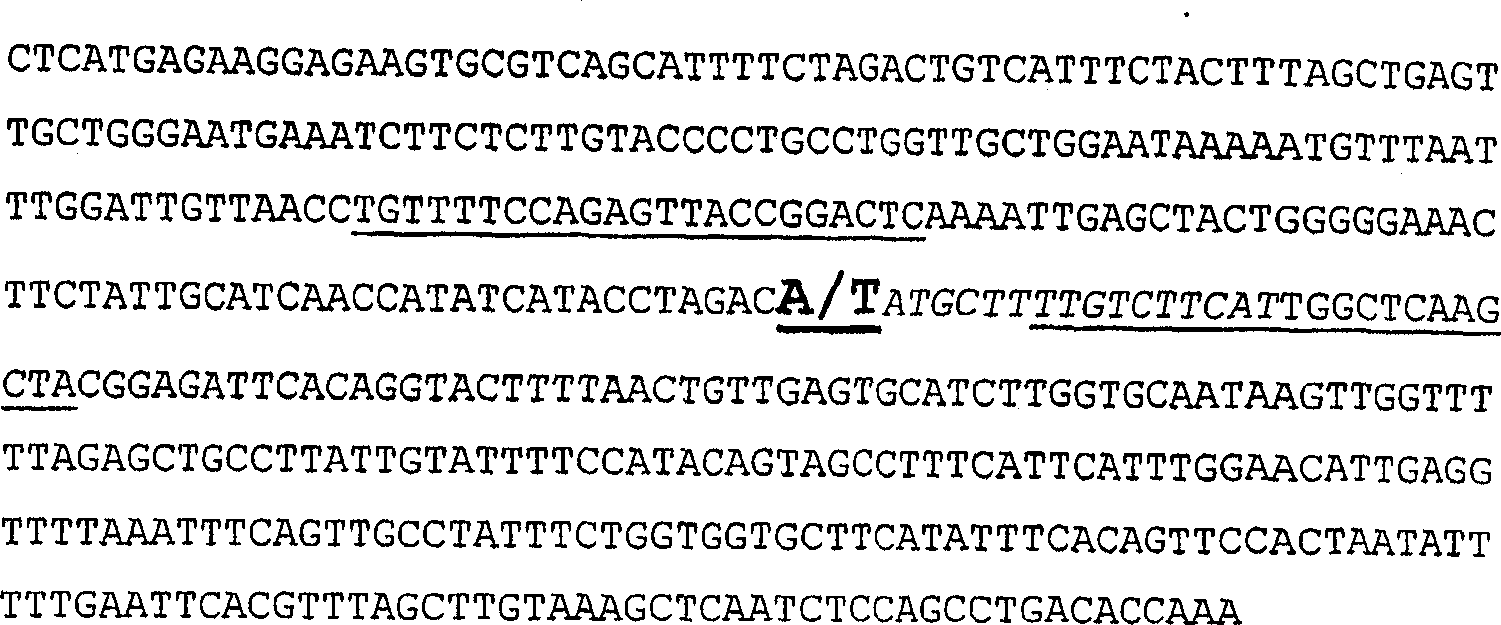Patents
Literature
39 results about "Mutant phenotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
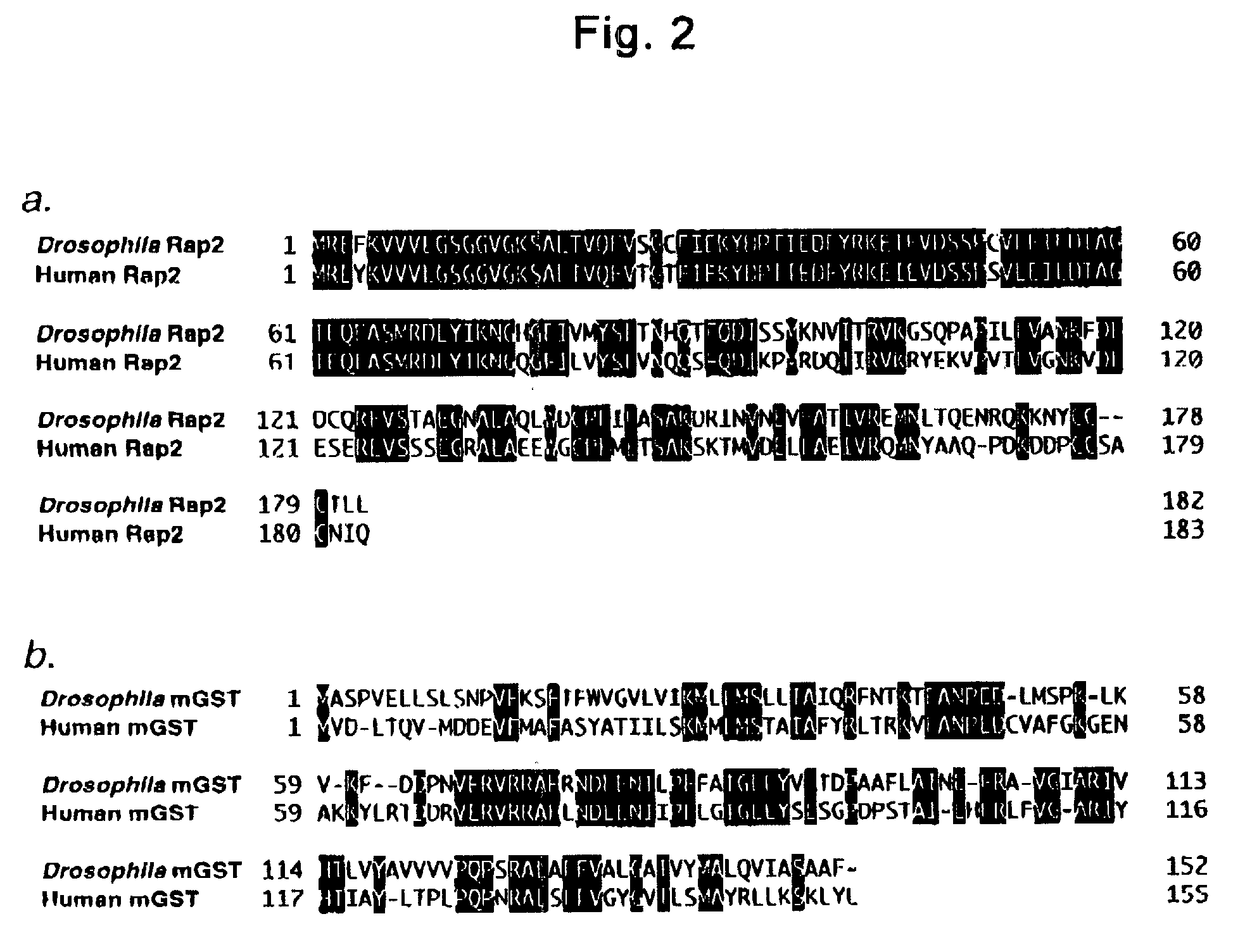
Phenotypes are observable characteristics of an organism that arise due to the interaction of its genotype with its environment. A mutant phenotype is an altered attribute resulting from changes in the genome. A mutant yeast phenotype can be any detectable feature of cells, colonies or cultures.
Method of Controlling Plant Growth and Architecture by Controlling Expression of Gibberellin 2-Oxidase
InactiveUS20100095406A1Reduce the overall heightIncrease the number ofBacteriaSugar derivativesGenetically modified riceMutant phenotype
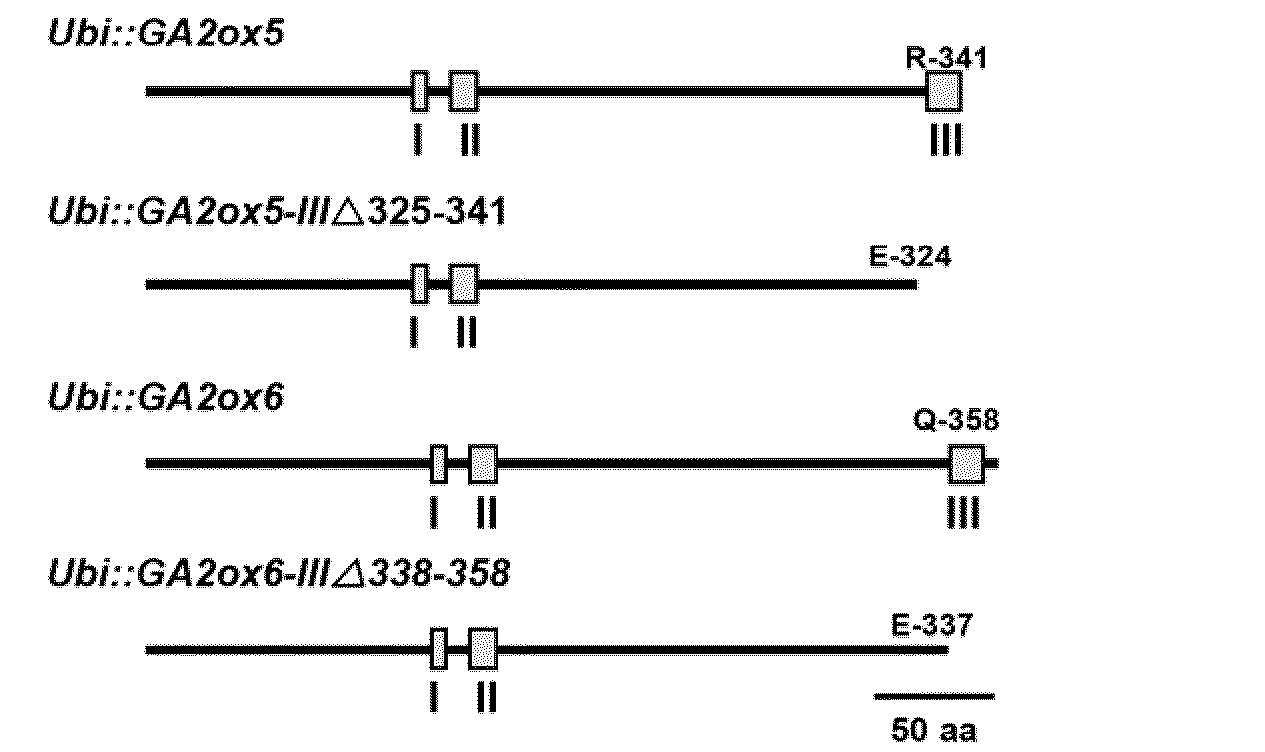
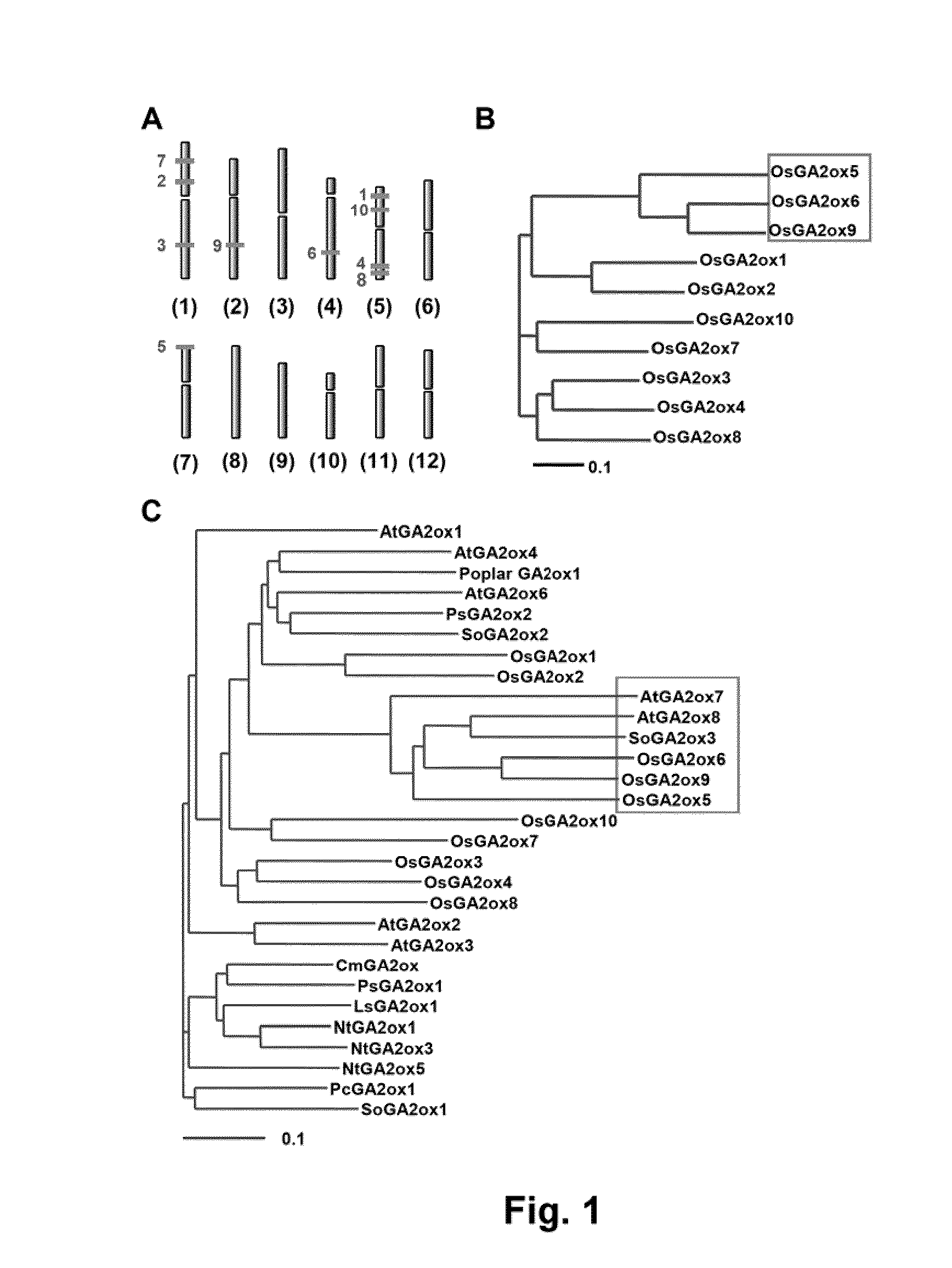
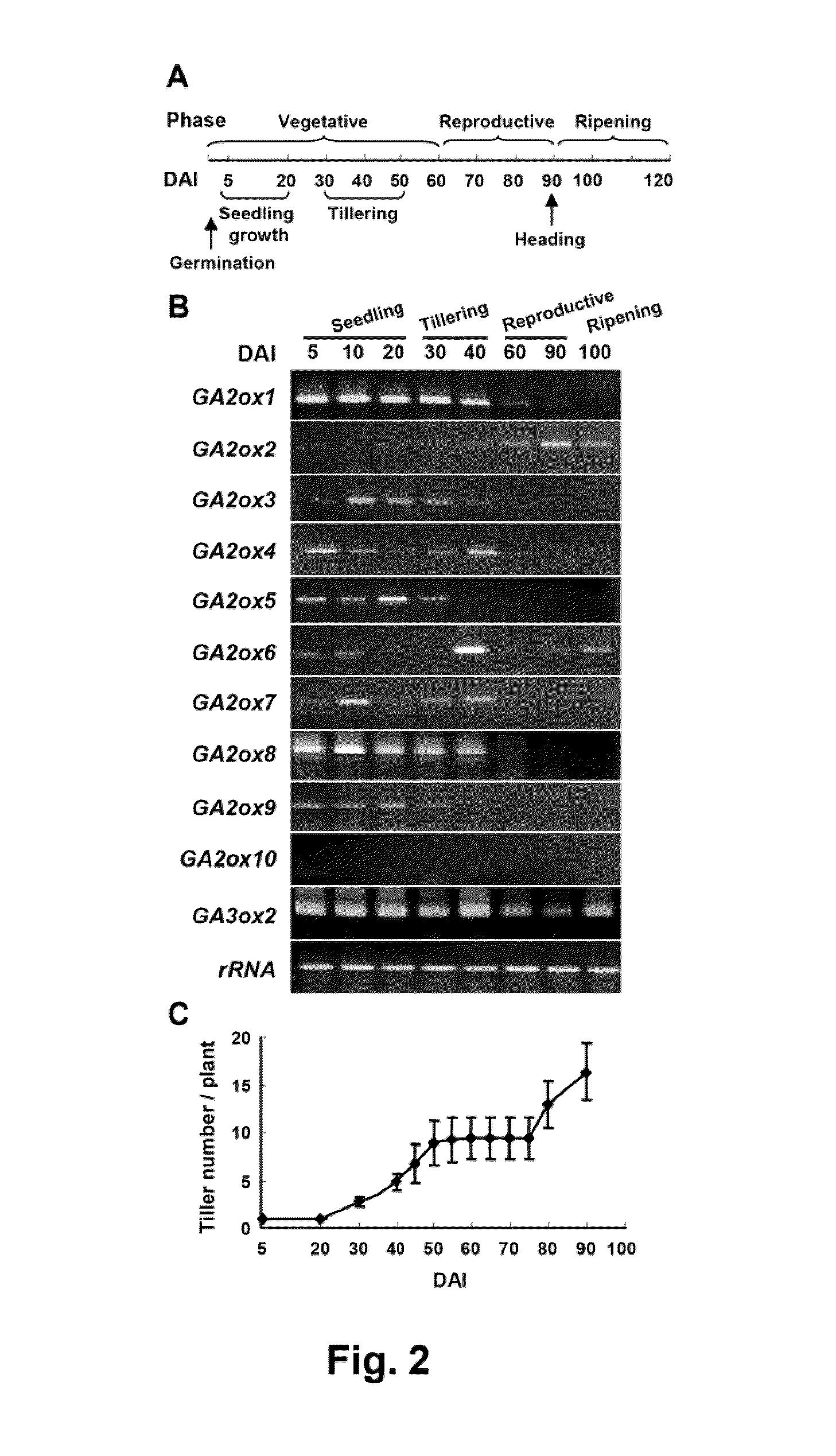
Novel gibberellin 2-oxidase (GA2ox) genes were identified. Differential expression of GA2ox genes correlated with flower development, seed germination, tiller growth and other developmental processes. In addition, the early and increased growth of tiller and adventitious root and altered root architecture caused by overexpression of GA2oxs further suggest the pleiotropic role of GA2oxs in controlling growth and architecture in plants such as rice. GA2ox5, GA2ox6 and GA2ox9 were three genes encoding class C20 GA2oxs in rice. Mutants or transgenic rice overexpressing class C20 GA2oxs exhibited a broad range of mutant phenotypes, including semi-dwarfism, increased root system and higher tiller numbers that may favor grain yield. Mutations in the conserved domain III were found to affect the physiological activity of class C20 GA2oxs. Methods are described for controlling plant growth and architecture by controlling gene expression of gibberellin 2-oxidase in the plant.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Kit, amplification method and detection method for detecting SNP sites related to tacrolimus and cyclosporine a personalized medicine
InactiveCN102277443AImprove detection efficiencyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typePolymerase L
The invention discloses a detection kit and a detection method for detecting SNP sites related to individualized drug use of tacrolimus and cyclosporine A by using multiplex PCR technology combined with SNP sensitive molecular switch technology. The kit is used to type three SNP loci associated with the administration of tacrolimus and cyclosporine A, including: rs2242480 SNP locus on the CYP3A4 gene, rs776746 SNP locus on the CYP3A5 gene, and rs776746 SNP locus on the MDR1 gene rs1045642 SNP site. The kit contains wild-type 2× amplification buffer, mutant 2× amplification buffer, and polymerase. The two buffers contain sequence-specific primers and internal reference primers corresponding to the SNP wild-type and mutant phenotypes, which can The typing of the above three SNP sites was completed in two multiplex PCR reactions, so as to provide a molecular biological basis for the rational use of tacrolimus and cyclosporine A.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG +1
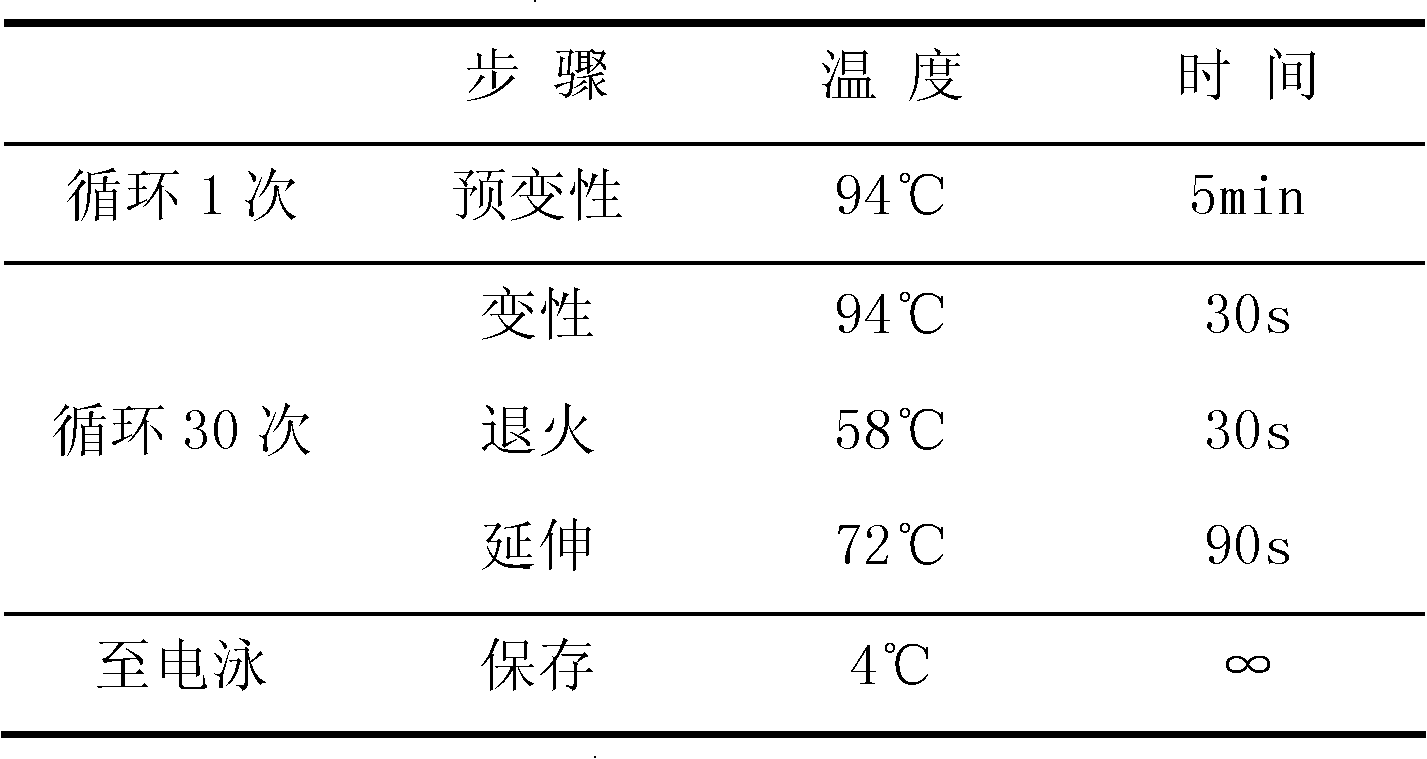
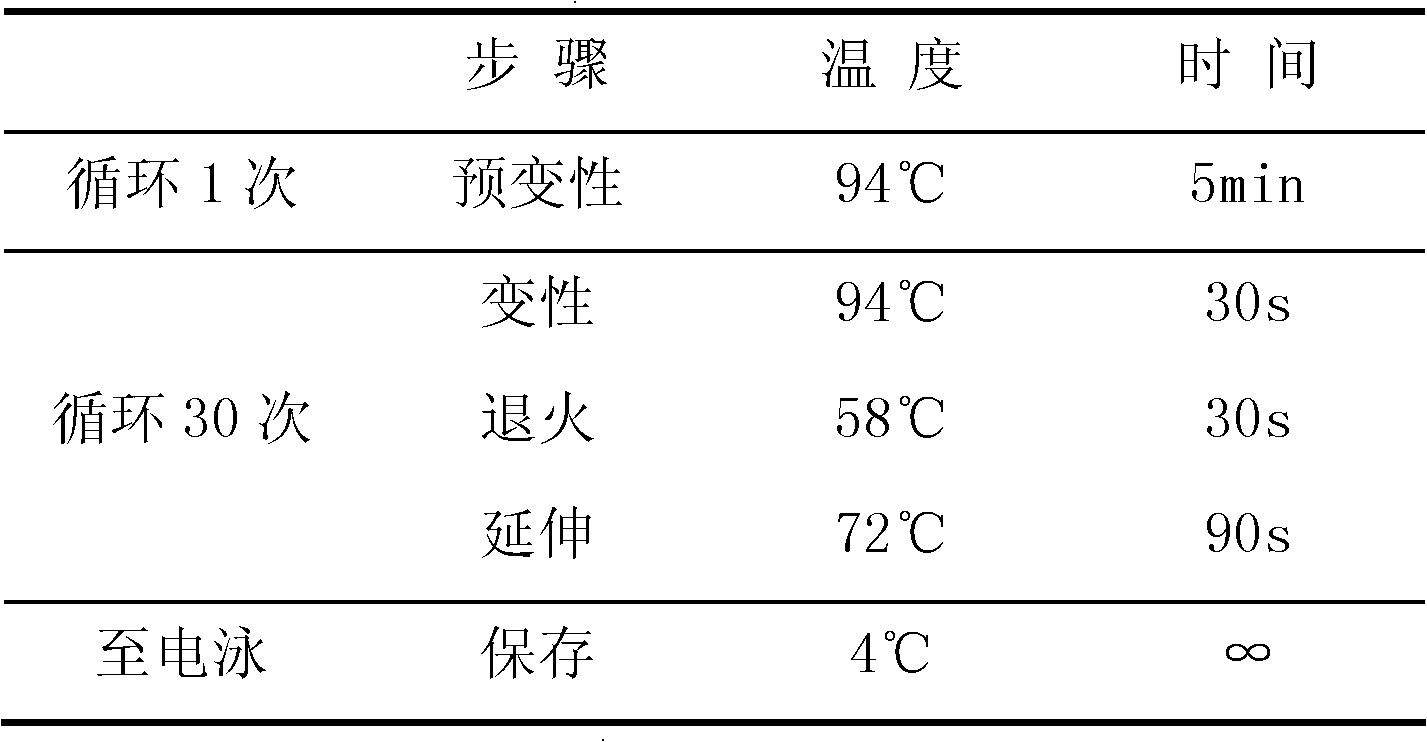
CYP2C19 gene detection kit, amplification method and detection method
