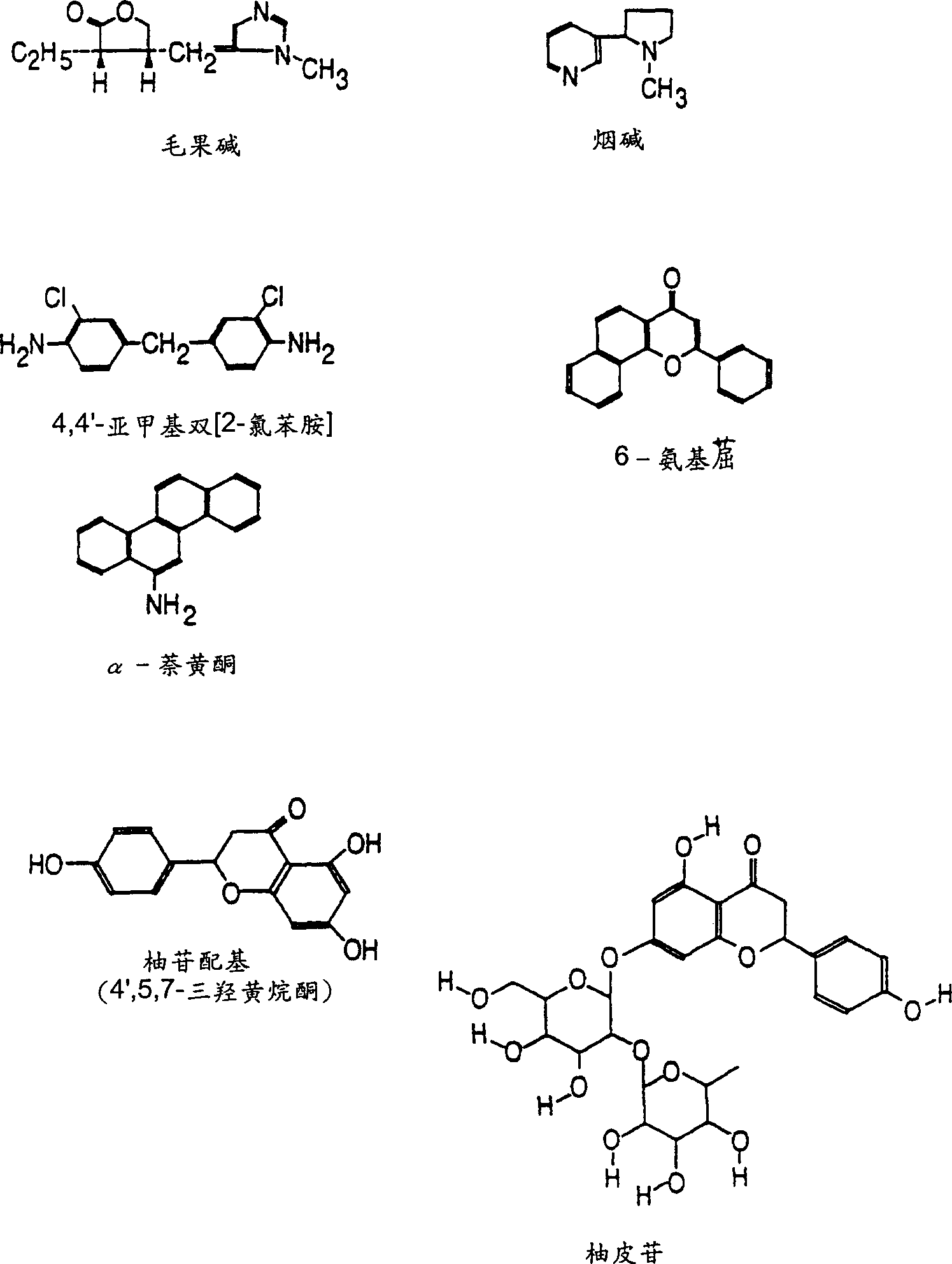
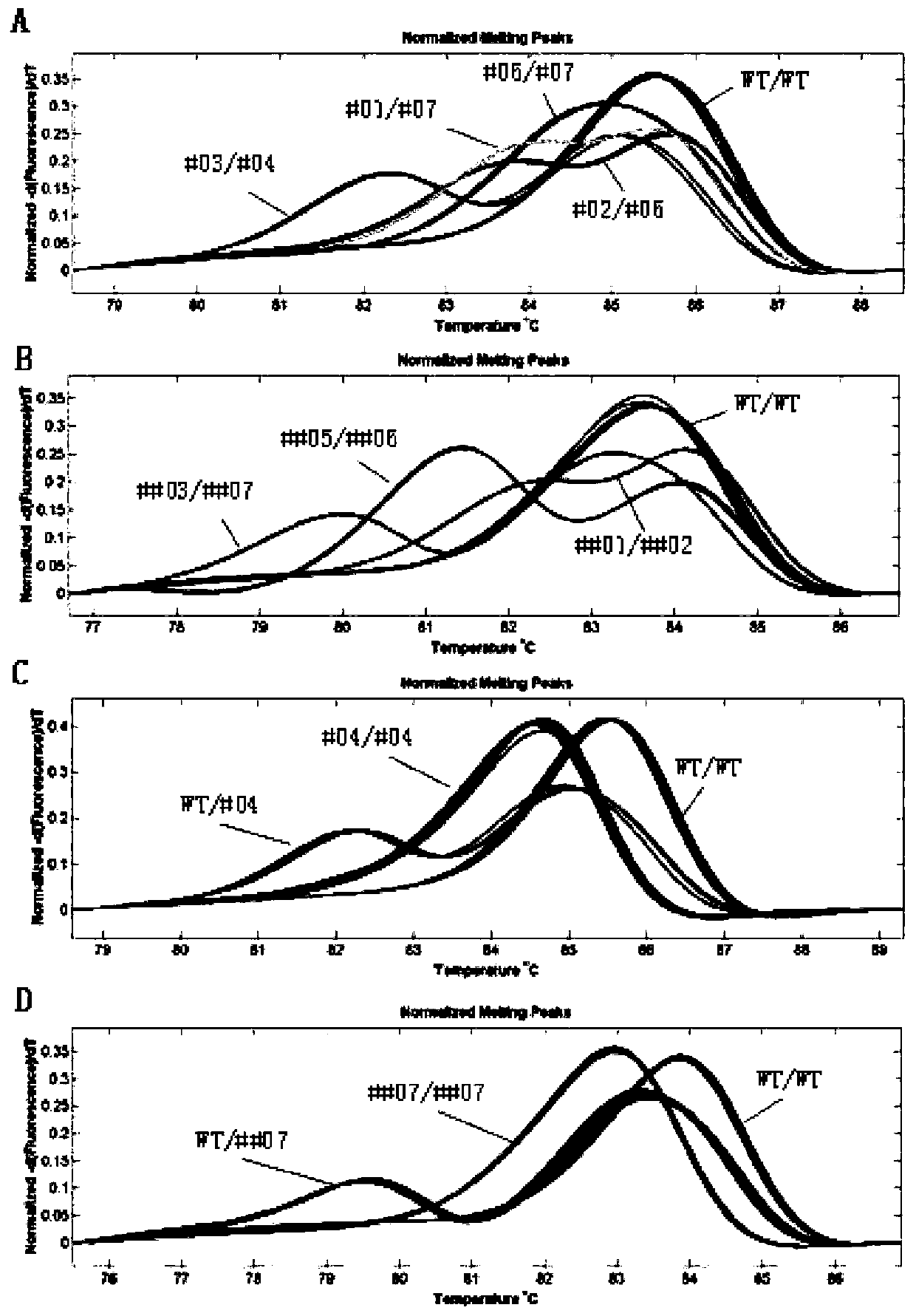
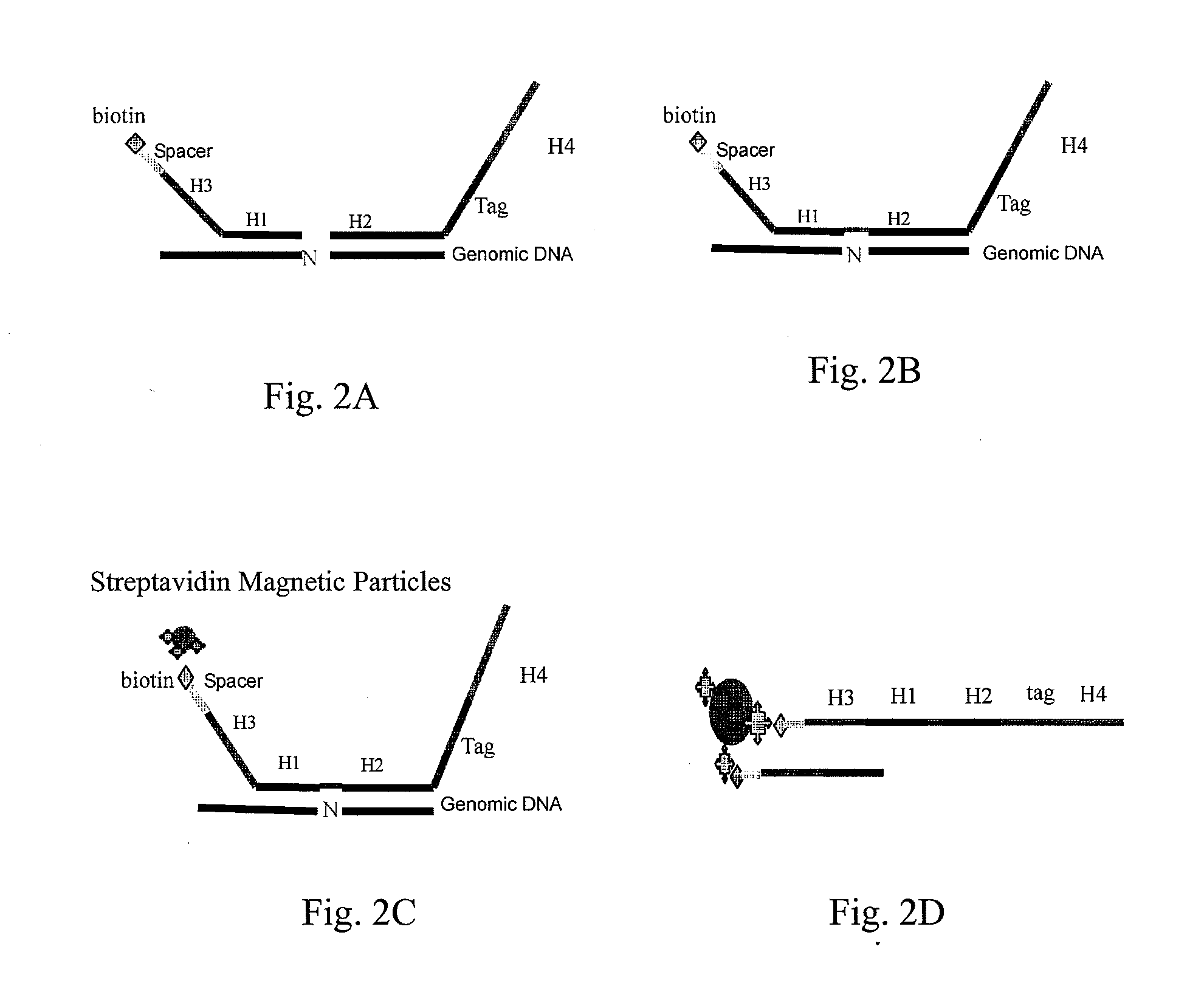
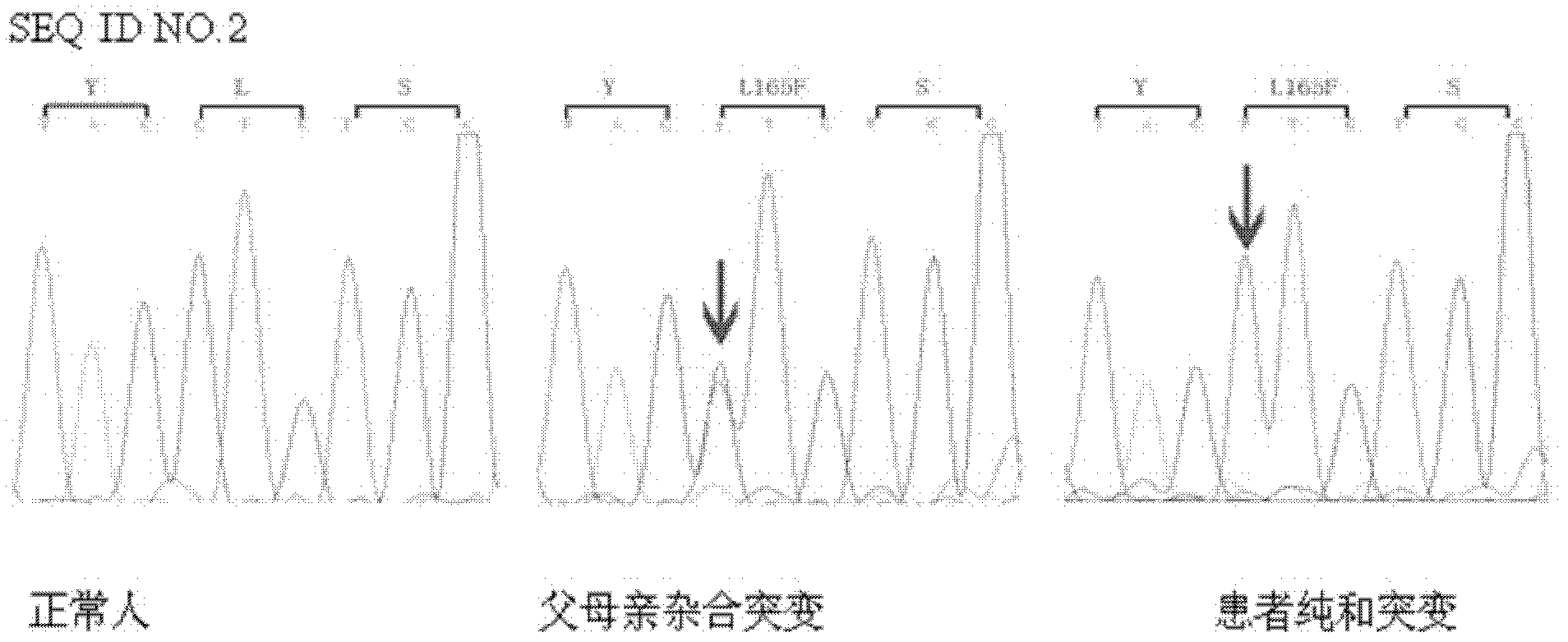
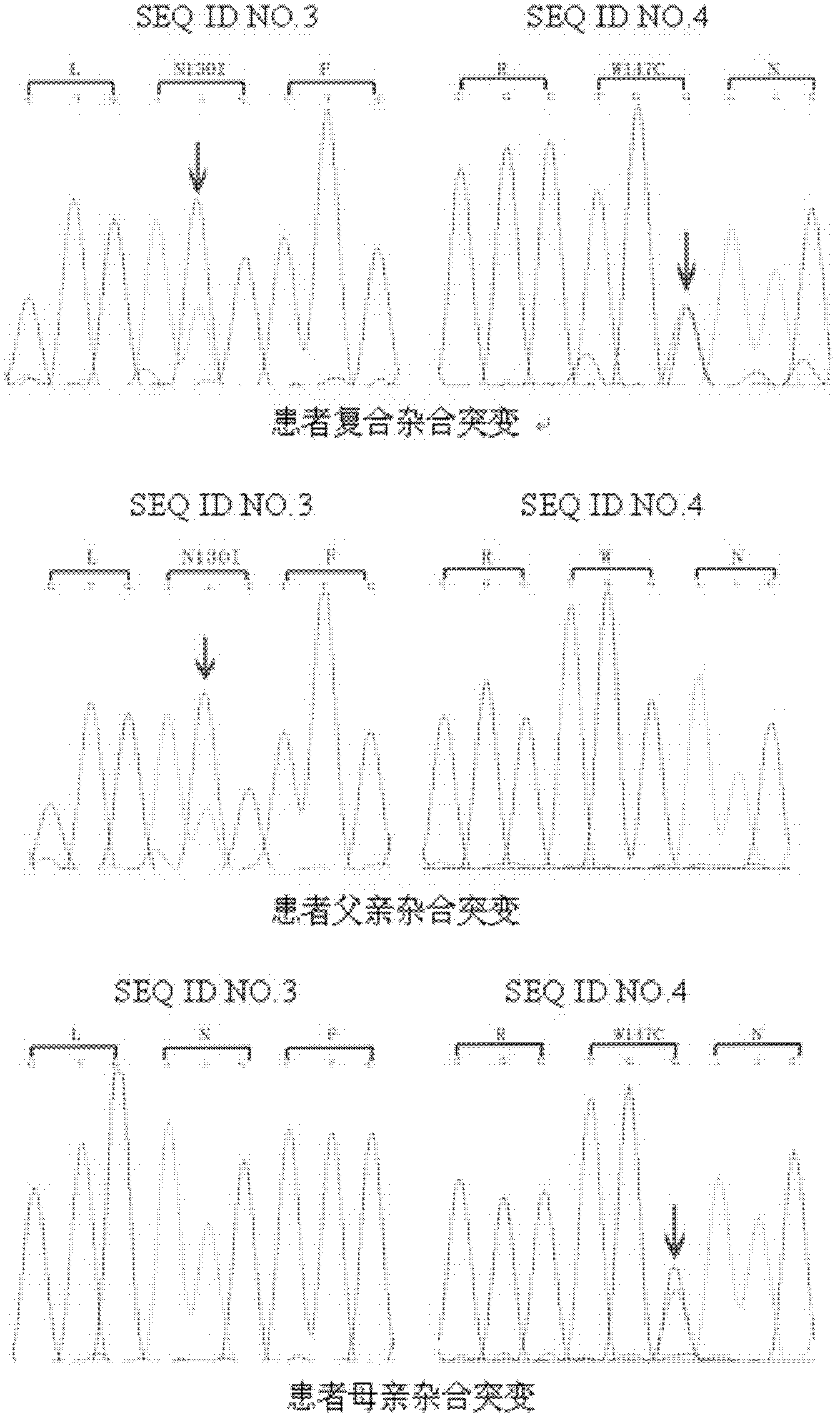
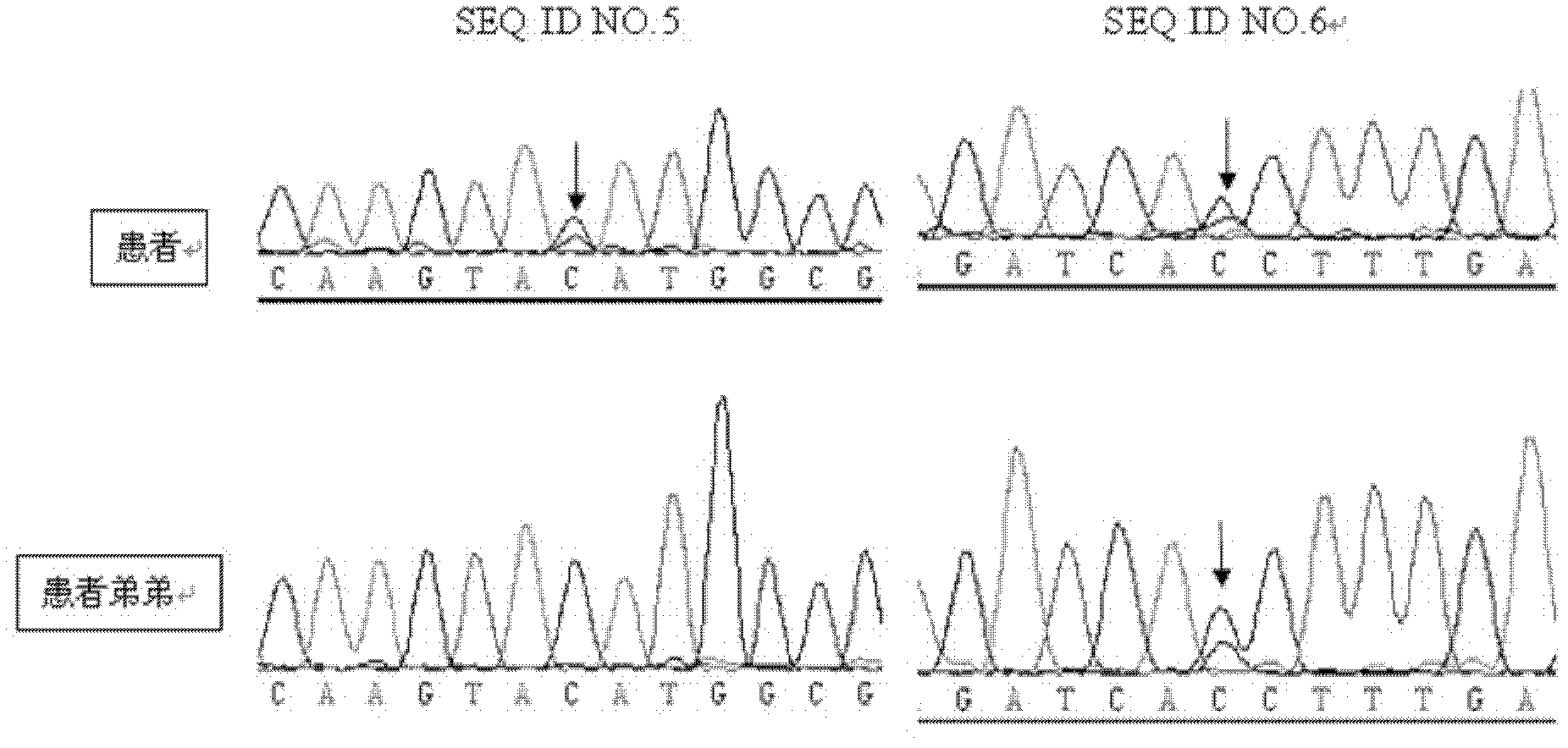
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Mutant genotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thalassemia gene detection method based on high-throughput sequencing technology
InactiveCN105886617ALess DNARealize detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingBeta thalassemia
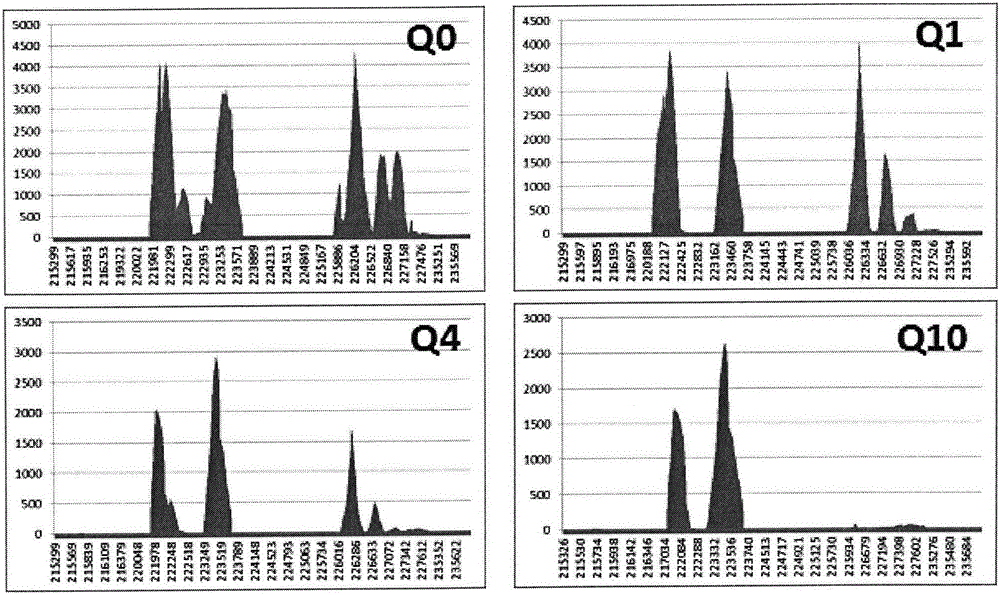
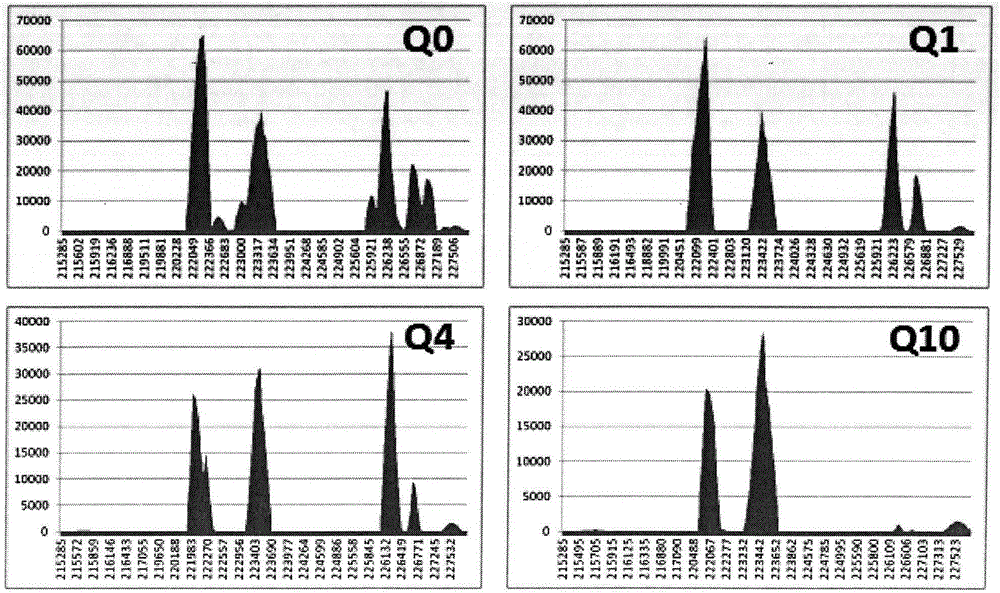
The invention discloses a thalassemia gene detection method based on a high-throughput sequencing technology. The thalassemia gene detection method mainly comprises the following steps that alpha & beta-thalassemia related gene fragments are specifically amplified based on PCR amplification primers of a span breakpoint and a mutation site designed by adopting a Gap-PCR method, library establishment is conducted on PCR products, library products are subjected to high-throughput sequencing, sequencing data uses a human genome hg19 as a reference sequence, sequencing depth values of gene loci in a target area chr16: 215000-236000 are analyzed according to a sequence alignment score Q10, and alpha-thalassemia deletion types are determined according to the distribution of the sequencing depth values of different loci; meanwhile sequence alignment is performed through the target area chr16: 215000-236000 and a target area chr16: 5246400-5248600, and alpha & beta-thalassemia mutation types are determined according to the basic types of specific sites. By the adoption of the thalassemia gene detection method, simultaneous