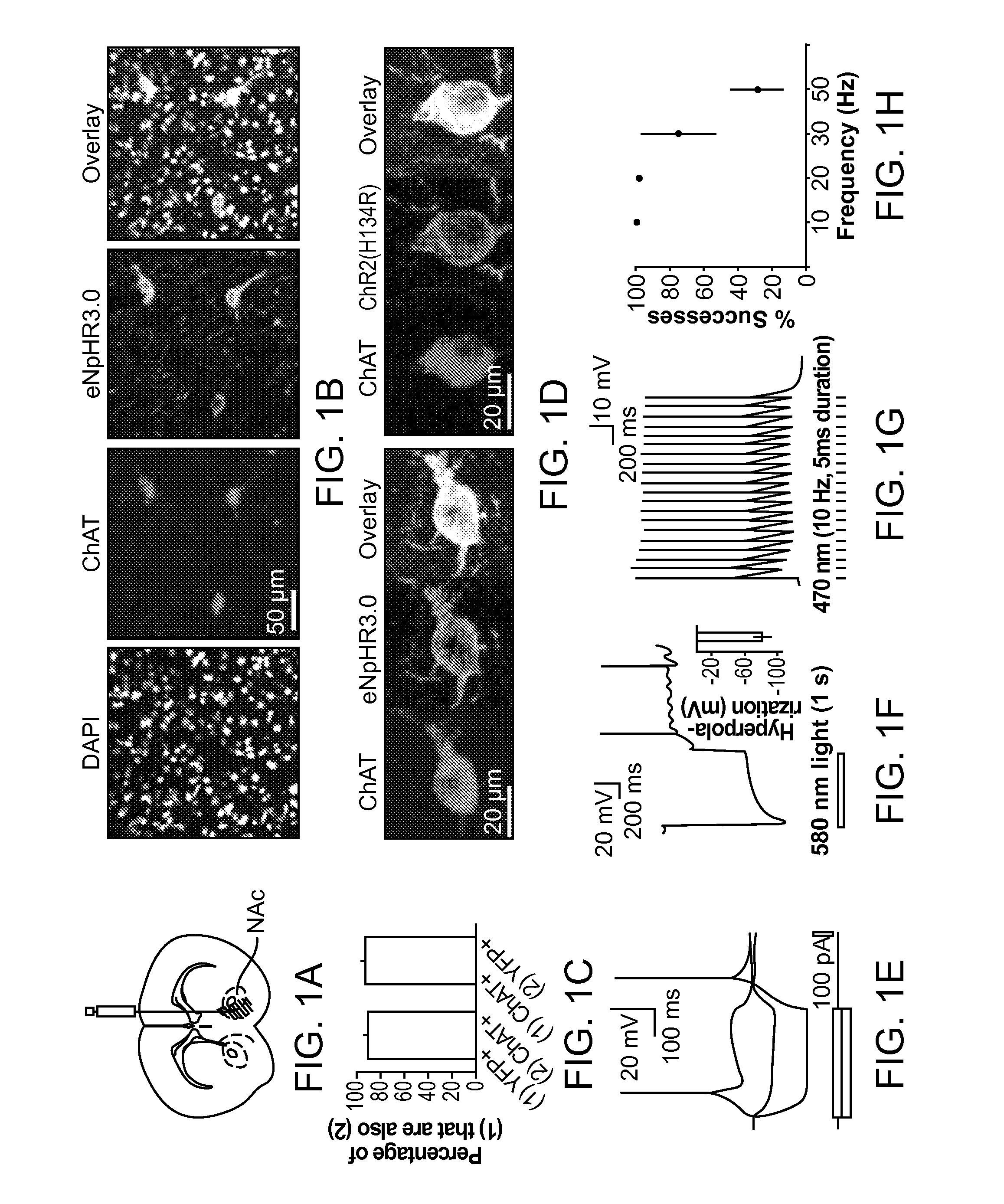
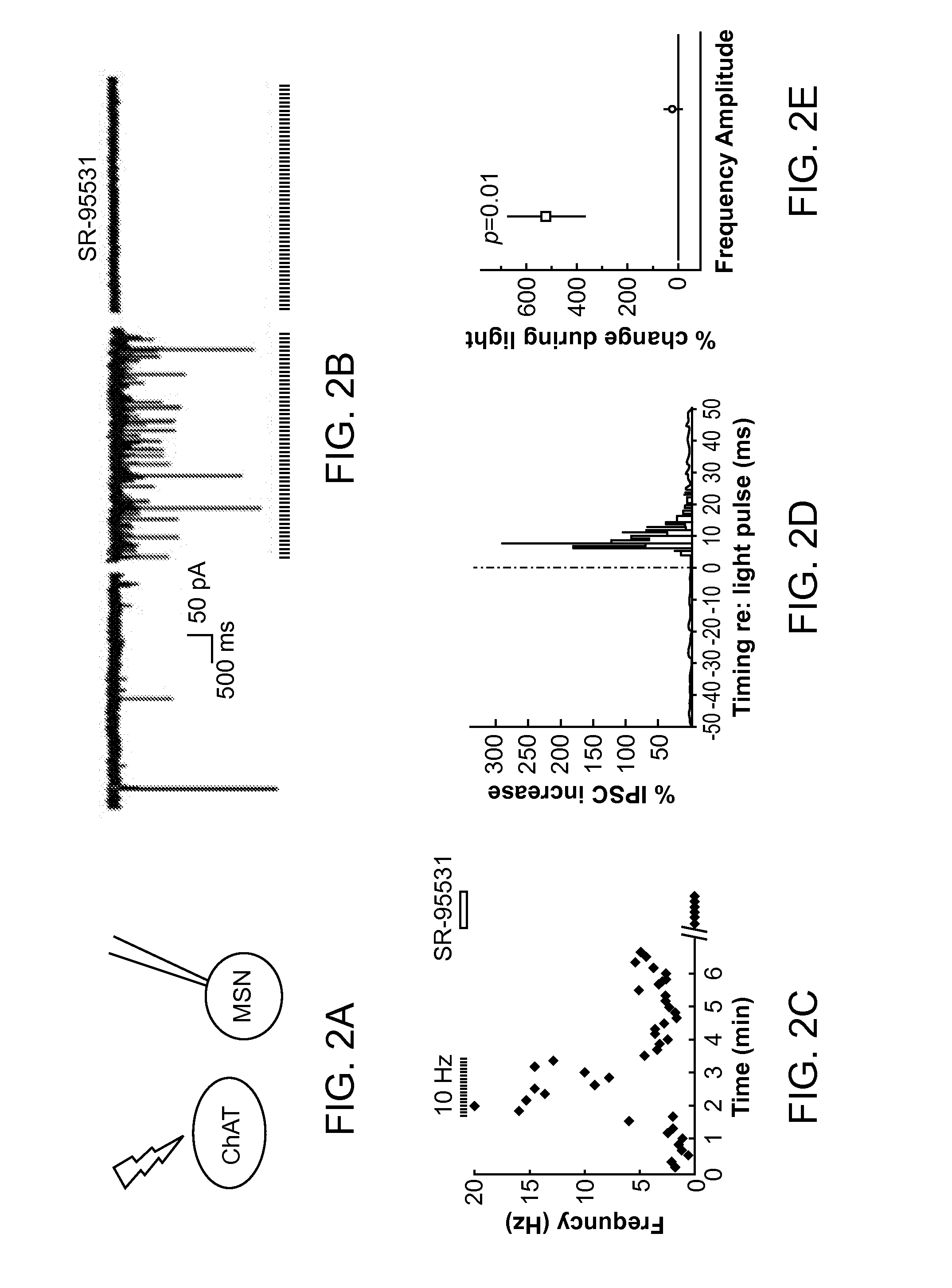
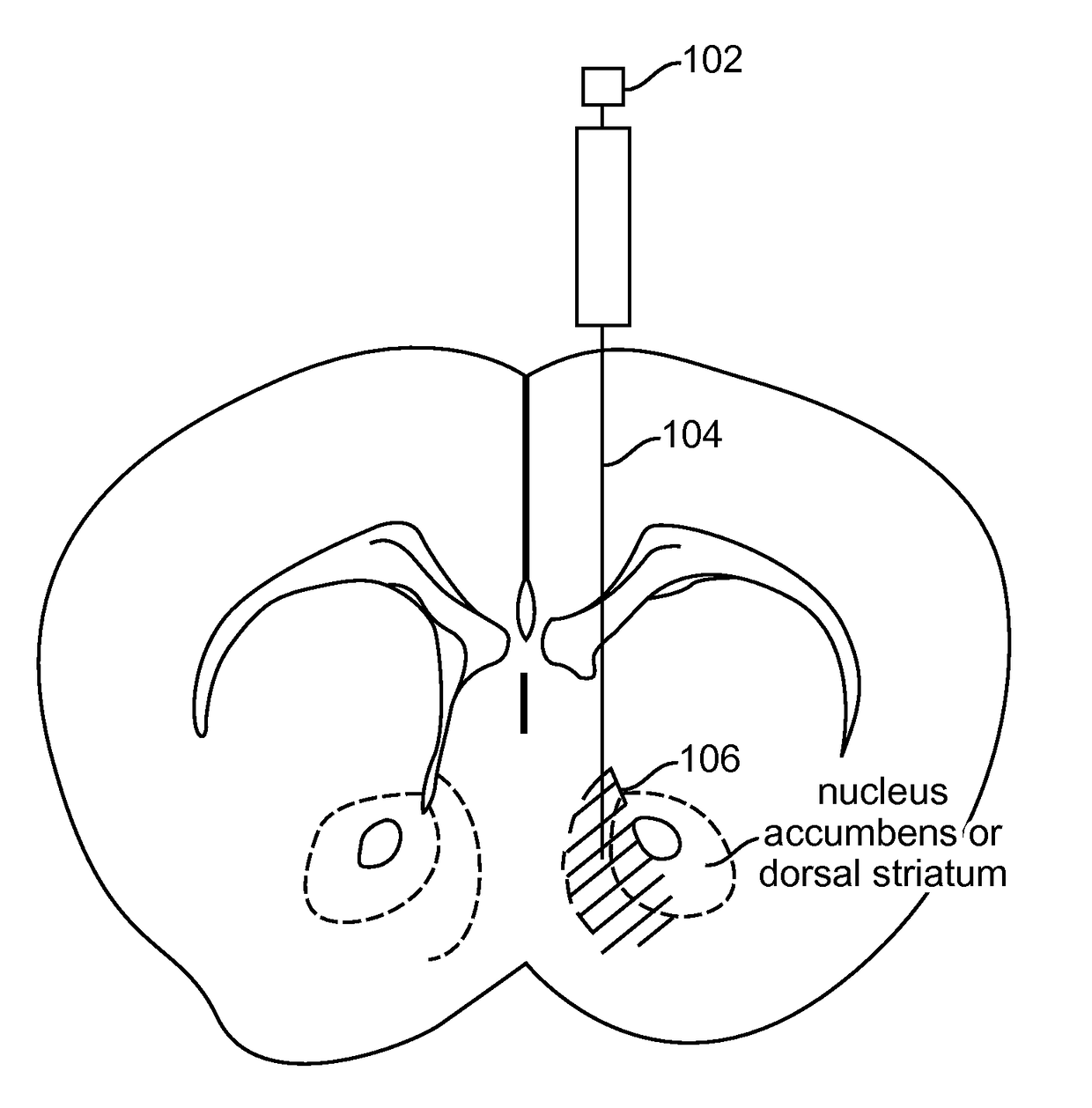
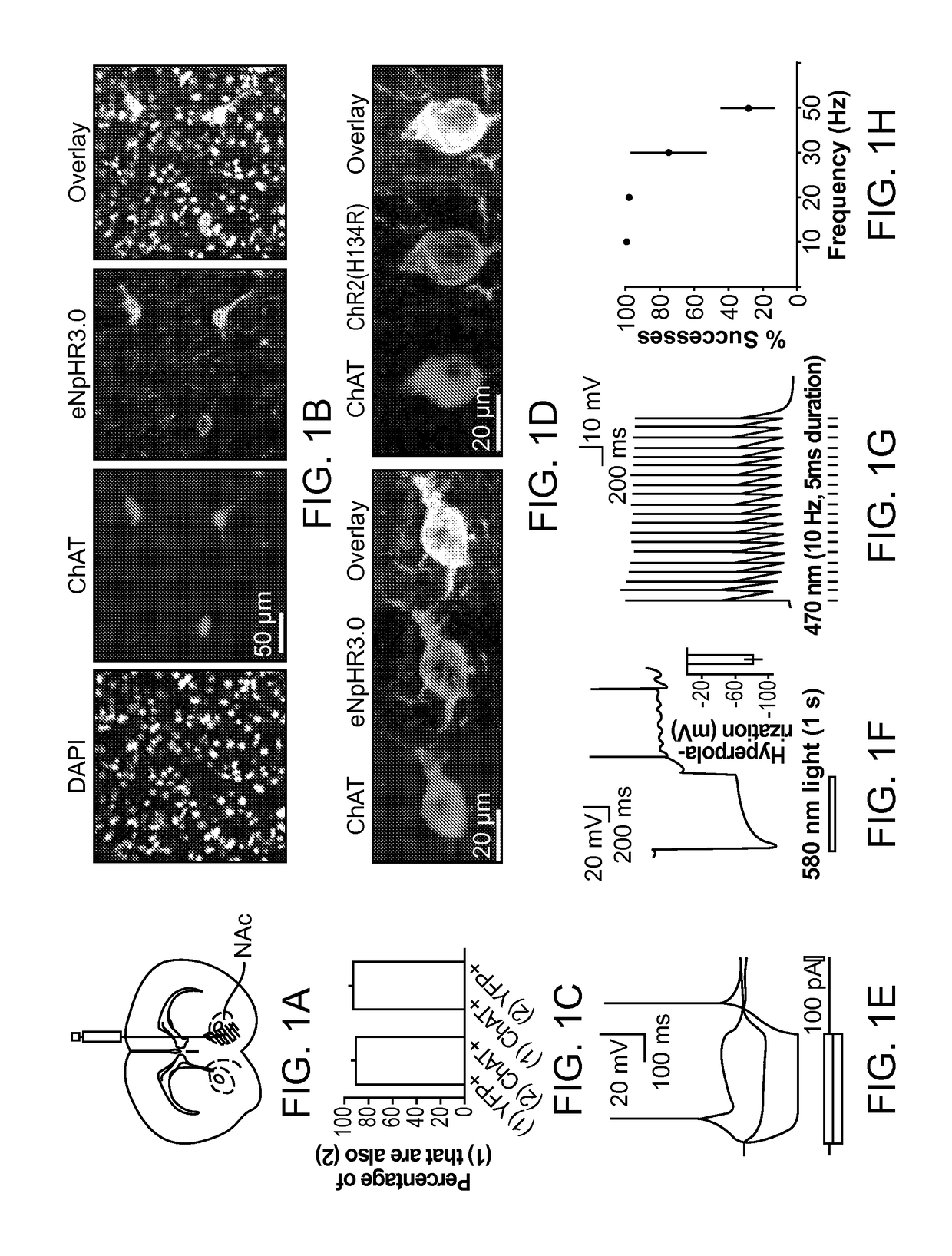
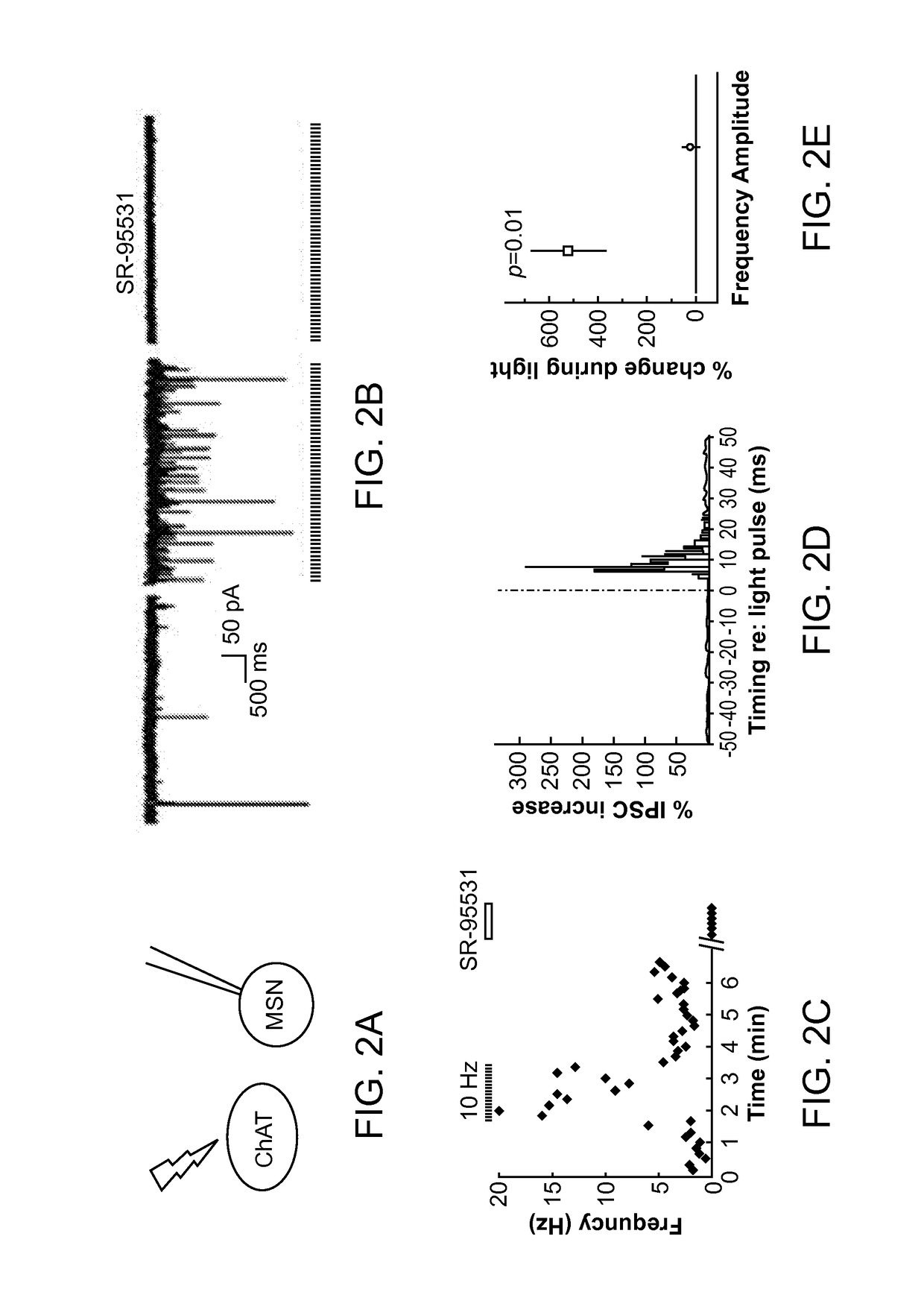
Optogenetic Control of Reward-Related Behaviors
ActiveUS20130317569A1Reduce and eliminate effectInhibition is effectiveNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsOptogeneticsInterneuron
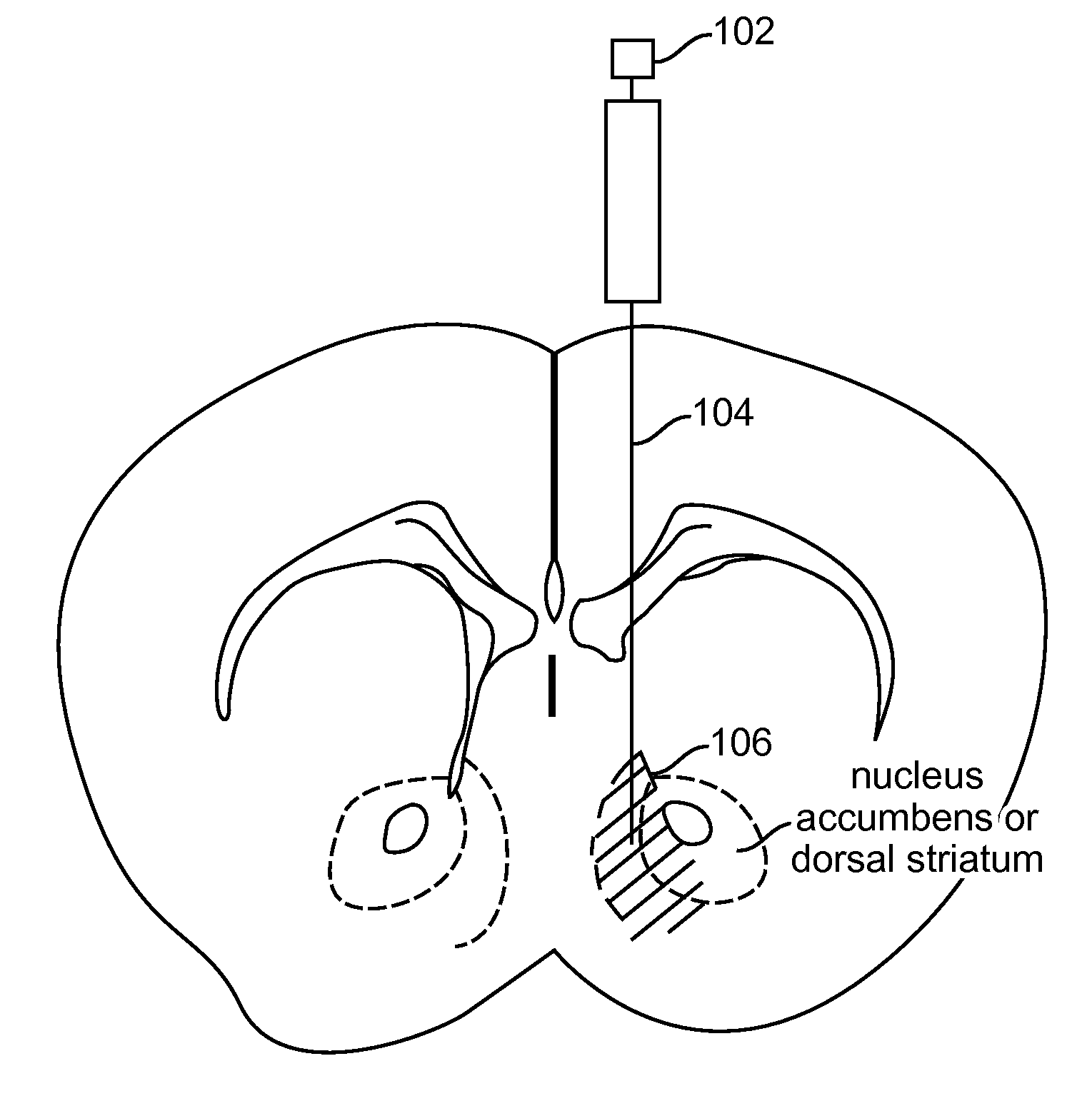
Provided herein are compositions and methods for disrupting at least one reward-related behavior in an individual through the use of light-responsive opsin proteins used to control the polarization state of the cholinergic interneurons of the nucleus accumbens or the striatum.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
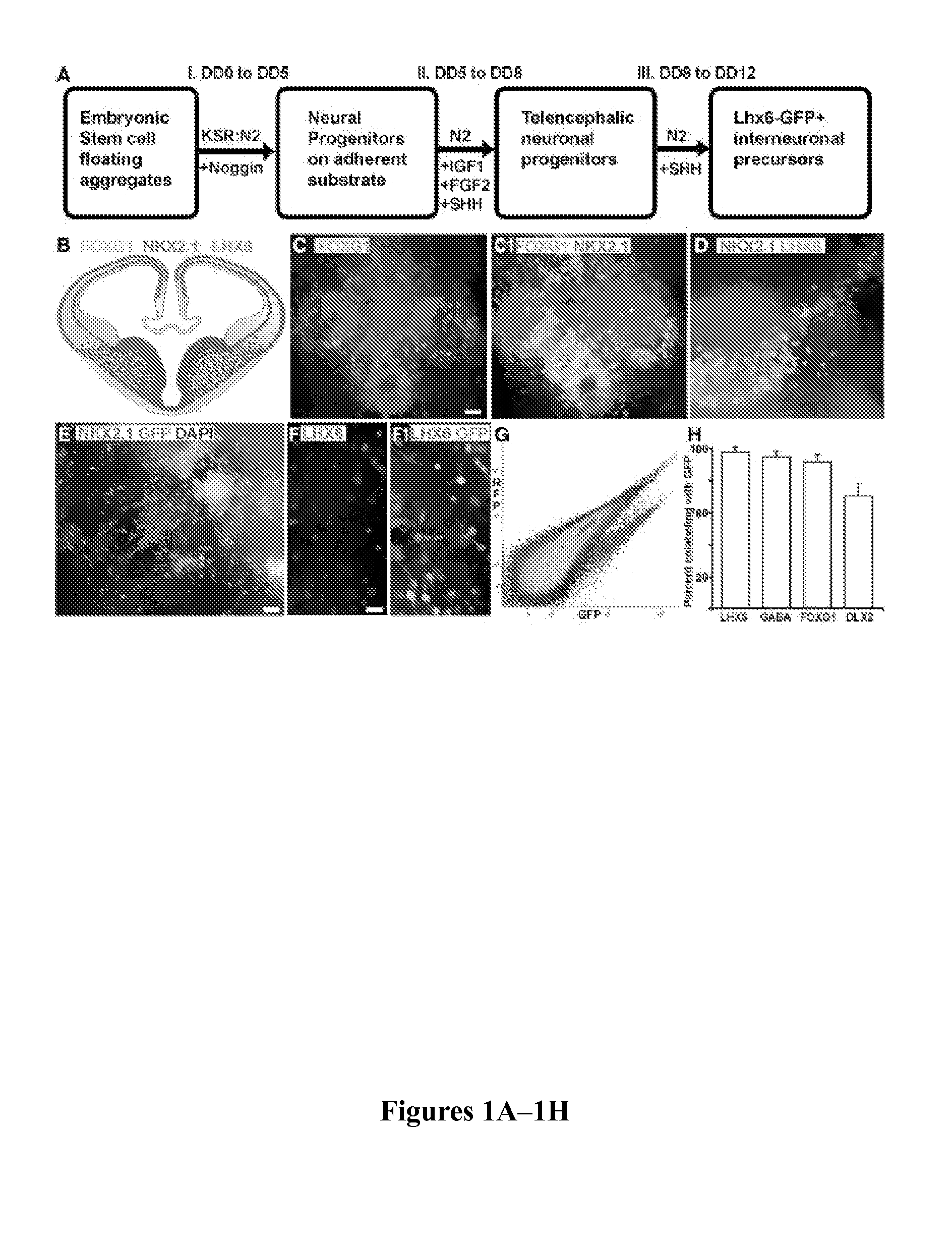
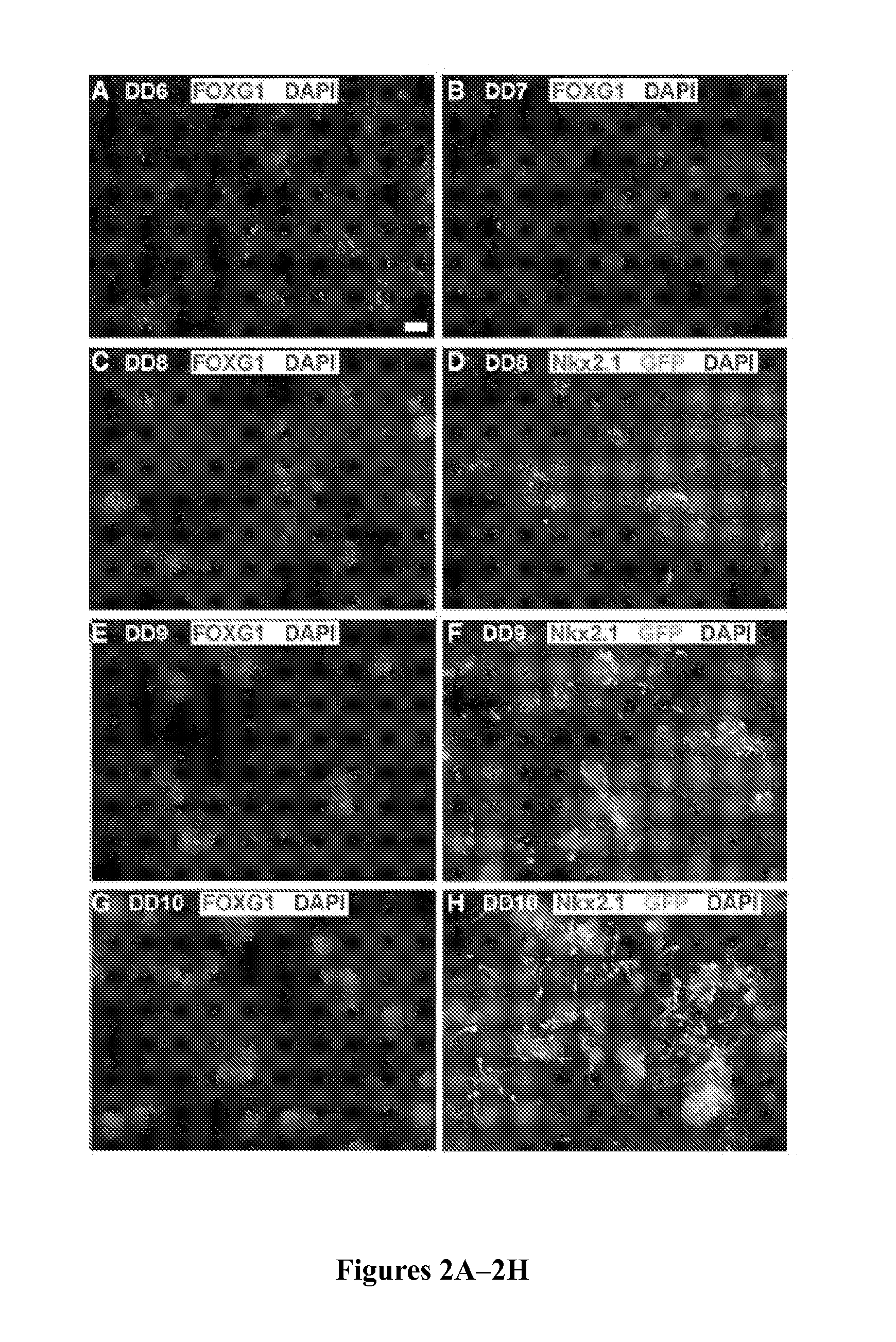
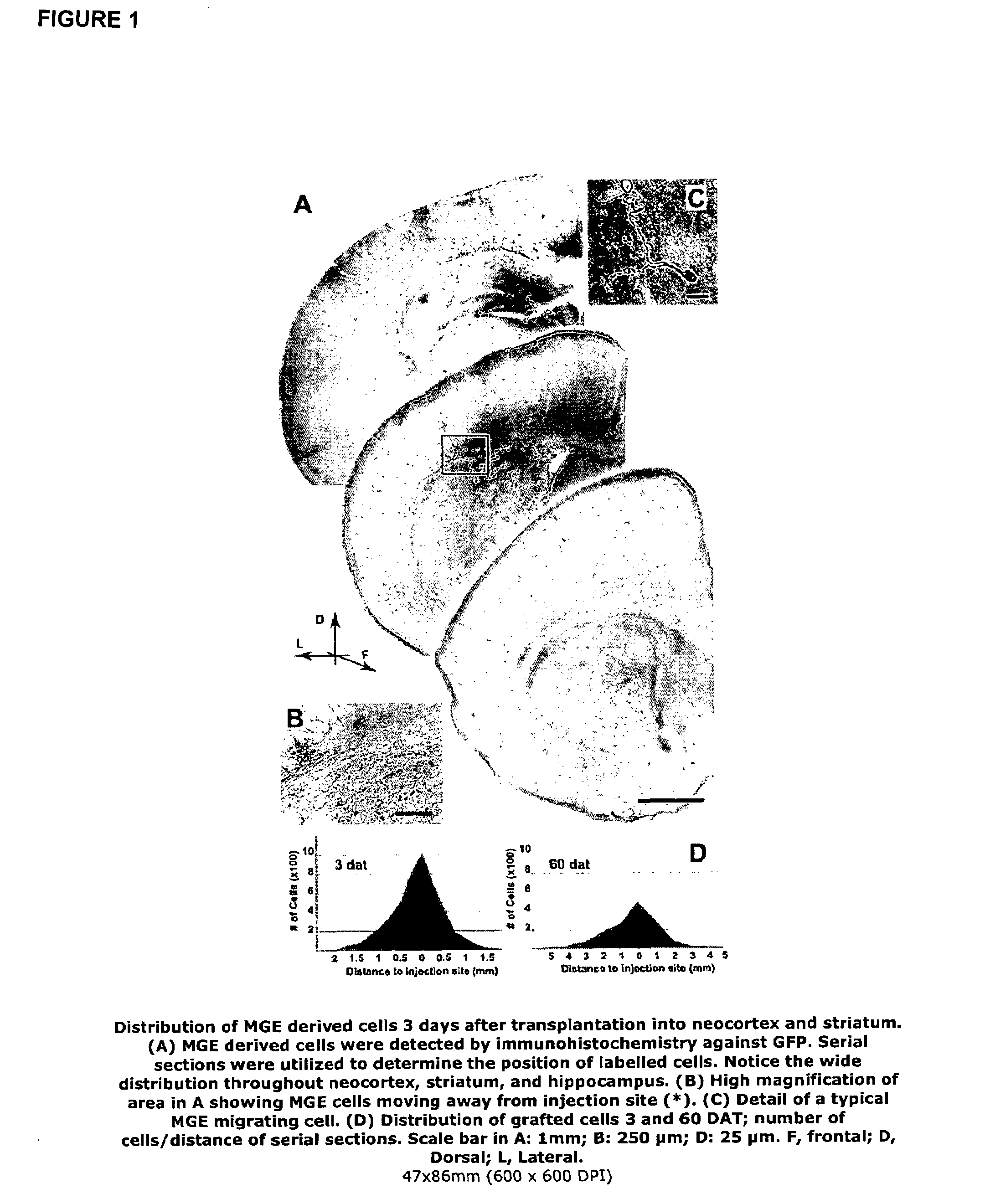
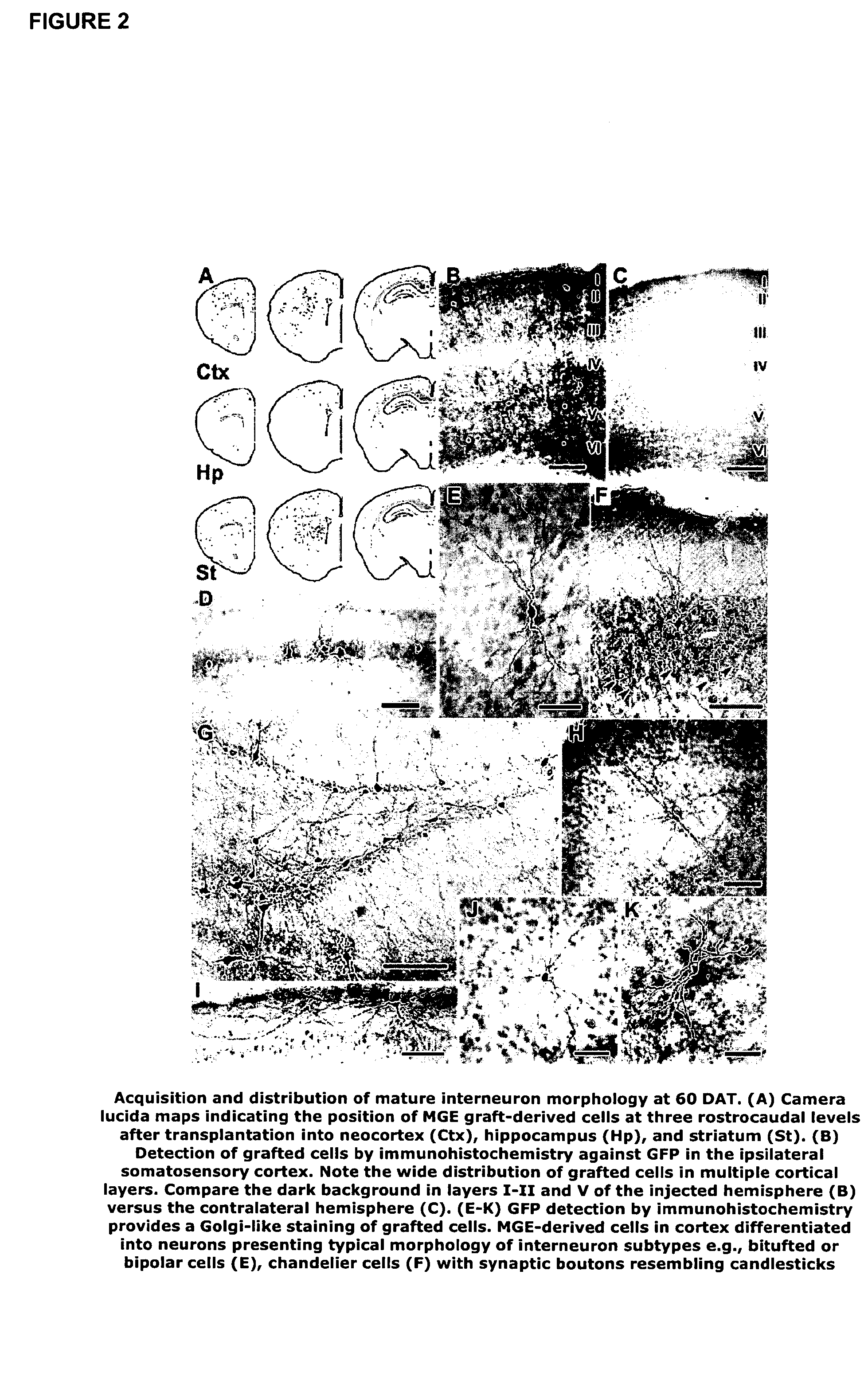
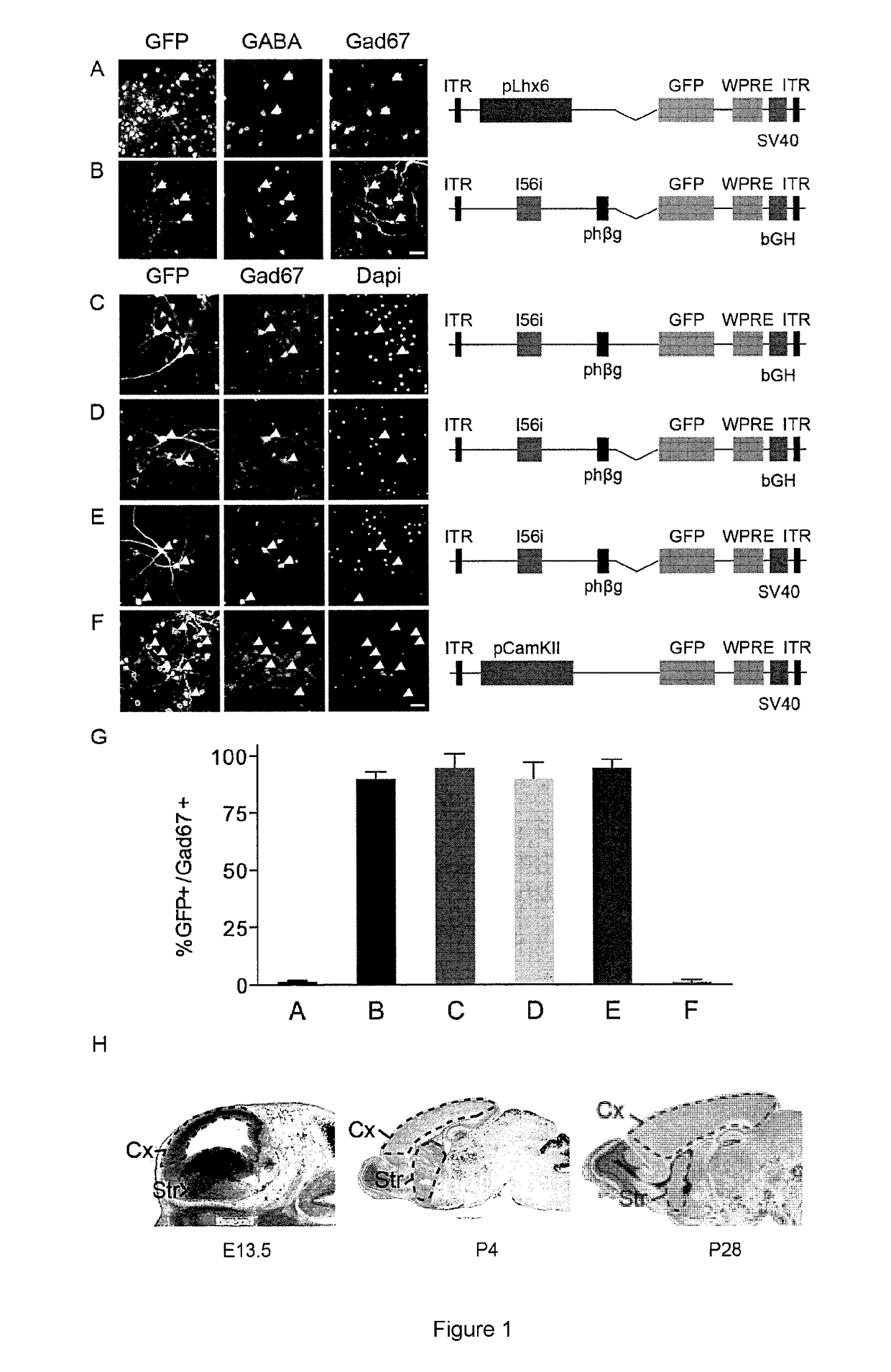
Method to isolate, identify, and use embryonic stem cells directed to forebrain interneuron fate
The present invention relates to methods of isolating a purified or enriched population of cortical or striatal immature interneuron progenitor cells and the isolated purified or enriched population of immature interneuron progenitor cells. Methods of treating a condition mediated by a loss or deficiency of interneuron function using the purified or enriched population of immature interneuron progenitor cells are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
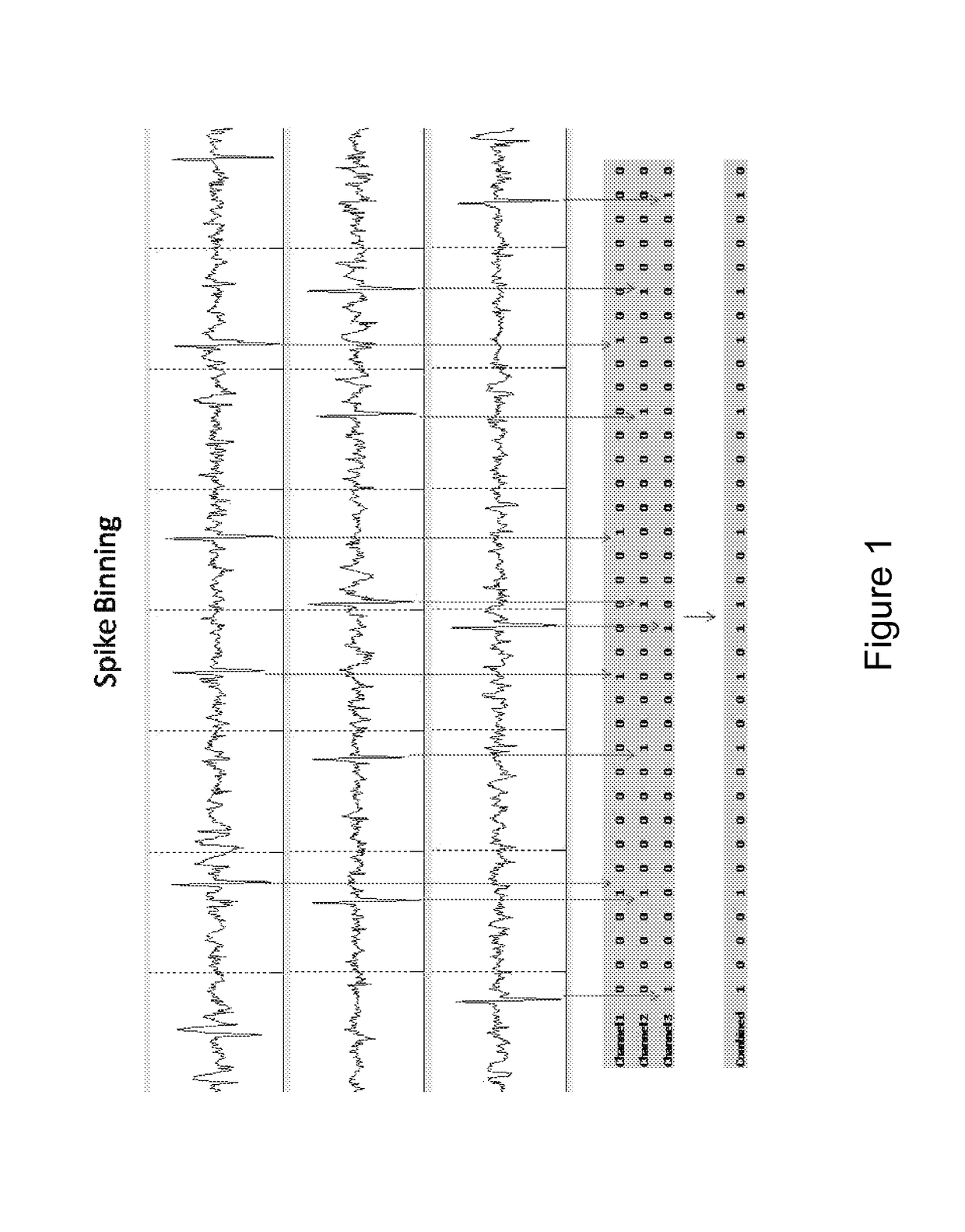
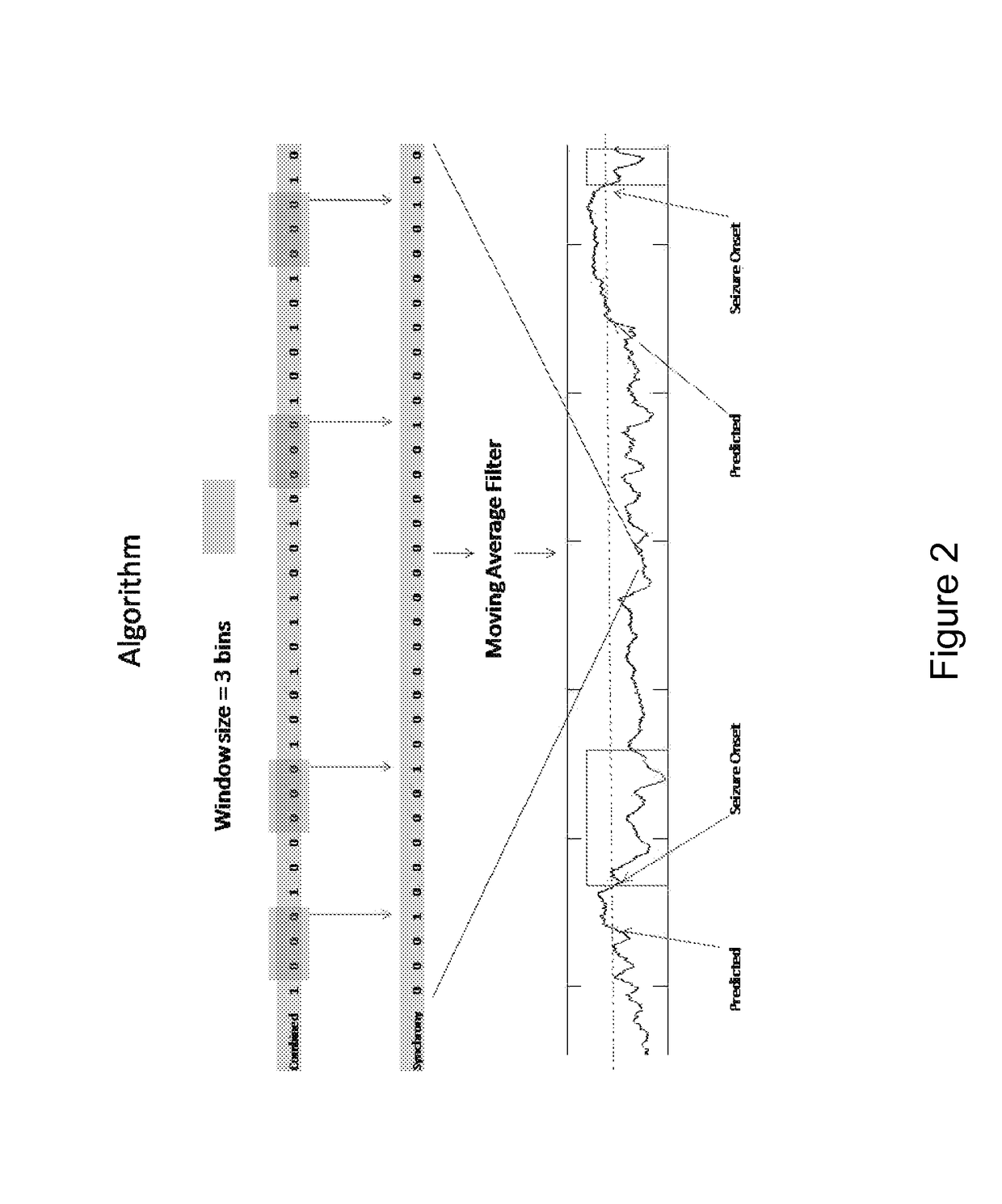
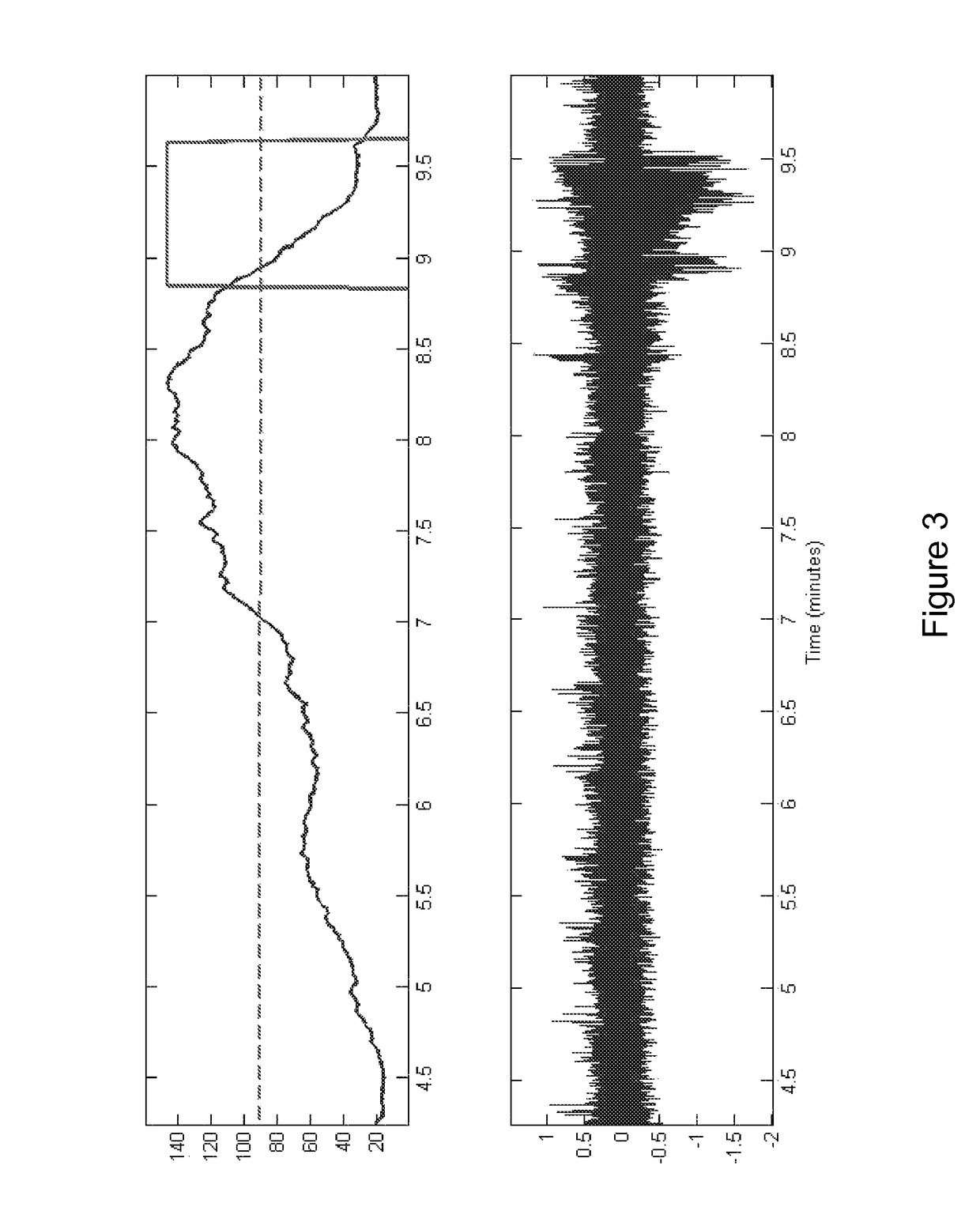
Methods, Computer-Readable Media, and Systems for Predicting, Detecting the Onset of, and Preventing a Seizure
InactiveUS20150351701A1Raise the possibilityImplantable neurostimulatorsMedical automated diagnosisMedicinePartial field
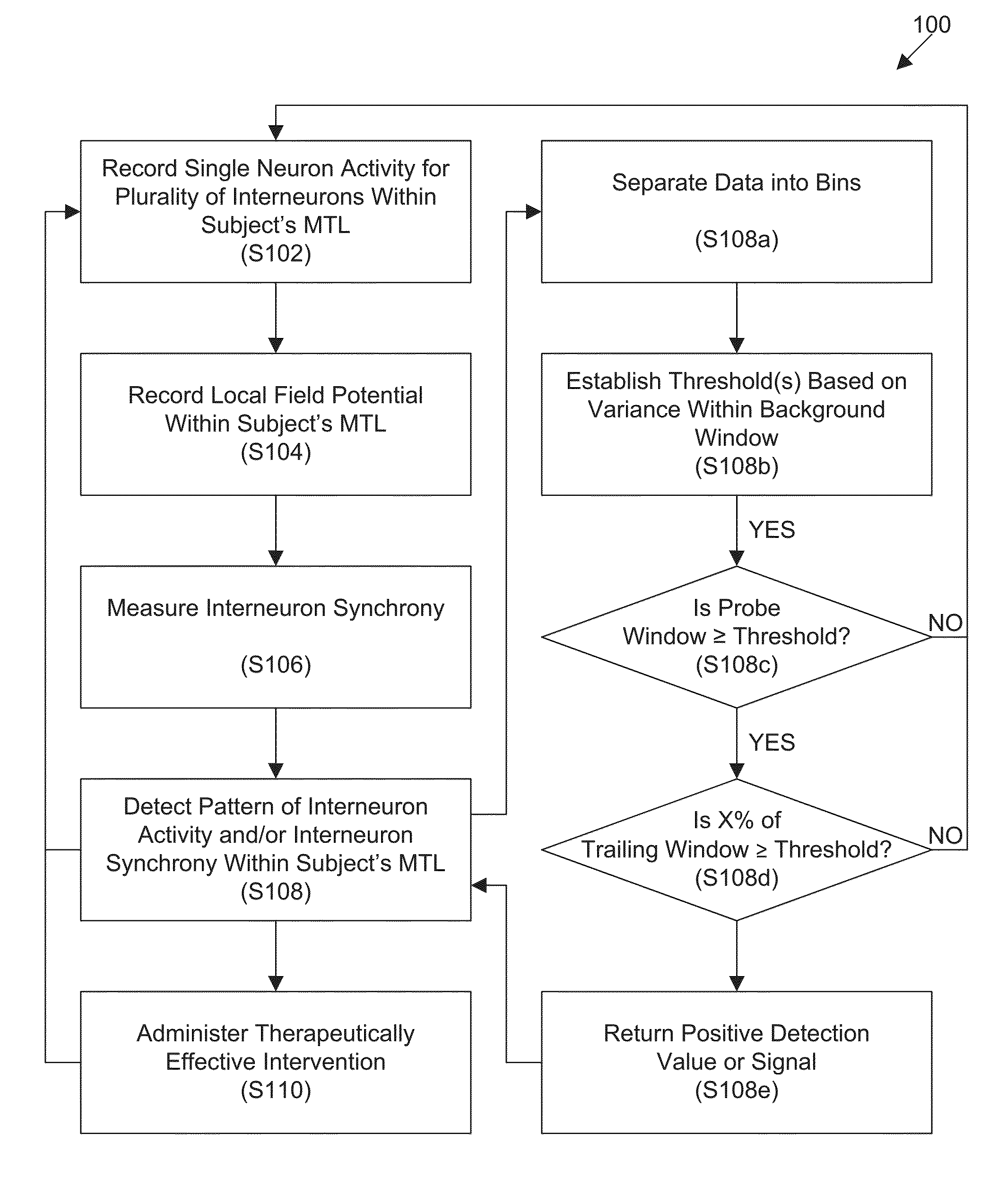
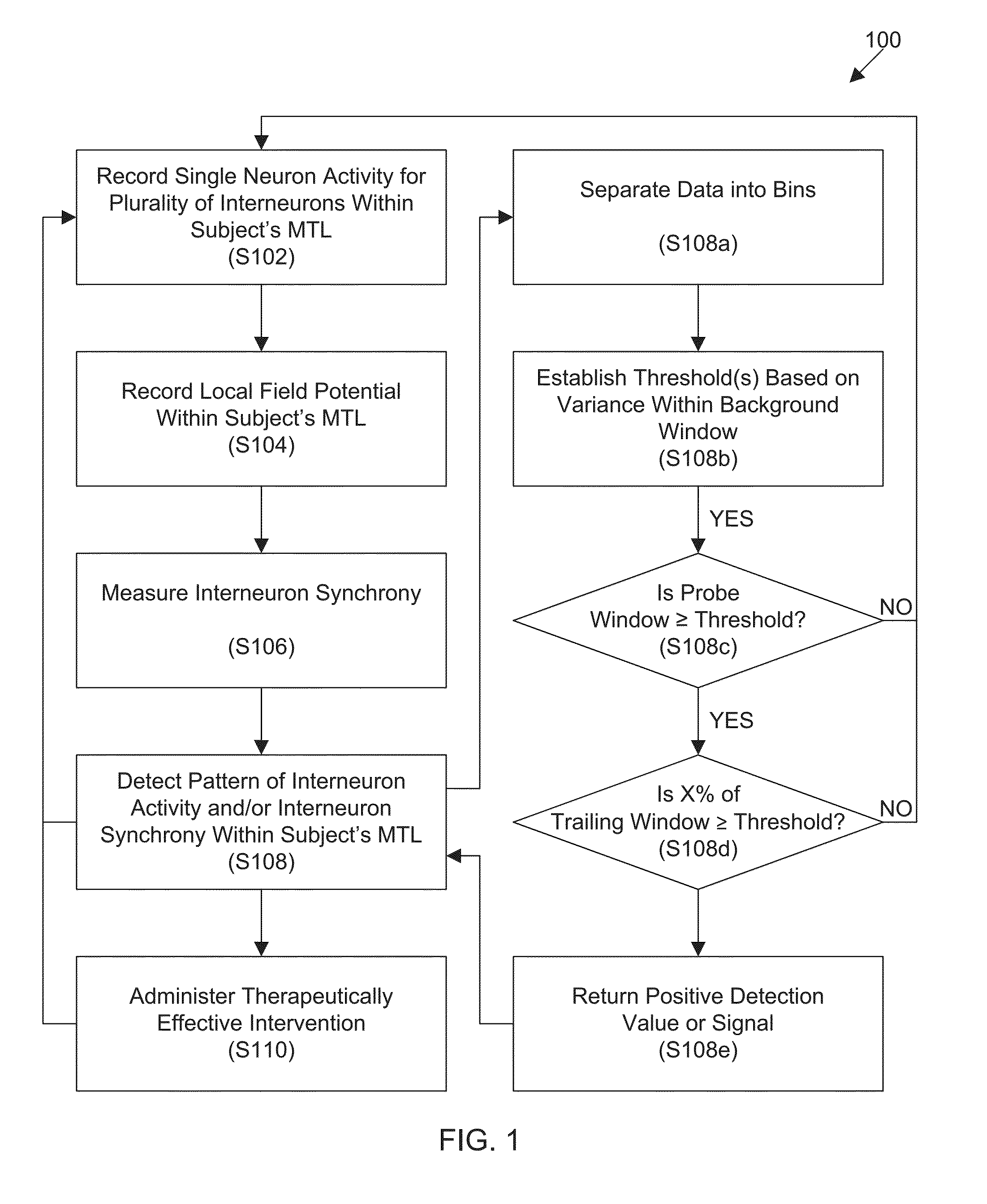
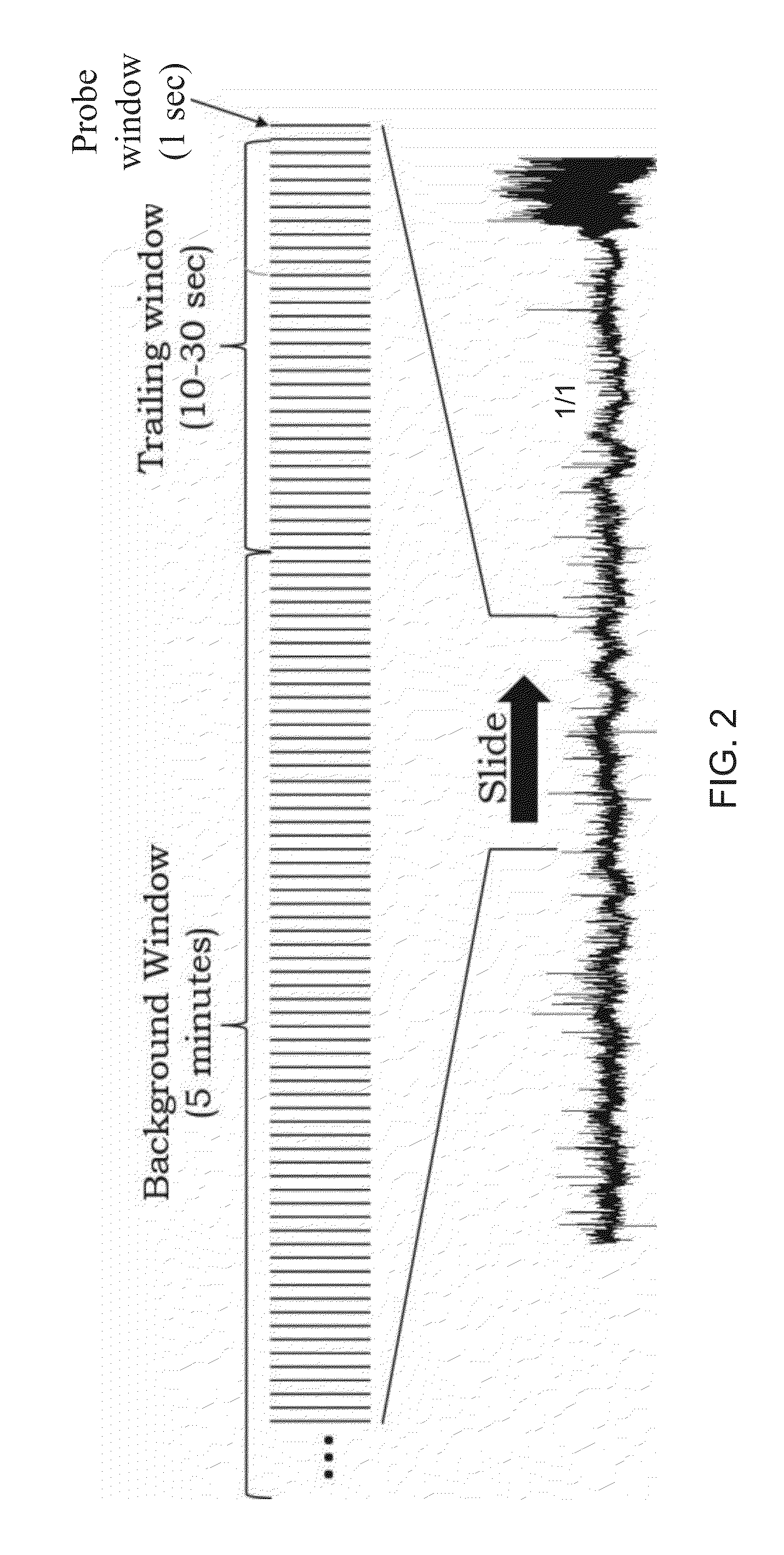
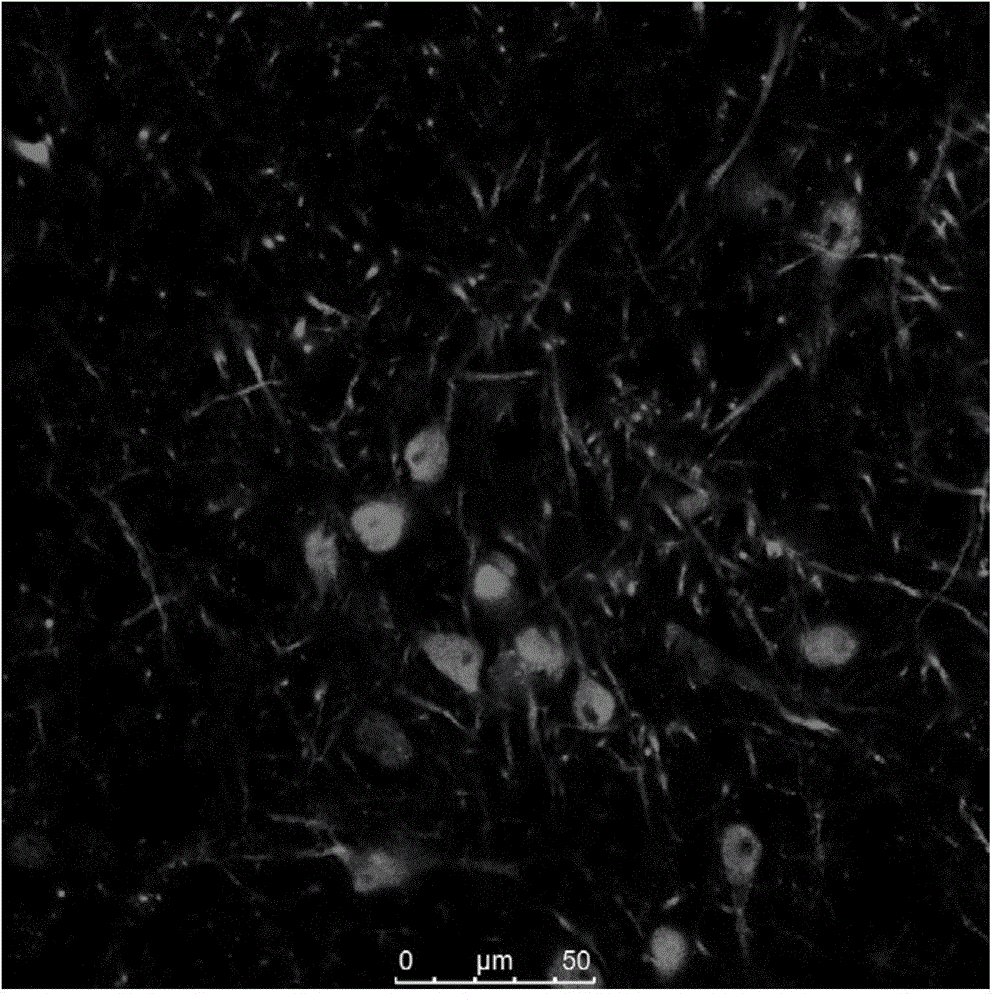
One aspect of the invention provides a method of predicting a seizure in a subject comprising: (a) recording single neuron activity for a plurality of interneurons within the subject's mesial temporal lobe; (b) recording local field potential (LFP) within the subject's mesial temporal lobe; (c) measuring interneuron synchrony within the subject's mesial temporal lobe; and (d) detecting a pattern of interneuron activity and interneuron synchrony within the subject's mesial temporal lobe associated with an increased likelihood of a seizure. Another aspect of the invention provides a method for preventing a seizure in a subject comprising: (a) performing any one of the methods described herein; and (b) upon detection of the pattern, administering a therapeutically effective intervention to the subject to prevent onset of a seizure. Another aspect of the invention provides a non-transitory computer readable medium containing computer-readable program code including instructions for performing any of the methods described herein.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
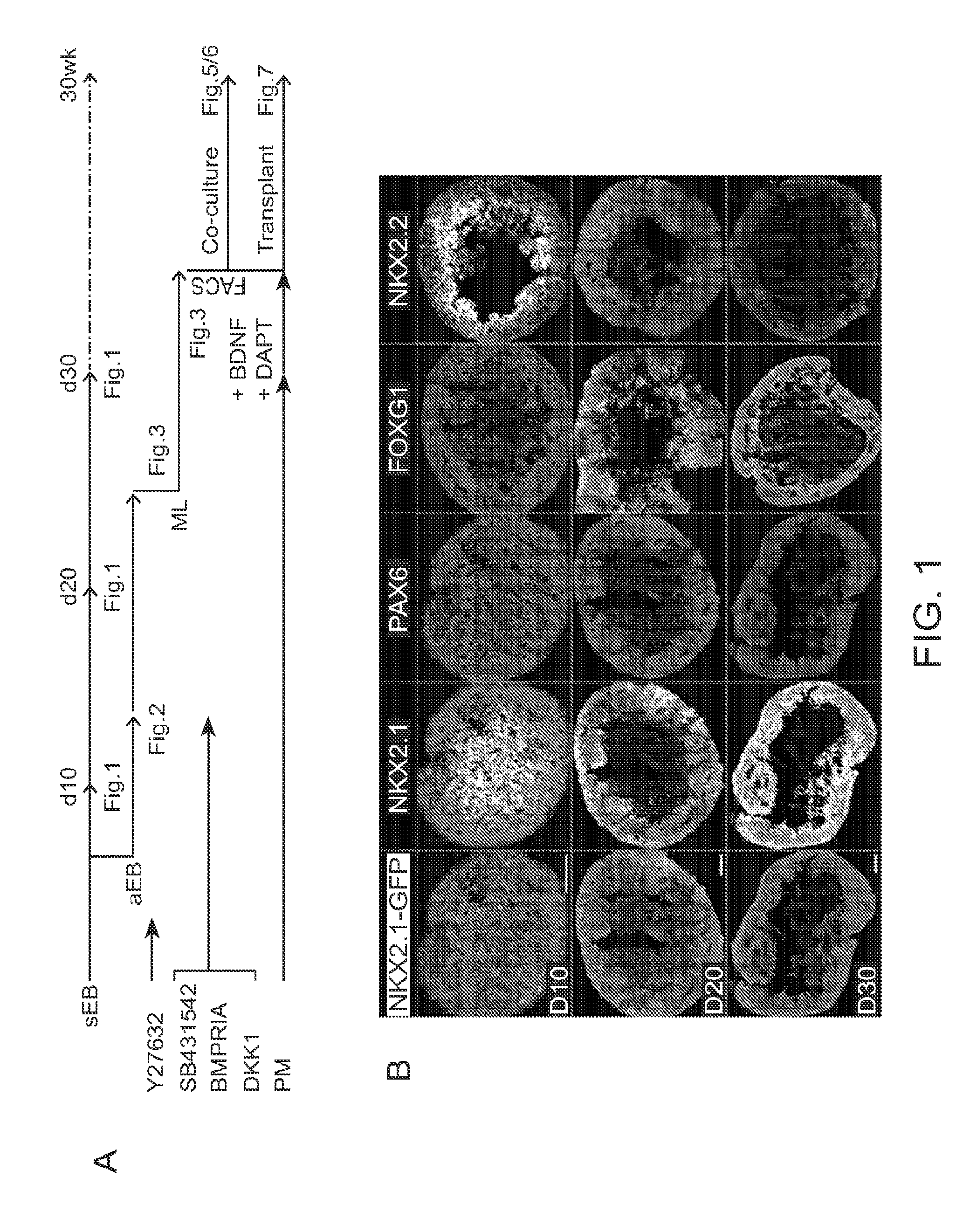
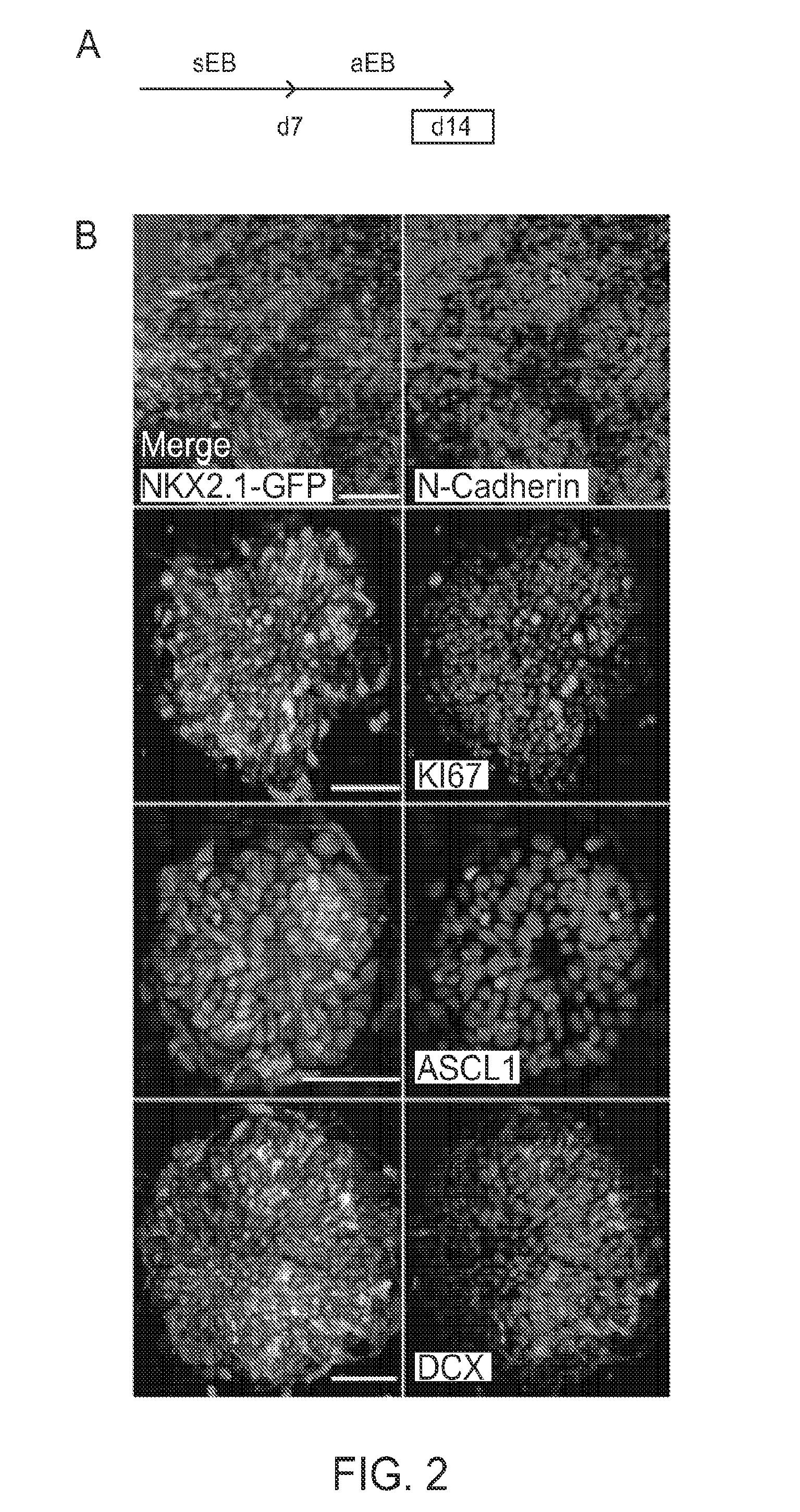
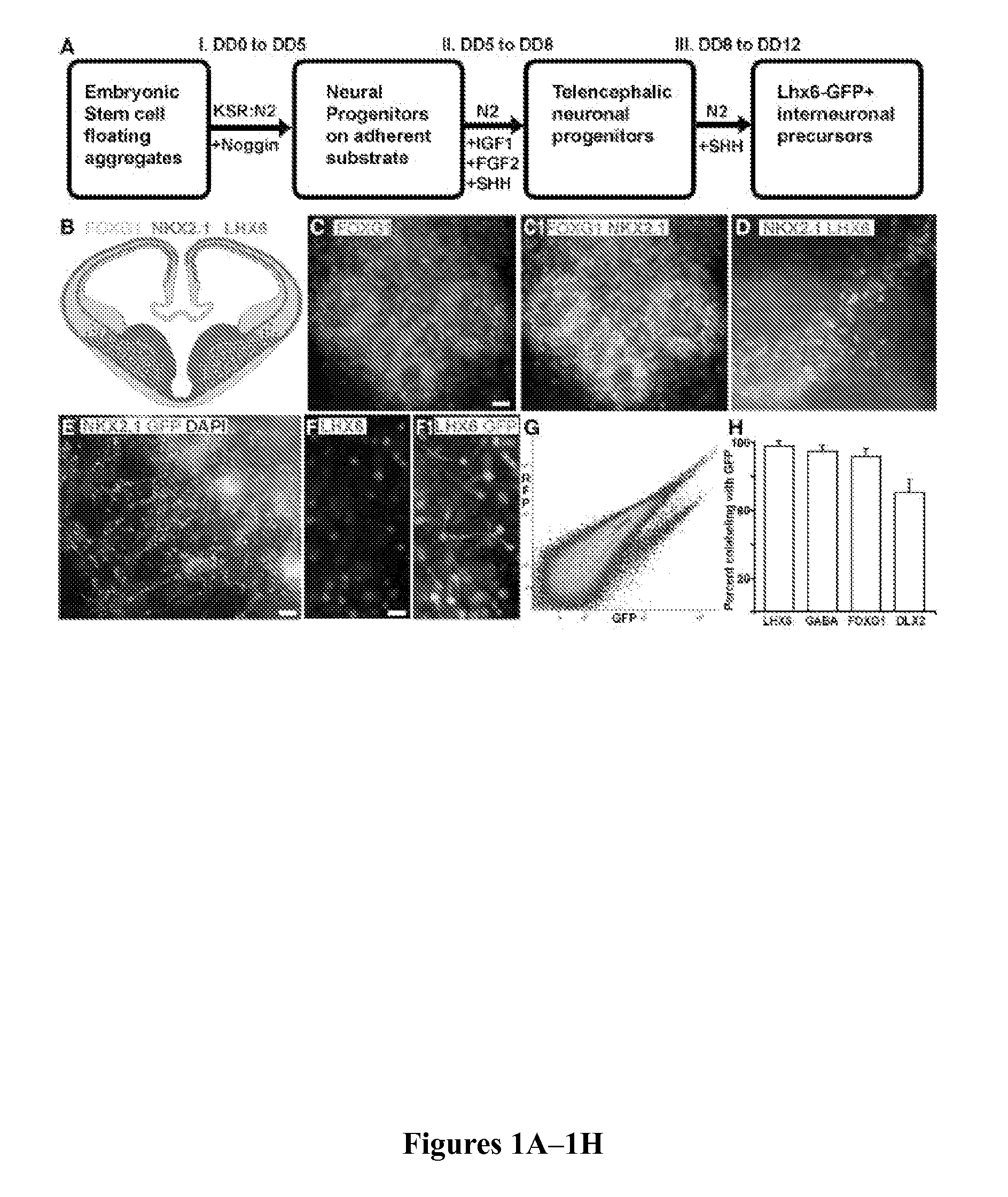
In Vitro Production of Medial Ganglionic Eminence Precursor Cells
Methods and systems for generating MGE precursor cells in vitro as well as compositions of enriched MGE precursor cells are provided. The methods and systems provide efficient production of MGE precursors. The methods and systems disclosed herein provide functional MGE precursors which differentiate into functional GABAergic interneurons.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
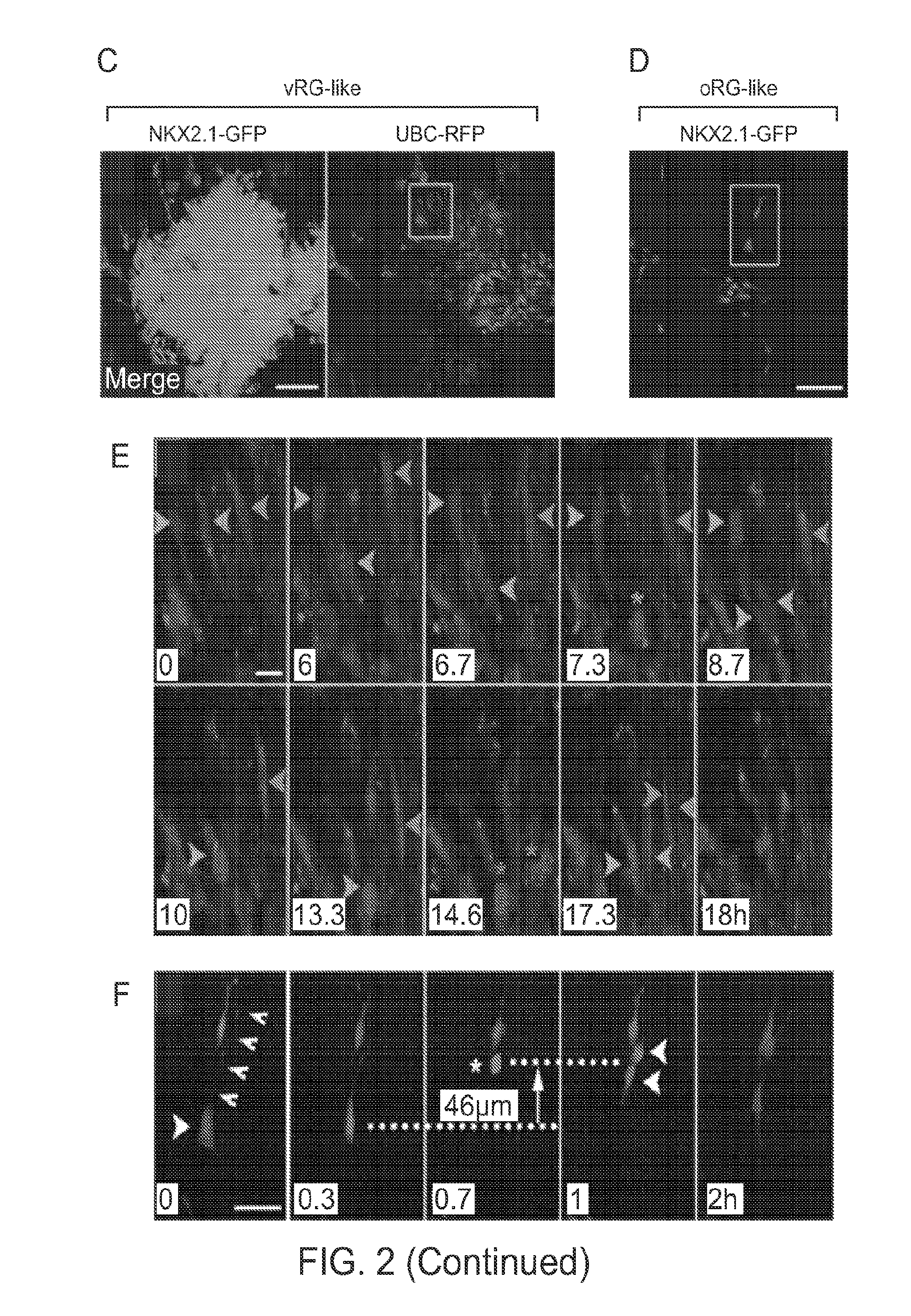
