Method for performing site-directed mutation on rice TDR gene by CRISPR\Cas9 system and detection method
A site-directed mutagenesis and detection method technology, applied in the field of high-resolution melting curve analysis, can solve the problems of difficult purification of genetic background, time-consuming and labor-intensive recessive male sterility gene tdr, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
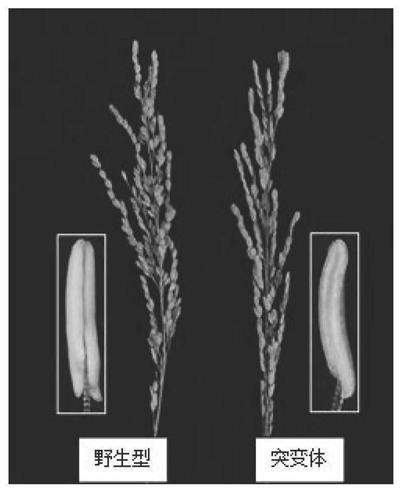
[0062] Example 1. Creating Recessive Male Sterile Lines in Rice by Knockout of TDR Gene by CRISPR\Cas9
[0063] Complete the knockout of the TDR gene (the gene number of the MSU rice genome database is LOC_Os02g02820; the number of the RAP rice genome database is Os02g0120500; its protein sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1) and obtain the male sterile plant by the following steps:
[0064] 1) Design CRISPR\Cas9 system sgRNA guide sequence
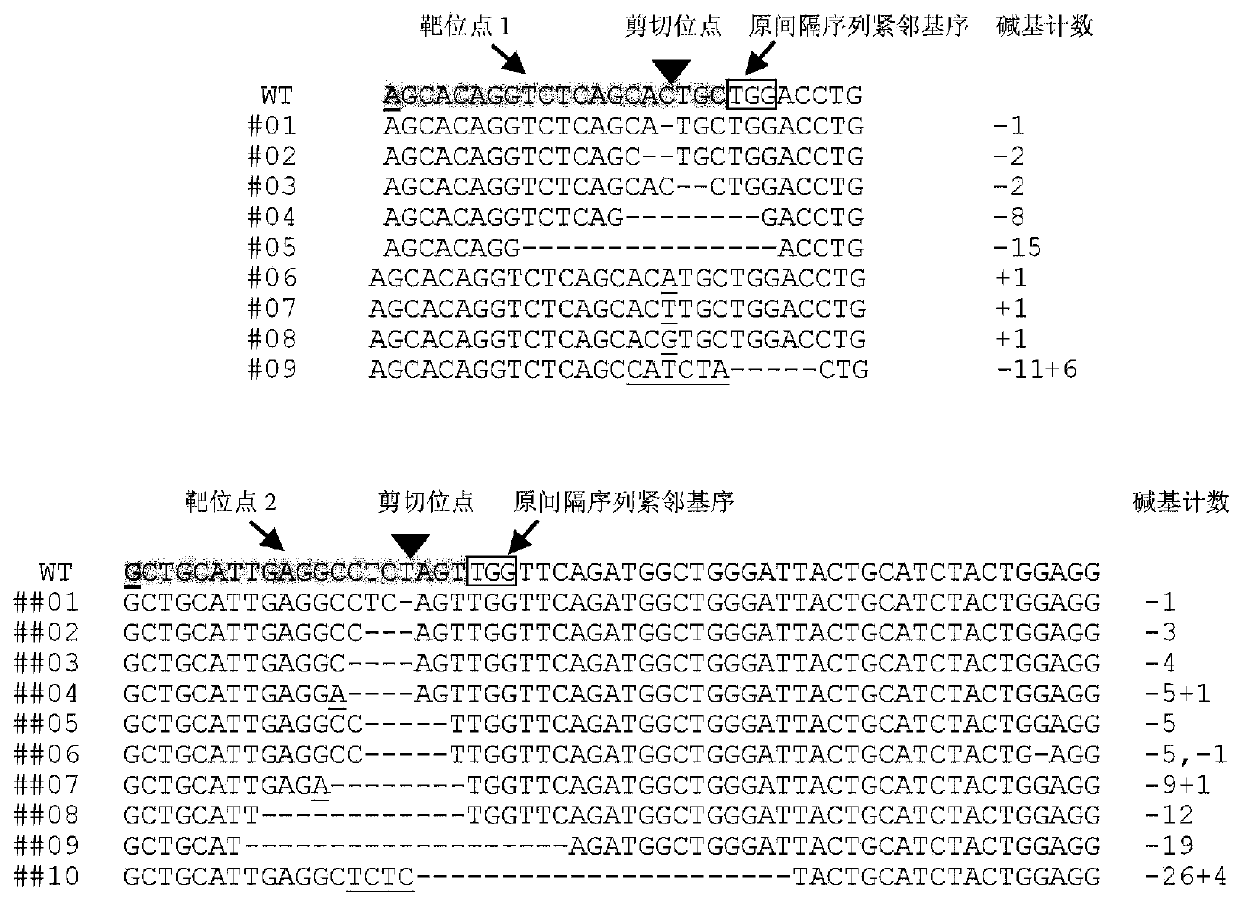
[0065] Using the online tool CRISPR-P ( http: / / cbi.hzau.edu.cn / crispr / ), according to the method provided by the developer, design the guide sequence of the CRISPR\Cas9 system for the TDR gene (also equivalent to the target site sequence). This embodiment selects two guide sequences (that is, selects two target sites) for implementation. They are AGCACAGGTCTCAGCACTGC (ie, the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 2, corresponding to target site 1) and GCTGCATTGAGGCCTCTAGT (ie, the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 3, corresponding to target site 2).