detection of 6 mutation genetypes of alpha-thalassemia and 26 mutation genetypes of beta-thalassemia can be achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Identification of white leghorns red plumage mutagenic mutant genotype and cultivation method for supporting system of red plumage pink shell layer chickens
PendingUS20210007334A1Broad prospect for promotionShorten the generation intervalHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
The present invention discloses a method for breeding the commercial strains of red feather pink-shell laying hens. It provides a primer pair for identifying the red feather causative mutation homozygous genotype of white leghorn chickens, which is composed of the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 2 of the Sequence List and the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 3 of the list. After the primer was designed according to the upstream and downstream nucleotide sequences of the 18,288,303rd deoxynucleotide in the positive-sense strand of the 11th chromosome as shown in the sequence information of the chicken reference genome Gallus_gallus-4.0 version published in NCBI, the genotype (SNP) at this site is tested through the restriction fragment length polymorphism, the genotype of the site (SNP) was tested through the restriction fragment length polymorphism; the offspring hens obtained by cross breeding the homogenous female parent (the homogenous female parent was obtained through expanded propagation of the white leghorn chickens with the red feather causative mutation homozygous genotype) and the Rhode Island Red rooster as a male parent are all of red feather phenotype, meeting the market demands and enjoying a broad prospect for promotion.