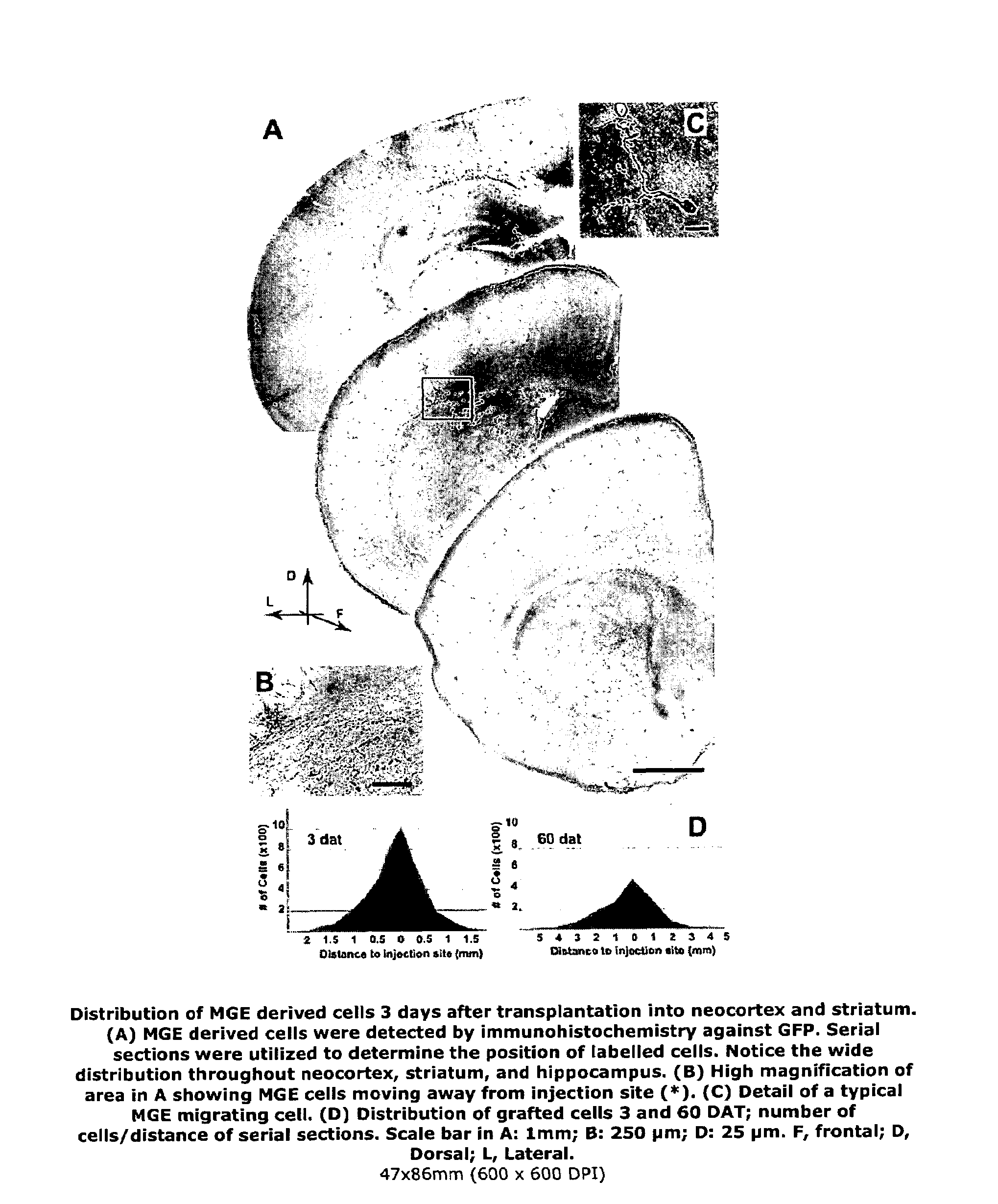
Transplantation of neural cells
ActiveUS20090311222A1Enhanced inhibitory interneuron activityIncrease in GABA mediated synaptic eventsBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseInhibitory interneuron
Restoration or increase of inhibitory interneuron function in vivo is achieved by transplantation of MGE cells into the brain. Compositions containing MGE cells are provided as are uses to treat various diseases characterised by abnormal inhibitory interneuron function or in cases where increase inhibition may ameliorate neural circuits that are abnormally activated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optogenetic control of reward-related behaviors
InactiveUS20170157269A1Reduce and eliminate effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderOptogeneticsInterneuron
Provided herein are compositions and methods for disrupting at least one reward-related behavior in an individual through the use of light-responsive opsin proteins used to control the polarization state of the cholinergic intemeurons of the nucleus accumbens or the striatum.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Automated Construction of Neural Network Architecture with Bayesian Graph Exploration
PendingUS20220004875A1Efficient searchPromote nuisance-robust feature extractionMathematical modelsNeural architecturesData setInterneuron
A system for automated construction of an artificial neural network architecture is provided. The system includes a set of interfaces and data links configured to receive and send signals, wherein the signals include datasets of training data, validation data and testing data, wherein the signals include a set of random number factors in multi-dimensional signals X, wherein part of the random number factors are associated with task labels Y to identify, and nuisance variations S. The system further includes a set of memory banks to store a set of reconfigurable deep neural network (DNN) blocks, hyperparameters, trainable variables, intermediate neuron signals, and temporary computation values including forward-pass signals and backward-pass gradients. The system further includes at least one processor, in connection with the interface and the memory banks, configured to submit the signals and the datasets into the reconfigurable DNN blocks, wherein the at least one processor is configured to execute a Bayesian graph exploration using the Bayes-Ball algorithm to reconfigure the DNN blocks such that redundant links are pruned to be compact by modifying the hyperparameters in the memory banks. The system realizes nuisance-robust variational Bayesian inference to be transferable to new datasets in semi-supervised settings.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
In vitro production of medial ganglionic eminence precursor cells
Methods and systems for generating MGE precursor cells in vitro as well as compositions of enriched MGE precursor cells are provided. The methods and systems provide efficient production of MGE precursors. The methods and systems disclosed herein provide functional MGE precursors which differentiate into functional GABAergic interneurons.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Systems and methods for treating dementia
ActiveUS10265497B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce tau phosphorylationMedical devicesVibration massageAmyloid betaInterneuron
