Patents
Literature
46 results about "Bacterial RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transfer-messenger RNA (abbreviated tmRNA, also known as 10Sa RNA and by its genetic name SsrA) is a bacterial RNA molecule with dual tRNA-like and messenger RNA-like properties. The tmRNA forms a ribonucleoprotein complex (tmRNP) together with Small Protein B (SmpB), Elongation Factor Tu (EF-Tu), and ribosomal protein S1.
Structure and use of 5' phosphate oligonucleotides
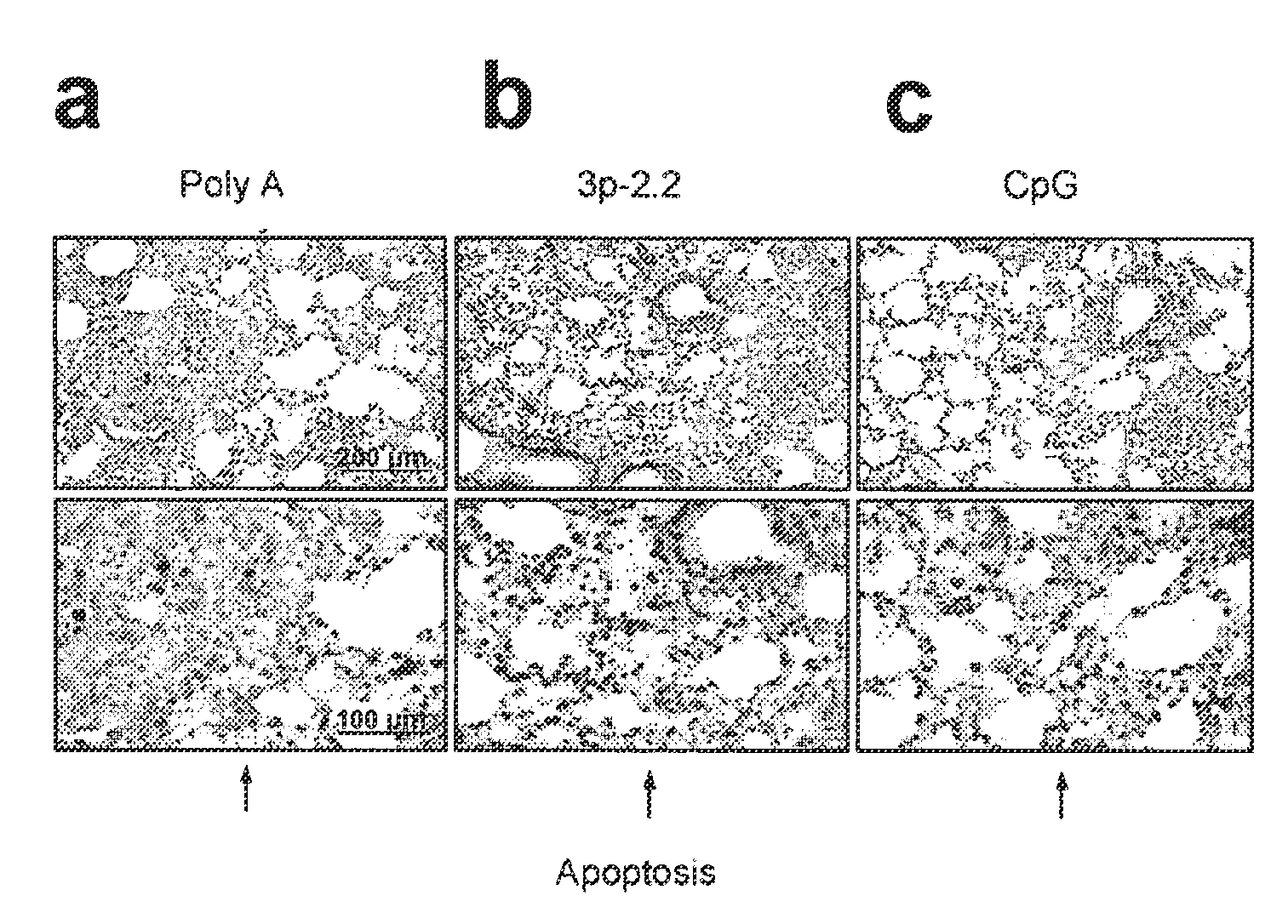
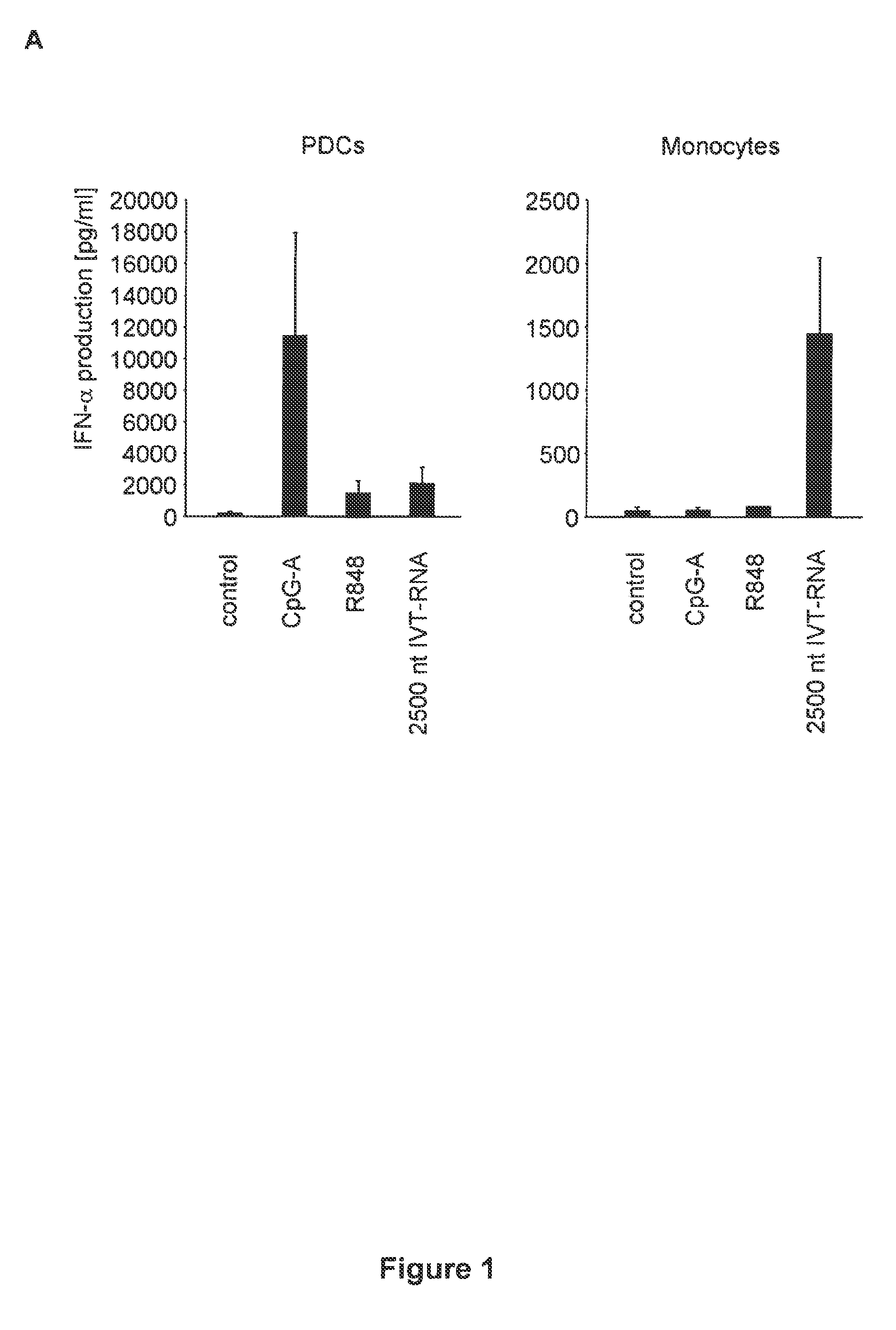
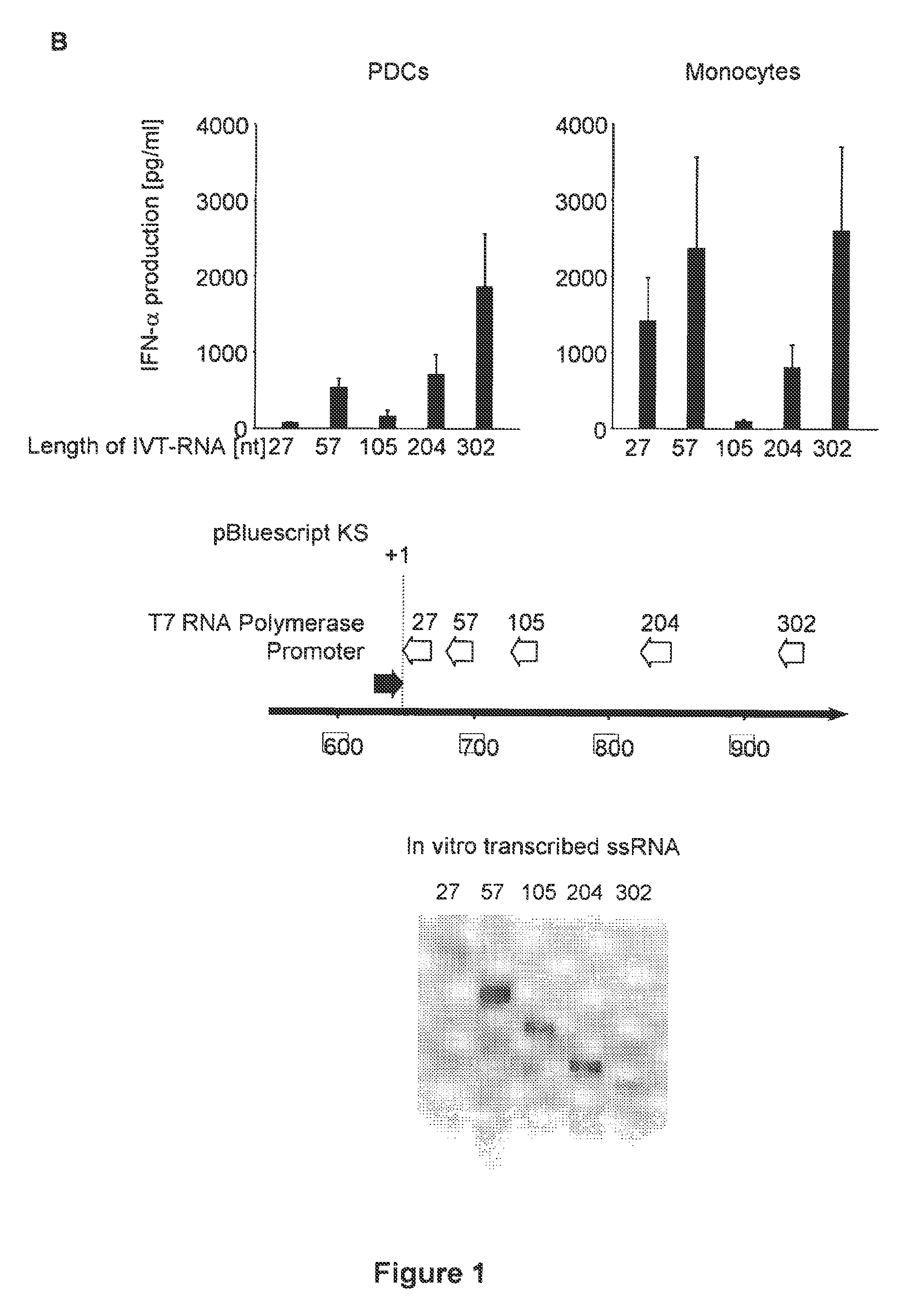
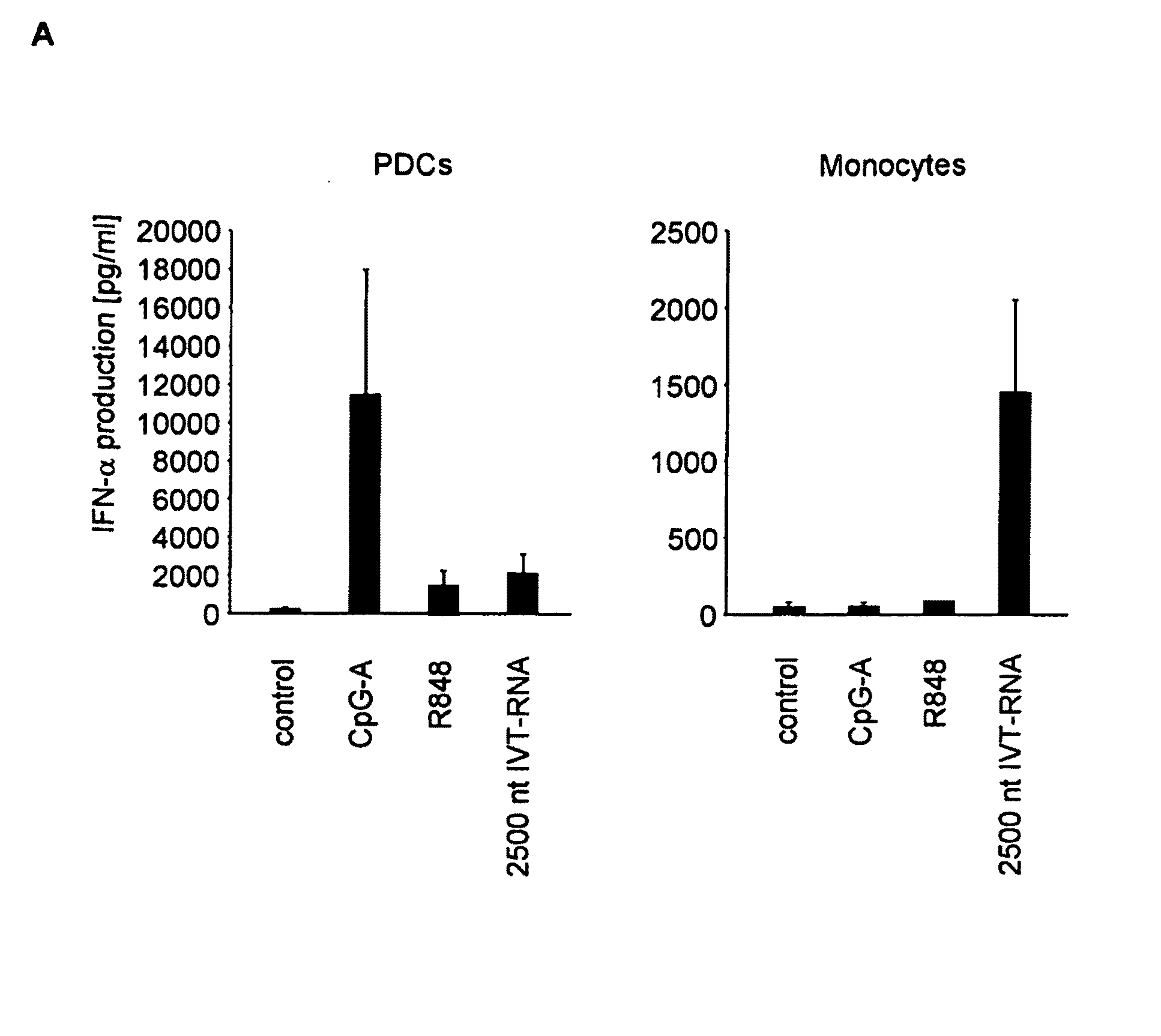
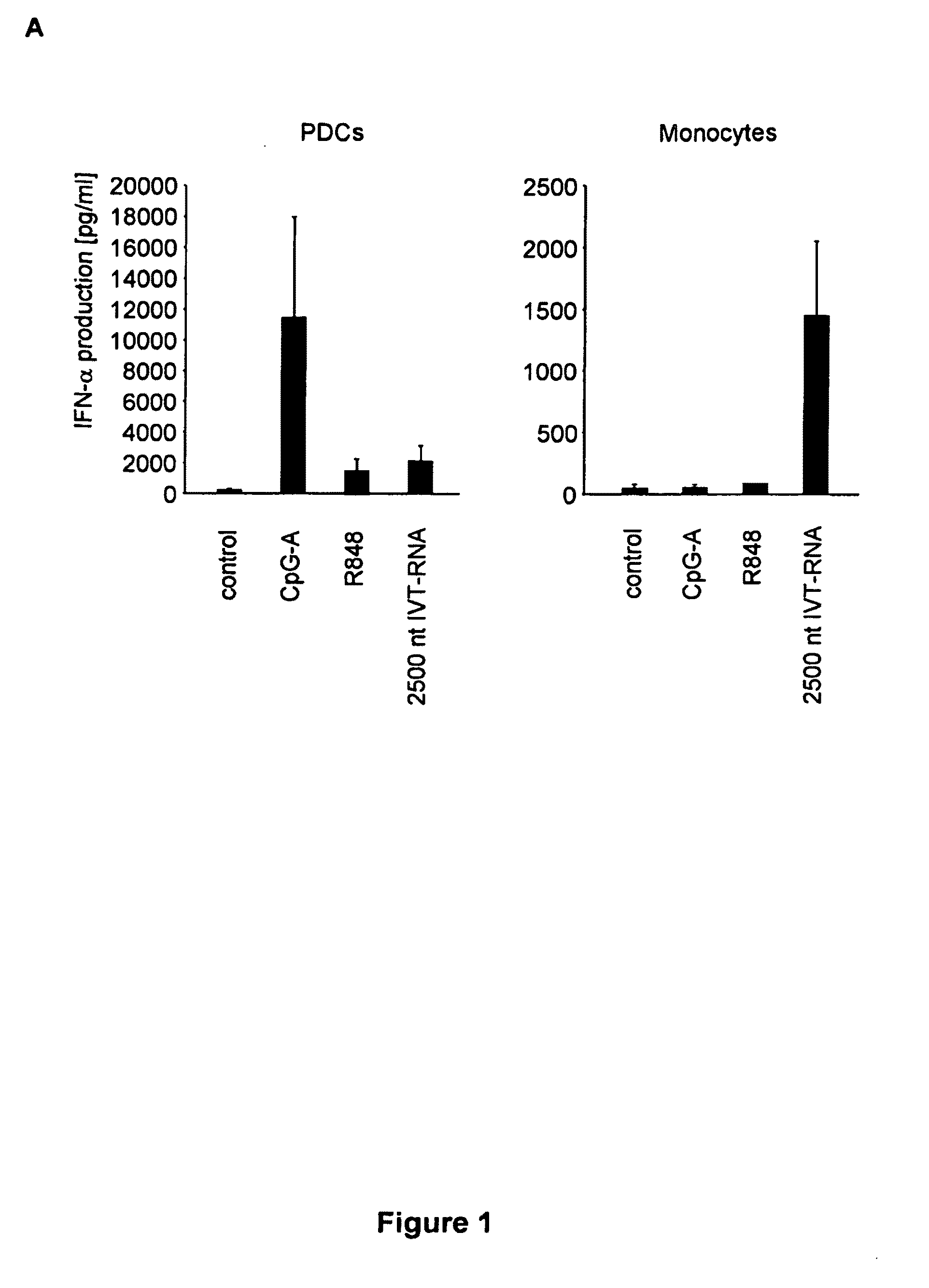
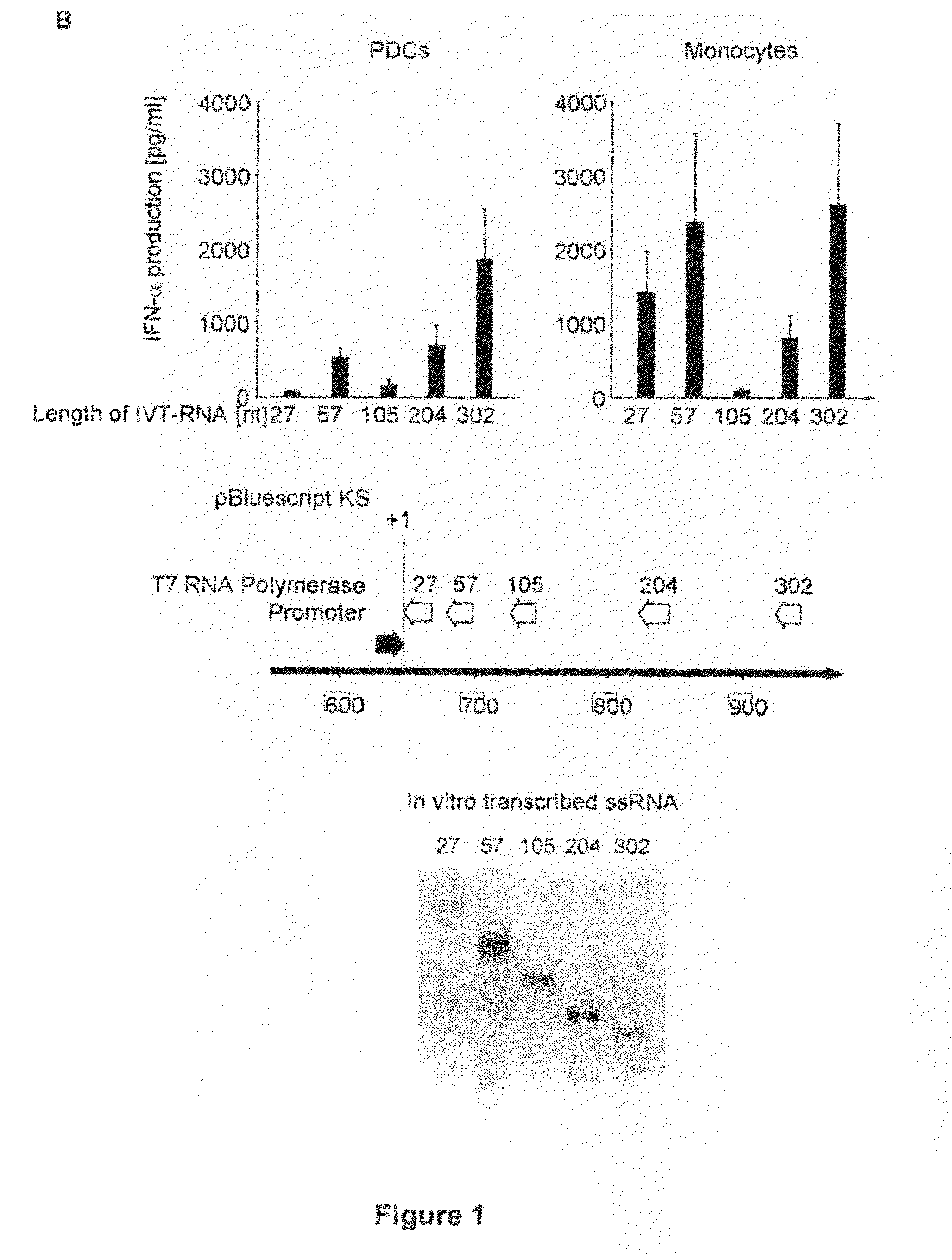
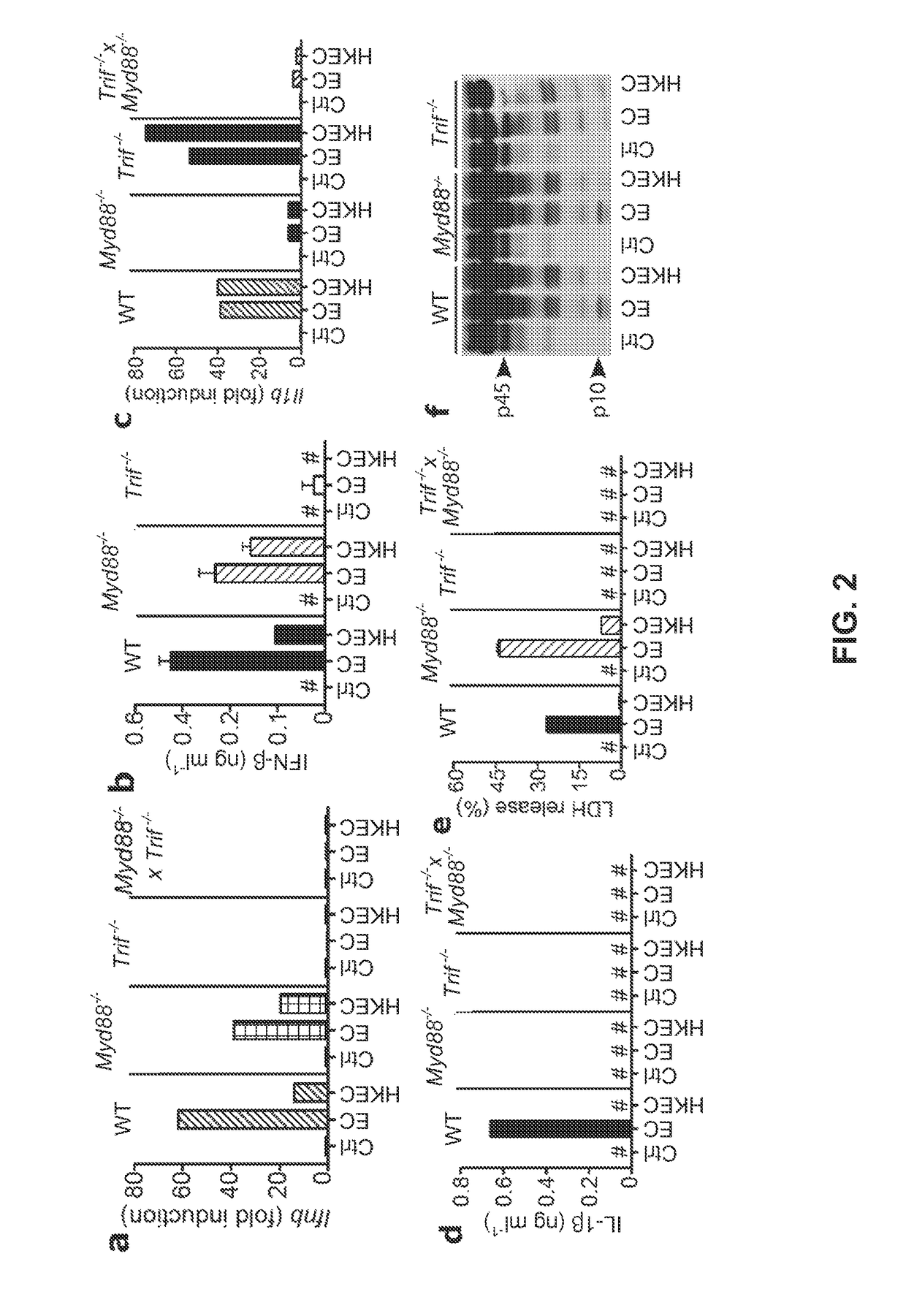
Oligonucleotides bearing free, uncapped 5′ phosphate group(s) are recognized by RIG-I, leading to the induction of type I IFN, IL-18 and IL-1β production. Bacterial RNA also induces type I IFN production. 5′ phosphate oligonucleotides and bacterial RNA can be used for inducing an anti-viral response or an anti-bacterial response, in particular, type I IFN and / or IL-18 and / or IL-1β production, in vitro and in vivo and for treating various disorders and diseases such as viral infections, bacterial infections, parasitic infections, tumors, allergies, autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiencies and immunosuppression. Single-stranded 5′ triphosphate RNA can be used for inducing an anti-viral response, an anti-bacterial response, or an anti-tumor response, in particular, type I IFN and / or IL-18 and / or IL-1β production, in a target cell-specific manner.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BONN
Structure and use of 5'phosphate oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20100178272A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
Owner:KLINISCHE PHARMAKOLOGIE
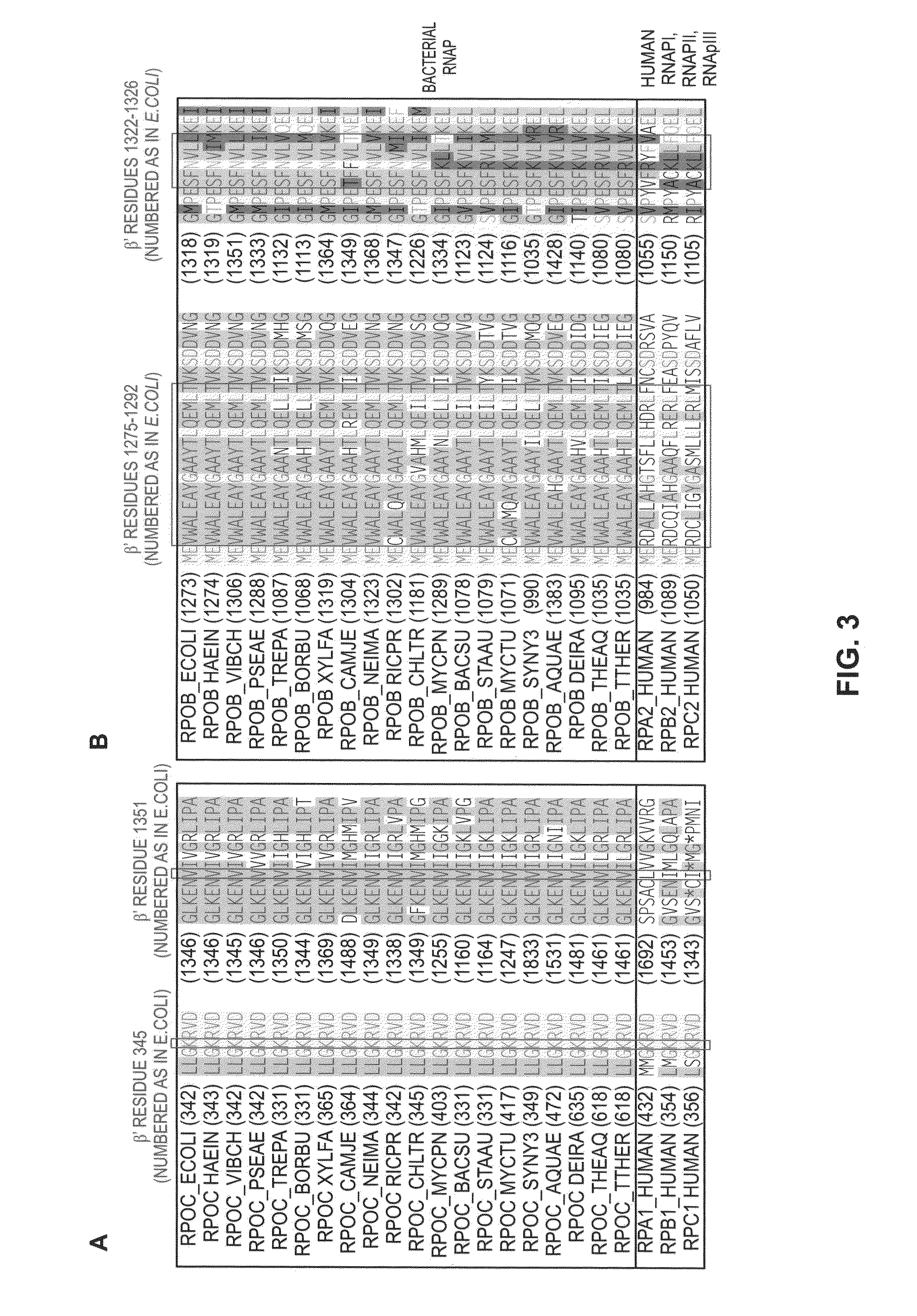
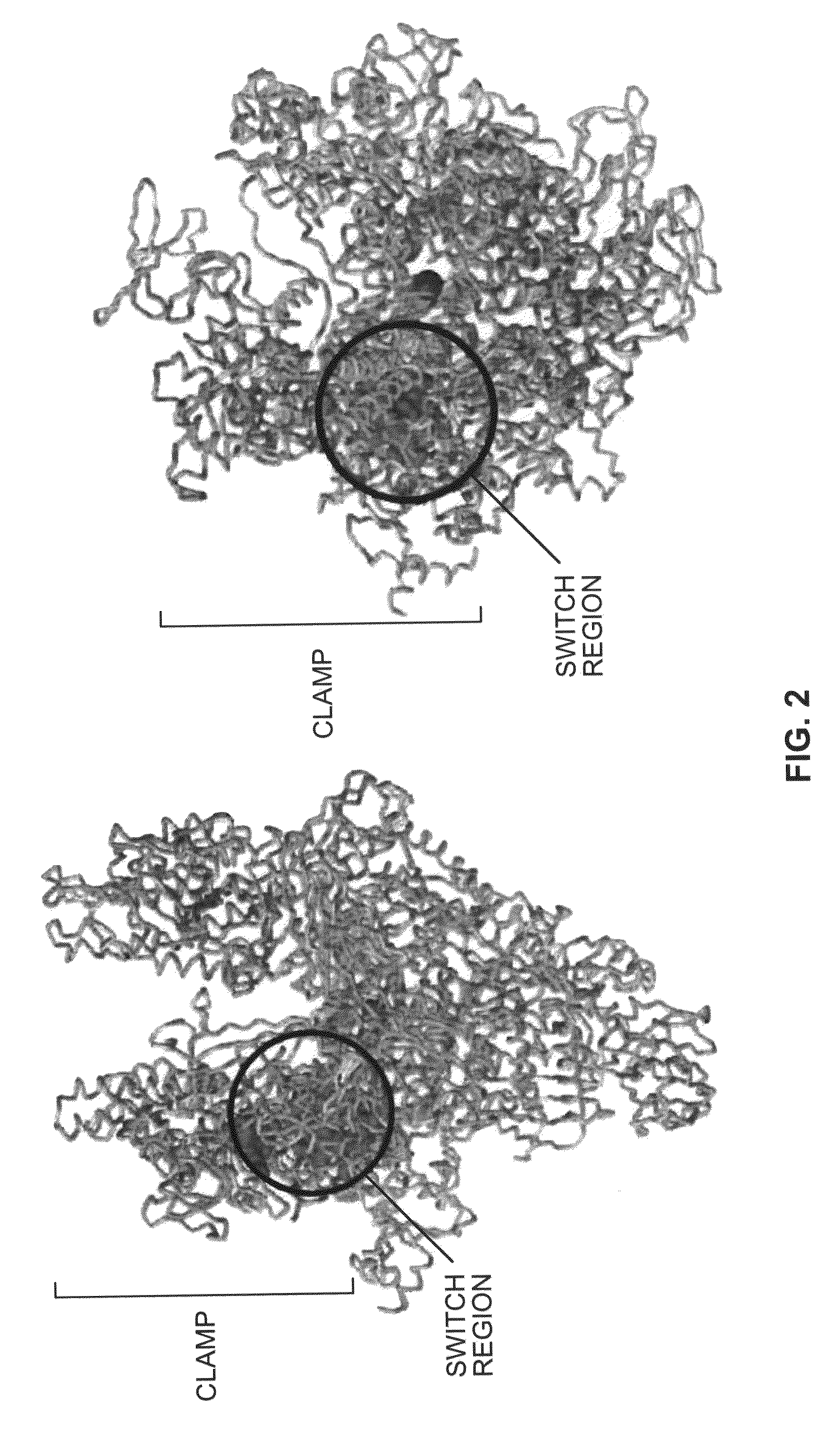
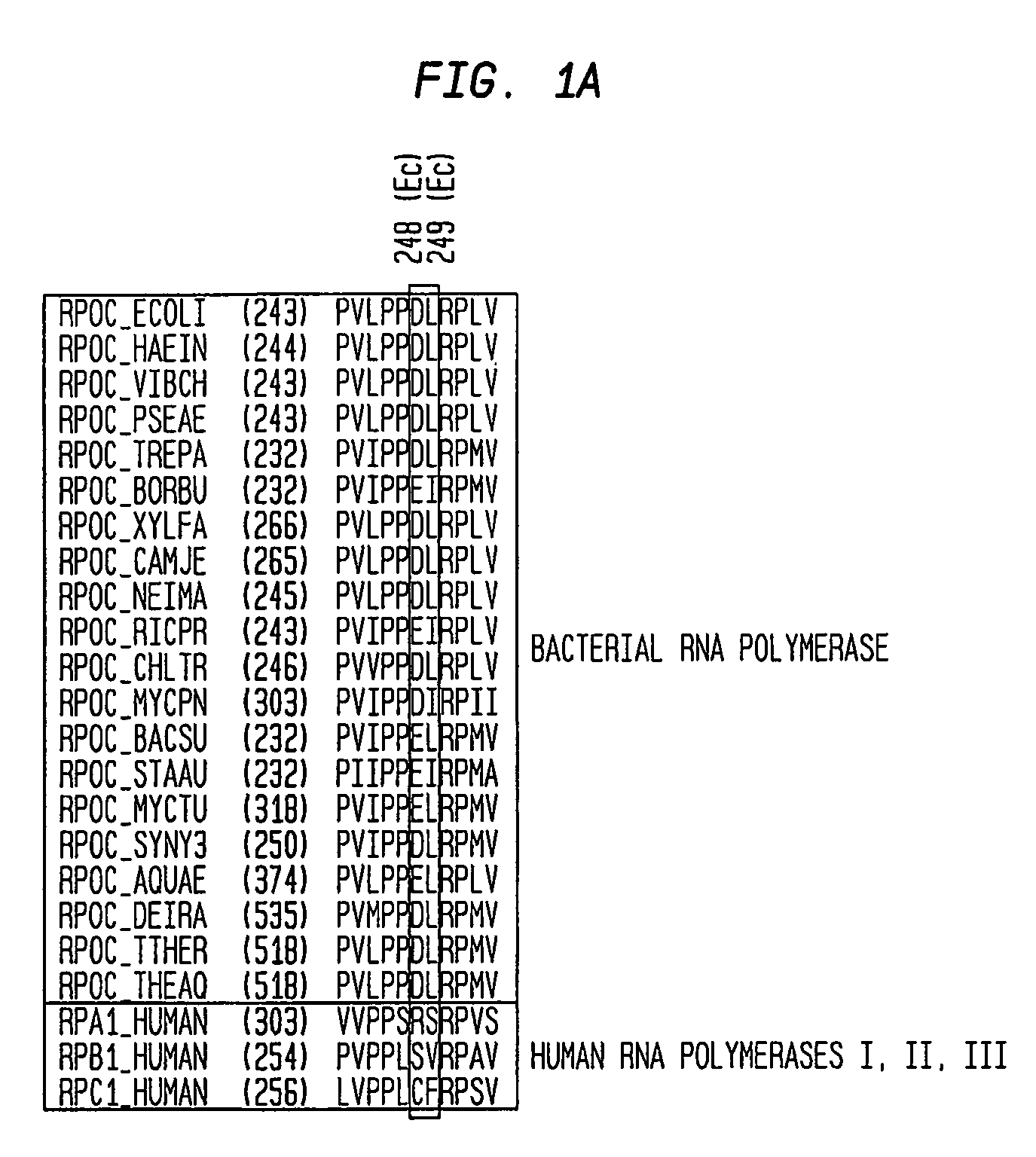
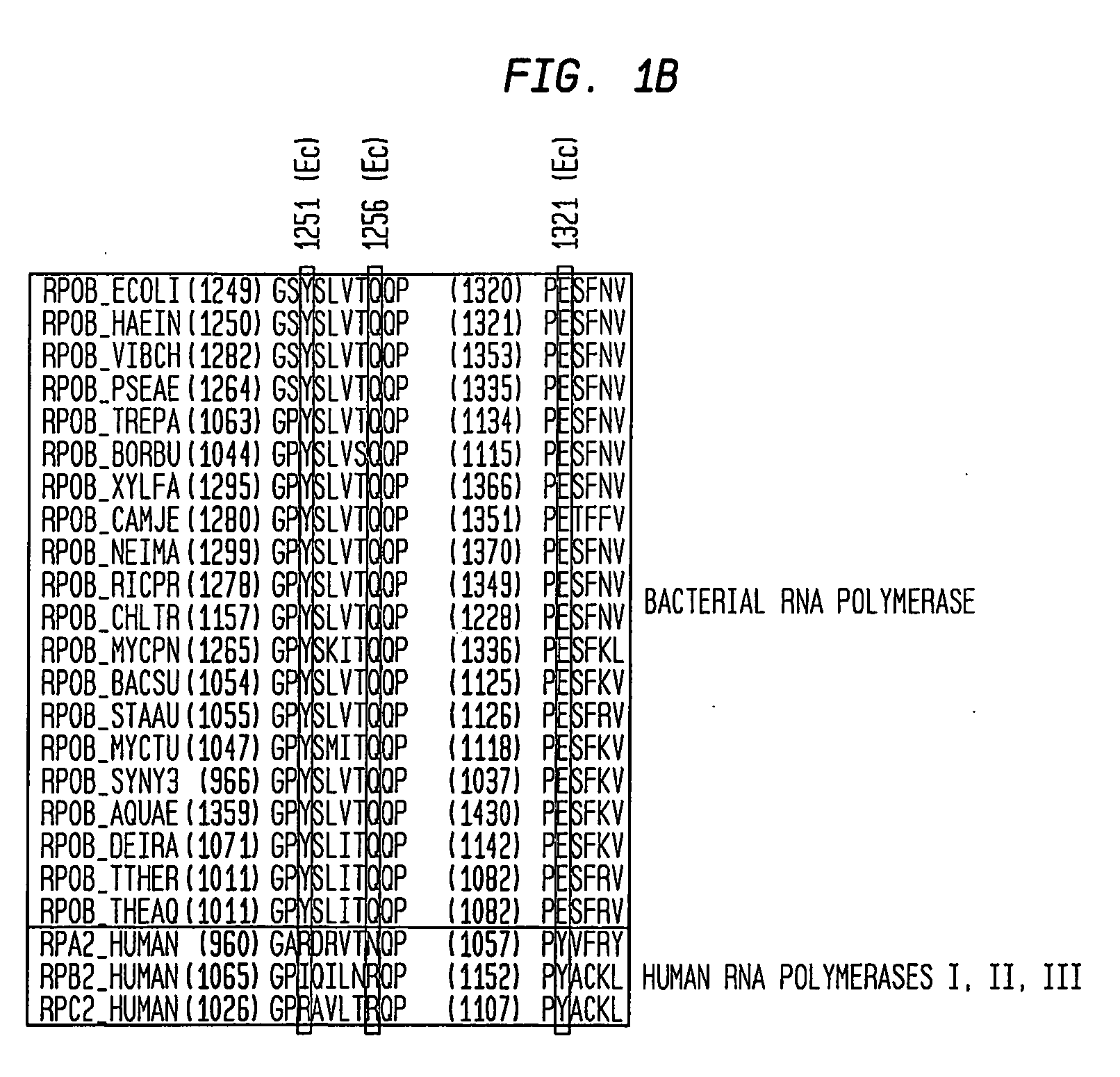
Target and method for inhibition of bacterial rna polymerase
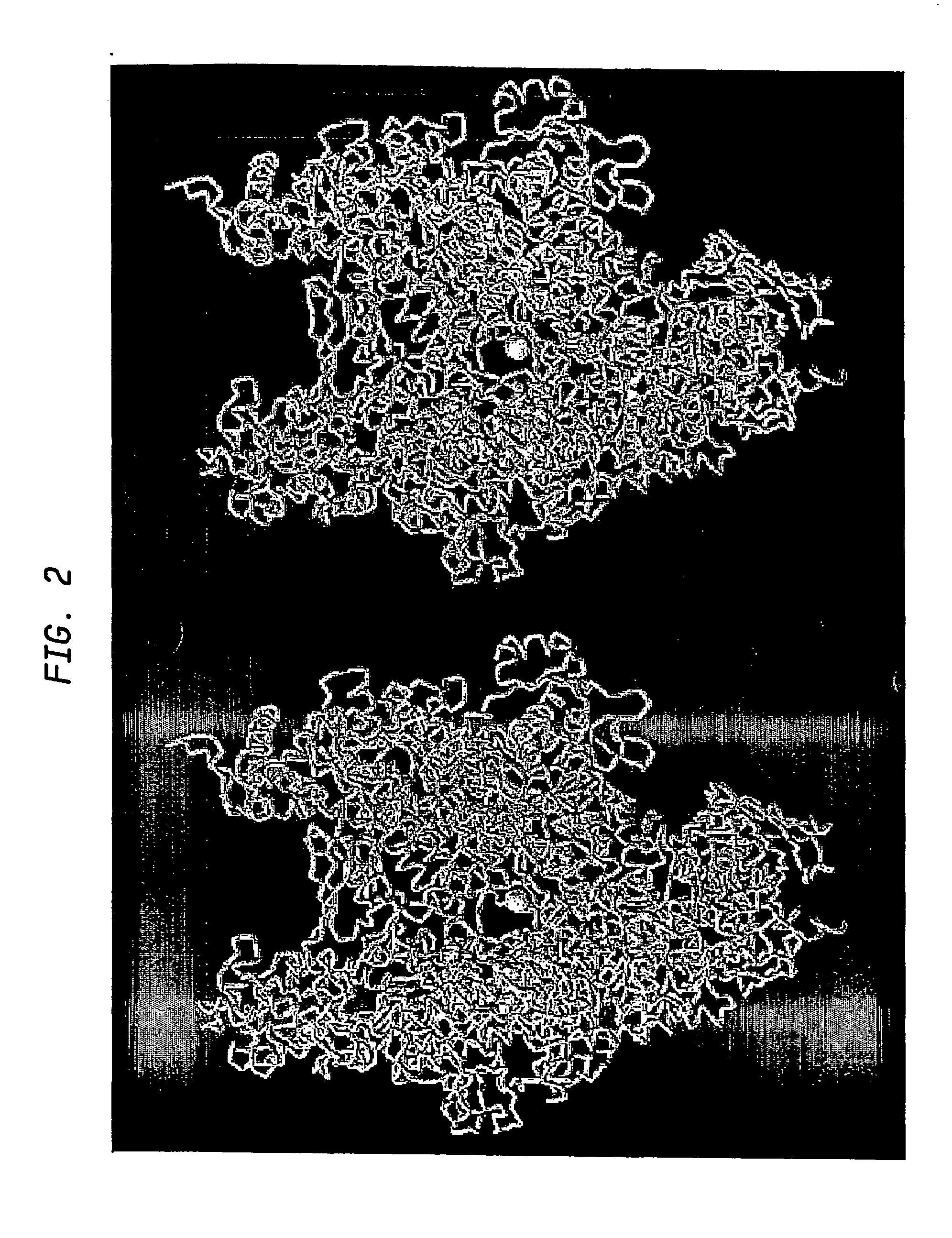
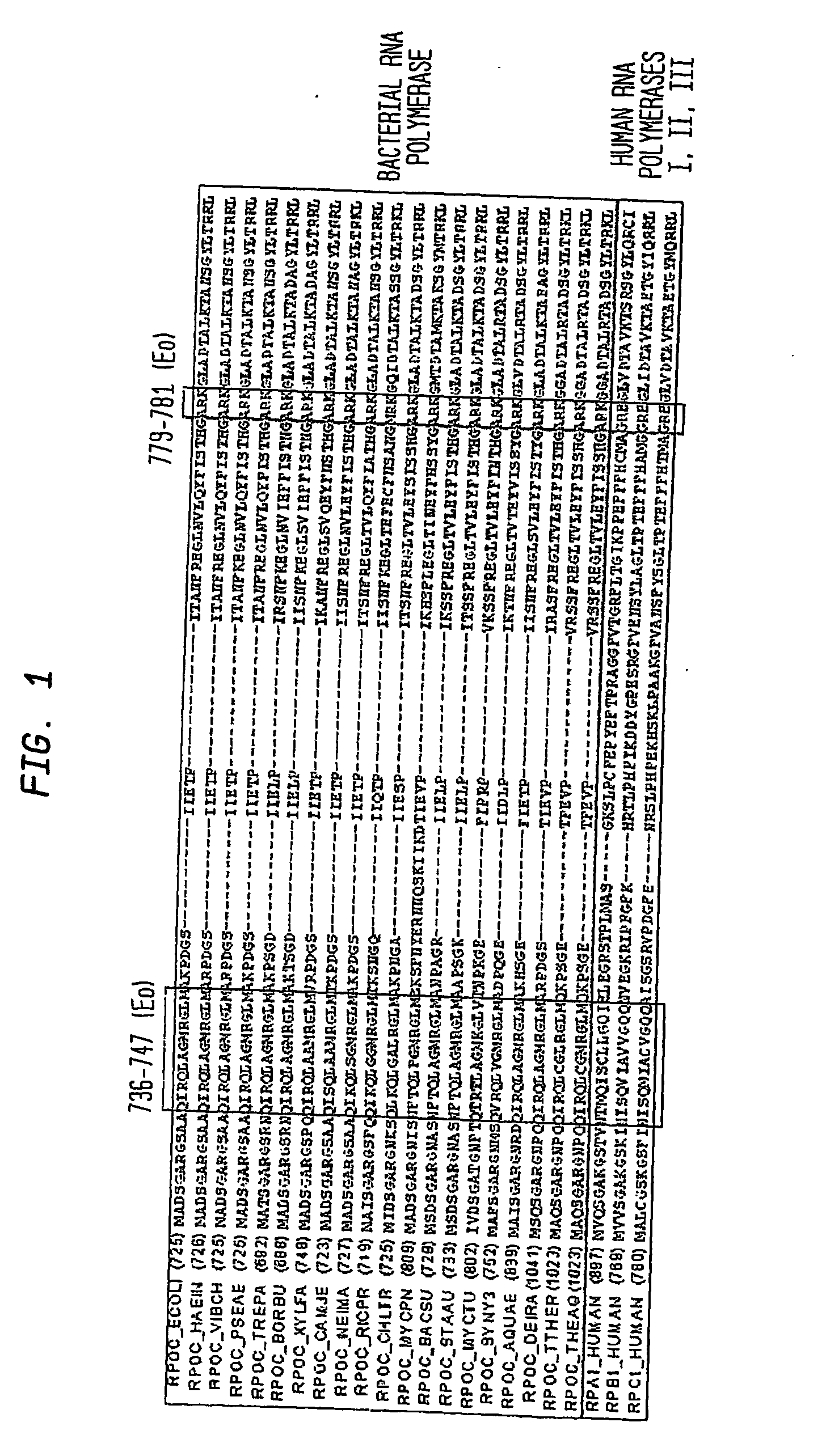
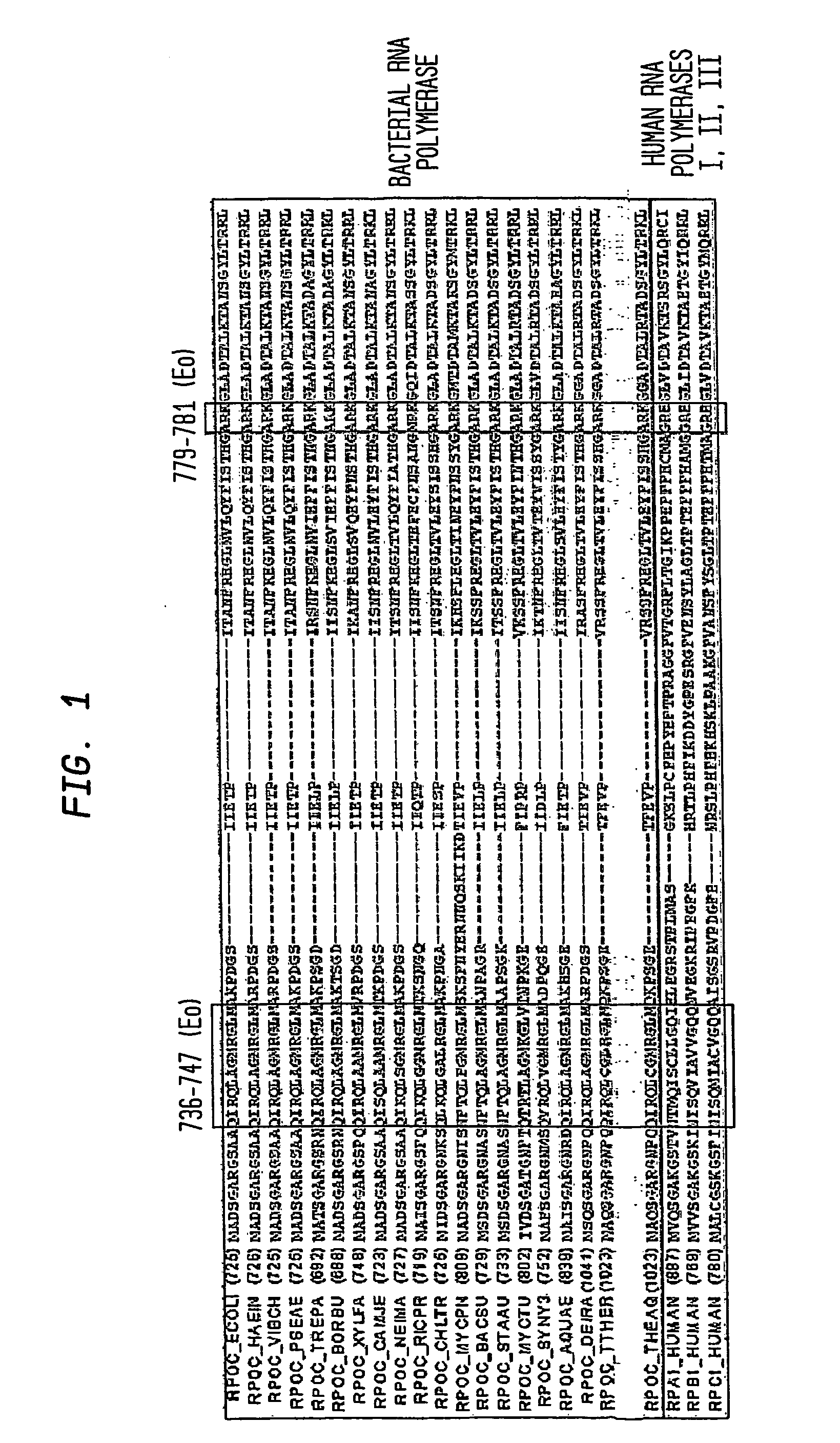
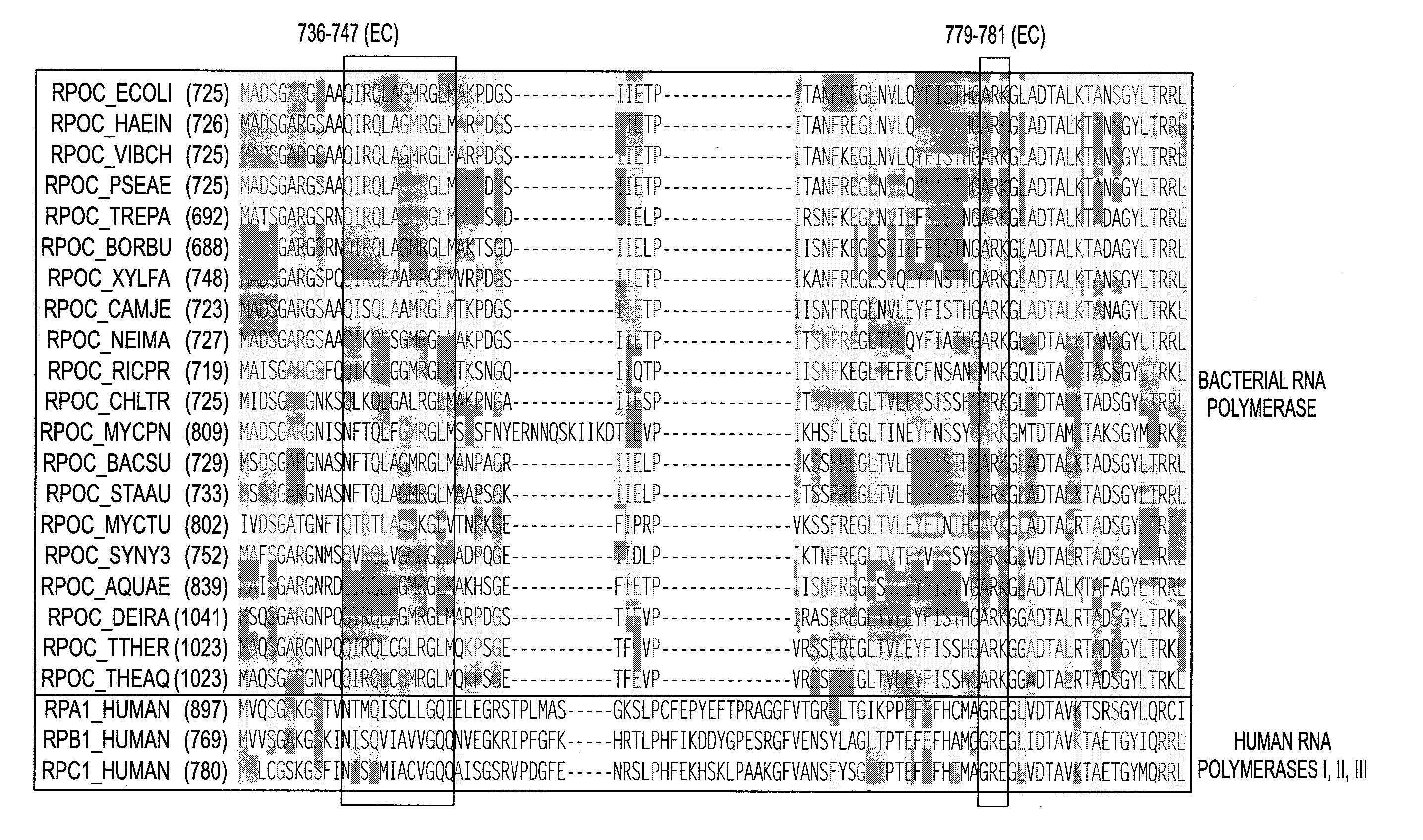
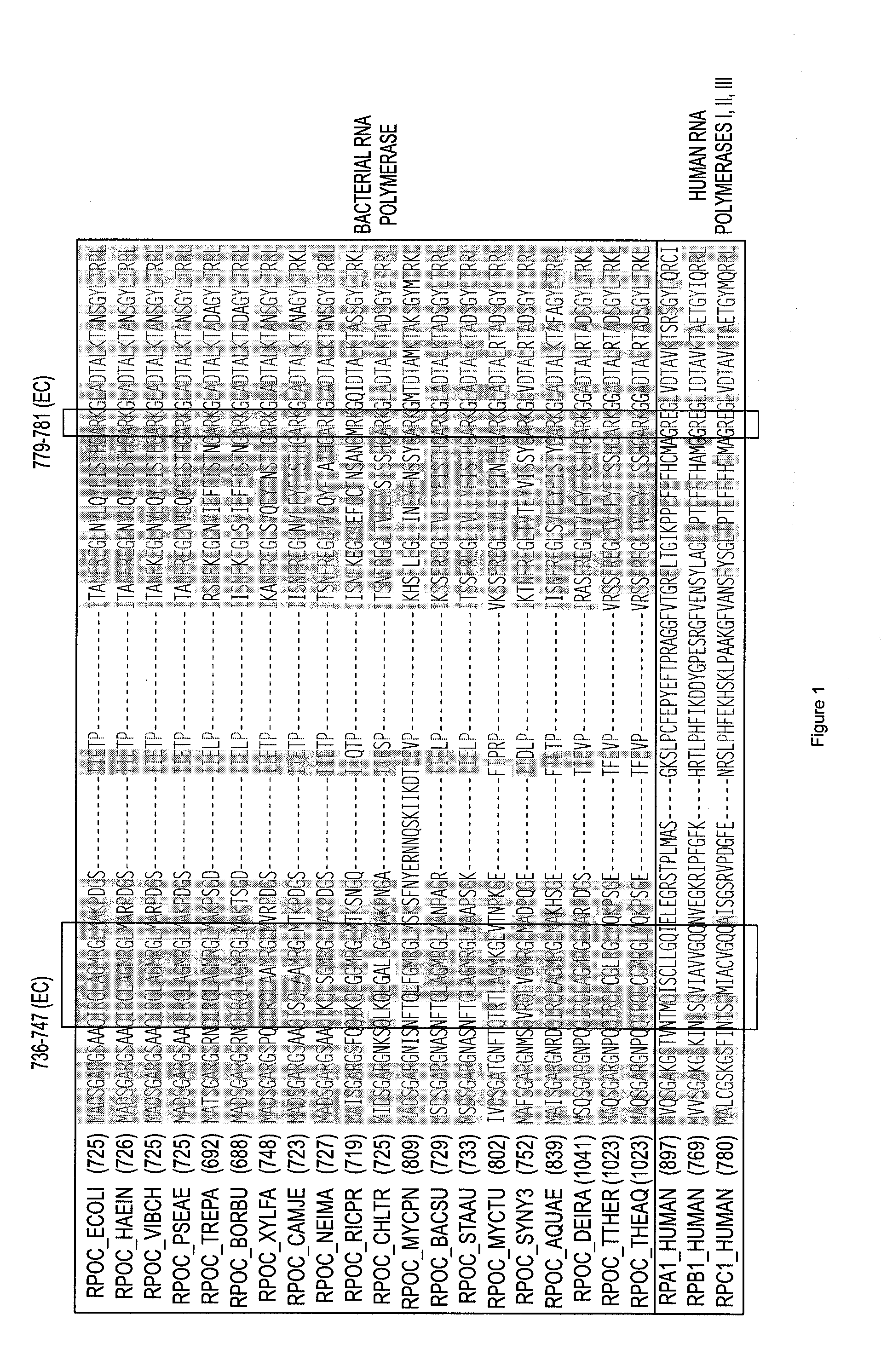
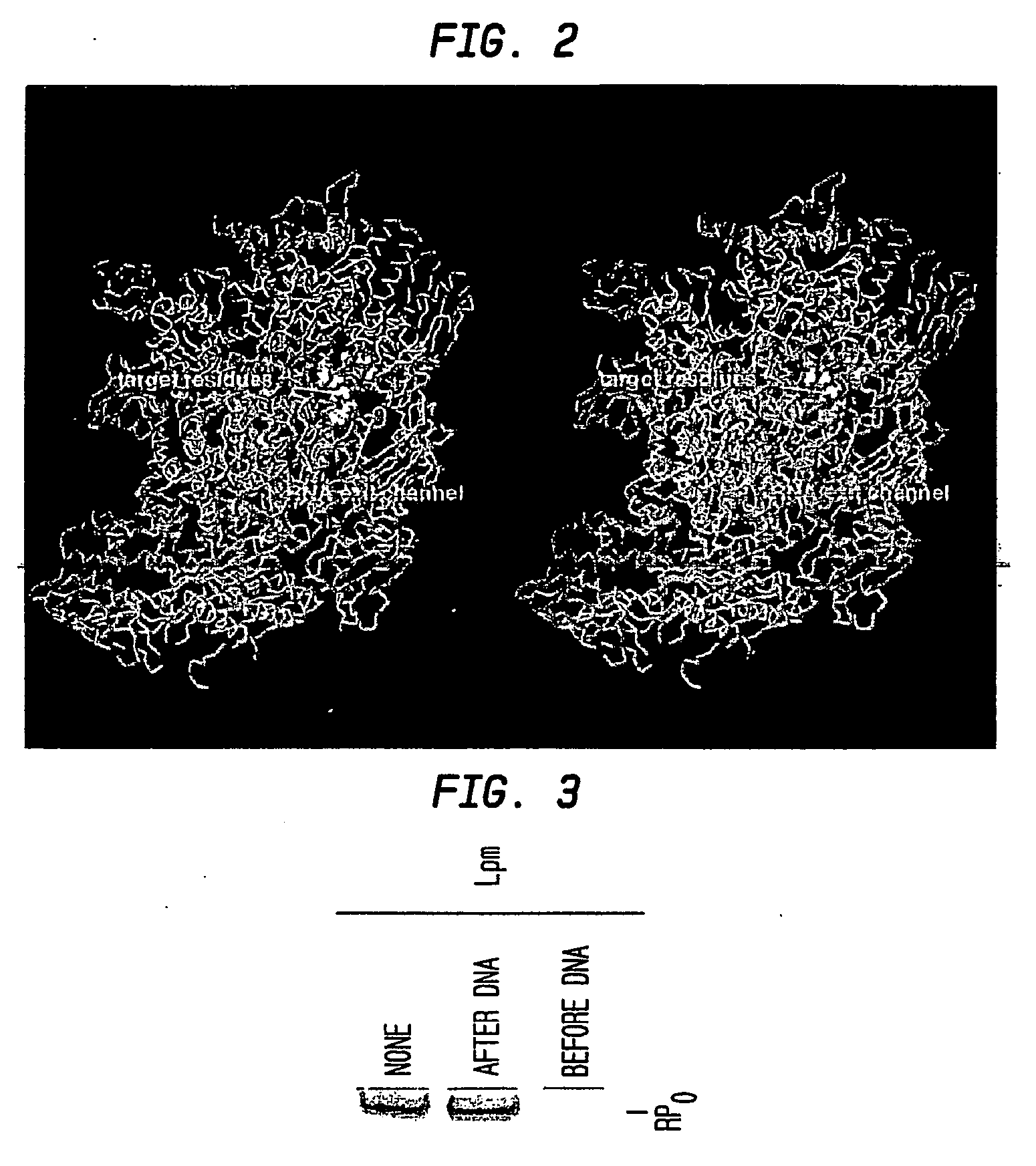
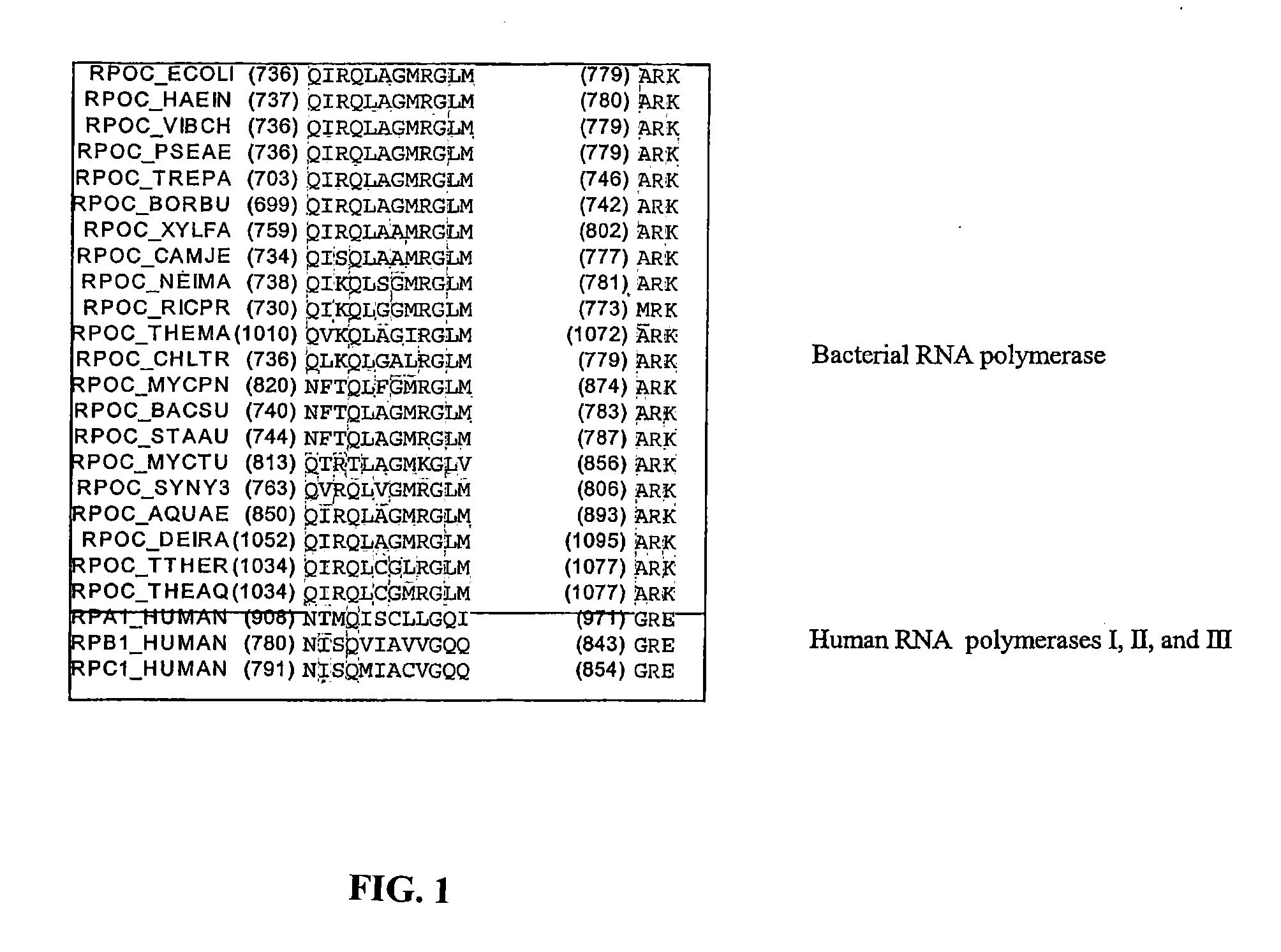
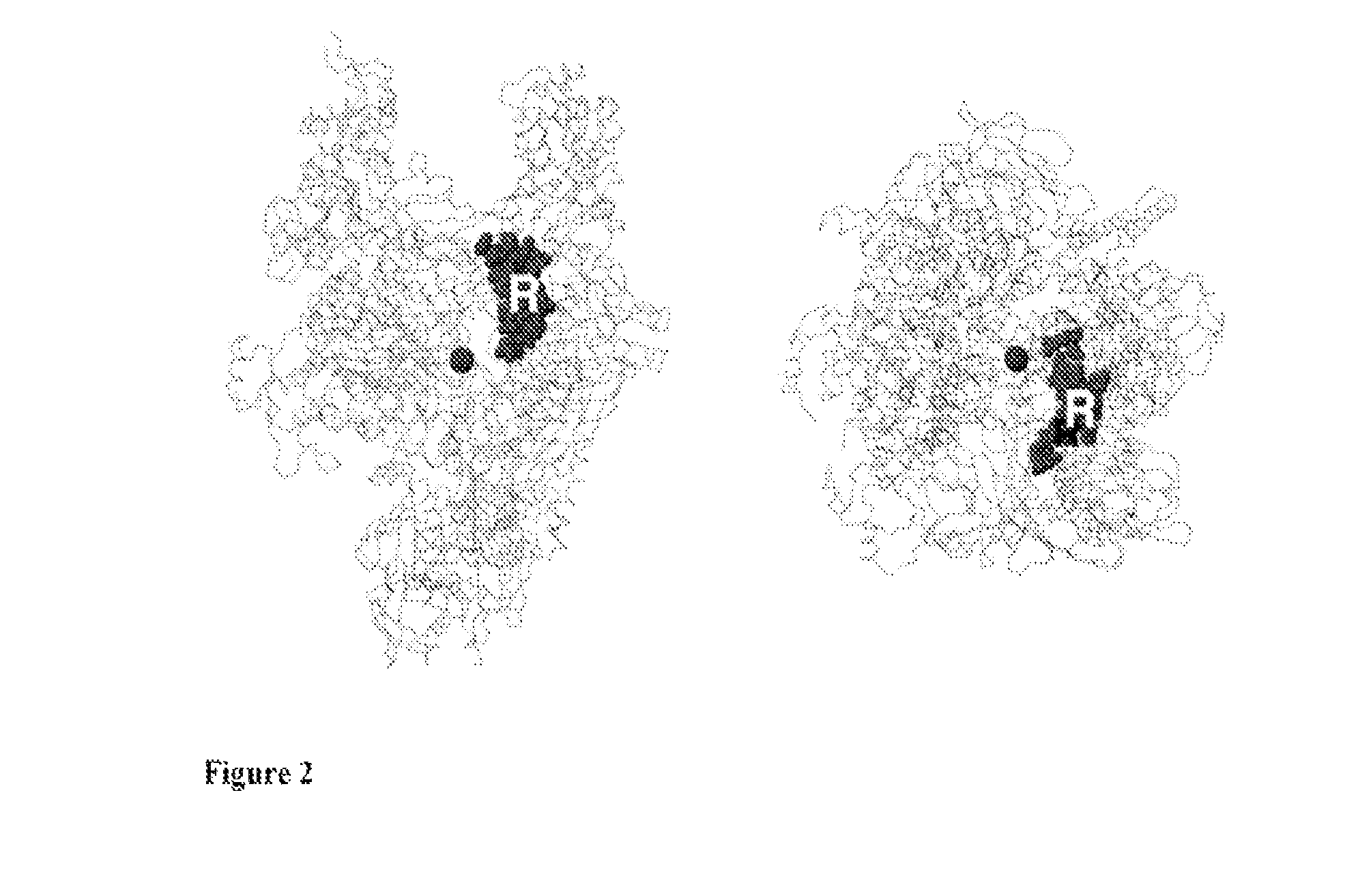
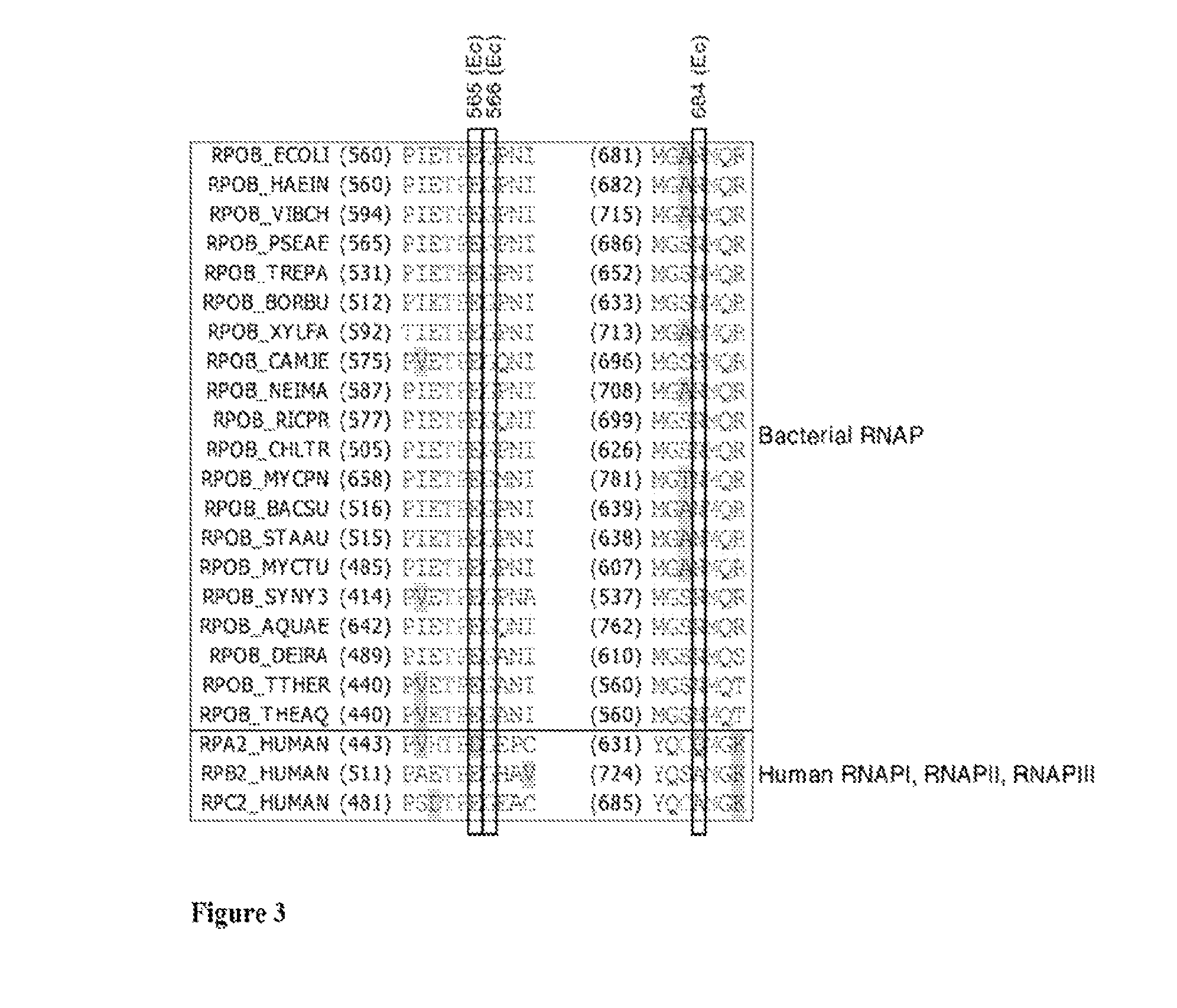
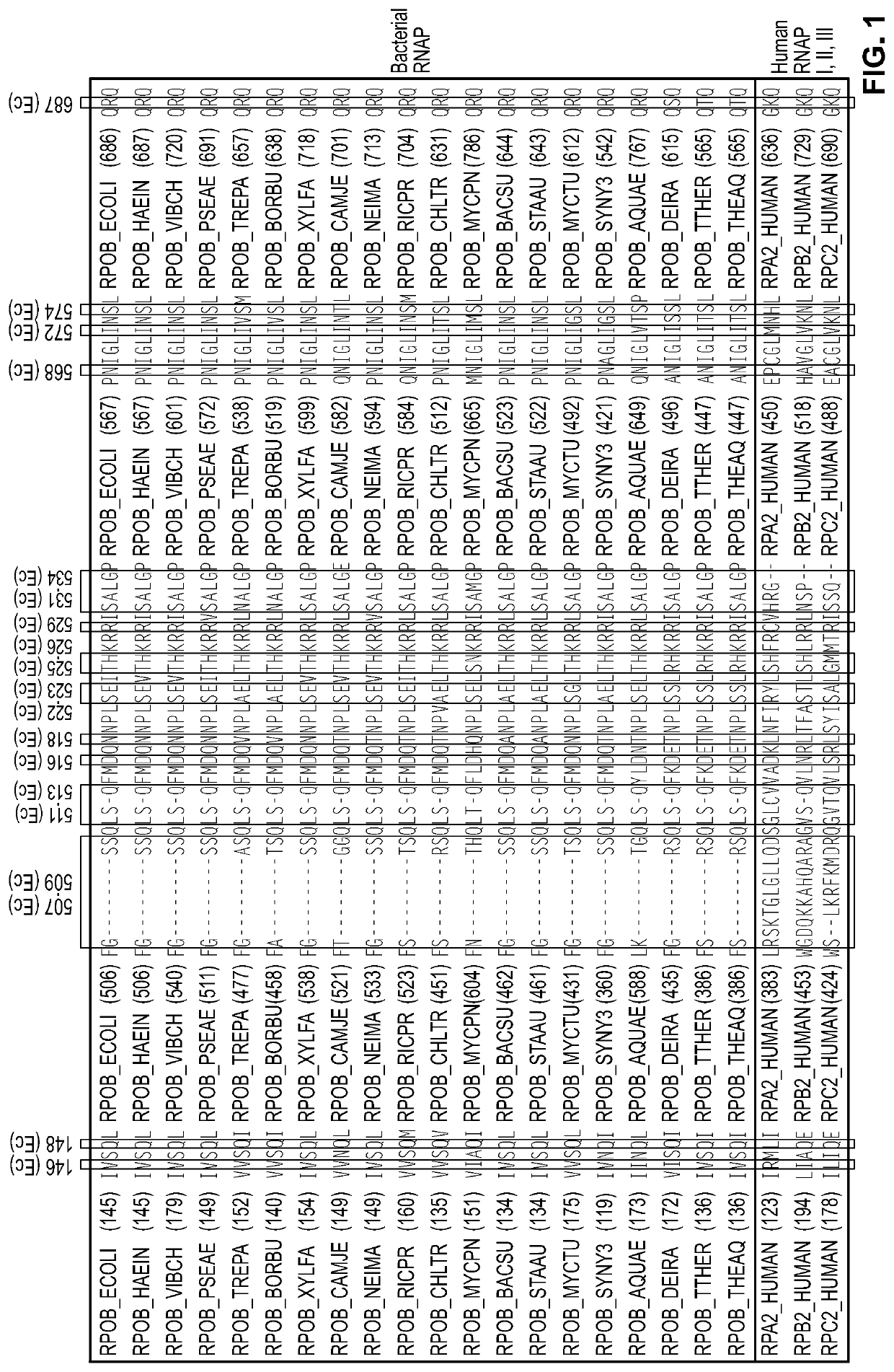
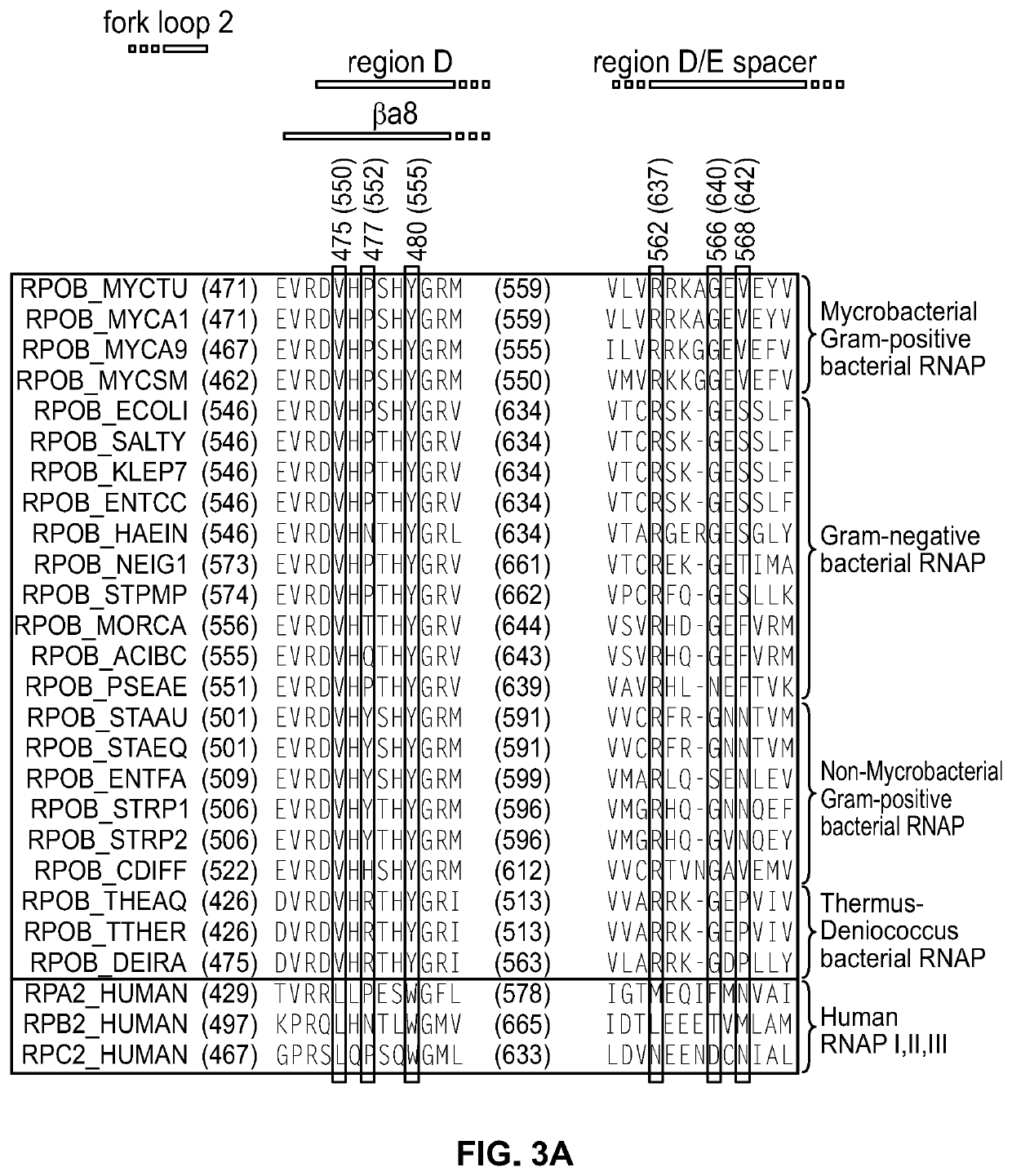
Target and method for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase disclosed are targets and methods for specific binding and inhibition of RNAP from bacterial species. Bacterial RNA polymeraseRPOC_ECOLI (736) QIRQLAGMRGLM (779) ARKRPOC_HAEIN (737) QIRQLAGMRGLM (780) ARKRPOC_VIBCH (736) QIRQLAGMRGLM (779) ARKRPOC_PSEAE (736) QIRQLAGMRGLM (779) ARKRPOC_TREPA (703) QIRQLAGMRGLM (746) ARKRPOC_BORBU (699) QIRQLAGMRGLM (742) ARKRPOC_XYLFA (759) QIRQLAAMRGLM (802) ARKRPOC_CAMJE (734) QISQLAAMRGLM (777) ARKRPOC_NEIMA (738) QIKQLSGMRGLM (781) ARKRPOC_RICPR (730) QIKQLGGMRGLM (773) MRKRPOC_THEMA(1010) QVKQLAGIRGLM(1072) ARKRPOC_CHLTR (736) QLKQLGALRGLM (779) ARKRPOC_MYCPN (820) NFTQLFGMRGLM (874) ARKRPOC_BACSU (740) NFTQLAGMRGLM (783) ARKRPOC_STAAU (744) NFTQLAGMRGLM (787) ARKRPOC_MYCTU (813) QTRTLAGMKGLV (856) ARKRPOC_SYNY3 (763) QVRQLVGMRGLM (806) ARKRPOC_AQUAE (850) QIRQLAGMRGLM (893) ARKRPOC_DEIRA(1052) QIRQLAGMRGLM(1095) ARKRPOC_TTHER(1034) QIRQLCGLRGLM(1077) ARKRPOC_THEAQ(1034) QIRQLCGMRGLM(1077) ARKHuman RNA polymerases I,II, and IIIRPA1_HUMAN (908) NTMQISCLLGQI (971) GRERPB1_HUMAN (780) NISQVIAVVGQQ (843) GRERPC1_HUMAN (791) NISQMIACVGQQ (854) GRE