InactiveCN103184265AImprove detection efficiencyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typePolymerase L
The present invention discloses a gene detection kit using the multiplex PCR technology combined with the SNP sensitive molecular switch technology for genotyping of cytochrome 4502C19 gene, an amplification method and a detection method. Three common polymorphic sites on the CYP2C19 gene significantly changing the product activity are genotyped by the kit, wherein the three common polymorphic sites include: rs4244285SNP site, rs4986893 site and rs12248560 site. The kit includes a wild-type 2*PCR buffer, a 2*mutant amplification buffer, and a polymerase. The two buffers respectively includes a sequence-specific primer and an internal reference primer corresponding to SNP wild and mutant phenotype, and can complete genotyping for the three SNP sites in two multiplex PCR reactions, and thus the CYP2C19 gene is genotyped, and molecular biological evidence is provided for the gene-expressed enzyme activity prediction.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG +1
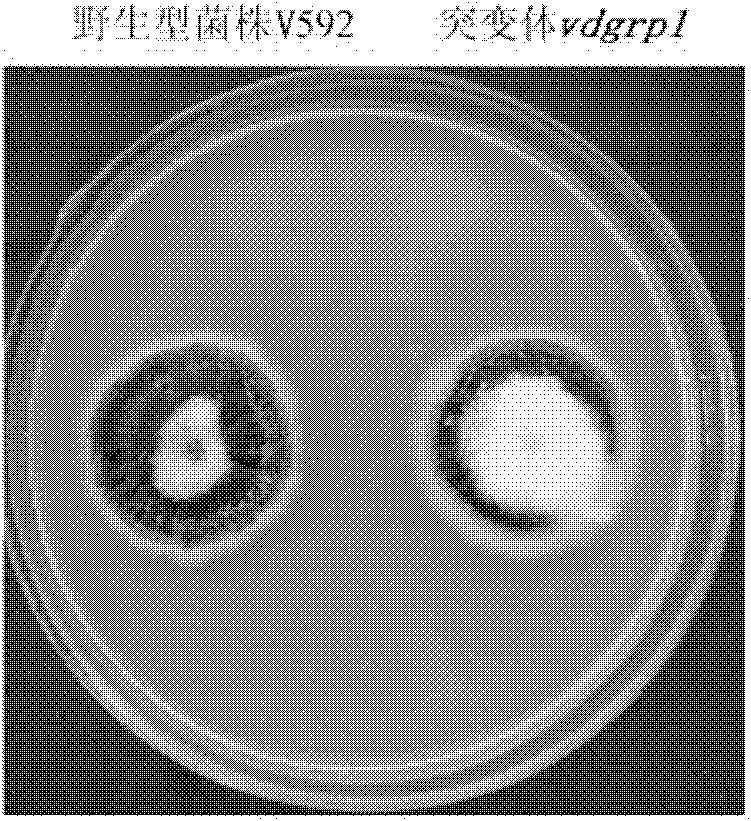
Pathogenic related protein VdGRP1 from verticillium dahliae kleb and coded gene thereof
ActiveCN102212121AReduce pathogenicityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMutant phenotype
The invention discloses a pathogenic related protein VdGRP1 from verticillium dahliae kleb and a coded gene thereof. The pathogenic related protein is the protein of 1) or 2): 1) the protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown as sequence 2 in a sequence table; and 2) the protein formed by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid residuesequence shown as sequence 2 in the sequence table, related to pathogenic fungi and derived from 1). A mutant strain vdgrpl of which the pathogenicity is weakened is obtained by screening a verticillium dahliae kleb mutant library mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and built through T-DNA insertion technology by the inventor. Southern hybridization proves that the mutant strain is a T-DNA single-insertion mutant. A gene causing mutant phenotype is obtained through TAIL-PCR technology by the inventor. Gene complementation tests prove that the mutation of the gene VdGRP1 weakens the pathogenicity of the strain vdgrpl which means that the gene VdGRP1 is a fungi pathogenic related gene.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
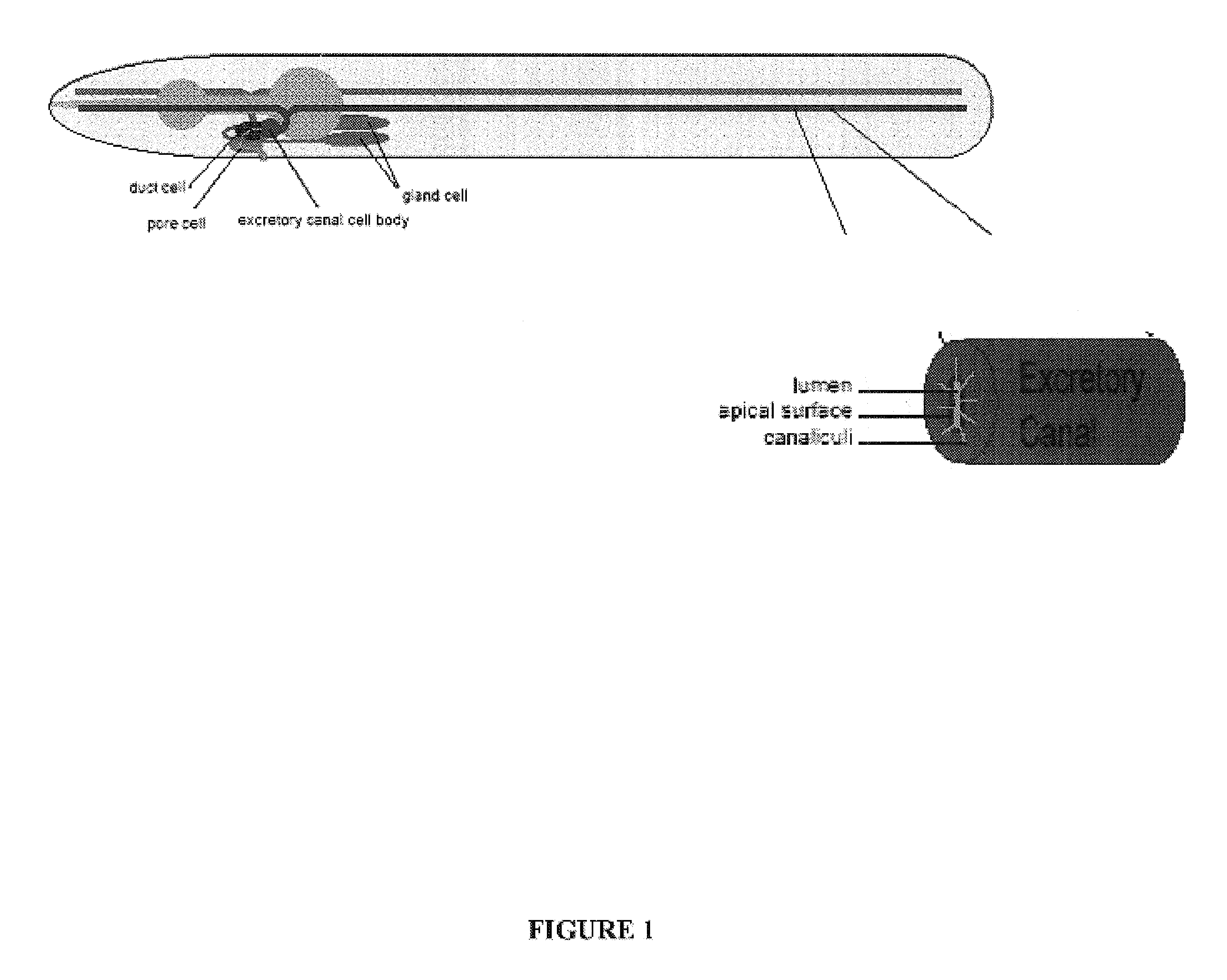
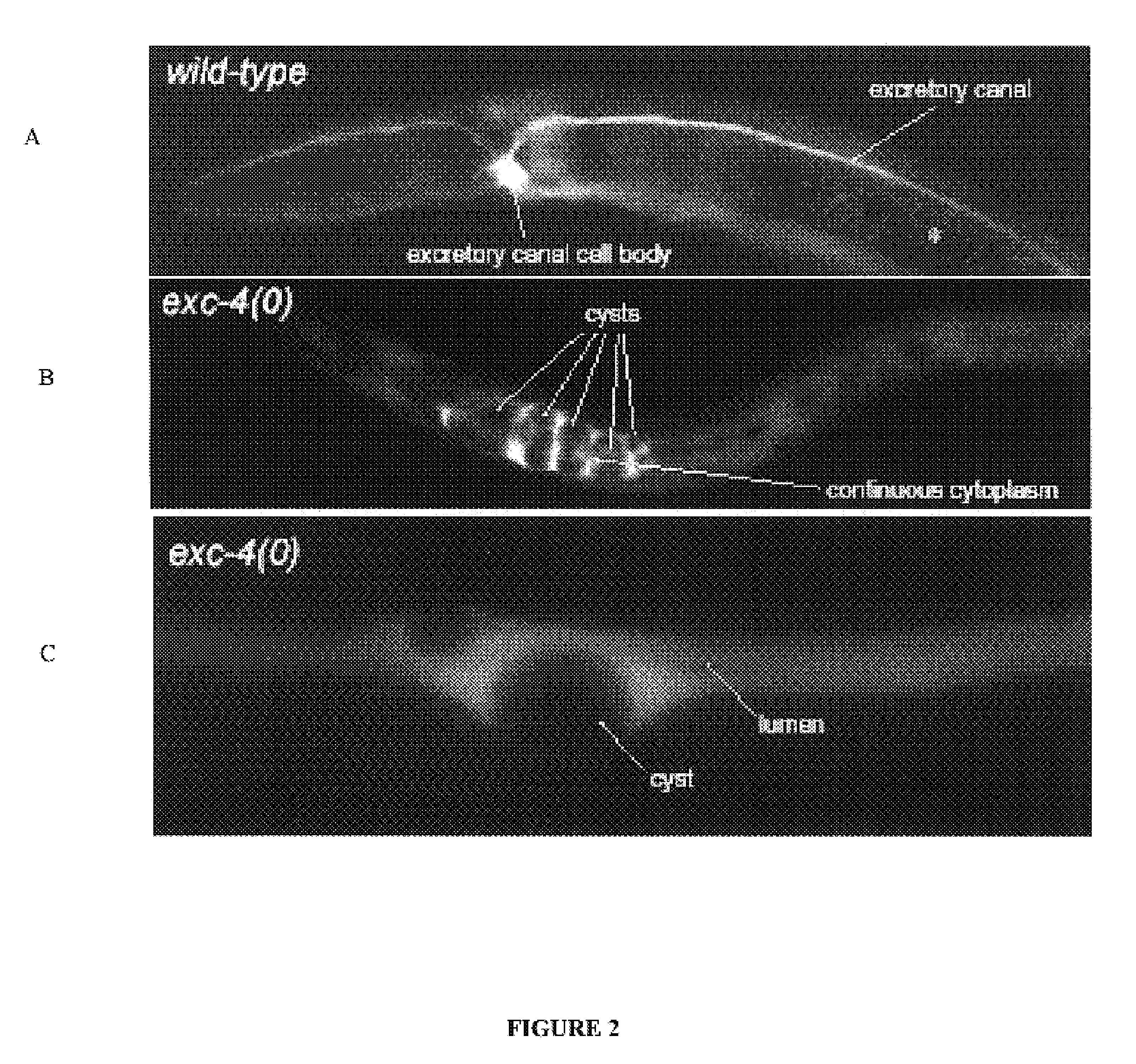
Method of screening for agents inhibiting chloride intracellular channels
InactiveUS20050003363A1Inhibit angiogenesisInhibiting tubulogenesisCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCell phenotypeMutant phenotype
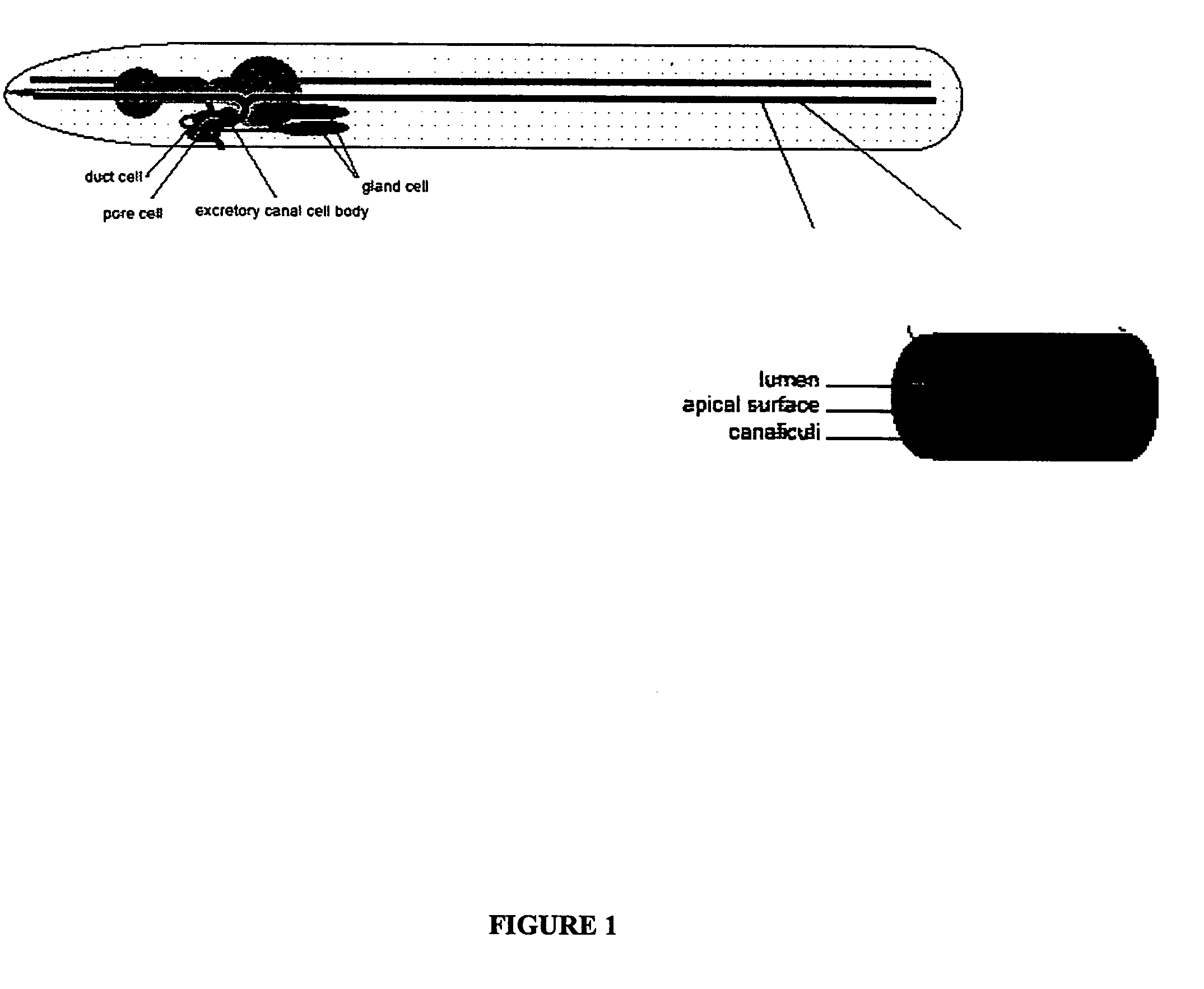
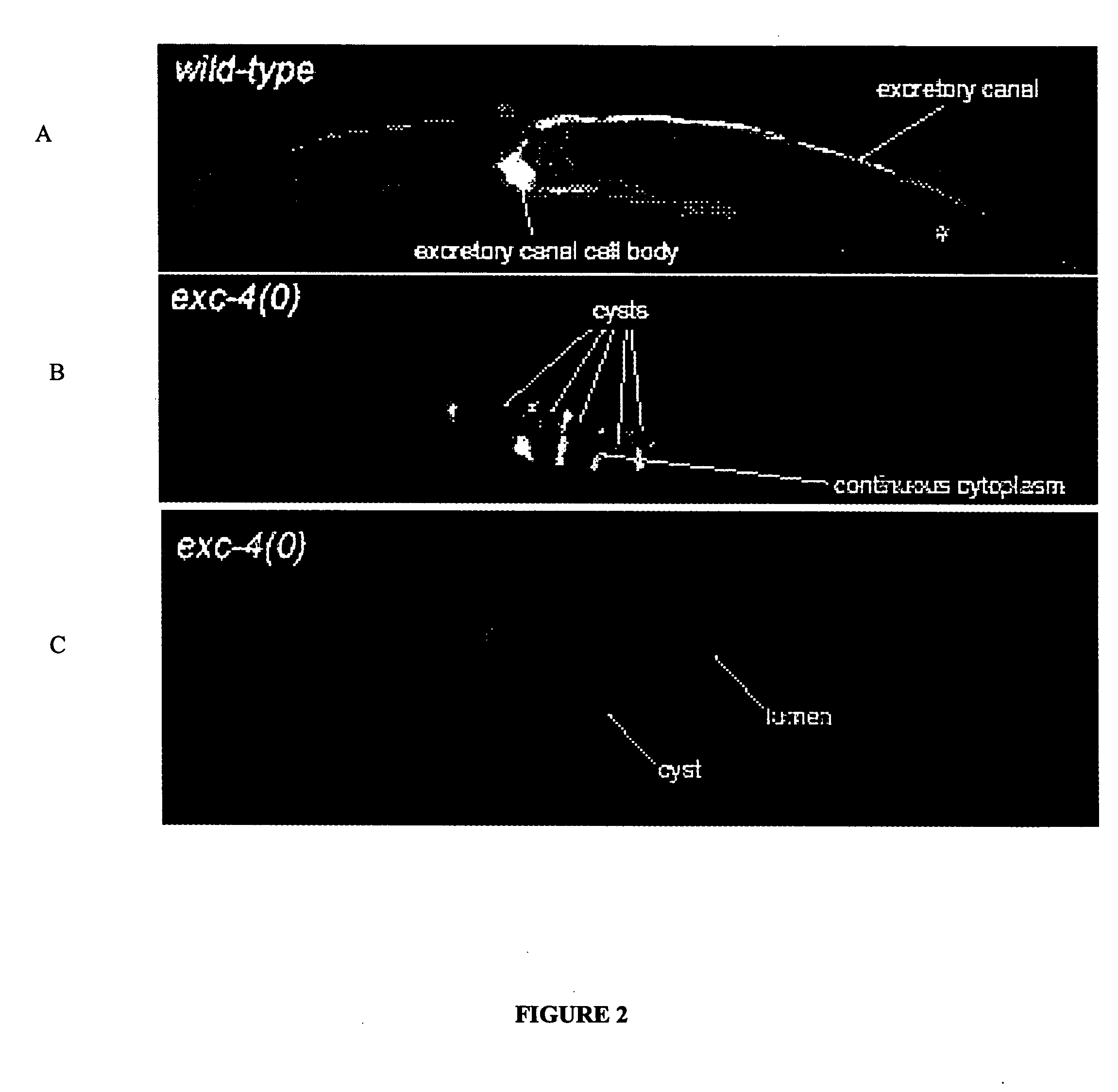
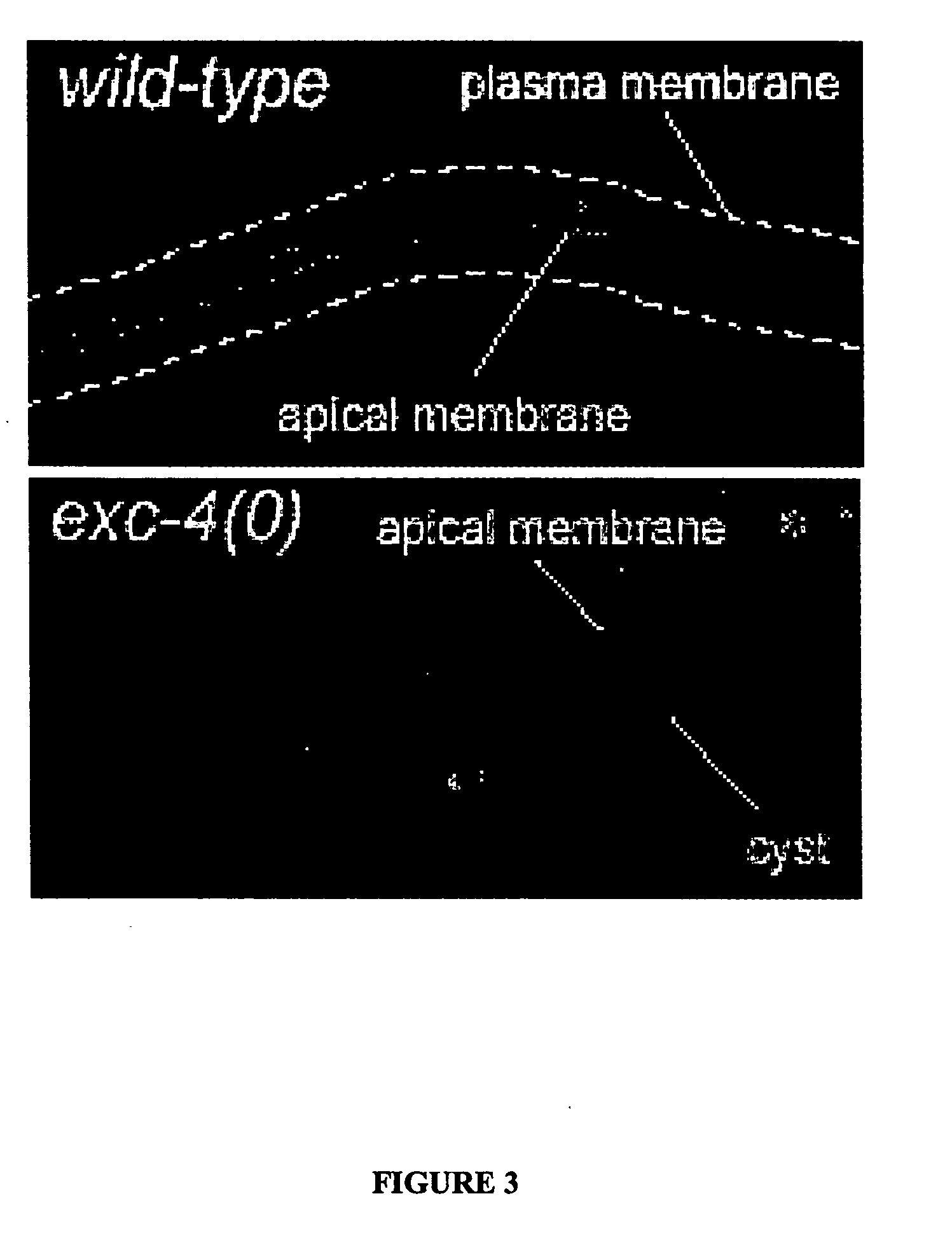