Owner:BEIJING HUADU YUKOU POULTRY
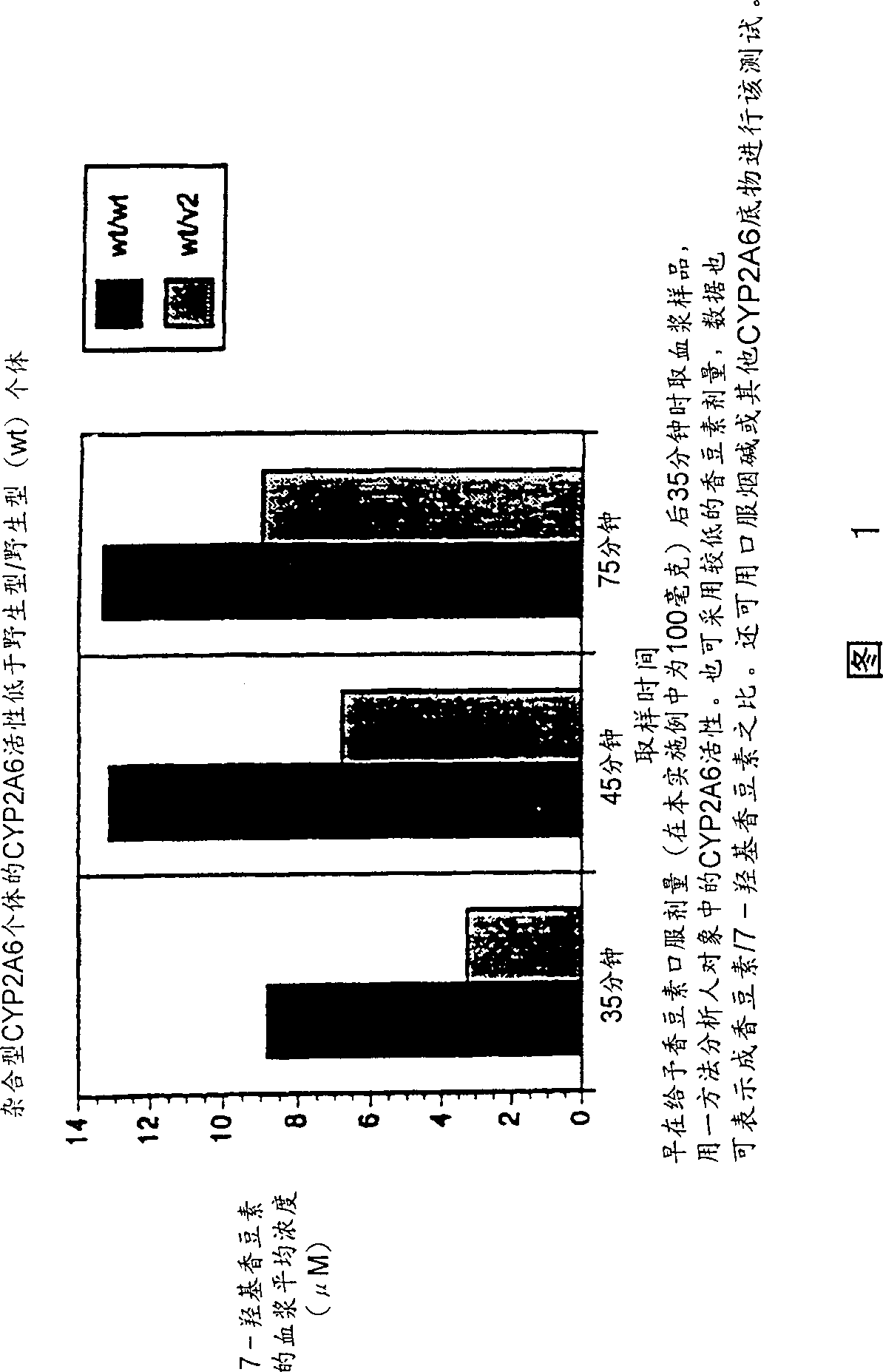
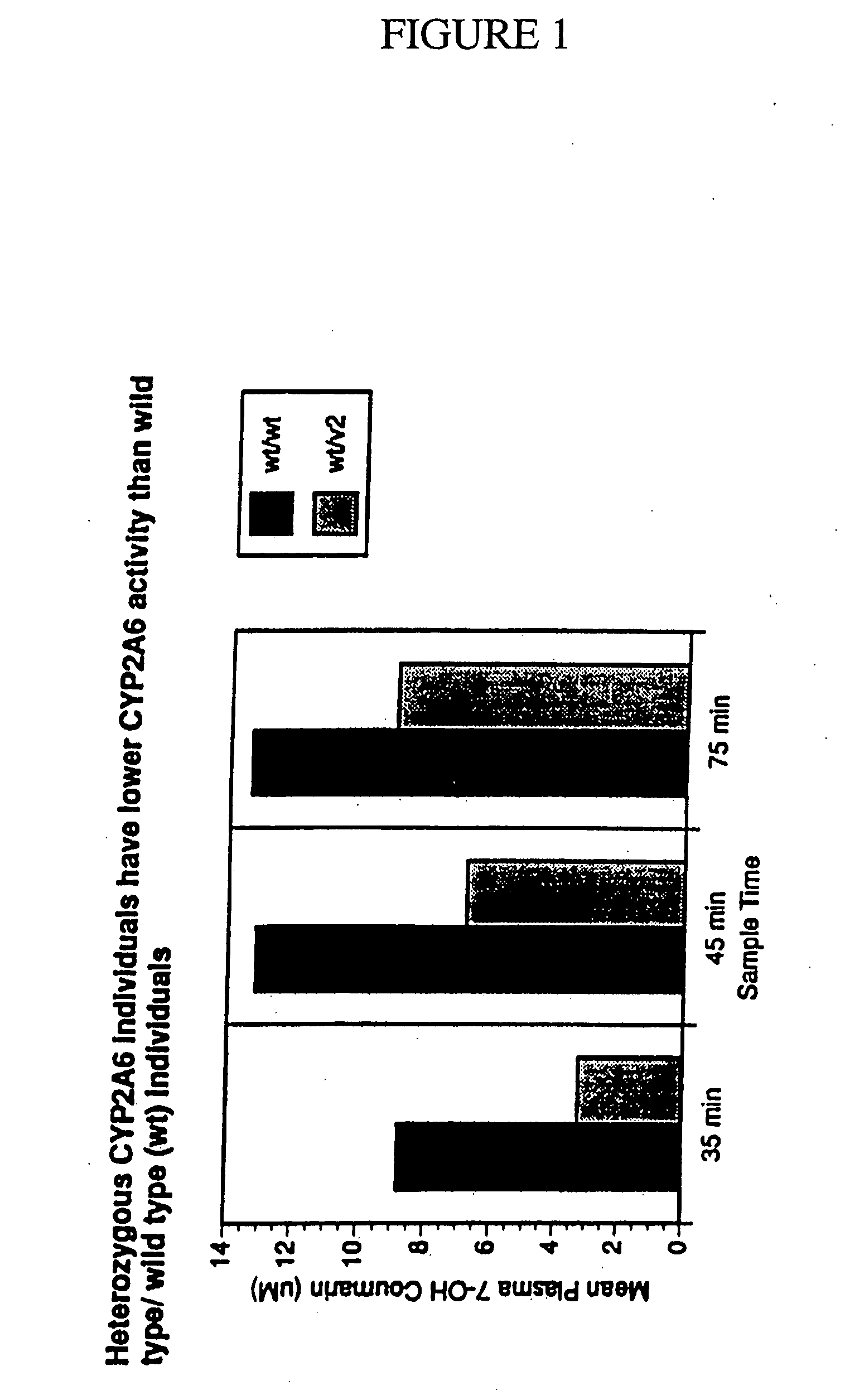
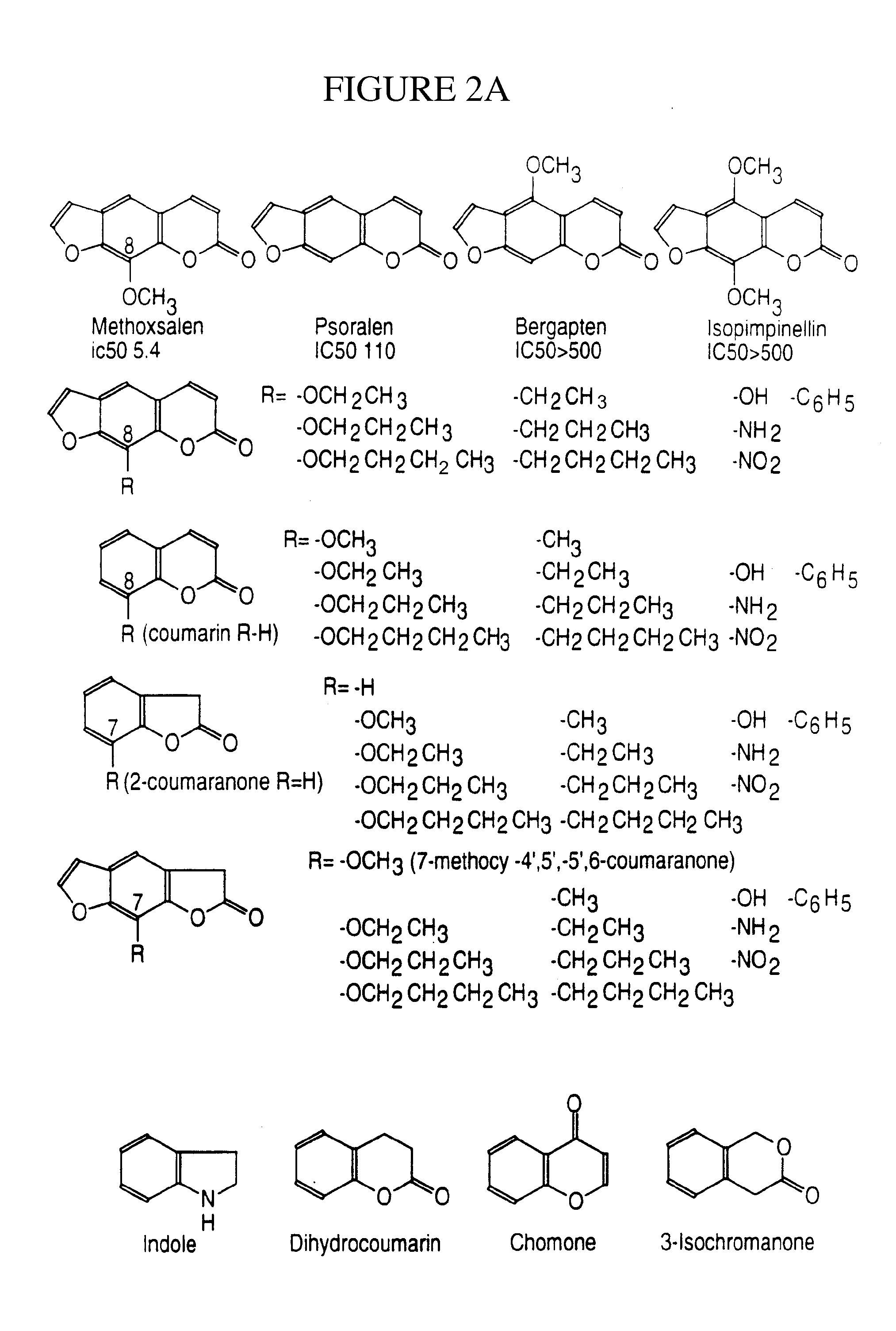
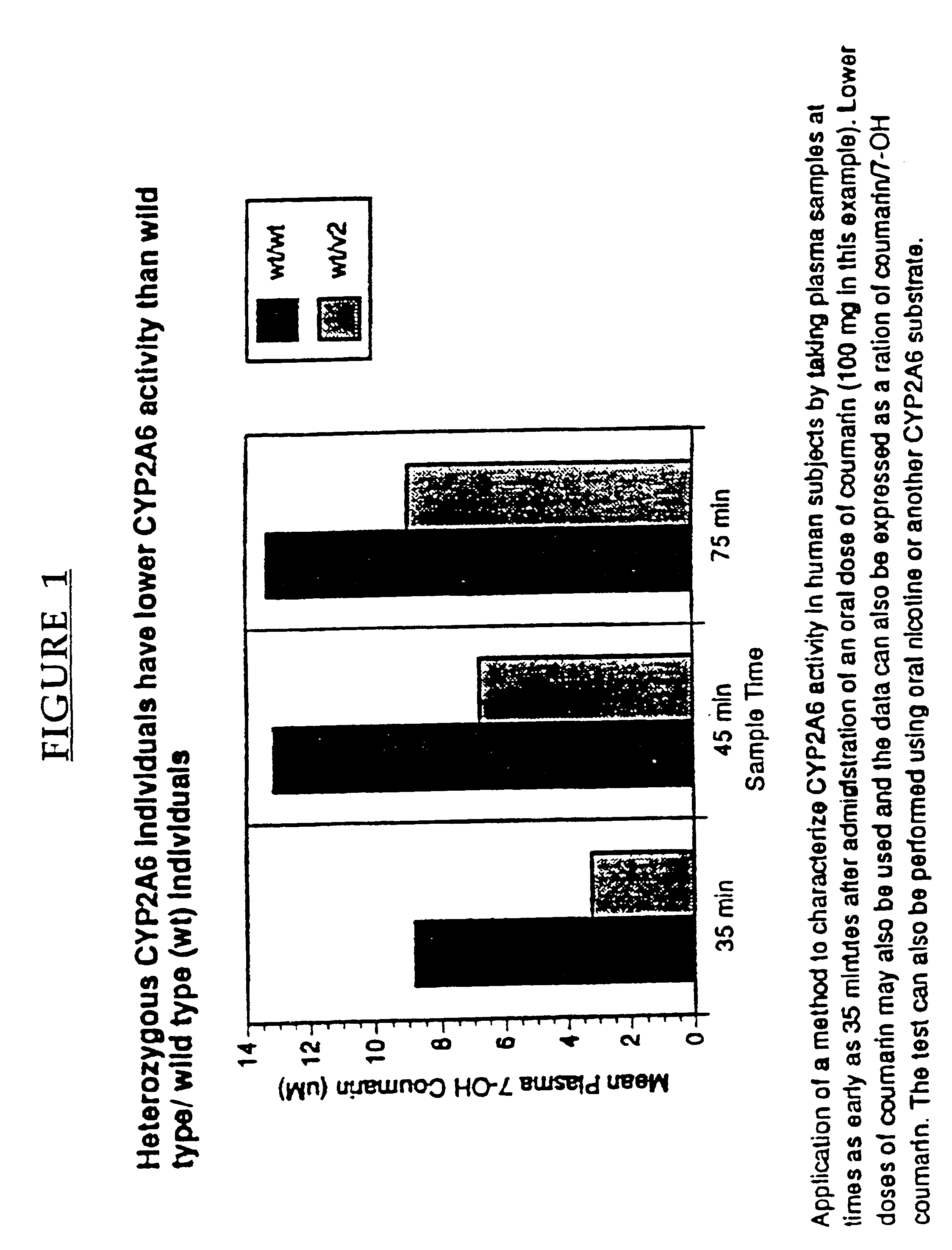
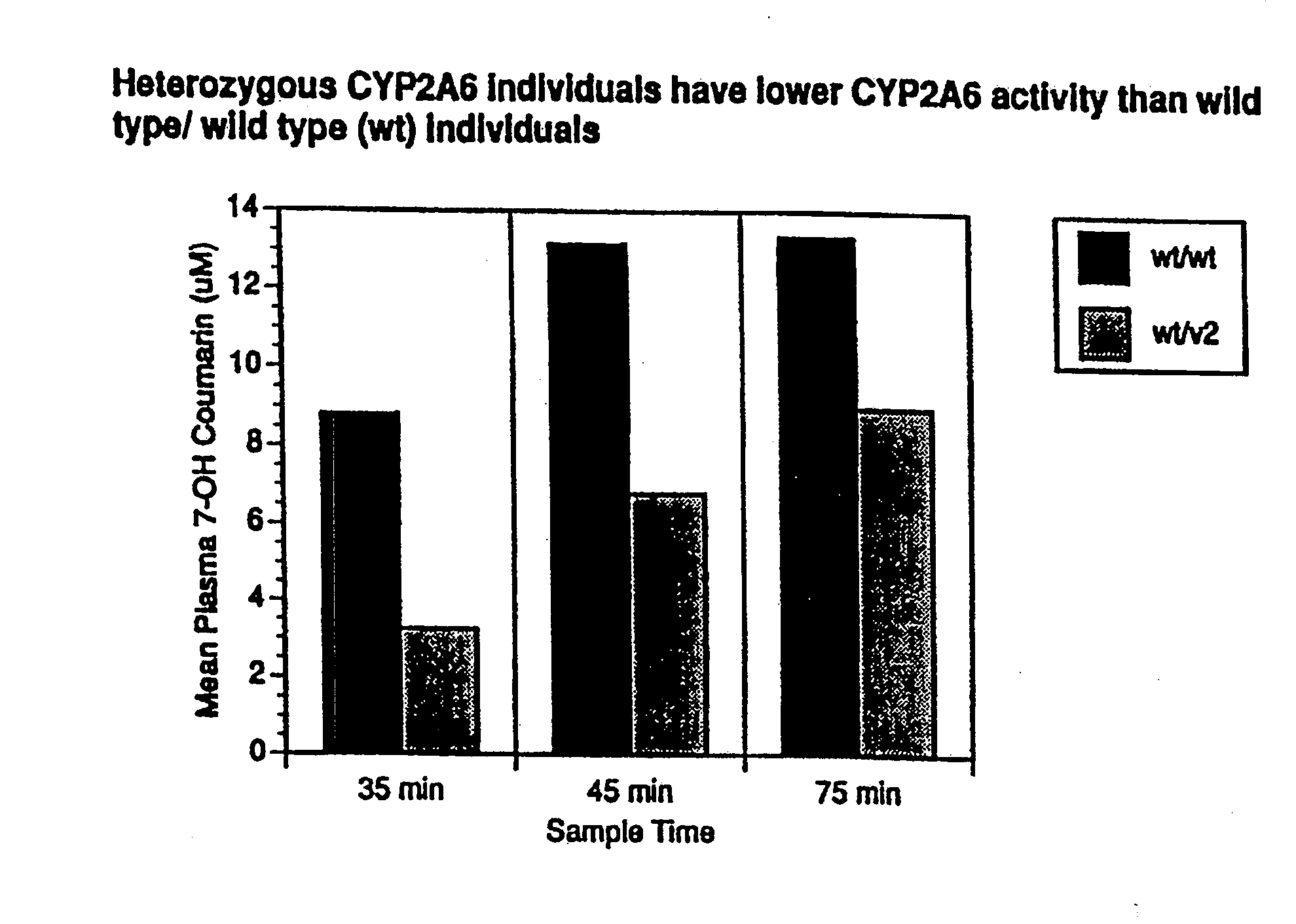
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on cyp2a enzymes
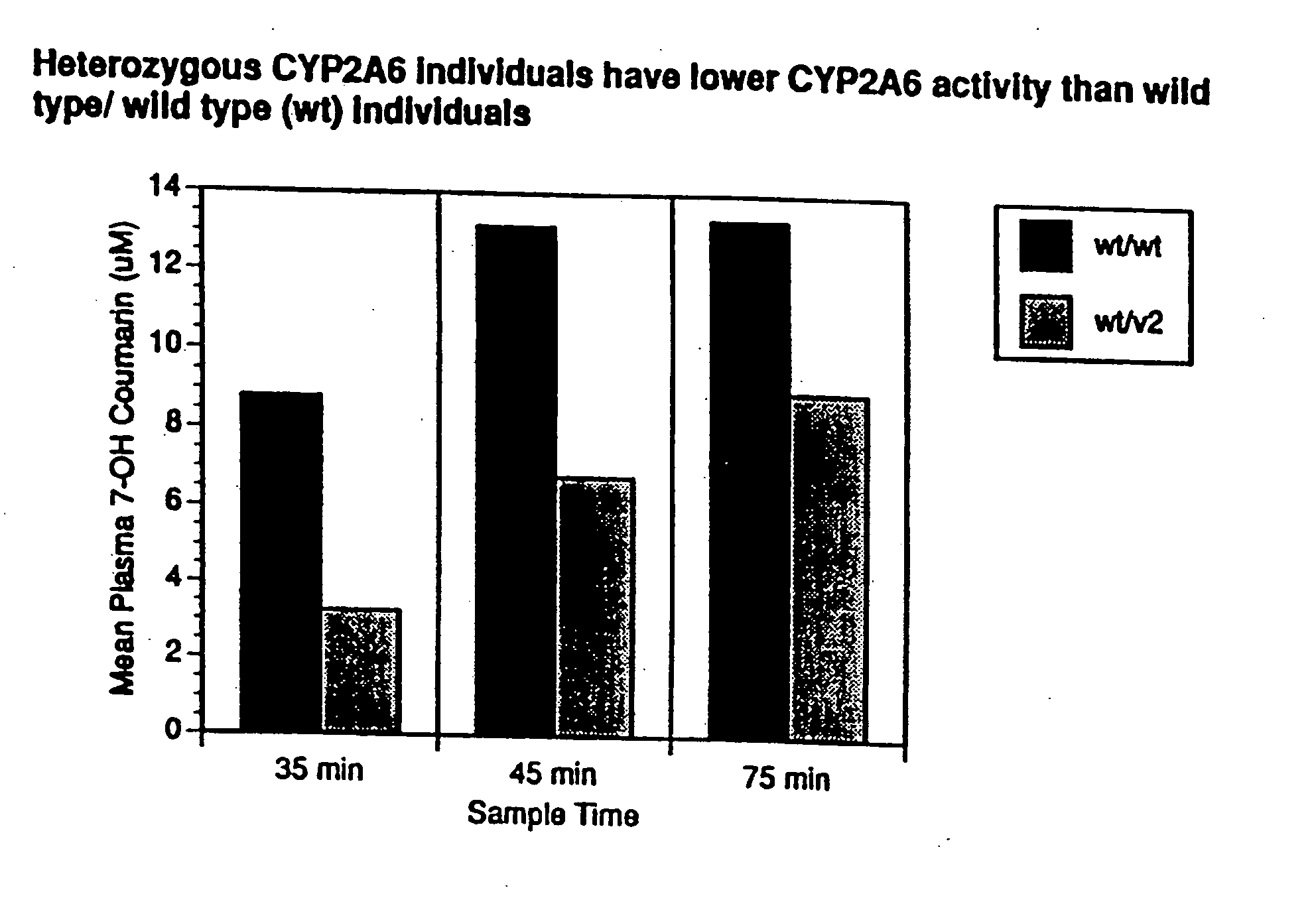
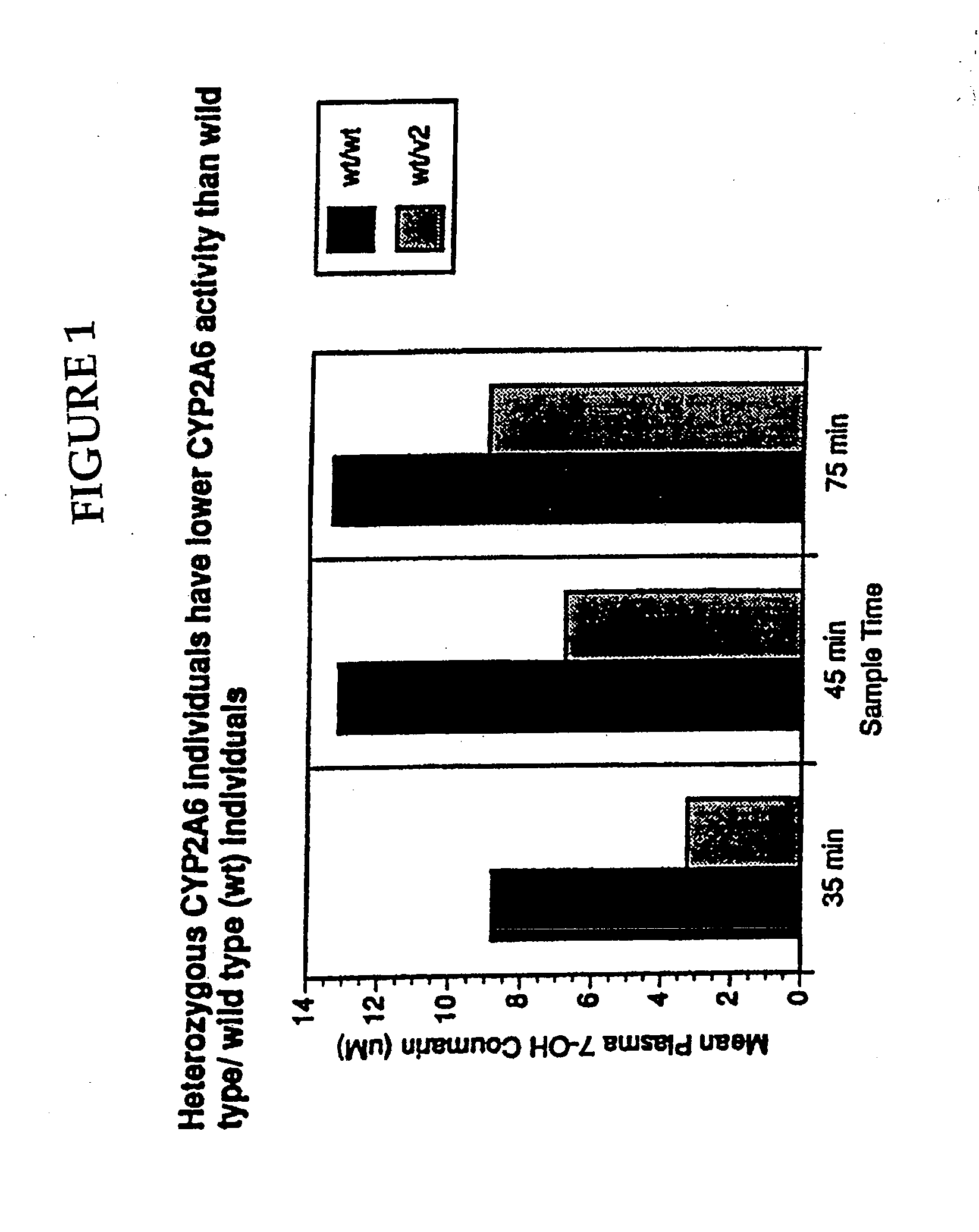
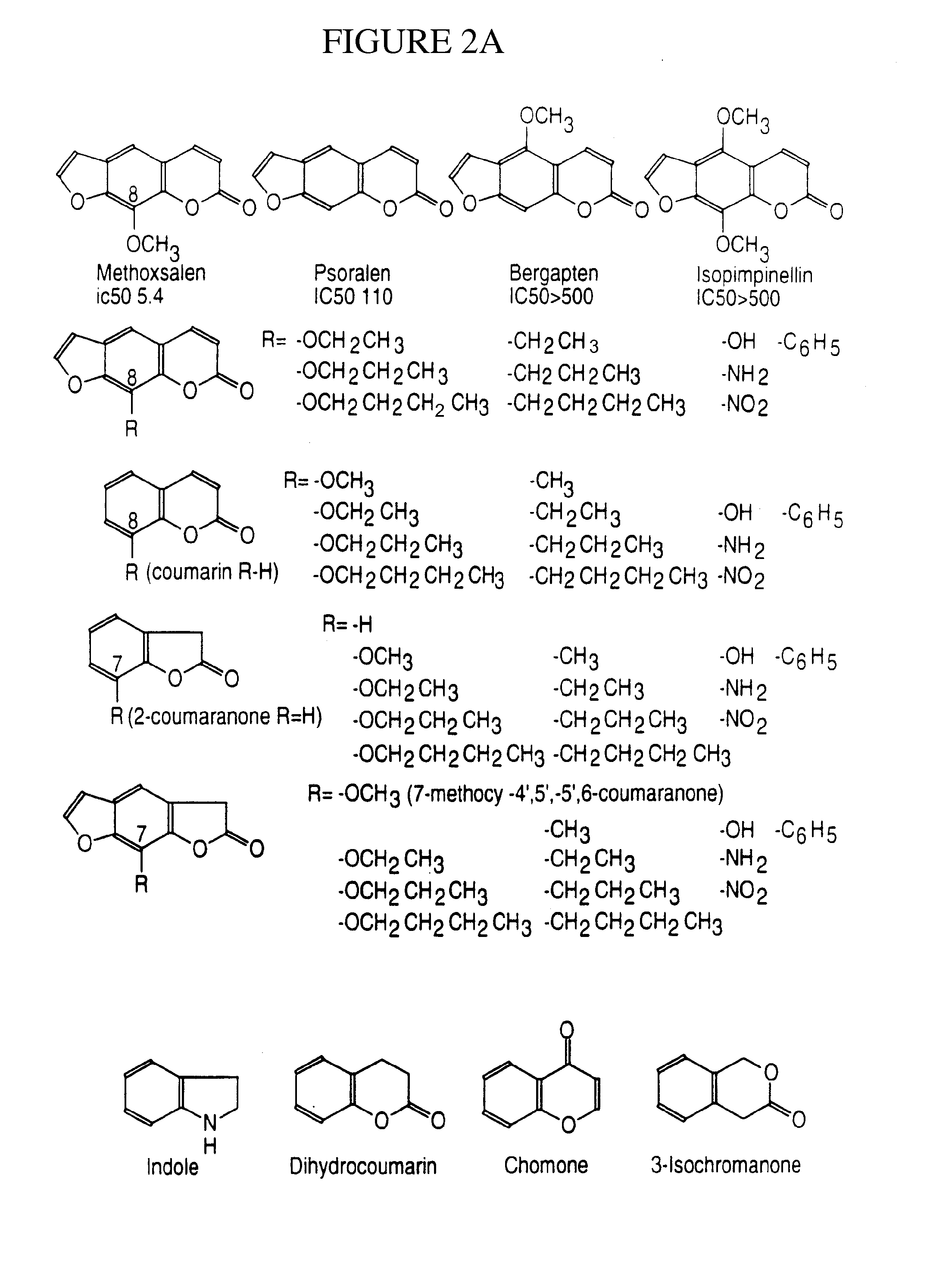
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
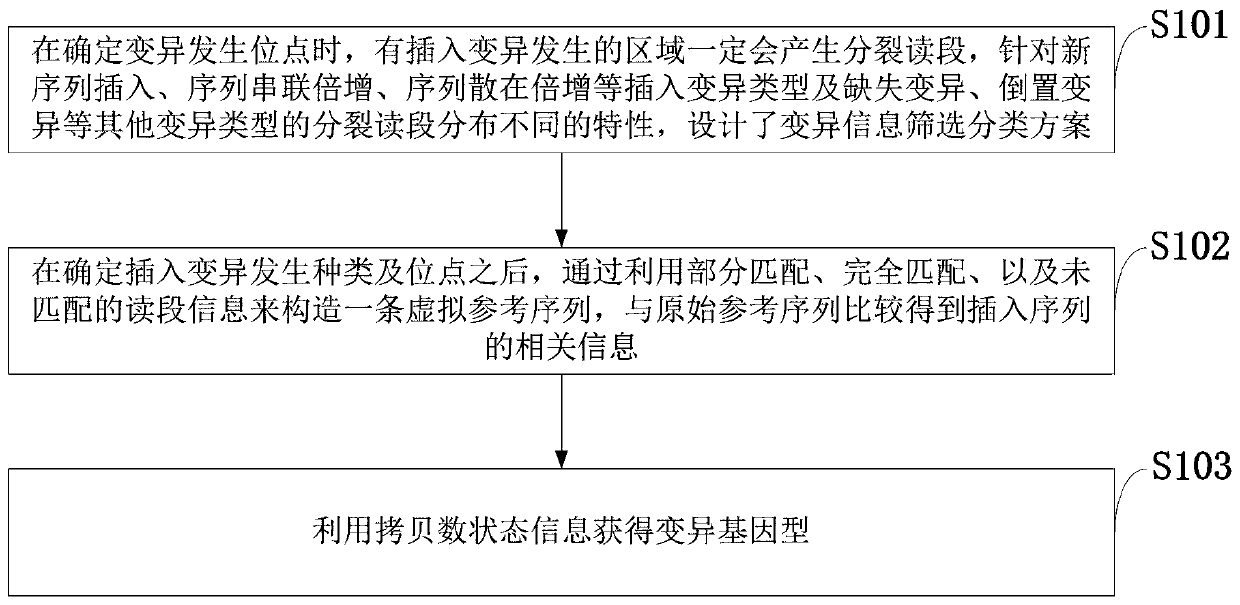
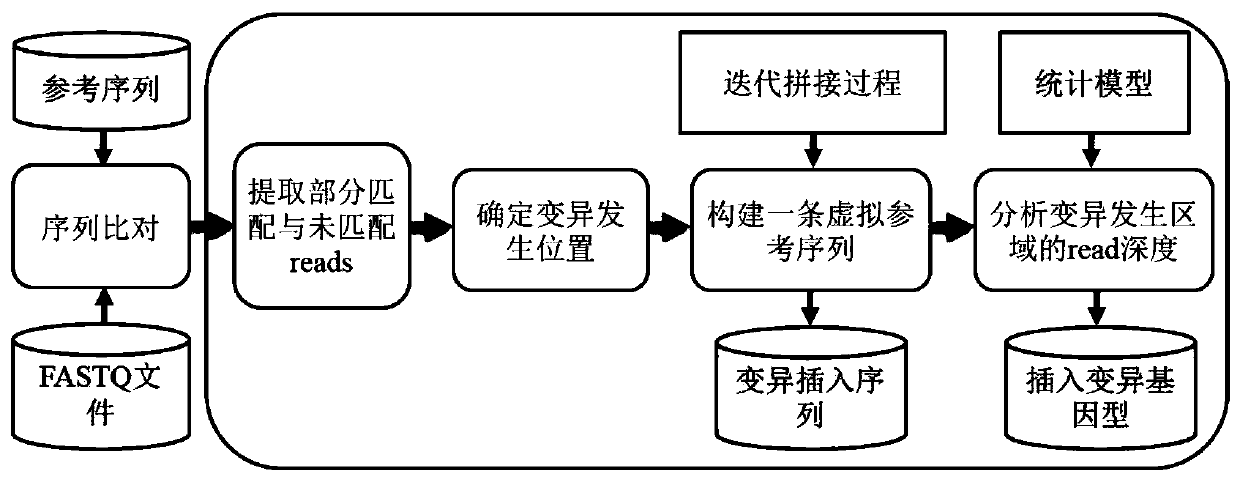
Insertion mutation detection method and system based on new-generation sequencing data
ActiveCN110299185ASolve the problem of inaccurate judgmentSolve the problem of detection errorProteomicsGenomicsGenomic sequencingRelevant information
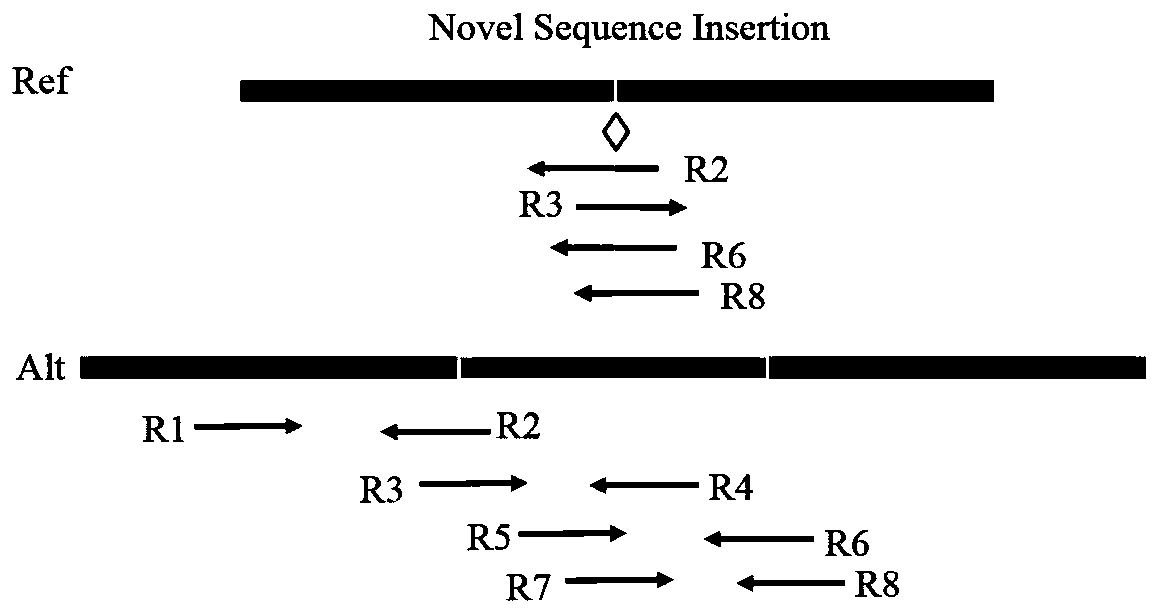
The invention belongs to the technical field of genome sequencing, and discloses an insertion mutation detection method based on new-generation sequencing data. The method comprises the steps: when amutation generation site is determined, a region where insertion mutation occurs certainly generates a split reading section, aiming at the characteristics that insertion variation types such as new sequence insertion, sequence series multiplication and sequence dispersion multiplication are different in distribution of missing variation and inverted mutation split reading sections, constructing avirtual reference sequence by utilizing partial matching, complete matching and unmatched read segment information after determining the insertion