Owner:EBRIGHT RICHARDH
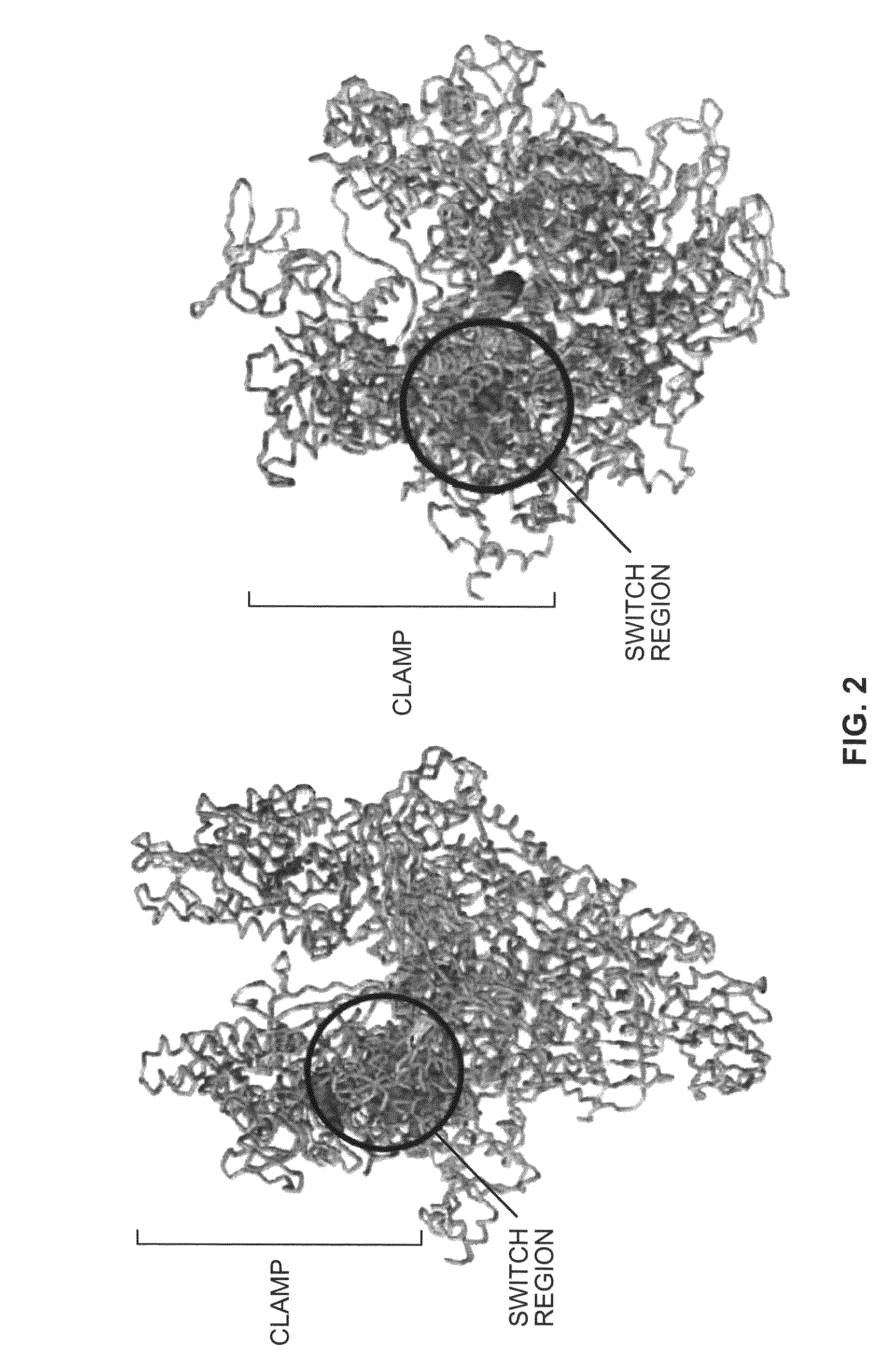
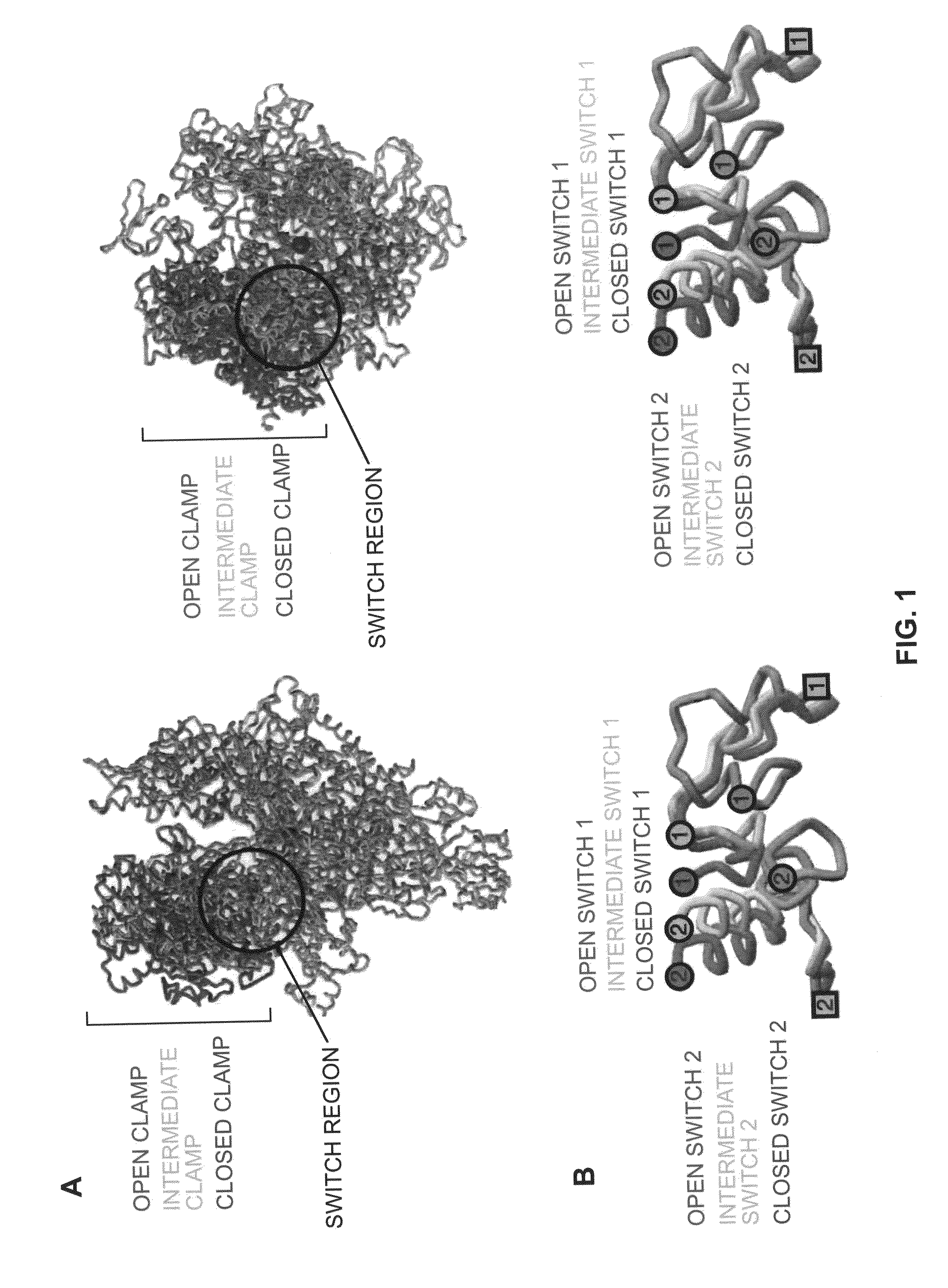
Switch-region: target and method for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase
ActiveUS8114583B2Inhibition is effectivePronounced antibacterial activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBacterial RNAMicrobiology
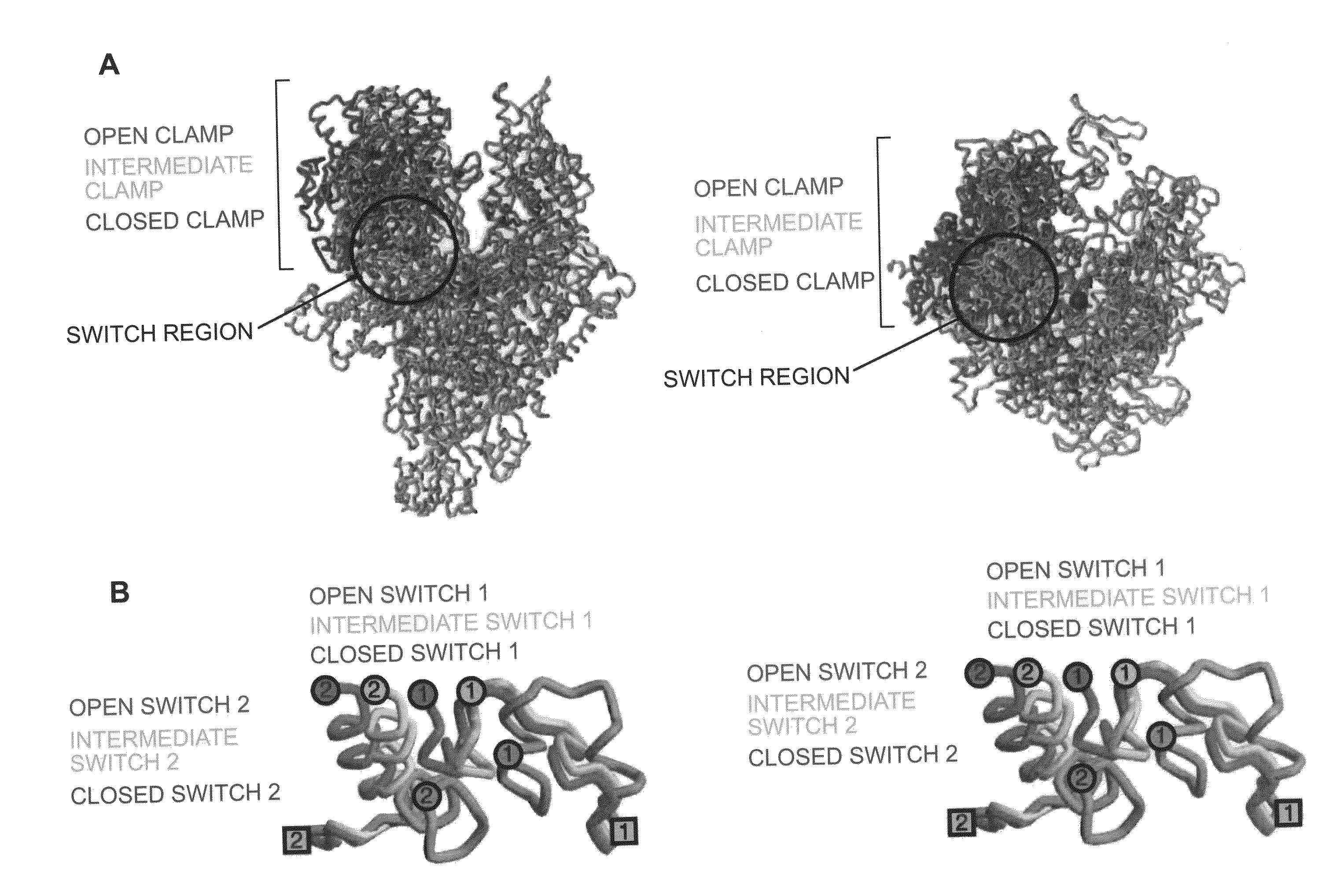
A target and methods for specific binding and inhibition of RNA polymerase from bacterial species are provided, including methods for identifying agents that bind to a bacterial RNA polymerase, and that inhibit an activity of a bacterial RNA polymerase, through interactions with a bacterial RNA polymerase homologous switch-region amino-acid sequence. The methods can include preparation of a reaction solution comprising the compound to be tested and an entity containing a bacterial RNAP homologous switch-region amino-acid sequence, and detection of binding or inhibition. Applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial viability, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy are also provided.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
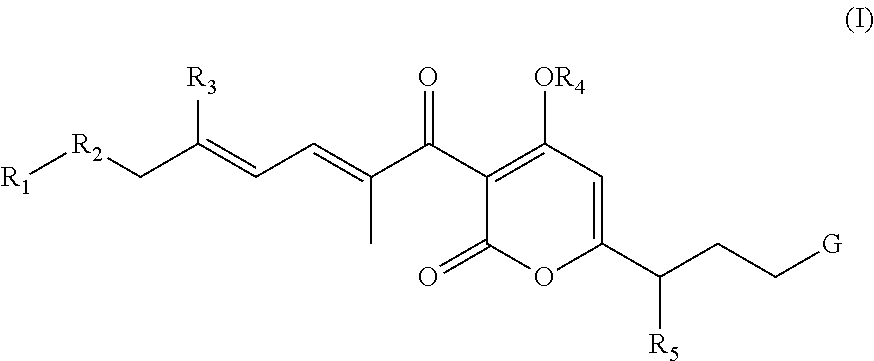
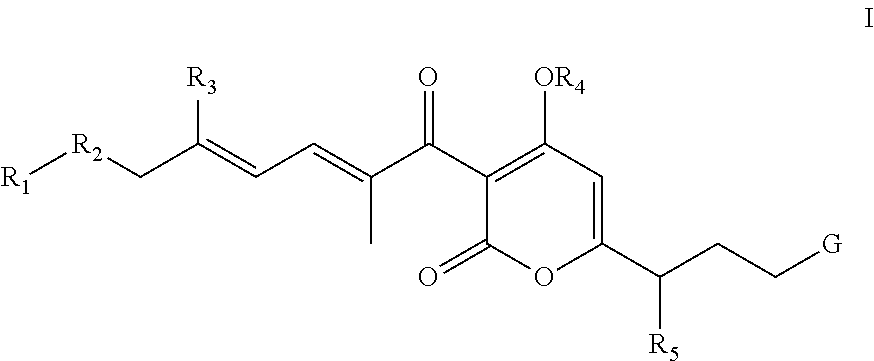
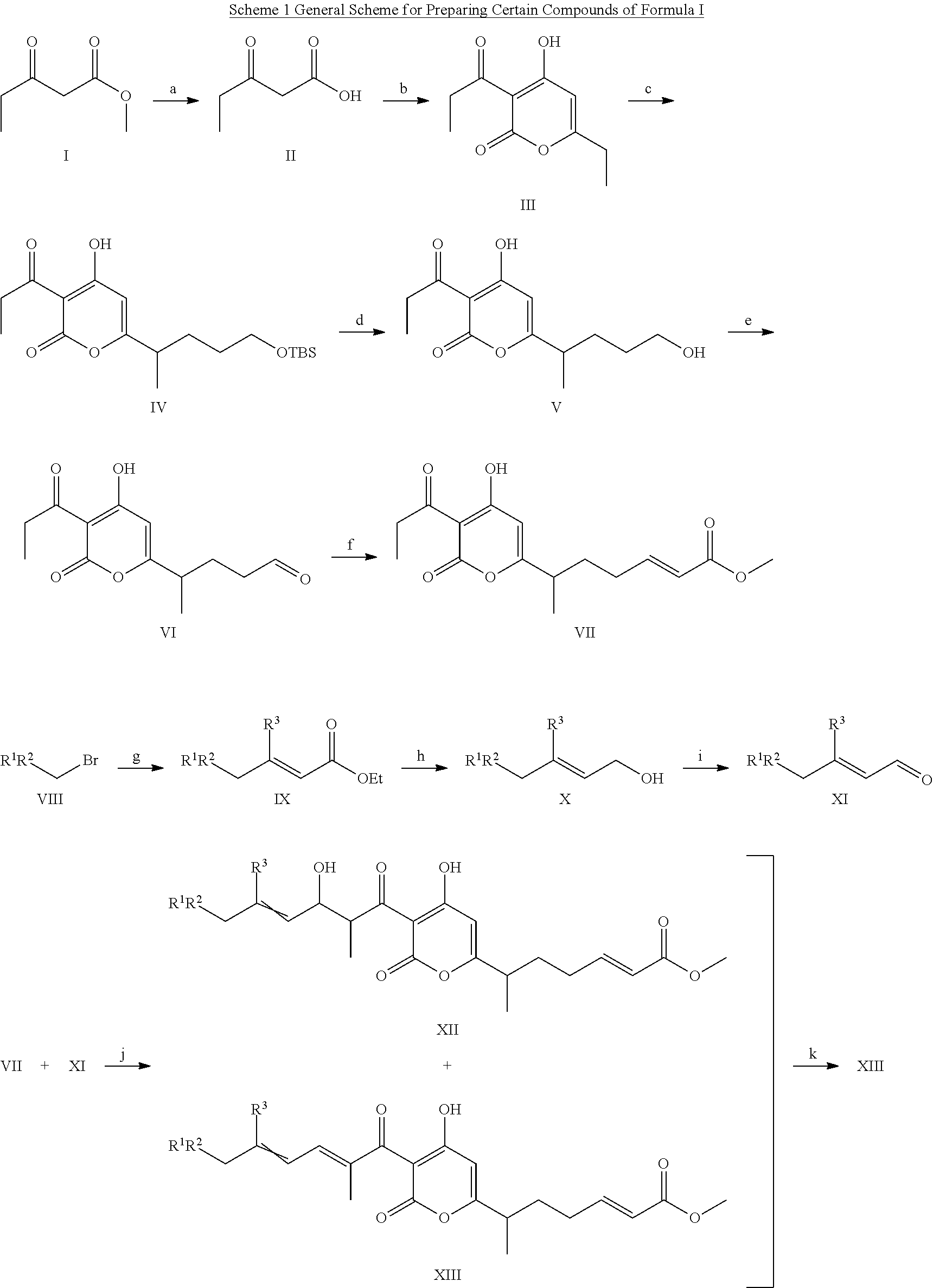
Antibacterial agents: sidechainfluorinated myxopyronin derivatives
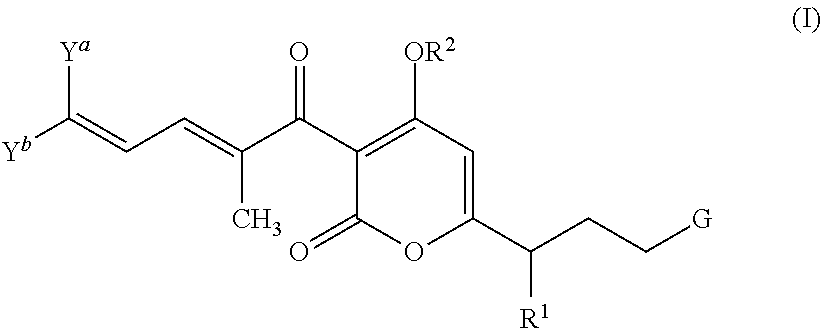
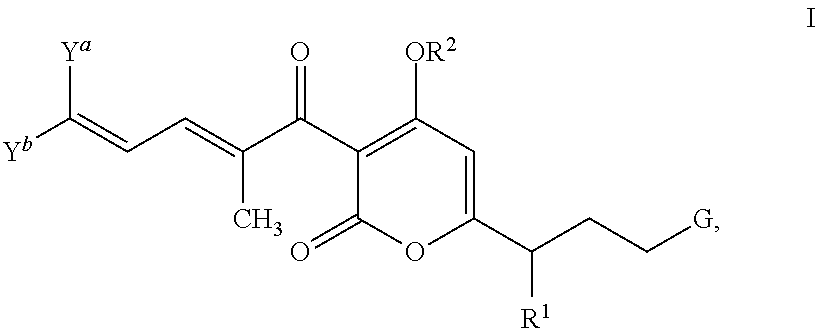
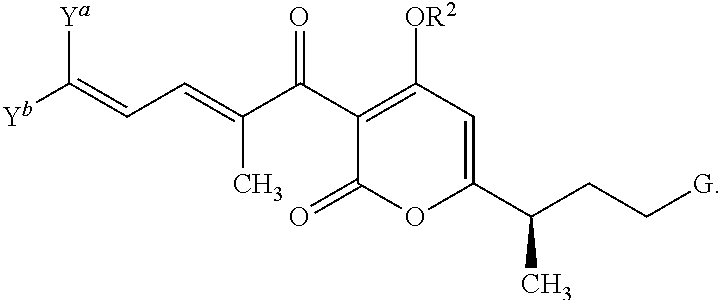
The invention provides compounds of Formula I: and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3 R4, R5, and G are as described in the specification, as well compositions comprising a compound of formula I, methods of making such compounds, and methods of using such compounds, e.g., as inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase and as antibacterial agents.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
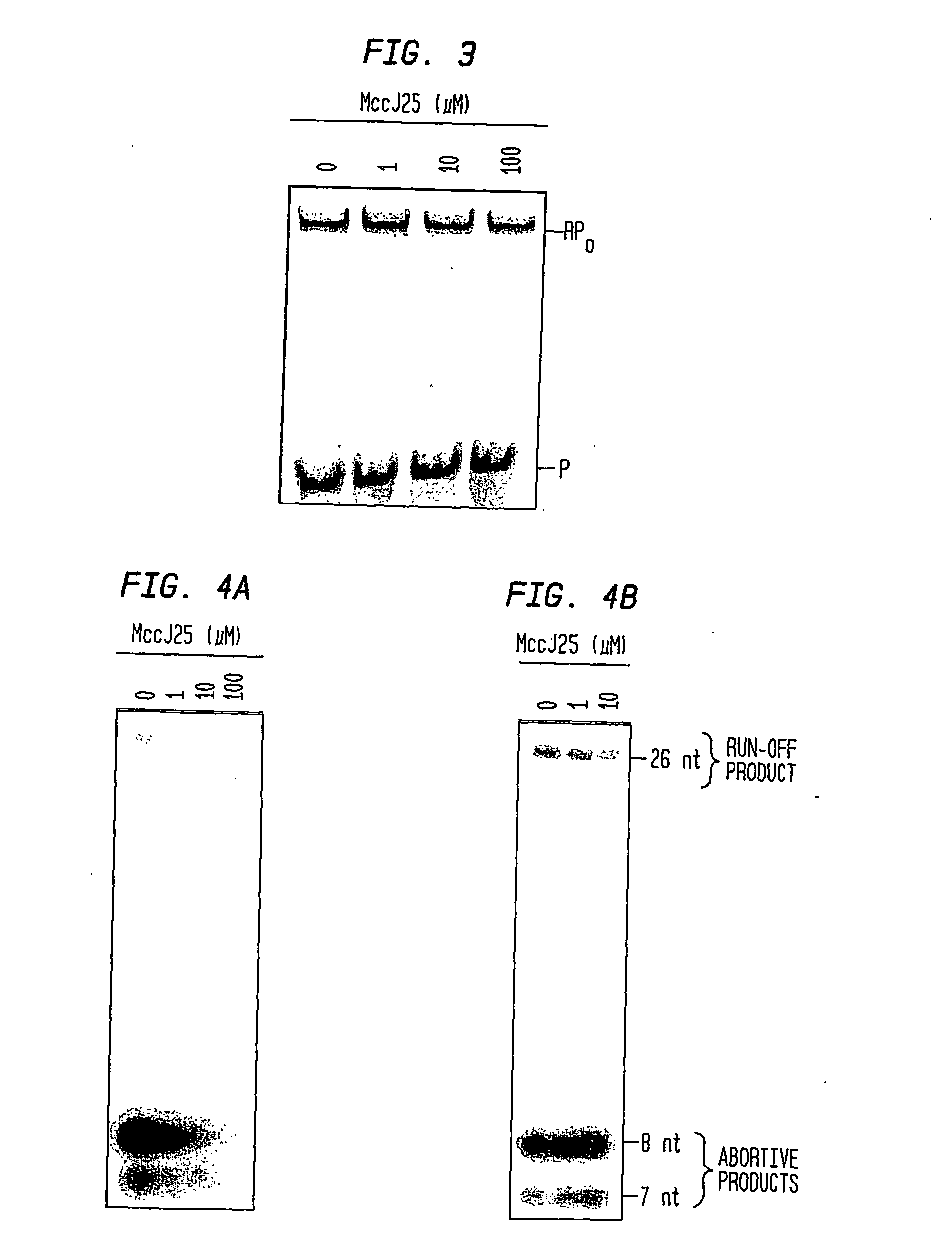
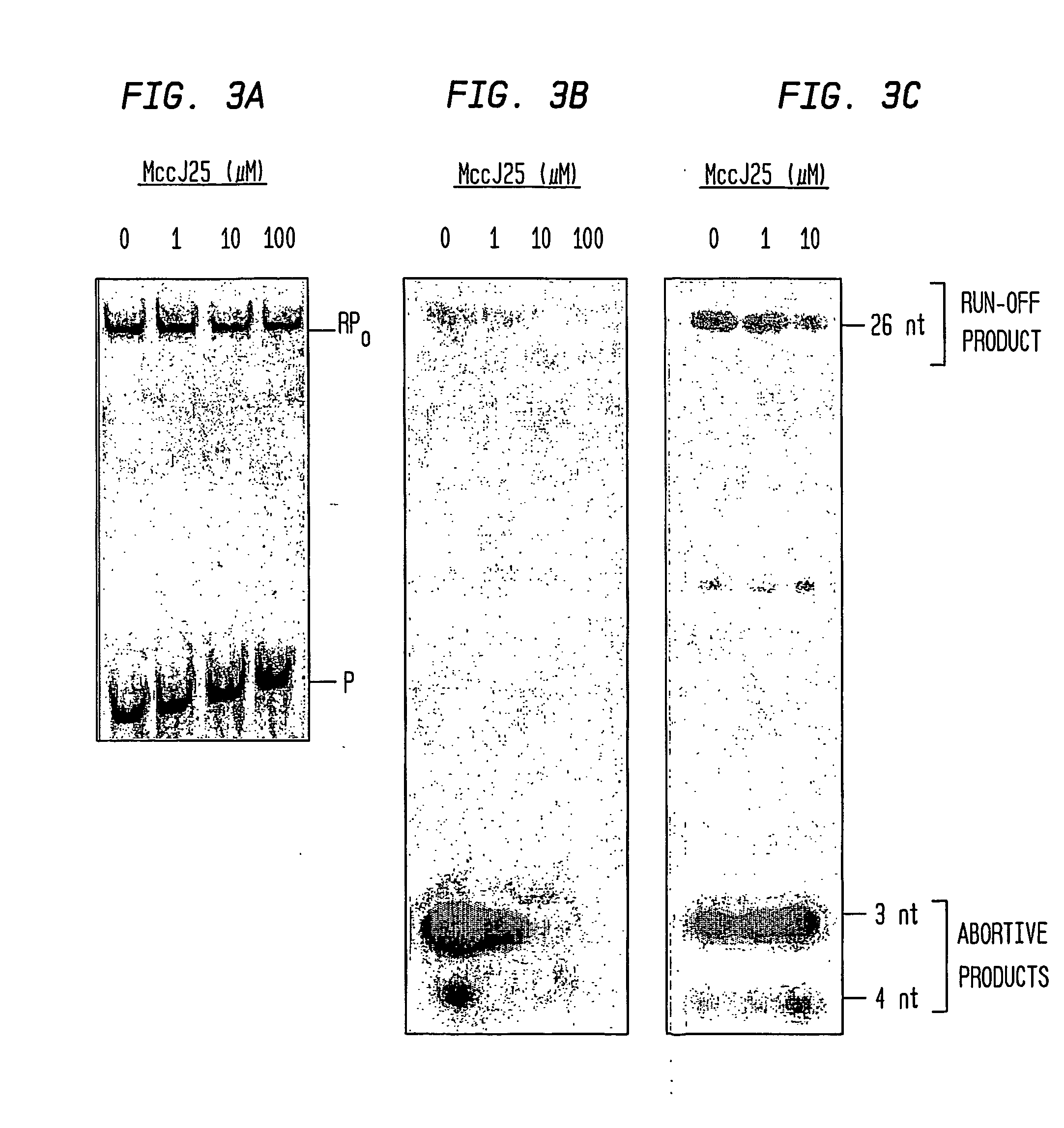
Target And Method For Inhibition Of Bacterial Rna Polymerase Minimized Derivatives Of Peptide Antibiotic Mccj25
InactiveUS20070196886A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacterial RNAPolymerase L
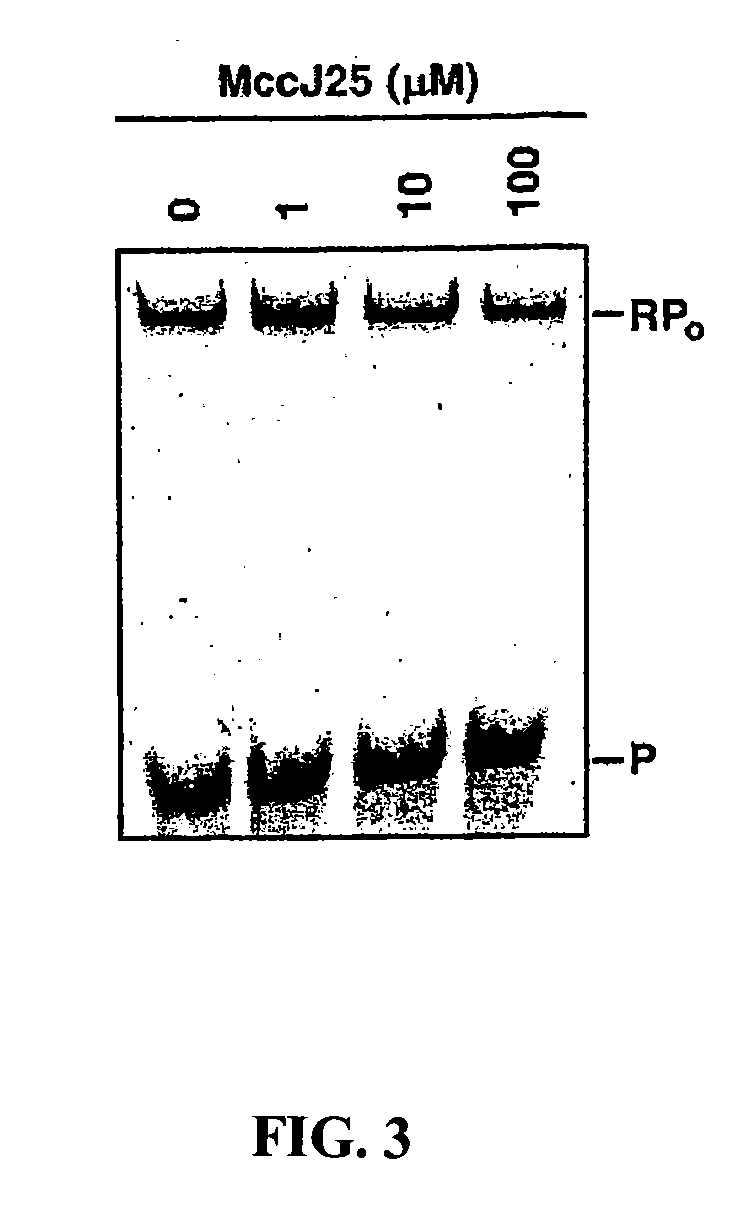
Disclosed are targets, methods, and reagents for specific binding and inhibition of RNAP from bacterial species. The invention has applications in analysis of RNAP structure and function, control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, antibacterial therapy, and drug discovery.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Antibacterial agents: high-potency myxopyronin derivatives
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method for the detection of group B Streptococcus (GBS) (Streptococcus agalactiae) in mammals
InactiveUS20090246764A1Reduce the numberMicrobiological testing/measurementStreptococcus agalactiaeMammal
