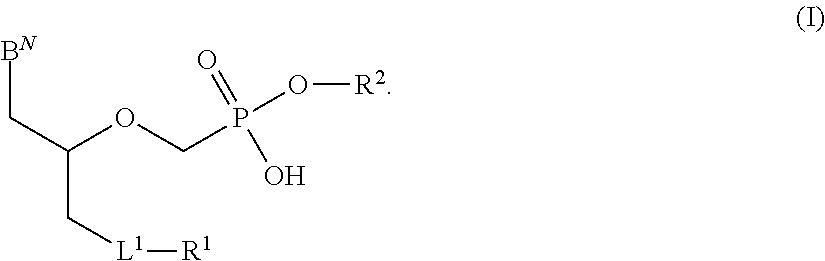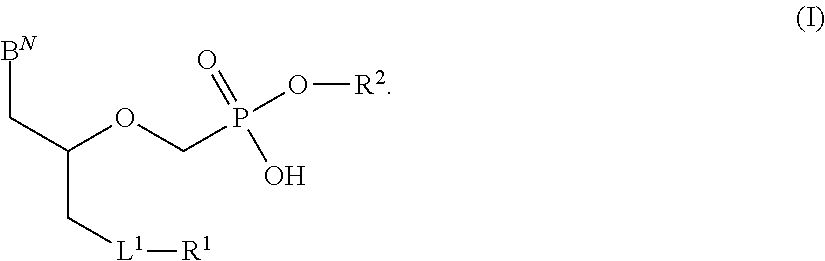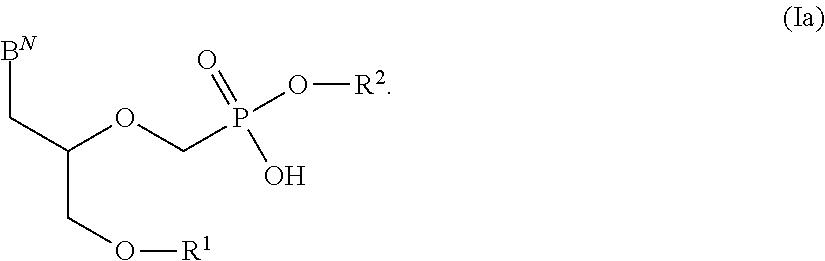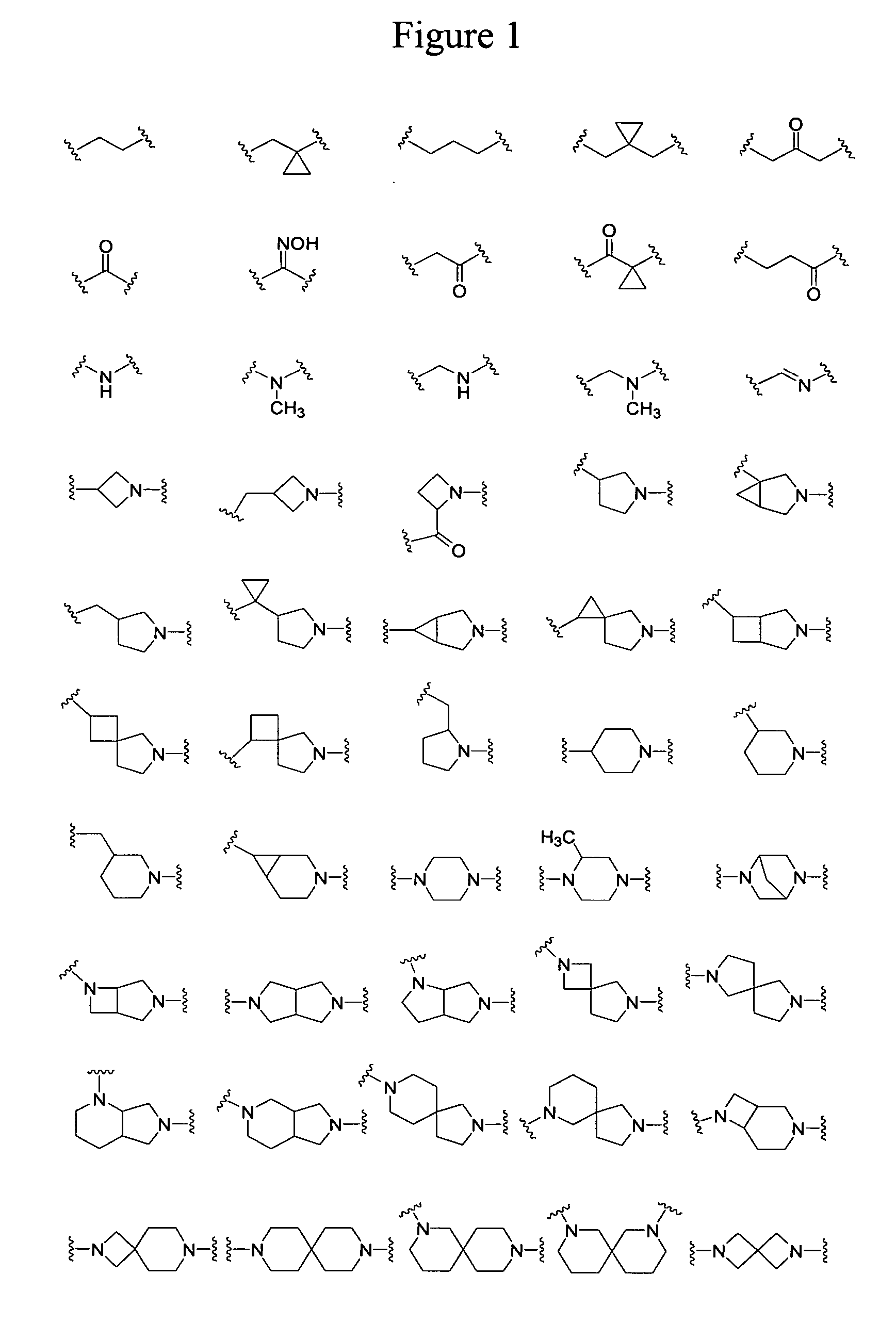Patents
Literature
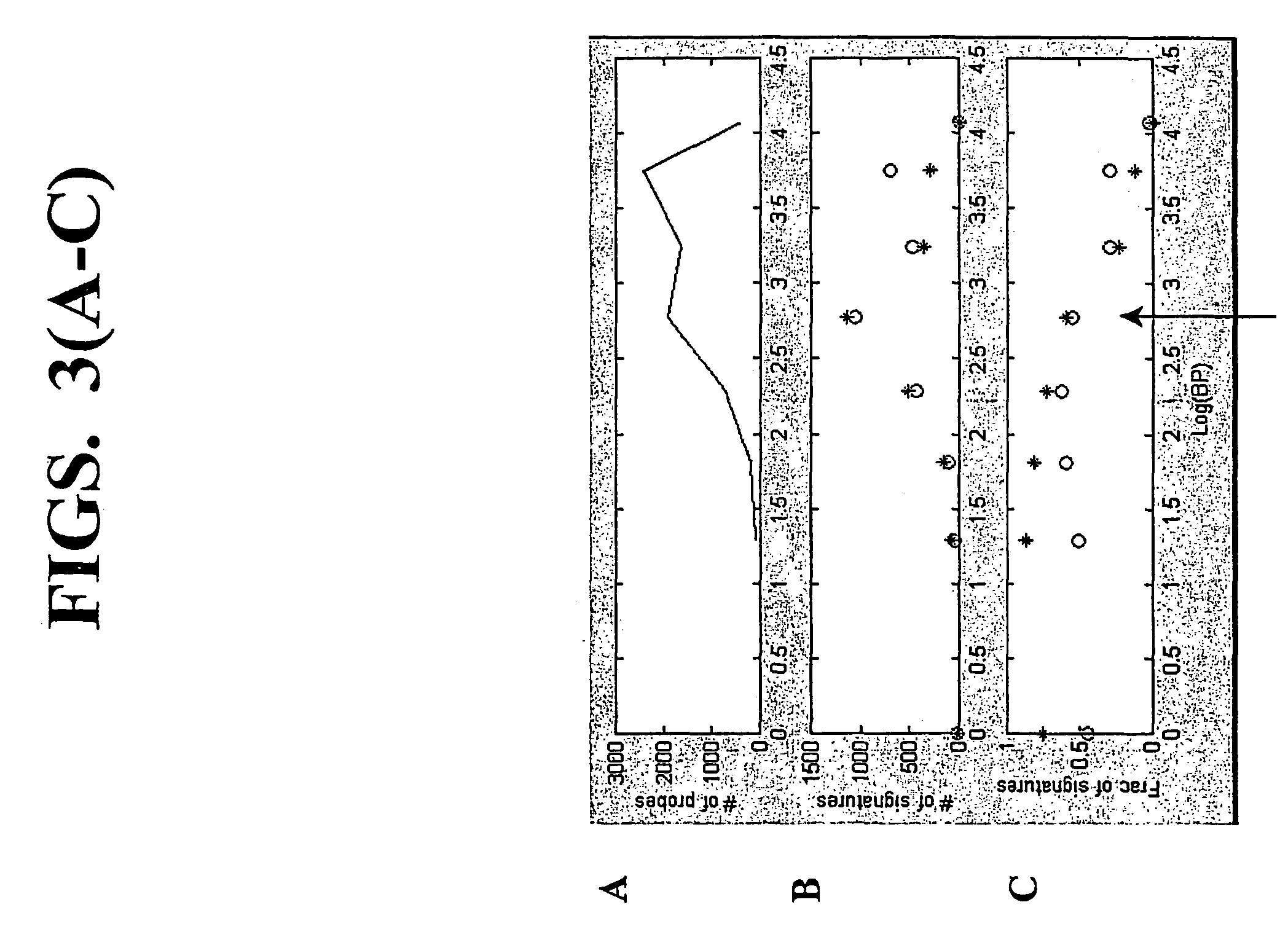
410 results about "RNA polymerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
RNA polymerase (ribonucleic acid polymerase), abbreviated RNAP or RNApol, officially DNA-directed RNA polymerase, is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA (usually about four turns of the double helix) so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides.
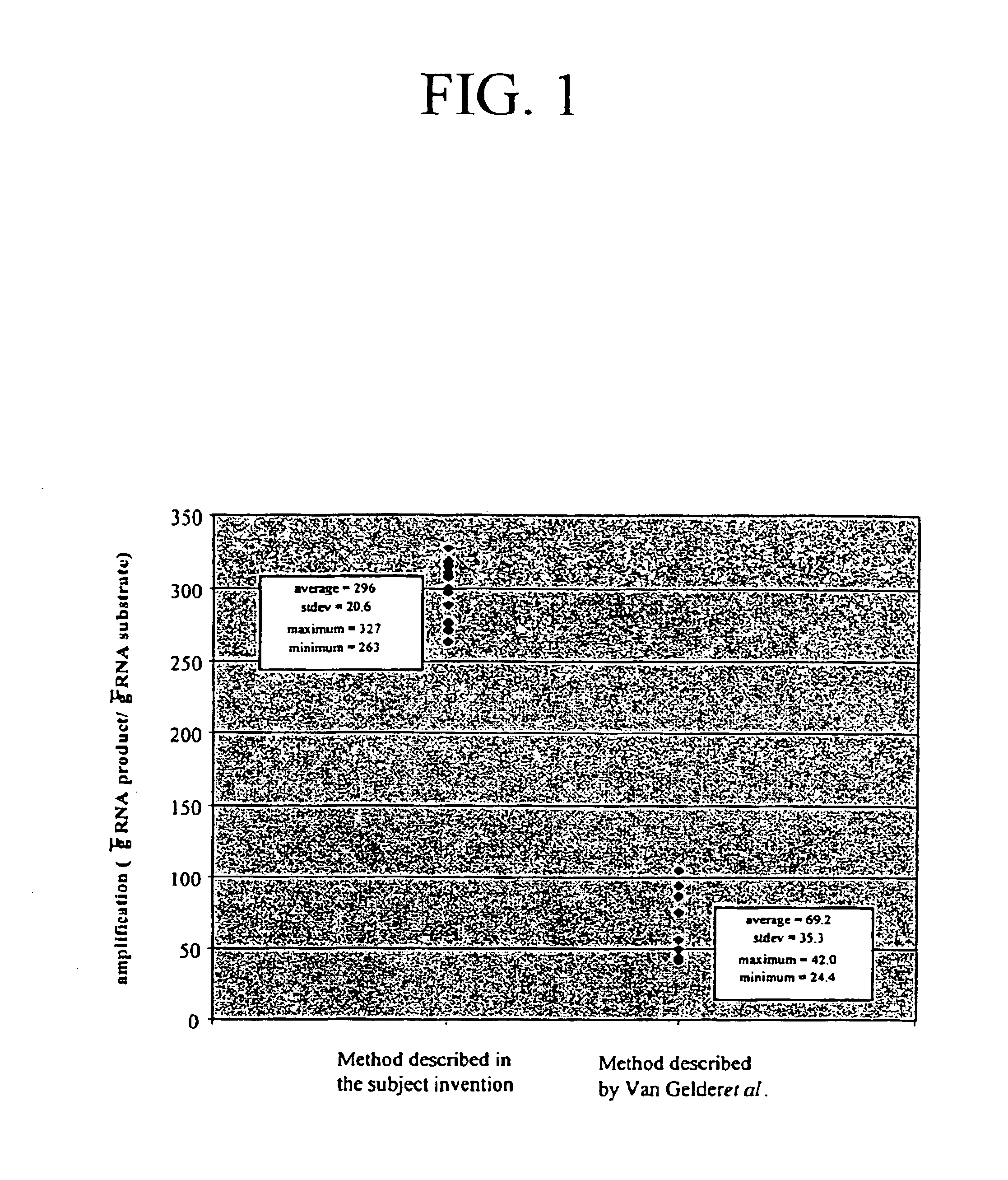
Method for linear mRNA amplification
InactiveUS6132997ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAReverse transcriptase
Methods for linearly amplifying mRNA to produce antisense RNA are provided. In the subject methods, mRNA is converted to double-stranded cDNA using a promoter-primer having a poly-dT primer site linked to a promoter sequence so that the resulting double-stranded cDNA is recognized by an RNA polymerase. The resultant double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into antisense RNA in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods find use a variety of different applications in which the preparation of linearly amplified amounts of antisense RNA is desired. Also provided are kits for practicing the subject methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection
InactiveUS7879815B2Effective penetrationLess susceptibleBiocideSugar derivativesHepatitis c viralPhosphoramidate
Owner:MSD ITAL +1
Pyrazolopyrimidines as protein kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of protein and / or checkpoint kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations including one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the protein or checkpoint kinases using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also relates to the inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication. In particular, embodiments of the invention provide compounds and methods for inhibiting HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzymatic activity. The invention also provides compositions and methods for the prophylaxis and treatment of HCV infection.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Isothermal DNA amplification
InactiveUS7579153B2Minimizes amplification biasThe process is fast and accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReverse transcriptaseNucleotide
The present invention provides for amplification of one or more polynucleotides by multi-staged linear amplifications using one or more RNA polymerases. At each stage RNA transcripts are accumulated at a linear rate, so that multiple stages provide for faster than linear transcript accumulation. In one aspect, the invention provides for polynucleotide amplification by ligating hairpin adaptors to an end of polynucleotides wherein the hairpin adaptors each contain a promoter sequence oriented so that transcription proceeds in the direction of the loop of the hairpin adaptor. Upon transcription through such loop region and to the complementary strand a replicate is made of the promoter sequence as well as the polynucleotide, thereby permitting exponential amplification upon reverse transcription, second strand synthesis, and repetition of the above cycle. Preferably such amplification is carried out under isothermal reaction conditions.