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for at least one of preventing, reducing, and treating a level of or change in at least one of amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide, C-terminal fragment-β (β-CTF), β-secretase (BACE1), γ-secretase, neuroinflammation, and / or dementia (e.g., Alzheimer's disease or age-related decline) in a subject by inducing synchronized gamma oscillations in the brain of the subject using, for example, a stimulus-emitting device to emit a stimulus (e.g., light, sound, and / or haptic) at a frequency (e.g., about 40 Hz) that synchronously activates in vivo a specific cell type (e.g., fast-spiking-parvalbumin (FS-PV) immunoreactive interneurons) and / or brain region (e.g., a sensory cortex and / or hippocampus) of the subject.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Generation of neuronal cells from pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20100166720A1High prevalenceIncrease incidenceBiocideNervous disorderCortical inhibitionInterneuron
The invention relates to in vitro methods for differentiating mammalian pluripotent stem cells into cells displaying a neuronal phenotype, more particularly into cortical-type neurons including inter alia pyramidal neurons and cortical inhibitory interneurons. The invention further encompasses so-obtained neuronal cells and cell population, compositions comprising such, and further uses of said neuronal cells and cell population.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Compositions and method for reducing seizures
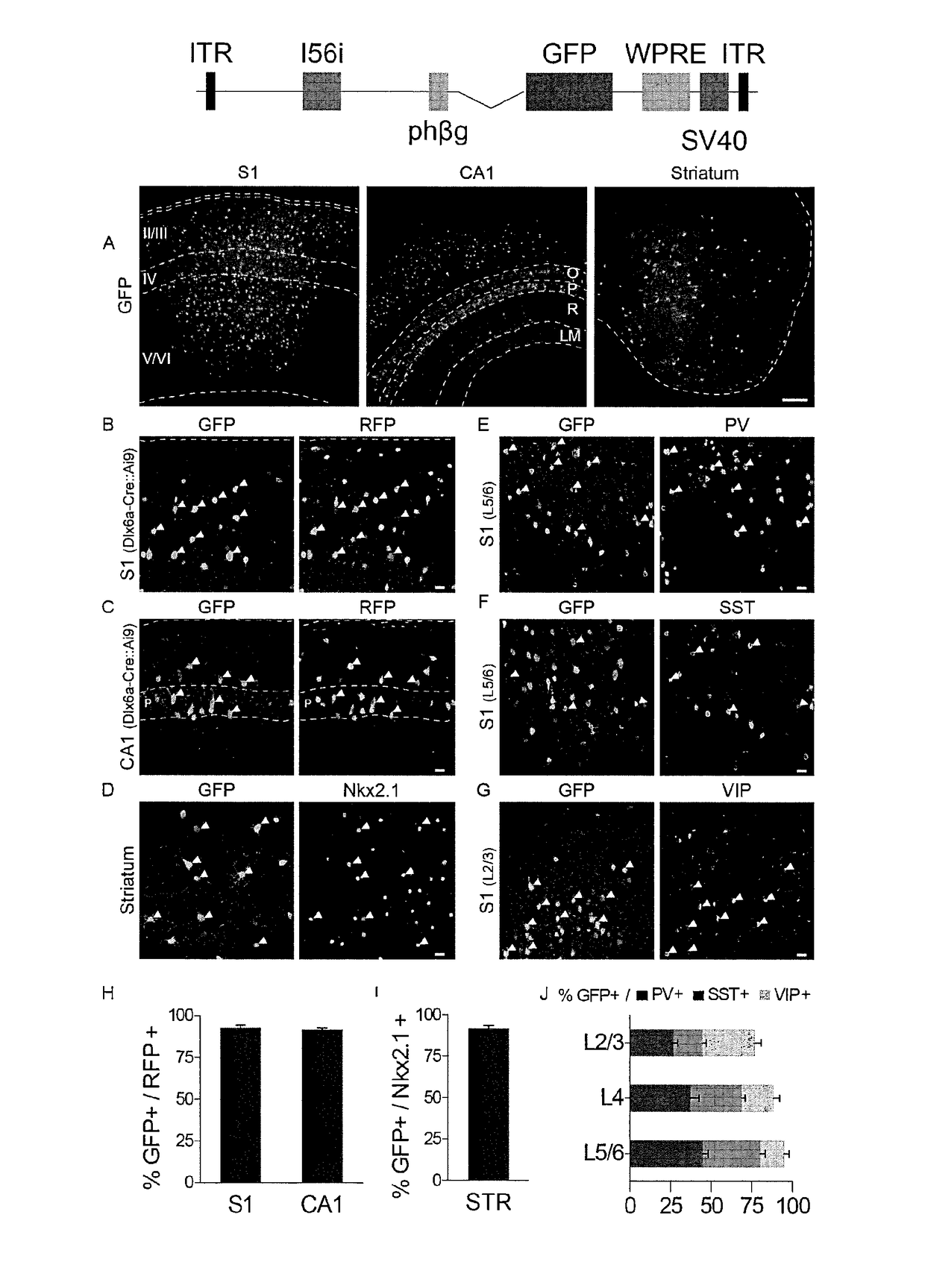
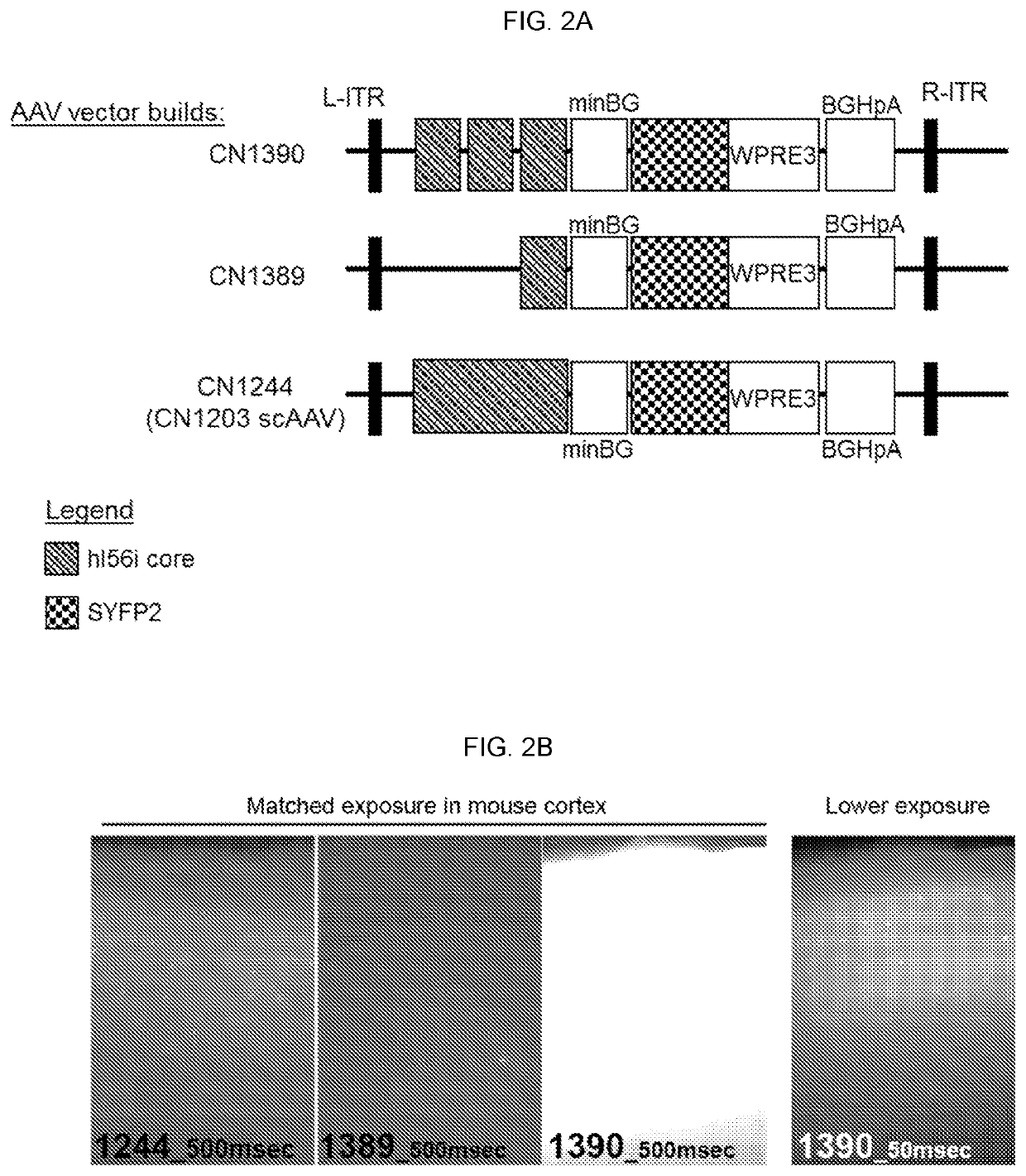
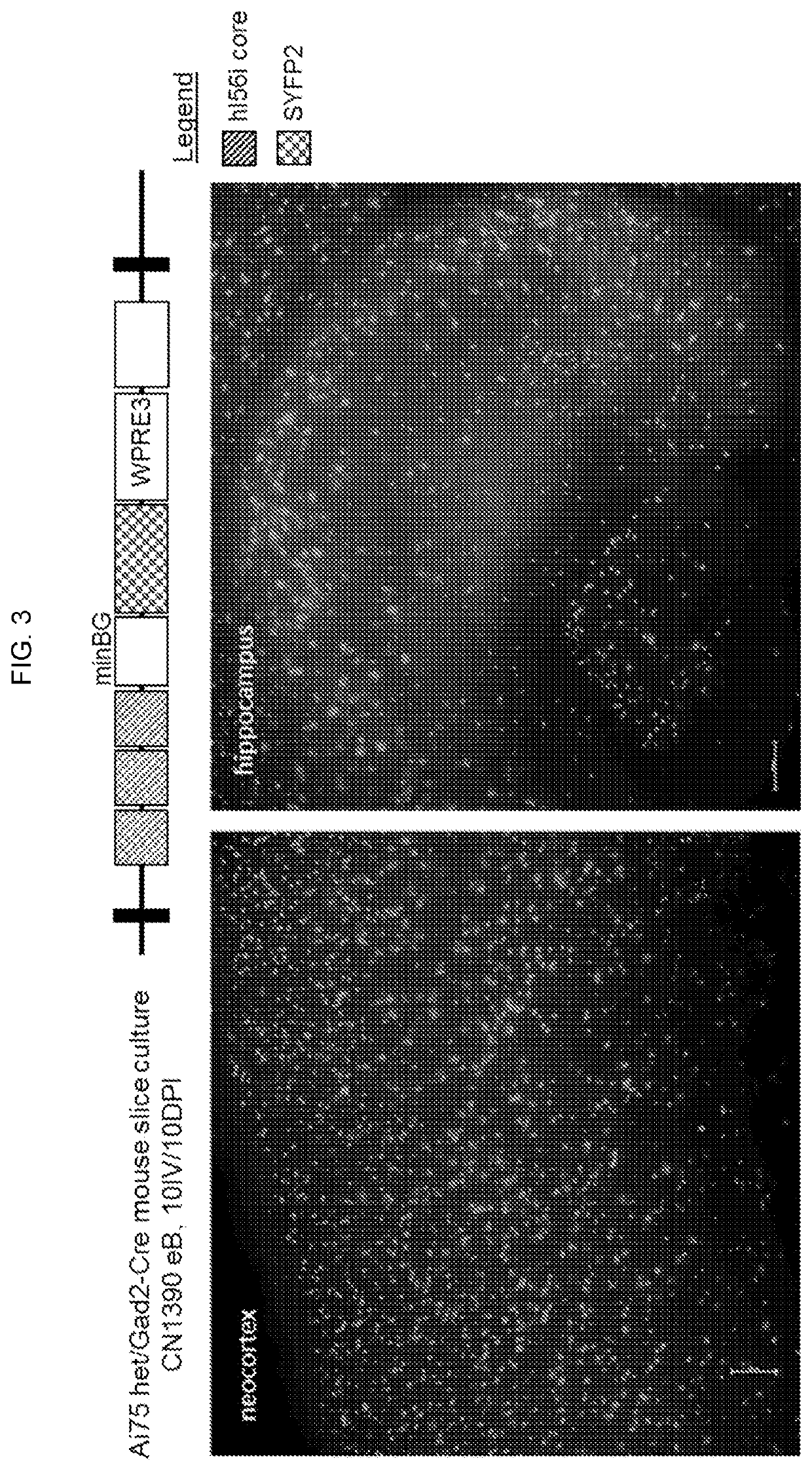
Provided are compositions and methods for prophylaxis and / or therapy of disorders that involve seizures. The compositions and methods relate to a recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) comprising a I56i enhancer sequence, and a sequence encoding hM3Dq modified muscarinic receptor (Gq-DREADD). The method includes introducing the rAAV into interneurons of an individual such that Gq-DREADD is expressed in interneurons of the individual. The method can further comprise administering to the individual an agonist of the Gq-DREADD, such for reducing or preventing seizures.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method to isolate, identify, and use embryonic stem cells directed to forebrain interneuron fate
The present invention relates to methods of isolating a purified or enriched population of cortical or striatal immature interneuron progenitor cells and the isolated purified or enriched population of immature interneuron progenitor cells. Methods of treating a condition mediated by a loss or deficiency of interneuron function using the purified or enriched population of immature interneuron progenitor cells are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
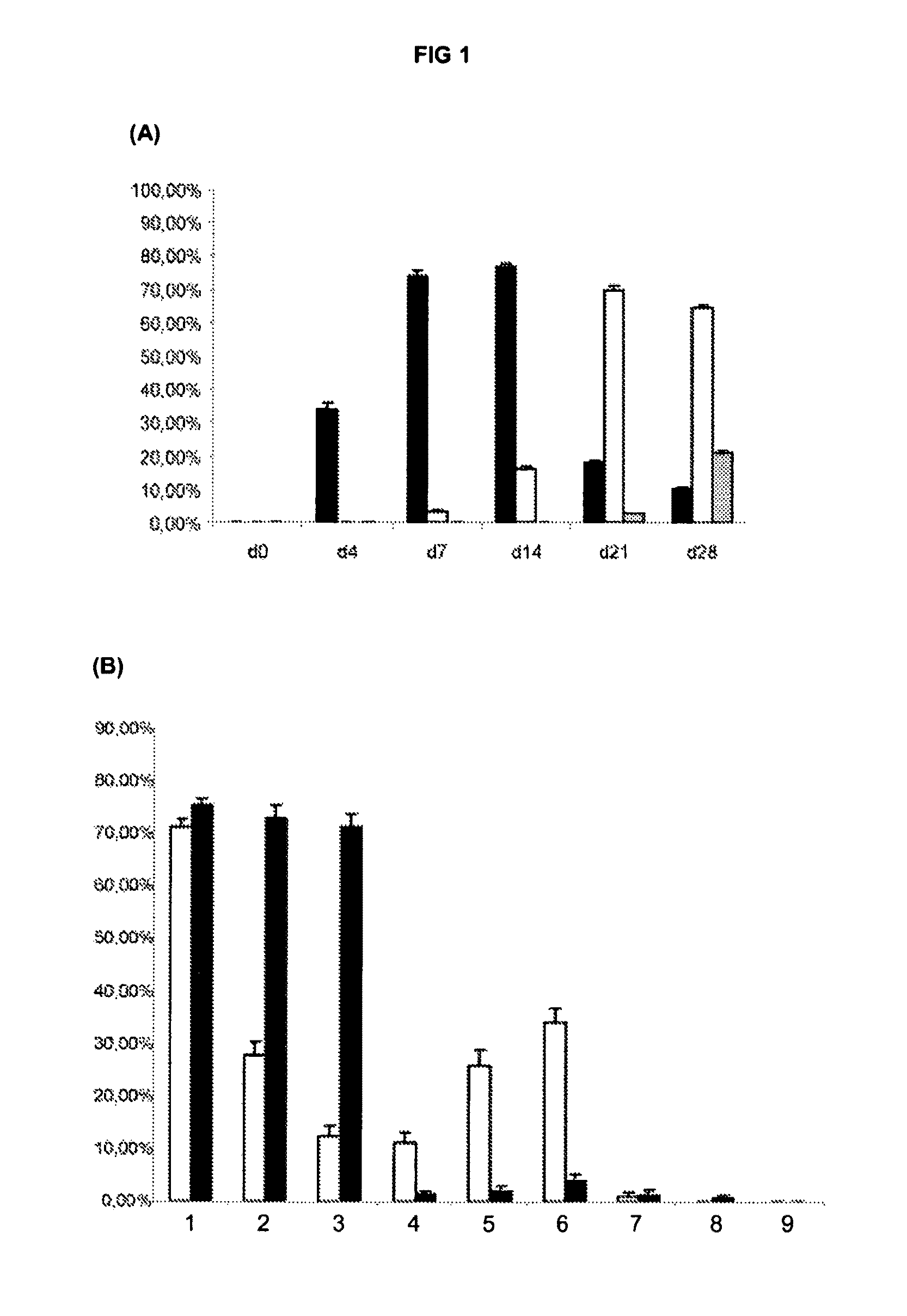
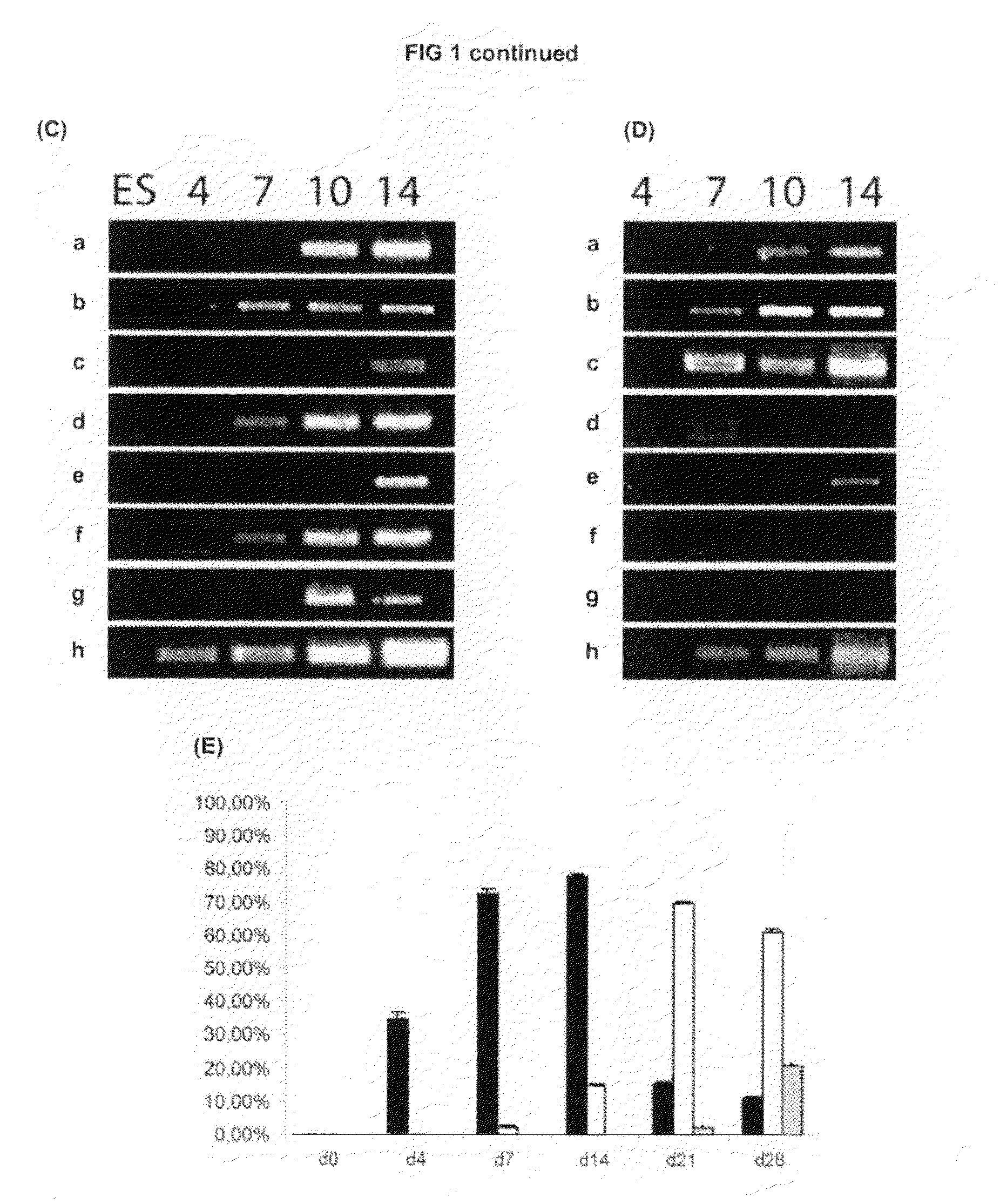
In vitro methods of differentiating stem cells into neurons and neurons generated using the same
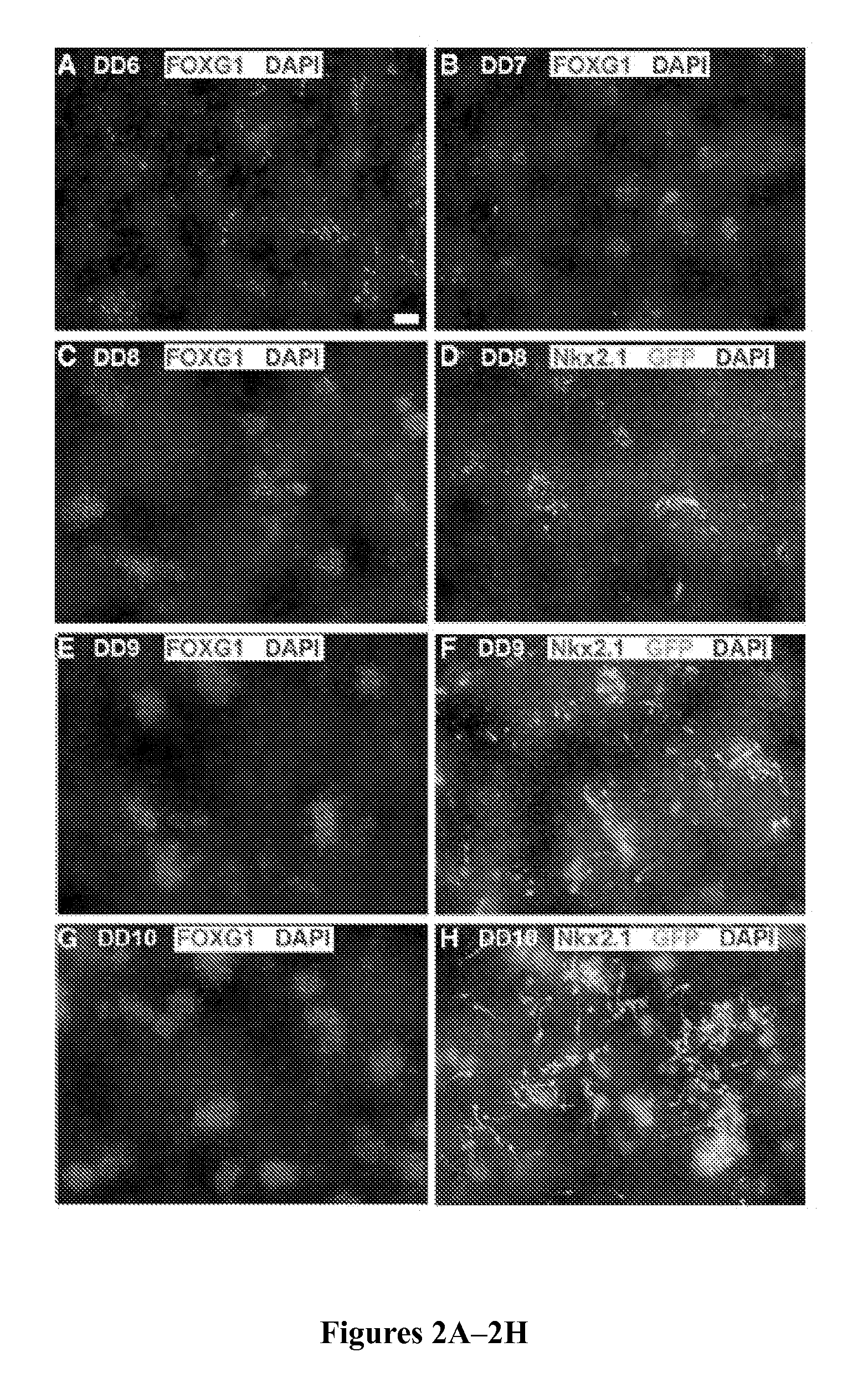
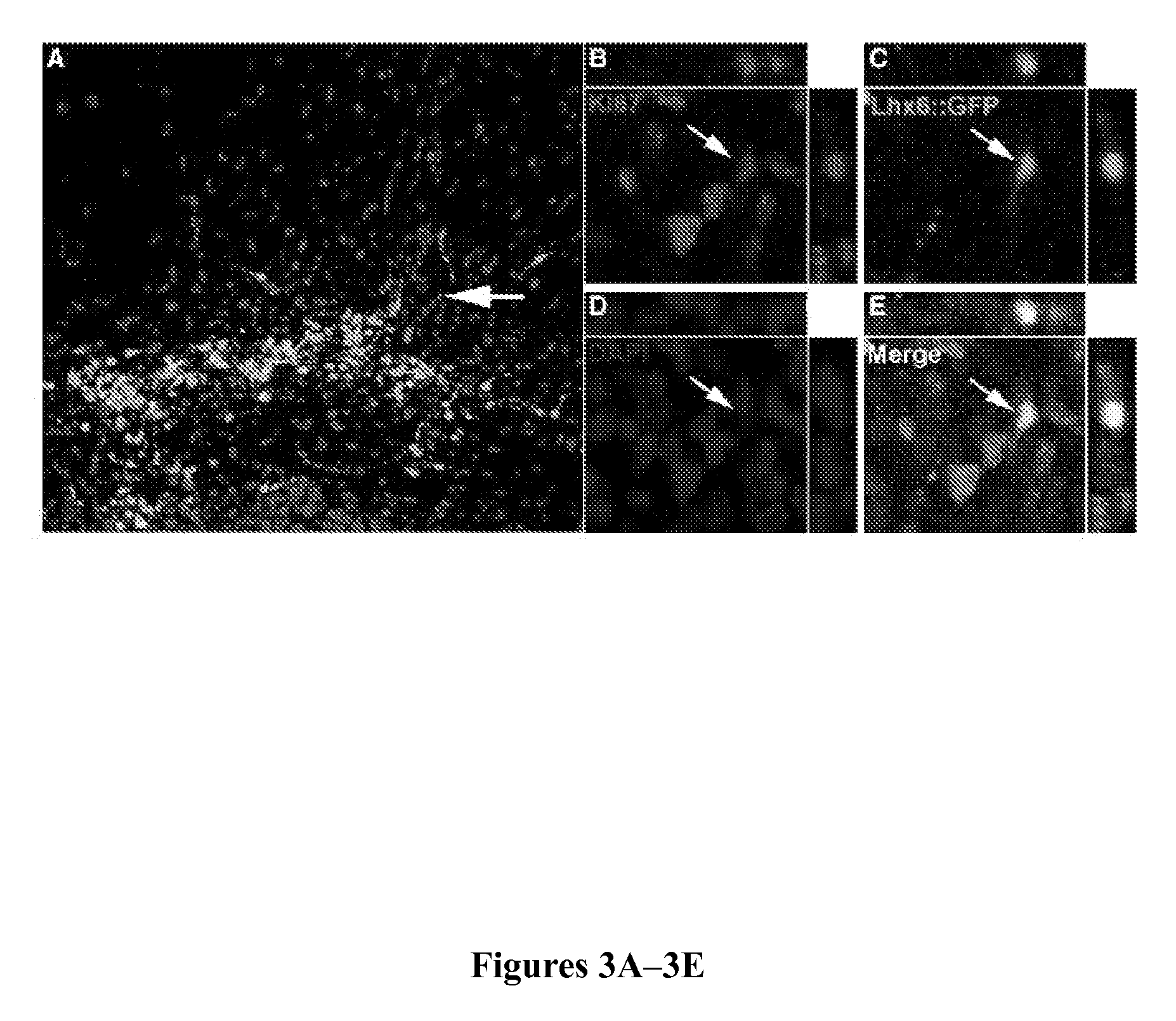
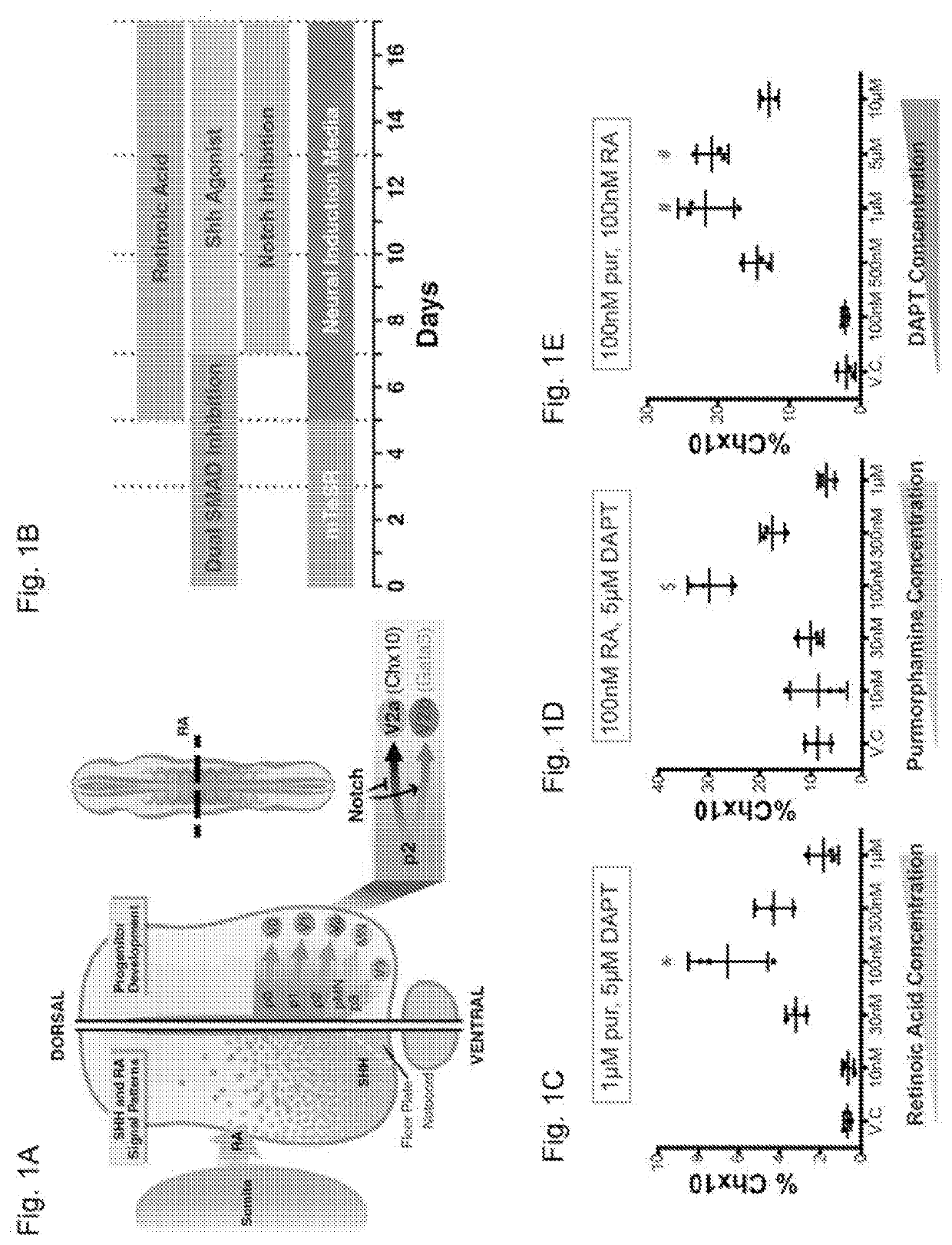
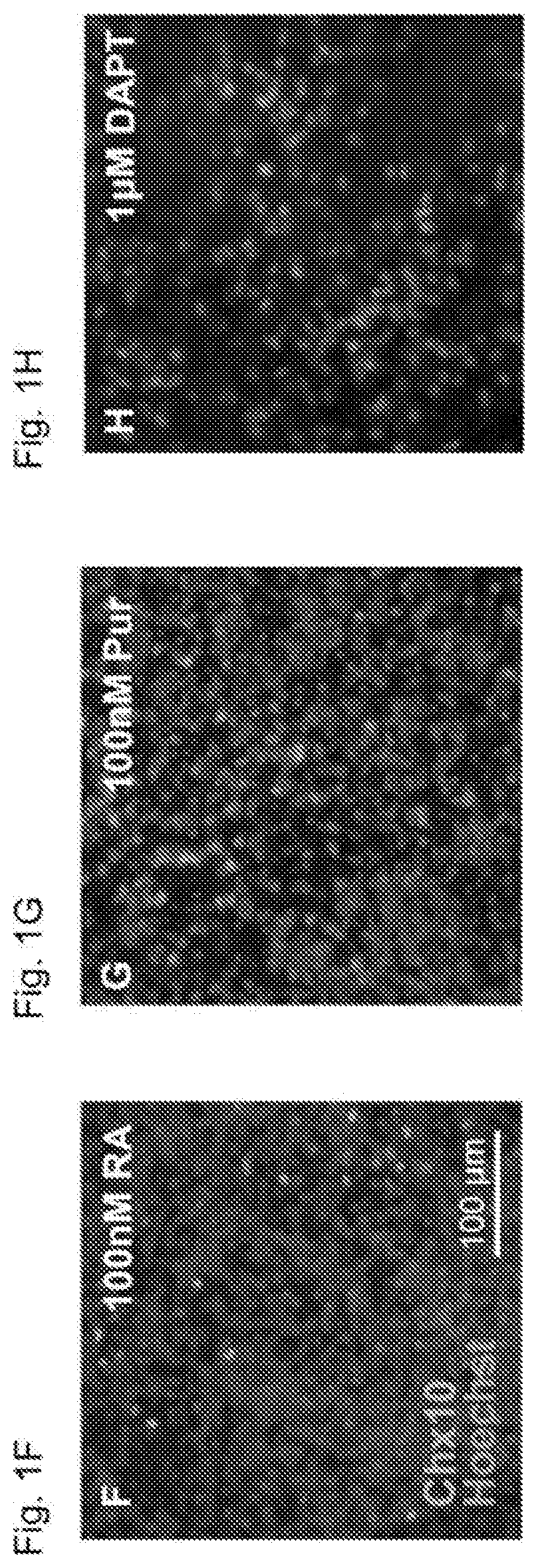
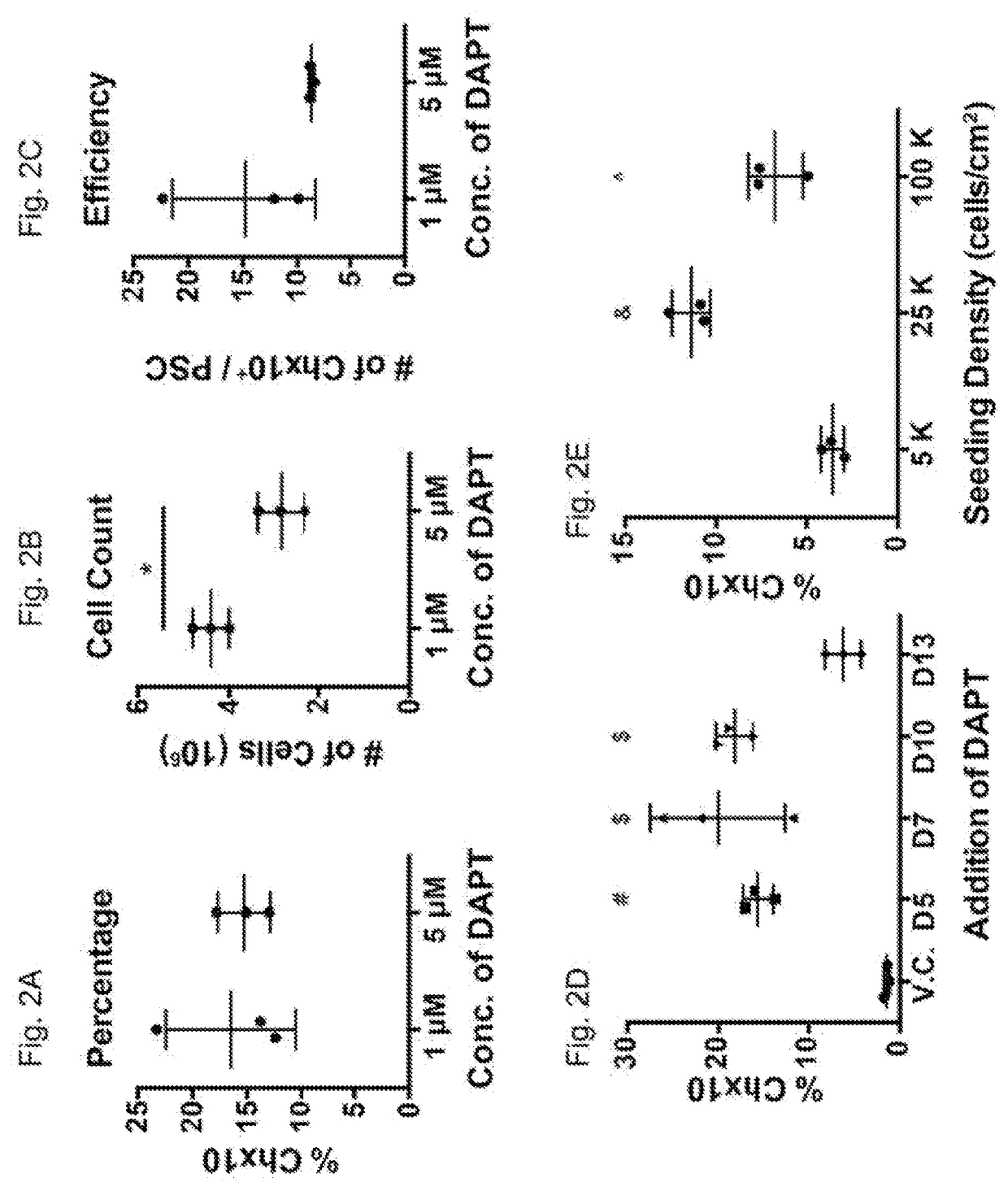
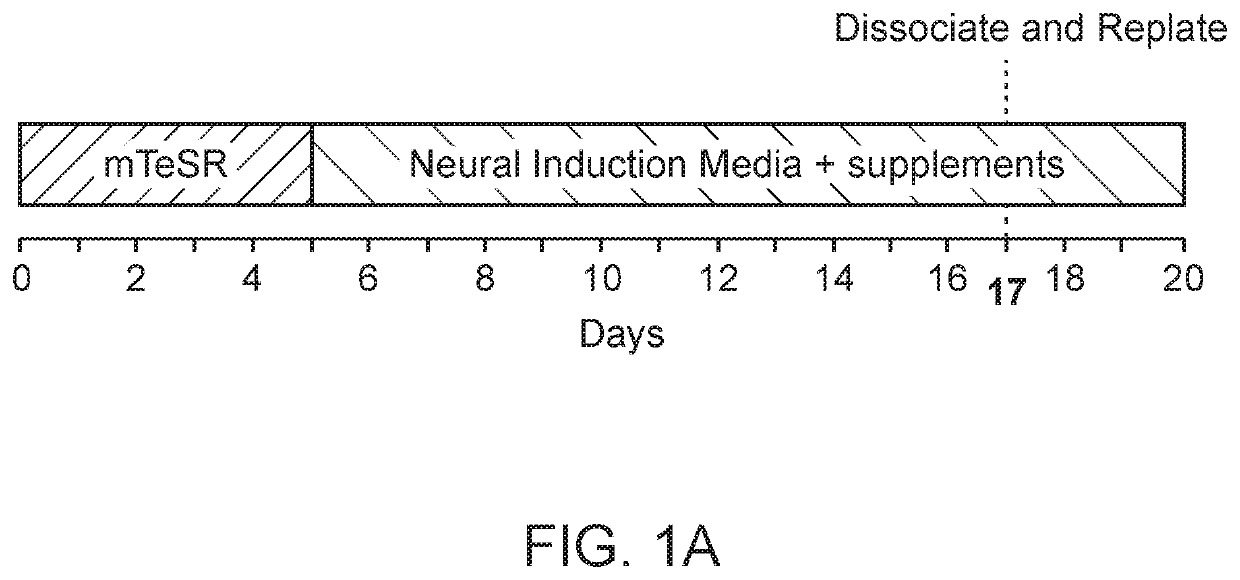
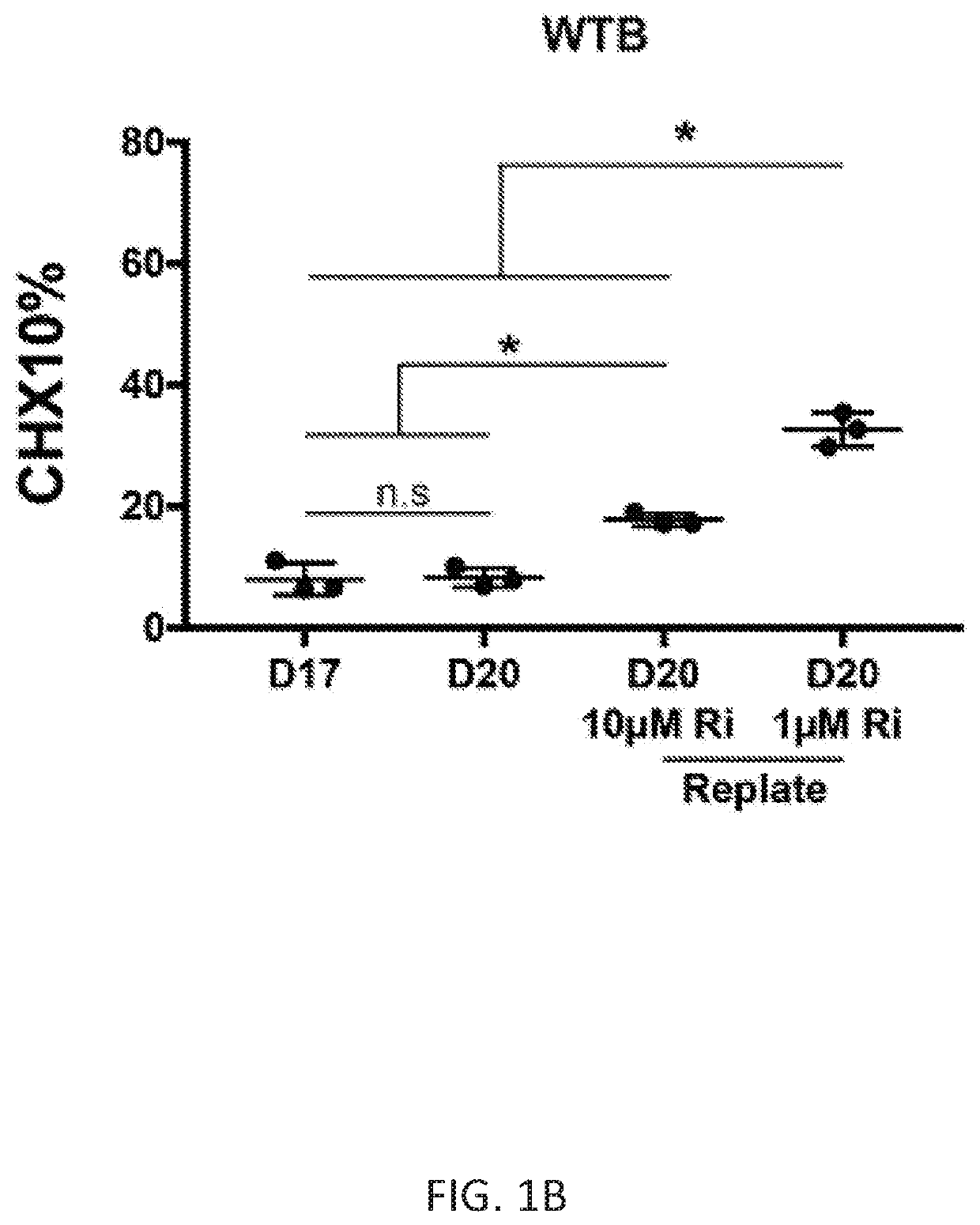
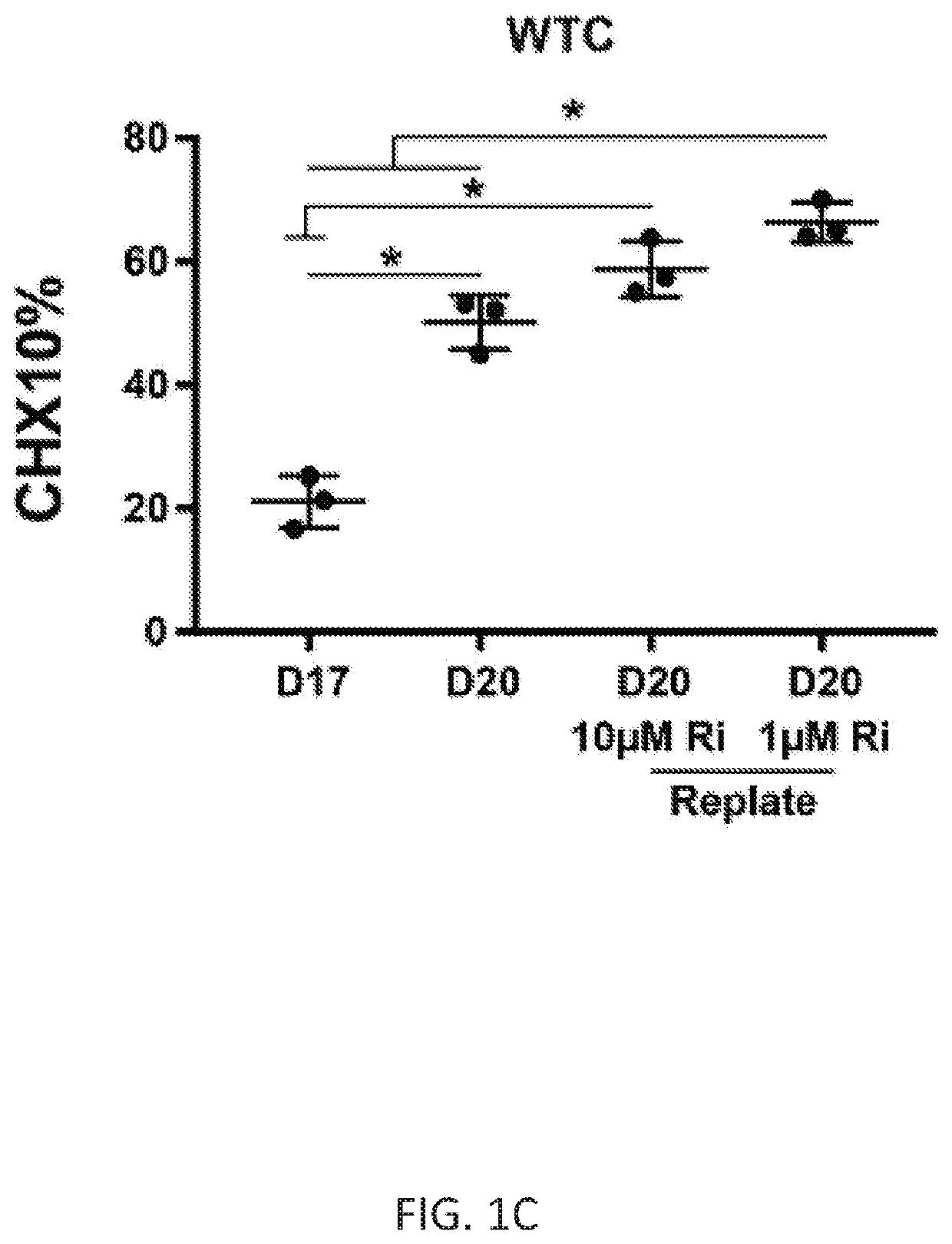
Methods of generating spinal cord glutamatergic interneurons (V2a interneurons) from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are provided. A method of the present disclosure may include culturing a first population of hPSCs in vitro in a neural induction medium that includes: a retinoic acid signaling pathway activator; a sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway activator; and a Notch signaling pathway inhibitor, wherein the culturing results in generation of a second population of cultured cells containing CHX10+ V2a interneurons. Also provided are non-human animal models that include the hPSC-derived spinal cord glutamatergic interneurons, and methods of producing the non-human animal models.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Generation of neuronal cells from embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS8633025B2High prevalenceIncrease incidenceBiocideNervous disorderPluripotential stem cellInhibitory interneuron