A method for the detection of all strains of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) (Streptococcus agalactiae) in a mammal comprises isolating nucleic acid from a biological sample obtained from the mammal, detecting in the isolated nucleic acid a specific target region of GBS ssrA gene or tmRNA, an RNA transcript of the GBS ssrA gene, which is indicative of the presence of GBS. The isolated nucleic acid can be contacted with at least one oligonucleotide complementary to the specific target region of the GBS ssrA gene or tmRNA allowing a probe assay to be performed directly on the biological sample. Alternatively, the isolated nucleic acid can be amplified with at least one primer complementary to a specific target region of the GBS ssrA gene or tmRNA in a PCR-based assay. The method according to the invention has the potential to be employed as a screening and / or diagnostic test for use inter alia in hospital laboratories, or as a point-of-care test in various settings where an individual's infection or colonization by GBS is required without delay.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Bipartite Inhibitors of Bacterial RNA Polymerase
The invention provides a compound having a structural formula (I): X-α-Y, wherein X is an moiety that binds to the Rif pocket of a bacterial RNA polymerase, Y is a moiety that binds to the secondary channel of a bacterial RNA polymerase, and α is a linker. The compound can act as an inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase. The invention has applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
SRNA marker for distinguishing mycobacterium tuberculosis and BCG vaccine and use thereof
ActiveCN110093432AEasy to trainEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesFluorescence
The invention discloses an sRNA marker for distinguishing mycobacterium tuberculosis and a BCG vaccine and a use thereof. For solving the problem that mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and BCG vaccination are difficult to distinguish, the type of sRNA in mycobacterium tuberculosis is detected and screened by bacterial RNA sequencing firstly, a specific primer and kit capable of detecting the sRNA of mycobacterium tuberculosis are designed according to the screened target sRNA sequence, and a corresponding real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method is established. After free sRNA is extracted from bacterial bodies and cDNA is synthesized, the content of sRNA is detected by the real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method. The experiment proves that the method can be used for distinguishing the mycobacterium tuberculosis and the BCG vaccine, has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, low cost, convenience in operation and the like, and is hopeful to further meet the clinical and laboratory needs for rapid diagnosis of the mycobacterium tuberculosis and the BCG vaccine.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Non-mccj25-related lariat-peptide inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase
The invention provides a method of inhibiting a bacterial RNA polymerases. The invention has applications in control of bacterial RNA polymerase activity, control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Ring mediated isothermality amplification fast detecting method for norovirus