Owner:POPULATION GENETICS TECH
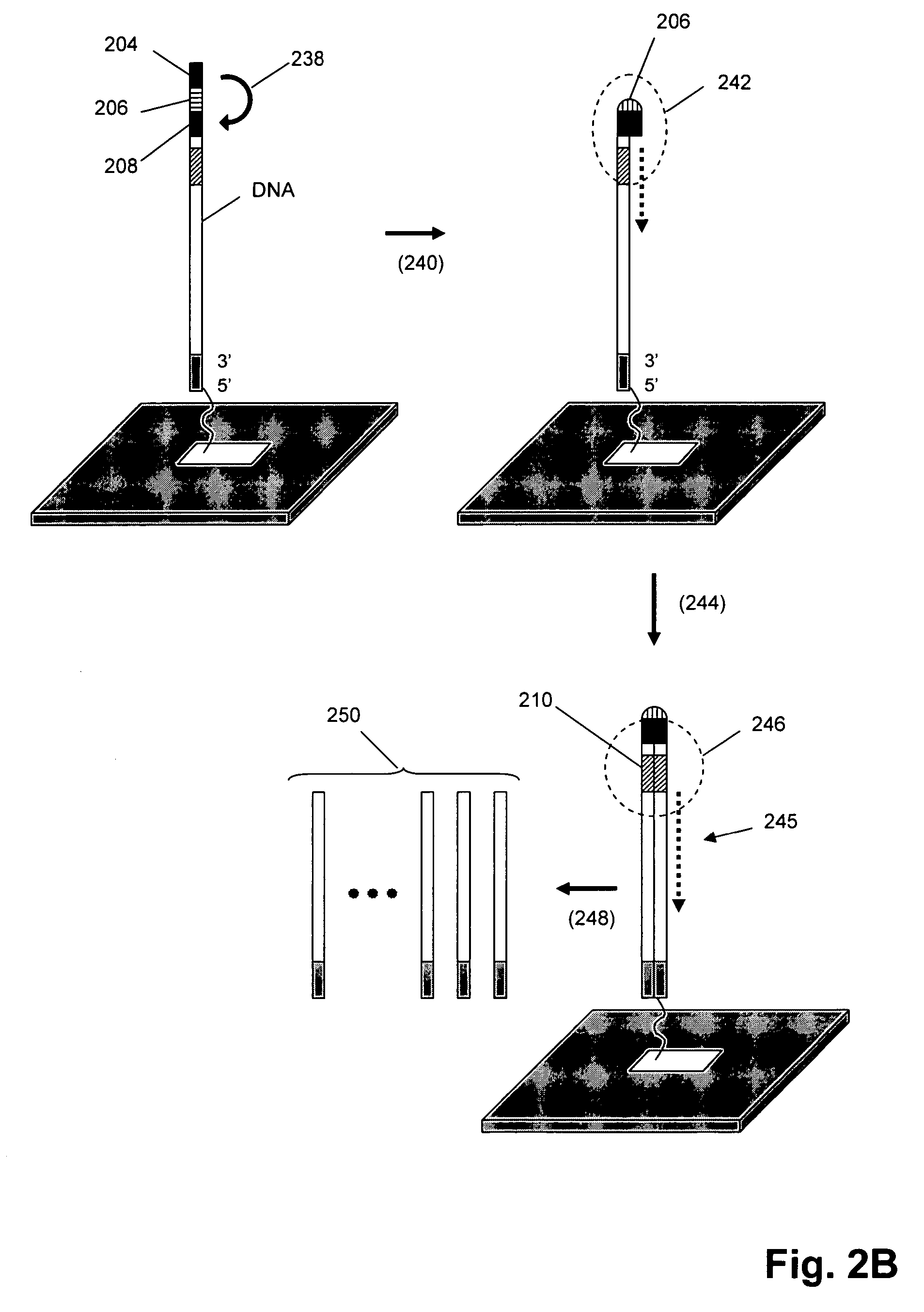
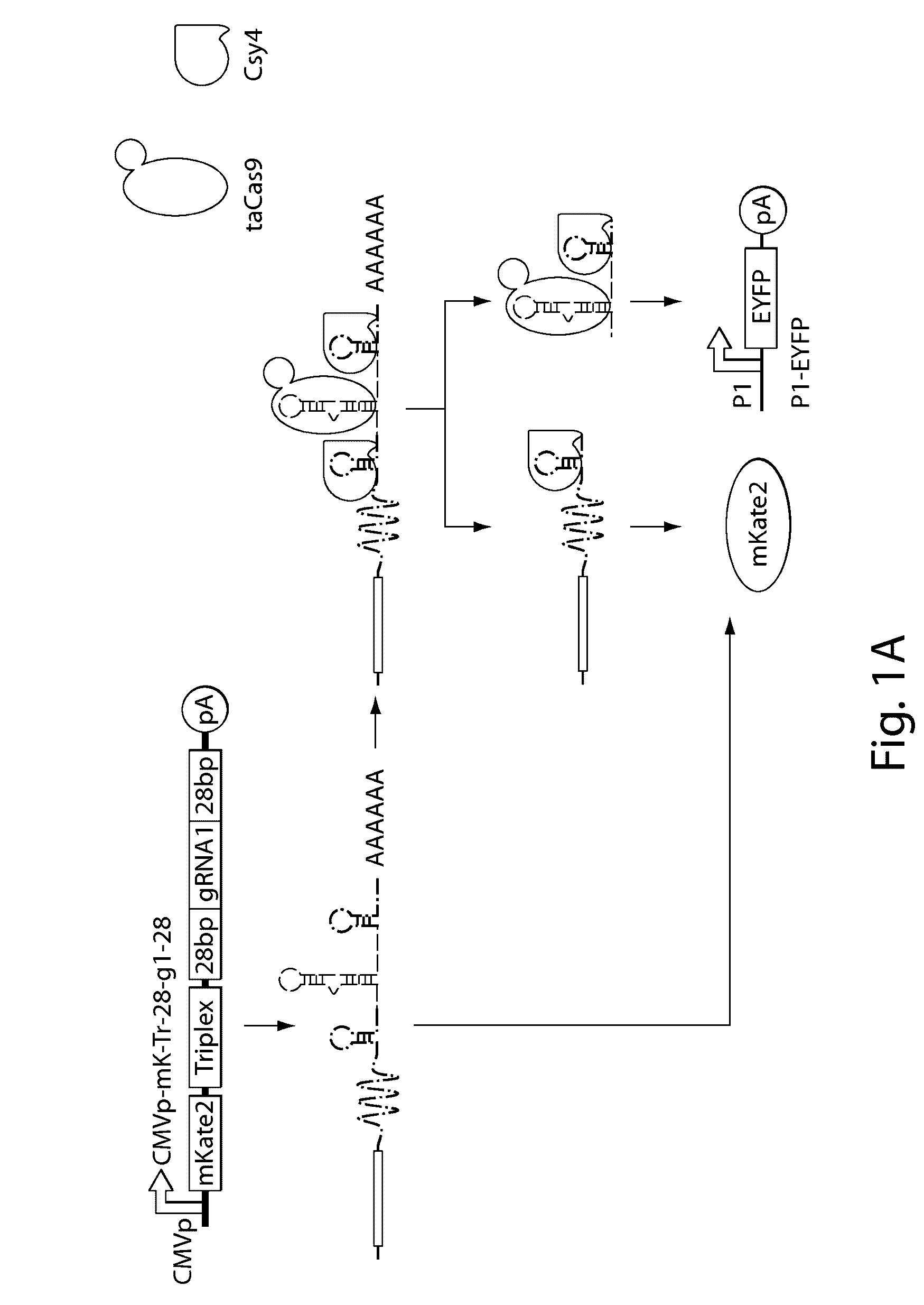
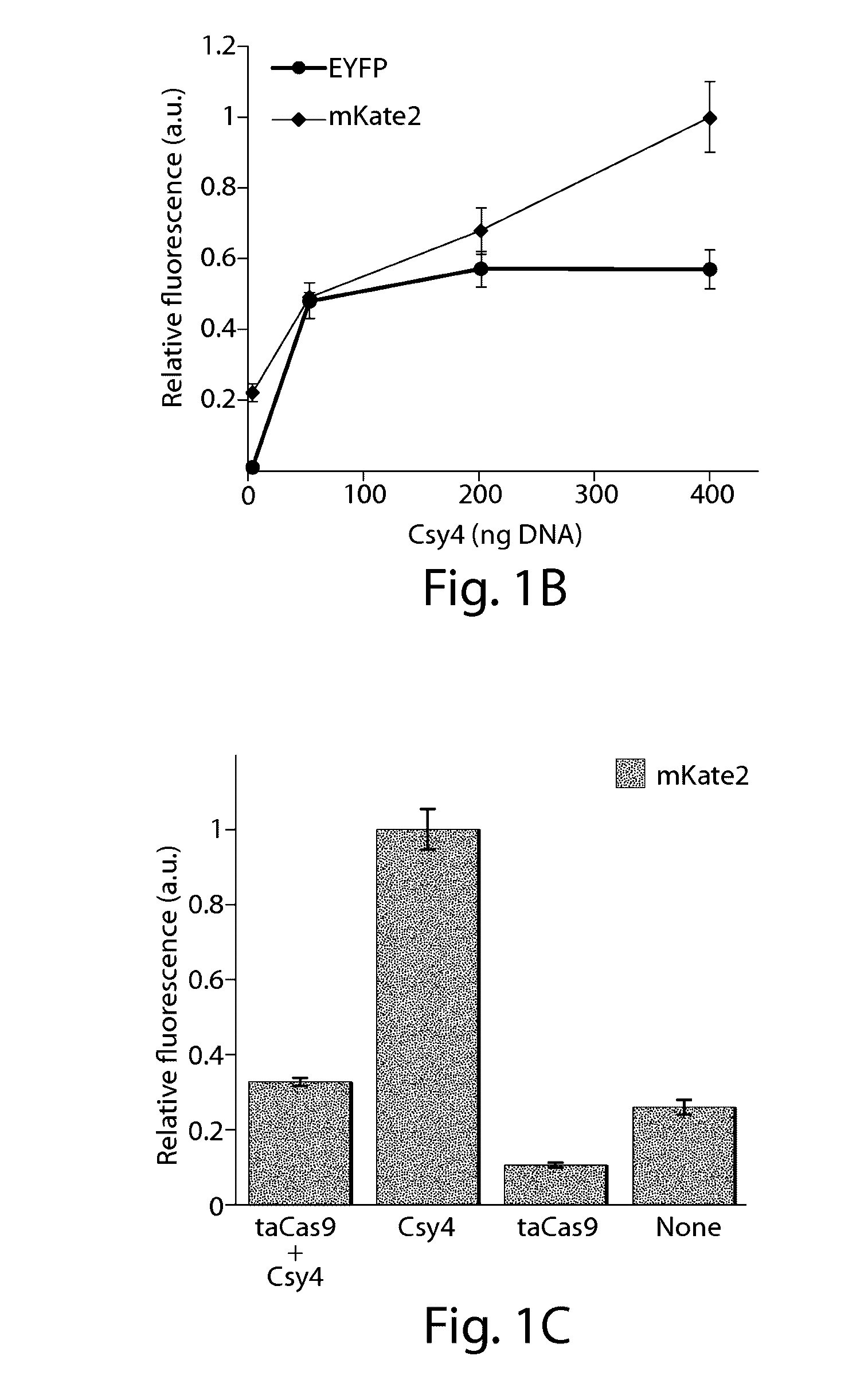
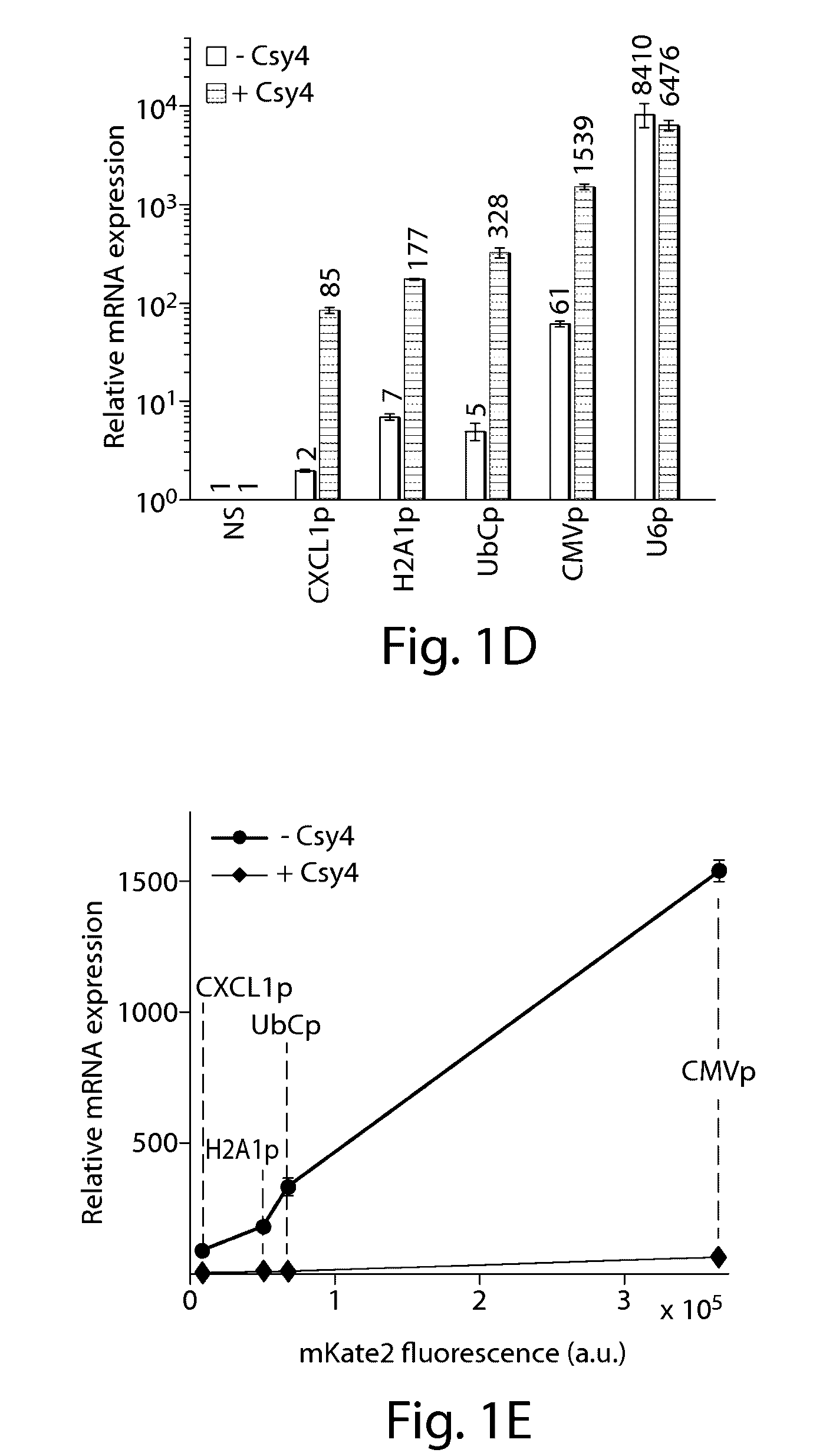
Methods and compositions for the production of guide RNA
Various aspects and embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods and compositions that combine multiple mammalian RNA regulatory strategies, including RNA triple helix structures, introns, microRNAs, and ribozymes with Cas-based CRISPR transcription factors and ribonuclease-based RNA processing in human cells. The methods and compositions of the present disclosure, in some embodiments, enable multiplexed production of proteins and multiple guide RNAs from a single compact RNA-polymerase-II-expressed transcript for efficient modulation of synthetic constructs and endogenous human promoters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Dinucleotide inhibitors of de novo RNA polymerases for treatment or prevention of viral infections
InactiveUS20060074035A1Inhibits viral replicationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotidePurine
Contemplated dinucleotide compounds have a general structure of A-B and inhibit synthesis of an RNA-dependent polymerase that initiates RNA replication de novo. In preferred dinucleotides, A comprises a purine or modified purine heterocyclic base and B comprises a pyrimidine or modified pyrimidine heterocyclic base.
Owner:VALEANT RES & DEV
Nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection
ActiveUS20100035835A1Efficient cell penetrationWider therapeutic indexBiocideSugar derivativesPolymerase LStructural formula
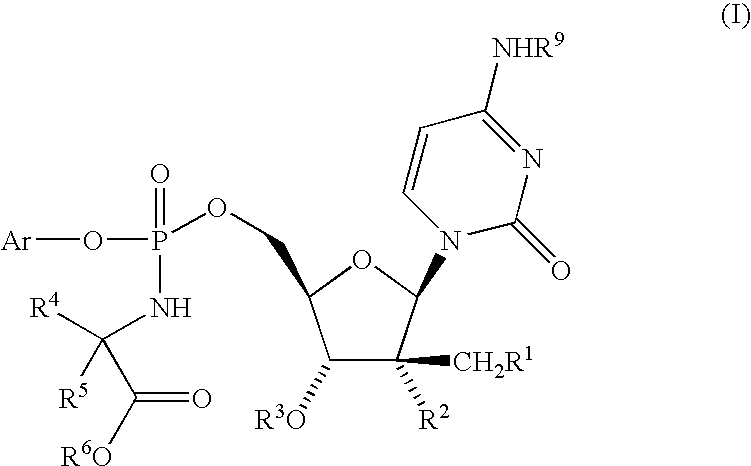
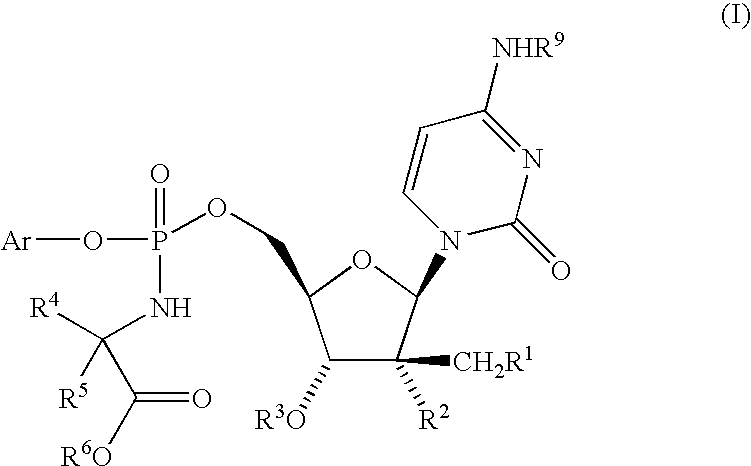
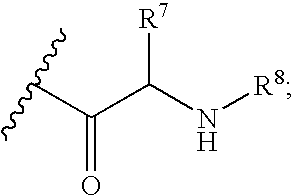
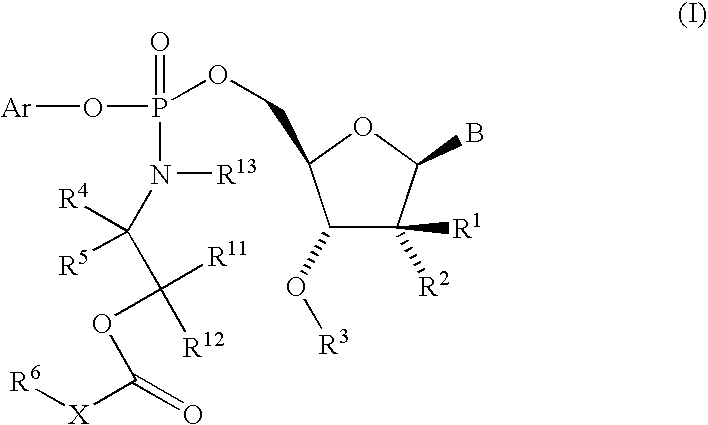
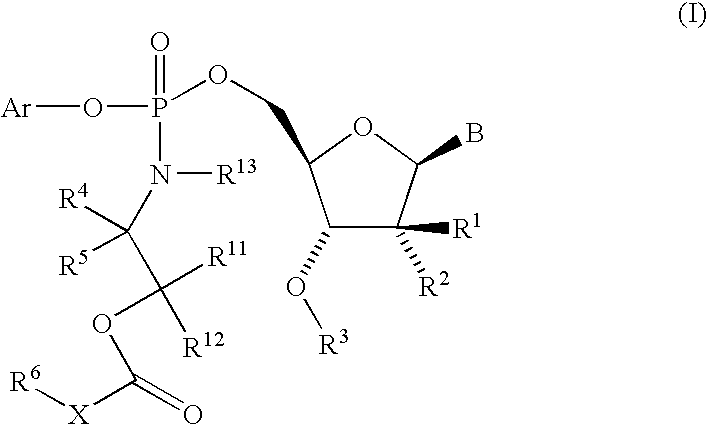
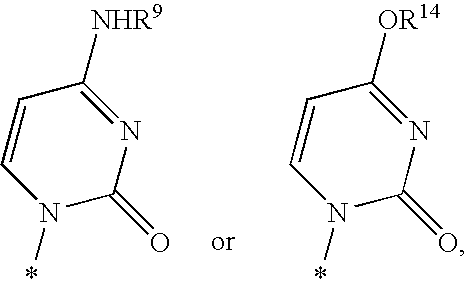
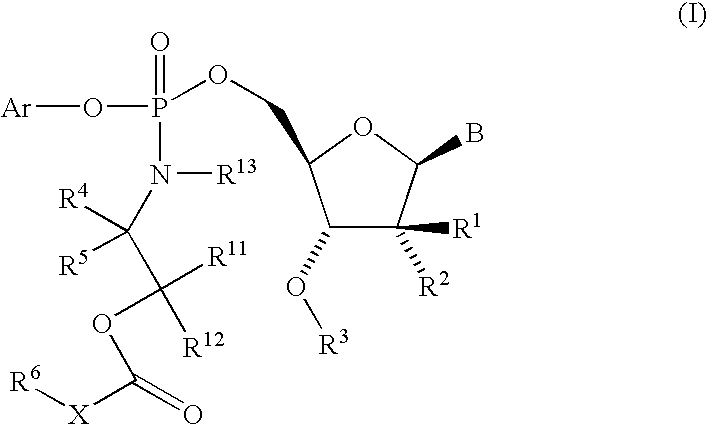
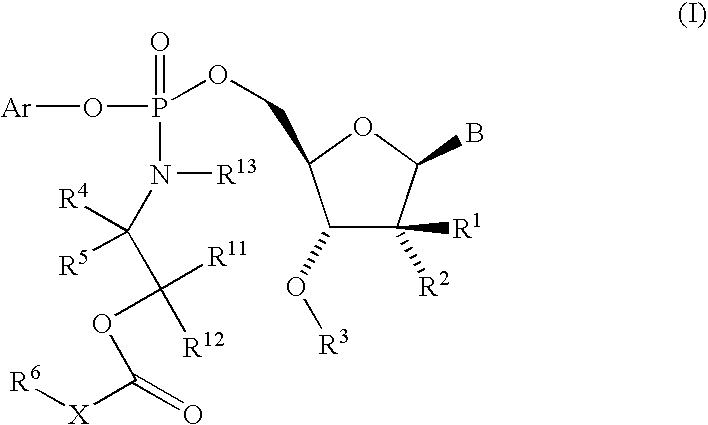
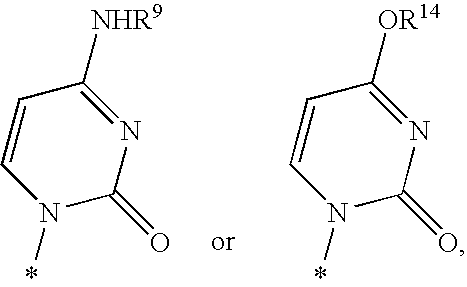
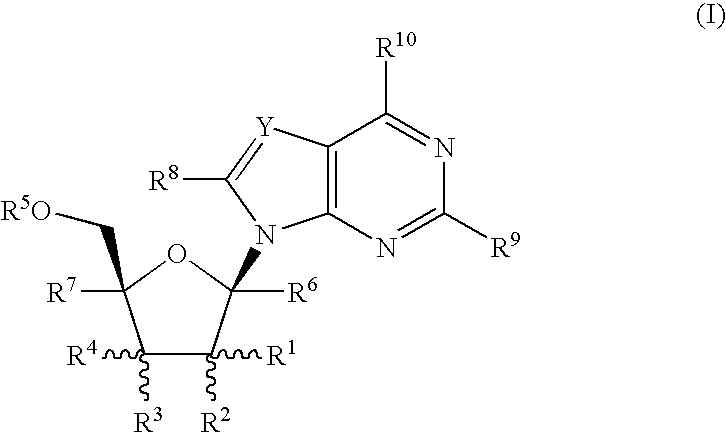
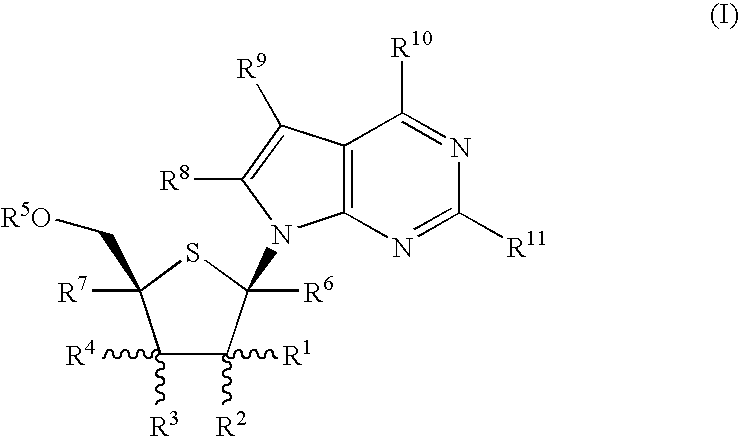
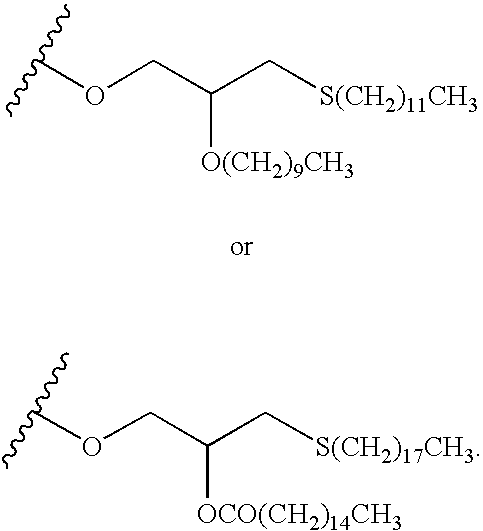
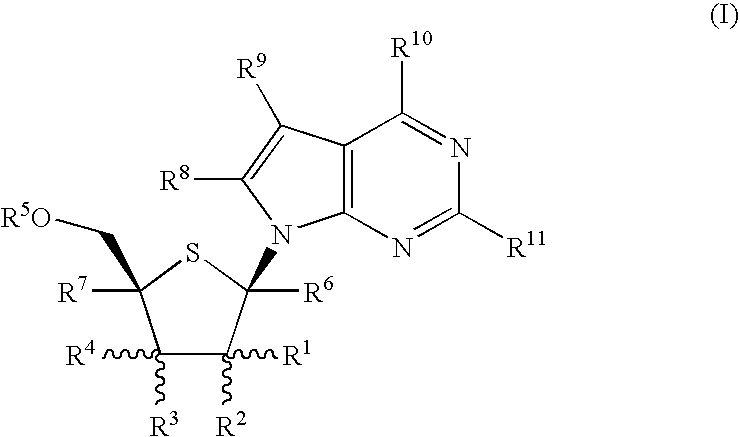
The present invention provides nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates of structural formula (I) which are precursors to inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase. These compounds are precursors to inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral replication and are useful for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection. They are particularly useful as precursors to inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, as precursors to inhibitors of HCV replication, and / or for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. The invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions containing such nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates alone or in combination with other agents active against RNA-dependent RNA viral infection, in particular HCV infection. Also disclosed are methods of inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA viral replication, and / or treating RNA-dependent RNA viral infection with the nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates of the present invention.