mutation generation type and site, and comparing thevirtual reference sequence with the original reference sequence to obtain related information of the insertion sequence; and obtaining a mutant genotype by utilizing the copy number state information. According to the invention, the problem of inaccurate insertion mutation point judgment can be solved; the problem of omission caused by insertion mutation detection of an SR method can be solved; the problem that in the prior art, repeated sequences may cause detection errors can be solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Breeding method for culturing good-taste and brown stripe-resisting rice
InactiveCN102172216AImprove accuracyImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention relates to a breeding for culturing good-taste and brown stripe-resisting rice and belongs to the field of genetic improvement of rice and application of biological technology. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting Wujing 13 and Guangdong 194 for matched hybridization; performing individual mixed harvest in the F2 and F3 generations, and performing the molecular mark auxiliary selection of dark albumen mutant genes and brown stripe-resisting genes at the F4 and F5 generations to obtain the double-gene homozygote, of which the dark albumen mutant genotype is Wx-mqWx-mq and the brown stripe-resisting genotype is Stv-biStv-bi; and performing the selection of yield and agronomic character at following generations until the new variety of high-yield rice, namely Nanjing 5055, with stabile and consistent agronomic character, good taste and brown stripe resistance is cultured in the F7 generation. The variety of rice has the advantages of high yield, brown stripe resistance, the combination of the softness of glutinous rice and the elasticity of non-glutinous rice, excellent taste and quality and wide application prospect in proper plantations of riverside areas and southern part of Jiangsu Province.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
PIK3CA gene mutation fluorescence quantitative PCR genotype detection kit and detection method
InactiveCN102851368AHigh detection sensitivityReduce false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMutant genotype
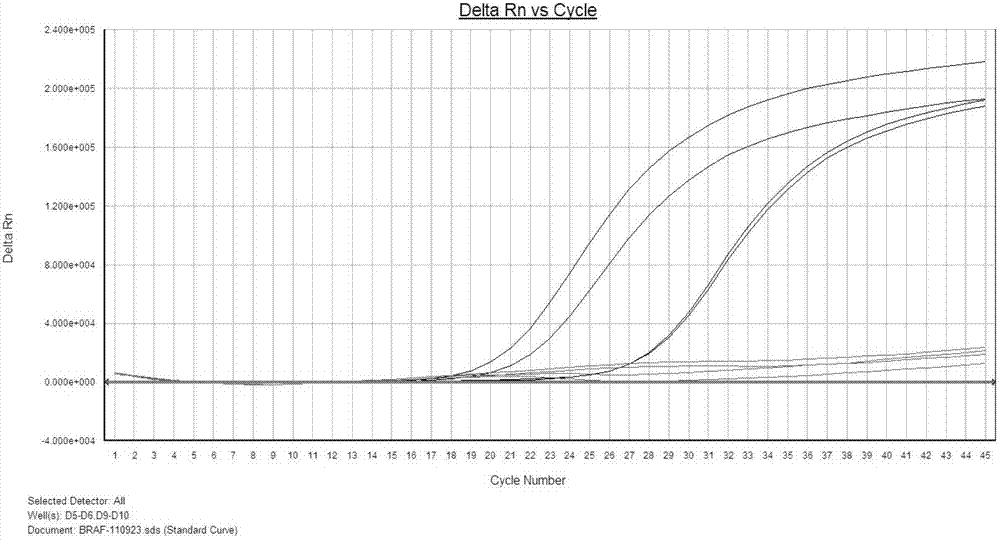
The invention discloses a PIK3CA gene mutation fluorescence quantitative PCR genotype detection kit comprising a PCR mixed reaction liquid, a positive control, and a fluorescent probe used for detecting PIK3CA gene mutant genotypes. The PCR mixed reaction liquid comprises PCR primers used for amplifying PIK3CA gene segments where the mutation sites exist. The invention also discloses a PIK3CA gene mutation fluorescence quantitative PCR genotype detection method. According to the method, PIK3CA gene mutant genotypes are subjected to fluorescence quantitative PCR detections by using the kit provided by the invention. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, detections can be carried out upon tissue PIK3CA gene mutations, and especially rapid, accurate, and high-sensitively detections upon PIK3CA gene 542,545 and 1047 nucleotide mutations can be realized.