InactiveCN101403014AGuaranteed reliabilityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBacterial RNALoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to a rapid detection method of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification of a G II type norovirus. Reagents thereof comprise a reaction solution of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification, Bst DNA polymerase and a color development agent; wherein, the reaction solution comprises a reaction buffer solution, dNTP, bitter salt, an upstream inner primer 5-CGGGCTCCAGAGCCATAACCT-ACGCCAACCCATCTGATG-3, a downstream inner primer 5-GTGGCGGGCCAACAAAACGTA-CACTGTGAACTCTCCACCAG-3, an upstream outer primer 5-GTGAATGAAGATGGCGTCGA-3 and a downstream outer primer 5-CTGGAGCGTTTCTAGGGGA-3, and lycine. The detection method of the G II type norovirus includes the extraction of bacterial RNA, the loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the G II type norovirus, and color development detection. The method has the advantages of fast speed, strong specificity, high sensitivity and low cost.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Switch-region: target and method for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase
ActiveUS20100311074A1Inhibition is effectivePronounced antibacterial activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBacteroidesPolymerase L
The invention provides a target and methods for specific binding and inhibition of RNA polymerase from bacterial species. The invention provides methods for identifying agents that bind to a bacterial RNA polymerase, and that inhibit an activity of a bacterial RNA polymerase, through interactions with a bacterial RNA polymerase homologous switch-region amino-acid sequence. Said methods comprise preparing a reaction solution comprising the compound to be tested and an entity containing a bacterial RNAP homologous switch-region amino-acid sequence, and detecting binding or inhibition. The invention has applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial viability, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Rna-exit-channel: target and method for inhibition of bacterial rna polymerase
The invention provides a target and methods for specific binding and inhibition of RNAP from bacterial species. The invention is directed to a method for identifying agents that bind to a bacterial RNAP homologous RNA-exit-channel amino-acid sequence, comprising preparing a reaction solution comprising the agent to be tested and an entity comprising a bacterial RNAP homologous RNA-exit-channel amino-acid sequence, and detecting presence or amount of binding. The invention has applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Target and method for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase
Target and method for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase disclosed are targets and methods for specific binding and inhibition of RNAP from bacterial species.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Bipartite inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase
The invention provides a compound having a structural formula (I): X-α-Y, wherein X is an moiety that binds to the Rif pocket of a bacterial RNA polymerase, Y is a moiety that binds to the secondary channel of a bacterial RNA polymerase, and α is a linker. The compound can act as an inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase. The invention has applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Antibacterial agents: soluble salts and aqueous formulations of pyronins
PendingUS20210002266A1Good water solubilityHighly solubleAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacterial RNABiochemistry
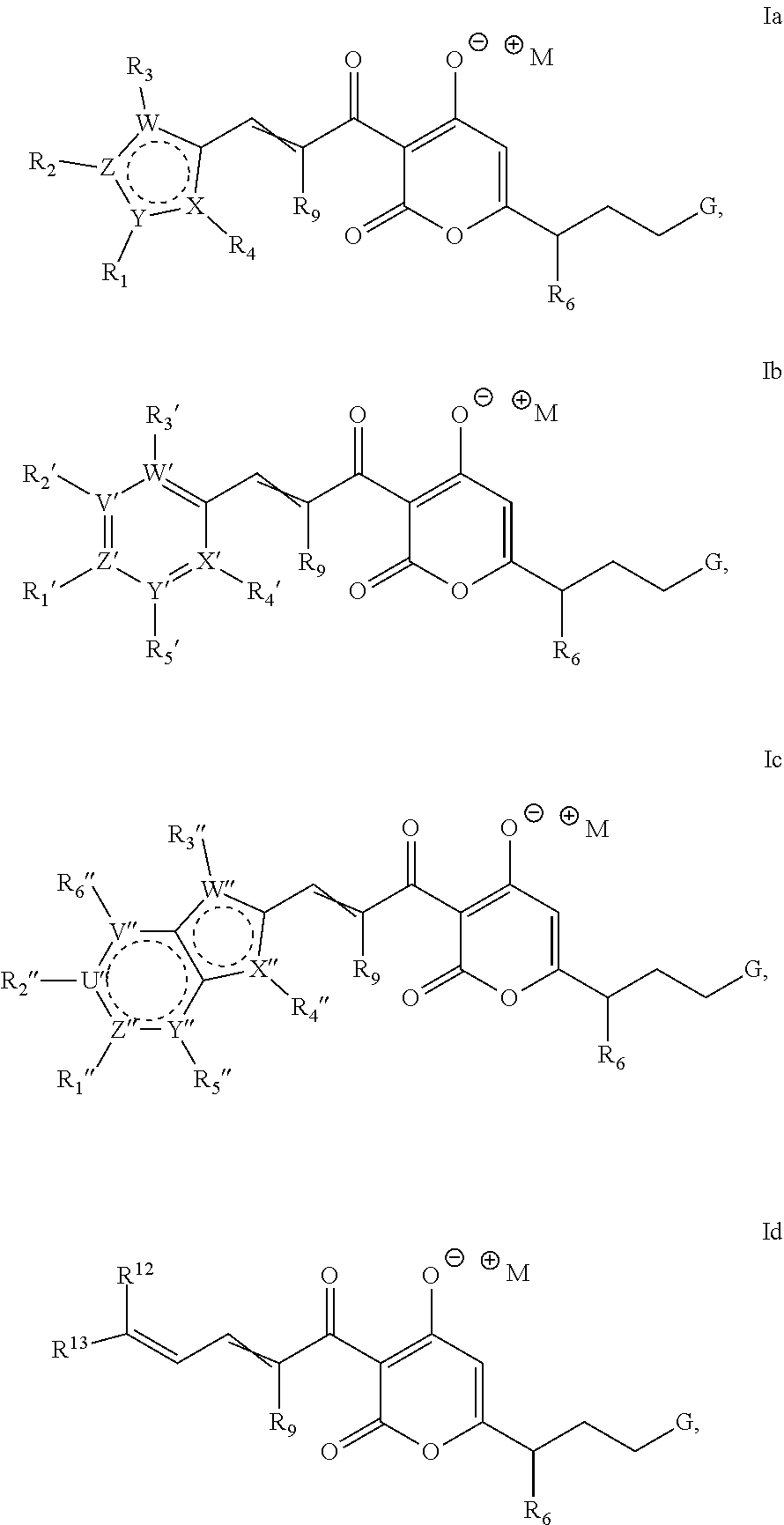
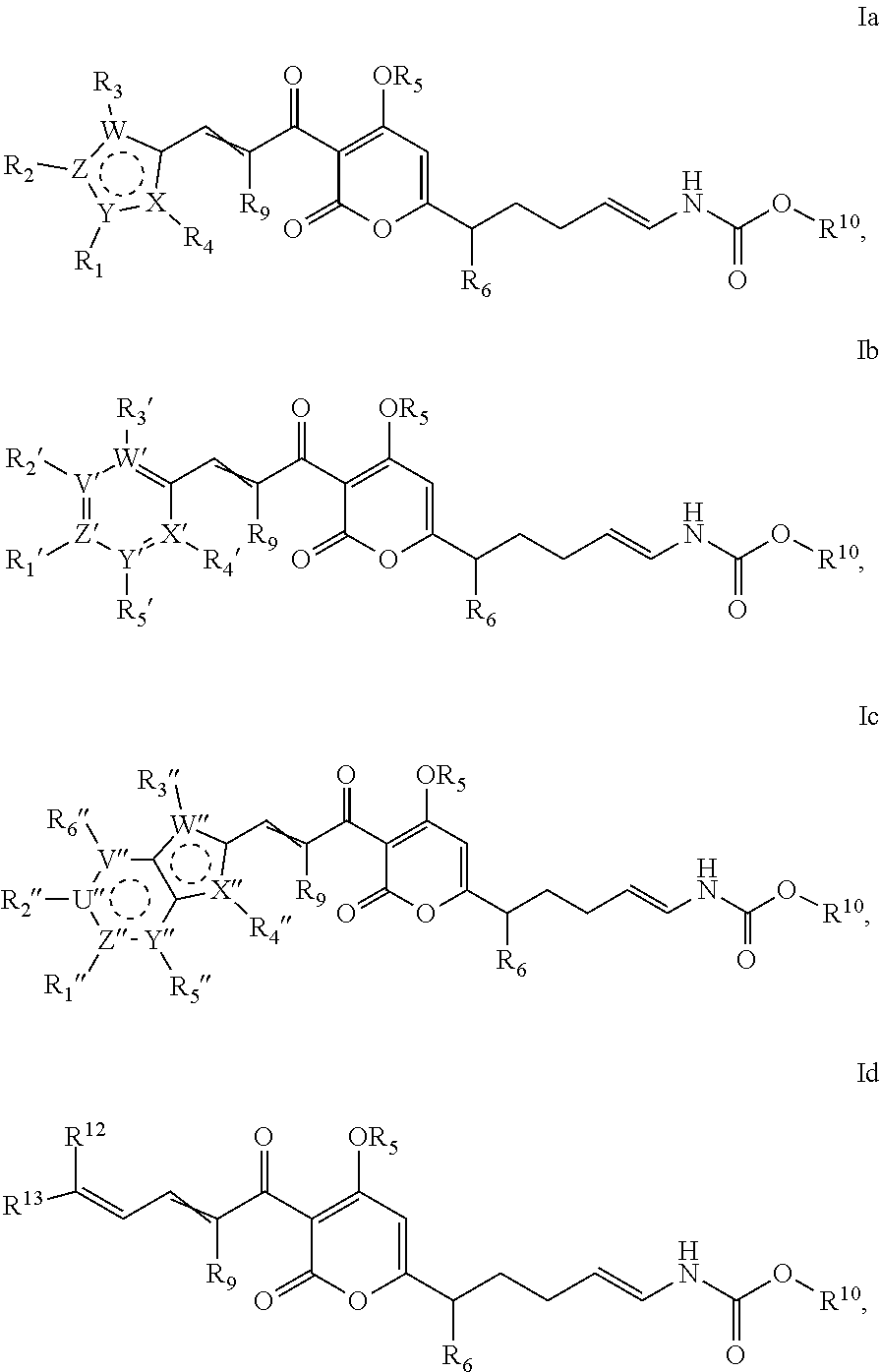
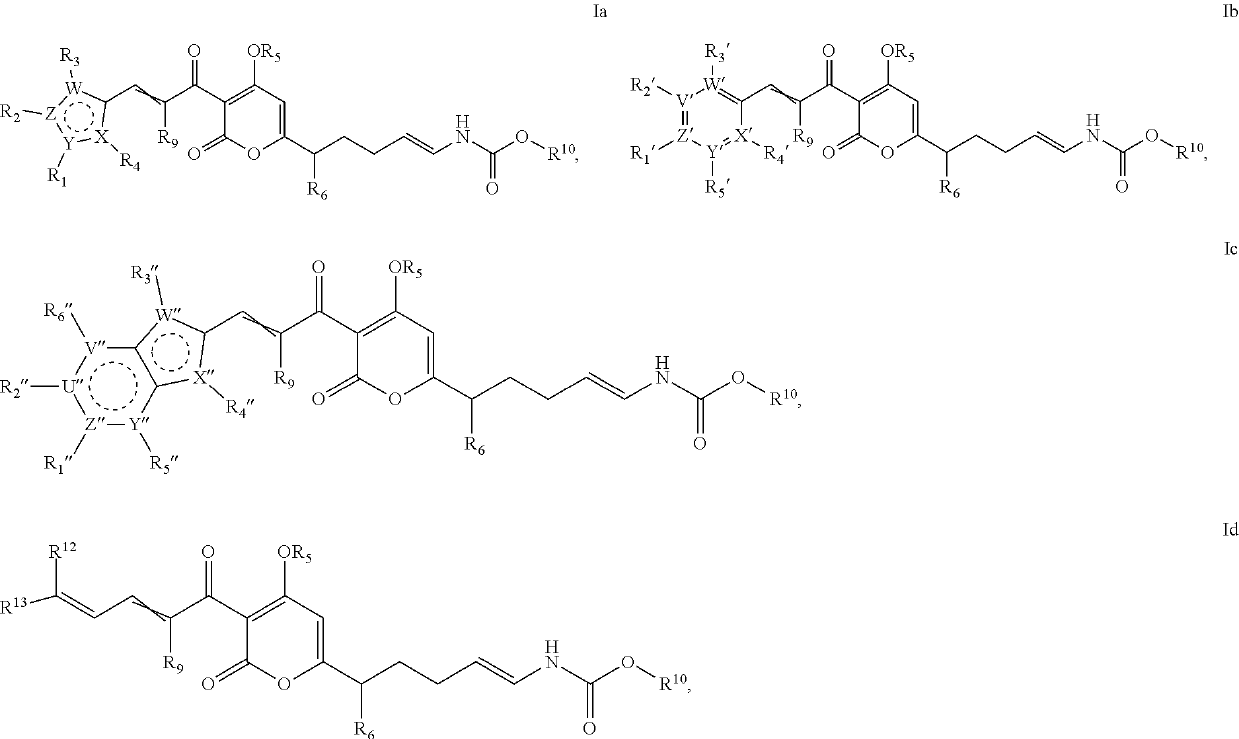
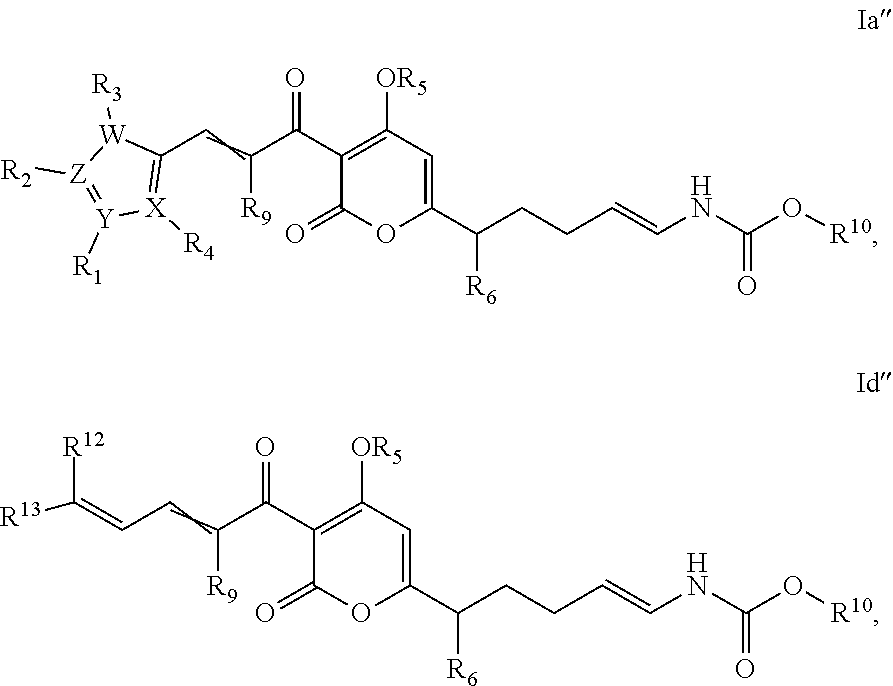