The present invention isolates and characterizes the exc-4 gene of C. elegans, and identifies exc-4 as an orthologue of the human CLIC family of chloride intracellular channels. Accordingly, a nucleic acid having the sequence of SEQ ID NO.: 1 is disclosed, as well as recombinant vectors and host cells comprising the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.: 1. Further, a number of screening methods are disclosed to identify putative agents that inhibit vertebrate, and preferably human, CLICs using C. elegans and exc-4 inhibition as a loss-of-function model for CLIC activity. Also disclosed is a method of determining whether a specific member of the CLIC gene family is involved in tubulogenesis, where the rescue of a C. elegans exc-4 excretory cell phenotype via expression of a transgenic CLIC gene of interest indicates that the CLIC gene of interest is involved in tubulogenesis. Finally, a method is disclosed of identifying putative vertebrate, and preferably human, CLIC inhibitors using transgenic C. elegans exc-4 mutant embryos, where expression of the transgene yields a CLIC product that rescues the exc-4 mutant phenotype. Agents of interest resulting in a reversionary exc-4 mutant phenotype are putative agents that inhibit CLIC expression or function.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
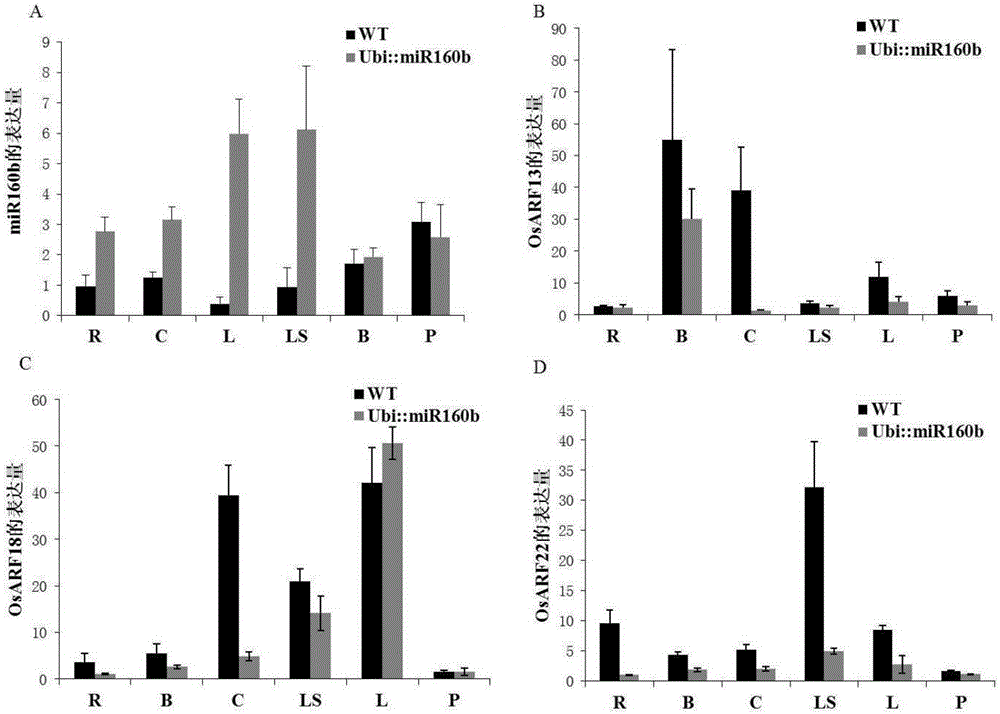
Application of paddy rice miR160b gene in regulation and control on tillering angle
InactiveCN105985954AAnalyzing Biological FunctionsEasy to breedMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceMutant phenotype
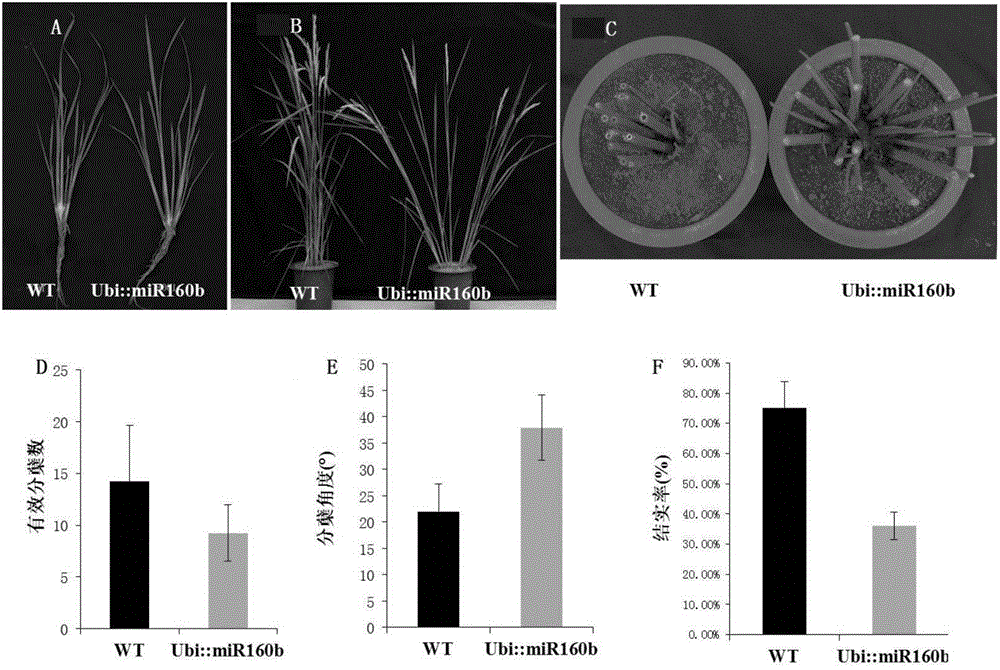
The invention belongs to the field of plant gene engineering and particularly relates to an application of a paddy rice miR160b gene in regulation and control on tillering angle. Through over-expression of the miR160b gene, a normal paddy rice plant has a phenotypic change of increased tillering angle, and through inhibition of the miR160b gene, the mutant phenotype of the over-expressed miR160b plant is recovered. The miR160b gene has the function of regulating and controlling plant type of paddy rice, wherein a stem-loop structure DNA sequence of the gene is represented as the SEQ ID No.1, a stem-loop structure precursor RNA sequence formed after transcription is represented as the SEQ ID No.2, and the sequence of a core region in mature miR160b formed after transcription and cutting is represented as the SEQ ID No.3. The invention discloses an expression mode of changing the paddy rice miR160b gene or the genes in other members of the family through gene engineering technology, so that the tillering angle of the paddy rice is regulated and controlled to form an ideal plant type, thereby increasing yield.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
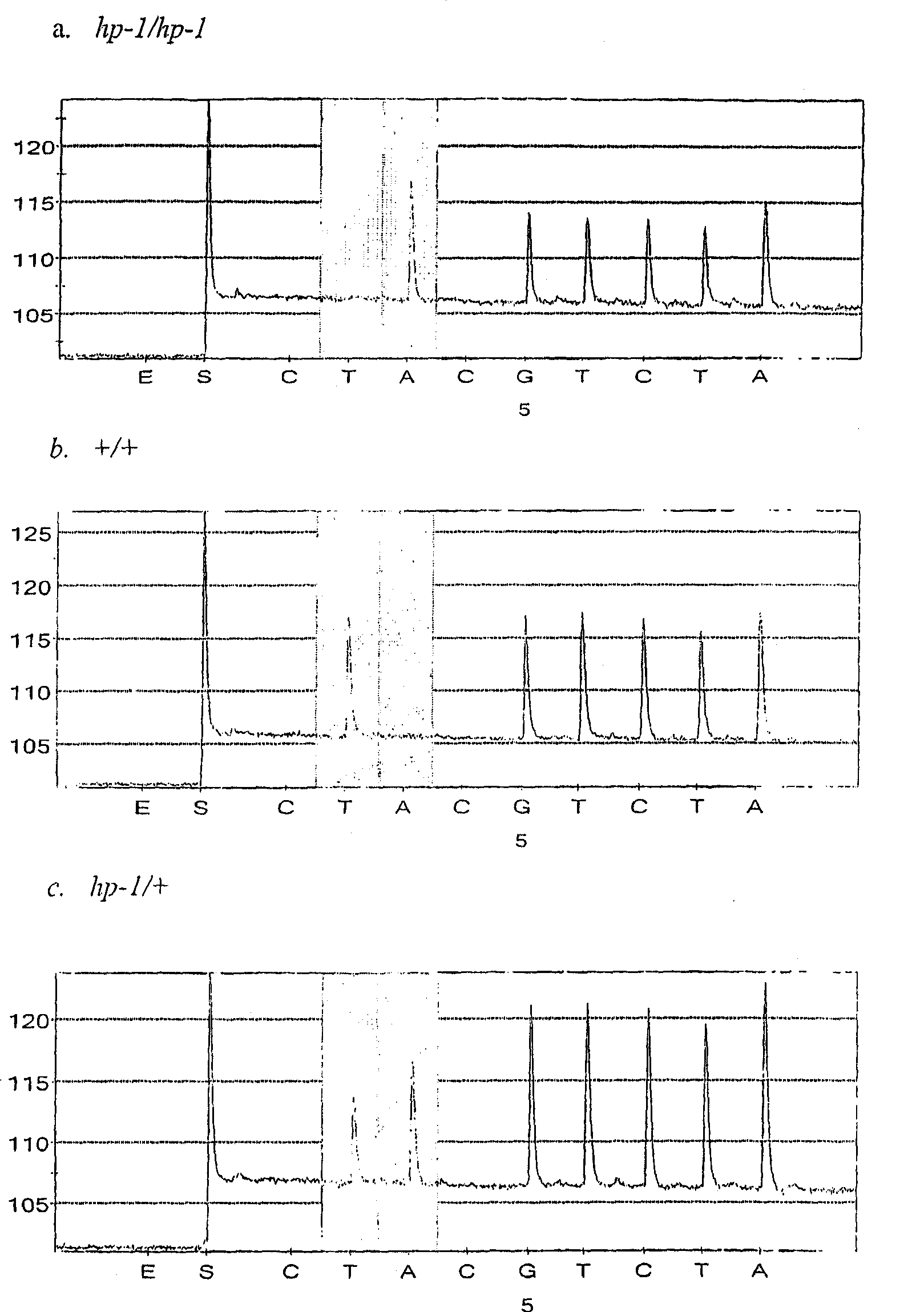
Isolated nucleotide sequences responsible for the tomato high pigment-1 mutant phenotypes (hp-1 and hp-1w) and uses thereof
InactiveCN101415826AMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesMutant phenotypeNucleotide sequencing
The present invention provides isolated nucleotide sequences responsible for the tomato high pigment 1 (hp-1) and high pigment 1<w> (hp-1<w>) phenotypes, wherein said sequences comprises an altered tomato DDB1 gene sequence or fragment thereof, wherein said the alteration in said altered sequence or fragment comprises an A-to-T transversion at nucleotide 931 of said DDB1 gene sequence in the case of hp-1 and a G-to-A transition at nucleotide 2392 of said DDB1 gene sequence in the case of hp-1<w>.