Owner:广州达健生物科技有限公司
Special CAPS marker for identifying wild type or mutant paddy rice salt resistant gene OSRR22, primer, and primer applications
ActiveCN107988409AEfficient identificationNo errorMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention relates to a special CAPS marker for identifying a wild type or mutant paddy rice salt resistant gene OSRR22, a primer, and primer applications. The marker comprises a marker Cas-Osrr22-1 for detecting a wild type site and the nucleotide sequence of the marker Cas-Osrr22-1 is represented by SEQ ID No.2. The marker also comprises a marker Cas-Osrr-22-2 for detecting a mutant WDR58-cas-1 site, and the nucleotide sequence of the marker Cas-Osrr-22-2 is represented by SEQ ID No.3. Compared with the prior art, the provided maker, primer, and primer applications have the advantages that a molecular marker for differentiating mutant and wild type of WDR58-cas-1 is provided, high efficient identification of salt resistant gene Osrr22 mutant genotype is realized; and WDR58-cas-1 mutant can be applied to breeding of salt resistant species. The CAPS marker can be applied to assistant breeding for improving the salt resistant property of paddy rice, and can be applied to identification for crossbreeding and backcross separation groups, heterozygosis genotype and homozygosis genotype can be accurately differentiated, and the breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AGROBIOLOGICAL GENE CENT
Identification method and special marker for red feather mutagenic genotype of white leghorn
ActiveCN108085400AImprove use valueBreed fastMicrobiological testing/measurementGallus gallus gallusPhenotypic trait
The invention discloses a red feather mutant of white leghorn as well as a marker and a detection method of the red feather mutant. The invention provides application of a substance for detecting thegenotype of red feather SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) luci in a genome of the white leghorn in identification of color characters of feather of filial generations of to-be-detected white leghorns and Rhode Island Red cocks; the red feather SNP loci are the 18th,, 288th and 303rd loca of a positive-sense strand of No.11 chromosome of a chicken genome. The experiment of the invention proves that one SNP locus is found and can realize identification of the red feather mutagenic genotype; by using the method, the red feather mutagenic genotype of white leghorn strain chicken is successfullyidentified. The identification method is convenient and quick, can be used for quickly cultivating a novel red feather mutant homozygotic type strain and further is applied to cultivation of a novelcomplete strain of 100 percent red feather phenotype red feather pink egg-shell chickens; cultivation cost is reduced, cultivation time is shortened and variety benefits are increased.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Molecular marker related to dwarfing of corn plant
ActiveCN113481315ARapid identificationShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyArginine
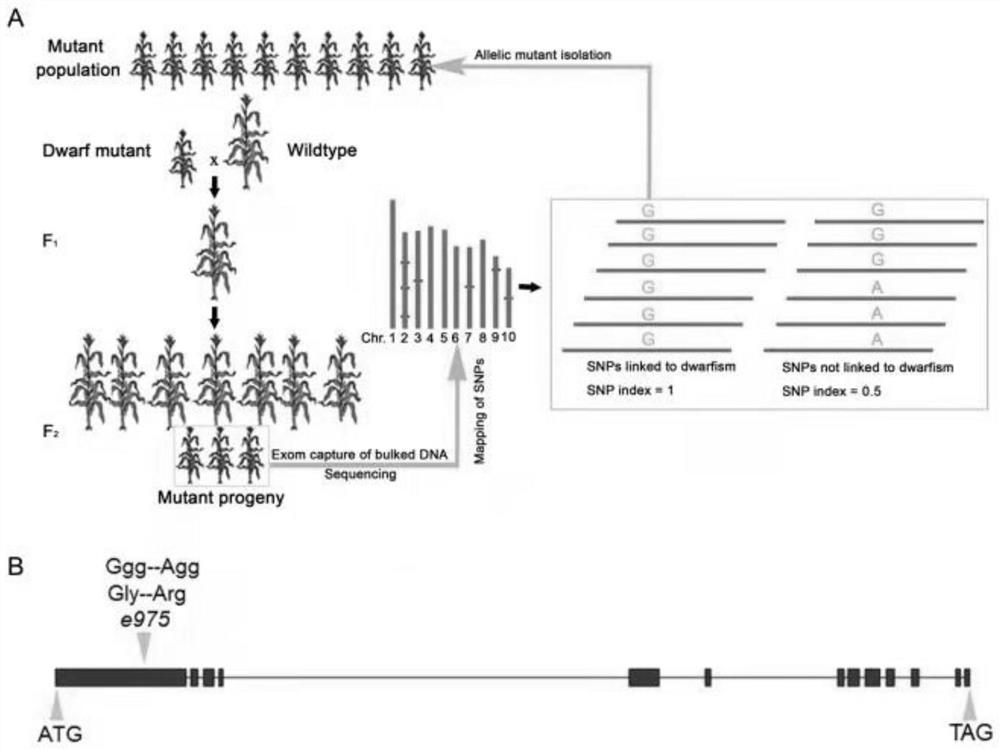
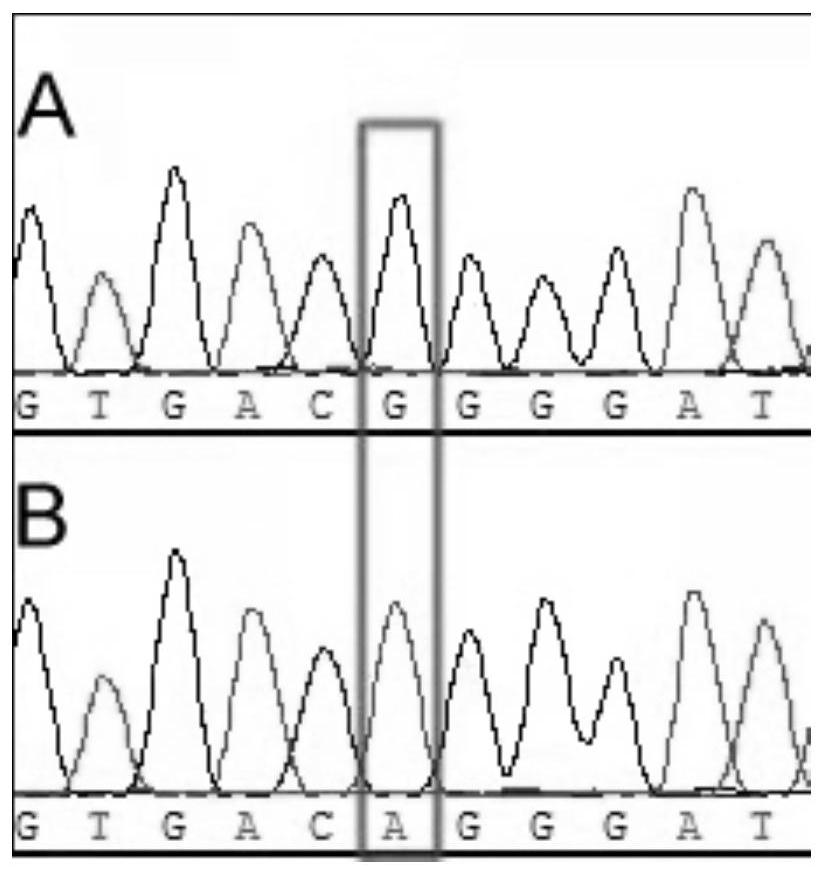
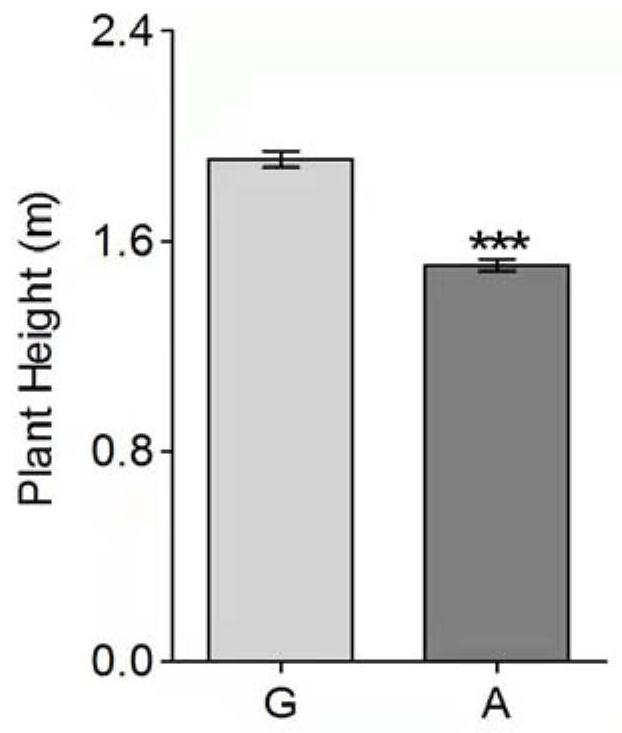
The invention discloses a molecular marker related to dwarfing of corn plant. According to the invention, a mutant e975 related to dwarfing of corn plant height is screened, although the section number of corn is obviously reduced, the height of the corn is obviously reduced, and the ear length of the corn is obviously reduced, the yield of the e975 is not obviously different from that of a wild type. Gene localization shows that the first exon of the Zm00001d027807 gene of the mutant has changed from G to A, so that non-polar glycine is changed into alkaline arginine. For the variation, a corresponding molecular marker primer (SEQ ID NO.3-4) is developed, and after PCR amplification, Sanger sequencing is utilized for genotype interpretation, so that the wild genotype and the mutant genotype of the filial generation contain corn dwarfing gene Zm00001d027807 can be identified. The molecular marker is beneficial to auxiliary breeding of new corn dwarfing varieties.
Owner:QILU NORMAL UNIV
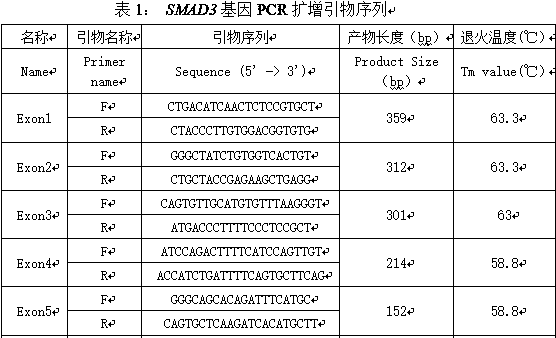
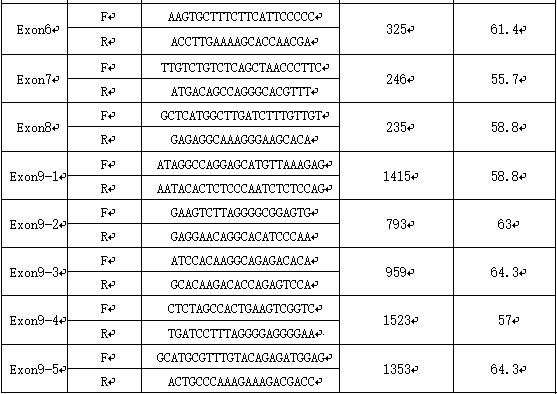
Muscovy duck egg laying performance associated gene SMAD3 molecular marker screening method
InactiveCN109868323AImproved egg production traitsImprove reproductive performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodCorrelation analysis
A muscovy duck egg laying trait associated gene SMAD3 molecular marker screening method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out DNA extraction: extracting female muscovy duck genome DNA in anegg laying period by adopting a phenol-chlorine method, and then determining an OD value and concentration of the purity of the genome DNA; (2) carrying out primer design: carrying out SMAD3 gene amplification primer design by applying NCBI online software and Primer 5.0, and sending a primer sequence to a related biological company for synthesis; (3) carrying out PCR amplification: adopting a 15[mu]L reaction system, setting PCR amplification conditions, carrying out PCR amplification, and carrying out electrophoresis detection on a product by using 1% agarose gel; (4) sequencing amplification product fragments and screening SNP sites; and (5) directly sequencing and typing the SNP mutation sites, carrying out correlation analysis on the SNP mutation sites and the egg laying performance,and determining the SNP closely correlated with the egg laying performance. When the molecular marker is applied to the muscovy duck seed selection and breeding process, the mutant genotype of the gene SMAD3 associated with the muscovy duck egg laying performance detected by the method is used as the molecular marker.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method for identifying red feather-induced mutant genotype of white leghorns and breeding method for complete set line of red feather pink shell laying hens
ActiveCN108192981ATo satisfy the market's needsAvoid the tediousness of test cross breedingHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand
Owner:BEIJING HUADU YUKOU POULTRY
Kit for accurately detecting polymorphism of ALDH2 (Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2) gene
InactiveCN108441553ASimple and fast operationStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection and discloses a kit for accurately detecting the polymorphism of an ALDH2 (Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2) gene. The kit for accurately detecting the polymorphism of the ALDH2 gene can be used for determining mutation gene types (G>A, G>T and G>C) of rs671 polymorphism sites of the ALDH2 gene in one step. In order to realize the function, the kit applies a method combining a multi-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology and a Taqman-MGB fluorescent probe labeling technology, and four pairs of specific primers and four specific probes for labeling different fluorescent dyestuffs are designed; the kit is characterized in that a target gene only can be combined with one pair of primers and one probe, so that the accuracy of a detection result is ensured. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of strong specificity, high accuracy, simplicity in operation and the like. A sample to be detected can be selected from whole blood or oral cells; the kit is clinically used for guiding rational drug use of nitroglycerin and guiding healthy wine drinking to prevent alcohol intoxication, and has great significance inthe aspect of prompting major diseases.
Owner:PRO MED BEIJING TECH
High-resolution-ratio dissolution curve detection method for mutation of OsNramp5 gene specific site
PendingCN110257488AImprove efficiencyShort detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementCurrent generationBioinformatics
The invention discloses a high-resolution-ratio dissolution curve detection method for mutation of an OsNramp5 gene specific site. By knocking out an OsNramp5 gene, low-cadmium paddy rice strains can be quickly created. In conventional CRISPR / Cas9-mediated gene knockout, if identification of current-generation mutants of transformed plants and screening of homozygous mutant genotypes of offsprings with markers removed are detected by a conventional sequencing method, time and labor are wasted and the cost is high. For overcoming the shortcomings, the invention provides the high-resolution-ratio dissolution curve detection method for rapidly detecting mutations in current generations of the transformed plants and rapidly identifying homozygous mutant individuals in the mutant isolated offsprings in the work of knocking out the OsNramp5 gene by CRISPR / Cas9. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of large flux, fast speed and low cost.
Owner:江西省超级水稻研究发展中心
CYP2A enzymes and their use in therapeutic and diagnostic method
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as 'CYP2A6' for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Therapeutic and diagnostic methods dependent on CYP2A enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease the production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme. Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (1) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6 -mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analyzing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Method for detecting genotype of polymorphic sites of corneal dystrophy gene and its kit
ActiveCN108085375AIncrease the number of mismatched basesImprove low efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceWild type
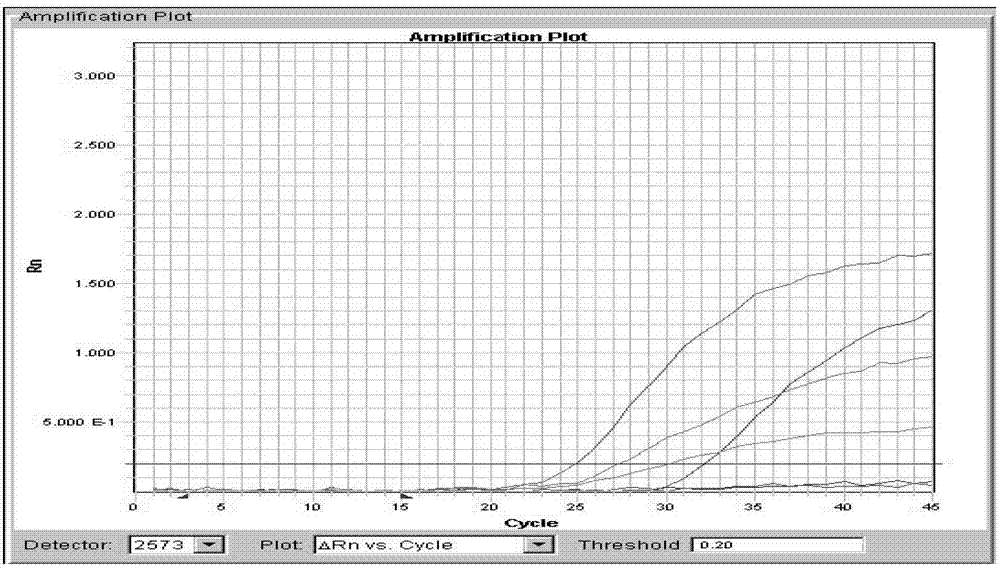
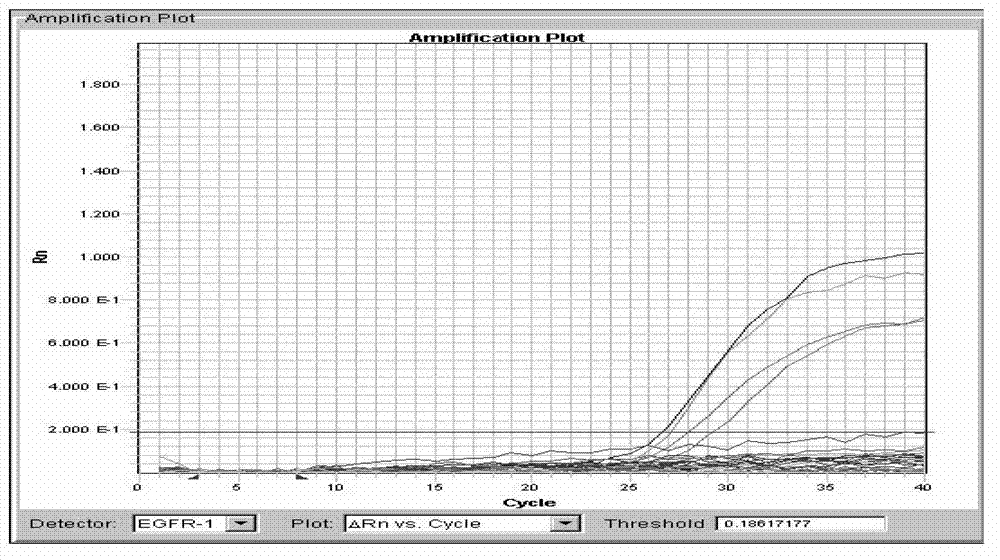
The invention discloses a method for detecting a genotype of polymorphic sites of a corneal dystrophy gene and its kit. In a same reaction system, real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection is respectively carried out on a same to-be-detected sample by an enhanced ARMS primer aiming at a gene wild type template for polymorphic sites of corneal dystrophy and an enhanced ARMS primer aimingat a mutant template; according to a Ct mutant type detected by the real-time fluorescence quantification detection by the enhanced ARMS primer aiming at the gene wild type template, a Ct wild type detected by the real-time fluorescence quantification detection by the enhanced ARMS primer aiming at the mutant template, and a difference delta-Ct value of the Ct mutant type and the Ct wild type, and the mutant genotype of the corneal dystrophy gene can be determined according to the types of the polymorphic site. The method has the advantages of simple operation and high accuracy.