Owner:MSD ITAL +1
Methods and means for enhancing RNA production
ActiveUS20170114378A1Improved and economical meanImproved and economical and methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibonucleosideFiltration membrane
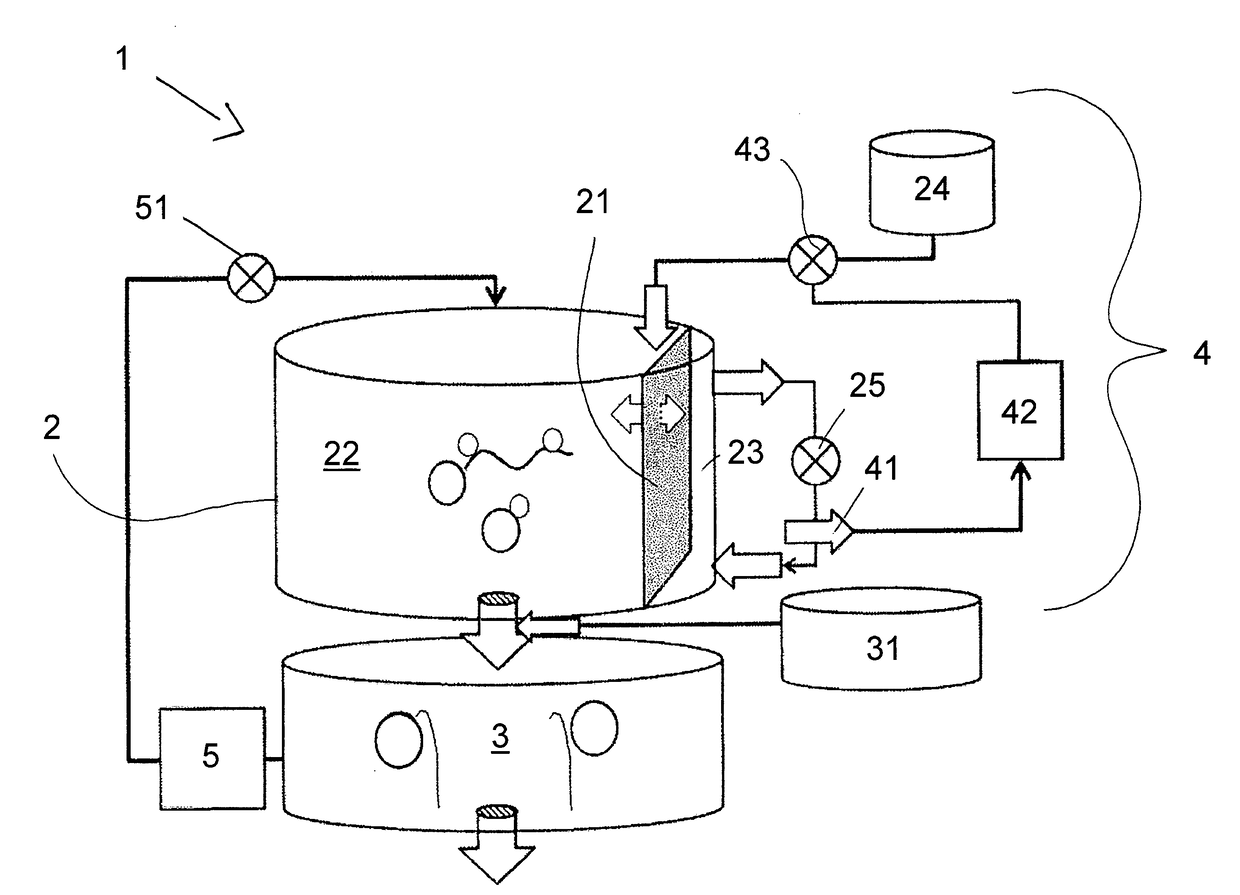
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing an RNA molecule of a given sequence, comprising the step of determining the fraction (1) for each of the four nucleotides G, A, C and U in said RNA molecule, and the step of synthesizing said RNA molecule by in vitro transcription in a sequence-optimized reaction mix, wherein said sequence-optimized reaction mix comprises the four ribonucleoside triphosphates GTP, ATP, CTP and UTP, wherein the fraction (2) of each of the four ribonucleoside triphosphates in the sequence-optimized reaction mix corresponds to the fraction (1) of the respective nucleotide in said RNA molecule, a buffer, a DNA template, and an RNA polymerase. Further, the present invention relates to a bioreactor (1) for synthesizing RNA molecules of a given sequence, the bioreactor (1) having a reaction module (2) for carrying out in vitro RNA transcription reactions in a sequence-optimized reaction mix, a capture module (3) for temporarily capturing the transcribed RNA molecules, and a control module (4) for controlling the infeed of components of the sequence-optimized reaction mix into the reaction module (2), wherein the reaction module (2) comprises a filtration membrane (21) for separating nucleotides from the reaction mix, and the control of the infeed of components of the sequence-optimized reaction mix by the control module (4) is based on a measured concentration of separated nucleotides.
Owner:CUREVAC REAL ESTATE GMBH
Nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection
ActiveUS8071568B2Effective penetrationLess susceptibleBiocideSugar derivativesPolymerase LPhosphoramidate
The present invention provides nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates of structural formula (I) which are precursors to inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase. These compounds are precursors to inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral replication and are useful for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection. They are particularly useful as precursors to inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, as precursors to inhibitors of HCV replication, and / or for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. The invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions containing such nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates alone or in combination with other agents active against RNA-dependent RNA viral infection, in particular HCV infection. Also disclosed are methods of inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA viral replication, and / or treating RNA-dependent RNA viral infection with the nucleoside aryl phosphoramidates of the present invention. (I)
Owner:MSD ITAL +1
2′-branched nucleosides and Flaviviridae mutation
ActiveUS7824851B2High sensitivityReduce Flaviviridae infectionBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAmino acidMutant strain
The present invention discloses a method for the treatment of Flaviviridae infection that includes the administration of a 2′-branched nucleoside, or a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug and / or salt thereof, to a human in need of therapy in combination or alternation with a drug that directly or indirectly induces a mutation in the viral genome at a location other than a mutation of a nucleotide that results in a change from seine to a different amino acid in the highly conserved consensus sequence, XRXSGXXXT (Sequence ID No. 63), of domain B of the RNA polymerase region, or is associated with such a mutation. The invention also includes a method to detect a mutant strain of Flaviviridae and a method for its treatment.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