Owner:沃尔坎尼中心-以色列农业部农业研究组织
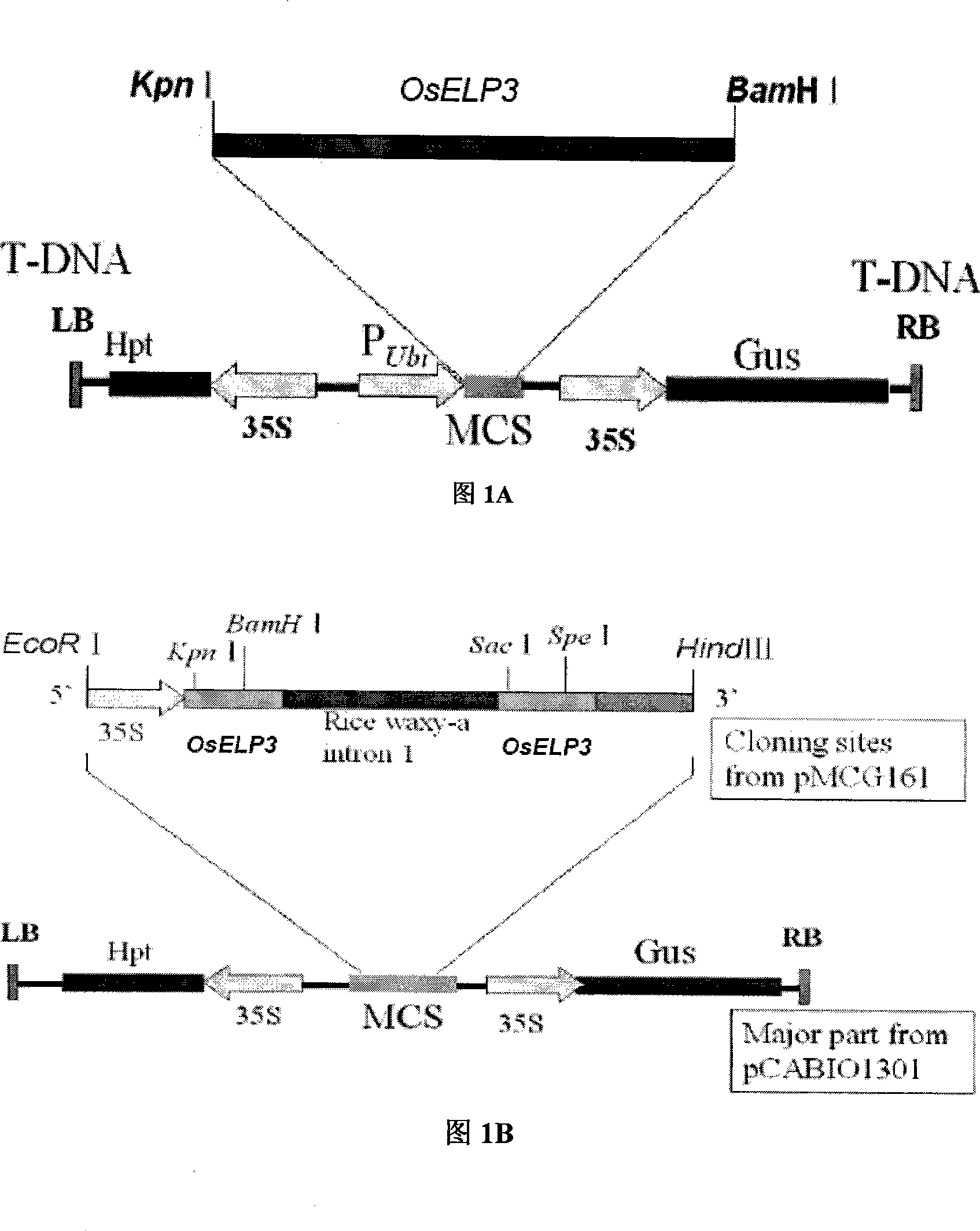
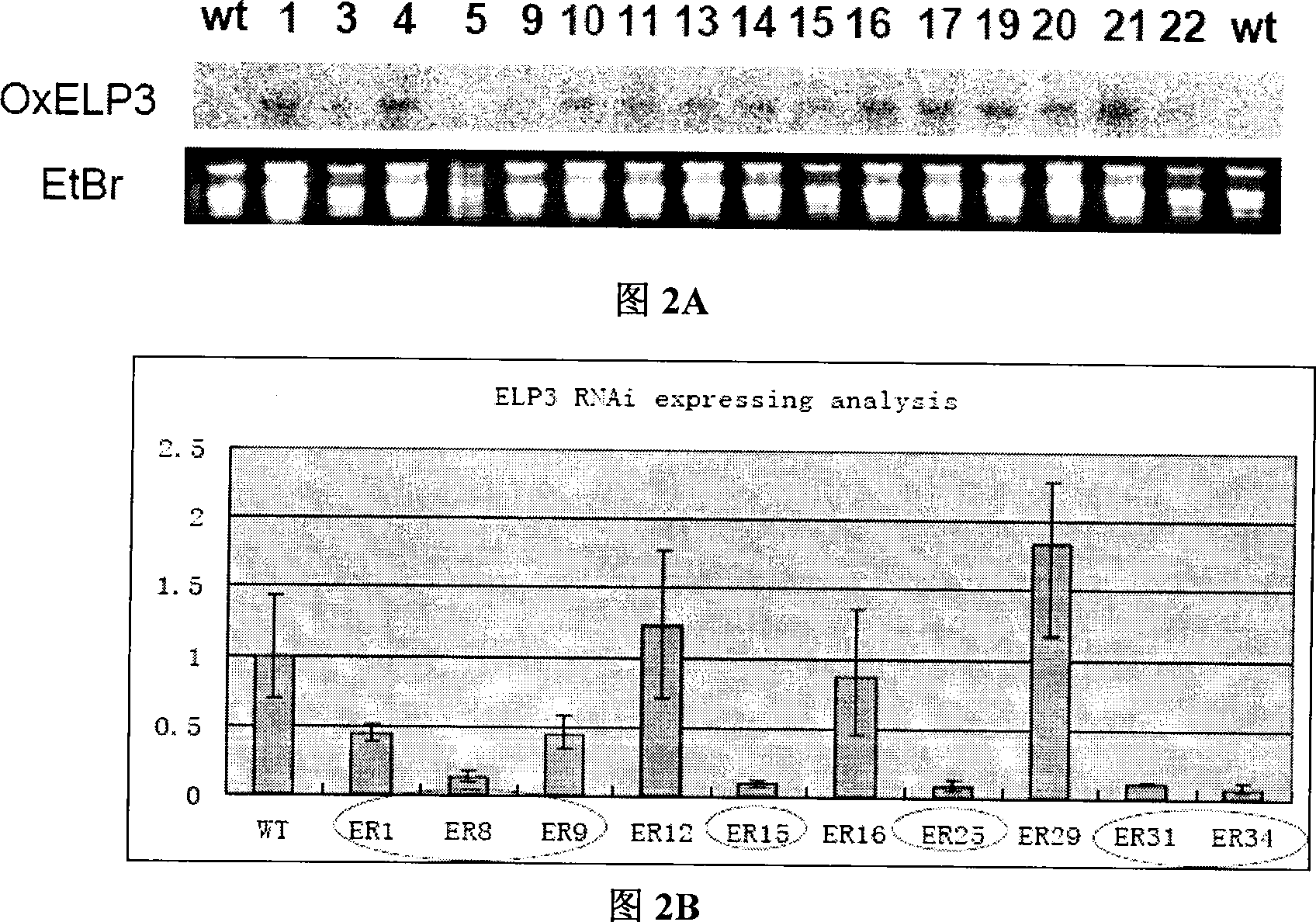
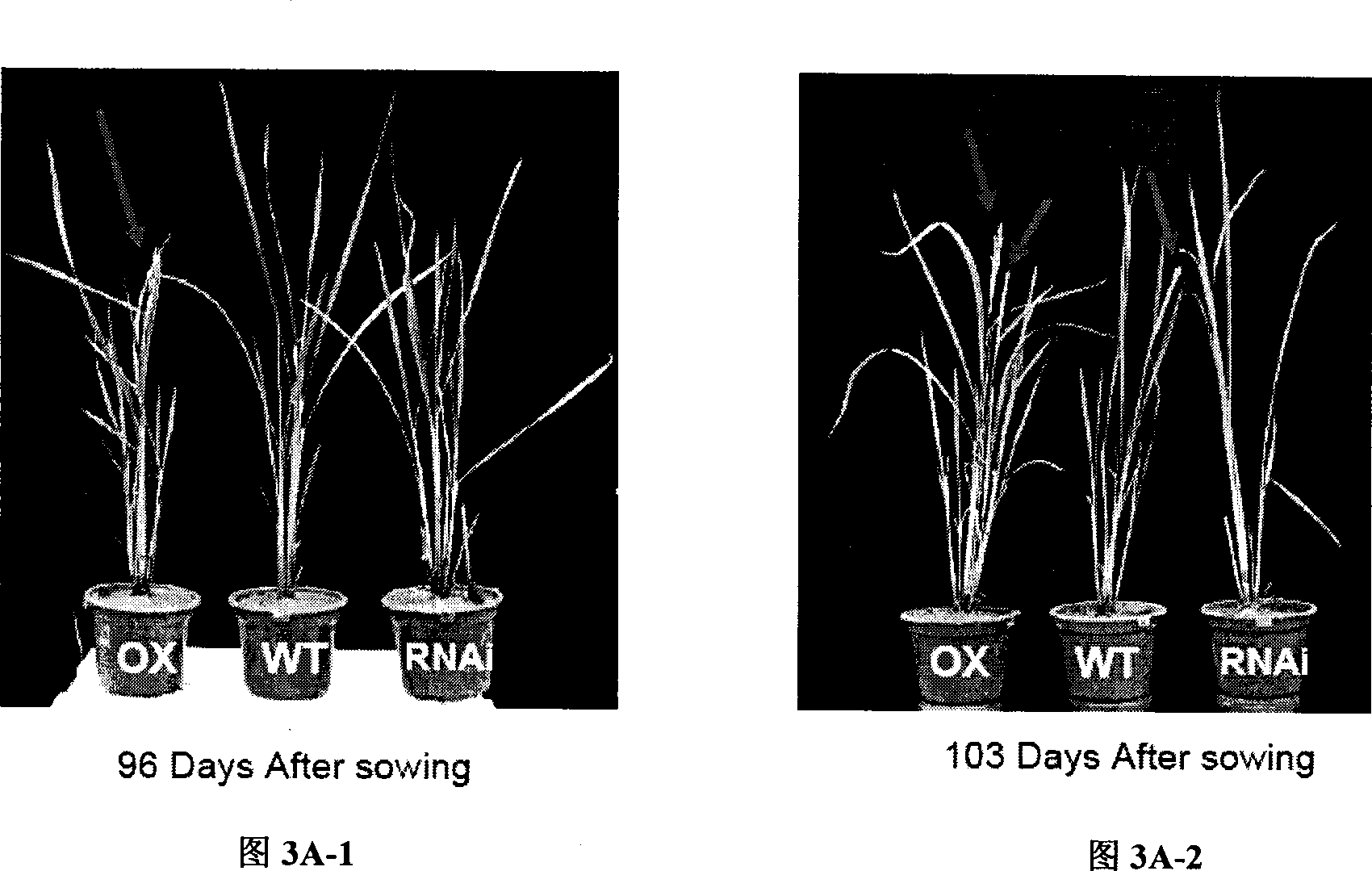
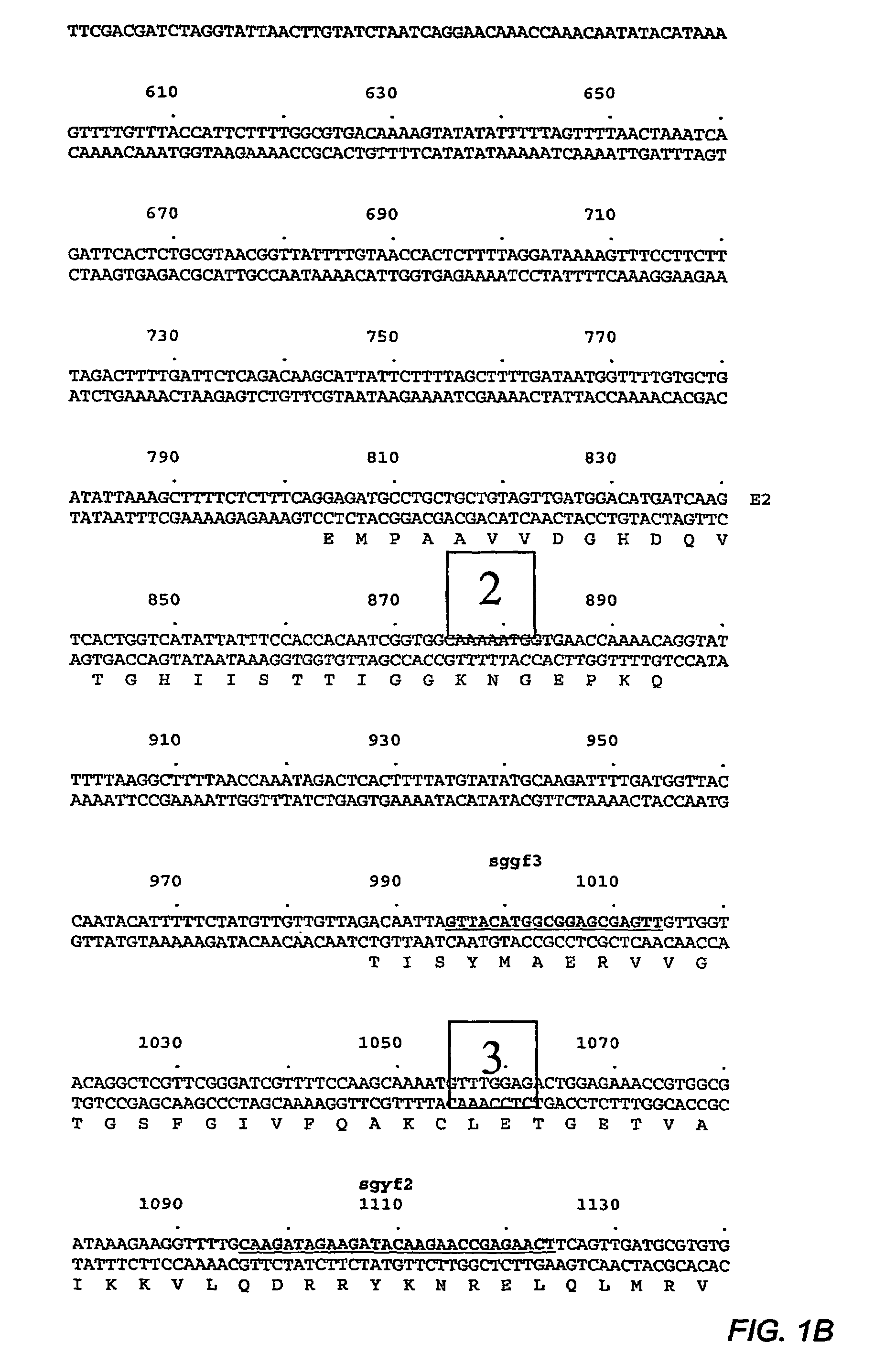
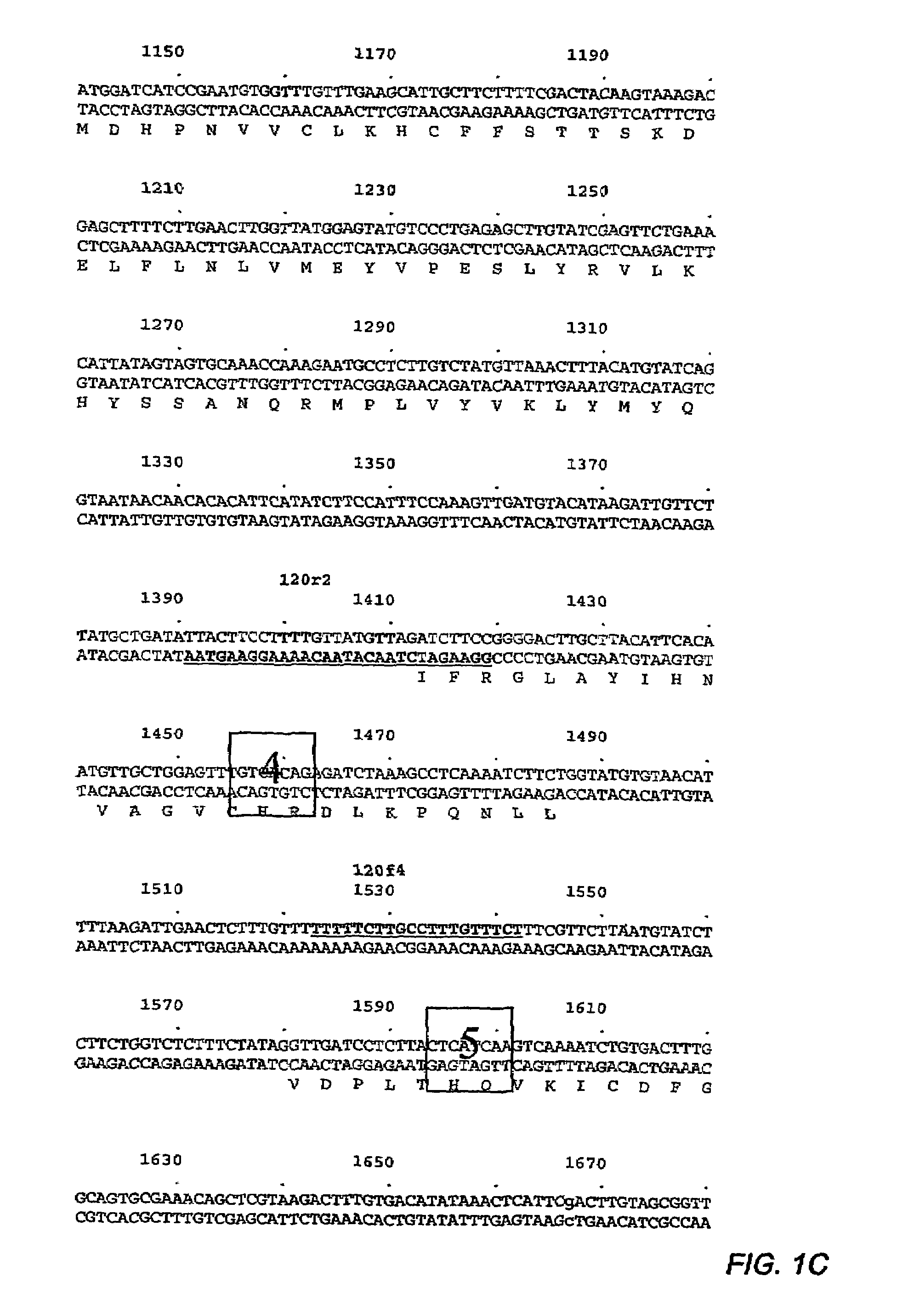
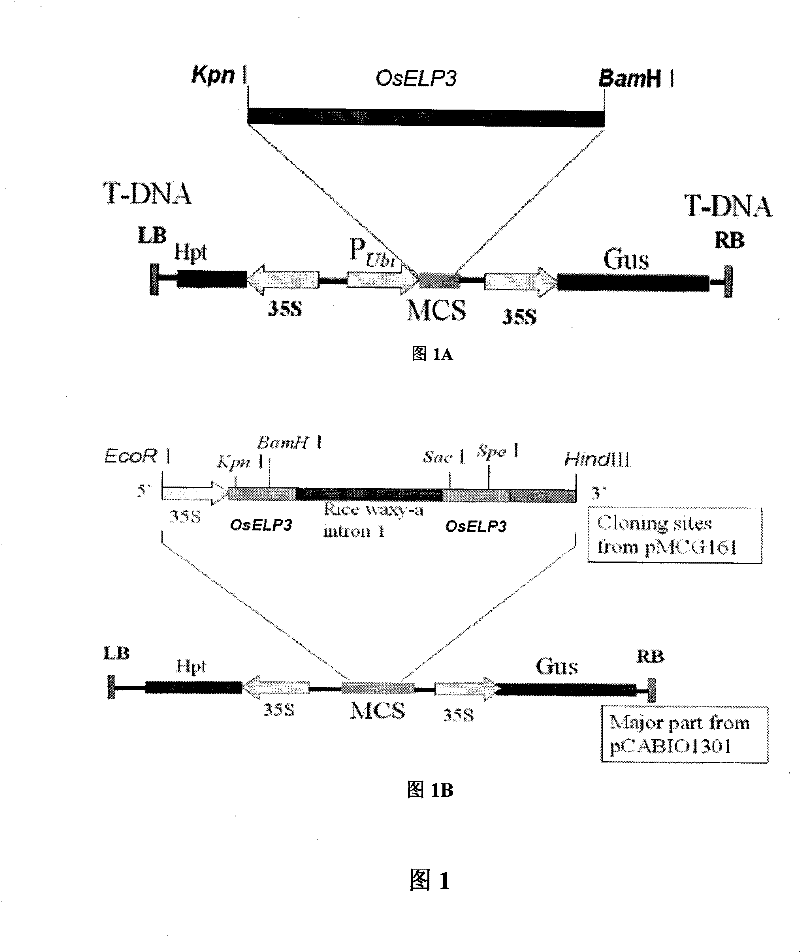
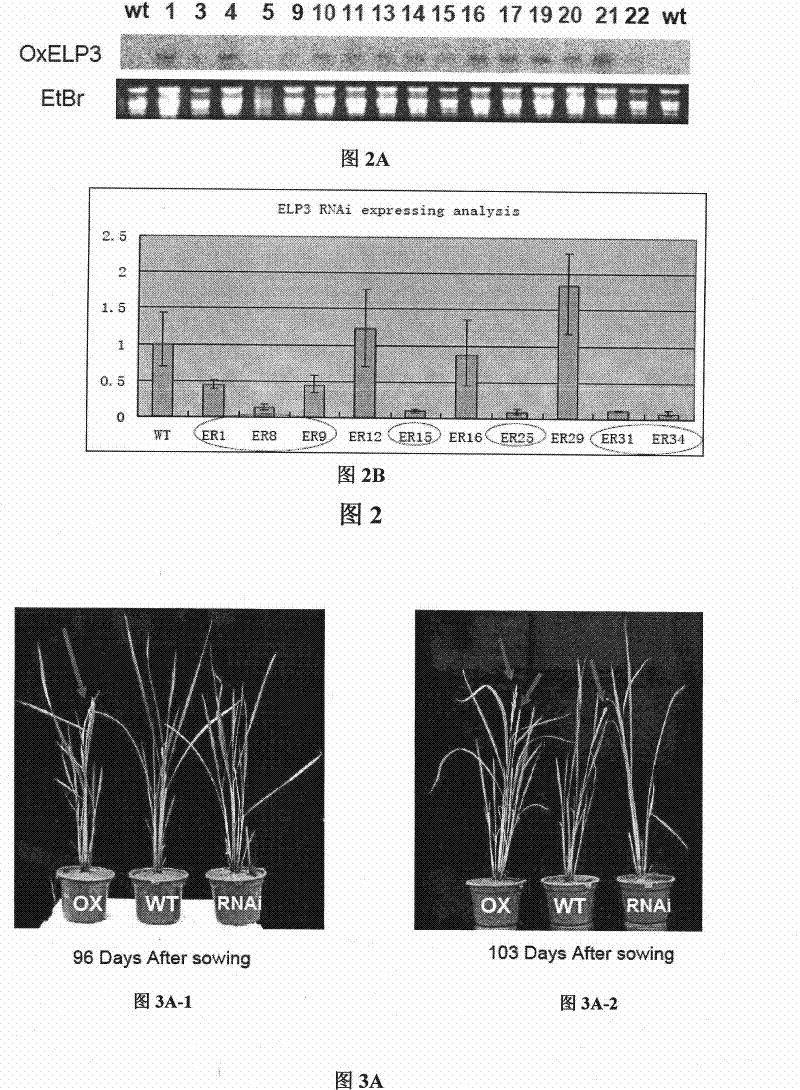
Use of histone acetylation enzyme gene OsELP3 in rice anthesis regulation
InactiveCN101434963AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEnzyme GeneHistone Acetylase
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a rice histone acetyltransferase gene, encoding protein functions and applications thereof. The invention discloses the rice histone acetyltransferase gene OsELP3, which is related to plant florescence. Under long-day sunlight, overexpression of the gene can bring rice blooming forward, and inhibition of the gene expression can delay rice blooming. After being processed under short-day sunlight, mutant phenotype of an inhibiting material is recovered to be wild. Analysis discovers that the OsELP3 gene can influence the expression levels of three blooming genes Hd3a, Hd1 and OsGI, and take rhythmic variation of self expression under short-day sunlight. The Western Blot experiment analysis shows that the gene has the histone acetylation function and the functionary locus on H3K9.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
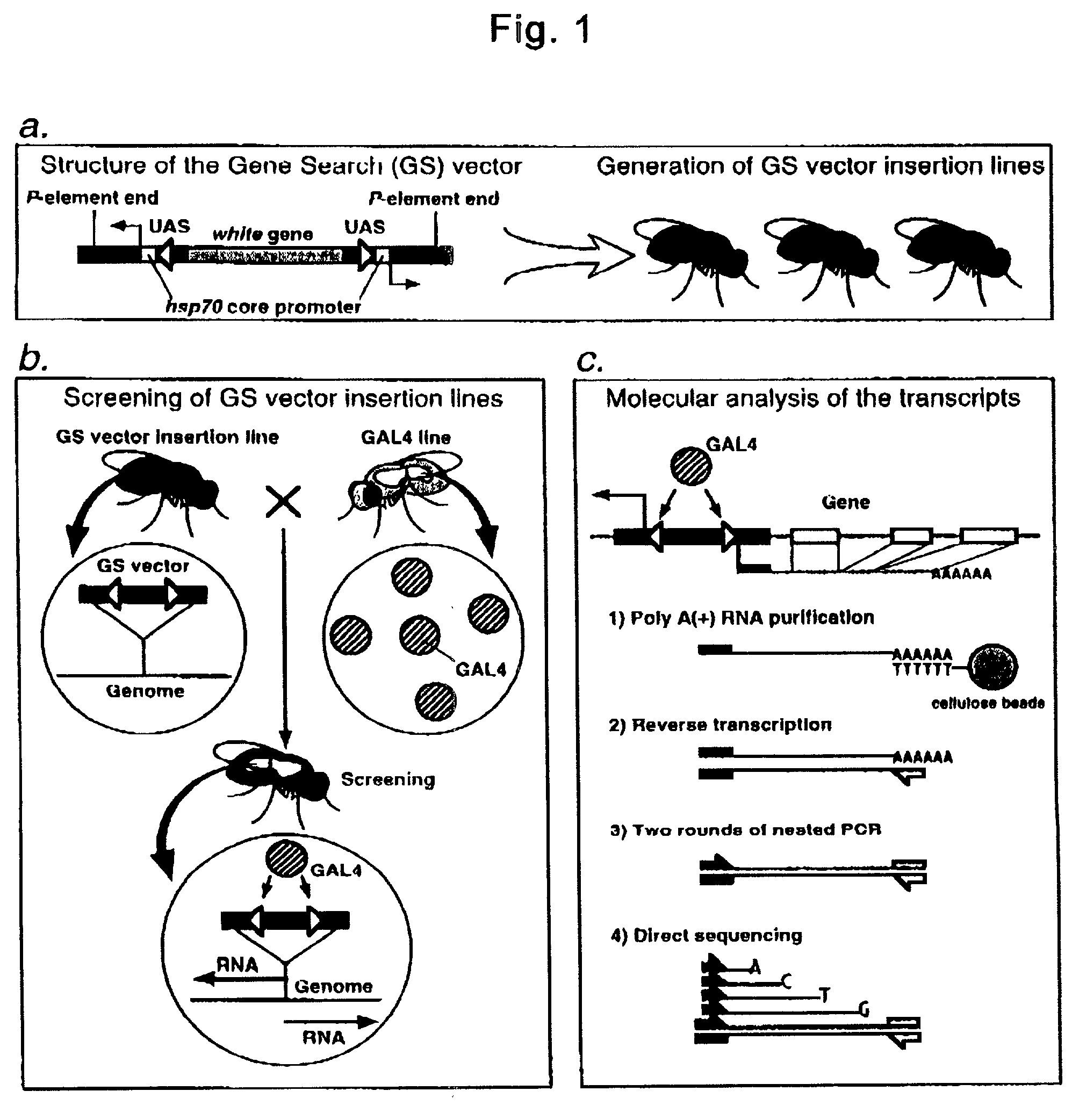
Gene Search Vector and Gene Search Method
InactiveUS20020032913A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeMutant phenotype
The present invention provides a gene search method comprising P-element insertion and being capable of efficiently identifying a novel gene regulating various biological functions of Drosophila and specifying a function corresponding to the novel gene. An unknown gene of Drosophila can be searched by the method comprising a step of inserting in the genome of Drosophila a gene search vector carrying two sets of an expression regulatory sequence comprising UAS sequence for GAL4 transcription factor GAL4 and a promoter sequence, as integrated in the P-element sequence in such a manner that their downstreams are in opposite directions, mating the vector-inserted Drosophila with a Drosophila expressing the GAL4 to create progeny individuals, and identifying a vector-inserted line with a phenotype different from those of wild-type Drosophila, and determining the nucleotide sequence of the gene for the mutant phenotype.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for identifying plant gene functions in total genome ranges
ActiveCN105734130AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSingle nucleotide mutationNucleotide
The invention relates to a method for identifying plant gene functions in total genome ranges.The method includes 1), mutating single nucleotide of starting plants and establishing plant mutant libraries; 2), detecting phenotypes of mutants in the plant mutant libraries and establishing plant mutant phenotype databases; 3), detecting genotypes of the mutants in the plant mutant libraries and establishing plant mutant genotype databases; 4), determining functions of genes where SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) sites caused by mutation of the single nucleotide in the starting plants by the aid of the plant mutant phenotype databases and the plant mutant genotype databases.The method has the advantages that the genes related to plant development procedures and biological procedures of stress-tolerant reaction or metabolic pathways or the like can be accurately and quickly found by the aid of the plant mutant phenotype databases and the plant mutant genotype databases which are established by the method, and novel ways can be created for plant functional genome research.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