The invention provides salts of formula Ia, Ib, Ic, or Id: wherein variables are as described in the specification, as well as compositions comprising a salt of formula Ia-Id, methods of making such salts, and methods of using such salts as, e.g., inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase and as antibacterial agents.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
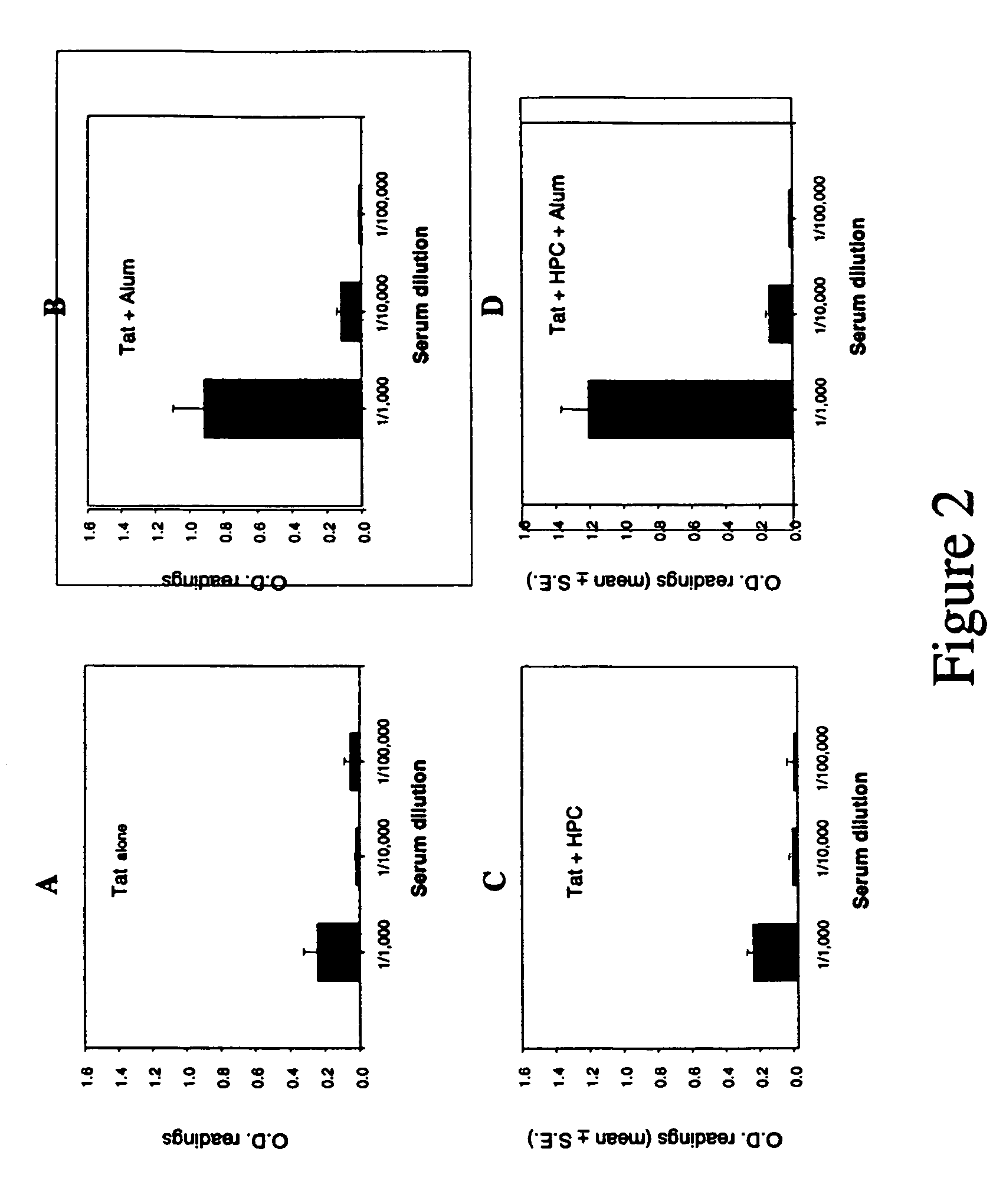
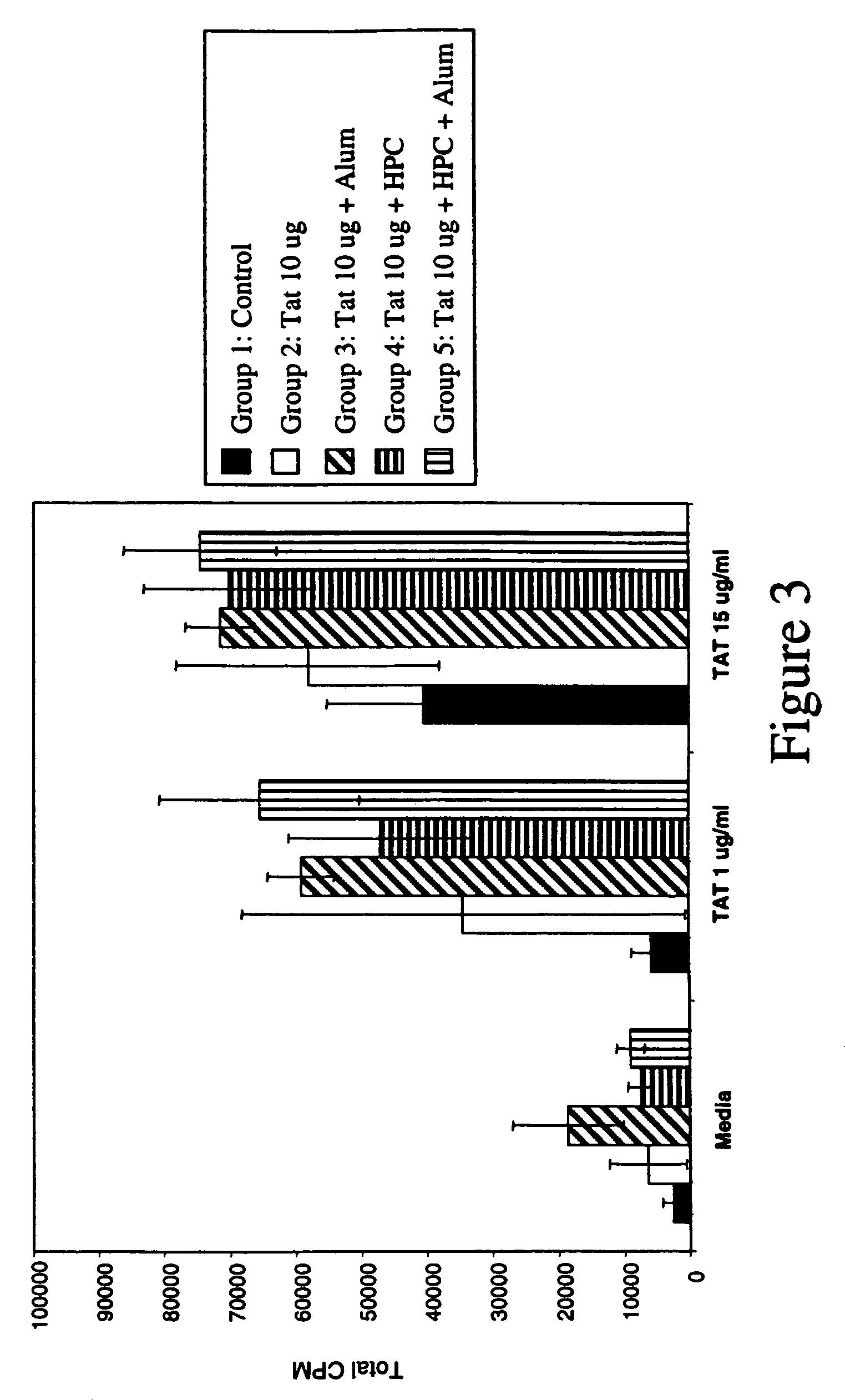
Compositions comprising human immunodeficiency virus Tat adsorbed to the surface of anionic nanoparticles
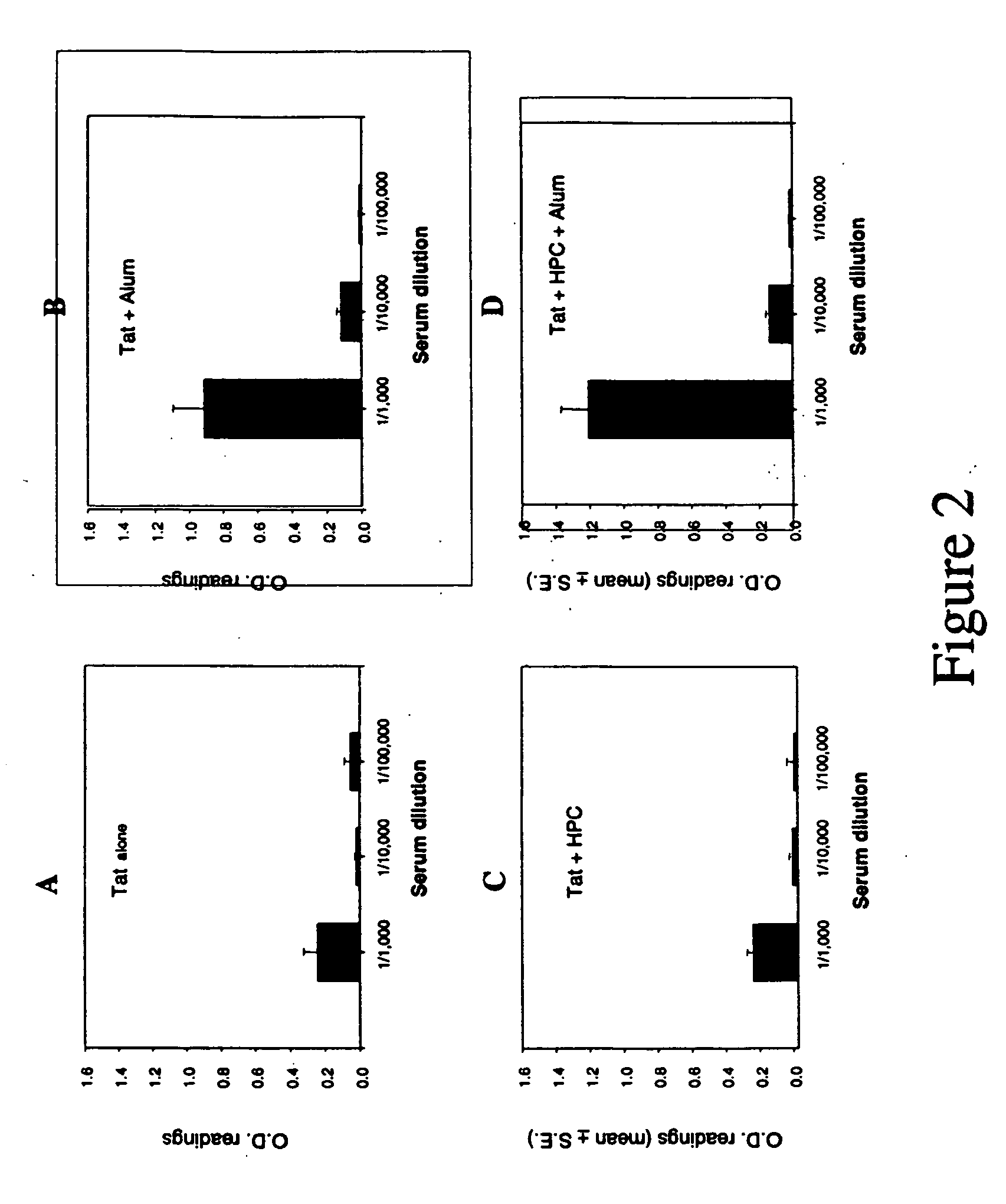
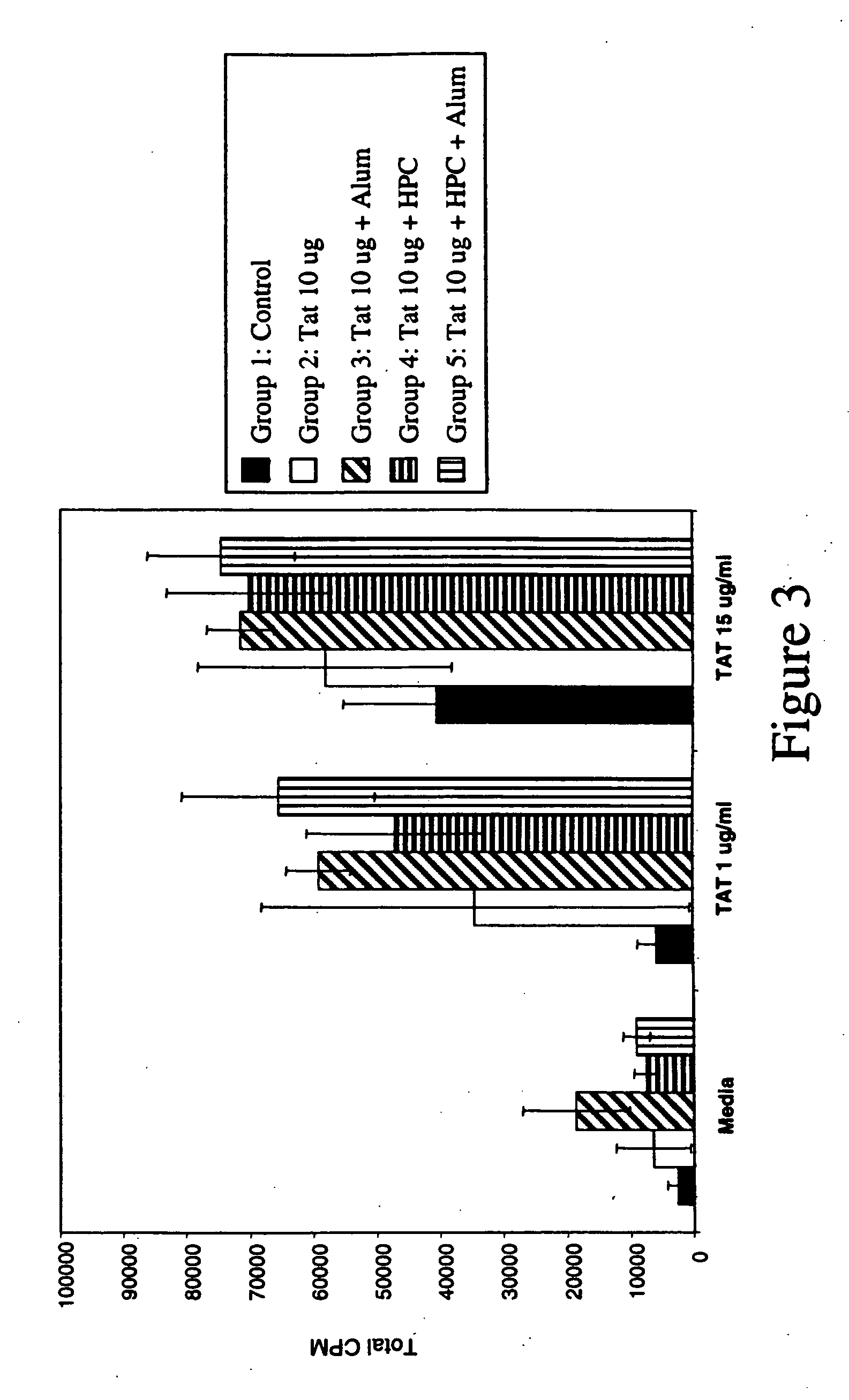
Non-denatured, recombinant human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Tat that is free of bacterial RNA and endotoxin is employed in an anti-HIV vaccine. A process of producing the recombinant Tat protein includes steps for removing bacterial RNA from the recombinant Tat and for removing endotoxin from the recombinant Tat protein. A Tat-adsorbed nanoparticle formulation and method of making the same. A method of vaccinating against and / or treating HIV infection comprises administering to a subject in need of such vaccination or treatment an immune-response inducing effective amount of the recombinant Tat protein.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
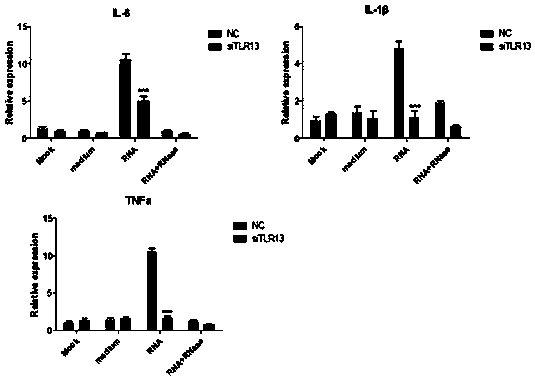
Innate immune TLR13 (toll-like receptor 13) gene of epinephelus coioides as well as eukaryotic expression vectors and application of innate immune TLR13 gene
ActiveCN107557366AHighlight Substantial ProgressFermentationAnimals/human peptidesInflammatory factorsNucleotide
The invention discloses an innate immune TLR13 (toll-like receptor 13) gene of epinephelus coioides as well as eukaryotic expression vectors and an application of the innate immune TLR13 gene for thefirst time. The nucleotide sequence of the TLR13 gene is shown as SEQ. ID.NO:1, the full-length cDNA sequence of the TLR13 gene is shown as SEQ. ID.NO:2, sequences of a pair of primers contained on the full-length cDNA sequence are shown as SEQ. ID.NO:4-5, and the amino acid sequence of the TLR13 protein is shown as SEQ. ID.NO:3. The two eukaryotic expression vectors containing the full-length cDNA sequence of the TLR13 gene are provided, namely, pEGFP-N3-TLR13 and pcDNA3.1-TLR13. Besides, the TLR13 gene or the TLR13 protein is applied to research of regulation of inflammatory factor expression, recognition of bacterial RNA, recognition of vibrio parahaemolyticus RNA and regulation of inflammatory factors.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutation prediction method based on naive Bayes model
ActiveCN112749833APredictableImprove accuracyForecastingProteomicsEscherichia coliRNA polymerase beta subunit
The invention discloses an Escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutation prediction method based on a naive Bayes model. The method comprises the following steps: collecting Escherichia coli RNA polymerase beta subunit rifampicin resistance positive mutants in an existing report; collecting mutants of a bacterial RNA polymerase beta subunit in an existing report, removing sites consistent with positive mutation of escherichia coli, and taking the mutants as negative mutants; predicting a protein property parameter data set of the obtained positive mutant and negative mutant; and training a naive Bayesian model by using the obtained protein property parameter data set, and predicting a mutation phenotype after amino acid mutation at each position in a rifampicin resistance interval in escherichia coli RpoB by using the model. The model constructed by the invention has good prediction performance on escherichia coli rifampicin resistance mutation phenotypes, and the AUC value under an ROC curve in model evaluation is 0.77; and the accuracy is high and can reach 75.4%.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Tat as an immunogen