The invention relates to in vitro methods for differentiating mammalian pluripotent stem cells into cells displaying a neuronal phenotype, more particularly into cortical-type neurons including inter alia pyramidal neurons and cortical inhibitory interneurons. The invention further encompasses so-obtained neuronal cells and cell population, compositions comprising such, and further uses of said neuronal cells and cell population.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
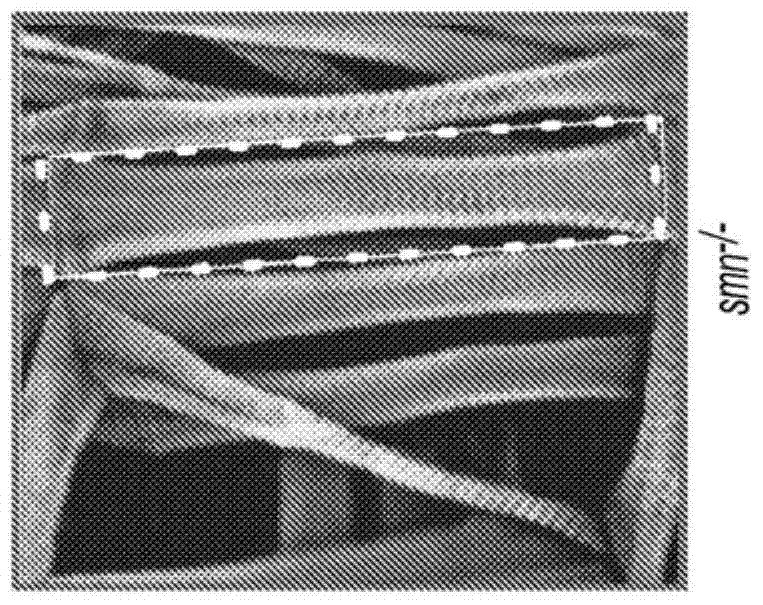
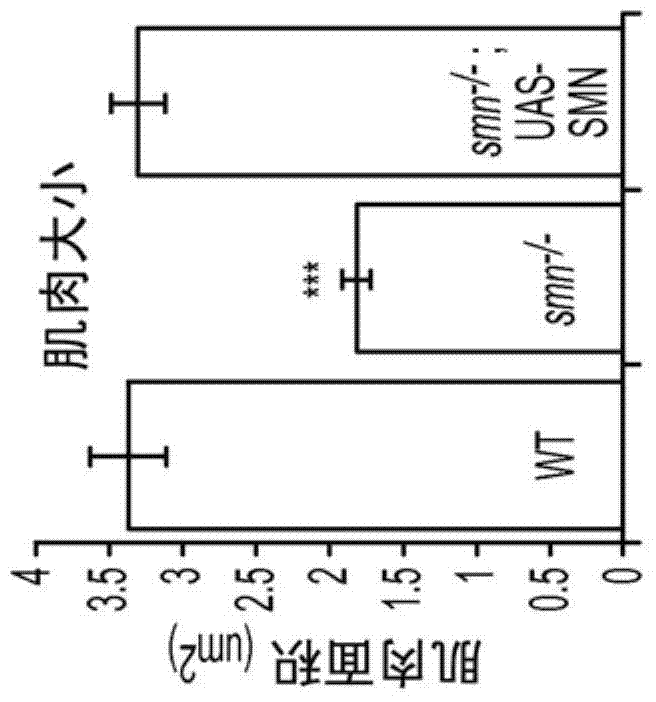
4-aminopyridine as a therapeutic agent for spinal muscular atrophy
It has been discovered that pharmacological inhibition of K+ channels (using the FDA-approved broad-spectrum K+ channel antagonist 4-AP) positively benefitted smn mutant phenotypes, a result that is consistent with the defective excitability of motor circuits by their interneuron or sensory neuron inputs being a critical consequence of SMN depletion. Based on these observations, certain embodiments of the invention are directed to methods of treatment of SMA by administering therapeutically effective amounts of one or more potassium channel antagonists, including 4-aminopyridine, 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine, 4-(methylamino)pyridine, and 4-(aminomethyl)pyridine. Other embodiments are directed to new pharmaceutical formulations comprising two or more potassium channel antagonists.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Illumination regulating and controlling composition for specifically regulating and controlling internuncial neuron activity of hypothalamus and application of illumination regulating and controlling composition
ActiveCN104593419AAffect anxiety-like behaviorElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceInterneuron
The invention provides an illumination regulating and controlling composition for specifically regulating and controlling internuncial neuron activity of hypothalamus and an application of the illumination regulating and controlling composition. The internuncial neuron activity of the hypothalamus is specifically regulated and controlled by an optogenetic regulation and control technology to affect an anxiety behavior. The illumination regulating and controlling composition for specifically regulating and controlling the internuncial neuron activity of the hypothalamus comprises a virus vector and an illumination device, wherein the virus vector is used for infecting photoesthetic genes carried by internuncial neurons or precursor cells of the internuncial neurons; the carrier comprises a promoter, the photoesthetic genes and a green fluorescence marker gene; the promoter is a VGAT promoter; and the illumination device is used for carrying out illumination regulation and control on the infected internuncial neuron cells or precursor cells of the internuncial neuron cells to change the activity. According to the technique provided by the invention, the internuncial neurons of the hypothalamus can be accurately and specifically regulated and controlled; and anxiety-like behaviors can be effectively affected.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
System and method of detecting and predicting seizures
InactiveUS10172567B2Raise the possibilityIncrease firing rateElectroencephalographyImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicinePartial field