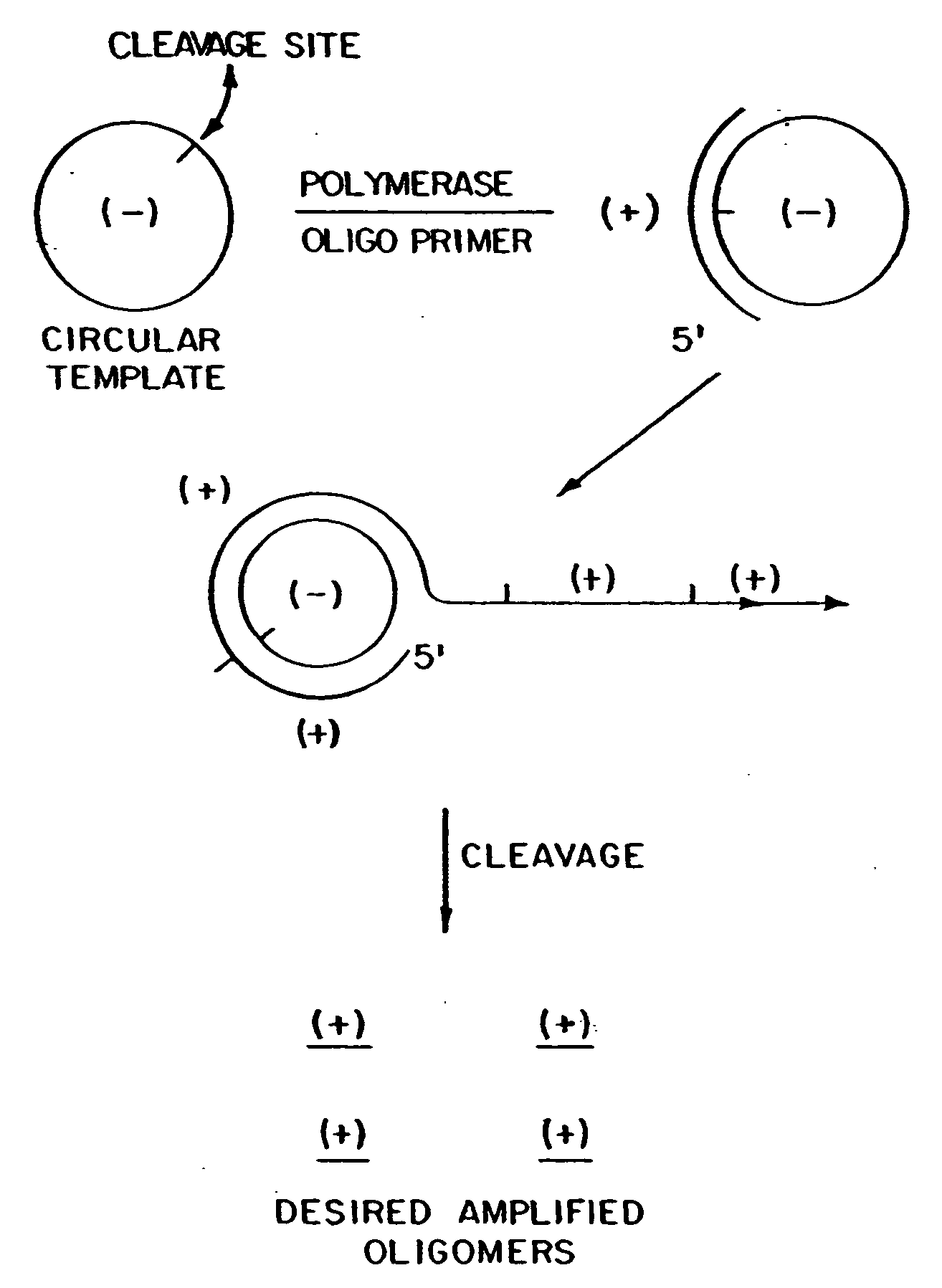
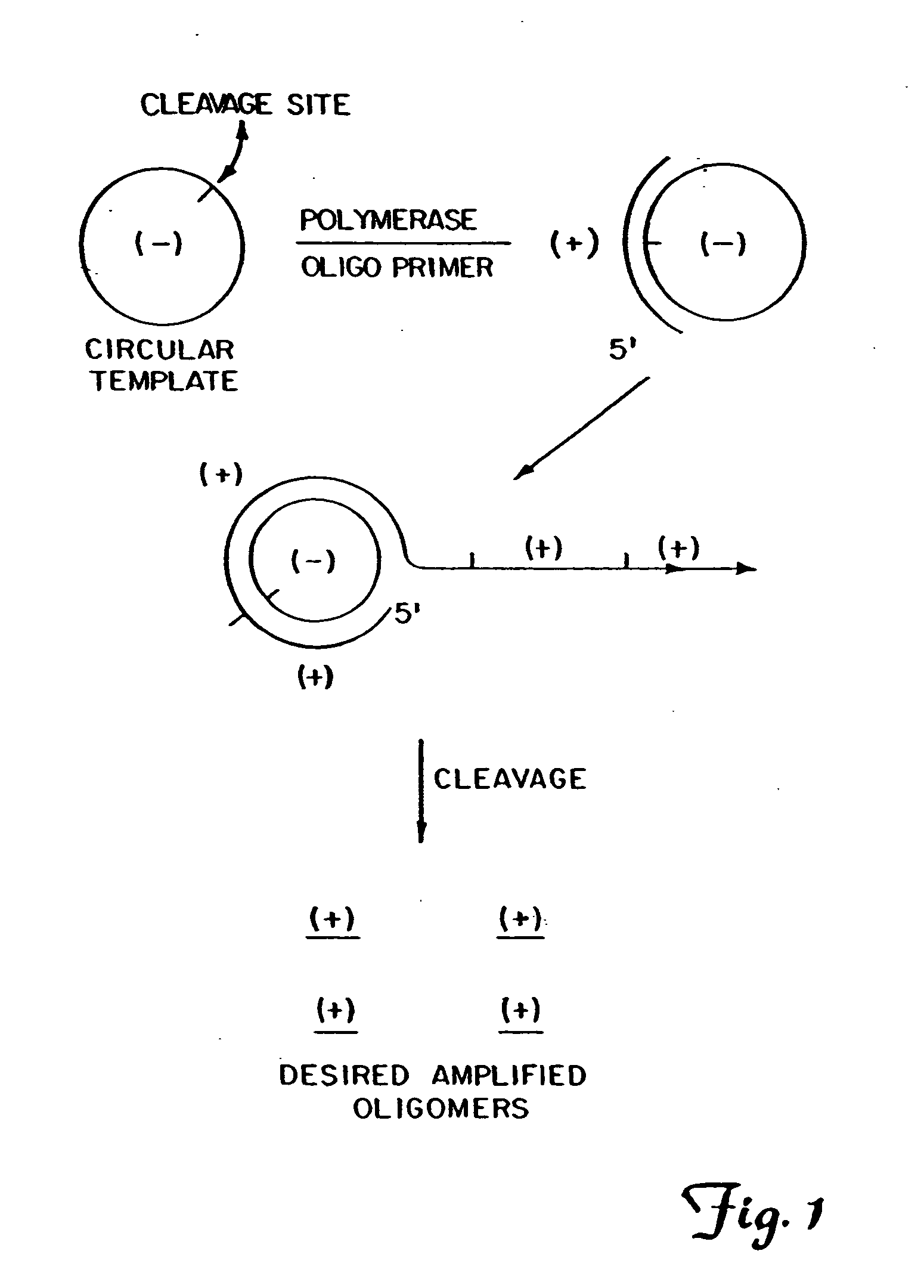
Circular DNA vectors for synthesis of RNA and DNA
InactiveUS20080227160A1Low-cost and efficientEasy to identifySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRibonucleotide synthesisRibonucleotide
The present invention provides methods for synthesis and therapeutic use of DNA and RNA oligonucleotides and analogs. RNA oligonucleotides are synthesized using a small, circular DNA template which lacks an RNA polymerase promoter sequence. The RNA synthesis is performed by combining a circular single-stranded oligonucleotide template with an effective RNA polymerase and at least two types of ribonucleotide triphosphate to form an RNA oligonucleotide multimer comprising multiple copies of the desired RNA oligonucleotide sequence. Preferably, the RNA oligonucleotide multimer is cleaved to produce RNA oligonucleotides having well-defined ends. Preferred RNA oligonucleotide multimers contain ribozymes capable of both cis (autolytic) and trans cleavage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
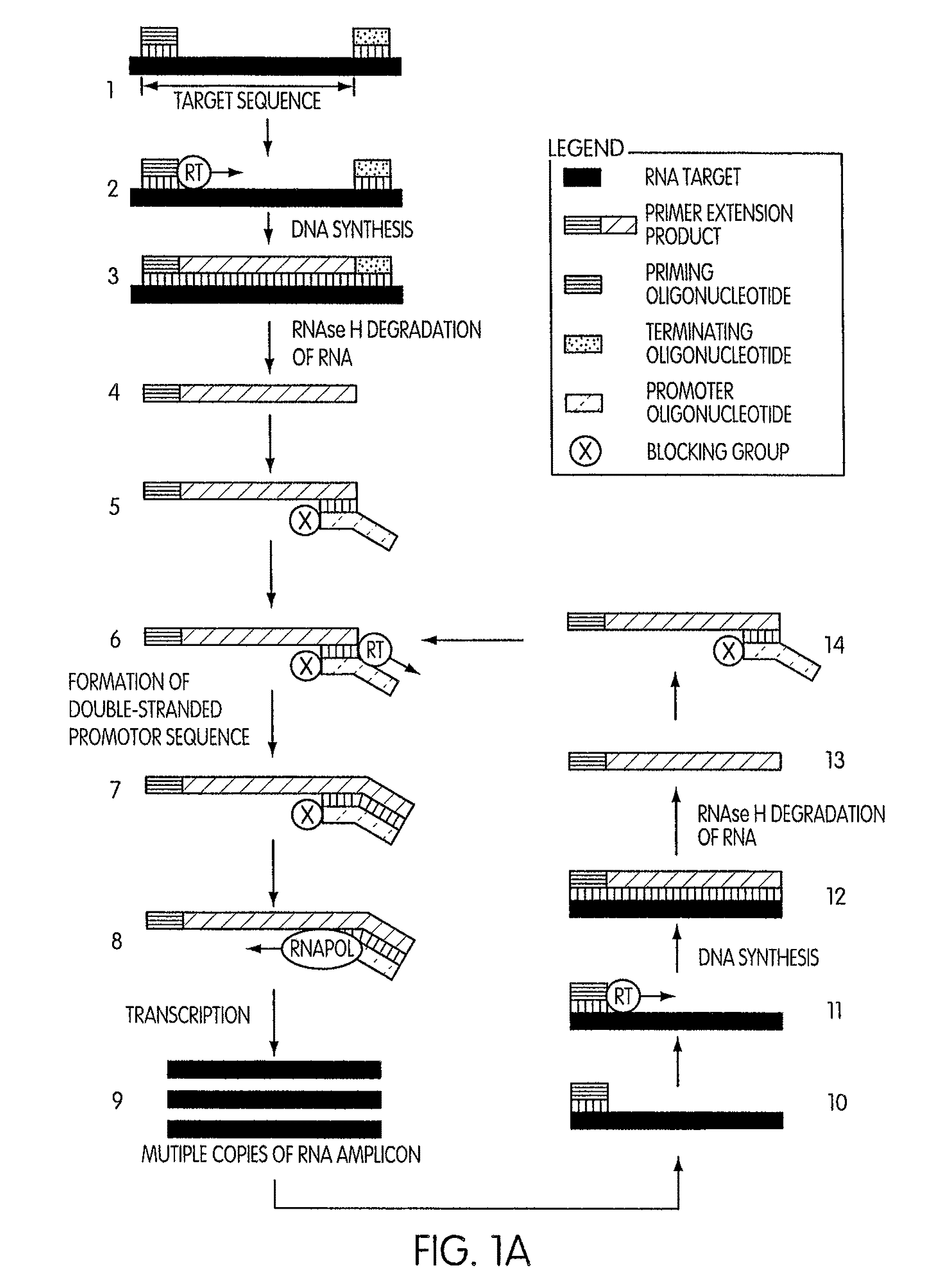
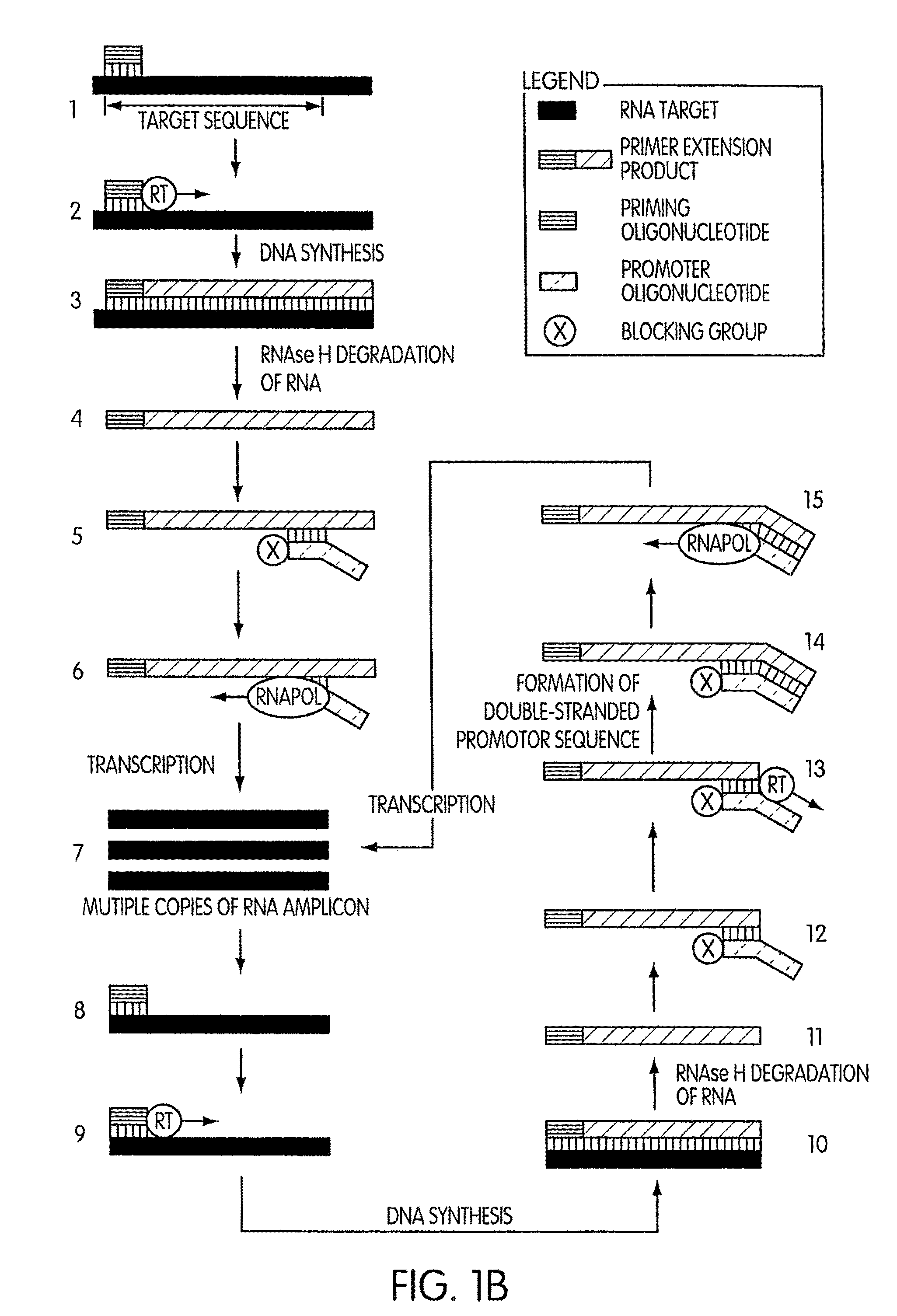
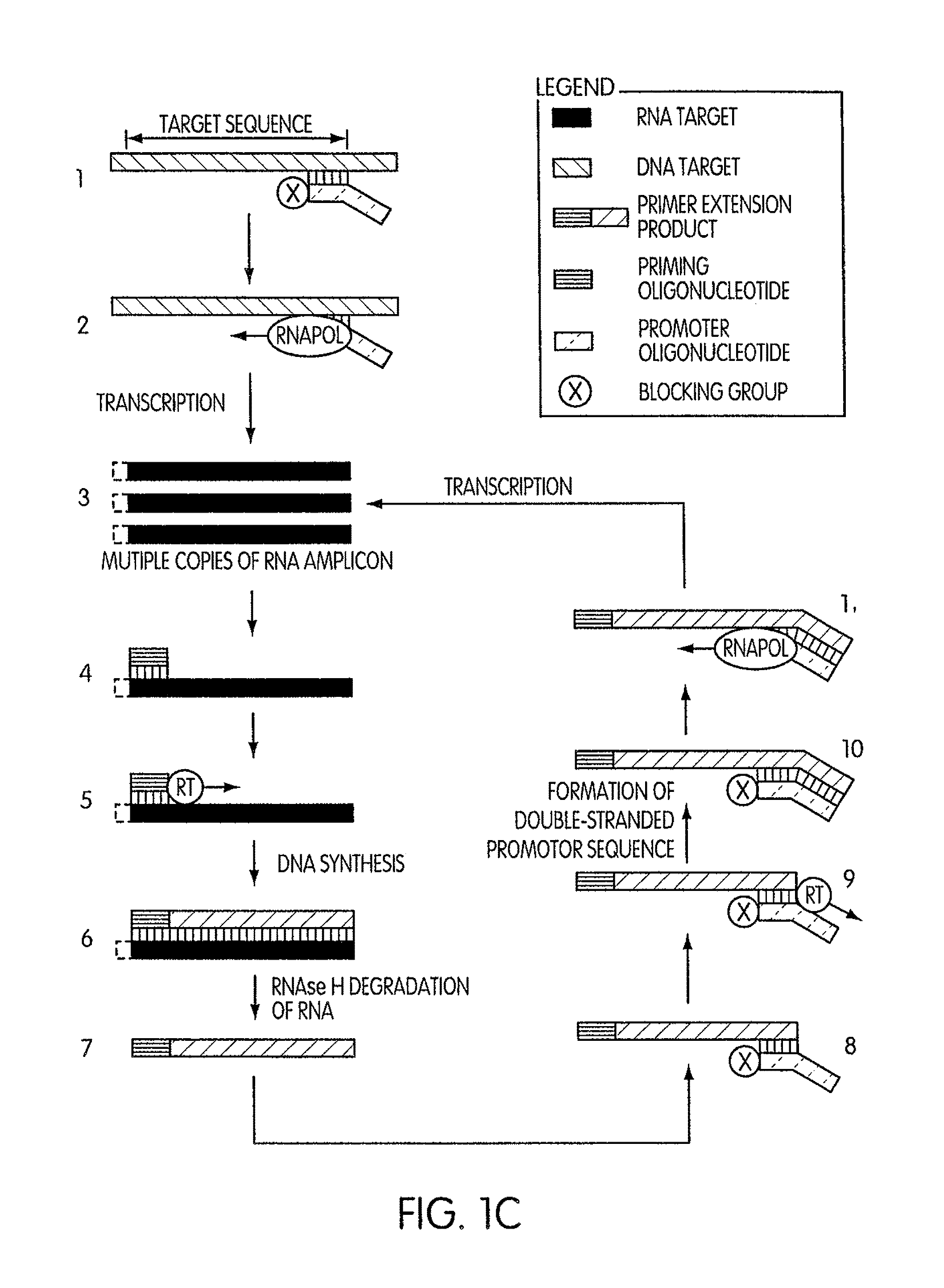
Amplification of ribonucleic acids
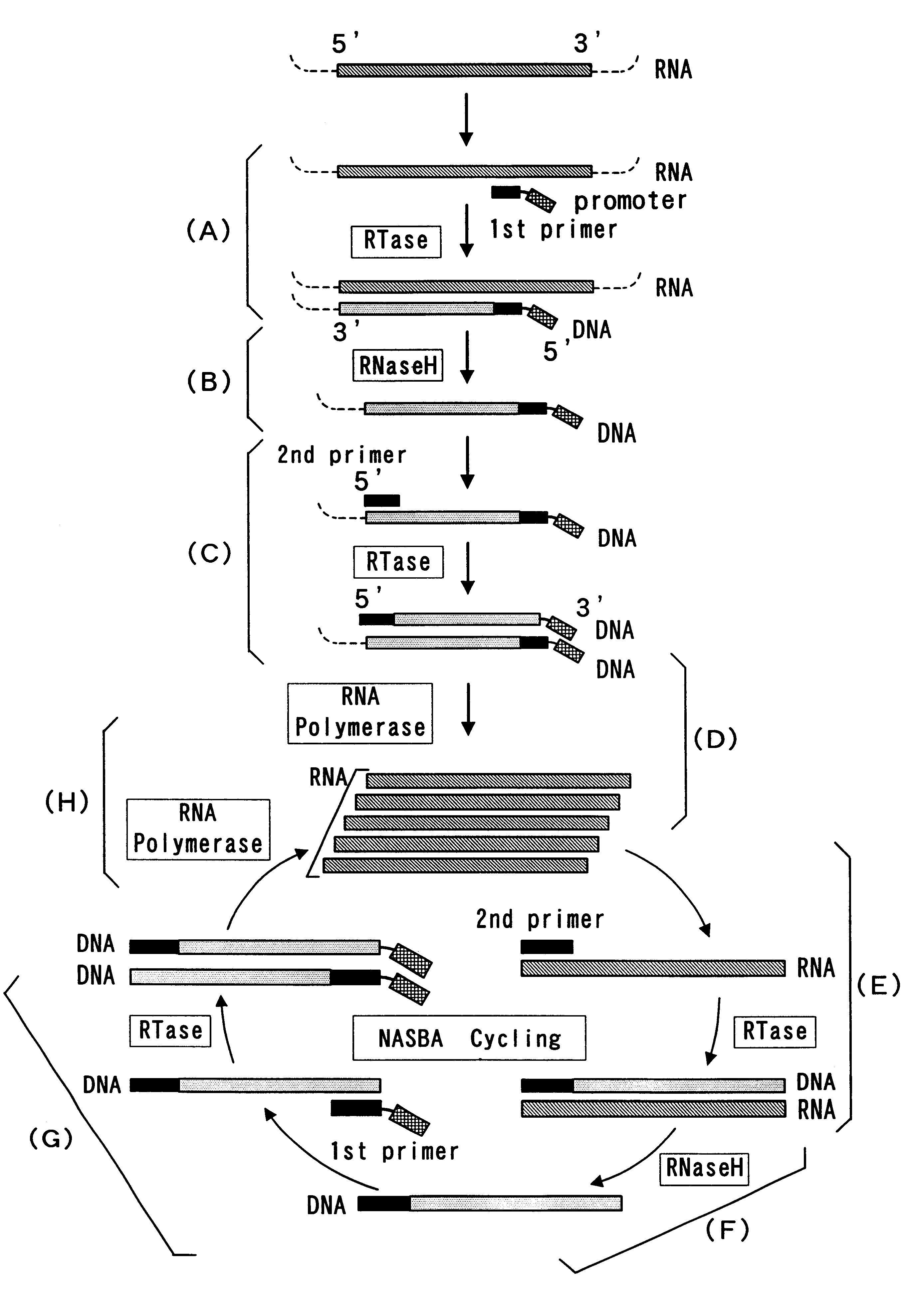
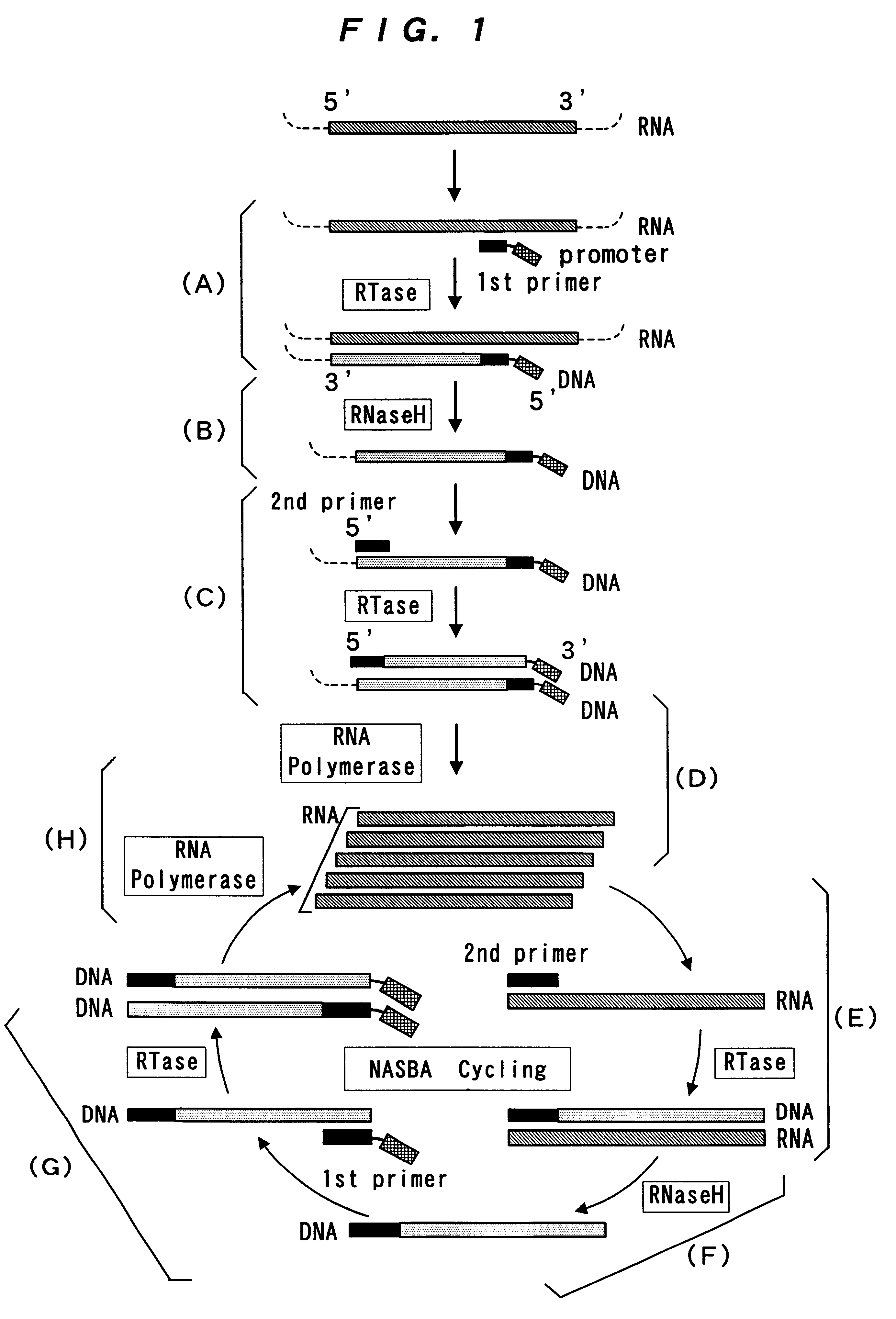
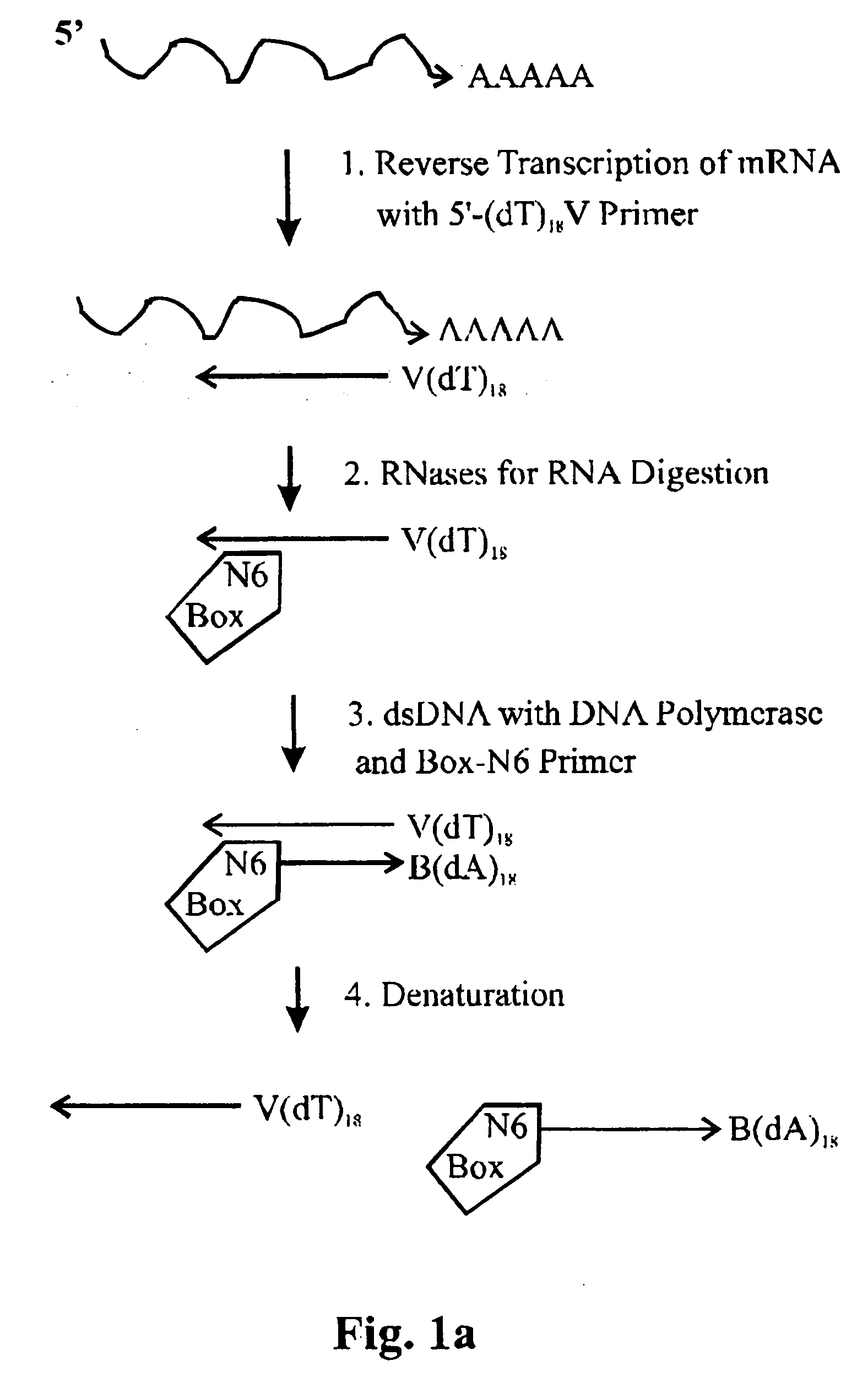
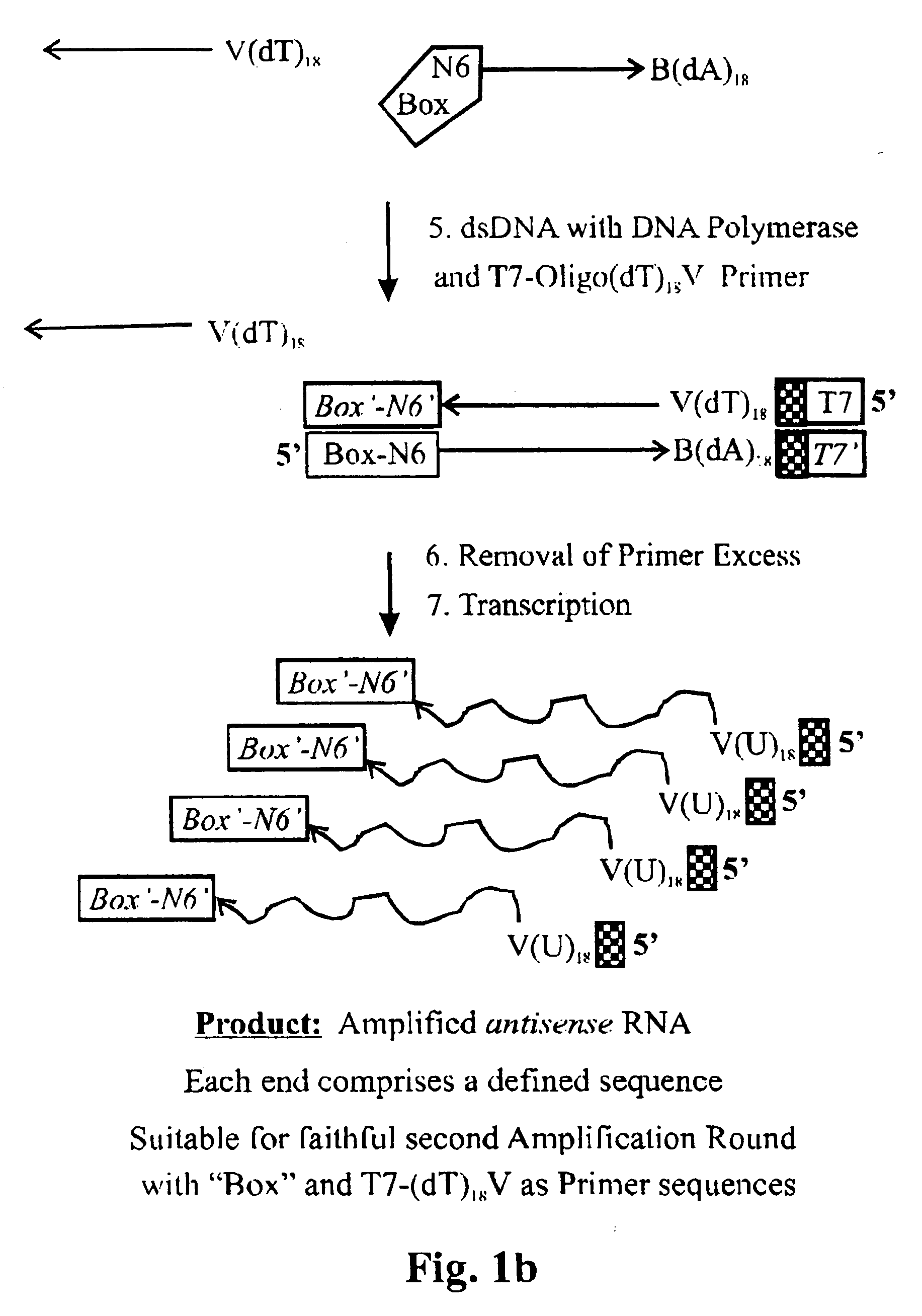
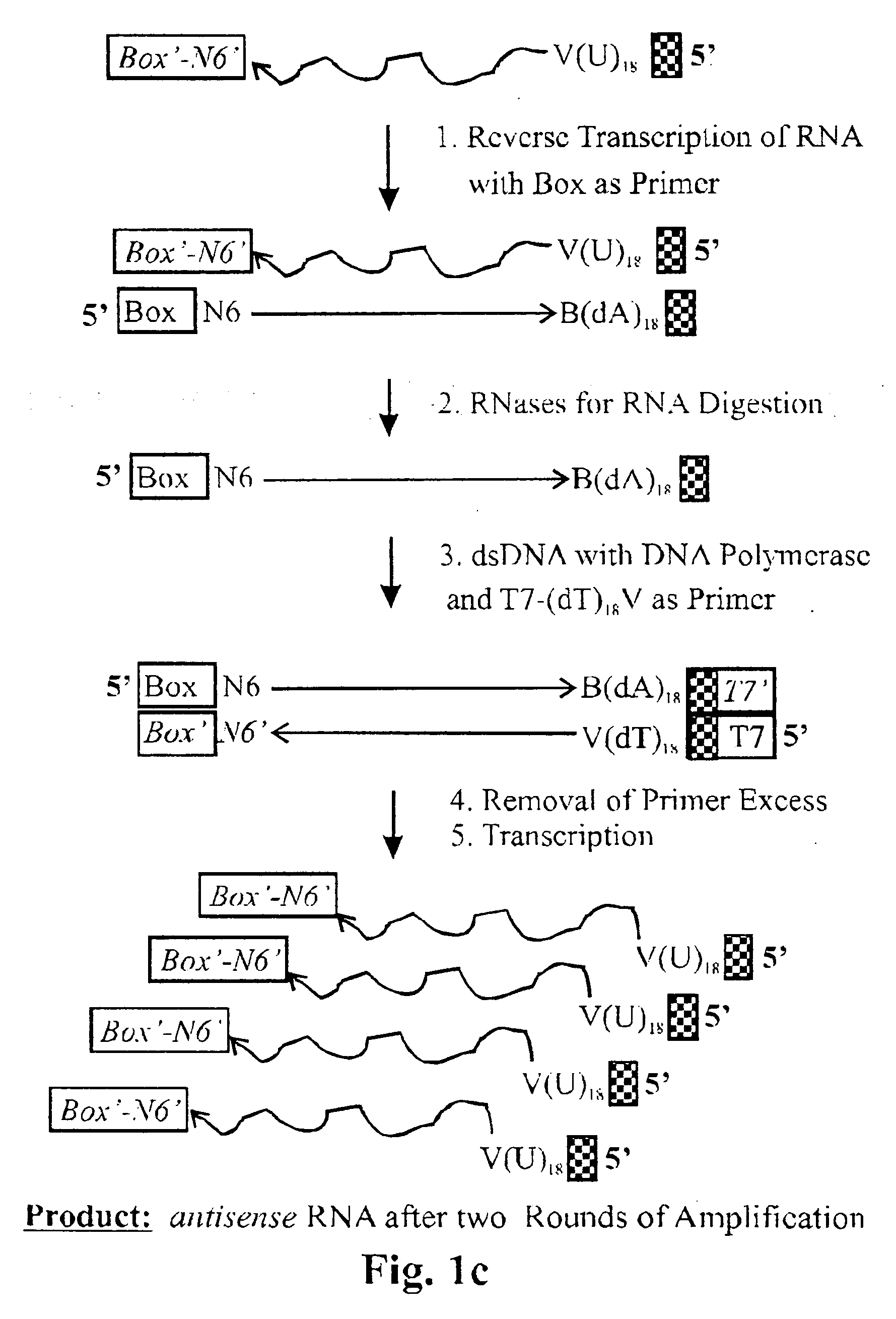
The invention relates to methods for the amplification of ribonucleic acids, comprising the following steps: (a) a single stranded DNA is produced from an RNA by means of reverse transcription, using a single-stranded primer having a defined sequence, an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates; (b) the template RNA is removed; (c) a DNA duplex is produced by means of a single-stranded primer comprising a box sequence, a DNA polymerase and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates; (d) the duplex is separated into single-stranded DNAs; (e) DNA duplexes are produced from one of the single-stranded DNAs obtained in step (d) by means of a single-stranded primer comprising a promoter sequence at its 5′end and the same defined sequence as the primer used in step (a) at its 3′end, a DNA polymerase and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates; (f) a plurality of RNA single strands, both ends of which comprise defined sequences, are produced by means of an RNA polymerase and ribonucleoside triphosphates. The invention also relates to kits for amplifying ribonucleic acids according to one of said methods, said kits comprising the following components: (a) at least at least one single-stranded primer, which contains a promoter sequence; (b) at least one single-stranded primer comprising a box sequence; (c) an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase; (d) deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates; (e) a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase; (f) an RNA polymerase; and (g) ribonucleoside triphosphates.
Owner:AMPTEC
Nucleoside derivatives as inhibitors of rna-dependent rna viral polymerase
The present invention provides nucleoside compounds and certain derivatives thereof which are inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase. These compounds are inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral replication and are useful for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection. They are particularly useful as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, as inhibitors of HCV replication, and / or for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. The invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions containing such nucleoside compounds alone or in combination with other agents active against RNA-dependent RNA viral infection, in particular HCV infection. Also disclosed are methods of inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA viral replication, and / or treating RNA-dependent RNA viral infection with the nucleoside compounds of the present invention.