...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2. Using high-resolution melting curve analysis to detect and propagate TDR mutation types that are easy to type with wild type
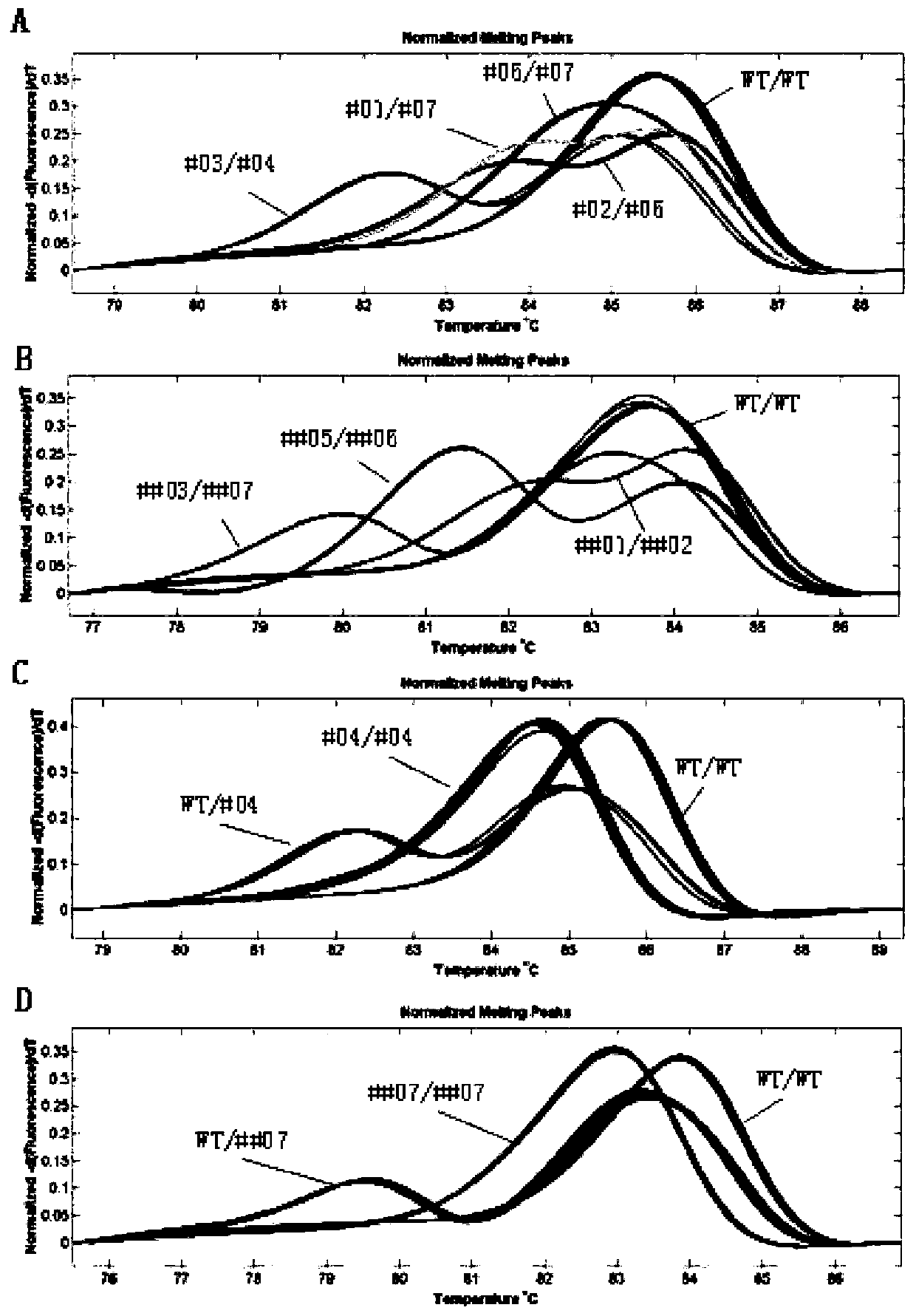
[0114]In Example 1, after obtaining sterile strains (homozygous mutant strains) of different gene-edited strains, the high-resolution melting curve method provided by the present invention is used to analyze the sterile strains of different strains together with the wild type to screen Mutant genotypes that are easy to type with wild type. The results showed that an easy-to-type mutation type was obtained from the mutant lines of target site 1 and target site 2 respectively, and the mutation numbers were #04 and ##07, respectively. Further genotyping detection was carried out on the fertile strains in the easy-to-type mutant lines, and heterozygous mutants were screened out (results of high-resolution melting curve analysis, see image 3 C and D), and then hybridize the heterozygous mutant fertile plants with the same line of sterile...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Example 3. Preliminary detection of TDR site-directed mutation T by high-resolution melting curve analysis 0 Gene mutations at the target sites of the subgenerational transformants
[0122] The TDR gene obtained in Example 1 was knocked out by the same method as described in Example 2. 0 The transformed seedlings were detected, and compared with the sequencing results, it was found that the high-resolution melting curves of all the plants with gene mutations were significantly different from those of the wild type (see image 3 A&B), therefore, using the method provided by the present invention to detect the site-directed mutation contemporary transformed plantlets can quickly determine whether there is a gene mutation at the target site of the transformant.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com