The present invention describes systems and methods for predicting and detecting a seizure in a subject. The methods of the invention comprise measuring interneuron synchrony in terms of the coherence between interneuron action potentials and local field potential oscillations. In one embodiment, the detection of specific patterns of coherence, correlation and firing rate of interneurons predicts an upcoming seizures.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Generation of a population of hindbrain cells and hindbrain-like organoids from pluripotent stem cells
PendingUS20210284962A1Gene expression in the population of hindbrainCatalytic crackingNervous system cellsBiotechnologyPluripotential stem cell
Provided herein are methods of generating hindbrain cells, including respiratory hindbrain cells, from pluripotent stem cells. Also provided are methods of generating a three-dimensional organoid comprising a population of hindbrain cells including a heterogeneous population of interneurons.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS +1
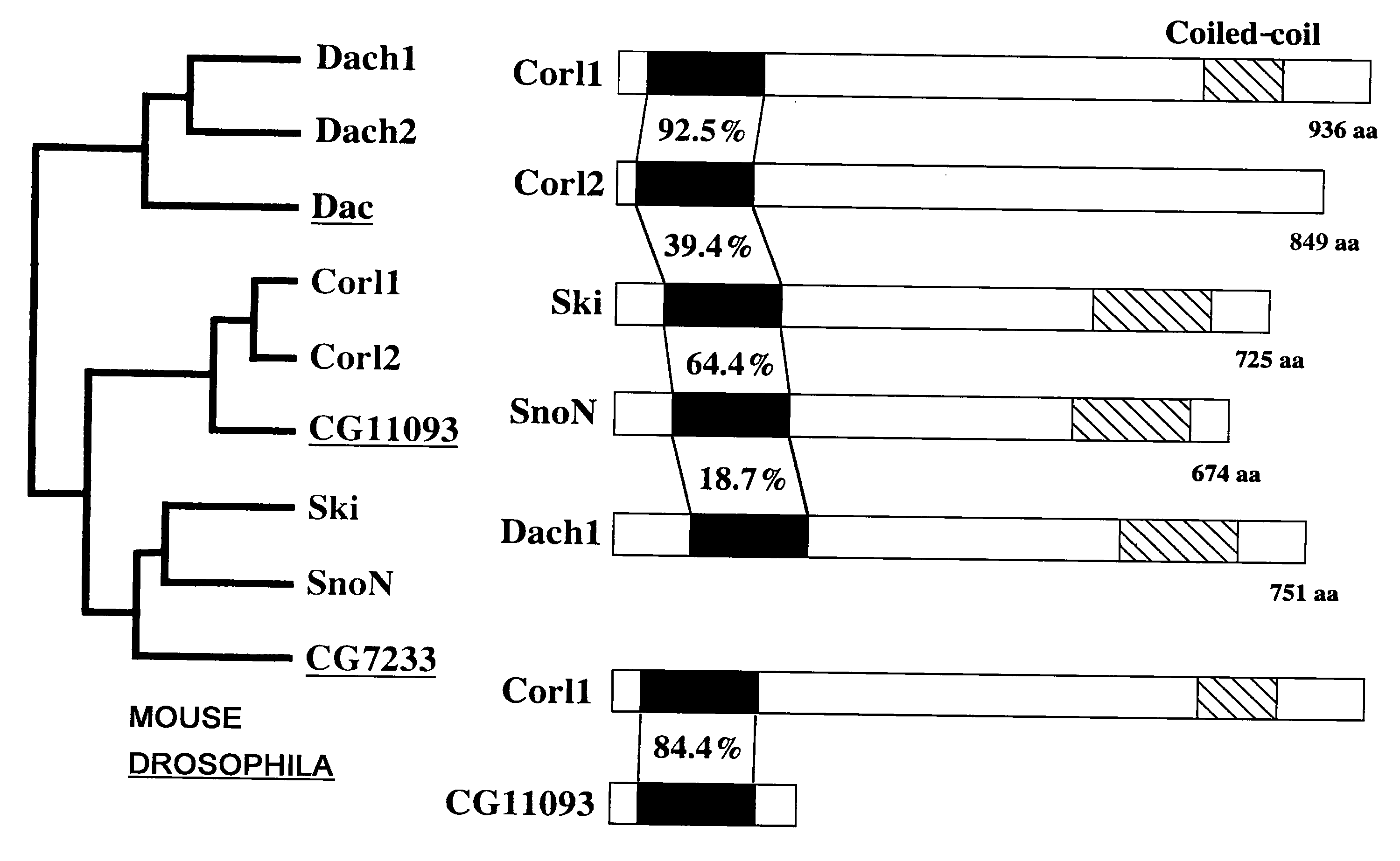
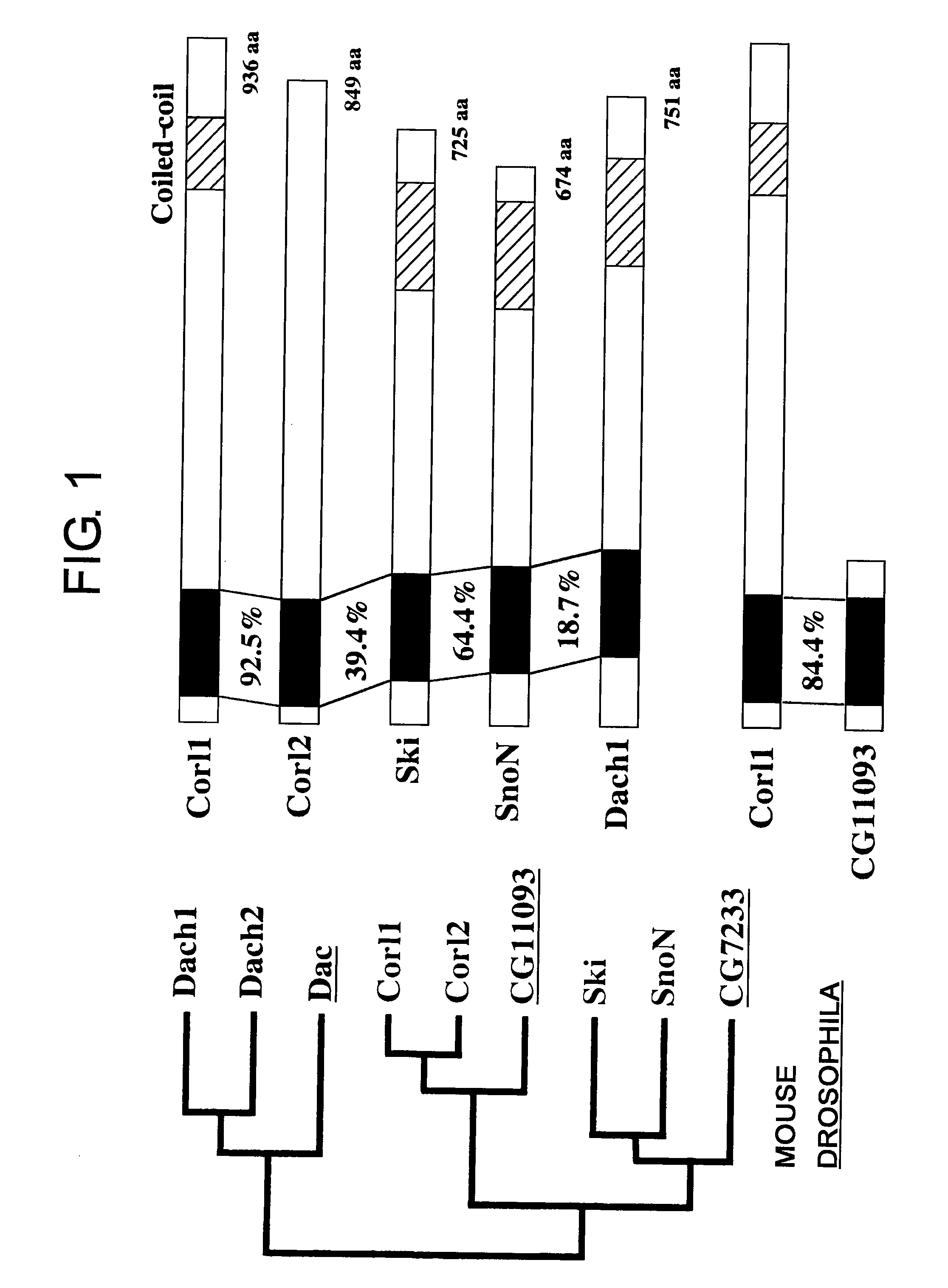
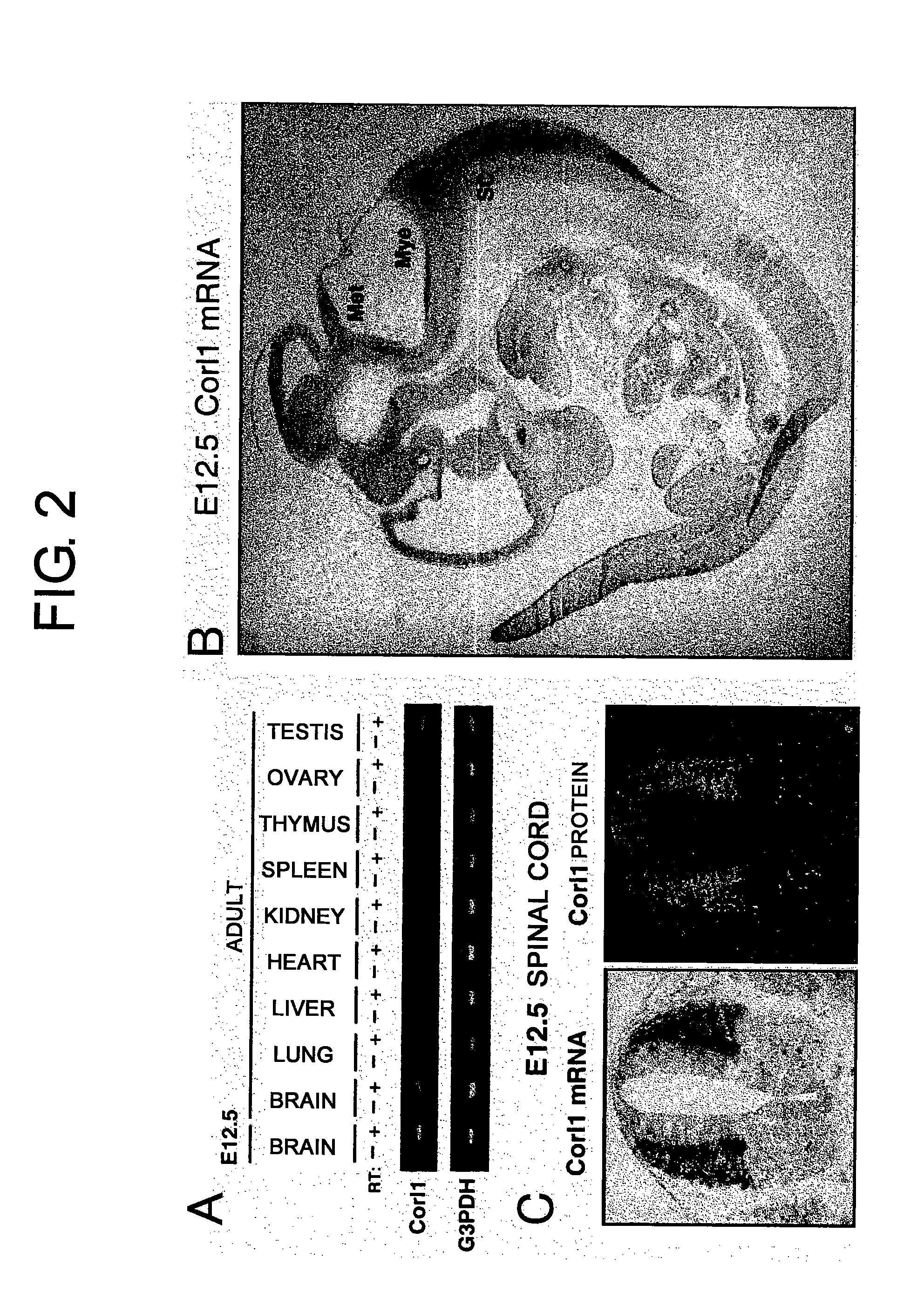
Methods of Distinguishing Types of Spinal Neurons Using Corl1 Gene as an Indicator
InactiveUS20080213757A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisEmbryonic StageInterneuron
As a result of screening for genes that are selectively expressed in fetal mouse brain region by subtraction method, the present inventors obtained a cDNA fragment encoding Corl1. The expression of Corl1 was examined by RT-PCR, in situ hybridization, and immunostaining using polyclonal antibodies. The results demonstrated that Corl1 was especially expressed at a high level of selectively in the central nervous system during embryonic stages. The expression patterns of Corl1 determined using various markers in embryonic spinal cord were compared to identify types of neurons expressing Corl1. The results revealed that Corl1 was specifically expressed in spinal cord interneurons dI4, dI5, dILA, and dILB. Accordingly, the present invention provides for discrimination between dI4 and dI6, neurons which previously could only be discriminated based on developmental location, using the expression of Corl1 as an indicator.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
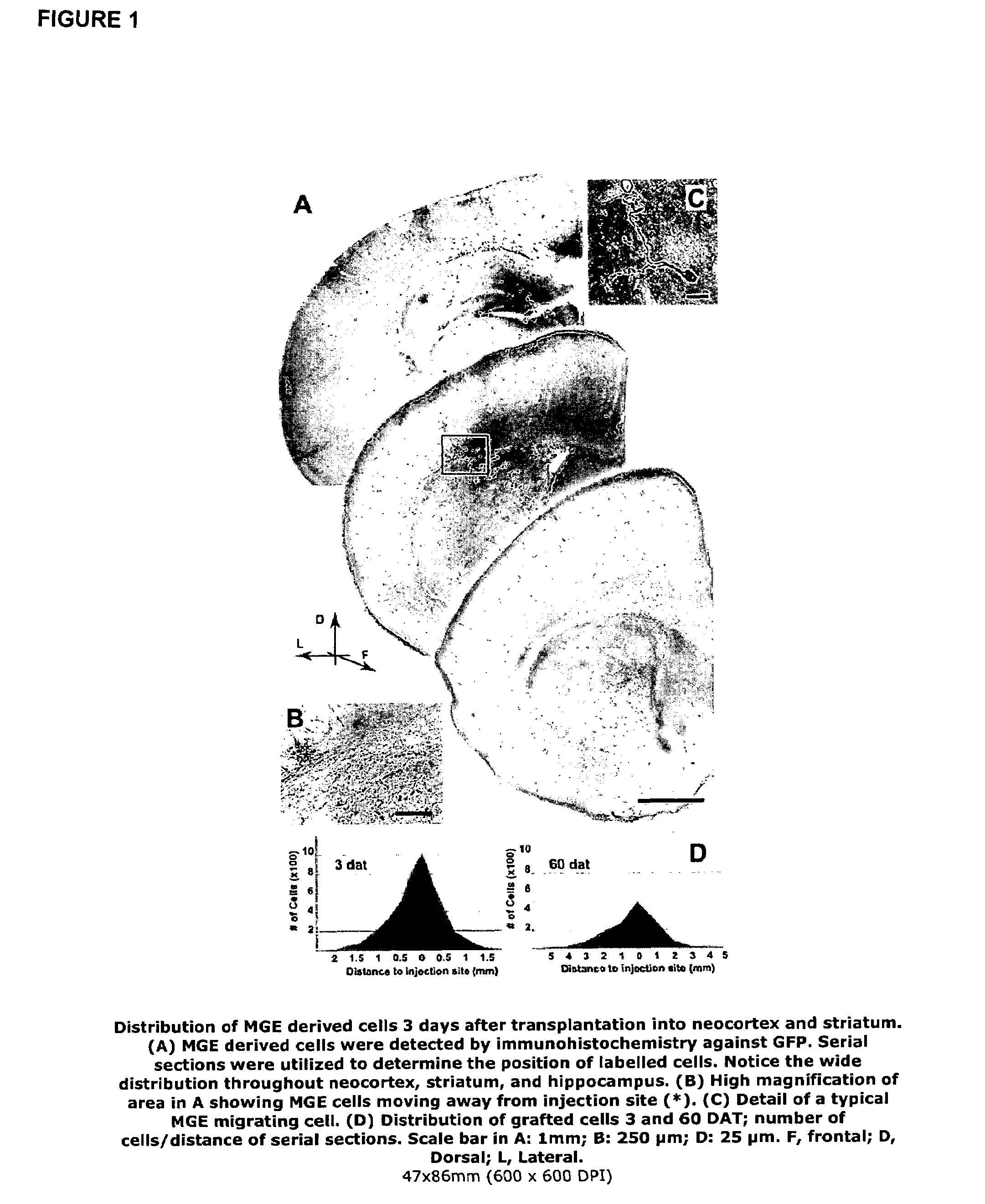
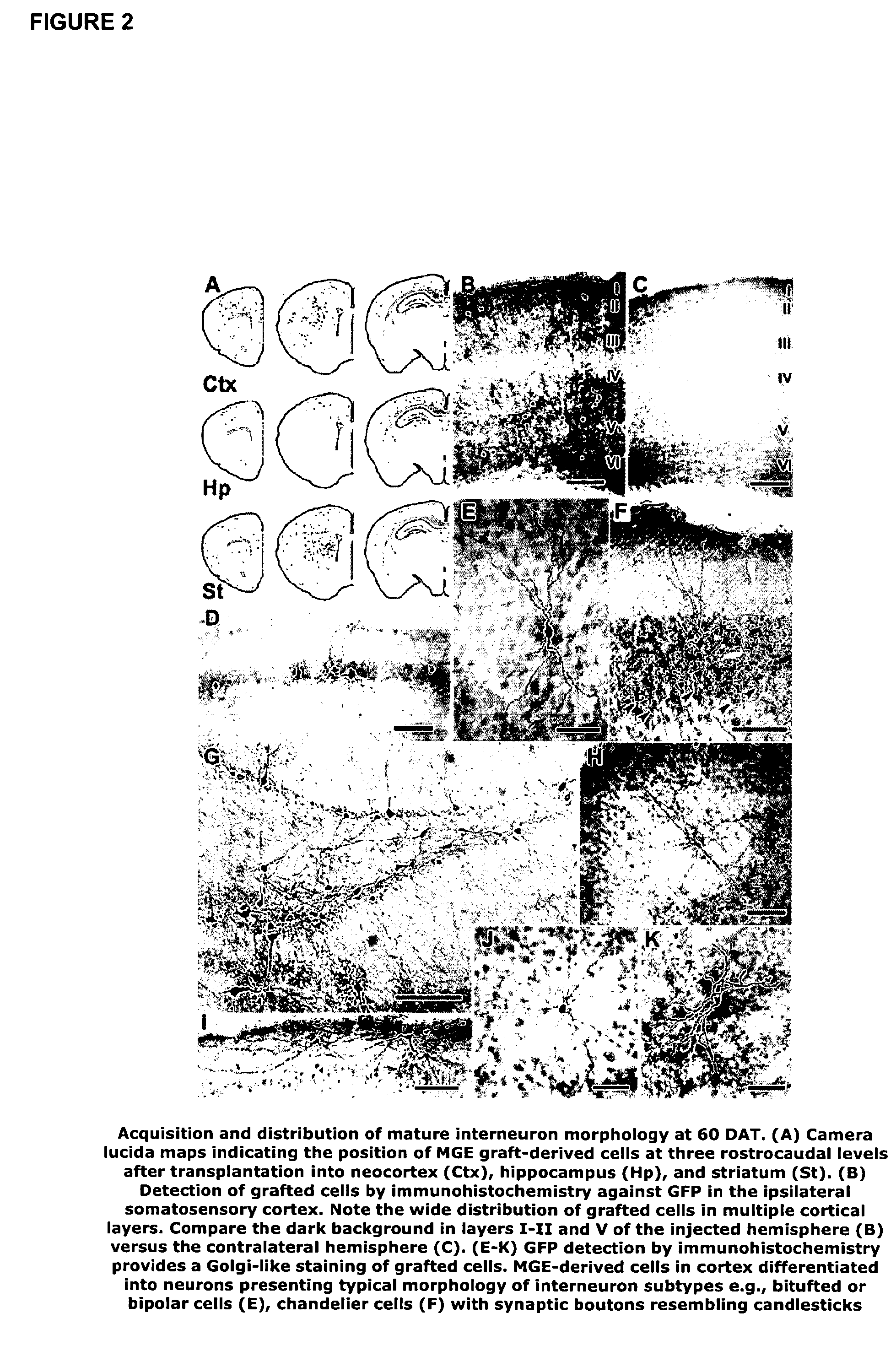
Transplantation of neural cells
ActiveUS9192630B2Enhanced inhibitory interneuron activityIncrease in GABA mediated synaptic eventsBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseInhibitory interneuron
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of neuron-imitating enterprise data hierarchy representation and system thereof
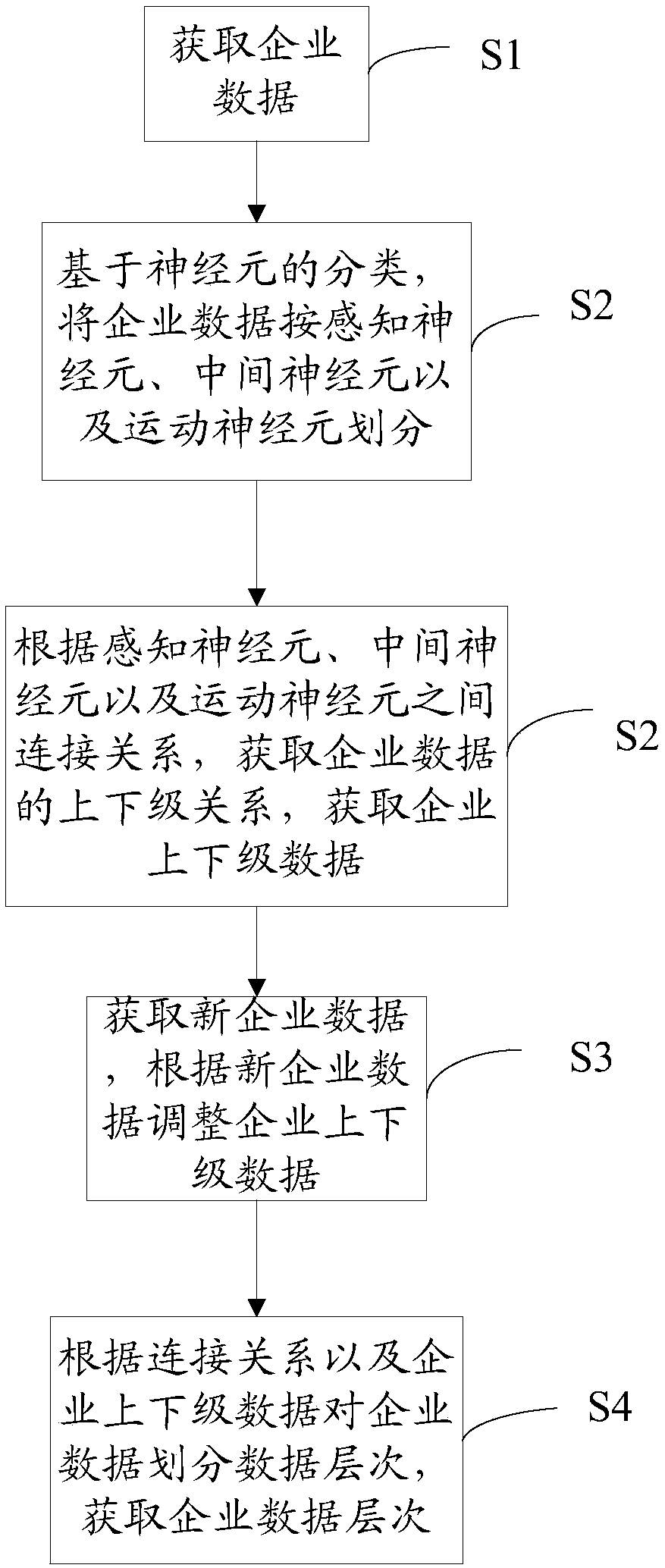
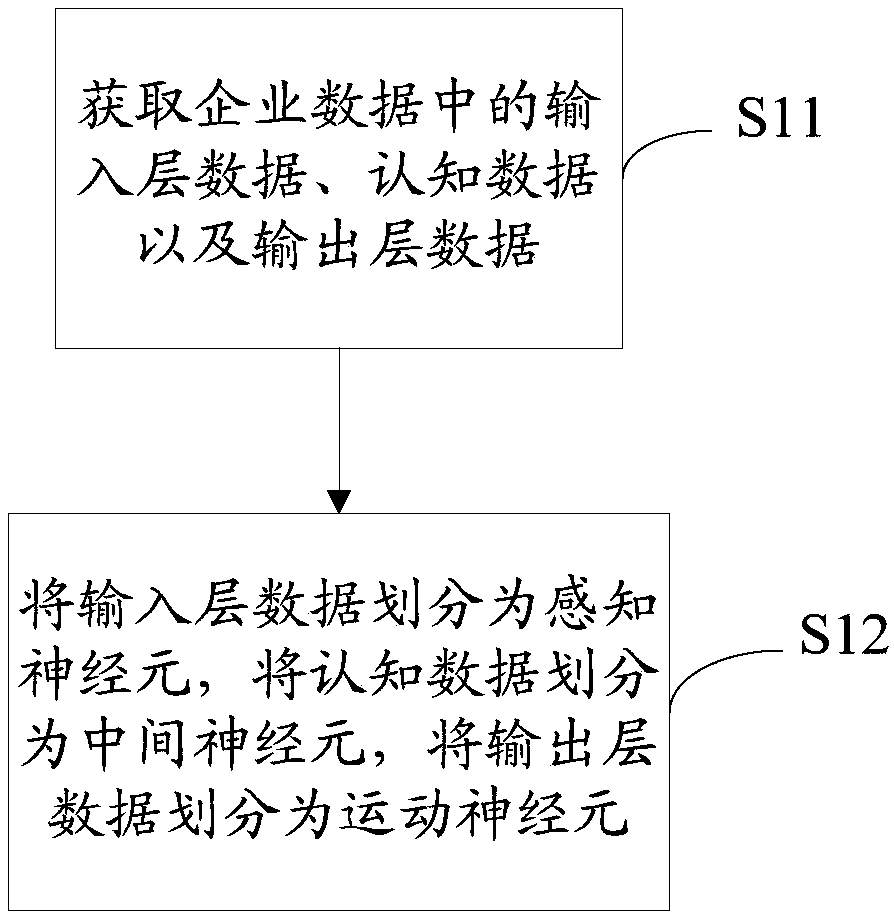
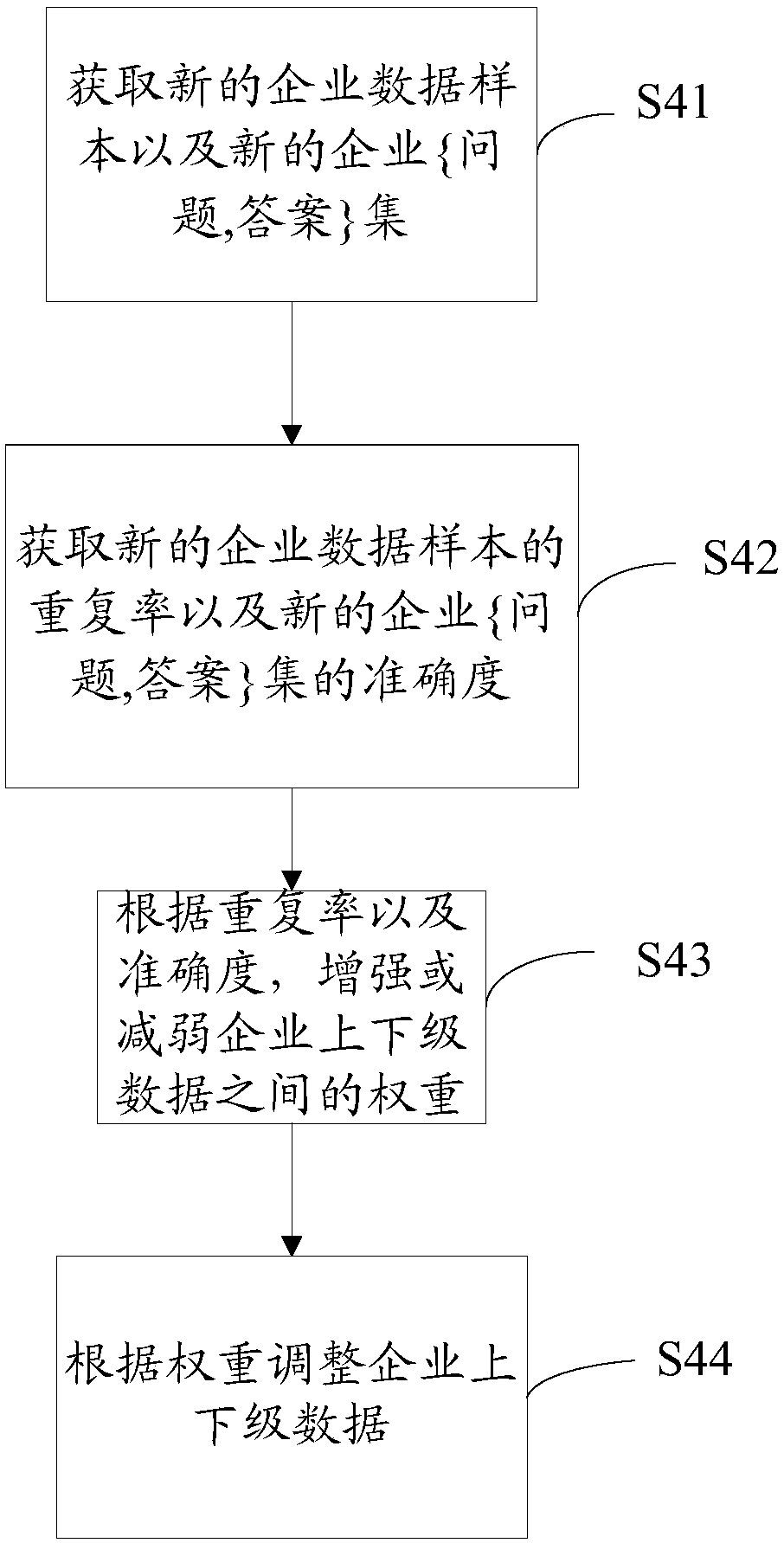
InactiveCN107609639AGuaranteed atomicityReduce redundancyPhysical realisationOriginal dataInterneuron
The invention relates to a method of neuron-imitating enterprise data hierarchy representation and a system thereof. The method includes: acquiring enterprise data; dividing the enterprise data on thebasis of neuron categories according to perceiving neurons, interneurons and motor neurons; acquiring upper / lower-level relationships of the enterprise data according to connection relationships between the perceiving neurons, the interneurons and the motor neurons, and acquiring enterprise upper / lower-level data; and carrying out data hierarchy dividing on the enterprise data according to the connection relationships and the enterprise upper / lower-level data to acquire an enterprise data hierarchy. According to the method, utilizing a human brain neural-network to build the enterprise data hierarchy is realized, guaranteeing atomicity of the data is facilitated, redundancy of data storage is reduced, comprehensiveness and organization of evaluation of an enterprise service institution ororganization on an enterprise are improved, and correctness, accuracy and high efficiency of the original data hierarchy are more efficiently guaranteed.