Owner:OLSEN DAVID B +3
C-purine nucleoside analogs as inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase
ActiveUS7534767B2BiocideSaccharide with heterocyclic radicalsRNA Virus InfectionsRNA-dependent RNA polymerase
The present invention provides C-purine nucleoside analogs and certain derivatives thereof which are inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase. These compounds are inhibitors RNA-dependent RNA viral replication and are useful for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection. They are particularly useful as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, as inhibitors of HCV replication, and / or for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. The invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions containing such C-nucleoside compounds alone or in combination with other agents active against RNA-dependent RNA viral infection, in particular HCV infection. Also disclosed are methods of inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA viral replication, and / or treating RNA-dependent RNA viral infection with the C-nucleoside compounds of the present invention.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC +1
Thionucleoside derivatives as inhibitors of rna-dependent rna viral polymerase
The present invention provides thionucleoside compounds and certain derivatives thereof which are inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral polymerase. These compounds are inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA viral replication and are useful for the treatment of RNA-dependent RNA viral infection. They are particularly useful as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, as inhibitors of HCV replication, and / or for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. The invention also describes pharmaceutical compositions containing such thionucleoside compounds alone or in combination with other agents active against RNA-dependent RNA viral infection, in particular HCV infection. Also disclosed are methods of inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting RNA-dependent RNA viral replication, and / or treating RNA-dependent RNA viral infection with the thionucleoside compounds of the present invention.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC +1
Method for linear mRNA amplification
InactiveUS6916633B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntisense RNAReverse transcriptase
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Amplification method
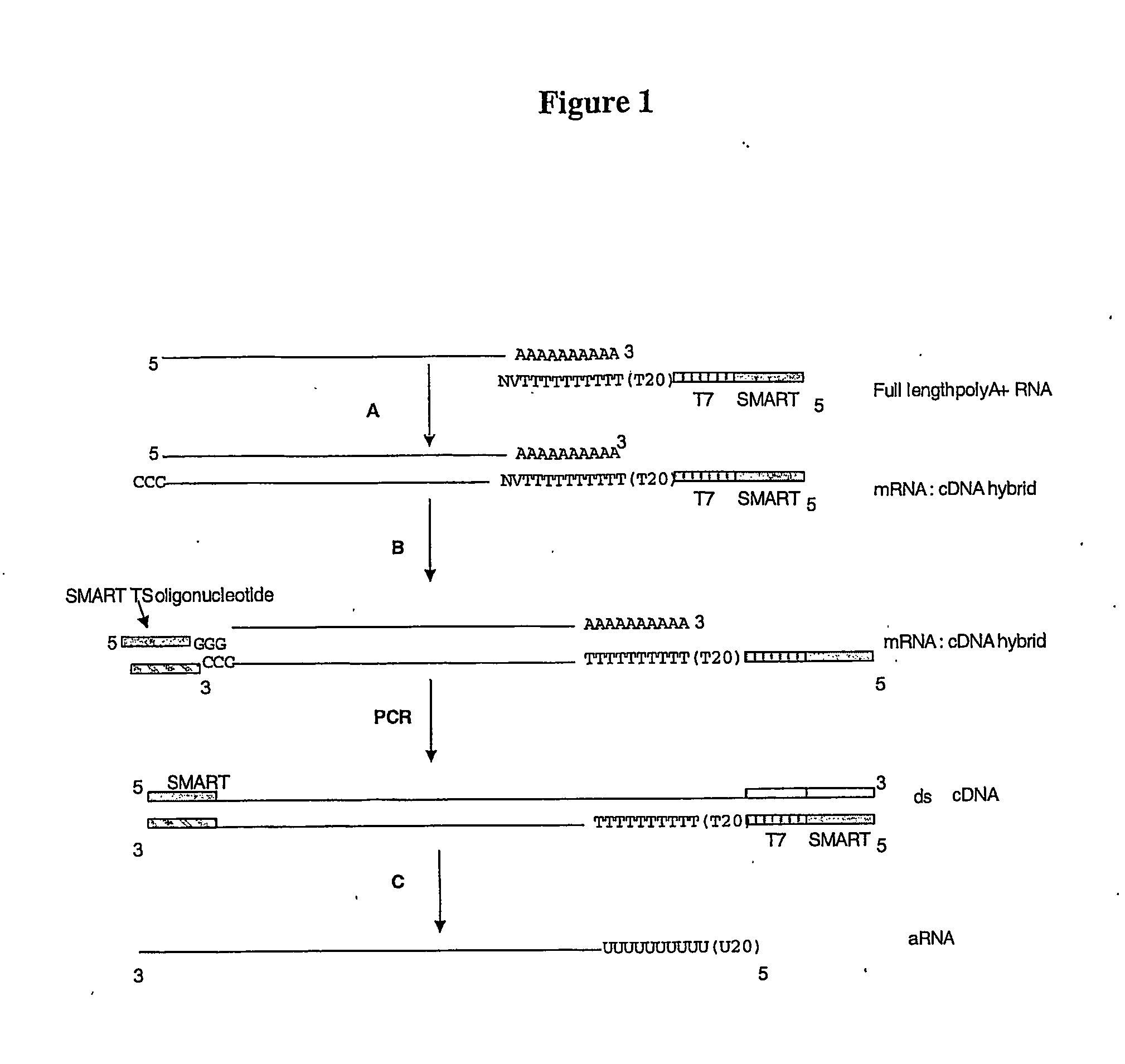
InactiveUS20070105090A1Maintaining representationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTemplate switchingPolymerase
The present invention combines the use of template switching with nucleic acid amplification—such as PCR—to generate amplification products representative of an entire RNA population. An RNA polymerase promoter sequence allows transcription-based amplification to be performed on the derived amplification products such that antisense amplified RNA (aRNA) or complementary RNA (cRNA) is produced for subsequent downstream applications.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
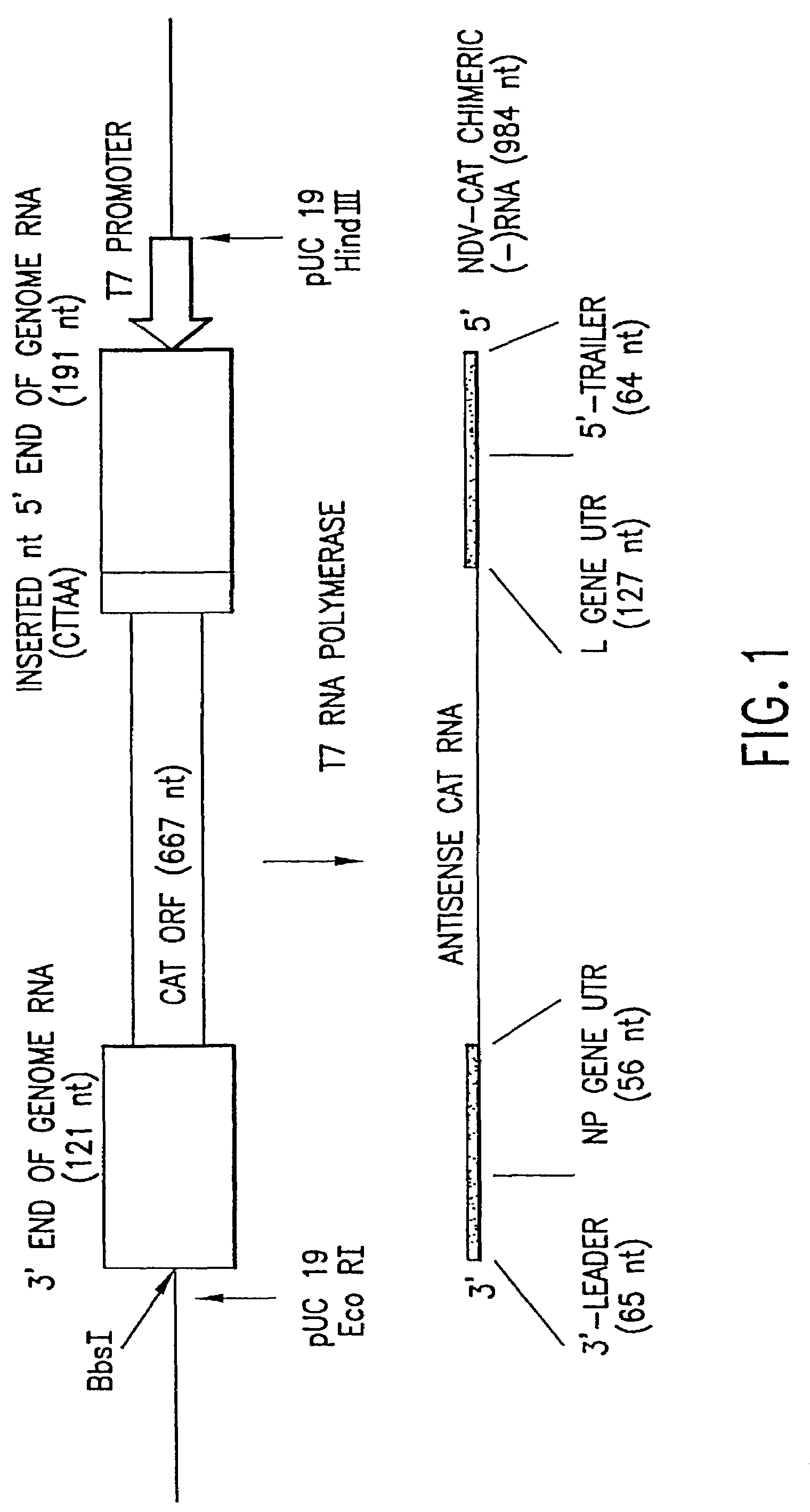
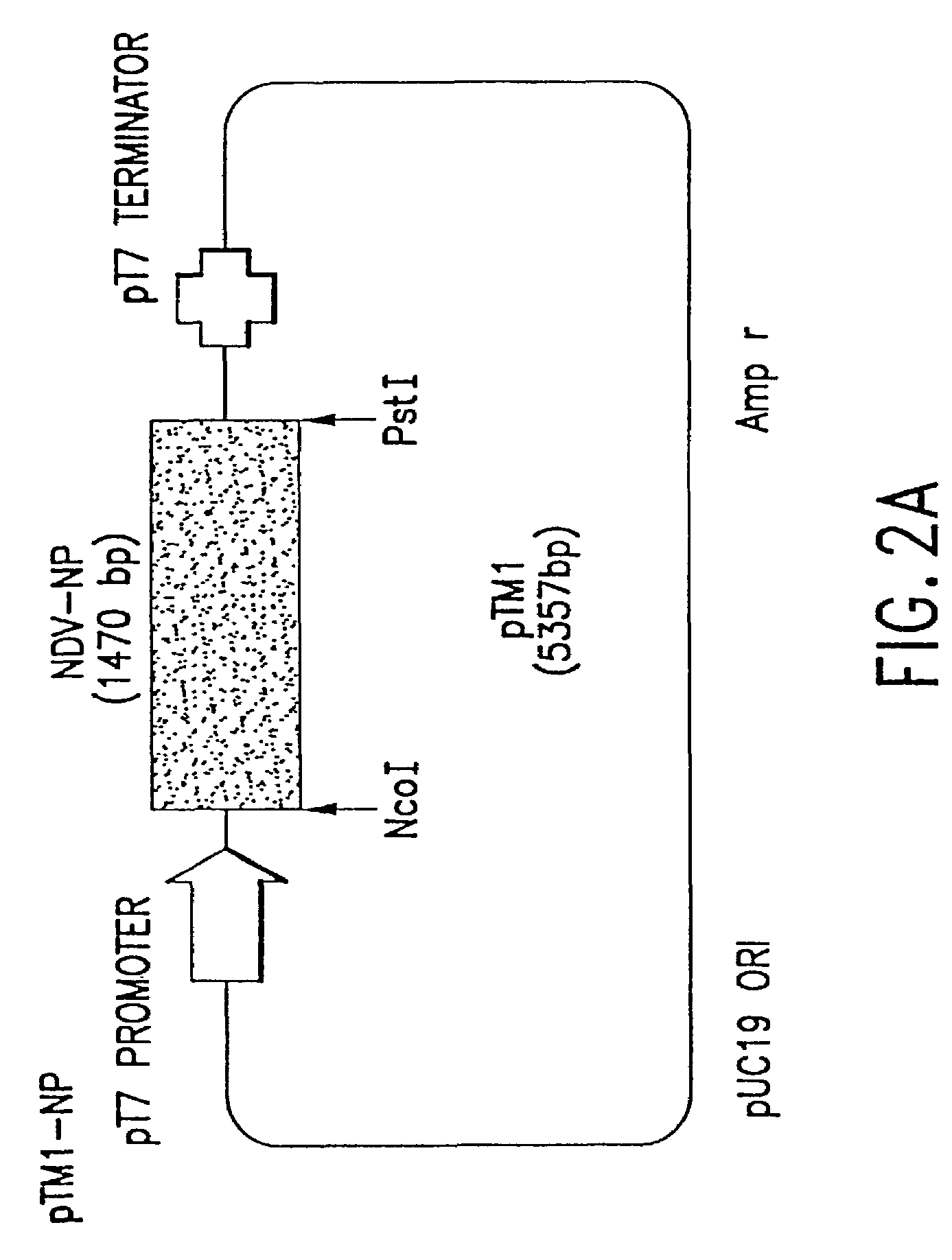
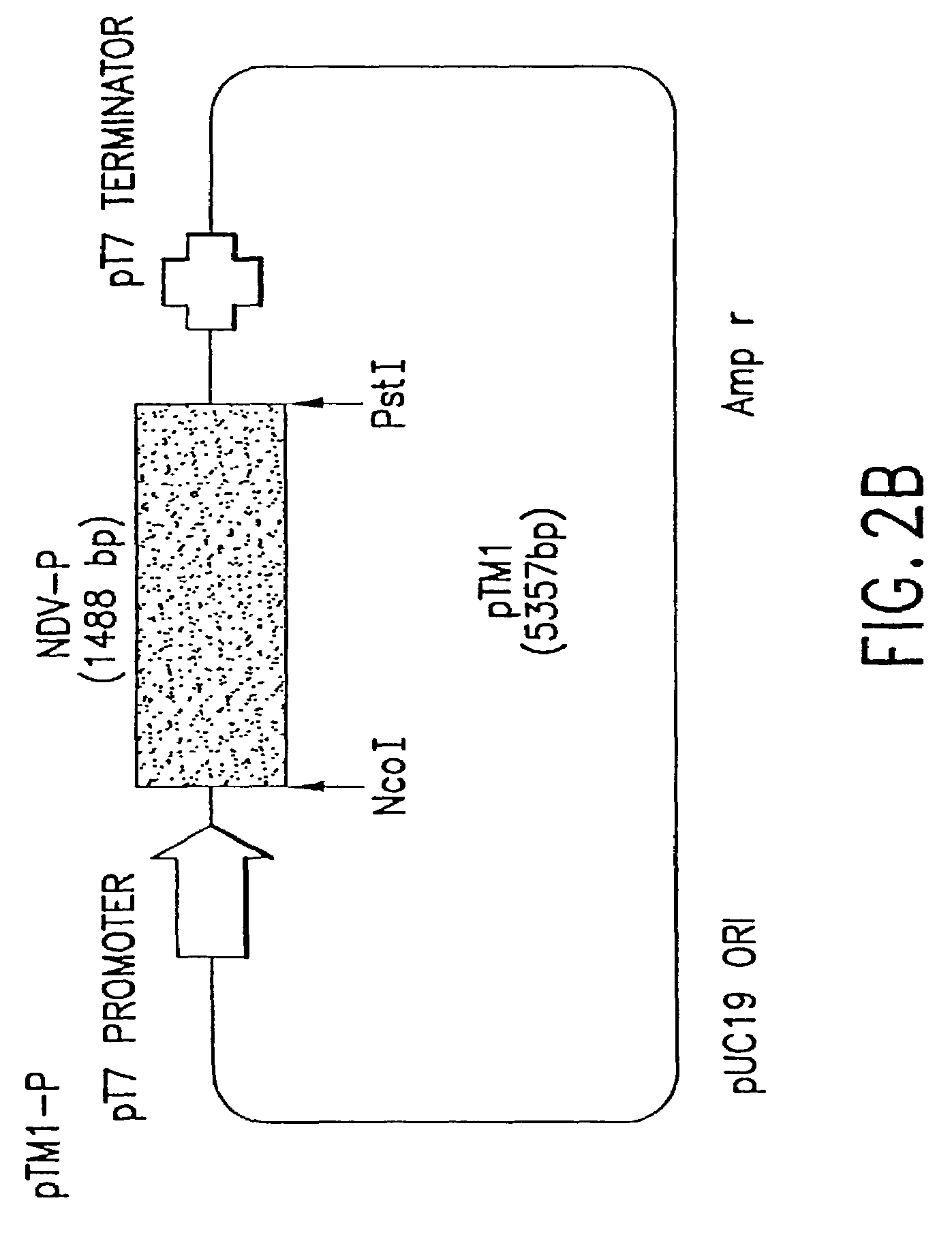
Recombinant Newcastle disease virus RNA expression systems and vaccines