Owner:北京华大通瀛科技有限公司
Method for screening disease phenotype related mutation sites and application thereof
PendingCN112735594ASmall sample sizeAvoid allele frequency effectsMedical data miningProteomicsDisease phenotypeDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformatics, in particular to a method for screening disease phenotype related mutation sites and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sequencing data of a plurality of disease samples and normal samples, and carrying out variation detection; performing association rule mining by taking the phenotype of the samples and the mutation type of the detected mutation site as a total project set to obtain a mutation site having a strong association relationship with the phenotype of the disease samples; and performing modeling analysis on the mutation sites obtained through association rule mining and screening to obtain mutation sites related to disease phenotypes. Alleles are converted into classification variables for association rule mining, and then modeling analysis is carried out on sites strongly associated with disease phenotypes, so that the total quantity of analyzed samples can be effectively reduced, and the influence of allele frequency on an analysis result is avoided; and screening and analysis of disease phenotype related sites can be completed only by obtaining mutation genotype information.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Method for identifying plant gene functions in total genome ranges
ActiveCN105734130AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSingle nucleotide mutationNucleotide
The invention relates to a method for identifying plant gene functions in total genome ranges.The method includes 1), mutating single nucleotide of starting plants and establishing plant mutant libraries; 2), detecting phenotypes of mutants in the plant mutant libraries and establishing plant mutant phenotype databases; 3), detecting genotypes of the mutants in the plant mutant libraries and establishing plant mutant genotype databases; 4), determining functions of genes where SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) sites caused by mutation of the single nucleotide in the starting plants by the aid of the plant mutant phenotype databases and the plant mutant genotype databases.The method has the advantages that the genes related to plant development procedures and biological procedures of stress-tolerant reaction or metabolic pathways or the like can be accurately and quickly found by the aid of the plant mutant phenotype databases and the plant mutant genotype databases which are established by the method, and novel ways can be created for plant functional genome research.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
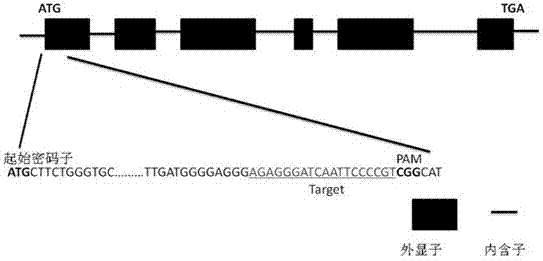
Method for performing site-directed mutation on rice TDR gene by CRISPR\Cas9 system and detection method
InactiveCN111575313AReduce the impactKnockout is complete and permanentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenes mutationAnimal science
Recessive male sterility has an important utilization value in plant breeding. TDR gene function deficits in rice can cause thorough recessive male sterility, and is thus an important target of creating the recessive male sterility in genetic engineering. The invention discloses a method for performing site-directed mutation on a rice TDR gene by a CRISPR\Cas9 system. By using the site-directed mutation method provided by the invention, a TDR gene mutant can be fast and efficiently created so as to obtain a recessive male sterility material. The invention further provides a detection method ona specific TDR mutation genotype obtained by the site-directed mutation method. The detection method can be used for fast identifying whether the mutation exists in the target in a current generationtransformant of the TDR site-directed mutation, and can also be used for genotyping identification of the later-generation specific mutation genotype.
Owner:江西省超级水稻研究发展中心
Test probes, common oligonucleotide chips, nucleic acid detection method, and their uses
ActiveUS20110218115A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligonucleotide chipDna polymerasen
High-throughput detection for the interesting base or the mutation site in the nucleic acid sample can be achieved by the linear test probe pairs P1 and P2. The test probe pairs P1 and P2 respectively comprise either of the flanking complementary sequences which are adjacent to the interesting base or the mutation site in the nucleic acid sample. When the test probe pairs P1, P2 are annealed and hybridized to the nucleic acid sample, a gap will be generated at the interesting base or the mutation site position between the probe pairs and the sample. Divide the annealed hybrid sample into four equal reaction systems to which add dATP, dTTP, dCTP, dGTP, respectively. The test probe pairs P1 and P2 will be ligated into one single probe when adding the complementary nucleotide system under the DNA polymerase or ligase. After purified and amplified, the generated single probes are hybridized to the corresponding area in a common oligonucleotide microarray. The generated single probe will give a signal in the hybrid area, and therefore detect and analyze the hybrid signal to determine the base type or the mutation genotype at the detection position. The invention can be applied to the re-sequencing the target nucleic acid sequence, the detection and analysis for the mutation, insertion, or deletion sites of a known nucleic acid sequence, and the genotyping of the pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:SHANXI LIFEGEN
Related genes of autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia
InactiveCN102618559AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesDiseaseRelated gene
The invention discloses five mutant genes of a novel ARCA (autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia) subtype disease-causing gene, and further discloses a recombinant vector comprising mutant CHIP (carboxyl terminus of Hsc70interacting protein) of the ARCA subtype disease-causing gene, a recombinant cell comprising the recombinant vector, encoding protein of the related genes of ARCA and a kit for detecting the mutant genes.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Therapeutic and Diagnostic Methods Dependent on CYP2A Enzymes
A method of regulating the activity of human cytochrome P450 isozyme CYP2A6 to control nicotine metabolism or decrease to production of carcinogens from procarcinogens, such as those present in tobacco smoke, in an individual by selectively inhibiting CYP2A6. Various prophylactic (i.e., prevention and treatment) compositions and methods are also described, including an improved oral nicotine composition and method comprising the use of nicotine together with an inhibitor of the CYP2A6 enzyme.Furthermore, it has been discovered that the presence in an individual of a mutant allele of human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 (referred to throughout this specification as “CYP2A6” for brevity) is predictive of an individual who: (i) has a decreased risk of becoming a smoker, (ii) will smoke less if he / she becomes dependent, and / or (iii) may be at relatively lower risk for cancer due to both decreased smoke exposure and decreased CYP2A6-mediated activation of tobacco smoke and other procarcinogenic substrates. This invention provides diagnostic methods for predicting tobacco dependence risk and risk for cancers related to CYP2A6 substrates in an individual by analysing for the presence of a mutant genotype for human cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2A6 in an individual, ranging from gene duplication (multiple copies of CYP2A6) to single or even no copies due to null alleles or gene deletion.
Owner:NICOGEN
Use of multiple target nucleic acid detection method using clamping probe and detection probe
PendingCN106536758AGrowth inhibitionEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeNon invasive
Owner:PANAGENE INC
Screening method of molecular marker of circadian rhythm behavior related gene Cry1 of egg ducks
The invention discloses a screening method of a molecular marker of a circadian rhythm behavior related gene Cry1 of egg ducks. The screening method comprises the following steps: (1) extraction of DNA: extracting DNA by using a blood / cell / tissue genome DNA kit, and then assaying the OD value and concentration; (2) designing of a primer: designing the primer by using Primer Primer 5.0, and delivering the primer to a biology company for synthesis; (3) PCR amplification: conducting PCR amplification by using a 20mu L reaction system and setting the PCR amplification conditions, and taking and detecting the product by agarose gel electrophoresis; (4) fragment purification of the amplification product, vector linking, conversion, positive clone screening and sequencing; and (5) SNP mutant site screening and correlation analysis for determining the circadian rhythm behavior related SNP of egg ducks. In the molecular breeding process, the mutant gene type of the circadian rhythm behavior related gene Cry1 detected by the method is regarded as the molecular marker.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