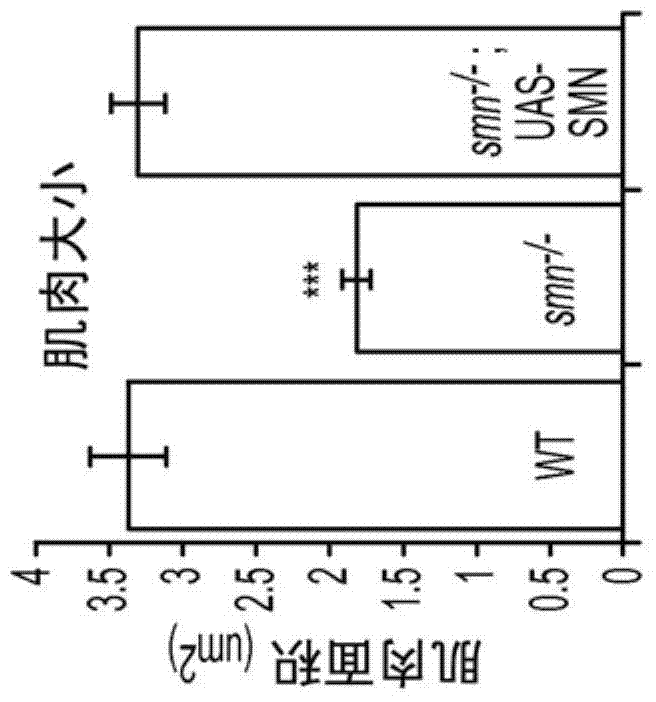
4-aminopyridine as a therapeutic agent for spinal muscular atrophy
It has been discovered that pharmacological inhibition of K+ channels (using the FDA-approved broad-spectrum K+ channel antagonist 4-AP) positively benefitted smn mutant phenotypes, a result that is consistent with the defective excitability of motor circuits by their interneuron or sensory neuron inputs being a critical consequence of SMN depletion. Based on these observations, certain embodiments of the invention are directed to methods of treatment of SMA by administering therapeutically effective amounts of one or more potassium channel antagonists, including 4-aminopyridine, 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine, 4-(methylamino)pyridine, and 4-(aminomethyl)pyridine. Other embodiments are directed to new pharmaceutical formulations comprising two or more potassium channel antagonists.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
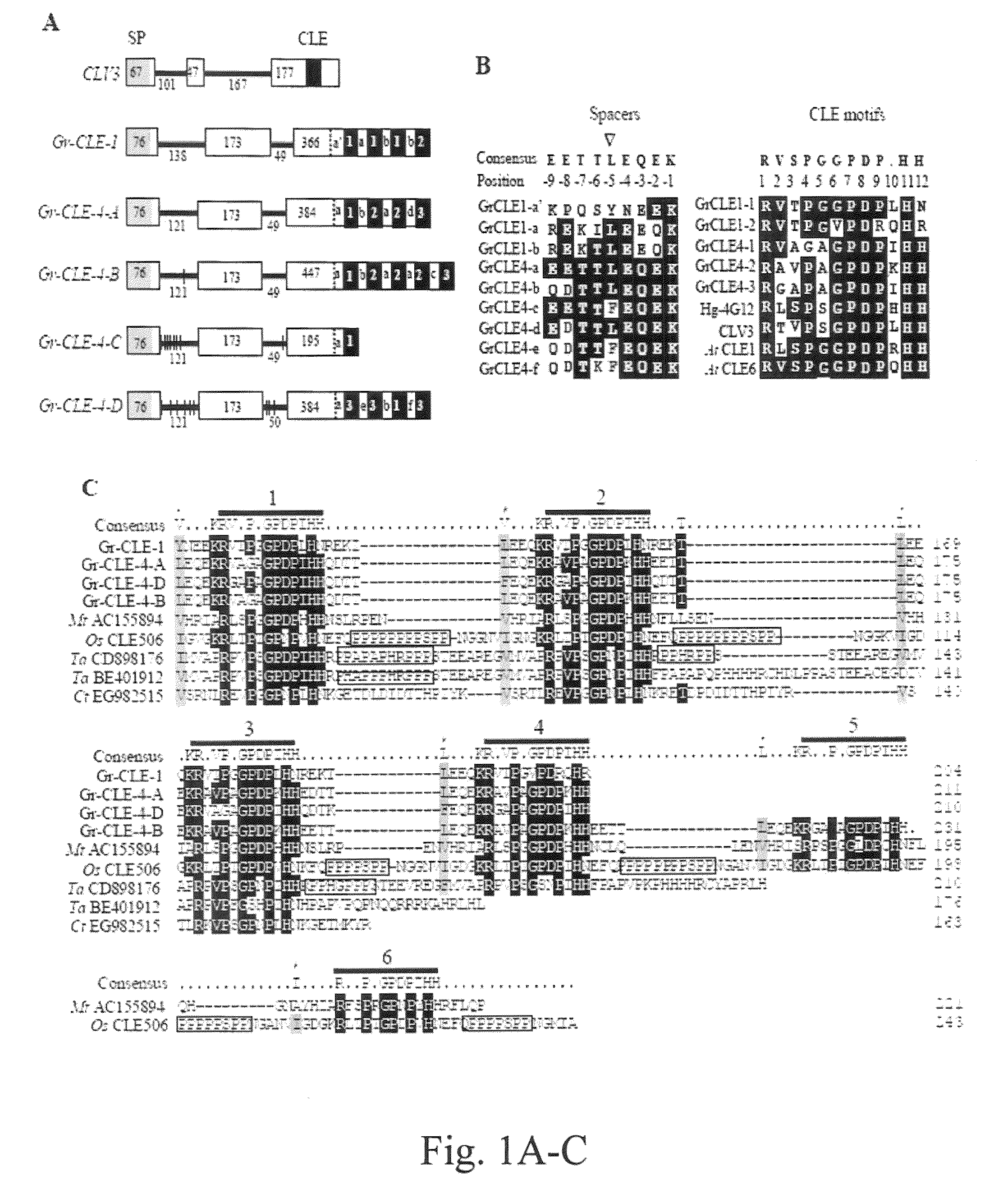
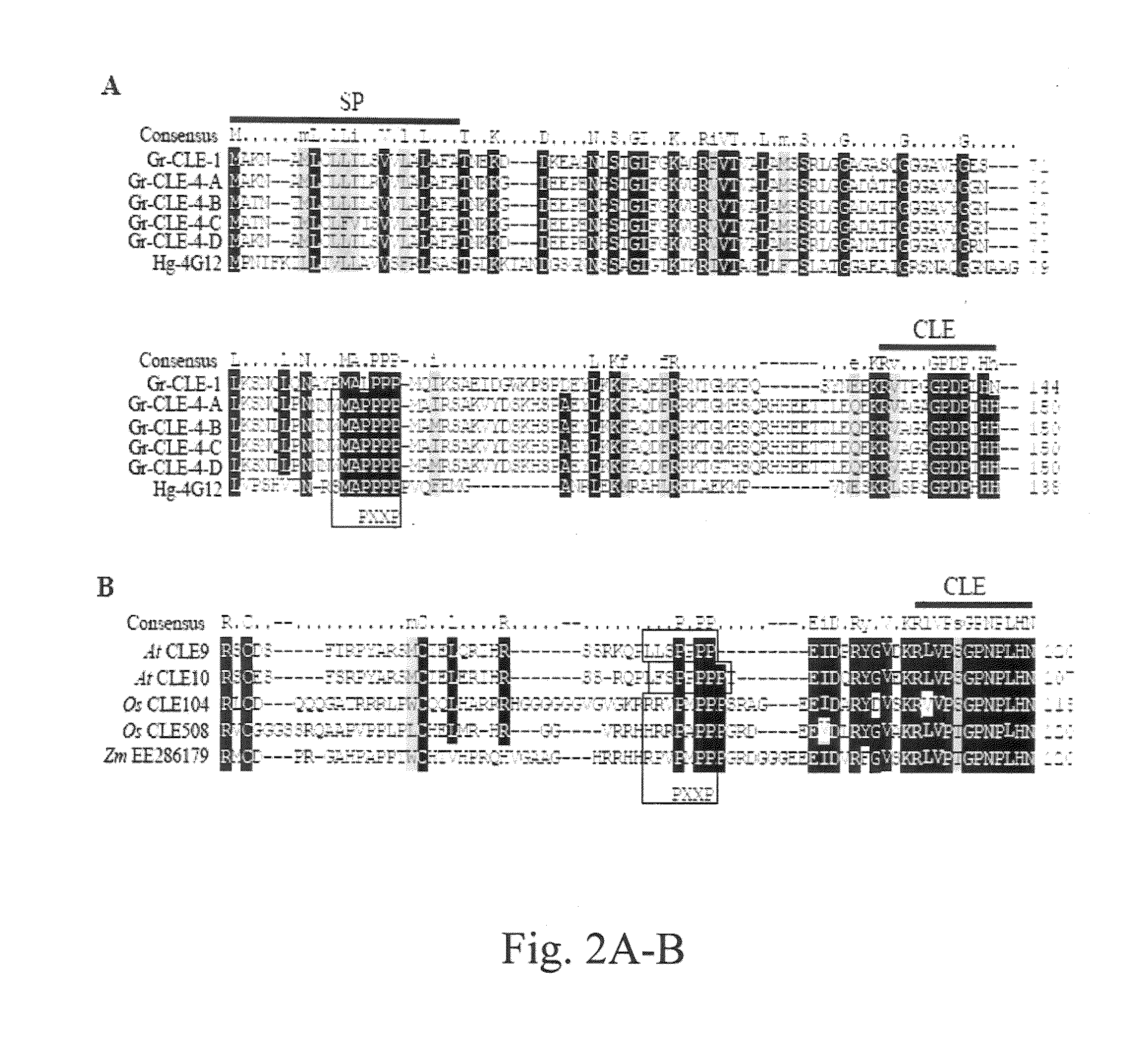
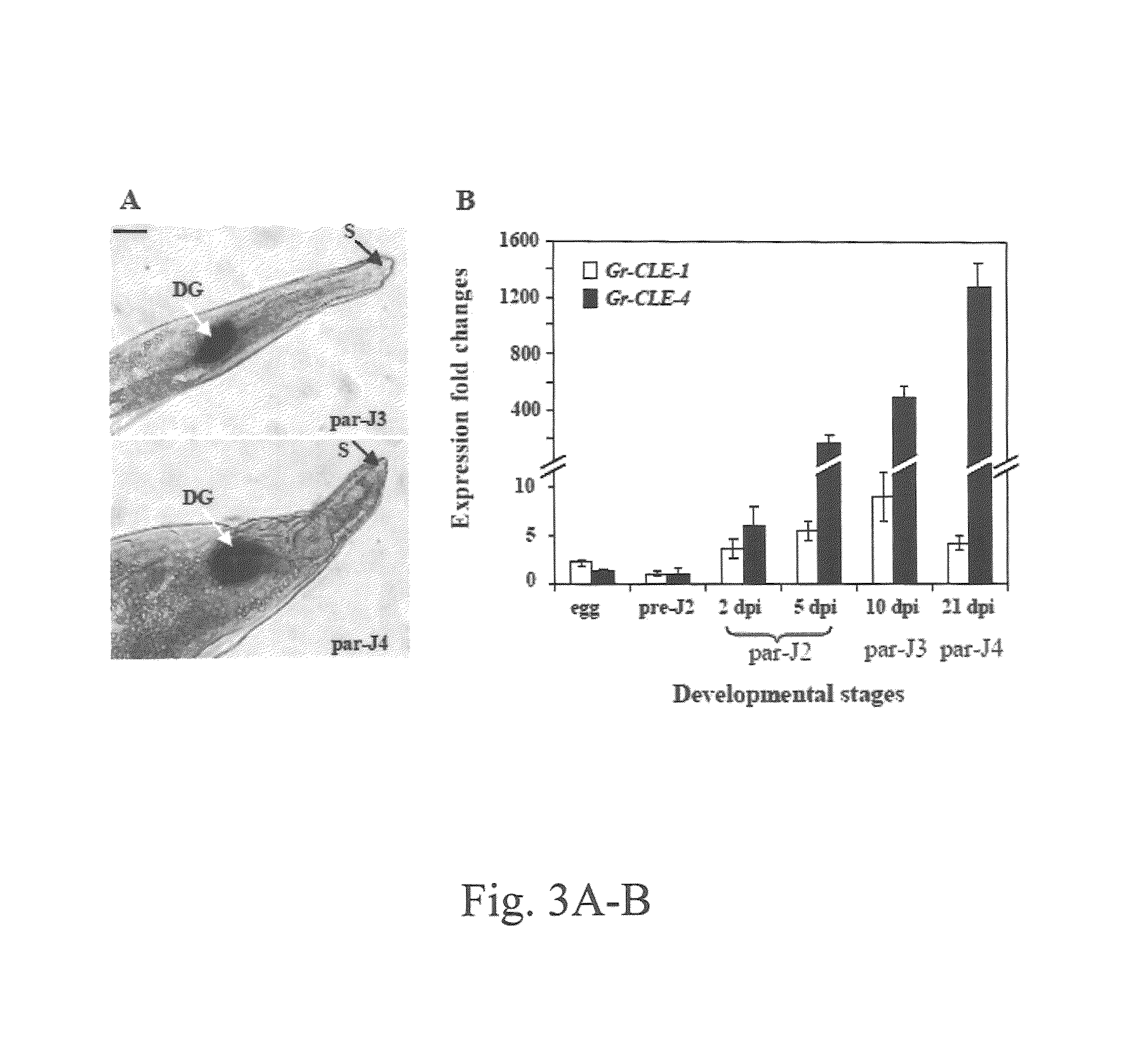
Generating transgenic potatoes with novel resistance to potato cyst nematodes by silencing nematode parasitism genes of CLE -1 and CLE-4s
Plant CLAVATA3 / ESR-related (CLE) peptides have diverse roles in plant growth and development. We have isolated and characterized the function of five new CLE genes from the potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Unlike typical plant CLEs that contain a single CLE motif, four of the five Gr-CLE genes encode CLE proteins with multiple CLE motifs. These Gr-CLEs were found to be specifically expressed within the dorsal esophageal gland cell of nematode parasitic stages, suggesting a role for their encoded proteins in plant parasitism. Overexpression of Gr-CLEs in Arabidopsis mimicked overexpression of plant CLEs and Gr-CLE proteins could rescue the Arabidopsis clv3-2 mutant phenotype when expressed within meristems. A short root phenotype was observed when synthetic GrCLE peptides were exogenously applied to roots of Arabidopsis or potato similar to the overexpression of Gr-CLEs in Arabidopsis and potato hairy roots. These results reveal that G. rostochiensis CLEs with either single or multiple CLE motifs function similarly to plant CLEs and that CLE signaling components are conserved in both Arabidopsis and potato roots. Transgenic potato hairy roots expressing Gr-CLE-1 or Gr-CLE-4 dsRNA were generated. There was an approximately 50% reduction in the average number of cysts per root in the Gr-CLE-1 or Gr-CLE-4 dsRNA transgenic lines when compared with the infected control lines, indicating that silencing nematode CLE genes through host-derived RNAi may generate novel resistance against potato cyst nematodes in transgenic potatoes.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
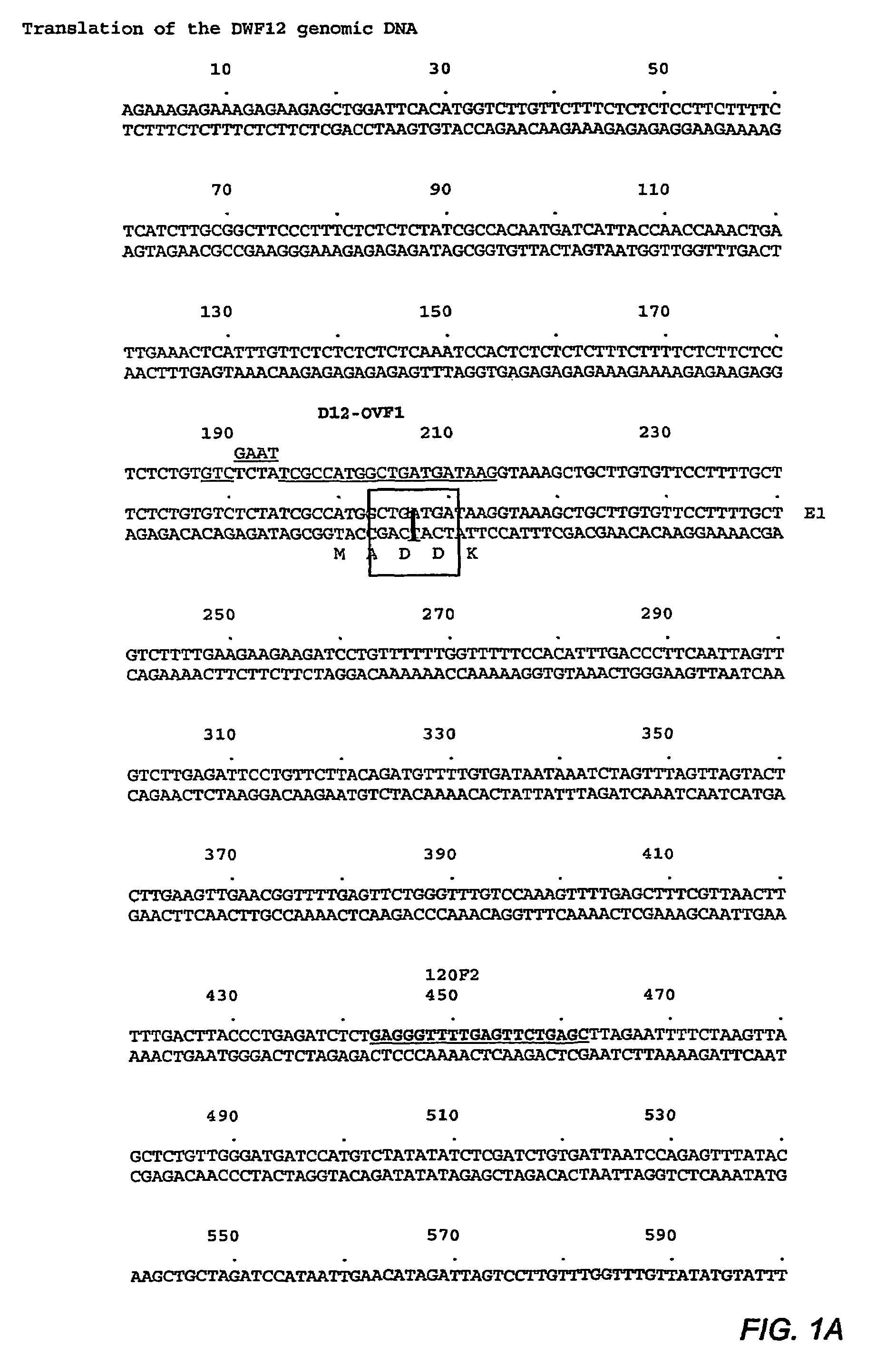
DWF12 and Mutants Thereof
InactiveUS20090025100A1Reduced and increased kinase activityShort robust statureTransferasesTissue cultureBiotechnologyNucleotide
DWARF12 (DWF12) sequences, mutants and methods of using the same are disclosed. The dwf12 polynucleotides can be used in the production of transgenic plants which display at least one dwf12 mutant phenotype, so that the resulting plants have altered biochemistry, structure or morphology.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Transposable element-anchored, amplification method for isolation and identification of tagged genes
InactiveUS6881539B1Labor moreLess manipulationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCDNA libraryMutant phenotype