This invention relates to genetically engineered Newcastle disease viruses and viral vectors which express heterologous genes or mutated Newcastle disease viral genes or a combination of viral genes derived from different strains of Newcastle disease virus. The invention relates to the construction and use of recombinant negative strand NDV viral RNA templates which may be used with viral RNA-directed RNA polymerase to express heterologous gene products in appropriate host cells and / or to rescue the heterologous gene in virus particles. In a specific embodiment of the invention, the heterologous gene product is a peptide or protein derived from the genome of a human immunodeficiency virus. The RNA templates of the present invention may be prepared by transcription of appropriate DNA sequences using any DNA-directed RNA polymerase such as bacteriophage T7, T3, SP6 polymerase, or eukaryotic polymerase I.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
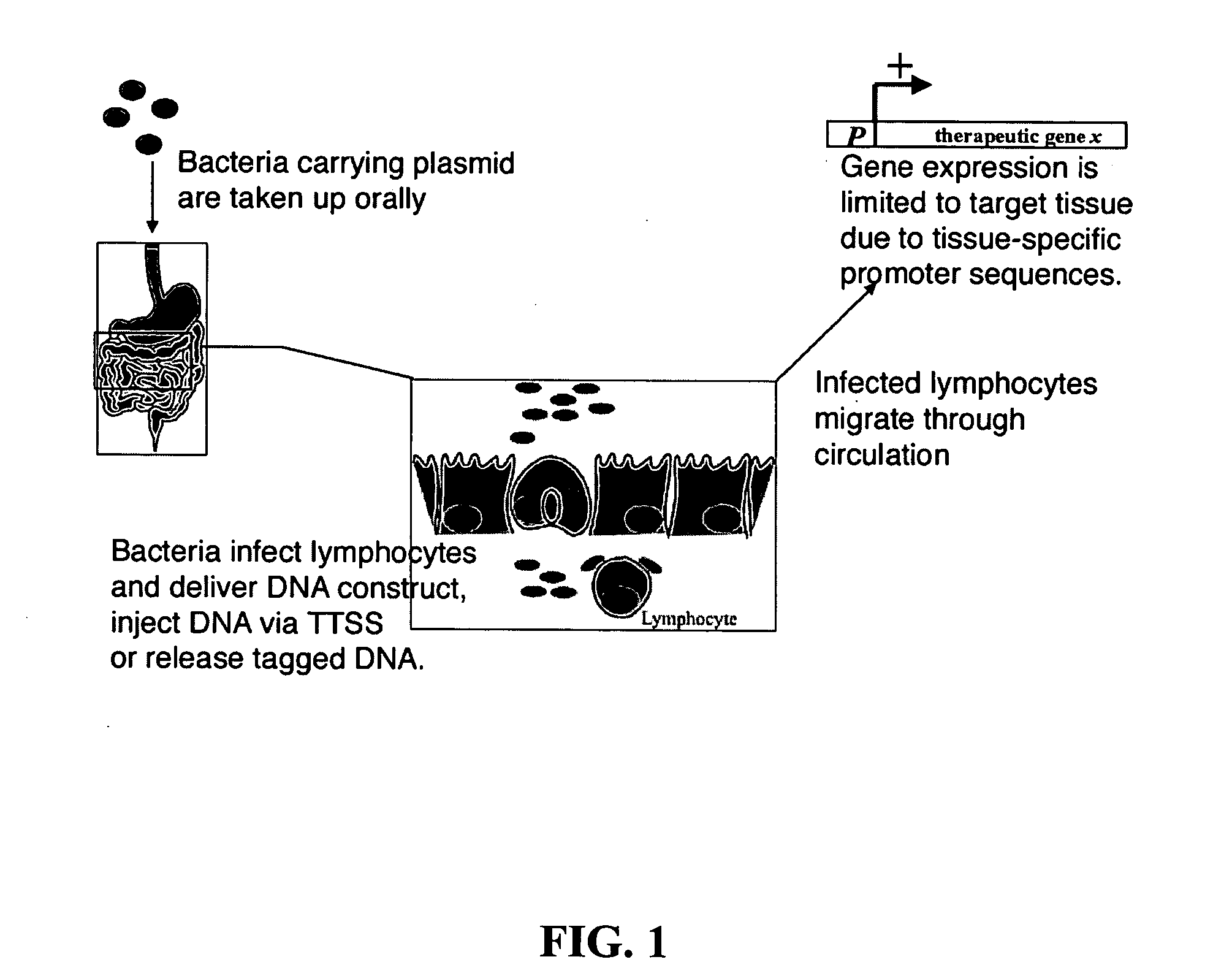
Bacterial vector systems
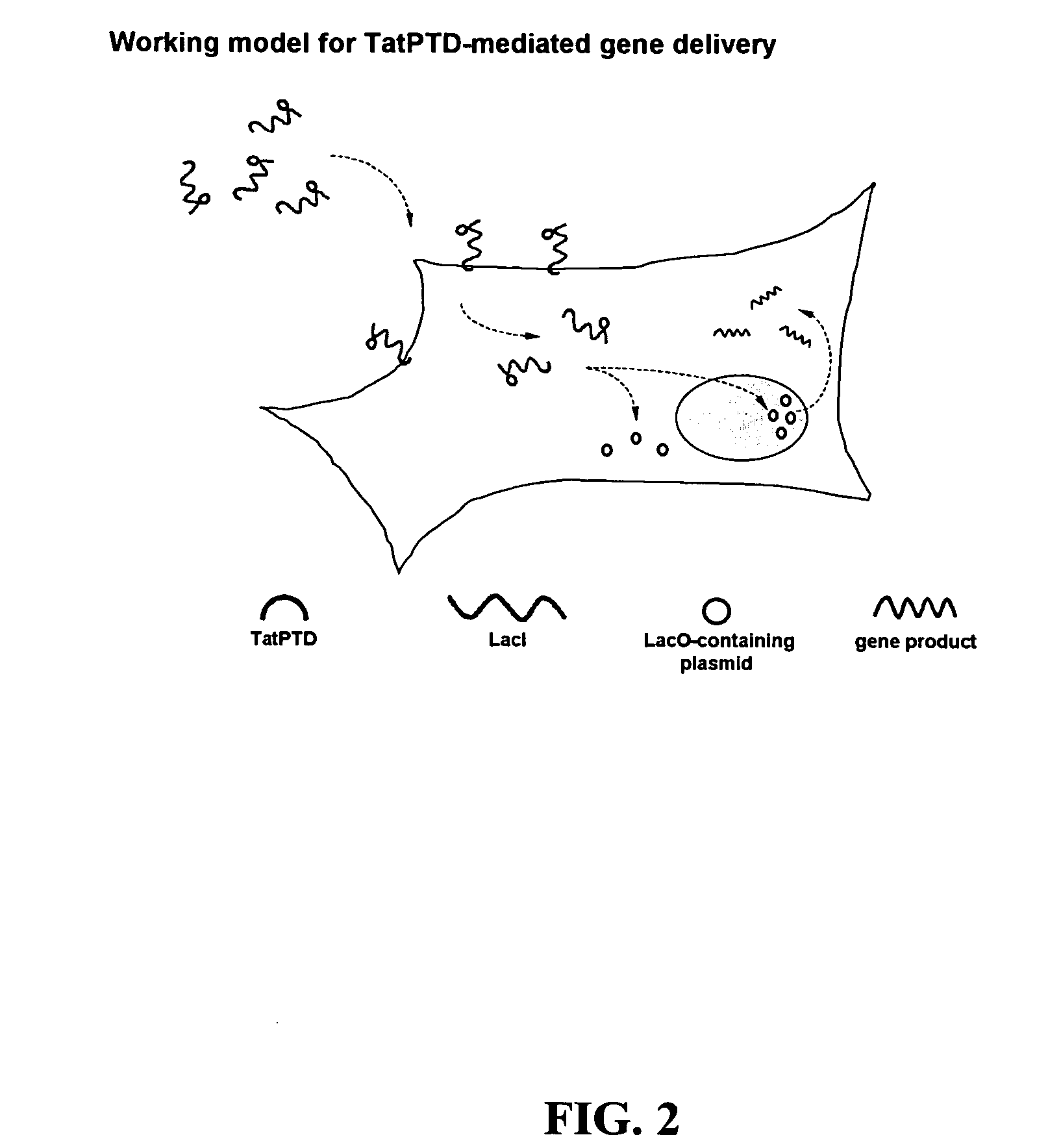
InactiveUS20060068469A1Efficient rapid deliveryFusion with DNA-binding domainBacteriaGene deliveryGene targets
The present invention provides bacterial vectors and fusion proteins containing a TTSS polypeptide, compositions of such fusion proteins including polynucleotides, and methods of delivering one or more genes into a target cell that involve contacting the cell with a composition that includes such a fusion protein. Compositions and methods of gene delivery that involve a bacterium and a TAT, Antp, or HSV VP22 polypeptide are also disclosed. The invention also concerns methods of delivering one or more genes into a target cell utilizing a bacterium capable of becoming internalized within the cell, wherein the bacterium includes one or more genes targeted for delivery to the cell, a gene encoding an RNA polymerase, and a gene that causes lysis of the bacterium.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Isothermal exponential RNA amplification in complex mixtures
Methods and compositions are provided for performing isothermal amplification of a nucleic acid target employing probes characterized by having a masked RNA polymer promoter unable to bind to a complementary initiator oligonucleotide and RNA polymerase and initiate transcription, a dsDNA sequence which when invaded by the target nucleic acid exposes the masked promoter to initiate transcription, and a template sequence, a portion of which is normally included in the dsDNA region, which when copied produces a product that can reinitiate the process of invading the dsDNA region and initiating transcription of another copy.
Owner:DISCOVERX INC
Constant temperature synchronous amplification detecting process for nucleic acid and use thereof
ActiveCN101333565AAvoid pollutionShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNegative strandFluorescence
Owner:SHANGHAI RENDU BIOTECH
Method for determining DNA nucleotide sequence
InactiveUS6294337B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRoom temperatureDNA fragmentation
A method for sequencing a target DNA fragment in which along with amplification of the target DNA fragment, nucleic acid transcripts are generated using an RNA polymerase and the amplified target DNA fragments are used as templates in the presence of terminators for nucleic acid transcription reaction and the generated nucleic acid transcripts are analyzed, characterized in that the amplification of target DNA fragments and the generation of nucleic acid transcripts are carried out at a constant temperature is disclosed. The amplification of target DNA fragments and the generation of nucleic acid transcripts can be carried out around the room temperature. A DNA sequencing method using a novel method in which without using a thermo-resistant RNA polymerase, the amplification of target DNA fragments and generation of nucleic acid transcript can be carried out simultaneously in parallel is provided.