Owner:前海梧桐(深圳)数据有限公司
Robot stepping priority control method
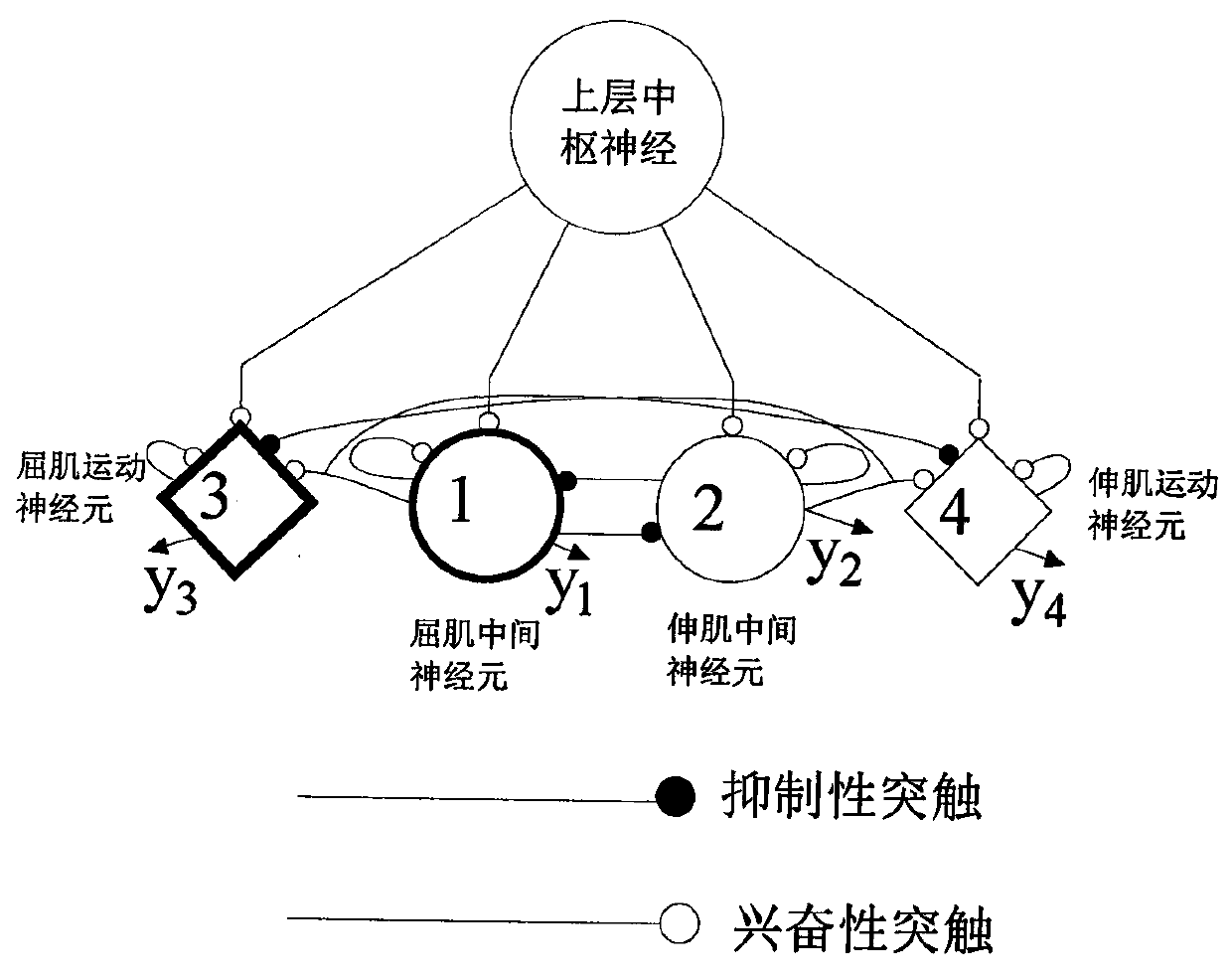
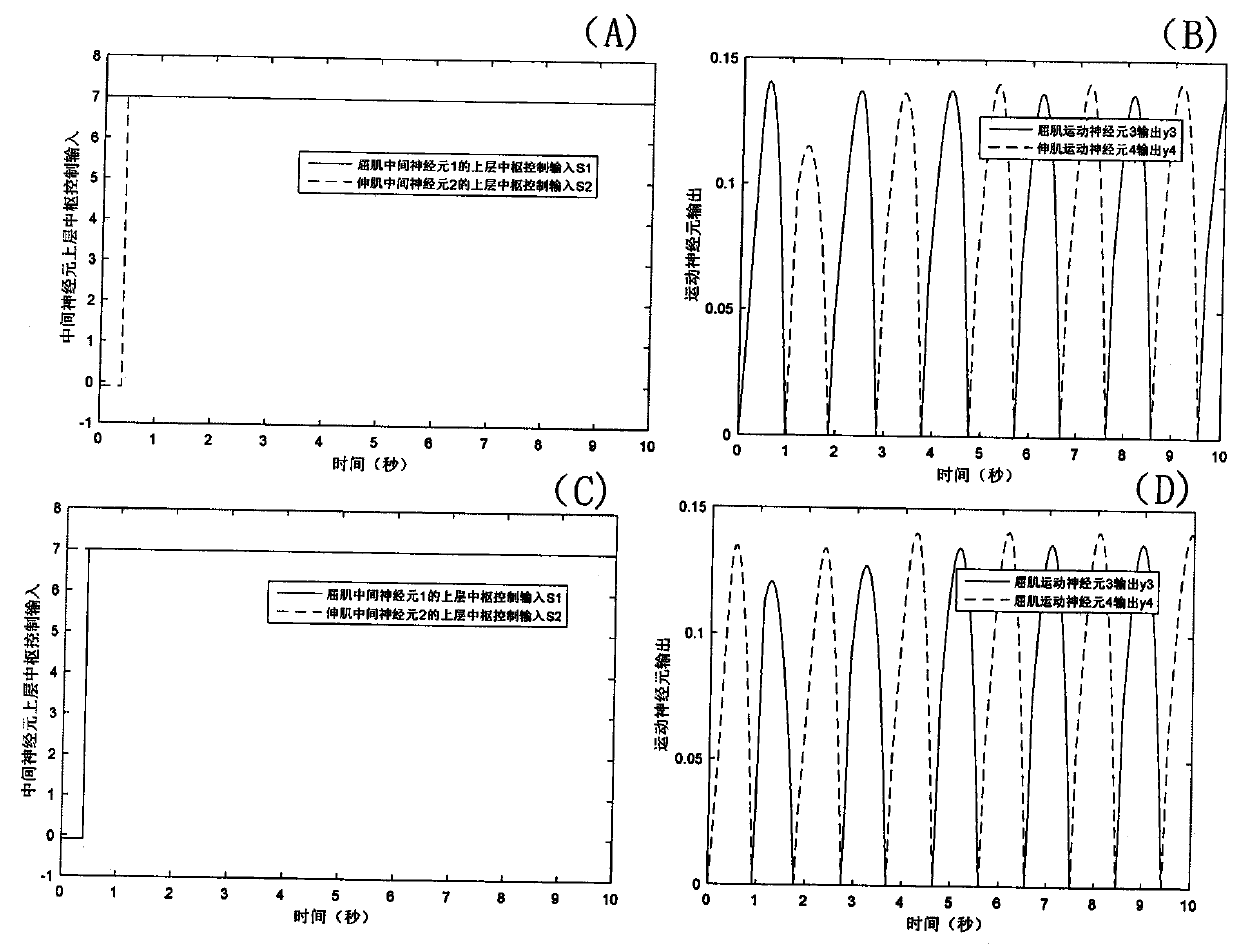
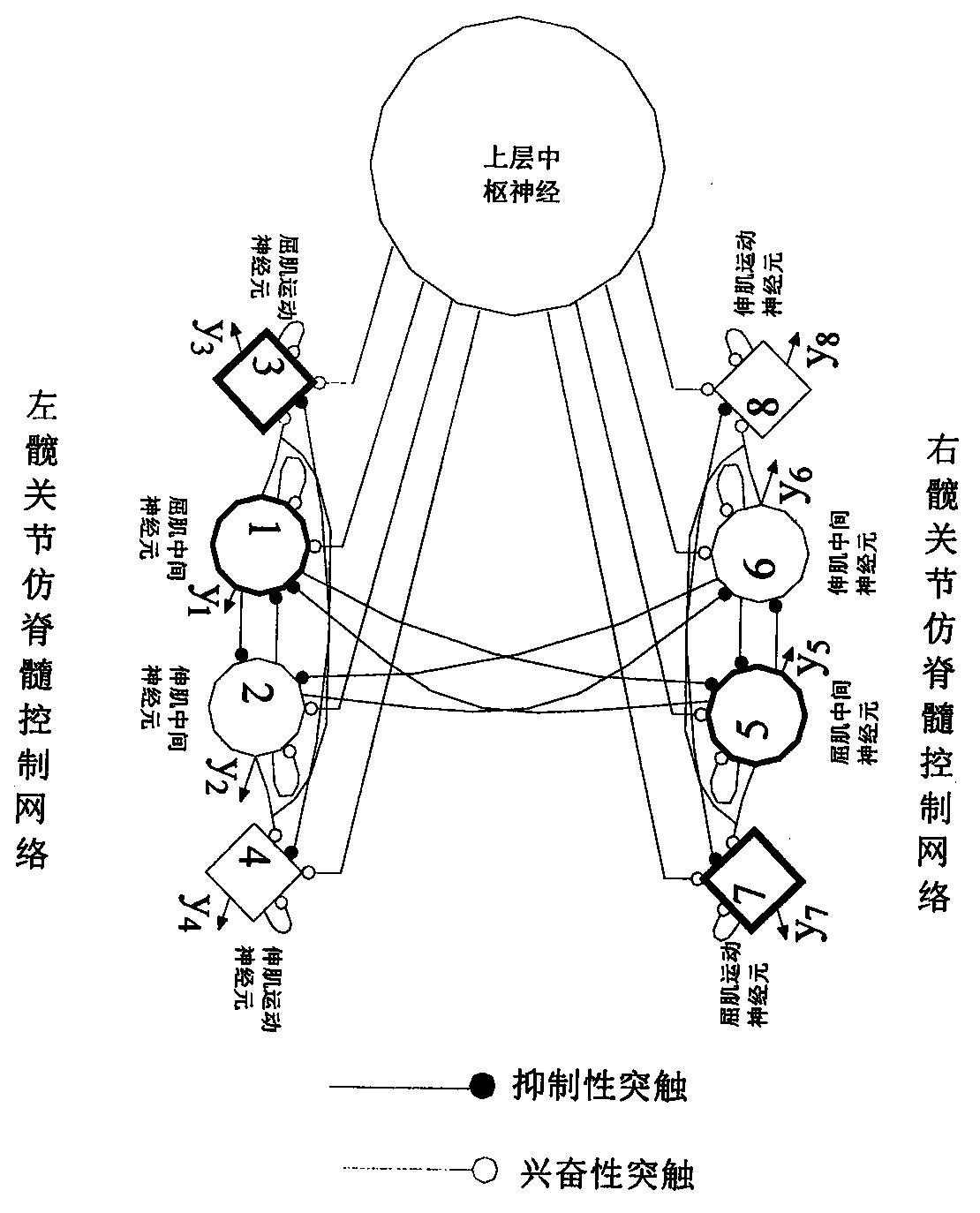
ActiveCN111037572AImprove motor flexibilityEasy to controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorNeuron networkExoskeleton robot
The invention discloses a robot stepping priority control method, and relates to the technical field of robots. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a spinal cord imitationcontrol network of robot joints, including an intermediate neuron network and a motor neuron network, and utilizing a robot joint flexor muscle and extensor muscle preferential contraction sequence control method to directly design upper-layer central nervous control input with a limited sequence for a robot alternate swing joint flexor muscle and extensor muscle intermediate neuron control network so as to realize stepping priority control; or indirectly controlling the phase relation between the outputs of the leg middle neuron networks by designing the input priority sequence of the upper-layer central control signals of the flexor muscle and the extensor muscle middle neurons of the guide network by utilizing the guide effect between the middle neuron networks so as to control the stepping priority sequence of the robot. The method is convenient to control, and the movement flexibility of the foot type bionic robot and various exoskeleton robots can be effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV +1
Application of Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) in preparation of product to enhance Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily C Member 6 (TRPC6) channel activity
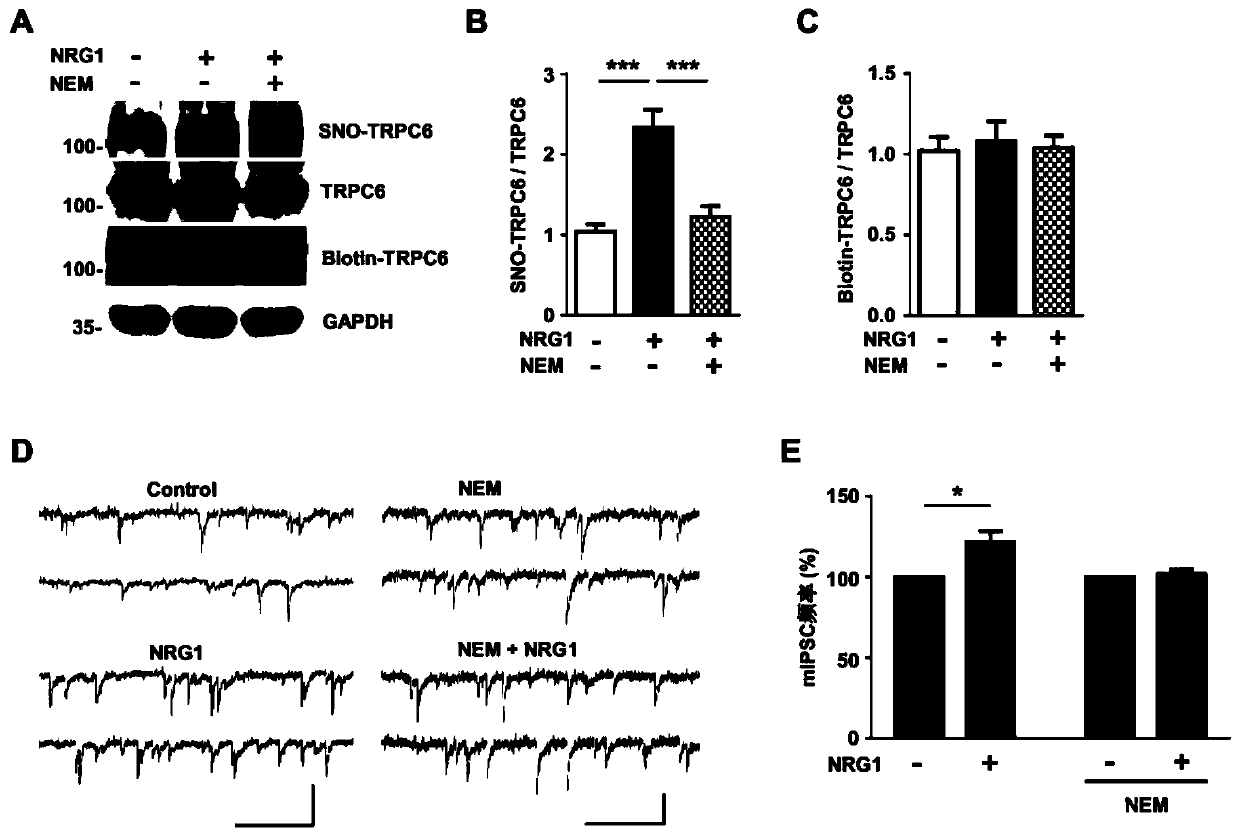
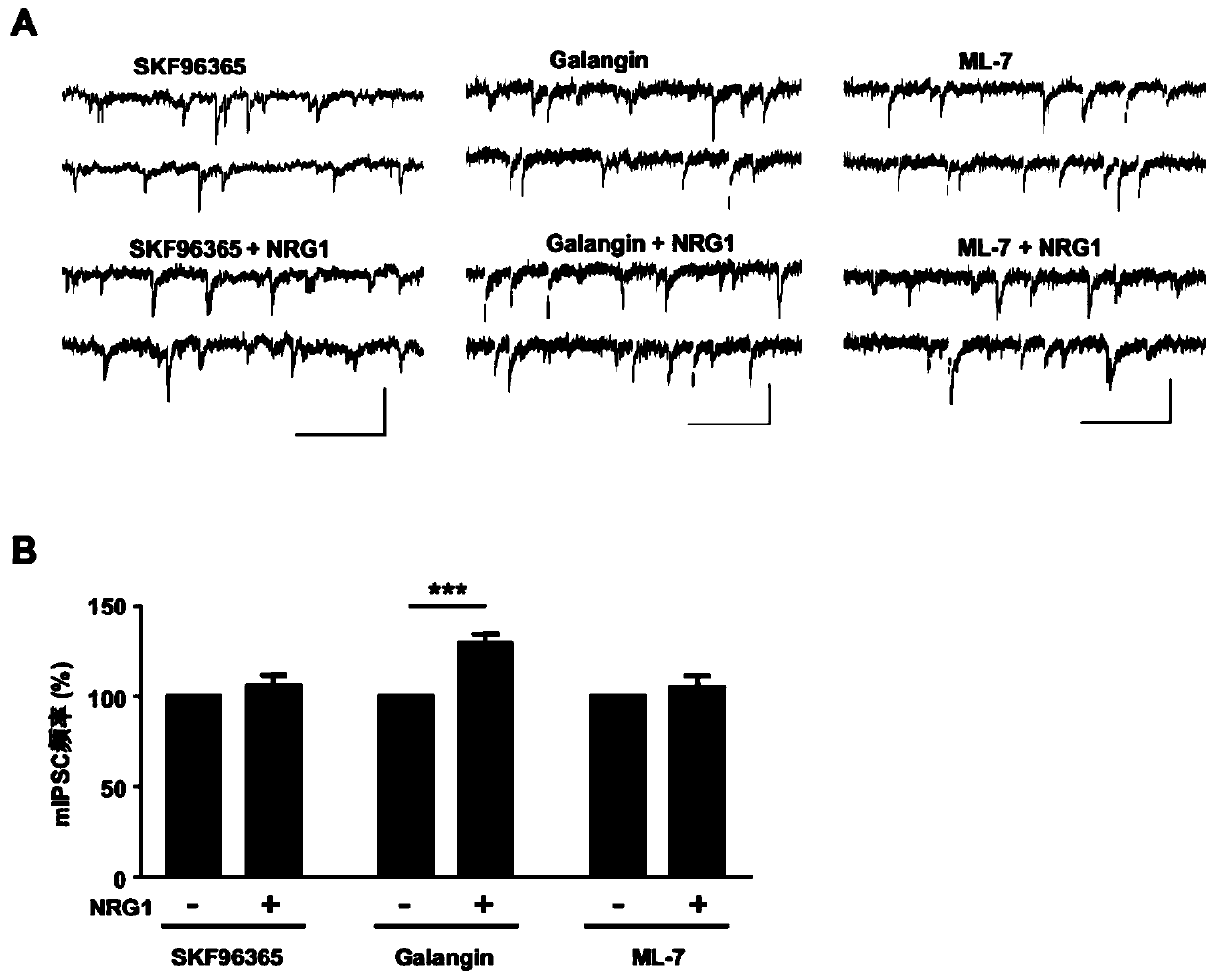
InactiveCN110721307AFacilitated releasePromote nitrosylationPowder deliveryNervous disorderNeuregulinHippocampal region
The invention provides application of Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) in preparation of a product to enhance Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily C Member 6 (TRPC6) channel activity. The invention discovers that TRPC6 channel protein is co-labeled with ErbB4 receptor of NRG1 in hippocampus through immunofluorescence experiment; and moreover, it is further proven by Western blot that the NRG1can promote nitrosylation of the TRPC6 channel protein. Then, it is proven by whole cell patch clamp experiment that both nitrosylation inhibitors and TRPC6 channel blockers can block the NRG1-ErbB4 pathway as well as promote release of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA); and moreover, TRPC6 channel is knocked-out on intermediate neurons expressing the ErbB4 receptor so as to block effect of the NRG1on GABA release, thereby leading to neuronal rhythmic oscillations and schizophrenia-like behavioral abnormalities. Research results of the invention show that the NRG1 can activate the TRPC6 channelby promoting nitrosylation of the TRPC6 channel protein, thereby increasing the release of the GABA.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Generation of pgc-1α mice with conditional knockout of GABAergic neurons
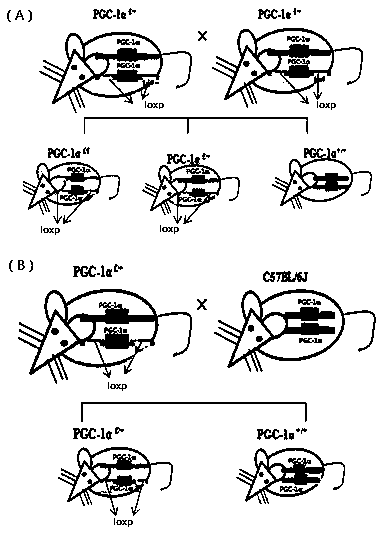
InactiveCN105684993BExpand the populationRapidly expanding populationMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryDLX5Interneuron