A method for the rapid isolation and identification of the DNA sequence of transposable element-tagged genes is provided. The method comprises a modified AFLP approach using a transposable element-anchored amplification to identify and clone an amplification product that is associated with a mutant phenotype. Once cloned, the amplification product of interest may be used to screen a cDNA library directly or may be sequenced and compared to available databases for sequence homology. A modification of this approach provides a method for the identification of the location of an additional type of insertion event into genomic DNA, more specifically transgene insertion into the genome of a host organism.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutation prediction method based on naive Bayes model
ActiveCN112749833APredictableImprove accuracyForecastingProteomicsEscherichia coliRNA polymerase beta subunit
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutation prediction method based on a naive Bayes model. The method comprises the following steps: collecting Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit rifampicin resistance positive mutants in an existing report; collecting mutants of a bacterial RNA polymerase beta subunit in an existing report, removing sites consistent with positive mutation of escherichia coli, and taking the mutants as negative mutants; predicting a protein property parameter data set of the obtained positive mutant and negative mutant; and training a naive Bayesian model by using the obtained protein property parameter data set, and predicting a mutation phenotype after amino acid mutation at each position in a rifampicin resistance interval in escherichia coli RpoB by using the model. The model constructed by the invention has good prediction performance on escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutation phenotypes, and the AUC value under an ROC curve in model evaluation is 0.77; and the accuracy is high and can reach 75.4%.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Application of isolated gene sequence in preparation of albino strain of Japanese oryzias latipes
InactiveCN108018315AHigh mutation rateShort breeding timeHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAMutant phenotypeEmbryo
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to an application of an isolated gene sequence in preparation of an albino strain of Japanese oryzias latipes. The gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. Gene mutation is performed based on the gene as shown in SEQ ID No.1 as a target gene, F0 embryos with obvious pigment deletion are selected and cultured into parent fish, F1 embryos are produced by hybridization of F0 mutant parents, the F1 embryos with pigment deletion are screened out to be cultured continuously, and the stable genetic oryzias latipes albinostrain with red eyes can be produced. Compared with an oryzias latipes albino strain obtained with a traditional method, the oryzias latipes albino strain obtained with a gene mutation method has theadvantages of high mutation rate (90% or higher mutation rate), short breeding time (the mutant phenotype can be observed in 2-3 days for subsequent screening), low cost and the like, and has basic value and application value of scientific research.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Peanut mutant creation method and application
InactiveCN111670806APlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyMethane sulfonate