Non-denatured, recombinant human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Tat that is free of bacterial RNA and endotoxin is employed in an anti-HIV vaccine. A process of producing the recombinant Tat protein includes steps for removing bacterial RNA from the recombinant Tat and for removing endotoxin from the recombinant Tat protein. A Tat-adsorbed nanoparticle formulation and method of making the same. A method of vaccinating against and / or treating HIV infection comprises administering to a subject in need of such vaccination or treatment an immune-response inducing effective amount of the recombinant Tat protein.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Bipartite inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase
The invention provides bipartite inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase having the general structural formula (I): X-α-Y (I) wherein X is an moiety that binds to the rifamycin binding site of a bacterial RNA polymerase, Y is a moiety that binds to the GE23077 binding site of a bacterial RNA polymerase, and is a linker. The invention also provides compositions comprising such compounds, methods of making such compounds, and methods of using said compounds. The invention has applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Extraction method of bacterial RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
The invention discloses an extraction method of bacterial RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The extraction method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting thallus and then putting the thallus into a centrifuge tube; secondly, adding 50 to 200mu l of EB buffer solution containing lysozyme into the centrifuge tube for thoroughly resuspending the thallus; thirdly, adding 200 to 600mu l of buffer A into the centrifuge tube and then uniformly mixing by vortex oscillation; if the insoluble precipitate occurs, centrifuging the insoluble precipitate, and transferring supernatant obtained by centrifuging into another centrifugal tube; fourthly, adding 200 to 600mu l of buffer B into the centrifuge tube, uniformly mixing, then adding a magnetic bead solution, oscillating, uniformly mixing and the like. According to the extraction method of the bacterial RNA, provided by the invention, the thallus can be quickly cracked, and further the RNA is released; in addition, the magnetic bead is combined with the advantages of nucleic acid, so that the extraction concentration is increased, the operation is simple and quick, and the extraction efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:成都晟博源生物工程有限公司
Application of Hfq protein of staphylococcus aureus in preventing and treating staphylococcus aureus infection
InactiveCN101711859AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiHost immunity
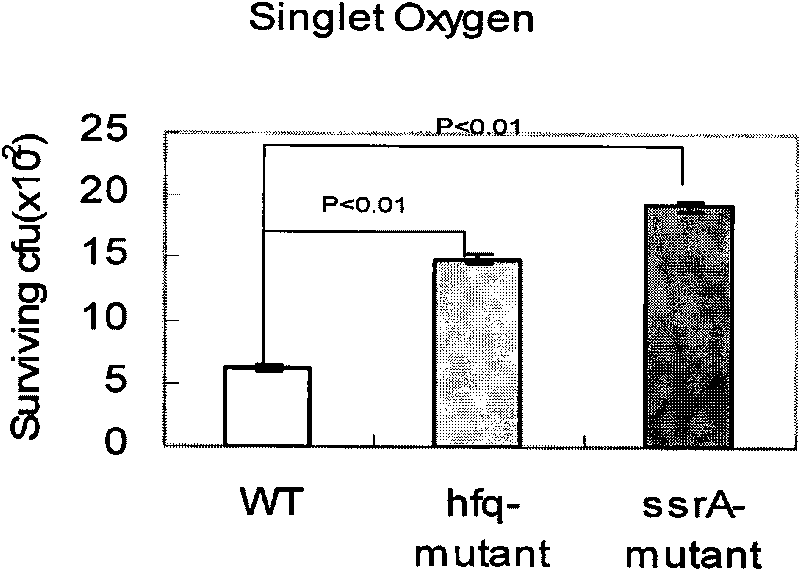
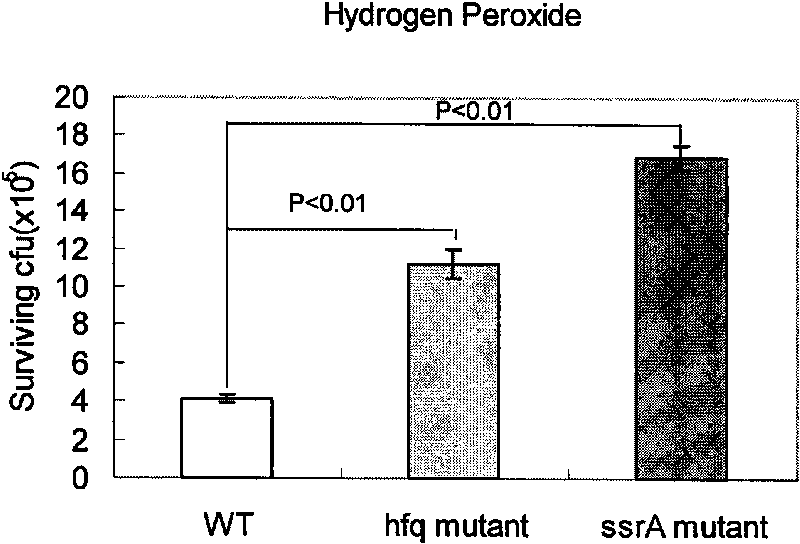