The invention relates to a GABAergic neuron conditional knockout gene PGC-1 alpha mouse model and a construction method thereof and belongs to the field of animal models and application thereof. The construction method includes the steps that a PGC-1 alpha <flox / flox> mouse is obtained in the first place; then, a PGC-1 alpha <flox / +> is mated with a C57BL / 6J, and the PGC-1 alpha <flox / +> is obtained, then the PGC-1 alpha <flox / +> and the C57BL / 6J are mated with a Dlx5 / 6<Cre-IRES-EGFP> mouse, and the full knockout D1x5 / 6< Cre-IRES-EGFP >, PGC-1 alpha <flox / flox>, semi knockout D1x5 / 6< Cre-IRES-EGFP > and a PGC-1 alpha <flox> mouse are obtained; as a result, a gene knockout mouse on GABAergic internuncial neuron conditional knockout PGC-1 alpha is prepared, and a credible animal model is provided for mechanism research on neurodevelopment and neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Interneuron-specific therapeutics for normalizing neuronal cell excitability and treating dravet syndrome
Provided are therapeutic virus vectors, particularly, recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors, designed to contain an enhancer sequence that specifically restricts expression of an effector gene (e.g., an SCN1A-encoding polynucleotide, Gq-DREADD-encoding polynucleotide, or PSAM-encoding polynucleotide) contained in the vector to PV-expressing GABAergic interneuron or to neuron cell populations in the brain. The rAAV vectors, compositions and methods thereof are useful for treating subjects afflicted with neuropathologies, seizures, pharmacologically-intractable forms of epilepsy including Dravet syndrome (DS), a form of infantile epilepsy associated with severe seizures, cognitive impairment and premature death, as the cause of DS involves loss of function of a sodium channel encoded by the SCN1A gene. The described vectors restore expression of effector genes to the appropriate interneuron or neuron cell populations with specificity and sensitivity, advantageously to address the root cause of the disease by restoring the excitation-inhibition balance by means of gene-therapy (with SCN1A) or pharmacogenetics.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Prediction method and device based on multi-modal extreme learning machine, equipment and medium
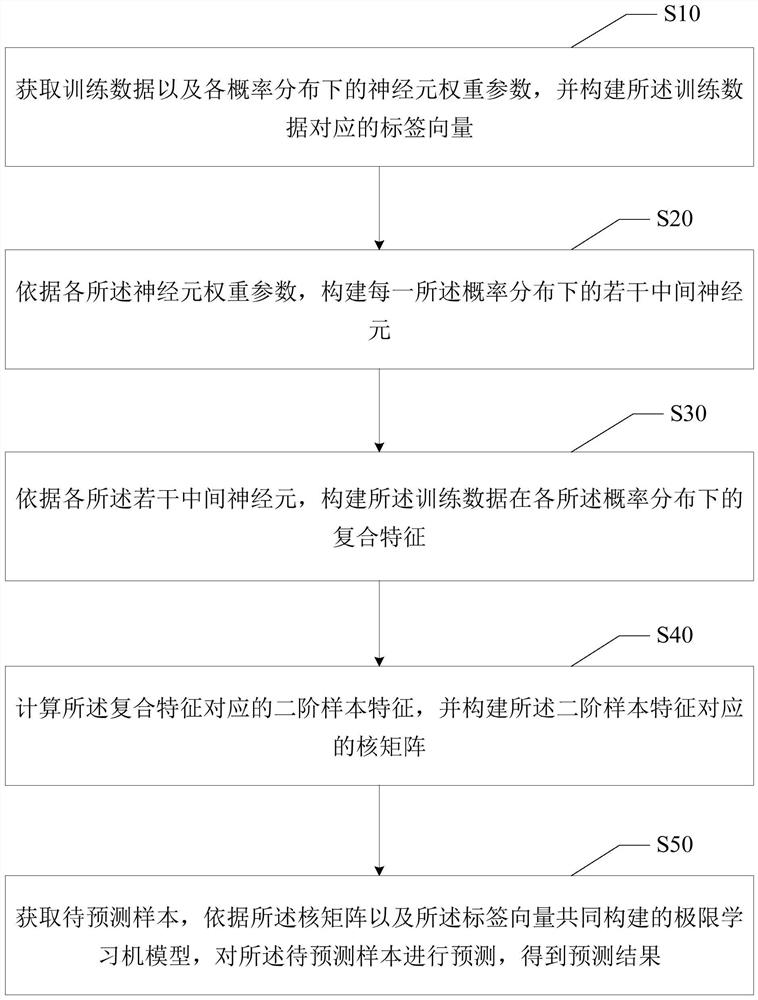
PendingCN114386523ASolve the technical problem of unstable precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesLearning machineInterneuron
The invention discloses a prediction method and device based on a multi-mode extreme learning machine, equipment and a medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining training data and neuron weight parameters under probability distribution, and constructing a tag vector corresponding to the training data; constructing a plurality of intermediate neurons under each probability distribution according to the weight parameters of the neurons; according to the plurality of interneurons, constructing composite features of the training data under each probability distribution; second-order sample features corresponding to the composite features are calculated, and a kernel matrix corresponding to the second-order sample features is constructed; and obtaining a to-be-predicted sample, and predicting the to-be-predicted sample according to an extreme learning machine model jointly constructed by the kernel matrix and the label vector to obtain a prediction result. The method can be applied to solving data-driven modeling problems, such as image classification, sequence prediction, geophysics, credit evaluation and the like. The technical problem of unstable precision caused by random mapping of an extreme learning machine model in the prior art is solved.
Owner:INST OF ADVANCED TECH UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A Probabilistic Calculation-Based Artificial Neural Network Hardware Realization Device