The invention relates to a peanut mutant creation method and application. The peanut mutant creation method can be used for creating peanut mutant groups with rich phenotypes. The peanut mutant creation method comprises the following steps: (1) soaking peanut seeds with an EMS (ethyl methane sulfonate) aqueous solution with the concentration of 0.4-0.5% and treating the peanut seeds for 8-10 h through a shaking table; (2) washing the seeds with running water for 3-5 h and removing residual EMS; (3) germinating the treated seeds in an illumination culture box; (4) picking out the germinated andwhite seeds and planting the seeds; (5) planting M1 generations; in a peanut growth period, investigating the phenotypes of mutants and counting the ratio of the various mutant phenotypes to the groups; and (6) randomly selecting one seed from each single plant of M2 generations and planting the; investigating the phenotypes of the mutants and counting the ratio of the various mutant phenotypes to the groups to obtain peanut EMS mutant groups with the rich phenotypes. By adopting the peanut mutant creation method, the EMS mutation groups with variation of plant height, plant type, branch number, pod size and the like can be obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Screening methods for compounds useful in the treatment of polycystic kidney disease
The present invention provides cell-based screening assays designed to identify agents that regulate the activity of the polycystic kidney disease proteins encoded by the PKD-1 and PKD-2 genes and that may be useful in the treatment of polycystic kidney disease. The assays of the invention comprise the contacting of genetically engineered cells expressing a mutant or truncated PKD gene product with a test agent and assaying for a decrease in the PKD mediated mutant phenotype. Characteristics associated with such a mutant phenotype include increased adherence to type I collagen coated surfaces; apical expression of NaK-ATPase on the cell membrane; increased expression of β-2-NaK-ATPase; and decreased focal adhesion kinase (FAK) incorporation into focal adhesion complexes, and inability to form tubular structures in a gel matrix. To facilitate the screening methods of the invention, cells may be genetically engineered to express epitope tagged PKD gene products and / or epitope tagged PKD interacting proteins (PKD-IP). Such interacting proteins include, for example, focal adhesion complex proteins such as FAK, paxillin, vinculin, talin and the like.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
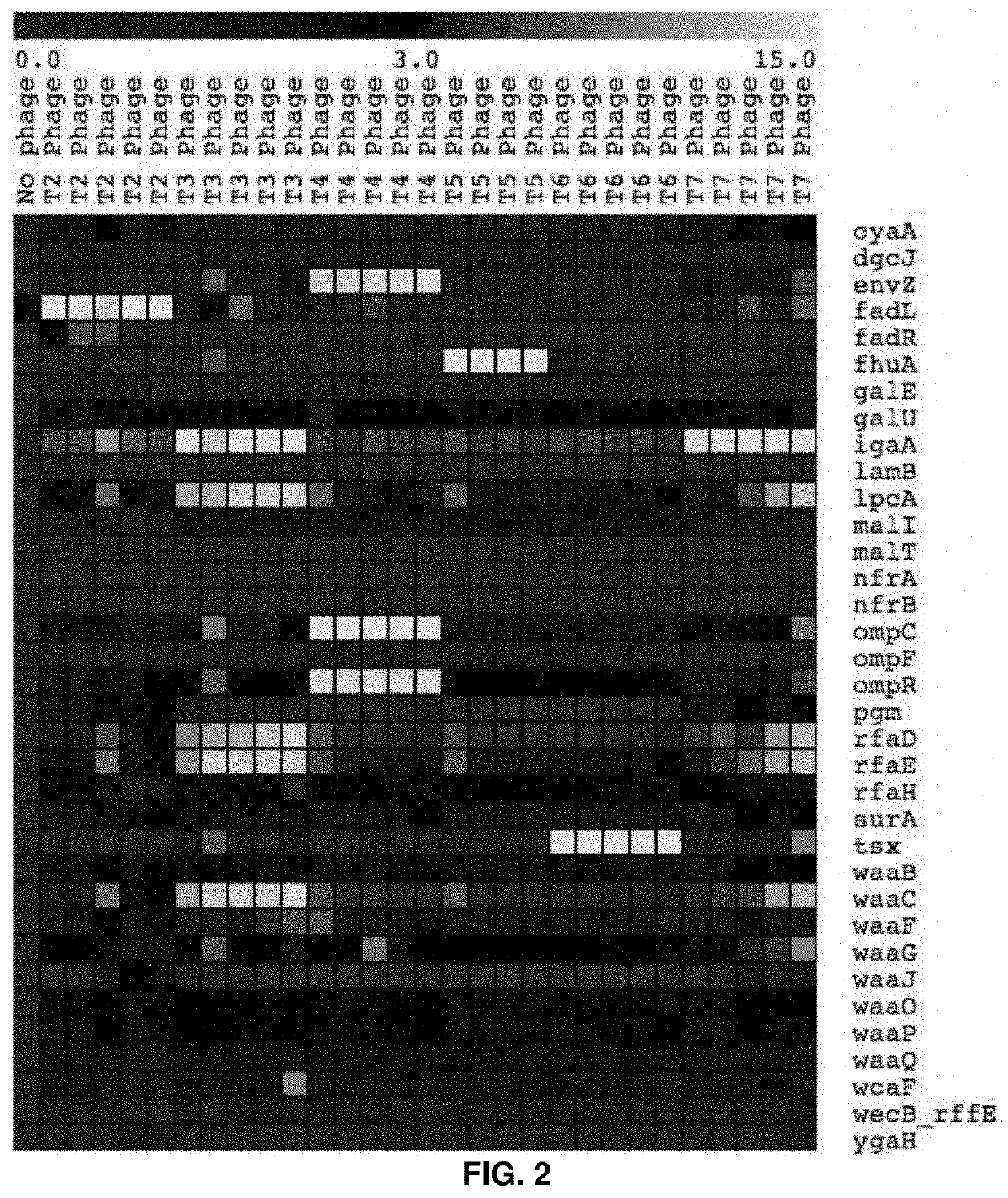
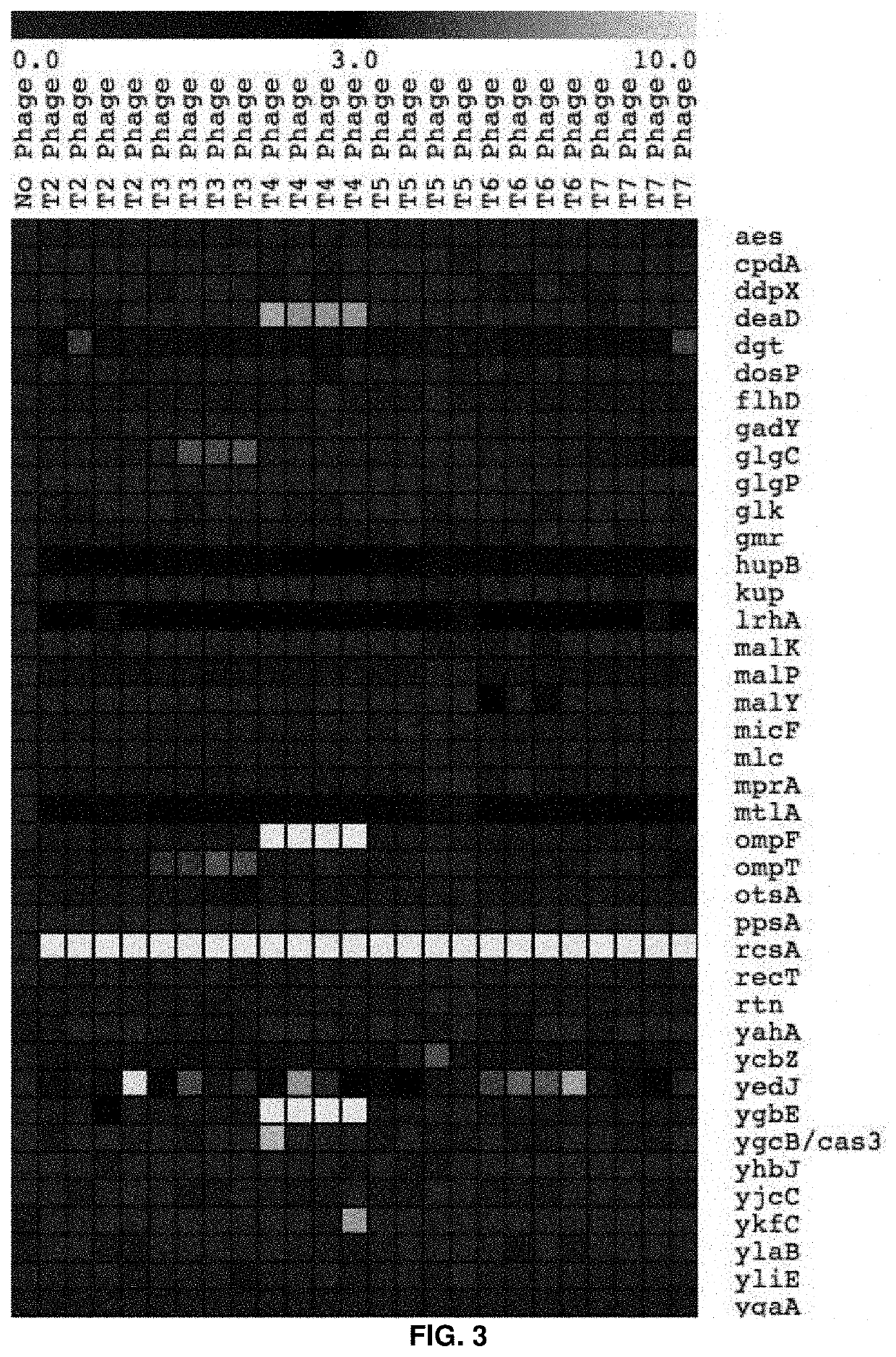
High-throughput methods to characterize phage receptors and rational formulation of phage cocktails
PendingUS20210403995A1Cost-effective and genome-wide assayMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism librariesPhage ReceptorsMutant phenotype
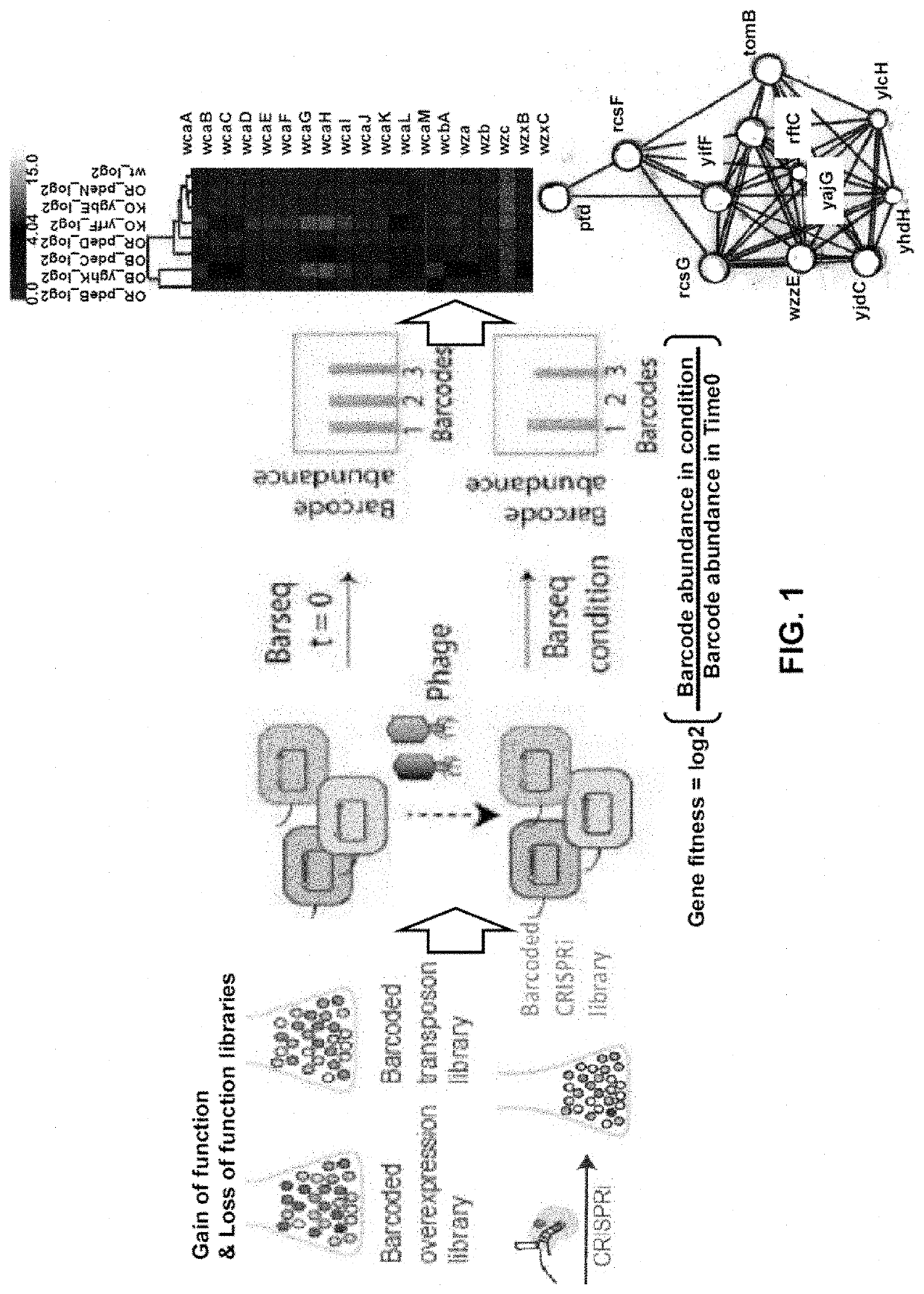
The present invention provides for a method for screening for gene function for a bacteriophage, the method comprising: (1) (a) providing one or more host organism, such as a species or strain, libraries, (b) providing randomly barcoded transposon sequencing (such as RB-TnSeq), and (c) screening for loss-of-function (LOF) mutant phenotypes; or (2) (a) providing one or more DNA barcoded overexpression strain libraries (such as Dub-seq) using DNA of the host organism and / or phage, and (b) screening for gain-of-function (GOF).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
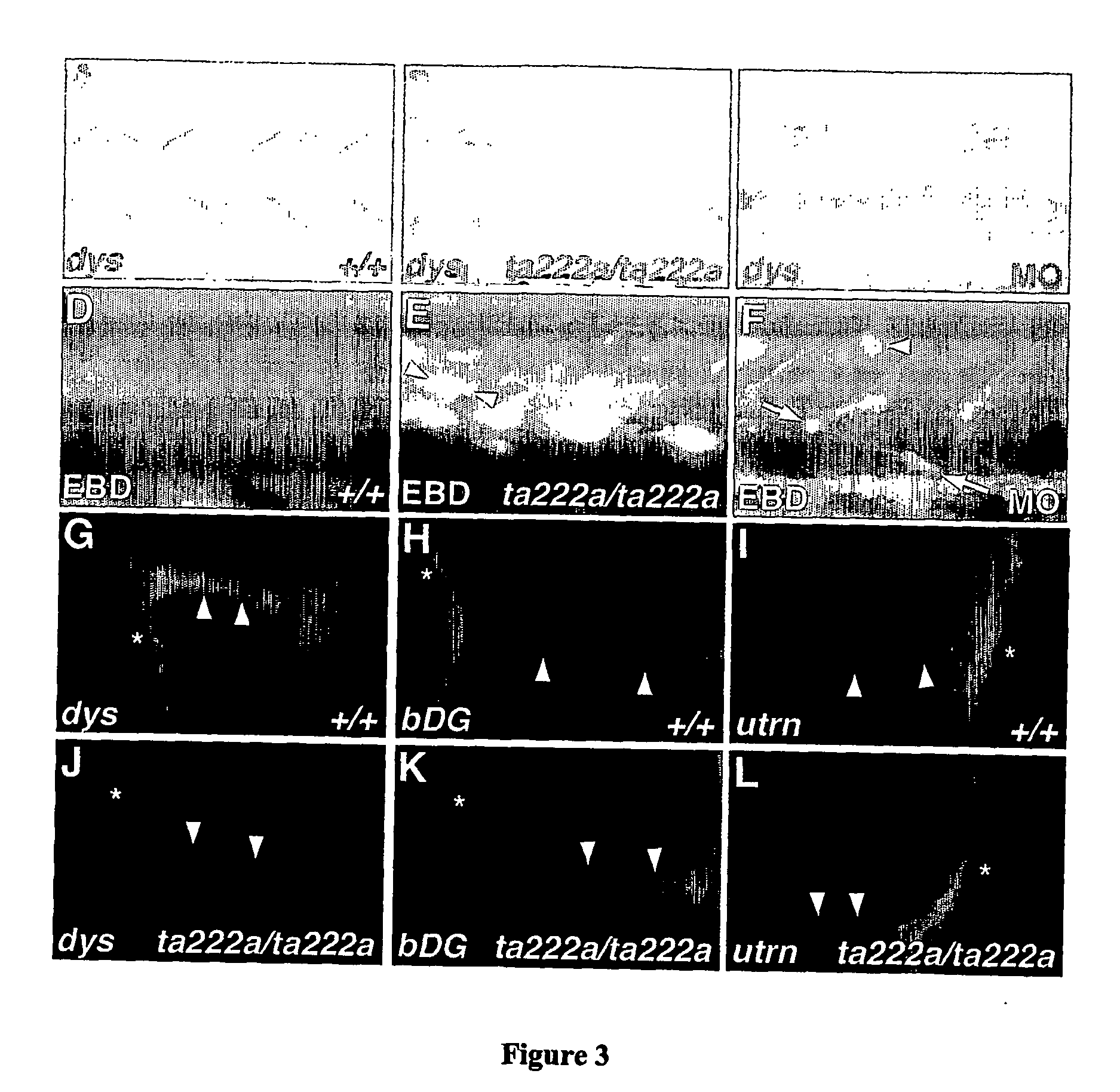
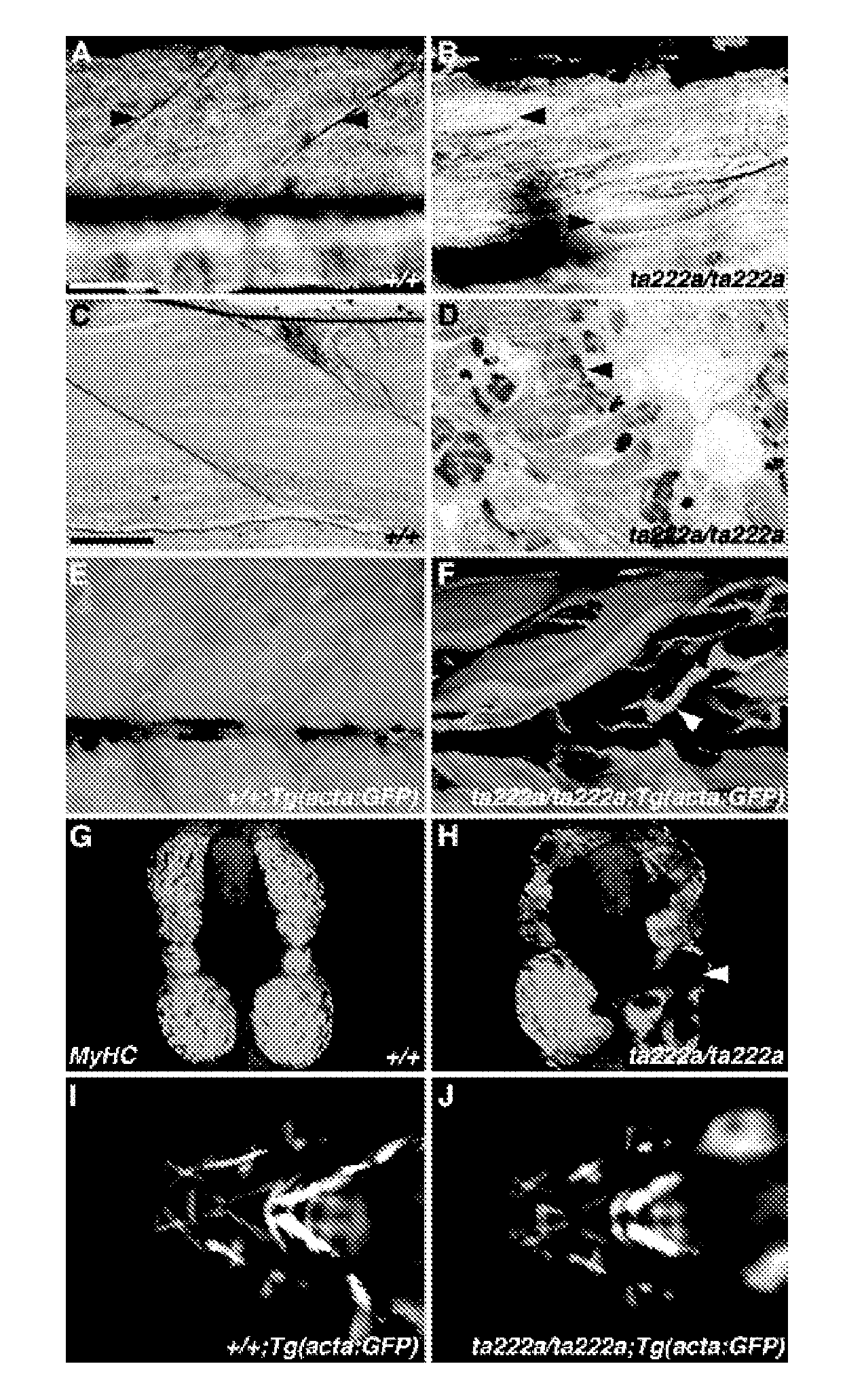
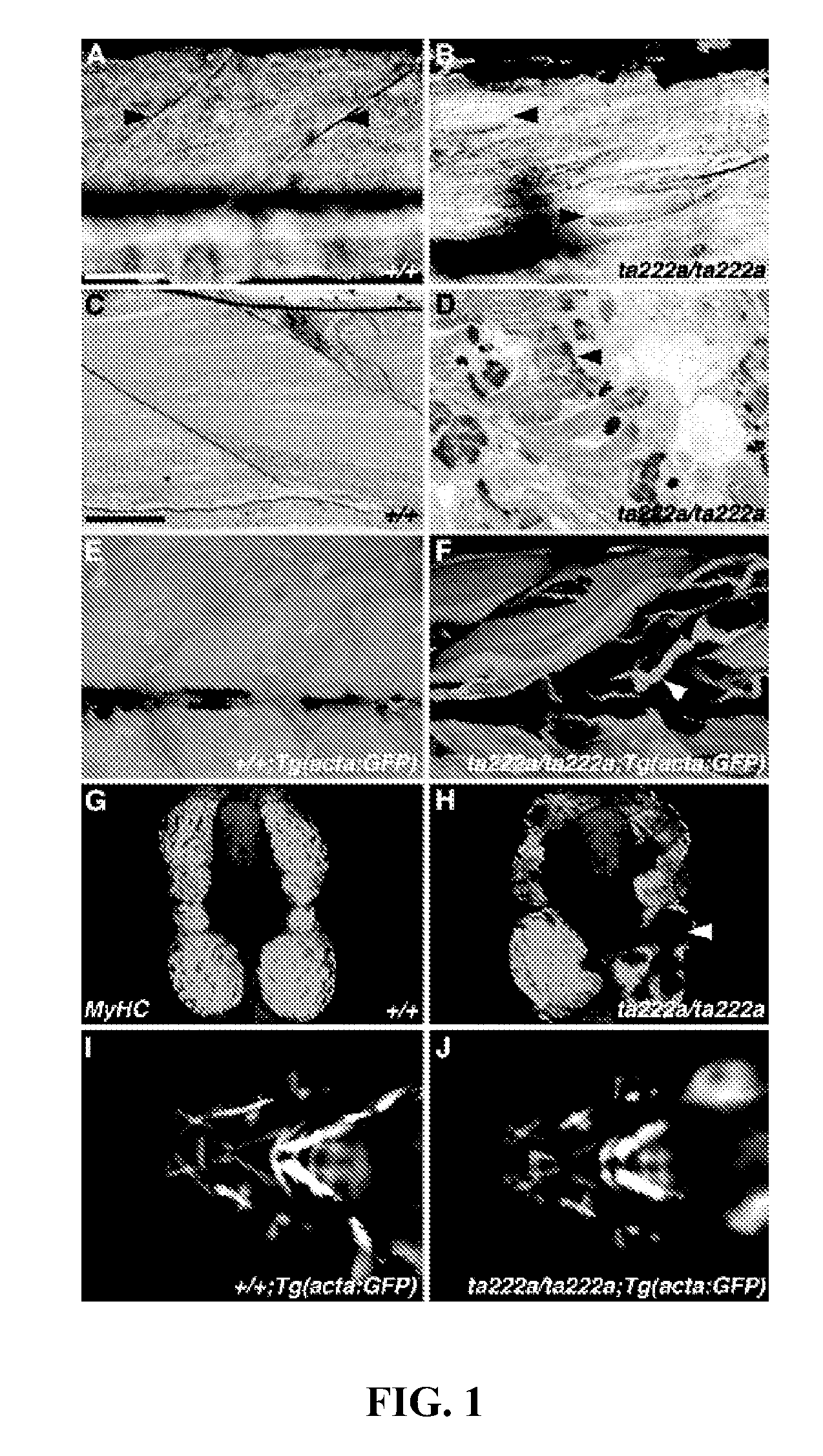
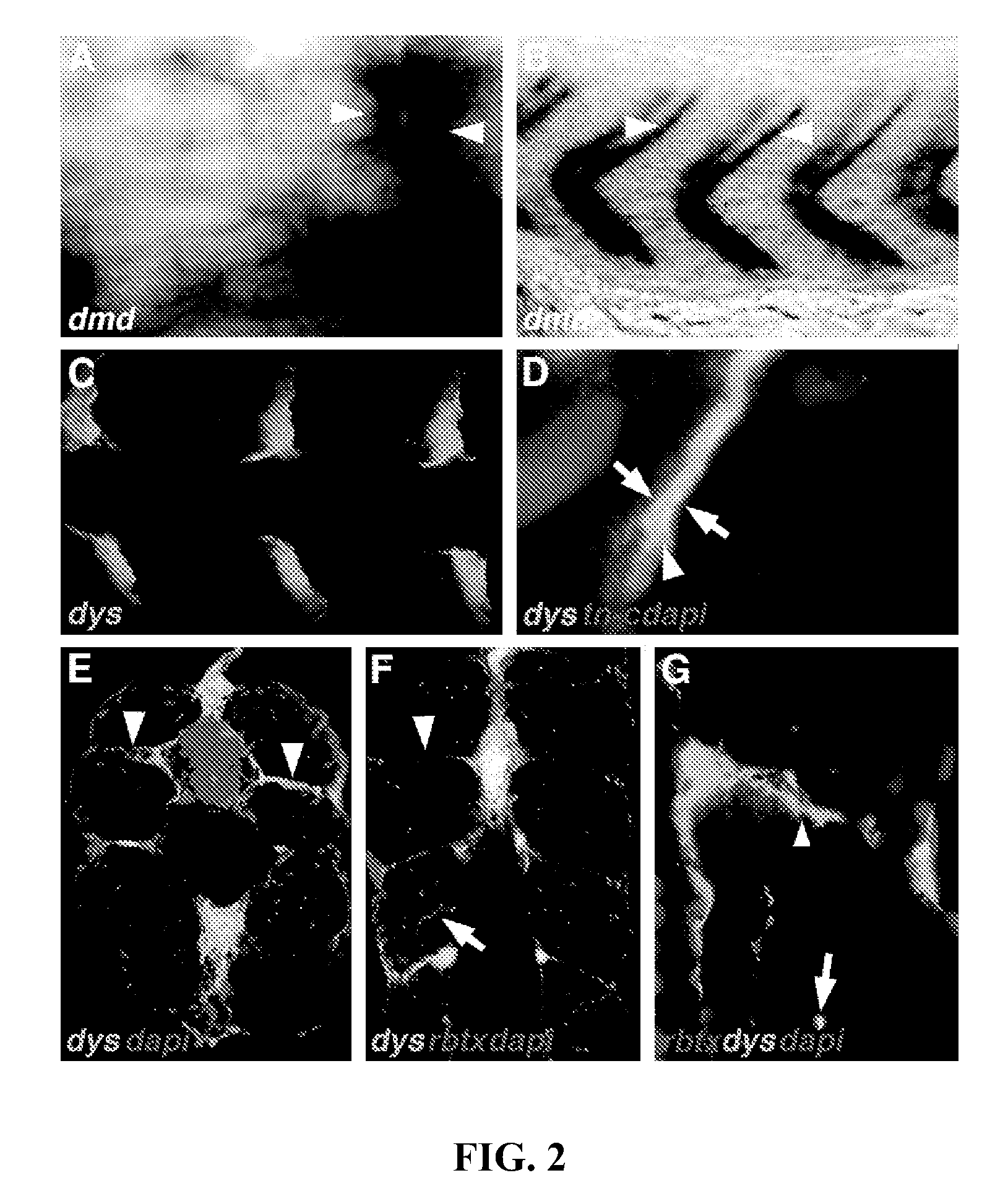
Model for muscular dystrophy and cardiomyopathy
InactiveUS20070056054A1Improve fertilityMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureDuchenne muscular dystrophyMuscular dystrophy
An isolated zebrafish genetic strain having a dystrophin mutant phenotype and fish models useful for screening or assaying agents having potential activity on muscular dystrophy or cardiomyopathy.
Owner:VICTOR CHANG CARIDAC RES INST LTD
Model for muscular dystrophy and cardiomyopathy
An isolated zebrafish genetic strain having a dystrophin mutant phenotype and fish models useful for screening or assaying agents having potential activity on muscular dystrophy or cardiomyopathy.