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, relating to the application of Hfq protein of staphylococcus aureus. Used as chaperone molecule of tmRNA-ssrA in staphylococcus aureus, the Hfq protein Hfq protein participates in the synthesis of adjusting and controlling staphylococcus aureus superficial pigment, thereby affecting the capability of graft-versus-host immunity of the staphylococcus aureus. Thus, the Hfq protein has good application prospect in the field of preventing and treating the staphylococcus aureus infection.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Bacterial RNAs as vaccine adjuvants
ActiveUS9844592B2Increase heightStimulate immune responseIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCancer antigen ingredientsBacteroidesMicroorganism
The disclosure features vaccine adjuvants comprising prokaryotic mRNA, and methods of vaccination using the adjuvants. More specifically, the disclosure provides a vaccine composition comprising a nonviable immunogen (e.g., heat-killed bacterium), a tumor antigen, or an immunogenic peptide of microbial or mammalian origin, and an adjuvant, wherein adjuvant comprises prokaryotic mRNA (e.g., bacterial mRNA), as well as the methods of using the vaccine compositions. Further disclosed are the structural features of the prokaryotic mRNA used as the adjuvants.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Antibacterial agents: o-alkyl-deuterated pyronins
PendingUS20210002246A1Good metabolic stabilityImprove antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacterial RNABiochemistry
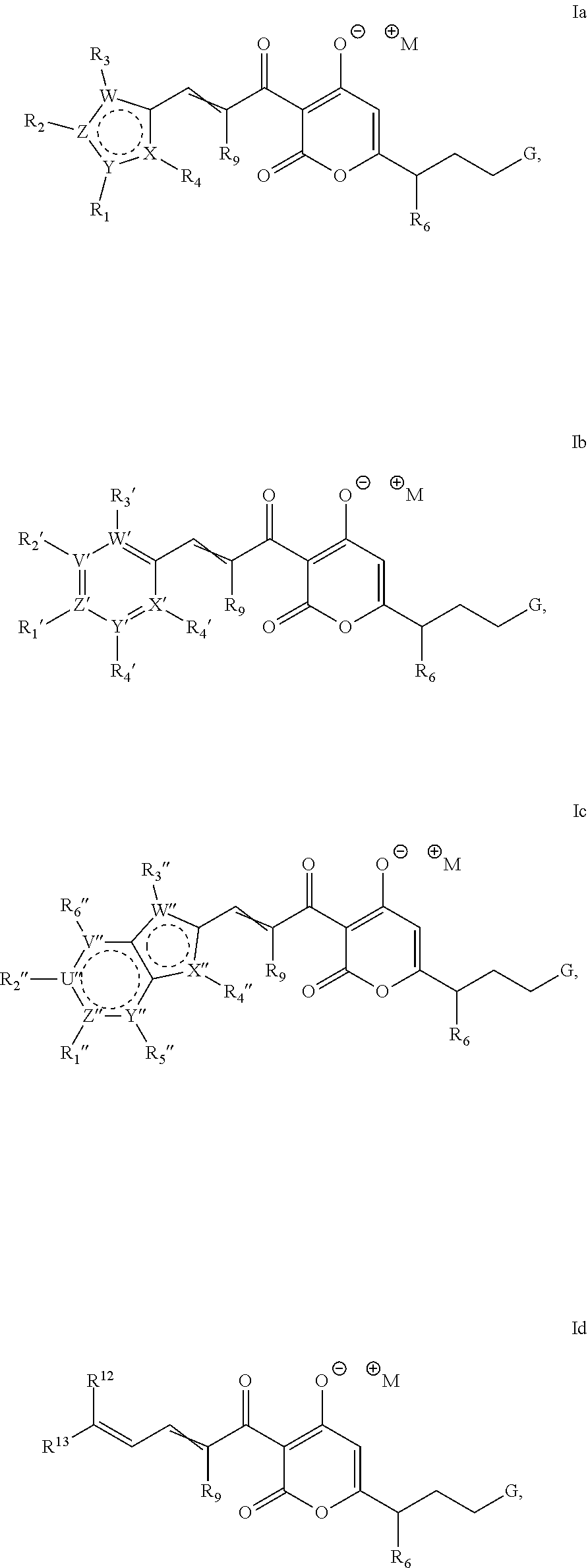
The invention provides compounds of formula Ia, Ib, Ic, or as well as compositions comprising a compound of formula Ia-Id, methods of making such compounds, and methods of using such compounds, e.g., as inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase and as antibacterial agents.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Pyridoindole derivative and antibacterial application thereof
The invention relates to the fields of medicine design science, medicinal chemistry and medicine science. A molecule capable of inhibiting the activity of bacterial ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase is searched by computer virtual screening on the basis of a crystal three-dimensional structure of the bacterial RNA polymerase, and the screened compound is derived, so that a pyridoindole derivative which can inhibit the activity of the bacterial RNA polymerase and has a structure shown as a formula (I) and pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the derivative are provided. The invention also relates to a medicinal composition of the pyridoindole derivative with the structure shown as the formula (I) and application of the composition. The compound can be used as an inhibitor for the bacterial RNA polymerase and selectively inhibits bacterial growth and propagation by inhibiting the activity of the bacterial RNA polymerase, so the compound and the medicinal composition can be used as an active substance for effectively treating and / or preventing bacterial infectious diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition, substrate comprising a pharmaceutical composition, and use of a pharmaceutical composition