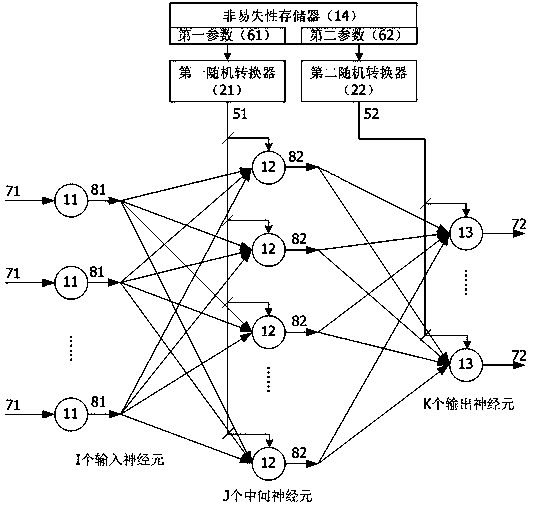
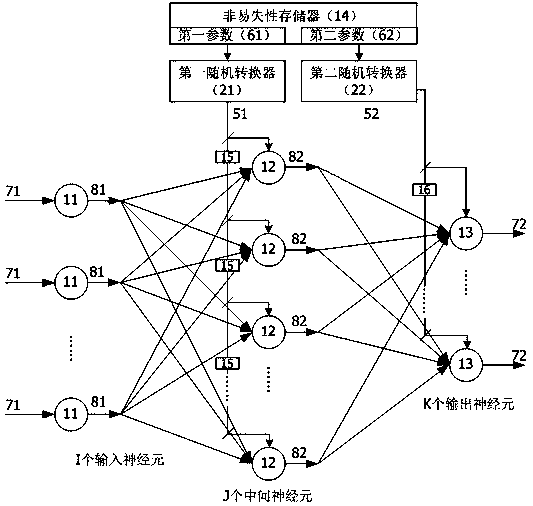
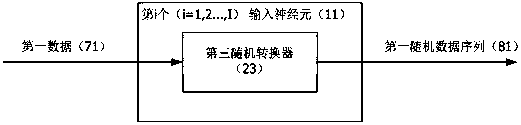
The invention relates to an artificial neural network hardware implementation device based on probability calculation. The artificial neural network hardware implementation device based on probability calculation comprises input, intermediate and output modules. The input module is formed by I input neurons, and the input neurons receive first data and output a first random data sequence; the intermediate module is formed by J intermediate neurons, and the intermediate neurons receive the first random data / parameter sequence and output a second random sequence; and the output module is formed by K output neurons, and the output neurons receive the second random data / parameter sequence and output the second data, wherein I, J and K are integers greater than or equal to 1. The output end of the input neurons is connected with the input end of the intermediate neurons, the output end of the intermediate neurons is connected with the input end of the output neurons, and a complete or partial connection mode is adopted. The first and second random data sequences and the first and second random parameter sequences are expressed by the probability values of 0 or 1 appearing in the data sequences within a period of time. According to the neural network device, hardware logic and wiring resources can be greatly reduced, and circuit cost and power consumption can be reduced so that implementation of a super-large-scale neural network through small and medium-sized circuits is enabled to be possible.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
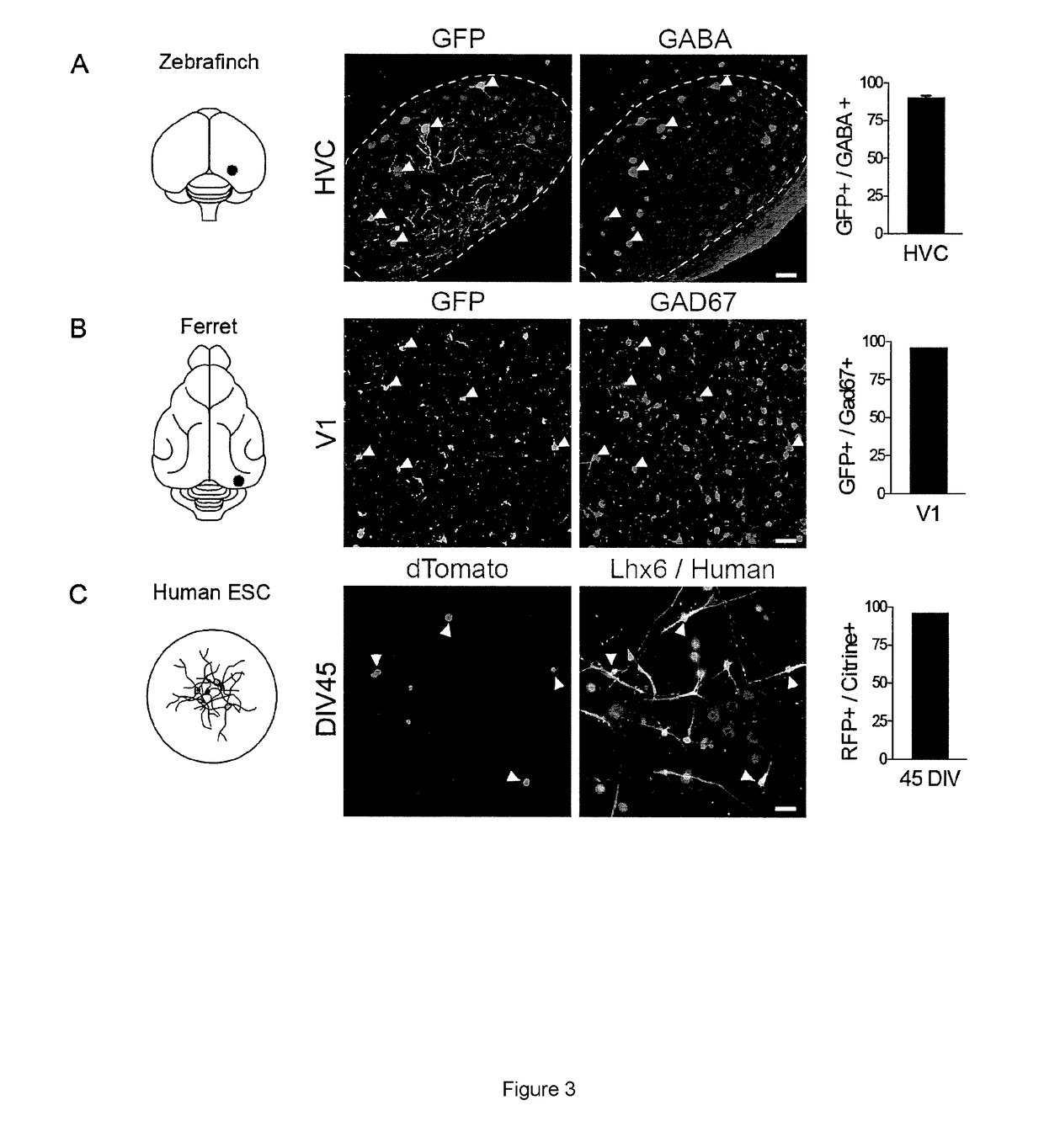
Artificial expression constructs for selectively modulating gene expression in interneurons
PendingUS20210348195A1Rapid and strong cell-specific expressionRapid onsetGenetically modified cellsNervous system cellsInterneuronExpression gene
Artificial expression constructs for selectively modulating gene expression in selected central nervous system cell types are described. The artificial expression constructs can be used to selectively express synthetic genes or modify gene expression in GABAergic interneurons.
Owner:ALLEN INST +1
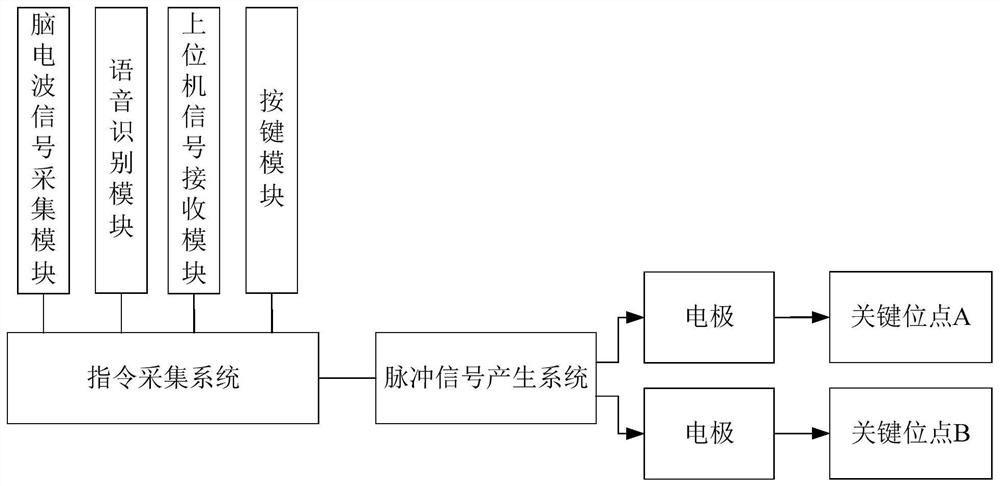
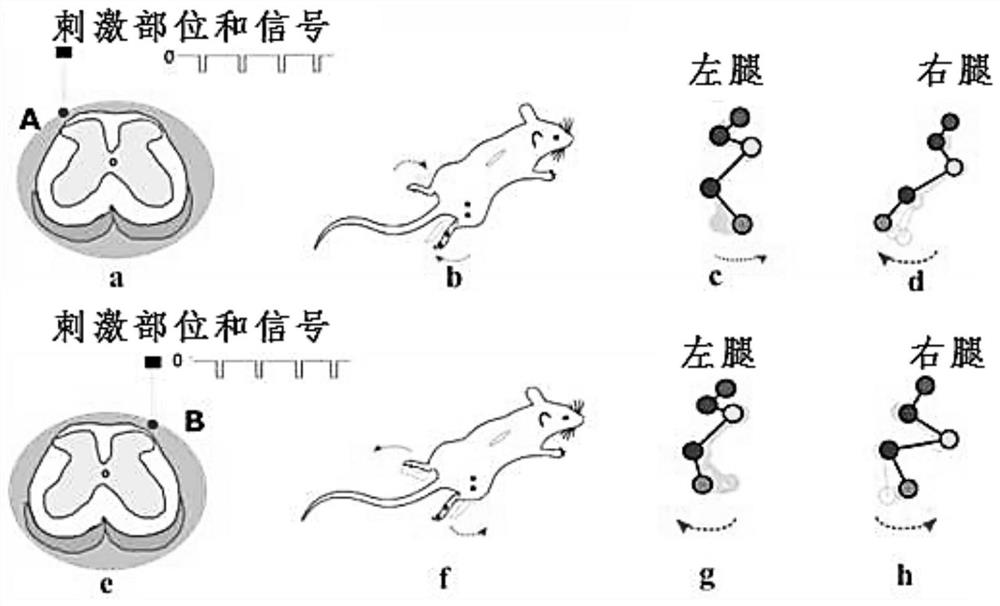
Double-electrode electronic system for reconstructing gait motion function
PendingCN111683714AEfficient reconstructionAchieve neurological reconstructionSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesInterneuronSpinal cord
The invention relates to a double-electrode electronic system for reconstructing a gait motion function. The double-electrode electronic system comprises an instruction acquisition system, a pulse signal generation system, two biological stimulation electrodes and a reference electrode. The instruction acquisition system generates a control instruction according to instruction information and sends the control instruction to the pulse signal generation system; the pulse signal generation system generates a pulse signal according to the control instruction and sends the pulse signal to the biological stimulation electrodes; alternate electric pulse excitation is carried out on two key sites for inducing gait motion in spinal cord by the biological stimulation electrodes, the key sites for generating coordinated action of an inherent intermediate neural network for generating lower limb rhythm motion in spinal cord nerves are activated, and reconstruction of a lower limb gait motion function is effectively carried out in a mode of being closer to physiological conditions. The electronic system can be applied to animal experiments or rehabilitation training.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com