Escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutation prediction method based on naive Bayes model
A Bayesian model, E. coli technology, used in prediction, genomics, instrumentation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0037] A method for predicting Escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutations based on naive Bayesian model, comprising the following steps:
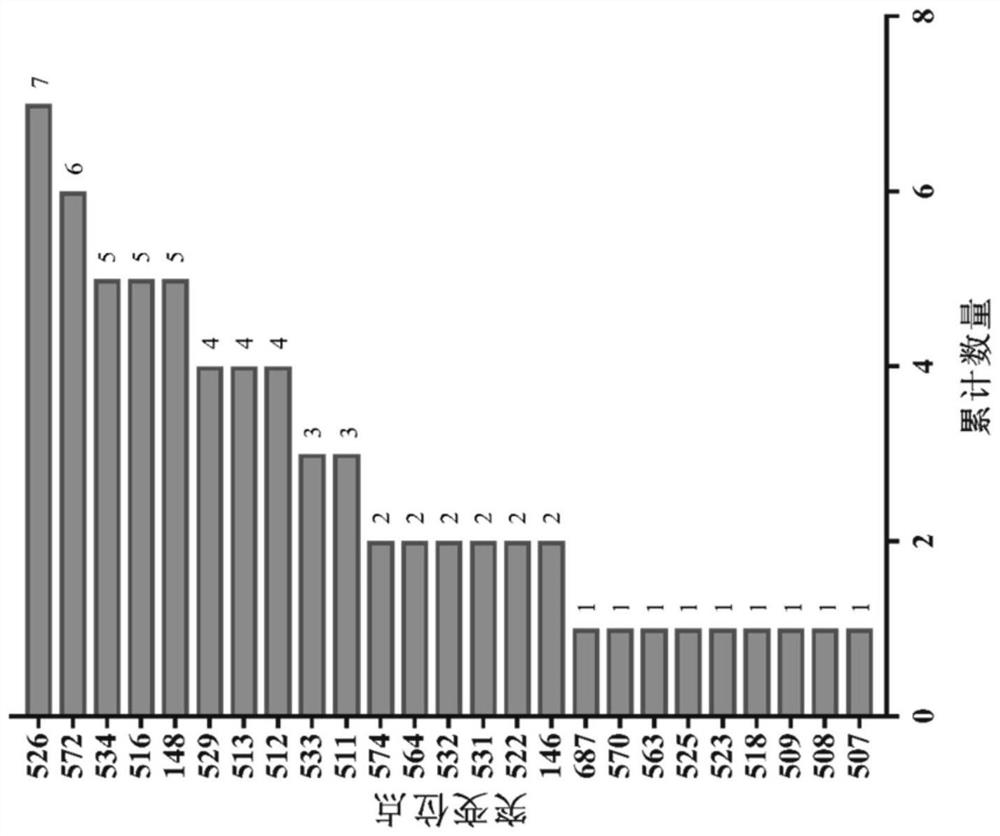
[0038] (1) Collect literature (Garibyan, L., Use of the rpoB gene to determine the specificity of base substitution mutations on the Escherichia colichromosome. DNA Repair, 2003.2(5): p.593-608.) Reports that can cause rifampicin Amino acid mutation sites and mutations in Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit (RpoB) of resistance results (positive mutations); figure 1 It is the statistical result of the mutation times of each amino acid in the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase β subunit in the above-mentioned literature; Table 1 is the mutation site and result of each amino acid of RpoB in the above-mentioned literature (67 kinds in total):
[0039] Table 1: Mutation sites and results of each amino acid of RpoB in the literature
[0040]
[0041] Table 2
[0042]
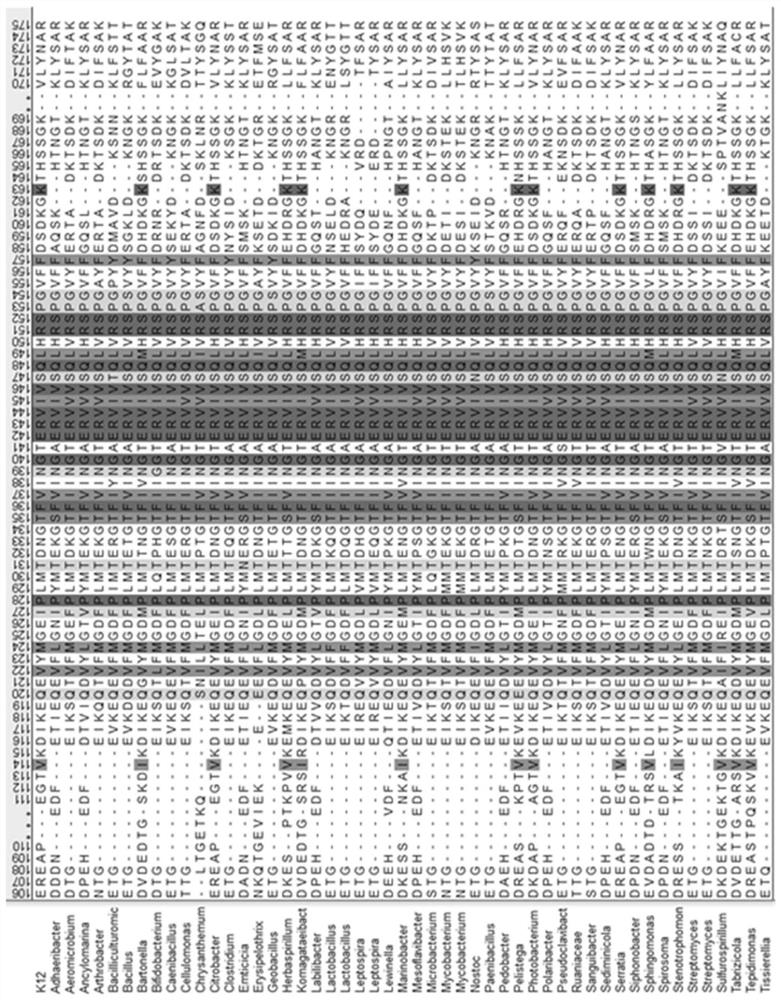
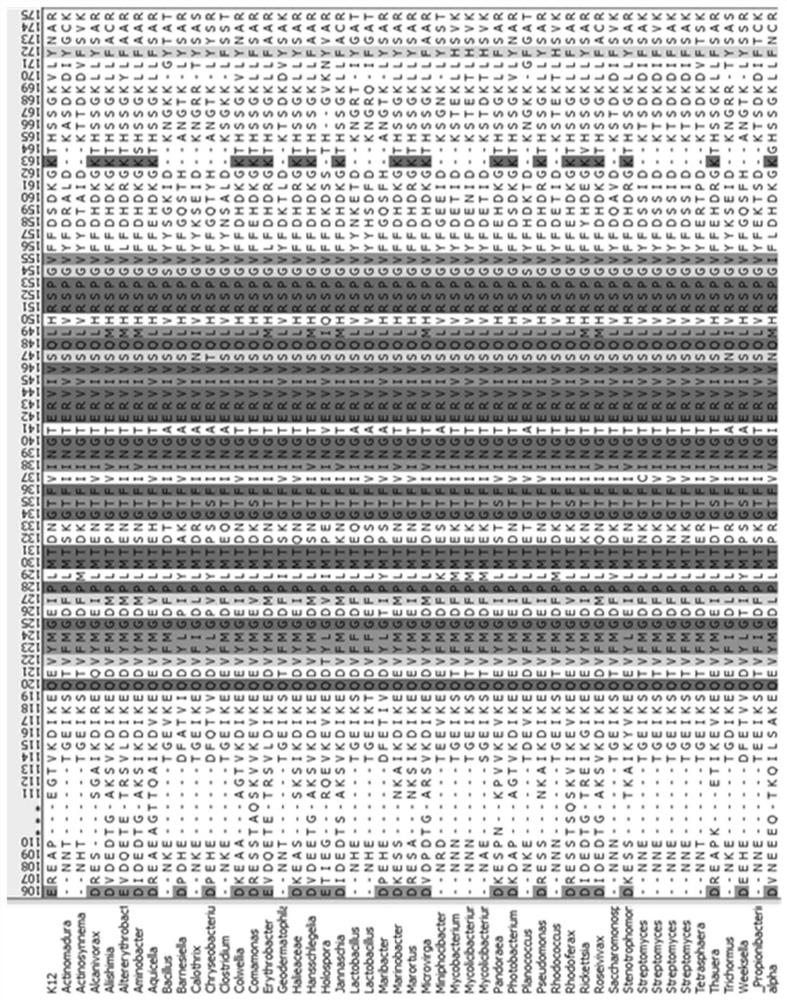
[0043] (2) On the NCBI website, search for Protein with R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com