The invention relates to the use of a pharmaceutical composition for the local treatment or prevention of a tissue infection at an infection site, the pharmaceutical composition comprising at least two different antibiotics of group A or pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof, or an antibiotic of group A and at least one antibiotic of group B or pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof. Group A comprises primarily intracellular active antibiotics working as inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase; as inhibitor of gyrase; or as inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis. Group B comprises primarily extracellular active antibiotics working as inhibitor of bacterial cell wall synthesis; or inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis; or by direct destabilization or rupture of the bacterial cell wall.The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of extracellular and / or intracellular microbial infected cells and / or for the prevention of microbial cell infections comprising at least one antibiotic acting as an inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase and / or at least one antibiotic affecting the bacterial cell wall or its synthesis, and a substrate carrying a pharmaceutical composition.The invention also relates to the use of a combination of at least one antibiotic acting as an inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase and at least one antibiotic affecting the bacterial cell wall or its synthesis as anti-adhesive against microorganisms on surfaces.
Owner:BIOMET DEUTLAND
Antibacterial agents: dual-targeted RNA polymerase inhibitors
ActiveUS20210198279A1Potent effect against drug-sensitivePotent effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryBacterial RNAAntibacterial agent
The invention provides bipartite, dual-targeted inhibitors of bacterial RNA polymerase having the general structural formula (I): X-α-Y (I) wherein X is an moiety that binds to the Rif target of a bacterial RNA polymerase; Y is a moiety that binds to the bridge-helix N-terminus target of a bacterial RNA polymerase; and is a covalent bond or a linker. The invention also provides compositions comprising such compounds, methods of making such compounds, and methods of using said compounds. The invention has applications in control of bacterial gene expression, control of bacterial growth, antibacterial chemistry, and antibacterial therapy.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Novel bacterial RNA (ribonucleic acid) extraction reagent and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN104845966AIncrease contentImprove extraction efficiencyDNA preparationBacterial RNACell wall
The invention relates to a novel bacterial RNA (ribonucleic acid) extraction reagent and a preparing method thereof. The reagent is composed of bacterial cell wall breaking reagent, binding liquid and cleaning solution. The bacterial cell wall breaking reagent is composed of extract A and extract B. The extract A is a mixture of Tris, EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid), SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate), Tween 80, Triton X-100, glycine, sarcosyl, Beta-mercaptoethanol and water; the extract B is a mixture of water phenol, ethanol and pyrrolidone. The binding liquid is guanidinium isothiocyanate solution. The cleaning solution is ethanol water. The novel bacterial RNA extraction reagent has the advantages that during extraction of total RNA of the gram-positive bacterium, the content of total RNA in the finally acquired gene group DNA and total RNA is evidently increased, extraction efficiency of the total RNA is increased, and wide application is benefited.
Owner:上海泰坦科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com