Owner:RIKEN
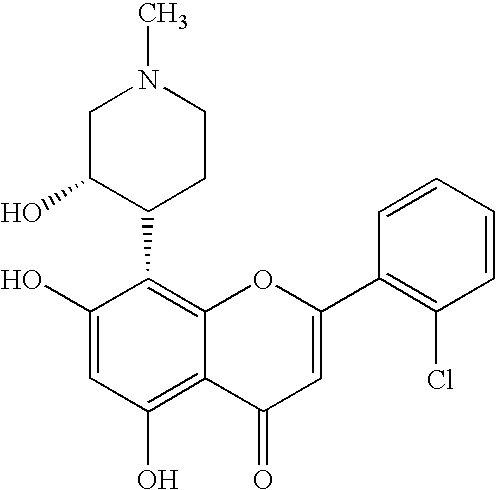
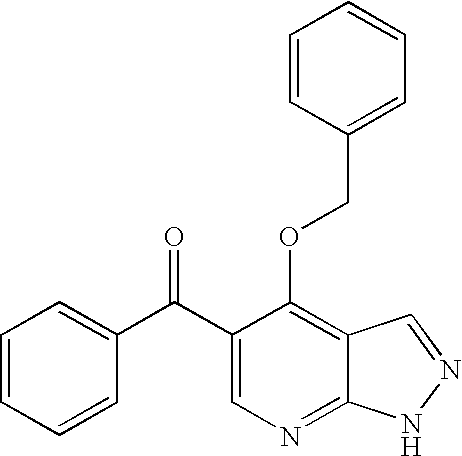
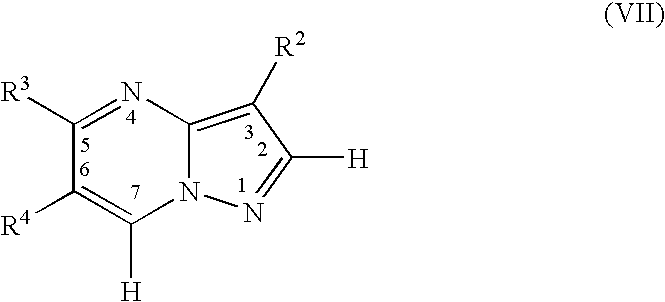
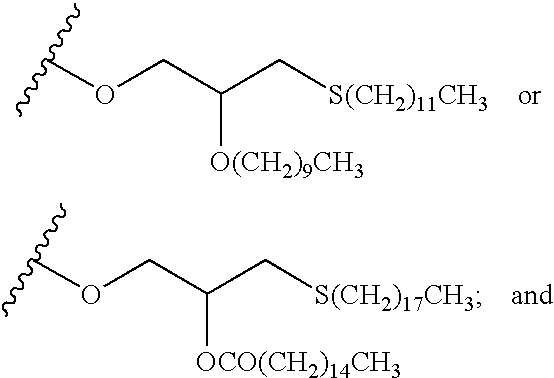
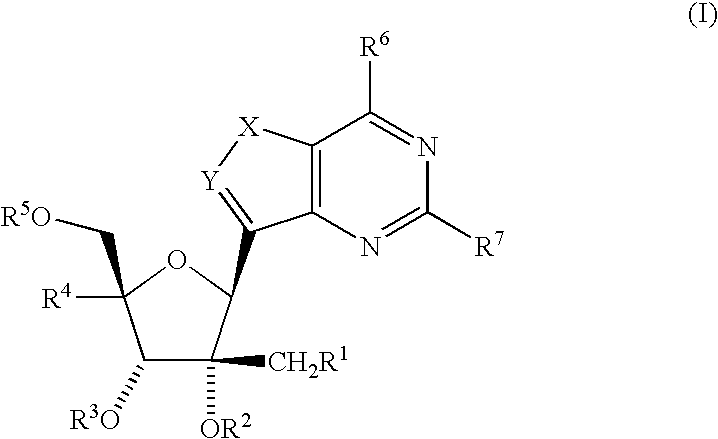
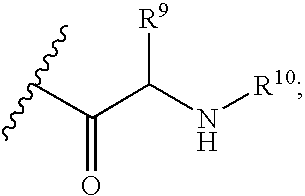
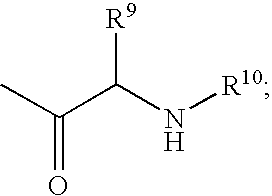
Substituted 5-carboxyamide pyrazoles and [1,2,4]triazoles as antiviral agents
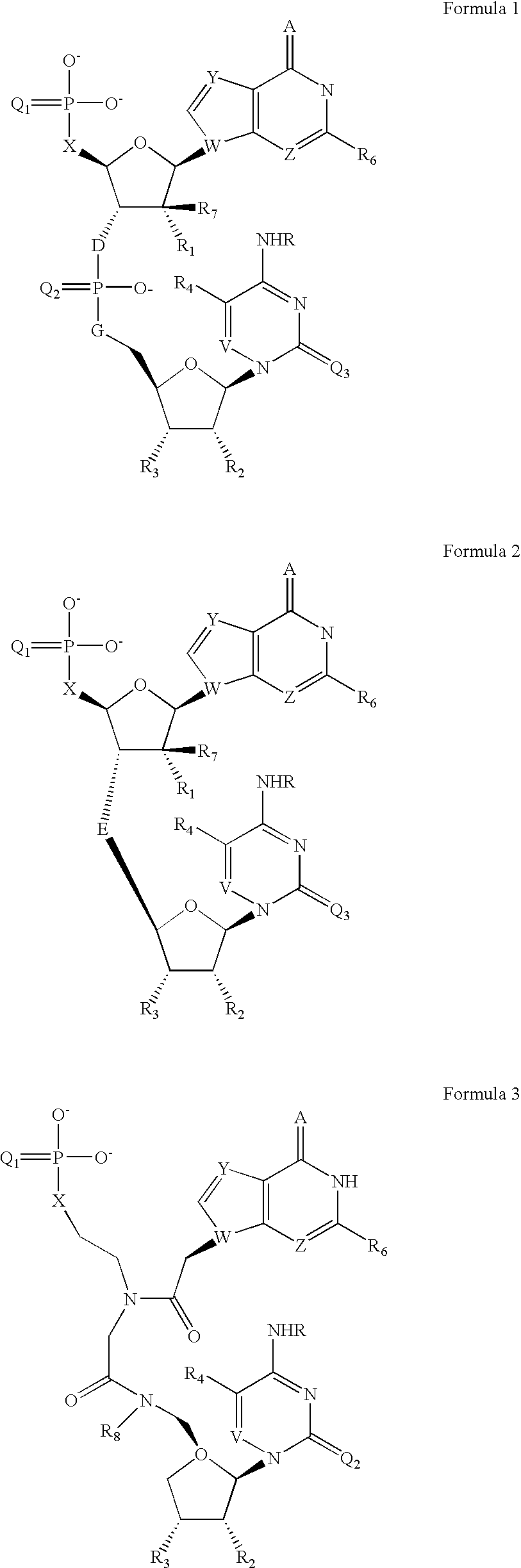
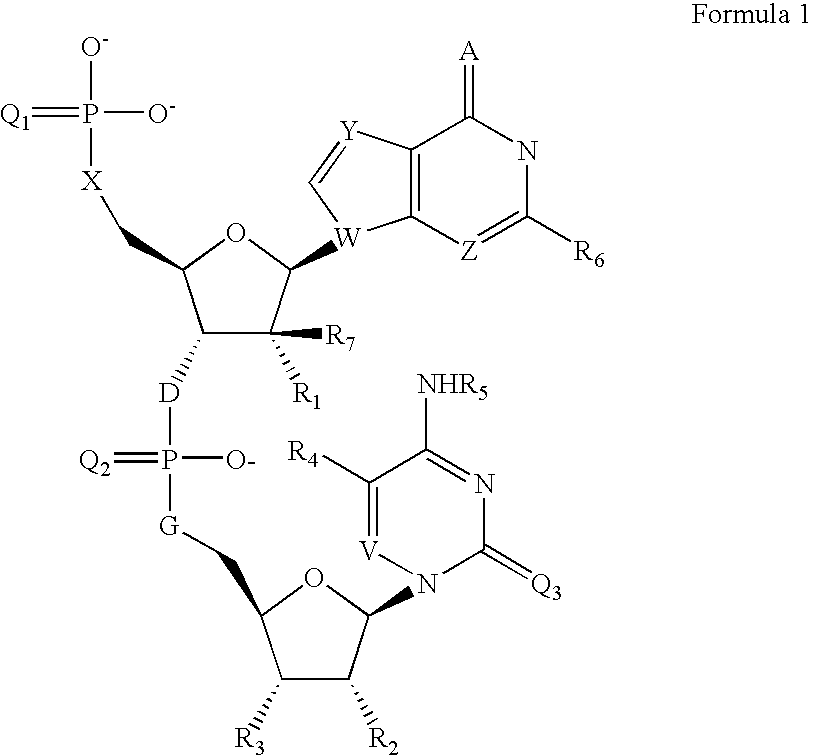
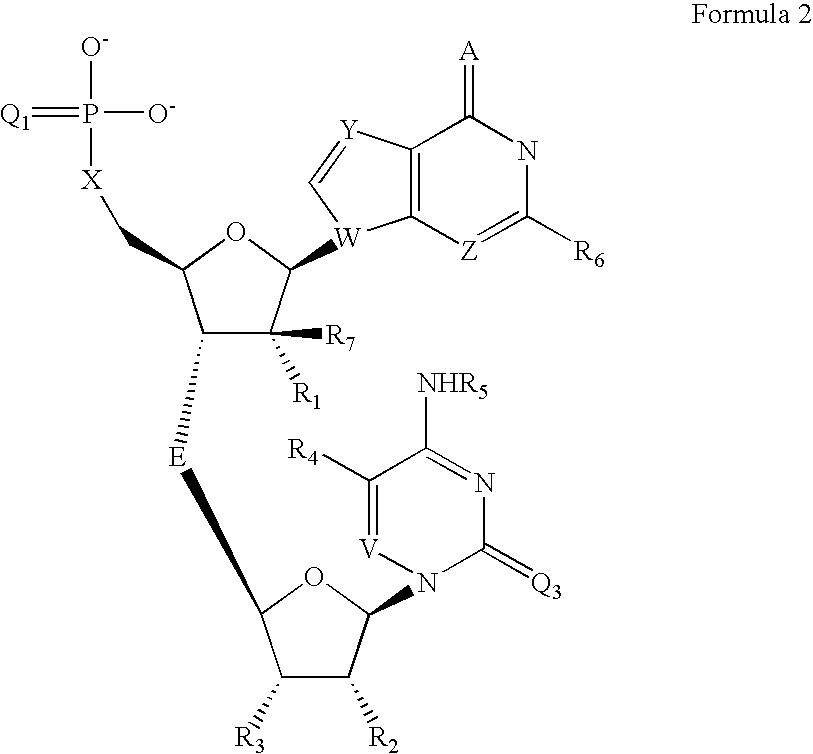
The present invention provides compounds of formula I wherein X, Y, R1-R7 are as defined herein. Compositions containing these compounds, and methods for inhibiting HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and treating hepatitis C and related disorders using these compounds and compositions are also provided.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Reagent for nucleic acid amplification and process for nucleic acid amplification
InactiveUS6261773B1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerPolymerase L
The present invention provide a process for sequence-specific nucleic acid amplification capable of improving the detection sensitivity and increasing the signal. In particular, the present invention provides a reagent for nucleic acid amplification containing at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts, specifically a reagent for nucleic acid amplification comprising, in addition to the at least one compound, a forward primer having a DNA sequence homologous to a sequence of a target RNA; a reverse primer having a DNA sequence complementary to a sequence of the target RNA and having a promoter for RNA polymerase attached to its 5' end; ribonucleotides; deoxyribonucleotides; a reverse transcriptase or RNA-directed DNA polymerase; a RNase H; a DNA polymerase or a reverse transcriptase having DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity; and a RNA polymerase. The present invention also provides a process for nucleic acid amplification characterized by carrying out a nucleic acid amplification reaction in the presence of at least one member selected from the group consisting of EDTA, NTA, UDA, CyDTA, DTPA, GEDTA, TTHA and their salts.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Phosphonates with reduced toxicity for treatment of viral infections
There are provided, inter alia, acyclic nucleoside phosphonate compounds having reduced toxicity and enhanced antiviral activity, and pharmaceutically accepted salts and solvates thereof. There are also provided methods of using the disclosed compounds for inhibiting viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting viral reverse transcriptase, inhibiting replication of virus, including hepatitis C virus or a human retrovirus, and treating a subject infected with a virus, including hepatitis C virus or a human retrovirus.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nucleic acid construct for endogenously expressing RNA polymerase in cells
The invention provides a nucleic acid construct for endogenously expressing RNA polymerase in cells, and particularly discovers a novel nucleic acid construct capable of greatly enhancing protein translation efficiency. The nucleic acid construct consists of a promoter with specific promotion intensity (such as RNR2, ADH1, GAPDH, TEF1, PGK1 and SED1) and coding sequences of proteins of RNAP (suchas T7RNAP, T3RNAP, T4RNAP and T5RNAP), if the nucleic acid construct of the invention is applied into a yeast extracorporeal protein synthesis system, the activity of synthesized luciferase is quite high relative to light unit value (RLU), and the effect can be the same as the effect of T7RNAP added exogenously. The effect can reach up to 6.6* 107.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Kits for amplifying DNA
ActiveUS8183359B2Reduce appearance problemsMinimize and substantially eliminate emergenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaA-DNA