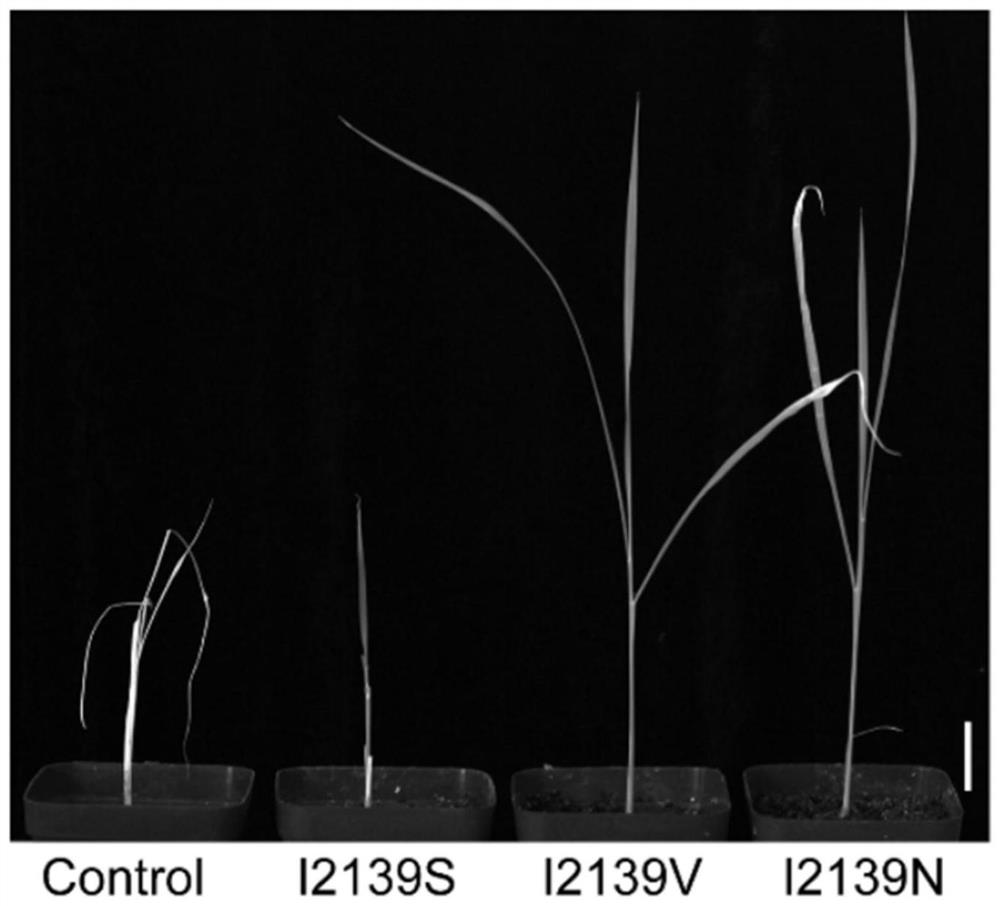
Method for guiding editing system to mediate crops to generate endogenous herbicide resistance
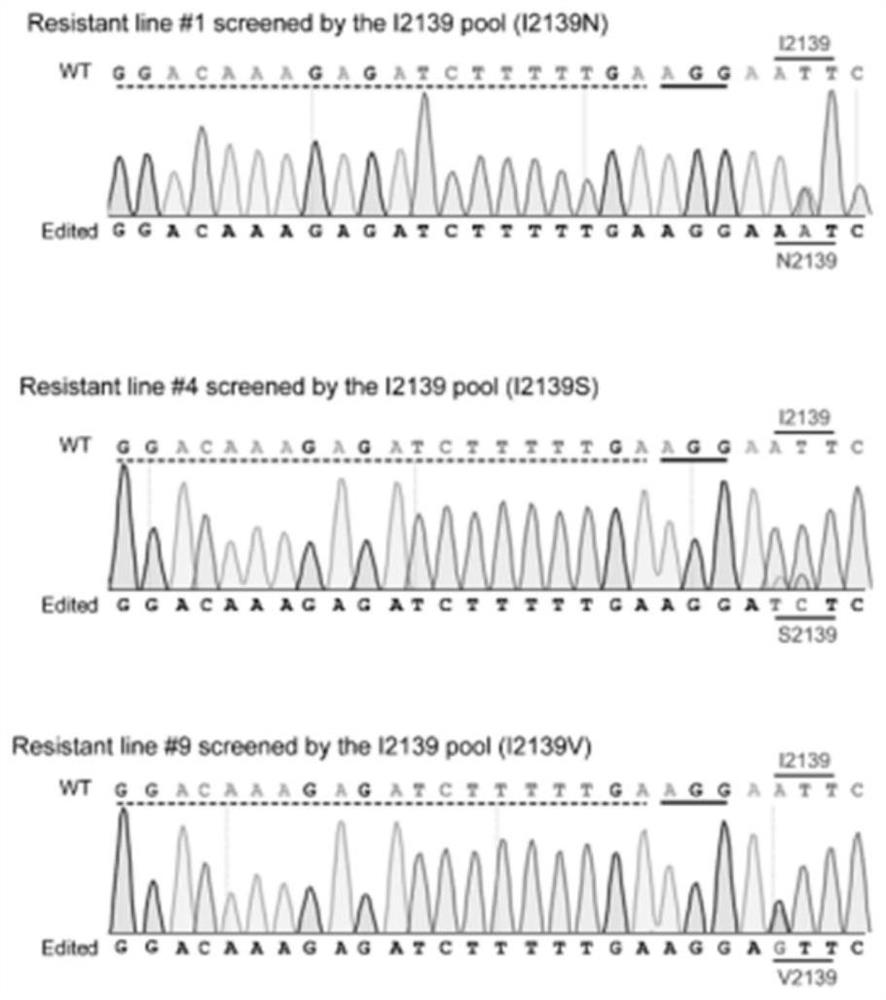
The invention discloses a method for guiding an editing system to mediate crops to generate endogenous herbicide resistance. According to the invention, various herbicide-resistant ACCase mutant genotypes are obtained, and the ACCase mutant genes respectively obtain single amino acid mutation at different sites. The ACCase mutant gene is obtained by utilizing a CRISPR-mediated guide editing system, specifically, the 1879th amino acid is mutated into leucine, threonine, valine, serine, methionine and the like from isoleucine, the 1927th amino acid is mutated into tyrosine or phenylalanine from proline, the 2097th amino acid is mutated into glycine, serine or leucine from tryptophan, and the ACCase mutant gene is mutated into leucine, threonine, valine, serine, methionine and the like from tryptophan. The 2139th site is mutated into aspartic acid, valine and serine from isoleucine, the 2176th site is mutated into glycine from aspartic acid, and the 2194th site is mutated into serine and alanine from glycine. These ACCase mutant genes endow receptor plants with resistance (tolerance) to acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor herbicides to varying degrees.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting fat coverage rate of Simmental cattle carcass by using DLK1 gene markers
The invention discloses a method for detecting a fat coverage rate of Simmental cattle carcass by using DLK1 (Dalta Like non-canonical Notch ligand 1) gene markers. The method comprises the followingsteps: designing a pair of primers by using a DNA sequence of DLK1 gene of a Chinese Simmental cattle; performing strict PCR amplification and electrophoresis of samples on a PCR reaction system; screening and finding out two SNP sites by sequencing; screening from a population to obtain a restriction endonuclease Msp I at a DLK1-478 C / T site, wherein an excision base defined by the restriction endonuclease is CCGG; and screening to obtain a restriction endonuclease Ase I at a DLK1-609 T / G site, wherein T allele and TT mutant genotype individuals carrying the DLK1-478 C / T site in the Chinese Simmental cattle population have relatively high fat coverage rates and relatively good marbling; and G allele and GG mutant genotype individuals carrying the DLK1-609 T / G site have relatively high fatcoverage rates. According to the invention, the two mutation sites of the DLK1 gene can be used as genetic markers for predicting the fat coverage rate and marbling traits of the Chinese Simmental cattle, and are used for early marker assisted selection of beef cattle.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
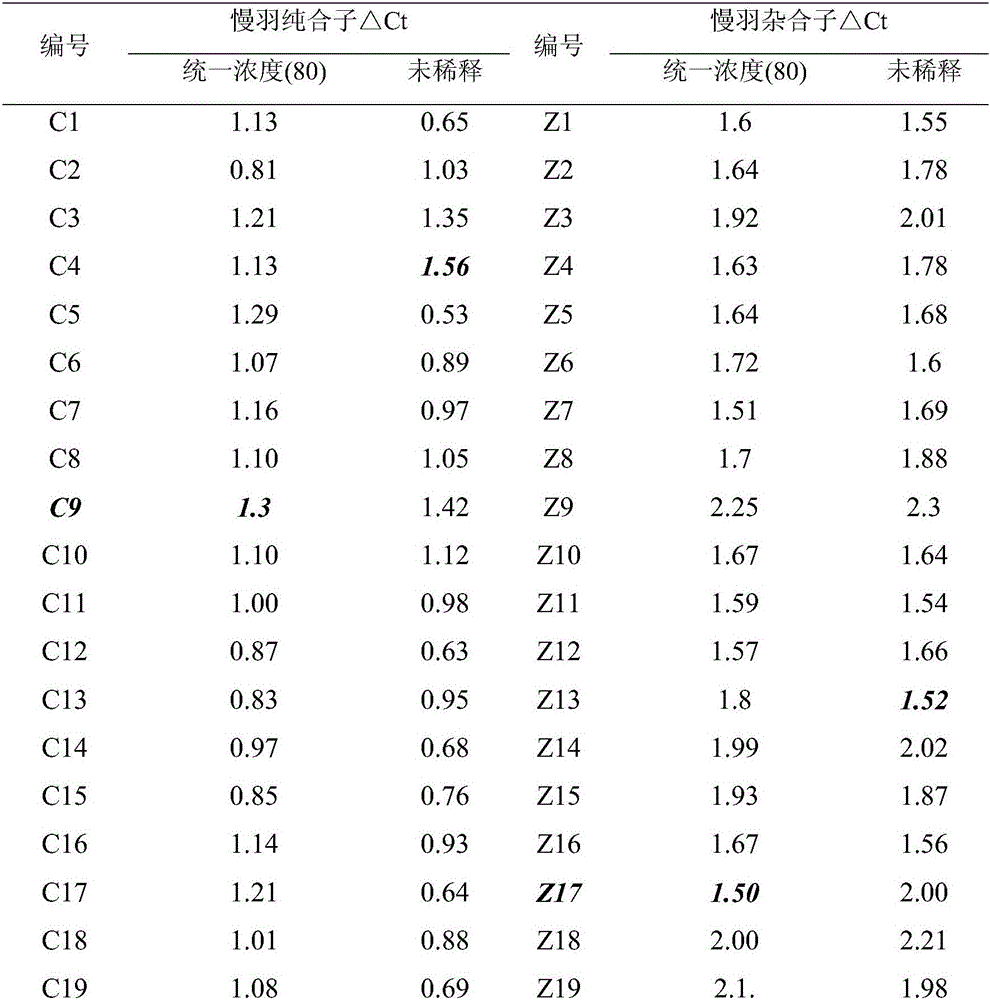
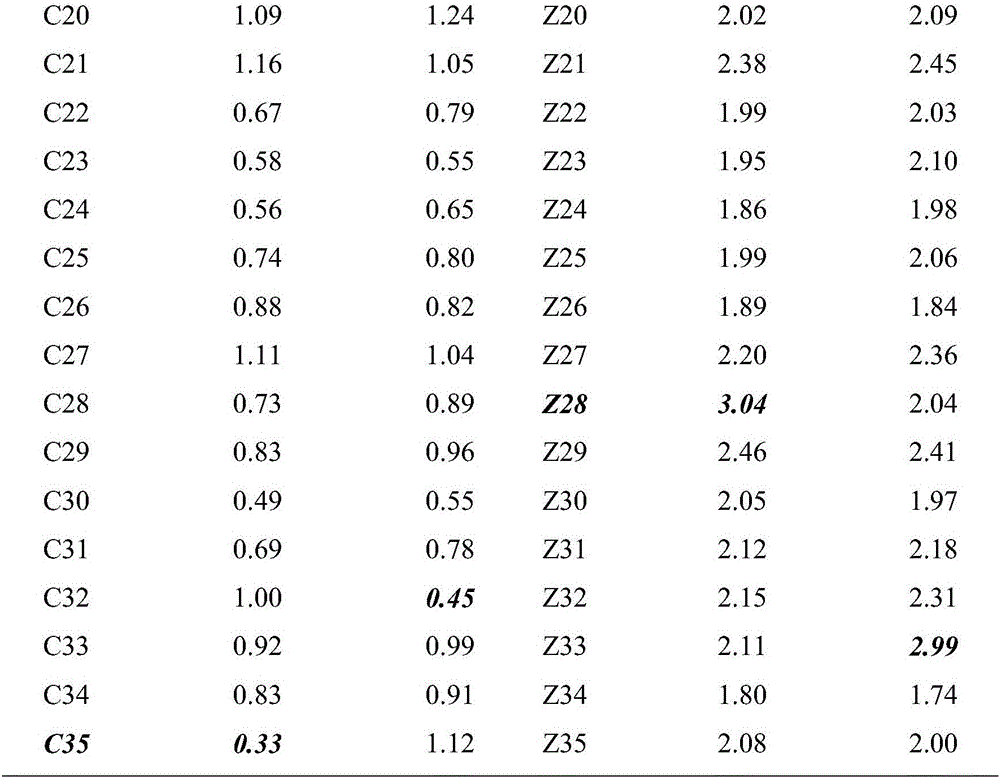
Method for detecting slow-feathering mutation genotypes of cocks
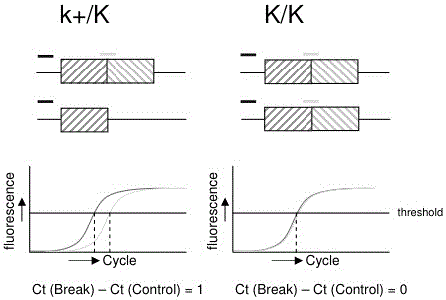
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal breeding test and particularly discloses a method for detecting slow-feathering mutation genotypes of cocks. The method includes the following steps of S1, extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of blood samples of detected individuals and diluting the DNA to be 40-100nmol / mu L; S2, performing real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction), wherein the type of a fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument is United States Bio-rad CFX96, a fluorescence quantitative reagent is Bio-rad SYBR Green fluorescence quantitative PCR Mix, a fluorescence quantitative primer sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-4; S3, calculating delta Ct value of the detected individuals, and judging the genotypes of the individuals according to the delta Ct, where when the delta Ct is greater than 1.5, the genotypes are heterozygotes, when 0.3 is less than delta Ct which is less than 1.3, the genotypes are homozygotes, and when 1.5 is greater than or equal to delta Ct which is greater than or equal to 1.3, the genotypes are eliminated. The method has the advantages of short period, high speed, 100% of accuracy, less steps, less proneness to making mistakes and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
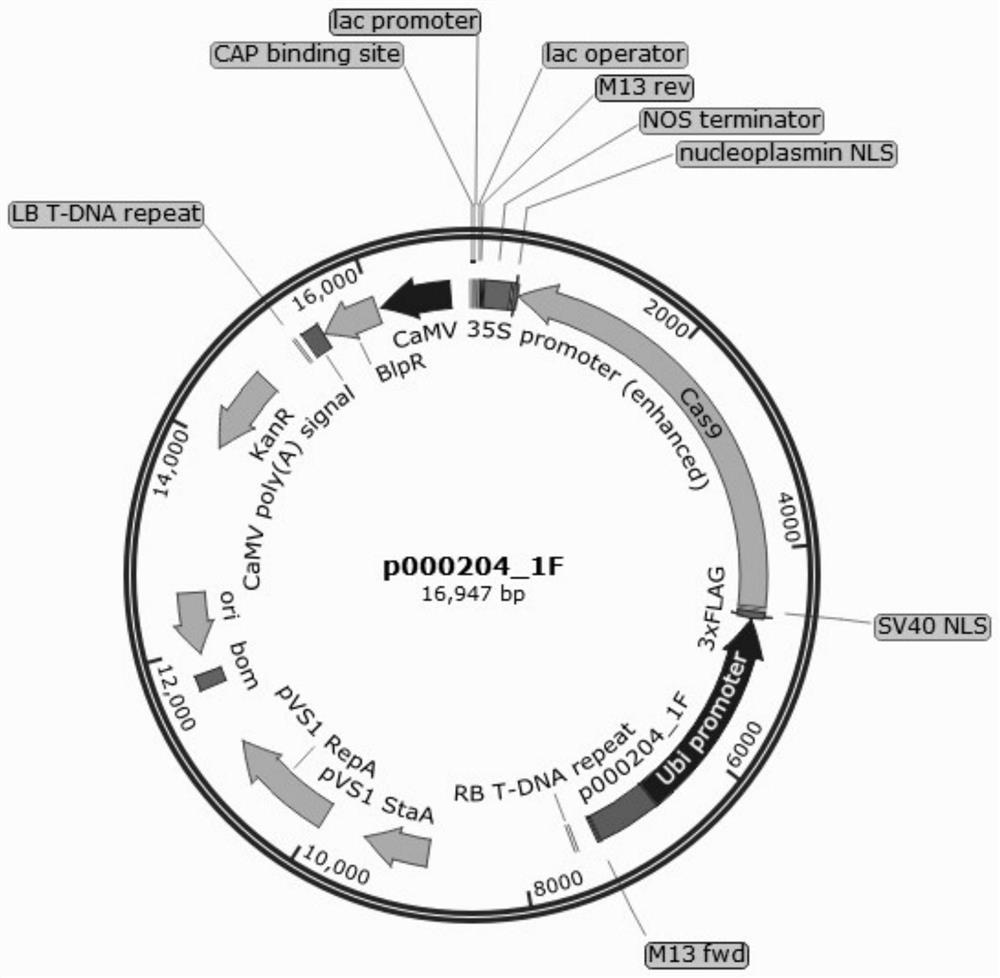
A gene controlling maize female traits and a kit, mutant genotype and method for creating a maize female sterile line
ActiveCN110903368BDiscovery of Regulatory FunctionsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyHybrid seed
The invention discloses a gene for controlling female properties of corn, and a kit, a mutant genotype and a method for creating a female sterile line of corn. The invention provides a Zm00001d000204gene nucleic acid and amino acid sequence, and CRISPR-Cas9 method for editing the Zm00001d000204 gene sequence. The invention discloses the method for creating the female sterile line of corn, and discloses an edited corn genotype sequence with female sterility properties. According to the invention, the corn sulfate transport protein coding gene Zm00001d000204 is mutated by using the CRISPR / Cas9method, and regulation and control functions of the Zm00001d000204 gene on the female properties of the corn are found. By utilizing the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing method, the corn female sterile line can be created, so that the method is used for corn hybrid seed production, and the seed production efficiency is improved. The invention also provides Zm00001d000204 mutant genotypes with female sterility properties, the sequences of the mutant genotype can cause female sterility of corn, and can be used for creating the new female sterile line.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
Hbv B genotype 1799G>C mutation as molecular marker application and kit
InactiveCN103451319BImprove relevanceFacilitate monitoring of prognostic goalsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseHepatitis B virus
The invention discloses an application of HBV (hepatitis B virus) B genetype 1799G>C mutation as a molecular marker and a kit, based on extremely high correlation of the mutation at the site 1799 of the HBV B genetype with liver cirrhosis / liver cancer; the polymorphism of the 1799th site G / C as the molecular marker can be applied to preparing a reagent or a kit for prompting the disease progress and tendency of an HBV B genetype infected person, and also serves as a target spot for preparing a reagent or a medicament for reminding the HBV B genetype infected person of the possibility of the progress of evolving into liver cirrhosis / liver cancer; as a result, the progress of the course of disease of being infected by genetype B hepatitis B virus can be predicted at the early stage of infection; furthermore, assistance can be provided for treating the patient at the initial stage of infection, the progress of the liver diseases is prevented from accelerating to evolving into heavy liver diseases and even the liver cancer; moreover, the monitoring of a prognosis target can be carried out smoothly.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method and kit for promoting flowering time of rice and mutation genotypes
ActiveCN110423751AEarly floweringShortened reproductive periodPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceF-box protein
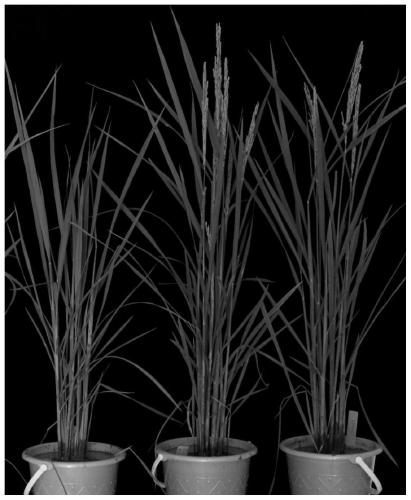
The invention discloses a method and a kit for promoting flowering time of rice and mutation genotypes. The invention provides a method for achieving early flowering of rice by editing OsFBO14 gene sequences with CRISPR-Cas9 method and discloses genotype sequences having early flowering traits of rice after editing. The method of the invention mutates F-box protein-encoding genes OsFBO14 of rice with CRISPR / Cas9 method and discovers the regulation effect of the OsFBO14 genes on flowering time of rice. By CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing method, the rice can flower in advance, thereby shortening growthperiod of rice, reducing planting cost and improving ecological adaptability of rice. The invention also provides the OsFBO14 mutation genotypes of gene-edited plants with early flowering time, and these mutation genotype sequences can promote rice to flower in advance, and be used to improve flowering traits of rice.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com