Owner:VICTOR CHANG CARIDAC RES INST LTD
Method of screening for agents inhibiting chloride intracellular channels
InactiveUS7125976B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCell phenotypeMutant phenotype
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
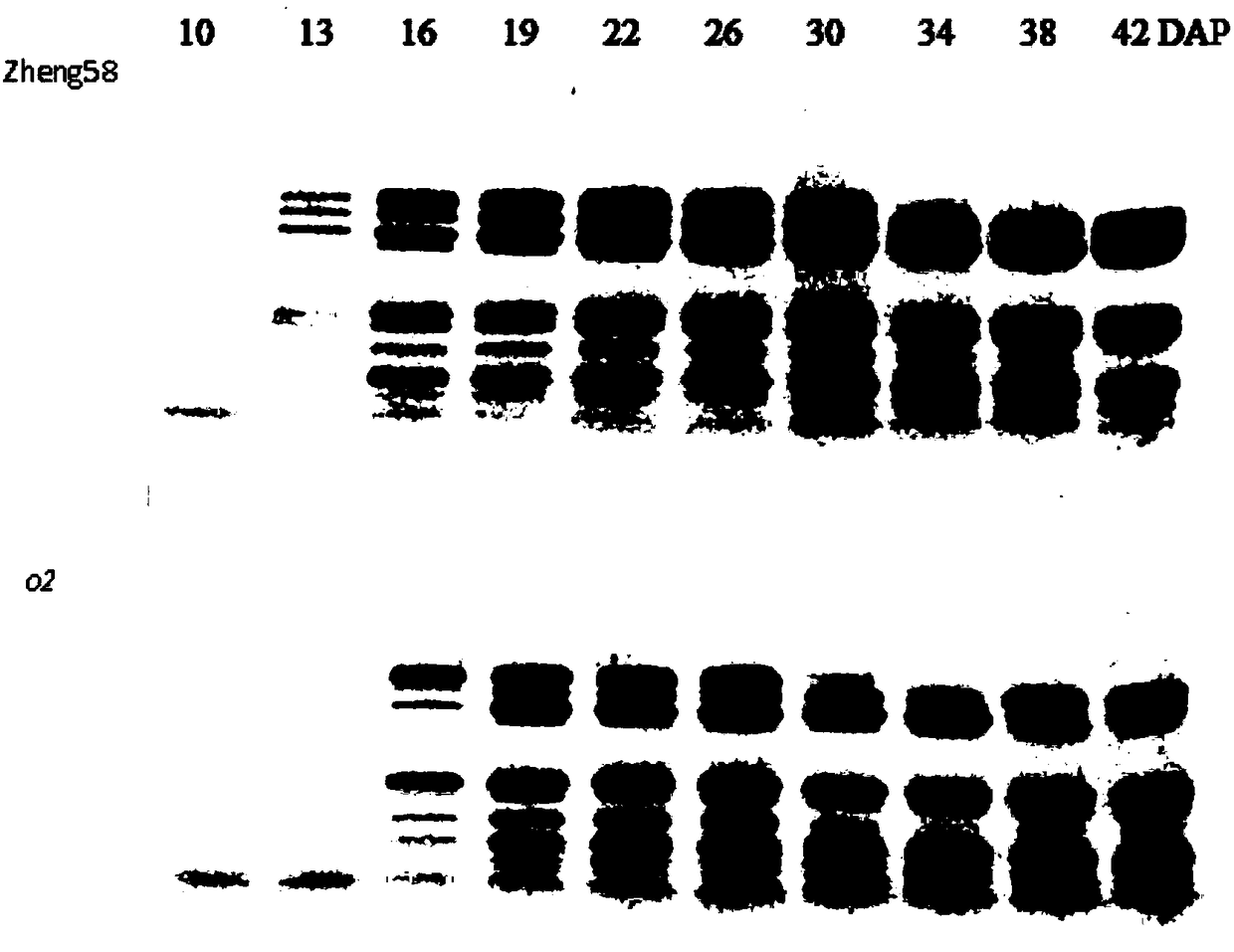
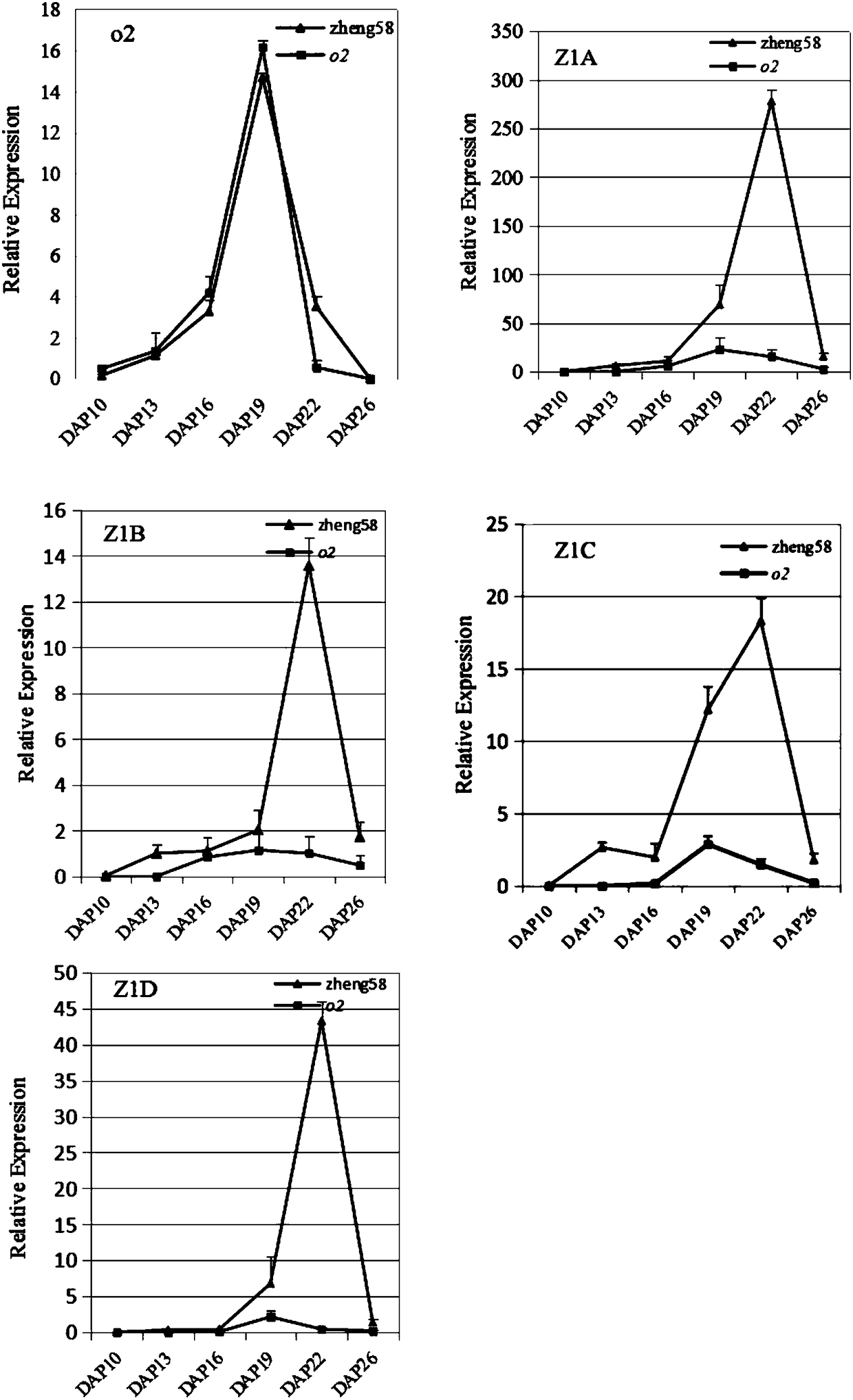
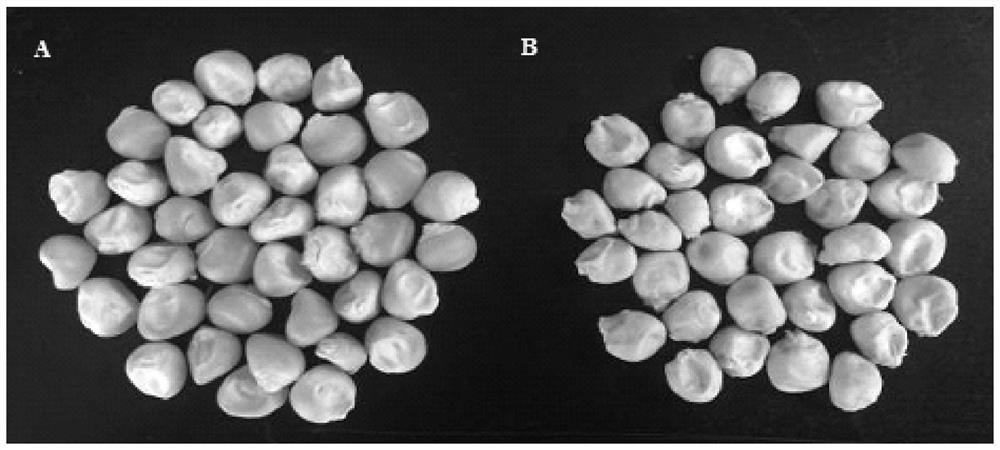
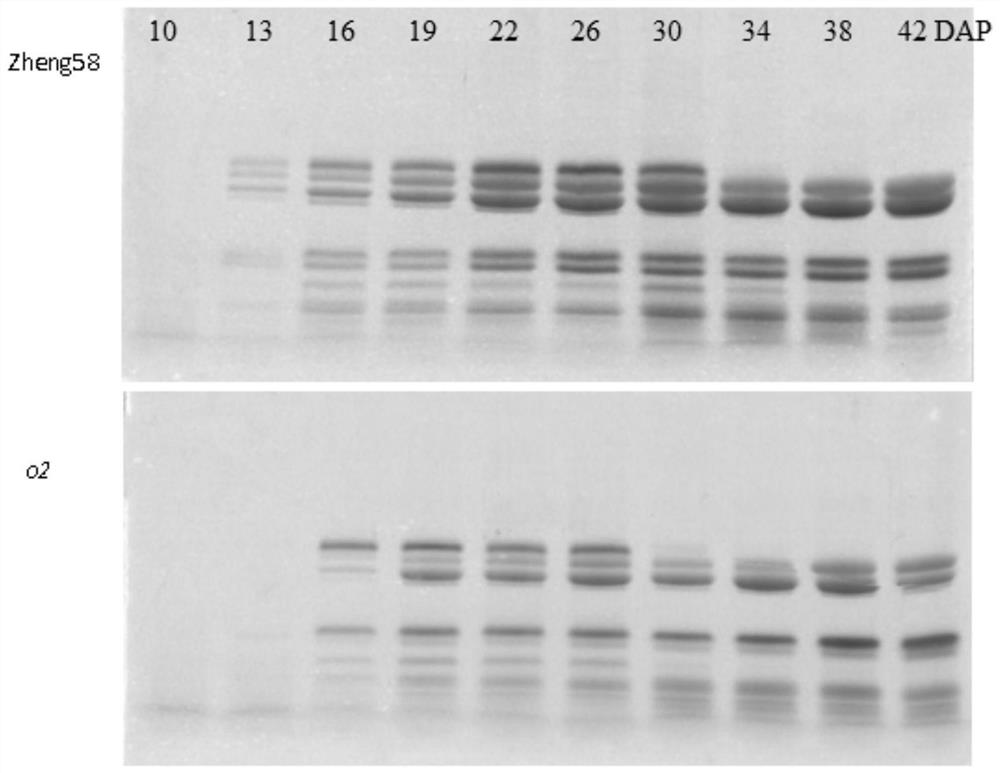
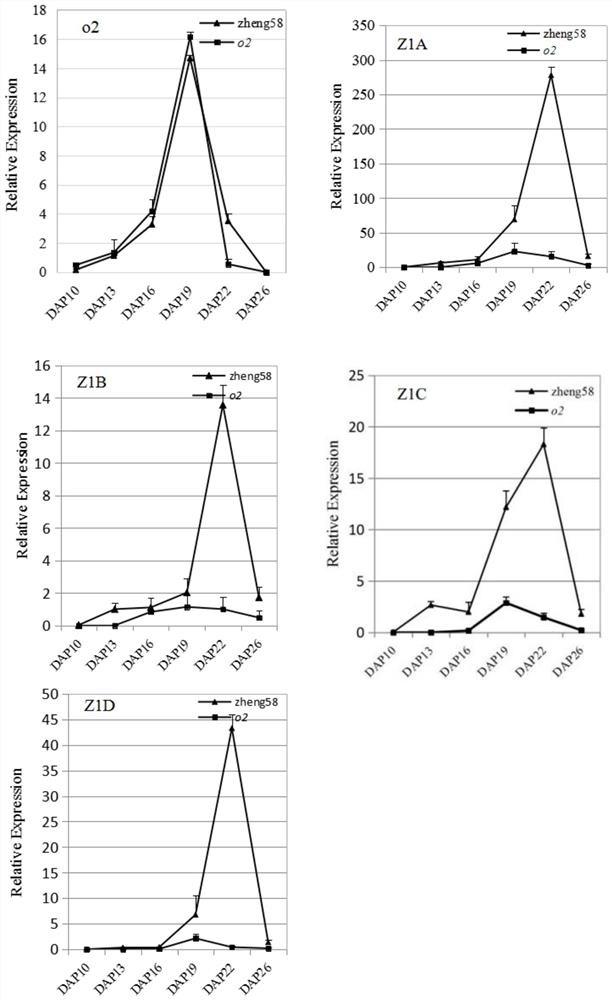
Opaque2 gene mutation site in Zheng 58/opaque2 near-isogenic line and application thereof
ActiveCN108559751AImprove breeding selection efficiencyHigh in lysineMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesSequence analysisMutant phenotype
The invention discloses an opaque2 gene mutation site in a Zheng 58 / opaque2 near-isogenic line and a high-performance molecular marker and application thereof. By virtue of sequencing analysis, ten basic groups are omitted at 713bp site after ATG of o2 gene in Zheng 58 / o2, and ORF predicts that O2 protein translation is terminated in advance. A co-dominance molecule marker o2-indel-1 in the gene is developed for the mutation omission site, the marker is used for backcross transformation, the result shows that o2-indel-1 and o2 mutant phenotype are completely linked, and an error rate is 0. Therefore, the parsing of the opaque2 gene mutation site facilitates the development of the high-performance molecular marker, and can improve the high-quality protein corn breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
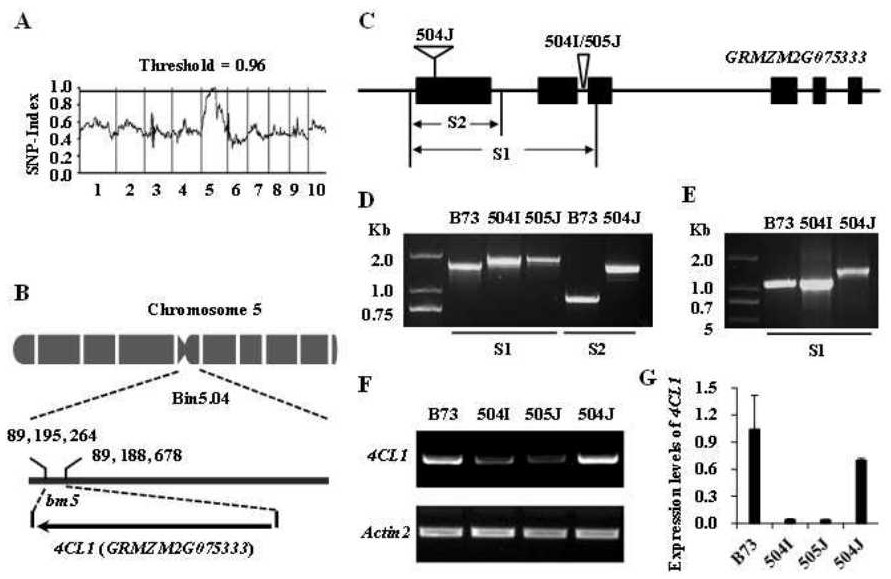
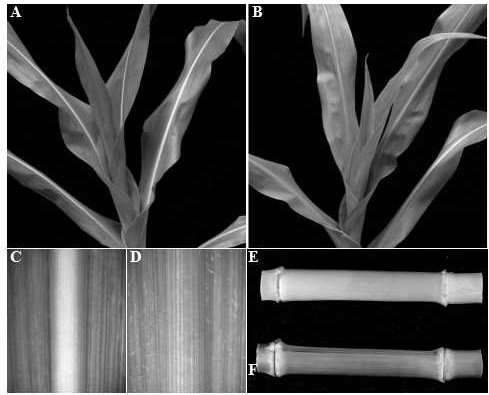
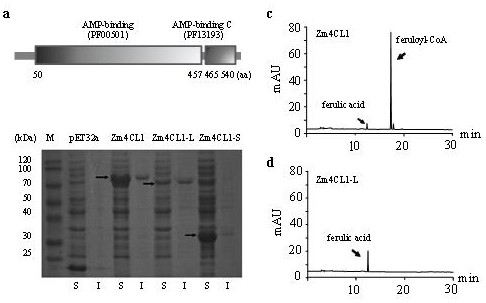
Mutant gene identification, variation and molecular markers of maize brown midrib5 (bm5) mutant
This application involves bm5 Identification of mutant genes associated with mutant phenotypes, variation and their molecular markers. It is specifically divided into the following four aspects: the content of the present invention focuses on specific naturally occurring mutants of maize bm5 , cloned its mutant gene BM5 , the gene causes the phenotype of lignin composition change in a specific maize line due to the insertion of transposons (Mu elements and Ac elements); the present invention provides a rapid detection method for the identification of the transposons; 4-coumaric acid : The enzyme activity level of coenzyme A ligase (Zm4CL1) directly affects the lignin composition and saccharification efficiency of maize; Zm4CL1 It can be used as one of the target genes for directional molecular genetic breeding of lignin, providing new targets for molecular breeding in the future, and providing practical guidance for directional molecular genetic breeding.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Pathogenic related protein VdGRP1 from verticillium dahliae kleb and coded gene thereof
ActiveCN102212121BReduce pathogenicityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesMutant phenotypeBacilli
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mutation site of opaque2 gene in Zheng 58/opaque2 near-isogenic line and its application
ActiveCN108559751BImprove breeding selection efficiencyHigh in lysineMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesSequence analysisBase J
The present invention discloses the opaque2 gene mutation site in Zheng 58 / opaque2 near-isogenic line and its high-efficiency molecular marker and application. The sequencing analysis of this application found that 10 bases were missing at 713bp after the ATG of the o2 gene in Zheng 58 / o2, and ORF prediction O2 protein translation is prematurely terminated. The intragenic co-dominant molecular marker o2-indel-1 was developed for the mutation deletion site, and the marker was used for backcross breeding. The results showed that o2-indel-1 was completely linked to the o2 mutant phenotype, and the misselection rate was 0. Therefore, the analysis of the mutation site of opaque2 gene is helpful for the development of high-efficiency molecular markers and improves the selection efficiency of high-quality protein maize breeding.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DWF12 and mutants thereof
InactiveUS7304205B2Reduced and increased SHAGGY kinase activityReduced activityClimate change adaptationTransferasesMutant phenotypePolynucleotide
DWARF12(DWF12) sequences, mutants and methods of using the same are disclosed. The dwf12 polynucleotides can be used in the production of transgenic plants which display at least one dwf12 mutant phenotype, so that the resulting plants have altered biochemistry, structure or morphology.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
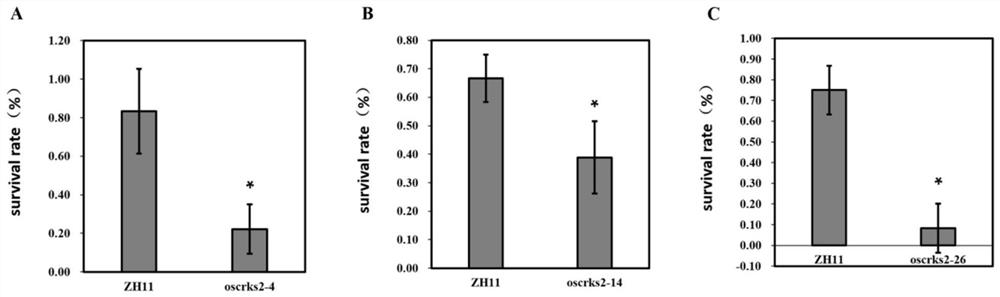
Application of OsCRKS2 gene in controlling drought resistance of rice
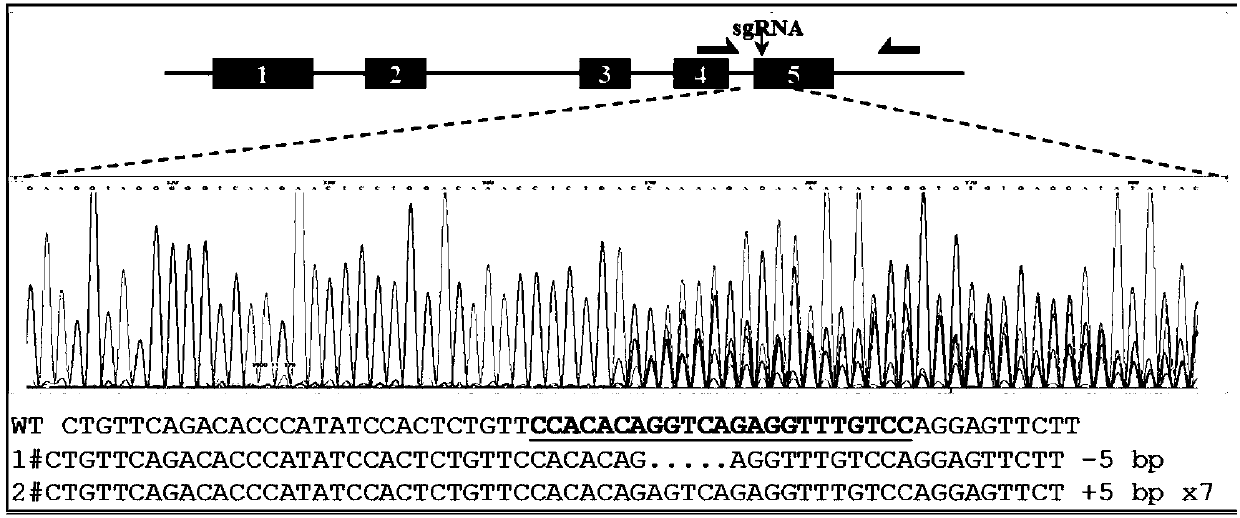
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The invention particularly relates to application of the OsCRKS2 gene in controlling the drought resistance of rice. According to the invention, the OsCRKS2 gene capable of improving the drought tolerance of rice is obtained through separation, cloning and functional verification. The nucleotide sequence of the OsCRKS2 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the sequence of protein coded by the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The rice drought response control gene OsCRKS2 is cloned, CRISPR mutant phenotype identification is carried out on candidate genes, drought stress phenotype identification in the seedling stage and the adult-plant stage shows that when a gene segment is deleted, the drought stress resistance of rice is reduced, and the function and the application way of the gene are proved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Use of histone acetylation enzyme gene OsELP3 in rice anthesis regulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a rice histone acetyltransferase gene, encoding protein functions and applications thereof. The invention discloses the rice histone acetyltransferase gene OsELP3, which is related to plant florescence. Under long-day sunlight, overexpression of the gene can bring rice blooming forward, and inhibition of the gene expression can delay rice blooming. After being processed under short-day sunlight, mutant phenotype of an inhibiting material is recovered to be wild. Analysis discovers that the OsELP3 gene can influence the expression levels of three blooming genes Hd3a, Hd1 and OsGI, and take rhythmic variation of self expression under short-day sunlight. The Western Blot experiment analysisshows that the gene has the histone acetylation function and the functionary locus on H3K9.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
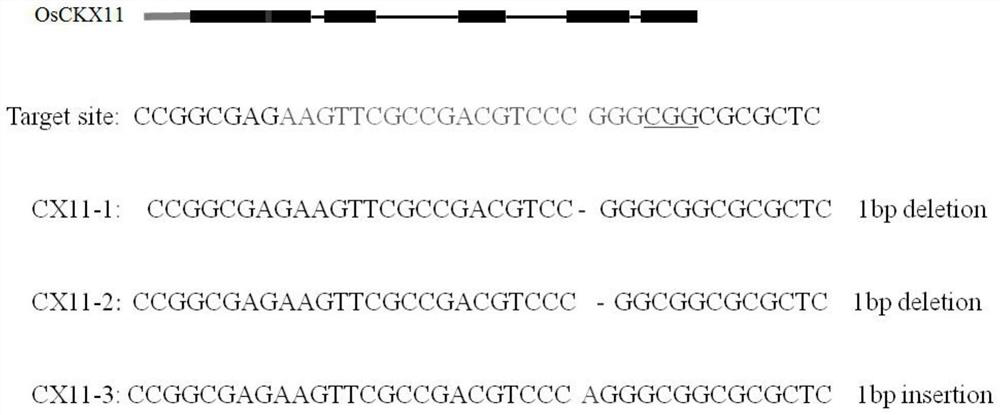
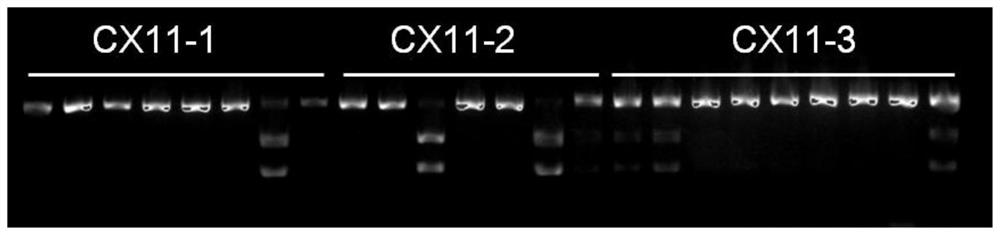
A kind of rice senescence control gene osckx11 and its application
ActiveCN109402078BRegulates the aging processAdjust development periodBacteriaOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyPremature aging
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and discloses a rice leaf senescence control gene OsCKX11 and its application. The amino acid sequence of the rice leaf senescence control gene OsCKX11 has at least 70% homology with the amino acid sequence shown in the amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.1 sex. The present invention conducts site-directed mutation of rice cytokinin oxidase coding gene OsCKX11, analyzes the phenotypic changes of its mutants, and finds that the lack of function of this gene will cause late senescence of rice leaves; in some premature senescence cultivars, OsCKX11 is knocked out by genetic engineering technology It can purposely regulate the aging process of plants and adjust the development period of plant populations to achieve the purpose of increasing production, which has very important application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com