Kits for amplifying DNA which include a priming oligonucleotide that hybridizes to a 3′-end of a DNA target sequence, a displacer oligonucleotide that hybridizes to a target nucleic acid containing the DNA target sequence at a position upstream from the priming oligonucleotide, and a promoter oligonucleotide that includes a region that hybridizes to a 3′-region of a DNA primer extension product that includes the priming oligonucleotide and a promoter for an RNA polymerase. The priming oligonucleotide does not include an RNA region that hybridizes to the target nucleic acid and is selectively degraded by an enzyme activity when hybridized to the target nucleic acid. The kits do not include a restriction endonuclease and oligonucleotides that include a promoter for an RNA polymerase are all modified to prevent the initiation of DNA synthesis therefrom.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method for rna amplification
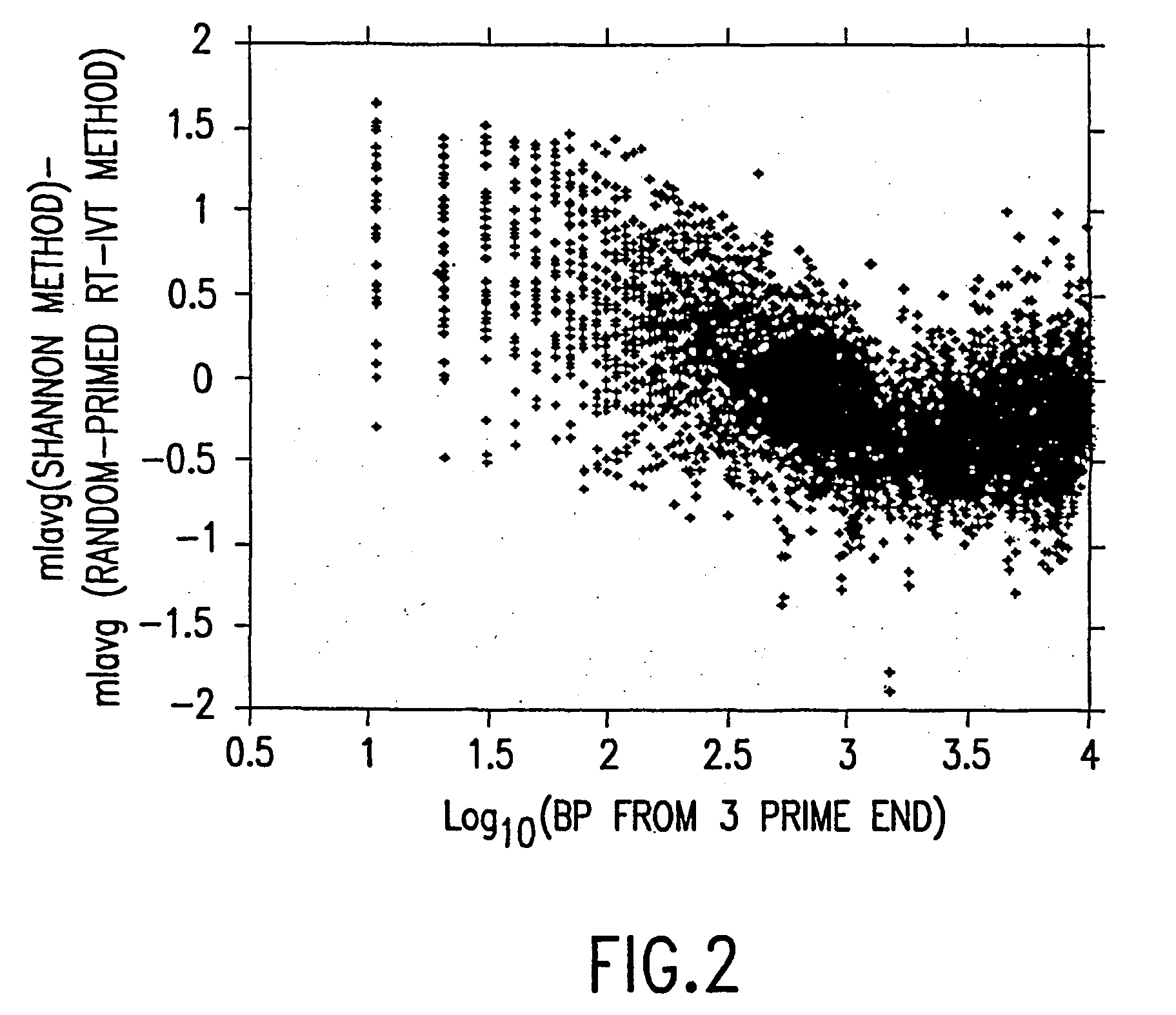
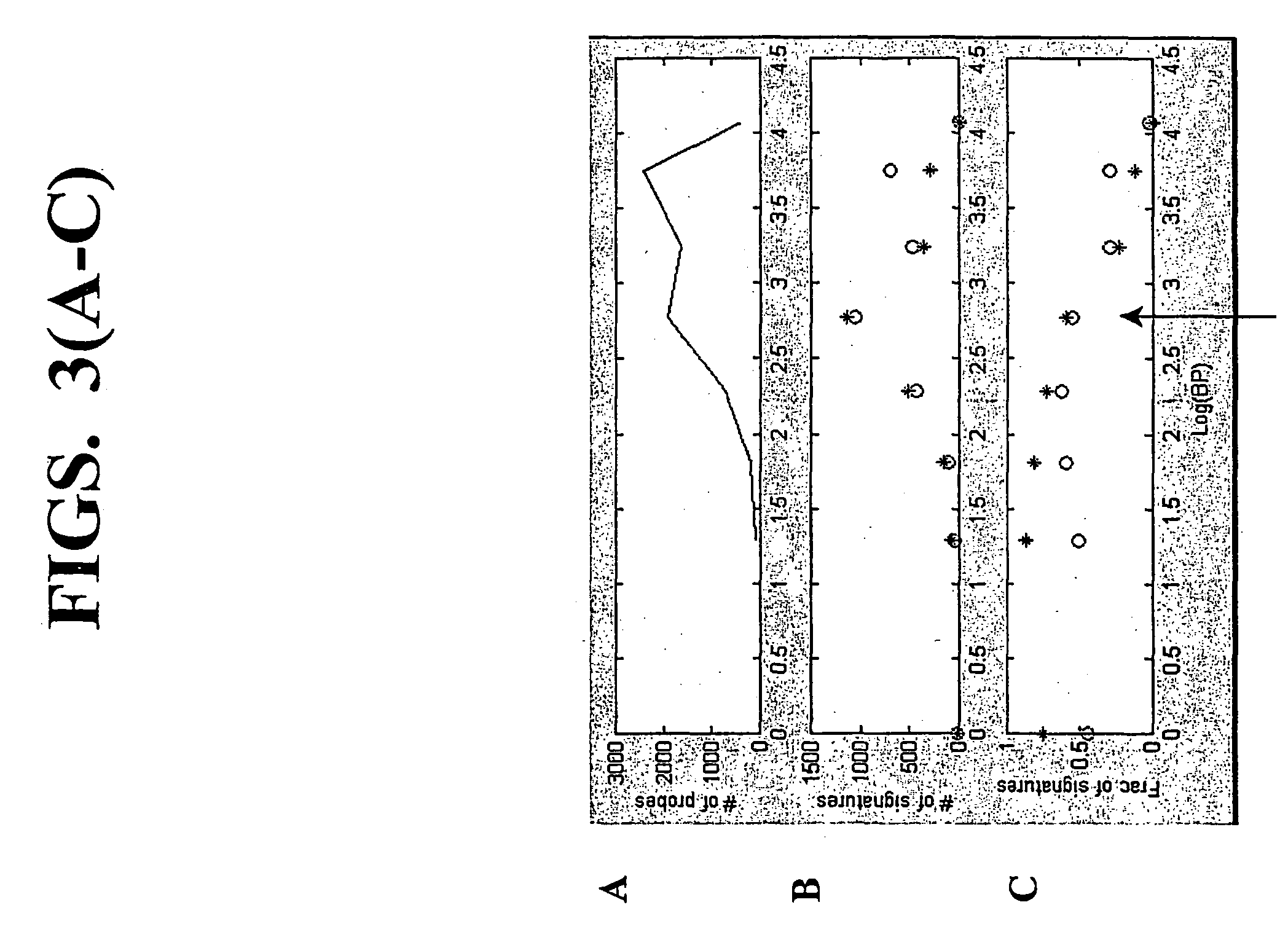
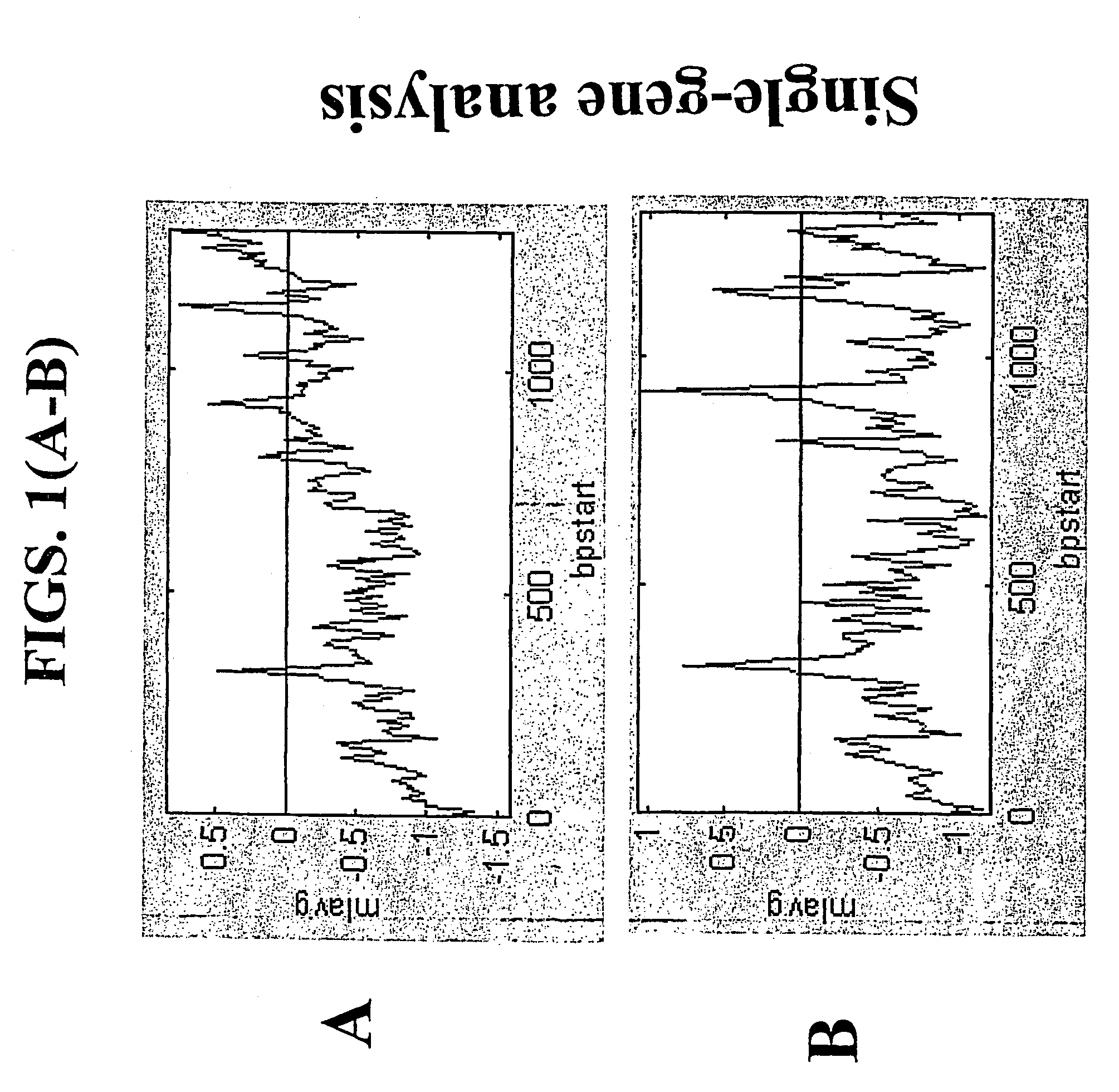
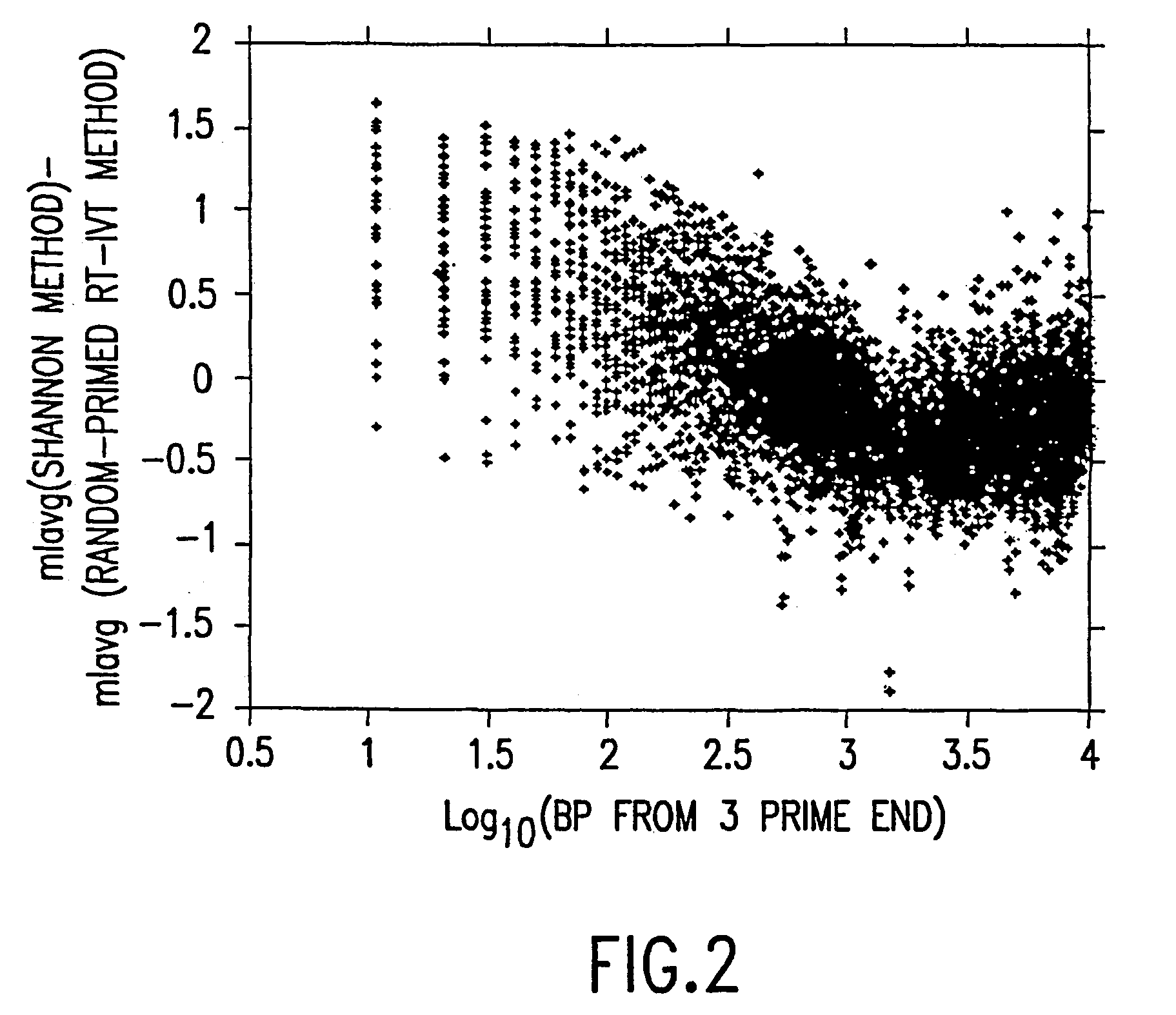
InactiveUS20040081978A1Improve representationImprove abilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReverse transcriptaseSingle strand
A random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method of linearly amplifying RNA is provided. According to the methods of the invention, source RNA (or other single-stranded nucleic acid), preferably, mRNA, is converted to double-stranded cDNA using two random primers, one of which comprises a RNA polymerase promoter sequence ("promoter-primer"), to yield a double-stranded cDNA that comprises a RNA polymerase promoter that is recognized by a RNA polymerase. Preferably, the primer for first-strand cDNA synthesis is a promoter-primer and the primer for second-strand cDNA synthesis is not a promoter-primer. The double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into RNA by the RNA polymerase, optimally in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods produce linearly amplified RNA with little or no 3' bias in the sequences of the nucleic acid population amplified.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method for RNA amplification
InactiveUS7229765B2Improve abilitiesImprove representationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReverse transcriptaseSingle strand
A random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method of linearly amplifying RNA is provided. According to the methods of the invention, source RNA (or other single-stranded nucleic acid), preferably, mRNA, is converted to double-stranded cDNA using two random primers, one of which comprises a RNA polymerase promoter sequence (“promoter-primer”), to yield a double-stranded cDNA that comprises a RNA polymerase promoter that is recognized by a RNA polymerase. Preferably, the primer for first-strand cDNA synthesis is a promoter-primer and the primer for second-strand cDNA synthesis is not a promoter-primer. The double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into RNA by the RNA polymerase, optimally in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods produce linearly amplified RNA with little or no 3′ bias in the sequences of the nucleic acid population amplified.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
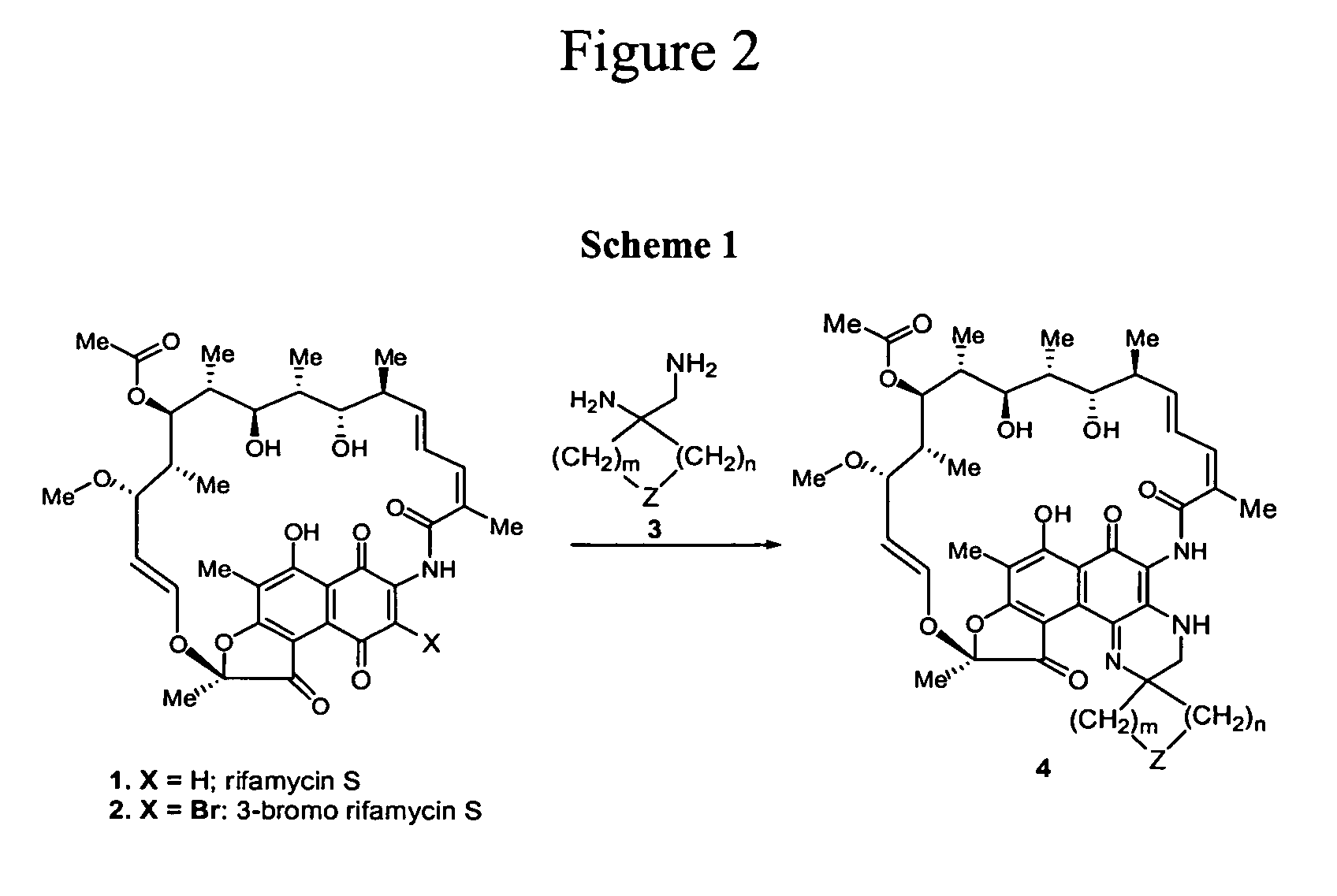
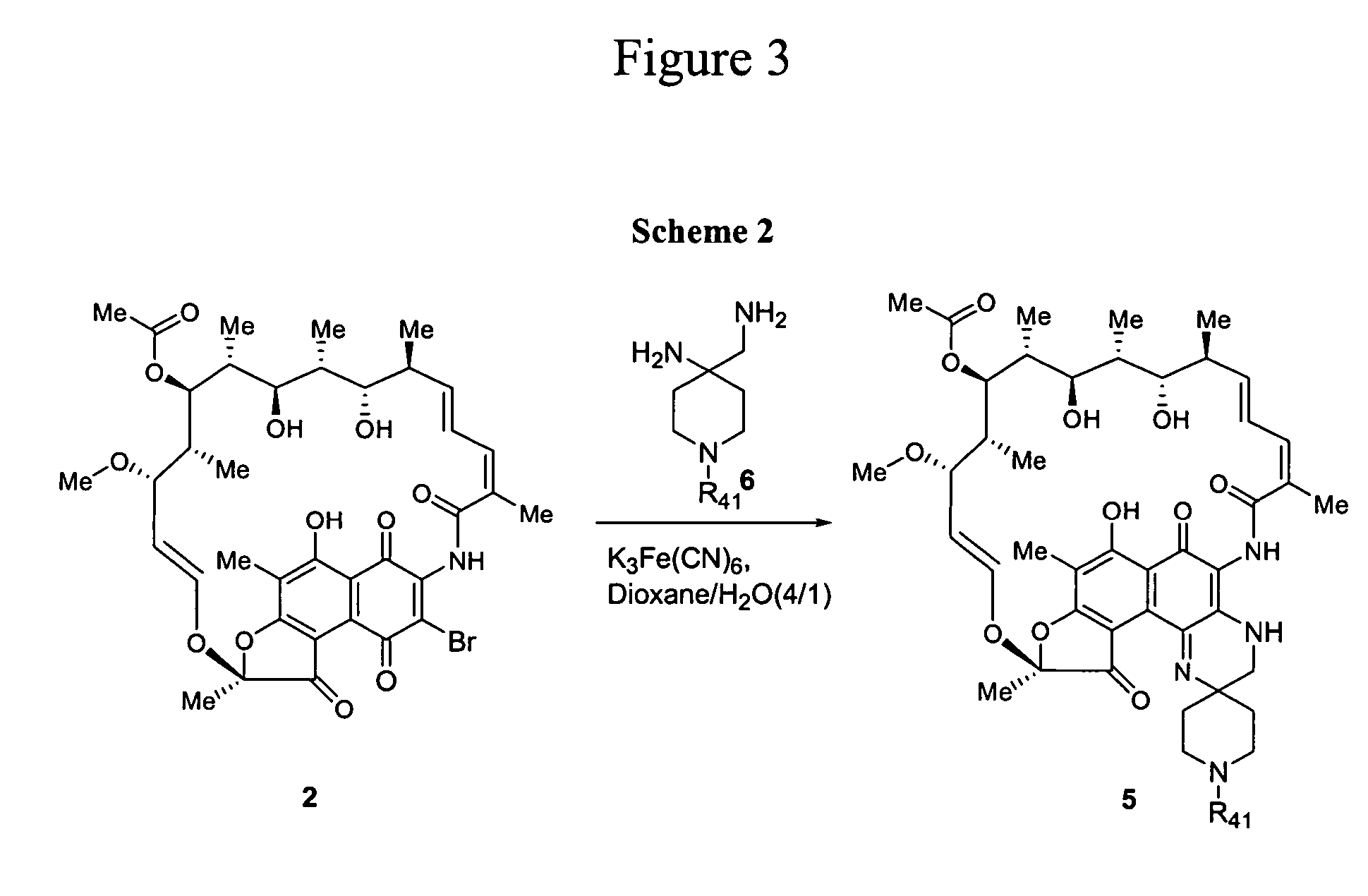
Spiro-rifamycin derivatives targeting RNA polymerase
Compounds of the current invention relate to rifamycin derivatives having antimicrobial activities, including activities against drug-resistant microorganisms. More specifically, compounds of the current invention relate to a series of novel spiro rifamycin derivatives which have demonstrated potent antimicrobial activity.
Owner:TENNOR THERAPEUTICS (SUZHOU) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



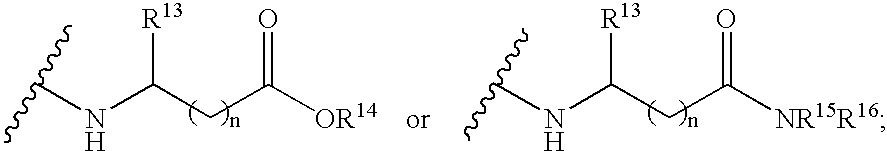
![Substituted 5-carboxyamide pyrazoles and [1,2,4]triazoles as antiviral agents Substituted 5-carboxyamide pyrazoles and [1,2,4]triazoles as antiviral agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f9f59a89-1354-406c-b580-94652b9b0025/US20060111411A1-20060525-C00001.png)
![Substituted 5-carboxyamide pyrazoles and [1,2,4]triazoles as antiviral agents Substituted 5-carboxyamide pyrazoles and [1,2,4]triazoles as antiviral agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f9f59a89-1354-406c-b580-94652b9b0025/US20060111411A1-20060525-C00002.png)
![Substituted 5-carboxyamide pyrazoles and [1,2,4]triazoles as antiviral agents Substituted 5-carboxyamide pyrazoles and [1,2,4]triazoles as antiviral agents](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f9f59a89-1354-406c-b580-94652b9b0025/US20060111411A1-20060525-C00003.png)